Analysis Report: pgKDN-inf vs pgwt-inf
WANG Ziyi
Date: 17 12月 2022
Summary: pgKDN-inf vs pgwt-inf
1. Differentially Expressed Genes
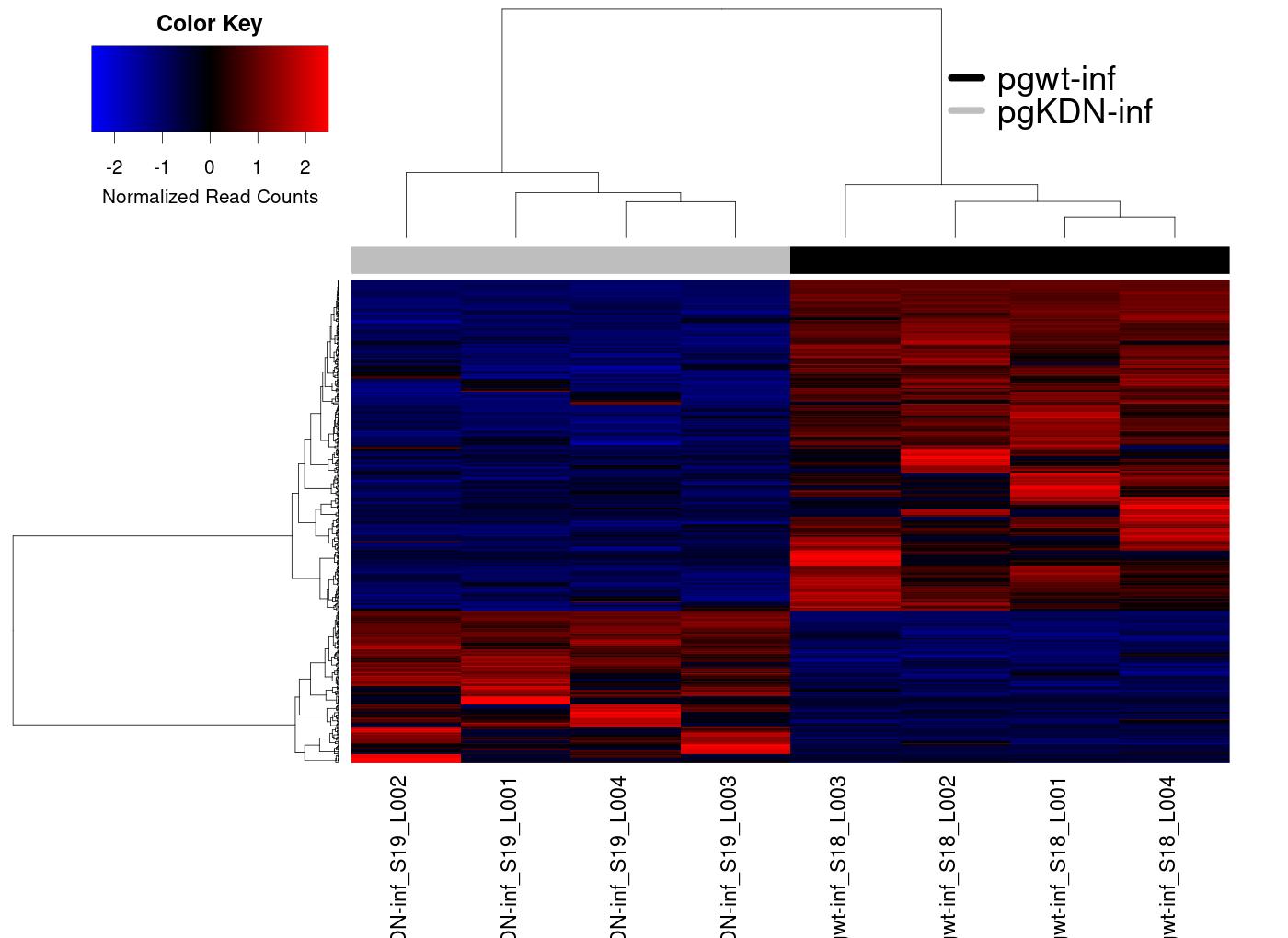
Heatmap
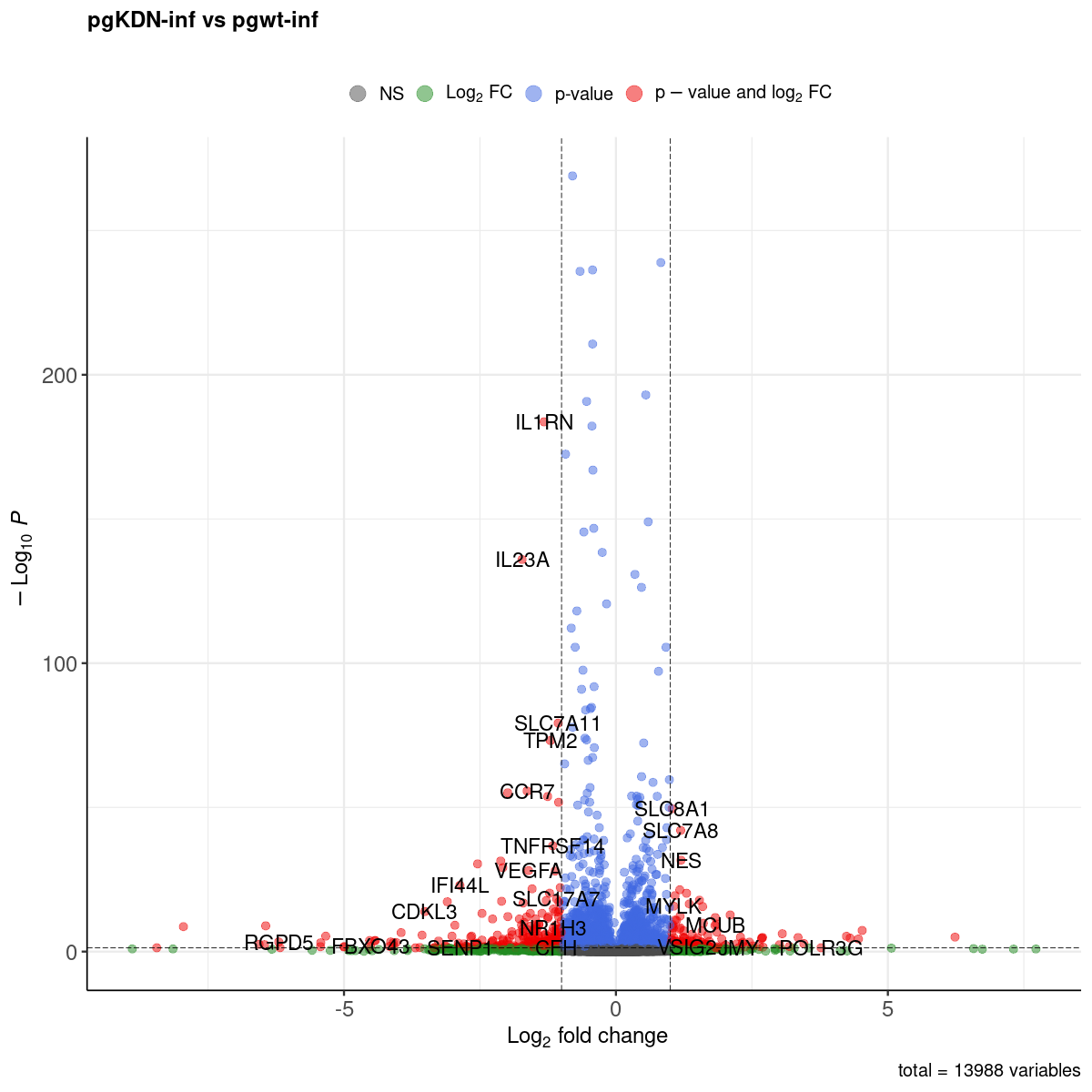
Volcano plot
DEGs list
Spreadsheet
| Ensembl gene ID | Entrez ID | Gene Name | Biotype | UniProtKBID | UniProtFunction | UniProtKeywords | UniProtPathway | RefSeqSummary | KEGG | GO | GeneRif | H.sapiens homolog ID | H.sapiens homolog symbol | baseMean | Fold Change | log2FC | lfcSE | stat | pvalue | padj | Is.Sig. | Has.Sig.AS | Intercept_pgKDN-inf | SE_Intercept_pgKDN-inf | Intercept_pgwt-inf | SE_Intercept_pgwt-inf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSG00000000971 | 3075 | CFH | protein_coding | P08603 | FUNCTION: Glycoprotein that plays an essential role in maintaining a well-balanced immune response by modulating complement activation. Acts as a soluble inhibitor of complement, where its binding to self markers such as glycan structures prevents complement activation and amplification on cell surfaces (PubMed:21285368, PubMed:25402769). Accelerates the decay of the complement alternative pathway (AP) C3 convertase C3bBb, thus preventing local formation of more C3b, the central player of the complement amplification loop (PubMed:19503104, PubMed:26700768). As a cofactor of the serine protease factor I, CFH also regulates proteolytic degradation of already-deposited C3b (PubMed:18252712, PubMed:28671664). In addition, mediates several cellular responses through interaction with specific receptors. For example, interacts with CR3/ITGAM receptor and thereby mediates the adhesion of human neutrophils to different pathogens. In turn, these pathogens are phagocytosed and destroyed (PubMed:9558116, PubMed:20008295). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18252712, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19503104, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20008295, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21285368, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25402769, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26700768, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28671664, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9558116}. | 3D-structure;Age-related macular degeneration;Alternative splicing;Complement alternate pathway;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hemolytic uremic syndrome;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Innate immunity;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Sulfation;Sushi | This gene is a member of the Regulator of Complement Activation (RCA) gene cluster and encodes a protein with twenty short consensus repeat (SCR) domains. This protein is secreted into the bloodstream and has an essential role in the regulation of complement activation, restricting this innate defense mechanism to microbial infections. Mutations in this gene have been associated with hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS) and chronic hypocomplementemic nephropathy. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. | hsa:3075; | blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; serine-type endopeptidase complex [GO:1905370]; complement component C3b binding [GO:0001851]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding [GO:0043395]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; complement activation [GO:0006956]; complement activation, alternative pathway [GO:0006957]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of complement activation [GO:0030449]; regulation of complement activation, alternative pathway [GO:0030451]; regulation of complement-dependent cytotoxicity [GO:1903659] | 10781834_This paper (PMID 10781834) was the first to describe the detailed structure of the human CFH gene. 11825898_Three SIBLINGs (small integrin-binding ligand, N-linked glycoproteins) enhance factor H's cofactor activity enabling MCP-like cellular evasion of complement-mediated attack. 11851332_molecular modelling of the C-terminal domains of factor H of human complement: a correlation between haemolytic uraemic syndrome and a predicted heparin binding site 11921353_acts as adrenomedullin binding protein - review 12391176_Recombinant factor H with deletions at the carboxyl-terminal end loses the ability to control the spontaneous activation of the alternative complement pathway on host-like surfaces, a functional defect that leads to acute renal failure in HUS. 12424708_structural and functional characterization of three different factor H proteins purified from the plasma of patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome who carry the factor H mutations W1183L, V1197A, or R1210C 12471127_The site and putative residues on factor H (FH) essential for the interaction of the C-terminal end of FH with C3d, C3b, and heparin have been identified; the heparin- and C3d-binding sites are overlapping. 12630812_two specific binding sites for adrenomedullin were found in factor H 12960213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12960213_Screening for factor H gene (FH1) mutations contributes to the classification of atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome (aHUS). 14583443_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14638802_promoted entry of Fba(+) group A streptococci into epithelial cells in a dose-dependent manner but did not affect invasion by an isogenic fba mutant 14974950_CFH deficiency my favor acute allograft glomerulopathy. 15163532_Review. Factor H is an essential regulatory protein for complement homeostasis in plasma & for the protection of bystander host cells & tissues from damage by complement activation. Genetic & structural data delineate the functional domains responsible. 15331938_Complement factor H contributes to the control mechanism of in situ complement activation and prevents renal damage in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. 15557185_Human complement regulatory factor H binds to Streptococcal pyogenes M18 surface protein Emm18. 15634279_Binding to platelets is mediated by the C-terminal region of factor H and factor H mutated at the C-terminus exhibited reduces binding 15749837_Factor H is cleaved by a dermatan sulfate-mediated protease identified in blood. 15754282_A novel nucleotide substitution 3254T-->C causing a Ser1061Pro substitution in the short consensus repeat SCR18was found in a girl with hemolytic uremic sundrome. 15761120_a common coding variant, Y402H, that significantly increases the risk for age-related macular degeneration (AMD)with odds ratios between 2.45 and 5.57 was revealed; this common variant likely explains approximately 43% of AMD in older adults 15761121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15761121_tested single-nucleotide polymorphisms in CFH for association with age-related macular degeneration (AMD) in two case-control populations; possession of at least one histidine at amino acid position 402 increased the risk of AMD 2.7-fold 15761122_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15761122_identified a tyrosine-histidine polymorphism in which the histidine variant almost always occurs in the context of the age-related macular degeneration risk haplotype 15784724_there are naturally occurring susceptibility factors in CFH and MCP for the development of atypical haemolytic-uraemic syndrome 15870199_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15895326_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16174643_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16192651_Binding of CFH to endothelial cells is mediated by the carboxy-terminal glycosaminoglycan binding site. 16229850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16229850_no association of the complement factor H Y402H gene polymorphism with risk of incident thromboembolic events, nor with baseline levels of C-reactive protein 16263173_Three heparin-binding sites were identified in complement factor H1. 16267773_results suggest that the interaction with pneumococci PspC contributes to pneumococcal virulence. 16299065_Deficiency of and mutations and variations in the complement factor H (CFH) gene are associated with the development of membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis type II. 16299065_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16300415_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16310045_Keratinocytes are capable of synthesizing factor H and that this synthesis is regulated by IFN-gamma. 16379025_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16379025_These results suggest the contribution of the Y402H polymorphism of the CFH gene to exudative AMD susceptibility also in the French population 16386793_Mutations in the complement regulators factor H, membrane cofactor protein (MCP), and factor I are associated with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. 16431947_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16431947_The CFH Y402H variant is strongly associated with both GA(geographic atrophy) and CNV (choroidal neovascularization) in the U.K. population. 16470555_gene conversion is responsible for functionally significant CFH mutations in atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome 16519819_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16528247_Two different factor H mutations associated with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome were examined: in one, factor H accumulated in cells, and in the other, membrane binding was reduced. 16533809_three-dimensional solution structure of the C-terminal module pair of factor H 16541016_Four previously found haplotypes and one additional haplotype were found. Haplotype frequencies were significantly different from those in found Americans affected with macular degeneration. Two were risk factors and one was protective. 16541016_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16621965_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16630992_CFH gene determines susceptibility to myocardial infarction. HisHis homozygotes had a hazard ratio of 1.77 for myocardial infarction. 16630992_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16642439_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16710702_CFH does not appear to be a primary hereditary contributor to age-related macular degeneration {ARMD} in Japanese, and the absence of CFH contribution to ARMD in Japanese may correlate with the findings in ethnic differences of ARMD phenotypes. 16710702_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16723442_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16730735_No evidence was found to associate the complement factor H Y402H gene polymorphism with coronary artery disease and atherosclerosis. 16751403_When bound to Neisseria meningitidis, factor H retains its activity as cofactor of alternative complement pathway factor I and contributes to the ability of N. meningitidis to avoid complement-mediated killing in the presence of human serum. 16754848_Results describe age-related macular degeneration (AMD) genetic risk factors through identification of polymorphisms in ERCC6 and in complement factor H. 16774956_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16785547_Factor H (fH) binds to an approximately 29-kDa outer membrane protein on Neisseria meningitidis identified as GNA1870; binding of down-regulator protein fH correlates with levels of neisserial GNA1870 expression. 16787919_amino acid 384 is adjacent to a heparin-binding site in CCP7 of factor H and demonstrate that the allotypic variants differentially recognize heparin 16816528_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16828512_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16828512_Results indicate that CFH (complement factor H) increases the risk of developing GA (grade 4) as well as neovascular (grade 5) and milder (grade 3) disease. 16849663_CFH Y402H polymorphism may account for a substantial proportion of age-related macular degeneration and may confer particular risk in the presence of environmental and genetic stimulators of the complement cascade. 16849663_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16865697_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16877387_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16877387_The allele frequency of Y402H polymorphism in CFH (complement factor H)has an ethnic variation, with much lower 1277C frequency in Chinese than in white patients. 16885922_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16885922_The CFH gene polymorphism seems to be an important etiologic factor for AMD also in the isolated Finnish population. 16889549_combined liver-kidney transplantation offers the prospect of a favorable long-term outcome for patients with hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with complement factor H mutations 16905558_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16909242_We suggest that protracted administration of exogenous factor H might not be a long-term strategy in homozygous factor H deficiency. 16936080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16936080_The CFH polymorphism Tyr402His appears indicative of AMD (age-related macular degeneration) pathogenesis. 16936129_A significant level of CFH expression is maintained in different ocular tissues during development and aging. 16936732_Common variation in three genes, including a noncoding variant of CFH, strongly influences risk of age-related macular degeneration. 16936732_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16936733_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16954704_Results further support the notion that CFH (complement factor H) and LOC387715 genes are the major risk factors for ARMD. 17000705_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17000705_study provides additional support for the CFH and LOC387715 genes in age-related maculopathy (ARM) susceptibility via the evaluation of cohorts that had different ascertainment schemes regarding ARM status and through the meta-analyses 17003406_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17003406_The C allele of Y402H represents a significant risk factor in individuals with AMD, and this effect is most pronounced in individuals with neovascular disease. 17022693_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17056561_Factor H domains 19-20 alone are capable of discriminating between host-like and complement-activating cells. 17076561_Heterozygous CFH/CFHL1 hybrid gene in which exons 1-21 are derived from CFH and exons 22/23 from CFHL1 causing Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. 17079491_age-related macular degeneration(AMD) risk-conferring allele alters the binding properties of complement factor H gene (CFH), thereby leading to choroidal C-reactive protein deposition, contributing to AMD pathogenesis 17132743_extracellular NS1 may function to minimize Soluble and cell-surface-associated nonstructural protein 1 binds to and recruits the complement regulatory protein factor H 17137217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17151483_(Complement factor H)CFH gene polymorphism is not associated with AMD (age-related macular gegeneration) in the Japanese population. 17151483_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17157600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17157600_The CFH gene and Hemicentin-1 genes do not appear to be involved in a statistically significant fraction of dry AMD (age-related macular degeneration) cases in the Japanese population. 17167412_Differences in association between CFH gene and exudative age-related macular degeneration(AMD) in Chinese from Caucasians and Japanese. SNP rs3753394 in CFH promoter carrying significantly increased risk for exudative AMD. 17167412_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17198853_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17198853_Our data suggest that the CFH Tyr402His is not a major risk factor for overall early AMD (age-related macular degeneration) in this Latino population, but may play a role in susceptibility to phenotypes of early AMD likely to progress to late AMD. 17208302_Data show the role of the factor H C-terminus in host cell recognition and protection. 17210851_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17210852_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17210858_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17229916_Mutant factor H causes defective complement control and in hemolytic uremic syndrome--particularly under condition of inflammation and complement activation-causes endothelial cell damage. 17241667_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17241667_results suggest that cigarette smoking and CFH T1277C polymorphism are independent risk factors for age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and that both risk factors are associated more strongly with neovascular AMD than all forms of AMD combined 17266113_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17285240_findings suggest that the combined effect of variants in the CFH and LOC 387715 genes may contribute to the age-related macular degeneration phenotype in this family 17293598_complement control protein 6-8 is able to interact with DNA and necrotic cells, but in contrast the His-384 allotype binds these ligands more strongly than the Tyr-384 variant 17306880_Complement factor H polymorphism T1277C (tyrosine-402 --> histidine-402) is strongly associated with both dry and wet age-related macular degeneration(AMD) and points to a possible role for inflammation in the pathogenesis of AMD. 17306880_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17314151_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17314151_findings are consistent with evidence that, in addition to the widely described Y402H variant, there is at least one and, most probably, several other mutations in the CFH gene which determine disease manifestation in age-related macular degeneration 17339482_Y402H polymorphism affects binding affinity to C-reactive protein; it could lead to an impaired targeting of FH to cellular debris and enhanced inflammation along the macular retinal pigmented epithelium-choroid interface 17352366_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17360715_causal link between H402Y and age-related macular degeneration in which variation at position 402 modulates the response of factor H to age-related changes in the glycosaminoglycan composition and apoptotic activity of the macula 17362990_His402 allotype may self-associate more readily than the Tyr402 allotype, short complement regulator (SCR)-6/8 is partly responsible for the folded-back structure of intact FH, and SCR-6/8 changes conformation upon heparin binding. 17396242_CFH genotype and allele frequencies were similar in cases and controls. These results do not support an involvement of common nonsynonymous polymorphisms of the CFH gene in predisposition to CAD and its complications 17396242_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17398321_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17398321_Our data suggest that the CFH Y402H polymorphism is a major risk factor for exudative AMD in a Central European population. 17399790_Factor H-like protein 1 (FHL-1), an alternative splice product of the CFH gene, is identified as an additional protein that includes risk residue 402 and confers risk for age-related macular degeneration. 17426452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17438519_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17438673_We identify and characterize a large, common deletion that encompasses both the CFHR1 and CFHR3 genes. The absence may account for the protective effects against age-related macular degeneration. 17442969_The acquisition of factor H by pneumococci via PspC occurs via two contact sites located in SCR8-11 and SCR19-20, and factor H attached to the surface of the pneumococcus promotes adhesion to both host epithelial and endothelial cells. 17456821_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17464302_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17464302_the CFH Y402H variant was significantly enriched in patients with predominantly classic CNV. Patients homozygous for the CFH Y402H genotype seem to have worse visual acuity after PDT. 17472578_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17483111_CFH Y402H was inversely associated with CHD among women, but not men. This inverse association was observed in both populations with earlier age of CHD. 17483111_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17558024_Oxidative stress modulates complement factor H expression in retinal pigmented epithelial cells by acetylation of FOXO3 17562771_Adherence assays demonstrated that preincubation of Streptococcus pneumoniae with complement factor H (FH) increased adherence to human umbilical vein endothelial cells 5-fold and to lung epithelial cells 18-fold. 17580967_A common variant (Y402H) of complement factor H was tested for differences in binding various ligands. 17591618_N-glycan characterization of human complement factor H 17591627_Complement factor H appear to play a role in both age-related macular degeneration and renal pathophysiology. 17591627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17591866_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17591866_The findings do not support the hypothesis that the His(402) allele is related to larger retinal venular diameters. The association with smaller retinal venular diameters most likely is a chance finding, because it was present only among never-smokers 17599974_outcome of hemolytic uremic syndrome in patients with CFH mutation is catastrophic 17631852_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17631852_The Y402H CFH variant carried a significantly increased risk for developing AMD in our population. 17679948_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17697822_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17697822_population-based study suggests that the combined presence of unfavorable CFH and CRP genetic profiles is associated with risk of MI. 17699195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17724217_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17724217_Replication of the association between the protective haplotypes and decreased AMD susceptibility provides increased evidence that these associations have biological meaning 17767156_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17846368_Both ARMS2 polymorphism and complement factor H polymorphism are independently associated with progression of age-related macular degeneration. 17846371_Single nucleotide polymorphism of complement factor H gene indicates a greater risk of age-related macular degeneration. 17869048_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17877809_In this family-based study, we found no evidence of an association between variants of the CFH gene and early-onset coronary heart disease 17877809_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17915330_the binding of Factor H and C4bp to Aspergillus spp. appears to be even stronger than to Candida spp. and different, albeit possibly nearby, binding moieties mediate this surface attachment. 17962488_Although the Y402H variant was not significantly associated with age-related macular degeneration (AMD), other coding and noncoding variants in the CFH gene including rs1410996 and smoking moderately influenced the risk of AMD in a Japanese population. 17962488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17973958_Heterozygous R1215Q mutation is found in atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, with incomplete penetrance of the disease. 17995985_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17995985_no clear impact of the CFH Y402H polymorphism on recent exudative age-related macular degeneration lesion characteristics 17999207_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17999207_Variant in this gene may modify susceptibility for late-onset Alzheimer's disease. 18005991_The regulatory SCR-1/5 and cell surface-binding SCR-16/20 fragments of CFH reveal partially folded-back solution structures and self-associative properties. 18006700_either lacked the CFHR1/CFHR3 completely (n = 14) or showed extremely low CFHR1/CFHR3 plasma levels (n = 2) are positive for factor H (CFH) autoantibodies 18039838_The binding of factor H and factor H-like protein 1 (FHL-1) from human sera to Aspergillus fumigatus conidia was shown by adsorption assays and immunostaining. 18050121_The dysfunction of the CFH related to the risk of age-related macular degeneration and caused by the Y402H polymorphism does not modify the outcome of photodynamic therapy. 18054635_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18054635_The Age-related macular degeneration associated complement factor H Y402H and LOC387715 A69S variants were associated with differences in choroidal neovascular lesion size in this study. 18067970_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18067970_The complement factor H, Y402H polymorphism is associated with peripheral reticular pigmentary change, suggesting that age-related macular degeneration changes are not limited to the macula. 18093091_we have identified a functional interaction between Scl1 and plasma FH, which may contribute to GAS evasion of complement-mediated opsonization and phagocytosis. 18161619_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18162041_CFH and ARMS2 haplotypes and smoking exerted large effects on AMD risk. Common haplotypes of CFH conferred ORs from 1 to 4.17. Homozygotes for ARMS2 were at very high risk for AMD. Risk rose to 15.5% in 1/10 of the population with highest predicted risk. 18162041_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18162041_Polymorphisms in the complement factor H gene, LOC387715, and the HTRA1 promoter are strongly associated with age-related macular degeneration. 18163432_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18163432_The CFH 1277C allele may predispose patients for co-morbidity in Alzheimer disease and age-related macular degeneration. 18164066_Independent of CFH genotype or smoking history, an individual's risk of AMD (age-related macular degeneration) could be increased or decreased, depending on their genotype or haplotype in the 10q26 region. 18164066_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18183578_important role of FH/FHL (Complement Factor H) in colon cancer cells defense against complement-mediated cytotoxicity, and in metastatic process. 18203751_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18203751_This demonstrates for the first time the existence of a gene environment-interaction between pathogenic load of C. pneumoniae and the CFH gene in the aetiology of AMD 18211923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18211923_The CFH Y402H polymorphism showed a genotype-phenotype association for some drusen features. Additional genetic factors are likely to influence drusen phenotype. 18223247_In Korean subjects, CFH polymorphism appears to be a considerable hereditary contributor to exudative age-related macular degeneration. 18223247_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18235016_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18235085_The R1210C mutation is a prototypical atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome mutation that is present as a rare polymorphism in geographically separated human populations. 18248681_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18263814_The FH Y402H polymorphism associated with AMD (age-related macular degeneration) causes a reduction in binding of FH (factor H)and FHL-1 to CRP (c-reactive protein) and (atreptococcal M protein) M protein. 18268093_mutated FH enables complement activation on the surface of platelets and their activation, which may contribute to the development of thrombocytopenia in Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. 18292569_Direct-binding specificity of human factor H only to gonococci that prevent serum killing (i.e., Neisseria gonorrhoeae) is restricted to humans and may in part explain species-specific restriction of natural gonococcal infection. 18292760_Association of the complement factor H Y402H polymorphism with cardiovascular disease is dependent upon hypertension status. 18292760_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18292785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18316707_A high impact of the additive effect of CFH and HTRA1 in the development of exudative AMD was shown. The HTRA1-smoking additive effect found in this study further suggests the importance of this environmental risk factor in AMD. 18316707_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18325906_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18336910_These data recapitulate a prototypical complement genetic profile, including a partial factor H deficiency and the presence of major risk factors for age-related macular degeneration and membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis type II. 18340363_Complement factor H polymorphisms associated with deleterious renal phenotypes and age-related macular degeneration. 18340363_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18362109_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18362109_Possible association between occult or minimally classic choroidal neovascularization(CNV) and CFH polymorphism and between classic and predominantly classic CNV and HTRA1 polymorphism. 18378209_Both VEGF +936 C/T and CFH Y402H polymorphisms are dependently associated with wet age-related macular degeneration in the Taiwan Chinese population. 18378209_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18406463_various conformational isoforms (native, amyloid fibrils, and beta-oligomers) of recombinant human PrP (90-231 and 121-231) bind C1q and activate complement. 18413232_Kallikrein is responsible for the cleavage of factor H. 18421087_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18421087_The findings support prior evidence that the CFH gene is one of the AMD-associated genes. There is a different distribution pattern of CFH variants in the Chinese compared with other populations. 18422436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18423869_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18423869_The findings of this study indicate that an individual's response to age-related eye disease supplements may be related to complement factor H genotype. 18433936_Lack of an association of the CFH Y402H polymorphism with Alzheimer's disease. 18433936_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18436811_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18436811_The present data provided an independent validation of the association of LOC387715 and HTRA1 SNPs, along with their risk estimates among Indian patients with AMD. 18452766_our results showed that in Spanish patients with AMD the associations of both polymorphisms are not equal: Y402H is associated with early and wet AMD, whereas A69S is associated only with wet AMD. 18461138_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18493315_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18493315_adding C2 to the two-factor model of CFH and LOC387715 increases the sensitivity (from 63% to 73%) of assessing risk of AMD 18502988_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18515590_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18515590_The SNPs rs3753394 and rs800292 of CFH and rs11200638 of HTRA1 are significantly associated with the risk of PCV (polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy) in Chinese patients. 18538409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18538409_This study confirmed associations of the Y402H CFH gene variant with age-related macular degeneration (AMD) in nonwhite populations, but neither explained the lack of association between inflammatory factors and AMD in the cohort 18541031_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18566420_H. influenzae interferes with the alternative complement activation pathway by binding FH and FHL-1 18596911_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18604638_CFH Y402H polymorphism is associated with early-onset CAD in Chinese. 18604638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18627285_Complement factor H variant p.Y402H is not a genetic risk factor for pseudoxanthoma elasticum. 18627285_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18658028_An abnormal control of the complement alternative pathway is a risk factor for the occurrence of HELLP syndrome. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18682806_Both the HTRA1 and LOC387715/ARMS2 single nucleotide polymorphysms appear to contribute equally to disease risk (both geographic atrophy and choroidal neovascularization) with no evidence of interaction with CFH. 18682806_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18682812_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18682812_The purpose of this study was to investigate the association of reported common single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in CFH, LOC387715, and HTRA1 with exudative age-related macular degeneration in a northern Chinese population. 18704199_If elevated serum/plasma levels of CRP are associated with neovascular age-related macular degeneration, it is likely not due to genetic variation within CRP, but likely due to variations in some other genetic as well as epidemiological factors. 18704199_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18718667_Findings from multiple samples support an AMD genetic variant harbored within HtrA1. The risk of advanced AMD increased when the presence of risk alleles from HtrA1 was combined with eith | 18.208074 | 0.468034694 | -1.095313 | 0.41526728 | 6.974125 | 0.0082696643135666825230600807117298245429992675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0427796096221045724083964501005539204925298690795898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 11.4172299 | 4.7744441 | 24.5167293 | 9.6658238 | |||
| ENSG00000001084 | 2729 | GCLC | protein_coding | P48506 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the ATP-dependent ligation of L-glutamate and L-cysteine and participates in the first and rate-limiting step in glutathione biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9675072}. | Acetylation;ATP-binding;Disease variant;Glutathione biosynthesis;Hereditary hemolytic anemia;Ligase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | PATHWAY: Sulfur metabolism; glutathione biosynthesis; glutathione from L-cysteine and L-glutamate: step 1/2. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:9675072}. | Glutamate-cysteine ligase, also known as gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase is the first rate-limiting enzyme of glutathione synthesis. The enzyme consists of two subunits, a heavy catalytic subunit and a light regulatory subunit. This locus encodes the catalytic subunit, while the regulatory subunit is derived from a different gene located on chromosome 1p22-p21. Mutations at this locus have been associated with hemolytic anemia due to deficiency of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase and susceptibility to myocardial infarction.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2010]. | hsa:2729; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; glutamate-cysteine ligase complex [GO:0017109]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ADP binding [GO:0043531]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; glutamate binding [GO:0016595]; glutamate-cysteine ligase activity [GO:0004357]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; aging [GO:0007568]; blood vessel diameter maintenance [GO:0097746]; cell redox homeostasis [GO:0045454]; cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus [GO:0044344]; cellular response to follicle-stimulating hormone stimulus [GO:0071372]; cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0071333]; cellular response to hepatocyte growth factor stimulus [GO:0035729]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular response to thyroxine stimulus [GO:0097069]; cysteine metabolic process [GO:0006534]; glutamate metabolic process [GO:0006536]; glutathione biosynthetic process [GO:0006750]; L-ascorbic acid metabolic process [GO:0019852]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of hepatic stellate cell activation [GO:2000490]; negative regulation of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1901029]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031397]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; regulation of mitochondrial depolarization [GO:0051900]; response to activity [GO:0014823]; response to arsenic-containing substance [GO:0046685]; response to cadmium ion [GO:0046686]; response to heat [GO:0009408]; response to hormone [GO:0009725]; response to human chorionic gonadotropin [GO:0044752]; response to interleukin-1 [GO:0070555]; response to nitrosative stress [GO:0051409]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410] | 11820781_Expression of the gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase heavy subunit gene is inducible by certain nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., indomethacin) in colon cancer cells. 11844594_Genetic determinants of lung cancer short-term survival: the role of glutathione-related genes 11972604_Oxidant stress induces gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase and glutathione synthesis in human bronchial epithelial NCI-H292 cells. 12070177_identification of a variant antioxidant response element in the promoter region 12500194_redox-sensitive elements directing expression of the glutamate cysteine ligase in CYP2E1-expressing cells are present in the ARE4 distal portion of the 5'-flanking region, perhaps a reflection of metabolic adaptation to CYP2E1-generated oxidative stress. 12598062_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12663448_A new gamma-GCSH mutation from gamma-GCS deficiency, a C>T missense mutation at nucleotide 379, encodes a predicted Arg127Cys amino acid change. The mutated amino acid lies within a cleft on the protein surface of gamma-GCSH, containing Cys249. 14676828_GCS is up-regulated by antiestrogens mediated by estrogen receptor beta. 15451055_Review. The most important element in both Gclc and Gclm expression is the electrophile response element in their promoters. 15485876_data provide the first report of glutamylcysteine ligase (GCLC) expression in the islet and demonstrate that adenoviral overexpression of GCLC increases intracellular glutathione levels and protects the beta cell from adverse effects of IL-1 beta 16322067_Adrenomedullin regulates cellular glutathione content via modulation of gamma-glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit expression 16403949_Results suggest that TNF-alpha elevates the expression of lens epithelium-derived growth factor (LEDGF) and that LEDGF is one of the transactivators of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase heavy subunit gene. 16491484_Drug-resistant cells have the inherent ability to maintain increased gamma-GCS activity. 16599007_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16690975_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16690975_This study found an association between variants in GCLC, a novel candidate gene, and cystic fibrosis lung function; this effect was observed only in patients with a mild CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator) genotype 16766924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17109620_Activation of insulin signaling through PI3K/Akt/mTOR/Nrf2/ GCLc pathway affords significant cell protection by maintaining cellular redox balance. 17207022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17207022_The genetic polymorphism in GCLC -129C/T is not associated with susceptibility to COPD in a southern Chinese population of Han nationality. 17333241_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17344309_upregulation of gamma-glutamate-cysteine ligase as part of the long-term adaptation process to iron accumulation in neurons 17479437_GCLC promoter polymorphisms may influence glutamate decarboxylase 65 autoantibody levels the age at which type 1 diabettes is diagnosed. 17479437_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17643973_The -588TT/-23TT genotype was found to be associated with decreased risk of allergic asthma after adjustment for age, gender and smoking status using regression analysis (OR=0.33 95% CI 0.15-0.70, p=0.036) but with increased risk of non-allergic asthma. 17921251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17961430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18035085_GCLC T allele, together with hypertension and male sex, is associated with cardiovascular events in our study population. 18035085_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18066575_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18276794_Glutamate cysteine ligase iz induced by hydroxynonenal through the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway in respiratory epithelium. 18420959_GCLC is a novel susceptibility gene for low level of lung function in copd 18420959_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18549827_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18549827_decreasing trend of GCL activity was observed in the order of 7/7>7/9>9/9 (P=0.04) 18560528_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18926903_results support the functional importance of insulin in Nrf2-dependent transcriptional upregulation of GCLc in GSH recovery during oxidative challenge and suggest a possible role for hypoglycemia in promoting insulin-mediated GCLc upregulation 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19041695_study of consequences of impaired glutathione synthesis, due to GAG trinucleotide repeat polymorphism in catalytic subunit of glutamate cysteine ligase, on regulation of the proteome; findings show altered proteome reaction in response to oxidative stress 19347979_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19515364_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19567187_PD98059 and erythromycin could block AP-1 transduction pathway, but increase the synthesis of gamma-GCS induced by 4-hydroxynonenal in bronchial epithelial cells. 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19817962_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19817962_Polymorphisms of glutamate-cystein ligase and microsomal triglyceride transfer protein genes may be associated with non-alcoholic liver disease progression. 20180881_Regulation of GCL(cat) by MYCN accounts for the survival of neuroblastoma cells against oxidative damage; GCL should be considered a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma. 20200426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20615707_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20655259_An ethnic-specific polymorphism in the catalytic subunit of glutamate-cysteine ligase impairs the production of glutathione intermediates in vitro. 20655259_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20659789_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673128_high-risk glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit GAG trinucleotide repeat genotypes lead to alterations of plasma thiols levels that reflect a dysregulation of redox control 20689807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20712757_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20732852_Data show that activation of the PPARgamma/PGC-1alpha pathway may protect against COPD progression by upregulating gamma-GCS and relieving oxidative stress. 20970495_Posttranslational modification and regulation of glutamate-cysteine ligase by the alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehyde 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. 21105962_SNPs not associted with schizophrenia in Japanese individuals 21156206_These results provide evidence that interaction of the two variations can efficiently impair GCLC expression and thus suggest its involvement in the pathogenesis of diseases related to GSH metabolism. 21277635_SNPs not associated with self-reported depression 21438662_the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) -129C/T (rs17883901) in glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC) and SNPs I128T (rs3816873) and Q95H (rs61733139) in microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTTP) in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease 21444626_Results suggest that GAG polymorphism affects GCLC expression via translation, and thus may be associated with altered risk for GSH-related diseases and toxicities. 21555518_GCLC is a target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq analysis in HEK 293 cells. 21657237_The impacts of four clinical missense mutations on GCLC enzymatic function in vivo and in vitro, was evaluated. 21871559_insulin increased GCLc promoter activity, which required a prerequisite increase or decrease in medium glucose 21962117_The functional SNPs CYBA -675 T --> A and GCLC rs17883901, probably associated with cellular redox imbalances, modulate the risk for renal disease in the studied population of type 1 diabetes patients 22249522_Data show for the first time that GCLC may serve a dual role, as a surrogate marker for cellular redox state as well as malignant potential of melanoma cells. 22452920_Data suggest that microRNA/mRNA pairs in hsa-miR-140-3p/RAD51AP1/, hsa-miR-145/E2F3, hsa-miR-139-5p/TOP2A, and hsa-miR-133a/GCLC were correlated with ovarian tumorigenesis. 22610501_A functional trinucleotide repeat polymorphism in the 5'-untranslated region of the glutathione biosynthetic gene GCLC is associated with increased risk for lung and aerodigestive tract cancers. 22824134_rs761142 in GCLC was found to be associated with reduced GCLC mRNA expression and with SMX-induced hypersensitivity in HIV/AIDS patients. 23255485_Genistein up-regulated HO-1 and Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase expression through the EKR1/2 and PKC /Nrf2 pathways during oxidative stress. 23443115_The Kaplan-Meier analysis shows that rs3736729 on GCLC presents a significant association with disease-free survival and overall survival. 23448276_These data strongly indicate a discrepancy between the regulation of GCLC and of GGT following the oxidative stress situation due to mitochondrial uncoupling. 23758905_Polymorphisms in GCLC, GSTM1, GSTT1, and GSTP1 genes associated with metabolism of glutathione act on cystic fibrosis severity. 23770363_1,25 (OH) vitamin D significantly upregulated expression of GCLC and GR and lowered secretion of IL-8 and MCP-1 in high-glucose exposed U937 monocytes. 24068433_the CYP1A1 (rs2606345, rs4646903, rs1048943), GCLC, AGT, and AGTR1 genes was associated with pleuritis, empyema, acute respiratory distress syndrome, all PC and acute respiratory failure (ARF). 24665821_H2S upregulates GCLC and GSH and inhibits IL-1beta levels, which may be what mediates the beneficial effects of H2S-rich compounds in mitigating the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome and atherosclerosis 25353619_miR-433 targets both catalytic (GCLc) and regulatory (GCLm) subunits of GCL. 26059756_GCLC and GSS were expressed at higher levels in colon cancer tissue, as compared with normal mucosa. 26087411_Cigarette smoke-induced hypermethylation of the GCLC promoter is related to the initiation and progression of COPD. 26365678_Data suggest expression of hepatocyte GCLC and GCLM can be regulated by dietary component; alpha-lipoic acid, a vitamin B complex nutrient, protects against oxidative stress/cytotoxicity induced by cadmium via restoration of GCLC and GCLM expression. 26520442_Glutaminolysis is activated in ES2 and OVCAR3, though ES2 exclusively synthesizes amino acids and GSH. ES2 cells are more resistant to carboplatin than OVCAR3 and the abrogation of GSH production by BSO sensitizes ES2 to carboplatin. HNF1beta regulates the expression of GCLC, but not GCLM, and consequently GSH production in ES2 26894974_High GCLC expression is associated with chemotherapy resistance in breast cancer. 27069063_GCLC polymorphisms correlated with brain GSH and Glu levels in psychosis. 27117941_(i) melatonin counteracted UVR-induced alterations in the ATP synthesis and reduced free radical formation; (ii) melatonin induced the translocation of Nrf2 transcription factor from the cytosol into the nucleus resulting in, (iii) melatonin enhanced gene expression of phase-2 antioxidative enzymes including gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase (gamma-GCS), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), and NADPH: quinone dehydrogenase-1 (NQO1... 28103909_A panel consisting of IGFBP1, KIM1, GCLC and GSTM1 genes could be used in combination for early screening of CKDu, whereas these genes in addition with FN1, IGFBP3 and KLK1 could be used to monitor progression of CKDu. The regulation of these genes has to be studied on larger populations to validate their efficiency for further clinical use. 28185919_Knockdown of CD44 reduced the protein level of xCT, a cystine transporter, and increased oxidative stress. However, an increase in GSH was also observed and was associated with enhanced chemoresistance in CD44-knockdown cells. Increased GSH was mediated by the Nrf2/AP-1-induced upregulation of GCLC, a subunit of the enzyme catalyzing GSH synthesis 28265008_Taken together, our findings provide evidence that G9a protects head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC)cells against chemotherapy by increasing the synthesis of GSH, and imply G9a as a promising target for overcoming cisplatin resistance in HNSCC 28411284_NQO1 and GCLC were both functionally sufficient to autonomously confer a tamoxifen-resistant metabolic phenotype, characterized by i) increased mitochondrial biogenesis, ii) increased ATP production and iii) reduced glutathione levels. 28457937_The findings indicate that expression of the transcription factor NRF2 and its effector GCL are both profoundly deregulated in endometriotic lesions towards increased growth and fibrogenetic processes. 28993271_Glutathione biosynthesis during the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in THP-1 macrophages is tightly and differentially regulated via GCLC and GCLM subunits of glutamate cysteine ligase. 29023060_Study found that the frequency of C/T polymorphism genotype of GCLC gene in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis is 36.4%. 29039508_the present study demonstrated that cells transformed by chronic exposure to 3MC exhibited inhibition of GSH biosynthesis by suppression of GCL protein expression and reduction of cysteine availability, which may subsequently render cells vulnerable to oxidative stress. 29474642_High expression of GCLC in tumor tissue may be a potential predictor of treatment failure. 29549912_gamma-GCS has a role in chemo- and radio-resistance of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells 30959073_Results provide evidence that the functional SNPs rs17883901 in GCLC and rs713041 in GPX4 modulate the risk for diabetic retinopathy in the studied population of type 1 diabetes individuals, widening the spectrum of candidate genes for this complication. 32054366_Genetic susceptibility analysis of GCLC rs17883901 polymorphism to preeclampsia in Chinese Han women. 32715377_Genetic variants in glutamate cysteine ligase confer protection against type 2 diabetes. 33357455_Non-canonical Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase Activity Protects against Ferroptosis. 34642912_Association of Polymorphisms of Glutamate Cysteine Ligase Genes GCLC C-129 T and GCLM C-588 T with Risk of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Chinese Women. 35386070_Genetic variation at the catalytic subunit of glutamate cysteine ligase contributes to the susceptibility to sporadic colorectal cancer: a pilot study. 36359768_Ferroptosis-Related Gene GCLC Is a Novel Prognostic Molecular and Correlates with Immune Infiltrates in Lung Adenocarcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000032350 | Gclc | 481.555634 | 0.490820384 | -1.026733 | 0.28804986 | 12.444720 | 0.0004191750687125748932489177622784382037934847176074981689453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0035994797453244940094174708633545378688722848892211914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 320.0610522 | 72.7373869 | 655.3614236 | 148.1584591 |
| ENSG00000001617 | 6405 | SEMA3F | protein_coding | Q13275 | FUNCTION: May play a role in cell motility and cell adhesion. | Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | This gene encodes a member of the semaphorin III family of secreted signaling proteins that are involved in axon guidance during neuronal development. The encoded protein contains an N-terminal Sema domain, an immunoglobulin loop and a C-terminal basic domain. This gene is expressed by the endothelial cells where it was found to act in an autocrine fashion to induce apoptosis, inhibit cell proliferation and survival, and function as an anti-tumorigenic agent. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. | hsa:6405; | extracellular space [GO:0005615]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; chemorepellent activity [GO:0045499]; semaphorin receptor binding [GO:0030215]; axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048846]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; branchiomotor neuron axon guidance [GO:0021785]; facial nerve structural organization [GO:0021612]; negative chemotaxis [GO:0050919]; negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048843]; nerve development [GO:0021675]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; neural crest cell migration involved in autonomic nervous system development [GO:1901166]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; regulation of postsynapse organization [GO:0099175]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway [GO:0071526]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway involved in axon guidance [GO:1902287]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway involved in neuron projection guidance [GO:1902285]; sympathetic ganglion development [GO:0061549]; sympathetic neuron projection extension [GO:0097490]; sympathetic neuron projection guidance [GO:0097491]; trigeminal nerve structural organization [GO:0021637]; ventral trunk neural crest cell migration [GO:0036486] | 12659673_SEMA3F and VEGF have antagonistic actions affecting motility in primary tumor cell 15520858_SEMA3F is a potent metastasis inhibitor that targets both tumor and stromal cells 15967098_SEMA3F suppresses lung neoplasm progression in an experimental model 17308083_Results suggest that p53 negatively regulates tumor vessel formation and cell growth via the SEMA3F-NRP2 pathway. 17569671_combinations of sema3A and sema3F may be able to inhibit tumor angiogenesis more effectively than single semaphorins. 17693432_Semaphorin 3F mRNA forms a G quartet-containing structure, which is recognized with high affinity and specificity by the RGG box domain of the fragile X mental retardation protein. 18476556_Transient SEMA-3F gene transfection may inhibit the proliferation of Tca8113 cells. 18660502_ABL2/ARG is a novel mediator of SEMA3F-induced RhoA inactivation and collapsing activity. 18818766_Sema3F inhibits tumor development from MDA-MB-435 and MDA-MB-231 and but not MCF-7 or MDA-MB-68 cancer cells. It inhibits tumor angiogenesis in all of the formed tumors. The inhibition is correlated with the expression of neuropilins of the tumors cells. 19177200_SEMA3F loss was associated with changes in cell signaling: increased phospho-AKT in normoxia and hypoxia-induced factor 1alpha protein. Exogenous addition of SEMA3F could modulate ZEB-1-induced angiogenesis in a chorioallantoic membrane assay. 19657188_Semaphorin3F reverses Multicellular resistance by regulating alpha(v)beta3 19683737_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19683737_These data indicate that polymorphisms in SEMA3F are associated with prostate cancer risk and poor prognosis in Hispanic and nonHispanic white men 19790074_Soluble neuropilin-2Fc did not inhibit repulsion but increased the repellent effect of semaphorin 3F. 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20036365_SEMA3F, CLEC16A, LAMA3, and PCSK2 variants have roles in myocardial infarction in Japanese individuals 20124444_semaphorin-3B and semaphorin-3F have roles in ovarian cancer 20198310_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20388805_Metastatic tumor cells overexpress c-myc, leading to upregulation of Id2 expression; the aberrantly elevated amount of Id2 represses SEMA3F expression and, as a consequence, enhances the ability of tumor cells to migrate and invade. 21349996_Endogenous SEMA3F acts as a suppressor of the growth and metastasis of human colorectal cancer cells. 21610314_It was concluded that hypoxia regulates VEGF and SE MA3F activities through transcriptional repression of their common receptor NRP2, providing a novel mechanism by which hypoxia induces tumor angiogenesis, growth and metastasis. 22093159_This study demonstrated a marked loss of noradrenergic and sensory nerve fibers in polyp mucosa, which was associated with a strong increase of semaphorin 3F and 3A. 22350413_showed that transcription of SEMA3F is directly regulated by RORalpha 22431917_we found that merlin regulated expression of SEMA3F through Rho GTPase family member Rac1 23603393_A functional role for Semaphorin 3F in the outer retina where it acts as a vasorepulsive cue to maintain physiologic avascularity. 24079887_Data suggest that SEMA3F C-terminal domain exhibits high-affinity binding of neuropilin-1 (NRP1; thus inhibiting binding of vascular endothelial growth factor A to NRP1); this interaction may be involved in anti-angiogenic activity of SEMA3F. 25068647_Data indicate that semaphorin 3F (SEMA3F) and its receptor neuropilin-2 (NRP2) are expressed in the thymus. 25529012_Our findings demonstrate the ability of SEMA3F to inhibit the stemness of human CRC cells by suppressing Rac1 activation, which suggests a novel therapeutic approach for colorectal cancer 25866254_SEMA3F functions as a suppressor of colorectal cancer metastasis by down-regulating the ASCL2-CXCR4 signaling axis. 25952650_SEMA3F may represent an antilymphangiogenic metastasis suppressor gene widely lost during cancer progression, hence serving as a prognostic biomarker and an attractive target for therapeutic intervention to halt metastasis. 26086095_Infantile hemangioma-derived stem cells and endothelial cells are inhibited by SEMA3E and SEMA3F. 26156437_SEMA3F-NRP2 interactions inhibit intracellular PI-3K activity, mTORC2-dependent signaling, RhoA activity and cytoskeletal stress fiber formation. 26447612_Study demonstrates an anti-tumoral role of SEMA3F in ileal NETs. We thus suggest that SEMA3F and/or its cellular signaling pathway could represent a target for ileal NET therapy. 26722466_SEMA3F was downregulated in colorectal cancer tissues as compared to matched adjacent non-tumor tissues 26784191_A new SEMA3F transcript is expressed in all breast cell lines and breast cancer biopsies, and is translated into a new semaphorin 3F isoform. 27558236_in situ hybridization analysis revealed that Sema 3C and Sema 3F are expressed at the RNA level in the endometriosis affected peritoneum 28350837_Semaphorin 3F placenta tissue expression was significantly reduced in preeclampsia. In addition, semaphorin 3F level at delivery was significantly lower in serum, amniotic fluid and venous umbilical blood of preeclamptic patients compared with normal pregnant women. 28698137_There is a positive association between the expression of AKAP12 and Semaphorin 3F in prostate cancer, suggesting that the activation of Semaphorin 3F by AKAP12 may be involved in prostate cancer progression and metastasis. 29299034_SEMA3F plays a role as a tumor suppressor in Oral squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion. 30663199_Familial chronic megacolon appears to be associated with SEMA3F, which is associated with genes impacting enteric nerve or pacemaker function. 31420803_SEMA 3F is recommended as an important therapeutic agent for the prevention of pathological angiogenesis. SEMA 3F may offer an effective and efficient anti-angiogenic intervention that can be administered at a lower dose alternative to typical VEGF blocking agents. 31563162_The level of SEMA3F was significantly higher in normal prostate tissues compared with that in prostate cancer cells. 31968181_SEMA3F was significantly upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue and was associated with poor survival. SEMA3F promoted hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by activating focal adhesion pathway. 32098168_Endothelial Semaphorin 3F Maintains Endothelial Barrier Function and Inhibits Monocyte Migration. 32191647_Semaphorin 3F signaling actively retains neutrophils at sites of inflammation. 32441221_Semaphorin 3F Serves as a Tumor Suppressor in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and is Associated With Lymph Node Metastasis in Disease Progression. 33595613_Semaphorin 3fa Controls Ocular Vascularization From the Embryo Through to the Adult. 33856648_Semaphorin3F Drives Dendritic Spine Pruning Through Rho-GTPase Signaling. | ENSMUSG00000034684 | Sema3f | 16.990851 | 0.400111159 | -1.321527 | 0.43792276 | 9.205744 | 0.0024125686637045543406210335035666503245010972023010253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0158436668863377004556891591846579103730618953704833984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 10.2437116 | 2.8310300 | 25.4873406 | 6.2323558 | |
| ENSG00000005059 | 55013 | MCUB | protein_coding | Q9NWR8 | FUNCTION: Negatively regulates the activity of MCU, the mitochondrial inner membrane calcium uniporter, and thereby modulates calcium uptake into the mitochondrion. Does not form functional calcium channels by itself. Mitochondrial calcium homeostasis plays key roles in cellular physiology and regulates cell bioenergetics, cytoplasmic calcium signals and activation of cell death pathways. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q810S1}. | Calcium;Calcium transport;Coiled coil;Ion transport;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | Predicted to enable calcium channel inhibitor activity. Predicted to be involved in calcium import into the mitochondrion and mitochondrial calcium ion homeostasis. Located in mitochondrion and nucleoplasm. Is integral component of mitochondrial inner membrane. Part of uniplex complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:55013; | calcium channel complex [GO:0034704]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; uniplex complex [GO:1990246]; calcium channel inhibitor activity [GO:0019855]; calcium import into the mitochondrion [GO:0036444]; mitochondrial calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0051560]; mitochondrial calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0006851] | 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20332099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24231807_MCUb (also known as CCDC109b) is a paralogue of MCU (CCDC109a). MCUb physically resides within the mitochondrial uniporter complex (uniplex), which consists of the MCU, MCUb, EMRE, MICU1, and MICU2. 28754121_This study elucidated a role for CCDC109B as an oncogene and a prognostic marker in human gliomas. 31533452_MCUB-dependent changes in mitochondrial calcium uniporter stoichiometry are a prominent regulatory mechanism to modulate mitochondrial Ca(2+) uptake and cardiac myocyte cellular physiology. | ENSMUSG00000027994 | Mcub | 72.117498 | 3.534632763 | 1.821560 | 0.26923719 | 44.484617 | 0.0000000000256363651357329876864498086359704133452286356487093144096434116363525390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000008224804484372317353618028026353021370242757370760955382138490676879882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 109.5501442 | 17.3022370 | 31.0452269 | 5.1984248 | |
| ENSG00000006837 | 51265 | CDKL3 | protein_coding | Q8IVW4 | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of cyclin-dependent protein kinase (CDK) family. CDK family members are highly similar to the gene products of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cdc28, and Schizosaccharomyces pombe cdc2, and are known to be important regulators of cell cycle progression. This gene was identified as a gene absent in leukemic patients with chromosome 5q deletion. This loss may be an important determinant of dysmyelopoiesis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:51265; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004693]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; dendrite extension [GO:0097484]; negative regulation of axon extension [GO:0030517]; positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0050775]; protein modification process [GO:0036211]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468] | 12927787_NKIAMRE is a member of a conserved family of kinases with homology to both MAP kinases and cyclin-dependent kinases 17945021_cdkl3 transfected in anchorage-independent (suspension) HeLa cells overexpressed relative to attached cells and lead to elevated proliferation and faster transition G0/G1 phases to S phase relative to controls. Same in two HEK-293 and a CHO cell lines. 18412109_data suggest that the CDKL3 gene is a strong candidate for nonsyndromal autosomal dominant mild mental retardation 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 32234750_CDKL3 promotes osteosarcoma progression by activating Akt/PKB. 33232736_CircTP53 promotes colorectal cancer by acting as a miR-876-3p sponge to increase cyclin-dependent kinase-like 3 expression. 34097336_Identification of CDKL3 as a critical regulator in development of glioma through regulating RRM2 and the JNK signaling pathway. 34329837_Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-secreted exosomal microRNA-205-5p exerts inhibitory effect on the progression of liver cancer through regulating CDKL3. 34427098_Cyclin-dependent kinase like 3 promotes triple-negative breast cancer progression via inhibiting the p53 signaling pathway. | ENSMUSG00000020389 | Cdkl3 | 25.155900 | 0.087494992 | -3.514656 | 0.41807554 | 67.239689 | 0.0000000000000002404249551503615873184308547776017218685512023823580562975621432997286319732666015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000128853037266025203178022929658463169865937952493495366468323481967672705650329589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 3.6937963 | 2.0332761 | 41.5028586 | 22.5823427 | ||
| ENSG00000008086 | 6792 | CDKL5 | protein_coding | O76039 | FUNCTION: Mediates phosphorylation of MECP2 (PubMed:15917271, PubMed:16935860). May regulate ciliogenesis (PubMed:29420175). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15917271, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16935860, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29420175}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Intellectual disability;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase | This gene is a member of Ser/Thr protein kinase family and encodes a phosphorylated protein with protein kinase activity. Mutations in this gene have been associated with X-linked infantile spasm syndrome (ISSX), also known as X-linked West syndrome, and Rett syndrome (RTT). Alternate transcriptional splice variants have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:6792; | centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; ciliary tip [GO:0097542]; dendrite cytoplasm [GO:0032839]; dendritic growth cone [GO:0044294]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004693]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; positive regulation of axon extension [GO:0045773]; positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0050775]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of cilium assembly [GO:1902017]; regulation of dendrite development [GO:0050773]; regulation of postsynapse organization [GO:0099175] | 15492925_CDKL5 mutations are associated with epilepsy, X-linked mental retardation and a clinical phenotype that overlaps Rett syndrome. 15635068_A proportion of Rett syndrome atypical cases may result from mutations in CDKL5. (review) 15917271_demonstrate that MeCP2 and CDKL5 interact both in vivo and in vitro and that CDKL5 is indeed a kinase, which is able to phosphorylate itself and to mediate MeCP2 phosphorylation 16015284_novel pathogenic CDKL5 mutations were identified in three girls, two of whom had initially been diagnosed with the early onset seizure variant of Rett Syndrome (RTT) and the other with early onset seizures and some features of RTT 16326141_Patients with the CDKL5 mutation have an early onset, epileptic encephalopathy in infancy that evolves into myoclonic seizures in childhood with a unique EEG pattern. 16611748_CDKL5 mutations are a significant cause of infantile spasms and early epileptic seizures in female patients, and of a later intractable seizure disorder, irrespective of whether they have suspected Rett syndrome. 16611748_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16935860_CDKL5 phosphorylation is required for its entrance into the nucleus whereas a portion of the COOH-terminal domain is responsible for a stable residency in this cellular compartment probably through protein-protein interactions 17049193_The observation of this study and review of the literature suggest that a broader polymorphic electroclinical pattern with both generalized and focal seizures may occur in patients with CDKL5 mutations. 17089071_CDKL5 mutations may a rare cause of Rett syndrome. 17089071_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17993579_screened entire coding region of CDKL5 in 151 affected girls with a heterogeneous phenotype ranging from encephalopathy with epilepsy to atypical Rett syndrome, and identified 3 novel missense mutations in catalytic domain Ala40Val, Arg65Gln, Leu220Pro 18063413_clinical features & electroencephalographic findings of 2 patients affected by a previously unreported CDKL5 mutation; both manifest Hanefeld variant Rett syndrome & had early-onset seizures, hand stereotypies, congenital psychomotor delay & hypotonia 18266744_Epileptic phenotype in CDKL5 mutations, and a potential relationship between the phenotype and the genotype. 18701457_CDKL5 expression is modulated during neuronal development and its subcellular distribution is tightly regulated by the C-terminal tail 18790821_18 different mutations (7 novel ones) were identified in 20 unrelated girls. These mutations were identified in eight patients with encephalopathy with RTT-like features, five with infantile spasms and seven with encephalopathy with refractory epilepsy. 18809835_CDKL5 gene mutations may represent a cause of severe or profound mental retardation and early-onset intractable seizures, also in boys. 19241098_Results describe the correlation of genotype and phenotype in CDKL5 mutated female carriers. 19428276_a novel p.Arg970X mutation in the last exon of the CDKL5 gene resulting in late onset seizure disorder. 19471977_Data demonstrate the first instance of genomic deletion as the molecular basis of CDKL5 deficiency in females. 19552836_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19564592_We report CDKL5 mutations in boys with severe encephalopathy and early-onset intractable epilepsy. 19734009_CDKL5 mutations are not responsible for early onset severe myoclonic epilepsy in infancy 19740913_CDKL5 is involved in pre-mRNA processing, by controlling splicing factor dynamics. 19780792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19780792_We found CDKL5 mutations in 8.2% (4 of 49) of patients and genomic deletions in 8.2% (4 of 49). Overall, abnormalities of the CDKL5 gene accounted for 16.3% (8 of 49) of patients. 19793311_The CDKL5 mutation rate is high (28%) in women with early-onset seizures and infantile spasms. 20397747_seven polymorphic variations and four de novo mutations of the CDKL5 gene were identified, and in all instances of the latter the clinical phenotype was that of an epileptic encephalopathy. 20493745_Two patients (one female, one male) with CDKL5 mutations have epileptic spasms after tonic seizures but never present infantile spasms as the main seizure type or hypsarrhythmia in electroencephalography. 20513142_Data indicate that MEF2C missense de novo mutations in severe mental retardation showed diminished MECP2 and CDKL5 expression. 20602487_CDKL5 mutation is associated with epileptic encephalopathy. 20728410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21107515_CDKL5 deficit may induce changes in synaptic plasticity in the patient's brain. 21124335_CDKL5 exon 16b should now be considered in the genetic screening of patients presenting with a CDKL5-related disease profile. 21293276_We report the first case of an exonic deletion of CDKL5 in a male and emphasize the importance of underappreciated mosaic exonic copy number variation in patients with early-onset seizures and RTT-like features of both genders. 21309761_Infants with CDKL5-related early epileptic encephalopathy can present in the first year of life with an unusual. 21318334_A novel CDKL5 exon and pathogenic mutations in patients with severe mental retardation, early-onset seizures and Rett-like features. 21502606_the distinctive hypermotor-tonic-spasms sequence is a feature of CDKL5 epileptic encephalopathy. 21750574_female CDKL5-mutated iPSCs maintain X-chromosome inactivation and clones express either the mutant CDKL5 allele or the wild-type allele that serve as an ideal experimental control. 21765152_This study present clinical phenotype of 5 girls having a mutation in the CDKL5 gene 21770923_mutations in early onset epileptic encephalopathy 21775177_A novel CDKL5 mutation is identified in an ambulatory girl who had severe mental retardation and multiple types of seizures without Rett-like features. 22264704_sought to determine the historic, clinical, and prognostic features of epilepsy secondary to CDKL5 mutations. all children developed infantile spasms. All children demonstrated developmental delay and visual impairment. 22430159_The patients with clinical features of Rett syndrome, with epileptic encephalopathy before 6 months of age, regardless the presence of genetic abnormalities (mutations in MeCP2 or CDKL5 or both) or even in their absence. 22678952_Recurrent mutations in the CDKL5 gene in patients with epileptic encephalopathies can be associated with either a milder or a more severe phenotype. 22779007_This review surveys the current state of CDKL5 research with emphasis on the clinical symptoms associated with mutations in CDKL5, the different mechanisms regulating its functions, and the connected molecular pathways. 22832775_CDKL5 mutations cause severe epilepsy in infancy with subsequent epileptic encephalopathy. 22867051_The importance of CDKL5 mutations as etiological factors in neurodevelopmental disorders was shown. The CDKL5 gene sequence and its rearrangements should be thoroughly analyzed in females with Rett syndrome, severe encephalopathy and epilepsy. 22921766_a functional axis between MYCN and CDKL5 governing both neuron proliferation rate and differentiation. 22922712_CDKL5 is localized at excitatory synapses and contributes to correct dendritic spine structure and synapse activity. 23064044_Identification of eleven novel sequence variations including four pathogenic mutations in the CDKL5 gene. 23151060_study examines the presence of breathing and sleep abnormalities in a small series of patients with CDKL5 mutations 23242510_3 known & 3 new (V966Im A1911V, H589H)mutations in the C-terminal domain of CDKL5 were found in Indian patients with Rett syndrome negative for MECP2. 23583054_aberrations of CDKL5 and ARX combined are an important consideration in the genetic forms of early-onset epilepsy in boys 23756444_CDKL5 gene is not useful in practical molecular diagnosis of atypical Rett syndrome. 23828526_study described the clinical condition and characterization of two first Brazilian patients with CDKL5 mutations, including the first Brazilian case of atypical Rett related to abnormalities in this gene 24564546_Mutations in the CDKL5 gene associtaed with Hanefield variants of Rett syndrome and early-onset epileptic encephalopathies. 24738188_Its mutation causes Rett syndrome.(review) 25266480_CDKL5 gene mutations accounted for 5.4% of boys with early onset epileptic encephalopathy 25315662_Data suggest that the increased dosage of cyclin dependent kinase like 5 protein(CDKL5) might have affected interactions of this kinase with its substrates, leading to perturbation of neurodevelopmental and neurobehavioral abnormalities. 25762588_study presents the genotype of 2 sisters, a CDKL5 mutation c. 283-3_290del, but different phenotype 25864828_It was indicated that CDKL5 controls excitatory synaptic transmission and the conditions associated with CDKL5 deviation in man indicates synaptic abnormalities. 26239053_Rett syndrome with early epilepsy and the congenital variant are mainly due to variations in the CDKL5 and FOXG1 genes, respectively 26701947_Mutations in exon 8 of cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 gene were determined to be disease-causing in epileptic encephalopathy. 27062609_In the asymptomatic mother, the mutated copy of the CDKL5 gene was inactivated in 90% of blood cells. We also identified a premature stop codon (p.Arg926*) in IQSEC2 in a patient with a Rett-like phenotype. Finally, exome sequencing enabled us to characterize a heterozygous de novo missense (p.Val408Ala) in KCNA2 in a girl with infantile-onset seizures variant of Rett syndrome (RTT) 27171548_The genetic etiology of Rett syndrome (RTT) without MECP2, CDKL5, and FOXG1 mutations is heterogeneous, overlaps with other NDDs, and complicated by a high mutation burden. Dysregulation of chromatin structure and abnormal excitatory synaptic signaling may form two common pathological bases of RTT. 27265524_The results suggested the mutant CDKL5 was responsible for the Rett syndrome disease. 27315173_We have characterised the predominant brain isoform of CDKL5, a 9.7 kb transcript comprised of 18 exons with a large 6.6 kb 3'-untranslated region (UTR), which we name hCDKL5_1. In addition we describe new exonic regions and a range of novel splice and UTR isoforms 27528505_Although abilities were markedly impaired for the majority with the CDKL5 disorder, some females and a few males had better functional abilities. This variability may be related to underlying gene variants, with females with a late truncating variant having better levels of ability than those with no functional protein. 28780406_mutations in the CDKL5 gene in complex genotypes associated with West syndrome with variable phenotype 29444904_The implication that mutations in an alternative exon of CDKL5 can be clinically important should be considered when selecting appropriate genetic tests for patients suspected of having a CDKL5-related disorder. 29510241_CDKL5 truncation was identified in a case of encephalopathy manifesting transient methylmalonic acidemia. 29618004_a dramatic reduction of expression of the GluA2 subunit occurs concomitantly with its hyper-phosphorylation on Serine 880 and increased ubiquitination. Consequently, Cdkl5 silencing skews the composition of membrane-inserted AMPA-Rs towards the GluA2-lacking calcium-permeable form 30266825_These data reveal the first cellular substrates of CDKL5, which may represent important biomarkers in the diagnosis and treatment of CDKL5 disorder, and illuminate the functions of this poorly characterized kinase. 30377159_new consensus for evaluating CDKL5/STK9-dependent signalling mechanisms. 30378547_diaper changing-induced reflex seizures as one of the presenting features in a case of CDKL5-related epilepsy 30561084_Twenty-five parents of individuals registered in the International CDKL5 Disorder Database participated in semi-structured telephone interviews to explore areas that supported or challenged their child's QOL 30928302_Pathogenic variants include deletions, truncations, splice variants, and missense variants. Pathogenic missense variants occur exclusively within the kinase domain or affect splice sites. The CDKL5 protein is widely expressed in the brain, predominantly in neurons, with roles in cell proliferation, neuronal migration, axonal outgrowth, dendritic morphogenesis, and synapse development. Review. 30929312_CDKL5 is a gene identified as causative genes in atypical forms of Rett syndrome. 31108505_we showed that selective cortical deletion of CDKL5 from excitatory cells is sufficient to produce abnormalities of visual cortical responses, demonstrating that the normal function of cortical circuits is dependent on CDKL5. 31225800_that CDKL5 mutations likely play a direct role in psychomotor development, whereas epilepsy is one of the clinical features associated with this complex disorder 31717404_the evolution and molecular features of MeCP2, CDKL5, and FOXG1 and their binding partners, were analyzed. 31858726_CDKL5 promotes proliferation, migration, and chemotherapeutic drug resistance of glioma cells via activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. 31925439_Targeting of CDKL5 promoter causes significant reactivation of the inactive allele affected by X chromosome inactivation; this change is associated with removal of methyl groups from CpG dinucleotides. 31942678_Progressive EEG Changes in CDKL-5 Related Epileptic Encephalopathy. 32002787_Increased DNA Damage and Apoptosis in CDKL5-Deficient Neurons. 32034940_Expanding the phenotype of the CDKL5 deficiency disorder: Are seizures mandatory? 32105570_Rett Syndrome, a Neurodevelopmental Disorder, Whole-Transcriptome, and Mitochondrial Genome Multiomics Analyses Identify Novel Variations and Disease Pathways. 32111237_Novel CDKL5 mutations were found in patients in China: retrospective investigation in cases of CDKL5-related disorders. 32125365_study provides the first evidence that gene therapy mediated by Adenovirus vectors can be used for treating CDKL5 disorder. 32445745_Unusual double mutation in MECP2 and CDKL5 genes in Rett-like syndrome: Correlation with phenotype and genes expression. 32588892_Dopaminergic loss of cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 recapitulates methylphenidate-remediable hyperlocomotion in mouse model of CDKL5 deficiency disorder. 32641489_Cyclin-dependent-like kinase 5 is required for pain signaling in human sensory neurons and mouse models. 33044867_Involvement of the CDKL5-SOX9 signaling axis in rhabdomyolysis-associated acute kidney injury. 33047306_Exploring genotype-phenotype relationships in the CDKL5 deficiency disorder using an international dataset. 33106377_Phenotypes in adult patients with Rett syndrome: results of a 13-year experience and insights into healthcare transition. 33341033_Exploring quality of life in individuals with a severe developmental and epileptic encephalopathy, CDKL5 Deficiency Disorder. 33989939_CDKL5 deficiency disorder in males: Five new variants and review of the literature. 34229227_Clinical manifestation of CDKL5 deficiency disorder and identified mutations in a cohort of Slovak patients. 35483386_CDKL5 deficiency disorder: clinical features, diagnosis, and management. 36202289_Neuronal hyperexcitability and ion channel dysfunction in CDKL5-deficiency patient iPSC-derived cortical organoids. 36417806_CDKL5 deficiency causes epileptic seizures independent of cellular mosaicism. | ENSMUSG00000031292 | Cdkl5 | 24.565060 | 0.475945573 | -1.071131 | 0.32883414 | 10.602507 | 0.0011293440680460445010857561953798722242936491966247558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0083760683053171105377776584077764709945768117904663085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 14.1191315 | 3.9382253 | 29.6523473 | 7.9349292 | |
| ENSG00000013619 | 10046 | MAMLD1 | protein_coding | Q13495 | FUNCTION: Transactivates the HES3 promoter independently of NOTCH proteins. HES3 is a non-canonical NOTCH target gene which lacks binding sites for RBPJ. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18162467}. | Activator;Alternative splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation | This gene encodes a mastermind-like domain containing protein. This protein may function as a transcriptional co-activator. Mutations in this gene are the cause of X-linked hypospadias type 2. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2010]. | hsa:10046; | centrosome [GO:0005813]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 8789451_Deletion of the F18 (MAMLD1) and MTM1 genes in two patients with congenital myopathy and hypospadias 9169146_The identification and genomic characterization of the F18 (MAMLD1) gene in human 17086185_identified three different nonsense mutations of CXorf6 in individuals with hypospadias 18162467_CXorf6 transactivates the Hes3 promoter, augments testosterone production 18635673_CXorf6 mutations are associated with isolated hypospadias of varying severity 18635673_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19339788_MAMLD1 mutations cause hypospadias primarily because of compromised testosterone production around the critical period of sex development, and provide useful information for the molecular network involved in fetal testosterone production.[review] 20347055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20347055_mutational analysis of the MAMLD1-gene in hypospadias 22479329_Data suggest that MAMLD1 should be routinely sequenced in 46,XY disorders of sex development (DSD) patients with otherwise normal AR, SRD5A2 and NR5A1 genes. 22934520_The single-nucleotide polymorphisms of MAMLD1 bear no obvious correlation with hypospadias, and MAMLD1 is not a candidate gene in its pathogenesis in the Chinese population. 23044878_MAMLD1 mutations cause 46,XY disorders of sex development primarily because of compromised testosterone production around critical period for sex development; in addition, SNP in MAMLD1 may constitute a susceptibility factor for hypospadia. [REVIEW] 25833151_These results imply that the pathogenic events resulting from MAMLD1 mutations include splice errors. 26580071_MAMLD1 sequence variations may not suffice to explain the phenotype in carriers and MAMLD1 may also have a role in adult life 26815876_occurrence of MAMDL1 gene polymorphisms, specially of c.2960C>T in 3' UTR of its exon 7 is associated with a higher risk of isolated hypospadias in Indian children, probably by lowering androgenic levels 27490115_Study provides evidence that MAMLD1 transcription is up-regulated in patients with 46,XX testicular and ovotesticular disorders of sex development. 28199199_By direct sequencing of PCR products, we assessed and found mutations that occur in 220 sporadic cases of hypospadias. The mutation p.N589S (c.1766A>G) was found at a significantly higher rate among patients with hypospadias. 30911995_Attenuation of MAMLD1 Expression Suppresses the Growth and Migratory Properties of Gonadotroph Pituitary Adenomas. 31477715_Nuclear localization of Yes associated protein 1 (YAP1)-mastermind like domain containing 1 (MAMLD1) protein is mediated by MAMLD1 and independent of YAP1-Ser127 phosphorylation. 31924698_Xq28 copy number gain causing moyamoya disease and a novel moyamoya syndrome. 32690052_Clinical and molecular spectrum of 46,XY disorders of sex development that harbour MAMLD1 variations: case series and review of literature. 33424767_Disorders of Sex Development in Individuals Harbouring MAMLD1 Variants: WES and Interactome Evidence of Oligogenic Inheritance. 34487543_[Advance in research on the role of MAMLD1 gene in disorders of sex development]. 34517852_The genomic profiling and MAMLD1 expression in human and canines with Cushing's disease. 34695834_MAMLD1 and Differences/Disorders of Sex Development: An Update. | ENSMUSG00000059401 | Mamld1 | 43.050709 | 0.357595831 | -1.483598 | 0.28545079 | 27.094086 | 0.0000001937899012894293333841741174342065967550752247916534543037414550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000036336905351696210048691604993509329801781859714537858963012695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 21.8098131 | 4.7624650 | 61.3372204 | 12.4488584 | |
| ENSG00000015568 | 84220 | RGPD5 | protein_coding | Q99666 | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat | RAN is a small GTP-binding protein of the RAS superfamily that is associated with the nuclear membrane and is thought to control a variety of cellular functions through its interactions with other proteins. This gene shares a high degree of sequence identity with RANBP2, a large RAN-binding protein localized at the cytoplasmic side of the nuclear pore complex. It is believed that this RANBP2 gene family member arose from a duplication event 3 Mb distal to RANBP2. Alternative splicing has been observed for this locus and two variants are described. Additional splicing is suggested but complete sequence for further transcripts has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:729540;hsa:84220; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear pore [GO:0005643]; NLS-bearing protein import into nucleus [GO:0006607]; regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0050790] | 191.679251 | 0.013609072 | -6.199287 | 1.23054275 | 17.019771 | 0.0000369926093676563923912103959423802734818309545516967773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0004262377428622550457580631100285017964779399335384368896484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 4.8969501 | 4.9962621 | 345.6463355 | 339.9443906 | |||||
| ENSG00000019102 | 23584 | VSIG2 | protein_coding | Q96IQ7 | Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Predicted to be located in membrane. Predicted to be integral component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:23584; | membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629] | 20659327_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) | ENSMUSG00000001943 | Vsig2 | 13.090050 | 2.463671426 | 1.300810 | 0.44131762 | 8.886275 | 0.0028732238422134923593043165368499103351496160030364990234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0182381354196147309199016461889186757616698741912841796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 18.5010141 | 2.9980032 | 7.5929063 | 1.6424262 | ||
| ENSG00000025434 | 10062 | NR1H3 | protein_coding | Q13133 | FUNCTION: Nuclear receptor that exhibits a ligand-dependent transcriptional activation activity (PubMed:19481530, PubMed:25661920). Interaction with retinoic acid receptor (RXR) shifts RXR from its role as a silent DNA-binding partner to an active ligand-binding subunit in mediating retinoid responses through target genes defined by LXRES (By similarity). LXRES are DR4-type response elements characterized by direct repeats of two similar hexanuclotide half-sites spaced by four nucleotides (By similarity). Plays an important role in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis, regulating cholesterol uptake through MYLIP-dependent ubiquitination of LDLR, VLDLR and LRP8 (PubMed:19481530). Interplays functionally with RORA for the regulation of genes involved in liver metabolism (By similarity). Induces LPCAT3-dependent phospholipid remodeling in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membranes of hepatocytes, driving SREBF1 processing and lipogenesis (By similarity). Via LPCAT3, triggers the incorporation of arachidonate into phosphatidylcholines of ER membranes, increasing membrane dynamics and enabling triacylglycerols transfer to nascent very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles. Via LPCAT3 also counteracts lipid-induced ER stress response and inflammation, likely by modulating SRC kinase membrane compartmentalization and limiting the synthesis of lipid inflammatory mediators (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z0Y9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19481530, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25661920}. | 3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the NR1 subfamily of the nuclear receptor superfamily. The NR1 family members are key regulators of macrophage function, controlling transcriptional programs involved in lipid homeostasis and inflammation. This protein is highly expressed in visceral organs, including liver, kidney and intestine. It forms a heterodimer with retinoid X receptor (RXR), and regulates expression of target genes containing retinoid response elements. Studies in mice lacking this gene suggest that it may play an important role in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. | hsa:10062; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sterol response element binding [GO:0032810]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; apoptotic cell clearance [GO:0043277]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; hormone-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0009755]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088]; mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0042789]; negative regulation of cholesterol storage [GO:0010887]; negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120163]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of lipid transport [GO:0032369]; negative regulation of macrophage activation [GO:0043031]; negative regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation [GO:0010745]; negative regulation of pancreatic juice secretion [GO:0090188]; negative regulation of pinocytosis [GO:0048550]; negative regulation of proteolysis [GO:0045861]; negative regulation of response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:1903573]; negative regulation of secretion of lysosomal enzymes [GO:0090341]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060336]; phosphatidylcholine acyl-chain remodeling [GO:0036151]; positive regulation of cholesterol efflux [GO:0010875]; positive regulation of cholesterol transport [GO:0032376]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0045723]; positive regulation of lipoprotein lipase activity [GO:0051006]; positive regulation of protein metabolic process [GO:0051247]; positive regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway [GO:0034145]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transporter activity [GO:0032411]; positive regulation of triglyceride biosynthetic process [GO:0010867]; regulation of circadian rhythm [GO:0042752]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570]; sterol homeostasis [GO:0055092]; triglyceride homeostasis [GO:0070328] | 11875109_data suggest a model in which LXR ligands trigger an autoregulatory loop leading to selective induction of hLXRalpha gene expression 12032151_studies demonstrate that activated LXR induces the expression of the apoE/C-I/C-IV/C-II gene cluster in both human and murine macrophages 12054659_Different regulation of the LXRalpha promoter activity by isoforms of CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins 12117567_interaction of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha with liver X receptor alpha antagonizes the stimulatory effect of their respective ligands on the murine cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene promoter 12161442_LXRa is regulated by fatty acids in human cells 12198243_SHP is able to interact with LXR and to modulate its transcriptional activity. 12470296_PGC-1 alpha serves as a co-activator for the liver X receptor (LXR) alpha 12932788_These data enable the identification of the amino acids that coordinate the interaction of both steroidal and non-steroidal ligands in the ligand-binding pocket of liver X receptor alpha. 12957674_hLXRalpha and hLXRgeta transactivated a reporter gene bearing a truncated FPPS promoter containing a putative direct repeat 4 (DR4) LXR response element, and direct interaction was demonstrated 14699103_LXRalpha and LXRbeta regulate transcription of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene in macrophages 15319359_unliganded TRbeta1 suppresses promoter activity driven by LXRalpha and its ligand, whereas transactivation by T3-bound TRbeta1 is not affected by LXRalpha in the presence or absence of oxysterols 15353176_LXRalpha plays an important role in the cAMP-mediated regulation of human renin gene transcription by binding to cAMP responsive element in the promoter. 15539633_LXRs are expressed and functional in primary human coronary artery smooth muscle cells; their ligands inhibit cell proliferation and neointima formation 15548517_activation of the liver X receptors (LXR) dramatically promoted lipid accumulation in vascular smooth muscle cells 15625283_In the human body, the LXRalpha protein is highly expressed in macrophage lineage cells and foam cells in atherosclerotic lesions 16054077_The beneficial effect of hepatic LXRalpha was abrogated by a synthetic LXR agonist, which activated SREBP-1c and its target genes. 16106051_liver X receptor-alpha in mouse kidney and HK-2 proximal tubular cells is downregulated by LPS and cytokines 16170053_expression of alternative LXRalpha transcripts in certain biological contexts may impact LXR signaling and lipid metabolism 16249184_LXRalpha is a negative modulator of Abcd2, acting through a novel regulatory mechanism involving overlapping SREBP and LXRalpha binding sites 16354658_competitive binding of coactivators and corepressors can explain the tissue-specific behavior of partial liver X receptor alpha and beta agonists 16482468_LXR agonists may lead to increased utilisation of lipids and glucose in muscle cells without affecting the mechanism of action of insulin. 16567856_Data demonstrate that LXR-alpha activation altered all of the cellular cholesterol fluxes. 16758300_LXR-alpha gene plays a crucial role in the regulation of innate immunity at the genomic level. 16904112_Results provide evidence that liver X receptors alpha and beta are phosphorylated proteins. 16920108_Data show that liver X receptor alpha regulates the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene, which mediates the endocytic uptake of LDL cholesterol in the liver. 16941683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16941683_in the investigated German sample, no evidence of association of ABCB11 and LXRA to gallstone susceptibility was detected. The gallstone trait is not allelic to progressive familial cholestasis at the ABCB11 locus. 16956579_myeloperoxidase is regulated by LXR and PPARalpha ligands 16973760_LXR-alpha and LXR-beta independently interfere with the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis regulation at the level of the pituitary and the adrenal gland 17108812_One LXRA single nucleotide polymorphism, rs2279238, and one common haplotype, CAAGCC, as well as two LXRB single nucleotide polymorphisms, LB44732G>A and rs2695121, were associated with obesity phenotypes. 17110595_novel mechanism of inflammatory gene regulation (C-reactive protein) by LXR ligands 17135302_ROS and NF-kappaB, but not LXR, mediate the IL-1beta-induced downregulation of ABCA1 via a novel transcriptional mechanism, which might play an important role of proinflammation in the alteration of lipid metabolism. 17217555_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17218271_These studies define parallel but functionally distinct pathways that are utilized by PPARgamma and LXRs to differentially regulate complex programs of gene expression that control immunity and homeostasis. 17255360_LXR is a potent modulator of dendritic cells maturation and function mediated in part by blocking the expression of fascin. 17272748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17296605_LXRalpha is regulated not only by oxysterol derivatives but also by PKA-mediated phosphorylation, which suggests that nutritional regulation of SREBP-1c and lipogenesis could be regulated at least partially through modulation of LXR 17391100_Results suggest that co-repression of LXR activity by RIP140 involves an atypical binding mode of RIP140 and a repression element in the RIP140 C-terminus. 17396233_These data indicate for the first time that human macrophage aP2 promoter is a direct target for the regulation by LXR/RXR heterodimers. 17405904_We show here that primary hASM cells express liver X receptor (LXR; alpha and beta subtypes), an oxysterol-activated nuclear receptor that controls expression of genes involved in lipid and cholesterol homeostasis, and inflammation. 17416342_The LXR agonist T0901317, therefore, acts as an antiandrogen in human prostate cancer cells. 17452725_Haplotype 2 associated with reduced mortality from infectious disease. Haplotype 2 also associated with higher levels of plasma apolipoprotein E, a target gene of the LXRalpha (p =.018), and higher levels of triglycerides (p =.041). 17628006_This novel insight that thyroid hormone regulates LXR-alpha mRNA levels and promoter activity should shed light on a cross talk between LXR-alpha and TR-beta1 as a new therapeutic target against dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis. 17644777_atorvastatin reduces LPL and EL expression by reducing the activation of LXRalpha and NF-kappaB, respectively 17724434_It was proposed that LXR is a key regulator of cytokine release in LPS-challenged human monocytes, possibly by interfering with translational events. 17766241_In summary, this study is the first to demonstrate anti-inflammatory actions of LXRs in the lung. 17845217_LXRalpha and LXRbeta are expresed in the majority of the cell types in human skin. 17960176_important roles of LXRalpha in differentiation and inflammatory signaling in sebaceous glands 18007013_Upregulation of ABCG5/ABCG8 in gallstone patients, possibly mediated by increased liver X receptor (LXR) alpha, may contribute to the cholesterol supersaturation of bile, a prerequisite for gallstone formation. 18024509_May modulate the bile acid biosynthetic pathway at a unique site downstream of cholesterol 7-alpha- ydroxylase (CYP7A1) and 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (AKR1C4) and may also modulate the metabolism of steroid hormones and certain xenobiotics. 18096827_Laminar flow increases LXR function via a PPARgamma-CYP27 dependent mechanism, which reveals an atheroprotective role for laminar flow exerting on endothelium. 18182682_review of role of activation of PPARalpha, -beta/delta, or -gamma or LXRs in skin physiology and cytology and disease 18209740_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18209740_results suggest that NR1H3 plays an important role in the HDL-cholesterol metabolism and in the genetic susceptibility to metabolic syndrome. 18250151_reveal a previously unrecognized role for phosphorylation in restricting the repertoire of LXRalpha-responsive genes 18276933_LXR (as a heterodimer with the retinoid X receptor) is able to bind the ENG promoter on an LXR response element and mediates the activation of ENG gene expression by LXRalpha in JAR cells. 18327405_CRP modulates the expression of genes that contribute to both pro- and anti-inflammatory responses in human monocytes. Among these novel anti-inflammatory effects, we show clearly that CRP activates the LXRalpha pathway. 18372238_Protein kinase C alpha modulates liver X receptor alpha transactivation. 18511497_These data identify Rev-erbalpha as a new LXR target gene, inhibiting LXR-induction of TLR-4 in a negative transcriptional feedback loop, but not cholesterol homeostasis gene expression. 18562803_FXRalpha down-regulates CETP gene expression via binding to the DR4RE sequence within the CETP 5' promoter and this FXRalpha binding is essential for FXRalpha inhibition of LXRalpha-induced CETP expression. 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18669643_Data show that, at sufficiently high concentration, the NR corepressor (NCoR) influences the activity of the liver X receptor (LXR) even in the presence of a potent full agonist that destabilizes NCoR binding. 18789440_IFN-gamma down-regulates ABCA1 expression by inhibiting LXRalpha in a JAK/STAT signaling pathway-dependent manner 18854425_25-Hydroxycholesterol-3-sulfate regulates macrophage lipid metabolism via the LXR/SREBP-1 signaling pathway. 19060910_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19105208_mediates HBV-associated hepatic steatosis 19119143_Suppression of 2,3-oxidosqualene cyclase by high fat diet contributes to liver X receptor-alpha-mediated improvement of hepatic lipid profile. 19164445_Data suggest that LXR ligands prevent LXRalpha from ubiquitination and degradation by detaching BARD1/BRCA1, which may be critical for early transactivation of ligand-stimulated LXRalpha through binding of LXRalpha to the promoters of target genes. 19201410_PPARg, PPARd and LXRa are involved in the regulation of ABCA1 expression and HDL biogenesis in a cooperative signal transduction pathway 19211025_The present study was directed to explore the functional genomics of LXR-alpha gene within blood mononuclear cells of subjects suffering from coronary heart disease (CHD). 19261092_the inhibitory activity of liver X receptor alpha, ATP-binding cassette transporter and macrophage scavenger receptor A by LPS may be related to the transformation of human macrophages into foam cells. 19292929_Common genetic variation in LXRA is unlikely to affect the risk of developing type 2 diabetes or quantitative phenotypes related to glucose homeostasis 19292929_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19360318_Cholesterol synthesis was activated in NAFLD liver, meaning that cholesterol metabolism is dysregulated in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. 19366697_A mechanism for LXRalpha in controlling the gene expression of LGK that involves activation through SREBP-1c and PPARgamma and inhibition through SHP, is proposed. 19380774_Liver X receptors alpha and beta are constitutively expressed and functional in human B cells. 19426978_LXR-activating oxysterols induce the expression of inflammatory markers in endothelial cells through LXR-independent mechanisms. 19481530_Data describe the requirement of GPS2 for ABCG1 gene transcription and cholesterol efflux from macrophages, and implicate GPS2 in facilitating LXRalpha/beta recruitment to an ABCG1-specific promoter/enhancer unit upon ligand activation. 19645823_The expression of LXR-alpha at both mRNA and protein level was significantly higher in perilesional skin as compared to the normal skin of vitiligo patients. 19697157_LXRbeta protein expression was unaltered in photoaged skin (p = 0.75). Our data therefore suggest that, while not playing a major role in skin aging, robust cutaneous expression implies a fundamental role for LXRbeta in epidermal biology. 19796621_Deletion of liver X receptors (Lxralpha and beta) reduced cell cycle progression and ventral midbrain neurogenesis, resulting in decreased dopaminergic neurons at birth. 19798078_LXR-alpha gene knockdown within normal human keratinocytes simulated the genomic profile observed in psoriatic skin lesions. 19837721_LXRalpha and LXRbeta control cholesterol homeostasis. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19933273_O-GlcNAcylation of LXR is a novel mechanism by which LXR acts as a glucose sensor affecting LXR-dependent gene expression, substantiating the crucial role of LXR as a nutritional sensor in lipid and glucose metabolism. 20005944_sauchinone has the capability to inhibit LXRalpha-mediated SREBP-1c induction and SREBP-1c-dependent hepatic steatosis 20037595_production in tumors inhibits functional expression of CCR7 in dendritic cells and dampens antitumor responses 20057170_results provide evidence that TGF-beta1 up-regulates expressions of ABCA1, ABCG1 and SR-BI through the LXR alpha pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells 20080977_DAX-1 acts as a novel corepressor of liver X receptor alpha and inhibits hepatic lipogenesis 20118482_activation of LXRalpha stimulates renin expression and induces mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into renin-secreting, juxtaglomerular-like cells 20139031_Data clarified the PAR-2 expression of human macrophages and suggested that tryptase might promote lipid accumulation in macrophages and foam cell formation by suppressing LXRalpha activation via PAR-2/LXRalpha/LXRalpha target genes signaling pathway. 20190811_Liver X Receptor activation downregulates AKT survival signaling in lipid rafts and induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells. 20219900_Results suggest that liver X receptors play a regulatory role in fatty acid metabolism by direct regulation of ACSL3 in human placental trophoblast cells. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20364260_LXR activation inhibits chemokine-induced migration of CD4-positive lymphocytes by reducing PI-3 kinase activity and activation of Rac-1 with subsequent inhibition of MLC phosphorylation, f-actin formation and ICAM3 translocation. 20410489_Activation of LXR alpha represents a novel lipid-signaling paradigm that alters the inflammatory response of human dendritic cells. 20494359_Indicate that LXRalpha has an essential role in the regulation of CETP expression and maintaining reverse cholesterol transport. 20506155_Data suggest that berberine abrogates the formation of foam cells by macrophages by enhancing LXRalpha-ABCA1-dependent cholesterol efflux. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20655109_Gene expression of LXRalpha was significantly decreased in placental tissues, while increased expression was observed for LXRalpha in adipose tissue, from pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. 20836841_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20837115_Results establish for the first time that LPCAT3 is specifically regulated by LXRalpha. 20855565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20868688_Data suggest the ability of FoxO1 to inhibit LXRalpha binding with the LXRE in the SREBP-1c promoter. 20945144_Data suggest LXRalpha has a role in regulation of lipid synthesis in keratinocytes; activation of LXRalpha via a ligand leads to accumulation of lipid droplets and increases expression of SREBP-1c, FAS, PPARalpha, PPARbeta, and PPARgamma. 21042792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21125317_the Liver X Receptor-alpha gene activated in cancerous cells of diverse origin results in the regulation of genes forcing these cells to enter into the state of apoptosis 21136146_elevated expression of LXRalpha may be involved in the progression of diabetic cardiomyopathy, and demethylation of LXRalpha is likely to be responsible for its increased expression in myocardial tissues. 21187453_an important role of LXRs in the coordinated regulation of lipid metabolic and inflammatory gene programs in macrophages 21245992_PXR and LXR polymorphisms, but not NF-kB or PPARgamma, may contribute to risk of IBD, especially among never smokers 21266776_This study reports a novel signaling pathway underlying liver X receptor-mediated regulation of Th17 cell differentiation and autoimmunity. 21310851_the expression of hsa-miR-613 can be transcriptionally activated by LXR-alpha 21315073_CIDEA binds to liver X receptors and regulates their activity in vitro. 21316679_Genetic polymorphisms in NR1H3 and its target genes ABCA1, APOE, CETP and LPL contribute to the genetic variance for HDL-cholesterol concentrations in adolescence. 21349840_Liver X receptor-retinoid X receptor (LXR-RXR) heterodimer cistrome reveals coordination of LXR and AP1 signaling in keratinocytes 21350215_Different regulatory activities of the liver X receptoralpha (and PPARgamma) pathways identified a distinct macrophage subpopulation with a low susceptibility to become foam cells. 21356276_we concluded that LXR-alpha/beta gene expression ratio is a critical factor to activate POMC gene expression in ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas. 21440016_This increase in hepatitis B virus transcription and replication was directed by nuclear receptor LXRalpha induction in the presence of oxysterols. 21562465_LXRA genotypes were associated with variable risk for cardiovascular outcomes and pharmacogenetic effect. 21625070_decreased expression in atherosclerotic artery macrophages infected with Chlamydia pneumoniae 21775116_The mRNA levels of LXRalpha and SREBP-1c, transcription factors that regulate SCD-1, were decreased by 10,12 conjugated linoleic acid in human adipocytes. 21889884_FGF21 gene expression was negatively regulated by LXR in HepG2 cells and mouse primary hepatocytes. 21903943_Functional genetic variation in liver X receptor alpha (LXRalpha) predicts risk of ischemic vascular disease in the general population. 21937108_RXRalpha and LXR activate two promoters in placenta- and tumor-specific expression of PLAC1. 21951066_LXR alpha/beta play a role in the regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase and alpha-synuclein expression; the extent to which the oxysterol 27-hydroxycholesterol utilizes these pathways to modulate expression levels of these two proteins is characterized. 22027013_Te results of this study suggested taht genetic variations in MMEL1, ECE1, ECE2, AGER, PLG, PLAT, NR1H3, MMP3, LRP1, TTR, NR1H2, and MMP9 genes do not play major role among the Finnish AD patient cohort. 22137263_Data suggest that expression of LXRalpha in androgen-independent prostate neoplasm cells can be regulated by dietary factors (here, the carotenoid lycopene). 22257474_LXR are involved in the metabolism and inflammation in human diseases; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is classically associated with lipid metabolic disorders and inflammatory responses. 22311022_Two genetic variants in LXRalpha independently influence the susceptibility to metabolic risk factors of polycystic ovary syndrome patients. 22367754_liver x receptors are activated by phospholipase A2 modified low density lipoproteins in human macrophages 22399489_Regulation of LXRalpha pre-mRNA splicing may be involved in the pathogenesis of LXRalpha-related diseases 22503545_PAPP-A may first down-regulate expression of LXRalpha through the IGF-1/PI3-K/Akt signaling pathway and then decrease expression of ABCA1, ABCG1, SR-B1 and cholesterol efflux in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. 22547570_Lxralpha regulates the androgen response in prostate epithelium 22569763_serum LXRa ligand oxysterol levels could be surrogate markers of insulin resistance, and high oxysterol levels in the circulation may play an important role in the development of hepatic and peripheral insulin resistance followed by NAFLD 22610535_Activation of LXR-alpha and LXR-beta Suppresses Proliferation of Human Colon Cancer Cells. 22634718_Liver X receptor regulates rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte invasiveness, matrix metalloproteinase 2 activation, interleukin-6 and CXCL10. 22641099_Studied the effect of HCV NS5A protein, core protein, and viral replication on the intracellular lipid accumulation and the LXRalpha-regulated expression of lipogenic genes. 22707265_Data suggest that taurine, a dietary component, is a direct ligand of LXR-alpha and appears to control gene expression of LXR-alpha and it's responsive genes (e.g., ATP-binding cassette transporters) in enterocytes, macrophages, and hepatocytes. 22723445_Pharmacological activation of endothelial LXRs reduces angiogenesis by restraining cholesterol-dependent vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 compartmentation and signaling. 22749359_The induction of ABCG1 and its mediated 7-ketocholesterol efflux from endothelial cells by cyanidin-3-O-beta-glucoside resulted from liver X receptor alpha activation. 22766509_Discussion of the role of LXR in orchestrating lipid homeostasis and neuroinflammation in the brain. The ability of LXR to attenuate Alzheimer disease pathology makes them potential therapeutic targets for this neurodegenerative disease. [Review Article] 22916038_An allele-specific regulatory polymorphism within NR1H3 (coding for LXR-a), rs7120118, coincides with causal SNPs for HDL-C levels associated with cardiovascular disease in Caucasian patients. 22984430_The regulation of SREBP-1c gene expression by SIRT1 may require the deacetylation of LXR transcription factors. 22990668_Activation of LXRalpha during inflammatory response may constitute an endogenous protective mechanism in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. 23018104_Activation of LXR reduced the binding of the transcriptional factors AP-1 and NF-kappaB to the ET-1 gene promoter region, thereby regulating gene expression. 23041609_LXRalpha transactivates the expression of CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 through common two cis-elements 23099324_activation of the LXR could have a beneficial, therapeutic effect in the prevention of bacterial-induced bone erosion 23163651_Higher expression of LXR-alpha in perilesional melanocytes decreases adhesion, proliferation, and matrix metalloproteinases, and increases apoptosis leading to vitiligo lesions. 23185273_Three new cell surface markers that could be useful to monitor LXR activation, were identified. 23313547_LXRalpha levels appear as a limiting factor for macrophage cholesterol efflux in humans. 23393188_The study identified highly integrated LXRalpha ligand-dependent transcriptional networks, including the APOE/C1/C4/C2-gene cluster, which contribute to the reversal of cholesterol efflux and the dampening of inflammation processes in foam cells to prevent atherogenesis. 23416078_TR-beta and LXR-alpha competitively up-regulate the human Seladin-1 promoter, sharing the same response element, site A. 23451202_STX4 is a new LXRalpha-ligand to study transcriptional regulation of anti-atherogenic processes in cell or ex vivo models, and provides a promising lead structure for pharmaceutical development 23496987_MiR-613 suppresses lipogenesis by directly targeting LXRalpha in HepG2 cells. 23564066_LXRalpha plays a central role in neopterin-induced downregulation of ABCA1 and ABCG1 in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. 23680128_PGC-1b, a coactivator of both LXR-alpha and SREBP-1, was markedly down-regulated by OEPAs compared with EPA. 23686114_Treatment of human THP-1 macrophages with endogenous or synthetic LXR ligands stimulates both transcriptional and posttranscriptional pathways that result in the selective recruitment of the LXRalpha subtype to LXR-regulated promoters. 23732298_Liver x receptor alpha positively regulates the basal expression of CYP3A4 in hepatocytes. 23733886_evidence for the existence of an LXR-IDOL-mediated internalization pathway for the LDLR that is distinct from that used for lipoprotein uptake 23812424_LXRalpha-mediated downregulation of FOXM1 suppresses the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 23838803_Data indicate that LXR-beta genotypes (rs35463555) and (rs2695121) were associated with risk of gallbladder cancer (GBC) as compared to healthy controls whereas LXR-alpha (rs7120118) was not associated with GBC risk. 23867395_LXRalpha activates FoxO1 transcription through a direct binding on its promoter region. 24036496_Liver X receptor activation stimulates iron export in human alternative macrophages. 24100084_Variants in LXRalpha and LXRbeta genes are not potential contributors to the risk of metabolic syndrome and related traits in an Iranian population. 24118845_The liver X receptor activation has anti-inflammatory effects on CXC10, CCL5 and IL-10 production from alveolar macrophages. 24180251_There was no significant association between two NR1H3 single nucleotide polymorphisms and obesity, even after adjustment for age and sex. The odds ratios for obesity were: 1.32 (0.85-2.74) for rs11039155 and 0.77 (0.30-1.99) for rs2279238. 24265317_Results indicate that Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) activates SMILE gene expression, which leads to repression of liver X receptor alpha (LXRalpha)-mediated hepatic lipogenic enzyme gene expression. 24278306_genetic variation in NR1H3 modulates the expression of LXRalpha and the levels of soluble Abeta42. 24289152_Data suggest PAF (platelet activating factor)/PAF receptor signaling exerts proinflammatory effect on neutrophil via downregulation of LXRa/target genes (ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABC) A1, ABC G1, sterol response element binding protein 1c). 24533572_The rsl2221497 polymorphism in LXRalpha gene is associated with susceptibility of coronary heart disease in Han population. 24618263_Activation of LXRs interfered with the release of interleukin-6 from macrophages and, thus, inhibited fibroblast activation and collagen release. 24713062_PPARalpha and LXRalpha interact with high affinity, resulting in altered protein conformations, the affinity of this interaction and the resulting conformational changes could be altered by endogenous PPARalpha ligands, namely long chain fatty acids. 24751522_PPARgamma negatively regulates the expression of miR-613 at transcriptional level, and miR-613 suppressed LXRalpha and ABCA1 by targeting the 3'-UTR of their mRNAs. 24832115_Studies indicate that no liver X receptor (LXR) modulator has successfully progressed beyond phase I clinical trials. 24842676_Report significant reduction in LXR-alpha transcript in testes of men with azoospermia. 24886807_Data indicata that -1830 T>C polymorphism within liver X receptors alpha gene (NR1H3) promoter region may be involved in regulation of NR1H3 expression. 24996838_LXRalpha rather than LXRbeta plays a predominant role in mediating cholesterol efflux in human macrophages. 25005769_SREBP-2 rs2228314 G to C change and variant C genotype as well as LXRalpha rs11039155 G to A change and variant A may contribute to PCOS in Chinese Han population 25028566_The expression of liver X receptor alpha is a potential predictor for the expression of hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase 2a1 in human liver. 25035925_study suggests that the anti-atherogenic properties of IL-10 may include enhancing effects on cholesterol efflux mechanism that involves cross-talk with LXRalpha activation 25073010_NR1H3 accelerates hepatic differentiation through an HNF4alpha-dependent reciprocal network. 25102981_This research suggests that LXR is an attractive target for treatment and regulation of hepatic inflammation and fibrosis. 25187371_PRMT3 translocation by palmitic acid is coupled to the binding of LXRalpha, which is responsible for the onset of fatty liver. 25255963_ligands selectively regulate placenta gene targets and functional pathways 25264165_The data indicate a direct inhibitory interaction of polyunsaturated fatty acids with LXRalpha, a consequent reduction of SREBP-1 and of its binding to SCD1 promoter. 25283515_An increase of 55% in LXR-alpha gene expression at RNA level was observed in Atorvastatin + 22-R hydroxycholestrol compared to 24% in Ascorbic acid + 22-ROH cholesterol. 25332231_FHL2 is a transcriptional coactivator of LXRs and may be an important determinant of cholesterol metabolism in SMCs 25437875_TRAP80 is a selective regulator of hepatic lipogenesis and is required for LXR-dependent SREBP-1c activation. 25450400_data suggest that ASXL3 is another corepressor of LXRalpha, promoting to the regulation of lipid homeostasis 25600616_Propofol up-regulates expression of ABCA1, ABCG1, and SR-B1 through the PPARgamma/LXRalpha pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. 25659329_LXRb is the dominant isoform in the rat myocardium and the expression of both LXR isoforms (LXRa and LXRb) did not change after administration of T0901317 25661920_These results clearly indicate a novel mechanism in which CCAR2 may regulate the transcriptional activation function of LXRalpha due to its specific inhibition of SIRT1 and serve to regulate cellular proliferation. 25729942_the rsl2221497 polymorphism in the LXRalphagene was associated with the susceptibility to stroke in a Chinese population. 25779847_treatment with Ang-(1-7) promoted cholesterol efflux in Ang II-treated THP-1 macrophages, partly through inactivation of p38 and JNK signaling and by inducing the expression of PPARg and LXRa. 25867319_The rs12221497 polymorphism in the LXRalpha gene was associated with the susceptibility to stroke in a Han Chinese population. 25962847_Data show that menin, encoded by the MEN1 gene, inhibits the transcriptional activity of nuclear receptor liver X receptor alpha (LXRalpha). 25980575_This study provides the first evidence to show LXR activation reduces cadmium-induced apoptotic cell death of human renal proximal tubular cells by inhibition of reactive oxygen species production and JNK activation. 26160456_These results identify LXRalpha as a key cardiac transcriptional regulator that helps orchestrate an adaptive metabolic response to chronic cardiac stress. 26261553_Lipoxin A4 increases ABCA1 expression and promotes cholesterol efflux through LXRalpha pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. 26379423_Suggest that blocking cholesterol deposition and inhibiting the LXRalpha pathway-induced inflammatory response might be one of the main mechanisms by which anthocyanins exert their protective effects in diabetic nephropathy. 26595172_Studied the role of LXRalpha with Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in adipogenesis of MSCs. 26602218_Intestinal activation of LXR reduces the production of chylomicrons by a mechanism dependent on the apical localization of SR-B1. 26635040_The anti-inflammatory effects of platelet-derived microparticles in human plasmacytoid dendritic cells involve liver X receptor activation. 26669941_LXR-alpha might downregulate S1PR2 expression via miR-130a-3p in quiescent HUVECs. Stimulation of TNF-alpha attenuates the activity of LXR-alpha and results in enhanced S1PR2 expression. 26692490_In conclusion, our data indicate that HNF-4alpha may have a wider role in cell and plasma cholesterol homeostasis by controlling the expression of LXRalpha in hepatic cells. 26756785_PPARalpha and LXRalpha may be mediators by which omega3PUFA attenuate bile acid-induced hepatocellular injury 26814197_these data identify a new mechanism of LXR regulation that involves TIPARP, ADP-ribosylation and MACROD1. 26964694_these data show that YXS is effective in mitigating MI/R injury by suppressing mitochondrial mediated apoptosis and oxidative stress and by upregulating LXRalpha, thereby providing a rationale for future clinical trials and clinical applications 26991262_RXRalpha negatively regulates the transcription and expression by directly binding to the RARE in the promoter of Cx43 27016616_combined PPARgamma C1431T, PGC-1alpha G482S, and LXRalpha -115G/A polymorphisms increase the risk of coronary artery disease and predicted the severity of coronary atherosclerosis in Thais 27253448_mutant NR1H3 (LXRA) alters gene expression profiles, suggesting a disruption in transcriptional regulation as one of the mechanisms underlying Multiple Sclerosis pathogenesis. 27343431_AMPK activates LXRalpha and ABCA1 expression in human macrophages 27351826_this study shows that show that H2O2 exerts a du | ENSMUSG00000002108 | Nr1h3 | 98.418273 | 0.450411995 | -1.150683 | 0.18109349 | 40.373288 | 0.0000000002097898074060800541660310149230596506175761106760546681471168994903564453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000061136246374921825824573901303048834021680590922187548130750656127929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 60.7541302 | 9.1275249 | 135.0891908 | 19.4042663 | |
| ENSG00000025708 | 1890 | TYMP | protein_coding | P19971 | FUNCTION: May have a role in maintaining the integrity of the blood vessels. Has growth promoting activity on endothelial cells, angiogenic activity in vivo and chemotactic activity on endothelial cells in vitro. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1590793}.; FUNCTION: Catalyzes the reversible phosphorolysis of thymidine. The produced molecules are then utilized as carbon and energy sources or in the rescue of pyrimidine bases for nucleotide synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1590793}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Chemotaxis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Glycosyltransferase;Growth factor;Neuropathy;Phosphoprotein;Primary mitochondrial disease;Progressive external ophthalmoplegia;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase | PATHWAY: Pyrimidine metabolism; dTMP biosynthesis via salvage pathway; dTMP from thymine: step 1/2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1590793}. | This gene encodes an angiogenic factor which promotes angiogenesis in vivo and stimulates the in vitro growth of a variety of endothelial cells. It has a highly restricted target cell specificity acting only on endothelial cells. Mutations in this gene have been associated with mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. | hsa:1890; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; 1,4-alpha-oligoglucan phosphorylase activity [GO:0004645]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; pyrimidine-nucleoside phosphorylase activity [GO:0016154]; thymidine phosphorylase activity [GO:0009032]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; dTMP catabolic process [GO:0046074]; mitochondrial genome maintenance [GO:0000002]; pyrimidine nucleobase metabolic process [GO:0006206]; pyrimidine nucleoside metabolic process [GO:0006213]; regulation of gastric motility [GO:1905333]; regulation of myelination [GO:0031641]; regulation of transmission of nerve impulse [GO:0051969] | 9857235_dThdPase activity in gastric cancer cells was found to be correlated with venous invasion, supporting previous findings that it plays a role in tumor angiogenesis 11920479_induction in tumoral stroma, but not in tumor cells, may promote angiogenesis in adenocarcinoma of the lung; may be important prognostic factor in adenocarcinoma of the lung 11925935_inhibits the intracellular apoptotic signal transduction in the Fas-induced apoptotic pathway 11957147_COX-2 is upregulated in endometrial cancer and facilitates tumor growth via angiogenesis produced in associated with VEGF and TP. 11986782_thymidine phosphorylase is a major angiogenic factor in prostate carcinoma and its upregulation is likely to occur in the context of host immune response 11992400_TK1 gene expression together with TS, TP and DPD gene expression may play important roles in influencing the malignant behavior of epithelial ovarian cancer. 12174926_summary of research advances concerning thymidine phosphorylase in breast carcinoma (review) 12177387_Biochemical defects of thymidine phosphorylase (hPD-ECGF) and a pathogenic G-to-A transition mutation at nucleotide 435 in the hPD-ECGF gene have been identified in two affected siblings with mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy (MNGIE). 12429983_Development of oral cancer epithelia is associated with a significant increase in thymidine phosphorylase expression 12466967_Sp1 transcription factor contributes to its expression in human colon carcinoma cells. 12520153_MCP-1-positive myxoma and stromal cells and TP-positive myxoma and stromal cells significantly correlated with increased microvessel count. In cardiac myxoma, MCP-1 and thymidine phosphorylase may be important angiogenic signals accompanying growth. 12565868_These findings indicate that thymidine phosphorylase has cytoprotective functions against cytotoxic agents which are independent of its enzymatic activity. 12639965_experiments are the first to demonstrate a direct effect of thymidine phosphorylase and 2-deoxyribose on signaling pathways associated with endothelial cell migration 12684660_This enzyme is expressed and mediates angiogenesis regulated by enzyme inhibitors in human ovarian cancer cells in vivo. 12813027_point mutations in mtDNA of tissues and cultured cells from patients with thymidine phosphorylase deficiency and mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy 12820387_Overexpression of TP mRNA by stromal cells within tumors plays an important role in tumor angiogenesis of prostate cancer. 12918063_overexpression of thymidine phosphorylase is associated with invasiveness and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma 14702180_There is no prognostic significance to TP mRNA expression in breast neoplasms. 14719072_Activity of thymidine kinase, thymidine phosphorylase and thymidilate synthase in human cancer xenografts to investigate the contribution of these enzymes to the sensitivity of TAS-102. 14966914_Tumor associated macrophages are the most important source of dThdPase in colorectal cancer tissues. 15069545_There were no significant differences between TP levels in the tumor specimens of the two groups, whereas in stages III and IV, those of the gastric cancer group tended to be higher than those of colorectal cancer group 15123637_Results describe the inhibitory activity of the purine riboside derivative KIN59 (5'-O-tritylinosine) against human and bacterial recombinant thymidine phosphorylase (TPase) and TPase-induced angiogenesis. 15201953_Enzyme expression can precisely predict 5'-dFUR sensitivity in colorectal cancer. 15254700_Thymidine phosphorylase and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase have roles in progression of liver metastasis 15262124_Thymidine phsoporylase activity is significantly higher in more advanced neoplasmatic disease (FIGO III and IV) although no correlation between TP activity and grading or histopathological type of ovarian tumor was observed. 15289834_TP expression in tumor tissue is high in proportion to TP expression in primary tissue 15374822_We conclude that genetic approaches using PD-ECGF to target the myocardium are effective for alleviating chronic myocardial ischemia. 15375582_vascular endothelial growth factor and TP expression was also associated with a significantly higher level of Cyclooxygenase-2, as well as greater intratumoral microvessel density 15474072_Hypoxia increased both VEGF secretion and number of cells containing VEGF and thymidine phosphorylase. 15571233_Thymidine phosphorylase deficiency has a role in causing MNGIE, an autosomal recessive mitochondrial disorder 15571260_thymidine phosphorylase mRNA and activity expression is upregulated 2-3 fold after treatment with interferon alpha 15571282_TP has no role in trifluorothymidine sensitivity, but activates 5'-deoxy-5-fluorouridine and to a lesser extent 5FU 15607208_Genetic analysis revealed a novel 18-base pair (bp) duplication (5044-5061 dup) in exon 8 of the thymidine phosphorylase (TP) gene in the patient of mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy. 15756429_TP/PD-ECGF may support or modify tumor growth through angiogenesis in cooperation with other factors 15756433_thymidine phosphorylase may have a role in efficacy of adjuvant doxifluridine in advanced colorectal cancer 15781193_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15879300_TP overexpression upregulated HO-1 expression and consequently increased p27(KIP1) in cultured VSMCs, and inhibited VSMC migration and proliferation in vitro and in vivo 15978330_an increased expression of mRNA, specific for thymidine kinase 1, deoxycytidine kinase, and thymidine phosphorylase, may be involved in carcinogenic processes in the human thyroid 16132996_Association of mRNA expresion patterns with tumor stage and suggested new prognostic and predictive markers for patients with colorectal cancer. 16198108_Increased muscle nucleoside levels associated with a novel frameshift mutation in the thymidine phosphorylase gene in a Spanish patient with MNGIE. 16317434_TP expression significantly predicted metastasis-free survival, but not local control; this is consistent with role as tumor angiogenesis promotor 16369467_results show a local increase in the expressions of IGF-1 and PDEGF in the muscularis propria of the pyloric muscle in children with IHPS, which may have implications to the pathogenesis of the disease 16458893_cytoprotective function of TP is mediated, at least in part, by regulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway; TP molecules confer resistance to DNA damage-induced apoptosis in cancer cells 16685420_TP enhances the invasion of tumor cells through the induction of invasion-related genes. 16798057_Thymidine phosphorylase and uridine phosphorylase were both responsible for converting 5'dFUrd/5FU into 5FU/FUrd, respectively. 16803458_The structure of human thymidine phosphorylase (HTP) from crystals grown in the presence of thymidine, was determined. 16969493_thymidine phosphorylase levels are more elevated relative to dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase levels in squamous cell carcinoma than in adenocarcinoma 17103175_GLS/TP and VEGF have synergistic effects on angiogenesis in rheumatoid synovitis, and GLS/TP has a role in regulating VEGF 17437622_We present the first detailed report of a Brazilian MNGIE patient, harboring a novel ECGF1 homozygous mutation (C4202A, leading to a premature stop codon, S471X). 17497037_Data Show thymidine phosphorylase was expressed in regenerative hepatocytes, but not in fibroblasts, suggesting its role in promoting oxidative stress produced by hepatocytes may contribute to the development of fibrous bands in hepatic cirrhosis. 17681069_The PyNpase levels of bladder tumor tissue significantly correlated to the tumor grade and growth pattern (papillary/non-papillary), while stage, multiplicity, and tumor shape (peduncle/sessile) were not independent factors 17688376_Expected role of TP in the activation of capecitabine and known promoting role of TP in tissue fibrosis frequently associated with tumor regression in rectal carcinoma. 17854149_Expression of thymidylate synthase and thymidine phosphorylase mRNA is a useful predictive parameter for the survival of postoperative gastric cancer patients after 5-fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy. 17923735_thymidine phosphorylase expression in cancer-infiltrating inflammatory cells could affect lymph node metastasis and patients' survival in gastric cancer 17999375_Patients with high levels of tumour cell thymidine phosphorylase expression were significantly associated with a favorable outcome. 18019682_dThdPase, but not mutant p53, plays an important role in tumor angiogenesis in ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas 18341568_The lack of TP protein expression in basal cell carcinoma tumoral cells is linked to transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. 18359286_These findings suggest that the suppression of BNIP3 expression by TP prevents, at least in part, hypoxia-induced apoptosis. 18476626_Both TP and MK are important for angiogenesis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. The expression of TP, MK and CD105 were all correlated with T-stage and lymph node metastasis. 18559600_Cytoplasmic hnRNP K and high thymidine phosphorylase may be potential prognostic and therapeutic markers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 18725595_We used carrier erythrocyte entrapped thymidine phosphorylase therapy for MNGIE. The treatment failed. 18765464_Thymidine phosphorylase expression and benefit from capecitabine in patients with advanced breat cancer is reported. 18848756_adventitial delivery of the PD-ECGF/TP gene after grafting may be promising method for preventing vein graft failure. 18922971_TP increases the migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells, especially in TP-expressing cells. 18955007_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18986516_The cytosol thymidine phosphorylase activity in endometrial cancer is significantly higher than in normal endometrium, with no relation as to the stage and grade of tumors 19023133_Thymidine phosphorylase plays a key role in endothelial progenitor cell survival and proangiogenic potential. 19056268_Mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by loss-of-function mutations in the thymidine phosphorylase gene (TYMP). We report here a patient compound heterozygous for two TYMP mutations. 19093516_Clinicopathological significance of the progesterone receptor and its association with thymidine phosphorylase expression in colorectal cancer. 19295266_There was no relationship between primary colorectal lesions and synchronous liver metastases in terms of thymidine phosphorylase(TP) mRNA levels and TP protein levels 19330019_Results collectively establish the regulation and role of ERK-mediated cytoplasmic accumulation of hnRNP K as an upstream modulator of TP, suggesting that hnRNP K may be an attractive candidate as a future therapeutic target for cancer. 19344718_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19555658_the crystal structures of recombinant hTP and its complex with a substrate 5-iodouracil (5IUR) at 3.0 and 2.5A, respectively were reported. 19654105_the relationship between the expression of TK1 and TP as they relate to proliferation (Ki-67 labeling index) and angiogenesis (Chalkley count of CD31-stained blood vessels) in a series of 110 non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tumors 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20112501_Increased thymidine phosphorylase expression is associated with bladder cancers. 20151198_Case Report: thymidine phosphorylase deficiency is a multisystem and ultimately fatal disease. 20355241_TP may have a role in angiogenesis-dependent growth and migration of cholangiocarcinoma and in response to 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy 20372793_thymidine phosphorylase has a role in the induction of early growth response protein-1 and thrombospondin-1 by 5-fluorouracil in human cancer carcinoma cells 20488166_Thymidine phosphorylase-derived sugars from overexpressing tumor cells accumulate in the cytoskeleton and to some extent in the cell membrane, enabling endothelial cells to migrate and invade towards tumor sites. 20585803_MNGIE is caused by mutations in the gene encoding thymidine phosphorylase, which lead to absolute or nearly complete loss of its catalytic activity, producing systemic accumulations of its substrates, thymidine and deoxyuridine. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20714877_TYMP and TYMS mRNA and protein expression levels were significantly higher in epithelial ovarian cancer, and DPYD mRNA and protein expression levels were significantly lower. 20837458_Thymidylate synthase, thymidine phosphorylase, and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase play a role in the prognosis of non-small-cell lung cancer. 20955617_thymidine phosphorylase is expressed differently in gallbladder and bile duct cancer 21068389_altered function of hnRNP H1/H2 in tumor cells is a novel determinant of aberrant thymidine phosphorylase splicing thereby resulting in acquired chemoresistance to TP-activated fluoropyrimidine anticancer drugs. 21222488_transition state for the arsenolytic reaction 21252618_Thymidine phosphorylase involvement in the enhancement of IgE production 21362301_A significant correlation was noticed between HIF-1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor expression while the expression levels of thymidine phosphorylase, cyclooxygenase and microvessel density were significantly higher in high HIF-2alpha tumors. 21386840_Thymidine phosphorylase did not increase the tumour invasion, but stimulated the migration and invasion of endothelial cells by two different mechanisms. 21586171_In Chinese advanced gastric cancer, Thymidine Phosphorylase positive & beta-tubulin III negative might predict response and prognosis to capecitabine plus paclitaxel chemotherapy. 21809665_In grade 3 samples of CIN (Cervical Intraepithalial Neoplasia), expression of TP (separately or in combination with Ki-67 antigen) appeared to be related to imminent progression to invasive cancer. TP levels were shown to correlate directly with CIN grade 21837996_PD-ECGF and VEGF have a synergetic effect in the proliferation of micro-vessels, and they play an important role in the proliferation and involution of hemangioma. 22321252_Elevated cytoplasmic hnRNP K and TP overexpression are associated with poorer survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients 22340655_The expression of PD-ECGF may play an important role in the development and invasion of renal cell carcinoma. 22534375_Sp1 binding sites in the gliostatin (GLS)promoter are essential for GLS mRNA expression. 22593457_mRNA expression of TYMS, DPYD, and TYMP is associated with distinct characteristics and may be useful for predicting survival in patients with stage IV colorectal cancer. 22595739_High TP/PD-ECGF expression and thrombocytosis can be regarded as valuable tools for predicting overall survival in patients with gastric carcinoma. 22610353_Data indicate that high thymidine phosphorylase (TP) tumor gene expression was associated with obtaining pathological complete response (pCR). 22618301_A report of two brothers in whom novel TYMP gene mutations (c.215-13_215delinsGCGTGA; c.1159 2T > A) were associated with different clinical presentations and outcomes. 22668509_Thymidine phosphorylase induced STAT3 phosphorylation and increased total amount of unphosphorylated-STAT3 in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC), which may play a critical role in inhibiting VSMC proliferation 22751949_The enzymatic activity of thymidine phosphorylase was required for the enhanced expression of IL-8 in human cancer cells. 22752215_TP gene expression levels in primary CRC tissues and the primary tumor site may be useful predictors of the efficacy of oral UFT/LV chemotherapy. 23160694_These findings suggest that thymidine phosphorylase plays an important role in angiogenesis, extracellular matrix remodeling and in the prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer 23813863_the first evidence of the significant impact of the TYMP genotype upon the clinical outcome of patients treated with HLA-identical sibling allo-SCT. 24024441_The expressions of PD-ECGF and VEGF are higher in the colorectal carcinoma patients with schistosomiasis than in the colorectal carcinoma patients without schistosomiasis. 24027750_our study shows that IFN-alpha enhanced 5'-DFUR-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by upregulation of TP expression, which is partially regulated by activation of ERK signaling 24448160_These results demonstrate that the use of AAV to direct TYMP expression in liver is feasible as a potentially safe gene therapy strategy for Mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy. 24455740_We suggest that a chip including DPYD, TYMS, TYMP, TK1, and TK2 genes is a potential tool to predict response in LARC following fluoropyrimidine-based CCRT 24617035_thymidine phosphorylase is more likely expressed by malignant B cells in higher-grade lymphomas 24798152_thymidine phosphorylase could strongly influence gastric cancer progression via the dual activities of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis 24819505_action of thymidine phosphorylase in non-small cell lung cancer: crosstalk with Nrf2 and HO-1 25027354_Gastrointestinal cancer patient carriers of the thymidine phosphorylase rs11479 T allele, with a low platelet count, could be at risk of a poor outcome. 25304388_4-methylumbelliferone exerts its antitumor effect on ovarian cancer through suppressing thymidine phosphorylase expression. 26617778_Pretreatment expression of thymidine phosphorylase/HIF-1alpha were found to predict pathologic response and outcomes in clinical stage II/III rectal cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. 26676225_High VEGF expression was subsequently correlated with a short overall survival rate for patients exhibiting lymph node metastasis (P=0.0128); however, there was no significant difference in overall survival rate regarding the expression levels of TP and CD34 26676887_the highest expression of GGH and EGFR was noted in the left-sided colon; the highest expression of DHFR, FPGS, TOP1 and ERCC1 was noted in the rectosigmoid, whereas TYMP expression was approximately equivalent in the right-sided colon and rectum 27127154_Increases in gene expression levels of TYMP, DPYD, and HIF1A in tumor tissues at 7 days after the start of CRT may be useful for predicting the efficacy of CRT including S-1 or UFT 27283904_Data show that thymidine phosphorylase (TYMP) positive patients had higher systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) score. 27532673_TP expression is associated with tumor stage, histological grade and thrombocytosis in patients with renal cell carcinoma 27559096_Investigated the contribution of myeloma-expressed thymidine phosphorylase (TP) to bone lesions. In osteoblast progenitors, TP up-regulated the methylation of RUNX2 and osterix, leading to decreased bone formation. In osteoclast progenitors, TP up-regulated the methylation of IRF8, leading to increased bone resorption. 27658717_TP(thymidine phosphorylase ) curbed the expression of three proteins-IRF8, RUNX2, and osterix. This downregulation was epigenetically driven: High levels of 2DDR, a product of TP secreted by myeloma cells, activated PI3K/AKT signaling and increased the methyltransferase DNMT3A's expression 28530649_Studied the role of thymidine phosphorylase (TP) in promoting the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). It was shown that TP correlated with MMP2 and MMP9 expression, and that TP mediated the migration of tumor cells through activity of MMPs in HCC cell lines. 30642883_These results indicated that hDHFR is not the only target of Pyr. We further found that thymidine phosphorylase (TP), an enzyme that is closely associated with the EMT of cancer cells, is also a target protein of Pyr. The data retrieved from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database revealed that TP overexpression is associated with poor prognosis of patients with lung cancer 30849523_Kinetics mechanism and regulation of native human hepatic thymidine phosphorylase 31366497_Sp1-binding sites in the TP promoter were methylated in epidermoid carcinoma. 5-Aza-CdR demethylated Sp1-binding sites and enhanced sensitivity to 5-FU 32476180_Thymidine phosphorylase promotes angiogenesis and tumour growth in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 33825174_Novel Mutations of the TYMP Gene in Mitochondrial Neurogastrointestinal Encephalomyopathy: Case Series and Literature Review. 35341481_Loss of thymidine phosphorylase activity disrupts adipocyte differentiation and induces insulin-resistant lipoatrophic diabetes. 35567733_Impact of thymidine phosphorylase and CD163 expression on prognosis in stage II colorectal cancer. | ENSMUSG00000022615 | Tymp | 250.458389 | 0.264979593 | -1.916047 | 0.31775933 | 34.141812 | 0.0000000051238384305890661220787892101390104127034419434494338929653167724609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000001231481992561509615046448249883748182753606670303270220756530761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 91.8879012 | 26.5916750 | 347.6028398 | 99.7384479 |
| ENSG00000027869 | 9047 | SH2D2A | protein_coding | Q9NP31 | FUNCTION: Could be a T-cell-specific adapter protein involved in the control of T-cell activation. May play a role in the CD4-p56-LCK-dependent signal transduction pathway. Could also play an important role in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Could be an adapter protein that facilitates and regulates interaction of KDR with effector proteins important to endothelial cell survival and proliferation. | Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;SH3-binding | This gene encodes an adaptor protein thought to function in T-cell signal transduction. A related protein in mouse is responsible for the activation of lymphocyte-specific protein-tyrosine kinase and functions in downstream signaling. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. | hsa:9047; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098] | 11528519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15129233_'short' alleles of the promoter could contribute to the genetic susceptibility to Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis 15129233_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15752554_TSAd appears to contribute to interleukin-2 synthesis at multiple different levels 17327418_upon chemokine stimulation, Lad acts as an adaptor protein that links the G protein beta subunit to the tyrosine kinases Lck and Zap-70, thereby mediating T-cell migration 18160104_SH2D2A expression is regulated both at the transcriptional and translational level. 18533279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18533279_This study found a significant association between CIDP and the genotype GA13-16 homozygote (OR 3.167; p 0.013). 18541536_lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase binds to T cell-specific adapter protein (TSAd) prolines and phosphorylates and interacts with the three C-terminal TSAd tyrosines 18554728_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18554728_the present study shows that the SH2D2A gene may contribute to susceptibility to MS. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19561400_TSAd associates with laminin binding protein and mediates T lymphocyte migration during T cell activation 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20305788_TSAd, through its interaction with both Itk and Lck, primes Itk for Lck mediated phosphorylation and thereby regulates CXCL12 induced T cell migration and actin cytoskeleton rearrangements 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21696499_in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy we found an association with a homozygous genotype for a low repeat number of tandem GA in the SH2D2A gene 24910151_Data indicate the expression pattern of T cell-specific adapter protein (TSAd) in various healthy lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissues. 25492967_The kinase Itk and the adaptor TSAd change the specificity of the kinase Lck in T cells by promoting the phosphorylation of Tyr192. 26163016_TSAD binds to and co-localizes with Nck. Expression of TSAD increases both Nck-Lck and Nck-SLP-76 interaction in T cells. 27896837_Data indicate that the T cell-specific adaptor protein (TSAd) SH2 domain interacts with CD6 antigen and linker for activation of T cells protein (LAT) phosphotyrosine (pTyr) peptides. 31484725_The ITK SH3 and LCK SH3 domains can both competefor and simultaneously bind to adjacent binding sites on TSAD encompassing aa 242-268. 33046503_TSAd Plays a Major Role in Myo9b-Mediated Suppression of Malignant Pleural Effusion by Regulating TH1/TH17 Cell Response. | ENSMUSG00000028071 | Sh2d2a | 24.961808 | 0.327849090 | -1.608896 | 0.33459060 | 24.005060 | 0.0000009608286909664223149801819470749997265102138044312596321105957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000158866096090287399239700250053175523134996183216571807861328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 12.0443821 | 3.2989925 | 37.0171017 | 9.0224548 | |
| ENSG00000047597 | 7504 | XK | protein_coding | P51811 | FUNCTION: Recruits the lipid transfer protein VPS13A from lipid droplets to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32845802}. | Amino-acid transport;Blood group antigen;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | This locus controls the synthesis of the Kell blood group 'precursor substance' (Kx). Mutations in this gene have been associated with McLeod syndrome, an X-linked, recessive disorder characterized by abnormalities in the neuromuscular and hematopoietic systems. The encoded protein has structural characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic membrane transport proteins. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:7504; | endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; amino acid transport [GO:0006865]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular magnesium ion homeostasis [GO:0010961]; myelination [GO:0042552]; regulation of axon diameter [GO:0031133]; regulation of cell size [GO:0008361]; skeletal muscle fiber development [GO:0048741] | 17379193_In human cortex, the results show expression of XK in cortical neurons with an apparent cytoplasmic localization. 17469188_Sequence analysis demonstrated a 5 bp deletion in exon 2 of the XK gene in McLeod syndrome. 21145924_This study identified one non-synonymous and one intron variant in mood disorder and schizophrenia subjects, respectively, in XK. 21463873_Novel XK protein mutations are reported in two patients who exhibit typical clinical characteristics of McLeod syndrome. 24635891_study reports the clinical findings and a novel nonsense hemizygous mutation, c.154C>T (p.Gln52X) at exon 1 of XK gene in a Taiwanese family with McLeod syndrome 24816235_The XK gene was not linked to hypermutability in red cells from patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. 26308465_the expression of KX is critical to normal morphology, and null mutations are associated with the McLeod neuroacanthocytosis syndrome. 32845802_XK is a partner for VPS13A: a molecular link between Chorea-Acanthocytosis and McLeod Syndrome. 35994651_A partnership between the lipid scramblase XK and the lipid transfer protein VPS13A at the plasma membrane. | ENSMUSG00000015342 | Xk | 117.220177 | 2.045365615 | 1.032359 | 0.16249399 | 40.498979 | 0.0000000001967187866374712407145725191913898828588447287302187760360538959503173828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000057566995554078405394932413721969383102461392809345852583646774291992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 157.8260187 | 10.9648409 | 77.5710794 | 6.1627569 | |
| ENSG00000057704 | 57458 | TMCC3 | protein_coding | Q9ULS5 | Coiled coil;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Enables 14-3-3 protein binding activity and identical protein binding activity. Located in endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:57458; | endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; 14-3-3 protein binding [GO:0071889]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802] | 20306291_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 27697108_TMCC3 proteins are localized in endoplasmic reticulum through transmembrane domains and polymerized with other TMCC3 protein an 1-3-3 proteins. 31696206_A TMCC3 mutant lacking the N-terminal coiled-coil domain abolished localization to tubular network of the endoplasmic reticulum, suggesting that TMCC3 localized independently of binding to atlastins. 33742122_Transmembrane and coiled-coil domain family 3 (TMCC3) regulates breast cancer stem cell and AKT activation. | ENSMUSG00000020023 | Tmcc3 | 15.645267 | 0.379198949 | -1.398973 | 0.47346706 | 8.780128 | 0.0030452976761375667030806724255853623617440462112426757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0190935113822556165596999733224947704002261161804199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 6.3220108 | 3.6925885 | 16.6001958 | 9.3338823 | ||
| ENSG00000064547 | 9170 | LPAR2 | protein_coding | Q9HBW0 | FUNCTION: Receptor for lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), a mediator of diverse cellular activities. Seems to be coupled to the G(i)/G(o), G(12)/G(13), and G(q) families of heteromeric G proteins. Plays a key role in phospholipase C-beta (PLC-beta) signaling pathway. Stimulates phospholipase C (PLC) activity in a manner that is independent of RALA activation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15143197, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19306925}. | 3D-structure;Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a member of family I of the G protein-coupled receptors, as well as the EDG family of proteins. This protein functions as a lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptor and contributes to Ca2+ mobilization, a critical cellular response to LPA in cells, through association with Gi and Gq proteins. An alternative splice variant has been described but its full length sequence has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | Mouse_homologues mmu:53978; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone membrane [GO:0048787]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; lysophosphatidic acid receptor activity [GO:0070915]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035025]; regulation of metabolic process [GO:0019222] | 12123830_demonstrate that two biological fluids, blood plasma and seminal plasma, differentially activate LPA receptors 12668280_results suggested that LPA(2) and LPA(3) may be involved in VEGF expression mediated by LPA signals in human ovarian oncogenesis 12759391_LPA may directly increase the level of cyclin D1 in ovarian cancer cells, increasing their proliferation. 15535846_Upregulation of LPA2 may play a role in carcinogenesis, particularly in postmenopausal breast cancer. 15728708_LPA2 is the major LPA receptor in colon cancer cells and cellular signals by LPA2 are largely mediated through its ability to interact with NHERF2. 15755723_formation of the LPA receptor/PDZ domain-containing RhoGEF complex plays a pivotal role in LPA-induced RhoA activation 16904289_These results demonstrate that MAGI-3 interacts directly with LPA(2) and regulates the ability of LPA(2) to activate Erk and RhoA. 17496233_EDG4 and EDG2 cooperate to promote LPA-stimulated chemotaxis in breast tumor cell lines. 17765657_data suggest that LPA receptor-dependent expression of CTGF and CYR61 represents a common host response after interaction with bacteria. 17965021_lysophosphatidic acid 2 receptor mediates down-regulation of Siva-1 to promote cell survival 18703779_A role for the transgenic lysophosphatidic acid (LPA)2 receptor is identified in regulating smooth muscle cell migratory responses in the context of vascular injury. 18754873_LPA and LPA receptors, LPA(2) as well as LPA(1), represent potential therapeutic targets for patients with MPM 19001604_Expression of LPA2 during ovarian carcinogenesis contributes to ovarian cancer aggressiveness, suggesting that the targeting of LPA production and action may have potential for the treatment of ovarian cancer. 19025891_Switching of LPA receptor expression from LPA3 to LPA1, may be involved in prostate cancer progression and/or androgen independence 19081821_LPA(1) receptor, LPA(2) and LPA(3) receptors-induced VASP phosphorylation is a critical mediator of tumor cell migration initiation 19116446_LPA2 and Gi/Src pathways are significant for LPA-induced COX-2 expression and cell migration that could be a promising drug target for ovarian cancer cell metastasis. 19860625_Data show that CLL cells express LPA receptors LPA(1-5) and VEGF receptors, and the plasma levels of VEGF are elevated in CLL patients. 19899077_show that human microglia express LPA receptor subtypes LPA(1), LPA(2), and LPA(3) on mRNA and protein level. LPA activation of C13NJ cells induced Rho and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation and enhanced cellular ATP production. 20890765_LPA2 gene mutation may play some role in the pathogenesis of colon cancer. 21134377_MAGI-3 competes with NHERF-2 to negatively regulate LPA2 receptor signaling in colon cancer cells. 21234797_This work shows for the first time that key components of the LPA pathway are modulated following traumatic brain injuries in humans. 21964883_found that LPA receptor 2/3-mediated IL-8 expression occurs through Gi/PI3K/AKT, Gi/PKC and IkappaB/NF-kappaB signaling 23084965_LPA2 and LPA6 receptor subtypes are predominant in both HPAECs and HMVECs 23569130_Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) increased hepatocellular carcinoma cells cell invasion, which was LPA-receptor dependent. 24061591_LPA1 and LPA2 are major LPA receptor subtypes compared with low-expressed LPA3 in PANC-1 tumor cells. 24613836_Crystal structure of NHERF2 PDZ1 domain complex with C-terminal LPA2 sequence. The PDZ1-LPA2 binding specificity is achieved by hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic contacts with the last four LPA2 residues contributing to specific interactions. 24950964_the RhoA-regulated formin Dia1 is involved in entosis downstream of LPAR2 25463482_Suggest that LPA2 and LPA3 may function as a molecular switch and play opposing roles during megakaryopoiesis of K562 cells. 26327335_Data show high expression levels of LPAR2 and LPAR1 in endometrial cancer tissue with positive correlations with FIGO stage suggesting them as potential biomarkers for endometrial cancer progression. 26937138_LPAR2 mRNA is up-regulation in colorectal cancer. 27124742_epithelial dysplasia was observed in founder mouse intestine, correlating LPA2 overexpression with epithelial dysplasia. The current study demonstrates that overexpression of LPA2 alone can lead to intestinal dysplasia. 27244685_The results indicate that LPA2 and LPA3 receptors play opposing roles during red blood cells differentiation. 27583415_LPA2 mRNA levels were associated with poorer differentiation, and higher LPA6 levels were associated with microvascular invasion in HCC; both became a risk factor for recurrence after surgical treatment when combined with increased serum ATX levels 27805252_LPA2 expression was associated with HIF-1alpha expression and that a high level of LPA2 was associated with shorter overall survival and was an independent prognostic predictor for breast cancer in Chinese women. 28205098_These results suggest that LPA signaling via LPA2 may play an important role in the regulation of cellular functions in HT1080 cells treated with cisplatin. 29621954_Study shows that due to the high LPAR2 and LPAR4 transcript and protein expression in endometriotic ovarian cysts and positive correlations of both these receptors with the PR-B and ERbeta, respectively, those receptors seem to be the most promising predictors of the endometriotic cysts. 29859140_Investigated the roles of LPA receptors in the regulation of cellular functions during tumor progression in osteosarcoma cell lines. MG63-R7-C cell activities were inhibited by LPA2 knockdown, suggesting that LPA signaling via LPA2 plays an important role in the acquisition of malignant properties during tumor progression in MG-63 cells. 30093116_LPAR2 and LPAR5 regulate cellular functions during tumor progression in fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells. 31115486_It was revealed that LPA may stimulate the expression of Notch1 and Hes family bHLH transcription factor 1, and the phosphorylation of protein kinase B which belongs to the Notch pathway. 31235682_The positive expression rate of LPA2 and KLF5 were statistical different in gastric adenocarcinoma, GIN, and normal gastric tissue (P | ENSMUSG00000031861 | Lpar2 | 196.676404 | 0.404252011 | -1.306673 | 0.35193098 | 13.273824 | 0.0002691376294669853936822323525746014638571068644523620605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0024509747141824166256907080452265290659852325916290283203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 104.2783116 | 22.5392950 | 259.8588173 | 55.5857312 | |
| ENSG00000065534 | 4638 | MYLK | protein_coding | Q15746 | FUNCTION: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase implicated in smooth muscle contraction via phosphorylation of myosin light chains (MLC). Also regulates actin-myosin interaction through a non-kinase activity. Phosphorylates PTK2B/PYK2 and myosin light-chains. Involved in the inflammatory response (e.g. apoptosis, vascular permeability, leukocyte diapedesis), cell motility and morphology, airway hyperreactivity and other activities relevant to asthma. Required for tonic airway smooth muscle contraction that is necessary for physiological and asthmatic airway resistance. Necessary for gastrointestinal motility. Implicated in the regulation of endothelial as well as vascular permeability, probably via the regulation of cytoskeletal rearrangements. In the nervous system it has been shown to control the growth initiation of astrocytic processes in culture and to participate in transmitter release at synapses formed between cultured sympathetic ganglion cells. Critical participant in signaling sequences that result in fibroblast apoptosis. Plays a role in the regulation of epithelial cell survival. Required for epithelial wound healing, especially during actomyosin ring contraction during purse-string wound closure. Mediates RhoA-dependent membrane blebbing. Triggers TRPC5 channel activity in a calcium-dependent signaling, by inducing its subcellular localization at the plasma membrane. Promotes cell migration (including tumor cells) and tumor metastasis. PTK2B/PYK2 activation by phosphorylation mediates ITGB2 activation and is thus essential to trigger neutrophil transmigration during acute lung injury (ALI). May regulate optic nerve head astrocyte migration. Probably involved in mitotic cytoskeletal regulation. Regulates tight junction probably by modulating ZO-1 exchange in the perijunctional actomyosin ring. Mediates burn-induced microvascular barrier injury; triggers endothelial contraction in the development of microvascular hyperpermeability by phosphorylating MLC. Essential for intestinal barrier dysfunction. Mediates Giardia spp.-mediated reduced epithelial barrier function during giardiasis intestinal infection via reorganization of cytoskeletal F-actin and tight junctional ZO-1. Necessary for hypotonicity-induced Ca(2+) entry and subsequent activation of volume-sensitive organic osmolyte/anion channels (VSOAC) in cervical cancer cells. Responsible for high proliferative ability of breast cancer cells through anti-apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11113114, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11976941, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15020676, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15825080, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16284075, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16723733, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18587400, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18710790, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19826488, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20139351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20181817, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20375339, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20453870}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Actin-binding;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Aortic aneurysm;ATP-binding;Calcium;Calmodulin-binding;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase | This gene, a muscle member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, encodes myosin light chain kinase which is a calcium/calmodulin dependent enzyme. This kinase phosphorylates myosin regulatory light chains to facilitate myosin interaction with actin filaments to produce contractile activity. This gene encodes both smooth muscle and nonmuscle isoforms. In addition, using a separate promoter in an intron in the 3' region, it encodes telokin, a small protein identical in sequence to the C-terminus of myosin light chain kinase, that is independently expressed in smooth muscle and functions to stabilize unphosphorylated myosin filaments. A pseudogene is located on the p arm of chromosome 3. Four transcript variants that produce four isoforms of the calcium/calmodulin dependent enzyme have been identified as well as two transcripts that produce two isoforms of telokin. Additional variants have been identified but lack full length transcripts. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:4638; | actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cleavage furrow [GO:0032154]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; stress fiber [GO:0001725]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; myosin light chain kinase activity [GO:0004687]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; aorta smooth muscle tissue morphogenesis [GO:0060414]; bleb assembly [GO:0032060]; cellular hypotonic response [GO:0071476]; positive regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051928]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of wound healing [GO:0090303]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; smooth muscle contraction [GO:0006939]; tonic smooth muscle contraction [GO:0014820] | 11976941_a novel function in regulating the activation of volume-sensitive organic osmolyte/anion channels by mediating Ca2+ entry in response to hypotonicity 12460991_activation by Pro33 polymorphism of integrin beta3 14741352_Increasing [Ca(2+)](i) increases MLCK activation. 15056655_cortactin and EC myosin light chain kinase have roles in mediating lung vascular barrier augmentation evoked by S1P 15087444_myosin light chain kinase has a role in ATP- augmented von Willebrand factor-dependent shear-induced platelet aggregation 15507455_MLCK1 is the isoform responsible for tight junction regulation in absorptive enterocytes 15681825_IFN-gamma can prime intestinal epithelial monolayers to respond to TNF-alpha by disrupting tight junction morphology and barrier function via MLCK up-regulation and MLC phosphorylation 15817725_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15825080_Complementary roles for these kinases in purse-string closure of experimental and in vivo oligocellular epithelial wounds; rho and ROCK are critical for actin ring assembly, while the activity of MLCK drives contraction. 16284075_findings suggest intracellular Ca(2+)-calmodulin activates MLCK thereby maintaining TRPC5 activity by the promotion of plasma membrane TRPC5 distribution under control of phosphorylation/dephosphorylation equilibrium of myosin light chain 16306123_Results suggest that calmodulin and myosin light chain kinase modulate the activation process of transient receptor potential channel 5. 16399953_MYLK genetic variants are implicated to confer increased risk of sepsis and sepsis-associated ALI. 16399953_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16723733_These studies demonstrate a newly discovered role for MLCK in the generation of pro-survival signals in both untransformed and transformed epithelial cells 16835238_Data show that either AP-1 or NFkappaB can up-regulate long MLCK transcription, but the mechanisms by which TNF up-regulates intestinal epithelial long MLCK transcription from exon 1A are differentiation-dependent. 17244674_MLC2 phosphorylation is regulated by both ROCK and MLC kinase and plays an important role in platelet biogenesis by controlling proplatelet formation and fragmentation. 17266121_MYLK genetic variants studied in European and African Americans with asthma and severe asthma and identified a single polymorphism (Pro147Ser) restricted to African populations and which was associated with severe asthma in African Americans. 17472811_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18218860_Protein kinase A activity prevents activation of beta2 integrins and cell adhesion by inhibiting myosin light chain kinase in neutrophils. 18363837_These studies provide novel insight into the cellular and molecular mechanisms that regulate basal and TNF-alpha-induced modulation of MLCK gene activity. 18496125_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18521921_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18710790_Myosin light-chain kinase contributes to the proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells through cross-talk with activated ERK1/2. 18828194_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19011151_Selective overexpression of airway smooth muscle genes in asthmatic airways leads to increased Vmax, thus contributing to the airway hyperresponsiveness observed in asthma. 19264973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19277499_MYLK polymorphism is associated with high blood eosinophil level among asthmatic patients. 19277499_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19429448_LNCaP cells express both long (non-muscle) and short (smooth muscle) isoforms, and that both isoforms are down-regulated by androgens. 19549383_MLCK inhibits the restoration of GPIbalpha in PAR1 pathway during the course of thrombin receptor activation in platelets. 19706030_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19826488_hARD1 is a bona fide regulator of MLCK, and hARD1 plays a crucial role in the balance between tumor cell migration and stasis 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20053363_Data provide insights into the molecular basis for vascular barrier-regulatory cytoskeletal responses and quantified the critical interactions between non-muscle MLCK isoenzymes and cortactin during vascular barrier regulation. 20081554_No association between snps in the myosin light chain kinase gene and either the need for positive-pressure ventilation or the development of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome was observed in children with community-acquired pneumonia. 20081554_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20098615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20181817_membrane blebbing in response to AT(1)R signaling is dependent on beta-arrestin2 and is mediated by a RhoA/ROCK/MLCK-dependent pathway 20207250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453870_study concludes MLCK is responsible for high proliferative ability of breast cancer cells through anti-apoptosis, in which p38 pathway was involved 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20861316_Studies indicate an essential role for Abl kinase in vascular barrier regulation via posttranslational modification of nmMLCK. 21055718_genetic and functional studies support the conclusion that heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in MYLK are associated with aortic dissections. 21297165_Data identify a novel interaction between cardiac-specific Ig-like domain C0 and the regulatory light chain of myosin, thus placing the N terminus of the protein in proximity to the motor domain of myosin. 21652678_Results provide evidence that neutrophil transmigration is regulated by myosin light chain kinase-mediated endothelial cell contraction and that this event depends on subendothelial cell matrix stiffness. 22015949_MYLK SNPs downregulate smooth muscle MLCK promoter activity due to interruption of a FOXN1 binding site. These data provide new insights into the contribution of MYLK SNPs to inflammatory disease susceptibility. 22135309_IL-18 may potentiate inflammation in the context of inflammatory bowel disease by facilitating neutrophil transepithelial migration via MLCK-dependent disruption of tight junctional occludin. 22219181_MLCK is essential for the translocation and association of cortactin and p47phox. 22377736_Hypermethylated FAM5C and MYLK in serum are strongly associated with the development of gastric cancer and can be used as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and pre-warning. 22808459_The approximate time period of changes in the ratios of MLCK-108 and MLCK-210 was revealed (between 8-9 and 13 weeks), that can be associated with functional changes in the developing myocardium. 23306855_Claudin-2 assumes an important role in colorectal inflammation, and furthermore implicates the involvement of MLCK in colon inflammation. 23492194_Increased human lung endothelial cell expression of MYLK by bioactive agonists (excessive mechanical stress, TNF-alpha) is regulated in part by specific miRNAs (miR-374a, miR-374b, miR-520c-3p, and miR-1290). 23656735_these studies show that the IL-1beta-induced increase in intestinal tight junction permeability was regulated by p38 kinase activation of ATF-2 and by ATF-2 regulation of MLCK gene activity 23951055_Results suggest that Aurora B, but not Rho/MLCK (myosin-light-chain kinase) signaling, is essential for the localization of 2P-MRLC (myosin regulatory light chains) to the midzone in dividing HeLa cells. 24722483_IgE has a role in regulating smMLCK in HASM cells 24911373_epithelial MLCK-activated brush border fanning by IFN-gamma promotes adherence and internalization of normally noninvasive enteric bacteria 25179839_These findings suggested that low MYLK and MYL9 expressions might be associated with the development of NSCLC. 25181625_Data suggest that expression of MLCK, myosin light chain, and myosin heavy chain 11 (MYH11) is up-regulated in uterine myoma as compared to adjacent smooth muscle cells; phosphorylation/activation of MLCK appears to be involved in cell proliferation. 25271083_nmMLCK variant (721C) mRNA secondary structure exhibits increased stability and greater efficiency in protein translation initiation. 25483583_The Smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) contributes to Ca(2+) flux regulation in vascular smooth muscle (VSM) and in non-muscle cells, where cytoskeleton has been suggested to help Ca(2+) channels trafficking. 25562159_Melatonin protects the esophageal epithelial barrier by suppressing the transcription, translation and activity of MLCK through ERK1/2 signal transduction 25582918_inhibition of p38 MAP kinase attenuated the histamine response in all three EC types. Inhibition of RhoA, ROCK, or MLCK also prevented the histamine-induced decrease in TER in HDMEC. 25696011_serum MLCK is associated with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. 26025125_Fine mapping of the myosin light chain kinase (MYLK) gene replicates the association with asthma in populations of Spanish descent. 26111161_These structure-function studies suggest novel mechanisms for nmMLCK regulation, which may confirm MYLK as a candidate gene in inflammatory lung disease and advance knowledge of the genetic underpinning of lung-related health disparities. 26147384_Gene-based association analyses shows nominal significant association with multifocal fibromuscular dysplasia for myosin light chain kinase. 26334100_TKS5 and MYLK represent two mediators of invasive behavior of cancer cells that are regulated by the ZEB1/miR-200 feedback loop 26334299_study demonstrates that G. duodenalis-mediated disruption of villin is, at least, in part dependent on activation of myosin light chain kinase (MLCK). 26468005_We speculate that the drop of the ROCK-to-MLCK ratio may occur as an attempt to compensate for the increased Rho kinase activity. 26607798_suggest a novel role for myosin light chain and myosin light chain kinase in advanced glycation end product-induced endothelial hyperpermeability 26854089_Likely pathogenic variants included a TGFB2 variant in one patient and a SMAD3 variant in another. These variants have been reported previously in individuals with similar phenotypes. Variants of uncertain significance of particular interest included novel variants in MYLK and MFAP5, which were identified in a third patient 26876209_loss of MLCK contributes to the migratory properties of epithelial cells resulting from changes in cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesions, and increased epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. 27375035_Its phosphorylation and dephosphorylation regulate smooth muscle contraction and relaxation. 27440420_PXR regulates the intestinal epithelial barrier during inflammation by modulating cytokine-induced MLCK expression and JNK1/2 activation 27483374_Sixty-seven experienced runners competed in a marathon race. The MLCK genotype (C37885A) of these marathoners was determined. CA heterozygotes for MLCK C37885A might present higher exercise-induced muscle damage after a marathon competition than CC counterparts. 27529643_mechanical stress and MYLK single nucleotide polymorphism regulate MYLK alternative splicing. 27543902_these Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)-associated MYLK cytosine-guanine dinucleotides with effect modification by ethnicity and local modified cytosine quantitative trait loci suggest that MYLK epigenetic variation and local genetic background may contribute to health disparities observed in ARDS. 27563827_High expression of MLCK is correlated with metastatic triple negative breast cancer. 27586135_A 2-bp deletion in myosin light chain kinase (c3272_3273del, p.Ser1091*) that led to a premature stop codon have a high risk of presenting with an acute aortic dissection or rupture. 27869798_Data show that alterations in myosin light chain kinase activity, claudin-15 and claudin-2 expression are associated with gluten-induced symptomatology and intestinal permeability changes in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D). 28260490_In contrast to mylk2 and mylk3, mylk1 has a complex structure, and multiple protein products of the mylk1 gene are expressed in most if not all cell types. This review deals with the mylk1 gene and its protein products- multiple MLCK isoforms and noncatalytic KRP/telokin protein. [Review] 28391269_Rebeccamycin attenuates TNF-alpha-induced disruption of intestinal epithelial barrier integrity by inducing claudin-5 expression and suppressing MLCK production via Chk1 activation. 28401540_We identified 2 novel disease-causing MYLK mutations using TAAD gene panel sequencing, 3explaining the cardiovascular phenotype in 0.6% of the cases (n = 358). Both heterozygous point mutations result in a pre-mature termination codon, probably leading tononsense-mediated mRNA decay and, hence, haploinsufficiency 28602422_three Megacystis microcolon intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome (MMHS)-affected subjects from two consanguineous families with no variants in the known MMIHS-associated genes. 28696205_Interaction between kinase domain and regulatory light chain (RLC) substrate is identified in the absence of calmodulin, indicating restored substrate-binding capability due to mechanically induced removal of the auto-inhibitory regulatory region. 29057883_nmMLCK is a potential molecular target to counteract early stages of atherosclerosis, such as endothelial dysfunction, inflammation through its capacity to increase transendothelial migration of monocytes and, most importantly, through the reorganization of VAMP-dependent vesicles associated with the release of IL-6 in modeled obstructive sleep apnea. 29077485_Report direct role for hnRNPA1 in MYLK alternative splicing in lung endothelial cells. 29262413_Recombinant human MLCK was concentration- and time-dependently degraded by recombinant human MMP9 in vitro, and this process was prevented by the MMP9 inhibitor. 29544503_This study found that MYLK gene Ala1491Ser mutation affect the kinase activity and clinically, it presents with vascular aneurysms and dissection. 29767236_the MAPKspecific inhibitor SB203580 attenuated the inhibitory effects of 4HPR on the migration of HepG2 cells. Moreover, we also observed that 4HPR inhibited the activation and expression of myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) in HepG2 cells. 29901087_miR155 directly suppressed the expression of MYLK without affecting the RhoA pathway. 29925964_These data further define the aortic phenotype associated with MYLK pathogenic variants. Given minimal aortic enlargement before dissection, an alternative approach to guide the timing of aortic repair is proposed based on the probability of a dissection at a given age 30737779_that AR-v12 is highly expressed in gastric cancer tissues and promotes migration and invasion through directly regulating MYLK 30936544_a unique domain within the MLCK splice variant MLCK1 directs perijunctional actomyosin ring (PAMR) recruitment. 31742692_Silencing of long noncoding RNA SRRM2-AS exerts suppressive effects on angiogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via activating MYLK-mediated cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. 32086378_Cardiac myosin regulatory light chain kinase modulates cardiac contractility by phosphorylating both myosin regulatory light chain and troponin I. 32495861_CircRNA_MYLK promotes malignant progression of ovarian cancer through regulating microRNA-652. 33438217_Silencing of long noncoding RNA MYLK-AS1 suppresses nephroblastoma via down-regulation of CCNE1 through transcription factor TCF7L2. 33800915_MYLK and PTGS1 Genetic Variations Associated with Osteoporosis and Benign Breast Tumors in Korean Women. 34000008_A novel tumor suppressor role of myosin light chain kinase splice variants through downregulation of the TEAD4/CD44 axis. 34056735_CircMYLK promotes the growth, migration, invasion, and survival of bladder cancer cells by upregulating CCND3 level via competitively binding to miR-34a. 34319762_Myosin light chain kinase-driven myosin II turnover regulates actin cortex contractility during mitosis. 34588420_CHD1L prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatocellular carcinomar cell death by activating hnRNP A2/B1-nmMYLK axis. 34747428_Procyanidin A1 and its digestive products prevent acrylamide-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction via the MAPK-mediated MLCK pathway. 35278271_SIK2 promotes ovarian cancer cell motility and metastasis by phosphorylating MYLK. 36170767_The m(6)A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes trophoblast cell invasion by regulating MYLK expression. | ENSMUSG00000022836 | Mylk | 571.573622 | 2.089107499 | 1.062887 | 0.12120171 | 75.869150 | 0.0000000000000000030309861334269849780901003898795980577890775888586427297410885728368157288059592247009277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000001867728371558443506910188290843527990428800248431245867308803099149372428655624389648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 819.7944355 | 56.9357918 | 394.2737019 | 28.3764130 | |
| ENSG00000066056 | 7075 | TIE1 | protein_coding | P35590 | FUNCTION: Transmembrane tyrosine-protein kinase that may modulate TEK/TIE2 activity and contribute to the regulation of angiogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20227369}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase | This gene encodes a member of the tyrosine protein kinase family. The encoded protein plays a critical role in angiogenesis and blood vessel stability by inhibiting angiopoietin 1 signaling through the endothelial receptor tyrosine kinase Tie2. Ectodomain cleavage of the encoded protein relieves inhibition of Tie2 and is mediated by multiple factors including vascular endothelial growth factor. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. | hsa:7075; | plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; aortic valve morphogenesis [GO:0003180]; branching involved in lymph vessel morphogenesis [GO:0060854]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; lymphatic endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0060836]; mesoderm development [GO:0007498]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; plasma membrane fusion [GO:0045026]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001936]; regulation of extracellular matrix assembly [GO:1901201]; response to retinoic acid [GO:0032526]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; tissue remodeling [GO:0048771]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570] | 11866538_Vascular endothelial growth factor modulates the Tie-2:Tie-1 receptor complex 11920509_high expression independently associated with shorter survival in patients with early chronic phase CML 17724803_Results describe the expression of angiopoietin-1, 2 and 4 and Tie-1 and 2 in gastrointestinal stromal tumors, leiomyomas and schwannomas. 17728252_Activation of Tie1 ectodomain cleavage increases cartilage oligomeric protein angiopoietin 1 activation of Tie2. 17786322_Overexpression and activation of Tie1 is associated with breast and colonic neopalsms 18675456_the trophoblastic shell of the very early human placenta, as well as endothelial cells and ACC exhibited strong staining intensity for Tie-1 19236867_Tie-1 has an inflammatory function in endothelial cells. 19880500_A natural antisense transcript was identified for tyrosine kinase containing immunoglobulin and epidermal growth factor homology domain-1 (tie-1), tie-1AS long noncoding RNA in zebrafish, mouse, and humans. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20164029_The Tie-1 immunoreactivity was dominantly observed in the heamangiogenic cells and cells cords, whereas the matured villi showed immunoreactivity only in other components. 20227369_Provide evidence for Tie1-Tie2 complex formation on the cell surface and identify molecular surface areas essential for recognition. The Tie1-Tie2 interactions are dynamic, inhibitory, and differentially modulated by angiopoietin-1 and -2. 20346360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22235284_the effects of factors activating ectodomain cleavage on both Tie1 and Tie2 within the same population of cells, and their impact on angiopoietin signalling 22342979_these results suggest that the expression level of Tie1 and its physical interaction with Tie2 defines whether Ang2 functions as a Tie2 agonist or antagonist, thereby determining the context-dependent differential endothelial sensitivity to Ang2. 22421998_Data propose that EndMT associated with Tie1 downregulation participates in the pathological development of stroma observed in tumours. 22987233_The decreasing expression of Tie1 may play an important role in the pathogenesis of primary lower extremity varicose veins. 26436659_T794A-expressing human umbilical vein endothelial cells formed significantly shorter tubes with fewer branches in three-dimensional Matrigel cultures, but did not alter Tie1 or Tie2 tyrosine phosphorylation or downstream signaling. 26489611_The inhibition of Tie-2 exerted by Tie-1can be relieved by Tie-1 ectodomain cleavage mediated by tumor- and inflammatory-related factors, which causes destabilization of vessels and initiates vessel remodeling in cancer. (Review) 27548530_Tie1 directly interacts with Tie2 to promote ANG-induced vascular responses under noninflammatory conditions, whereas in inflammation, Tie1 cleavage contributes to loss of ANG2 agonist activity and vascular stability 27695111_In vitro binding assays with purified components reveal that Tie-integrin recognition is direct, and further demonstrate that the receptor binding domain of the Tie2 ligand Ang-1, but not the receptor binding domain of Ang-2, can independently associate with a5b1 or aVb3. cooperative Tie/integrin interactions selectively stimulate ERK/MAPK signaling in the presence of both Ang-1 and fibronectin 27941161_Ang,Tie1 and Tie2 play roles in vascular development and pathogenesis of vascular diseases.[review] 28464467_We identified colorectal cancer as a novel Tie1-expressing tumor, with Tie1-positive cells hardly detectable in the normal intestine. Tie1 expression did not influence cancer cell proliferation in regular in vitro cultures, but significantly affected malignant growth of transplanted tumors in vivo. 29355844_Tie1 has regulatory functions in angiogenesis and vascular abnormalization as well as metastasis 30806032_Results found deregulated expression of TIE1 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tissues to be associated with poor clinical outcome. 31340773_Study in metastatic breast cancer patients treated with a taxane-bevacizumab combination chemotherapy revealed that overall and progression-free survival was significantly shorter in patients with a high baseline Tie1 level demonstrating the prognostic value of baseline Tie1 plasma concentration in patients with metastatic breast cancer. 32947856_TIE1 as a Candidate Gene for Lymphatic Malformations with or without Lymphedema. 33812182_Involvement of small extracellular vesicle-derived TIE-1 in the chemoresistance of ovarian cancer cells. 34942230_A novel cis-regulatory variant modulating TIE1 expression associated with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in Han Chinese children. | ENSMUSG00000033191 | Tie1 | 22.153402 | 0.475453051 | -1.072625 | 0.40433379 | 6.857285 | 0.0088280601694472118912138114410481648519635200500488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0450025166363803158509071522530575748533010482788085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 13.8309551 | 3.2112025 | 29.0233783 | 6.8686582 | |
| ENSG00000067840 | 57595 | PDZD4 | protein_coding | Q76G19 | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | Predicted to be located in cell cortex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:57595; | cell cortex [GO:0005938]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] | 15077175_Might play an important role in the proliferation of SS cells and might be a suitable target for SS drugs. 15138636_PDZRN4L showed 49.9% total-amino-acid identity with PDZRN4 short isoform (PDZRN4S). PDZ, PR34H1 and PR34H2 domains were conserved between PDZRN4L and PDZRN4S. | ENSMUSG00000002006 | Pdzd4 | 44.871600 | 0.481597633 | -1.054100 | 0.28973405 | 13.186926 | 0.0002819088833762946788748238180488669968326576054096221923828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0025424509739958799613146478435510289273224771022796630859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 28.8324189 | 8.2901528 | 60.2451548 | 16.8912857 | ||
| ENSG00000069493 | 29121 | CLEC2D | protein_coding | Q9UHP7 | FUNCTION: Receptor for KLRB1 that protects target cells against natural killer cell-mediated lysis (PubMed:20843815, PubMed:16339513). Inhibits osteoclast formation (PubMed:14753741, PubMed:15123656). Inhibits bone resorption (PubMed:14753741). Modulates the release of interferon-gamma (PubMed:15104121). Binds high molecular weight sulfated glycosaminoglycans (PubMed:15123656). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14753741, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15104121, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15123656, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16339513, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20843815}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Lectin;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA | This gene encodes a member of the natural killer cell receptor C-type lectin family. The encoded protein inhibits osteoclast formation and contains a transmembrane domain near the N-terminus as well as the C-type lectin-like extracellular domain. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2010]. | hsa:29121; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; natural killer cell lectin-like receptor binding [GO:0046703]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166] | 15104121_LLT1 induces Interferon Type II production by natural killer cells. 15123656_Data show that osteoclast inhibitory lectin (OCIL) binds a range of physiologically important glycosaminoglycans, and this property may modulate OCIL actions upon other cells [OCIL]. 16339512_Engagement of CD161 on NK cells with LLT1 expressed on target cells inhibited NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity and IFN-gamma secretion. LLT1/CD161 interaction in the presence of a TCR signal enhanced IFN-gamma production by T cells 16339513_LLT1 on target cells can inhibit NK cytotoxicity via interactions with CD161. LLT1 activates NFAT-GFP reporter cells expressing a CD3zeta-CD161 chimeric receptor; reciprocally, reporter cells with a CD3zeta-LLT1 chimeric receptor are stimulated by CD161 18453569_Expression of LLT1 on activated dendritic cells and B cells suggests that it might regulate the cross-talk between NK cells and APCs 18465072_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18465072_Women with a lysine (GG genotype) at position 19 of the OCIL protein displayed lower bone mineral density at femoral neck and at lumbar spine sites than women having an asparagine residue. 18593762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20415786_LLT1 used Src-PTK, p38 and ERK signalling pathways, but not PKC, PI3K or calcineurin pathways, to increase production of IFN-gamma by human natural killer cells. 20843815_Data show that only CLEC2D isoform 1 (LLT1) is expressed on the cell surface. 21572041_Molecular basis for LLT1 protein recognition by human CD161 protein (NKRP1A/KLRB1). 21930700_LLT1 and CD161 have roles in modulating immune responses to pathogens; and interferon-gamma contributes to modulate immune responses 22664939_One polymorphism in LLT1 was found to be associated with our Crohn's Disease population (P | ENSMUSG00000030155+ENSMUSG00000030157+ENSMUSG00000030364+ENSMUSG00000030365+ENSMUSG00000000248 | Clec2e+Clec2d+Clec2h+Clec2i+Clec2g | 82.114527 | 0.388008835 | -1.365839 | 0.33726810 | 16.074318 | 0.0000609044370373185644336119781705463083198992535471916198730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0006634978701542150469894210118582122959196567535400390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 48.4542481 | 12.8331200 | 124.3242367 | 32.0614456 |
| ENSG00000070018 | 4040 | LRP6 | protein_coding | O75581 | FUNCTION: Component of the Wnt-Fzd-LRP5-LRP6 complex that triggers beta-catenin signaling through inducing aggregation of receptor-ligand complexes into ribosome-sized signalsomes. Cell-surface coreceptor of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, which plays a pivotal role in bone formation. The Wnt-induced Fzd/LRP6 coreceptor complex recruits DVL1 polymers to the plasma membrane which, in turn, recruits the AXIN1/GSK3B-complex to the cell surface promoting the formation of signalsomes and inhibiting AXIN1/GSK3-mediated phosphorylation and destruction of beta-catenin. Required for posterior patterning of the epiblast during gastrulation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11357136, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11448771, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15778503, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16341017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16513652, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17326769, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17400545, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19107203, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19293931, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19801552}. | 3D-structure;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Endocytosis;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Isopeptide bond;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation;Wnt signaling pathway | This gene encodes a member of the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor gene family. LDL receptors are transmembrane cell surface proteins involved in receptor-mediated endocytosis of lipoprotein and protein ligands. The protein encoded by this gene functions as a receptor or, with Frizzled, a co-receptor for Wnt and thereby transmits the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling cascade. Through its interaction with the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling cascade this gene plays a role in the regulation of cell differentiation, proliferation, and migration and the development of many cancer types. This protein undergoes gamma-secretase dependent RIP- (regulated intramembrane proteolysis) processing but the precise locations of the cleavage sites have not been determined.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2009]. | hsa:4040; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; Wnt signalosome [GO:1990909]; Wnt-Frizzled-LRP5/6 complex [GO:1990851]; coreceptor activity involved in canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:1904928]; coreceptor activity involved in Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0071936]; frizzled binding [GO:0005109]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0019210]; low-density lipoprotein particle receptor activity [GO:0005041]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; toxin transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0019534]; Wnt receptor activity [GO:0042813]; Wnt-protein binding [GO:0017147]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in neural crest cell differentiation [GO:0044335]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in regulation of cell proliferation [GO:0044340]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cellular response to cholesterol [GO:0071397]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:0071542]; midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:1904948]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; negative regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071901]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0034392]; neural crest cell differentiation [GO:0014033]; neural crest formation [GO:0014029]; positive regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045787]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; receptor-mediated endocytosis involved in cholesterol transport [GO:0090118]; response to peptide hormone [GO:0043434]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055]; Wnt signaling pathway involved in midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:1904953]; Wnt signaling pathway involved in somitogenesis [GO:0090244] | 12897152_Wnt canonical signaling through LRP6 establishes a novel mechanism for receptor activation which is opposite to the general paradigm of ligand-induced receptor oligomerization 15271658_role for an LDL receptor-related protein in the regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and survival through the evolutionary conserved Wnt signaling cascade. 15516984_LRP6 may function as a potential oncogenic protein by modulating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling 15908424_SOST antagonizes Wnt signaling by binding to the extracellular domain of the Wnt coreceptors LRP5 and LRP6 and disrupting Wnt-induced Frizzled-LRP complex formation. 16263759_Together our results show that in addition to serving as a folding chaperone, Mesd can function as a receptor antagonist by inhibiting ligand binding to mature LRP6. 16355283_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16365045_a direct interaction between LRP6 and GSK3 results in an attenuation of GSK3 activity 16384981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16384981_These data suggest that LRP6, VEGF, and VLDLR may play a role in the risk of developing (age-related macular degeneration)AMD. 16513652_active CKIepsilon generation may induce a negative feedback loop by phosphorylation of sites on LRP5/6 that modulate axin binding and hence beta-catenin degradation 16564009_LRP6 is required for anthrax toxin lethality; LRP6 enables toxin internalization by interacting at the cell surface with PA receptors 16989816_Mesd and LRP6 modulate Wnt signaling. 17326769_These findings suggest a novel mechanism for LRP6 in Wnt signaling: induction of ectodomain shedding of LRP6, followed by the gamma-secretase involved proteolytic releasing its intracellular domain. 17332414_results link a mutation in LRP6 which encodes a co-receptor in the Wnt signaling pathway to coronary artery disease and multiple cardiovascular risk factors 17376403_The finding that GRB10 interferes with the binding of Axin to LRP6 indicated a possible molecular mechanism by which the overexpression of GRB10 suppresses Wnt signaling. 17517621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17517621_report the association between common LRP6 variants and late-onset Alzheimer's disease in a multicenter case-control series as well as in a large family-based series ascertained 17569865_it is proposed that Wnts induce coclustering of receptors and Dvl in LRP6-signalosomes, which in turn triggers LRP6 phosphorylation to promote Axin recruitment and beta-catenin stabilization 17698587_Results identify a novel feedback mechanism by which Wnt, including Wnt3a, negatively regulates LRP6 at the mRNA level. 17765217_While secreted Wise either synergizes or inhibits the Wnt signals depending on the partner ligand, ER-retained Wise consistently blocks the Wnt pathway. ER-retained Wise reduces LRP6 on the cell surface, making cells less susceptible to the Wnt signal. 17804805_RSPO1 regulates Wnt signaling by inhibiting internalization of LRP6. 18077588_Both Fz and Dvl functions are critical for Wnt-induced Lrp6 phosphorylation through Fz-Lrp6 interaction. Axin, a key scaffolding protein in the Wnt pathway, is required for Lrp6 phosphorylation via its ability to recruit Gsk3. 18083125_each LRP6 PPPS/TP motif contributes in a combinatorial fashion to activate the canonical Wnt-beta-catenin pathway 18350154_data argue against a human-specific role for LRP6 in anthrax toxin entry and suggest instead that involvement of this protein may be restricted to certain cell types independently of their species of origin 18362152_PPPSP motifs represents a built-in amplifier for Wnt signaling by the LRP6 family of receptors. 18378904_propose that palmitoylation serves to tilt the long, 23-residue transmembrane domain of LRP6 with respect to the plane of membrane to prevent a hydrophobic mismatch and subsequent recognition by the ER quality control 18406176_No association was seen between FRZB, LRP5 and LRP6 variants with radiographic osteoarthritic outcomes in two population-based cohorts 18406176_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18493104_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18493104_We found no evidence for a substantial effect of LRP5 or LRP6 SNPs on susceptibility to type 2 diabetes or clinical characteristics of diabetic subjects in Japanese population. 18502762_Kremen may not be essential for Dkk1-mediated Wnt antagonism and Kremen may only play a role when cells express a high level of LRP5/6 18505732_DKK1 inhibition of LRP6 is independent of LRP6 internalization and degradation 18524778_analysis of the structural basis of the interaction between Dkk and low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) 5/6 18606139_WNT3 and DKK1 regulate distinct internalization pathways of LRP6 to tune the activation of beta catenin signaling. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18717822_The authors show that LRP6 can indeed form a complex with anthrax toxin receptors, and that this interaction plays a role both in Wnt signalling and in anthrax toxin endocytosis. 18772438_Wnt3a stimulates formation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate through frizzled & dishevelled; in turn PtdIns (4,5)P2 regulated phosphorylation of LRP6 at Thr1479 & Ser1490; study reveals signaling mechanism for Wnt to regulate LRP6 phosphorylation 18838381_BAMBI interacts with Wnt receptor Frizzled5, coreceptor LRP6, and Dishevelled2 and increases the interaction between Frizzled5 and Dishevelled2 18981475_PTH treatment led to phosphorylation of LRP6 and an increase in amount of beta-catenin in osteoblasts with a concurrent increase in bone formation in rat. Thus, LRP6 coreceptor is a key element of the PTH signaling that regulates osteoblast activity. 19015224_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19107203_Phosphorylated LRP6/5 both recruits and directly inhibits GSK3beta using two distinct portions of its cytoplasmic sequence. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19293931_propose a working model that Axin recruitment to the phosphorylated LRP6 places GSK3 in the vicinity of multiple phosphorylated PPPSPXS motifs 19339249_These studies reveal unique properties of the LRP6 beta-propeller domains and provide novel tools to understand LRP6 function in ligand binding and Wnt signaling. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19477926_Results identify the first propeller domain as a novel regulatory domain for DKK1 binding to LRP6. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19667113_A common variant in low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 gene (LRP6) is associated with LDL-cholesterol. 19667113_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19711366_PPP(S/T)P motif phosphorylation of the free LRP6 intracellular domain is not required to activate the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and attenuate GSK3beta activity 19801552_Results identify GRK5/6 as novel kinases for the single transmembrane receptor LRP6 during Wnt signaling. 19833493_LRP6 variants with impaired Wnt/beta-catenin signaling appear to be involved in early coronary and carotid artery atherosclerosis, at least in hypertensive patients. 19833493_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19881541_found that mammary glands from mouse mammary tumor virus-LRP6 mice exhibit significant Wnt activation evidenced by the translocation of beta-catenin from membrane to cytoplasmic/nuclear fractions. 19898734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19898734_results suggest that SNP in LRP6, is not associated with bone mineral density in the Slovenian population 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20053636_Results suggest that Dkk1 induces the internalization of LRP6 to suppress its phosphorylation in the lipid raft and allows subsequent recycling of LRP6 so that it can be reused for signaling. 20057906_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20093360_analysis of the frizzled8.Wnt3a.LRP6 signaling complex reveals multiple Wnt and Dkk1 binding sites on LRP6 20137080_The canonical Wnt-signaling proteins LRP6 and Dvl2 and Dvl3 are involved in the regulation of beta-catenin. 20194742_Expression of the Wnt signaling coreceptor LRP6 is up-regulated in a subpopulation of human breast cancers. 20351274_SERPINA3K is a high-affinity, endogenous antagonist of LRP6 20388731_Dishevelled signals through LRP5/6 in human cells and Drosophila embryos. 20390408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20460648_Gbetagamma activates GSK3 to promote LRP6-mediated beta-catenin transcriptional activity 20543981_results reveal a novel role for Dkk1 in preventing Wnt ligand-induced LRP6 down-regulation and contribute significantly to our understanding of Dkk1 function in Wnt/LRP6 signaling 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20676368_Results suggest that LRP6-ICD can differentially modulate Wnt pathway transcriptional activity depending upon its subcellular localization and differential protein-protein interactions. 20846389_The mRNA expression levels of DKK-1 binding receptor LRP5/6 and Krm1/2 in SCs from patients with MM were significantly higher than those in myeloma cells and in SCs from healthy donors. 20926594_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20926594_We found common polymorphisms of LRP5 associated with osteoporotic fractures, and polymorphisms of the LRP6 gene associated with BMD, thus suggesting them as likely candidates to contribute to the explaination of the hereditary influence on osteoporosis. 20974802_direct phosphorylation of LRP6 by MAPKs provides a unique point for convergence between WNT/beta-catenin signaling and mitogenic pathways 21245321_findings implicate LRP6 as a critical modulator of PDGF-dependent regulation of cell cycle in smooth muscle and indicate that loss of this function contributes to development of early atherosclerosis in humans 21397183_Two structural and functional domains of MESD required for proper folding and trafficking of LRP5/LRP6. 21536646_these results identified TMEM198 as a membrane scaffold protein that promotes LRP6 phosphorylation and Wnt signaling activation. 21887268_These studies uncover a new and important molecular tuning mechanism for differential regulation of LRP5 and LRP6 phosphorylation and signaling activity. 21944579_The consensus E1 binding sequence motif is important for DKK1 and SOST binding to LRP6 and for inhibitory function. 21984209_Results provide key insights for understanding LRP5/6 structure and the interaction of LRP5/6 with DKK1, as well as for drug discovery. 22000855_The LDL-receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6), alongside Frizzled receptors, transduces Wnt signaling across the plasma membrane. 22000856_The Wnts bound to either portion of the LRP6 ectodomain likely bear a similar spatial relationship to Frizzled coreceptors. 22128165_LRP6 protein regulates low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor-mediated LDL uptake. 22372892_The conformation of the LRP6 intracellular domain is elongated before activation; this is based on the intrusion of the Frizzled complex into the ensemble space of the proline rich region of LRP6, which alters the shape of its available ensemble space. 22393312_LRP6 as a new candidate gene in ileal Crohn's Disease; an association of a non-synonymous SNP (rs2302685; Ile1062Val) with early onset ileal Crohn's Disease 22490400_The C allele of the rs11054731 within the LRP6 gene was associated with increased risk and extent of CAD in Chinese. 22570728_overexpression of LRP6 contributes to the hyperactivation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in human HCCs and suggest it may play a role in hepatocarcinogenesis. 22589387_Crystal structures of the LRP6 ectodomain in complex with DKK1, along with mutagenesis studies, provide considerable insights into the molecular basis for DKK-mediated inhibition and Wnt signaling through LRP5/6 22606268_sLRP6E1E2, by inhibiting interaction between Wnt and its receptor, suppressed Wnt-induced cell proliferation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. 22696217_peptide derived from the loop 2 region of sclerostin blocked the interaction of sclerostin with LRP5/6 and also inhibited Wnt1 but not Wnt3A or Wnt9B signaling. This suggests that these Wnts interact with LRP6 in different ways 22871567_These results demonstrate LRP6 as the predominant Wnt3a LRP-receptor in human mesenchymal stem cells, which cannot be substituted by LRP5. 22907437_Arf modulates LRP6 phosphorylation for the transduction of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 23077088_Data indicate that LRP6, BCL2L14, DUSP16, CREBL2, and CDKN1B were involed in centromeric (12p11.21-12p13.2) deletion in ETV6-RUNX1 B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL). 23218566_The LRP6delta3 isoform is a novel splice variant which shows diminished wnt signaling activity and is associated with Alzheimer's disease. 23302227_results show that Cav-1 interacts with LRP6 to generate an integrated signaling module that leads to the activation of IGF-IR/IR and results in stimulation of Akt-mTORC1 signaling and aerobic glycolysis in prostate cancer 23306204_SOX9 regulates low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6) and T-cell factor 4 (TCF4) expression and Wnt/beta-catenin activation in breast cancer. 23395167_the LRP6(R611C) mutation diminishes TCF7L2-dependent transcription of the IR while it increases the stability of IGFR and enhances mTORC1 activity. 23638027_Wnt3a-induced transcriptional responses and induction of alkaline phosphatase activity, an early marker of osteoblast differentiation, require the Wnt co-receptors LRP5 and LRP6 23666756_A novel role of kallistatin in preventing breast tumor growth and mobility by direct interaction with LRP6. 23703864_Americans with early onset familial coronary artery disease and metabolic syndrome and healthy Northern European controls were screened for nonconservative mutations in LRP6; 3 novel mutations were identified which cosegregated with the metabolic traits in the kindreds of affected subjects and none in controls 23754096_Pantoprazole treatment caused a decrease in phospho-LRP6, but not in LRP6. 23773994_Results indicate that Lrp6 mediates not only canonical Wnt signaling, but can also modulate non-canonical pathways involving RhoA-dependent mechanisms to impact neurulation, possibly through intracellular complexes with DAAM1. 23811937_Data indicate that upregulated miR-126 upon coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) infection targets SPRED1, LRP6, and WRCH1 genes, mediating cross-talk between ERK1/2 and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways, and thus promoting viral replication. 23987510_Lypd6 appears to control Lrp6 activation specifically in membrane rafts, which is essential for downstream signaling. 24203697_This study demonstrates the association of rare and novel missense mutations in LRP6 that is an inhibitor rather than an activator of the non-canonical planar cell polarity pathway with human neural tube defects. 24265322_Data show that beta-arrestins regulate Wnt3a-induced low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (Lrp6) phosphorylation by the regulation of the membrane dynamics of Amer1. 24392029_Syndecan-1 modulates the cancer stem cell phenotype via regulation of the Wnt and IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathways 24412065_GSK3 is sequestered into multivesicular bodies through and interaction between p120-catenin/cadherin and LRP5/6. 24427284_results demonstrated that the novel loss-of-function variants identified in this study might contribute to disease liability in a subset of coronary artery disease (CAD) and defects in Wnt signal activation might be important contributing factors for the onset of CAD 24457908_LRP6 may influence glucose metabolism in type II fibers of human skeletal muscles. 24607787_Rottlerin is a novel LRP6 inhibitor, promoting protein degradation. 24704686_Data indicate that miR-202 suppresses the expression of LRP6 (low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6) by binding to the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of its mRNA. 24743782_The results suggested that the lack of affinity between human DKK3 and human LRP5/6 results from: i) insertion of the 7 amino acids, and ii) P258 in human DKK3. 24843317_The LRP6 rs10845498 SNP is associated with a reduced risk of lung SCC, while tobacco smoke increases the risk 24906453_Data provides the first evidence that LRP6 rs2302685 polymorphism is associated with an increased risk of MI in Chinese subjects, and the association is more evident among younger individuals, which probably due to the elevated LDL-C levels. 25143377_The LRP6 tyrosine mutant increased in signaling activation in response to Wnt3a/beta-catenin stimulation. 25240815_the metastasis and angiogenesis functions of miR-126-3p were mediated by LRP6 and PIK3R2. 25242217_LRP6 (and Wnt signaling) are significantly downregulated in Alzheimer's disease brains. 25301448_High LRP6 expression is associated with glioblastoma. 25358452_Particularly for TNBC associated with Skp2/LRP6 overexpression. 25425204_The interaction between Wnt isoforms and their LRP6 cognate receptor depends on the jutting loop present in Wnt3a but absent in Wnt5b. 25500543_LRP6 phosphorylation by ERK1/2 may provide a unique point of convergence between KRAS/MAPK and Wnt/beta-catenin signalings during oncogenesis 25546815_LRP6 variants outside of YWTD repeats could potentially predispose embryos to neural tube defectss, whereas Lrp6 modulation of Wnt/planar cell polarity signaling would be more essential than its canonical pathway role in neural tube closure. 25783012_No mutations in LRP5 and LRP6 could be identified 25902418_Lrp6 binds to Frizzled, preventing Frz-regulated non-canonical Wnt pathway activation and further non-canonical pathway-mediated tumour metastasis. 25959626_findings suggest that rescuing LRP5/6-mediated Wnt signaling improves neuronal cell survival and reduces tau phosphorylation, which support the hypothesis that Wnt signaling might be an attractive therapeutic strategy for managing AD 26031789_LRP6 variants may be associated with risk of ischaemic stroke. 26063413_miR513c functions as a tumor suppressor miRNA, mediated predominantly through the direct suppression of the expression of LRP6. 26120271_LRP6 and VEGF levels in the vitreous body from patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy were increased and correlated mutually. 26387593_Loss-of-Function Mutations in the WNT Co-receptor LRP6 Cause Autosomal-Dominant Oligodontia. 26797284_Accordingly, we propose that the anti-fibrotic activity of adiponectin may be mediated through AdipoR1/R2 receptors 26963285_We identified a frameshift (c.4594delG, p.Cys1532fs) and a canonical splice-site mutation (c.3398-2A>C, p.?) in LRP6, respectively, in the patient with tooth agenesis (TA) and orofacial clefting (OFC) and in the patient with severe TA only. Mutations in LRP6 cause TA in humans 27089893_results suggest that miR-29b inhibits expression of LRP6 and HuR post-transcriptionally, thus playing a role in the regulation of IEC proliferation and intestinal epithelial homoeostasis. 27285107_sustained activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling due to abrogation of Merlin-mediated inhibition of LRP6 phosphorylation may be a cause of Neurofibromatosis type II disease. 27455246_Mutant LRP6 Impairs Endothelial Cell Functions Associated with Familial Normolipidemic Coronary Artery Disease. 27524201_Structure of the dual-mode Wnt regulator Kremen1 and insight into ternary complex formation with LRP6 and DKK1 have been presented. 27751231_The authors show that folding of the Wnt signaling coreceptor LRP6 is promoted by ubiquitination of a specific lysine, retaining it in the ER while avoiding degradation. 27821587_findings revealed an unrecognized role of Caprin-2 in facilitating LRP5/6 constitutive phosphorylation at G2/M through forming a quaternary complex with CDK14, Cyclin Y, and LRP5/6. 28042322_Taken together, this study reveals evidence demonstrating a mechanism by which the LPR6/ GSK3beta/E2F1 axis-upregulated LSH promoted gliomas. 28052259_LRP6 ectodomain becomes highly compact upon complexation with the Wnt antagonist Dkk1, suggesting a potential role for the ectodomain conformational change in the regulation of receptor oligomerization and signaling. 28187755_LncRNA PTCSC3 inhibits the proliferation and migration of glioma cells and suppresses Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway by targeting LRP6 28247948_data suggest that LRP6 promotes negative breast cancer cell migration and invasion by regulating the expression and function of S100A4 via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway 28387660_Increased LRP6 gene expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 28418856_High Expressions of LRP6 is associated with cancer. 28425175_VAP1 cleaved the extracellular region of LRP6 at Glu1196-Leu1197, the C-terminus of the 4th propeller domain. This cleavage removes four inhibitory beta-propeller structures, resulting in activation of LRP5/6. 28696417_we focus on the role of LRP6 genetic polymorphisms and Wnt signaling in complex diseases, and the mechanisms from mouse models and cell lines. It is also highly anticipated that LRP6 variants will be applied clinically in the future 28821575_LRP6 endocytosis proceeds by two routes, depending on the presence of LDL, and that LRP6 controls the intracellular destination of NPC1L1 in hepatocytes. 28870205_CCN2 plays a promoting role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)progression through activating LRP6 in a HSPGs-dependent manner. Heparin in combination with chemotherapy has a synergic effect and could be a treatment choice for HCCs with a high CCN2 expression. 28880263_LRP6 expression was found to be upregulated in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissues, and correlated with a cluster of clinicopathologic parameters, including smoking, drinking, tumor differentiation status, lymph node metastasis and survival time. 28960852_Three rare missense mutations (c.1514A>G, p.Y505C); c.2984A>G, p.D995G; and c.4280C>A, p.P1427Q) of the LRP6 gene were identified in Chinese NTD patients. The Y505C mutation is a loss-of-function mutation on both WNT/beta-catenin and PCP signaling. The D995G mutation partially lost inhibition on PCP signaling without affecting WNT/beta-catenin signaling. The P1427Q mutation dramatically increased WNT/beta-catenin signa... 29017031_identify ANGPTL4 as a Wnt signaling antagonist that binds to syndecans and forms a ternary complex with the Wnt co-receptor Lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 29402412_Therefore, our study demonstrates that miR-183 is a tumor suppressor microRNA that plays a major role in OS. 29439617_Study shows that low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 Is essential for trophoblast survival and invasion. 29500247_We identified rare damaging variants in four genes known to be mutated in syndromic lip and/or cleft palate (syCL/P) : TP63 (one family), TBX1 (one family), LRP6 (one family) and GRHL3 (two families), and clinical reassessment confirmed the isolated nature of their lip and/or cleft palate (CL/P). 29864925_knockdown of LRP6 inhibited the cell viability by activation of Drp1 in glucose deprived-cardiomyocytes. 30039844_LRP6 rs2302685 (V1062I) variant carriers are associated with an increased risk of hyperlipidemia in Iranian children and adolescents. 30069874_Results indicate the key role in the interaction of LY6/PLAUR domain containing 6 (LYPD6) with LDL receptor related protein 6 (LRP6). 30070011_LRP6 regulates alternative pre-mRNA splicing. 30361437_oligomerizations of FZDs and LRP5/6 can integrate the cytoplasmic protein Dishevelled into the LRP5/6 signalosome, resulting in a robust activation of ligand-independent beta-catenin signaling 30474181_association of LRP5 intronic rs4988319 and rs3736228 (Ala1330Val) with attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (cADHD) was observed among girls, whereas in boys association between LRP6 rs2302685 (Val1062Ile) and cADHD was present (OR = 1.66, CI = 1.20-2.31, p = .0024). In the PGC-ADHD dataset tendency of associations were observed only among females for LRP5 rs3736228 and for LRP6 rs2302685. 30583072_High LRP6 expression is associated with hepatocarcinogenesis. 30605688_Authors show that AAK1 promotes clearance of LRP6 from the plasma membrane to suppress the WNT pathway. 30684559_low-expressed LRP6 may be responsible of lower migration and invasion of extravillous trophoblasts and subsequent preeclampsia. 30711569_MEG3 functions as a potential hepatocyte lipid degeneration suppressor. MEG3 helps to alleviate lipid over-deposition, probably by binding to miR-21 to regulate the expression of LRP6. 30976847_We found that the rs2302685 mutation, which impaired the function of LRP6, was present in higher frequency among alcoholics with alcoholic liver disease than those without alcoholic liver disease 31085352_New explanation for autosomal dominant high bone mass: Mutation of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6. 31332306_the results together with previous data such as the development of Split-hand/foot malformation (SHFM) in Lrp6 knockout mice, the presence of SHFM in two subjects with 19q13 deletions involving UBA2, and strong mouse Uba2 expression in the developing limb buds, imply that LRP6 and UBA2 represent plausible candidate genes for SHFM. 31544984_LRP6 regulates Rab7-mediated autophagy through the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway to modulate trophoblast cell migration and invasion. 31588233_VSTM2A suppresses colorectal cancer and antagonizes Wnt signaling receptor LRP6. 31744930_Dynamic palmitoylation controls the microdomain localization of the DKK1 receptors CKAP4 and LRP6. 31811407_Cardiac-specific LRP6 knockout induces lipid accumulation through Drp1/CPT1b pathway in adult mice. 32076828_Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6-mediated signaling pathways and associated cardiovascular diseases: diagnostic and therapeutic opportunities. 32319541_LRP6 is involved in the proliferation, migration and invasion of trophoblast cells via miR346. 32573887_The rs2302685 polymorphism in the LRP6 gene is associated with bone mineral density and body composition in Iranian children. 32844563_A novel missense mutation of LRP6 identified by whole-exome sequencing in a Chinese family with non-syndromic tooth agenesis. 32945478_MicroRNA590 inhibits migration, invasion and epithelialtomesenchymal transition of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting lowdensity lipoprotein receptorrelated protein 6. 33065966_TRAP1 Regulates Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway through LRP5/6 Receptors Expression Modulation. 33097721_Sclerostin inhibits Wnt signaling through tandem interaction with two LRP6 ectodomains. 33118644_Clinical Phenotype and Relevance of LRP5 and LRP6 Variants in Patients With Early-Onset Osteoporosis (EOOP). 33136328_PAR1&2 driven placenta EVT invasion act via LRP5/6 as coreceptors. 33164649_Lrp6 Dynamic Expression in Tooth Development and Mutations in Oligodontia. 33391525_ERK1/2 inhibition reduces vascular calcification by activating miR-126-3p-DKK1/LRP6 pathway. 33391533_Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 regulates cardiomyocyte-derived paracrine signaling to ameliorate cardiac fibrosis. 33400244_MiR-30a suppresses clear cell renal cell carcinoma proliferation and metastasis by targeting LRP6. 33501755_Circ-LRP6 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and autophagy in oral squamous cell carcinomas. 33545636_Distinct roles of LRP5 and LRP6 in Wnt signaling regulation in the retina. 33676964_Hsa_circ_0099198 facilitates the progression of retinoblastoma by regulating miR-1287/LRP6 axis. 34042263_The complex role of Wnt ligands in type 2 diabetes mellitus and related complications. 34180138_Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 6 Cell Surface Availability Regulates Fuel Metabolism in Astrocytes. 34359960_Unveiling the Roles of Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 6 in Intestinal Homeostasis, Regeneration and Oncogenesis. 34615853_Transmembrane protein 97 exhibits oncogenic properties via enhancing LRP6-mediated Wnt signaling in breast cancer. 34671210_Lrp6 Genotype affects Individual Susceptibility to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Silibinin Therapeutic Response via Wnt/beta-catenin-Cyp2e1 Signaling. 34734756_PUM1 modulates trophoblast cell proliferation and migration through LRP6. 34896607_Variants in the Wnt co-receptor LRP6 are associated with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. 34930169_MicroRNA-513c-5p is involved in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia by regulating of low-density lipoprotein receptor-associated protein 6. 35211755_circLRP6 contributes to osteosarcoma progression by regulating the miR1413p/HDAC4/HMGB1 axis. 35277657_SIK2 maintains breast cancer stemness by phosphorylating LRP6 and activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 35840698_An LRP6 mutation (Arg360His) associated with low bone mineral density but not cardiovascular events in a Caucasian family. 35961235_Mutations in LRP6 highlight the role of WNT signaling in oral exostoses and dental anomalies. | ENSMUSG00000030201 | Lrp6 | 68.177093 | 2.045642067 | 1.032554 | 0.37131380 | 7.551012 | 0.0059976377838132748088195711488879169337451457977294921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0332652487390880588491448577315168222412467002868652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 97.3529076 | 22.3539159 | 48.1166466 | 11.1132226 | |
| ENSG00000074181 | 4854 | NOTCH3 | protein_coding | Q9UM47 | FUNCTION: Functions as a receptor for membrane-bound ligands Jagged1, Jagged2 and Delta1 to regulate cell-fate determination (PubMed:15350543). Upon ligand activation through the released notch intracellular domain (NICD) it forms a transcriptional activator complex with RBPJ/RBPSUH and activates genes of the enhancer of split locus. Affects the implementation of differentiation, proliferation and apoptotic programs (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R172, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15350543}. | 3D-structure;Activator;ANK repeat;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Notch signaling pathway;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes the third discovered human homologue of the Drosophilia melanogaster type I membrane protein notch. In Drosophilia, notch interaction with its cell-bound ligands (delta, serrate) establishes an intercellular signalling pathway that plays a key role in neural development. Homologues of the notch-ligands have also been identified in human, but precise interactions between these ligands and the human notch homologues remains to be determined. Mutations in NOTCH3 have been identified as the underlying cause of cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:4854; | actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; artery morphogenesis [GO:0048844]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; forebrain development [GO:0030900]; glomerular capillary formation [GO:0072104]; negative regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045665]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuroblast differentiation [GO:0014016]; neuron fate commitment [GO:0048663]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944] | 11032621_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11861701_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11861701_Results indicate that T6746C polymorphism in the intracellular domain of the Notch3 gene is not associated with increased risk for CVDD. 11891328_Combined expression of pTalpha and Notch3 in T cell leukemia identifies the requirement of preTCR for leukemogenesis 11978185_Notch signalling involved in differentiation of normal adult human epidermis is altered under experimental conditions and pathologies which modify this program. 12210282_Notch3 does not appear to be a candidate gene for BPD in this family. 12480758_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12480758_Polymorphism is not associated with cerebrovascular disease in Japanese patients. 12511775_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12678157_Notch 3 gene is responsible for CADASIL among patients of different ethncis. 12810003_Genetic, clinical and pathological studies of CADASIL in Japan: a partial contribution of Notch3 mutations and implications of smooth muscle cell degeneration for the pathogenesis. 14767686_This is the first missense mutation in codon 1006 of exon 19 of the Notch3 gene to be described in Italy and the second reported in the literature. 15096408_Acute visual loss due to nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) has not previously been reported in CADASIL (heterozygotes for the C406T mutation on exon 3 of the Notch3 gene). 15304596_This 12-bp deletion in the extracellular domain mutation is the first CADASIL-associated Notch3 mutation not involving a cysteine residue in the EGF-like repats. 15378071_The mutation in position 133 (R133C) of the NOTCH3 gene, which maps to 19p13.1, is found in Finnish families with CADASIL. 15694192_Our findings emphasize the importance of genetic analysis of NOTCH3 for Asians with a phenotype typical of CADASIL. 15987768_Notch promotes changes in hVSMC phenotype via activation of CBF-1/RBP-Jkappa-dependent pathways in vitro and contributes to the phenotypic response of VSMCs to cyclic strain-induced changes in VSMC differentiation. 16009764_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16107360_subtle abnormalities seen in furin processing of mutant Notch3 receptor, although both heterodimeric and full length receptors are present on cell surface, are capable of interacting with soluble forms of three ligands, and retain ability to activate CBF1 16426270_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16492242_Findings support the view that functional polymorphism T6746C in Notch3 gene is not involved in increasing the risk of migraine or migraine subtypes. 16492242_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16717210_The novel Korean mutation of R75P, not involving a cysteine residue, is related to less frequent involvement of the anterior temporal area, thus broadening the spectrum of CADASIL. 16796587_a 44-year-old patient with clinical features of CADASIL who was a carrier of a new Notch3 mutation: cys128-->gly. 16807713_Our results show that mtDNA sequence variation is increased within CADASIL pedigrees. These findings suggest a relationship between NOTCH3 and mtDNA. 16833034_The defective gene in CADASIL is Notch 3, which encodes a large transmembrane receptor. 16899352_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16998728_Italian CADASIL families from Central Italy with mutation CGC-TGC at codon 1006 in the exon 19 Notch3 gene. 17158237_Notch-3 expression is dysregulated in breast cancer. 17292860_Role for the conserved N-terminal sequence of Notch3: targeting of the protein to the secretory pathway and reduction of cytoplasmic Notch3 expression which may inhibit cytoplasmic functions. 17301032_with supervised resistance exercise training, expression of Notch1 and Hes6 genes were increased and Delta-like 1 and Numb expression were decreased. 17331978_A model that invokes novel pathogenic roles for the mutant NOTCH3 protein rather than compromised NOTCH3 function as the primary determinant of the CADASIL arteriopathy. 17390743_Genetic analysis of Notch3 revealed an R141C missense mutation and she was diagnosed with CADASIL complicated with IgA nephropathy. 17573339_NOTCHES N1, N2, and N3 all bound to FIH; results suggest the possibility that Notch ICDs are FIH substrates. 17690848_This study describe the genetical, clinical,neuropsychological and neuroimaging findings in an Italian CADASIL patient with a rare mutation in exon 10 leading to a Gly528Cys substitution. 17696940_Suggest an aberrant expression of Notch3 and Notch4 in HCC and allow the hypothesis of an activation of Notch signalling by Notch3. 17804716_Notch pathway plays an important role in lung cancer biology. 17822320_Overexpression of notch3 is associated with breast cancer 17822871_Notch3 promotes cell growth and survival by activating PI3-kinase/AKT pathway; N-cadherin participates in the change of cell growth caused by Notch3 activation; and Notch3 signalling has dual-effects on the Wnt/TCF pathway. 17853970_Results describe a Spanish family reported with CADASIL, caused by the 346C > T mutation in NOTCH3 gene. 17854869_This review focuses on recent findings of Notch3 in vascular development and in regulating vascular smooth muscle cell behavior and phenotype. 17878719_In CADASIL patients, Notch3 mutations were associated with mitochondrial disease, particularly affecting the skeletal muscle. 17920003_Cytoplasmic expression of Notch 3 receptors was detected and Notch signaling might be involved in development of hepatocellular carcinoma. 17939118_Rgs5 and Notch3 are expressed in pericytes of developing and injured teeth and have roles along with vascular-derived stem cells during pulp healing 17996090_Positive MRI findings in asymptomatic individuals or in-patients who presented with depression or a psychiatric problem indicated that NOTCH3 gene signalling may start early and may have different clinical presentations 18022198_We report for the first time a mutation on exon 21 of the NOTCH3 gene that leads to a cysteine substitution in the EGF-like repeat 29 of the NOTCH3 receptor extracellular domain, and that causes CADASIL in a functionally independent elderly man. 18060036_IL-6 treatment triggered Notch-3-dependent upregulation of the Notch ligand Jagged-1 and promotion of MS and MCF-7-derived spheroid growth 18069660_we conclude that in the ectatic ducts of CP, PDH activates signalling pathways such as Notch, which have transforming potential. 18075987_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18184405_NOTCH2, NOTCH3 and NOTCH4 genes are rarely mutated in common human cancers. 18339869_NOTCH3-mediated signaling rather than NOTCH1-mediated signaling plays an important role in the proliferation of ErbB2-negative breast tumor cells. 18483410_PDGF receptor (PDGFR)-beta is a novel immediate Notch target gene. PDGFR-beta expression was upregulated by Notch ligand induction or by activated forms of the Notch receptor; dysregulated Notch signaling perturbs VSMC differentiation and function. 18499132_NOTCH3 analysis disclosed a new missense mutation within exon 7, leading to the substitution of cysteine 366 with a tryptophan (Cys366Trp) in CADSIL patient. 18572291_The presence of GOM strongly suggests that renal lesions were related to the NOTCH3 mutation. 18626519_CADASIL in Arabs without Notch 3 mutation. 18632624_Jagged-1 is the primary Notch3 ligand in ovarian carcinoma and Jagged-1/Notch3 interaction constitutes a juxtacrine loop promoting proliferation and dissemination of ovarian cancer cells within the intraperitoneal cavity 18758477_Relationships between the structural differences & the nonredundant roles that Notch3 plays in the pathogenesis of cerebral autosomal-dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts & leukoencephalopathy are reviewed. Review. 18765654_cysteine-sparing mutation (A1020P) in association with a CADASIL-compatible phenotype in two German families. 18941948_Patient with clinical features of CADASIL and a positive family history who was a carrier of a new mutation at the exon 4 of the NOTCH3 gene: C162R. 18948701_there could be a relation between right-to-left shunt and specific Notch3 mutations, such as Arg141Cys. 18974129_findings indicate that Pbx1 is a direct Notch3-regulated gene that mediates the survival signal of Notch3 in ovarian cancer 19006080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19006080_analyzed the NOTCH3 gene in a large group of CADASIL patients, and identified 20 different mutations, 22 polymorphisms, and 8 genetic variants of unknown pathological significance never reported previously 19018300_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19043263_R75P mutation is reported in two Japanese CADASIL families not directly involving cysteine residues located within the first epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like repeats. 19054571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19056668_We used Conventional MRI and NOTCH3 gene screening in sporadic CADASIL. We found 13% of Cadasil patients carried a Notch3 mutation. 19139365_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19150886_NOTCH3 expression is induced in mural cells through an autoregulatory loop that requires endothelial-expressed JAGGED1. 19167727_exon 3 and exon 4 of the NOTCH3 gene are the mutation hotspots in Mainland Chinese cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) patients 19174371_Granular osmiophilic material was detected in the skin biopsy of all 131 patients, in whom the NOTCH3 mutation had been identified and a representative skin biopsy was available. 19208840_Escape of human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells from dormancy is associated with Dll4 expression. 19242647_A population-specific mutational spectrum of CADASIL was found in the Chinese patients on Taiwan. The Chinese patients carrying NOTCH3 R544C may descend from a common ancestor. 19242647_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19293235_Results highlight distinguishing functional and phenotypic features of CADASIL mutations in the Notch3 ligand-binding domain. 19372454_study describes differences in clinical phenotype in a pair of monozygotic CADASIL twins; causative NOTCH3 mutation was a novel c.752G>A -substitution (p.Cys251Tyr); findings suggest environmental & lifestyle factors influence clinical course of CADASIL 19373490_MTHFR C677T, ALOX5AP T2354A and NOTCH3 C381T were significant combinational contributors to thrombotic stroke. 19404845_The levels of expression of Notch2 and Notch3 were minimally detected in renal cell carcinoma tumours and non-neoplastic tissues 19417009_CADASIL-associated mutations significantly enhance multimerization of NOTCH3. 19576955_we report the high recurrence of R1006C NOTCH3 mutation in ten families all originate from a restricted area of central Italy 19603167_Notch3 expression were elevated in immune thrombocytopenic purpura. 19735738_critical role for lysosomes in the degradation 19816816_Notch3-specific siRNA suppressed Notch3 expression & increased gemcitabine-induced, caspase-mediated apoptosis. PI3K/Akt activity was decreased by the suppression of Notch3 expression. 19825845_These findings suggest that prolonged retention of mutant Notch3 aggregates in the endoplasmic reticulum decreases cell growth and increases sensitivity to other stresses. 19835636_MSX2 activates NOTCH3-signaling in leukemic T-cells. 19855400_this study demonstrated that high steady-state levels of NOTCH3 are associated with the development of PAH in humans and that Notch3 expression is required for the development of pulmonary hypertension in two experimental models of this disease 19859875_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19881544_provide evidence that Notch3 regulates Bim, a BH-3-only protein, via MAPK signaling. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20038773_CADASIL was diagnosed in 16/81 (20%) probands by finding a mutation leading to a cysteine substitution within the epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like repeats of the NOTCH3 receptor 20040020_Notch signaling may participate in controlling cell differentiation and proliferation in normal bone and COF of the jaws. Notch signaling disorder may be a molecular incident in COF occurrence and development. 20069356_The pattern of Notch gene expression mirrors the progression from immature cells to endothelial-lined vascular channels (i.e., endothelial differentiation) that characterizes the growth and involution of infantile hemangioma. 20167921_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20169447_Here we report clinical and molecular data of 18 CADASIL patients from 10 unrelated families with exon 10 mutations. The phenotypic spectrum included a high frequency of psychiatric symptoms (12/18) and peripheral vascular involvement (6/18). 20329594_a case of CADASIL who presented with migrainous headache, behavioral disorder, and familial history of stroke characteristic white matter lesions and a mutation in the NOTCH 3 gene. 20359736_Patients with cervical carcinomas with Notch3 expression had shorter survival than those whose tumors did not express nuclear Notch3. Inactivation of Notch3 decreased cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in cell lines that overexpressed Notch3. 20472562_LRP1 and TSP2 stimulate Notch activity by driving trans-endocytosis of the Notch ectodomain into the signal-sending cell 20554499_Notch3 receptors and their ligands play differential roles in the cytodifferentiation of squamous odontogenic tumors of the mandible. 20614134_Notch3 activation cooperatively takes part in the LiCl-induced cell cycle changes, at least partially, associated with c-MYC, Skp2 and p21. 20624166_Results indicate that the Notch 3 signaling pathway is involved in the tumor progression of ovarian serous carcinoma. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20651241_our results suggest that enhanced Notch3 expression in breast cancer cells, triggered by osteoblasts and their secretion of TGFbeta1 in the bone marrow niche, may stand as a novel mechanism for promoting bone metastasis. 20671266_Notch3 pathway activation reprograms tumor cells to assume an array of embryonic stem cell markers and participates in development of chemoresistance in ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma. 20689064_Notch3 is important for the investment of mural cells and is a critical regulator of developmental and pathological blood vessel formation 20801121_the cross talk of N3 with N1 during differentiation provides novel, mechanistic insights into Notch signaling and esophageal squamous epithelial biology 20813781_Further investigation of the G684A variant and the Notch 3 gene is warranted to understand their role in migraine. 20813781_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20819128_The expression Notch3 protein in tongue carcinoma was higher than adjacent non-neoplastic tongue tissues. Expression of Notch3 and Jagged2 were highly correlated in tongue carcinoma tissues. 20935329_mutational spectrum and primary clinical features of patients with CADASIL from mainland China 21078731_The Notch3 gene encodes a transmembrane surface protein that plays a major role in cellular signaling pathways that depend on cellular context in a tissue-specific manner. It is primarily expressed in vascular smooth vessel cells. 21103979_Results suggest that common variants in NOTCH3 are not strongly associated with diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes among white individuals. Findings cannot exclude these genes from involvement in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. 21118965_Data show that shRNA against NOTCH3 resulted in a significant decrease in ALDH(+) lung cancer cells, commensurate with a reduction in tumor cell proliferation and clonogenicity. 21124806_Data show no detectable difference in the DNA binding site preferences of CSL before and after loading of four different Notch receptors and MAML1 proteins. 21169401_The physiological role of Notch3 may be in mediating developmental maturation of vascular smooth muscle cells. 21217157_An inherited pattern of cord lesions in association with CADASIL is caused by a novel NOTCH3 missense mutation, C212Y. 21245095_Results highlight the differential ability of Notch receptor paralogs to initiate malignant tumor formation, and suggest that glial precursors of the optic nerve, but not the brain, are susceptible to transformation by Notch3. 21409506_A missense mutation involving exon 24 of NOTCH3/CADASIL causes cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy. 21471519_Data show that Notch1 to -3 may have potential use as a strong prognostic fact 21508102_MUC16 biosynthesis is posttranscriptionally regulated by Notch signaling at early stages of epithelial cell differentiation, suggesting that Notch activation contributes to maintaining a mucosal phenotype at the ocular surface 21551231_Data suggest that control of NOTCH3 expression through miR-150 may have important impact on T-cell development and physiology. NOTCH3 expression in T-cells in acute lymphoblastic leukemia appears to be regulated by miR-150. 21602525_The stromal cell-mediated antiapoptotic effect on B- ALL cells is mediated by Notch-3 and -4 or Jagged-1/-2 and DLL-1 in a synergistic manner. 21616505_Data confirm the importance of screening the whole epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domains region of NOTCH3 for the molecular diagnosis of CADASIL among the Italian population. 21628316_Spontaneous aggregation is limited to CADASIL-mutant N3, recapitulating a central aspect of CADASIL pathology in vitro. 21673954_HCV NS3 protein is involved in the activation of the Notch-signaling pathway through the targeting to both SRCAP and p400 21702048_data support the expression of Notch3 in adult cell types, and suggests that PBLs and fibroblasts could provide readily available cells for the study of the role of Notch3 expression in pathogenetic mechanisms 21705670_Endothelial cells downregulate apolipoprotein D expression in mural cells through paracrine secretion and Notch3 signaling. 21726900_The receptors Notch2, -3, -4 and their ligands Jagged1, -2 and Delta1, -4 were detected at both the mRNA and protein level in early and late placenta 21743488_Data show that HER2 overexpression enhances Notch3 promoter activity in mammary epithelial cells. 21852154_Our data demonstrate the diversity of clinical stroke presentation according to ethnicity and vascular risk factors in Korean CADASIL patients. 21890822_NOTCH3-mediated signaling prevents expansion of a unique subset of ZEB-expressing cells. 21920521_HGF induces vascular smooth muscle cell osteogenic differentiation via c-Met/Akt/Notch3 signalling, highlighting these pathways as potential targets for intervention of vascular calcification. 21940234_Results indicate that inhibition of Notch3 expression can result in potent antitumor activity in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). 21940951_Notch3 Arg170Cys knock-in mice display pathologic and clinical features of the neurovascular disorder cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy. 21951372_This review discusses mutations in several genes that lead to monogenic disorders manifesting white matter lesions, such as CADASIL. 22006983_common variants at the NOTCH3 gene increase the risk of age-related white matter lesions in hypertensives. 22079340_This study revealed the NOTCH3 R1006C mutation has several peculiarities that may condition clinical course of CADASIL. 22079830_ese results indicated that the process of degradation of mutant N3ECD on the cell surface is disturbed due to impairment of transendocytosis 22082899_clinical and neuroradiological findings of 2 subjects of two unrelated Japanese families who shared a common p.Arg332Cys mutation 22117196_Inhibition of Notch3 signalling induces rhabdomyosarcoma cell differentiation promoting p38 phosphorylation and p21(Cip1) expression and hampers tumour cell growth in vitro and in vivo. 22120716_acetylation/deacetylation balance represents a regulatory switch of Notch3 signaling, providing the molecular basis for the pharmacological use of HDACi in human T-ALL treatment. 22133740_NOTCH3 gene mutations are frequently found in Korean acute stroke patients who present with neuroimaging features consistent with advanced small-vessel disease. 22153798_Notch3 is expressed at a higher level in non-functioning pituitary adenomas than in normal human pituitary tissue. 22153900_Whole exome sequencing in a Turkish patient clinically diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease from a consanguineous family reveals a complex history of neurological and immunological disorders and identifies a mutation in NOTCH3 (p.R1231C). 22159056_NOTCH3 mutation is the longest duplication yet and 1st reported case in african-american with CADASIL 22204979_Both Notch3 and vascular smooth muscle cells differentiation marker proteins were upregulated, which were abrogated by Jagged1-specific siRNA. 22218279_CADASIL mutation and Balo concentric sclerosis: a link between demyelination and ischemia. 22292737_Notch3 mutation precipitates age-related pericytic degeneration that might result in cellular injury and trigger autophagic apoptosis. 22310065_Report down-regulation of Notch signaling components NOTCH3 and HEY2 in abdominal aortic aneurysms. 22367839_Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, frontotemporal lobe degeneration and cerebral dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy are reported in a family with NOTCH3 mutation. 22373597_Three novel mutations in NOTCH3 in cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy. 22396495_Findings define direct target genes of NOTCH3 and highlight the role of DLGAP5 in mediating the function of NOTCH3 in ovarian cancer. 22422895_In an outbred Western European population of patients with CADASIL in the northeast of England, most NOTCH3 mutations are in exon 4. 22493555_Data suggest that Notch3 may regulate the activation of hepatic stellate cells, and the selective interruption of Notch3 may provide an anti- fi brotic strategy in hepatic fi brosis. 22526456_immunohistochemical analysis of NOTCH1-3, JAGGED1, cMET, and phospho-MAPK in 100 carcinomas of unknown primary 22623959_Members of a 5-generational Han Chinese family with CADASIL patients had an R133C mutation in the NOTCH3 gene but only individuals exposed to known vascular risk factors developed CADASIL. 22664156_study added on to the genetic heterogeneity of CADASIL by describing 21 NOTCH3 mutations identified in 53 index Italian patients; also characterized the NOTCH3 haplotypes to investigate possible influences of the genetic background on the recurrence of mutations 22691042_Immunohistochemistry showed a reverse correlation between MUC2 and Notch3 or Jagged1 (P = 0.033 and P = 0.005, respectively) and between MUC5AC and Jagged1 or Hes1 22705236_Down-regulation of Notch1 and Notch3 in two hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines resulted in Hes1 down-regulation, CDKN1C/P57 up-regulation, and reduced cell growth. 22806125_Notch-3 receptor activation drives inflammation and fibrosis following tubulointerstitial kidney injury. 22948298_CADASIL mutations and shRNA silencing of NOTCH3 affect actin organization in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. 23010708_Notch3 expression may be related to chemoresistance and the Notch3 pathway may represent a novel therapeutic target for advanced stage chemoresistant ovarian cancer. 23019585_Our study suggests important clinical applications for targeting Notch as part of novel treatment strategies upon diagnosis of ovarian cancer and at recurrence 23028706_CADASIL mutants of NOTCH3 complex with NOTCH1, 3, and 4, slow NOTCH3 clearance, and that overexpressed wild type and mutant NOTCH3 protein interfere with key NOTCH-mediated functions in smooth muscle cells 23036509_Cellular and mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cell lines (VSMCs) established from CADASIL mutation carriers (R133C) and healthy controls. 23226563_These data further support a central role for Notch signalling in pancreatic cancer and suggest that nuclear expression of Notch3 and its target gene, HEY-1, merit validation in biomarker panels for diagnosis, prognosis and treatment efficacy. 23314443_FAM172A may be a novel tumor-suppressor gene that plays an important role in cell cycle mediated, at least partially, by the Notch 3 signaling pathway. 23319290_A novel NOTCH3 Gly89Cys mutation located in exon 3 was identified in a Serbian family with cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL). 23412372_Parkinsonism is a late, not rare, feature of CADASIL: a study on Italian patients carrying the R1006C mutation 23444212_Data indicate that the expression of Notch-2 and Notch-4 receptors was higher in the GFP-bright population whereas Notch-1 and Notch-3 receptors were more expressed in GFP-dim population. 23460375_Diagnosis is confirmed by genetic testing and the finding of the Notch3 mutation or by skin biopsy. 23465844_Case Report: clinical manifestations/pathologic alterations in subjects with NOTCH3 mutations giving rise to CADASIL. 23468978_hypothesize that targeting Notch1 may be more useful than Notch3 for designing novel preventive and therapeutic strategies for HCC in the near future 23492684_hENT1 and Notch3 mRNA expressions in biopsy specimens were the key predictive biomarkers of gencitabine effect and gemcitabine sensitivity in patients with unresectable pancreatic ductal carcinoma. 23572112_Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy conforms to the classical definition of dominant diseases, according to which homozygotes and heterozygotes for the G528C NOTCH3 mutation are phenotypically indistinguishable. 23584202_NOTCH3 fragments are major components of granular osmiophilic material deposits in brain samples from CADASIL patients. 23587639_NOTCH3 mutations in the genetically undefined cases with CADASIL may be located deep in the introns. 23602593_Homozygosity of the NOTCH3 p.R544C has a modestly deleterious effect on the cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy 23610446_Results reveal a novel function of Notch3 in senescence regulation and tumor suppression. 23637910_Notch3 and Hes5 are hypermethylated in human B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). 23645556_Studied Notch3 expression in NSCLC tissues and adjacent non-cancerous normal lung tissues over a period of 5 yrs. Notch3 had high expression in 67 of 131 cases of NSCLC, which was significantly higher than in adjacent noncancerous lung tissues. 23649002_The NOTCH3 transcription factor is a master regulator of motility in neuroblastoma. 23649698_NOTCH3 aggregation in the brain vessels promotes abnormal recruitment of extracellular matrix proteins in CADASIL patients. 23729168_Notch3 pathway represents a promising target for adjuvant therapy in patients with PC. 23747483_Complexation of the Notch3 NRR with an inhibitory antibody retards deuteration not only across its discontinuous binding epitope but also around the S2 site. 23773728_Notch3 mediates melanoma-endothelial cell communication and tumor cell migration. 23836039_Findings suggest that Notch3 might be an important regulator in the development of HCC, and a potential therapeutic target for patients with HCC. 23845442_Notch3 plays a nonredundant role in tumor cell propagation in two mouse models and in human non-small-cell lung cancer. 23847153_Migraine was found in only 3.8% of CADASIL patients with the R544C mutation. 23975424_Par-4/THAP1 complex and Notch3 competitively regulated pre-mRNA splicing of CCAR1 and affected inversely the survival of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. 23999936_the study describes novel NOTCH1-3 rearrangements in benign and malignant, visceral, and soft tissue glomus tumors 24026140_We report a comprehensive evaluation of several individuals in the CADASIL family whose member was identified to have the new mutation of NOTCH3 receptor on exon 6 24041655_Notch3 activation activates nitric oxide/soluble guanylyl cyclase signalling in immortalized ovarian surface epithelial cells and ovarian cancer cells. 24086431_common NOTCH3 variants may be associated with risk of ischemic stroke warrants further study. 24138322_3D coculture induced an upregulation of Notch3 receptor in human coronary artery smooth muscle cells and its ligand Jagged1 in human coronary artery endothelial cells. 24139282_Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) is caused by mutations in the NOTCH3 gene on chromosome 19. 24143218_the prognostic value and the oncogenic function of NOTCH3 in gliomagenesis 24151014_NOTCH3 expression is decreased in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and amygdala from suicide victims compared to control brain. 24244701_Data show that microRNA-1 (miR-1) is down-regulated in colorectal tumors and that miR-1 has the potential to suppress NOTCH3 expression through direct binding to its 3'-UTR region. 24336671_A significant increase in Notch3 expression was found in the placentas from patients with early-onset preeclampsia. 24367688_Notch3 plays a role in the cell proliferation and apoptosis induced by CHIR99021 in non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines. 24480794_Study demonstrated a pattern of cognitive deficits in Asian CADASIL patients with R544C mutation consistent with previous studies in Caucasian CADASIL patients 24525742_NOTCH3 signaling regulates MUSASHI-1 expression in metastatic colorectal cancer cells. 24671051_Expression of Notch1, -2, and -3, CDK2, and CCNE1 was significantly decreased by upregulation of ALDH1A1 in A549 cells, but increased by its interruption in A549s cells. 24728738_High nuclear Notch3 expression is associated with tumor recurrence in patients with stage II and III colorectal cancer. 24743243_Notch3 pathway alterations are prevalent and significantly related to poor clinical outcome in patients with ovarian cancer. 24788939_Data suggest that extracellular signal-regulated kinases ERK1/2 signaling can cross-interact with the transforming growth factor beta2/Smad2/3 and the Jagged-1/Notch-3 signaling in retinal pigment epithelium cells epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 24797362_These results strongly suggest that high levels of Notch3 activation increase the proliferative potential of RMS cells. 24810798_Our findings indicate that Notch3 signaling, associated with MUC5AC expression, could be a more favorable prognostic factor in small intestinal adenocarcinoma. 24816653_Two novel mutations located in exons 6 and 15 of the NOTCH3 gene were found in two patients with suspected CADASIL. 24844136_This review discusses and provide recommendations for the interpretation of NOTCH3 mutations in the diagnosis of cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL). 24984200_results provide novel insights into the determinants of NOTCH3 overexpression in cancer cells, by revealing a key role for BORIS as the main mediator of transcriptional deregulation of NOTCH3 25096610_This study showed that the new mutation of NOTCH3 gene in patients of CZDASIL. 25098330_By screening the entire coding region of NOTCH3, a novel missense mutation p.G149V (c.446G>T) was found. 25105908_The NOTCH3 mutation spectrum in our group was diverse and consistent with those in Caucasians but differed from those in Korea and Taiwan. 25150590_Results show that CADASIL arteries feature latent N-terminal NOTCH3 epitopes, suggesting the first evidence in vivo of NOTCH3 structural alterations 25169943_Reduction of COL4A2 expression by RNAI-mediated knockdown induces cell death. Finally, elevated Notch3 expression levels correlate with higher COL4A2 expression in human ovarian tumor specimens 25171754_NOTCH3 regulates the cellular behavior, including, proliferation, marker to predict | ENSMUSG00000038146 | Notch3 | 19.117411 | 0.181384116 | -2.462880 | 0.54005533 | 20.092248 | 0.0000073795184397965073286426891663314364677717094309628009796142578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001015991180471196333708408521268040658469544723629951477050781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 2.4698000 | 1.2283157 | 13.5641497 | 6.3131470 | |
| ENSG00000074660 | 8578 | SCARF1 | protein_coding | Q14162 | FUNCTION: Mediates the binding and degradation of acetylated low density lipoprotein (Ac-LDL). Mediates heterophilic interactions, suggesting a function as adhesion protein. Plays a role in the regulation of neurite-like outgrowth (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is a scavenger receptor that is expressed in endothelial cells. It regulates the uptake of chemically modified low density lipoproteins, including acetylated low density lipoprotein (Ac-LDL), and it may be involved in atherogenesis. This gene is regulated by the transcription factors ZNF444/EZF-2 and SP1. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2013]. | hsa:8578; | endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; low-density lipoprotein particle binding [GO:0030169]; scavenger receptor activity [GO:0005044]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cholesterol catabolic process [GO:0006707]; dendrite development [GO:0016358]; neuron remodeling [GO:0016322]; positive regulation of axon regeneration [GO:0048680]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898] | 11978792_Characterization of the gene and its regulation by a novel transcription factor, endothelial zinc protein-2 12154095_SRECI binds to SRECII and has a similar tissue distribution pattern 21190681_GP2 is a binding partner of the scavenger receptor expressed on endothelial cells I (SREC-I) but not of SR-AI and SR-BI. Dendritic cells express SREC-I and also bind and internalize GP2. 24788600_In several assay systems this type F-scavenger receptor, termed SREC-I, bound to cell wall techoic acid in a charge dependent manner and mediated adhesion to nasal epithelial cells in vitro. 25155057_These studies in addition to our earlier findings showed SREC-I to play a primary role in chaperone-associated antigen uptake both through cross priming of MHC class I molecules and entry into the class II pathway. 25641411_Scavenger receptor SREC-I promotes double stranded RNA-mediated TLR3 activation in human monocytes 29242513_SCARF-1 promotes adhesion of CD4(+) T cells to human hepatic sinusoidal endothelium under conditions of shear stress 32296440_Molecular and Cellular Interactions of Scavenger Receptor SR-F1 With Complement C1q Provide Insights Into Its Role in the Clearance of Apoptotic Cells. 34236384_The Role of SREC- in Innate Immunity to Aspergillus fumigatus Keratitis. 35082161_SCARF1-Induced Efferocytosis Plays an Immunomodulatory Role in Humans, and Autoantibodies Targeting SCARF1 Are Produced in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. | ENSMUSG00000038188 | Scarf1 | 49.371927 | 0.340960271 | -1.552324 | 0.50632354 | 8.892982 | 0.0028626882153761539287484261251393036218360066413879394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0181944330360817550784613416681168018840253353118896484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 23.9826964 | 8.0081483 | 70.1438596 | 22.9508862 | |
| ENSG00000075790 | 55973 | BCAP29 | protein_coding | Q9UHQ4 | FUNCTION: May play a role in anterograde transport of membrane proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi. May be involved in CASP8-mediated apoptosis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Coiled coil;Endoplasmic reticulum;ER-Golgi transport;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | Involved in osteoblast differentiation. Located in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:55973; | endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006888]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum exit site [GO:0070973] | 18097552_Bap29varP acts as an essential chaperone, influencing the processing and trafficking of Pgp to the cell surface. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21068099_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 28415823_we believe that in contrast to traditional gene fusions, DUS4L-BCAP29 cannot be used as a cancer biomarker. Instead, it is a fusion transcript that exists in normal physiology and that its pro-growth effect is not unique to cancer cells. | ENSMUSG00000020650 | Bcap29 | 308.428550 | 2.015898476 | 1.011423 | 0.30786211 | 10.551994 | 0.0011606282012036484973388494879031895834486931562423706054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0085807966587931466806438152161717880517244338989257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 424.3843341 | 121.6840171 | 211.5530144 | 60.7244570 | |
| ENSG00000077984 | 8530 | CST7 | protein_coding | O76096 | FUNCTION: Inhibits papain and cathepsin L but with affinities lower than other cystatins. May play a role in immune regulation through inhibition of a unique target in the hematopoietic system. | 3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Thiol protease inhibitor | The cystatin superfamily encompasses proteins that contain multiple cystatin-like sequences. Some of the members are active cysteine protease inhibitors, while others have lost or perhaps never acquired this inhibitory activity. There are three inhibitory families in the superfamily, including the type 1 cystatins (stefins), type 2 cystatins and the kininogens. The type 2 cystatin proteins are a class of cysteine proteinase inhibitors found in a variety of human fluids and secretions. This gene encodes a glycosylated cysteine protease inhibitor with a putative role in immune regulation through inhibition of a unique target in the hematopoietic system. Expression of the protein has been observed in various human cancer cell lines established from malignant tumors. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:8530; | cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; multivesicular body [GO:0005771]; cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004869]; endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004866]; peptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0030414]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inhibition of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0097340]; negative regulation of microglial cell activation [GO:1903979]; negative regulation of peptidase activity [GO:0010466]; positive regulation of myelination [GO:0031643] | 12423348_cystatin F is an intracellular cysteine peptidase inhibitor with readily regulated expression 15212960_CST7 is secreted, but artificial modification of its C-terminus can induce its endocytic targeting. 15752368_Cystatin F was not colocalized with cystatin C shich suggests distinct functions for these two cysteine protease inhibitors in U937 cells. 16601115_analysis of reduction-dependent activation of human cystatin F 18256700_A latent protease inhibitor which is itself regulated by proteolysis in the endocytic pathway. 19192250_Data demonstrate the addition of N-linked sugars to an Asn-X-Cys motif in cystatin F and suggest that the mannose 6-phosphate sorting machinery is used to divert cystatin F from the secretory pathway and to mediate its uptake from extracellular pools. 21344476_Transgenic cystatin F is expressed in model mice only during demyelination; in chronic demyelination, remyelinating ability is lost. 22365146_Regulation of cathepsins S and L by cystatin F during maturation of dendritic cells. 30033148_during monocyte to macrophage differentiation, the endosomal/lysosomal proteolytic activity can be regulated by cystatin F whose expression is under the control of transcriptional factor C/EBP alpha. 31059105_Cystatin F was identified as the key subunit of family 2 cystatins in survival analysis. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) patients who harbored a higher expression level of CST7 had a lower risk in overall survival. The prognostic nomogram indicated that the CST7 expression model effectively predicted the outcomes of patients with earlystage PDAC. 32947653_Exploring the factors underlying remyelination arrest by studying the post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms of cystatin F gene. 33868254_Transcriptomic Profiling Identifies Neutrophil-Specific Upregulation of Cystatin F as a Marker of Acute Inflammation in Humans. 34189679_Cystatin F acts as a mediator of immune suppression in glioblastoma. | ENSMUSG00000068129 | Cst7 | 25.987026 | 0.454110736 | -1.138884 | 0.32692699 | 12.332559 | 0.0004451256692416582843793704249435450037708505988121032714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0037891429102377910745347300291996361920610070228576660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 16.7904922 | 7.9327211 | 37.0305456 | 17.0646322 | |
| ENSG00000078487 | 55063 | ZCWPW1 | protein_coding | Q9H0M4 | FUNCTION: Dual histone methylation reader specific for PRDM9-catalyzed histone marks (H3K4me3 and H3K36me3) (PubMed:32744506, PubMed:20826339). Facilitates the repair of PRDM9-induced meiotic double-strand breaks (DSBs) (By similarity). Essential for male fertility and spermatogenesis (By similarity). Required for meiosis prophase I progression in male but not in female germ cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6IR42, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20826339, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32744506}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosome;Coiled coil;Differentiation;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Spermatogenesis;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Enables methyl-CpG binding activity and methylated histone binding activity. Predicted to be involved in meiosis I; positive regulation of DNA metabolic process; and spermatogenesis. Predicted to act upstream of or within homologous chromosome pairing at meiosis. Predicted to be located in XY body. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:55063; | chromosome [GO:0005694]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; methyl-CpG binding [GO:0008327]; methylated histone binding [GO:0035064]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; homologous chromosome pairing at meiosis [GO:0007129]; meiosis I [GO:0007127]; positive regulation of DNA recombination [GO:0045911]; positive regulation of double-strand break repair [GO:2000781]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] | 24743338_Of those 394 variants, 34 showed strong evidence of regulatory function (RegulomeDB score | ENSMUSG00000037108 | Zcwpw1 | 61.235549 | 0.215446969 | -2.214595 | 0.70482585 | 8.396093 | 0.0037602841778145408915823288964475068496540188789367675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0227307066029687997177344271904075867496430873870849609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 22.0619457 | 12.5115003 | 102.9855204 | 58.4372644 | |
| ENSG00000079387 | 29843 | SENP1 | protein_coding | Q9P0U3 | FUNCTION: Protease that catalyzes two essential functions in the SUMO pathway (PubMed:10652325, PubMed:15199155, PubMed:16253240, PubMed:16553580, PubMed:21829689, PubMed:21965678, PubMed:23160374, PubMed:24943844, PubMed:25406032, PubMed:29506078). The first is the hydrolysis of an alpha-linked peptide bond at the C-terminal end of the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) propeptides, SUMO1, SUMO2 and SUMO3 leading to the mature form of the proteins. The second is the deconjugation of SUMO1, SUMO2 and SUMO3 from targeted proteins, by cleaving an epsilon-linked peptide bond between the C-terminal glycine of the mature SUMO and the lysine epsilon-amino group of the target protein. Deconjugates SUMO1 from HIPK2 (PubMed:16253240). Deconjugates SUMO1 from HDAC1 and BHLHE40/DEC1, which decreases its transcriptional repression activity (PubMed:21829689). Deconjugates SUMO1 from CLOCK, which decreases its transcriptional activation activity (PubMed:23160374). Deconjugates SUMO2 from MTA1 (PubMed:21965678). Deconjugates SUMO1 from METTL3 (PubMed:29506078). Desumoylates CCAR2 which decreases its interaction with SIRT1 (PubMed:25406032). Deconjugates SUMO1 from GPS2 (PubMed:24943844). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10652325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15199155, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16253240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16553580, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21829689, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21965678, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23160374, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24943844, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25406032, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29506078}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Thiol protease;Ubl conjugation pathway | This gene encodes a cysteine protease that specifically targets members of the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) protein family. This protease regulates SUMO pathways by deconjugating sumoylated proteins. This protease also functions to process the precursor SUMO proteins into their mature form. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2012]. | hsa:29843; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; deSUMOylase activity [GO:0016929]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; SUMO-specific endopeptidase activity [GO:0070139]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097190]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein desumoylation [GO:0016926]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] | 12466471_co-localizes with Herpes simplex virus 1 ICP0 in cell nucleus 15199155_SENP1's ability to enhance AR-dependent transcription is not mediated through desumoylation of AR, but rather through its ability to deconjugate histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1), thereby reducing its deacetylase activity. 15701643_p300 is essential for SENP1 to enhance c-Jun-dependent transcription because SENP1 can desumoylate the CRD1 domain of p300, thereby releasing the cis-repression of CRD1 on p300 15917269_as a result of (12;15)(q13;q25)translocation, the SUMO/Sentrin-specific protease 1 gene (SENP1) on chromosome 12 and the embryonic polarity-related mesoderm development gene (MESDC2) on chromosome 15 are disrupted and fused 16253240_HIPK2 is a desumoylation target for the SUMO-specific protease SENP1 that shuttles between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. 16553580_x-ray crystallographic structure of SENP1-SUMO-2 complex demonstrates structural basis for discrimination between SUMO paralogues during processing 16712526_A study evalution the mechanisms of regulation of the sumoylation pathway by the SUMO-specific proteases is presented. 16925949_studies indicate that overexpression of SENP1 is associated with prostate cancer developme 17099698_discrimination between unprocessed SUMO-1 and SUMO-2 by SENP1 is based on a catalytic step rather than substrate binding and is likely to reflect differences in the ability of SENP1 to correctly orientate the scissile bonds in SUMO-1 and SUMO-2 17704192_SENP1 may act as redox sensors and effectors modulating the desumoylation pathway and specific cellular responses to oxidative stress 18219322_SENP1 mediates TNF-induced desumoylation and translocation of HIPK1, leading to an enhanced ASK1-dependent apoptosis. 18474224_SENP1 restored the promyelocytic leukemia protein mediated suppression of STAT3 activation. 18616636_Sentrin-specific protease Senp1 repression induces tumor suppressor protein p53-mediated premature senescence; SUMO proteases may thus be required for proliferation of normal human cells. 19116244_SENP1 reverses the ligand-induced SUMOylation of AR and helps fine tune the cellular responses to androgens in a target promoter-selective manner. 20079608_epigenetic control of MMP-1 expression via histone H4 acetylation 20337593_Results demonstrate that SENP1 is the most efficient SUMO protease acting on Elk-1, and that SENP3 has little effect on Elk-1. SENP2 has an intermediate effect, but its ability to activate Elk-1 is independent from its SUMO-deconjugating activity. 20841360_Induction of SENP1 in endothelial cells contributes to hypoxia-driven VEGF expression and angiogenesis. 21106093_Could use the urinary hTERT, SENP1, PPP1CA, and MCM5 mRNA to detect bladder cancer recurrence. 21505236_crystal structure of human SENP1 was redetermined at 2.4 A degrees resolution with Rwork and Rfree values of 23.1% and 31.3%, respectively 21669491_SENP1 might play a role in cell cycle regulation of colon cancer cells 22370484_de-SUMOylation is essential for SENP1 modulating XBP1 transcriptional activity. 22688647_The SENP1 levels are influenced by the presence of Nup153, whereas SENP2 is not sensitive to changes in Nup153 abundance. 22733136_Results show the contribution of SENP1 to the progression of prostate cancer, and suggest that SENP1 may be a prognostic marker. 22748127_mutation of K364 to arginine (R) or deSumoylation by small ubiquitin-like modifier (Sumo)-specific protease-1, a nuclear deSumoylase, enhanced the transactivation capacity of LEDGF and its cellular abundance 23002208_Data show that the loss of OCT4 expression under hypoxia can be triggered by sumoylation, which was regulated by the SUMO1 peptidase SENP1. 23089540_Data suggest that small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO)-specific protease 1 (SENP1) expression might contribute to the malignant progression of prostate cancer and as a potential prognostic factor for biochemical recurrence after prostatectomy. 23633483_A critical role for SENP1-mediated desumoylation in promoting Pin1 function during tumorigenesis. 24048451_Chromosome segregation depends on precise spatial and temporal control of sumoylation in mitosis; SENP1 and SENP2 are important mediators of this control. 24196834_Many nucleoporins are mislocalized and, in some cases, reduced in level when SENP1 and SENP2 are codepleted. 24691972_our data demonstrate that the miR-138/SENP1 cascade is relative to radiosensitization in lung cancer cells and is a potential radiotherapy target. 25014244_cadmium-induction enhances AR transcriptional activity by decreasing AR SUMOylation 25082844_SENP1 deficiency exacerbates ischemia-reperfusion injury in cardiomyocytes via a HIF1alpha-dependent pathway. 25139051_Data suggest that up-regulation of SENP1 down-regulates insulin secretion and impairs intracellular calcium signaling in islet beta-cells; this secretory dysfunction is due to SENP1-induced apoptosis of islet beta-cells. 25217324_SENP1 was upregulated in PDAC tissues; overexpressed SENP1 was associated with lymph node metastasis and TNM stage. 25225945_results provide independent evidence in support of a role for SENP1 in chronic mountain sickness in individuals of Quechua ancestry and suggest the SENP1 and ANP32D signatures of selection are in tight linkage disequilibrium (LD). 25263960_SENP1 uses remote substrate binding for conformational flexibility and activation 25430449_Over-expression of small ubiquitin-like modifier proteases 1 predicts chemo-sensitivity and poor survival in non-small cell lung cancer.( 25446185_SENP1 up-regulation in diseased heart is mediated via calcineurin-NFAT/MEF2C-PGC-1alpha pathway. 25645686_low expression of miR-145 was correlated with high expression of SENP1 in Prostate cancer cell line and the SENP1 3'-untranslated region was a regulative target of miR-145 in vitro. 25791478_results delineate a key role for Senp1in IL-6 induced proliferation and survival of MM cells, suggesting it may be a potential new therapeutic target in MM 25816890_a significant role of SENP1 in the regulation of cell migration and invasion in neuroblastoma 26202067_SENP1 expression has strong prognostic impact in a molecularly defined subset of cancers. This is per se not surprising as the biologic impact of each individual molecular event is likely to be dependent on its cellular environment. 26389676_SENP1 was expressed in human islets, and its mRNA level was unchanged in islets from donors with T2D. In cultured islets, overexpressed SENP1-GFP colocalized with secretory granules at the plasma membrane 26548925_SENP1 desensitizes hypoxic ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin by up-regulating HIF-1alpha 26695141_Hepatocellular carcinoma cells express a high level of Senp1 which is induced by HGF/c-Met signals. Senp1 silencing reduces the HGF-induced proliferation and migration of HCC cells, induces HCC cell apoptosis and growth arrest, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, with increase of E-cadherin and ZO-1 expression, decrease of fibronectin and N-cadherin expression. 26852650_Genetic interactions of SNPs in CARD14, SENP1 and VEGFA might represent a functional mechanism in the pathogenesis of high altitude polycythemia. 27177472_miRNA1236 regulates hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transformation and metastasis by repressing HDAC3 and SENP1 expression. 27178176_The variability of the SENP1 and SENP2 genes may play a role in breast cancer occurrence. 27573572_this study elucidated that SENP1 is essential for triple-negative breast cancer cell proliferation and migration in vitro, as well as tumor formation and metastasis in vivo 27576863_Molecular dynamics simulations showed that binding of the beta-grasp domain of SUMO1 induces significant conformational and dynamic changes in SENP1, including widening of the exosite cleft and quenching of nanosecond dynamics in all but a distal region. 27693211_A key role for SENP1 in astrocytoma development and apoptosis.SENP1 inhibition promotes cell apoptosis by regulating NF-kappa B/Akt signaling pathways. 27741516_SENP1 promotes cell proliferation and disease progression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma, possibly through deSUMOylating and stabilizing HIF-1alpha, leading to increased expression of key glycolytic enzymes and enhanced glycolytic flux. 27821551_GATA1 is an essential downstream target of SENP1 and that the differential expression and response of GATA1 and Bcl-xL are a key mechanism underlying chronic mountain sickness pathology. 28417919_SENP1 deSUMOylated SMAD4 to promote EMT via up-regulating E-cadherin in prostate cancer cells. Therefore, SENP1 is a potential target for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. 28550686_miR-185 was significantly downregulated in RCC tissues and cell lines. SENP1 was a direct target of miR-186, and SENP1 mRNA expression was reversely correlated with miR-186 in RCC tissues. 28569748_endothelial SENP1-mediated SUMOylation drives graft arteriosclerosis by regulating the synergistic effect of GATA2 and NF-kappaB and consequent endothelial dysfunction. 28576968_Despite the requirement of all three nucleoporins for accurate NHEJ, only Nup153 is needed for proper nuclear import of 53BP1 and SENP1-dependent sumoylation of 53BP1. Data support the role of Nup153 as an important regulator of 53BP1 activity and efficient NHEJ. 28748780_These results suggest that the miR-133a-3p-SENP1 axis might play a role in cell proliferation and cell cycle regulation of colorectal cancer cells. 28796315_Results showed that the expression of SENP1 was remarkably upregulated in osteosarcoma cells (OS) cells. SENP1 positively regulated HIF-1alpha expression level in the setting of hypoxic; subsequently, its depletion markedly ameliorated VEGF production triggered by hypoxia. 29472234_KLF15 is a critical regulator of pulmonary endothelial homeostasis via repression of endothelial Arg2 expression. KLF15 abundance and nuclear compartmentalization are regulated by SUMOylation/deSUMOylation-a hypoxia-sensitive process that is controlled by SENP1. 29481054_Treatment of cells with streptonigrin resulted in increased global SUMOylation levels and reduced level of hypoxia inducible factor alpha (HIF1alpha). These findings inform both the design of SENP1 targeting strategy and the modification of streptonigrin to improve its efficacy for possible future clinical use. 30043429_Results in this present study showed that SENP1 was a risk factor for poor non-small cell lung cancer prognosis. And also demonstrated that the overexpression of SENP1 in non-small cell lung cancer was related to chemotherapy resistance. 30082317_It has been proposed that the functional link between chromatin remodeling by CHD3 and deSUMOylation by SENP1 provides another level of control of gene expression. 30226577_Study revealed a significant decrease in the expression of SUMO1 specific peptidase 1 (SENP1) in osteosarcoma tissues and osteosarcoma cell lines, and SENP1 expression was much lower in osteosarcoma stem cells than in noncancer stem cells. 30305424_SENP1 is a crucial c-Myc deSUMOylating enzyme that positively regulates c-Myc's stability and activity. 30921636_These findings suggest that the absence of SELENON together with a high-fat dietary regimen increases susceptibility to insulin resistance by triggering a chronic ER stress in skeletal muscle and muscle weakness 31045562_Noncovalent structure of SENP1 in complex with SUMO2 has been described. 31186231_Findings show that increased SUMOylation of CD45 via loss of SENP1 suppresses CD45-mediated dephosphorylation of STAT3, which promotes MDSC development and function, leading to tumorigenesis. 31953908_SENP1/HIF-1alpha axis works in angiogenesis of human dental pulp stem cells. 32462635_Regulation of ALS-Associated SOD1 Mutant SUMOylation and Aggregation by SENP and PIAS Family Proteins. 33154164_SUMOylation of the ubiquitin ligase IDOL decreases LDL receptor levels and is reversed by SENP1. 33371766_SENP1 is required for the growth, migration, and survival of human adipose-derived stem cells. 33686713_Long noncoding RNA MCM3AP-AS1 enhances cell proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer by regulating miR-193a-5p/SENP1. 34037277_SENP1 participates in Irinotecan resistance in human colon cancer cells. 34049792_Momordin Ic induces G0/1 phase arrest and apoptosis in colon cancer cells by suppressing SENP1/c-MYC signaling pathway. 34516314_Circular RNA circ_0089153 acts as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate colorectal cancer development by the miR-198/SUMO-specific peptidase 1 (SENP1) axis. 35342335_SENP1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer invasion and metastasis via enhancing CSN5 transcription mediated by GATA1 deSUMOylation. 35807394_Insights into the Allosteric Effect of SENP1 Q597A Mutation on the Hydrolytic Reaction of SUMO1 via an Integrated Computational Study. | ENSMUSG00000033075 | Senp1 | 144.851599 | 0.138198595 | -2.855185 | 1.02323881 | 6.655153 | 0.0098869485856944386986677741901985427830368280410766601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0490768760882518903509996732736908597871661186218261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 42.9881326 | 26.6765605 | 311.6440233 | 193.4176619 | |
| ENSG00000080573 | 50509 | COL5A3 | protein_coding | P25940 | FUNCTION: Type V collagen is a member of group I collagen (fibrillar forming collagen). It is a minor connective tissue component of nearly ubiquitous distribution. Type V collagen binds to DNA, heparan sulfate, thrombospondin, heparin, and insulin. | Collagen;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal | This gene encodes an alpha chain for one of the low abundance fibrillar collagens. Fibrillar collagen molecules are trimers that can be composed of one or more types of alpha chains. Type V collagen is found in tissues containing type I collagen and appears to regulate the assembly of heterotypic fibers composed of both type I and type V collagen. This gene product is closely related to type XI collagen and it is possible that the collagen chains of types V and XI constitute a single collagen type with tissue-specific chain combinations. Mutations in this gene are thought to be responsible for the symptoms of a subset of patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type III. Messages of several sizes can be detected in northern blots but sequence information cannot confirm the identity of the shorter messages. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:50509; | collagen type V trimer [GO:0005588]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring tensile strength [GO:0030020]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; proteoglycan binding [GO:0043394]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; skin development [GO:0043588] | 15136578_analysis of processing of the Pro-alpha1(V)Pro-alpha2(V)Pro-alpha3(V) procollagen heterotrimer 15316020_CBF/NF-Y and two repressors regulate the core promoter of the human pro-alpha3(V) collagen gene 19012342_Absence of obvious disease-causing mutations and null alleles in a cohort of 13 patients with h-EDS is consistent with exclusion of COL5A3 as a candidate gene for this disease. 29168291_This study identified significant interaction between two new genes, COL5A3 and MMP9, which may be accounted for by a degradation of COL5A3 by MMP9 influencing eczema susceptibility | ENSMUSG00000004098 | Col5a3 | 33.316912 | 0.432152920 | -1.210386 | 0.43514040 | 7.473363 | 0.0062618477698302144052178164201905019581317901611328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0344981199702186075439769297190650831907987594604492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 19.7105546 | 9.0071244 | 45.9296121 | 20.7506721 | |
| ENSG00000081923 | 5205 | ATP8B1 | protein_coding | O43520 | FUNCTION: Catalytic component of a P4-ATPase flippase complex which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled to the transport of phospholipids, in particular phosphatidylcholines (PC), from the outer to the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane (PubMed:25315773, PubMed:17948906). May participate in the establishment of the canalicular membrane integrity by ensuring asymmetric distribution of phospholipids in the canicular membrane (By similarity). Thus may have a role in the regulation of bile acids transport into the canaliculus, uptake of bile acids from intestinal contents into intestinal mucosa or both and protect hepatocytes from bile salts (By similarity). Involved in the microvillus formation in polarized epithelial cells; the function seems to be independent from its flippase activity (PubMed:20512993). Participates in correct apical membrane localization of CDC42, CFTR and SLC10A2 (PubMed:25239307, PubMed:27301931). Enables CDC42 clustering at the apical membrane during enterocyte polarization through the interaction between CDC42 polybasic region and negatively charged membrane lipids provided by ATP8B1 (By similarity). Together with TMEM30A is involved in uptake of the synthetic drug alkylphospholipid perifosine (PubMed:20510206). Required for the preservation of cochlear hair cells in the inner ear (By similarity). May act as cardiolipin transporter during inflammatory injury (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q148W0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17948906, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20510206, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20512993, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25239307, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27301931}. | 3D-structure;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;Hearing;Intrahepatic cholestasis;Lipid transport;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | This gene encodes a member of the P-type cation transport ATPase family, which belongs to the subfamily of aminophospholipid-transporting ATPases. The aminophospholipid translocases transport phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine from one side of a bilayer to another. Mutations in this gene may result in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 1 and in benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:5205; | apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; phospholipid-translocating ATPase complex [GO:1990531]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; stereocilium [GO:0032420]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity [GO:0140326]; cardiolipin binding [GO:1901612]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; phosphatidylcholine flippase activity [GO:0140345]; phosphatidylcholine floppase activity [GO:0090554]; phosphatidylserine flippase activity [GO:0140346]; phosphatidylserine floppase activity [GO:0090556]; apical protein localization [GO:0045176]; bile acid and bile salt transport [GO:0015721]; bile acid metabolic process [GO:0008206]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; inner ear receptor cell development [GO:0060119]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; phospholipid translocation [GO:0045332]; regulation of chloride transport [GO:2001225]; regulation of microvillus assembly [GO:0032534]; regulation of plasma membrane organization [GO:1903729]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; vestibulocochlear nerve formation [GO:0021650]; xenobiotic transmembrane transport [GO:0006855] | 12880872_three homologues found and two sequenced and two RNA transcript sizes analysed by northern blot: APT8B2, APT8B3, APT8B4 14988830_Loss of familial intrahepatic cholestasis-1 leads to diminished nuclear translocation of farnesoid X receptor(FXR), with subsequent potential for pathologic alterations in intestinal and hepatic bile acid transporter expression 15239083_54 distinct disease mutations: 10 mutations predicted to disrupt splicing, 6 nonsense mutations, 11 small insertion or deletion mutations predicted to induce frameshifts, 1 large genomic deletion, 2 small inframe deletions, and 24 missense mutations. 15888793_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15946126_Loss of familial intrahepatic cholestasis-1 leads to diminished nuclear translocation of farnesoid X receptor(FXR), with subsequent potential for pathologic alterations in intestinal and hepatic bile acid transporter expression 17948906_Coexpression with CDC50 proteins resulted in relocalization of ATP8B1 from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane. In the plasma membrane, ATP8B1 functions as a flippase for phosphatidylserine. 18668687_FIC1 signals to FXR via PKC zeta. FIC1-related liver disease is likely related to downstream effects of FXR on bile acid homeostasis. 19027009_ATP8B1 deficiency predisposes to cholestasis by favoring bile acid-induced injury in the canalicular membrane but does not directly affect FXR expression 19228886_Knockdown of ATP8B1 expression leads to specific downregulation of the bile acid sensor FXR in HepG2 cells: effect of the FXR agonist GW4064. 19381753_These results suggest that the PFIC1 mutants have a lower stimulatory effect on FXR activity and cannot interact with CDC50A, which may lead to the development of the features of PFIC1. 19478059_show that ATP8B1/Atp8b1 deficiency, both in patients and in Atp8b1(G308V/G308V) mutant mice, causes hearing loss, associated with progressive degeneration of cochlear hair cells 19479804_Post-liver transplantation steatosis may be due to a malfunction of the ATP8B1 product. 19731236_PFIC1 mutations lead to the complete absence of canalicular expression, whereas in BRIC1/ICP residual protein is expressed in the canalicular membrane. 19809379_Findings support the hypothesis that hepatocyte FIC1 enhances FXR signaling via a PKCzeta-dependent signaling pathway. 19918981_A surprisingly large proportion of ATP8B1 mutations resulted in aberrant folding and decreased expression at the plasma membrane. These effects were partially restored by treatment with 4-phenylbutyrate. 20038848_ATP8B1 gene mutations play an important role in Chinese patients with progressive intrahepatic cholestasis and low gamma-glutamyltransferase. The linked mutation P209T and IVS6+5G>T is a hot mutation in the Chinese population. 20216097_We now report evidence that heterozygous genetically determined alteration of ATP8B1 (encoding FIC1) may also represent a risk factor for transient neonatal cholestasis. 20232290_Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis types 1 & 2 differ clinically, biochemically, and histologically at presentation and/or during the disease course. A small proportion of normal-GGT PFIC is likely not due to ATP8B1 or ABCB11 mutations. 20414253_Data identified three novel mutations in BSEP, one novel mutation in MDR3, and one heterozygous mutation in ATP8B1 in PFIC patients. 20447715_facilitating diagnosis and elucidating the differing consequences of ATP8B1 and ABCB11 mutations in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis 20512993_critical role in apical membrane organization that is unrelated to its presumed aminophospholipid translocase activity 20683201_Sequence analysis of the genes identified 27% cholestasis subjects with missense, nonsense, deletion, and splice site variants associated with disease phenotypes based on the type of mutation in the JAG1, ATP8B1, ABCB11, or ABCB4 genes. 20852622_results unveil a new paradigm whereby Atp8b1 is a cardiolipin importer whose capacity to remove cardiolipin from lung fluid is exceeded during inflammation or when Atp8b1 is defective 23033845_Novel splice-site mutation in ATP8B1 results in atypical progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 1. 23060447_Biochemical analysis of P4-ATPase mutations identified in patients with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis 23197899_Case Report: missense ATP8B1 mutation in adult male with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 1. 23213138_FIC1 signals to FXR via a signaling pathway including PLD2 and PKCzeta 23251605_The basal expression of ATP8B1 is driven by a housekeeping-like promoter located 71 kb upstream of the first protein coding exon, and is independent of bile acids and farnesoid X receptor. 23750872_Case Report: suggest contribution of ATP8B1 mutations to drug-induced liver injury from anabolic androgenic steroids marketed as dietary supplements. 24260417_We did not find an association between heterozygous ATP8B1 variants and chronic pancreatitis in our cohort of patients with hereditary and idiopathic chronic pancreatitis. 25239307_Data indicate that the lipid flippase (ATP8B1)-transmembrane protein 30A (CDC50A) heterodimer is essential for the apical localization of sodium-dependent bile acid transporter (SLC10A2/ASBT) in Caco-2 cells. 25421123_We systematically characterized the molecular consequences of 14 ATP8B1 mutations at exon-intron boundaries associated with ATP8B1 deficiency and found that the majority resulted in total exon skipping 26050466_insufficient activity of Atp8b1/FIC1 increases susceptibility to bacterial pneumonia. 26240149_the predominant P4 ATPases in pure pancreatic beta cells and human and rat pancreatic islets were ATP8B1, ATP8B2, and ATP9A. ATP8B1 and CDC50A were highly concentrated in ISG 26382629_As hypothyroidism can be another extrahepatic feature of ATP8B1 deficiency, thyroid function should be monitored in these patients. 27050426_GGT levels in patients with ATP8B1 or ABCB11 deficiency varied with age. The peak GGT value was | ENSMUSG00000039529 | Atp8b1 | 192.001085 | 0.058842233 | -4.087004 | 1.05067361 | 10.205810 | 0.0013999885123013944623893145546844607451930642127990722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0100632267780431175485666983604460256174206733703613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 27.6194703 | 21.7767578 | 530.4534129 | 419.1831612 | |
| ENSG00000082458 | 1741 | DLG3 | protein_coding | Q92796 | FUNCTION: Required for learning most likely through its role in synaptic plasticity following NMDA receptor signaling. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Intellectual disability;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain | This gene encodes a member of the membrane-associated guanylate kinase protein family. The encoded protein may play a role in clustering of NMDA receptors at excitatory synapses. It may also negatively regulate cell proliferation through interaction with the C-terminal region of the adenomatosis polyposis coli tumor suppressor protein. Mutations in this gene have been associated with X-linked cognitive disability. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. | hsa:1741; | adherens junction [GO:0005912]; AMPA glutamate receptor complex [GO:0032281]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; establishment of planar polarity [GO:0001736]; establishment or maintenance of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity [GO:0045197]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; positive regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0061098]; receptor clustering [GO:0043113]; receptor localization to synapse [GO:0097120]; regulation of postsynaptic membrane neurotransmitter receptor levels [GO:0099072] | 15185169_Loss may lead to altered synaptic plasticity and may explain the intellectual impairment observed in individuals with DLG3 mutations 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19167192_The results of this study suggested a putative role for DLG3/SAP102 in cortical hyperexcitability and epileptogenicity of malformations of cortical development. 19795139_Results identified a novel splice site mutation in the disc-large homolog 3 (DLG3) gene, encoding the synapse-associated protein 102 (SAP102) in one out of 300 families with moderate to severe non-syndromic mental retardation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21252287_DLG3 was identified by genome-wide gene expression analyses as correlated with cellular sensitivity to cisplatin and carboplatin. DLG3 was also found to correlate with cellular sensitivity to platinating agents in NCI-60 cancer cell lines. 21369957_DLG3 did not associate with non-syndromic mental retardation in Chinese Han population; however, further studies are needed. 21384559_A total of six novel and 11 known single nucleotide polymorphisms were identified. Further studies are warranted to analyze the candidate genes at Xq11.1-q21.33. 22745750_Synapse associated protein 102 (SAP102) binds the C-terminal part of the scaffolding protein neurobeachin. 23103165_The PDZ-independent interaction between SAP102 and GluN2B mediates the synaptic clearance of GluN2B-containing NMDARs.(SAP102 protein) 24381070_The data of this study suggested that DLG3 is down-regulated in this cancer type. 24507884_This study identified DLG3 significantly associated loci with a biologically plausible role in schizophrenia. 24739954_miR-1246 might play a role in neurological pathogenesis of human enterovirus 71 by regulating DLG3 gene in infected cells. 25268382_Trans-homophilic interaction of CADM1 activates PI3K by forming a complex with MAGuK-family proteins MPP3 and Dlg. 25555912_These data shed new light on the role of SAP102 in the regulation of NMDAR trafficking. 27222290_Insertion of a guanine into the DLG3 5' UTR, 7 bp upstream of the start codon, down regulated DLG3 protein levels. This non-coding variant segregates with X-linked intellectual disability in a large family. 27222290_The dupG DLG3 variant segregated with non-syndromic X-linked intellectual disability in a large family and was predicted to disrupt folding of the mRNA. 27466188_Following the critical period NMDA receptor function was unaffected by loss of SAP102 but there was a reduction in the divergence of TC connectivity. These data suggest that changes in synaptic function early in development caused by mutations in SAP102 result in changes in network connectivity later in life. 28777483_This family broadens the mutational and phenotypical spectrum of DLG3-associated non-syndromic X-linked intellectual disability and demonstrates that heterozygous female mutation carriers can be as severely affected as males. 29282697_These data provide evidence for a novel mechanism in regulating SAP102 function and glutamate receptor trafficking. 31271664_High expression of DLG3 is associated with decreased survival from breast cancer. 32593652_Silence of lncRNA MIAT-mediated inhibition of DLG3 promoter methylation suppresses breast cancer progression via the Hippo signaling pathway. | ENSMUSG00000000881 | Dlg3 | 52.288280 | 2.965844581 | 1.568443 | 0.37344016 | 16.964701 | 0.0000380812799072379146191925924913590506548644043505191802978515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0004366237240511835625451919629114172494155354797840118408203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 85.3928928 | 17.1806362 | 28.4764065 | 6.0228390 | |
| ENSG00000085514 | 29992 | PILRA | protein_coding | Q9UKJ1 | FUNCTION: Paired receptors consist of highly related activating and inhibitory receptors and are widely involved in the regulation of the immune system. PILRA is thought to act as a cellular signaling inhibitory receptor by recruiting cytoplasmic phosphatases like PTPN6/SHP-1 and PTPN11/SHP-2 via their SH2 domains that block signal transduction through dephosphorylation of signaling molecules. Receptor for PIANP. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10903717, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21241660}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as an entry co-receptor for herpes simplex virus 1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18358807}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Cell signaling pathways rely on a dynamic interaction between activating and inhibiting processes. SHP-1-mediated dephosphorylation of protein tyrosine residues is central to the regulation of several cell signaling pathways. Two types of inhibitory receptor superfamily members are immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM)-bearing receptors and their non-ITIM-bearing, activating counterparts. Control of cell signaling via SHP-1 is thought to occur through a balance between PILRalpha-mediated inhibition and PILRbeta-mediated activation. These paired immunoglobulin-like receptor genes are located in a tandem head-to-tail orientation on chromosome 7. This particular gene encodes the ITIM-bearing member of the receptor pair, which functions in the inhibitory role. Alternative splicing has been observed at this locus and three variants, each encoding a distinct isoform, are described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:29992; | extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; MHC class I protein binding [GO:0042288]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 18097101_PILRalpha protein was successfully crystallized at 293 K using the sitting-drop vapour-diffusion method and the crystals diffracted to 1.3 A resolution. 18358807_The results demonstrate that cellular receptors for both gB and gD are required for HSV-1 infection and that PILRalpha plays an important role in HSV-1 infection as a coreceptor that associates with gB. 19244335_viral entry via PILRalpha appears to be conserved but that there is a PILRalpha preference among alphaherpesviruses 19457990_Insertional mutations of gB reduced cell fusion activity when PILRalpha was overexpressed much more than nectin-1. 21241660_These results suggest that PANP is involved in immune regulation as a ligand of the PILRalpha. 22396535_Data show that PILRalpha/ligand interactions require conserved PILRalpha arginine (Arg)-133 (mouse) and Arg-126 (human). 22695228_The authors show that the human ocular and highly neurovirulent HSV-1 strain McKrae enters substantially more efficiently into cells via the gB-specific human paired immunoglobulin-like type-2 receptor-alpha (hPILR-alpha). 23302878_The amino terminus of herpes simplex virus 1 gK is functionally and physically associated with the gB-PILRalpha protein complex and regulates membrane fusion of the viral envelope with cellular membranes during virus entry. 24253495_These results contribute our knowledge of the biological functions of HBVDNAPTP1 and provide novel data to aid in the further analysis of the regulatory mechanism of this protein. 24843130_We demonstrated that three residues (Y2, R95, and W108) presented on the surface of PILRalpha form the sialic acid binding site equivalent to those in siglecs but are arranged in a unique linear mode. 24889612_PILRalpha exhibits large conformational change to recognize simultaneously both the sTn O-glycan and the compact peptide structure constrained by proline residues 27029068_The interaction of NK cells with PILRalpha expressing targets lead to elevated IFNgamma secretion and cytotoxicity. In conclusion, PILRalpha is a novel NK activating ligand which binds and activates an unknown NK receptor expressed on a unique NK cell subset. 29046357_Data suggest that, although PILRA exhibits essentially the same recognition of different glycopeptides, slight modifications of linker sugar cause significant changes in a wide area of the binding interface, resulting in a reduction of binding affinity; analogs/fragments of gpb were used in these studies. (PILRA = paired immunoglobin like type 2 receptor alpha; gpb = envelope glycoprotein B, Herpes simplex virus type 1) 29181857_Exome-wide burden analysis revealed significant burden of variants in PILRA in patients with late-onset Alzheimer's disease 29202958_Transcriptome wide association study results identified two novel genes as statistically significantly associated with nonobstructive azoospermia susceptibility: PILRA and ZNF676. 30388101_We propose that PILRA G78R protects individuals from Alzheimer's disease risk via reduced inhibitory signaling in microglia and reduced microglial infection during HSV-1 recurrence. 31297637_Herpes simplex virus type 1 IgG are increased in Alzheimer's disease patients with the protective R78 PILRA genotype. 34602489_Inhibitory Fcgamma Receptor and Paired Immunoglobulin Type 2 Receptor Alpha Genotypes in Alzheimer's Disease. 35617401_The CD8alpha-PILRalpha interaction maintains CD8(+) T cell quiescence. 35918447_PILRA polymorphism modifies the effect of APOE4 and GM17 on Alzheimer's disease risk. | 77.001527 | 0.443901928 | -1.171687 | 0.20174083 | 33.926522 | 0.0000000057233159807144271291229849544200669608784437514259479939937591552734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000001363845722968201135644292654874876191684052173513919115066528320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 41.5483646 | 11.2805023 | 93.8431084 | 24.8780334 | |||
| ENSG00000085999 | 8438 | RAD54L | protein_coding | Q92698 | FUNCTION: Plays an essential role in homologous recombination (HR) which is a major pathway for repairing DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) gaps, and stalled or collapsed replication forks (PubMed:9774452, PubMed:24798879, PubMed:32457312, PubMed:11459989, PubMed:12205100, PubMed:27264870). Acts as a molecular motor during the homology search and guides RAD51 ssDNA along a donor dsDNA thereby changing the homology search from the diffusion-based mechanism to a motor-guided mechanism. Also plays an essential role in RAD51-mediated synaptic complex formation which consists of three strands encased in a protein filament formed once homology is recognized. Once DNA strand exchange occured, dissociates RAD51 from nucleoprotein filaments formed on dsDNA (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P32863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11459989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12205100, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24798879, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27264870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32457312, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9774452}. | Acetylation;ATP-binding;DNA damage;DNA repair;DNA-binding;Helicase;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the DEAD-like helicase superfamily, and shares similarity with Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad54, a protein known to be involved in the homologous recombination and repair of DNA. This protein has been shown to play a role in homologous recombination related repair of DNA double-strand breaks. The binding of this protein to double-strand DNA induces a DNA topological change, which is thought to facilitate homologous DNA paring, and stimulate DNA recombination. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008]. | hsa:8438; | nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity [GO:0140658]; ATP-dependent DNA/DNA annealing activity [GO:0036310]; DNA translocase activity [GO:0015616]; helicase activity [GO:0004386]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; chromosome organization [GO:0051276]; determination of adult lifespan [GO:0008340]; DNA recombination [GO:0006310]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; double-strand break repair via synthesis-dependent strand annealing [GO:0045003]; meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051321]; reciprocal meiotic recombination [GO:0007131]; response to ionizing radiation [GO:0010212]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410] | 12614485_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12614485_The RAD54L polymorphism (2290C/T) can be used as a genetic marker inside the consensus deletion region at 1p32 in human meningiomas. 15975611_Shortened telomeres in murine scid cells expressing mutant RAD54L coincide wirth reduction in recombination at telomeres. 16520463_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16540687_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16862129_hRad54, a Swi2/Snf2 protein, binds HJ-like structures with high specificity and promotes their bidirectional branch migration in an ATPase-dependent manner 17054727_Some immortal cells use the alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT) pathway to maintain their telomeres instead of telomerase. This is the first genetic evidence that Rad54 is dispensable for the ALT pathway. 17417655_RAD54 is recruited by RAD51-ssDNA filament to the chromatin of the intact chromosome and it remodels that chromatin to facilitate accessibility for strand exchange 17545145_analysis of human rad54 protein interactions with branched DNA molecules 17660833_Rad54 protein causes dissociation of joint molecules by ATP-dependent branch-migration and therefore plays an important role in double strand DNA break repair. 18203022_germline mutations in RAD51, RAD51AP1, RAD51L1, RAD51L3, RAD52 and RAD54L are unlikely to be causal of an inherited predisposition to CLL. 18270339_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18617519_Rad51 protein stimulates the branch migration activity of Rad54 protein.( 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19147782_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20496165_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20522537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20610542_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20813000_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24798879_Nap1 stimulates homologous recombination by RAD51 and RAD54 in higher-ordered chromatin containing histone H1. 25765654_support a model in which RAD54L and RAD54B counteract genome-destabilizing effects of direct binding of RAD51 to dsDNA in tumor cells 25965574_TAF12 and NFYC are transcription factors that regulate the epigenome, whereas RAD54L plays a central role in DNA repair 29295984_Data show that the RAD54 N-terminal domain (NTD) is responsible for initiation of branch migration (BM) through two coupled, but distinct steps; specific binding to Holliday junctions and RAD54 oligomerization. 32333827_Extended in vitro culture of primary human mesenchymal stem cells downregulates Brca1-related genes and impairs DNA double-strand break recognition. 33261027_E2F1 Promotes Progression of Bladder Cancer by Modulating RAD54L Involved in Homologous Recombination Repair. 34079088_Oct4 confers stemness and radioresistance to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the homologous recombination factors PSMC3IP and RAD54L. 34169999_Association of MTHFR, MTRR and RAD54L Gene Variations with Meningioma and Correlation with Tumor's Histopathological Characteristics on Turkish Cohort. 36071250_Rad54L promotes bladder cancer progression by regulating cell cycle and cell senescence. | ENSMUSG00000028702 | Rad54l | 153.898903 | 0.487253828 | -1.037255 | 0.33768735 | 9.038827 | 0.0026430515965829085023308664403884904459118843078613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0170332486977118925663976511941655189730226993560791015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 78.3366611 | 25.2164574 | 163.5204286 | 52.4917279 | |
| ENSG00000088179 | 5775 | PTPN4 | protein_coding | P29074 | FUNCTION: Phosphatase that plays a role in immunity, learning, synaptic plasticity or cell homeostasis (PubMed:25825441, PubMed:27246854). Regulates neuronal cell homeostasis by protecting neurons against apoptosis (PubMed:20086240). Negatively regulates TLR4-induced interferon beta production by dephosphorylating adapter TICAM2 and inhibiting subsequent TRAM-TRIF interaction (PubMed:25825441). Dephosphorylates also the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs/ITAMs of the TCR zeta subunit and thereby negatively regulates TCR-mediated signaling pathway (By similarity). May act at junctions between the membrane and the cytoskeleton. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WU22, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20086240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25825441, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27246854}. | 3D-structure;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Hydrolase;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This protein contains a C-terminal PTP domain and an N-terminal domain homologous to the band 4.1 superfamily of cytoskeletal-associated proteins. This PTP has been shown to interact with glutamate receptor delta 2 and epsilon subunits, and is thought to play a role in signalling downstream of the glutamate receptors through tyrosine dephosphorylation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:5775; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; cytoskeletal protein binding [GO:0008092]; glutamate receptor binding [GO:0035254]; non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004726]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470] | 18614237_PTPN4 is dispensable for T cell development and/or T cell effector functions. 23666597_These findings suggest that PTPN4 negatively regulates cell proliferation and motility through dephosphorylation of CrkI. 25158884_The physiologically active PTPN4 two-domain (the PDZ and the phosphatase domains) adopts a predominant compact conformation in solution. PDZ ligand binding restores the catalytic competence of PTPN4 disrupting the transient interdomain communication. 25424712_Deletion of PTPN4 has been reported in monozygotic twins with a Rett syndrome-like phenotype. 27246854_the p38gamma.PTPN4 interaction promotes cellular signaling, preventing cell death induction. 27923202_Binding assays confirmed that three (Cyto8-mtxd-1, Cyto8-mtxk-4 and Cyto8-mtxd-1k-4) out of the five designed peptides exhibit moderately or considerably increased affinity as compared to the native peptide Cyto8-RETEV 28801650_Data show that mutations affect the regulation of the protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 4 (PTPN4) bidomain and indicate that the PDZ-PDZ ligand regulation of PTPN4 is a linker-mediated mechanism. 31025789_Study identified a nonsense mutation of PTPN4 with mutation ratio of 90.90% from 1 case of rectal cancer. Overexpression of PTPN4 suppressed the growth of colorectal cancer cells. PTPN4 dephosphorylates pSTAT3 at the Tyr705 residue with a direct interaction and depresses the transcriptional activity of STAT3. 35089587_Structural and biochemical analysis of the PTPN4 PDZ domain bound to the C-terminal tail of the human papillomavirus E6 oncoprotein. 36042375_MicroRNA-375 is a therapeutic target for castration-resistant prostate cancer through the PTPN4/STAT3 axis. | ENSMUSG00000026384 | Ptpn4 | 46.218627 | 6.427945265 | 2.684358 | 0.52047712 | 23.740503 | 0.0000011023798400945599563458031713847340427037124754860997200012207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000179931029209366441046300671979807361822167877107858657836914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 82.4596832 | 30.4016314 | 12.6439167 | 4.6464403 | |
| ENSG00000088827 | 6614 | SIGLEC1 | protein_coding | Q9BZZ2 | FUNCTION: Acts as an endocytic receptor mediating clathrin dependent endocytosis. Macrophage-restricted adhesion molecule that mediates sialic-acid dependent binding to lymphocytes, including granulocytes, monocytes, natural killer cells, B-cells and CD8 T-cells. Preferentially binds to alpha-2,3-linked sialic acid (By similarity). Binds to SPN/CD43 on T-cells (By similarity). May play a role in hemopoiesis. {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endocytosis;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Lectin;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. The encoded protein is a lectin-like adhesion molecule that binds glycoconjugate ligands on cell surfaces in a sialic acid-dependent manner. It is a type I transmembrane protein expressed only by a subpopulation of macrophages and is involved in mediating cell-cell interactions. The protein plays an important role in multiple human diseases and bacterial and viral infections has been shown to enhance SARS-CoV-2 infection. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2021]. | hsa:6614; | early endosome [GO:0005769]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; virion binding [GO:0046790]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell [GO:0075512]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954] | 16002716_Inhibitory signals delivered from human rhinovirus HRV14-treated dendritic cells to cocultured T cells via sialoadhesin (Sn) are critical for induction of T-cell anergy. 17328080_Increased expression of Siglec-1 in circulating systemic sclerosis (SSc) monocytes and tissue macrophages suggests type I IFN-mediated activation of monocytes occurs in SSc, possibly through toll-like receptor (TLR) activation of interferon secretion. 17330143_Sialoadhesin is induced to high levels on CD14(+) cells early after HIV-1 infection in vivo. 18383365_SIGLEC1, used as a surrogate marker for type I interferon, is a potential biomarker to assess disease acitvity in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). SIGLEC1+ resident monocytes could act as antigen presenting cells in SLE. 18383365_Siglec-1 (sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin 1) expression in resident blood monocytes is a potential biomarker for monitoring disease activity, displaying type I IFN responses, and estimating levels of anti-dsDNA antibodies 18414664_Increased sialoadhesin expression on CD14(+) monocytes occurs in response to HIV-1 infection with maximum expression associated with high viral load 19285973_Siglec-1 may be considered as a potential non-invasive indicator for monitoring disease severity and a biomarker for predicting the relative risk of cardiovascular events. 19950173_Data show that the combinatorial signal delivered by R-DC to T cells via B7-H1 and sialoadhesin is crucial for the induction of IL-35(+) Treg. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20653431_Increased expression in monocytes of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22249367_Monocytes overexpress sialoadhesin nonspecifically during intestinal transplant rejection and systemic or enteritic inflammatory states. 22933622_Based on increased SIGLEC1 expression in circulating monocytes, findings suggest a role for SIGLEC1 in the chronic progressive phases of multiple sclerosis. 23271952_These findings identify Siglec-1 as a key factor for HIV-1 spread via infectious dendritic/T-cell synapses. 23593001_downregulation of CD169 expression or neutralizing CD169 function abrogated dendritic cell-mediated HIV-1 capture and trans infection, while exogenous expression of CD169 in receptor-naive cells rescued glycosphingolipid-dependent capture and trans infection. 23610394_the CD169/Sn endocytic pathway is conserved and capable of presenting lipid antigens to iNKT cells 23734742_CD169(+) macrophages in RLNs promote CD8(+) T-cell-mediated antitumor immunity. 24196391_Siglec-1 may play a proinflammatory role in stimulating lymphocyte proliferation and activation in rheumatoid arthritis. 24947940_GM3-CD169 binding is a gp120-independent signal for sequestration and preservation of HIV-1 infectivity. 25033082_evidence identifying sialyllactose-containing gangliosides in the viral membrane and the cellular lectin Siglec-1 as critical determinants for HIV-1 capture and storage by mature DCs and for DC-mediated trans-infection of T cells 25354152_The most abundant cytokine present in semen (TGF-beta1) is able to enhance specifically the expression of an important molecule (CD169) involved in the capture and transmission of HIV-1 particles from the mucosal lumen to the submucosal compartment. 25760631_Our study suggests that HIV-1 capture by CD169 can provide virus evasion from both innate (phagocytosis) and adaptive immune responses 25947229_Siglec-1 on myeloid cells could fuel novel CD4(+) T-cell infections and contribute to HIV-1 dissemination in vivo. 26667473_These results highlight the importance of sialic acids on the V1V2 region in binding to sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin. 26752092_Siglec-1 and Siglec-2 are potential biomarkers in autoimmune disease. (Review) 27174787_CD169 might act as a co-stimulatory molecule for cytotoxic T-cell activation, and could define a population of tumour-infiltrating macrophages with potential anti-tumour properties in human hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. 27510803_classical HIV-1 infectious routes may compensate for the lack of Siglec-1 in fuelling HIV-1 dissemination within infected individuals 27551071_the antibody-sialidase conjugate desialylated tumor cells in a HER2-dependent manner, reduced binding by natural killer (NK) cell inhibitory sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin (Siglec) receptors, and enhanced binding to the NK-activating receptor natural killer group 2D (NKG2D). 27601677_The results reveal marked differences between afferent and efferent ymphatic endothelial cells and identify molecules on lymphatic vessels. Further characterizations of Siglec-1 (CD169) and macrophage scavenger receptor 1 (MSR1/CD204), show that they are discriminatively expressed on lymphatic endothelium of the subcapsular sinus but not on lymphatic vasculature of the lymphatic sinus 27861544_These findings suggest that CD169+ macrophages in RLNs might be a useful marker for assessing clinical stage, including LN states, in patients with breast cancer. 27993350_this study shows that binding of monoclonal antibodies to Sn results in delayed and reduced phagocytosis of fluorescent beads, and that no effect is observed on Fc-mediated phagocytosis or phagocytosis of bacteria by macrophages 28002629_In colorectal tumor, malignant melanoma, and endometrial tumor, it was shown that a high density of CD169-positive macrophages in the lymph node sinus was a predictive factor for better clinical prognosis. 28129379_These data demonstrate a prominent role for Siglec-1 in the internalization of HIV-1 to the virus-containing compartment in infected monocyte-derived macrophages 28501799_High expression of SIGLEC1 in pregnant women with autoantibodies against Ro/SS-A indicates an enhanced risk for autoimmune congenital heart block development. 28794041_High CD169 expression is associated with HIV-1. 28880401_CD169 expression in regional LNs was not associated with PSA-relapse. 28964857_Our findings evidenced for the first time the novel association between SIGLEC1 rs3859664 SNP and active pulmonary TB. Intriguingly, carriers of the polymorphism produced less IL-1ss than non-carriers, suggesting the possible involvement of Siglec-1 signalling pathway with inflammasome complex. 29037117_SIGLEC1 mRNA levels have potential as a novel predictive biomarker for Graves disease relapse. 29266251_In vitro, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) increased expression of Siglec-1 on healthy newborn and adult monocytes. RSV-induced Siglec-1 on monocytes inhibited Interferon gamma production by adult CD4(+) T cells. In contrast,Interferon gamma production by RSV in newborns was not affected by Siglec-1. 30516869_suggest that high expression of CD169 in lymph node sinus macrophages reflects a high potential for anti-cancer immune responses in esophageal cancer patients 31591213_circulating dendritic cell precursors, but not other blood dendritic cell subsets, are susceptible to infection by HIV-1 in a Siglec-1-dependent manner. This constitutes a unique functional feature that might represent a preferential relationship of this emerging cell type with viruses. 31992280_Decreased expression of a phagocytic receptor Siglec-1 on alveolar macrophages in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 32223897_Tuberculosis-associated IFN-I induces Siglec-1 on tunneling nanotubes and favors HIV-1 spread in macrophages. 33081587_SIGLEC1 (CD169) is a sensitive biomarker for the deterioration of the clinical course in childhood systemic lupus erythematosus. 33206973_Monocyte CD169 Expression as a Biomarker in the Early Diagnosis of Coronavirus Disease 2019. 33489013_Dissemination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is associated to a SIGLEC1 null variant that limits antigen exchange via trafficking extracellular vesicles. 33491921_CD169 and CD64 could help differentiate bacterial from CoVID-19 or other viral infections in the Emergency Department. 33547747_Monocyte CD169 expression in COVID-19 patients upon intensive care unit admission. 33986412_SIGLEC1 (CD169): a marker of active neuroinflammation in the brain but not in the blood of multiple sclerosis patients. 34160241_CyTOF Profiling of Zika and Dengue Virus-Infected Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Identifies Phenotypic Signatures of Monotype Subsets and Upregulation of the Interferon-Inducible Protein CD169. 34387304_Siglec-1 expression on monocytes is associated with the interferon signature in juvenile dermatomyositis and can predict treatment response. 34607536_Prognostic value of CD169-positive macrophages in various tumors: a meta-analysis. 35177553_SIGLEC1 enables straightforward assessment of type I interferon activity in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. 35695299_The role of activated monocyte IFN/SIGLEC1 signalling in Graves' disease. 36279285_CD169-mediated restrictive SARS-CoV-2 infection of macrophages induces pro-inflammatory responses. | ENSMUSG00000027322 | Siglec1 | 38.503522 | 0.181418431 | -2.462607 | 0.31869606 | 64.137688 | 0.0000000000000011602077191844247039670739305161142622112324142291672757210108102299273014068603515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000573462387842817494380362755242766893882698162054900592465855879709124565124511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 12.0362199 | 2.4321441 | 65.7544946 | 9.8300503 | |
| ENSG00000088882 | 56265 | CPXM1 | protein_coding | Q96SM3 | FUNCTION: May be involved in cell-cell interactions. No carboxypeptidase activity was found yet (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Carboxypeptidase;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Zinc | This gene likely encodes a member of the carboxypeptidase family of proteins. Cloning of a comparable locus in mouse indicates that the encoded protein contains a discoidin domain and a carboxypeptidase domain, but the protein appears to lack residues necessary for carboxypeptidase activity.[provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. | hsa:56265; | extracellular space [GO:0005615]; metallocarboxypeptidase activity [GO:0004181]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; peptide metabolic process [GO:0006518]; protein processing [GO:0016485] | 10073577_This paper deals with mouse CPXM. 27006448_These findings establish CPX-1 as a positive regulator of adipogenesis situated downstream of FGF-1/BAMBI that may contribute to hyperplastic adipose tissue expansion via affecting extracellular matrix remodeling. | ENSMUSG00000027408 | Cpxm1 | 128.034979 | 0.498224697 | -1.005132 | 0.14075837 | 51.681789 | 0.0000000000006526531448271620739746075474523338486032564276229095412418246269226074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000245411618006514582884302366401439439262677222330921722459606826305389404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 85.0342743 | 11.8255912 | 171.4403672 | 22.8063976 | |
| ENSG00000092068 | 23428 | SLC7A8 | protein_coding | Q9UHI5 | FUNCTION: Sodium-independent, high-affinity transport of small and large neutral amino acids such as alanine, serine, threonine, cysteine, phenylalanine, tyrosine, leucine, arginine and tryptophan, when associated with SLC3A2/4F2hc. Acts as an amino acid exchanger. Has higher affinity for L-phenylalanine than LAT1 but lower affinity for glutamine and serine. L-alanine is transported at physiological concentrations. Plays a role in basolateral (re)absorption of neutral amino acids. Involved in the uptake of methylmercury (MeHg) when administered as the L-cysteine or D,L-homocysteine complexes, and hence plays a role in metal ion homeostasis and toxicity. Involved in the cellular activity of small molecular weight nitrosothiols, via the stereoselective transport of L-nitrosocysteine (L-CNSO) across the transmembrane. Plays an essential role in the reabsorption of neutral amino acids from the epithelial cells to the bloodstream in the kidney. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10391915, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10574970, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11311135, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12117417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12716892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15081149, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15769744, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15918515}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Amino-acid transport;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | Enables several functions, including neutral amino acid transmembrane transporter activity; thyroid hormone transmembrane transporter activity; and toxin transmembrane transporter activity. Involved in L-alanine import across plasma membrane; L-leucine import across plasma membrane; and thyroid hormone transport. Located in plasma membrane. Part of basolateral plasma membrane and microvillus membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:23428; | apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; microvillus membrane [GO:0031528]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015171]; glycine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015187]; L-alanine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015180]; L-amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015179]; L-leucine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015190]; neutral amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015175]; organic cation transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015101]; peptide antigen binding [GO:0042605]; thyroid hormone transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015349]; toxin transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0019534]; amino acid import across plasma membrane [GO:0089718]; amino acid transport [GO:0006865]; glycine transport [GO:0015816]; L-alanine import across plasma membrane [GO:1904273]; L-leucine import across plasma membrane [GO:1903801]; leucine import across plasma membrane [GO:0098713]; leucine transport [GO:0015820]; metal ion homeostasis [GO:0055065]; neutral amino acid transport [GO:0015804]; proline transmembrane transport [GO:0035524]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; thyroid hormone transport [GO:0070327]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104]; tryptophan transport [GO:0015827]; valine transport [GO:0015829] | 12716892_the interaction of CD98/LAT2 with ICAM-1, found to be expressed to the basolateral domain, and the potential of such interaction on intracellular signal activation in Caco2-BBE cell monolayers 15769744_identify LAT1 and LAT2 as members of system L that mediate transmembrane movement of l-CSNO 17558306_Genetic variation in LAT1 and LAT2 does not appear to be a major cause of inter-individual variability in pharmacokinetics and of adverse reactions to melphalan. 17558306_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19808856_LAT2 genes may play important roles in leiomyoma cell proliferation and regulate leiomyoma growth 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21486766_Compared with the adult cerebral cortex, mRNAs encoding OATP1A2, OATP1C1, OATP3A1 variant 2, OATP4A1, LAT2 and CD98 were reduced in fetal cortex at different gestational ages, whilst mRNAs encoding MCT8, MCT10, OATP3A1 variant 1 and LAT1 were similar. 25299125_The detergent-induced stabilization of the purified human 4F2hc-LAT2 complex presented here paves the way towards its crystallization and structure determination at high-resolution 26050671_LAT1 and LAT2 are present and functional in the syncytiotrophoblast MVM, whereas LAT2 is also expressed in the BM and in the fetal capillary endothelium. 27224648_LAT1 and LAT2 were overexpressed in both pheochromocytoma and medullary thyroid carcinoma by comparison with normal tissues. 29355479_These preliminary data suggest that a relevant proportion of age-related hearing loss cases could be explained by SLC7A8 mutations. 30419950_Data reveal that LAT2 functions as an oncogenic protein and could regulate glutamine-dependent mTOR activation to promote glycolysis and decrease GEM sensitivity in pancreatic cancer 31701662_Abnormalities in the genes that encode Large Amino Acid Transporters increase the risk of Autism Spectrum Disorder. 32200487_The solute carrier SLC7A8 is a marker of favourable prognosis in ER-positive low proliferative invasive breast cancer. 32993041_Sub-Nanometer Cryo-EM Density Map of the Human Heterodimeric Amino Acid Transporter 4F2hc-LAT2. 33001560_Small molecule inhibitors provide insights into the relevance of LAT1 and LAT2 in materno-foetal amino acid transport. 33066406_The Heavy Chain 4F2hc Modulates the Substrate Affinity and Specificity of the Light Chains LAT1 and LAT2. 34494553_Genomic and epigenomic evolution of acquired resistance to combination therapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000022180 | Slc7a8 | 362.656850 | 2.281944813 | 1.190264 | 0.08517601 | 198.106256 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000054087746304000498031200491795580596680467017253321421984558402216098988809571194907769880396947757506993822110708935307910039114176470320671796798706 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000009457242441254487054929892587333529244931792143555735035550490127292064590983889478246313426159474119184498780085745828216658992459997534751892089844 | Yes | No | 497.0705347 | 24.3687550 | 218.8370664 | 12.0303687 | |
| ENSG00000092445 | 7301 | TYRO3 | protein_coding | Q06418 | FUNCTION: Receptor tyrosine kinase that transduces signals from the extracellular matrix into the cytoplasm by binding to several ligands including TULP1 or GAS6. Regulates many physiological processes including cell survival, migration and differentiation. Ligand binding at the cell surface induces dimerization and autophosphorylation of TYRO3 on its intracellular domain that provides docking sites for downstream signaling molecules. Following activation by ligand, interacts with PIK3R1 and thereby enhances PI3-kinase activity. Activates the AKT survival pathway, including nuclear translocation of NF-kappa-B and up-regulation of transcription of NF-kappa-B-regulated genes. TYRO3 signaling plays a role in various processes such as neuron protection from excitotoxic injury, platelet aggregation and cytoskeleton reorganization. Also plays an important role in inhibition of Toll-like receptors (TLRs)-mediated innate immune response by activating STAT1, which selectively induces production of suppressors of cytokine signaling SOCS1 and SOCS3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20546121}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for lassa virus and lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus, possibly through GAS6 binding to phosphatidyl-serine at the surface of virion envelope. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22156524, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22673088, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25277499}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Ebolavirus, possibly through GAS6 binding to phosphatidyl-serine at the surface of virion envelope. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17005688}. | 3D-structure;ATP-binding;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase | The gene is part of a 3-member transmembrane receptor kinase receptor family with a processed pseudogene distal on chromosome 15. The encoded protein is activated by the products of the growth arrest-specific gene 6 and protein S genes and is involved in controlling cell survival and proliferation, spermatogenesis, immunoregulation and phagocytosis. The encoded protein has also been identified as a cell entry factor for Ebola and Marburg viruses. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. | hsa:7301; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding [GO:0043548]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; apoptotic cell clearance [GO:0043277]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; forebrain cell migration [GO:0021885]; natural killer cell differentiation [GO:0001779]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045824]; negative regulation of lymphocyte activation [GO:0051250]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0034122]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neuron apoptotic process [GO:0051402]; neuron cellular homeostasis [GO:0070050]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; neuropeptide signaling pathway [GO:0007218]; ovulation cycle [GO:0042698]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014065]; platelet activation [GO:0030168]; platelet aggregation [GO:0070527]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of viral life cycle [GO:1903902]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein kinase B signaling [GO:0043491]; secretion by cell [GO:0032940]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:0034446]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169]; vagina development [GO:0060068] | 12768229_Gas6 receptors were not upregulated in any of the allograft groups, except for the Axl receptor, which increased only in acute tubular necrosis. 14623883_Tyro3 may have roles in signal transduction and cell adhesion 15733062_Axl, Sky and Mer are Gas6 receptors that enhance platelet activation and regulate thrombotic responses 15964779_Results identify and characterise a novel interaction between RanBPM and the related receptor tyrosine kinases, Axl and Sky. 17005688_Here we show the involvement of members of the Tyro3 receptor tyrosine kinase family-Axl, Dtk, and Mer-in cell entry of filoviruses. 18620092_Possible strategies for targeted inhibition of the TAM family in the treatment of human cancer. 19805117_Results identified the receptor protein tyrosine kinase TYRO3 as an upstream regulator of MITF expression by a genome-wide gain-of-function cDNA screen. 20348395_Protein S controls hypoxic/ischemic blood-brain barrier disruption through the TAM receptor Tyro3 and sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor. 20546121_Gas6 and Tyro3, Axl and Mer (TAM) receptors have roles in human and murine platelet activation and thrombus stabilization 20637106_correlation of decreased protein S levels with lupus disease activity is consistent with a role for the TAM receptors in scavenging apoptotic cells and controlling inflammation 20664904_Findings indicate genetic association between MERTK and TYRO3 allelic variants and carotid atherosclerosis. 20664904_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21343401_Our findings suggest that a TYRO3/AXL-GAS6 autocrine circuit sustains the malignant features of thyroid cancer cells 21384080_expression is downregulated in atherosclerotic carotid plaque 21496228_plasma concentrations of sMer and sTyro3 were significantly increased in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosis and Rheumatoid arthritis 22119469_analysis of novel and selective spiroindoline-based inhibitors of Sky kinase 22156524_Axl,Tyro3,DC-SIGN and LSECtin are identified as new virus receptors for Lassa virus cell entry. 23354874_Gas6, a ligand of Tyro3, exerts an autocrine activities though Tyro3 and Axl in a subgroup of leiomyosarcoma. 23570341_data indicate that Tyro3 may confer increased survival signals in melanoma cells and can be stymied using inhibitory mAbs 23632195_These findings indicate that Tyro3 is a critical signal for synovial hyperplasia, osteoclast differentiation and bone erosion during arthritis. 23662598_[review] Receptor tyrosine kinases Tyro-3, Axl and Mer, collectively designated as TAM, are involved in the clearance of apoptotic cells. 23865365_Low expression of the Syk gene may play an important role in tumorigenesis in esophageal cancer. 24982338_The effects of TYRO3-knockdown by small interfering RNA (siRNA) on proliferation, cell-cycle distribution, and cell signaling in different breast neoplasm cell lines were compared. 25074926_These studies demonstrate that, despite their similarity, TYRO3, AXL, and MER are likely to perform distinct functions in both immunoregulation and the recognition and removal of ACs. 25211072_Tetherin phosphorylation induces the recruitment of Syk which is required for downstream NF-kappaB activation. 25815442_the results of the present study demonstrated that the acquired taxol resistance of ovarian cancer cells was associated with ROS-dependent upregulation in the expression of Tyro3 RTK and the subsequent activation of Akt. 25878564_Significantly increased levels of sMer, sTyro3 and sAxl may be important factors contributing to the deficit in phagocytosis ability in systemic lupus erythematosus . 25881761_The mRNA expression levels of Tyro-3, Axl were decreased in pSS patients. When considering the plasma level, increased levels of soluble Mer was observed with statistically significant difference. 26573872_these data suggest that Tyro3 contributes significantly to tumor growth, aggressiveness and liver dysfunction 26656104_Tyro3 gene dosage modulates Mertk-associated retinal degeneration, provide strong evidence for a direct role for TYRO3 in RPE phagocytosis, and suggest that an eQTL can modify a recessive Inherited photoreceptor degenerations. 27034374_genetic ablation of a receptor tyrosine kinase encoded byTyro3in mice or the functional neutralization of its ortholog in human dendritic cells resulted in enhanced type 2 immunity. 27132510_TYRO3 is overexpressed in the early stage of colon cancer development and aberrant expression of TYRO3 promotes tumorigenesis and induces EMT through the regulation of SNAI1. 27486820_Study identified the Gas6/TAM receptor pathway with Tyro3 and Mer as novel targets in colorectal cancer. 27801848_In this paper, we review the biology of the Gas6/Tyro3, Axl, and MerTK(collectively named TAM system)and the current evidence supporting its potential role in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis . 28184013_Phosphatidylserine mediated hyperactivation of TYRO3.TYRO3 promotes epithelial cell efferocytosis in a tyrosine kinase-dependent manner.TYRO3 role in AKT-dependent drug resistance. 28537534_Taken together, our data indicate that elevated plasma Gas6 levels is associated with the severity of disease during HTNV infection in humans, suggesting that Gas6 may play an important role by binding with Tyro3 on monocytes. 28668213_Patients with macroalbuminuria diabetes had higher circulating levels of sMer and more urinary soluble Tyro3 and sMer than normoalbuminuric diabetics. Increased clearance of sTyro3 and sMer was associated with loss of tubular Tyro3 and Mer expression in diabetic nephropathy tissue. During in vitro diabetes, human kidney cells had down-regulation of Tyro3 and Mer mRNA and increased shedding of sTyro3 and sMer. 29024938_These results show that TYRO3, AXL and GAS6 are expressed at higher levels in LMS and expression of its ligands correlates to a worse PFS in LMS patients. 29148078_Serum sTyro3 levels were elevated in rheumatoid arthritis patients and correlated positively with disease activity and bone destruction, which may serve as an important participant in rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. 29274473_Data suggest that TYRO3-mediated phosphorylation of ACTN4 is involved in invasiveness of melanoma cells; TYRO3-mediated phosphorylation of ACTN4 requires FAK activation at tyrosine 397. (TYRO3 = TYRO3 protein tyrosine kinase; ACTN4 = actinin alpha 4; FAK = focal adhesion kinase isoform FAK1) 30082152_A meta-analysis of 3 Japanese populations (a total of 2403 Japanese adults) revealed that TYRO3 rs2297377 was associated with atopy and allergic rhinitis (OR = 1.29 and 1.31; P = 0.00041 and 0.0010, respectively). 30226533_TYRO3 is upregulated in colorectal cancer cells and is a direct target gene of miR-7. 30429374_TYRO3 plays a critical role in maintaining normal podocyte function and may be a potential new drug target to treat glomerular diseases 30541554_Axl and Tyro3, but not Mertk, have an important role in platelet activation and thrombus formation 30619243_data do not support a particular role for TAM receptors or for activated CD11b in the association of platelet-derived EVs with monocytes and granulocytes in the circulation. 30765874_TYRO3 plays a critical role in maintaining cell growth and inhibiting apoptosis and is a potential therapeutic target to treat bladder cancer. 30765874_There was a significantly higher expression of TYRO3, in both non-muscle invasive bladder cancers (MIBCs) and MIBCs, compared to normal urothelium. Loss-of-function experiments identified a TYRO3-dependency of bladder carcinoma-derived cells both in vitro and in a mouse xenograft model. 30898992_Results found the protein levels of Syk and inflammatory factors expression in the NSTE-ACS and STEMI groups were higher than those in the SAP and control groups. The protein levels of Syk and inflammatory factors expression in the SAP group were higher than those in the control group. 31230815_we identify an unexpected role of TAM kinases (Tyro3, Axl, and Mer)as promoters of necroptosis, a pro-inflammatory necrotic cell death. Pharmacologic or genetic targeting of TAM kinases results in a potent inhibition of necroptotic death in various cellular models. We identify phosphorylation of MLKL Tyr376 as a direct point of input from TAM kinases into the necroptosis signaling 31451482_TAM Family Receptor Kinase Inhibition Reverses MDSC-Mediated Suppression and Augments Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Melanoma. 31655933_Increased sMer, but not sAxl, sTyro3, and Gas6 relate with active disease in juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus. 31765735_Oncogenic role of TYRO3 receptor tyrosine kinase in the progression of pancreatic cancer. 31831556_Functional Genomics Identifies Hepatitis-Induced STAT3-TYRO3-STAT3 Signaling as a Potential Therapeutic Target of Hepatoma. 32018224_TYRO3 facilitates cell growth and metastasis via activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in human gastric cancer cells. 32051695_New Insights into the Role of Tyro3, Axl, and Mer Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. 32664510_Galectin-3 Stimulates Tyro3 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase and Erk Signalling, Cell Survival and Migration in Human Cancer Cells. 32964059_Selective Increment of Synovial Soluble TYRO3 Correlates with Disease Severity and Joint Inflammation in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. 32988883_Prognostic Significance of TYRO3 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Expression in Gastric Cancer. 33011564_TAM and TIM receptors mRNA expression in Zika virus infected placentas. 33109549_TYRO3 Truncation Resulting From a t(10;15)(p11;q15) Chromosomal Translocation in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. 33234241_Recent advancements in role of TAM receptors on efferocytosis, viral infection, autoimmunity, and tissue repair. 33234243_TAM receptors and their ligand-mediated activation: Role in atherosclerosis. 33234244_Post-translational modifications of the ligands: Requirement for TAM receptor activation. 33234245_Immunological role of TAM receptors in the cancer microenvironment. 33532004_Role of the Gas6/TAM System as a Disease Marker and Potential Drug Target. 33855973_TYRO3 induces anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy resistance by limiting innate immunity and tumoral ferroptosis. 35039980_Circ_0000467 Exerts an Oncogenic Role in Colorectal Cancer via miR-330-5p-Dependent Regulation of TYRO3. 35346994_TYRO3 Knockdown Suppresses the Growth of Myeloid Leukaemia Cells. | ENSMUSG00000027298 | Tyro3 | 38.504996 | 0.356586574 | -1.487676 | 0.46039103 | 9.830180 | 0.0017167158800667949979795734449794508691411465406417846679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0119707984697778307275894960071127570699900388717651367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 21.5531179 | 5.9961693 | 59.7065406 | 16.3149281 | |
| ENSG00000092929 | 201294 | UNC13D | protein_coding | Q70J99 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in cytotoxic granule exocytosis in lymphocytes. Required for both granule maturation and granule docking and priming at the immunologic synapse. Regulates assembly of recycling and late endosomal structures, leading to the formation of an endosomal exocytic compartment that fuses with perforin-containing granules at the immunologic synapse and licences them for exocytosis. Regulates Ca(2+)-dependent secretory lysosome exocytosis in mast cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15548590, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17237785}. | Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Exocytosis;Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis;Lysosome;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat | This gene encodes a protein that is a member of the UNC13 family, containing similar domain structure as other family members but lacking an N-terminal phorbol ester-binding C1 domain present in other Munc13 proteins. The protein appears to play a role in vesicle maturation during exocytosis and is involved in regulation of cytolytic granules secretion. Mutations in this gene are associated with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 3, a genetically heterogeneous, rare autosomal recessive disorder. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:201294; | azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; exocytic vesicle [GO:0070382]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; secretory vesicle [GO:0099503]; Weibel-Palade body [GO:0033093]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; germinal center formation [GO:0002467]; granuloma formation [GO:0002432]; natural killer cell degranulation [GO:0043320]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; positive regulation of exocytosis [GO:0045921]; positive regulation of regulated secretory pathway [GO:1903307]; positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900026]; regulation of mast cell degranulation [GO:0043304]; secretion [GO:0046903] | 14622600_HMunc13-4 mutations were shown to cause familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; HMunc13-4 is essential for the priming step of cytolytic granules secretion preceding vesicle membrane fusion. 14699162_Rab27 regulates the dense core granule secretion in platelets by employing its binding protein, Munc13-4 15466010_MUNC13-4 mutations play a role in the development of familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis subtype 3 through a defective cytotoxic pathway 16278825_A large group of 63 unrelated patients with Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL) was analysed for mutations in STX11, PRF1, and UNC13D. 16630545_These observations decisively prove that Rab27a inhibits ENaC function through a complex mechanism that involves GTP/GDP status, and protein-protein interactions involving Munc13-4 and SLP-5 effector proteins. 16778144_CD107a surface expression has a role in Munc13-4 defect in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis 16825436_12 novel and 4 known Munc13-4 mutations spread throughout the gene were found in haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis patients. 17993578_Biallelic UNC13D mutations were found in 18% of the PRF1/STX11-negative familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis families. 18240215_girl with systemic juvenile arthritis without macrophage activation syndrome was found to have compound heterozygous mutations of UNC13D and reduced NK cell cytotoxic function 18311812_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18311812_The genes PRF1, GZMB, UNC13D, and Rab27a involved in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis do not confer a significant risk of association with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 18432499_Fatal sibling cases of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL) with MUNC13-4 mutations 18453599_a role for Munc13-4 as a component of the secretory machinery in neutrophils. 18492689_UNC13D mutations leading to splicing errors represent the majority of mutations observed in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis 18710388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18759271_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18759271_The data suggest an association between MUNC13-4 polymorphisms and macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 19120489_mutated in type III hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, a severe inflammatory disease of infectious etiology with fatal outcome 19131769_UNC13D mutations are associated with primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 19704116_Rab27a or Munc13-4 recruitment to lytic granules is preferentially regulated by different receptor signals, demonstrating that individual target cell ligands regulate discrete molecular events for lytic granule maturation. 20015888_rRecurrent splicing mutations in UNC13D gene is associated with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 20823128_Data show that all but one patient with atypical familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis carried at least one splice-site mutation in UNC13D or STXBP2. 21370424_Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with MUNC13-4 gene mutation or reduced natural killer cell function prior to onset of childhood leukemia. 21646258_study reports recurrent fetal hydrops caused by familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with Munc13-4 mutation 21674762_Seven novel mutations in PRF1, UNC13D, and XIAP were identified in Chinese EBV-HLH patients. Only a fraction of Chinese children with EBV-HLH have genetic defects in PRF1, UNC13D, and XIAP. 21693760_Data show that point mutations in the binding motif of munc13-4 have severely impaired rab27a binding, allowing dissection of rab27a requirements in munc13-4 function. 21755595_novel Dutch founder mutation leads to severe early onset of FHL3 due to misfolding and degradation of munc13-4(1-899). 21881043_Missense and splice-site sequence variants in PRF1, MUNC13-4, and STXBP2 were found in 25 (14%) of the adult patients. The A91V-PRF1 genotype was found in 12 of these patients (48%). 21931115_Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 3 (FHL3) caused by deep intronic mutation and inversion in UNC13D. 22271450_Data indicate that Munc13-4 reinternalization is required for the maintenance of an intracellular pool that is functional to guarantee the serial killing potential. 22508512_study reports that Munc13-4 bound Ca(2 ) and restored Ca(2 )-dependent granule exocytosis to permeable cells (platelets, mast, and neuroendocrine cells) dependent on putative Ca(2 )-binding residues in C2A and C2B. 23180437_The deep intronic mutation UNC13D:c.118-308C>T accounts for the majority of previously missing mutations and is the most frequent mutation in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 3 in Korea. 23672263_Novel deep intronic and missense UNC13D mutations are reported in familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 3. 23810987_Defects in cargo trafficking caused by mutations in RAB27A and UNC13D genes, encoding Rab27a and its effector Munc13-4, cause severe immunodeficiencies in humans. (Review) 23840885_These data suggest that rare loss-of-function variations of UND13D are risk factors for autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome development. 23924873_this is the first report of HLH in association with EVC syndrome, and the IVS13+5G>A mutation that we believe is causative of EVC in our patient is also unreported. 24043286_This patient the patient carried mutations in FAS, XIAP, and UNC13D genes inherited from his mother who had rheumatoid arthritis; UNC13D is involved in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis 24470399_The prevalence of a 253-kb inversion and two deep intronic mutations, c.118-308C > T and c.118-307G > A, in UNC13D was determined in 1709 North American patients with type 3 hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 8 new mutations were also found. 24842371_Data indicate that Munc13-4 is highly expressed in differentiated NK cells and effector CD8(+) T lymphocytes. 25312756_These studies highlight the need for RAB27A sequencing in patients with FHL with normal pigmentation and identify a critical binding site for Munc13-4 on Rab27a, revealing the molecular basis of this interaction. 25573973_These data support an important role for Munc13-4 in human platelet degranulation 25980904_Synergistic defects of UNC13D and AP3B1 leading to adult hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 26377049_A newly defined mutation in the UNC13D (c.175G>C; p.Ala59Pro) was found in an asymptomatic heterozygote father and his homozygous daughter who had hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 26637270_Munc13-4 conveys Ca(2+) sensitivity to platelet SNARE-mediated membrane fusion and reveal a potential mechanism by which Munc13-4 bridges and stabilizes apposing membranes destined for fusion. 26637356_Data (including data from studies in knockout mice) suggest Munc13-4 binds to Rab11 and regulates trafficking of Rab11-containing vesicles; Munc13-4 appears to regulate final steps of Rab11-positive vesicle docking at plasma membrane in exocytosis. 26959483_analysis of sudden infant death syndrome brains shows downregulation of MyD88 in tissue from SIDS brains, as well as the downregulation of the genes encoding CCL3 and UNC13 in the liver 27016801_A novel Rab27a mutation binds melanophilin, but not Munc13-4, causing immunodeficiency without albinism. 27799161_Gene-corrected human Munc13-4-deficient CD8+ T cells can efficiently restrict EBV-driven lymphoproliferation in immunodeficient mice 28450451_Findings indicate that Munc13-4 supports acute WPB exocytosis by tethering WPBs to the plasma membrane via AnxA2-S100A10. 29549174_the results presented herein show that the munc13-4 protein expression assay is a reliable tool for FHL3 screening. 29665027_The present study describes a distinct variant spectrum in Chinese patients with Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), whereby UNC13D is the most frequently mutated gene with missense variants that are the most common molecular defects. The variant profile of Chinese HLH patients is quite different from that of Western cohorts but similar to that of Korean patients, yet showing its own uniqueness 29767240_The results of the present study indicate that Munc132 may be an essential regulator of basal MUC5AC exocytosis, while Munc134 appears to be a Munc13 protein subtype that may to be sensitive to hNE stimulation during airway MUC5AC hypersecretion. 29783935_Compound heterozygosity in the UNC13D gene was identified in trans and considered a causative mutation in a female patient with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). The nonsense mutation (NM_199242.2:c.2206C > T, p.Gln736X) was novel in cases of HLH. This mutation along with the splicing mutation (NM_199242.2:c.2709 + 1G > A) were inherited from the parents. 29930202_Depletion of Munc13-4 in highly aggressive breast carcinoma MDA-MB-231 cells reduced the size of CD63(+) multivesicular bodies (MVBs), indicating a role for Munc13-4 in MVB maturation. 30758854_Results indicate that haploinsufficiency of UNC13D required for lymphocyte cytotoxicity can predispose patients to lymphoma, suggesting the importance of cytotoxic lymphocyte-mediated surveillance of cancer. 30892133_Cross-regulation of defective endolysosome trafficking and enhanced autophagy through TFEB in UNC13D deficiency. 31171812_Defective Zn(2+) homeostasis in mouse and human platelets with alpha- and delta-storage pool diseases. 31651726_Different Clinical Presentation of 3 Children With Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis With 2 Novel Mutations. 32245292_Five mutations were detected in UNC13D. 32253931_Lentiviral Gene Therapy for Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Type 3, Caused by UNC13D Genetic Defects. 32582217_Alternative UNC13D Promoter Encodes a Functional Munc13-4 Isoform Predominantly Expressed in Lymphocytes and Platelets. 33093239_Unc-13 homolog D mediates an antiviral effect of the chromosome 19 microRNA cluster miR-517a. 33867526_Germline variants in UNC13D and AP3B1 are enriched in COVID-19 patients experiencing severe cytokine storms. 34339548_Spectrum mutations of PRF1, UNC13D, STX11, and STXBP2 genes in Vietnamese patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 35293882_Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis With Heterozygous STX11 and Homozygous UNC13D Mutations Diagnosed in the Neonatal Period. | ENSMUSG00000057948 | Unc13d | 292.253410 | 0.417017200 | -1.261821 | 0.34723434 | 12.796877 | 0.0003471985099390214614921423841309433555579744279384613037109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0030679802634409549140503958852832511183805763721466064453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 152.5074390 | 34.3671486 | 366.9701805 | 82.4821792 | |
| ENSG00000092969 | 7042 | TGFB2 | protein_coding | P61812 | FUNCTION: [Transforming growth factor beta-2 proprotein]: Precursor of the Latency-associated peptide (LAP) and Transforming growth factor beta-2 (TGF-beta-2) chains, which constitute the regulatory and active subunit of TGF-beta-2, respectively. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P01137, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04202}.; FUNCTION: [Latency-associated peptide]: Required to maintain the Transforming growth factor beta-2 (TGF-beta-2) chain in a latent state during storage in extracellular matrix (By similarity). Associates non-covalently with TGF-beta-2 and regulates its activation via interaction with 'milieu molecules', such as LTBP1 and LRRC32/GARP, that control activation of TGF-beta-2 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P01137, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04202}.; FUNCTION: [Transforming growth factor beta-2]: Multifunctional protein that regulates various processes such as angiogenesis and heart development (PubMed:22772371, PubMed:22772368). Activation into mature form follows different steps: following cleavage of the proprotein in the Golgi apparatus, Latency-associated peptide (LAP) and Transforming growth factor beta-2 (TGF-beta-2) chains remain non-covalently linked rendering TGF-beta-2 inactive during storage in extracellular matrix (By similarity). At the same time, LAP chain interacts with 'milieu molecules', such as LTBP1 and LRRC32/GARP, that control activation of TGF-beta-2 and maintain it in a latent state during storage in extracellular milieus (By similarity). Once activated following release of LAP, TGF-beta-2 acts by binding to TGF-beta receptors (TGFBR1 and TGFBR2), which transduce signal (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P01137, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04202, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22772368, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22772371}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Aortic aneurysm;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Mitogen;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | This gene encodes a secreted ligand of the TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) superfamily of proteins. Ligands of this family bind various TGF-beta receptors leading to recruitment and activation of SMAD family transcription factors that regulate gene expression. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate a latency-associated peptide (LAP) and a mature peptide, and is found in either a latent form composed of a mature peptide homodimer, a LAP homodimer, and a latent TGF-beta binding protein, or in an active form consisting solely of the mature peptide homodimer. The mature peptide may also form heterodimers with other TGF-beta family members. Disruption of the TGF-beta/SMAD pathway has been implicated in a variety of human cancers. A chromosomal translocation that includes this gene is associated with Peters' anomaly, a congenital defect of the anterior chamber of the eye. Mutations in this gene may be associated with Loeys-Dietz syndrome. This gene encodes multiple isoforms that may undergo similar proteolytic processing. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. | hsa:7042; | axon [GO:0030424]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; platelet alpha granule lumen [GO:0031093]; transforming growth factor beta complex [GO:0099126]; transforming growth factor beta ligand-receptor complex [GO:0070021]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0005160]; type II transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0005114]; type III transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0034714]; activation of protein kinase activity [GO:0032147]; ascending aorta morphogenesis [GO:0035910]; atrial septum morphogenesis [GO:0060413]; atrial septum primum morphogenesis [GO:0003289]; atrioventricular valve morphogenesis [GO:0003181]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cardiac epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0060317]; cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060038]; cardiac right ventricle morphogenesis [GO:0003215]; cardioblast differentiation [GO:0010002]; cell death [GO:0008219]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cell-cell junction organization [GO:0045216]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; cranial skeletal system development [GO:1904888]; dopamine biosynthetic process [GO:0042416]; embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching [GO:0009792]; embryonic digestive tract development [GO:0048566]; embryonic limb morphogenesis [GO:0030326]; endocardial cushion fusion [GO:0003274]; endocardial cushion morphogenesis [GO:0003203]; epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0001837]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; eye development [GO:0001654]; generation of neurons [GO:0048699]; glial cell migration [GO:0008347]; hair follicle development [GO:0001942]; hair follicle morphogenesis [GO:0031069]; heart development [GO:0007507]; heart morphogenesis [GO:0003007]; heart valve morphogenesis [GO:0003179]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; inner ear development [GO:0048839]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; membranous septum morphogenesis [GO:0003149]; negative regulation of alkaline phosphatase activity [GO:0010693]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation [GO:1905006]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0010936]; negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046580]; neural retina development [GO:0003407]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; neuron development [GO:0048666]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; outflow tract septum morphogenesis [GO:0003148]; pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0060389]; pharyngeal arch artery morphogenesis [GO:0061626]; positive regulation of cardioblast differentiation [GO:0051891]; positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033630]; positive regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045787]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010634]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation [GO:1905007]; positive regulation of heart contraction [GO:0045823]; positive regulation of immune response [GO:0050778]; positive regulation of integrin biosynthetic process [GO:0045726]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043525]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; positive regulation of ossification [GO:0045778]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; positive regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade [GO:0032874]; positive regulation of timing of catagen [GO:0051795]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; pulmonary valve morphogenesis [GO:0003184]; regulation of apoptotic process involved in outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:1902256]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of timing of catagen [GO:0051794]; regulation of transforming growth factor beta2 production [GO:0032909]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570]; response to wounding [GO:0009611]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; salivary gland morphogenesis [GO:0007435]; secondary palate development [GO:0062009]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395]; somatic stem cell division [GO:0048103]; substantia propria of cornea development [GO:1903701]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; uterine wall breakdown [GO:0042704]; uterus development [GO:0060065]; ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0060412]; ventricular trabecula myocardium morphogenesis [GO:0003222]; wound healing [GO:0042060] | 11716069_TGFB2 induces MMP-2 expression and suppresses TIMP-2 expression. It promotes invasion of cultured glioma cells in a dose-dependent way. 11795478_The main source of myofibroblast-like cells and ECM production in the liver is the perisinusoidal stellate cell, which responds to injury with a pleiotypic change termed activation. Activation is orchestrated by cytokines, like tgfb2 11895345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11991670_no correlation between the concentration of either isoform of TGFbeta in milk and the corresponding TGFbeta in plasma 12011061_a transcriptional target for Akt/protein kinase B via forkhead transcription factor. 12021923_TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2 and TGF-beta3 isoforms are produced by chondrosarcomas and could have a potential role as autocrine growth stimulators in these neoplasms 12060054_present in diabetic foot ulcer 12060393_Involvement of transforming growth factor-beta2 in catagen induction during the human hair cycle. 12064833_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12420205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12489185_investigated TGF-beta 1, -beta 2, and -beta 3 latency-associated peptides (LAP)expression in sound and carious human teeth 12545247_Immunohistochemical double-staining of human renal sections revealed that most Tgfb2-positive cells in control glomeruli were podocytes with few Tgfb2-positive mesangial cells. 12607775_TGF-beta2 expression in peritoneal fibroblasts was increased by hypoxia plus TGF-beta1, but decreased by TGF-beta1 alone. 12772773_Glucocorticoids significantly inhibited TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2 production and reduced expression of the up-regulated TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2 mRNA induced by exogenous TGF-beta1, -beta2, or -beta3 12802400_Data report the location and level of interleukin (IL)-8 and TGF-beta2 expression in the fimbrial compartment of fallopian tubes and IL-10 expression in the endometrium of women with pyoinflammatory adnexal diseases. 12911534_All three TGF-beta isoforms have fibrogenic effects on renal cells. TGF-beta2 and TGF-beta3 effects may be partially mediated by TGF-beta1. Blockade of all isoforms together may yield best therapeutic effect in reducing renal fibrosis. 14507446_Biological dressing effect of cultured epidermal sheets(CESs) is mediated by EGF family, TGF-beta, and VEGF. 14510802_In the confluent state, TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2 stimulated the cells to progress to the S-phase of the cell cycle through platelet-derived growth factor-B (PDGF-B) chain production and protein kinase C. 15009106_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15113633_increase of serum immunoglobulin A in newborns during 1 month of life was well correlated with levels of both transforming growth factor-beta1 and transforming growth factor-beta2 15290353_Repression of promoter activity by HPV type 16 E6 and E7 proteins. 15389580_PSA-mediated activation of latent TGFbeta2 may be an important mechanism for autocrine TGFbeta regulation in the prostate and may potentially contribute to the formation of osteoblastic lesions in bone metastatic prostate cancer. 15695166_Recombinant TGF-beta 2 passes through the mouse blood-brain barrier after peripheral injection and is widely distributed throughout the brain, with highest concentrations in the hypothalamus and nerves and lowest in the cerebral hemispheres. 15816823_upregulation of the potent catagen inducer, transforming growth factor beta2 (TGFbeta2) by BDNF in hair follicles 15896309_Human TGF-beta2 but not human TGF-beta1, or -beta3 promotes cardiac myocyte differentiation from mouse ES cells. 16210002_TGF-beta 2 may promote endometrial tissue repair through the inhibition of the proliferation, expansion, and migration of endometrial stromal cells, and through stimulation of contraction of the collagen gel matrix by these cells. 16260601_TGF-beta-dependent nuclear accumulation of Smad2 is caused exclusively by selective nuclear trapping of phosphorylated, complexed Smad2 16463680_The expression of TGF-beta2 mRNA was higher in cortex cataract than in nuclear cataract. 16467496_In conclusion, increased TGF-beta2 transcription in response to serum stimulation in KFs appears to be mediated by the p38 MAPK pathway. 16608413_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16778279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16885354_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16891397_TGF-beta2 is secreted in response to injury, significantly alters the bulk optical properties of the extracellular matrix, and its tight regulation may be required for normal collagen homeostasis. 16998703_The mRNA expressions of TGFbeta1 in hMSCs increased with the length of cell culture. 17192487_ombined effects of TGF-beta2 and connective tissue growth factor appear to be involved in the pathogenesis of proliferative vitreoretinal diseases 17201588_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17217916_The results presented in this paper provide evidence for the involvement of an oxidative process in the apoptosis elicited by TGF-beta(2) in HLECs. 17401695_BMP-2, TGF-beta2, and TGF-beta3 are involved in bone formation in heterotopic ossifications. 17431704_No evidence for association with susceptibility or progression of MS, but have demonstrated a trend towards association of the 5' region of the gene with susceptibility to PD. 17431704_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17453002_TGF-beta2 triggers the malignant phenotype of high-grade gliomas by induction of migration, and that this effect is, at least in part, mediated by versican V0/V1. 17532297_These results suggest that FGF-2 suppresses the hMSCs cellular senescence dependent on the length of culture through down-regulation of TGF-beta2 expression. 17611697_Am-80-induced cell-type non-specific growth inhibition is mediated by TGF-beta2, where the total mass of RARalpha could be an important regulatory factor in hematologic malignant cells 17651146_TGF-beta(2) may therefore be involved in the development of childhood atopic asthma by means of functional genetic polymorphism. 17679942_The highest levels of active TGF-beta2 were found in keratoconus eyes. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17960115_TGF-beta2 promoted human lens epithelial cell adhesion and migration in vitro. Integrin beta1 and integrin-mediated signaling are necessary for TGF-beta2-promoted adhesion and migration in human lens epithelial cells. 18039789_TGF-beta2 and -beta3 are differentially expressed during the menstrual cycle and regulated by progesterone in epithelial vs stromal cells. 18040277_The early induction of TGF-beta1 at the point of SCI suggests a role in the acute inflammatory response and formation of the glial scar, while the later induction of TGF-beta2 may indicate a role in the maintenance of the scar. 18043895_TGFbeta2 and TbetaRII have roles in the antiestrogenic activity of tamoxifen metabolites in breast cancer 18078367_TGF-beta 2 is closely related to cellular differentiation in human developing teeth 18080134_TGF-beta 2 was detected since the bud stage of the salivary gland. Its expression was observed in ductal cells and increased along gland differentiation. 18174230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18223299_TGF-beta(2) is a potent growth factor for lens epithelial cell(LEC) epithelial mesenchymal transition(EMT); TGF-beta(2)-induced EMT in LECs is mediated by the downregulation of connexin 43, which is regulated through the PI3K/Akt pathway 18292822_The endometria from women with idiopathic infertility TGFbeta2 expression was 2.8 fold higher than in endometria from control group and 2.1 fold higher in endometrial samples from women with unexplained recurrent miscarriage compared to the control group. 18348727_IL-13 may contribute to subepithelial fibrosis in asthma by stimulating biologically significant TGF-beta2 secretion from the airway epithelium. 18358889_may affect the growth and differentiation of dental pulp cells via an autocrine fashion by activation of the transforming growth factor beta receptor protein kinase/receptor regulated Smad proteins signal transduction pathways 18384390_in gingival crevicular fluid and peri-implant crevicular fluid did not change significantly after a period of de novo plaque accumulation 18431253_Taken together, these in vitro and in vivo results indicate that glioma-derived factors may induce MMPs and downregulate endothelial tight junction protein and, thus, play a key role in glioma-induced impairment of the blood-brain barrier. 18498721_study found different expression of the TGF-beta1, -2 and -3 isoforms in the human corneal epithelium; such differential expression of TGF-betas suggests that each of them may play a specific role in corneal tissue 18505915_the TGF-beta1-2-3/Smad3 pathway has a role in mediating ovarian oncogenesis by enhancing metastatic potential 18563556_Genes more highly expressed in BRCA1-associated tumors included stathmin, osteopontin, TGFbeta2 and Jagged 1 18694919_A dominant increase in TGF-beta2 expression in cord tissue was seen in Dupuytren's disease. 19031438_BMP4 blocked the TGF-beta2 induction of extracellular matrix proteins in optic nerve head cells; the BMP antagonist gremlin reversed this inhibition 19062040_TGF-beta cytokines may be involved in postsurgical adhesion formation 19161338_High-affinity binding of TGF-beta1/3 to TGF-betaRII is primarily due to hydrogen bonding between Arg25 and 94 of TGF-beta1/3, and Glu119 and Asp32 of TbetaR-II. Arg25 and 94 are substituted by Lys in TGF-beta2, which binds with low affinity to TbetaR-II. 19212830_Report expression of decorin in esophageal cancer in relation to the expression of three isoforms of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta1, -beta2, and -beta3) and matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity. 19249525_Expression levels of Tgfb2 in circulating lymphocytes are not sufficiently specific to diagnose transitory postsurgical complications such as symptomatic infection after liver transplantation. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19438810_These results suggest an important role for TGF-beta(2) in hair follicle morphogenesis. 19444386_The TGF-beta2 signal pathway participates in the apoptotic signal transfer and might be an initiator of cellular apoptosis of human lens epithelial cells. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19472023_Variations of the stress distribution in cancellous bone correlate with the variation of the concentrations of TGF-beta2 and IGF-I in bone matrix. 19572226_PRDX6 attenuates oxidative stress- and TGFbeta-induced abnormalities of human trabecular meshwork cells. 19651985_Ladybird homeobox 1 (LBX1), a developmentally regulated homeobox gene, directs expression of the known EMT inducers ZEB1, ZEB2, Snail1, and transforming growth factor beta2 (TGFB2). 19710942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19937272_Our data provide evidence that TGF-beta signaling patterns vary by age and pathologic features of prognostic significance including ER expression. 19959123_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19965872_Data show that TNF-alpha induces the formation of fibrotic foci by cultured retinal pigment epithelial cells through activation of transforming growth factor-TGF-beta signaling in a manner dependent on hyaluronan-CD44-moesin interaction. 20059631_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20134268_high prechemotherapy serum levels associated with improved survival in advanced epithelial ovarian cancer 20142847_TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2, and TGF-beta3 mRNAs were detected in both normal and pseudophakic bullous keratopathy (PBK) corneas. 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20543478_Carbachol can promote and atropine can inhibit the expression and secretion of TGF-beta2 in human retinal pigment epithelium cells. 20585394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20585394_results represent the first report on CM genetic risk factors in Angolan children and suggest the novel hypothesis that genetic variants of the TGFB2 and HMOX1 genes may contribute to confer a specific risk of developing the CM syndrome 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20630504_A variant in the fibrillin-3 gene is associated with TGF-beta and inhibin B levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20875417_TGF-beta2 suppressed macrophage cytokine production in the developing intestine and protected against inflammatory mucosal injury. 21034224_elevated levels of TGF-b2 within the anterior segment contribute to the development of glaucoma; the increased risk for developing glaucoma as one ages may in part be related to the rise of this cytokine 21087804_The TGF-beta1 mediated secretion of endothelin-1 and TGF-beta2 is mediated by Rho kinase activation in hepatic stellate cells. 21087928_autocrine stimulation of myeloid progenitors by Tgfbeta2 as one mechanism by which HoxA10 expands this population. 21088899_Data suggest that glioma stem cells are likely to be the major tumor source of immunosuppressive cytokines such as TGF-beta2 and IL-10 and thereby play a crucial role in determining glioma malignancy. 21106846_Aqueous humor regulates dendritic cell maturation and function by the combined actions of cortisol and TGF-beta2, a pathway that is likely to contribute to the maintenance of immune privilege in the eye. 21161068_Study revealed a correlation between the localization of transforming growth factor-beta2 and the development of intraocular hyaloid vascular network, its regression, formation of the vitreous body, and development of definite retinal vessels. 21207416_quantitative increase in promoter methylation levels of TGFbeta2 is associated with prostate cancer progression 21212630_BMP-2 and TGFbeta2 shared pathways regulate endocardial cell transformation 21305699_TGFbeta subtypes (1, 2 and 3) affect terminal differentiation of in vitro cultured hBMSCs differently 21360509_Degranulation of skin mast cells can be an important mechanism of TGFbeta secretion in systemic sclerosis. 21411746_Data show that TGF-beta pathways operate during ovarian fetal development, and fibrillin 3 is highly expressed at a critical stage early in developing human and bovine fetal ovaries. 21446058_differential expression pattern of TGFbeta2 in the lens and retina is correlated with the cell type and differentiation state. 21585337_The present paper showed that TGF-beta2 stimulates endothelial-mesenchymal transition through multiple signalling pathways. 21642622_Gremlin employs canonical TGFbeta2/Smad signaling to induce extracellular matrix protein genes and proteins in cultured human trabecular meshwork cells. 21693611_The present study reveals that TGFbeta2 and NGF are associated with idiopathic epiretinal membranes, suggesting a novel compensatory mechanism so far never proposed. 21738403_Transforming growth factor-beta2 increases extracellular matrix proteins in optic nerve head cells via activation of the Smad signaling pathway. 21917933_A total of 853 proteins were quantified. TGFbeta treatment significantly altered the abundance of 47 proteins, 40 of which have not previously been associated with TGFbeta signaling in the eye. 22180604_Myxomatous mitral valves are characterized by reduced levels of MT1/2 accompanied by an up-regulation of TGF-beta2. 22464821_The aim of the study was to determine temporal TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3 gene expression profiles in the anterior lens capsule of paediatric patients with posttraumatic cataract. 22487836_The genotypic and allelic frequencies of transforming growth factor beta 2 gene rs6658835 were associated with VSD (P 0.05). 22504005_identified transforming growth factor-beta2 secreted by normal kidney and ADPKD cells as an inhibitor of cystogenesis in 3D culture system using ADPKD cells from kidneys 22582395_RFX1 reduces cell proliferation through inhibiting the TGFbeta2-ERK signaling pathway. RFX1 blocks TGFbeta2 expression through its direct action on TGFbeta2 transcription. 22653295_data permit us to suggest an important role of TbetaRII expression in the maintenance of chondrocyte phenotype, which is altered with age, and bring new insights in our understanding of chondrogenesis process. 22706080_TGF-beta2 is abundant in seminal plasma as a key agent in seminal plasma that signals induction of proinflammatory cytokine synthesis in cervical cells. 22736943_No significant associations were identified between FOXC1, TGFbeta2, and BMP4 alleles and haplotypes and primary open-angle glaucoma. 22739237_the microenvironment at the verge between inflammation (IL-1beta) and tissue remodeling (TGFbeta2) can strongly promote the process of EndMT. 22772368_report heterozygous mutations or deletions in the gene encoding the TGF-beta2 ligand for a phenotype within the Loeys-Dietz syndrome spectrum 22772371_haploinsufficiency for TGFB2 predisposes to thoracic aortic disease, suggesting that the initial pathway driving disease is decreased cellular TGF-beta2 levels leading to a secondary increase in TGF-beta2 production in the diseased aorta 22786655_Transcriptional profiling of human glioblastoma vessels indicates a key role of VEGF-A and TGFbeta2 in vascular abnormalization. 22823397_TGF beta-2 inhibits the expression of the clock genes Period (Per)1, Per2, and Rev-erb-alpha, and of the clock-controlled genes D-site albumin promoter binding protein (Dbp) and thyrotroph embryonic factor (Tef ) 22955109_TGF-beta may contribute to aneurysm formation by promoting the generation of myofibroblasts that mediate damage to the arterial wall through recruitment of pro-inflammatory cells. 23099432_TGFbetaRIIb expression is a regulatory mechanism for TGFbeta2 signal transduction. 23102774_TGFbeta2 protein and localization of mutations are identified in patients with thoracic aortic aneurysm and/or dissection. 23249391_TGF-beta decreases baseline and IL-13-stimulated mucin production by primary human bronchial epithelial cells. 23257207_TGF-beta(2) reduces proliferation but stimulates migration of cultured corneal endothelial cells via p38MAPK phosphorylation. 23297089_SDC-2 modulates TGFbeta2 transcriptional regulation via Smad2 signaling to facilitate fibrosarcoma cell adhesion. 23306609_the suppression of TGF-b1 induced TGF-b3 upregulation, and the suppression of TGF-b2 induced another unexpected downregulation of both TGF-b1 and TGF-b3. 23322721_TGFbeta2 increased NFkappaB reporter activity in control cells, but betaglycan expression suppressed both basal and TGFbeta2-stimulated NFkappaB activity. 23387555_Mutation or removal of the G-quadruplex sequence from the 5' UTR of the gene diminished the level of expression of this gene at the translational level. 23651239_Data show expression of TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2, BMP-4, and BMP-7 was increased in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) cocultured with pancreatic cancer cells, and vasohibin-1, VEGF-A, and vVEGF-C expression in pancreatic cancer cells was upregulated by TAMs. 23668958_Endothelial cells may play a role in the induction and maintenance of EMT in tumor cells by constitutively releasing TGFbeta1 and TGFbeta2 23687438_MMP-2 and -9 are involved in the translocation of MRTF-A in lens epithelial cellsduring TGFbeta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. 23690072_These data do not confirm a crucial role of TGF beta1 and TGF beta2 release in the development of posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus 23712828_germline mutation of the TGFbeta2 gene is not a common cause of CTD in humans and that the TGFbeta2 expression level may be less critical in humans than in animals for the pathogenesis of CTD. 23880103_Serum TGFB2 was elevated in patients with classic prolapse as compared with the control group and the non-classic mitral valve prolapse group. 24045946_HD3alpha directly interacts with HDAC3 and Akt1 and selectively activates transforming growth factor beta2 (TGFbeta2) secretion and cleavage. 24193348_TGFB2 is a rarely mutated gene in patients with syndromic TAAD, and the clinical features of our TGFB2 mutation-positive individuals fit in the scheme of LDS, rather than MFS-related disorders. 24223867_Data indicate that glioma cell migration is mediated by Thrombospondin-1 (THBS-1) and TGF-beta2. 24311892_The expression of TGFB1 and TGFB2 increase significantly in benign prostatic hyperplasia treated with 5-alpha reductase inhibitor. 24314882_Inhibition of miR-21 has no effect on thrombospondin (TSP)-1-stimulated expression of TGFbeta2. 24402195_Compared to controls, plasma levels of TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2 were significantly lower in patients with recurrent VTE (p | ENSMUSG00000039239 | Tgfb2 | 34.691883 | 2.334586386 | 1.223167 | 0.41947150 | 8.322130 | 0.0039164958813229433162717008087838621577247977256774902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0234653935335608423984332659983920166268944740295410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 45.0472871 | 9.2136566 | 19.5806769 | 4.2130302 | |
| ENSG00000099985 | 5008 | OSM | protein_coding | P13725 | FUNCTION: Growth regulator. Inhibits the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines. Stimulates proliferation of AIDS-KS cells. It regulates cytokine production, including IL-6, G-CSF and GM-CSF from endothelial cells. Uses both type I OSM receptor (heterodimers composed of LIFR and IL6ST) and type II OSM receptor (heterodimers composed of OSMR and IL6ST). Involved in the maturation of fetal hepatocytes, thereby promoting liver development and regeneration (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1542792, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1542793}. | 3D-structure;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth regulation;Mitogen;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | This gene encodes a member of the leukemia inhibitory factor/oncostatin-M (LIF/OSM) family of proteins. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protein. This protein is a secreted cytokine and growth regulator that inhibits the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines. This protein also regulates the production of other cytokines, including interleukin 6, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor in endothelial cells. This gene and the related gene, leukemia inhibitory factor, also present on chromosome 22, may have resulted from the duplication of a common ancestral gene. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes an isoform that is proteolytically processed. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. | hsa:5008; | extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; oncostatin-M receptor binding [GO:0005147]; immune response [GO:0006955]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of hormone secretion [GO:0046888]; oncostatin-M-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038165]; positive regulation of acute inflammatory response [GO:0002675]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032740]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; regulation of hematopoietic stem cell differentiation [GO:1902036] | 11777927_We conclude that STAT1 activation is necessary but not sufficient for induction of transcription of IFN gamma-responsive genes; signals provided by IFN gamma other than STAT1 activation cannot be provided in trans to complement the response to OnM. 11811789_Oncostatin M and leukemia inhibitory factor regulate the growth of normal human breast epithelial cells 11818668_Il-6 and oncostatin M act synergistically to promote growth in a new human myeloma cell line. 11839742_role in identifying sterol-indendent regulatory elements in human ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 promoter 11936950_role in inducing alpha1-antitrypsin gene expression 12061840_expression and evidence for STAT3 activation in human ovarian carcinomas 12061841_produced in human dendritic cells in response to bacterial products 12090757_Oncostatin M induces tissue-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in lung tumor cells 12138373_Oncostatin M induces procoagulant activity in human vascular smooth muscle cells by modulating the balance between tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor. OSM might be involved in the thrombotic complications associated with plaque rupture. 12218157_Oncostatin M stimulates (45)Ca release and enhances mRNA expression of receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL) and osteoprotegerin in neonatal mouse calvarial bone cultures, but has no effect on the expression of RANK. 12391243_Raised intraperitoneal levels of OSM during bacterial infections originate from infiltrating neutrophils and regulate mesothelial expression of inflammatory cytokines. 12531804_Kaposi sarcoma-associated viral cyclin K overrides cell growth inhibition mediated by this protein through STAT3 inhibition. 12640208_Increased production of this protein is found in lymphomononuclear cells from HIV-1-infected patients with neuroAIDS. 12692260_oncostatin M, which transmits its signal via the gp130 cell surface receptor, and results in the selective down-modulation of the melanocyte lineage antigens 12707269_Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), cardiotrophin-1, and oncostatin M share structural binding determinants in the immunoglobulin-like domain of LIF receptor 15146412_this important cytokine is released from neutrophils as they infiltrate rheumatoid joints and, thus, contribute to the complex cytokine network that characterizes rheumatoid arthritis 15712220_IL-6 stimulates proliferation of prostate cancer 22Rv1 cells, in part through activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-K) signaling pathway. 15809742_Effects of OSM in 5 glioma cell lines and 7 short-term cultures of human gliomas and in normal cultured human astrocytes. 15831292_The expression of OSM and its receptor in ovarian tissue from fetuses and women suggests a possible role of OSM in growth initiation of human primordial follicles. 15837947_IL-6 and OSM upregulate PAI-1 protein and mRNA in adipose tissue 15863389_OSM may play a role in modulating the inflammatory cascade of chronic periodontitis. 16369169_Oncostatin M is expressed in the human nasal mucosa and is upregulated in the setting of allergic nasal inflammation. 16713283_OSM induces a motile/invasive phenotype in T-47D human breast cancer cells in vitro; OSM may enhance metastasis in vivo. 16802343_Pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor (PBEF) is regulated via IL-6 trans-signaling and the IL-6-related cytokine OSM. PBEF is also actively expressed during arthritis. 17009243_data suggest that OSM promotes angiogenesis and endothelial cell migration and potentiates the effects of IL-1beta in promoting extracellular matrix turnover and human cartilage degradation 17028186_sOSMR is able to bind OSM and interleukin-31 when associated to soluble gp130 or soluble interleukin-31R, respectively, and to neutralize both cytokine properties 17081797_These results suggest that OSM inhibits adiponectin expression by inducing dedifferentiation of adipocytes through signaling pathways involving JAK3 and MEK, but not JAK2. 17372020_OSM and its receptor play an important role in cutaneous inflammatory responses in general and the specific effects of OSM are associated with distinct inflammatory diseases depending on the cytokine environment. 17471233_in addition to growth arrest and induced differentiation, OSM also sensitizes normal and transformed osteoblasts to apoptosis by a mechanism implicating (i) activation and nuclear translocation of STAT5 and p53 and (ii) an increased Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. 17604327_If the effect of oncostatin M on PAI-1 in smooth muscle cells is operative in vivo, it could, via fibrinolysis and proteolysis, be involved in plaque progression, destabilization, thrombus formation, restenosis, and neointima formation. 17761945_Oncostatin M directly lowers the plasma triglycerides in hyperlipidemia by stimulating the transcription of ACSL3/5 in the liver. 17881458_In human proximal tubular cells ERK1/2 signaling represents an important component of oncostatin M inhibitory effect on N-cadherin expression. 17979974_Increased expression of some IL-6 cytokine family members (oncostatin M, gp130, CT-1, LIF) in cutaneous inflammation might contribute to the promotion of hair loss. 18028996_Production of OSM by human mast cells might represent one link between T cell-induced mast cell activation and development of spectrum of structural changes in T cell-mediated inflammatory processes in which mast cells have been found to be involved. 18187666_Our data establish a link between the complement system and the gp130 receptor cytokine family with possible implications for the pathology of inflammatory diseases. 18317962_secretion of OSM and LIF by both epithelial and stromal (paracrine manner) cells seems to promote tumor growth in human breast carcinoma 18398932_Mtb infection of monocytes results in prostaglandin-dependent OSM secretion, which synergizes with TNF-alpha to drive functionally unopposed fibroblast MMP-1/-3 secretion. 18499891_loss of repopulating activity during KIT-ligand stimulation is counteracted by Oncostatin M through the downregulation of ERK pathway signaling 18564531_Oncostatin M is expressed in both chronic obstructive sialadenitis and normal submandibular gland, and is up-regulated in chronic obstructive sialadenitis. 18637848_expressed in epithelialized apical periodontitis lesions 18772145_hXOR is a tumor suppressor-targeted gene and the phosphorylation of SAFB1 is regulated by OSM, which provides a molecular basis for understanding the role of SAFB1-regulated hXOR transcription in cytokine stimulation and tumorigenesis 18981157_human OSM is able to induce CCL1, CCL7, and CCL8 expression to levels comparable to those found for IL-1beta and TNF-alpha 19019853_These data suggest that oncostatin M might play a key role in repair and tissue regeneration via the induction of stromal cell derived factor 1. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19148539_by conducting site-directed mutagenesis, bioassays and molecular modeling we have defined 4 OM residues that are differently involved in the activation of ERK or STAT signaling pathway in HepG2 cells. 19158240_Oncostatin M enhances the antiviral effects of type I interferon and cooperates with it in the induction of adaptive immune responses to pathogens. 19158344_The renal parenchyma is capable of generating a strong acute phase response, likely mediated via OSM/OSMR. 19342253_Results indicate that leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and Oncostatin M increase the expression of MMP-1, MMP-3, and TIMP-1 several fold, and that their expression is reduced to basal levels in the presence of the LIF antagonist MH35-BD. 19565514_Oncostatin M can strongly up-regulate the expression of CCL13, a chemokine recently identified in the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. 19652200_The coagulation enzyme thrombin up-regulates oncostatin M via AP-1 activation in macrophages. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19916861_Sputum oncostatin M is increased in asthma with irreversible airflow obstruction and is present in airway neutrophils and macrophages 20088942_Findings provide evidence that the inflammatory cytokine oncostatin M is involved in modulation of the Ang-Tie system by increasing Ang2 expression in human endothelial cells in vitro, and in murine hearts and human hearts in vivo. 20101226_Inflammatory cytokines oncostatin-M and interleukin-6 can regulate S100A7 expression and that S100A7 may mediate some of their effects in breast cancer. 20149034_OSM may play a biological marker for severe preeclampsia, and its action may be predominantly on the trophoblasts and endothelium of placenta villi in preeclampsia. 20189410_The greater the amount of periodontal tissue destruction there is substantial increase in gingival crevicular fluid OSM concentrations. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20408777_oncostatin M is a gp 130 cytokine inflammatory biomarker that has a role in periodontal disease 20626292_elevated expression in kidneys from patients with urinary obstruction 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20650266_OSM, and to a lesser degree IL-6, induces the expression of Grp78/BiP, an ER chaperone associated with tumor development and poor prognosis in cancer. 20661773_The expression and secretion of oncostatin M and of its receptor were strongly up-regulated by Helicobacter pylori or by Helicobacter pylori culture supernatant. Oncostatin M secretion was independent of the CagA, VacA or Type IV secretion system. 21196532_a cytokine-triggered regulatory network for PCSK9 expression that is linked to JAKs and the ERK signaling pathway 21376322_OSM is expressed in atherosclerotic lesions and may contribute to the progression of atherosclerosis by promoting SMC proliferation, migration and extracellular matrix protein synthesis through the STAT pathway 21399864_The purpose of this study was to investigate the possible suppressive or stimulatory role of OSM in the ovarian cancer model of SKOV3 cells, as well as the involvement of the ERK1/2, p38 and STAT3 signaling pathways. 21457934_Taken together, our data show that KIT D816V promotes expression of OSM through activation of STAT5. 21481226_promotes STAT3 activation, VEGF production, and invasion in osteosarcoma cell lines 21775705_This report uses an in vitro model with human umbilical vein endothelial cells and isolated human neutrophils to examine the effects of two locally derived cytokines, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and G-CSF, on oncostatin M expression. 21965736_A possible interaction between IL-6, OSM, u-PA and VEGF in prostate cancer was investigated. 21975934_c-MYC is an important molecular switch that alters the cellular response to OSM-mediated signaling from tumor suppressive to tumor promoting. 22051730_JAK2 V617F-mediated up-regulation of OSM may contribute to fibrosis, neoangiogenesis, and the cytokine storm observed in myeloproliferative neoplasms. 22056139_Oncostatin M (OSM) is a major mediator of cardiomyocyte dedifferentiation and remodeling during acute myocardial infarction (MI) and in chronic dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). 22267310_Oncostatin M (OSM), a cytokine of the IL-6 family, was identified as a major coupling factor produced by activated circulating CD14+ or bone marrow CD11b+ monocytes/macrophages. 22267707_Oncostatin M signaling may cause suppression of estrogen receptor-alpha and disease progression i breast cancer. 22829597_A unique loop structure in oncostatin M determines binding affinity toward oncostatin M receptor and leukemia inhibitory factor receptor. 22931588_Data suggest that OSM enhances invasion activities of extravillous trophoblasts during placentation through increased enzyme activity of MMP-2 (primarily) and MMP-9 (to some extent). 22982441_OSM induced proliferation of Ewing sarcoma cell lines. 23313749_These data show that OSM and IL-1beta are not only a biological characteristic signature of hypertensive leg ulcer, but these cytokines reflect a specific inflammatory state, directly involved in the pathogenesis. 23584474_OSM may promote a clinically relevant EMT/CSC-like phenotype in human breast cancer via a PI3K-dependent mechanism 23621172_Oncostatin M is a FIP1L1/PDGFRA-dependent mediator of cytokine production in chronic eosinophilic leukemia. 23735324_TGFBI and periostin, extracellular matrix proteins implicated in tumorigenesis and metastasis, were identified as oncostatin M-induced secreted proteins in mesenchymal stem cells. 23867565_Data indicate that pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL6 or OSM could activate pathways associated with prostate cancer progression and synergize with cell-autonomous oncogenic events to promote aggressive malignancy. 24297795_white adipose tissue macrophages are a source of OSM and OSM levels are significantly induced in obesity/type 2 diabetes. OSM produced from immune cells in WAT may act in a paracrine manner on adipocytes to promote inflammation in adipose tissue. 24418171_oncostatin M is a cytokine possessing vigorous antiviral and immunostimulatory properties which is released by APC upon interaction with CD40L present on activated CD4+ T cells. 24600984_data suggest that increased serum OSM levels are associated with the coronary stenosis score and that circulating levels of this chemokine may reflect the extent of coronary atherosclerosis 24710357_OSM promotes STAT3-dependent intestinal epithelial cell proliferation and wound healing in vitro. 25252914_Autocrine activation of STAT3 in MCF-7 cells ectopically expressing OSM-induced cellular scattering. 25735629_Data suggest that OSM promotes osteoblastic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells through JAK3/STAT3 pathway and may contribute to the development of atherosclerotic calcification. 25804939_In patients with diabetes, bone marrow plasma OSM levels were higher and correlated with the bone marrow to peripheral blood stem cell ratio. 25840724_OSM promotes mucosal epithelial barrier dysfunction, and its expression is increased in patients with eosinophilic mucosal disease. 25845347_The Notch signaling pathway was found to be one of the signaling pathways that inhibit OSM-induced MC3T3-E1 cell proliferation and differentiation. 25849622_Oncostatin M can regulate airway smooth muscle responses alone or in synergy with IL-17A. 25954856_we demonstrated that recombinant human OSM (rhOSM) promoted tumor angiogenesis in EC cell lines by activating STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3) and enhanced both cell migration and cell inva 26198770_Oncostatin M and interleukin-31: Cytokines, receptors, signal transduction and physiology. 26304992_OSM expression in osteoblasts increases in response to Osteopontin-induced inflammation in vitro. 26311783_Oncostatin M regulates neuronal function and confers neuroprotectin in an animal model of ischemic stroke. 26355153_administration of Fstl1 induced airway remodeling and increased OSM, whereas administration of an anti-OSM Ab blocked the effect of Fstl1 on inducing airway remodeling, eosinophilic airway inflammation 26399567_Nucleolin stabilizes oncostatin-M mRNA by binding to a GC-rich element in its 3'UTR. 27349249_This result demonstrates that HPV16 oncoproteins upregulate oncostatin M and play an important role to promote oral squamous cell carcinoma development 27486982_our findings suggested that OSM suppresses SLUG expression and tumor metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells through inducing the inhibitory effect of the STAT1-dependent pathway and suppressing the activating effect of STAT3-dependent signaling 27676154_Genistein (a specific Tyr phosphorylation inhibitor) leads to the interaction of CHOP (C/EBP Homologous Protein) with C/EBP-beta, thus negatively regulating it. Knockdown of C/EBP-beta also leads to inhibition of PMA-mediated OSM induction. 27892764_a novel STAT3/SMAD3-signaling axis is required for OSM-mediated senescence. 27993536_Neutrophils are a major source of OSM-producing cells in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis and severe asthma. 28053127_Data provide evidence that OSM regulates an epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell plasticity program that promotes tumorigenic properties in pancreatic cells. 28106823_The identification of the OSM inflammatory pathway as an important mediator of epithelial mesenchymal transition in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) may provide a novel potential opportunity to improve therapeutic strategies. 28288136_OSM-induced plasticity was Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3)-dependent, and also required a novel intersection with transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta)/SMAD signaling. Removal of OSM or inhibition of STAT3 or SMAD3 resulted in a marked reversion to a non-invasive, epithelial phenotype. 28368383_OSM and OSMR are highly expressed in inflammatory bowel disease intestinal mucosa compared to control mucosa. OSM promotes inflammatory behavior in human intestinal stroma. 28471981_Study showed that in atrial fibrillation (AF) with thrombus, the atrial tissue infiltration of M1 macrophages increased significantly; the OSM expression was also found to increase simultaneously; downstream tissue factor (TF) increased and tissue factor pathway inhibitors (TFPI)decreased, leading to an imbalance between TF and TFPI eventually. OSM might be related to thrombosis in patients with AF mediated by TF and TFPI 28560754_Oncostatin M induces RIG-I and MDA5 expression and enhances the double-stranded RNA response in fibroblasts. 28729401_IL6 family cytokine oncostatin-M (OSM) induced a switch to the EMT phenotype and protected cells from targeted drug-induced apoptosis in OSM receptors (OSMRs)/JAK1/STAT3-dependent manner 28972028_downregulation of miR-20a-5p is caused by promoter hypermethylation. MiR-20a-5p could also suppress the production of IL-17 by targeting OSM and CCL1 production in CD4(+) T cells in patients with active VKH. 29269396_The mechanism of prostaglandin E2-induced transcriptional up-regulation of Oncostatin-M by CREB and Sp1 has been described. 29511087_Because most of the key amino acid residues identified here are conserved between LIF and OSM, we concluded that comparatively minor differences in a few amino acid residues within binding site III account for the differential biological effects of OSM and LIF 29526757_The IL-6-type cytokine oncostatin M (OSM) indeed induces cellular properties associated with tumorigenesis and disease progression in non-transformed human prostate epithelial cells, including morphological changes, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), enhanced migration and pro-invasive growth patterns. 29898744_our findings suggest that OSM plays a crucial role in the early steps of metastatic breast cancer progression, resulting in increased circulating tumor cell (CTC) and lung metastases as well as reduced survival. Therefore, early therapeutic inhibition of OSM in patients with breast cancer may prevent breast cancer metastasis. 30091322_OSM [oncostatin M]might be involved in the invasiveness of extravillous trophoblasts under hypoxia conditions via increasing MMP-2 and MMP-9 enzymatic activities through STAT3 signaling. Increased MMP-9 activity by OSM seems to be more important in primary trophoblasts. 30142324_H3N2 influenza virus infection enhances oncostatin M expression in human nasal epithelium. 30373773_data reveal that individual amino acids within the AB loop of OSM determine species-specific activities. These mutations might reflect a key step in the evolutionary process of this cytokine, in which receptor promiscuity gives way to ligand-receptor specialization. 30670533_Our results reveal a paracrine-signaling mechanism by which neutrophil-released OSM rapidly influences endothelial cell function during physiological and pathological inflammation. 30930146_Subset of TREM2(+) Dermal Macrophages Secretes Oncostatin M to Maintain Hair Follicle Stem Cell Quiescence and Inhibit Hair Growth 31461490_Gene expression analysis on human normal arteries (n = 10) and late stage/advanced carotid atherosclerotic arteries (n = 127) and in situ hybridization on early human plaques (n = 9) showed that OSM, and its receptors, OSM receptor (OSMR) and Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Receptor (LIFR) are expressed in normal arteries and atherosclerotic plaques. 31861914_Oncostatin M, A Profibrogenic Mediator Overexpressed in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Stimulates Migration of Hepatic Myofibroblasts. 31930328_Oncostatin M Is a Prognostic Biomarker and Inflammatory Mediator for Sepsis. 32325460_Plasma Oncostatin M, TNF-alpha, IL-7, and IL-13 Network Predicts Crohn's Disease Response to Infliximab, as Assessed by Calprotectin Log Drop. 32359099_Oncostatin M upregulates Livin to promote keratinocyte proliferation and survival via ERK and STAT3 signalling pathways. 32652496_Association of serum regenerating islet-derived protein 3-beta and oncostatin-M levels with the risk of acute coronary syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus - A pilot study. 32678942_Treponema denticola stimulates Oncostatin M cytokine release and de novo synthesis in neutrophils and macrophages. 32690652_Osteal Tissue Macrophages Are Involved in Endplate Osteosclerosis through the OSM-STAT3/YAP1 Signaling Axis in Modic Changes. 32703406_Oncostatin M enhances osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells derived from supernumerary teeth. 33216732_Oncostatin M expression and TP53 mutation status regulate tumor-infiltration of immune cells and survival outcomes in cholangiocarcinoma. 33624092_Oncostatin M Is a Biomarker of Diagnosis, Worse Disease Prognosis, and Therapeutic Nonresponse in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. 33923774_Myocardial Accumulations of Reg3A, Reg3gamma and Oncostatin M Are Associated with the Formation of Granulomata in Patients with Cardiac Sarcoidosis. 33990221_Serial Lipocalin 2 and Oncostatin M levels reflect inflammation status and treatment response in axial spondyloarthritis. 34011405_Novel mechanism for OSM-promoted extracellular matrix remodeling in breast cancer: LOXL2 upregulation and subsequent ECM alignment. 34037532_TCF-3-mediated transcription of lncRNA HNF1A-AS1 targeting oncostatin M expression inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition via TGFbeta signaling in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. 34102284_Oncostatin M promotes hepatic progenitor cell activation and hepatocarcinogenesis via macrophage-derived tumor necrosis factor-alpha. 34117193_Oncostatin-M Does Not Predict Treatment Response in Inflammatory Bowel Disease in a Pediatric Cohort. 34301760_Endothelial Reprogramming Stimulated by Oncostatin M Promotes Inflammation and Tumorigenesis in VHL-Deficient Kidney Tissue. 34534575_Oncostatin M Improves Cutaneous Wound Re-Epithelialization and Is Deficient under Diabetic Conditions. 34547509_Oncostatin M suppresses browning of white adipocytes via gp130-STAT3 signaling. 34674925_Oncostatin M sensitizes keratinocytes to UVB-induced inflammation via GSDME-mediated pyroptosis. 34921158_Heterocellular OSM-OSMR signalling reprograms fibroblasts to promote pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis. 35020406_Oncostatin M expression induced by bacterial triggers drives airway inflammatory and mucus secretion in severe asthma. 35064579_Oncostatin M is overexpressed in NASH-related hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cancer cell invasiveness and angiogenesis. 35163735_The Role of Oncostatin M and Its Receptor Complexes in Cardiomyocyte Protection, Regeneration, and Failure. 36054964_Exogenous Oncostatin M induces Cardiac Dysfunction, Musculoskeletal Atrophy, and Fibrosis. | ENSMUSG00000058755 | Osm | 16.569883 | 0.433771792 | -1.204992 | 0.45370303 | 7.075331 | 0.0078152364470478481034421136541823216248303651809692382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0410204605708462677338133062221459113061428070068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 8.5746491 | 3.9688941 | 19.9702349 | 8.8668224 | |
| ENSG00000100154 | 23331 | TTC28 | protein_coding | Q96AY4 | FUNCTION: During mitosis, may be involved in the condensation of spindle midzone microtubules, leading to the formation of midbody. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23036704}. | Acetylation;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Mitosis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat | Enables kinase binding activity. Involved in regulation of mitotic cell cycle. Located in midbody. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:23331; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; midbody [GO:0030496]; spindle pole [GO:0000922]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell division [GO:0051301]; regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0007346] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23036704_observations indicated that a novel big protein TPRBK is essential for the formation and integrity of the midbody, hence we postulated that TPRBK plays a critical role in the progress of mitosis and cytokinesis during mammalian cell cycle | ENSMUSG00000033209 | Ttc28 | 154.102813 | 0.465094119 | -1.104405 | 0.19050430 | 33.142870 | 0.0000000085629783812438732144484468920830888549744486226700246334075927734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000001979817216476682841172621057576619385542926465859636664390563964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 94.5313236 | 16.3863189 | 204.3247449 | 34.9422366 | |
| ENSG00000100522 | 64841 | GNPNAT1 | protein_coding | Q96EK6 | 3D-structure;Acyltransferase;Disease variant;Dwarfism;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transferase | PATHWAY: Nucleotide-sugar biosynthesis; UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine biosynthesis; N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate from alpha-D-glucosamine 6-phosphate (route I): step 1/2. | Enables identical protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in UDP-N-acetylglucosamine biosynthetic process. Predicted to act upstream of or within cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor. Predicted to be located in late endosome. Predicted to be active in Golgi apparatus; endoplasmic reticulum; and endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:64841; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment [GO:0005793]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; glucosamine 6-phosphate N-acetyltransferase activity [GO:0004343]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; monosaccharide binding [GO:0048029]; N-acetyltransferase activity [GO:0008080]; UDP-N-acetylglucosamine biosynthetic process [GO:0006048] | 18675810_Crystal structures of human GNA1, including apo GNA1, the GNA1-GlcN6P complex and an E156A mutant were reported. 26935656_The Glucosamine-6-phosphate N-acetyltransferase1 (GNA1) catalyses the transfer of an acetyl group from acetyl coenzyme A to glucosamine-6-phosphate to form N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate which is an essential intermediate in UDP-GlcNAc biosynthesis. 32591345_Novel form of rhizomelic skeletal dysplasia associated with a homozygous variant in GNPNAT1. 33178836_Independent Prognostic Potential of GNPNAT1 in Lung Adenocarcinoma. 33686019_Potential role of glucosamine-phosphate N-acetyltransferase 1 in the development of lung adenocarcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000037722 | Gnpnat1 | 339.393418 | 2.311907470 | 1.209084 | 0.28436814 | 17.557728 | 0.0000278715741293023015659035407365351488806481938809156417846679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0003332201529236586108953521723208268667804077267646789550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 400.1180128 | 120.1596941 | 172.5979312 | 51.9012870 | |
| ENSG00000100628 | 51676 | ASB2 | protein_coding | Q96Q27 | FUNCTION: Substrate-recognition component of a SCF-like ECS (Elongin-Cullin-SOCS-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins (PubMed:16325183, PubMed:15590664). Mediates Notch-induced ubiquitination and degradation of substrates including TCF3/E2A and JAK2 (PubMed:21119685). Required during embryonic heart development for complete heart looping (By similarity). Required for cardiomyocyte differentiation (PubMed:32179481). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K0L0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15590664, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16325183, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21119685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32179481}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Involved in myogenic differentiation and targets filamin FLNB for proteasomal degradation but not filamin FLNA (PubMed:19300455). Also targets DES for proteasomal degradation (By similarity). Acts as a negative regulator of skeletal muscle mass (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K0L0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19300455}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Targets filamins FLNA and FLNB for proteasomal degradation (PubMed:21737450, PubMed:22916308, PubMed:24044920, PubMed:24052262). This leads to enhanced adhesion of hematopoietic cells to fibronectin (PubMed:21737450). Required for FLNA degradation in immature cardiomyocytes which is necessary for actin cytoskeleton remodeling, leading to proper organization of myofibrils and function of mature cardiomyocytes (By similarity). Required for degradation of FLNA and FLNB in immature dendritic cells (DC) which enhances immature DC migration by promoting DC podosome formation and DC-mediated degradation of the extracellular matrix (By similarity). Does not promote proteasomal degradation of tyrosine-protein kinases JAK1 or JAK2 in hematopoietic cells (PubMed:22916308). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K0L0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21737450, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22916308, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24044920, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24052262}. | Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. | This gene encodes a member of the ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing (ASB) protein family. These proteins play a role in protein degradation by coupling suppressor of cytokine signalling (SOCS) proteins with the elongin BC complex. The encoded protein is a subunit of a multimeric E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that mediates the degradation of actin-binding proteins. This gene plays a role in retinoic acid-induced growth inhibition and differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]. | hsa:51676; | cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000151]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; cullin family protein binding [GO:0097602]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0055013]; cardiac muscle cell differentiation [GO:0055007]; dendritic cell migration [GO:0036336]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; podosome assembly [GO:0071800]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; skeletal muscle atrophy [GO:0014732]; skeletal muscle cell differentiation [GO:0035914]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] | 18799729_ASB2 may regulate hematopoietic cell differentiation by modulating cell spreading and actin remodeling through targeting of filamins A and B for degradation. 21119685_By shifting monomeric E3 ligase complexes to dimeric forms through activation of Asb2 transcription, Notch could effectively control the turnover of a variety of substrates and it exerts diverse effects on cell proliferation and differentiation. 21737450_ASB2alpha is a novel regulator of integrin-dependent adhesion of hematopoietic cells 22174154_A model whereby ASB2 contributes to hematopoietic differentiation, in part, through MLL degradation and HOX gene down-regulation. 22382022_These results suggest that ASB2beta but not ASB2alpha might be monoubiquitinated and that the ASB2beta UIM motif, but not its E3 Ub ligase activity, plays a pivotal role in this monoubiquitination. 22916308_Data show that neither endogenous nor exogenously expressed ASB2alpha induces degradation of JAK proteins in hematopoietic cells 24044920_Phosphorylation of serine 323 of ASB2 alpha by Erk kinases is critical for ASB2alpha-mediated degradation of FLNA. 24052262_data therefore reveal ubiquitin acceptor sites in FLNa and establish that ASB2alpha-mediated effects on cell spreading are due to loss of filamins. 26537633_Using ASB2 conditional knockout mice. 29955039_functionally relevant miRNA/mRNA interactions were identified in skeletal muscles of myotonic dystrophy type 1 patients, highlighting the dysfunction of miR-29c and ASB2. 30116272_Notch signaling can initiate Asb2 transcription and NF-kappa B activation in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. | ENSMUSG00000021200 | Asb2 | 14.836637 | 0.442944655 | -1.174802 | 0.40982413 | 8.403907 | 0.0037441537628510562600581135228594575892202556133270263671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0226527780427165092991259598420583643019199371337890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 8.6585053 | 3.7414017 | 19.6060742 | 7.9782859 |
| ENSG00000100784 | 9252 | RPS6KA5 | protein_coding | O75582 | FUNCTION: Serine/threonine-protein kinase that is required for the mitogen or stress-induced phosphorylation of the transcription factors CREB1 and ATF1 and for the regulation of the transcription factors RELA, STAT3 and ETV1/ER81, and that contributes to gene activation by histone phosphorylation and functions in the regulation of inflammatory genes (PubMed:11909979, PubMed:12569367, PubMed:12763138, PubMed:9687510, PubMed:18511904, PubMed:9873047). Phosphorylates CREB1 and ATF1 in response to mitogenic or stress stimuli such as UV-C irradiation, epidermal growth factor (EGF) and anisomycin (PubMed:11909979, PubMed:9873047). Plays an essential role in the control of RELA transcriptional activity in response to TNF and upon glucocorticoid, associates in the cytoplasm with the glucocorticoid receptor NR3C1 and contributes to RELA inhibition and repression of inflammatory gene expression (PubMed:12628924, PubMed:18511904). In skeletal myoblasts is required for phosphorylation of RELA at 'Ser-276' during oxidative stress (PubMed:12628924). In erythropoietin-stimulated cells, is necessary for the 'Ser-727' phosphorylation of STAT3 and regulation of its transcriptional potential (PubMed:12763138). Phosphorylates ETV1/ER81 at 'Ser-191' and 'Ser-216', and thereby regulates its ability to stimulate transcription, which may be important during development and breast tumor formation (PubMed:12569367). Directly represses transcription via phosphorylation of 'Ser-1' of histone H2A (PubMed:15010469). Phosphorylates 'Ser-10' of histone H3 in response to mitogenics, stress stimuli and EGF, which results in the transcriptional activation of several immediate early genes, including proto-oncogenes c-fos/FOS and c-jun/JUN (PubMed:12773393). May also phosphorylate 'Ser-28' of histone H3 (PubMed:12773393). Mediates the mitogen- and stress-induced phosphorylation of high mobility group protein 1 (HMGN1/HMG14) (PubMed:12773393). In lipopolysaccharide-stimulated primary macrophages, acts downstream of the Toll-like receptor TLR4 to limit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (By similarity). Functions probably by inducing transcription of the MAP kinase phosphatase DUSP1 and the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin 10 (IL10), via CREB1 and ATF1 transcription factors (By similarity). Plays a role in neuronal cell death by mediating the downstream effects of excitotoxic injury (By similarity). Phosphorylates TRIM7 at 'Ser-107' in response to growth factor signaling via the MEK/ERK pathway, thereby stimulating its ubiquitin ligase activity (PubMed:25851810). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8C050, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11909979, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12569367, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12628924, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12763138, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12773393, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15010469, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18511904, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25851810, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9687510, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9873047}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Inflammatory response;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Stress response;Transferase;Ubl conjugation | Enables ATP binding activity and protein serine/threonine kinase activity. Involved in several processes, including histone-serine phosphorylation; positive regulation of histone modification; and regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Located in cytoplasm and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:9252; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; histone H2AS1 kinase activity [GO:0044024]; histone H3S10 kinase activity [GO:0035175]; histone H3S28 kinase activity [GO:0044022]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070498]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001818]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; positive regulation of CREB transcription factor activity [GO:0032793]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; post-translational protein modification [GO:0043687]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of postsynapse organization [GO:0099175] | 12690113_IL1beta and TNFalpha activation of MSK1 and CREB and cAMP-response element signaling cascades occurs via ERK/p38 MAP kinases and are crucial aspects of the intracellular mechanisms that mediate MUC5AC gene expression 15010469_acetylation of histones may stimulate transcription by suppressing an inhibitory phosphorylation by MSK1 15133024_MSK1 has a role in transforming growth factor-beta-mediated responses through p38alpha and Smad signaling pathways 16479592_essential role of the C-terminal domain of MSK1 for its constitutive interaction with group V secretory phospholipase A(2), which appears essential to support VEGF-mediated PAF synthesis 16532028_Plays a positive role in the control of cell proliferation of both HaCaT keratinocytes and the A431 human epidermoid carcinoma line. 16543895_As MSK1 regulates the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, it may play a role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. 16762916_MSK1 has a role downstream of p38 in the regulation of As2O3 responses 17117922_Thr700 phosphorylation relieves the inhibition of MSK1 by a C-terminal autoinhibitory helix and helps induce a conformational shift that protects Thr581 from dephosphorylation 17495961_Dimethylfumarate specifically inhibits MSK1 and 2 activations and subsequently inhibits NF-kappaB-induced gene-transcriptions, which are believed to be important in the pathogenesis of psoriasis 18424438_the induction of inflammatory genes by farnesol is mediated by the activation of the NF-kappaB pathway and involves MEK1/2-ERK1/2-MSK1-dependent phosphorylation of p65/RelA(Ser(276)) 19015318_the action of 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) on colon carcinoma cells depends on the dual action of VDR as a transcription factor and a nongenomic activator of RhoA-ROCK and p38MAPK-MSK1. 19197368_This study provides therefore a direct link between MSK1-mediated phosphorylation of Ser276 p65 of NF-kappaB, allowing its binding to the SCF intronic enhancer, and pathophysiological SCF expression in inflammation. 19251839_IL-17F may be involved in airway inflammation and remodeling via the induction of IL-11, and RafI-MEK1/2-ERK1/2-MSK1-CREB is identified as a novel signaling pathway. 19633291_Data reveal that TPA activates transcription of TBX2 through activating MSK1, which leads to an increase in phosphorylated histone H3 and the recruitment of Sp1 to the TBX2 gene. 19672773_Data provide evidence that p38 Map kinase pathway is activated leading to increased upregulation of mixed lineage kinase 3, MKK3/6, MSK1, and Mapkapk2, upon treatment of BCR/ABL expressing cells with dasatinib. 19706715_We conclude that RSV induces RelA activation in the innate inflammatory response via a pathway separate from that controlling RelA cytoplasmic release, mediated by ROS signaling to cytoplasmic MSK1 activation and RelA Ser-276 phosphorylation. 19933278_MSK1 and MSK2 are differentially regulated by CK2 during the UV response and that MSK2 is the major protein kinase responsible for the UV-induced phosphorylation of p65 at Ser(276) that positively regulates NF-kappaB activity in MDA-MB-231 cells 20044958_The MSK1 can be phosphorylated and activated in cells by both ERK1/2 and p38alpha. 20089855_CREB controls MSK1-mediated phosphorylation of histone H3 at the c-fos promoter in vitro 20198339_Bile acid regulates MUC2 transcription in colon cancer cells via positive EGFR/PKC/Ras/ERK/CREB, PI3K/Akt/IkappaB/NF-kappaB and p38/MSK1/CREB pathways and negative JNK/c-Jun/AP-1 pathway. 20200978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20354165_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20406806_MiR-148a attenuates paclitaxel resistance of hormone-refractory, drug-resistant prostate cancer PC3 cells by regulating MSK1 expression 20408143_In this study, by applying a novel method, we have identified the phosphorylation sites in human MSK1 mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase 1, and show that MRK-beta could also activate MSK1 through direct interaction. 20805296_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20864036_MSK1- and MSK2-mediated H3K27me3S28 phosphorylation serves as a mechanism to activate a subset of PcG target genes determined by the biological stimuli and thereby modulate the gene expression program determining cell fate. 21282660_MSK1 is a direct and potent transcriptional activator when targeted to c-fos promotor, and when targeted to alpha-globin promoter induces H3 S28 phosphorylation reactivating expression of this polycomb-silenced gene. 22312446_MSK1 is an important downstream kinase involved in CS-induced NF-kappaB activation 22626465_Astaxanthin attenuates the UVB-induced secretion of prostaglandin E2 and interleukin-8 in human keratinocytes by interrupting MSK1 phosphorylation in a ROS depletion-independent manner 23604116_MSK1 plays an important role for hormone-dependent breast cancer growth 23643942_Angiopoietin 2-mediated signaling via survivin/ref-1/MSK-1 pathway promotes doxorubicin resistance in HepG2 cells. 23675462_MSK1 and MSK2 are required for maximal TFF 1 induction. 24792438_Data suggest that MSK1 and MSK2 are the major CREB kinases in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients stimulated with lysophosphatidic acid and that phosphorylation of CREB1 at Ser-133 plays a significant role in IL-8 production. 24953041_These results highlight the relevance of MSK1 in the up-regulation of RARbeta by prostaglandin E2. 25520509_Authors conclude that paramyxoviruses trigger the DNA damage response, a pathway required for MSK1 activation of phospho Ser 276 RelA formation to trigger the IRF7-RIG-I amplification loop necessary for mucosal interferon production. 25958199_Increased MSK1 activity is critically important for Epstein-Barr virus LMP1-promoted cell proliferation and transformation. 26030901_Interrupting MSK1 activation is a new target for antioxidants. 26109721_KSHV activates the MSK1/2-CREB1 pathway during primary infection and that it depends on this pathway for viral lytic replication. I 27196759_Our findings indicate that MSK1/beta-catenin signaling serves as an escape survival signal upon PI3K inhibition and provides a strong rationale for the combined use of PI3K and MSK1/beta-catenin inhibition to induce lethal growth inhibition in human GBM cells. 27588146_Results show that MSK1 phosphorylates H3S10 through p38-MAPK pathway in gastric cancer patients. 28314603_MSK1 was overexpressed in 148 out of 329 colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. CRC patients with high MSK1 expression had shorter overall survival than those with low MSK1, especially among patients with stage III tumors. Overexpression of MSK1 is associated with poor prognosis in CRC and is connected to tumor aggressiveness. 29327245_High MSK1 is associated with improved breast cancer-specific survival in early stage invasive breast cancer patients, and has additional prognostic value in HER2-negative and non-basal like disease. 29358704_We show that MSK1 downregulation impairs the differentiation of breast cancer cells, increasing their bone homing and growth capacities. MSK1 controls the expression of genes required for luminal cell differentiation, including the GATA3 and FOXA1 transcription factors, by modulating their promoter chromatin status. 30305627_These studies suggest that MSK1 acts through a direct interaction with p53 to function as a transcriptional coactivator and that MSK1 activation by upstream MAPK signaling is important for efficient p21 gene expression. 30679314_show that expression of nuclear PKCdelta activates ERK and MSK1, that ERK activation is required for MSK1 activation, and that both ERK and MSK1 activation are required for apoptosis 31281310_MicroRNA-130a Contributes to Type-2 Classical DC-activation in Sjogren's Syndrome by Targeting Mitogen- and Stress-Activated Protein Kinase-1. 33560725_Overexpression of the MSK1 Kinase in Patients With Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction and Its Confirmed Role in a Murine Model. 33634591_14q32.11 microdeletion including CALM1, TTC7B, PSMC1, and RPS6KA5: A new potential cause of developmental and language delay in three unrelated patients. 34445361_Mitogen and Stress-Activated Kinases 1 and 2 Mediate Endothelial Dysfunction. | ENSMUSG00000021180 | Rps6ka5 | 47.420776 | 0.187060116 | -2.418426 | 0.75912623 | 8.936073 | 0.0027959315891139843550383670134351632441394031047821044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0178500643854524951303908153477095765992999076843261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 16.5412612 | 9.2541293 | 88.2292855 | 49.2742068 | |
| ENSG00000101152 | 80331 | DNAJC5 | protein_coding | Q9H3Z4 | FUNCTION: Acts as a general chaperone in regulated exocytosis (By similarity). Acts as a co-chaperone for the SNARE protein SNAP-25 (By similarity). Involved in the calcium-mediated control of a late stage of exocytosis (By similarity). May have an important role in presynaptic function. May be involved in calcium-dependent neurotransmitter release at nerve endings (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P60904, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q29455}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene is a member of the J protein family. J proteins function in many cellular processes by regulating the ATPase activity of 70 kDa heat shock proteins. The encoded protein plays a role in membrane trafficking and protein folding, and has been shown to have anti-neurodegenerative properties. The encoded protein is known to play a role in cystic fibrosis and Huntington's disease. A pseudogene of this gene is located on the short arm of chromosome 8. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. | hsa:80331; | azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; chromaffin granule membrane [GO:0042584]; clathrin-sculpted gamma-aminobutyric acid transport vesicle membrane [GO:0061202]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; ATP-dependent protein binding [GO:0043008]; chaperone-mediated protein folding [GO:0061077]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; neuron apoptotic process [GO:0051402]; regulated exocytosis [GO:0045055]; regulation of synaptic vesicle cycle [GO:0098693]; synaptic vesicle exocytosis [GO:0016079] | 10194413_Has a role in exocytosis of large dense core vesicles. 12039948_Csp has a role in regulated CFTR trafficking at the plasma membrane. [CYSTEINE STRING PROTEIN] 14570907_Cysteine string protein inhibits N-type calcium channels, but is blocked by mutant huntingtin 15972823_CSP modulates G protein function by preferentially targeting the inactive GDP-bound form of G alpha(s) and promoting GDP/GTP exchange; the guanine nucleotide exchange activity of full-length CSP is regulated by Hsc70-SGT 16469739_Cysteine string protein monitors late steps in cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator biogenesis 18314541_First evidence that CSP and HSP70, and their interactions with MARCKS, are involved in mucin secretion from airway epithelium. 18596047_palmitoylation of CSP is enhanced specifically by co-expression of the Golgi-localized palmitoyl transferases DHHC3, DHHC7, DHHC15, or DHHC17 19098309_Csp not only regulates the exit of CFTR from the ER, but this action is accompanied by Hsc70/Hsp70 and CHIP-mediated CFTR degradation. 21820099_A neuroprotective role for CSPalpha in humans is confirmed. 22073189_This is the first replication study of the identification of DNAJC5 as the disease-causing gene for autosomal dominant ANCL. The identification of the novel gene in ANCL will allow us to gain a better understanding of the pathological mechanism of ANCLs 22235333_association of DNAJC5 mutations with autosomal dominant Kufs disease 22902780_Palmitoylation-induced aggregation of mutant CSP-alpha proteins may underlie the development of adult-onset neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis 22978711_Results indicate of a p.L116del mutation in DNAJC5 from families with autosomal dominant Kufs disease. 24126164_Missense mutations in DNAJC5 does not play a major role in PD in the Chinese population. 25631211_the presynaptic vesicle protein CSPalpha is a key player in synaptic degeneration and protection in Alzheimer's disease. 26610600_These results suggest that the degeneration seen in the patients with AD-ANCL reported here might be a consequence of both the early effects of CSPalpha mutations at the cellular soma. 26659577_This study demonstrated that Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis with DNAJC5/CSPalpha mutation has PPT1 pathology and exhibit aberrant protein palmitoylation. 27261198_In fact, DnaJC5 overexpression induced tau release in cells, neurons, and brain tissue, but only when activity of the chaperone Hsc70 was intact and when tau was able to associate with this chaperone. 27452402_Phosphorylation of CSP triggers a major conformational switch that modulates its protein interactions. 28127059_The importance of specific residues in the cysteine-string domain was investigated, revealing that a central core of palmitoylated cysteines is essential for aggregation of adult-onset neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis CSPalpha L115R/L116 mutants. 28424476_Results indicate that by assisting local lysosome/proteasome processes, CSPalpha-mediated removal of toxic proteins via extracellular vesicles plays a central role in synaptic proteostasis. 28740222_Study demonstrate that primary dermal fibroblasts from asymptomatic mutation carriers recapitulate features of adult-neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (AD-ANCL) in vitro including CSPalpha-p.L115R/CSPalpha-WT aggregates and the structural and functional lysosomal dysfunction found in the brains of AD-ANCL patients. Further findings support a gain-of-function mechanism for CSPalpha mutations leading to AD-ANCL. 29506599_This report describes the clinical history of autosomal dominant Kufs disease, the genetic mutation within the DNAJC5 gene, and the neuropathological findings demonstrating depletion of choline acetyltransferase in the brain. 30561534_Clinical distinction of type A (progressive myoclonus epilepsy) and type B (dementia with motor disturbance) Kufs disease was supported by molecular diagnoses. Type A is usually caused by recessive pathogenic variants in CLN6 or dominant variants in DNAJC5. Type B Kufs is usually associated with recessive CTSF pathogenic variants. 31919451_Autosomal-dominant adult neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis caused by duplication in DNAJC5 initially missed by Sanger and whole-exome sequencing. 32042150_Point mutations in cysteine string protein-alpha (CSP alpha) cause dominantly inherited adult-onset neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (ANCL). Normally palmitoylated cysteine string region of cysteine string protein alpha loses palmitoylation in ANCL mutants. 32783189_Autosomal dominant neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis: Clinical features and molecular basis. 33662413_DNAJC5 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells proliferation though regulating SKP2 mediated p27 degradation. | ENSMUSG00000000826 | Dnajc5 | 582.651704 | 3.154596262 | 1.657455 | 0.43460300 | 13.822645 | 0.0002009002660758334624264975776242181382258422672748565673828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0019027525861184154797739465081463094975333660840988159179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 997.2832013 | 356.9615502 | 313.2410432 | 112.2097531 | |
| ENSG00000101654 | 8731 | RNMT | protein_coding | O43148 | FUNCTION: Catalytic subunit of the mRNA-capping methyltransferase RNMT:RAMAC complex that methylates the N7 position of the added guanosine to the 5'-cap structure of mRNAs (PubMed:9790902, PubMed:9705270, PubMed:10347220, PubMed:11114884, PubMed:22099306, PubMed:27422871). Binds RNA containing 5'-terminal GpppC (PubMed:11114884). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10347220, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11114884, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22099306, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27422871, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9705270, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9790902}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Methyltransferase;mRNA capping;mRNA processing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase | Enables RNA binding activity and mRNA (guanine-N7-)-methyltransferase activity. Involved in 7-methylguanosine mRNA capping. Located in fibrillar center and nucleoplasm. Part of mRNA cap binding activity complex; mRNA cap methyltransferase complex; and receptor complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:8731; | fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; mRNA cap binding complex [GO:0005845]; mRNA cap methyltransferase complex [GO:0031533]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; mRNA (guanine-N7-)-methyltransferase activity [GO:0004482]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; 7-methylguanosine mRNA capping [GO:0006370]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830] | 15767670_Nuclear localization of cap methyltransferase is mediated by alternative nuclear localization signal motifs 19161160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23863084_The RNMT N-terminal domain is required for transcript expression, translation and cell proliferation. 24200467_Data suggest the C-terminal nuclear localization domain (QYP) is critical for RAM (RNMT-activating mini protein) to enter the cell nucleus where RAM activates RNMT resulting in mRNA cap methylation. TNPO1/TNPO2 mediate RAM nuclear entry. 24763612_High RNMT expression is associated with liver cancer. 26942677_CDK1-Cyclin B1 activates RNMT, coordinating mRNA cap methylation with G1 phase transcription. 27899423_MYC promotes mRNA cap methylation and protein production of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling transcripts through recruitment of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) and consequently RNMT to gene promoters. 27934633_RNMT-RAM complex coordinates mRNA processing with ribosome production. 28981715_Results identify a cytoplasmic pool of RNMT which is a component of the cytoplasmic capping complex, and demonstrate its function as the methyltransferase that catalyzes the final maturation step in cap homeostasis. 29719263_These findings suggest that multiple interactions among RNMT-RAM, RNA Pol II factors, and RNA along the transcription unit stimulate transcription. 30991934_Data show that most of the cell lines which exhibited enhanced dependency on RNA guanine-7 methyltransferase (RNMT) harboured oncogenic mutations in phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic 110-KD alpha (PI3Kalpha). 31329932_Mechanism of allosteric activation of human RNMT by RAM has been reported. 35026230_Identification and Characterization of the Interaction Between the Methyl-7-Guanosine Cap Maturation Enzyme RNMT and the Cap-Binding Protein eIF4E. | ENSMUSG00000009535 | Rnmt | 309.365324 | 2.033019065 | 1.023624 | 0.25779453 | 15.419038 | 0.0000861163364821210833245299087757018696720479056239128112792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0009077583381400976736061436689340098382672294974327087402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 282.9999682 | 72.8728752 | 140.6708926 | 36.2157021 | |
| ENSG00000101901 | 79868 | ALG13 | protein_coding | Q9NP73 | FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Possible multifunctional enzyme with both glycosyltransferase and deubiquitinase activities.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: May be involved in protein N-glycosylation, second step of the dolichol-linked oligosaccharide pathway. | Alternative splicing;Congenital disorder of glycosylation;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Epilepsy;Glycosyltransferase;Hydrolase;Multifunctional enzyme;Protease;Reference proteome;Thiol protease;Transferase;Ubl conjugation pathway | The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of a bipartite UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transferase. It heterodimerizes with asparagine-linked glycosylation 14 homolog to form a functional UDP-GlcNAc glycosyltransferase that catalyzes the second sugar addition of the highly conserved oligosaccharide precursor in endoplasmic reticulum N-linked glycosylation. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2009]. | hsa:79868; | endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; cysteine-type deubiquitinase activity [GO:0004843]; N-acetylglucosaminyldiphosphodolichol N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0004577]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] | 16100110_ALG13 and ALG14 form a functional endoplasmic reticulum UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transferase 24501762_We report on a novel missense variant in the ALG13 gene in a nonconsanguineous Arab family that co-segregates with nonsyndromic intellectual disability. 28178702_ALG13-is2 could be an important modifier of renal filtration defects 28778787_A female patient heterozygous for ALG13 Asn107Ser variant presented with infantile spasms, developmental delay, and dysmorphic features. The patient showed normal pattern of glycosylated transferrin and random pattern of X-inactivation. 31444733_X-Linked ALG13 Gene Variant as a Cause of Epileptic Encephalopathy in Girls. 33410528_The phenotypic spectrum of X-linked, infantile onset ALG13-related developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. 33583022_Expanding the phenotype, genotype and biochemical knowledge of ALG3-CDG. 33734437_ALG13 X-linked intellectual disability: New variants, glycosylation analysis, and expanded phenotypes. | ENSMUSG00000041718 | Alg13 | 225.406453 | 2.912522881 | 1.542269 | 0.41382751 | 13.225306 | 0.0002761946322114837448248592099986353787244297564029693603515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0025054542901259625915788564753938771900720894336700439453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 352.3753773 | 114.2896057 | 121.8136275 | 39.4975373 | |
| ENSG00000102271 | 56062 | KLHL4 | protein_coding | Q9C0H6 | Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Kelch repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat | This gene encodes a member of the kelch family of proteins, which are characterized by kelch repeat motifs and a POZ/BTB protein-binding domain. It is thought that kelch repeats are actin binding domains. However, the specific function of this protein has not been determined. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:56062; | centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; actin binding [GO:0003779] | 32753315_KLHL4, a novel p53 target gene, inhibits cell proliferation by activating p21(WAF/CDKN1A). | ENSMUSG00000025597 | Klhl4 | 12.084794 | 3.194445277 | 1.675565 | 0.48478896 | 12.401319 | 0.0004290306111281458681383504938366968417540192604064941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0036727540933050822728744844170023498008958995342254638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 18.8828562 | 3.5262418 | 5.8884603 | 1.5422799 | ||
| ENSG00000102890 | 79767 | ELMO3 | protein_coding | Q96BJ8 | FUNCTION: Involved in cytoskeletal rearrangements required for phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and cell motility. Acts in association with DOCK1 and CRK. Was initially proposed to be required in complex with DOCK1 to activate Rac Rho small GTPases. May enhance the guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activity of DOCK1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Phagocytosis;Reference proteome;SH3-binding | The protein encoded by this gene is similar to a C. elegans protein that functions in phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and in cell migration. Other members of this small family of engulfment and cell motility (ELMO) proteins have been shown to interact with the dedicator of cyto-kinesis 1 protein to promote phagocytosis and effect cell shape changes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:79767; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell motility [GO:0048870]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909] | 20127720_The present study reports the first characterization of the ELMO3 promoter and suggests a significant role of CDX2 in the basal transcriptional regulation of the intestine-specific expression of ELMO3, possibly through interaction with SP1. 26191257_The over-expression of ELMO3 was a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker for non-small cell lung cancer. 27999268_the silencing of ELMO3 inhibited cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and F-actin polymerization, and induced Gap 1 (G1) phase cell cycle arrest, demonstrating that ELMO3 is involved in the processes of growth, invasion and metastasis of Colorectal Cancer 28039609_The purpose of this study was to asses ELMO3 expression in postoperatively irradiated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients. 30345300_the results indicate that ELMO3 participates in the processes of cell growth, invasion, and migration, and ELMO3 is expected to be a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker for gastric cancer. 30374620_ELMO3 might serve as a clinical prognostic marker of patients with minor salivary gland carcinoma | ENSMUSG00000014791 | Elmo3 | 31.634702 | 0.485963691 | -1.041080 | 0.31938796 | 10.623927 | 0.0011163372022149364339027588499675402999855577945709228515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0083016080726116582566564972012201906181871891021728515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 21.5071010 | 4.1296329 | 44.2926308 | 7.7929872 | |
| ENSG00000102931 | 23568 | ARL2BP | protein_coding | Q9Y2Y0 | FUNCTION: Together with ARL2, plays a role in the nuclear translocation, retention and transcriptional activity of STAT3. May play a role as an effector of ARL2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18234692}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Reference proteome | ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF)-like proteins (ARLs) comprise a functionally distinct group of the ARF family of RAS-related GTPases. The protein encoded by this gene binds to ARL2.GTP with high affinity but does not interact with ARL2.GDP, activated ARF, or RHO proteins. The lack of detectable membrane association of this protein or ARL2 upon activation of ARL2 is suggestive of actions distinct from those of the ARFs. This protein is considered to be the first ARL2-specific effector identified, due to its interaction with ARL2.GTP but lack of ARL2 GTPase-activating protein activity. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:23568; | centrosome [GO:0005813]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; midbody [GO:0030496]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; spindle [GO:0005819]; GTPase regulator activity [GO:0030695]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; maintenance of protein location in nucleus [GO:0051457]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 19368893_Crystal structure of the ARL2-GTP-BART complex reveals a novel recognition and binding mode of small GTPase with effector. 21665939_overexpression of the amino (N)-terminal region of G3BP, including the binding region for BART mRNA, dominant-negatively inhibits formation of the complex between endogenous G3BP and BART mRNA, and increases the expression of BART. 21833473_Our results imply that BART increases active RhoA by inhibiting ARL2 function, which in turn inhibits invasiveness of cancer cells. 21901094_We identify a subset of BART miRNAs that are restricted to Latency III in normal infection but are up regulated in tumors that express Latency I and II. 22532868_These results imply that BART contributes to regulating PKCalpha activity through binding to ANX7, thereby affecting the invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells. 22745590_Our results imply that BART regulates actin-cytoskeleton rearrangements at membrane ruffles through modulation of the activity of Rac1, which, in turn, inhibits pancreatic cancer cell invasion. 23685147_EBV-miR-BART1 could influence the expression of metabolism-associated genes and might be involved in cancer metabolism in nasopharyngeal carcinoma 23849777_Mutations in ARL2BP cause autosomal-recessive retinitis pigmentosa. 24899173_EBV also downregulates two immediate early genes by miR-BART20-5p. 26135619_Alteration of EBV encoded miR-BART1 expression results in an increase in migration and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro and causes metastasis in vivo. EBV-miR-BART1 directly targets the cellular tumour suppressor PTEN. 27790702_Subsequent analysis of 844 index cases did not reveal further pathogenic chances in ARL2BP indicating that mutations in ARL2B are a rare cause of arRCD (about 0.1%) in a large cohort of French patients. 30210231_This study identified two homozygous variants in ARL2BP as a rare cause of autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Further studies are required to define the underlying disease mechanism causing retinal degeneration as a result of mutations in ARL2BP and any phenotype-genotype correlation associated with residual levels of the wild-type transcript. 31425546_Study identified multiple ciliopathy phenotypes associated with mutations in ARL2BP in human patients and in a mouse knockout model. Spermiogenesis is impaired, resulting in abnormally shaped heads, shortened and mis-assembled sperm tails, and loss of axonemal doublets. ARL2BP is required for the structural maintenance of cilia as well as of the sperm flagellum, and that its deficiency leads to syndromic ciliopathy. 33438581_ARL3 activation requires the co-GEF BART and effector-mediated turnover. 34681596_Epstein-Barr Virus miR-BART1-3p Regulates the miR-17-92 Cluster by Targeting E2F3. | ENSMUSG00000031776 | Arl2bp | 295.323963 | 3.227141515 | 1.690257 | 0.30948058 | 28.378123 | 0.0000000997866081845426045655544325559127560865135819767601788043975830078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000019604144315805926416693919650535704590765817556530237197875976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 511.9397993 | 99.0126004 | 159.5636479 | 30.9653603 | |
| ENSG00000102962 | 6367 | CCL22 | protein_coding | O00626 | FUNCTION: May play a role in the trafficking of activated/effector T-lymphocytes to inflammatory sites and other aspects of activated T-lymphocyte physiology. Chemotactic for monocytes, dendritic cells and natural killer cells. Mild chemoattractant for primary activated T-lymphocytes and a potent chemoattractant for chronically activated T-lymphocytes but has no chemoattractant activity for neutrophils, eosinophils, and resting T-lymphocytes. Binds to CCR4. Processed forms MDC(3-69), MDC(5-69) and MDC(7-69) seem not be active. | Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | This antimicrobial gene is one of several Cys-Cys (CC) cytokine genes clustered on the q arm of chromosome 16. Cytokines are a family of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The CC cytokines are proteins characterized by two adjacent cysteines. The cytokine encoded by this gene displays chemotactic activity for monocytes, dendritic cells, natural killer cells and for chronically activated T lymphocytes. It also displays a mild activity for primary activated T lymphocytes and has no chemoattractant activity for neutrophils, eosinophils and resting T lymphocytes. The product of this gene binds to chemokine receptor CCR4. This chemokine may play a role in the trafficking of activated T lymphocytes to inflammatory sites and other aspects of activated T lymphocyte physiology. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. | hsa:6367; | extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; CCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0048020]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; lymphocyte chemotaxis [GO:0048247]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 11981828_Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells are endowed with the capacity to attract CD4+, CD40L+ T cells by producing CCL22, suggesting a vicious circle, leading to the progressive accumulation of the neoplastic cells. 12642832_Neither MDC release nor MDC mRNA was detected in any of the 3 types of fibroblasts stimulated with any of the cytokines examined. 12715916_important role in the production of antigen specific IgE by T-B cell interaction and in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis 12949249_CCL22 is an antimicrobial protein with bacteriocidal activity against E. coli and S. aureus. 14747532_selectively induced in EBV-infected B cells by LMP-1 protein 14962085_IL-4/IL-13 and IFN-gamma induce alternations in the distribution of adherens junctions in a different fashion and thereby contribute to the reciprocal regulation of TARC/MDC production. 15113590_Serum levels of TARC and MDC in atopic dermatitis patients were significantly higher than those found in normal controls. 15187160_CCL22 induced accumulation of phosphatidylinositol-(3,4,5)-trisphosphate in the leukemic T cell line CEM. CCL22 also had the ability to chemoattract human Th2 cells and CEM cells in a pertussis toxin-sensitive manner. 15210758_CCL17 and CCL22, which are constitutively produced by immature DCs, mediate both T cell polarization and attraction. 15813816_findings indicate TARC and MDC are actively involved in pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis and their expression, opposite to that of eotaxin, is strongly associated with clinical picture of atopic dermatitis. 15944327_Elevated bronchial mucosal expression of MDC/CCL22 is implicated in asthma pathogenesis; its action is partly through selective development and retention, or recruitment of T helper type 2, not Th1, receptor-bearing cells. 16453150_MDC/CCL22 has a role in inhibiting progression of lung cancer 16583210_Both a Th1 chemoattractant (CXCL9) and Th2 chemoattractants, CCL17 and CCL22, cooperatively play a role in the development of autoimmune blistering disease. 16614259_CCL22 stimulates phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase-independent phosphorylation of the novel delta isoform of PKC at threonine 505, situated within its activation loop--an event closely associated with increased catalytic activity. 17008059_These data suggest that the CCL22 level produced by monocyte derived dendritic cells thus reflects the disease activity of Atopic dermatitis (AD) and it may also play an important role regarding the production of CCL22 in the pathogenesis of AD. 17517104_Ragweed stimulation significantly increased the production of the Th2-associated cytokines IL-5, IL-9 and IL-13, the chemokines CCL17 and CCL22 and the regulatory cytokine IL-10 in allergic patients 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17967467_A trend towards a decreased allelic frequency of the A allele of the CCL22 C/A SNP as well as of the T allele of the CCL17 C/T SNP was found in MS patients compared with controls. 17967467_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17979978_There were no significant differences in CCL17 and CCL22 expression in PBMCs, sera and lesional skins of patients with intrinsic and extrinsic atopic dermatitis. 18047937_CCL19, CCL20 and CCL22 factors could play an additive role in the pathogenesis of the inflammatory process leading to bronchiolar fibro-obliteration in lung transplant patients 18178833_HTLV-1-infected T cells produce CCL22 through Tax and selectively interact with CCR4+CD4+ T cells, resulting in preferential transmission of HTLV-1 to CCR4+CD4+ T cells. 18208895_MDC/CCL22 is likely to play a role in the development of multiple sclerosis in females only, possibly influencing the intracerebral recruitment of Th2 cells, which produce anti-inflammatory cytokines 18224687_Significantly higher CCL22 expression is associated with gastric cancer 18266834_Serum concentrations of CCL17, CCL22, and CCL27 correlate well with the extent and intensity of Atopic dermatitis (AD) in infants. Of the three Th2 chemokines examined, serum CCL27 correlated most significantly with the severity of AD 18271928_Latent membrane protein 1-expressing tumor cells in age-related Epstein-Barr virus-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorder were selectively positive for CCL17 and CCL22. 18287226_although IE86 does repress the UL144-mediated activation of a synthetic NFkB promoter, it is unable to block UL144-mediated activation of the CCL22 promoter, and this lack of responsiveness to IE86 appears to be regulated by binding of CREB. 18435706_serum CCR4 ligands (CCL17 and CCL22)may be useful inflammatory markers for assessing atopic dermatitis severity in children 18515987_There are elevated concentrations of the chemokines MDC, eotaxin, I-TAC, and MCP-1 in malignant pleural effusions. 18547160_The increased level of CCL17 and CCL22 release was important for acute myelogenous leukemia dendritic cell (AML-DC) chemotaxis of normal T cells. 19175890_Development of allergic disease is associated with a more marked Th2-like deviation already at birth, shown as increased levels of cord blood IgE and MDC (CCL22) and higher ratios of MDC (CCL22) to IP-10 (CXCL10) and I-TAC (CXCL11). 19244125_Regulatory T cells recruited through CCL22/CCR4 are selectively activated in lymphoid infiltrates surrounding primary breast tumors and lead to an adverse clinical outcome. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19298002_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19371952_The adenylyl cyclase-cAMP system has an inhibitory role in IFN-gamma plus TNF-alpha-stimulated production of TARC and MDC in HaCaT keratinocytes by inhibiting NF-kappaB activation through p38 MAPK pathway. 19756997_Endocrine disrupting chemicals suppressed CCL22 and IP-10 levels in cultured monocytes via, at least in part, the MKK1/2-ERK MAPK pathway and histone H4 acetylation. 19942450_Data show that MDC/CCL22 is present in the synovial membrane of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients and in synovial fluid of patients with RA and PsA, which would enable migration of CCR4 expressing memory cells. 20002703_CCL17 and CCL22 within the tumor are related to the increased population of Foxp3(+) T-regs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20337996_CCL22 may be responsible for the infiltration of CD4(+)CD25(high) T cells into the pleural space of patients with tuberculous pleurisy. 20348247_chemokine CCL22 may have a role in abdominal aortic aneurysm 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20525891_Plasma concentration of CCL22 correlates with the frequency of circulating CD4-positive FoxP3-positive (CD4+FoxP3+) regulatory T cells (Tregs) in human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV) type 1-infected subjects. 20625996_These results indicate that intracellular reactive oxygen species and MAPK kinases both contribute to IFN-gamma-stimulated production of TARC and CCL22 by increasing NF-kappaB activation. 21129807_Contact between monocyte-derived dendritic cells and HCV-JFH1-infected Huh7 cells induced the expression of CCL17 and CCL22. 21327296_Data show that, for the small macrophages in COPD, increased transcript and protein levels for CCL2, CCL7, CCL13 and CCL22 with a more than 100-fold increase for CCL13 mRNA. 21823987_results suggested that suppression of the CCL22 gene using Salmonella induced anti-inflammatory effects 22125604_Data suggest that variants of C-C motif chemokine 22 (CCL22) play a role in susceptibility to atopic dermatitis (AD) in a gain-of-function manner. 22322668_Data show that PD-1, PD-L1, PD-L2, CCL17, and CCL22 mRNA was identified in papillomas. 22975373_findings suggest that HBV infection and activity of the TGF-beta-miR-34a-CCL22 axis serve as potent etiological factors to predispose hepatocellular carcinoma patients for the development of portal vein tumor thrombus 23106659_High cord blood levels of the Th2 related chemokine CCL22 were significantly associated with high total- IgE levels during the first 6 years of life, but not with specific sensitization, asthma, eczema or allergic rhinitis. 23180648_lymph node metastasis of CCR4(+) HNSCC is promoted by CCL22 in an autocrine or M2-like macrophage-dependent paracrine manner. 23265706_Data suggest that decreased levels of plasmatic CCL22 may contribute to CD4(+) lymphopaenia. 23268288_genetic polymorphism is not associated with breast carcinoma in Southern Iranian population 23340773_These data reveal an elevated serum concentration of Th2-attracting chemokines CCL22 and CCL17 in opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome. 23782855_Autistic children had significantly higher serum levels of MDC than healthy controls 24124553_both CCL22 and TGF-beta1 are candidate chemoattractants for intratumoral Foxp3 (+)Tregs infiltration; however, unlike the later, CCL22 is an independent prognostic predictor of BC patients. 24254331_Suggest that lower CCL22 levels may play an important role in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis in women. 24397961_increased expression in the thymus of myasthenia gravis patients 25117529_Sesamin suppressed lipopolysaccharide induced CCL22 expression in monocytes through the ER/PPAR-a, the MAPK-p38 pathway, the NFkB-p65 pathway and the epigenetic regulation by suppressing histone H3/H4 acetylation in the CCL22 promoter region. 25136780_CCL22 is a novel mediator of lung inflammation following hemorrhage and resuscitation 25148803_CCR4 C1014T and CCL22 C16A genetic variations were neither associated with the risk, nor with the progression of colorectal cancer in Iranian population 25352172_CCL22 could be an immune marker in ANCA-associated vasculitis. 25604093_Circulating CCL22 levels are related to both glioma risk and survival duration independent of age, histology, grade and IDH mutation status. CCL22 should be considered a marker of immune status with potential prognostic value 25647263_Elevated levels of CCL22 found in the ascites could create a chemokine gradient aiding in Treg cells migration. Increased Tregs percentage in the local microenvironment of ovarian cancer might be an important mechanism of immunosuppression. 25722218_The serum CCL22 levels were affected by genetic variations at SNP rs223818. Accordingly, SNP rs223818 may play a role in the susceptibility to breast cancer. 25922986_Our results demonstrate that CCL22 is expressed in human placenta. Decidual expression was only observed in miscarriage conditions and correlates with Treg infiltration. 25970596_First-episode psychosis patients had higher serum CCL22, which decreased substantially following antipsychotic treatment. 26093920_Distinctive Treg associated CCR4-CCL22 expression profile with altered frequency of Th17/Treg cell in the immunopathogenesis of Pemphigus Vulgaris. 26341115_increased amounts released by neutrophils from fibromyalgia patients 26432403_type I IFN blocks the regulatory T cell-attracting chemokine CCL22 and thus helps limit the recruitment of regulatory T cells to tumors 26827189_Data suggest that Th1 (IFN-gamma-inducible protein-10 IP-10/CXCL10) and Th2 (thymus and activation regulated chemokine TARC/CCL17) and (macrophage derived chemokine MDC/CCL22) cooperatively play a role in the development of ankylosing spondylitis (AS). 27152707_These results showed that the higher levels of CXCL10, CCL20 and CCL22 were associated with ischemic heart disease. The serum levels of chemokines may influence by the certain traditional risk factors of IHD and some studied SNPs, but did not influence by treatment and gender of patients. 27499437_CCL22 and IL-37 with a co-localization in non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells inhibited the proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition process 27634754_The CCL22-mediated enhancement of antitumor responses is however not due to conversion, but rather to redirection of existing regulatory T cells to the site of cutaneous overexpression. 27811371_Elevations in serum MDC and BLC were independently associated with the significant risk of early stage lung adenocarcinoma, even in non-smokers and in stage IA patients. 27863395_blood CCL22 levels were positively associated with IgE sensitization at age 2. A high cord blood CCL22/CXCL10 chemokine ratio was significantly associated with a higher risk of allergic sensitization at age 3. 28039457_Tumor-associated macrophages promote prostate cancer migration through activation of the CCL22-CCR4 signaling axis. 28383711_Data suggest that high levels of CCL17 and CCL22 in endometrium in women with endometriosis promote (1) recruitment of Tregs, (2) immunosuppression of Tregs, and (3) angiogenesis in endometrium. (Tregs = regulatory T cells) 28501127_CCL22 plays an important role in supporting gastric cancer development presumably by increasing the percentage of regulatory T cells in the tumor microenvironments. CCL22 levels in sera have a predictive value for gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis and the early recurrence. 28898872_MDC might serve as a marker of pharmacological therapy response in major depressive disorder 29099057_This review presents key clinical studies of Multiple sclerosis together with experimental studies in animals that have demonstrated functional roles of CCR4, CCL17, and CCL22 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis pathogenesis. [review] 29662241_Th2-associated chemokine CCL22 levels appear to be inversely related to mite sensitization and the risk of asthma development in early childhood. 29794410_High level of CCL22 is associated with histamine receptor 2 stimulation and thus atherosclerosis. 29945324_The frequency of CC genotypes at both SNPs rs4359426 and rs2228428 in C-C motif chemokine 22 (CCL22) and chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 4 protein (CCR4) genes was significantly higher in myocardial infarction (MI) patients compared to other genotypes. 30572845_Both CCL1 and CCL22 were expressed in most breast cancer tissues. CCL1 was significantly over-expressed in invasive breast cancer as compared to normal breast tissue. CCL1, but surprisingly not CCL22, showed a significant correlation with the number of tumor-infiltrating FoxP3+ Treg 30623804_CCL22 may be an early factor in the onset/pathogenic process of cartilage degeneration and/or related to pain OA. 30928379_macrophage-derived CCL22 plays an important role in the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment via IL-8 in malignant pleural effusion 30953706_Study demonstrates that PAL cell lines express and secrete CCL17 and/or CCL22 chemokines, the ligands of C-C motif chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4), in contrast to EBV-negative DLBCL cell lines 31131048_A positive association between the psoriasis area and severity index score with three serum proteins (PI3, CCL22, IL-12B) has been found. 31134686_expression of CCL22 in the tumor microenvironment led to a deterioration in the prognosis of patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma by influencing the balance of M1- and M2-like macrophages 31325403_In oral cancer specimens, CCL22 mRNA was upregulated. Release of IL-1beta from cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) induces CCL22 mRNA expression in oral cancer cells by activating NF-kappaB. Data support a model in which CAF-derived IL-1beta, CCL22, and its receptor CCR4 foster a protumor environment by promoting cell transformation and Treg infiltration. 31769216_p65/miR-23a/CCL22 axis regulated regulatory T cells recruitment in hepatitis B virus positive hepatocellular carcinoma. 32060848_REVIEW: CCL22 Signaling in the Tumor Environment 32179746_Elevated serum chemokine CCL22 levels in first-episode psychosis: associations with symptoms, peripheral immune state and in vivo brain glial cell function. 32480426_Systematic reassessment of chemokine-receptor pairings confirms CCL20 but not CXCL13 and extends the spectrum of ACKR4 agonists to CCL22. 32725764_Serum CCL22 levels decreased in parallel with disease activity in CCR4-positive mycosis fungoides treated with mogamulizumab. 33264064_Rhinovirus-induced CCL17 and CCL22 in Asthma Exacerbations and Differential Regulation by STAT6. 33597749_Affinity-coupled CCL22 promotes positive selection in germinal centres. 34781732_Toxoplasma gondii GRA28 Is Required for Placenta-Specific Induction of the Regulatory Chemokine CCL22 in Human and Mouse. 35962191_Tumor-associated macrophage (TAM)-derived CCL22 induces FAK addiction in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). 36224014_Spatial Transcriptomics Analysis Reveals that CCL17 and CCL22 are Robust Indicators of a Suppressive Immune Environment in Angioimmunoblastic T Cell Lymphoma (AITL). | ENSMUSG00000031779 | Ccl22 | 13.671207 | 0.236953659 | -2.077323 | 0.46751712 | 21.764542 | 0.0000030824462388276656800835482524769659562480228487402200698852539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000465629135947315155995979152336872175510507076978683471679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 5.5870613 | 1.8361466 | 23.3123074 | 5.9970904 | |
| ENSG00000103269 | 9028 | RHBDL1 | protein_coding | O75783 | FUNCTION: May be involved in regulated intramembrane proteolysis and the subsequent release of functional polypeptides from their membrane anchors. {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Membrane;Protease;Reference proteome;Serine protease;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a protein similar to Rhomboid in Drosophila which is involved in signalling in the Spitz/epidermal growth factor receptor/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. The Rhomboid family of proteins consists of intramembrane serine proteases containing several transmembrane domains. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. | hsa:9028; | membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | ENSMUSG00000025735 | Rhbdl1 | 11.829550 | 0.351219551 | -1.509555 | 0.57073980 | 6.937772 | 0.0084394146534952484833835839594939898233860731124877929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0434660715628215968409087111012922832742333412170410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 6.1212353 | 1.9079141 | 16.8481815 | 4.6999256 | ||
| ENSG00000103742 | 57722 | IGDCC4 | protein_coding | Q8TDY8 | Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:57722; | plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609] | 20658536_identified Nope as a novel oncofetal surface marker for murine and human HCC. Nope is specifically expressed by epithelial tumor cells but not in preneoplastic stages and is a promising marker 32986656_First evaluation of Neighbor of Punc E11 (NOPE) as a novel marker in human hepatocellular carcinoma. 35246597_Expression of Neighbor of Punc E11 (NOPE) in early stage esophageal adenocarcinoma is associated with reduced survival. | ENSMUSG00000032816 | Igdcc4 | 78.867631 | 0.478715311 | -1.062760 | 0.27419363 | 14.796924 | 0.0001197306668440480733207192942657570711162406951189041137695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0012074928390876310882462441043116996297612786293029785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 41.6595043 | 12.7866170 | 87.4349960 | 26.3789580 | ||
| ENSG00000104140 | 171177 | RHOV | protein_coding | Q96L33 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in the control of the actin cytoskeleton via activation of the JNK pathway. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z1Y0}. | Cell membrane;Endosome;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | Predicted to enable GTP binding activity and GTPase activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including Cdc42 protein signal transduction; cell projection assembly; and endocytosis. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:171177; | endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; Cdc42 protein signal transduction [GO:0032488]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; establishment or maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0007163] | 11956592_cloning and characterization of WRCH2 on human chromosome 15q15 15664990_Data suggest that Chp is implicated in cell transformation, and the unique amino and carboxyl termini of Chp represent atypical mechanisms of regulation of Rho GTPase function. 17355222_Results demonstrate a novel mechanism of signal termination mediated by the Rho-family GTPases Chp and Cdc42, which results in ubiquitin-mediated degradation of one of their direct effectors, Pak1. 22339630_CDC42 homologous protein does not enhance the level of Ser60 phosphorylation in Pak6. (RHO V protein) 24388711_Authors propose that the RHOV gene could be validated as a diagnostic or prognostic marker for NSCLC, and that observed overexpression of RHOV might contribute to tumorigenesis. 26555387_This review addresses the developmental roles of 2 GTPases of the Rho family, RhoV/Chp and RhoU/Wrch. 30113035_Our results suggest that the effector domain of RhoV mediates its binding to Pak1, complementing the current view of the molecular basics of RhoV binding to effectors of the Pak family. 34326698_RHOV promotes lung adenocarcinoma cell growth and metastasis through JNK/c-Jun pathway. 34834920_A CRISPR Activation Screen Identifies an Atypical Rho GTPase That Enhances Zika Viral Entry. | ENSMUSG00000034226 | Rhov | 14.343843 | 0.354344516 | -1.496775 | 0.44255427 | 11.773425 | 0.0006008233674976046169088905735122807527659460902214050292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0049321110707491160746185343555225699674338102340698242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 7.6733307 | 4.2081880 | 21.7469678 | 11.3617252 | |
| ENSG00000104219 | 51201 | ZDHHC2 | protein_coding | Q9UIJ5 | FUNCTION: Palmitoyltransferase that catalyzes the addition of palmitate onto various protein substrates and is involved in a variety of cellular processes (PubMed:18508921, PubMed:18296695, PubMed:19144824, PubMed:21343290, PubMed:22034844, PubMed:23793055). Has no stringent fatty acid selectivity and in addition to palmitate can also transfer onto target proteins myristate from tetradecanoyl-CoA and stearate from octadecanoyl-CoA (By similarity). In the nervous system, plays a role in long term synaptic potentiation by palmitoylating AKAP5 through which it regulates protein trafficking from the dendritic recycling endosomes to the plasma membrane and controls both structural and functional plasticity at excitatory synapses (By similarity). In dendrites, mediates the palmitoylation of DLG4 when synaptic activity decreases and induces synaptic clustering of DLG4 and associated AMPA-type glutamate receptors (By similarity). Also mediates the de novo and turnover palmitoylation of RGS7BP, a shuttle for Gi/o-specific GTPase-activating proteins/GAPs, promoting its localization to the plasma membrane in response to the activation of G protein-coupled receptors. Through the localization of these GTPase-activating proteins/GAPs, it also probably plays a role in G protein-coupled receptors signaling in neurons (By similarity). Also probably plays a role in cell adhesion by palmitoylating CD9 and CD151 to regulate their expression and function (PubMed:18508921). Palmitoylates the endoplasmic reticulum protein CKAP4 and regulates its localization to the plasma membrane (PubMed:18296695, PubMed:19144824). Could also palmitoylate LCK and regulate its localization to the plasma membrane (PubMed:22034844). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P59267, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JKR5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18296695, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18508921, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19144824, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21343290, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22034844, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23793055}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Promotes Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) replication by mediating viral nsp1 palmitoylation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30404808}. | Acyltransferase;Cell membrane;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Synapse;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Enables protein homodimerization activity and protein-cysteine S-palmitoyltransferase activity. Involved in several processes, including peptidyl-L-cysteine S-palmitoylation; regulation of protein catabolic process; and regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane. Located in Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:51201; | endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; postsynaptic recycling endosome [GO:0098837]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; palmitoyltransferase activity [GO:0016409]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein-cysteine S-myristoyltransferase activity [GO:0019705]; protein-cysteine S-palmitoyltransferase activity [GO:0019706]; protein-cysteine S-stearoyltransferase activity [GO:0140439]; peptidyl-L-cysteine S-palmitoylation [GO:0018230]; positive regulation of AMPA glutamate receptor clustering [GO:1904719]; positive regulation of endosome to plasma membrane protein transport [GO:1905751]; positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:1900273]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein localization to postsynaptic membrane [GO:1903539]; protein metabolic process [GO:0019538]; protein palmitoylation [GO:0018345]; protein targeting to membrane [GO:0006612]; regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022407]; regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity [GO:0048168]; regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0042176]; regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903076]; synaptic vesicle maturation [GO:0016188] | 18296695_Identification of CKAP4/p63 as a substrate of DHHC2, a putative tumor suppressor. 18508921_DHHC2 affects palmitoylation, stability, and functions of tetraspanins CD9 and CD151 19144824_DHHC2-mediated palmitoylation of CKAP4 has a role in opposing cancer-related cellular behaviors. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21343290_Gi/o signaling and the palmitoyltransferase DHHC2 regulate palmitate cycling and shuttling of RGS7 family-binding protein. 21471008_The palmitoyl transferase DHHC2 targets a dynamic membrane cycling pathway: regulation by a C-terminal domain 22034844_DHHC2 localizes primarily to the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus suggesting that it is involved in S-acylation of newly-synthesized or recycling Lck involved in T cell signalling. 23457560_reduced ZDHHC2 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis and independently predicts an unfavorable prognosis in gastric adenocarcinoma patients 24995331_These results suggest an important role for ZDHHC2 as a tumor suppressor in metastasis and recurrence of HCC. 32180374_Fine-mapping of ZDHHC2 identifies risk variants for schizophrenia in the Han Chinese population. 33488612_Zdhhc2 Is Essential for Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Mediated Inflammatory Response in Psoriasis. | ENSMUSG00000039470 | Zdhhc2 | 182.692193 | 2.657444770 | 1.410040 | 0.32911702 | 17.633011 | 0.0000267897702601473962683541196749814616850926540791988372802734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0003222143649174048080086052436854515690356492996215820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 263.6286970 | 52.6359166 | 99.1133248 | 20.0596859 | |
| ENSG00000104888 | 57030 | SLC17A7 | protein_coding | Q9P2U7 | FUNCTION: Multifunctional transporter that transports L-glutamate as well as multiple ions such as chloride, proton, potassium, sodium and phosphate (PubMed:10820226). At the synaptic vesicle membrane, mainly functions as an uniporter which transports preferentially L-glutamate but also phosphate from the cytoplasm into synaptic vesicles at presynaptic nerve terminals of excitatory neural cells (By similarity). The L-glutamate or phosphate uniporter activity is electrogenic and is driven by the proton electrochemical gradient, mainly by the electrical gradient established by the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase across the synaptic vesicle membrane (By similarity). In addition, functions as a chloride channel that allows a chloride permeation through the synaptic vesicle membrane that affects the proton electrochemical gradient and promotes synaptic vesicles acidification (By similarity). Moreover, may function as a K(+)/H(+) antiport allowing to maintain the electrical gradient and to decrease chemical gradient and therefore sustain vesicular glutamate uptake (By similarity). The vesicular K(+)/H(+) antiport activity is electroneutral (By similarity). At the plasma membrane, following exocytosis, functions as a symporter of Na(+) and phosphate from the extracellular space to the cytoplasm allowing synaptic phosphate homeostasis regulation (PubMed:10820226). The symporter activity is driven by an inside negative membrane potential and is electrogenic (By similarity). Is necessary for synaptic signaling of visual-evoked responses from photoreceptors (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3TXX4, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62634, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10820226}. | Alternative splicing;Antiport;Cell membrane;Chloride;Chloride channel;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Neurotransmitter transport;Phosphate transport;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sodium;Sodium transport;Symport;Synapse;Synaptosome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | The protein encoded by this gene is a vesicle-bound, sodium-dependent phosphate transporter that is specifically expressed in the neuron-rich regions of the brain. It is preferentially associated with the membranes of synaptic vesicles and functions in glutamate transport. The protein shares 82% identity with the differentiation-associated Na-dependent inorganic phosphate cotransporter and they appear to form a distinct class within the Na+/Pi cotransporter family. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:57030; | chloride channel complex [GO:0034707]; clathrin-sculpted glutamate transport vesicle membrane [GO:0060203]; excitatory synapse [GO:0060076]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; chloride channel activity [GO:0005254]; L-glutamate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005313]; L-glutamate uniporter activity [GO:0140788]; neurotransmitter transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005326]; phosphate ion uniporter activity [GO:0140787]; potassium:proton antiporter activity [GO:0015386]; sodium:inorganic phosphate symporter activity [GO:0015319]; sodium:phosphate symporter activity [GO:0005436]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; anion transport [GO:0006820]; brain development [GO:0007420]; chloride transport [GO:0006821]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; L-glutamate transmembrane transport [GO:0015813]; neural retina development [GO:0003407]; neurotransmitter loading into synaptic vesicle [GO:0098700]; neurotransmitter transport [GO:0006836]; phosphate ion homeostasis [GO:0055062]; phosphate ion transport [GO:0006817]; potassium ion transport [GO:0006813]; regulation of synapse structure or activity [GO:0050803]; regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis [GO:1900242]; sodium-dependent phosphate transport [GO:0044341]; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0035249] | 15653259_In schizophrenia, VGLUT1 mRNA was decreased in hippocampal formation and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. In the hippocampus, the loss of VGLUT1 mRNA supports data indicating that glutamatergic presynaptic deficits are prominent. 15961236_Alterations in the pattern of vesicular glutamate transporter 1-immunoreactivity that perfectly matched the neuronal loss and gliosis, as well as the decrease in the number of asymmetrical synapses identified by electron microscopy in this tissue 17531353_Our results suggest that VGLUT1 expression in the prefrontal cortex could be used as a valuable neurochemical marker of dementia in AD. 17660252_Docking and homology modeling explain the inhibition of VGLUT1. 18155679_We found increased VGLUT1 transcript and reduced VGLUT1 protein expression in the ACC, but not DLPFC, in schizophrenia. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19156168_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19720501_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19720501_this study suggests that the common genetic variants of the VGLUT1 gene appear not play a major role in conferring susceptibility to schizophrenia in Han population of Taiwan. 19839996_This study found decreased VGLUT1 mRNA expression in both major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder in the entorhinal cortex. 21396926_We examined the ratio of excitatory to inhibitory vesicular neurotransmitter transporter mRNAs (VGluT1 to VGAT) and their ratio in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex during normal human development and in people with schizophrenia 22510271_Data indicate that GABAergic axons were labeled with vesicular inhibitory aa transporter (VIAAT) antibodies, whereas glutamatergic axons were detected with antisera against the major vesicular glutamate transporter (VGLUT) isoforms, VGLUT1 and VGLUT2. 23022470_Depressed patients showed significant decreases in synaptophysin (SYN) and VGLUT1 expression, whereas in bipolar patients, decreases in VGLUT1 expression have also been found. 25749033_Loss of SLC17A7 expression is associated with glioblastoma. 26836159_Results suggest that activation of JNK in Alzheimer's disease (AD) inhibits insulin signaling which could lead to a decreased expression of VGLUT1, therefore contributing to the glutamatergic deficit in AD 27029226_This study was the first to demonstrate an association between genetic polymorphism at rs7417284 SNP in the promoter region of the SLC17A7 gene and concussion severity and duration. Based upon these findings, rs74174284 is a potential predictive genetic marker for identifying athletes who are more susceptible for altered recovery times and worse motor speed ImPACT scores after sport-related concussion. 27258819_Study revealed susceptibility of glutamatergic nerve terminals to Abeta induced toxicity and underlined the importance of VGLUT1 in the progression of Alzheimer's disease, as the decrease of this protein levels could increase the susceptibility to subsequent deleterious inputs by exacerbating Abeta induced neuroinflammation and synaptic plasticity disruption. 29890994_The findings of this study indicate that Slc17A7 located on 1p/19q may simultaneously influence tumor development. 31663854_In mammals, VGLUT1 gained a proline-rich sequence that recruits endophilinA1 and turns the transporter into a regulator of synaptic vesicles organization and spontaneous release. | ENSMUSG00000070570 | Slc17a7 | 219.254202 | 0.469375830 | -1.091185 | 0.11712256 | 87.539758 | 0.0000000000000000000082602599366466554606492804289220446080423953258237882259825551889420580664591398090124130249023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000006017943541344449363752524347228128536769205633494327425947467702371795894578099250793457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 135.0476768 | 16.3068806 | 289.1155525 | 33.6250327 | |
| ENSG00000104936 | 1760 | DMPK | protein_coding | Q09013 | FUNCTION: Non-receptor serine/threonine protein kinase which is necessary for the maintenance of skeletal muscle structure and function. May play a role in myocyte differentiation and survival by regulating the integrity of the nuclear envelope and the expression of muscle-specific genes. May also phosphorylate PPP1R12A and inhibit the myosin phosphatase activity to regulate myosin phosphorylation. Also critical to the modulation of cardiac contractility and to the maintenance of proper cardiac conduction activity probably through the regulation of cellular calcium homeostasis. Phosphorylates PLN, a regulator of calcium pumps and may regulate sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium uptake in myocytes. May also phosphorylate FXYD1/PLM which is able to induce chloride currents. May also play a role in synaptic plasticity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10811636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10913253, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11287000, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15598648, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21457715, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21949239}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cataract;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Kinase;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sarcoplasmic reticulum;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is a serine-threonine kinase that is closely related to other kinases that interact with members of the Rho family of small GTPases. Substrates for this enzyme include myogenin, the beta-subunit of the L-type calcium channels, and phospholemman. The 3' untranslated region of this gene contains 5-38 copies of a CTG trinucleotide repeat. Expansion of this unstable motif to 50-5,000 copies causes myotonic dystrophy type I, which increases in severity with increasing repeat element copy number. Repeat expansion is associated with condensation of local chromatin structure that disrupts the expression of genes in this region. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. | hsa:1760; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nuclear outer membrane [GO:0005640]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0033017]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; myosin phosphatase regulator activity [GO:0017020]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010657]; nuclear envelope organization [GO:0006998]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of excitatory postsynaptic membrane potential involved in skeletal muscle contraction [GO:0014853]; regulation of heart contraction [GO:0008016]; regulation of myotube differentiation [GO:0010830]; regulation of skeletal muscle contraction by calcium ion signaling [GO:0014722]; regulation of sodium ion transport [GO:0002028]; regulation of synapse structural plasticity [GO:0051823] | 11121205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11748308_eight years' experience of direct molecular testing for myotonic dystrophy in Wales 11766468_Gene for myotonic dystrophy 11768386_presymptomatic testing in myotonic dystrophy: genetic counselling approaches 11768387_trinucleotide repeat contraction of a paternal expanded DMPK allele back to the normal range detected in the fetus: a pitfall in prenatal diagnosis of myotonic dystrophy 11781699_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11793472_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11793472_negative linear correlation of age at onset and average expansion size in juvenile-adult DM1 patients (35 out of 46) whose progenitor allele is less than 245 repeats long 11903110_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11903304_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12427866_conclude that mutant DMPK 3'-UTR transcripts disrupt myoblast differentiation by reducing MyoD levels below a threshold required to activate the differentiation program 12598332_Levels of this enzyme are altered, along with muscle development, in congenital myotonic dystrophy. 12697816_These studies indicate that homologous recombination strongly destabilizes long tracts of CTG repeats from DMPK 12832055_enhancement of activity through homodimerization of coiled-coil regions 14510658_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14607980_the N-terminus of DMPK plays an important role in DMPK kinase activity, and that the C-terminus of DMPK determines the intracellular localization of the protein 14657503_DMPK mutant RNA binds and sequesters transcription factors (TFs) with up to 90% depletion of selected TFs from active chromatin 14701736_used transgenic DM1 mice carrying more than 300 unstable CTG repeats within their large human genomic environment to investigate the dynamics of CTG repeat germinal mosaicism in males 15017064_Ribozymes can be applied to repair mutations at the RNA level, and therefore can restore normal cellular functions in myotonic dystrophy. 15039975_Observational study of healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 15079005_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15210527_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15284213_The number of CTG repeats in the normal or mutational range of DM1PK gene is associated with neither idiopathic male subfertility nor with clinical characteristics of male subfertility. (DM1PK) 15317754_Continuous overexpression of hDMPK generated pathologic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and myotonic muscle myopathy in transgenic mice. 15462191_Trinucleotide Repeat Expansion at 3 untranslated region of myotonic dystrophy protein kinase is associated with myotonic dystrophy 15476170_In twenty-six individuals from a family with DM, the CTG repeats in DMPK were found in normal range. 15583383_preliminary X-ray analysis of the coiled-coil domain of dystrophia myotonica kinase 15598648_DMPK phosphorylates phospholamban and regulates calcium uptake in cardiomyocyte sarcoplasmic reticulum 15722335_with DMPK in myotonic dystrophy cells, there may be a link between processing of the shRNA and nuclear import or a separate pathway for processing shRNAs in the nuclei 15824798_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15894391_Transfected into Saccharomyces cerevisiae overexpresses two forms of human DMPK, full-length (DMFL) and a C-terminal truncated form (DMTand affects growth and cell morphology. 15981568_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16099181_role in muscle differentiation by controlling the rearrangement of the cytoskeleton that takes place during elongation and fusion of myblasts into myotubes 16193250_Myotonic dystrophy is an autosomal dominant disease caused by a trinucleotide repeat-expansion, cytosine-thymine-guanine (CTG)n, in the 3' untranslated region of a gene encoding DMPK. 16519679_Our findings indicate that the coiled-coil domain modulates myotonic dystrophy protein kinase multimerization, substrate binding, kinase activity and subcellular localization characteristics. 16636244_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16946708_coordinated physical and functional interactions between hnRNP H, CUG-BP1 and MBNL1 dictate IR splicing in normal and DM1 myoblasts 17192963_It is important to use more than one linked polymorphic marker in PGD-PCR protocols to identify the DM1 mutation. 17204048_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17433680_Subjects who presented large CTG expansion in regions of the DMPK gene correlated with significant extensive cognitive deficits in intelligence scales. 17825047_the expanded CUG repeats in DMPK mRNA are blocking a stage in its export pathway that would normally occur at the speckle periphery 17846170_In DM1, DMPK mutant transcripts detach from the gene but accumulate in granules that abut but do not enter SC-35 domains, suggesting that RNA entry into the domain is blocked. 18184345_subcortical WMLs are correlated with focal dementia in classic DM1(CTG repeat expansion ) patients. 18228241_Further studies are warranted to elucidate the molecular etiology causing neurodevelopmental symptoms such as autism spectrum disorder and mental retardation in myotonic dystrophy type 1. 18474935_Mutation analysis revealed 2 copies of expansion mutation of 1260 and 60 cytosine-thymine-guanine repeats in the myotonic dystrophy protein kinase gene. 18574937_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18577525_Data show that an important instability of the CTG repeat CTG repeat in DMPK gene was detected during prolonged in vitro culture, showing stepwise increases of the repeat number in consecutive passages as well as a higher range of variability. 18611984_The length of the (CTG)n repetition located in the 3'UTR of the DM protein kinase gene (DMPK) is associated with the degree of splicing misregulation in myotonic dystrophy type 1. 18648326_In transgenic mice the respiratory impairment associated with DM-1 may be partially due to pathologic alterations in neuromuscular junctions and phrenic nerves. 18798829_DMPK Allelic frequencies in the Chilean sample studied were intermediate between those of the two ancestral populations (European and Pehuenche). 18798829_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19127114_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19166838_Altered splicing of Tau in DM1 is different from the fetal splicing process. 19309729_The crystal structure of the kinase domain of DMPK bound to the inhibitor bisindolylmaleimide VIII (BIM-8) revealed a dimeric enzyme associated by a conserved dimerization domain. 19514047_The identification of interruptions in the DMPK repeat has important consequences for molecular genetic testing where they can lead to false negative conclusions. 19626675_DMPK is a kinase with pronounced expression in diverse muscle and neural tissues that are affected in myotonic dystrophy type 1 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19946639_a tail-anchored myotonic dystrophy protein kinase isoform induces perinuclear clustering of mitochondria, autophagy, and apoptosis 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20228473_Steinert's disease caused by a dynamic mutation of (CTG) trinucleotide repeats in the 3' untranslated region of the myotonic dystrophy protein kinase gene (DMPK). 20231114_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20346670_This study showedthat an abnormal activation of the proteolytic Fbox32/ubiquitin-proteasome pathway may contribute to muscle atrophy in these mice and could be involved in the progressive muscle loss observed in the myotonic dystrophy type 1 patients. 20421627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20635151_analysis of CTG repeats at the DMPK gene in myotonic dystrophy patients and healthy individuals from the Mexican population 20644219_Methylation of the CpG sites in DMPK locus does not correlate with CTG expansion size or with the congenital form of the disease. The size range of the repeat expansions with methylation was from as small as 300 to as large as 2800 repeats. 20685272_An aberrant MTMR1 expression and signs of altered myofiber maturation were documented in DM1. There was more severe dysregulation of MTMR1 expression in DM1. 20801043_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20801043_Only seven typical patients with myotonic dystrophy from six unrelated families were identified, all with large pathological CTG repeat expansions (> 400 repeats) in the DMPK gene 21204525_NMR spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulation show that the 5'CUG/3'GUC motif found in DM1 RNAs is dynamic. 21760538_The results of this study suggested that peripheral neuropathy can be linked to a large CTG expansion and a severe form of DM1. 21949239_reduced DMPK may contribute to NE instability, a common mechanism of skeletal muscle wasting in muscular dystrophies. 22354993_In the DMPK/SIX5 locus, the presence of two potential replication origins presents an opportunity to screen for trans-acting second-site genes and therapeutic agents affecting chromatin structure, DNA replication, and trinucleotide repeats stability 23196502_This work may shed light on the alteration of this class of non-coding RNA as an additional molecular mechanisms involved in DM1 pathophysiology. 23209425_These data demonstrate that the human DM1 locus carrying very large expansions induced a variety of molecular and physiological defects in transgenic mice, reflecting DM1 to a certain extent. 23263591_The results of this study supported the conclusion that different patterns of CCG interruptions within the CTG array could modulate the DM1 clinical phenotype, variably affecting the mutational dynamics of the variant repeat. 23680132_DMPK alleles in the samples cover four of five DM1 clinical categories: normal (5 to 34 repeats), mild (50 to 100 repeats), classical (101 to 1000 repeats), and congenital (>1000 repeats 23933738_The mismatch repair components MSH2, MSH3 and MSH6 were highly expressed in iPSCs compared with fibroblasts, and only occupied the DMPK1 gene harboring longer CTG.CAG triplet repeats 24136222_Together with HK II and Src, mitochondrial DMPK is part of a multimolecular complex endowed with antioxidant and pro-survival properties. 24139022_This study demonstrates the feasibility of carrying out longitudinal in vivo studies of muscle function over several months in a mouse model of myotonic dystrophy confirming the feasibility of this method to test preclinical therapeutics. 24274137_In conclusion, our data suggest that the frequency of DMPK mutation carriers and the prevalence of DM1 in the Korean population might be higher than those reported in other ethnicities. Supporting 24417793_This study found a correlation between CTG expansion and age of onset, temporalis wasting and mental disability. 24792155_The results show that a DEAD-box helicase, DDX6, interacts with CUG-expanded DMPK-mRNA in primary fibroblasts from dystrophia myotonica type 1 patients. 25702800_that genome modification may be used to generate genetically modified progenitor cells as a first step toward autologous cell transfer therapy for Myotonic dystrophy type 1 26214024_This study supports the idea that genetic abnormalities in DM1mainly target the white matter, but gray matter involvement is also crucial in determining the clinical characteristics of myotonic dystrophy type 1. 26304544_miR-206 and miR-148a regulate the DMPK transcript and may functionally cooperate. 26310035_Three SNP loci (rs915915, rs1799894, and rs10415988) associated with a high chance of myotonic dystrophy in Yakut population. 26339785_Sense DMPK RNA foci clearly co-localize with MBNL1 and MBNL2 proteins and accumulate in myotonic dystrophy 1 tissues during development. 26756355_Study shows DMPK expression with a complex pattern of tissue-specific epigenetics consistent with evidence that normal tissue require careful regulation of its RNA and protein levels which might include cis-acting regulatory elements in neighboring genes. 27330968_The patients with DM1 nucleotide expansion (CTG) mutation showed widespread abnormalities of all DTI parameters in the white matter, which were associated with reduced gray matter volume in all brain lobes and thinning in parieto-temporo-occipital cortices. 27876818_Analysis of five intergenerational transmissions revealed a substantial intrafamilial stability of the DM1 mutation among relatives. 27991661_Interruptions within the DMPK expanded alleles could also interfere with the chromatin structure, the transcriptional activity of the Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) locus and the interaction with RNA CUG-binding proteins 28257691_Methylation upstream of the expanded DMPK CTG repeat occurs exclusively with maternal transmission and that it is somehow linked to the development of congenital myotonic dystrophy. 28363916_(CTG)>18 frequency of 3.60%, 1.57% and 4.00% in the Malay, Chinese and Indian subpopulations of Malaysia were discovered. 28376341_A second point is that DM mutations, although located in noncoding regions, may reduce the expression of mutant alleles, raising questions whether loss-of-function may contribute to the phenotype, or possibly impose a safety limit on knockdown therapies that create or aggravate a DMPK or CNBP deficiency state 28435090_findings thus suggest that nuclear retention may be a common feature of regulation of DMPK RNA expression. The typical forced nuclear residence of expanded DMPK transcripts affects this regulation in tissues of DM1 patients, but not through hyperadenylation. 28617590_Data, including data from studies on synthetic RNA modeling RNA repeat expansions found in patients with Huntington's disease (mRNA for exon 1 of Huntingtin protein) and myotonic dystrophy type 1 (mRNA for 3prime untranslated region of dystrophia myotonica-protein kinase), suggest internal loops of r(3xCAG) are stabilized by one-hydrogen bond AA pairs, while those of r(3xCUG) prefer one- or two-hydrogen bond UU pairs. 28886202_Our work suggests that DM1 patients are at risk for Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy (FECD). DMPK mutations contribute to the genetic burden of FECD but are uncommon. We establish a connection between two repeat expansion disorders converging upon RNA-MBNL1 foci and FECD. 28942489_Variant repeats might explain a part of the phenotypic variability in a small percent of myotonic dystrophy type 1 patients and likely display a stabilizing effect on the meiotic instability of DMPK expanded alleles 29029879_Patients with myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) may have a slight decrease in renal function that cannot be explained by a higher occurrence of risk factors for renal failure such as diabetes, hypertension or age. In addition, there was no correlation between CTG repeats, a marker of disease severity, and renal function. 29054426_Haplotype analysis using various polymorphic-markers in proximity to DMPK gene indicates that a single founder mutation originates myotonic dystrophy type 1 in Mexico; however, Y-STR haplogroups data and the presence of pre-mutated and large normal alleles in Amerindians support the hypothesis that both European and Amerindian ancestral chromosomes might have introduced the disease to the Mexican population. 29651162_The abnormal expansion of CTG repeats in the 3'-UTR of the DMPK gene elicits Myotonic Dystrophy 1, whereas elongated CCTG repeats in intron 1 of ZNF9 triggers Myotonic Dystrophy 2. 29771332_We have developed an inducible, skeletal muscle-specific mouse model of DM1 (CUG960) that expresses 960 CUG repeat-expressing animals (CUG960) in the context of human DMPK exons 11-15. 30094526_The motor function (MRCSS and 6MWT) and CTG repeat length of DMPK significantly correlated with LV diastolic dysfunction in patients with myotonic dystrophy type 1. 30274788_paired gRNA-CRISPR/Cas9 caused frequent inversion of expanded CTG repeats at the Dystrophia Myotonica protein kinase(DMPK) locus, and this approachwas not suitable for in vivo therapeutic genome editing. 30700578_Expanded CUG repeats in DMPK transcripts adopt diverse hairpin conformations without influencing the structure of the flanking sequences. 31164682_Robust and accurate detection and sizing of repeats within the DMPK gene using a novel TP-PCR test. 31220271_Allele length of the DMPK CTG repeat is a predictor of progressive myotonic dystrophy type 1 phenotypes. 31480541_These results suggest the existence of p53-p73-DMPK axis which mediates DNA-damage induced actomyosin contraction at the cortex and concomitant cell death. 31608518_A DM1 family with interruptions associated with atypical symptoms and late onset but not with a milder phenotype. 31936870_DM1 Phenotype Variability and Triplet Repeat Instability: Challenges in the Development of New Therapies. 33301350_DNA methylation at the DMPK gene locus is associated with cognitive functions in myotonic dystrophy type 1. 33497365_Reversible cardiac disease features in an inducible CUG repeat RNA-expressing mouse model of myotonic dystrophy. 34776509_DMPK hypermethylation in sperm cells of myotonic dystrophy type 1 patients. 35054778_DM1 Transgenic Mice Exhibit Abnormal Neurotransmitter Homeostasis and Synaptic Plasticity in Association with RNA Foci and Mis-Splicing in the Hippocampus. 35741732_High Resolution Analysis of DMPK Hypermethylation and Repeat Interruptions in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1. | ENSMUSG00000030409 | Dmpk | 196.735297 | 0.473241804 | -1.079351 | 0.23977108 | 19.904106 | 0.0000081425262805721334934518432224770378979883389547467231750488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001105802501093621371258679531024426978547126054763793945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 126.8852799 | 18.3347431 | 269.7152884 | 37.8437271 | |
| ENSG00000105419 | 56917 | MEIS3 | protein_coding | Q99687 | FUNCTION: Transcriptional regulator which directly modulates PDPK1 expression, thus promoting survival of pancreatic beta-cells. Also regulates expression of NDFIP1, BNIP3, and CCNG1. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97368}. | Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a homeobox protein and probable transcriptional regulator. The orthologous protein in mouse controls expression of 3-phosphoinositide dependent protein kinase 1, which promotes survival of pancreatic beta-cells. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. | hsa:56917; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; brain development [GO:0007420]; embryonic pattern specification [GO:0009880]; eye development [GO:0001654]; negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001234]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 20553494_This work suggests that the transcriptional activity of all members of the Meis/Prep Hth protein family is subject to autoinhibition by their Hth domains, and that the Meis3.2 splice variant encodes a protein that bypasses this autoinhibitory effect. 26354419_Findings support a model in which Meis3 is required for neural crest proliferation, migration into, and colonization of the gut such that its loss leads to severe defects in enteric nervous system development. 33376716_Inhibition of MEIS3 Generates Cetuximab Resistance through c-Met and Akt. | ENSMUSG00000041420 | Meis3 | 33.135769 | 0.486704308 | -1.038883 | 0.33798894 | 9.349366 | 0.0022306257599817832029676090144221234368160367012023925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0148787107607790472507680590297240996733307838439941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 20.7378773 | 5.3689627 | 42.7478924 | 10.6797470 | |
| ENSG00000105877 | 8701 | DNAH11 | protein_coding | Q96DT5 | FUNCTION: Force generating protein of respiratory cilia. Produces force towards the minus ends of microtubules. Dynein has ATPase activity; the force-producing power stroke is thought to occur on release of ADP. | ATP-binding;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Dynein;Kartagener syndrome;Microtubule;Motor protein;Nucleotide-binding;Primary ciliary dyskinesia;Reference proteome;Repeat | This gene encodes a ciliary outer dynein arm protein and is a member of the dynein heavy chain family. It is a microtubule-dependent motor ATPase and has been reported to be involved in the movement of respiratory cilia. Mutations in this gene have been implicated in causing Kartagener Syndrome (a combination of situs inversus totalis and Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia (PCD), also called Immotile Cilia Syndrome 1 (ICS1)) and male sterility. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2013]. | hsa:8701; | 9+0 motile cilium [GO:0097728]; 9+2 motile cilium [GO:0097729]; axoneme [GO:0005930]; dynein complex [GO:0030286]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; motile cilium [GO:0031514]; proximal portion of axoneme [GO:0120134]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; dynein intermediate chain binding [GO:0045505]; dynein light intermediate chain binding [GO:0051959]; minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity [GO:0008569]; cardiac septum morphogenesis [GO:0060411]; cilium movement [GO:0003341]; determination of left/right asymmetry in nervous system [GO:0035545]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; epithelial cilium movement involved in determination of left/right asymmetry [GO:0060287]; flagellated sperm motility [GO:0030317]; learning or memory [GO:0007611]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018]; protein localization to motile cilium [GO:0120229]; regulation of cilium beat frequency [GO:0003356] | 12142464_mutations in the DNAH11 gene cause one form of situs inversus totalis and most likely primary ciliary dyskinesia 15304525_Dynein plays an unexpected role in the regulation of mitochondrial morphology in living cells, by controlling the recruitment of Drp1 to these organelles. 15375157_a specific requirement for p150(Glued)/dynein/functional microtubules in activation of MKK3/6 and p38 MAPKs in vivo. 18022865_These findings support the view that DNAH11 mutations indeed cause Primary ciliary dyskinesia and Kartagener syndrome, and that the reported DNAH11 nonsense mutations are associated with a normal axonemal ultrastructure. 18492703_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19060911_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19410201_Two 'major' genes, DNAI1 and DNAH5, underlie PCD in nearly half of the patients with ODA defects 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20513915_mutations: splice site in acceptor splice site of exon 5 and nonsense mutation located in exon 23 for DNAH11 in primary ciliary dyskinesia 22184204_Mutations in DNAH11 are a common cause of PCD in patients without ciliary ultrastructural defects; thus, genetic analysis can be used to ascertain the diagnosis of PCD in this challenging group of patients. 26729821_In an epithelial cell line engineered to contain the DNAH11 target site, TALENs cleaved over 80% of the mutated DNAH11 sequence and replaced the mutated sequence with wild-type sequence in about 50% of cells. This study demonstrates that gene editing can rescue ciliary beating ex vivo, opening up new avenues for treating Primary ciliary dyskinesia. 26909801_DNAH11 mutations result in a subtle outer dynein arm defect in only the proximal region of respiratory cilia. 27340223_Dnah11(avc)(4) did not disrupt SHF Hh signaling and caused Atrioventricular septal defects (AVSDs) only concurrently with heterotaxy, a left/right axis abnormality. In contrast, Mks1(avc)(6) disrupted SHF Hh signaling and caused AVSDs without heterotaxy.We speculate that cilia gene mutations contribute to both syndromic and non-syndromic AVSDs in humans 29467202_DNAH11 mutations result in a characteristic abnormality of the ciliary ultrastructure detectable by electron tomography, but not traditional transmission electron microscopy 31040315_DNAH11 variants and its association with congenital heart disease and heterotaxy syndrome. 31053115_study demonstrated that the polymorphisms rs2494938 at 6p21.1 and rs2285947 at 7p15.3 may serve as independent prognostic biomarkers for ESCC, implying the potential biological role of their related genes (LRFN2 and DNAH11) in the process of ESCC development 31160482_The variant c.9484-1 G>T was confirmed as a novel virulence variant which was predicted to affect splicing by Human Splicing Finder 3.1. And c.12428 T>C was predicted to be mildly pathogenic in silico analysis. We found that DNAH11 polymorphisms display strong associations with asthenozoospermia, and may contribute to an increased risk of male infertility in Chinese patients. 31605628_The rs2285947 variant of DNAH11 was found to be significantly associated with both ovarian and breast cancers in a cohort of women in India. 32357925_We identified two rare nonsynonymous variants in the dynein axonemal heavy chain 5 gene (DNAH5): a previously reported variant c.7502G > C; p.(R2501P), and a novel variant c.12043 T > G; p.(Y4015D). . Individual 2 had non-syndromic SI and DD. In individual 2, one rare variant (c.9110A > G;p.(H3037R)) in the dynein axonemal heavy chain 11 gene (DNAH11), coding for another component of the outer dynein arm, was identified. 33243178_Two novel mutations in the DNAH11 gene in primary ciliary dyskinesia (CILD7) with considerable variety in the clinical and beating cilia phenotype. 34133440_DNAH11 compound heterozygous variants cause heterotaxy and congenital heart disease. 34405951_Identification of compound heterozygous DNAH11 variants in a Han-Chinese family with primary ciliary dyskinesia. 36140829_Clustering of Genetic Anomalies of Cilia Outer Dynein Arm and Central Apparatus in Patients with Transposition of the Great Arteries. | ENSMUSG00000018581 | Dnah11 | 15.866826 | 3.907959500 | 1.966416 | 0.62773180 | 8.802564 | 0.0030080758291444859540975098610715576796792447566986083984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0188770590839269052085835909338129567913711071014404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 25.1824470 | 14.5779226 | 7.1622803 | 4.1912779 | |
| ENSG00000106415 | 113263 | GLCCI1 | protein_coding | Q86VQ1 | Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a protein of unknown function. Expression of this gene is induced by glucocorticoids and may be an early marker for glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in this gene are associated with a decreased response to inhaled glucocorticoids in asthmatic patients. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. | hsa:113263; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737] | 21991891_A functional GLCCI1 variant is associated with substantial decrements in the response to inhaled glucocorticoids in patients with asthma. 22304573_Variation at GLCCI1 and FCER2 could lead personalized asthma treatment. 22660954_GLCCI1 nucleotide polymorphisms associated with steroid-responsiveness in asthmatic patients are unlikely to have a clinically actionable impact in pediatric nephrotic syndrome. 22796022_Studied the influence of GLCCI1 SNP rs37972 on dexamethasone efficacy in bacterial meningitis patients.Results show rs37972 in GLCCI1 is associated with death in patients with CA bacterial meningitis treated with adjunctive dexamethasone therapy. 23836780_Novel association was found between intraocular pressure and a common variant at 7p21 near to GLCCI1 and ICA1. 24131825_GLCCI1 rs37973 does not influence treatment response to inhaled corticosteroids in white subjects with asthma. 24673601_GLCCI1 variant accelerates pulmonary function decline in patients with asthma receiving inhaled corticosteroids. 24897287_GLCCI1 rs37972 T allele was not significantly associated with an increased risk of oral corticosteroid use. 25134782_the minor alleles 'T' and 'G' of rs37972 and rs37973 SNPs, respectively, were not significantly associated with increased asthma risk in asthma patients from Saudi Arabia 25724472_Carriers of the GLCCI1-C allele had lower levels of baseline rheumatoid arthritis disease activity, suggesting a role for the GLCCI1 gene in regulation of glucocorticoid sensitivity to endogenously produced cortisol. 25843653_Carriers of the rs41423247 GLCCI1 polymorphism had a higher probability of responding to glucocorticoids, whereas all other polymorphisms did not affect the likelihood of response to treatment of graft-versus-host disease patients. 27133712_GLCCI1 variations may affect inhaled corticosteroid response by modulating GLCCI1 expression. 28488322_A worsening of pulmonary function caused by GLCCI1 variants could be prevented due to recently used medications based on new action mechanisms. 29224020_CC/CT genotype was significantly associated with post-transplant hypertension 29345236_this study found the GG genotype of GLCCI1 to be associated with better inhaled corticosteroids treatment response in asthma patients 29384926_The genetic variant rs37973 in GLCCI1 is associated with poorer clinical therapeutic response to inhaled glucocorticoids in a Chinese asthma population. 29981236_The GLCCI1 rs37973 variant is a risk factor for glucocorticoid resistance in Chinese patients with SAR who receive short-term intranasal corticosteroids treatment. one genotype of GLCCI1, rs37973, was significantly associated with the INCS response. The effective rate of the GG group was lower than those of the AA and AG groups (AA vs. GG: 73.7% vs. 51.6%, P=0.007; AG vs. GG: 78.8% vs. 51.6%, P=0.000). 30229311_GLCCI1 variant was associated with a significant decrease of the total lung capacity at 3 years after lung transplantation 30256538_The rs37973 polymorphism of GLCCI1 is related to postoperative recovery from chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) for individual sensitivity to glucocorticoids. Furthermore, AA genotype was associated with better treatment response in CRS. 30860871_GLCCI1 is a downstream molecule of the GC-GR cascade that acts as an antiapoptotic mediator in thymic T cells. Phosphorylated GLCCI1colocalized with microtubules in transfected cells. GR-dependent upregulation of GLCCI1 was proapoptotic in a cultured thymocyte cell line. Transgenic mice overexpressing human GLCCI1 had enlarged thymi with many thymocytes. GLCCI1 bound to both LC8 and PAK1. It reduced BIM expression. 31516081_GLCCI1 and STIP1 variants are associated with asthma susceptibility and inhaled corticosteroid response in a Tunisian population. 33208131_Effects of STIP1 and GLCCI1 polymorphisms on the risk of childhood asthma and inhaled corticosteroid response in Chinese asthmatic children. 33725570_Hsa_circ_001659 serves as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. 34529984_GLCCI1 gene body methylation in peripheral blood is associated with asthma and asthma severity. | ENSMUSG00000029638 | Glcci1 | 199.345690 | 2.061466950 | 1.043671 | 0.35749156 | 8.326668 | 0.0039067259452040771147696140985772217391058802604675292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0234334304223997487437447517777400207705795764923095703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 250.7992557 | 54.2672182 | 121.8312719 | 26.6202109 | ||
| ENSG00000107317 | 5730 | PTGDS | protein_coding | P41222 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the conversion of PGH2 to PGD2, a prostaglandin involved in smooth muscle contraction/relaxation and a potent inhibitor of platelet aggregation (PubMed:20667974). Involved in a variety of CNS functions, such as sedation, NREM sleep and PGE2-induced allodynia, and may have an anti-apoptotic role in oligodendrocytes. Binds small non-substrate lipophilic molecules, including biliverdin, bilirubin, retinal, retinoic acid and thyroid hormone, and may act as a scavenger for harmful hydrophobic molecules and as a secretory retinoid and thyroid hormone transporter. Possibly involved in development and maintenance of the blood-brain, blood-retina, blood-aqueous humor and blood-testis barrier. It is likely to play important roles in both maturation and maintenance of the central nervous system and male reproductive system (PubMed:20667974, PubMed:9475419). Involved in PLA2G3-dependent maturation of mast cells. PLA2G3 is secreted by immature mast cells and acts on nearby fibroblasts upstream to PTDGS to synthesize PGD2, which in turn promotes mast cell maturation and degranulation via PTGDR (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O09114, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20667974, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9475419}. | 3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Fatty acid biosynthesis;Fatty acid metabolism;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Isomerase;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Mast cell degranulation;Membrane;Nucleus;Prostaglandin biosynthesis;Prostaglandin metabolism;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transport | The protein encoded by this gene is a glutathione-independent prostaglandin D synthase that catalyzes the conversion of prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) to postaglandin D2 (PGD2). PGD2 functions as a neuromodulator as well as a trophic factor in the central nervous system. PGD2 is also involved in smooth muscle contraction/relaxation and is a potent inhibitor of platelet aggregation. This gene is preferentially expressed in brain. Studies with transgenic mice overexpressing this gene suggest that this gene may be also involved in the regulation of non-rapid eye movement sleep. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:5730; | endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; rough endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005791]; fatty acid binding [GO:0005504]; prostaglandin-D synthase activity [GO:0004667]; retinoid binding [GO:0005501]; small molecule binding [GO:0036094]; cyclooxygenase pathway [GO:0019371]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; mast cell degranulation [GO:0043303]; negative regulation of male germ cell proliferation [GO:2000255]; prostaglandin biosynthetic process [GO:0001516]; regulation of circadian sleep/wake cycle, sleep [GO:0045187]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384] | 11751991_Pronounced eosinophilia and Th2 cytokine release in human lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase transgenic mice 12900000_Study performed in patients with kidney function ranging from normal to advanced renal failure suggests that serum beta-trace protein is an indicator of impaired glomerular filtration rate. 15081423_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15325247_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15453544_The circadian lipocalin-type PGDS pattern and its suppression by total sleep deprivation indicate an interaction of the prostaglandin D system and human sleep regulation. 15718494_Shear stress induces l-PGDS expression by transcriptional activation through the AP-1 binding site. 17093043_Results show that the lipocalin-type prostaglandin D2 synthase (PGDS)/PGD2/prostaglandin D receptor (DP1R) system plays pivotal roles in the regulation of physiological sleep. 17230501_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17230501_Our data do not support the involvement of the PTGDS gene in the etiology of schizophrenia. 17307169_PGD2 synthetases, as well as receptors for PGD2, are described in testicular interstitial cells of men with spermatogenic damage and infertility. 17404210_Lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase/beta-trace is a major amyloid beta-chaperone in human cerebrospinal fluid and the disturbance of this function may be involved in the onset and progression of Alzheimer's disease. 17499437_expression of L-PGDS in degenerating neurons implies that L-PGDS functions as an early stress protein to protect against neuronal death in the hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy brain 17532558_The embryonic male prostaglandin D synthase (Pgds)/SOX9 pathway is expressed at both the RNA and protein levels in different types of human ovarian tumors. 17574780_L-PGDS gene expression in TE671 cells was activated by USF1 through the aE-box within intron 4 and cooperatively by AP-2beta in the promoter in a cell-type-specific manner. 17588556_Data confirm the potential of Beta-trace protein as an endogenous Glomerular Filtration Rate marker in children. 17852800_The cystatin C, beta2-microglobulin and beta-trace protein levels displayed changes with increased levels in the third trimester but unaltered levels during the first and second trimesters. 18077799_Thirteen different proteins with 3-NT modification were identified in the CSF of HIV Dementia patients. L-PGDS was the most abundant. 18349703_A single nucleotide polymorphism, rs3814500 (MspI site) ws found in the promoter region of the PTGDS gene among Chinese schizophrenic families. No association with schizophrenia was seen. 18436228_Lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase may have a role in coronary artery disease 18448869_Quantifying the prostaglandin-D-synthase/transthyretin complex in ventricular cerebrospinal fluid may be useful in the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease, possibly in its early stages. 18552976_Among gene transcripts elevated in depressed episodes were prostaglandin D synthetase (PTGDS) and prostaglandin D2 11-ketoreductase (AKR1C3), both involved in hibernation. We hypothesized them to account for some of the rapid cycling symptoms. 18802357_These results suggest that expression of DP and CRTH2 is associated with the pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis, and the expression of these receptors may be regulated by h-PGDS and PGD. 18817855_Enhancement of PGD2 production through COX-2 and LPGDS by USF1 in human brain-derived TE671 cells under serum starvation are reported. 18830622_Prostaglandin D synthase-mediated SOX-9 upregulation could provide a reasonable explanation for the presence of testicular differentiation in ovarian ovarian sex cord-stromal tumours. 19015601_an increase in serum L-PGDS concentration is associated with the progression of atherosclerosis 19094210_Lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase might have an important role in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19131342_Biochemical, functional, and pharmacological characterization of AT-56, an orally active and selective inhibitor of lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase. 19132521_CC16 did not inhibit eosinophil migration towards PGD(2). 19276290_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19598000_As the CSF is in contact with axons and mitochondria of the optic nerve, we postulate that a change in the concentration of CSF protein such as L-PGDS could exercise a harmful effect on these structures. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19949816_This beta-trace protein based formula was found to estimate GFR with reasonable precision 19958607_protein levels in nasal fluids can serve for diagnosis of cerebrospinal fluid leak 20008150_The expression of H-PGDS in human dendritic cells (DCs) and the regulatory mechanisms by which DCs produce prostaglandin D2, is demonstrated. 20144489_Using RT-PCR we demonstrated that L-PGDS gene expression decreased proportionately with tumor progression in lung cancer. 20403807_L-PGDS may fine-tune the retinoic acid signalling in melanocytes. 20596612_This study included 62 persons aged 18-30 years and cell phone exposure. EMF emissions may down-regulate the synthesis of beta-trace protein. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20667974_Met64 seems to function as a kinetic clamp, pushing the thiol group of Cys65 close to the site of nucleophilic attack during catalysis. 21104585_RBP-4, lipocalin-2 and L-PGDS do not regulate insulin sensitivity in healthy men. Rather their expression seemed to reflect inflammatory activity and were inversely correlated with alcohol intake and serum HDL levels. 21163901_Report the presence of L-PGDS in the COX-2-expressing cells in the mucosa of active ulcerative colitis patients in parallel with disease activity. 21192373_It may be feasible to test for perilymphatic fluid fistula using PTGDS in samples from the tympanic cavity. 21271676_Proteomic profiling of cerebrospinal fluid identifies prostaglandin D2 synthase as a putative biomarker for pediatric medulloblastoma. 21325722_Lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase is associated with coronary vasospasm and vasomotor reactivity in response to acetylcholine 21501068_Ascites and pleural effusion contain high concentrations of beta-TP that exceed the levels in corresponding plasma 21603615_two genes involved in cardiovascular diseases, ADORA1 and PTGDS, were differentially up-regulated in epicardial adipose tissue compared to mediastinal and subcutaneous adipose tissue 21745310_Beta-trace protein can be used as an alternative diagnostic tool to detect moderate or severe glomerular filtrate rate reduction in patients after liver transplantation. 22248185_these results demonstrate that L-PGDS protected against neuronal cell death by scavenging reactive oxygen species without losing its ligand-binding function 22299829_L-PGDS expression may contribute to the restricted proliferation of epidermal melanocytes, but conversely its overexpression may reflect the dysregulated proliferation of melanoma cells. 22342541_The DHEA metabolite 7beta-hydroxy-epiandrosterone exerts anti-estrogenic effects on breast cancer cell lines. 22370065_The gene coding for PTGDS was found to be more expressed in patients with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)relative to patients with bipolar disorder indicating a possible link with the differential etiology of ADHD. 22498882_Urinary PGDS, not ZA2G, may serve as a biomarker for active LN and upon validation in larger studies, may become the non-invasive test to evaluate the disease activity in future management of LN. 22664386_Delta(12)-PGJ(2) is a dominant metabolite of L-PGDS-produced PGD(2) during adipogenesis and acts as an activator for adipogenesis through both PPARgamma-dependent and -independent mechanisms 22677050_Data suggest that L-PGDS binds small lipophilic ligands with both high-affinity and low-affinity interactions; molecular models are proposed from studies that include binding of hemin, biliverdin, and bilirubin. 22745274_The serum level of beta-trace protein is an independent predictor of death and cardiovascular disease mortality in incident hemodialysis patients. 22818840_Elevated plasma level of beta-trace protein associated with all cause of death in patients with acute coronary syndrome. 22960220_Low PTGDS expression is associated with testis cancer. 22989106_no overall evidence of an association between wireless phone use and serum concentrations of beta-trace protein 23076868_The results we obtained from mice led to our investigation of PTGDS in 29 human cryptorchid patients but we failed to find any mutation that supported an involvement of this gene in human testicular descent. 23335043_betaTP, beta2M, CysC, and creatinine differ in their associations with demographic and clinical factors, suggesting variation in their non-glomerular filtration rate determinants. 23518194_All-cause and cardiovascular mortality are strongly associated with beta-trace protein marker levels and beta-microglobulin in a representative sample of US adults. 23526831_Structural and dynamic insights into substrate binding and catalysis of human lipocalin prostaglandin D synthase. 23698027_Among NSTE-ACS patients, BTP and CysC were superior to conventional renal parameters for predicting MB, and improved clinical stratification for hemorrhagic risk. 24438498_These data indicate that scalp is spatially programmed via mast cell prostaglandin D-synthase distribution in a manner reminiscent of the pattern seen in androgenetic alopecia. 24493589_Lipocalin-type prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) synthase (L-PGDS) interacts intracellularly with the G protein-coupled receptor DP1 in an agonist-independent manner. 24521203_involved in pathogenesis of androgenetic alopecia [review] 25005874_These results suggest that L-PGDS acted as a scavenger of biliverdin, which is a molecule not found in normal CSF. 25522430_PTGDS mRNA expression was down-regulated in rapid-cycling bipolar disorder patients in a euthymic, depressive, and manic/hypomanic state compared with healthy control subjects. 25964109_levels of L-PGDS in cervicovaginal secretions of pregnant women at different stages of parturition correlate with preterm birth. 25966493_Expression of MR and prostaglandin D2 synthase is strongly correlated in adipose tissues from obese patients. 26211517_Given that uPGDS levels fall after treatment of LN, uPGDS may be used to monitor the efficacy of therapy. It can also differentiate patients with active nephritis and active non renal lupus. 26431580_Hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase defines a proeosinophilic pathogenic effector human T(H)2 cell subpopulation with enhanced function 26800100_BTP and B2M levels are less affected than serum by amputation, and should be considered for future study of GFR estimation 26924065_Serum levels of beta trace protein and beta 2 microglobulin can be used to predict residual kidney function in hemodialysis patients. 27271931_Thus, our results suggest decreased NK cell-mediated eosinophil regulation, possibly through an increased level of PGD2, as a previously unrecognized link between PG dysregulation and eosinophilic inflammation in CRS. 27614217_The cut off value for betaTP in the diagnosis and follow-up of cerebrospinal fluid leaks should be modified depending on the type of secretion (sample type), for a better diagnostic accuracy 29124765_These observations suggest that tumor cell-derived inflammatory cytokines increase L-PGDS expression and subsequent PGD2 production in the tumor endothelial cells (ECs). This PGD2 acts as a negative regulator of the tumorigenic changes in tumor ECs. 29421771_Measurement of serum BTP can be a reliable tool for detecting kidney function in neonates. 29621631_High lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase expression is associated with Spontaneous intracranial hypotension. 29668081_Lipocalin-type PGD synthase is a novel phytocannabinoid-binding protein. 30393234_The expression levels of CDC20 and PTGDS were able to predict overall survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. 30720106_Prostaglandin D2 synthase 21 kDa (brain) (PTGDS) was found to be expressed at a significantly higher level in the tumors of highgrade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC) patients with a short diseasefree survival time. Inverse profile, with positivity for PTGDS product prostaglandin D2 strongly associated with an increase in diseasefree survival, the absence of relapse and sensitivity to platinumbased therapy. 30730082_Herein, we found that PTGDS is overexpressed in AGA. 30734298_that in the HCl-induced murine ALI model PGD2 was produced locally by inflamed endothelial and epithelial L-PGDS and this enhanced the endothelial barrier through the DP receptor 30996283_Galectin-3 and beta-trace protein concentrations are higher in clinically unaffected patients with Fabry disease. 31467325_Abundant neuroprotective chaperone Lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase (L-PGDS) disassembles the Amyloid-beta fibrils. 31575663_-type prostaglandin D synthase regulates the trafficking of the PGD2 DP1 receptor by interacting with the GTPase Rab4 31755786_Evidence for shrunken pore syndrome in children. 32334026_GGA3 interacts with L-type prostaglandin D synthase and regulates the recycling and signaling of the DP1 receptor for prostaglandin D2 in a Rab4-dependent mechanism. 32389118_COX and PTGDS Gene Expression Levels in PGD2 Synthesis Pathway are Correlated with miR-520 in Patients with Vessel Restenosis. 32851567_YAP promotes self-renewal of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting expression of L-PTGDS and PTGDR2. 33175978_Lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase levels increase in patients with narcolepsy and idiopathic hypersomnia. 34116656_SNX10 and PTGDS are associated with the progression and prognosis of cervical squamous cell carcinoma. 34743203_Glycoprotein PTGDS promotes tumorigenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by MYH9-mediated regulation of Wnt-beta-catenin-STAT3 signaling. | ENSMUSG00000015090 | Ptgds | 51.120604 | 0.496204467 | -1.010993 | 0.22575529 | 20.290554 | 0.0000066528213244281750722531817987537294811772881075739860534667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000923460851193139679480778592157719231181545183062553405761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 33.4642912 | 4.7131275 | 67.7470189 | 8.5233061 | |
| ENSG00000108679 | 3959 | LGALS3BP | protein_coding | Q08380 | FUNCTION: Promotes integrin-mediated cell adhesion. May stimulate host defense against viruses and tumor cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11146440, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8034587, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9501082}. | 3D-structure;Cell adhesion;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | The galectins are a family of beta-galactoside-binding proteins implicated in modulating cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions. LGALS3BP has been found elevated in the serum of patients with cancer and in those infected by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). It appears to be implicated in immune response associated with natural killer (NK) and lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cell cytotoxicity. Using fluorescence in situ hybridization the full length 90K cDNA has been localized to chromosome 17q25. The native protein binds specifically to a human macrophage-associated lectin known as Mac-2 and also binds galectin 1. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:3959; | blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; platelet dense granule lumen [GO:0031089]; scavenger receptor activity [GO:0005044]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 11867635_structural and functional properties of M2BP 11980646_Expression of 90K (Mac-2 BP) correlates with distant metastasis and predicts survival in stage I non-small cell lung cancer patients. 14758079_REVIEW: role in tumor progression and metastasis 15231701_90K plays an important role in the maintenance of an appropriate level of immune response. 16518858_a possible mechanism by which Tumor-associated antigen 90K may contribute to colon cancer progression is by modulating tumor cell adhesion to extracellular proteins, including galectin-3 17091455_There is no difference in Gal-3 expression in peripheral blood lymphocytes in patients with papillary thyroid cancer 17131321_Elevated Mac-2 binding protein is associated with distant metastasis and higher tumor stage in gastric cancer 17949550_serum galectin 3 binding protein (G3BP) levels were increased in Behcet's patients when compared with healthy controls and patients with inactive disease 18450743_galectin-3-binding protein as a factor secreted by neuroblastoma cells that stimulates the expression of interleukin-6 in bone marrow stromal cells and provides a novel function for this protein in cancer progression. 18490383_identified extracellular endosialin ligands and identified Mac-2 BP/90K as a specific interaction partner 18594176_EGF signal is critical for the Mac-2BP expression, and more importantly, STAT3 protein could work as a negative regulator, while human telomerase reverse transcriptase as a positive regulator in Mac-2BP transcription. 18646789_Mac-2 binding protein was found to be overexpressed in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) specimens and significantly elevated in the sera of OSCC patients compared to healthy controls 19017490_NGF induces Mac-2BP expression via the PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathway. 19153476_High serum 90K (median value >or=1,249.50 ng/ml) showed a significant association with stage III/IV, >or=2 extranodal involvements and risk of high/high-intermediate international prognostic index 19291534_the Mac-2 BP may play a role in the development and progression of mucinous ovarian tumours 19544526_Engineered enhancement of LGALS3BP expression in EWS cells resulted in inhibition of anchorage independent cell growth/reduction of cell migration and metastasis. Silencing of LGALS3BP expression reverted cell behavior with respect to in vitro parameters 20019050_Initial assessment showed that serum Mac-2BP is significantly elevated in patients with NET (neuroendocrine tumors) and is expressed by the majority of NET tissues. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20583127_Serum Mac-2BP does not appear to originate in the prostate and it is unlikely that Mac-2BP can be used for the differential diagnosis of prostate cancer versus benign prostatic hyperplasia. 21094132_These results suggest that galectin-3 binding protein may be a potential therapeutic target for treatment of, at least, colon cancer patients with high expression of galectin-3 binding protein. 21474793_serum changes of three glycoproteins, galectin-3 binding protein, insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3, and thrombospondin 1, was associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma 21515679_Mac-2BP was detected as a predominant DC-SIGN ligand expressed on some primary colorectal cancer tissues 21660451_LGALS3BP gene was expressed by neuroblatoma cell lines and patients' neuroblasts 22447108_results show that NF-kappaB regulated the expression of G3BP and that G3BP increased the adhesion of T47D breast cancer cells to fibronectin 22496229_Adeno-associated virus type 6 interacts with G3BP in human and dog sera but not in macaque serum. 22864925_LGALS3BP induces vascular endothelial growth factor in human breast cancer cells and promotes angiogenesis. 22970241_breast cancer cells express Mac-2BP as a novel E-selectin ligand, potentially revealing a new prognostic and therapeutic target for breast cancer 23184915_The expression of serum Mac-2 binding protein is a potential therapeutic target and biomarker for lung cancer. 23233740_MIR596 is frequently observed in oral squamous cell carcinoma and regulates expression of LGAL3BP. 23443559_LGALS3BP suppresses assembly of centriolar substructures. 23775887_Serum Mac-2 binding protein levels as a novel diagnostic biomarker for prediction of disease severity and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis 23830458_Recombinant 90K showed an apparent molecular weight of approximately 78kDa which was much smaller than that ( approximately 97kDa) of the natural 90K. It is suggested that recombinant 90K has small N-glycans with about half the molecular weight of N-glycans of natural 90K. 23899964_Studied levels of galectin-3 binding protein in milk from 247 HIV-infected Zambian mothers. Levels were higher in those mothers who transmitted HIV through breast-feeding. 24156545_Thus, 90K constitutes a novel antiviral factor that reduces the particle infectivity of HIV-1, involving interference with the maturation and incorporation of HIV-1 Env molecules into virions. 24302979_LGALS3BP is enriched in human ovarian carcinoma exosomes. 24362527_LGALS3BP-mediated integrin activation results into signal transmission via Akt, JNK and the Ras cascade via the Raf-ERK axis while p38 activity is kept at baseline levels 25013204_Gal-3BP levels in patients with haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome correlated with increased complement activation and with clinical variables reflecting the severity of acute hantavirus infection. 25320078_These findings suggest a novel immunoinhibitory function for LGALS3BP that might be important for immune evasion of tumor cells during cancer progression. 26070204_Post-Tx WFA+-M2BP (> 2.0 COI) is associated with the risk for development of HCC among patients with SVR. The WFA+-M2BP values could be a new predictor for HCC after SVR. 26124285_Results provide direct evidence for the involvement of CALU and LGALS3BP as potential negative regulators in the virus-triggered induction of the typeI interferons. 26168351_study elucidates the specificity of Gal-3BP interacting with galectin-1 and the role of Gal-3BP in cancer cell aggregation and metastasis 26219351_These results provide evidence that low expression of LGALS3BP participates in malignant progression of colorectal cancer. 26448934_90K/Mac-2BP correlated with the size of colorectal cancer. 26502662_findings may help clarify the molecular mechanism of the tumor-suppressive effect through down-regulation of LGALS3BP by miR-596 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma 26503549_three uniquely identified proteins (CDK6 , galectin-3-binding protein and LDH C) were found, which show tight connection with prostate cancer and presence of all of them was previously linked to certain aspects of prostate cancer 27176937_In this study, we addressed this question by analysing sLex expression together with two glycoproteins (BST-2 and LGALS3BP).Concomitant high expression of BST-2 with sLex defined a sub-group of patients with ER-negative tumours displaying higher risks of liver and brain metastasis and a 3-fold decreased survival rate 27240351_Results showed that in acute febrile phase, galectin-9 and galectin-3BP were induced in dengue patients compared to healthy controls suggesting that both molecules might be important inflammatory mediators in acute dengue virus infection. 27344370_serum M2BP may reflect silent atherosclerosis in apparently healthy subjects 27588936_the serum M2BP-adiponectin complex is elevated in men with coronary artery disease 27604950_M2BP inhibits both HIV-1 Env processing and virion production.M2BP traps HIV-1 Gag to vimentin filaments to inhibit the transportation of HIV-1 Gag to the plasma membrane. 27665173_Serum M2BP can be a useful biomarker for the diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and the prediction of disease progression since it potentially reflects altered pro-oncologic glycosylation enzymes 27668402_Our present results highlight the action of 90K on promoting degradation of mutant beta-catenin lacking the phosphorylation sites in the N-terminus. 28008658_WFA + -M2BP from hepatic stellate cells induces Mac-2 expression in Kupffer cells, which in turn activates hepatic stellate cells to be fi brogenic. 28336809_the combination of 17-AAG and PI3K/Akt inhibitor would effectively suppress acquired resistance to 17-AAG. In conclusion, targeting of LGALS3BP-mediated-specific survival signaling pathway in resistant cells may provide a novel therapeutic model for the cancer therapy. 28537900_A higher pre-treatment WFA+-M2BP level was associated with an increased risk of HCC development in patients with undetectable HBV DNA under NA therapy. 28731888_Elevated plasma M2BP levels might be predictive of unstable plaque and were associated independently with poor cardiovascular outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes. 28756229_The Mac-2BP may have a role in regulating the extracellular spreading and storage of the Wnts, thereby modulating their bioavailability and stability. 28811008_Serum Mac-2-binding protein expression predicts disease severity in chronic hepatitis C patients. 29207493_Results showed that 90K destabilizes E-cadherin and affects cell adhesion and invasion in subconfluent cancer cells via dissociation of the E-cadherin-p120-catenin complex, suggesting that 90K drives less confluent tumor cells into the early steps of cancer metastasis. 29233037_Serum M2BP might contribute to the inflammatory process in systemic lupus erythematosus. 29288305_M2BPGi is a very useful, easily applicable clinical indicator associated with hepatocellular carcinoma development in chronic hepatitis B patients virologically well controlled with nucleot(s)ide analogues therapy; higher levels of serum M2BPGi at 48 weeks was independent risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma development. 29318378_M2BPGi is a surrogate marker for assessing hepatic stellate cells (HSC) activation. These findings may reveal the roles of HSCs in extrahepatic fibrotic disease progression. [Review] 29679552_Data suggest that serum levels of RBP4 and LGAL3BP are up-regulated after menopause when complicated by NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease); RBP4 and LGAL3BP may serve as biomarkers of NAFLD in postmenopausal women. (RBP4 = retinol binding protein 4; LGAL3BP = galectin-3 binding protein) 29679592_that Multiple coagulation factor deficiency protein 2 promotes cancer metastasis by regulating lectin mannose binding 1 and level of galactoside-binding soluble 3 binding protein expression levels 29743357_Low LGALS3BP expression is associated with HIV infections. 29882603_Gal-3BP expression is induced in viral infection and by a multitude of molecules that either mimic or are characteristic for an ongoing inflammation and microbial infection. It belongs to the scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) domain-containing protein family, by virtue of its N-terminal SRCR domain. Review. 30101431_Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer is a novel liver fibrosis marker 30161179_In a large cohort of patients with the full spectrum of NAFLD, WFA+ -M2BP levels predicted the presence of advanced disease and correlated strongly with fibrosis stage. 30306612_Serum M2BPGi level significantly decreases after nucleoside analogue treatment in chronic hepatitis B patients. 30530049_M2BP is highly expressed in advanced carotid artery plaques and significantly correlated with clinical ischemic manifestations. 30585730_adhesion protein LGALS3BP was found to be significantly enriched in circulating EVs from a cohort of EC patients with a high risk of recurrence by targeted proteomics (multiple reaction monitoring), highlighting its potential in liquid biopsy in EC. 30775897_Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer (M2BPGi] might be able to detect liver fibrosis with great sensitivity 30786068_useful to identify high risk patients on antiviral treatment for subsequent hepatocellular carcinoma development 30848102_Results showed that LGALS3BP was upregulated at both RNA and protein levels in glioblastoma (GBM) tissue and generally associated with shorter overall survival (OS) in GBM patients. 30918432_High serum levels of Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer (M2BPGi) increased hepatocellular carcinoma risk by 4-5 folds. If M2BPGi is below the threshold (0.68 cut-off index), there is > 99% chance that the patient will not develop liver cancer in the subsequent 15 years. 31019124_Our results showed that serum Gal-3 and Gal-9 should not be considered biomarkers of inflammatory bowel disease. Despite not being a specific marker for Crohn's Disease, serum Gal-3BP might be used as an adjuvant biomarker for disease activity. 31302247_Increased LGALS3BP promotes proliferation and migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma via PI3K/AKT pathway. 31393964_Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2-binding protein had a good performance in distinguishing liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients. 31653515_Elevated serum M2BP levels reflects one of the contributors to the progression of silent atherosclerosis. 31681284_Stimulation of Mononuclear Cells Through Toll-Like Receptor 9 Induces Release of Microvesicles Expressing Double-Stranded DNA and Galectin 3-Binding Protein in an Interferon-alpha-Dependent Manner. 31752995_High Gal3BP levels were associated with female sex, increasing sCD163 and total cholesterol levels, and decreasing HDL-cholesterol levels in patients with type 1 diabetes. The prevalence of high Gal3BP was more than twice as high in the women as in the men. 31894262_The GALNT6LGALS3BP axis promotes breast cancer cell growth. 31996371_Galectin 3-binding protein suppresses amyloid-beta production by modulating beta-cleavage of amyloid precursor protein. 32221402_Investigating LGALS3BP/90 K glycoprotein in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neurological diseases. 32444247_Serum Mac-2-binding protein glycosylation isomer predicts esophagogastric varices in cirrhotic patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection treated with IFN-free direct-acting antiviral agent: M2BPGi levels predict varices in SVR patients. 32455631_Wisteria floribunda Agglutinin-Positive Mac-2 Binding Protein but not alpha-fetoprotein as a Long-Term Hepatocellular Carcinoma Predictor. 32550761_M2BPGi for assessing liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C treated with direct-acting antivirals. 32847841_Serum levels of mac-2 binding protein are associated with diabetic microangiopathy and macroangiopathy in people with type 2 diabetes. 33208911_Plasma exosomes from endometrial cancer patients contain LGALS3BP to promote endometrial cancer progression. 33247961_Serum Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer as a biomarker of fibrosis in living donor liver transplant graft. 33337998_Galectin-3-binding protein is a novel predictor of venous thromboembolism in systemic lupus erythematosus. 33354779_Microvesicles in active lupus nephritis show Toll-like receptor 9-dependent co-expression of galectin-3 binding protein and double-stranded DNA. 33686953_90K predicts the prognosis of glioma patients and enhances tumor lysate-pulsed DC vaccine for immunotherapy of GBM in vitro. 33910911_Serum galectin-3BP as a novel marker of obesity and metabolic syndrome in Chinese adolescents. 34052527_LGALS3BP/Gal-3 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. 34192302_N-glycan structures of Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac2 binding protein in the serum of patients with liver fibrosisdagger. 34565385_Role of galectin 3 binding protein in cancer progression: a potential novel therapeutic target. 34728600_Extracellular LGALS3BP regulates neural progenitor position and relates to human cortical complexity. 34858323_Association of Serum Galectin-3-Binding Protein and Metabolic Syndrome in a Chinese Adult Population. 34874835_Human herpesvirus infections and circulating microvesicles expressing galectin-3 binding protein in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. 34969731_Mac-2 Binding Protein Glycosylation Isomer as a Prognostic Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Sustained Virological Response. 35038949_Lectin galactoside-binding soluble 3 binding protein mediates methotrexate resistance in choriocarcinoma cell lines. 35346341_Urinary galectin-3 binding protein (G3BP) as a biomarker for disease activity and renal pathology characteristics in lupus nephritis. 35895036_LGALS3BP in Microglia Promotes Retinal Angiogenesis Through PI3K/AKT Pathway During Hypoxia. | ENSMUSG00000033880 | Lgals3bp | 81.504201 | 0.466088394 | -1.101325 | 0.23288165 | 22.175268 | 0.0000024885901770546624559227785050685710643847414758056402206420898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000382952688631910001613306571144335066492203623056411743164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 51.2543420 | 7.7735067 | 109.0691027 | 15.4078326 | |
| ENSG00000109107 | 230 | ALDOC | protein_coding | P09972 | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Glycolysis;Lyase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Schiff base | PATHWAY: Carbohydrate degradation; glycolysis; D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and glycerone phosphate from D-glucose: step 4/4. | This gene encodes a member of the class I fructose-biphosphate aldolase gene family. Expressed specifically in the hippocampus and Purkinje cells of the brain, the encoded protein is a glycolytic enzyme that catalyzes the reversible aldol cleavage of fructose-1,6-biphosphate and fructose 1-phosphate to dihydroxyacetone phosphate and either glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate or glyceraldehyde, respectively. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:230; | cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; cytoskeletal protein binding [GO:0008092]; fructose-bisphosphate aldolase activity [GO:0004332]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; fructose 1,6-bisphosphate metabolic process [GO:0030388]; fructose metabolic process [GO:0006000]; gluconeogenesis [GO:0006094]; glycolytic process [GO:0006096] | 15589842_Diverse ALDOC promoter regions are required to direct specific LacZ expression in the hippocampus and Purkinje cells if transgenic mice. 19034380_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the temporal lobe from patients with schizophrenia. 19110265_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19405953_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the Wernicke's Area from patients with schizophrenia. 19686046_Results identified fructose bisphospate aldolase C that showed elevated levels of protein carbonyls in inferior parietal lobule (IPL) from subjects with early stage-Alzheimer's disease. 20381070_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the anterior cingulate cortex in men patients with schizophrenia. 24525694_residues 85-102 harbor the epitope-containing region recognized by MAb 9F 24993527_ALDOC, Aldolase A (ALDOA) and Aldolase B (ALDOB) activate Wnt signaling. 30396920_NME1 enhanced ALDOC transcription, evidenced by increased expression of ALDOC pre-mRNA and activity of an ALDOC promoter-luciferase module. This is the first study to indicate that NME1 induces transcription through its direct binding to the promoter region of a target gene. 32502493_MUC16 C-terminal binding with ALDOC disrupts the ability of ALDOC to sense glucose and promotes gallbladder carcinoma growth. 33242559_EPB41 suppresses the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in non-small cell lung cancer by sponging ALDOC. 33274599_The melanoma brain metastatic microenvironment: aldolase C partakes in shaping the malignant phenotype of melanoma cells - a case of inter-tumor heterogeneity. 33664453_BCDIN3D RNA methyltransferase stimulates Aldolase C expression and glycolysis through let-7 microRNA in breast cancer cells. 34456184_Identification of 4-methylation driven genes based prognostic signature in thyroid cancer: an integrative analysis based on the methylmix algorithm. 35147255_Overexpression of aldolase, fructose-bisphosphate C and its association with spheroid formation in colorectal cancer. | ENSMUSG00000017390 | Aldoc | 18.136591 | 0.490443723 | -1.027840 | 0.35610333 | 8.447262 | 0.0036559335004437815662414745787600622861646115779876708984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0222441051779937448706903069250984117388725280761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 11.7150051 | 2.8212615 | 23.9502841 | 5.2309004 | |
| ENSG00000109158 | 2557 | GABRA4 | protein_coding | P48169 | FUNCTION: GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel. | 3D-structure;Cell membrane;Chloride;Chloride channel;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Ligand-gated ion channel;Membrane;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian brain where it acts at GABA-A receptors, which are ligand-gated chloride channels. Chloride conductance of these channels can be modulated by agents such as benzodiazepines that bind to the GABA-A receptor. At least 16 distinct subunits of GABA-A receptors have been identified. This gene encodes subunit alpha-4, which is involved in the etiology of autism and eventually increases autism risk through interaction with another subunit, gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor beta-1 (GABRB1). Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found in this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. | hsa:2557; | chloride channel complex [GO:0034707]; dendrite membrane [GO:0032590]; GABA-A receptor complex [GO:1902711]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynapse [GO:0098794]; postsynaptic specialization membrane [GO:0099634]; synapse [GO:0045202]; benzodiazepine receptor activity [GO:0008503]; excitatory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity [GO:0005231]; GABA-A receptor activity [GO:0004890]; GABA-gated chloride ion channel activity [GO:0022851]; inhibitory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity [GO:0005237]; neurotransmitter receptor activity [GO:0030594]; transmitter-gated ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential [GO:1904315]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; chloride transmembrane transport [GO:1902476]; gamma-aminobutyric acid signaling pathway [GO:0007214]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; nervous system process [GO:0050877]; regulation of membrane potential [GO:0042391]; regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential [GO:0060078]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; synaptic transmission, GABAergic [GO:0051932] | 12242096_truncated alpha 4 N-terminus may play a post-translational regulatory role in intracellular folding/glycosylation/assembly of the alpha 4 subunit 16080114_GABRA4 is involved in the etiology of autism and potentially increases autism risk through interaction with GABRB1. 16080114_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16770606_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16770606_These results confirmed our earlier findings, indicating GABRA4 and GABRB1 as genes contributing to autism susceptibility, extending the effect to multiple ethnic groups and suggesting seizures as a stratifying phenotype. 17124266_alpha4beta3gamma2L receptors have unique kinetic properties that limit the range of GABA applications to which they can respond maximally. 17135278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18334916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18482426_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19078961_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19207358_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19207358_Only two of the newly genotyped SNPs, rs10517173, rs16851647, were associated with nicotine dependence (observed P-values of 0.002, corrected FDR-BH P-values of 0.02). However, these SNPs were in complete LD with each other and with rs11731576. 19289452_Lower delta mRNA levels in schizophrenia might reflect a reduced number of alpha(1)beta(x)delta GABA(A) receptors that could contribute to deficient tonic inhibition and prefrontal cortical dysfunction in schizophrenia. 19736351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19874574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21422964_single nucleotide polymorphisms studied in the GABRA4, GABRE, and GABRQ genes are not related to the risk for familial ET. 22273344_Association between premenstrual symptom severity and two genes from the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) pathway: steroid-5-alpha-reductase, alpha polypeptide 1 (SRD5A1) and gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-4 (GABRA4). 23561058_The pathway by which GABRA2 initially confers risk for eventual alcohol problems begins with a predisposition to sensation-seeking early in adolescence. 24431441_Transgenic mice with the alpha4betadelta GABAA receptor subunit deletion show increased conditioned place preference, but not from delta-deficient or alpha4-deficient knockout mice. 24778259_The ability of neurosteroids to modulate the phosphorylation and membrane insertion of alpha4 subunit-containing GABAARs may underlie the profound effects these endogenous signaling molecules have on neuronal excitability and behavior. 26239769_GABRA4 is associated with autism spectrum disorder in a dataset from Argentina. 29135068_rs505474, rs1398175, and rs4868029 in the GABRA2, GABRA4, and GABRP genes, respectively, allele frequencies were significantly different between patients and controls.Four haplotypes were significantly associated with Bipolar Disorder TA and AG for rs3815762 and rs4868029 in GABRP, GG for rs11636988 and rs8024256 in GABRB3 and GAGG for rs2197414, rs4921195, rs13188991, and rs11956731 in GABRA6. 29151244_Study identified a rare noncoding sequence variants in gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor, alpha 4 subunit in autism spectrum disorder. GABRA4 rare variants in noncoding DNA may be variants of modest physiological effects in ASD etiology. 29299688_GABRA4 rs2229940 did not show association with migraine risk 29720720_These results suggest association between GABRR3 rs832032 polymorphism and the risk for restless legs syndrome , and a modifier effect of GABRA4 rs2229940 on the age of onset of restless legs syndrome . 31690811_Steady-state activation of the high-affinity isoform of the alpha4beta2delta GABAA receptor. 32028044_Further evidence of GABRA4 and TOP3B as autism susceptibility genes. 35152403_A de novo missense variant in GABRA4 alters receptor function in an epileptic and neurodevelopmental phenotype. | ENSMUSG00000029211 | Gabra4 | 70.550770 | 2.012067231 | 1.008679 | 0.36673085 | 7.347786 | 0.0067145405405649484509300606305259861983358860015869140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0362637038924411153617555214623280335217714309692382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 100.1296485 | 23.0307899 | 50.2965905 | 11.9261882 | |
| ENSG00000109339 | 5602 | MAPK10 | protein_coding | P53779 | FUNCTION: Serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in various processes such as neuronal proliferation, differentiation, migration and programmed cell death. Extracellular stimuli such as pro-inflammatory cytokines or physical stress stimulate the stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAP/JNK) signaling pathway. In this cascade, two dual specificity kinases MAP2K4/MKK4 and MAP2K7/MKK7 phosphorylate and activate MAPK10/JNK3. In turn, MAPK10/JNK3 phosphorylates a number of transcription factors, primarily components of AP-1 such as JUN and ATF2 and thus regulates AP-1 transcriptional activity. Plays regulatory roles in the signaling pathways during neuronal apoptosis. Phosphorylates the neuronal microtubule regulator STMN2. Acts in the regulation of the amyloid-beta precursor protein/APP signaling during neuronal differentiation by phosphorylating APP. Participates also in neurite growth in spiral ganglion neurons. Phosphorylates the CLOCK-BMAL1 heterodimer and plays a role in the photic regulation of the circadian clock (PubMed:22441692). Phosphorylates JUND and this phosphorylation is inhibited in the presence of MEN1 (PubMed:22327296). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11718727, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22327296, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22441692}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Biological rhythms;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Epilepsy;Intellectual disability;Kinase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the MAP kinase family. MAP kinases act as integration points for multiple biochemical signals, and thus are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes, such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. This kinase is specifically expressed in a subset of neurons in the nervous system, and is activated by threonine and tyrosine phosphorylation. Targeted deletion of this gene in mice suggests that it may have a role in stress-induced neuronal apoptosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. A recent study provided evidence for translational readthrough in this gene, and expression of an additional C-terminally extended isoform via the use of an alternative in-frame translation termination codon. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2017]. | hsa:5602; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; JUN kinase activity [GO:0004705]; MAP kinase activity [GO:0004707]; MAP kinase kinase activity [GO:0004708]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cellular senescence [GO:0090398]; Fc-epsilon receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038095]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of circadian rhythm [GO:0042752]; regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051090]; response to light stimulus [GO:0009416]; rhythmic process [GO:0048511]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 12436199_Shares a promoter region with the tightly linked gene encoding Fas-associated phosphatase-1. 16737965_interaction of free arrestins with JNK3 and Mdm2 and their ability to regulate subcellular localization of these proteins may play an important role in the survival of photoreceptors and other neurons 17680991_Arrestin in all conformations binds JNK3 comparably, whereas Mdm2 preferentially binds cone arrestin 'frozen' in the basal state. 18408005_JNK3 recruits MKK4 to the beta-arrestin-2 scaffold complex by binding to the MAPK docking domain (D-domain) located within the N terminus of MKK4. 19001375_the molecular interactions of arrestin2 and arrestin3 and their individual domains with the components of the two MAPK cascades, ASK1-MKK4-JNK3 and c-Raf-1-MEK1-ERK2 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20525557_JNK1, JNK2, and JNK3 are involved in P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 21041242_The results suggest the possible involvement of CaMKII and JNK3 in soman-induced long-term neurotoxicity. 21166945_results suggest that MAPK10 may have a proapoptotic function and could function as a tumor-suppressor gene in chromophobe renal cell carcinoma 21321401_[review] This review focuses on delineating the role of scaffold proteins, especially that of JNK3 as a target, on the regulation of JNK signaling in neurons. 22047447_Arrestin-3 acts as a 'true' scaffold, facilitating JNK3alpha2 phosphorylation by bringing it and MAP kinase kinase (MKK)4 together. 22523077_Silent scaffolds: inhibition OF c-Jun N-terminal kinase 3 activity in cell by dominant-negative arrestin-3 mutant. 23142346_Subtle structural mechanisms for allosteric signaling between the peptide-binding site and activation loop of human JNK3. 23329067_reduced JNK3 activity has potentially deleterious effects on neuronal function via altered regulation of a set of post-synaptic proteins. 24412749_Mitogen-activated protein kinase 10 JNK3 alpha (JNK3apha2)binds to both domains of arrestin-3. 24767251_miR-29b mRNA, MAPK10 protein expression, and ATG9A protein expression are closely related to chemosensitivity of ovarian carcinoma. 25025079_JNK3 is required for the antiapoptotic effects of exendin 4 25178256_analysis of the unique mechanisms by which JNK1beta1 is regulated 25455349_Study found that JNK3 levels are increased in brain tissue and CSF from patients with Alzheimer disease and CSF levels could reflect the rate of cognitive decline 25475894_Data indicate that tetra-substituted pyridinylimidazoles were designed as dual inhibitors of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) 3 and p38alpha mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase, and both kinases may be involved in the progression of Huntington's disease. 26868142_Peptide mini-scaffold facilitates JNK3 activation in cells. 28393229_Mapk10 expression was regulated by miR27a-3p in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Mapk10 gene was down-regulated in the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. 30591558_phosphorylation rate of JNK3 at Thr-221 by MKK7 is two orders of magnitude faster than the corresponding phosphorylation of Tyr-223 by MKK4 with or without arrestin-3 31080119_Structural mechanisms of the arrestin-3/JNK3 interactions have been reported. 31432180_the present study identified a novel significant association between the increased expression levels of MAPK10, TUBB2B and RASL11B, and neuroblastoma cells. 32040807_Identification and neuroprotective evaluation of a potential c-Jun N-terminal kinase 3 inhibitor through structure-based virtual screening and in-vitro assay. 32066630_MicroRNA-4516-mediated regulation of MAPK10 relies on 3' UTR cis-acting variants and contributes to the altered risk of Hirschsprung disease. 32468043_Propofol suppresses the progression of nonsmall cell lung cancer via downregulation of the miR215p/MAPK10 axis. 32572915_Circ_0000515 drives the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating MAPK10. 32998477_JNK3 as Therapeutic Target and Biomarker in Neurodegenerative and Neurodevelopmental Brain Diseases. 33774030_Genetic variants in MAPK10 modify renal cell carcinoma susceptibility and clinical outcomes. 34502556_The Roles of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) in Infectious Diseases. | ENSMUSG00000046709 | Mapk10 | 128.836925 | 0.469894546 | -1.089591 | 0.17582161 | 38.280277 | 0.0000000006127887973097699448176860675995339389210414537956239655613899230957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000162650658382714647004173156219150597756595288956305012106895446777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 80.2496969 | 15.9295289 | 171.1753491 | 33.2831271 | |
| ENSG00000109787 | 51274 | KLF3 | protein_coding | P57682 | FUNCTION: Binds to the CACCC box of erythroid cell-expressed genes. May play a role in hematopoiesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Activator;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Enables sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:51274; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cellular response to peptide [GO:1901653]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 15684403_The recruitment of CtBP and sumoylation are required for full repression by BKLF. 15937668_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21360637_KLF3 is an important regulator of several biological processes, including adipogenesis, erythropoiesis, and B cell development. (Review) 21470678_Low KLF3 is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 22003205_B cell differentiation is significantly impaired in the bone marrow, spleen, and peritoneal cavity of Klf3 null mice; the defects are cell autonomous. 23918807_A feedback loop consisting of microRNA 23a/27a and the beta-like globin suppressors KLF3 and SP1 regulates globin gene expression. 25979369_Among the mechanosensitive genes, the two transcription factors, HoxA5 and Klf3, contain cAMP-response-elements methylation of which could serve as a mechanosensitive master switch in gene expression in atherosclerosis. (Review) 26314219_Klf-3 expression is downregulated in human metastatic sarcomas, and Klf-3 levels negatively correlate with miR-182 expression. 28423541_Low KLF3 expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 30485570_These data demonstrate that miR-326/Sp1/KLF3 regulatory axis is involved in the development of lung cancer. miR-326 could bind to 3'UTR of Sp1 but not KLF3 and decreased the accumulation of Sp1, which further indirectly reduced KLF3 expression and inactivated JAK2/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways in vitro and in vivo. 31486564_bioinformatics analysis and in vitro experiments indicated that the role of KLF3 in lung cancer metastasis is dependent on the STAT3 signaling pathway. Overall, our data indicated the crucial function of KLF3 in lung cancer metastasis and suggested opportunities to improve the therapy of patients with lung cancer. 31646570_LncRNA NEAT1/miR-1224/KLF3 contributes to cell proliferation, apoptosis and invasion in lung cancer. 32101374_Expression of human Kruppel-like factor 3 in peripheral blood as a promising biomarker for acute leukemia. 33490232_Unravelling Structure, Localization, and Genetic Crosstalk of KLF3 in Human Breast Cancer. 33728488_microRNA-21-5p from M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles promotes the differentiation and activity of pancreatic cancer stem cells by mediating KLF3. 34407548_Hepatic Meteorin-like and Kruppel-like Factor 3 are Associated with Weight Loss and Liver Injury. 34937039_Exosome miR-23a-3p from Osteoblast Alleviates Spinal Cord Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Down-Regulating KLF3-Activated CCNL2 Transcription. 35311620_Fat mass and obesity associated (FTO)-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of Kruppel-like factor 3 (KLF3) promotes osteosarcoma progression. 35549815_Bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs)-derived exosomal microRNA-21-5p regulates Kruppel-like factor 3 (KLF3) to promote osteoblast proliferation in vitro. | ENSMUSG00000029178 | Klf3 | 200.319799 | 2.125907571 | 1.088079 | 0.11321008 | 93.191999 | 0.0000000000000000000004745958798540006379325818740347725633130487013402586810029148978173907380551099777221679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000000355007869914318715427357020802717016579344767573132233802815638235017559054540470242500305175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 269.3091832 | 17.1474961 | 127.2399059 | 8.9099398 | |
| ENSG00000110944 | 51561 | IL23A | protein_coding | Q9NPF7 | FUNCTION: Associates with IL12B to form the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-23 that plays different roles in innate and adaptive immunity (PubMed:11114383). Released by antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells or macrophages, binds to a heterodimeric receptor complex composed of IL12RB1 and IL23R to activate JAK2 and TYK2 which then phosphorylate the receptor to form a docking site leading to the phosphorylation of STAT3 and STAT4 (PubMed:32474165, PubMed:29287995, PubMed:33606986). This process leads to activation of several pathways including p38 MAPK or NF-kappa-B and promotes the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-17A/IL17A (PubMed:12023369). In turn, participates in the early and effective intracellular bacterial clearance (PubMed:32474165). Promotes the expansion and survival of T-helper 17 cells, a CD4-positive helper T-cell subset that produces IL-17, as well as other IL-17-producing cells (PubMed:17676044). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11114383, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12023369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16424222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17676044, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29287995, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32474165, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33606986}. | 3D-structure;Antiviral defense;Cytokine;Disulfide bond;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Tissue remodeling | This gene encodes a subunit of the heterodimeric cytokine interleukin 23 (IL23). IL23 is composed of this protein and the p40 subunit of interleukin 12 (IL12B). The receptor of IL23 is formed by the beta 1 subunit of IL12 (IL12RB1) and an IL23 specific subunit, IL23R. Both IL23 and IL12 can activate the transcription activator STAT4, and stimulate the production of interferon-gamma (IFNG). In contrast to IL12, which acts mainly on naive CD4(+) T cells, IL23 preferentially acts on memory CD4(+) T cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:51561; | endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; interleukin-23 complex [GO:0070743]; interleukin-23 receptor complex [GO:0072536]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; interleukin-23 receptor binding [GO:0045519]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032693]; positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation [GO:0042104]; positive regulation of activation of Janus kinase activity [GO:0010536]; positive regulation of defense response to virus by host [GO:0002230]; positive regulation of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production [GO:0032725]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032733]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032740]; positive regulation of memory T cell differentiation [GO:0043382]; positive regulation of natural killer cell activation [GO:0032816]; positive regulation of natural killer cell proliferation [GO:0032819]; positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090023]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of NK T cell activation [GO:0051135]; positive regulation of NK T cell proliferation [GO:0051142]; positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045672]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001916]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of T-helper 1 type immune response [GO:0002827]; positive regulation of T-helper 17 cell lineage commitment [GO:2000330]; positive regulation of T-helper 17 type immune response [GO:2000318]; positive regulation of tissue remodeling [GO:0034105]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042509]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098]; tissue remodeling [GO:0048771] | 12162874_Elevated expression of mRNA for IL-23(p19)was found in trigeminal ganglia of BALB/C mice infected with HSV-1 from early acute infection to the beginning of the latent phase. 12847224_In BALB/c mice, single chain (sc) IL-23-transduced CT26 cells grow progressively until day 26, then the tumors start to regress in most animals; scIL-23 transduction also significantly suppresses lung metastases of CT26 and B16F1 tumor cells. 14707118_IL-23 plays a more dominant role than IL-12 in psoriasis, a Th1 type of human inflammatory disease. 15070757_Macrophages produce neither IL-23 nor IL-12 but predominantly secrete IL-10. 15583831_IL-23 p19 mRNA is inducible in colonic myofibroblasts by IL-1beta and Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha 15731058_synthesis induced by Bordetella pertussis in monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MDDC) 16300465_This overview provides the historical background and current understanding of the roles of IL-12, IL-23, and T-helper type 1 (TH1) cell development in inflammation and autoimmunity. 16339539_IL-23 plays an important role in the FasL-induced IL-17 production. 16424222_Augmented expression of IL-23 by keratinocytes and cutaneous antigen-presenting cells may contribute to the perpetuation of inflammatory lesions in psoriatic skin. 16670765_IL-23 and IL-17 have roles in inflammation [commentary] 16751425_An abnormal type-1 T helper (Th1) cell bias exists related to IL-23-expressing dendritic cells from multiple sclerosis (MS) patients, which may play an important role in the pathogenesis of human autoimmune diseases such as MS. 16772281_Increased concentrations of p40 subunit of IL-23 in follicles containing oocytes suggest an important role of this cytokine in reproduction. 17007011_This review summarizes information on the expression and role of IL-12 both in patients with Crohn's diease and experimental models of colitis, thus emphasizing differences between IL-12 and IL-23 activity on the development of intestinal inflammation. 17021762_Abnormal IL-23 expression may play a role in the pathogenesis and progression of mycosis fungoides to Sezary syndrome. 17182554_c-Rel controls IL-23 p19 gene expression through two kappaB sites in the p19 promoter, and propose a c-Rel-dependent enhanceosome model for p19 gene activation. 17187052_IL-22 is preferentially produced by T(H)17 cells and mediates the acanthosis induced by IL-23 17236132_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17564777_mRNA levels of IL23 subunit p19 in active SLE patients was significantly higher compared with those in the inactive SLE patients 17606463_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17763202_Upregulated IL-23p19 in synovial fluid may be involved in joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. 17945537_results here show that IL-23 is elevated in children with malarial anemia, and that IL-10 and IL-12 appear to have important regulatory effects on IL-23 production during childhood malaria 18054783_Data suggest that the p38 MAP kinase and NF-kappaB signaling pathways play an important role in regulation of IL-23p19 expression on human microglia, and are thus potential therapeutic targets in the treatment of MS. 18180107_These data indicate that IL23R represents a novel shared susceptibility gene as its association with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) has recently been verified. 18190588_an increased expression of IL-12 p40, IL-12 p35 and IL-23 p19 mRNA was observed in bone marrow mononuclear cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with aplastic anemia compared with the corresponding one in normal controls. 18311793_Immunohistochemical stainings of submandibular glands from C57BL/6.NOD-Aec1Aec2 mice and of salivary gland biopsy specimens from Sjogren's syndrome patients revealed IL-17 and IL-23 staining within lymphocytic foci and epithelial tissues. 18319400_NK cells require in vivo priming with IL-12/23 to acquire their full spectrum of functional reactivity, while T cells are dependent upon IL-12/23 signals for the differentiation and/or the maintenance of CD56(+) effector memory T cells 18373953_The activated IL-23/IL-17 axis is important for the inflammatory immunity in systemic lupus erythematosus. 18408745_IL-23 stimulates survival and proliferation of Th17 cells and thus serves as a key master cytokine regulator for psoriasis 18490716_findings show that lactic acid secreted by tumor cells enhances the transcription of IL-23p19 and IL-23 production in monocytes/macrophages and in tumor-infiltrating immune cells that are stimulated with TLR2 and 4 ligands 18497880_intestinal macrophages expressing CD14 contribute to the pathogenesis of Crohn disease via IL-23/IFN-gamma axis 18579762_Levels of IL-23, IL-17, and IFN-gamma are elevated in Behcet disease(BD) with active uveitis. IL-23/IL-17 pathway together with IFN-gamma is associated with active intraocular inflammation in BD patients. 18606709_study demonstrates that oxidative stress induced by soluble cigarette smoke components potently inhibits the production of IL-12 and IL-23 by maturing dendritic cells 18680750_Data suggest that the structure of interleukin-23 reveals the molecular basis of p40 subunit sharing with interleukin-12. 18708069_Results describe the crystal structures of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-23 and its complex with a high-affinity neutralizing antibody. 18752933_Serum levels of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and IL-23p19 were higher in psoriatic arthritis patients than in rheumatoid arthritis patients. 18754016_Identification of potentially functional splice variants of IL23 receptor (IL-23R) will aid in understanding possible pathogenic mechanisms of IL-23R's contribution to disease susceptibility. 18786233_The role of the IL23/IL17 axis in bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung transplantation is reported. 18825388_The greatest upregulation of IL-23p19, Foxp3 and survivin mRNA was seen in colorectal carcinomas than normal mucosa. 19034457_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19040306_Significant associations between Arg381Gln SNP and haplotypes encoding this variant were noted in psoriatic arthritis 19088061_IL-23 in synergy with IL-18 elicits IFN-gamma production in NK T cells but not in NK cells; upregulates IL-18Ra and CD56 expression 19169254_Expanded catalog of genetic loci implicated in psoriasis susceptibility. 19169254_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19201028_Fibroblast-like synoviocytes are potently regulated by inflammatory cytokines to specifically express IL-23 p19. 19247658_IL-23 and IL-17 may play critical roles in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis and IL-23-stimulated production of IL-17 by PBMCs may be responsible for the development of AS. 19262574_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19264456_Bioactive forms of IL-12 and IL-23 are highly expressed in various DC and macrophage subsets and their marked in situ production suggest that both cytokines have crucial pathogenic role in psoriasis. 19322214_The IL-23/Th17 axis has a role in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis [review] 19333939_overexpression of IL-23, but not IL-17, is a pivotal feature of subclinical gut inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis 19426392_Association of the CagA status of Helicobacter pylori and serum levels of interleukin (IL)-17 and IL-23 in duodenal ulcer patients. 19431078_This review summarizes the critical role of the IL-23/IL-17 axis in progressing to chronic destructive arthritis, as well as the dominant cell type in arthritis development and pathology. 19479806_IL-23 and IL-17 are up-regulated during acute hepatic rejection after liver transplantation. 19542049_Synergistic production of IL-23 by dendritic cells derived from cord blood in response to costimulation with LPS and IL-12 is reported. 19542431_Evaluating IL-23 production by dendritic cells (DC) in conjunction with IL-12p70 subunit may be important to elucidate the exact nature of DCs ability to regulate the immune response. 19587005_binding of NKG2D to UL-16 binding protein (ULB)1 contributes to IL-23-dependent IL-17 production by CD4(+) cells in human M. tuberculosis infection. 19605880_these results suggest that the IL-23-induced Th17 pathway is stimulated in inflammatory periodontal lesions 19657406_Levels of IFNgamma, TNFalpha, IL-6, IL-15, IL-18, and IL-23 were increased (above healthy controls) in both affected and unaffected areas from Inflammatory Bowel Diseas. 19705136_genes encoding components of the IL23-mediated inflammatory pathway are important determinants of psoriasis pathogenesis across multiple racial groups. 19797506_Results desceibe the gene expression of interleukins-17A, -23, and -12 and determine the proximity of IL-17A- and IL-23-producing cells in rheumatoid synovial tissue. 19845828_In the most severely affected group of Huntington's disease patients there were increased blood levels of IL-23. 19900478_induces RANKL expression in synoviocytes of rheumatoid arthritis patients via STAT3 and NF-kappaB signal pathways 19915944_the concentration of soluble form of vascular endothelial cadherin and IL-23 are raised in sera of patients with Behcet's disease compared with healthy controls 19929695_interleukin 17 and interleukin 23 were statistically significantly decreased in tuberculin skin test(TST)-positive individuals, compared with TST-negative individuals 20027291_The IL-23 induced cytokines allow for the subsequent production of IL-12 and amplify the IFN-gamma production in the type-1 cytokine pathway. 20054003_Data show that that 4-trifluoromethyl-celecoxib can inhibit secretion but not transcription of IL-12 (p35/p40) and IL-23 (p40/p19 heterodimers), and that this is associated with HERP function in the endoplasmic reticulum. 20071030_CD40-triggering of immature and mature DC but not of primary monocytes induced a rapid expression of high levels of IL-23, free p40, and minor levels of IL-12. 20106535_higher expression in peripheral blood lymphocytes and decidua of recurrent spontaneous abortion patients 20154336_IL23A may have undergone positive selection pressure directed towards conservation, suggesting that functional genetic variants within IL23A will have a significant impact on the host immune response. 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20428758_IL-23 up-regulates the growth and cell proliferation of oral cancer by promoting the nuclear transactivation of RelA. 20603238_Data from a large patient cohort rather suggest that high intra-tumoral expression levels of p35 mRNA and p19 mRNA are associated with a superior clinical outcome. 20624950_Data indicate dendritic cells from TLR7(-/-) animals showed activated IL-23, and neutralization of IL-17 in the TLR7(-/-) resulted in a significant decrease in the mucogenic response in the lungs. 20682175_serum IL-23 levels are significantly elevated in colorectal carcinoma (CRC) vs. control patients and are strongly associated with overexpression of VEGF, thus they may play an important role in carcinogenesis of CRC 20682672_Data show that IL-17 levels are elevated in SLE patients with elevated serum IL-23 in patients with inflammatory manifestations, but lack of correlation between Th17, Th1, and Th2 cytokines suggested independent regulatory mechanisms for these cytokines. 20701979_results suggest a possible regulatory role for IL-23 in the menstrual cycle and in early pregnancy, although the extent and function of this role are yet to be determined 20840651_SAA is a significant inducer of IL-23 and IL-1beta in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synoviocytes and potentially activates the IL-23/IL-17 pathway in the RA synovium. 20873540_IL-23 may contribute to the chronic inflammation and airway remodelling in allergic rhinitis. 20886035_Beta-glucan exposure in the cell wall of fungi is essential for the generation of IL-23 producing dendritic cells and TH-17 immune responses. 20956338_our results identify a critical functional role for IL-23 in psoriasis 21116820_IL-21 and IL-23 levels are increased in the plasma of spondyloarthritis (SpA) patients compared with healthy volunteers, but not that of IL-17A; no evidence is found that the level of any of these cytokines reflects SpA activity. 21145044_semiquinone glucoside derivative dose dependent study showed approximately similar level of induction in IL-12p40, IL-12p35, IL-23p19 and RelA proteins expression at all tested concentration (30-90 microg/ml) compared to control 21145111_Human periodontal ligament fibroblasts are a target of Th17, and that IL-17 appears to up-regulate the expression of IL-23 p19 via a homeostatic mechanism involving Akt-, p38 MAPK-, and ERK 1/2-dependent NF-kappaB signalling versus the JNK/AP-1 pathway. 21161669_Our results indicate increased serum IL-23 levels in ankylosing spondylitis patients 21227898_Expression of IL-23p19 was increased significantly in inflamed mucosa of crohn Disease. 21231819_IL-17 and IL-23 levels are increased in early as compared to established disease providing evidence that IL-17/IL-23 may play a crucial role in autoimmune diseases. 21302302_This work investigated, for the first time, the role of IL-23 in colorectal cancer resection and chemotherapy, showing no correlation with the severity of disease, tumor removal, and chemotherapeutic treatment. 21387004_IL-23 was an essential cytokine in mediating Th17 cell development by IFN-induced dendritic cells. 21402701_IL-23 induction by beta-glucans is due to activation of c-Rel associated with Ser-10-histone H3 phosphorylation in the il23a promoter mediated by MAPK and SAPK or PKA, and inhibition of il12a transcription 21515794_Data show that deletion of TTP completely abolishes IFN-gamma-mediated p19 mRNA degradation. 21516111_Data show that IL-23 induced a positive feedback loop whereby GM-CSF secreted by T(H)17 cells stimulated the production of IL-23 by antigen-presenting cells. 21518507_The imbalance of T cell subsets in chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpurapatients is mainly associated with IL-12, but not with IL-23 and IL-17. 21531892_Data indicate that Th17 cells convert to Th1 cells through IL-17 induction of mucosal innate IL-12 and IL-23 production. 21547355_The IL-23/IL-23R pathway is a potential route to facilitate the malignant progression of cancers. 21560441_IL-23 and IL-17 participates in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis. IL-23 may play a critical role in the development of UC through inducing production of IL-17. 21576383_IL-23-responsive innate lymphoid cells are increased in inflammatory bowel disease 21623003_The IL23A and TNIP1 genes showed convincing evidence for association SNPs mapping to previously reported psoriasis loci show evidence for association to PSA. 21641076_IL-12 and IL-23 were found to be abundantly expressed by macrophages infiltrating papillary and reticular dermis of hidradenitis suppurativa lesional skin 21670317_Systemic IL-23 transgene exposure induces chronic arthritis, severe bone loss and myelopoiesis, which results in increased osteoclast differentiation and systemic bone loss. 21740501_Primary immunodeficiencies that impair interleukin-23 (IL-23)-dependent pathways are associated in humans with disseminated non-typhoidal Salmonella bloodstream infections (bacteraemia). 21747388_The individual contributions of these cytokines to specific pathologies require investigation and clinical evaluation of the role of IL-12- and IL-23-specific inhibitors. 21931205_IL-23 plays an important role in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis and is a marker of disease activity in these patients. 22003203_IL-23 and IL-1beta are identified as critical factors in the generation of egg antigen-specific transgenic T helper (Th)17 cells involved in the pathogenesis of severe schistosomiasis. 22127978_Patients with SLE display enhanced IL-23p19 expression as a result of hyperactivation of TBK-1, resulting in increased binding of IRF-3 to the promoter. 22144400_Since IL-23 is a maturation and growth factor for IL-17-producing cells, increased IL-23R expression may regulate the function of this putative pathogenic gamma-delta T cell population. 22174449_A new molecular mechanism for hepatitis B virus-induced IL-23 expression involves activation of the ERK/NF-kappaB pathway by hepatitis B x protein, leading to the transactivation of the IL-23 p19 and p40 promoters. 22177788_IL-23, a regulatory element that bridges the innate and adaptive arms of the immune system, might be involved in the inflammatory process observed in fetal abdominal aortic wall. 22209993_These data gives reason to believe there is an involvement of IL-23 in peripheral arterial disease. 22262980_These results demonstrate an involvement of IL-17/-23 system in the early primary Sjogren's syndrome pathogenesis. 22298331_study found a significant higher systemic IL-23 value in women with breast cancer compared to the control group; patients with shorter overall survival presented higher IL-23 values, suggesting a negative prognostic correlation 22417709_Production of IL-23 was increased in the peripheral mononuclear blood cells of primary Sjogren's syndrome patients compared to controls. 22505413_human IL-23 crystal belonged to space group P61 or P65, with unit-cell parameters a = b = 108.94, c = 83.79 A degrees , = 120 22559912_These data demonstrate that IL-23/IL-17 axis, stimulated independently of TGF-beta increase IL-17A gene polymorphism and antiphospholipid antibody production, might contribute to vascular manifestations of primary antiphospholipid syndrome. 22621182_IL-27 was found to be the only IL-12 family member that acts on antigen-presenting cells as a priming signal for IL-23. 22678234_IL-23 levels were higher in asthmatic than in healthy children (p 0.05). 27146815_High IL-23 expression is associated with polycystic ovary syndrome. 27155366_Interleukin 17A (Il17a) and interleukin-23 (IL-23) - dependent interleukin-17 Receptor C (IL-17RC) are expressed by sputum and neutrophils in deltaF508-CFTR protein (F508del) cystic fibrosis patients. 27240992_suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid significantly inhibited IL-12p40 and IL-23p19 mRNA synthesis and did not change IL-12p35 mRNA transcription. 27245439_An increase in CSF mean levels of IL-23 was observed in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. 27315572_TNF-alpha plays an important role for the autocrine stimulation of IL-23 production by 6-sulfo LacNAc(+) dendritic cells. 27343994_this study shows that double-negative T cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients are more expanded when stimulated in vitro with recombinant IL-23 than controls 27388654_Data show that the number of interleukin 17 (IL-17) positive cells significantly correlated positively with the number of interleukin-23 (IL-23) positive cells in skin 27400195_our results suggest that IL-39 induces differentiation and/or expansion of neutrophils in lupus-prone mice. 27515793_The expression of IL-17 and IL-12 in patients with lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei is reported in patients and healthy controls. 27551155_IL-23 released by keratinocytes in response to endogenous TLR4 ligands caus | ENSMUSG00000025383 | Il23a | 580.078077 | 0.302223944 | -1.726310 | 0.07020877 | 631.511473 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002344717214334076723963145890050106488195004737580289000 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001130962220486381531252149980962706158073485726658312226 | Yes | No | 264.8343831 | 41.3490477 | 880.3103210 | 135.4412955 | |
| ENSG00000111335 | 4939 | OAS2 | protein_coding | P29728 | FUNCTION: Interferon-induced, dsRNA-activated antiviral enzyme which plays a critical role in cellular innate antiviral response (PubMed:10464285, PubMed:9880569). Activated by detection of double stranded RNA (dsRNA): polymerizes higher oligomers of 2'-5'-oligoadenylates (2-5A) from ATP which then bind to the inactive monomeric form of ribonuclease L (RNASEL) leading to its dimerization and subsequent activation (PubMed:10464285, PubMed:9880569, PubMed:11682059). Activation of RNASEL leads to degradation of cellular as well as viral RNA, resulting in the inhibition of protein synthesis, thus terminating viral replication (PubMed:10464285, PubMed:9880569). Can mediate the antiviral effect via the classical RNASEL-dependent pathway or an alternative antiviral pathway independent of RNASEL (PubMed:21142819). In addition, it may also play a role in other cellular processes such as apoptosis, cell growth, differentiation and gene regulation (PubMed:21142819). May act as a negative regulator of lactation, stopping lactation in virally infected mammary gland lobules, thereby preventing transmission of viruses to neonates (By similarity). Non-infected lobules would not be affected, allowing efficient pup feeding during infection (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:E9Q9A9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10464285, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11682059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19923450, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9880569, ECO:0000303|PubMed:21142819}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Lipoprotein;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Myristate;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleotidyltransferase;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;Transferase | This gene encodes a member of the 2-5A synthetase family, essential proteins involved in the innate immune response to viral infection. The encoded protein is induced by interferons and uses adenosine triphosphate in 2'-specific nucleotidyl transfer reactions to synthesize 2',5'-oligoadenylates (2-5As). These molecules activate latent RNase L, which results in viral RNA degradation and the inhibition of viral replication. The three known members of this gene family are located in a cluster on chromosome 12. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:4939; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase activity [GO:0001730]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; interleukin-27-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070106]; negative regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045071]; nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process [GO:0006139]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; regulation of lactation [GO:1903487]; regulation of ribonuclease activity [GO:0060700]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; RNA catabolic process [GO:0006401]; type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060337] | 12447867_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16014697_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19559055_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19853919_2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase type 2 (OAS2), a dsRNA binding protein involved in the pathway that activates RNase-L, is identified as a new binding partner for NOD2. 20588308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21050126_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21050126_The data suggest a possible association between OAS2 and OAS3 single nucleotide polymorphisms and the outcome of tick-borne encephalitis virus infection in a Russian population. 23337612_The results suggest that OAS1-OAS3-OAS2 haplotypes are associated with differential susceptibility to clinical outcomes of dengue infection. 24328427_Primary mononuclear cells from patients with systemic sclerosis have increased basal levels of OASL and OAS2 genes. 24594345_Data obtained suggest that the OAS2 rs1293762 and CD209 rs2287886 SNPs are associated with predisposition to chronic hepatitis C in Russian population. 26595239_Suggest 2'5'-oligoadenylate synthetase 2 mediates T-cell receptor CD3-zeta chain down-regulation via caspase-3 activation in oral cancer. 27572959_Epigenetic regulation of OAS2 shows disease-specific DNA methylation profiles at individual CpG sites. 27899133_we characterized the functional consequences of the Neandertal haplotype in the transcriptional regulation of OAS genes at baseline and infected conditions. We found that cells from people with the Neandertal-like haplotype express lower levels of OAS3 upon infection, as well as distinct isoforms of OAS1 and OAS2 28139728_Mx1 and OAS1-2 polymorphisms were associated with the severity of liver disease in HIV/HCV-coinfected patients, suggesting a significant role in the progression of hepatic fibrosis. 30128873_OAS2 rs739901 5'-flanking C/A genetic polymorphisms involve the susceptibility to EV71 infection, and A allele might be a risk factor of the susceptibility to EV-71 infection. 30148861_Low OAS2 expression is associated with colorectal cancer metastasis, mediating perineural and lymphovascular invasion. 30965010_The OAS2 showed a marked increase in activity with increasing dsRNA length with a minimum requirement of 35 bp. 32413313_Structural and Hydrodynamic Characterization of Dimeric Human Oligoadenylate Synthetase 2. 32849499_Quantitative Proteomic Profile of Psoriatic Epidermis Identifies OAS2 as a Novel Biomarker for Disease Activity. 34516354_Long noncoding RNA SATB1-AS1 contributes to the chemotherapy resistance through the microRNA-580/ 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase 2 axis in acute myeloid leukemia. 35305973_OAS1, OAS2, and OAS3 Contribute to Epidermal Keratinocyte Proliferation by Regulating Cell Cycle and Augmenting IFN-1Induced Jak1Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 1 Phosphorylation in Psoriasis. | ENSMUSG00000032690 | Oas2 | 245.035865 | 0.462585926 | -1.112207 | 0.13577799 | 66.888394 | 0.0000000000000002873214834299077875241389215412417524265063675618925298493877562577836215496063232421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000153398966038837804195211951210780467628536690577467638263442495372146368026733398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 152.7918193 | 14.5695145 | 331.9471716 | 29.8722828 | |
| ENSG00000111344 | 8437 | RASAL1 | protein_coding | O95294 | FUNCTION: Probable inhibitory regulator of the Ras-cyclic AMP pathway (PubMed:9751798). Plays a role in dendrite formation by melanocytes (PubMed:23999003). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23999003, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9751798}. | Alternative splicing;Calcium;Differentiation;GTPase activation;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger | The protein encoded by this gene is member of the GAP1 family of GTPase-activating proteins. These proteins stimulate the GTPase activity of normal RAS p21 but not its oncogenic counterpart. Acting as a suppressor of RAS function, the protein enhances the weak intrinsic GTPase activity of RAS proteins resulting in the inactive GDP-bound form of RAS, thereby allowing control of cellular proliferation and differentiation. This particular family member contains domains which are characteristic of the GAP1 subfamily of RasGAP proteins but, in contrast to the other GAP1 family members, this protein is strongly and selectively expressed in endocrine tissues. Alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different isoforms have been described [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. | hsa:8437; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046580]; positive regulation of dendrite extension [GO:1903861]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 12221082_Galpha and Gbeta gamma require distinct Src-dependent pathways for its activation 16009725_RASAL preservs of Ca2+ frequency information 17640920_RASAL constitutes a tumor suppressor gene and therefore further emphasized the importance of Ca(2+) in the regulation of Ras signaling and has established that deregulation of this pathway is an important step in Ras-mediated tumorigenesis 18992247_Decreased expression of the RAS-GTPase activating protein RASAL1 is associated with colorectal tumor progression. 20473946_Reduced expression of RAS protein activator like-1 is associated with gastric cancer. 22825043_decreased RASAL1 expression is a characteristic of gastric cancer and regulated by epigenetic mechanisms 23251034_Ras GTPase activating (RasGAP) activity of the dual specificity GAP protein Rasal requires colocalization and C2 domain binding to lipid membranes. 23665422_Hypermethylations of RASAL1 and KLOTHO is associated with renal dysfunction in a Chinese population environmentally exposed to cadmium 24136889_We identified RASAL1 as a major tumor suppressor gene that is frequently inactivated by hypermethylation and mutations, providing a new alternative genetic background for thyroid cancer, particularly FTC and ATC. 24377515_Promoter hypermethylation of the RASAL1 gene was detected in MKN-28, SGC-790l and BGC-823 cancer cells. 24531877_It is a tumor suppressor gene which influences the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by regulating RAS/ERK signaling pathway. 24712574_Germline RASAL1 alterations are uncommon in patients with Cowden syndrome but may not be infrequent in patients with apparently sporadic follicular-variant papillary thyroid cancer. 24925056_large chromosome 12 rearrangement, spanning MDM2 and RASAL1, is the first recurrent molecular abnormality to be reported in juvenile ossifying fibroma 25616414_Transcriptional suppression of RASAL1 through aberrant promoter methylation contributes to endothelial-mesenchymal transition and ultimately to progression of cardiac fibrosis. 25735335_Loss of RASAL1 expression is associated with gastric carcinogenesis. 26008146_These findings suggest that Ebp1 suppressed thyroid cancer cell lines by upregulating RASRAL expression. 26997440_Report a new subtype of high-grade mandibular osteosarcoma with RASAL1/MDM2 amplification. 27012941_HIF1alpha and transforming growth factor (TGF)/SMAD signalling pathways synergistically regulate hypoxia-induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition through both DNMT3a-mediated hypermethylation of RASAL1 promoter and direct SNAIL induction. 27124111_DNA methylation, TGFbeta1 and RASAL1 appear to have an interacting relationship. 27878301_RASAL1 role in in sorafenib-resistance of liver cancer cells 28011578_our study showed significantly longer overall survival times for oesophagogastric adenocarcinoma patients without RASAL1 expression 28885980_Domain topology of human Rasal | ENSMUSG00000029602 | Rasal1 | 44.385629 | 0.252212742 | -1.987287 | 0.26188868 | 58.959079 | 0.0000000000000160985367162137678949434725756272402989938748868459228447136410977691411972045898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000007103669766132434237671933342274032486879029035797827873466303572058677673339843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 14.1390463 | 8.5573117 | 56.3021714 | 33.6893262 | |
| ENSG00000111732 | 57379 | AICDA | protein_coding | Q9GZX7 | FUNCTION: Single-stranded DNA-specific cytidine deaminase. Involved in somatic hypermutation (SHM), gene conversion, and class-switch recombination (CSR) in B-lymphocytes by deaminating C to U during transcription of Ig-variable (V) and Ig-switch (S) region DNA. Required for several crucial steps of B-cell terminal differentiation necessary for efficient antibody responses (PubMed:18722174, PubMed:21385873, PubMed:21518874, PubMed:27716525). May also play a role in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression by participating in DNA demethylation (PubMed:21496894). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18722174, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21385873, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21496894, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21518874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27716525}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;mRNA processing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation;Zinc | This gene encodes a RNA-editing deaminase that is a member of the cytidine deaminase family. AICDA is specifically expressed and active in germinal center-like B cells. In the germinal center, AICDA is involved in somatic hypermutation, gene conversion, and class-switch recombination of immunoglobulin genes. An epigenetic role in neoplastic transformation and lymphoma progression has been experimentally ascribed to AICDA using mouse models. Defects in this gene are the cause of autosomal recessive hyper-IgM immunodeficiency syndrome type 2 (HIGM2). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2020]. | hsa:57379; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; P-body [GO:0000932]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; cytidine deaminase activity [GO:0004126]; deoxycytidine deaminase activity [GO:0047844]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cytidine to uridine editing [GO:0016554]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; DNA cytosine deamination [GO:0070383]; DNA demethylation [GO:0080111]; isotype switching [GO:0045190]; mRNA processing [GO:0006397]; negative regulation of DNA methylation-dependent heterochromatin formation [GO:0090310]; negative regulation of single stranded viral RNA replication via double stranded DNA intermediate [GO:0045869]; negative regulation of transposition [GO:0010529]; regulation of nuclear cell cycle DNA replication [GO:0033262]; somatic diversification of immunoglobulins [GO:0016445]; somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes [GO:0016446] | 11823785_required for somatic hypermutation in the centroblast-like Ramos cells; sufficient to induce somatic hypermutation in hybridoma cells, which represent a later stage of B-cell differentiation that does not normally undergo SHM 12097915_AID mutates E. coli suggesting a DNA deamination mechanism for antibody diversification. 12114543_Internal IgH class switch region deletions are position-independent and enhanced by expression 12202747_Somatic hypermutation of the AID transgene in B and non-B cells 12511417_AID is highly regulated during normal B-cell development & is constitutively expressed in human germinal center B-NHL & in subsets of nongerminal center B-NHL. This constitutive expression may cause illegitimate recombination & somatic mutation in B-NHL. 12521993_Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells that express this enzyme display dissociation between class switch recombination and somatic hypermutation 12715918_has the function to induce spontaneous IgM production in B cells 12799424_Activation-induced cytidine deaminase causes transcription-dependent, strand-biased C to U deaminations. 12855567_data suggest that AID-mediated DNA alterations may occur in a variably sized, minor subset of B-CLL cells at any given time. 12873980_Expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase is confined to B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas of germinal-center phenotype. 12928399_Activation-induced cytidine deaminase plays a crucial role in the induction of DNA breakage during immunoglobulin class switch recombination. 12973929_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14536088_there is an essential role for the C-terminal domain of AID in CSR that is independent of its cytidine deaminase activity and that is not required for either gene conversion or somatic hypermutation 14551145_AID transcripts, including a splice variant, were common to both unmutated or mutated VH genes in mantle cell lymphoma. 14769937_AID is a nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein with a bipartite nuclear localization signal and a nuclear export signal in its N and C termini, respectively 14990977_AID expression was associated with the ongoing mutation in follicular lymphoma (FL) fresh cells. Results suggest the switch off of AID expression may start in the B-lineage differentiation stage counterpart of FL after optimizing somatic hypermutation 15061213_expression of AID in 15 Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines by RT-PCR 15087440_Activation-induced cytosine deaminase (AID) is actively exported out of the nucleus but retained by the induction of DNA breaks 15148397_results suggested both AID and APOBEC-1 are equally likely to bind single-stranded DNA or RNA, which has implications for the identification of natural AID targets 15182647_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15195091_separate domains of AID interact with specific cofactors to regulate these two distinct genetic events in a target-specific way 15304391_AID protein is specifically expressed in normal and transformed germinal center B cells 15371439_wild type AID retains its specificity for mutated hot spot motifs within the confines of a moving transcription bubble while introducing clusters of multiple deaminations predominantly on the nontranscribed strand 15372234_novel mutation found in the gene encoding for activation-induced cytidine deaminase in a Tunisian family with hyper-IgM type 2 syndrome 15448152_Aid and perhaps some of its family members may have roles in epigenetic reprogramming 15593119_AID overexpression by itself does not automatically lead to the onset of a mutator phenotype. 15613101_expression in acute lymphoblastic leukemia L2 with t(14;18)(q32;q21) 15944282_Direct evidence is presented for the DNA deamination from Escherichia coli expressing AID; uracils are preferentially generated at cytosines in the nontranscribed strand during transcription. 15949042_AID-mediated deamination of DNA is a major cause of mutations at G-C base pairs in immunoglobulin genes during somatic hypermutation. Its intrinsic substrate specificity is a primary determinant of mutational hotspots at G-C base pairs during SHM. 16122802_AID can interact with MDM2, an oncoprotein that shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm and targets p53 for nuclear export and degradation. 16269615_interfollicular large B cells and AID-expressing B lymphocytes of the thymic medulla could give rise to mature B-cell malignancies. 16314506_Somatic hypermutation on both DNA strands is the natural outcome of AID action on a transcribed gene. 16387847_control of T cell-dependent immune responses may be modulated, via AID, by signals that activate protein kinase A 16439679_The distribution of nuclear AID is consistent with the topography of somatic hypermutation and class switch recombination in activated B cells. 16541139_The AID expression and ASHM are associated with higher-grade transformation of CLL and provide further evidences that AID expression and ASHM may be activated during the clonal history of B-cell lymphomas. 16624806_review of the role of AICDA in producing high affinity isotype-switched antibodies [review] 16705187_AID binds DNA exposed by the transcribing polymerase, implicating the polymerase itself as the vehicle which distributes AID on DNA as it moves away from the promoter. 16785531_Features of activation-induced deaminase (AID) mapping within the noncatalytic domain, but outside the chromosome region maintenance 1-dependent nuclear export signal at the C-terminus, influence its function. 16999936_APOBEC3G is not a nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling protein like APOBEC-1 and AID 17060445_AID may persist on immunoglobulin and other target sequences after deamination, possibly acting as a scaffolding protein to recruit other factors 17066440_Findings suggest that the aberrant expression of AID is observed in human hepatocytes with several pathological settings, including chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. 17132718_cells may be the founder cells of the germinal center reaction (a pro-GC cell) and may be the normal counterpart of the mantle cell lymphoma cell 17161027_AID is alone unable to act processively on any of a number of DNA substrates 17485517_AID is a BCR-ABL1-induced mutator in Philadelphia chromosome(+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells, which may be relevant to the particularly unfavorable prognosis of this leukemia subset. 17638864_primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBL), an immunoglobulin (Ig)-negative lymphoma that possesses hypermutated, class-switched Ig genes, expresses high levels of AID with an intact primary structure but does not do class switch recombination 17878393_AID retains its exclusive association with numerous, residual germinal centers in parotid Sjogren's syndrome-MALT lymphomas, whereas neoplastic marginal zone-like B cells are consistently AID negative 18213388_generation of phase 1 mutations is not a prerequisite for the expression of phase 2 mutations 18306229_The proinflammatory cytokine-induced aberrant production of AID might link bile duct inflammation to an enhanced genetic susceptibility to mutagenesis, leading to cholangiocarcinogenesis 18329947_aberrant AID expression can be triggered by several pathogenic factors, including Helicobacter pylori infection & proinflammatory cytokines, in human epithelial cells, but AID expression is absent in those cells under physiologic conditions[review]. 18390709_results obtained with activated CD19(+) B cells show that the expression of E47, activation-induced cytidine deaminase, and Iggamma1 circle transcripts progressively decrease with age 18391550_Aberrant expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase may contribute to the development of gastric cancers and induce p53 nuclear expression 18417471_analysis of the effect of phosphorylation and phosphorylation-null mutants on the activity and deamination specificity of activation-induced cytidine deaminase 18722174_The results, therefore, identify residues in AID involved in its in vivo targeting and suggest they might act through interaction with CTNNBL1, giving possible insight into the linkage between AID recruitment and target-gene transcription. 18757891_Results identify non-conservative homologous recombination as a novel DNA transaction pathway promoted by activation-induced cytidine deaminase. 18760480_AID and Ung generate staggered double-strand DNA breaks (DSBs) not only by cleaving intact double-strand DNA, but also by processing blunt DSB ends. 18772346_AID can cause single-base substitutions or multiple clustered mutations depending on the transcriptional activity of T7 RNA polymerase. 18776814_expressed in bone marrow infiltrates of malignant lymphoma 18940926_results lead to a model for exonuclease 1 function in class switch recombination in which cleavage at activation-induced deaminase (AID)-initiated nicks produces gaps that become substrates for further attack by AID and subsequent repair 19017972_V(H)4 replacement in preimmune human B cells is mediated by an AICDA-independent mechanism resulting from inefficient but selective RAG activity. 19023113_in the absence of CD40-CD154 interactions, there is a marked reduction in SHM and, specifically, mutations of AICDA-targeted G residues in RGYW motifs along with a decrease in transversions normally related to UNG2 activity. 19139166_Estrogen regulates gene expression of AID at the transcriptional level. 19196959_class switch recombination activity of AID requires an ACF-like cofactor that specifically interacts with the carboxy-terminal domain of AID 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19266080_sensitive gel electrophoresis (CSGE) and sequencing analysis of AICDA coding sequences demonstrated sequence heterogeneity due to 5923A/G and 7888C/T polymorphisms, but did not reveal any novel mutation that might explain the selective IgE deficit. 19309412_The expression of activation induced cytidine deaminase in follicular lymphoma is independent of prognosis and stage. 19336552_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19363484_HoxC4 directly activates the Aicda promoter 19380635_AID acts processively in naked DNA and DNA organized within transcribed nucleosomes. 19412186_Two other mechanisms involved in controlling AID subcellular localization, are identified. 19443686_AID targeting of hot and cold spots is a key part of the mutation process, our results suggest that the sequence environment plays an equally important role 19561087_When recognition loop of 9-11 amino acids is grafted from the donor APOBEC3F or 3G proteins into the acceptor scaffold of AID, the mutational signature of AID changes toward that of the donor proteins. 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19575287_in hyper-IgM syndrome, one novel AICDA mutation (E122X) was detected 19578742_abnormal over-expression of GANP together with AID might be associated with rigorous DNA damage, potentially causing the malignant development of Cholangiocarcinoma (CCAs) during long-term inflammation. 19667096_Both mice and humans share a latent, AID-dependent pathway for the preimmune diversification of B lymphocytes. 19703021_The higher levels of AID expression in B cells of Reumatoid Arthritis patients correlate with the higher levels of T helper cell cytokines IFN-gamma and IL-17. 19732723_ACIDA promotes B lymphoid blast crisis and drug resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia. 19734146_SLIP-GC is a replication-related protein in germinal center B cells whose reduction is toxic to cells through an AICDA-dependent mechanism. 19741596_However, no activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) expression (an absolute requirement for class switching) was detected in lamina propria 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19859091_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19898425_AID expression is an indicator of an unfavorable prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma patients 19911124_Studies indicate the APOBEC family consists of 11 members: APOBEC-1 (Apo1), APOBEC-2 (Apo2), activation induced cytidine deaminase (AID), APOBEC- 3A, -3B, -3C, -3DE, -3F, -3H (Apo3A-H) and APOBEC- 4 (Apo4). 19966806_Aicda is regulated by the balance between B cell-specific and stimulation-responsive elements and ubiquitous silencers. 20027182_data provide new evidence that mammalian AID is required for active DNA demethylation and initiation of nuclear reprogramming towards pluripotency in human somatic cells 20048284_Altering the spectrum of immunoglobulin V gene somatic hypermutation by modifying the active site of AID. 20117026_Expression of at least one AID-mRNA isoform predominated among mutated IgG vs. mutated IgMD. AID splice variants may inhibit somatic hypermutation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells of the unmutated subtype. 20118283_Findings underscore that AID splice variants are unlikely to have preservation of catalytic activity. 20233972_High expression of AID and active class switch recombination might account for a more aggressive disease in unmutated CLL patients: link with an activated microenvironment in CLL disease. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237507_Higher expression levels of activation-induced cytidine deaminase distinguish hairy cell leukemia from hairy cell leukemia-variant and splenic marginal zone lymphoma. 20338830_the sequence selectivity of APOBEC family of enzymes 20373075_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20373075_The researchers found no evidence of an association between the AICDA 7888 C/T polymorphism and the risk of gastric atrophy or gastric neoplasms in the study group. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20491788_The ectopic expression of AICDA in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RA-FLS) causes TP53 somatic mutations & dysfunction, leading to acquisition of tumour-like properties by RA-FLS. 20507984_GANP may serve as an essential link required to transport AID to B-cell nuclei and to target AID to actively transcribed IgV regions 20637757_AID-mediated genotoxic effects appear to occur frequently at the CDKN2b-CDKN2a locus and contribute to malignant transformation of the gastric mucosa 20729863_14-3-3 proteins specifically bound 5'-AGCT-3' repeats, were upregulated in B cells undergoing class switch DNA recombination (CSR) and were recruited with AID to the switch regions that are involved in CSR events 20855884_Esr1 bind to and activate the HOXC4 promoter to potentiate HoxC4-mediated AID induction, immunoglobulin class switch and somatic hypermutation. 20864035_Exogenous and intrinsic AID-induced DNA strand breaks in B-cells activate ATM, which signals through an LKB1 intermediate to inactivate CRTC2, resulting in repression of germinal center B-cell differentiation, while opposing lymphomagenesis. 20878190_findings suggest that pro-inflammatory cytokine-mediated aberrant expression of AICDA in colonic epithelial cells plays a role as a genotoxic factor that enhances genetic instability during chronic colonic inflammation, leading to colorectal cancer 20927319_Low Cytidine Deaminase is associated with gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer. 20974684_The constitutive expression of AID in ATL cells can be speculated to result from mutations induced by the Tax-activated AID and/or other Tax-associated mutagenic mechanisms 21041454_Hsp90 inhibition provides the first pharmacological means to down-regulate AID expression and activity. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21109971_AID and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in cancer cells may be modified by epigenetic mechanisms 21133730_AID overexpression promotes chromosomal abnormalities and is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression 21255825_Study implicates the RNA exosome, a cellular RNA-processing/degradation complex, in targeting AID to both DNA strands. 21268017_Ig class-switch recombination, as well as the stabilisation of AID, depend on an interaction between the AID C-terminal decapeptide and factor(s) additional to Crm1. 21290192_High expression and mutation-inducing activity of AID is associayed with human lung cancer. 21570118_Activation-induced deaminase (AID) expression is correlated with Bcr-Abl expression in chronic myelocytic leukemia-B-lymphoid blast cells. 21659520_Phosphorylation directly regulates the intrinsic DNA cytidine deaminase activity of activation-induced deaminase and APOBEC3G protein 21700883_identified a major and previously unsuspected role for AID in the removal of developing autoreactive B cells 21831295_Findings demonstrate that miR-93 and miR-155 constitutively suppress AID translation in MCF-7 cells, suggesting widespread roles for these miRs in preventing genome cytidine deaminations, mutagenesis, and oncogenic transformation. 21984922_Analysis of co-regularities and creation of AID-associated functional network gives an integrated view of biological processes and might be further applied to assess role of altered AID expression in etiology of other diseases. 22034886_Activation-induced cytidine deaminase is associated with inflammation in ulcerative colitis, whereas it may not specifically contribute to carcinogenesis 22080610_Activation-induced cytidine deaminase -induced decrease in Top1 is critical for somatic hypermutation. 22168746_AID may act as a negative regulator of cell survival in follicular lymphoma when sufficient c-myc is expressed 22198384_Data suggest that AID may generate DNA damage with variable efficiencies in different organisms, identify residues critical in regulating AID activity, and provide insights into the evolution of the APOBEC family of enzymes. 22234692_Data show that interaction between myeloma and dendritic cell (DC), but not monocytes, leads to rapid induction of the genomic mutator activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) and AID-dependent DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) in myeloma cell. 22308462_Along with known AID targets, this screen identified a set of unique genes (SNHG3, MALAT1, BCL7A, and CUX1) and confirmed that these loci accumulated mutations as frequently as Ig locus after AID activation 22363466_Lysine modification may represent a novel level of AID regulation. 22391874_Hypermutable bases (both paired and unpaired) are made accessible to activation-induced cytidine deaminase in stabilised DNA secondary structures formed with increasing transcription levels 22446380_The data suggested that the present-day human APOBEC3B enzyme retained the nuclear import mechanism of an ancestral activation-induced cytosine deaminase during the expansion of the APOBEC3 locus in primates. 22466889_aberrant AID expression may play an important role in the dysplasia-carcinoma sequence in the oral cavity 22469133_Findings suggest that activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) plays an integral role in inflammation-associated carcinogenesis and is therefore a potential target molecule for the prevention and treatment of cancers. 22492685_An ortholog of AID was, evolutionarily, the first enzyme to generate acquired immune diversity by catalyzing gene conversion and probably somatic hypermutation. (Review) 22715099_A structural analysis is presented that shows how localized defects in different regions of AID can contribute to loss of catalytic function. 22798497_While APOBEC3A was a strong deaminator of both C and 5-methylcytosine, AID was much weaker in it's ability to deaminate this modified base. 22843687_Spt6 is a unique histone chaperone capable of regulating the histone epigenetic state of both AID targets and the AID locus. 22899287_We suggest that duodenal follicular lymphoma cells are in the memory B-cell stage, and require BACH2 instead of AID for ongoing mutation. 22962683_DNA sequence preference may serve as an additional layer of AID regulation by restricting its mutagenic activity to specific sequences, despite the observation that AID has the potential to access the genome widely. 22992148_report of two siblings of a Tajik family with a hyper-immunoglobulin M (HIGM) syndrome phenotype in which a novel missense mutation in the activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AICDA) gene was detected 23008333_Data show that activation-induced deaminase (AID) associates with RNA polymerase-associated factor 1 (PAF1) through its N-terminal domain. 23017209_RBM5 promotes exon 4 skipping of AID pre-mRNA by competing with the binding of U2AF65 to the polypyrimidine tract. 23071276_Data suggest that the production of fully functional activation-induced deaminase (AID) protein by IGHV-unmutated (U-CLL) and IGHV-mutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (M-CLL) cells could be involved in clonal evolution of the disease. 23133680_LINE-1 retroelements are complexed and inhibited by activation induced cytidine deaminase 23166356_Among BCL6 validated targets, miR-155 and miR-361 directly modulate AID expression, indicating that via repression of these miRNAs, BCL6 up-regulates AID. 23190037_B cell defects, as measured by the autonomous AID reporter, in IBD patients contribute to reduced humoral responses to the influenza vaccine, as we have previously shown for elderly individuals. 23198547_H. pylori infection induces ectopic AID expression in the gastric mucosal cells via NFkappaB activation, resulting in various gene mutations and aberrations in the gastric mucosal cells leading to gastric cancer development. 23212122_a critical role for AID activity in the initiation of reprogramming to iPSCs. 23263985_AID enzymatic activity is important for the fragility at the the human bcl-2 major breakpoint region. 23277564_identify a unique cofactor, RING finger protein 126 (RNF126), verify its interaction by traditional techniques, and show that it has functional consequences as RNF126 is able to ubiquitylate activation-induced cytidine deaminase 23341589_C-to-T and G-to-A mutations accumulated in hepatitis B virus (HBV) nucleocapsid DNA when AICDA was expressed in HBV-replicating hepatic cell lines. 23363221_LMP1 induces AID up-regulation and genomic instability via Egr-1. 23399385_High levels of AID specifically increased mutations at A, but not T, leading to strand bias. 23408445_genetic polymorphisms in AICDA and CASP14 are associated with risk for brain tumor in Korean children. 23476051_Both WGCW/WRC and CpG/CGC breaks at BCL6 are most likely initiated by AID in germinal center B-cells, and their differential use suggests subtle mechanistic differences between Ig-BCL6 and non-Ig-BCL6 rearrangements. 23589568_This reveals a novel antineoplastic role of AID that can be triggered by inhibition of homologous recombination. 23593411_5-FC combined gene therapy with TNF-alpha and CD suicide gene should be an effective treatment on Laryngeal carcinoma. 23634222_Aberrant AID expression in the oral epithelium would contribute to the initiation of oral squamous cell carcinoma 23652018_GANP-mediated chromatin modification promotes transcription complex recruitment and positioning at immunoglobulin variable loci to favour AID targeting. 23662991_Results show that activation induced cytidine deaminase (AID) expression may be associated with deletions in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). 23731676_There was no significant association between the previously reported genetic variant of AICDA gene and the development of Common variable immunodeficiency or selective IgA deficiency 23803409_Two patients, sisters from a consanguineous family, were diagnosed with HIGM2 syndrome, and found to be homozygous for a transversion mutation. 23820005_aberrant AID expression triggers an auto-activation circuit to consolidate self-expression 23882083_Data indicate that knockdown of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) suppresses expression of several key epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) transcriptional regulators and increased methylation of CpG islands of these genes. 23942124_data suggest a role for nucleotide sugar pucker in explaining the molecular basis for AID's DNA selectivity and, more generally, suggest how other nucleic acid-modifying enzymes may distinguish DNA from RNA 24025329_proinflammatory cytokines IL-1/TNFalpha trigger a novel antiviral mechanism involving AID to regulate host cell permissiveness to HBV infection. 24244169_findings reveal additional functions for AID in innate immune defense against KSHV with implications for a broader involvement in innate immunity to other pathogens. 24349193_DNA repair pathways which are in vitro activated by AID-induced lesions are reminiscent of those found during AID-induced in vivo immunoglobulin diversification. 24351917_findings suggest that AID has a role in the development of oral epithelial dysplasia and promotes progression of oral cancer 24434356_AID physically associates with the major spliceosome subunits (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins, snRNPs), as well as other essential splicing components, in addition to the transcription machinery. 24507160_[review] In a B cell that produces AID protein and undergoes mutation of the V regions of the expressed Ig heavy and light chain genes, only some of the transcription complexes initiating at the active V-region promoters are associated with AID. 24684646_analysis of a possible association between AID expression and BRAF mutation in melanoma 24923561_B cells hijack to supply ssDNA substrates for AID to mutate at immunoglobulin V regions during somatic hypermutation. 24973444_AID lacking the C terminus is impaired in its ability to recruit nonhomologous end joining repair factors, resulting in accumulation of double-strand breaks that undergo aberrant resection. 25099163_demonstrates that intensity of malaria transmission correlates with AID expression levels in the presence of Epstein-Barr virus 25154417_Results show that both AID mRNA levels and DNA-cytosine deamination activities follow the same general pattern of increase and decline after stimulation in the two genetic backgrounds. 25179679_data demonstrate that AID is active in CLL in vivo and thus, AID likely contributes to clonal evolution of CLL. 25237741_In yeast, AID and the catalytic domain of APOBEC3G preferentially mutate transcriptionally active genes within narrow regions, 110 base pairs in width, fixed at RNA polymerase initiation sites. 25483776_Study reports that the majority of detectable AID off-target activity in a variety of mouse and human lymphoid or nonlymphoid cell types occurs within focal regions of overlapping sense/antisense transcription within intragenic super enhancers. 25483777_AID activity and its relationship to chromosome folding and the B cell regulome was studied; find that AID-mediated lesions occur predominantly within B cell super-enhancers and regulatory clusters; further show that the structural and transcriptional features of these domains help explain AID tumorigenic activity in the B cell compartment of mice and humans. 25486549_Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID)-induced mutagenic U:G mismatches in DNA may be a fundamental and common cause of mutations in B-cell malignancies. 25849121_These findings indicated that TNF-alpha-induced AID expression is involved with class switch recombination in cancer. 25902538_hnRNP K and hnRNP L may serve as A1CF-like cofactors in AID-mediated class switch recombination and somatic hypermutation 25912253_HSP90 inhibitors indirectly target AID in vivo 25990957_Surges in ERK activity induced by extracellular cues enhance Arp2/3-mediated actin polymerization to generate protrusion power phases sufficient to promote sustained cell motility. 26077666_High expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase is associated with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. 26113087_Data indicate that both the amount and intensity of the activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) protein expression increased with the progression from precancerous to cancerous lesions in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) tissues. 26166388_The high levels of memory and activated B cells and follicular helper T cells were positively associated with the progression of immunoglobulin A nephropathy. This may be mediated by the overexpression of AID, which is potentially regulated by IL21. 26219420_aberrant expression of AID may reflect continuous B cell activation and sustained survival signals in HCV-related CV patients. 26223652_Data show that microRNAs miR-155 and miR-16 downregulate activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) and transcription factor E47 in B Cells through binding of the 3'-untranslated regions. 26355458_identify AID derivatives that accelerate somatic hypermutation with minimal impact on viability, which will be useful tools for engineering genes and proteins by iterative mutagenesis and selection 26365193_DNA methylation dynamics of germinal center B cells are mediated by AID. 26398702_AICDA/APOBEC family of cytidine deaminases is significant in innate immunity, as it restricts numerous viruses, including HBV, through hypermutationdependent and independent mechanisms. (Review) 26537386_Studies indicate that gene conversion mediated by activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) has been found to contribute to generation of the primary antibody repertoire. 26545377_AID mutations leading to AID deficiency are the most frequent underlying molecular basis of hyper IgM syndrome in consanguineous Tunisian patients. 26638776_Mutations in activation-induced cytidine deaminase is associated with indolent chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. 26867650_Data suggest novel mechanism in innate immunity allows cytokine TGF-beta to restrict viral circular DNA in hepatocyte nuclei via innate immunity; AID deaminates circular DNA of hepatitis B virus leading to DNA degradation; mechanism depends on UNG. 26936395_We also report that AID activity results in epigenetic, genetic and genomic damage in fallopian tube epithelial cells 26980048_AID protein is expressed in a large proportion of Philadelphia chromosome-positive B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cases at levels detectable by immunohistochemistry. 27142677_Finnish founder allele causing HIGM2 identified. 27217538_These data, showing the direct targeting and induction of functional AID by EBNA3C, suggest a novel role for EBV in the etiology of B cell cancers, including endemic Burkitt lymphoma 27258794_Structural analysis of AID protein required in immunoglobulin diversification has been reported. 27716525_the His130Pro mutation allows the enzyme to retain its mutagenic activity and would prevent the interaction of AID with specific cofactors required for class switch recombination but not for somatic hypermutation. Thus, there would be no contradiction between maintaining the catalytic and mutagenic activity of AID and the presence of function defects at the genomic level. 27789066_this study reports a case of growth hormone deficiency with an autosomal recessive Hyper-immunoglobulin M syndrome by phenotype and genotype, with a novel mutation in AICDA that has not been reported formerly 28077417_silencing of AID in human bone marrow cells skews differentiation toward myelomonocytic lineage. However, in contrast to Tet2 loss, Aid loss does not contribute to enhanced HSC self-renewal or cooperate with Flt3-ITD to induce myeloid transformation. Genome-wide transcription and differential methylation analysis uncover the critical role of Aid as a key epigenetic regulator 28140712_we reported high AID, low miR-181b and high miR-155 expression in de novo adult B-ALL patients. Univariate high AID or low miR-181b expression was an unfavorable prognostic factor. High AID with low miR-181b or with low miR-155 expression is better in predicting unfavorable OS than univariate factor. High AID with low miR-181b and low miR-155 expression confers worst prognosis. 28388279_AID expression was increased in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients with del17p or del11q who have poor prognosis. 28490810_induction of AID expression would result in chromosomal translocations in the process of differentiation from B cell derived induced pluripotent stem cells. 28757211_Data implicate intrinsic preference of AID for structured substrates and uncover the importance of G4 recognition and oligomerization of AID in class switch recombination. 28779685_The authors found that the viral epsilon RNA and C-terminus of AID are required for AID-mediated hepa | ENSMUSG00000040627 | Aicda | 24.187258 | 0.357719225 | -1.483100 | 0.32988590 | 20.885839 | 0.0000048748529651287389116709469760735373711213469505310058593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000703709424935199204806726691607821067009354010224342346191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 12.6998296 | 7.2581443 | 35.6932839 | 19.8816806 | |
| ENSG00000111788 | unprocessed_pseudogene | 50.300603 | 0.099428129 | -3.330202 | 1.09457024 | 7.060886 | 0.0078785045238431612724117059087802772410213947296142578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0413060424585900073934929821461992105469107627868652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 9.2527686 | 5.7296199 | 89.5825483 | 54.4255174 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000111817 | 29940 | DSE | protein_coding | Q9UL01 | FUNCTION: Converts D-glucuronic acid to L-iduronic acid (IdoUA) residues. Plays an important role in the biosynthesis of the glycosaminoglycan/mucopolysaccharide dermatan sulfate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16505484, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19004833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7092807, ECO:0000269|Ref.7}. | 3D-structure;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Ehlers-Danlos syndrome;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Isomerase;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Microsome;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | PATHWAY: Glycan metabolism; chondroitin sulfate biosynthesis. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:16505484, ECO:0000305|PubMed:19004833, ECO:0000305|PubMed:7092807, ECO:0000305|Ref.7}.; PATHWAY: Glycan metabolism; heparan sulfate biosynthesis. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:16505484, ECO:0000305|PubMed:19004833, ECO:0000305|PubMed:7092807, ECO:0000305|Ref.7}. | The protein encoded by this gene is a tumor-rejection antigen. It is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum and functions to convert D-glucuronic acid to L-iduronic acid during the biosynthesis of dermatan sulfate. This antigen possesses tumor epitopes capable of inducing HLA-A24-restricted and tumor-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in cancer patients and may be useful for specific immunotherapy. Mutations in this gene cause inmusculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. A related pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 9, and a paralogous gene exists on chromosome 18. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. | hsa:29940; | cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; chondroitin-glucuronate 5-epimerase activity [GO:0047757]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; chondroitin sulfate biosynthetic process [GO:0030206]; chondroitin sulfate metabolic process [GO:0030204]; dermatan sulfate biosynthetic process [GO:0030208]; dermatan sulfate metabolic process [GO:0030205]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0015012] | 19004833_Identification of the active site of DS-epimerase 1 and requirement of N-glycosylation for enzyme function. 22350411_Dermatan sulfate epimerase 1 was highly upregulated in esophagus squamous cell carcinoma 23704329_study identified a homozygous DSE missense mutation (c.803C>T, p.S268L) in a male child with musculocontractural type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome; data indicate mutation affects the epimerase activity, resulting in reduced dermatan sulfate (DS) biosynthesis and an increased synthesis or an accumulation or reduced conversion of chondroitin sulfate 29864158_Study showed that DSE is frequently upregulated in human glioma tissue and cell lines and associated with a worse tumor grade and poor overall survival. Its knockdown suppresses malignant phenotypes, whereas DSE overexpression enhances glioma cell malignancy, both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanically, DSE modulates HB-EGF-induced EGFR/ErbB2 activity and downstream signaling. 29976758_DS-epi1, DS-epi2, and D4ST1 form homomers and are all part of a hetero-oligomeric complex where D4ST1 directly interacts with DS-epi1, but not with DS-epi2. The cooperation of DS-epi1 with D4ST1 may therefore explain the processive mode of the formation of iduronic acid blocks. 31972438_Dermatan sulfate epimerase 1 expression and mislocalization may interfere with dermatan sulfate synthesis and breast cancer cell growth. | ENSMUSG00000039497 | Dse | 244.819152 | 0.335984713 | -1.573533 | 0.19336719 | 64.096844 | 0.0000000000000011845111738185703329712700908201552562688574398233609663577681203605607151985168457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000583413461245569003726108547667032698503218612895437900078832171857357025146484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 124.7350825 | 17.8654006 | 373.1823413 | 52.5490283 |
| ENSG00000111913 | 9750 | RIPOR2 | protein_coding | Q9Y4F9 | FUNCTION: Acts as an inhibitor of the small GTPase RHOA and plays several roles in the regulation of myoblast and hair cell differentiation, lymphocyte T proliferation and neutrophil polarization (PubMed:17150207, PubMed:24687993, PubMed:23241886, PubMed:24958875, PubMed:25588844, PubMed:27556504). Inhibits chemokine-induced T lymphocyte responses, such as cell adhesion, polarization and migration (PubMed:23241886). Involved also in the regulation of neutrophil polarization, chemotaxis and adhesion (By similarity). Required for normal development of inner and outer hair cell stereocilia within the cochlea of the inner ear (By similarity). Plays a role for maintaining the structural organization of the basal domain of stereocilia (By similarity). Involved in mechanosensory hair cell function (By similarity). Required for normal hearing (PubMed:24958875). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80U16, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17150207, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23241886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24687993, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24958875, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27556504}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Acts as an inhibitor of the small GTPase RHOA (PubMed:25588844). Plays a role in fetal mononuclear myoblast differentiation by promoting filopodia and myotube formation (PubMed:17150207). Maintains naive T lymphocytes in a quiescent state (PubMed:27556504). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17150207, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25588844, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27556504}. | Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Chemotaxis;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Deafness;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Hearing;Membrane;Myogenesis;Non-syndromic deafness;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal transduction inhibitor | This gene encodes an atypical inhibitor of the small G protein RhoA. Inhibition of RhoA activity by the encoded protein mediates myoblast fusion and polarization of T cells and neutrophils. The encoded protein is a component of hair cell stereocilia that is essential for hearing. A splice site mutation in this gene results in hearing loss in human patients. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. | hsa:9750; | apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; stereocilium [GO:0032420]; stereocilium membrane [GO:0060171]; 14-3-3 protein binding [GO:0071889]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cellular response to chemokine [GO:1990869]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; negative regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0007162]; negative regulation of establishment of T cell polarity [GO:1903904]; negative regulation of protein localization to cell leading edge [GO:1905872]; negative regulation of Rho guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:2001107]; negative regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035024]; negative regulation of T cell migration [GO:2000405]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; positive regulation of filopodium assembly [GO:0051491]; positive regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045663]; positive regulation of myoblast fusion [GO:1901741]; positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090023]; positive regulation of neutrophil extravasation [GO:2000391]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of establishment of cell polarity [GO:2000114]; regulation of mitotic spindle assembly [GO:1901673]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; skeletal muscle fiber development [GO:0048741] | 17150207_C6ORF32 is a novel protein likely to play multiple functions, including promoting myogenic cell differentiation, cytoskeletal rearrangement and filopodia formation 21190562_PC3 tumors are sustained by a small number of tumor-initiating cells with stem-like characteristics, including strong self-renewal and pro-angiogenic capability and marked by the expression pattern FAM65Bhigh/MFI2low/LEF1low. 24687993_Fam65b expression is necessary for the complex to form. 24958875_show that wild-type Fam65b is expressed during embryonic and postnatal development stages in murine cochlea, and that the protein localizes to the plasma membranes of the stereocilia of inner and outer hair cells of the inner ear 25588844_These data together elucidate a mechanism for RHOA and pMLC polarization in stimulated neutrophils through direct inhibition of RHOA by FAM65B at the leading edge. 25953057_In our analyses of the DYX2 locus, we observed associations of KIAA0319, ACOT13, and FAM65B with developing cortical thickness and/or functional anisotropy. 27269051_Mouse Ripor2 forms ring-like structures at the base of stereocilia and interacts with RhoC 27556504_FAM65B has a role in controlling proliferation of transformed and primary T cells 30254631_results show that Fam65b expression and phosphorylation can finely tune the amount of active RhoA in order to favor optimal T lymphocyte motility. 30720667_this is the first study to explore and validate the relationships between seven SNPs in the FAM65B, AGBL4, and CUX2 genes and ATDH in a Chinese population. On the basis of this case-control study, SNP rs10946737 in FAM65B may be associated with susceptibility to ATDH in Chinese Han anti-TB treatment patients. | ENSMUSG00000036006 | Ripor2 | 74.944837 | 0.374016277 | -1.418827 | 0.21167558 | 45.304972 | 0.0000000000168620553949770890284752940584689644316906953491752574336715042591094970703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000005510897917405128114924727267850794454329133031933452002704143524169921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 37.6310024 | 10.6134665 | 101.0560110 | 27.7744103 | |
| ENSG00000112715 | 7422 | VEGFA | protein_coding | P15692 | FUNCTION: Growth factor active in angiogenesis, vasculogenesis and endothelial cell growth. Induces endothelial cell proliferation, promotes cell migration, inhibits apoptosis and induces permeabilization of blood vessels. Binds to the FLT1/VEGFR1 and KDR/VEGFR2 receptors, heparan sulfate and heparin. NRP1/Neuropilin-1 binds isoforms VEGF-165 and VEGF-145. Isoform VEGF165B binds to KDR but does not activate downstream signaling pathways, does not activate angiogenesis and inhibits tumor growth. Binding to NRP1 receptor initiates a signaling pathway needed for motor neuron axon guidance and cell body migration, including for the caudal migration of facial motor neurons from rhombomere 4 to rhombomere 6 during embryonic development (By similarity). Also binds the DEAR/FBXW7-AS1 receptor (PubMed:17446437). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q00731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11427521, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16489009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17446437, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25825981}. | 3D-structure;Alternative initiation;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Heparin-binding;Mitogen;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | This gene is a member of the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family. It encodes a heparin-binding protein, which exists as a disulfide-linked homodimer. This growth factor induces proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells, and is essential for both physiological and pathological angiogenesis. Disruption of this gene in mice resulted in abnormal embryonic blood vessel formation. This gene is upregulated in many known tumors and its expression is correlated with tumor stage and progression. Elevated levels of this protein are found in patients with POEMS syndrome, also known as Crow-Fukase syndrome. Allelic variants of this gene have been associated with microvascular complications of diabetes 1 (MVCD1) and atherosclerosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. There is also evidence for alternative translation initiation from upstream non-AUG (CUG) codons resulting in additional isoforms. A recent study showed that a C-terminally extended isoform is produced by use of an alternative in-frame translation termination codon via a stop codon readthrough mechanism, and that this isoform is antiangiogenic. Expression of some isoforms derived from the AUG start codon is regulated by a small upstream open reading frame, which is located within an internal ribosome entry site. The levels of VEGF are increased during infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), thus promoting inflammation by facilitating recruitment of inflammatory cells, and by increasing the level of angiopoietin II (Ang II), one of two products of the SARS-CoV-2 binding target, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). In turn, Ang II facilitates the elevation of VEGF, thus forming a vicious cycle in the release of inflammatory cytokines. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2020]. | hsa:7422; | adherens junction [GO:0005912]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; platelet alpha granule lumen [GO:0031093]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; VEGF-A complex [GO:1990150]; chemoattractant activity [GO:0042056]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; extracellular matrix binding [GO:0050840]; fibronectin binding [GO:0001968]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; neuropilin binding [GO:0038191]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005161]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 binding [GO:0043183]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 binding [GO:0043184]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005172]; activation of protein kinase activity [GO:0032147]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; artery morphogenesis [GO:0048844]; basophil chemotaxis [GO:0002575]; branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0001569]; camera-type eye morphogenesis [GO:0048593]; cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0055013]; cardiac vascular smooth muscle cell development [GO:0060948]; cell maturation [GO:0048469]; cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002042]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; cellular stress response to acid chemical [GO:0097533]; commissural neuron axon guidance [GO:0071679]; coronary artery morphogenesis [GO:0060982]; coronary vein morphogenesis [GO:0003169]; dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:0071542]; endothelial cell chemotaxis [GO:0035767]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; eye photoreceptor cell development [GO:0042462]; heart morphogenesis [GO:0003007]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; induction of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050930]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; lactation [GO:0007595]; lung development [GO:0030324]; lymph vessel morphogenesis [GO:0036303]; macrophage differentiation [GO:0030225]; mammary gland alveolus development [GO:0060749]; mesoderm development [GO:0007498]; monocyte differentiation [GO:0030224]; motor neuron migration [GO:0097475]; negative regulation of adherens junction organization [GO:1903392]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of blood-brain barrier permeability [GO:1905604]; negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin [GO:2000048]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043154]; negative regulation of establishment of endothelial barrier [GO:1903141]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003151]; ovarian follicle development [GO:0001541]; positive chemotaxis [GO:0050918]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048842]; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration [GO:0043536]; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903589]; positive regulation of branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0090190]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell migration by vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:0038089]; positive regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090050]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cell proliferation by VEGF-activated platelet derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038091]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of CREB transcription factor activity [GO:0032793]; positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process [GO:2000573]; positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis by VEGF-activated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038033]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of epithelial tube formation [GO:1905278]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051894]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of histone deacetylase activity [GO:1901727]; positive regulation of leukocyte migration [GO:0002687]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of mast cell chemotaxis [GO:0060754]; positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation [GO:0002052]; positive regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900745]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation [GO:1900086]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042327]; positive regulation of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050927]; positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation [GO:0031954]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of protein kinase C signaling [GO:0090037]; positive regulation of protein kinase D signaling [GO:1903572]; positive regulation of protein localization to early endosome [GO:1902966]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; positive regulation of receptor internalization [GO:0002092]; positive regulation of retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:1902336]; positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903672]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to hypoxia [GO:0061419]; positive regulation of trophoblast cell migration [GO:1901165]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:1900748]; positive regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043117]; post-embryonic camera-type eye development [GO:0031077]; primitive erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0060319]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction [GO:0010749]; regulation of retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:0090259]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002040]; surfactant homeostasis [GO:0043129]; tube formation [GO:0035148]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048010]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 signaling pathway [GO:0036324]; vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:0038084]; vascular wound healing [GO:0061042]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570]; VEGF-activated neuropilin signaling pathway [GO:0038190] | 11146397_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11352659_Includes data regarding non-AUG translation initiation (CUG) of VEGF 11563986_Includes data regarding non-AUG translation initiation (CUG) of VEGF 11642726_upregulated in eye in experimental herpesvirus retinopathy 11686329_Thrombin induces increased expression and secretion of VEGF from human FS4 fibroblasts, DU145 prostate cells and CHRF megakaryocytes. 11705851_The VEGF levels were significantly higher in recurrent ALL compared with newly diagnosed ALL. 11705867_VEGF levels were elevated in patients with invasive cancer of ductal/no specific type, ductal carcinoma in situ, and estrogen receptor (ER)-positive tumors. 11731620_Includes data regarding non-AUG translation initiation (CUG) of VEGF 11741977_induction in human glioblastoma cells by acidic extracellular pH via ERK1/2 MAPK signaling pathway 11742492_Significant association with poor survival by VEGF. 11748975_Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in serous ovarian carcinoma: relationship with high mitotic activity and high FIGO stage. 11751905_both VEGF-induced PI 3-kinase activation and beta(1) integrin-mediated binding to fibronectin are required for the recruitment and activation of PKC alpha. 11783119_VEGF expression and intratumoral microvessel density (IMVD) can be considered as a biological indicator of malignant potential in brain astrocytoma. 11784713_Vascular endothelial growth factor modulates neutrophil transendothelial migration via up-regulation of interleukin-8 in human brain microvascular endothelial cells 11784722_modulation of signaling and angiogenic effects by PTEN 11806247_upregulation by interleukin-1 beta in vascular smooth muscle cells via the P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway 11809675_Vascular endothelial growth factor-A(165) induces progression of melanoma brain metastases without induction of sprouting angiogenesis. 11809713_Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase stimulates human glioma xenograft growth and angiogenesis. 11815711_essential for developmental angiogenesis and is also required for female reproductive functions and endochondral bone formation. 11819817_VEGF plays an important role in the oncogenesis of human gastric cancer. 11824377_Platelets and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): a morphological and functional study. 11831981_VEGF is highly related to PVBE and angiogenesis of meningoma. 11832343_bFGF and VEGF were synergistic in terms of DAF expression, resulting in enhanced endothelial cytoprotection 11834731_A 40-bp RNA element that mediates stabilization of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA by HuR. 11836562_Plasma vascular endothelial growth factor is useful in assessing progression of breast cancer post surgery and during adjuvant treatment. 11839635_VEGF and flt-1 are upregulated in blood vessels in many organs of acute Kawasaki Disease 11847008_Blood levels are elevated in myelodysplastic syndromes and in acute myeloid leukemia. VEGF corrected for the peripheral blood platelet count is a marker of disease progression in MDS. 11866530_NMR structure of a phage-derived peptide antagonist in complex with vascular endothelial growth factor 11866538_Vascular endothelial growth factor modulates the Tie-2:Tie-1 receptor complex 11867956_free plasma VEGF levels are high in chronic renal impairment; may contribute to the endothelial dysfunction of uraemia 11875709_prognostic value of matched preoperative serum and plasma vascular endothelial growth factor concentrations in patients with colorectal cancer. 11877311_Prognostic significance of VEGF expression in bone marrow cells in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. 11877669_VEGF upregulates BCL-2 expression and is associated with decreased apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. 11882460_Chemoattractive and proliferative effects of VEGF-A have been demonstrated on primary human osteoblasts. 11891801_Plasma VEGF levels are significantly increased in chronic myeloproliferative disorders. The highest levles were found in CMD with essential thrombocythemia. Levels were significantly higher in CMD patients with vascular complications. 11908876_VEGF may act as a growth factor for both endothelial cells and tumor cells. 11912213_Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor A transcription in tumorigenic glioblastoma cell lines by an enhancer with cell type-specific DNase I accessibility 11912219_overexpression in mesangial cells by advanced glycation end products 11920479_tumor cell-VEGF induction may promote angiogenesis in adenocarcinoma of the lung; tumor cell expression may be important prognostic factor in adenocarcinoma of the lung 11921018_expression of tissue factor (TF) and VEGF is frequently observed in colorectal cancer and TF expression is significantly related with VEGF expression and microvessel density 11930687_VEGF as a mediator of OHSS. 11930688_VEGF may play a role in pathogenesis of OHSS. 11940485_Cultured plasma cells from patients with advanced relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma who responded favorably to thalidomide secreted a significantly lower amount of VEGF than did plasma cells from resistant patients. 11956584_thrombin upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor 11956638_VEGF expression and vascular density in colon cancer 11957147_COX-2 is upregulated in endometrial cancer and facilitates tumor growth via angiogenesis produced in associated with VEGF and TP 11959648_copper sulfate induced VEGF expression in primary as well as transformed human keratinocytes 11960372_Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor angiogenesis 11961297_the role and intracellular signal pathway of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activation induced by VEGF 11961303_VEGF and p53 are highly expressed in esophageal carcinomas 11964077_VEGF is down regulated in ovarian carcinoma cells and in serous effusions 11964307_HTLV-I-transformed T cells, but not HTLV-I-negative CD4(+) T cells, secrete biologically active forms of VEGF and bFGF and induce angiogenesis in vitro. 11972026_A dynamic shift of VEGF isoforms with a transient and selective progesterone-induced expression of VEGF189 regulates angiogenesis and vascular permeability in human uterus 11978184_Increased expression of VEGF may be responsible for gastric carcinogenesis and tumor aggressiveness of gastric cancer in northern China. 11978667_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11980898_differential regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in bladder cancer cells (peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, beta) 11986954_level spontaneously secreted by patient CLL B-cells quantified; secreted in 2/3 patient samples; co-expression of VEGF and VEGF receptors suggests autocrine pathways of stimulation. 11999550_REVIEW: Association of expression of VEGF and receptors in human leukemia and lymphoma, resulting in the generation of autocrine loops that may support cancer cell survival and proliferation 12012273_investigation of the immediate effect of ovulation induction with hCG on peripheral VEGF levels in 6 women with primary infertility enrolled in the IVF/ET program 12014632_Overexpression of cyclin DI contributes to malignant properties of esophageal tumor cells by increasing VEGF production and decreasing Fas expression. 12016145_modulation of synthesis by sodium butyrate in colon cancer cell line HT29 12023772_findings suggest that products secreted by schistosome eggs may promote angiogenesis within hepatic granulomas by up-regulating endothelial cell VEGF 12038454_VEGF and IL-6 were both independent prognostic factors for overall survival of aggressive lymphoma. 12039075_Data suggest that VEGF-A may be more than angiogenic in prostate cancer and hence favor tumor progression by affecting tumor cells. 12042276_relationship between serum VEGF levels, alpha(2)M levels and the development of OHSS in hyperstimulated subjects undergoing IVF 12058259_Genotype may influence tumour growth in malignant melanoma, possibly via effects on tumour angiogenesis 12058259_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12062186_Comparison and modulation of angiogenic responses by FGFs, VEGF and SCF in murine and human fibrosarcomas. 12067896_VEGF-induced proliferation and angiogenesis requires activation of the protein kinase C (PKC) signaling pathway, whereas vascular permeability is enhanced by PKC blockade. 12067976_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12085210_Hyperthermia acts as an anti-angiogenic strategy by suppressing VEGF expression & thus inhibiting endothelial proliferation and blood vessel ECM remodeling. 12102661_results indicate opposite effects of IFN-gamma and IL-4 on VEGF expression from normal and activated keratinocytes and fibroblasts 12105188_Integrin (alpha 6 beta 4) regulation of eIF-4E activity and VEGF translation (Integrin alpha6beta4) 12114504_VEGF binds to CTGF and degrades MMPs, inducing physiological or pathologic angiogenesis 12117969_Induction of VEGF in THP-1 macrophages and human microvascular endothelial cells during Bartonella henselae infection 12119553_IL-10 gene expression in esophageal squamous cell cancer specimens was significantly correlated with VEGF121 gene expression. The results suggested that IL-10 stimulates angiogenic factor gene expression. 12127077_VEGF(121) contains a third interchain disulfide bond between Cys116 of each monomer. 12133473_VEGF promotes angiogenesis by paracrining in breast carcinoma, and takes part in tumor invasion and lymph node metastasis. 12133520_A new alternative splicing isoform of VEGF has been identified in the lung tissue of a legally aborted human fetus. 12133521_VEGF is associated with the development and prognosis of colorectal cancer. 12141529_effect of epidermal growth factor on vascular endothelial growth factor secretion by endometrial stromal cells 12149254_Data show that exposure of human colon carcinoma cells to insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) induces the expression of HIF-1 alpha, the regulated subunit of hypoxia-inducible factor 1, a known transactivator of the VEGF gene. 12151344_expression in colon carcinoma cells exposed to pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate 12151391_role of a variant in competitively and specifically antagonizing the mitogenic effect of the wild-type protein on endothelial cells 12163680_Green tea inhibits induction in human breast cancer cells. 12168088_PTEN modulates angiogenesis in prostate cancer by regulating VEGF expression. 12168808_vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) has been demonstrated to have a central involvement in the angiogenic process in rheumatoid arthritis 12168898_Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression correlates with p53 and ki-67 expressions in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. 12174362_expressions of iNOS and VEGF may serve as indexes for evaluating staging of gastric carcinoma and forecasting its risk of metastasis 12174901_data suggest that mutations of p53 and activation of the Ras/MAPK pathway may play a role in the induction of VEGF expression in human colorectal cancer 12187074_High level of vascular endothelial growth factor in hemorrhagic pleural effusion of cancer. 12197476_regulation and expression profile of 884 human genes under the influence of either bFGF or VEGF-A alone in the context of human endothelial cells 12207021_cystine knot promotes folding and not thermodynamic stability 12208766_The redox protein thioredoxin-1 (Trx-1) increases hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha protein expression: Trx-1 overexpression results in increased vascular endothelial growth factor production and enhanced tumor angiogenesis. 12209585_VEGF isoforms and mutations in human colorectal cancer. 12209725_Women with ovarian carcinoma who reported higher levels of social well being had lower levels of VEGF 12213806_These results suggest that the expression of HIF-1 and VEGF induced by Cr(VI) may be an important signaling pathway in the Cr(VI)-induced carcinogenesis. 12213874_may play important roles in placental biology and chorionic villus vascular development and remodeling in an autocrine/paracrine manner 12213878_findings implicate altered VEGF and KDR signaling in pituitary tumorigenesis; PTTG stimulation of FGF-2 and VEGF expression in the presence of up-regulated growth factor receptors may account for angiogenic growth and progression of human pituitary tumors 12215337_expression in uterine leiomyoma 12232762_The prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor in 574 node-negative breast cancer patients who did not receive adjuvant systemic therapy. 12235106_plays a role in bone formation elicited by bone morphogenetic protein 4, and can significantly enhance BMP4-elicited bone formation and regeneration 12239588_vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human esophageal cancer 12358602_findings underline an essential role of AP-2/Sp1 recognition sites in UVB-mediated VEGF expression by the keratinocyte-derived cell line HaCaT 12391145_Data describe a novel mechanism by which vascular endothelial growth factor induces DNA synthesis in a pathway where sphingosine kinase mediates signaling from protein kinase C to Ras in a manner independent of Ras-guanine nucleotide exchange factor. 12391545_Hb-induced synthesis of VEGF in TF-bearing malignant cells is mediated by protein tyrosine kinase and by MAP-kinase pathways 12393542_Inhibition of p38 MAPK inhibits IL-6 and VEGF secretion in bone marrow stromal cells triggered by adherence of multiple myeloma cells. 12400015_These results demonstrate a novel pathogenic mechanism whereby mutations in BRCA1, via their interaction with ER-alpha, could promote tumorigenesis through the hormonal regulation of mammary epithelial cell proliferation and impaired VEGF function 12406876_results suggest that in the hematopoietic microenvironment an autocrine vascular endothelial growth factor loop contributes to optimal megakaryocytic maturation through Flt1 12413884_Data demonstrate that the paracrine interaction between endothelial and mesenchymal cells potentiates angiogenesis in vitro and that this occurs with vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) but not with growth factor-2 (FGF-2). 12425822_The VEGF expression and tumour angiogenesis are correlated with peritumoural brain edema. 12427739_mediation of proliferation of human pulmonary valve endothelial cells by NFATc1 12427750_vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated gene induction and angiogenic responses of endothelial cells is inhibited by NAB2 12428103_FGF2 and VEGF release by platelets support cell survival and cell growth of vascular endothelium cells in coculture. 12429966_up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with submucosal carcinoma of esophagus 12430738_The malignant transformation of endothelial cells may be characterized by VEGF expression in the presence of p53 gene mutation. 12439912_The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors KDR and Flt-1 by gastric carcinoma tissues and cell lines was detected to elucidate the molecular mechanism of this growth factor in promoting tumor growth. 12445161_close relationship of VEGF expression with macrophage migration inhibitory factor expression in human glioblastoma 12446667_VEGF might contribute to breast cancer metastasis by enhancing the transendothelial migration of tumor cells through the down-regulation of endothelial integrity 12451991_The in vitro invasive ability of ovarian tumor cells appeared to be positive correlated to high expression of VEGF and MMP-2. 12452000_The high expression of VEGF in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma may promote the tumor progression and lead to dismal prognosis. 12453880_In vivo administration of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its antagonist, soluble neuropilin-1, predicts a role of VEGF in the progression of acute myeloid leukemia in vivo. 12453985_Vitreous levels are altered in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy 12456629_vascular endothelial growth factor does not discriminate ectopic from abnormal intrauterine pregnancies at 6 weeks gestation 12474525_Differential expression follows BCG immunotherapy in superficial papillary transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder 12481883_review discusses the impact of new vessel formation related to acute leukemia and the relation with various angiogenic factors with focus on VEGF/VEGF receptor signaling 12482858_VEGF is induced by p38 after stimulation by sodium arsenite 12482957_We show here that vascular endothelial growth factor but not basic fibroblast growth factor can induce gene expression of Notch1 and Dll4, in human arterial endothelial cells. The VEGF-induced specific signaling is mediated through VEGF receptors 1 and 2 12493399_This factor is transcribed and translated in chronic renal allograft rejection. 12496364_The induction of maximal neovascularization by VEGF requires the interaction between ephrin-A1 and EphA2. 12499259_Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes breast carcinoma invasion in an autocrine manner by regulating the chemokine receptor CXCR4. 12505748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12505748_results suggest that polymorphisms in the promoter region of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene together with the aldose reductase gene may be associated with the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy 12509426_regulation of transcription by oxidative stress via Sp1- and Sp3-dependent activation of two proximal GC-rich promoter elements 12509854_restoration of PTEN function in gliomas may induce therapeutic effect by downregulating VEGF. 12517803_PTEN mutation and epidermal growth factor receptor activation regulate mRNA expression in human glioblastoma cells by transactivating the proximal promoter 12545153_Stat3 directly regulates VEGF expression and hence angiogenesis, growth, and metastasis of human pancreatic cancer 12548213_VEGF impaired bradykinin-mediated dilatation and enhanced basal tone and permeability of isolated arteries which might indicate a potential role for VEGF in the development of endothelial dysfunction in pregnancy 12551914_A set of loop-1 and -3 structures in this protein family member, VEGF-ENZ-7, is essential for the activation of VEGFR-2 signaling. 12553038_Induction of VEGF seems to be regulated by the extent of the IL-6 receptor expression on pancreatic cancer cells. 12558813_We conclude that VEGF -460, -141 and +405 genotypes are not associated with susceptibility to childhood steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome 12563064_VEGF found in cerebrospinal fluid of SIDS infants (postmortem) suggests that a single or multiple hypoxic events may precede the SIDS event. 12568850_Progestins activate this gene transcription in endometrial adenocarcinoma cells 12574959_IL-6r and TNF-alpha increase in parallel to VEGF and FGF-2 with increasing stage of multiple myeloma. 12579315_VEGF-A is an estrogen responsive gene and modulation of this gene expression by estrogen is biphasic and can be mediated through ER-alpha dependent pathway. 12581744_exogenous VEGF-A(165) or VEGF-A(121) did not affect the rate of proliferation of either trophoblast cells or breast carcinoma cells, but did reduce their ability to invade through reconstituted ECM (Matrigel) 12590639_The relationship between pituitary tumour transforming gene (PTTG) expression and in vitro growth hormone and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion from human pituitary adenomas. 12591230_vascular endothelial growth factor indirectly stimulates smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration through the modulation of basic fibroblast growth factor and transforming growth factor beta(1) released by endothelial cells 12591731_We have analyzed the impact of the common -460/+405 polymorphism on both basal and stimulated VEGF transcription using the human breast cancer cell line MCF7. 12593846_expression in pancreatic carcinoma cell line evoked by insulin-like growth factor I receptor 12594002_We studied the association of endometriosis with circulating levels of human leukocyte antigens and VEGF in two generations of a single family (mother and three daughters). These markers were expressed distinctly in women with familial endometriosis. 12594815_Malignant mesothelioma growth inhibition by agents that target the VEGF and VEGF-C autocrine loops. 12597245_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12597245_Significant ethnic differences in C702T and G1612A allele frequencies, but C702T, C936T and G1612A polymorphisms in 3'-UTR of VEGF gene are not associated with risk of RCC in Japanese population. 12604407_A paracrine loop in the VEGF pathway triggers tumor angiogenesis and growth in multiple myeloma. 12607595_VEGF expression plays a role in promoting angiogenesis in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast, and p53 is likely to be involved in regulating VEGF expression. 12607599_VEGF, but not bFGF, was associated with higher tumor grading of NHL and high-grade transformation of low-grade lymphoma. 12615701_Cyclooxygenase-1 is overexpressed and promotes vascular endothelial growth factor production in ovarian cancer. 12629515_We conclude that IL-6 may promote cervical tumorigenesis by activating VEGF-mediated angiogenesis via a STAT3 pathway. 12631341_IGF-I induces VEGF gene expression and protein secretion in human mesangial cells via a Src-dependent mechanism. 12637571_extracellular pH might play an important role in regulating vascular endothelial growth factor interactions with cells and the extracellular matrix 12646239_These results demonstrate that a seven amino acid VEGF exon 6-derived peptide is an effective inhibitor of ocular neovascularisation in vivo. 12651930_expression is involved in angiogenesis in inflamed synovial tissue in the temporomandibular joint 12654193_expression levels of VEGF and bFGF were correlated with the biological behavior of superficial transitional cell bladder carcinoma. 12654197_expression levels of VEGF and bFGF were correlated with the biological behavior of superficial transitional cell bladder carcinoma. 12660426_mast cells may play an active role in the angiogenesis of basal cell carcinoma through the production of VEGF 12666706_increased in gingival tissues of diabetic patients, especially those with periodontal disease 12667326_The expression of EGF in hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC underlies the overexpression of VEGF in HCC. 12668286_Local VEGF expression was correlated significantly with tumor size, advanced stage and lymph node metastasis, but not correlated with peripheral VEGF levels 12670505_VEGF secreted by retinal pigment epithelial cells upregulates pigment epithelium-derived factor expression via VEGFR-1 in an autocrine manner. 12684660_expressed during angiogenesis in human ovarian cancer cells in vivo 12684689_Results suggest that up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor enables and supports the pathogenesis of external ear canal cholesteatoma. 12687277_Serum VEGF activity may be used to evaluate angiogenic and metastatic activity in breast cancer patients. 12696078_With the progression of tumor grade, the positive rate of VEGF gene expression significantly increased. 12700666_Distortion of autocrine transforming growth factor beta signal accelerates malignant potential by enhancing cell growth as well as PAI-1 and VEGF production in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 12708473_The expression of VEGF was significantly correlated with gastric cancer differentiation & vascular invasion. 12710853_In pregnancies complicated by trisomy 21 VEGF levels were significantly lower than in healthy controls. May be sign of imbalance of placental vascularization and altered endothelial function. 12711260_vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression is suppressed by pigment epithelium-derived factor through anti-oxidative properties, which inhibits leptin-induced angiogenesis 12716475_heme oxygenase activity up-regulates VEGF production and augments the capability of endothelial cells to respond to exogenous stimulation 12716911_ADAMTS1 significantly blocks VEGFR2 phosphorylation due to direct binding and sequestration of VEGF165, with consequent suppression of endothelial cell proliferation. 12719950_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12719950_Significant difference between normal individuals and stone patients in distribution of VEGF gene polymorphism as well as an odds ratio of 1.30 per copy of the 'T' allele. 12727858_Vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression in colon cancer cells exposed to prostaglandin E2 is mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. 12740269_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12742981_Gene transfer of VEGF during PTCA and stenting shows that intracoronary gene transfer can be performed safely; no differences in restenosis rate or lumen diameter were present after 6-month follow-up, and increased myocardial perfusion was detected 12756808_possible blood biological marker of Yersinia infection and may be involved in the development of chronic conditions 12763746_Submaximal exercise, suitable for humans with low cardiovascular fitness, induces decrease in VEGF arteriovenous balance that is likely to be of clinical significance in promoting angiogenic effects. 12767510_VEGF-A might play a main role in the COX-2 angiogenic pathway. 12788875_In the luteal phase, VEGF and IP-10, in the normal human breast, exhibit a proangiogenic profile. This may be one mechanism by which sex steroids contribute to breast cancer development. 12800229_Expression of VEGF has a significant correlation with microvascular density in colorectal carcinoma. 12810642_The promoter of human vascular endothelial growth factor contains 7 consensus binding sites for beta-catenin/TCF. Transfection of normal colon epithelial cells with activated beta-catenin up-regulated levels of VEGF-A mRNA and protein. 12810677_Tumor-derived VEGF interacts with Angs/Tie-2 system in host stromal endothelial cells & induces in a paracrine manner the remodeling of host vasculature to support angiogenesis during tumor growth. 12827055_Pterygia exhibit significantly lower PEDF but higher VEGF levels than those in normal corneas and conjunctivae. 12839933_Bombesin stimulates nuclear factor kappa B activation and expression of this angiogenic factor in prostate cancer cells. 12844492_VEGF has a regulatory role in focal adhesion complex assembly in human brain microvascular endothelial cells via activation of FAK and RAFTK/Pyk2 12845559_VEGF is produced locally and plays a fundamental, but not specific, role in diabetic retinal neovascularisation and proliferation. 12845639_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12847526_VEGF is a modifier of motoneuron degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 12850503_vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in osteolytic lesions of bone co-relates well with the extent of bone destruction and local recurrence 12855698_Vascular endothelial growth factor causes translocation of p47phox to membrane ruffles through WAVE1 12860293_human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells produce VEGF, which in turn regulates PEDF production, and this balance may be contributing to neovascularization in tumors. 12865814_expression or function in acute and chronic allograft rejection; an important proinflammatory cytokine after transplantation and its expression pattern might identify patients at risk for the development of GVD 12871382_thrombin-induced VEGF mRNA expression is associated with the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in vascular endothelial cells 12871881_Although VEGF seems to play a pivotal role locally in the implantation and development of endometriotic lesions, the disease is not associated with a significant modulation in the levels of circulating VEGF. 12883661_COX-2 and VEGF are expressed in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and may have a role in tumor invasiveness and angiogenesis 12883688_COX-2 or VEGF, but not cyclin D1 may play roles in breast cancer with poor prognosis 12883692_VEGF is regulated by her2/neu and contributes to Wilms tumor angiogenesis in vivo 12888890_VEGF has a role in pathologic angiogenesis and is downregulated by antisense oligonucleotides 12890905_Serum VEGF concentration was increased in arteriosclerosis obliterans (ASO) and thromboangitis obliterans, but increased concentration of M-CSF was seen only in ASO. 12893367_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12893367_VEGF gene C/T polymorphism is a suitable genetic marker of prostate cancer but cannot be used in the prediction of the outcome of patients who have received hormonal therapy. 12901801_Plasma VEGF levels are significantly higher than in gastric tumor patients than those in 10 healthy controls 12918061_Vascular endothelial growth factor expression correlates with matrix metalloproteinases MT1-MMP, MMP-2 and MMP-9 in human glioblastomas 12926153_In patients with advanced ovarian carcinoma, intense VEGF immunostaining was more often detected in peritoneal metastases than in primary tumors. 12937141_Secreted VEGF protein levels were significantly lower in IGF-IR dominant negative cells. Autocrine activation of IGF-IR system significantly affects VEGF expression and angiogenesis in human pancreatic cancer. 12949011_in humans: 1) VEGF, KDR, and Flt-1 mRNA are increased by acute systemic exercise; 2) the time course of the VEGF, KDR, and Flt-1 mRNA responses are different from those previously reported in rats 12957716_Our findings suggest that hyperhomocysteinemia could promote the development of atherosclerotic lesions through VEGF induction in macrophages. 14500349_Activated MMP9, and, to a lesser extent, MMP2, increased VEGF release by SKOV3 and OVCAR3 ovarian carcinoma cells. 14507446_Biological dressing effect of cultured epidermal sheets(CESs) is mediated by EGF family, TGF-beta, and VEGF. 14507641_High-level expression of angiopoietin-2 and VEGF receptors was observed in the endothelium of verruga peruana. Surprisingly, the major source of VEGF production in verruga peruana is the overlying epidermis. 14512169_Postmortem brain tissue analysis demonstrates activation of the proangiogenic VEGF signaling cascade in patients with cerebral malaria. 14512791_vascular endothelial growth factor expression is regulated by HIF1a and HIF2a, and has a role in nodular malignant melanomas of the skin 14513045_Progression of multiple myeloma to a vascular phase is accompanied by increase in microcirculation and and in VEGF. 14513053_Expressed in multiple myeloma cells and in bone marrow cells. 14514674_role of neuropilin-1 on endothelial cell migration 14530810_Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with myeloproliferative disorders 14532971_VEGF is upregulated by cyclooxygenase-2 in human gastric carcinoma 14555767_Hepatocyte growth factor mediates angiogenesis in cultured cancer cells by regulating the expression of this protein and thrombospondin 1. 14559444_VEGF may serve as an important modulator of mitogen-induced VSMC proliferation after vascular injury. 14572781_data suggest that human peritoneal mesothelial cells contribute to the development of peritoneal metastases and the accumulation of malignant ascites due to the production of vascular endothelial growth factor 14585871_VEGF may play an important role in the hydrosalpinx fluid formation, possibly by promoting vascular and epithelial permeability and therefore serum transudation. 14593238_in umbilical cord plasma, a developmental increase was evident in concentrations of vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF) and angiogenin during the last trimester of gestation, and VEGF level was lower in term fetuses born to mothers with diabetes 14602779_IGF-I stimulates VEGF synthesis in thyroid carcinomas in an Akt-dependent pathway via AP-1 and HIF-1 alpha 14604996_Both of the IRS proteins modulate VPF/VEGF expression in pancreatic cancer cells by different mechanistic pathways. 14607580_Intrauterine VEGF levels are regulated in a cycle-dependent way. Increasing levels in the late secretory phase are clearly correlated with decidualization. 14607712_the protein level of VEGF can reflect the compensation status of cirrhosis patients and may act as an anti-cirrhotic factor 14609725_VEGF express | ENSMUSG00000023951 | Vegfa | 689.605444 | 0.328202844 | -1.607340 | 0.13659429 | 133.428904 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000007284514722693250011435394368703960073979072906783609029474932975254008039111766484655086095756360009545460343360900878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000802329070401836000929763428138179869129560123164608551326025059052244466052065258176995143912790808826684951782226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 330.1248873 | 38.1993019 | 1010.5555115 | 114.4381821 | |
| ENSG00000113205 | 56132 | PCDHB3 | protein_coding | Q9Y5E6 | FUNCTION: Potential calcium-dependent cell-adhesion protein. May be involved in the establishment and maintenance of specific neuronal connections in the brain. | Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene is a member of the protocadherin beta gene cluster, one of three related gene clusters tandemly linked on chromosome five. The gene clusters demonstrate an unusual genomic organization similar to that of B-cell and T-cell receptor gene clusters. The beta cluster contains 16 genes and 3 pseudogenes, each encoding 6 extracellular cadherin domains and a cytoplasmic tail that deviates from others in the cadherin superfamily. The extracellular domains interact in a homophilic manner to specify differential cell-cell connections. Unlike the alpha and gamma clusters, the transcripts from these genes are made up of only one large exon, not sharing common 3' exons as expected. These neural cadherin-like cell adhesion proteins are integral plasma membrane proteins. Their specific functions are unknown but they most likely play a critical role in the establishment and function of specific cell-cell neural connections. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:56132; | membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0016339]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; synapse assembly [GO:0007416] | 29537081_PCDHB3 may function as a novel tumor suppressor in colorectal via inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway, and its expression and localization may serve as prognostic markers for advanced CRc. | ENSMUSG00000045498 | Pcdhb3 | 13.289074 | 3.148282349 | 1.654565 | 0.53218211 | 9.475424 | 0.0020824275738322004826452715775531032704748213291168212890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0140651844050047412221227105533216672483831644058227539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 20.3479005 | 6.6257502 | 6.5679410 | 2.2474970 | |
| ENSG00000113263 | 3702 | ITK | protein_coding | Q08881 | FUNCTION: Tyrosine kinase that plays an essential role in regulation of the adaptive immune response. Regulates the development, function and differentiation of conventional T-cells and nonconventional NKT-cells. When antigen presenting cells (APC) activate T-cell receptor (TCR), a series of phosphorylation lead to the recruitment of ITK to the cell membrane, in the vicinity of the stimulated TCR receptor, where it is phosphorylated by LCK. Phosphorylation leads to ITK autophosphorylation and full activation. Once activated, phosphorylates PLCG1, leading to the activation of this lipase and subsequent cleavage of its substrates. In turn, the endoplasmic reticulum releases calcium in the cytoplasm and the nuclear activator of activated T-cells (NFAT) translocates into the nucleus to perform its transcriptional duty. Phosphorylates 2 essential adapter proteins: the linker for activation of T-cells/LAT protein and LCP2. Then, a large number of signaling molecules such as VAV1 are recruited and ultimately lead to lymphokine production, T-cell proliferation and differentiation (PubMed:12186560, PubMed:12682224, PubMed:21725281). Required for TCR-mediated calcium response in gamma-delta T-cells, may also be involved in the modulation of the transcriptomic signature in the Vgamma2-positive subset of immature gamma-delta T-cells (By similarity). Phosphorylates TBX21 at 'Tyr-530' and mediates its interaction with GATA3 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q03526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12186560, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12682224, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21725281}. | 3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Immunity;Kinase;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;SH3 domain;Transferase;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes an intracellular tyrosine kinase expressed in T-cells. The protein contains both SH2 and SH3 domains which are often found in intracellular kinases. It is thought to play a role in T-cell proliferation and differentiation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:3702; | cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004715]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; B cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050853]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; gamma-delta T cell activation [GO:0046629]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; NK T cell differentiation [GO:0001865]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell activation [GO:0042110]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] | 11437596_Studies of Itk deletion mutants indicate that the amino acids in the N-terminal 152 residues and proline-rich domains enhance catalysis by affecting turnover rate rather than by substrate binding. 11830645_Itk catalytic activity is inhibited by the peptidyl prolyl isomerase activity of cyclophilin A (CypA). 16159638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16931156_In this review, the pathways are discussed by which Itk might impact the differentiation of T helper (Th) cells. 17060314_Itk forms dimers in the membrane and that receptors that recruit Itk do so to specific membrane regions 17237383_Vav phosphorylation correlates with calcium flux and Itk phosphorylation during mitogenic CD28 signalaing in Jurkat cells 17724684_Active signals from transgenic Tec kinase (ITK) regulate the development of memory-like CD8+ T cells with innate function. 17897671_Itk autophosphorylation on Y180 within the SH3 domain occurs exclusively via an intramolecular, in cis mechanism 18322190_In transgenic mice specifically lacking Itk kinase activity, active kinase signaling is required for control of T helper (Th)2 cell responses and development of allergic asthma. 18443296_These data suggest that inhibition of ITK blocks HIV infection by affecting multiple steps of HIV replication. 19222422_Analysis of SNPs in TCR pathway genes revealed that a haplotype that covers a major part of the coding sequence of ITK is a risk factor for seasonal allergic rhinitis. 19222422_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19425169_ITK deficiency as a result of a R335W missense mutation, causes a novel immunodeficiency syndrome that leads to a fatal inadequate immune response to Epstein-Barr virus. 19523959_The authors identify the residues on the surface of the Itk SH2 domain responsible for substrate docking and show that this SH2 surface mediates autophosphorylation in the full-length Itk molecule. 19535334_Findings identify ITK-SYK as an active, transforming FTK and suggest ITK-SYK as a rational therapeutic target for t(5;9)(q33;q22)-positive lymphomas. 19701889_these results provide an initial step in understanding the biological role of Itk-TFII-I signaling in T-cell function. 19714314_Data show that tacrolimus modified the expression levels of Foxp3-regulated T cell receptor signal related-genes, PTPN22 and Itk, in Treg cells. 19717557_The Tec family kinase Itk exists as a folded monomer in vivo. 20305788_TSAd, through its interaction with both Itk and Lck, primes Itk for Lck mediated phosphorylation and thereby regulates CXCL12 induced T cell migration and actin cytoskeleton rearrangements 20439541_Expression of patient-derived ITK in mice induces highly malignant peripheral T cell lymphomas. 20457812_T-cell receptor (TCR)-induced association between ITK and SLP-76, recruitment and transphosphorylation of ITK, actin polarization at the T-cell contact site, and expression of Th2 cytokines 21280324_Knocking down Itk expression inhibits Jurkat cell proliferation and cytokines production. 21323647_People with the -rare allele 196C>T may be more susceptible to asthma via transcriptional regulation of the ITK gene. 21674762_No detrimental mutations were identified in ITK in Chinese children with Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 21725281_These data suggest a sequential mechanism whereby ZAP-70-dependent priming of SLP-76 at three N-terminal sites triggers reciprocal regulatory interactions between Itk and SLP-76, which are ultimately required to couple active Itk to PLC-gamma1. 22289921_ITK mutations are distributed over the entire protein and include missense, nonsense and indel mutations, reminiscent of the situation in its sister kinase in B cells, Bruton's tyrosine kinase 22302878_These results indicate that Itk is required for efficient replication of influenza virus in infected T-cells. 22449075_This review focuses on Itk and its role in regulating T-cell signaling and function, especially the activation and development of alpha-beta T cells. 22829599_DEF6, a novel substrate for the Tec kinase ITK, contains a glutamine-rich aggregation-prone region and forms cytoplasmic granules that co-localize with P-bodies. 23260110_ITK and Gag colocalized at the plasma membrane and were concentrated at sites of F-actin accumulation and membrane lipid rafts in HIV-1 infected T cells 23293025_Data indicate that the intracellular signaling of ITK-SYK requires both SLP-76 and the adapter function of SYK/ZAP-70 kinases. 23454662_a new pathway regulated by Itk in cells, and suggest cross talk between Itk and G-protein signaling downstream of the TcR. 24076779_Case Report/Letter: ITK/SYK translocation in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. 24376268_T-cell-specific human ITK-Syk oncogene in mice leads to early polyclonal T cell lymphoproliferation with B cell expansion. It induces terminal T cell differentiation via Blimp-1, eliminating oncogene-expressing cells early in development. 24462896_Data indicate reduced T-cell activation by altered IL-2 inducible T-cell kinase (ITK) expression in vitro. 25061172_ITK deficiency is a genetic cause of idiopathic CD4+ T-cell lymphopenia. 25337257_Found that 38% and 14% of the Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma cases exhibited gains of ITK and SYK genes, respectively. 25492967_The kinase Itk and the adaptor TSAd change the specificity of the kinase Lck in T cells by promoting the phosphorylation of Tyr192. 25512530_approach identified 18 kinase and kinase-related genes whose overexpression can substitute for EGFR in EGFR-dependent PC9 cells, and these genes include seven of nine Src family kinase genes, FGFR1, FGFR2, ITK, NTRK1, NTRK2, MOS, MST1R, and RAF1. 25593320_These data indicate that PRN694 is a highly selective and potent covalent inhibitor of ITK and RLK, and its extended target residence time enables durable attenuation of effector cells in vitro and in vivo. 25934889_We conclude that ITK, formerly considered an immune cell-specific protein, is aberrantly expressed in melanoma and promotes tumor development and progression 27729219_The data indicate that increased ITK expression could act as a disease activity marker and as a risk factor for involvement in SLE, but it still needs further study to confirm. 27780854_These observations have significant therapeutic implications, as pharmacologic inhibition of ITK prevented the activation of this signaling axis and overcame chemotherapy resistance. 28213500_Our results provide new insight into the effect of ITK and suboptimal T-cell receptor signaling on CD8(+) T cell function, and how these may contribute to phenotypes associated with ITK deficiency 28635957_ITK signalling through the Ras/IRF4 pathway is required for functional development of type 1 regulatory T cells. 29453458_neither HS expression nor other attachment factors could explain the impaired HIV-1 binding to ITK-deficient Jurkat cells, which suggests that a more complex cellular process is influenced by ITK or that not yet discovered molecules contribute to restriction of HIV-1 binding and entry. 30242208_Specific ITKi had modest effects on apoptosis. 30778533_Loss of function in ITK can result in broad dysregulation of T-cell responses to oncogenic viruses, including beta-human papillomavirus and Epstein-Barr virus. 31022269_ITK knockdown decreased IL-17A production in T cells primed under Th17 conditions and promoted Th1 differentiation. 31484725_The ITK SH3 and LCK SH3 domains can both competefor and simultaneously bind to adjacent binding sites on TSAD encompassing aa 242-268. 32628964_ITK deficiency presenting as autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome. 32640487_BTK/ITK dual inhibitors: Modulating immunopathology and lymphopenia for COVID-19 therapy. 33017570_SUFU mediates EMT and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway activation promoted by miRNA-324-5p in human gastric cancer. 33931484_Itk Promotes the Integration of TCR and CD28 Costimulation through Its Direct Substrates SLP-76 and Gads. 34282055_Interleukin-2 inducible T-cell kinase: a potential prognostic biomarker and tumor microenvironment remodeling indicator for hepatocellular carcinoma. 34702300_Cytotoxic lymphocytes-related gene ITK from a systematic CRISPR screen could predict prognosis of ovarian cancer patients with distant metastasis. 35210549_ITK independent development of Th17 responses during hypersensitivity pneumonitis driven lung inflammation. 36326697_Inherited human ITK deficiency impairs IFN-gamma immunity and underlies tuberculosis. | ENSMUSG00000020395 | Itk | 17.926304 | 0.429388973 | -1.219643 | 0.46051664 | 6.882742 | 0.0087031967408093772325949899482111504767090082168579101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0444957295359801052736514748175977729260921478271484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 10.2970373 | 4.7563018 | 24.1558105 | 10.8381730 | |
| ENSG00000113356 | 10622 | POLR3G | protein_coding | O15318 | FUNCTION: DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Specific peripheric component of RNA polymerase III which synthesizes small RNAs, such as 5S rRNA and tRNAs (PubMed:20154270). May direct with other members of the RPC3/POLR3C-RPC6/POLR3F-RPC7/POLR3G subcomplex RNA Pol III binding to the TFIIIB-DNA complex via the interactions between TFIIIB and POLR3F. May be involved either in the recruitment and stabilization of the subcomplex within RNA polymerase III, or in stimulating catalytic functions of other subunits during initiation. Plays a key role in sensing and limiting infection by intracellular bacteria and DNA viruses. Acts as nuclear and cytosolic DNA sensor involved in innate immune response. Can sense non-self dsDNA that serves as template for transcription into dsRNA. The non-self RNA polymerase III transcripts, such as Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNAs (EBERs), induce type I interferon and NF- Kappa-B through the RIG-I pathway (PubMed:19609254, PubMed:19631370). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19609254, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19631370, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20154270}. | 3D-structure;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;DNA-directed RNA polymerase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription | Enables chromatin binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of innate immune response; positive regulation of interferon-beta production; and transcription by RNA polymerase III. Acts upstream of or within cell population proliferation. Located in cytosol and nuclear body. Part of RNA polymerase III complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:10622; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase III complex [GO:0005666]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity [GO:0003899]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; positive regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045089]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0006359]; transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0006383] | 21898682_Decreased levels of POLR3G result in loss of pluripotency and promote differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to all three germ layers but have no effect on cell apoptosis. 28494942_POLR3G regulates small non-coding RNAs and RNA splicing in human pluripotent stem cells. The primary function of POLR3G is in the maintenance rather than repression of transcription. 30820548_Depletion of POLR3G selectively triggers proliferative arrest and differentiation of prostate cancer cells, responses not elicited when POLR3GL is depleted. 30972912_FCER1A (rs7549785) and possibly POLR3G (rs7712322) are shown to be associated with peginterferon alfa-2a response in adult patients with chronic hepatitis B. 33626331_RNA polymerase III is required for the repair of DNA double-strand breaks by homologous recombination. 35637192_A cancer-associated RNA polymerase III identity drives robust transcription and expression of snaR-A noncoding RNA. | 99.622437 | 13.644675035 | 3.770266 | 1.29190636 | 6.838627 | 0.0089207387278782811906863159379099670331925153732299804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0453262961589398424844254975596413714811205863952636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 245.3424301 | 213.1097562 | 18.2040605 | 15.7741959 | |||
| ENSG00000113494 | 5618 | PRLR | protein_coding | P16471 | FUNCTION: This is a receptor for the anterior pituitary hormone prolactin (PRL). Acts as a prosurvival factor for spermatozoa by inhibiting sperm capacitation through suppression of SRC kinase activation and stimulation of AKT. Isoform 4 is unable to transduce prolactin signaling. Isoform 6 is unable to transduce prolactin signaling. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12580759, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20032052}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc | This gene encodes a receptor for the anterior pituitary hormone, prolactin, and belongs to the type I cytokine receptor family. Prolactin-dependent signaling occurs as the result of ligand-induced dimerization of the prolactin receptor. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different membrane-bound and soluble isoforms have been described for this gene, which may function to modulate the endocrine and autocrine effects of prolactin in normal tissue and cancer. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. | hsa:5618; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; endosome lumen [GO:0031904]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ciliary neurotrophic factor receptor binding [GO:0005127]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; leukemia inhibitory factor receptor activity [GO:0004923]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; peptide hormone binding [GO:0017046]; prolactin receptor activity [GO:0004925]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; activation of Janus kinase activity [GO:0042976]; activation of transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0007171]; cellular response to granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus [GO:0097011]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; lactation [GO:0007595]; localization [GO:0051179]; mammary gland alveolus development [GO:0060749]; mammary gland epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0060644]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; oncostatin-M-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038165]; positive regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030890]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation [GO:0031954]; prostate gland growth [GO:0060736]; receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0007259]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030856]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617]; steroid biosynthetic process [GO:0006694] | 11721697_Review: Prolactin receptor signal transduction 11997178_results presented are consistent with a role of the PRL-PRLR system in bone/cartilage formation/repair processes 12021177_Genomic regions containing exons for human prolactin receptor, and 5'-flanking and intronic sequences, were determined and their order was established in chromosome 5p14-13. 12351696_Given its apparent widespread expression, this PRLr isoform may contribute to PRL action. 12391112_Plasma prolactin elevated in exercise and correlated with total prolactin-receptor expression per B lymphocyte. Increase in prolactin-receptor per B lymphocyte in response to exercise. Increased circulating B lymphocytes expressing prolactin receptor. 12477494_Results demonstrate a stimulatory effect of estradiol on the expression of human prolactin receptor mRNA species with alternative exons-1, hE1(3) and hE1(N1)in breast cancer cells. 12559630_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12559630_To evaluate a possible role of prolactin receptor genes in SLE & MS formed an association study of PRLR SNPs was done. No statistically significant difference in the prolactin allele distribution was observed for any of the tested variations. 12668872_the interaction between Cyclophilin A and the PRLR plays a differential regulatory role in the various signaling pathways leading from the PRLR. 12679477_results demonstrate a direct effect of prolactin, via functional prolactin receptors, in reducing the lipoprotein lipase activity in human adipose tissue 12819209_prolactin signaling is attenuated by phosphorylation of the prolactin receptor on Thr391 12937675_expression in hepatocytes was maximum in secondary liver cancer, high in obstructive jaundice, and less in cholelithiasis; expression in cholangiocytes was higher than in hepatocytes and was maximum during obstructive jaundice 15082796_data indicate that the prolactin receptor is a novel SCF(beta-TrCP) substrate and implicate beta-TrCP as an important negative regulator of prolactin signaling and cellular responses to this hormone 15119991_A150C (Leu-->Ile) transversion at exon 6 of PRLR was detected.Polymorphism of prolactin receptors might play a role in mammary carcinogenesis 15119991_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15135067_transactivation occurs through an indirect interaction between erbB2 and prolactin or leptin receptors 15504038_Data support an 'induced-fit' model for prolactin receptor binding where binding of the first receptor to human prolactin induces a conformation change in the hormone creating the second receptor-binding site. 15618286_Prolactin receptor mediates the Vav2 and Nek3 interaction. 15700312_Responsiveness of ovarian carcinomas to prolactin suggest that the prolactin/prolactin receptor system may be a new therapeutic target of ovarian carcinomas. 16103113_prolactin binding initiates limited proteasomal cleavage of its receptor, generating a cell-associated fragment containing the extracellular domain; findings described new potential mediator of prolactin action 16278670_phosphorylation of prolactin receptor on Ser349 is decreased in breast cancer cells lines and primary cancer tissue that exhibit stabilization and accumulation of prolactin receptor 16434456_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16556730_Prolactin acts on the preformed Long Form homodimer to induce active signal transduction, while Short Form heterodimer lacks cytoplasmic sequences essential for activation. 16651265_a novel Estradiol-regulated non-estrogen responsive element-dependent transcriptional mechanism that mediates hPRLR expression 16785991_The data suggest that prolactin synergistically augments epidermal growth factor signaling in T47D breast cancer cells at least in part by lessening EGF-induced epidermal growth factor receptor downregulation. 17177141_An analysis of changes in the the expression of the prolactin receptor in liver fibrosis and liver cirrhosis. 17525486_The data revealed a widespread expresion of PRLR in normal and neoplastic human thyroid tissues. 17785459_residual agonism can be abolished either by further disrupting hormone site 2-receptor contacts by N-terminal deletion, as in Del1-9-G129R-human prolactin (hPRL), or by stabilizing hPRL and constraining its intrinsic flexibility, as in G129V-hPRL 18053149_In this comprehensive analysis covering 59 kb of the PRL locus and 210 kb of the PRLR locus, we found no significant association between common variation in these candidate genes and breast cancer risk or plasma PRL levels. 18053149_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18081308_Results demonstrate that altered extracellular domain conformation, and not just a change in bulk, produces altered conformation of the intracellular signaling region of the receptors. 18207134_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18207134_The resulting pattern of findings confirmed the hypotheses of the significance of the genes involved in the development of affiliative behaviors in the manifestation of ASD, the strongest results were obtained for allelic associations with the PRLR genes. 18252943_Prolactin promotes phosphorylation of PRLr on Ser349 and accelerates endocytosis of PRLr. Prolactin stimulated PRLr phosphorylation, endocytosis, and degradation in Jak2-null cells reconstituted with wild type Jak2. 18316598_GSK3 beta is a bona fide PRLr kinase that phosphorylates PRLr on Ser(349) and is required for the recognition of PRLr by beta Trcp, as well as for PRLr ubiquitination and degradation 18573876_The results of experiments using forced expression of ubiquitin mutants indicate that PRLr polyubiquitination via K63-linked chains is important for efficient interaction of PRLr with AP2 as well as for efficient internalization. 18596217_Mechanisms controlling PRLR isoform expression in the fallopian tube. 18613925_Prolactin receptor is significantly more expressed in male breast carcinoma than in gynaecomastia, and with different patterns of reactivity, suggesting a role for prolactin in male breast carcinogenesis. 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18681966_Autocrine prolactin appears to act as an inducible survival factor in a clonogenic subpopulation of breast cancer cells 18779591_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18779591_a heterozygous single nucleotide polymorphism in exon 6 of the PrlR gene, encoding Ile(146)-->Leu substitution in its extracellular domain confers constitutive activity to the receptor variant 19056863_Data indicate that src family kinases are key mediators of ligand-initiated prolactin receptor internalization, down-regulation, and signal transduction in breast cancer cells. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19153125_Even a very low level of PRLR expression was found to be sufficient to mediate PRL responsiveness in breast cancer cell lines. 19273600_Results suggest that the prolactin receptor conformation as stabilized by S-S bonds is required for the inhibitory action of S1b on prolactin-induced LF-mediated function and JAK2 association. 19276348_Human mammary epithelial cells harboring degradation-resistant PRLr display accelerated proliferation and increased invasive growth. 19574343_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19739126_Increased expression of short form 1b prolactin receptor in prostate cancer cells decreases cell growth and cell migration and reduced invasive capacity. 19897676_Characterization of two constitutively active prolactin receptor variants in a cohort of 95 women with multiple breast fibroadenomas. 19897676_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19906835_short form (sf)1b affects the end result of signaling through the long form(LF) receptor and the effects on cell number also support the concept that the LF:SF1b ratio may be relevant to tumor growth 20032052_four splice variants in spermatozoa 20053995_PRL structure will be a useful guiding tool for further investigations of the molecular mechanisms involved in PRLR dimerization and activation, as well as for the optimization of PRLR antagonists 20214633_Usually where breast STAT5a is present, PRLR is reduced; without STAT5a PRLR becomes abundant. Breast lesions lacking both were tested immunohistochemically for PRLR isoforms. The intermediate isoform was essentially only detected in these lesions. 20335148_The positive correlations in positivity rate between the PRL-R and ER/PR expressions are found only in CerbB-2 positive patients with breast cancer. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20427283_Results strongly support a conformationally mediated obligate-ordered prolactin receptor binding for each of the three lactogenic hormones: prolactin, growth hormone, and placental lactogen. 20453834_prolactin receptor expression is common in colorectal cancer 20547007_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634197_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20655519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20658264_Our study suggests the prolactin receptor gene is a molecular target that may be important in the pathogenesis and progression of lobular neoplasia 20716560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20826546_SIRPalpha modulates PRL receptor-associated signaling as a function of integrin occupancy by mediating integrin-PRL receptor cross-talk and contributing to breast cancer biology. 20846877_Blockade of the PRLR represents a novel treatment for patients with advanced breast or prostate cancer with limited therapeutic options. 20875426_This study allowed to visualize for the first time the loop L5 spanning PRLR2 residues Thr133-Phe140, revealing its central implication for the three intermolecular interfaces of the 1:2 complex between natural prolactin and two PRLR chains. 20889499_Two independent histidines, one in human prolactin and one in its receptor, are critical for pH-dependent receptor recognition and activation. 20962278_acetylation and deacetylation provide the rheostat-like regulation for the cytokine receptor PRLR in its cytoplasmic loop dimerization and subsequent STAT5 activation 21068074_Prolactin receptor signaling contributes to the local inflammatory response within the atherosclerotic plaque and thus to atherogenesis. 21125332_These findings suggest that the polymorphism rs10941235 in the PRLR gene is associated with breast cancer and cancer antigen 15-3 levels in Taiwanese women. 21144038_Rabbit antibodies have high titer and could specifically recognize each isoform of PRLR in breast cancer cell lines and human breast carcinoma biopsies. 21238538_Progesterone induces expression of the prolactin receptor gene through cooperative action of Sp1 and C/EBP transcription factors 21305610_Our results indicate no significant association of prolactin and PRLR polymorphisms with clozapine response, tardive dyskinesia diagnosis or its severity in patients with schizophrenia 21310852_Endogenous GH receptor(GHR) and PRLR associate, possibly as a GHR-PRLR heterodimer, in human breast cancer cells and GH signaling in these cells is largely mediated by the PRLR in the context of both PRLR-PRLR homodimers and GHR-PRLR heterodimers. 21470416_data provide limited support for an association between common variations in PRLR and breast cancer risk 21510945_both Zn(2+) and human PRLr binding influence human PRL conformers in an interdependent fashion 21591677_Functional impact of manipulation on the relative orientation of human prolactin receptor domains. 21670145_Enhanced complex formation of ERalpha dimer with SP1 and C/EBPbeta by E2 has an essential role in the transcriptional activation of the hPRLR gene. 21775057_Data show that cells expressing higher long:short PRLR ratios had increased growth, survival and migration in response to PRL and suggest that PRLR antagonists may be therapeutically beneficial in ovarian cancer. 21816901_The association of the PRLr with HMGN2 enables Stat5a-responsive promoter binding, thus facilitating transcriptional activation and promoting anchorage-independent growth. 21989556_PRL signaling through the long form prolactin receptor causes reduced fatty acid oxidation, increased lipid storage, glucose intolerance, and obesity. 22081226_These results demonstrate important contextual aspects of PRL-PRLR interactions with implications for the analysis of the role of PRL in breast cancer. 22325776_The structure of the human prolactin receptor reveals a structural link between the WSXWS motif, hormone binding, and receptor dimerization and we propose it as a general mechanism for class 1 receptor activation. 22577091_can be activated by three sequence-diverse human hormones: prolactin, GH, and placental lactogen [review] 22606260_PRLr isoforms expression and PRLr subcellular localisation are altered in parathyroid tumours 23159947_The prolactin receptor transactivation domain is associated with steroid hormone receptor expression and malignant progression of breast cancer 23192981_Our data suggest that prolactin receptor presence meaningfully affects growth hormone receptor use in breast cancer cells. 23651351_SNPs of the PRLR gene 5' UTR and promoter region are associated with increased risk for gestational diabetes in a population of Chilean subjects. 23775766_Results demonstrate a novel function for hepatic PRLR in the regulation of insulin sensitivity and provide important insights concerning the nutritional regulation of PRLR expression. 23849393_Data suggest that signal transduction via prolactin and prolactin receptor plays role in trophoblast cell migration and invasion; PRLR is expressed by extravillous cytotrophoblasts and first-trimester placental bed tissue. 24032713_Hypertrimethylation on H3K27 of the p53 gene promoter region due to elevated expression of DeltaS2 PRLR by alternative splicing of the pre-mRNA in its full-length form might serve as a new mechanism underlying prostate cancer 24142695_PRL-induced transient signaling in sensory neurons is governed by PI3K or PKCepsilon, mediated via the PRLR-S isoform, and transient effects mediated by PRLR-S are inhibited by presence of PRLR-L in these cells. 24195502_Thus, the familial hyperprolactinemia appears to be due to a germline, loss-of-function mutation in PRLR, resulting in prolactin insensitivity. 24249584_Negative/low expression is associated with poorly differentiated and larger breast tumors in Poland 24333596_PRL-R attenuation post-transcriptionally increased ZnT2 abundance and redistributed intracellular Zn pools into lysosomes and mitochondria. 24391856_High MFAB expression is associated with testicular germ cell tumor and glioblastomas. 24735798_Major changes in prolactin receptor conformation and dimerization affinity are triggered by single mutations in critical regions of D1. 24758841_PRL induced transient signaling pathways in neurons and modulated ion channels. [review] 24990775_There is a possible role for PRLR in the progression of cervical cancer. 24997655_exposure to prolactin increases TNF-alpha release from CD14(+) monocytes of rheumatoid arthritis patients, which can be abolished by PRLR gene silencing or treating with MAPK inhibitor. 25524456_Study shows that position 146 plays a central role in directing intrinsic properties of the PRLR, including extracellular domain folding, PRL-responsiveness, and ligand-independent activity of the receptor. 25784554_a residue quartet in the extracellular membrane proximal domain of the homodimeric cytokine receptor prolactin receptor is a key regulator of intracellular signaling discrimination 25846210_Data suggest that (1) cell membrane/lipid bilayer binding of PRLR and (2) tyrosine phosphorylation of PRLR intracellular domain are independent. 26095602_long PRLR plays an important role in breast cancer metastasis. 26317306_results highlight PRLR as an independent predictor of favorable prognosis in human breast cancer 26513615_Two markers for the PRL peptide gene and three markers for the prolactin receptor (PRLR) gene were genotyped. 26586670_PRL-PRLR can escalate the impact of breast cancer on bone metastasis and the presence of PRLR in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer bone metastasis has the potential to modulate the microenvironment to induce lytic osteoclast formation. 26641246_This study identified 4 PRLR variations (p.Ile76Val, p.Ile146Leu, p.Glu108Lys and p.Glu554Gln) in 16 Sporadic Prolactinoma in Humans. 26844452_The prolactin receptor is constitutively expressed on regulatory T and effector T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients, and this expression is higher than in healthy individuals. 27480353_Low PRLR expression is associated with Triple Negative Breast Cancer. 27575941_PRLRI146L and PRLRI176V variants are not associated with breast cancer or multiple breast fibroadenomas risk. 27788487_Prl receptor is expressed at different levels in the majority of glioblastoma multiforme tumors. Prolactin stimulation resulted in increased STAT5 phosphorylation and increased cellular invasion. 28377489_These results illustrate promising antitumor activity against PRLR-positive breast cancer xenografts and support the evaluation of anti-PRLR antibody-drug conjugate as potential therapeutic agents in breast cancer. 28980840_In a replication study of the association between the prolactin receptor gene intron C/T polymorphism (rs37389) and recurrent miscarriage, no association was found. 29901521_Prolactin-PRLR signaling may play a crucial role for the progression of type I endometrial cancer (EC) without involving the PTEN mutation in young hyperprolactinemic women without insulin resistance. 30445560_our results identify an association between a gain-of-function PRLR variant and prolactinomas and reveal a new etiology and potential therapeutic approach for these neoplasms. 30987013_loss of the co-expression of PRLR, TGFbetaRI and TGFbetaRII is indicative of aggressiveness and poor patient survival outcomes in breast cancer. 31389293_Association between prolactin receptor expression and proliferation in the endometrium of obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome. 32116231_PRLR probably plays a different role in the development and progression of breast cancer. In luminal A and luminal B HER2-positive subtypes PRLR may act as an oncogen, and in luminal B HER2-negative and ER-, PR-negative subtypes can play a tumor suppressor role. 32199279_Prolactin receptor expression as a novel prognostic biomarker for triple negative breast cancer patients. 32286456_Prolactin Acts on Myeloid Progenitors to Modulate SMAD7 Expression and Enhance Hematopoietic Stem Cell Differentiation into the NK Cell Lineage. 32360085_Upregulation of Prolactin Receptor Expression and Activation of Prolactin Signaling in an Aggressive Triple-Negative Breast Carcinoma During Pregnancy: A Case Report. 33259941_Immunohistochemical localization of prolactin receptor (PRLR) to Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's lymphoma. 33335078_Progesterone receptor isoform-dependent cross-talk between prolactin and fatty acid synthase in breast cancer. 33608185_Prolactin receptor expression and its role in trophoblast outgrowth in human embryos. 33664869_The short isoform of PRLR suppresses the pentose phosphate pathway and nucleotide synthesis through the NEK9-Hippo axis in pancreatic cancer. 33942735_Changes in prolactin receptor location in prostate tumors.', trans 'Cambios en la localizacion del receptor prolactina en tumores prostaticos. 35922139_Breast Cancer and Prolactin - New Mechanisms and Models. 36187116_Prolactin receptor gene transcriptional control, regulatory modalities relevant to breast cancer resistance and invasiveness. | ENSMUSG00000005268 | Prlr | 27.985078 | 0.195919303 | -2.351669 | 0.76608735 | 7.899803 | 0.0049440187978416292452488178810199315194040536880493164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0283134090120497686204892318073689239099621772766113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 10.4134081 | 5.1087254 | 51.7527842 | 24.7980010 | |
| ENSG00000114812 | 7433 | VIPR1 | protein_coding | P32241 | FUNCTION: This is a receptor for VIP. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase. The affinity is VIP = PACAP-27 > PACAP-38. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8926282}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a receptor for vasoactive intestinal peptide, a small neuropeptide. Vasoactive intestinal peptide is involved in smooth muscle relaxation, exocrine and endocrine secretion, and water and ion flux in lung and intestinal epithelia. Its actions are effected through integral membrane receptors associated with a guanine nucleotide binding protein which activates adenylate cyclase. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. | hsa:7433; | plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; G protein-coupled peptide receptor activity [GO:0008528]; peptide hormone binding [GO:0017046]; vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptor activity [GO:0004999]; adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007188]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger [GO:0007187]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284] | 11812772_Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor-1 (VPAC-1) is a novel gene target of the hemolymphopoietic transcription factor Ikaros. 11834941_VPAC1 is a cellular neuroendocrine receptor expressed on T cells that actively facilitates productive HIV-1 infection. 11859928_Thus, the highly diverged chemical properties of the hydrophobic 'YL' motif and charged 'DR(Y)' motif could be a crucial difference between the Secretin Receptor Family and the Rhodopsin Family with respect to receptor activation and G-protein coupling. 11930171_VPAC1 receptor mRNA is expressed in the trigeminal, otic and superior cervical ganglia (prejunctional) and cerebral arteries (postjunctional). 11981043_a small sequence in the third intracellular loop of the VPAC(1) receptor is responsible for the efficient agonist-stimulated intracellular calcium concentration increase 12094871_Genetic complexity of HVR1 quasispecies of hepatitis C virus in patients with cirrhosis. 12133828_a selective filter; Identification of a critical domain for restricting secretin binding 12225791_Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) inhibits the proliferation of bone marrow progenitors through the VPAC1 receptor. 12690118_the role of charged residues in the intracellular loop 3 and the proximal C-terminal tail of hVPAC1 receptor for agonist-induced adenylyl cyclase activation 14599709_cloning and sequencing of 5' flanking region; VPAC1 may play a functional role in development of both cerebellum and adrenal medulla 15171718_Data suggest that vasoactive intestinal peptide directly stimulates cortisol secretion from H295 cells via activation of the VPAC1 receptor subtype. 15247290_the hVPAC1 receptor binds to vasoactive intestinal peptide at its N-terminal ectodomain 15451021_Interaction of different G proteins with the recombinant VPAC1 receptor involves different receptor sub-domains. 15932876_the VPAC1 receptor carboxyl terminus has a role in agonist-induced receptor phosphorylation, internalization, and recycling 16037943_Farnesoid X receptor agonists may increase gallbladder fluid secretion through transcriptional activation of VPAC1. 16520374_analysis of the two-step activation mechanism of VPAC receptor and of class II G protein-coupled receptors 16554109_Thr429 phosphorylation has a role in activation of human VPAC1 16888162_125I-[Bpa28-vasoactive intestinal peptide] was covalently bonded to the 121-133 fragment within the N-terminal ectodomain of the receptor 16888167_Photoaffinity experiments clearly indicated that the 6-28 part of VIP physically interacts with the N-terminal ectodomain of VPAC1 receptor 16888206_MCF-7 cells have VPAC1 receptors that bound the VIP chemotherapeutic conjugate 16888207_observations provide additional evidence for a role of proapoptotic caspase adaptor protein and PAC1 R in the events determining the outcome of prostate cancer 16934434_identification and characterization of novel five-transmembrane(5TM) isoforms of VPAC1 17077178_expression of VIP receptor-1 (VPAC1) and VPAC2 in CD4+ T cells changed reciprocally in the context of the activation state 17611633_The differential expression of VIPR1 in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease mucosa suggests that the VIP system plays different roles in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. 17651798_Both intra- and extracellular Ca2+ play a role in controlling pro-inflammatory functions stimulated by PACAP which acts through a VPAC-1, FPRL1/Galphai/PI3K/ERK pathway and a VPAC-1/Galphas/PKA/p38 pathway to fully activate monocytes 17883247_analysis of VIP 16gamma-glutamyl diamino derivative positive charges on hVPAC1 and hVPAC2 receptor function 17885205_Structural studies provide a detailed molecular understanding of the VIP-VPAC1 receptor interaction. 18000164_VPAC1 signaling tempers normal megakaryopoiesis, and inhibition of this pathway stimulates megakaryocyte differentiation. 18174366_Proinflammatory effect of VIP is mediated via the specific G protein-coupled receptor VIP/pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating protein (VPAC1) receptor as well as via FPRL1. 18351280_VIP and PACAP levels were decreased in anterior vaginal wall of stress urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse patients,they may participate in the pathophysiology of these diseases. 18383379_deficient expression of VPAC1 (vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 1) in immune cells of Rheumatoid Arthritis was associated with the predominant proinflammatory Th1 mileu; reduced VPAC1 expression in RA is associated with genetic polymorphism 18597186_Results indicate that the N-terminal part of VIP physically interacts with the N-ted in the continuity of 6-28 VIP sequence; and the N-terminal part of VIP and its antagonist (PG97-269) have different sites of interaction with the VPAC1 receptor N-ted. 18663606_VIP acts in an autocrine fashion via VPAC1 to inhibit megakaryocyte proliferation and induce proplatelet formation 18668120_HLA-B (*)2705 and a functional polymorphism in VIPR1 gene, might be due to a founder effect or might be the result of a selective pressure. Consequent downregulation of this receptor in presence of a 'danger' signal might influence susceptibility to AS. 18668120_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19309439_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19309439_Patients with idiopathic achalasia show a significant difference in allele, genotype and phenotype of VIPR1 distribution of snps 19598235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20014941_We describe significant upregulation of the SPP1 gene, downregulation of VIPR1, and losses of the VIPR1 gene. 20026142_Results indicate that VPAC1, but not VPAC2 or PAC1, up-regulation in macrophages is a common mechanism in response to acute and chronic pro-inflammatory stimuli. 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20691743_Moreover, we report the markedly nuclear localization of VPAC(1) receptors in estrogen-dependent (T47D) and independent (MDA-MB-468) human breast cancer cell lines 20706588_role of in MicroRNA 525-5p down-modulating VPAC1 expressio 20922191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20922191_The VIPR1 polymorphism, previously linked to gastrointestinal dysmotility disorders, does not represent a common risk factor for gallstones in the general or in an elderly population. 21711977_increased expression in patients with allergic rhinitis 21769421_mRNA expression of the VPAC1 receptor was detected in 51% of the tumor specimens, while the incidence of mRNA expression for VPAC2 was 46%. 21896307_silencing of VPAC1 receptor inhibits vasoactive intestinal peptide effects on both EGF receptor and HER2 transactivation and vascular endothelial growth factor secretion in human breast cancer cells 22166542_The genetic association reported here indicates that VIP/VPAC1 signaling can be a relevant pathway in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes in females 22291440_hree residues play an important role in VPAC1 interaction with the first histidine residue of VIP. These data demonstrate that VIP and PG97-269 bind to distinct domains of VPAC1 22763881_The overexpression of VPAC1 and VPAC2 receptors and COX-2 in cancer tissue gives them a potential role as targets for diagnosis of prostate cancer. 23651810_VPAC1 receptor has a role in endotoxemia in peripheral blood mononuclear cells 24671823_These data suggest that VPAC1 overexpression is associated with poorer differentiation of colon cancer, which is likely caused by subsequent EGFR activation in cancer cells. 24788249_VIP regulates CFTR membrane expression and function in Calu-3 cells by increasing its interaction with NHERF1 and P-ERM in a VPAC1- and PKCepsilon-dependent manner. 25390694_variations at the 3'UTR of the VPAC-1 gene act synergistically to affect the expression of the luciferase as well as of the GFP reporter genes expressed in HEK293T cells. 26712708_VPAC1 rs9677 CC genotype could be correlated with a reduced response to statin therapy and seems to be involved in diabetes cardiomyopathy in female patients with type 2 diabetes. 26881970_The results reveal that more severe inflammation, based on high levels of IL-6, is associated with lower expression of VPAC1 and, conversely, with increased expression of VPAC2. 27381006_In vitro-polarized macrophages by GM-CSF (GM-MO), with a proinflammatory profile, expressed higher levels of VIP receptors, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptors 1 and 2 (VPAC1 and VPAC2, respectively), than macrophages polarized by M-CSF (M-MO) with anti-inflammatory activities. RA synovial macrophages, according to their GM-CSF-like polarization state, expressed both VPAC1 and VPAC2. 30407703_follicle-associated epithelium-adjacent villus epithelium in ileum of Crohn's disease possessed more mucosal mast cells and mucosal mast cells expressing VPAC1 but not VPAC2. 30583864_The promoter region of VIPR1 was methylated and DNA methylation inhibited VIPR1 gene transcription. Deacetylation of H3K27 in the promoter of VIPR1 inhibited the transcription of VIPR1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Low expression of VIPR1 had an adverse prognostic impact on HCC, and such expression is at least partially mediated by epigenetic modification. 30692637_Enhanced expression of VPAC1 in primary gastric cancer correlates with metastasis and poor prognosis.VPAC1 activation induces Ca2+ signaling to promote migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. 30810849_3D structure prediction of VAPC1 and identification of dual natural inhibitors for VPAC1 and EGFR. 31089161_Activation of Th lymphocytes alters pattern expression and cellular location of VIP receptors in healthy donors and early arthritis patients. 31408534_S. Typhimurium infection exploits host VPAC1/VIP to gain survival advantage in human monocytes. 31560089_Findings point out the tumor suppressor roles of VIPR1 in human LUAD pathogenesis. 32807782_Cryo-EM structure of an activated VIP1 receptor-G protein complex revealed by a NanoBiT tethering strategy. 35864952_Activation of VIPR1 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating arginine and pyrimidine metabolism. 35869757_[VIPR1 promoter methylation promotes transcription factor AP-2alpha binding to inhibit VIPR1 expression and promote hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth in vitro]. 36430275_PAC1, VPAC1, and VPAC2 Receptor Expression in Rat and Human Trigeminal Ganglia: Characterization of PACAP-Responsive Receptor Antibodies. | ENSMUSG00000032528 | Vipr1 | 24.828334 | 2.329134647 | 1.219794 | 0.31959173 | 14.791969 | 0.0001200456639129690957672538798028938344941707327961921691894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0012089263835958327566316716783489937370177358388900756835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 37.0258045 | 4.2188373 | 15.9622323 | 2.3135593 | |
| ENSG00000115008 | 3552 | IL1A | protein_coding | P01583 | FUNCTION: Cytokine constitutively present intracellularly in nearly all resting non-hematopoietic cells that plays an important role in inflammation and bridges the innate and adaptive immune systems (PubMed:26439902). After binding to its receptor IL1R1 together with its accessory protein IL1RAP, forms the high affinity interleukin-1 receptor complex (PubMed:2950091,PubMed:17507369). Signaling involves the recruitment of adapter molecules such as MYD88, IRAK1 or IRAK4 (PubMed:17507369). In turn, mediates the activation of NF-kappa-B and the three MAPK pathways p38, p42/p44 and JNK pathways (PubMed:14687581). Within the cell, acts as an alarmin and cell death results in its liberation in the extracellular space after disruption of the cell membrane to induce inflammation and alert the host to injury or damage (PubMed:15679580). In addition to its role as a danger signal, which occurs when the cytokine is passively released by cell necrosis, directly senses DNA damage and acts as signal for genotoxic stress without loss of cell integrity (PubMed:26439902). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14687581, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15679580, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17507369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26439902, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2950091, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3258335}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytokine;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Inflammatory response;Lipoprotein;Mitogen;Myristate;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Pyrogen;Reference proteome;Secreted | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the interleukin 1 cytokine family. This cytokine is a pleiotropic cytokine involved in various immune responses, inflammatory processes, and hematopoiesis. This cytokine is produced by monocytes and macrophages as a proprotein, which is proteolytically processed and released in response to cell injury, and thus induces apoptosis. This gene and eight other interleukin 1 family genes form a cytokine gene cluster on chromosome 2. It has been suggested that the polymorphism of these genes is associated with rheumatoid arthritis and Alzheimer's disease. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:3552; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; copper ion binding [GO:0005507]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; interleukin-1 receptor binding [GO:0005149]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to heat [GO:0034605]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular sodium ion homeostasis [GO:0006883]; connective tissue replacement involved in inflammatory response wound healing [GO:0002248]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; ectopic germ cell programmed cell death [GO:0035234]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:0097192]; fever generation [GO:0001660]; heart development [GO:0007507]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; keratinization [GO:0031424]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of establishment of Sertoli cell barrier [GO:1904445]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:2001240]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of immature T cell proliferation in thymus [GO:0033092]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0045840]; positive regulation of neutrophil migration [GO:1902624]; positive regulation of prostaglandin secretion [GO:0032308]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; positive regulation of steroid biosynthetic process [GO:0010893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010575]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0050999]; regulation of sensory perception of pain [GO:0051930]; response to copper ion [GO:0046688]; response to gamma radiation [GO:0010332]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to L-ascorbic acid [GO:0033591]; response to organonitrogen compound [GO:0010243]; response to ozone [GO:0010193]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] | 11065142_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11079552_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11138328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11145356_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11233912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11241561_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11264025_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11350500_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11350506_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11423389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11427627_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11436125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11448121_The level of IL-1 alpha is significantly higher in sera of cicatricial pemphigoid patients with active disease before intravenous immunoglobulin therapy compared to the post-treatment level. 11453239_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11640949_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11669478_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11703512_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11737511_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11774556_Allele specific regulation of cytokine genes: monoallelic expression of the IL-1A gene. Review. 11774564_Interleukin-1 alpha and beta system in testis--quantitative analysis. Expression of immunomodulatory genes in male gonad. 11777547_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11784248_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11790645_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11840488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11858158_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11895290_Meta-analysis of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11895546_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11911995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11921766_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11930657_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11940570_Lipopolysaccharide-mediated reactive oxygen species and signal transduction in the regulation of interleukin-1 gene expression. 11956022_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11991668_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11991668_data indicate that IL-1 gene polymorphisms known to affect the inflammatory response are highly related to plasma levels of CRP and fibrinogen in patients referred for coronary angiography 12028539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12034804_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12037600_Cloning and functional analysis of the allelic polymorphism in the transcription regulatory region 12047332_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12047332_Results suggest a role for the IL1A gene in modifying the clinical features of migraine. 12051868_Interleukin-1 system plays a role in sex steroid receptor gene expression in human endometrial cancer. 12052540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12052541_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12070246_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12100571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12101079_TNF-alpha promoter polymorphism is associated with Il-1 beta synthesis capacity in human leukocytees 12102486_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12115161_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12115182_Association of the interleukin-1 gene cluster on chromosome 2q13 with knee osteoarthritis. 12115182_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12140751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12149413_Review.inheritance of a specific IL-1A gene polymorphism increases risk for development of Alzheimer's disease by as much as sixfold. Moreover, this increased risk is associated with earlier age of onset of the disease. 12161036_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12164325_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12195069_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12209090_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12209090_The IL1A genotype associates with atopy in nonasthmatic adults 12210881_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12212456_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12218254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12220547_Review. The IL-1 family consists of IL-1alpha and IL-1beta, 2 receptors, and a specific receptor antagonist, IL-1Ra. The balance between IL-1 & IL-1Ra in local tissues plays an important role in the susceptibility to & severity of many diseases. 12242547_IL-1A allele 2 is a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease (AD) in a dose-dependent manner, the risk of developing AD with two copies of the IL-1A allele 2 being approximately double that of one copy of the IL-1A allele 2. 12242547_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12362317_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12362317_relationship between interleukin-1A (IL-1A) gene polymorphisms and the susceptibility of chronic periodontitis in Uighur minority in Xingjiang province of China 12370389_IL1-alpha induced during in vitro activation of mast cells by cystic fibrosis-associated Pseudomonas aeruginosa stimulates neutrophil transendothelial migration. 12390476_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12404162_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12425801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12445219_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12445604_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12445604_investigated interleukin polymorphisms in ovarian cancer but did not find any association between common polymorphisms of interleukin 1A, interleukin 1B, and interleukin 1 receptor antagonist and the occurrence of ovarian cancer 12453471_We have identified a novel regulatory sequence at -65 to -41 of the human IL-1alpha promoter 12519748_a 'defective' IL-1ra response to IL-1 may underlie, at least in part, the exaggerated prostaglandin-endoperoxide H synthase (PGHS)-2 induction in orbital fibroblasts 12528118_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12528118_the CTG haplotype of the IL1A gene may be an important marker for the susceptibility to, and the severity of, systemic sclerosis 12528119_that a DNA binding protein containing the Ets domain is constitutively expressed in fibroblasts from the skin of systemic sclerosis patients and regulates transcription of the IL1A gene, contributing to the fibrogenic phenotype of fibroblasts 12530978_soluble form of the IL-1 receptor accessory protein (AcP) increases the affinity of binding of human IL-1alpha and IL-1beta to the soluble human type II IL-1 receptor 12558814_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12558933_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12562360_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12598547_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12613995_In conjunctiva of keratoconjunctivitis sicca patients. 12622850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12626603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12631337_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12631337_The association of the TN7(delTTCA)A haplotype with higher levels of IL-1 alpha expression and reduced risk for ESRD is consistent with involvement of cytokines in risk for developing nephropathy. 12641660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12651617_may enhance the local production of CCL3, which may interact with CCR1 expressed on hepatoma cells, in an autocrine and/or paracrine manner 12667716_Low levels of IL-1 alpha mrna expression are associated with an increased risk for cancer specific death in patients with bladder cancer. 12673844_TNF-alpha & IL-1 produced by sickle leukocytes are the primary factors responsible for the observed CAM expression. This & the subsequent endothelial adherence of sickle erythrocytes play roles in the pathophysiology of sickle-related complications. 12702109_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12710950_IL-1A was used to stimulate epidermal keratinocytes in organ culture. 12714264_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12714264_no one particular polymorphism in the IL-1 gene cluster yields an advantage for survival in the last decades of life 12729191_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12730545_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12737276_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12742380_Activation of vascular endothelial cells by IL-1alpha released by a pulmonary epithelial cell line infected with respiratory syncytial virus. 12746420_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12749050_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12752101_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12752325_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12759172_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12782964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12794386_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12801479_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12824054_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12869004_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12874528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12890860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12899665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12901853_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12913118_the constitutively up-regulated expression of pre-IL-1 alpha in the nuclei of systemic sclerosis (SSc) fibroblasts up-regulates proliferation and matrix production of SSc fibroblasts through binding necdin 12928052_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12928381_Monoallelic expression of IL-1 alpha is observed in Th0, Th1, and Th2 cell clones from healthy individuals, as well as in synovial fluid of the knee joint derived from rheumatoid arthritis patients. 12930304_confirm the role of uPA in acantholysis and suggest an involvement of IL-1alpha/TNF-alpha in uPA induction 12930389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12931024_In pancreatic cancer, IL-1alpha enhanced alpha(6)beta(1)-integrin expression, probably via increased IL-1RI levels. 12946945_Proapoptotic stimuli upregulate MCP-1 expression by vascular smooth muscle cells through release of interleukin-1alpha. 12947160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12974682_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 13679381_IL-1alpha activity in chondrocytes is independent of any direct modification in UDPGD activity and manifests equally in human cartilage of all ages 14514232_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14533660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14566095_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14584862_Observational study of gene-gene interaction and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14633625_Cancer cell-derived cytokines, such as IL-1 alpha, induce cachexia by affecting leptin-dependent metabolic pathways. 14634838_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14639688_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14644395_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14656692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14664464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14672899_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14673470_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14674121_serum IL-1 alpha and IL-1 soluble receptor type 2 levels in women with ovarian cancers were significantly higher than those in cervical cancer, and in patients with benign disorders, and in healthy control 14688369_In IL-1 alpha transgenic mice, which may overproduce membrane-associated (MA)IL-1 as well as soluble IL-1 alpha, severity of arthritis highly correlates with MA-IL-1 activity rather than with soluble IL-1 alpha activity or serum IL-1 alpha concentration. 14693849_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14705223_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14705223_The IL-1alpha-889 polymorphism, previously shown to predispose to increased IL-1 protein expression, may be involved in susceptibility to systemic sclerosis 14735144_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14974822_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14983027_Precursor form of IL-1alpha was overexpressed in various cells and assessed for activity in the presence of saturating concentrations of IL-1 receptor antagonist 14984963_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14986816_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14997019_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15007345_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15007345_polymorphisms of IL1A (G/T at +4845) and IL4RA (T/C at +22446) show an epistatic effect on the risk of atopy 15009111_cells of keratinocyte origin (SCC 12F) respond to a single physiologic dose of solar-simulated irradiation with both early (8 h) and late (72 h) peaks of IL-1alpha mRNA induction 15036245_The presence of high amounts of intracellular IL-1alpha in human dermal fibroblasts suggests that these cytokines may carry out important function inside cells 15039285_(125)I fibrinogen demonstrated no specific interaction of IL-1alpha with fibrinogen 15050696_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15068111_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15082121_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15082121_The results suggest a possible contribution of the IL-1 gene locus polymorphisms to the pathogenesis of LBP. 15117956_IL-1beta is the critical regulator of tuberculosis-stimulated CCL5 secretion in the lung. 15130917_IL-1 evokes a complex gene expression program in endothelial cells that includes positive but also negative (feedback) regulators of diverse endothelial cell functions. 15170937_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15190266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15201366_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15219382_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15220553_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15238767_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15248873_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15270852_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15308963_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15338333_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15341923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15351436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15361128_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15377701_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15381245_Potential in tissue repair for injured human keratinocytes 15465625_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15468358_Data show that interleukin 1-alpha (IL-1a) is an important autocrine fibrogenic factor in systemic sclerosis (SSc) and suggest that inhibition of intracellular IL-1a may be a novel strategy for the treatment of SSc. 15476179_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15476179_The polymorphism distributions of IL-1alpha (-889C/T) showed no differences between the essential hypertension group and control group. 15489227_IL-1-inducible phosphorylation of p65 NFkB is mediated by multiple protein kinases including IKKalpha, IKKbeta, IKKepsilon, TBK1, and an unknown kinase and couples p65 to TAFII31-mediated IL-8 transcription 15514971_A potent cytokine stimulus for IL-8 RNA stabilization in breast cancer cells. 15551344_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15561982_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15562658_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15562910_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15563458_SHP-2 has a role in regulating IL-1-induced Ca2+ flux and ERK activation via phosphorylation of PLCgamma1 15566952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15581980_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15587751_serum IL-1 and TNF-alpha are reduced significantly by calcitriol during osteoporosis 15592292_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15633328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15638425_Cellular and subcellular expression of TNF-alpha, IL-1alpha and IL-6 in hepatocytes inx chronic hepatitis C. 15679580_IL-1alpha, TNF-alpha, CCL20, CCL27, and CXCL8 alarm signals are induced in human cells after allergen and irritant exposure 15679582_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15694997_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15723707_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15726267_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15727567_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15732864_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15732864_polymorphisms may play an important role in determining generalized aggressive periodontits susceptibility in Chinese males 15733644_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15737206_essential role for soluble factors, mainly IL-1alpha and bFGF, in the stimulation of dermal fibroblasts by human melanoma cells to secrete MMP-1. 15745939_The significant associations between VEGF and the levels of IL6 and IL1 alpha suggest an important role for these cytokines in the development of these tumours. 15777329_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15797878_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15830637_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15836820_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15854776_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15931231_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15951664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15951664_White carriers of the (+484)T haplotype were at increase risk of spontaneous preterm birth. 15954918_Two polymorphisms within the IL-1 gene cluster are associated with ESRD independent of race 15974847_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15974847_individuals carrying the positive genotype have significantly greater risk for developing periodontitis 15986200_Polymorphisms associated with control of gene expression and protein levels were not associated with occurrence of chronic idiopaathic leukemia in adults and were not responsible for the increased cytokines. 16021081_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16030091_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16046471_IKKbeta phosphorylates multiple p65 sites, as well as in an IkappaB-p65 complex, and S468 phosphorylation slightly reduces TNF-alpha- and IL-1beta-induced NF-kappaB activation 16078996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16100774_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16101131_Data demonstrates that IL-1alpha and COX-2 mRNA are frequently co-expressed in human gastric cancer tissues, and suggest that the IL-1alpha-COX-2 pathway might be involved in tumor progression by regulating cancer cell proliferation. 16106254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16115908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16155691_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16159520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16206345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16226351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16230423_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16246569_N-terminal IL-1alpha propiece increases ECV304 tumor cell motility. 16268484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16291395_The proteolytic activation of pro-MMP-9 in skin inflammatory diseases likely occurs via a pathway including IL-1alpha. 16304445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16317381_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16318580_GBF1 is recruited to the endogenous IRF-9 promoter, and interacts with C/EBP-beta, IL-1, and IL-6 16361815_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16369899_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16378839_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16378839_there is no genetic association between IL1A gene polymorphism and outcome after head injury 16384981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16389181_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16403098_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16410064_enhances tissue type plasminogen activator production in human pulp cells 16410066_induces alkaline phosphatase, osteonectin, and osteocalcin in tooth mineralization and may play a role in the cytoprotection of pulp cells via heme oxygenase-1 expression 16411061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16428739_significantly increases infective endocarditis incidence due to a platelet releasate-susceptible Streptococcus oralis strain, with rapidly increasing numbers of bacteria within the vegetations. 16433908_IL-1 alpha is secreted by middle ear epithelial cells upon exposure to NTHi components and that it can synergistically act with certain of these molecules to up-regulate beta-defensin 2 via the p38 MAP kinase pathway. 16464738_Genetic variations in pro-inflammatory IL-1alpha may predict the clinical outcome of breast carcinoma. 16464738_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16478776_In conclusion, incubation of normal or GD thyrocytes with Th1 cytokines induces a significant reduction in TSH-increased expression of both TPO and ThOXs, an effect partially mediated by NO. 16504015_IL-1alpha can induce selective upregulation of alpha6beta1-integrin and uPA/uPAR in pancreatic cancer cells and these changes may modulate the aggressive functions of pancreatic cancer. 16508980_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16510430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16517748_vitamin D modulates cutaneous inflammatory reactions, at least in part, by increasing the IL-1Ra to IL-1alpha ratio and suppressing IL-18 synthesis in keratinocytes 16546408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16564702_icIL-1ra1 does not act at an intracellular level to alter IL-1 mediated signalling, and is effective in inhibiting IL-1 responses only when released in an ATP-dependent and cell type specific manner 16564703_elevated production of IL-1alpha and TNF-alpha by in vitro stimulated whole blood cell cultures occurs in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease obese patients 16567828_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16573560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16619041_studies demonstrate a novel role for IL-1alpha in mediating a proliferative response to TGF-beta signaling 16636934_Interleukin-1 alpha gene single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with negative response to cyclophosphamide therapy scleroderma patients with alveolitis 16636934_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16684536_NF-kappaB is probably the primary transcription factor by which cAMP counteracts the inhibition of erythropoietin gene expression by IL-1. 16702372_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16708852_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16719905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16720107_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16733901_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16788102_allele-specific expression of IL-1alpha in CD4+ cells is achieved, at least in part, by differential methylation of the promoter 16814297_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16842617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16856121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16879223_the 4G/5G PAI-1 genotype influences the PAI-1 response to IL-1alpha and the modulatory effect of pravastatin 16885196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16888077_results suggest elevation of IL1 in myometrium at the end of pregnancy initiates process of down-regulation of oxytocin receptors in advanced labour resulting in desensitization of the myometrium to elevated levels of oxytocin in blood during lactation 16900886_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16905534_Tyr-542 of SHP-2 modulates IL-1-induced Ca2+ signals and association of the ER with focal adhesions 16907768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16911569_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16918024_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16930778_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16931944_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16938461_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16945028_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16945028_composite genotype was found to be significantly associated with severe chronic periodontitis 16961803_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16965524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16965825_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16965825_a common polymorphism of the interleukin-1alpha gene is associated with the presence of polycystic ovary syndrome 16971486_These findings reveal that nuclear localization of pre-IL-1alpha depends on the binding to HAX-1 and that biological activities might be elicited by the binding to both HAX-1 and IL-1RII in SSc fibroblasts. 16978691_IL-1, FN, and FN-derivatives have interrelated roles in determining biomaterial-modulated macrophage function [review] 17002905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17012236_This study proposes a novel mechanism of TIMP-1 regulation, which ensures an increased supply of the inhibitor after brain injury, and limits extracellular matrix degradation. 17034724_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17083033_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17138334_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17140155_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17141301_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17149369_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17179726_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17197697_Through the study of IRAK modification mutants, two parallel IL-1-mediated signaling pathways for NFkappaB activation, TAK1-dependent and MEKK3-dependent, were uncovered. These two pathways bifurcate at the level of IRAK modification. 17205326_All the polymorphisms within the IL-1alpha gene are in strong linkage disequilibrium and not convincingly associated with fracture risk, BMD, or bone turnover. 17205326_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17214636_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17244613_IL1 induced NF-kappaB activation is NEMO-dependent but does not require IKKbeta 17257312_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17290104_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17290104_PARP-1 haplotypes increased the risk of AD by interaction with the IL-1A -889 allele 2. 17293495_Autocrine actions of endogenous IL-1 alpha, mediated via IL-1RI signaling, contribute to a proproliferative and proinflammatory phenotypic shift in toll like receptor-activated human vascular smooth cells. 17309781_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17309781_the gene polymorphisms of the promotor region of IL-1 alpha at position (-889) are likely to play a pathogenic role in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and in modification of its clinical presentation and severity 17331078_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17335370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17335371_IL-1 genotypes are associated with cytokine levels in patients with aggressive periodontitis and chronic arthritis 17335371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17335373_+4845 alleles may influence post-scaling values of salivary aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase 17335373_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17348886_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17353161_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17355643_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 1736 | ENSMUSG00000027399 | Il1a | 47.566727 | 0.334179560 | -1.581305 | 0.24519713 | 42.997290 | 0.0000000000548157326813315803404632312789197161675969205418823548825457692146301269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000016741538618918475539103829686929728048916388161160284653306007385253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 24.5136135 | 19.0421318 | 73.7398234 | 56.7767551 | |
| ENSG00000115590 | 7850 | IL1R2 | protein_coding | P27930 | FUNCTION: Non-signaling receptor for IL1A, IL1B and IL1RN. Reduces IL1B activities. Serves as a decoy receptor by competitive binding to IL1B and preventing its binding to IL1R1. Also modulates cellular response through non-signaling association with IL1RAP after binding to IL1B. IL1R2 (membrane and secreted forms) preferentially binds IL1B and poorly IL1A and IL1RN. The secreted IL1R2 recruits secreted IL1RAP with high affinity; this complex formation may be the dominant mechanism for neutralization of IL1B by secreted/soluble receptors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10975853, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12530978, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7989776, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9862719}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine receptor that belongs to the interleukin 1 receptor family. This protein binds interleukin alpha (IL1A), interleukin beta (IL1B), and interleukin 1 receptor, type I(IL1R1/IL1RA), and acts as a decoy receptor that inhibits the activity of its ligands. Interleukin 4 (IL4) is reported to antagonize the activity of interleukin 1 by inducing the expression and release of this cytokine. This gene and three other genes form a cytokine receptor gene cluster on chromosome 2q12. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants and protein isoforms. Alternative splicing produces both membrane-bound and soluble proteins. A soluble protein is also produced by proteolytic cleavage. [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]. | hsa:7850; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; interleukin-1 binding [GO:0019966]; interleukin-1 receptor activity [GO:0004908]; interleukin-1, type II, blocking receptor activity [GO:0004910]; immune response [GO:0006955]; negative regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900016]; negative regulation of interleukin-1 alpha production [GO:0032690]; negative regulation of interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway [GO:2000660]; negative regulation of protein processing [GO:0010955]; protein processing [GO:0016485] | 11804955_reduced levels of mRNA in the endometrium of women suffering from endometriosis reveals a profound defect in gene expression with reduced capability of endometrial tissue to down-regulate IL-1 activity 11846196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12356774_the unique sIL1R-II binding ability of human IL-1beta is due to a single amino acid difference compared with monkey IL-1beta 12363051_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12372465_findings point toward a deficiency in the mechanisms involved in the down-regulation of IL-1 actions at the systemic level and reveal soluble interleukin-1 receptor type II as a key factor involved in that process 12377932_to evaluate whether the interleukin (IL)-1 decoy receptor (R)is correlated with severity of infection in critically ill patients and reflects the activation of anti-inflammatory pathways by glucocorticoid hormones 12530978_soluble form of IL-1R AcP contributes to the antagonism of IL-1 action by the type II decoy receptor 12794127_The type II IL-1 decoy receptor acts as a scavenger of IL-1, representing a novel autoregulatory mechanism of the IL-1 system in neutrophils. 14674121_serum IL-1 alpha and IL-1 soluble receptor type 2 levels in women with ovarian cancers were significantly higher than those in cervical cancer, and in patients with benign disorders, and in healthy control 15653174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15705625_a reduced release of sIL-1RII by the endometrial tissue of women with endometriosis and revealed a proteolytic post-translational mechanism which may be involved in the down-regulation of IL-1RII levels 16596202_Increased circulating levels of interleukin 1 receptor, type II is associated with Hepatitis C virus positive patients and with those affected also by non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and cryoglobulinemia syndrome 16971486_These findings reveal that nuclear localization of pre-IL-1alpha depends on the binding to HAX-1 and that biological activities might be elicited by the binding to both HAX-1 and IL-1RII in SSc fibroblasts. 17307738_BACE1 and BACE2 may act as alternative alpha-secretase-like proteases in proteolytic processing of IL-1R2 and APP 17324958_decreased IL1R2 expression is predominant in the eutopic and ectopic endometrium of women with endometriosis when compared with normal women. 17413037_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17482186_Suggest that IL-1RII can neutralize IL-1 beta and counteract its effect on endometrial stromal cells, and may provide a new clinical strategy for the treatment of endometriosis. 17517439_Abnormal interleukin 1 receptor types I and II gene expression in eutopic and ectopic endometrial tissues of women with endometriosis. 17702847_Chorionic gonadotropin down-regulates the expression of the decoy inhibitory interleukin 1 receptor type II in human endometrial epithelial cells. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17919610_Levels of interleukin-1beta and Il1R2in the peritoneal fluid of normal women and patients with endometriosis suffering from pelvic pain and infertility. 18096476_IL1R2 was greatly decreased with future rejection and FLT3, ITGAM, and PDCD1 showed borderline changes in future cardiac rejections. 18315432_was detected more often in chronic periodontitis gingival crevicular fluid than in aggressive periodontitis gingival crevicular fluid, and there was no correlation between gingival crevicular fluid concentration and clinical parameters. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19026558_Results suggest that interleukin-1 receptor type II overexpression is likely, through activation of the IL-1alpha precursor pathway, to enhance cell migration. 19180518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19401759_Alternate splicing of interleukin-1 receptor type II in vitro correlates with clinical glucocorticoid responsiveness in patients with autoimmune inner ear disease. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19489917_IL1R2 showed significant associations with Aspirin-intolerant asthma. 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20062062_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20353565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20652271_ANTXR2 and IL-1R2 polymorphisms are not associated with ankylosing spondylitis in Chinese Han population. 20652271_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20654748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21041274_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21083841_As already reported in endometriotic cells, endometrioid ovarian cancer cells exhibit a decrease in the expression of IL-1RII. These findings highlight a common signature between endometrioid ovarian cancer and implants of endometriosis. 21683158_Results suggest that under atherogenic conditions, there is a decrease in IL-1R2 expression in monocytes/macrophages and in the vascular wall that may facilitate IL-1 signaling. 21704385_interactions between TLR4 and IL-1R2 are associated with cervical pro-inflammatory cytokine concentrations. 22048455_The methylation statuses of the IL10 and IL1R2 genes were significantly reduced in the SLE patient samples relative to the healthy controls 23395675_Intracellular interleukin-1 receptor 2 binding prevents cleavage and activity of interleukin-1alpha, controlling necrosis-induced sterile inflammation. 24313836_Data indicate a significant increase in the levels of IL-8, TNF-alpha and IL-1R2 in the CSF of both meningitis groups as compared to controls, and the concentrations of IFN-gamma and IL-1 differed significantly only between the mumps group and control. 24411993_First study evaluating for associations between cytokine gene variations and the development of persistent breast pain in women following breast cancer surgery: 1 SNP (IL1R2 rs11674595) and 1 haplotype (IL10 haplotype A8) were associated with pain 24818754_A genetic susceptibility locus for AgP may lie within or close to the IL1R2 locus in Japanese aggressive periodontitis. 25432697_results suggested that IL1R2 could have oncogenic potential in osteosarcoma 25650410_Cerebrospinal fluid soluble interleukin-1 Receptor II, but not log interleukin-6, levels were positively correlated with a composite measure of aggression. 25736356_This is the first detection that the genetic variation rs2302589 in IL-1R2 gene was associated with ankylosing spondylitis in Northern Han Chinese. 25849954_Suggest IL-1R2 as potential biomarker of acute respiratory distress syndrome. 26209639_Data show that interleukin-1 receptor type 2 (IL1R2) forms a complex with c-Fos proto-oncogene protein and activates the interleukin-6 (IL-6) and vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) promoters. 26324711_Interleukin-1alpha Activity in Necrotic Endothelial Cells Is Controlled by Caspase-1 Cleavage of Interleukin-1 Receptor-2 26530134_these results reveal that the IL-1/IL-1R2 axis is differentially regulated in the remitting intestinal mucosa of ulcerative colitis patients 26590821_IL1R2 rs2310173 genotype GT was mildly protective against ankylosing spontylitis only in HLA-B27-negative patients. 26607028_reduced risk of preterm birth in Indian women with the minor allele of rs2072476 polymorphism 26888452_IL1R2 hypomethylation and androgen receptor hypermethylation may constitute an important determinant of disease severity, whereas NPR2 hypomethylation and SP140 hypermethylation may provide a biomarker for vulnerability to excessive daytime sleepiness in Obstructive Sleep Apnea 26967533_present study demonstrated the ability of Staphylococcus aureus to induce IL-1RII shedding in myeloid cells 27138824_No significant differences in the lymphocyte mRNA levels of IL-1R2, IL-6R, and Gp130 were observed between MDD patients and NC. These studies suggest abnormal gene expression of these cytokines and their membrane-bound receptors in the lymphocytes of MDD patients, and that their mRNA expression levels in the lymphocytes could be a useful biomarker for depression. 27461004_Data show that all the six inflammation-related CpG-SNPs genotypes including IL1B rs16944, IL1R2 rs2071008, PLA2G7 rs9395208, FAM5C rs12732361, CD40 rs1800686, and CD36 rs2065666 were associated with coronary heart disease (CHD), suggesting an important role of inflammation in the risk of CHD. 28341182_Expression level of IL1R2 was down regulated in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. 29853279_Plasma levels of soluble IL-1R2 are independently associated with parameters of left ventricular adverse remodeling following ST-elevation myocardial infarction. 29901123_The expression of SLC22A4, IL1R2 and VNN3, were independently associated with elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in chronic heart failure patients. 30256493_Data indicate the association between genetic polymorphisms of interleukin 1 receptor type 1 (IL1R1) and interleukin 1 receptor type 2 (IL1R2) and tuberculosis (TB) susceptibility in the Chinese Han population. IL1R1 and IL1R2 and TB susceptibility in the Chinese Han population. 30460760_IL1R2 SNPs rs719250 and rs3218896 are significantly associated with cervical cancer risk among Uygur females from China. 30623603_rs11674595 was significantly associated with the risk of femur head osteonecrosis in the Chinese Han population. 30672138_rs2072472 was significantly associated with a 0.73-fold decreased risk of high-altitude pulmonary edema. 30895747_rs3218977-GG was associated with a decreased risk of lung cancer in Chinese population. rs2072472 had a significant risk-increasing effect in the dominant model. 30895748_Two SNPs (rs4851527 and rs3218896) and haplotypes TGTC and TACT were significantly associated with endometrial cancer risk in Chinese population. 31021479_our data suggest that rs3917225 in IL1R1 , rs2072472 and rs11674595 in IL1R2 were potential risk markers associated with thyroid cancer risk in the Chinese Han population. Our findings provided new insights into the roles of IL1R1 and IL1R2 and the etiology of thyroid carcinoma. 31744444_IL1R2 Polymorphisms are Associated with Increased Risk of Esophageal Cancer. 32252823_The association of genetic polymorphisms in interleukin-1 receptors type 1 and type 2 with age-related hearing impairment in a Taiwanese population: a case control study. 32402117_Association of IL1R2 rs34043159 with sporadic Alzheimer's disease in southern Han Chinese. 32447774_Cell surface IL-1alpha trafficking is specifically inhibited by interferon-gamma, and associates with the membrane via IL-1R2 and GPI anchors. 32727543_Platelet concentrate and type II IL-1 receptor are risk factors for allergic transfusion reactions in children. 33057899_LncRNA A2M-AS1 lessens the injury of cardiomyocytes caused by hypoxia and reoxygenation via regulating IL1R2. 33507149_Induction of the IL-1RII decoy receptor by NFAT/FOXP3 blocks IL-1beta-dependent response of Th17 cells. 33704402_IL-1R2 expression in human gastric cancer and its clinical significance. 33809042_Cytokine Signature of Dengue Patients at Different Severity of the Disease. 34244037_Association of ITPKB, IL1R2 and COQ7 with Parkinson's disease in Taiwan. 34636689_Influence of Sociodemographic Characteristics and Inflammation-Related Gene Variants on the Comfort Level of Caregivers of Patients With Head and Neck Cancer. 34664761_IL1R2 polymorphisms and their interaction are associated with osteoporosis susceptibility in the Chinese Han population. 34865658_The association of genetic polymorphisms in interleukin-1 receptors type 1 and type 2 with sudden sensorineural hearing loss in a Taiwanese population: a case control study. 35087030_Cardiomyocyte IL-1R2 protects heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury by attenuating IL-17RA-mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis. 35943312_Over-expression of IL1R2 in PBMCs of Patients with Coronary Artery Disease and Its Clinical Significance. | ENSMUSG00000026073 | Il1r2 | 177.483452 | 0.429256624 | -1.220088 | 0.12494360 | 97.006884 | 0.0000000000000000000000690867182133892529794922267863560762568880181222815931142098308873067402657852653646841645240783691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000000054908239452777784220766181042662396980743880960062557560191071059918499486229848116636276245117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 93.0894476 | 66.5264427 | 217.9422582 | 155.4413756 | |
| ENSG00000116396 | 3749 | KCNC4 | protein_coding | Q03721 | FUNCTION: This protein mediates the voltage-dependent potassium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a potassium-selective channel through which potassium ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Potassium;Potassium channel;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel | The Shaker gene family of Drosophila encodes components of voltage-gated potassium channels and is comprised of four subfamilies. Based on sequence similarity, this gene is similar to the Shaw subfamily. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the delayed rectifier class of channel proteins and is an integral membrane protein that mediates the voltage-dependent potassium ion permeability of excitable membranes. It generates atypical voltage-dependent transient current that may be important for neuronal excitability. Multiple transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. | hsa:3749; | axon [GO:0030424]; dendrite membrane [GO:0032590]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuronal cell body membrane [GO:0032809]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; voltage-gated potassium channel complex [GO:0008076]; delayed rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:0005251]; potassium channel activity [GO:0005267]; voltage-gated potassium channel activity [GO:0005249]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071805]; potassium ion transport [GO:0006813]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765] | 15485486_Kv3.4 was overexpressed in early stages of Alzheimer disease and in advanced stages was present at high levels in neurodegenerative structures. This subunit regulates delayed-rectifier currents, primary determinants of spike repolarization in neurones 16449802_The characterization of a missense mutation in MiRP2 that affects its phosphorylation and consequent interactions with Kv3.4 is reported. 20093253_Kv3.4 channels exert a permissive role in the cell cycle progression of proliferating uterine vascular smooth cells. 21912965_Although all KV3 subunit transcripts are significantly expressed at embryonic age in whole mouse brain extracts, only KV3.1, KV3.2 and KV3.4 subunit transgenic proteins are present. 22473424_these data suggest that Kv3.4 and Cav1.2 may act together to control Ca(2) -dependent electrical activity of pioneer axons and play important roles during axon pathfinding. 23443853_Ionizing radiation-induced G2/M arrest was preceded by activation of Kv3.4-like voltage-gated potassium channels. 25609640_These results suggest a novel peripheral mechanism of post-spinal cord injury pain sensitization implicating Kv3.4 channel dysregulation and potential Kv3.4-based therapeutic interventions. 26648458_This study provides original evidence to demonstrate the early occurrence and high prevalence of abnormal Kv3.4 expression in oral leucoplakias. Our results support a role for Kv3.4 potassium channel in OSCC tumorigenesis rather than tumour progression and disease outcome. 31471334_HIF-1alpha regulates the invasion, migration and proliferation of oral cancer cells by regulating Kv3.4 expression. 33368632_PKCepsilon associates with the Kv3.4 channel to promote its expression in a kinase activity-dependent manner. | ENSMUSG00000027895 | Kcnc4 | 98.663655 | 0.421086532 | -1.247811 | 0.23737975 | 27.247641 | 0.0000001789934114652979375513204649689180669724919425789266824722290039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000033743394064374493596970838726889496683725155889987945556640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 59.9734921 | 20.2033682 | 143.7884180 | 47.8852800 | |
| ENSG00000116497 | 64766 | S100PBP | protein_coding | Q96BU1 | Alternative splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a protein that was originally identified by its interaction with S100 calcium-binding protein P. Expression of this protein has been reported to be associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. | hsa:64766; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306] | 15632002_can be added to the genetic progression model for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 18089492_S100P is a sensitive and specific marker for the detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma on FNAB specimens on cell-block and smear preparations. 22330678_S100P-binding protein mediates adhesion through regulation of cathepsin Z in pancreatic cancer cells. 25156441_Low S100PBP expression is associated with cervical cancer. | ENSMUSG00000040928 | S100pbp | 206.228004 | 6.238786623 | 2.641265 | 0.81508721 | 9.127290 | 0.0025182452420182571163620455223508542985655367374420166015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0163990756263274577164690271047220448963344097137451171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 365.1900793 | 249.3773978 | 58.1918612 | 39.7330974 | ||
| ENSG00000116701 | 4688 | NCF2 | protein_coding | P19878 | FUNCTION: NCF2, NCF1, and a membrane bound cytochrome b558 are required for activation of the latent NADPH oxidase (necessary for superoxide production). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12207919}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chronic granulomatous disease;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain;TPR repeat | This gene encodes neutrophil cytosolic factor 2, the 67-kilodalton cytosolic subunit of the multi-protein NADPH oxidase complex found in neutrophils. This oxidase produces a burst of superoxide which is delivered to the lumen of the neutrophil phagosome. Mutations in this gene, as well as in other NADPH oxidase subunits, can result in chronic granulomatous disease, a disease that causes recurrent infections by catalase-positive organisms. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. | hsa:4688; | acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; NADPH oxidase complex [GO:0043020]; phagolysosome [GO:0032010]; electron transfer activity [GO:0009055]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; superoxide-generating NAD(P)H oxidase activity [GO:0016175]; superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase activator activity [GO:0016176]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; respiratory burst [GO:0045730]; superoxide anion generation [GO:0042554]; superoxide metabolic process [GO:0006801] | 11483614_Transcriptional regulation of the p67phox gene: role of AP-1 in concert with myeloid-specific transcription factors. Identification of cis-regulatory elements regulating p67(phox), with identification of specific sequences of TF binding sites. 11705402_In a cell-free system, covalent binding between C-terminal-truncated p67phox and rac in the correct fusion order produces a more stable complex than the individual components and significantly influences the duration of fusion-produced oxidase activation. 11796733_detailed study of the protein-protein interactions that occur in the p40-p47-p67(phox) complex of the resting oxidase 11893732_p22(phox), gp91(phox), p47(phox), p67(phox), and p40(phox) existed as a functional complex in the cytoskeletal fraction. 11929750_Val204 in p67(phox), previously shown to be required for NADPH oxidase activity under cell-free conditions, was found to be essential for superoxide production by intact COS-phox cells. 12101222_effect of cPLA2 on its translocation 12130503_NAD(P)H oxidase subunits p47(phox) and p67(phox) are expressed in platelets; and NAD(P)H oxidase-dependent platelet superoxide anion release increases platelet recruitment. 12719414_p67phox and p47phox have roles in regulating a change of conformation in cytochrome b558, which initiates the electron transfer in NADPH oxidase activation 15181005_NOXO1, p47phox, and p67phox regulate Nox3 15256399_NAD(P)H oxidase activity is associated with increased protein levels of p22phox, p47phox, and p67phox, and increased p22phox and nox2 (gp91phox) mRNA expression. 16293794_Increased expression and activity of NAD(P)H oxidase subunits and xanthine oxidase, in part mediated through angiotensin II and PKC-dependent pathways, are important mechanisms underlying increased oxidative stress in human coronary artery disease 16297854_Here we show that the p47(phox)-p67(phox) interaction is disrupted not only by deletion of the PRR but also by substitution for basic residues in the extra-PRR (K383E/K385E). 16310324_Expression of p67(phox) is regulated through mechanisms that include modulation of transcription and translation. 16608528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16626305_These results indicate that Hcy (homocysteine)-stimulated superoxide anion production in monocytes is regulated through PKC-dependent phosphorylation of p47phox and p67phox subunits of NADPH oxidase. 16987007_NADPH oxidase assembly from p67phox was studies at the single-cell level. 17060455_chemoattractant-stimulated superoxide production can be amplified by a positive feedback loop in which p67(phox) targets Vav1-mediated Rac activation 17462995_These data clearly identify PLAGL2 as a novel regulator of NCF2/p67phox gene expression as well as NADPH oxidase activity and contribute to a greater understanding of the transcriptional regulation of NCF2. 17651608_There is an increased expression of NADPH oxidase p47(-PHOX) and p67(-PHOX) factor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17712795_a novel single nucleotide polymorphism in the promoter region 17910042_Single nucleotide polymorphism leads to alternative splicing without altering gene expression or respiratory burst activity. 18029359_p40(phox) translocates p67(phox) to the region of the cytochrome and subsequently switches the oxidase to an activated state dependent upon PtdIns(3)P and SH3 domain engagement. 18424721_As(2)O(3) induced phosphorylation and membrane translocation of the NADPH oxidase subunit p47(phox) and it also increased translocation of Rac1 and p67(phox). 18546332_mutations in CYBB, NCF1, CYBA or NCF2 may play a role in chronic granulomatous disease 18625437_autosomal recessive CGD due to NCF-2 gene mutations, and a novel homozygous and hypomorphic NCF-2 gene mutation was found. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19116138_p67(phox)-SH3(N) specifically functions in gp91(phox)/Nox2 activation probably via facilitating oxidase assembly. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19372141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423521_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19423540_Nine SNPs distributed across eight genetic regions (ALOX5, IRAK3, ITGB2, NCF2, NFKB1, SELP, SOD1, and STAT1) were associated with risk of glioma with P value of C) in NCF2 gene. We show that this mutation is responsible for a drastic decrease of p67phox mRNA and leads to the skipping of exon 3 detected in the low amount of residual mRNA. 27765769_Skeletal muscle protein expression of the NADPH oxidase subunits p22(phox), p47(phox), and p67(phox) was increased in obese relative to lean subjects, where p22(phox) and p67(phox) expression was attenuated by exercise training in obese subjects. 28035544_We analyzed the clinical and laboratory findings of CGD with mutations in the NCF2 gene from amongst our cohort of CGD patients. A homozygous mutation (c.835_836delAC, p.T279fsX294), a deletion in NCF2 gene was found in two cases. In the third case, two heterozygous mutations were detected, IVS13-2A>T on one allele and c.1099C>T (p.) on the other allele. 28096301_Phosphoinositol 3-phosphate regulates reactive oxygen species production by maintaining p40phox and p67phox at the phagosomal membrane. 29483646_Results show that NCF2 expression is highly upregulated in gastric cancer (GC) tumors. However, its mRNA is targeted by miR-532 and its expression repressed. More importantly, NCF2 can in turn upregulate LINC01410 expression via NF-kappaB in GC. 30323221_Activation of PAD4 by membranolytic insults that result in high levels of intracellular calcium (higher than physiological neutrophil activation) leads to rapid citrullination of p47(phox)/NCF1 and p67(phox)/NCF2, as well as their dissociation from PAD4 31245869_NCF2, MYO1F, S1PR4, and FCN1 as potential noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers in patients with obstructive coronary artery: A weighted gene co-expression network analysis. 31794672_Studies indicate that the G allele of neutrophil cytosolic factor 2 (NCF2) rs10911362 provided a protective role against tuberculosis (TB) risk in the Western Chinese Han population. 32666379_Novel NCF2 Mutation Causing Chronic Granulomatous Disease. 33145364_Association of NCF2, NCF4, and CYBA Gene Polymorphisms with Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Chinese Population. 33179520_Upregulation of glutaminase 2 and neutrophil cytosolic factor 2 is associated with the poor prognosis of glioblastoma. 33651148_Potentially functional variants of ERAP1, PSMF1 and NCF2 in the MHC-I-related pathway predict non-small cell lung cancer survival. 34708124_NCF1/2/4 Are Prognostic Biomarkers Related to the Immune Infiltration of Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma. 34971477_Neutrophil cytosolic factor 2 (NCF2) gene polymorphism is associated with juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus, but probably not with other autoimmune rheumatic diseases in children. | ENSMUSG00000026480 | Ncf2 | 311.575398 | 0.343534324 | -1.541474 | 0.14954642 | 104.043639 | 0.0000000000000000000000019790867240749827402740633482570959916125352159651811797332747759527865616391295588982757180929183959960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000000001698372091801279574350473941552679164160160303181783155975284604899400164867984130978584289550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 161.6148026 | 21.2630654 | 472.0538942 | 60.2930500 | |
| ENSG00000116833 | 2494 | NR5A2 | protein_coding | O00482 | FUNCTION: Nuclear receptor that acts as a key metabolic sensor by regulating the expression of genes involved in bile acid synthesis, cholesterol homeostasis and triglyceride synthesis. Together with the oxysterol receptors NR1H3/LXR-alpha and NR1H2/LXR-beta, acts as an essential transcriptional regulator of lipid metabolism. Plays an anti-inflammatory role during the hepatic acute phase response by acting as a corepressor: inhibits the hepatic acute phase response by preventing dissociation of the N-Cor corepressor complex (PubMed:20159957). Binds to the sequence element 5'-AACGACCGACCTTGAG-3' of the enhancer II of hepatitis B virus genes, a critical cis-element of their expression and regulation. May be responsible for the liver-specific activity of enhancer II, probably in combination with other hepatocyte transcription factors. Key regulator of cholesterol 7-alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7A) expression in liver. May also contribute to the regulation of pancreas-specific genes and play important roles in embryonic development. Activates the transcription of CYP2C38 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P45448, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15707893, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15723037, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15897460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16289203, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20159957}. | 3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Lipid-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | The protein encoded by this gene is a DNA-binding zinc finger transcription factor and is a member of the fushi tarazu factor-1 subfamily of orphan nuclear receptors. The encoded protein is involved in the expression of genes for hepatitis B virus and cholesterol biosynthesis, and may be an important regulator of embryonic development. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2016]. | hsa:2494; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription coregulator binding [GO:0001221]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; acinar cell differentiation [GO:0090425]; bile acid metabolic process [GO:0008206]; calcineurin-mediated signaling [GO:0097720]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching [GO:0009792]; homeostatic process [GO:0042592]; hormone-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0009755]; pancreas morphogenesis [GO:0061113]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045070]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; tissue development [GO:0009888] | 11927588_role in regulating aromatase expression in preadipocytes (liver receptor homologue-1) 12820970_Ligands are dispensabe for LRH-1 activation. 12852843_LRH-1 is a nuclear receptor which can assume an active conformation in the absence of a ligand agonist. 12853459_Liver receptor homolog 1 controls the expression of carboxyl ester lipase in pancreas 12972592_PDX-1 regulates expression of LRH-1 during pancreas development. 14671206_LRH-1 is highly expressed in corpus luteum, and it plays an essential role in the regulation of HSD3B2. 14728801_hBIF and HNF1 are involved together in the viral gene expression regulation of the Hepatitis B virus. 15117876_role for LRH-1 in the induction of the progesterone but not the estrogen biosynthetic pathway during granulosa cell differentiation. 15121760_LRH-1 is a positive transcription factor for ABCG5 and ABCG8 and, in conjunction with studies on LRH-1 activation of other promoters, identify LRH-1 as a 'master regulator' for genes involved in sterol and bile acid secretion from liver and intestine 15143151_important functional role of helix 1 in cofactor recruitment and a novel molecular mechanism of transcriptional regulation and cofactor recruitment mediated by hLRH-1 15181096_LRH-1 could be the major transcription factor responsible for the rapid and significant increase in ovarian StAR gene expression after ovulation. 15205472_The liver receptor homolog-1 has emerged as an essential regulator for the expression of cyp7a1 gene. 15218078_LHR-1 regulgates apolipoprotein A-1 transscription, and affects cholesterol homeostasis. 15613430_CYP11A1 expression in human granulosa cells is regulated by LRH-1. 15707893_Human LRH-1 receptor binds phosphatidyl inositol second messengers;ligand binding is required for maximal activity. 15723037_hLRH-1's control of gene expression is mediated by phospholipid binding 15923626_Data show that sumoylated LRH-1 is exclusively localized in promyelocytic leukemia protein nuclear bodies, and that this association is a dynamic process regulated in part by SUMO-1. 15963945_suppression of hLRH-1 resulted in cell cycle arrest mediated by the down-regulation of cyclin E1 16091743_LRH-1 is transcriptionally regulated by the estrogen receptor alpha reinforcing the hypothesis that LRH-1 could exert potential oncogenic effects in breast cancer formation. 16282330_LRH-1 and SHP1 regulate 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase promoter and have a role in regulation of cholesterol synthesis and uptake 16439367_phosphorylation of the hinge domain of the nuclear hormone receptor LRH-1 stimulates transactivation 16450584_siRNA interference studies suggested that nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 2 (hLRH-1) acts as a negative regulator in farnesyl pyrophosphate synthetase expression. 16469397_FTF and LRH-1 are two related but different transcription factors in human Caco-2 cells, suggesting that they may be homologues and not orthologues. 17095585_LRH-1 and SF-1 have qualitatively similar actions on FSH-stimulated estrogen and progesterone production. These factors may have overlapping actions in regulation of steroidogenesis that accompanies granulosa cell differentiation. 17522048_LRH-1 stimulation of the FAS LXR response is blocked by the addition of small heterodimer partner (SHP) and that FAS mRNA 17910058_LRH-1/phospholipid and LRH-1/SHP (fragments) interactions are analyzed by counting atomic contact number, identifying hydrogen bonds, and estimating binding free energies 17952562_The present study demonstrated for the first time the increased expression of hLRH-1v1 and hLRH-1 in human gastric cancer, an alteration which may implicate in tumorigenesis. 17977826_LRH-1 is a novel regulator of APOM transcription and further extend the role of this orphan nuclear receptor in lipoprotein metabolism and cholesterol homeostasis 18191017_Sphingosine-1-phosphate induces LRH-1 mRNA expression in MCF-7 cells in a prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)-dependent manner. 18270374_Liver receptor homolog 1 (LRH-1) is a key transcriptional factor required for the hepatic expression of CYP7A1. 18385139_PGC-1alpha is an important co-activator for LRH-1 and that SHP targets the interaction between LRH-1 and PGC-1alpha to inhibit CYP7A1 expression. 18410128_a study, by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, the impact of the ligand on the receptor and the interaction with different cofactor peptides 18508634_Possible unexpected new class of nuclear receptor signaling molecules, but broader functional roles of LRH-1 and these new ligands remain to be established.[REVIEW] 18665078_Differential expression of steroidogenic factors 1 and 2, cytochrome p450scc, and steroidogenic acute regulatory protein in the pancreas. 19015525_structure of the Dax-1:LRH-1 complex provides the molecular mechanism for the function of Dax-1 as a potent transcriptional repressor 19022561_both SF1 and LRH1 can transcriptionally cooperate with the AP-1 family members c-JUN and c-FOS, known to be associated with enhanced proliferation of endometrial carcinoma cells, to further enhance activation of the STAR, HSD3B2, and CYP19A1 PII promoters 19359379_The results indicate that LRH-1 could represent another key regulator of the steroidogenic lineage in MSCs and play a vital role in steroid hormone production in human Leydig cells. 19629617_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20101243_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20133449_results indicate that PGC-1alpha is involved in progesterone production in ovarian granulosa cells by potentiating transcriptional activities of LRH1 proteins. 20159957_selective synthetic agonists induce SUMOylation-dependent recruitment of either LRH-1 or LXR to hepatic APR promoters and prevent the clearance of the N-CoR corepressor complex upon cytokine stimulation 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20607599_Our findings extend this by highlighting LRH-1 as a key regulator of the estrogen response in breast cancer cells through the regulation of ER expression. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20817789_These findings suggest a new role of LRH-1 in promoting migration and invasion in breast cancer, independent of oestrogen sensitivity. 21129436_These results indicated that pluripotent stem cells could be differentiated into steroidogenic cells by the nuclear receptor 5A family of protein via the mesenchymal cell lineage. 21258413_Data indicate an important role of LRH-1 in colorectal tumor GC synthesis. 21392518_The results of this study support the hypothesis that suppression of LRH-1 may potentially be beneficial in the tissue specific regulation of aromatase expression in post menopausal breast cancer. 21536586_crucial role of the estrogen target gene nr5a2 in protecting human islets against-stressed-induced apoptosis 21614002_findings identify an LRH-1 dependent phosphatidylcholine signalling pathway that regulates bile acid metabolism and glucose homeostasis 21949357_LRH-1 transcription is activated up to 30-fold in pancreatic cancer cells compared to normal pancreatic ductal epithelium 21990348_findings demonstrate that signaling through RARs has critical roles in molecular reprogramming and that the synergistic interaction between Rarg and Lrh1 directs reprogramming toward ground-state pluripotency 22048972_NR5A2 modulates gene expression in osteoblasts and some allelic variants are associated with bone mass in Spanish postmenopausal women. 22125638_Data show that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in ABO, sonic hedgehog (SHH), telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 2 (NR5A2) were found to be associated with pancreatic cancer risk. 22187462_The three-dimensional structure of a beta-catenin armadillo repeat in complex with the liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1) ligand binding domain at 2.8 A resolution, is reported. 22359603_in ER-positive breast cancer cells, LRH-1 promotes cell proliferation by enhancing ERalpha mediated transcription of target genes such as GREB-1 22504882_The lipid-free receptor undergoes previously unrecognized structural fluctuations, allowing it to interact with widely expressed co-repressors. 23000165_this study indicates that LRH-1 acts as a transcriptional activator in the regulation of OCT4 gene expression through the cooperative interaction with three binding sites directly or/and indirectly. 23038264_HNF4alpha and LRH-1 promote active transcription histone marks on the Cyp7a1 promoter that are reversed by FGF19 in a SHP-dependent manner 23471216_Expression of human LRH-1 is regulated in a tissue-specific manner, and that the novel promoter region is controlled by the Sp-family, NR5A-family and PGC-1alpha in ovarian granulosa cells in a coordinated fashion. 23537609_Data conclude that SF-1 regulates aromatase expression in GCT; over-expression of LRH-1 suggests that this receptor may be involved in the pathogenesis of GCT by mechanisms other than the regulation of aromatase. 23667258_Experimental evaluation of the predicted ligands identified two compounds that inhibit the transcriptional activity of LRH-1 and diminish the expression of the receptor's target genes. 23737522_Data indicate that sequence divergence has differentially impacted ligand binding and protein dynamics in NR5A2. 23817023_Lrh-1 is necessary for maintenance of the corpus luteum, for promotion of decidualization and for formation of the placenta. 24520076_report the genome-wide location and molecular function of LRH-1 in breast cancer cells and reveal its therapeutic potential for the treatment of breast cancers, notably for tumors resistant to treatments currently used in therapies. 24564400_Data (including data from transgenic overexpression/gene silencing) suggest that NR5A2 modulates signal transduction/cell proliferation in mammary cells; mammary morphology exhibits significant reduction in lateral budding after NR5A2 overexpression. 24570488_during chronic colitis, TNF suppresses intestinal steroidogenic gene expression by inhibiting the activity of NR5A2, thus decreasing glucocorticoid synthesis and sustaining chronic inflammation. 24769073_LRH1 overexpression is associated with increased pancreatic cancer growth and metastatic spread 25435372_Analysis of breast cancer samples reveals that a high LRH-1 level is inversely correlated with CDKN1A expression in breast cancer patients and is associated with poor prognosis 25514243_the NR5A2 rs3790844 polymorphism is associated with increased OS of GC patients in the dominant model, and similar results were found among the female group and tumor size >5 cm group for NR5A2 rs3790843 polymorphism. 25675535_This study demonstrates a critical proproliferative role for LRH-1 in established colon cancer cell lines. 25869073_loss of LRH-1 by siRNA or miR-451 mimics significantly impaired Wnt/beta-catenin activity, leading to G0/G1 cell cycle arrest 25873311_Results identify LRH-1 as a critical component of the anti-inflammatory and fungicidal response of alternatively activated macrophages that acts upstream from the IL-13-induced 15-HETE/PPARgamma axis. 25896302_These findings demonstrate that in vitro LRH-1 can act like SF-1 and compensate for its deficiency. 25943101_AFPR may play a pivotal role in HBV-related hepatocarcinogenesis. 25951367_Studies indicate that liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1) is critical involvement in multiple types of cancer, and represents a desirable target for therapeutic applications. 25987835_our findings present supportive evidence that ApoM is a regulator of human LRH-1 transcription, and further reveal the importance of ApoM as a critical regulator of bile acids metabolism 26241054_these data demonstrate that copper-mediated nuclear receptor dysfunction disrupts liver function in WD and potentially in other disorders associated with increased hepatic copper levels. 26241668_in spermatozoa the LRH-1 effects are closely integrated with the estrogen signaling, supporting LRH-1 as a downstream effector of the estradiol pathway on some sperm functions. 26320367_Down-regulation of MicroRNA-381 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in colon cancer cells through up-regulation of LRH-1. 26398198_SERBP1 is a component of the LRH-1 transcriptional complex. 26400164_LRH-1 drives colon cancer cell growth by repressing the expression of the CDKN1A gene in a p53-dependent manner. 26421305_These findings show that POD-1/TCF21 regulates SF-1 and LRH-1 by distinct mechanisms, contributing to the understanding of POD-1 involvement and its mechanisms of action in adrenal and liver tumorigenesis. 26530052_demonstrate aberrant expressions of SF-1 and LRH-1 in endometriotic granulosa-lutein cells 26553876_Data suggest LRH1/NR5A2 exhibits phospholipid-mediated allosteric control of protein-protein binding interface in interactions with TIF2 (co-activator; transcription intermediary factor 2) and SHP (co-repressor; small heterodimer partner protein). 26592175_The SNPs rs3790843 and rs3790844 in the NR5A2 gene are associated with pancreatic cancer risk in Japanese subjects. 26677080_The present study indicates that miR-381 may be a novel tumor suppressor that blocks HCC growth and invasion by targeting LRH-1. 26761123_NR5A2 may be important in the pathophysiology of preterm birth and exploring noncoding regulators of NR5A2 is warranted 27049310_miR-376c inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer cell growth and invasion by targeting LRH-1 27586588_NR5A2-mediated cancer cell survival is facilitated through augmentation of GATA6 and anti-apoptotic factor BCL-XL levels. 27694446_The dramatic repositioning is influenced by a differential ability to establish stable face-to-face pi-pi-stacking with the LRH-1 residue His-390, as well as by a novel polar interaction mediated by the RJW100 hydroxyl group. The differing binding modes result in distinct mechanisms of action for the two agonists. 27809310_miR-27b-3p levels were found to be significantly negatively correlated with both NR5A2 and CREB1 levels in breast cancer tissues. 27983934_Our study suggests that miR-219-5p regulated the proliferation, migration, and invasion of human gastric cancer cells by suppressing LRH-1. 27984042_Additionally, the authors solved the structure of the human LRH-1 DNA-binding domain bound to a DR0 motif located within the Oct4 promoter. 27996162_The role of NR5A2 in regulating pancreatic cancer stem cell properties and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic carcinoma cells 28081303_The fusion transcript NR5A2-KLHL29FT was identified in normal and cancerous colonic epithelia. It is due to an uncharacterized polymorphic germline insertion of the NR5A2 sequence from chromosome 1 into the KLHL29 locus at chromosome 2, rather than a chromosomal rearrangement. NR5A2-KLH29FT expression levels were significantly lower in colon cancers than in matched normal colonic epithelia. 28363985_The first crystal structure of the LRH-1-PGC1alpha complex , which depicts hydrophobic contacts is identified and described. 28440426_Liver receptor homologue1 (LRH1) is a direct target of miR30d in colorectal carcinoma cells. 28531169_the expression level of LRH-1 can be used as a marker in the early diagnosis of unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion. 28710032_Liver receptor homolog-1 was identified as a direct target gene of miR-136 29048619_our data indicated that miR-381 inhibited migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)by targeting LRH-1, and may represent a novel potential therapeutic target and prognostic marker for NSCLC. 29128635_Results show that LRH-1 is a direct target gene of miR-374b and that decreased miR-374b expression may contribute to the promotion of LRH-1-mediated tumorigenesis of colon cancer. 29237721_Rev-erbalpha regulates Cyp7a1 and cholesterol metabolism through its repression of the Lrh-1 receptor. 29438990_These findings not only demonstrate the significant role of the nuclear receptor LRH-1 in the promotion of intratumoral androgen biosynthesis in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) via its direct transcriptional control of steroidogenesis, but also suggest targeting LRH-1 could be a potential therapeutic strategy for CRPC management. 29443959_transcriptional regulation by NR5A2 links differentiation and inflammation in the pancreas; findings support the notion that, in the pancreas, the transcriptional networks involved in differentiation-specific functions also suppress inflammatory programs; under conditions of genetic or environmental constraint, these networks can be subverted to foster inflammation 29515023_LRH-1-deficient adult mice fed high-fat diet displayed macrovesicular steatosis, liver injury, and glucose intolerance, all of which were reversed or improved by expressing wild-type human LRH-1. Results suggest that LRH-1 maintains the pool of arachidonoyl phospholipids, thus ensuring phospholipid diversity and normal lipid homeostasis in the adult liver. 29545602_LRH1 is highly expressed in chemotherapy-resistant breast cancer.LRH1 enhanced breast cancer cell chemoresistance by upregulating MDC1 and attenuating DNA damage. 29669824_Lrh-1 transcriptionally regulates Oat2. 30044146_rs2816948 not significantly associated with recurrent abortions 30273983_The results of our study indicate that LRH1 predicts NSCLC progression, metastasis, and a dismal prognosis, emphasizing its promising role as a novel target in NSCLC therapies. 30305617_LRH-1 maintains intestinal epithelial health and protects against inflammatory damage. 30320362_Results found the mRNA and protein expression levels of LRH1 were significantly higher in HepG2 and HuH6 hepatoblastoma cell lines and results suggest that LRH1 may contribute to cell proliferation in hepatoblastoma. Hepatoblastoma cells with higher LRH1 expression levels more susceptible to LRH1 inhibition. 30638865_study identified LRH1-driven pathway as a circuitry responsible for hepatocyte identity by using cistromic analysis, improving our understanding of liver pathophysiology and identifying novel therapeutic targets. 30740909_we have provided convincing evidence in vitro and in vivo demonstrating that Nr5a2 can induce lung CSC properties and promote tumorigenesis and progression through transcriptional up-regulation of Nanog. 30923324_Regulation of liver receptor homologue-1 by DDB2 E3 ligase activity is critical for hepatic glucose metabolism. 31058195_Using the cells derived from the model, novel SF-1/Ad4BP- and LRH-1-regulated genes were identified by combined DNA microarray and promoter tiling array analyses. The interaction of SF-1/Ad4BP and LRH-1 with transcriptional regulators in the regulation of ovarian steroidogenesis was also revealed. 31328159_This study describes a novel and critical role of LRH-1 in T cell maturation, functions, and immopathologies and proposes LRH-1 as an emerging pharmacological target in the treatment of T cell-mediated inflammatory diseases. 32037723_GATA6 enhances the stemness of human colon cancer cells by creating a metabolic symbiosis through upregulating LRH-1 expression. 32572717_Impact of NR5A2 and RYR2 3'UTR polymorphisms on the risk of breast cancer in a Chinese Han population. 32931651_Nuclear-mitochondrial crosstalk: On the role of the nuclear receptor liver receptor homolog-1 (NR5A2) in the regulation of mitochondrial metabolism, cell survival, and cancer. 33079429_Epithelial Nr5a2 heterozygosity cooperates with mutant Kras in the development of pancreatic cystic lesions. 33252195_Temporal activation of LRH-1 and RAR-gamma in human pluripotent stem cells induces a functional naive-like state. 33335203_Enantiomer-specific activities of an LRH-1 and SF-1 dual agonist. 34129175_LRH-1 high expression in the ovarian granulosa cells of PCOS patients. 34310734_NF-kappaB Regulation of LRH-1 and ABCG5/8 Potentiates Phytosterol Role in the Pathogenesis of Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Cholestasis. 34561301_Nuclear receptor NR5A2 negatively regulates cell proliferation and tumor growth in nervous system malignancies. 34643922_Nuclear receptor subfamily 5 group A member 2 (NR5A2): role in health and diseases. 35801407_LRH-1/NR5A2 interacts with the glucocorticoid receptor to regulate glucocorticoid resistance. | ENSMUSG00000026398 | Nr5a2 | 8.912102 | 3.140920277 | 1.651187 | 0.63951977 | 6.674823 | 0.0097784221536326952628481734564047656022012233734130859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0486417386504317678097564225936366710811853408813476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 13.6255252 | 2.5971309 | 4.2856483 | 1.1962942 | |
| ENSG00000117091 | 962 | CD48 | protein_coding | P09326 | FUNCTION: Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell surface glycoprotein that interacts via its N-terminal immunoglobulin domain with cell surface receptors including 2B4/CD244 or CD2 to regulate immune cell function and activation (PubMed:27249817, PubMed:12007789). Participates in T-cell signaling transduction by associating with CD2 and efficiently bringing the Src family protein kinase LCK and LAT to the TCR/CD3 complex (PubMed:19494291). In turn, promotes LCK phosphorylation and subsequent activation (PubMed:12007789). Induces the phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic immunoreceptortyrosine switch motifs (ITSMs) of CD244 initiating a series of signaling events that leads to the generation of the immunological synapse and the directed release of cytolytic granules containing perforin and granzymes by T-lymphocytes and NK-cells (PubMed:9841922, PubMed:27249817). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12007789, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19494291, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27249817, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9841922}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal | This gene encodes a member of the CD2 subfamily of immunoglobulin-like receptors which includes SLAM (signaling lymphocyte activation molecules) proteins. The encoded protein is found on the surface of lymphocytes and other immune cells, dendritic cells and endothelial cells, and participates in activation and differentiation pathways in these cells. The encoded protein does not have a transmembrane domain, however, but is held at the cell surface by a GPI anchor via a C-terminal domain which maybe cleaved to yield a soluble form of the receptor. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. | hsa:962; | external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; antigen binding [GO:0003823]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; defense response [GO:0006952]; regulation of adaptive immune response [GO:0002819]; T cell activation [GO:0042110] | 12072193_CM1-induced apoptosis is achieved via different initiation pathways, which are cell-type dependent 12496412_Signal-dependent adhesion of resting NK cells initiated by expression of ICAM-1 is greatly enhanced by coexpression of CD48, even in the absence of cytokines. 15356144_Engagement of natural killer (NK) cell receptor 2B4 by its counterreceptor, CD48, expressed on target cells leads to an inhibition in NK cytotoxicity independent of signaling lymphocytic activation molecule-associated protein (SAP) expression. 15760905_IL-18, IL-18 receptor alpha, and CD48 complex formation via glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor glycan triggers binding to IL-18 receptor beta, and thereby induces intracellular signal transduction and IFN-gamma production. 16081768_Review of recent studies suggests an important role for interactions between 2B4 and CD48 in the course of T cell activation and proliferation 16585556_2B4 (CD244) can stimulate NK cell cytotoxicity and cytokine production by interacting with NK cell expressed CD48 and adds CD48 to the growing number of activating NK cell receptors 16785501_CD48 is an interleukin (IL)-3-induced activating receptor on eosinophils and may be involved in promoting allergic inflammation. 16803907_CD48 is a CD2 and CD244 (2B4)-binding protein 16866884_In conclusion, we cannot confirm a role of human endogenous retrovirus-K18 superantigen polymorphisms or of the CD48 CA repeat for type 1 diabetes susceptibility. 16866884_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17222190_findings indicate that FimH induces host cell signalling cascades that are involved in E. coli K1 invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMEC) and CD48 is a putative HBMEC receptor for FimH 17599905_the mechanism of signal transduction by CD244 is to regulate FYN kinase recruitment and/or activity and the outcome of CD48/CD244 interactions is determined by which other receptors are engaged. 18617371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19494291_CD2 functions as the master switch recruiting CD48 and Lck 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20164429_The ligand (CD48) of the 2B4 receptor can exert both activating and inhibiting signals; natural killer (NK) cells might be at risk for self-killing were it not for the inhibiting signals generated by the 2B4-CD48 interaction. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20833258_Stimulation of CD48 induces rearrangement of signaling factors in lipid rafts, Lck-kinase activity, and tyrosine phosphorylation. 22495247_replication study of association of 2 SNPs in HERV-K18 and 19 tagSNPs in CD48 with schizophrenia (SZ)and type 2 diabetes (T2D) in patients with SZ in 2 Danish samples; no association was found with SZ or with T2D among individuals with SZ for any of the SNPs 23225218_Monocyte-induced natural killer cell dysfunction was markedly attenuated by blocking CD48 receptor 2B4 on NK cells, but not by blockade of NKG2D and NKp30. 24505299_Blockade of 2B4/CD48 interaction resulted in improvement in function via perforin expression and degranulation as measured by CD107a surface mobilization on HTLV-1 specific CD8+ T cells. 24670806_we propose that SLAMF2 engagement regulates adaptive immune responses 25255823_These data demonstrate the important role of CD48 in SA/exotoxins-eosinophil activating interactions that can take place during allergic responses and indicate CD48 as a novel therapeutic target for allergy and especially of AD. 26836239_Our data indicate sCD48 as a SEB-induced 'decoy' receptor derived from eosinophil and therefore as a potential anti-inflammatory tool in S. aureus-induced eosinophil inflammation often associated with allergy. 26860368_The present study provides further insights into the role of the 2B4-CD48 interaction in the fine regulation of CD8(+) T-cell effector function upon antigenic stimulation. 26926492_CD48 expression was increased in patients with a short disease duration compared to both controls and patients with longer disease duration. In patients with short disease duration, increased CD48 expression was associated with alveolar inflammation. 27249817_Data show that 2B4 not only can bind to CD48 in trans but also interacts with CD48 in cis by using the same binding interface. Also, the results demonstrated that constitutive phosphorylation of 2B4 occurs only in the presence of CD48, and that cis binding is sufficient to induce substantial levels of baseline phosphorylation. 27859399_mCD48 and sCD48 are differentially expressed in the peripheral blood of asthma patients of varying severity. sCD48 inhibits CD244-mediated eosinophil activation. These findings suggest that CD48 may play an important role in human asthma. 30306094_soluble CD48 levels were significantly elevated in patients with nonallergic asthma compared to control and to the allergic asthma cohort 31115879_immune receptor CD48 is overexpressed on MM cells together with SLAMF7, and that CD48 may be considered as an alternative target for treatment of MM in cases showing weak expression of SLAMF7. 31419545_this study demonstrates recurrent inflammatory disease caused by a heterozygous mutation in CD48 31922199_CD48 mRNA expression was significantly lower in patients than in normal healthy individuals. 33219153_Human innate lymphoid cell precursors express CD48 that modulates ILC differentiation through 2B4 signaling. 34477021_sCD48 is elevated in non-allergic but not in allergic persistent rhinitis. 34489334_GDF15 induces immunosuppression via CD48 on regulatory T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000015355 | Cd48 | 32.458695 | 0.484537390 | -1.045320 | 0.31133987 | 11.338613 | 0.0007591200357950217414426674622518476098775863647460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0059856657613871272136107926087333908071741461753845214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 21.5539432 | 17.3198148 | 44.6857034 | 35.6444440 | |
| ENSG00000117115 | 11240 | PADI2 | protein_coding | Q9Y2J8 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the deimination of arginine residues of proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12392711, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25621824, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30044909}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a member of the peptidyl arginine deiminase family of enzymes, which catalyze the post-translational deimination of proteins by converting arginine residues into citrullines in the presence of calcium ions. The family members have distinct substrate specificities and tissue-specific expression patterns. The type II enzyme is the most widely expressed family member. Known substrates for this enzyme include myelin basic protein in the central nervous system and vimentin in skeletal muscle and macrophages. This enzyme is thought to play a role in the onset and progression of neurodegenerative human disorders, including Alzheimer disease and multiple sclerosis, and it has also been implicated in glaucoma pathogenesis. This gene exists in a cluster with four other paralogous genes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:11240; | azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; euchromatin [GO:0000791]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; histone H3R26 arginine deiminase activity [GO:0140798]; nuclear estrogen receptor binding [GO:0030331]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein-arginine deiminase activity [GO:0004668]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030520]; negative regulation of chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070100]; negative regulation of lymphocyte chemotaxis [GO:1901624]; substantia nigra development [GO:0021762]; transcription initiation-coupled chromatin remodeling [GO:0045815] | 12392711_molecular cloning and gene organization; expressed by all the living epidermal layers, suggesting that PAD type II is functionally important during terminal differentiation of epidermal keratinocytes 15555572_first report to demonstrate a measurable response in the amounts of peptidylarginine deiminase type II mRNA, protein and activity in human astrocytes by prolonged hypoxic exposure 15629448_hPADI2 and hPADI4 have different roles under physiological and pathological conditions 17469138_The amount of peptidyl arginine deiminase type II enzyme and citrullinated myelin basic protein was increased in multiple sclerosis 17968929_PAD-2 & PAD-4 are only isotypes expressed in synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis & other arthritides; inflammatory cells are major source, but PAD-4 also comes from hyperplastic synoviocytes; both isotypes probably involved in citrullination of fibrin 18645041_These data provide new structure-function dimensions for chemokines in leukocyte mobilization, disclosing an anti-inflammatory role for PAD. 18668562_The citrullinating enzyme PAD-4 was detected in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and spondylarthritides. 18923545_Results describe the in vitro kinetic properties of the human peptidylarginine deiminase isoform 2 (hPAD2), and explore the putative inhibitory action of the methyl ester side chain of paclitaxel. 19478818_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19478818_PADI2 does not contribute to genetic susceptibility to schizophrenia. 19564157_PAD2 is expressed in human monocytic leukaemia THP-1 cells during differentiation into macrophages 20013286_PAD2 activation and aberrant citrullinated proteins could play a role in pathogenesis and have value as a marker for the postmortem classification of neurodegenerative diseases. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20806090_This is the first report demonstrating that like in primary open angle glaucoma, normal tension glaucoma also possesses elevated levels of both PAD2 and protein-bound citrulline. 21878453_Defective regulation of PAD2 in the periphery blood, without the immunological shelter of the blood-brain barrier, may contribute to the development of the autoimmune responses in MS. 22520816_Normal human and canine mammary epithelium showed strong cytoplasmic and nuclear expression of PAD2, but there was reduced PAD2 expression in mammary carcinomas from both species. 22614825_Contact between stimulated T cells and monocyte-macrophages or cytokine-activated monocyte-macrophages constitutes a highly likely source of PAD2 and PAD4, which are observed in inflamed synovial tissues. 22853951_17beta-estradiol stimulation induces the recruitment of PAD2 to target promoters by ERalpha, whereby PAD2 then citrullinates H3R26, which leads to local chromatin decondensation and transcriptional activation. 22911765_PAD2 binds directly to the promoters of the PTN and MAGEA12 genes and that the likely mechanism by which PAD2 regulates expression of these genes is via citrullination of arginine residues 2-8-17 on histone H3 tails. 23022892_These findings suggest that PAD2 and citrullinated proteins may play a key role in the brain pathology of prion diseases. [review] 23562679_Our observations show increased levels of protein deimination but not PAD2 in age related macular degeneration retinas and retinal pigment epithelium suggesting reduced rate of turnover of deiminated proteins. 24384061_Data suggest peptidylarginine deiminase 2 (PAD2) as a possible biomarker in various inflammatory diseases. 24594197_PAD2 and PAD4 have distinct substrate specificities. 24850148_PADI2 and vimentin participate in the apoptotic mechanisms of activated T lymphocytes. 24989433_PAD2 appears to use a substrate-assisted mechanism of catalysis in which the positively charged substrate guanidinium depresses the pKa of the nucleophilic cysteine 25213324_these studies provide the first genetic evidence that PAD2 functions as an oncogene and suggest that PAD2 may promote tumor progression by enhancing inflammation within the tumor microenvironment. 25475141_PAD2 activity was detected in synovial fluid samples from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. 25621824_Protein arginine deiminase 2 binds six calcium ions in an ordered fashion. 25897949_Report increased levels of extracellular PAD2 in the lungs of smokers. 26245941_PAD2 activity was significantly higher in cell-free synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients compared to osteoarthritis patients. 26255191_We identified the presence of PADI3 mRNA expression in synovial tissue and PADI2 and PADI4 mRNA expressions in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. 26927695_this study shows that a miR-4728 downregulates PADI2, a novel rheumatoid arthritis risk gene 27280713_Downregulation of PADI2 is an early event in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer associated with poor prognosis and points toward a possible role of citrullination in modulating tumor cells and their microenvironment. 27599511_Deimination of myelin basic protein (MBP) by peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD) prevents its binding to the proteasome and decelerates its degradation by the proteasome in mammalian cells. Potential anticancer drug tetrazole analogue of chloramidine 2, at concentrations greater than 1 microM inhibits the enzymatic activity of PAD in vitro. 27818200_Multiple proteins citrullinated by hypoxia-induced PADs were identified. In addition, the extracellular domain of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 was citrullinated by human PAD2 in vitro. CONCLUSION: Our data may contribute to understanding of pathophysiology of malignant gliomas from the aspects of protein citrullination. 28403548_Data suggest that protein-arginine deiminase 2 (PADI2) suppresses the proliferation of colonic epithelial cells through catalysis of protein citrullination, and that downregulation of PADI2 expression might therefore contribute to colon carcinogenesis. 28766045_These data suggest that overexpression of the human PAD2 transgene in the epidermis of transgenic mice increases the malignant conversion rate of benign tumors by promoting an inflammatory microenvironment. 28819028_Peptidyl arginine deiminase 2 (PADI2) is required for activation of androgen receptor (AR) signaling under androgen-deprived condition. 29084334_Brain gene expression of PADI2, ZNF385A, PSD2, and A2ML1 and DNA methylation dysregulations are implicated in the alteration of brain tissue properties associated with late-life cognitive decline above and beyond the influence of common neuropathologic conditions. 29148420_the mRNA expression of PADI2, PADI4 and Sp1 is upregulated in rheumatoid arthritis bone marrow CD34+ cells independently of the systemic inflammation or treatment regimen. 30064459_Chronic gingival inflammation is associated with increased local citrullination and PAD2 and PAD4 expression in periodontitis. 30161253_In most rheumatoid arthritis patients, PAD2 and PAD4 are equally efficient in generating citrullinated target sites for anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs) in fibrinogen and ENO1. The binding of autoantibodies to histone H3 was generally higher after citrullination with PAD4 than with PAD2. Citrullinated human serum albumin is not a target for ACPAs. 31243954_PAD2 translocates into the nucleus in response to calcium signaling. 31267364_Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase, Type II (PADI2) Is Involved in Urothelial Bladder Cancer. 31601253_PAD2 expression is upregulated in Tamoxifen resistant breast cancer cells. 31730822_citrullination of fibrinogen by peptidylarginine deiminase 2 impairs fibrin clot structure 31940417_This study shows that ubiquitous or nervous system expression of human PAD2 or PAD4 in Drosophila melanogaster have minimal impact on Drosophila melanogaster lifespan, fecundity, and the response to acute heat stress. 32079300_Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase 2 (PADI2)-Mediated Arginine Citrullination Modulates Transcription in Cancer. 32098295_Peptidylarginine Deiminase Isozyme-Specific PAD2, PAD3 and PAD4 Inhibitors Differentially Modulate Extracellular Vesicle Signatures and Cell Invasion in Two Glioblastoma Multiforme Cell Lines. 32341463_PAD enzymes in rheumatoid arthritis: pathogenic effectors and autoimmune targets. 32785008_The Essential Role of Peptidylarginine Deiminases 2 for Cytokines Secretion, Apoptosis, and Cell Adhesion in Macrophage. 33157227_Citrullination as a novel posttranslational modification of matrix metalloproteinases. 33573274_Peptidylarginine Deiminase Inhibitor Application, Using Cl-Amidine, PAD2, PAD3 and PAD4 Isozyme-Specific Inhibitors in Pancreatic Cancer Cells, Reveals Roles for PAD2 and PAD3 in Cancer Invasion and Modulation of Extracellular Vesicle Signatures. 34274450_PAD2-mediated citrullination of Fibulin-5 promotes elastogenesis. 34421923_PADI2 Polymorphisms Are Significantly Associated With Rheumatoid Arthritis, Autoantibodies Serologic Status and Joint Damage in Women from Southern Mexico. 34569542_The Clinical and Prognostic Significance of Protein Arginine Deiminases 2 and 4 in Colorectal Cancer. 35181688_Syndecan-2 regulates PAD2 to exert antifibrotic effects on RA-ILD fibroblasts. 35737372_Molecular Mechanism of Protein Arginine Deiminase 2: A Study Involving Multiple Microsecond Long Molecular Dynamics Simulations. 36076933_Peptidylarginine Deiminase 2 Gene Polymorphisms in Subjects with Periodontitis Predispose to Rheumatoid Arthritis. | ENSMUSG00000028927 | Padi2 | 58.037300 | 0.353982636 | -1.498250 | 0.24043627 | 39.448855 | 0.0000000003367651921364299817203418075929567329640512696187215624377131462097167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000093302783706225474412548543160471348212325892745866440236568450927734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 29.0995067 | 6.7434974 | 82.6366601 | 18.0363826 | |
| ENSG00000117152 | 5999 | RGS4 | protein_coding | P49798 | FUNCTION: Inhibits signal transduction by increasing the GTPase activity of G protein alpha subunits thereby driving them into their inactive GDP-bound form. Activity on G(z)-alpha is inhibited by phosphorylation of the G-protein. Activity on G(z)-alpha and G(i)-alpha-1 is inhibited by palmitoylation of the G-protein. | Alternative splicing;Lipoprotein;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Schizophrenia;Signal transduction inhibitor | Regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) family members are regulatory molecules that act as GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) for G alpha subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. RGS proteins are able to deactivate G protein subunits of the Gi alpha, Go alpha and Gq alpha subtypes. They drive G proteins into their inactive GDP-bound forms. Regulator of G protein signaling 4 belongs to this family. All RGS proteins share a conserved 120-amino acid sequence termed the RGS domain. Regulator of G protein signaling 4 protein is 37% identical to RGS1 and 97% identical to rat Rgs4. This protein negatively regulate signaling upstream or at the level of the heterotrimeric G protein and is localized in the cytoplasm. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:5999; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; G-protein alpha-subunit binding [GO:0001965]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; brain development [GO:0007420]; dorsal root ganglion development [GO:1990791]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; negative regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0061052]; negative regulation of dopamine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060160]; negative regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045744]; negative regulation of glycine import across plasma membrane [GO:1900924]; negative regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1901380]; positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:2000463]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of heart rate [GO:0010460]; regulation of actin filament organization [GO:0110053]; regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051924]; regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008277]; response to amphetamine [GO:0001975]; response to cocaine [GO:0042220]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to morphine [GO:0043278] | 12023979_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12422374_cytosolic and membrane levels of RGS4 may contribute to the regional differences in the coupling of muscarinic M1 receptors in Alzheimer's disease 12436019_A significant decrease in the transcript encoding regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) in the prefrontal cortex of patients with schizophrenia. 12642592_results suggest that palmitoylation of a Cys residue in the regulator of G protein signaling(RGS) box is critical for RGS16 and RGS4 GAPase activating protein activity and their ability to regulate G protein signaling in mammalian cells 14732600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14732600_The data of this research give modest support for the hypothesis that the regulator of G-protein signaling 4 is a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia. 14755443_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15182322_RGS4 mRNA distribution in human postmortem tissue from normal persons was very dense in most cortical layers examined, with lower density in the basal ganglia and thalamus. 15274033_Results could be interpreted as supporting evidence for the association between RGS4 and schizophrenia. 15369705_RGS4 and beta-tubulin modulate Galpha-GDP and Galpha-GTP states thus modulating MT1 melatonin receptor function. 15381923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15381923_RGS4 polymorphisms are associated with alterations in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (area 9) volumes among schizophrenic patients. 15383626_Although gross indices of signaling were unaffected by RGS4, it slowed the rate of increase in Ins(1,4,5)P3 levels. 15660667_In schizophrenia, significant case-control differences were not observed, though the TDT suggested transmission distortion. For bipolar disorder, an omnibus test suggested differences in the overall distribution of haplotypes bearing all four SNPs. 15660667_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16082709_No association is identified between RGS4 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers, genotypes, or haplotypes and schizophrenia 16082709_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16176390_Data do not directly replicate previous associations of RGS4, but association with SNP 7 in the Scottish population provides some support for a role in schizophrenia susceptibility. 16176390_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16246308_These results provide the first demonstration of a Ca(2+)-dependent interaction between RGS4 and CaM in vivo and show that association in lipid rafts of the plasma membrane might be involved in this physiological regulation of RGS proteins. 16380905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16508931_Finding weakens the evidence that mutations or variation in the RGS4 gene have an effect on schizophrenia susceptibility. 16508931_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16526029_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16526029_Results fail to support the RGS4 as a candidate gene for schizophrenia when evaluated with three SNP markers from promoter region and intron 1. 16604300_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16631129_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16791139_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16791139_this meta-analysis did not find statistically significant evidence for association between RGS4 and PRODH and schizophrenia on the basis of either allelic or genotypic analysis. 16860780_RGS4 is an example of a molecule that may underlie increased vulnerability through either genetic or non-genetic mechanisms, which we suggest may be typical of other genes in a complex, polygenic disorder such as schizophrenia. 16904822_Genetic polymorphisms within RGS4 are unlikely to confer an increased susceptibility to the etiology of schizophrenia. 16904822_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16905560_RGS4 mRNA was inversely correlated with COMT enzyme activity in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex 17006672_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17006672_SNPs in RGS4, G72, GRM3, and DISC1 showed evidence for significant statistical epistasis with COMT. 17055463_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17092693_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17106420_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17220356_examined function, receptor specificity, and expression of R4 subfamily RGS proteins, RGS2, -3, -4, -5, and -8 via missense mutations introduced 17301167_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17301167_RGS4 single nucleotide polymorphism impacts frontal lobe blood oxygenation level-dependent response and network coupling during working memory and results in reductions in gray, white matter structural volume in individuals carrying the A allele. 17408693_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17410640_In RGS4, the G-allele of the previously reported SNP RGS4-1 (single and as part of haplotypes with SNP RGS4-18) was associated with non-deficit schizophrenia but not with deficit schizophrenia. 17410640_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17515439_study identified all common RGS4 polymorphisms & evaluated patterns of linkage disequilibrium in relation to schizophrenia; 2 haplotypes reported to confer liability to SZ had significant promoter activity suggesting functional role for both haplotypes 17588543_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17588543_RGS4 genotypes predicted both the severity of baseline symptoms and relative responsiveness to antipsychotic treatment in patient with schizophrenia. 17707117_Full length cloning and expression analysis of splice variants of RGS4 were performed. 17707117_Multiple splice variant forms of RGS4 and Rgs4 are expressed in human and mouse brain and show differential expression across brain compartments. 17722013_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17722013_the association of regulator of G-protein signalling 4 protein polymorphisms with the phenotypic subgroups of schizophrenia. 18031991_The isolation and characterization of a novel human RGS4 mutant which displays enhanced or gain-of-function (GOF) activity, is described. 18198266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18204343_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18204343_RGS4 variances influence clinical manifestations of schizophrenia 18262772_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18434012_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18434012_RGS4 polymorphism was not associated with treatment response to electroconvulsive therapy in major depressive disorder 18443239_Transgenic overexpression of cardiac myocyte-specific RGS4 attenuates overexpression of hypertrophy-related genes in guanylyl cyclase A-knockout mice. 18470533_Data show that the expression of RGS4 decreases in the prefrontal cortex of postmortem brain samples spanning half a century of human aging (18-67 years). 18583979_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18584117_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18622782_Altered RGS4 expression is not universally present throughout the cortex of people with schizophrenia. 18804346_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18804346_We found evidence of a joint effect between IL3 (rs31400) and DTNBP1 18834502_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19041089_results suggest the possibility that alterations in the expression of RGS4-3 contribute to the development of SCZ. 19059885_Regulator of G-protein signaling 4 suppresses LPS-induced MUC5AC overproduction in the airway. 19201815_Prostaglandin E(2) can induce MUC5AC overproduction via the EP(4) receptor and that RGS4 may have suppressive effects in controlling MUC5AC overexpression in the airway. 19282471_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19282471_RGS4 polymorphisms are associated with variations in cognitive functions and contribute a small but statistically significant proportion of variance in a family-based sample. 19324084_RGS4 plays a key role in G protein coupling selectivity and signaling of the mu- and delta-opioid receptors. 19367581_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19416973_role for endogenous RGS4 protein in modulating delta-opioid receptor signaling in SH-SY5Y cells 19536175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19549919_Findings point to the existence of a mechanism for posttranslational regulation of RGS4 function, which may have important implications for the acquisition of a metastatic phenotype by breast cancer cells. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19937977_A homogeneous sample of 280 schizophrenia patients and 230 healthy controls of Hungarian, Caucasian descent were genotyped for polymorphisms in schizophrenia candidate genes NRG1, DTNBP1, RGS4, G72/G30, and PIP5K2A. 19937977_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20414142_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20414142_RGS4 is a potential susceptible gene for bipolar disorder. 20430014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20627871_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20630860_A novel mechanism involving coordinated regulation of nuclear levels and acetylation of NF-YA and Bcl6 activates RGS4 transcription. 20712983_Localization of Sst2 to the projection prevents excess G-protein activation during the pheromone response. 20816714_RGS4 and RGS10 proteins are detected in postmortem prefrontal cortex. 21041608_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21209077_Opioid-induced down-regulation of RGS4: role of ubiquitination and implications for receptor cross-talk. 21674833_The researchers found evidence that there were significant differences between the D1S1656 locus in the Maghreb population and other populations. 21910931_RGS4 gene variations specifically disrupt prefrontal control of saccadic eye movements. 22157635_Lack of association between the regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) rs951436 polymorphism and schizophrenia. 22253691_These studies indicate that increased RGS4 expression promotes a phenotypic switch of airway smooth muscle, evoking irreversible airway obstruction in subjects with severe asthma. 22753418_Cys-2 and Cys-12 play markedly different roles in the regulation of RGS4 membrane localization, intracellular trafficking, and G(q) inhibitory function via mechanisms that are unrelated to RGS4 protein stabilization. 23093381_The results suggest unaltered membrane RGS4 and cytosolic RGS10 proteins levels in schizophrenia and major depression. 23332465_genetic association study in Chinese Han population: Data suggest an SNP in RGS4 (rs10759) is associated with increased predisposition to schizophrenia via down-regulation of miroRNA (MIRN124) binding to 3-prime-untranslated region of RGS4 mRNA. 23630294_dramatic up-regulation of RGS4 expression in the nucleus accumbens of subjects treated with monoamine-directed antidepressants 23733193_Data indicate that Rab5, Rab7 and Rab11 are involved in RGS4 traffics through plasma membrane recycling or endosome. 23911251_RGS4 and COMT risk variants are associated with brain structural alterations in patient with schizophrenia. 24297163_ectopic expression of R4 subfamily members RGS2, RGS3, RGS4, and RGS5 reduced activated PAR1 wild-type signaling, whereas signaling by the PAR1 AKKAA mutant was minimally affected. 25289860_RGS2 and RGS4 are new interacting partners that play key roles in G protein coupling to negatively regulate kappa-OmicronR signaling. 26088132_RGS4 deletion results in a predisposition to atrial fibrillation from enhanced activity in the G-protein pathway, resulting in abnormal calcium release and corresponding electrical events. 26119705_After alphao dissociates from MOR, RGS4 remains bound to the C-terminal region of MOR 26640232_All of these results confirmed the critical role of RGS4 in NSCLC progression. 26910404_The results of this study demonstrated the association between the variation in the regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) gene, a putative candidate gene for psychosis previously associated with schizophrenia endophenotypes, and psychotic-like experiences (PLEs). 26987813_Data support the notion that the Galpha, but not Gbetagamma, arm of the Gi/o signalling is involved in TRPC4 activation and unveil new roles for RGS and RGS4 in fine-tuning TRPC4 activities. 28219718_Study investigated whether RGS4 could participate in signalling pathways to regulate neurotropic events. These observations suggest that RGS4 is implicated in opioid dependent neuronal differentiation and neurite outgrowth via a 'non-canonical' signaling pathway regulating STAT5B-directed responses. 31330059_MiR-21-3p modulates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and apoptosis via targeting TGS4 in retinal pigment epithelial cells. 31386272_A highly conserved delta-opioid receptor region determines RGS4 interaction. 31587286_lncRNA RPL34-AS1 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion while promoting apoptosis by competitively binding miR-3663-3p/RGS4 in papillary thyroid cancer. 32199913_RGS4 promotes allergen- and aspirin-associated airway hyperresponsiveness by inhibiting PGE2 biosynthesis. 32386256_miR-874-3p inhibits cell migration through targeting RGS4 in osteosarcoma. 32392739_Targeting RGS4 Ablates Glioblastoma Proliferation. 32501280_RGS4 controls Galphai3-mediated regulation of Bcl-2 phosphorylation on TGN38-containing intracellular membranes. 32517689_Regulators of G-protein signaling, RGS2 and RGS4, inhibit protease-activated receptor 4-mediated signaling by forming a complex with the receptor and Galpha in live cells. 35628613_Regulator of G-Protein Signaling-4 Attenuates Cardiac Adverse Remodeling and Neuronal Norepinephrine Release-Promoting Free Fatty Acid Receptor FFAR3 Signaling. | ENSMUSG00000038530 | Rgs4 | 102.260181 | 2.270331163 | 1.182903 | 0.18629866 | 40.363292 | 0.0000000002108659724072454100723606706767462512508437555425189202651381492614746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000061322104408161097911306985767422583766261823257082141935825347900390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 138.9588015 | 22.5141992 | 61.4938241 | 10.3282805 | |
| ENSG00000117298 | 1889 | ECE1 | protein_coding | P42892 | FUNCTION: Converts big endothelin-1 to endothelin-1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9396733}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hirschsprung disease;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc | The protein encoded by this gene is involved in proteolytic processing of endothelin precursors to biologically active peptides. Mutations in this gene are associated with Hirschsprung disease, cardiac defects and autonomic dysfunction. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. | hsa:1889; | early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome [GO:0005768]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; Weibel-Palade body [GO:0033093]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; peptide hormone binding [GO:0017046]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; axonogenesis involved in innervation [GO:0060385]; bradykinin catabolic process [GO:0010815]; calcitonin catabolic process [GO:0010816]; ear development [GO:0043583]; embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:0042733]; embryonic heart tube development [GO:0035050]; endothelin maturation [GO:0034959]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; heart development [GO:0007507]; hormone catabolic process [GO:0042447]; peptide hormone processing [GO:0016486]; pharyngeal system development [GO:0060037]; positive regulation of receptor recycling [GO:0001921]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure by endothelin [GO:0003100]; regulation of vasoconstriction [GO:0019229]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway involved in axon guidance [GO:1902287]; substance P catabolic process [GO:0010814]; sympathetic neuron axon guidance [GO:0097492] | 11723113_ECE-1alpha is expressed at significant levels in various types of human skin cells (including keratinocytes) and that it plays a constitutive role in the processing and UVB-inducible secretion of ET-1 by human keratinocytes 11906289_Toward an optimal joint recognition of the S1' subsites of endothelin converting enzyme-1 (ECE-1), angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), and neutral endopeptidase (NEP). 12011762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12244060_identification of potential residues involved in phosphorylation 12393864_Data demonstrate that the targeting signals specific for endothelin-converting enzyme 1b constitute a regulatory domain that could modulate the localization and the activity of other isoforms. 12464614_ECE1 has a role in limiting Abeta accumulation in the mouse brain 12609744_It is suggested that endothelial cells sense shear stress as oxidative stress and transduce signal for the regulation of the gene expression of ECE. 14597855_Cis-acting elements bind CAAT-box binding protein NF-YB, GATA-2, E2F-2, and a GC-box binding factor associated with transcriptional start sites of ECE-1c. Three polymorphic dinucleotide repeats. Methylation suppressed ECE-1c promoter in endothelium. 15010576_The main isoform to increase in response to high glucose was ECE-1c and it may be one of the factors contributing to the elevated ET-1 peptide levels observed in diabetes. 15126915_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15126915_This EVA-based study suggests that ECE1 interacts with ET1 to influence blood pressure in women. 15240857_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15340356_Neuronal ECE-1 expression was observed in various cortical regions of nondemented subjects. In a case-control study involving patients with late-onset AD, homozygous carriers of the A allele of ECE1 gene had a reduced risk of AD. 15665524_locally synthesized AII could be one of the mediators involved in the down-regulation of ECE-1 16023075_ECE-1 protein expression, prepro-endothelin-1 mRNA, and endothelin-1 peptide release were increased in response to native LDL or oxidized LDL. 16234608_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16526315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16531800_Observations strongly suggest that the expression of ECE is enhanced in neointimal smooth muscle cells at early stages after percutaneous coronary intervention injury in human coronary arteries. 16567585_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16698938_increased neuronal PKCepsilon activity can promote Abeta clearance and reduce AD neuropathology through increased endothelin-converting enzyme activity 16986361_These findings suggest that endothelin-converting enzyme (ECE) is upregulated in the neointima at early stages after percutaneous coronary intervension (PCI) injury. ECE may be one of the mediators in the repair processes after PCI in humans. 17264805_Homozygous carriers of the ECE-1 -839G variant allele exhibited a decreased risk of coronary artery disease 17264805_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17545092_Data show that CD133 and ECE expressions are associated with lymphoid metastasis and prognosis of NSCLC, and their overexpression often suggests unfavorable prognosis of NSCLC. 17592116_Endosomal peptidase ECE-1 degrades neuropeptides in endosomes to disrupt the peptide-receptor-beta-arrestin complex, thereby controlling postendocytic trafficking and signaling of receptors. 17618613_ECE-1b-338C to A variant might be associated with increased risk of CAD in Chinese population. 17618613_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17664854_genotyped 5 single nucleotide polymorphisms in the ECE1 gene in 1,873 individuals from a general Japanese population and identified one associated with hypertension in women 17701914_Endothelin-1 and endothelin-converting enzyme-1 have roles in human granulomatous pathology of eyelid 17712175_Spacio-temporal expression of two endopeptidases, ECE-1 and NEP, involved in the synthesis and degradation of ET-1, might regulate ET-1 action in human endometrium. 17761169_Results show catalytically active ECE-1 was detected in the media of human umbilical vein endothelial cells, and was confirmed by mass spectrometry based assays. 17977716_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18039931_A mechanism by which endosomal ECE-1 degrades neuropeptides in endosomes to disrupt the peptide/receptor/beta-arrestin complex, freeing internalized receptors from beta-arrestins and promoting recycling and resensitization, is proposed. 18334739_A allele was less present in LOAD patients than in controls, but an at limits statistically significant difference was achieved only in subjects aged less than 80 years 18334739_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18781169_Transient ECE-1c overexpression increased PC-3 invasiveness through matrigel, whereas transient ECE-1a expression suppressed invasion 18974277_Enhanced ECE-1 expression induced by hyperglycemia is partly due to activation of the PKC-delta isoform. Thus, inhibition of this PKC isoform may prevent diabetes-related increase in ET-1. 18992253_The crystal structure of the extracellular domain (residues 90-770) of human ECE-1 (C428S) with the generic metalloprotease inhibitor phosphoramidon determined at 2.38 A resolution. 19222484_By degrading endocytosed SP, ECE-1 promotes the recycling and re-sensitization of NK(1) receptors in endothelial cells, and thereby induces re-sensitization of the pro-inflammatory effects of SP. 19289136_C-338 polymorphism of the ECE1 gene might be associated with increased risk of carotid atherosclerosis in the Chinese population. 19289136_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19531493_Endosomal endothelin-converting enzyme-1 is a regulator of beta-arrestin-dependent ERK signaling 19889475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20037208_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20037208_study argues that the ECE1 338A allele is protective against late-onset Alzheimer disease in a Chinese population 20345647_any disease-specific contribution of ECE-1 to the accumulation of Abeta or reduction in local microvascular blood flow in Alzheimer disease or Vascular dementia is probably small. 20346360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20538960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20558134_These data indicate for the first time that PKC activation induces the trafficking and shedding of ECE to and from the cell surface, respectively. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20663017_ECE-1 is not correlated with amyloig beta or clinical diagnosis Alzheimer disease 20725143_ECE-1 influences prostate cancer cell invasion via both ET-1-mediated FAK phosphorylation and ET-1 independent mechanisms. 21554123_4,4'-dihydroxy-trans-stilbene strongly inhibits ECE-1 activity, whereas resveratrol is inactive. 21777246_Our results point to a regulatory function of ET-1, its type B receptor (ET(B)) and endothelin-converting enzyme-1 proteins in transendothelial passage of monocytes 21851036_Results of this study suggest lack of direct correlation of Lys198Asn ET-1 and Thr341lle ECE-1 gene polymorphisms with risk of gestational hypertension and preeclampsia in the studied population of Polish women 22027013_Te results of this study suggested taht genetic variations in MMEL1, ECE1, ECE2, AGER, PLG, PLAT, NR1H3, MMP3, LRP1, TTR, NR1H2, and MMP9 genes do not play major role among the Finnish AD patient cohort. 22322595_Degradation by ECE-1 is a novel mechanism by which CRF(1) receptor is protected from overactivation by physiologically relevant high concentrations of higher affinity ligand to mediate distinct resensitization and downstream signaling. 22416137_Endothelin-converting enzyme-1 (ECE-1) degrades NT in acidic conditions, and its activity is crucial for NTR1 recycling. 22693153_The Alzheimer's disease associated intronic haplotype is linked to the 338A variant of known ECE1b promoter variant, 338C>A (rs213045). 22728136_review of ECE-1 phosphorylation and other stimuli which act induce trafficking of ECE-1 to the cell surface [review] 22731820_results suggest that ECE1 polymorphisms may contribute to the susceptibility of sporadic congenital heart disease in a Chinese population 22972025_involved in the physiological degradation of atrial natriuretic peptide 23022525_The results complete a gap in our understanding of the mechanism(s) behind PKC induced trafficking of ECE-1. 23175834_we demonstrate that a CpG-CA repeat within the human ECE-1c promoter is highly polymorphic, harbors transcriptional start sites 23283972_Endothelin-converting enzymes degrade intracellular beta-amyloid produced within the endosomal/lysosomal pathway and autophagosomes 23360525_study suggests that the severity of periodontal disease may be associated with the expression of metalloendopeptidase genes, including NEP, ECE1 and ADAM17, in the buccal mucosal epithelium. 23816989_Although the presence of a soluble form of ECE-1 has been demonstrated in vitro, it is yet to be shown in any human biological fluid. This study, used a combination of mass spectrometry, Western blotting & quenched fluorescent substrate based enzyme assays & showed presence of catalytically active, soluble form of ECE-1 in CSF of subarachnoid hemorrhage subjects. 23863409_The altered expression of enzymes regulating the activity of ET-1, NEP and ECE-1, during parturition is controlled by inflammatory cytokines. 24000822_phosphoramidon and Abeta peptide binding to hECE-1 24026618_C-338A polymorphism of the ECE-1b gene was associated with an increased risk of ischemic stroke in the Chinese Han population. 24497914_Data indicate endothelin-converting enzyme-1 (ECE-1) as a target for alternative polyadenylation (APA), a regulatory mechanism aberrantly activated in cancer cells, and the mechanisms leading to ECE-1 overexpression in malignant cells. 24595843_Compared with rs213045 G homozygote, rs213045 TG genotype and rs213045 TT/TG genotypes are in dominant model significantly increased the risk of ischemic stroke. 24812665_identify the neural peptidase ECE-1 as a negative regulator of itch on sensory nerves by directly regulating ET-1-induced pruritus 24898255_the primary function of betaARRs and ECE-1 in SP-dependent inflammatory signaling is to promote resensitization, which allows the sustained NK1R signaling from the plasma membrane that drives inflammation 25179465_An arterial-specific enhancer of the human endothelin converting enzyme 1 (ECE1) gene is synergistically activated by Sox17, FoxC2, and Etv2 25226840_Nitric oxide inhibits the production of soluble endothelin converting enzyme-1 by endothelial cells. 25268585_confirmed that endothelin-converting enzyme 1 (ECE1), EDN1, and EDNRB were involved in SP-induced pigmentation and found that EDN1 secretion was affected by ECE1 and EDN1 siRNAs, but not by EDNRB siRNA 25469848_Thus, our findings suggest that ECE-1 may be a novel hypoxia-inducible factor-target gene. 25501500_Structural analysis of membrane-bound hECE-1 dimer using molecular modeling techniques: insights into conformational changes and Abeta1-42 peptide binding. 26543229_CK2-increased ECE-1c protein stability is related to augmented migration and invasion of colon cancer cells, shedding light on a novel mechanism by which CK2 may promote malignant progression of this disease. 26806547_results indicate that PKC-phosphorylated ECE-1 is a TIMAP-PP1c substrate and this phosphatase complex has an important role in endothelin-1 production of EC through the regulation of ECE-1 activity. 27036146_These results indicated that the ECE1 rs212528 and rs213045 polymorphisms had no major role to play in the genetic susceptibility to intracerebral haemorrhage. 28171705_ECE-1 and ECE-2 levels were significantly reduced in post-mortem brains from dementia with Lewy body patients. 29978582_overexpression of ECE-1 in head and neck cancer is a predictor of poor tumor differentiation and prognosis 30626614_Endothelin-converting enzyme-1 regulates glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor signalling and resensitisation. 30926432_current evidence suggests that ECE-1c contributes to cancer aggressiveness and plays a putative role as a key regulator of cancer progression. 31777301_Effects of ECE-1b rs213045 and rs2038089 polymorphisms on the development of contrast-induced acute kidney injury in patients with acute coronary syndrome. 31788944_Endothelin-converting enzyme-1c promotes stem cell traits and aggressiveness in colorectal cancer cells. 32107880_Association of ECE1 gene polymorphisms and essential hypertension risk in the Northern Han Chinese: A case-control study. 32170981_The role of Candida albicans candidalysin ECE1 gene in oral carcinogenesis. 32278308_Placental endothelin-converting enzyme-1 is decreased in preeclampsia. 35645613_Association of Endothelin-Converting Enzyme and Endothelin-1 Gene Polymorphisms with Essential Hypertension in Malay Ethnics. | ENSMUSG00000057530 | Ece1 | 165.640268 | 0.458219154 | -1.125890 | 0.21776598 | 26.303172 | 0.0000002918090607082304475499963739015818475763808237388730049133300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000052668711499183588168877638568954324682636070065200328826904296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 85.8737009 | 32.9562214 | 187.6269405 | 71.6119491 | |
| ENSG00000117318 | 3399 | ID3 | protein_coding | Q02535 | FUNCTION: Transcriptional regulator (lacking a basic DNA binding domain) which negatively regulates the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors by forming heterodimers and inhibiting their DNA binding and transcriptional activity. Implicated in regulating a variety of cellular processes, including cellular growth, senescence, differentiation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and neoplastic transformation. Involved in myogenesis by inhibiting skeletal muscle and cardiac myocyte differentiation and promoting muscle precursor cells proliferation. Inhibits the binding of E2A-containing protein complexes to muscle creatine kinase E-box enhancer. Regulates the circadian clock by repressing the transcriptional activator activity of the CLOCK-BMAL1 heterodimer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8437843}. | 3D-structure;Biological rhythms;Myogenesis;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation | The protein encoded by this gene is a helix-loop-helix (HLH) protein that can form heterodimers with other HLH proteins. However, the encoded protein lacks a basic DNA-binding domain and therefore inhibits the DNA binding of any HLH protein with which it interacts. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. | hsa:3399; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; bHLH transcription factor binding [GO:0043425]; leptomycin B binding [GO:1901707]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; transcription regulator inhibitor activity [GO:0140416]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to leptomycin B [GO:0072750]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; heart development [GO:0007507]; metanephros development [GO:0001656]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045662]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; notochord development [GO:0030903]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of DNA replication [GO:0006275]; response to wounding [GO:0009611] | 12952978_nuclear Id protein acts by sequestering pools of transiently diffusing bHLH protein to prevent reassociation with chromatin domains 15370294_Fluvastatin did not regulate p21 and p27, but down-regulated Id3 and p53 slightly. 15494533_Overexpression of Id3 enhances expression of ICAM-1 and E-selectin, and induces angiogenic processes such as transmigration, matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 expression, and tube formation in cultured vascular endothelial cells. 15583422_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15645115_Id1, 2 and 3 might play a role in the early stages of hepatocarcinogenesis, but not in the development of advanced carcinoma, and might consequently be related to HCC dedifferentiation 16271072_Id1, 3 double-knockdown significantly impaired the ability of gastric cancer cells to form peritoneal metastasis 16449966_ultraviolet radiation-induced apoptosis of immortalized keratinocytes is at least in part due to Id3 upregulation in these cells 16682435_ID proteins (ID1, ID2, ID3 and ID4) were significantly increased in Mecp2-deficient Rett syndrome brain; ID genes are ideal targets for MeCP2 regulation of neuronal maturation that may explain the molecular pathogenesis of Rett syndrome 17537403_PLZF upregulates apoptosis-inducer TP53INP1, ID1, and ID3 genes, and downregulates the apoptosis-inhibitor TERT gene 18281048_estrogen-induced tube formation in vascular endothelial cells requires the presence of Id3, a member of the helix-loop-helix family of transcriptional factors and estrogen increases Id3 phosphorylation via a redox-dependent process 18374504_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18477564_RhoA/Rho-associated kinase signaling plays positive and negative roles in myogenic differentiation, mediated by MRTF-A/Smad-dependent transcription of the Id3 gene in a differentiation stage-specific manner 19054058_There is a mechanism whereby reactive oxygen species upregulation of Id3 relieves repression of bax via E-box-binding factors. 19477940_RNA interference demonstrated that Id3 regulates differentiation and cell cycle (increased Neuro-D6 and p21 mRNA) in neuroblastoma cells 19515385_role in the development of peritoneal metastasis of pancreatic cancer 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20080245_The level of Id-3 protein expression was associated with the malignant potential of gastric tumors. 20185798_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20185798_Results provide novel evidence that Id3 is an atheroprotective factor and link a common SNP in the human ID3 gene to loss of Id3 function and increased carotid intima-media thickness. 20191379_Id1/3 peptide aptamer could represent a nontoxic exogenous agent that can significantly provoke antiproliferative and apoptotic effects in breast cancer cells, which are associated with deregulated expression of Id1 and Id3. 20512523_expression of vFLIP decreased the expression levels of Id2 and Id3 as well as cyclin E and cyclin A compared with the vFLIP-null cells 21030215_ID3 plays a role as an apoptosis inducer in response to X-ray irradiation via the regulation of endogenous beta-catenin level. 21191065_In serum samples of lung cancer patients, galectin 1-mediated Id3 induces expression of interleukin (IL)-10 in functionally altered signal pathways of monocytes and monocyte-derived dendritic cells. 21486943_Study uniquely identifies ID1 and ID3 as negative regulators of the hPSC-hematopoietic transition from a hemogenic to a committed hematopoietic fate, and demonstrates that this is conserved between hESCs and hiPSCs. 21498546_the data establish dysregulation of the Id/bHLH axis as an early and sustained feature of ductal pathogenesis 21837949_The ID3 protein is expressed in prostate cancer, and is elevated with the increase of Gleason score. 21975932_EGFR-AKT-Smad signaling promotes formation of glioma stem-like cells and tumor angiogenesis by ID3-driven cytokine induction. 21993163_Older muscle contained significantly more transcript for Forkhead Box O 1 (FoxO1, p=0.001), Inhibitor of DNA binding 1 (ID1, p=0.009), and Inhibitor of DNA Binding 3 (ID3, p=0.043) than young muscle. 22151756_Overexpression of Id3 triggered apoptosis in A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells, implicating Id3 in negative control of tumor growth. 22698403_Data show that regulation of p21 by ID1 and ID3 is a central mechanism preventing the accumulation of excess DNA damage and subsequent functional exhaustion of cancer-initiating cells (C-ICs). 22882857_Overexpression of Id3 markedly promoted the proliferation and invasive capacity of MCF-7 cells; however, these effects were significantly suppressed by the overexpression of FHL2. 23060149_These findings suggest an essential role of Id1 and Id3 in TGFbeta1 effects on proliferation and migration in prostate cancer cells. 23119064_Data indicate that ID2.K47A, ID2.Q55A and ID3.R52A, ID3.R60A had wildtype like expression levels in E. coli. 23143595_The findings suggested that cooperation between ID3 inactivation and immunoglobulin-MYC gene translocation is a hallmark of Burkitt lymphomagenesis. 23311395_Id1 and Id3 co-expression seems associated with a poor clinical outcome in patients with locally advanced NSCLC treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy 23342268_increased Id1 and Id3 expression attenuates all three cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKN2B, -1A, and -1B) resulting in a more aggressive PCa phenotype. 23768125_High ID3 expression is associated with medulloblastoma seeding and is a poor prognostic factor, especially in patients with Group 4 tumors 23771884_Id proteins, and particularly Id1 and Id3, are critical downstream effectors of BMP signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell. 24222112_ID3 mutations are recurrent events in double-hit B-cell lymphomas. 24292846_Importantly, the distinct ID3 expression patterns in acute leukemias (AL) indicate a specific deregulation of ID3 in the various types of AL and may support subtyping of AL. 24343358_study shows that Id2, Id3 and Id4 are each able to overcome TGF-beta dependence, and establish a role for Ids as key mediators of TGF-beta melanomagenesis 24493312_the combined immunohistochemical detection of VPREB3 and ID3 is applicable to the routine diagnostic in case of mature aggressive B-cell lymphomas. 24603695_Data indicate association of inhibitor of differentiation 3 (ID3) single nucleotide polymorphism rs11574 directly with coronary artery pathology. 24655651_Epigenetic changes in ID3, in combination with experiences of maltreatment, may confer risk for depression in children. 25090023_our data provide evidence that ID3 may play a critical role in regulating vascular endothelial cell survival and development of microvascular lesions induced by persistent environmental pollutants such as PCB153. 25239768_ID3 plays a potential role in the underlying regulatory mechanisms of metabolic health in human obesity. [Review] 25665868_ID3 has a role in the acquisition of molecular stem cell-like signature in microvascular endothelial cells 25778840_Inhibitor of differentiation 4 (ID4) acts as an inhibitor of ID-1, -2 and -3 and promotes basic helix loop helix (bHLH) E47 DNA binding and transcriptional activity. 26384138_Upon Id3 transfection, A549 cells displayed decreased migratory and invasive capabilities, however, co-transfection of miRId3 and Id3 into A549 cells reversed the Id3-induced inhibitions of migratory and invasive capabilities. 26992947_Immunohistochemical detection of inhibitor of DNA binding 3 mutational variants in mature aggressive B-cell lymphoma. 27044543_Results show that ID1, ID3 and IGJ genes are highly expressed in adult B-ALL and correlate with poor prognosis in Hispanic patients. 27176047_The results of the present study revealed that overexpression of Id3 may serve as a novel strategy for inhibiting cisplatinsensitive lung cancer. 28224680_Taken together, we found that Id3+ and CTLA-4+ endometrial cells were significantly higher in women with repeated implantation failure and recurrent miscarriage, suggesting the negative roles of these angiogenesis and immune tolerance markers involving in regulating endometrium receptivity. 29026069_The interactions between ID3 and the DNA damage mediator protein MDC1 suggest that ID3 participates in the DNA damage signaling pathway to maintain genomic stability. 29507860_This review will discuss the current understanding of ID3 in excess fat accumulation and the potential for Estrogenic Endocrine Disruptors to influence susceptibility to obesity or metabolic disorders via ID3 signaling 29593730_this study shows that CD5L promotes M2 macrophage polarization through autophagy-mediated upregulation of ID3 29907859_a critical role for highly altered Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL)-specific microRNA-10a in regulating the development of OPLL by modulating the ID3/RUNX2 axis. 30520117_blocks E47-mediated inhibition of beta-catenin transcription in choloangiocarcinoma cells 31215762_our results show that the suppressive effect of TGF-beta1 on the expression of MMP1 is mediated by a transcription factor, the inhibitor of differentiation 3 (ID3) protein. Our findings provide insights into the molecular interactions and mechanisms of TGF-b1 and ID3 during the regulation of MMP1 in human granulosa-lutein cells. 32039486_miR-212-5p exerts tumor promoter function by regulating the Id3/PI3K/Akt axis in lung adenocarcinoma cells. 32305567_The HBx and HBc of hepatitis B virus can influence Id1 and Id3 by reducing their transcription and stability. 32536579_Correlation of the levels of DNA-binding inhibitor Id3 and regulatory T cells with SLE disease severity. 32760207_LEF1/Id3/HRAS axis promotes the tumorigenesis and progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 33273801_Role of inhibitor of differentiation 3 gene in cellular differentiation of human corneal stromal fibroblasts. 34329970_Amphiregulin stimulates human chorionic gonadotropin expression by inducing ERK1/2-mediated ID3 expression in trophoblast cells. 34520124_ID1/ID3 mediate the contribution of skin fibroblasts to local nerve regeneration through Itga6 in wound repair. 34547407_Heme Oxygenase-1 (HMOX-1) and inhibitor of differentiation proteins (ID1, ID3) are key response mechanisms against iron-overload in pancreatic beta-cells. 34592230_Up-regulated DNA-binding inhibitor Id3 promotes differentiation of regulatory T cell to influence antiviral immunity in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. 34620174_EGF stimulates human trophoblast cell invasion by downregulating ID3-mediated KISS1 expression. 34718742_ID3 promotes homologous recombination via non-transcriptional and transcriptional mechanisms and its loss confers sensitivity to PARP inhibition. 34877804_Loss of ID3 in pancreatic cancer cells increases DNA damage without impairing MDC1 recruitment to the nuclear foci. 35219016_Expression of Id3 represses exhaustion of anti-tumor CD8 T cells in liver cancer. 35599595_Circadian Period 2 (Per2) downregulate inhibitor of differentiation 3 (Id3) expression via PTEN/AKT/Smad5 axis to inhibits glioma cell proliferation. 35678885_Brain infiltration of breast cancer stem cells is facilitated by paracrine signaling by inhibitor of differentiation 3 to nuclear respiratory factor 1. | ENSMUSG00000007872 | Id3 | 61.233906 | 2.381769543 | 1.252034 | 0.25854328 | 23.371700 | 0.0000013352864590649312765389695317752583036963187623769044876098632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000215432375886969533474411819806704215807258151471614837646484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 86.7755122 | 7.1821266 | 36.6387187 | 3.7495675 | |
| ENSG00000118162 | 11133 | KPTN | protein_coding | Q9Y664 | FUNCTION: As part of the KICSTOR complex functions in the amino acid-sensing branch of the TORC1 signaling pathway. Recruits, in an amino acid-independent manner, the GATOR1 complex to the lysosomal membranes and allows its interaction with GATOR2 and the RAG GTPases. Functions upstream of the RAG GTPases and is required to negatively regulate mTORC1 signaling in absence of amino acids. In absence of the KICSTOR complex mTORC1 is constitutively localized to the lysosome and activated. The KICSTOR complex is also probably involved in the regulation of mTORC1 by glucose. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28199306}. | Acetylation;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Lysosome;Membrane;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a filamentous-actin-associated protein, which is involved in actin dynamics and plays an important role in neuromorphogenesis. This protein is part of the KICSTOR protein complex that localizes to lysosomes. Mutations in this gene result in an autosomal recessive form of intellectual disability. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2017]. | hsa:11133; | KICSTOR complex [GO:0140007]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton [GO:0098871]; stereocilium [GO:0032420]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; cellular response to amino acid starvation [GO:0034198]; cellular response to glucose starvation [GO:0042149]; negative regulation of TORC1 signaling [GO:1904262]; protein localization to lysosome [GO:0061462] | 24239382_We have demonstrated that mutations in KPTN, encoding kaptin, cause a syndrome typified by macrocephaly, neurodevelopmental delay, and seizures. 28199306_identification of a protein complex (KICSTOR) that is composed of four proteins, KPTN, ITFG2, C12orf66 and SZT2, and that is required for amino acid or glucose deprivation to inhibit mTORC1 in cultured human cells 32358097_Pathogenic variants in KPTN gene identified by clinical whole-genome sequencing. 32808430_Pathogenic variants in KPTN, a rare cause of macrocephaly and intellectual disability. | ENSMUSG00000006021 | Kptn | 38.168533 | 0.449136193 | -1.154775 | 0.29901643 | 14.793302 | 0.0001199608335201497619172325559411262929643271490931510925292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0012089263835958327566316716783489937370177358388900756835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 24.3163024 | 5.2011626 | 54.3985127 | 11.1488258 | |
| ENSG00000119283 | 440730 | TRIM67 | protein_coding | Q6ZTA4 | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Predicted to enable zinc ion binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of protein localization. Predicted to act upstream of or within negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction; positive regulation of neuron projection development; and positive regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:440730; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046580]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:2000060]; regulation of protein localization [GO:0032880] | 31239268_TRIM67 functions as a pivotal tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer.Epigenetic silencing of TRIM67 correlates with poor survival in patients with colorectal cancer.TRIM67 stabilizes p53 and activates p53 signaling pathway.TRIM67 is a direct target gene of p53. 35806477_Loss of TRIM67 Attenuates the Progress of Obesity-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. | ENSMUSG00000036913 | Trim67 | 22.542093 | 2.421049540 | 1.275633 | 0.39355999 | 10.570180 | 0.0011492653952809574972176998031159200763795524835586547851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0085102828741080108893024558369688747916370630264282226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 32.5627617 | 6.1394199 | 13.5364186 | 2.9231446 | ||
| ENSG00000119508 | 8013 | NR4A3 | protein_coding | Q92570 | FUNCTION: Transcriptional activator that binds to regulatory elements in promoter regions in a cell- and response element (target)-specific manner. Induces gene expression by binding as monomers to the NR4A1 response element (NBRE) 5'-AAAAGGTCA-3' site and as homodimers to the Nur response element (NurRE) site in the promoter of their regulated target genes (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of proliferation, survival and differentiation of many different cell types and also in metabolism and inflammation. Mediates proliferation of vascular smooth muscle, myeloid progenitor cell and type B pancreatic cells; promotes mitogen-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation through transactivation of SKP2 promoter by binding a NBRE site (By similarity). Upon PDGF stimulation, stimulates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by regulating CCND1 and CCND2 expression. In islets, induces type B pancreatic cell proliferation through up-regulation of genes that activate cell cycle, as well as genes that cause degradation of the CDKN1A (By similarity). Negatively regulates myeloid progenitor cell proliferation by repressing RUNX1 in a NBRE site-independent manner. During inner ear, plays a role as a key mediator of the proliferative growth phase of semicircular canal development (By similarity). Mediates also survival of neuron and smooth muscle cells; mediates CREB-induced neuronal survival, and during hippocampus development, plays a critical role in pyramidal cell survival and axonal guidance. Is required for S phase entry of the cell cycle and survival of smooth muscle cells by inducing CCND1, resulting in RB1 phosphorylation. Binds to NBRE motif in CCND1 promoter, resulting in the activation of the promoter and CCND1 transcription (By similarity). Also plays a role in inflammation; upon TNF stimulation, mediates monocyte adhesion by inducing the expression of VCAM1 and ICAM1 by binding to the NBRE consensus site (By similarity) (PubMed:20558821). In mast cells activated by Fc-epsilon receptor cross-linking, promotes the synthesis and release of cytokines but impairs events leading to degranulation (By similarity). Also plays a role in metabolism; by modulating feeding behavior; and by playing a role in energy balance by inhibiting the glucocorticoid-induced orexigenic neuropeptides AGRP expression, at least in part by forming a complex with activated NR3C1 on the AGRP- glucocorticoid response element (GRE), and thus weakening the DNA binding activity of NR3C1. Upon catecholamines stimulation, regulates gene expression that controls oxidative metabolism in skeletal muscle (By similarity). Plays a role in glucose transport by regulating translocation of the SLC2A4 glucose transporter to the cell surface (PubMed:24022864). Finally, during gastrulation plays a crucial role in the formation of anterior mesoderm by controlling cell migration. Inhibits adipogenesis (By similarity). Also participates in cardiac hypertrophy by activating PARP1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P51179, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QZB6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20558821, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24022864}. | Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Proto-oncogene;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a member of the steroid-thyroid hormone-retinoid receptor superfamily. The encoded protein may act as a transcriptional activator. The protein can efficiently bind the NGFI-B Response Element (NBRE). Three different versions of extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcomas (EMCs) are the result of reciprocal translocations between this gene and other genes. The translocation breakpoints are associated with Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 4, Group A, Member 3 (on chromosome 9) and either Ewing Sarcome Breakpoint Region 1 (on chromosome 22), RNA Polymerase II, TATA Box-Binding Protein-Associated Factor, 68-KD (on chromosome 17), or Transcription factor 12 (on chromosome 15). Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. | hsa:8013; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; cAMP response element binding [GO:0035497]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; nuclear glucocorticoid receptor binding [GO:0035259]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; nuclear steroid receptor activity [GO:0003707]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; animal organ regeneration [GO:0031100]; cellular respiration [GO:0045333]; cellular response to catecholamine stimulus [GO:0071870]; cellular response to corticotropin-releasing hormone stimulus [GO:0071376]; cellular response to leptin stimulus [GO:0044320]; common myeloid progenitor cell proliferation [GO:0035726]; energy homeostasis [GO:0097009]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; gastrulation [GO:0007369]; mast cell degranulation [GO:0043303]; negative regulation of hydrogen peroxide-induced neuron death [GO:1903208]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048008]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy [GO:0010613]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of fatty acid oxidation [GO:0046321]; positive regulation of feeding behavior [GO:2000253]; positive regulation of glucose transmembrane transport [GO:0010828]; positive regulation of mast cell activation by Fc-epsilon receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038097]; positive regulation of mast cell cytokine production [GO:0032765]; positive regulation of monocyte aggregation [GO:1900625]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration [GO:1904754]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904707]; pyruvate oxidation [GO:0009444]; regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048660]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of type B pancreatic cell proliferation [GO:0061469] | 12543801_The homeotic protein Six3 is a coactivator of the nuclear receptor NOR-1 and a corepressor of the fusion protein EWS/NOR-1 in human extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcomas. 14525795_The genes identified here are novel candidates as key early mediators of VEGF-induced endothelial functions. 14962944_In vascular smooth muscle cells, LDL-induced mitogenesis involves NOR-1 upregulation through a CREB-dependent mechanism. Mutation of specific CRE sites in the NOR-1 promoter abolishes LDL-induced NOR-1 promoter activity. 15262426_Aberrant coexpression of NOR1 and SIX3 is a potential alternative mechanism underlying the development of extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcomas 15523651_different SIX3 mutations in HPE2 may affect different signaling pathways, and that one of these pathways may involve the nuclear receptor NOR1 15949808_Neuron-derived orphan receptor-1 (NOR-1) is a transcription factor over-expressed in human atherosclerotic plaques that is involved in vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. 15964844_NR4A nuclear receptors NR4A1, NR4A2, NR4A3 are potential transcriptional mediators of inflammatory signals in activated macrophages 16873729_Nur77, Nurr1, and NOR-1 are expressed in human atherosclerotic lesion macrophages and reduce human macrophage lipid loading and inflammatory responses, providing further evidence for a protective role of these factors in atherogenesis. 16945922_platelet-derived growth factor-induced NOR1 transcription in smooth muscle cell is mediated through cAMP-response element-binding protein-dependent transactivation of the NOR1 promoter 17515897_NOR-1 is a critical tumor suppressor of myeloid leukemogenesis that is downregulated in leukemic blasts from acute myeloid leukemia patients. 17596136_NOR-1 up-regulation plays a key role in thrombin-induced endothelial cell growth 17981763_NOR-1 is over-expressed in human atherosclerotic plaques and in porcine arteries subjected to angioplasty, is induced by growth factors in vascular cells and it has been involved in cell migration and proliferation 18325999_NOR-1 is necessary for oxidative metabolism in skeletal muscle. 19682370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19682370_common genetic variation within the NR4A3 locus determines insulin secretion 19720740_NOR-1 is a downstream effector of HIF-1 signaling involved in the survival response of endothelial cells to hypoxia. 19727524_NOR1 protein is frequently down-expressed in Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 19775727_These results suggest that FISH analysis of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimens using EWSR1 and NR4A3 probes is useful and convenient and may provide an ancillary method for the diagnosis of extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcomas. 20411565_Protein kinase C-regulated role in TCR-induced thymocyte apoptosis 20558821_A novel pathway is identified that establishes NOR1 orphan nuclear receptor in an atherogenic role by positively regulating monocyte recruitment to the vascular wall. 20659174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20659174_Results identified the NR4A3 gene is associated with the quantity of tobacco smoked in subjects with schizophrenia; this association was replicated in a population of individuals with bipolar disorder. 20668010_Loss of NR4A3 is associated with thyroid follicular neoplasia. 21621845_stimulation of peripheral blood mast cells caused a robust upregulation of NR4A2 and, in particular, NR4A3, while NR4A1 expression was only moderately affected 21725049_Data from patients with familial platelet disorder/acute myelogenous leukemia indicate a correlation between increased clonogenic potential of patient hematopoietic progenitor cells and NR4A3 expression. Data indicate NR4A3 is direct target of RUNX1. 21752397_Low expression of NR4A gene family members (NR4A1, NR4A3) and 1-alpha25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor (VDR) genes is demonstrated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of multiple sclerosis patients. 21873782_NOR1 isoform 1 and isoform 2 are both detected in fetal brain. NOR1 isoform 2 lacking exon 2 is the sole isoform in multiple tissues except for brain. 22143616_Data show altered adipose tissue expression of the NOR1 stress-responsive nuclear receptor in obesity, suggesting it may modulate pathogenic potential in humans. 22569967_The pathognomic rearrangement of NR4A3 is a useful diagnostic feature in identifying cellular extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcomas. 22789442_Pin1 enhances the transcriptional activity of all three NR4A nuclear receptors and increases protein stability of Nur77 through inhibition of its ubiquitination. 23247046_present work is the first report of a novel mechanism of HDAC inhibitor-induced apoptosis in AML that involves restoration of the silenced nuclear receptors Nur77 and Nor1 23390133_Over-expression of neuron-derived orphan receptor-1 (NOR-1) exacerbates neointimal hyperplasia after vascular injury 23462179_Nor-1 and its gene targets are also up-regulated in human HCC samples. 23554459_Results indicate that miR-638 is a key molecule in regulating vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by targeting the NOR1/cyclin D pathway. 23588370_We molecularly confirmed NR4A3/EWSR1 rearrangements as myxochondroid sarcoma, either osseous or extraskeletal variants. 24005216_NR4A nuclear receptors are involved in negative selection of thymocytes, Treg differentiation and the development of Ly6C monocytes. Nur77 and Nurr1 attenuate atherosclerosis in mice whereas NOR-1 aggravates vascular lesion formation. 24626568_Results indicate that DNA hypomethylation of the CpG island at Nr4a3 exon 3 is associated with low Nr4a3 expression, and correlates with poor prognosis of neuroblastoma. 24630523_These results reinforce the role of NOR-1 in vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and in vascular remodelling 24657653_NOR1 suppresses slug/vimentin expression to inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transformation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 24788728_NOR1 expression causes apoptosis of tumor cells in hypoxia by altering the expression of PDK1 expression and mitochondrial Bax-Bcl2 balance thus suppress tumor cell adaptation to hypoxia 24806827_Studies demonstrate that NOR1 deletion in hematopoietic stem cells accelerates atherosclerosis formation by promoting myelopoiesis in the stem cell compartment and by inducing local proatherogenic activities in the macrophage. 25089663_In this review, a concise overview of the current understanding of the important metabolic roles governed by NR4A members NR4A1, NR4A2 and NR4A3 including their participation in a number of diseases shall be provided 25118646_Study suggests that NOR1 modulates the proliferation and apoptosis of human prostate cancer PC3 cells through the MAPK signaling pathway. 25199433_placental expression not affected by obesity or gestational diabetes 25410408_The authors discuss the role of NR4A1 and NR4A3 as tumor suppressors in hematologic neoplasms.[Review] 25449536_identified 13 ADCC-activated genes. Six gene expression assays including 8 of the 13 genes (CCL3, CCL4/CCL4L1/CCL4L2, CD160, IFNG, NR4A3 and XCL1/XCL2) were analyzed in 127 kidney biopsies 25536180_Our data support a role for NOR-1 as a negative modulator of the acute response elicited by pro-inflammatory stimuli in the vasculature. 25809189_A2M is expressed in the vasculature and NR4A receptors modulate VSMC MMP2/9 activity by several mechanisms including the up-regulation of A2M. 25844690_NOR1 promotes the proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. 25852083_DNA-PK directly phosphorylates NOR-1, modulating vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. 25917081_NR4A2 is a key factor in multiple diseases, such as inflammation, cancer and cardiovascular diseases. 25941992_Data identify NOR1 as a transcription factor induced during alternative differentiation of human macrophages and demonstrate that NOR1 modifies the alternative macrophage phenotype. 26096603_accumulation of NR4A3 is specific to alpha-synucleinopathy. 26600038_miR-17 and -20a target NOR-1 thereby regulating NOR-1-dependent gene expression. 26634653_Identified Nur77/Nor1 as novel regulators of thrombomodulin expression and function in vascular endothelial cells. 27159982_Study found a marked down-regulated gene expression of the NR4A subfamily (NR4A1, NR4A2, and NR4A3) obtained from Parkinson's disease patients, but only a NR4A1 decrease in Alzheimer's disease patients compared to healthy controls. This study reports that the entire NR4A subfamily and not only NR4A2 could be systemically involved in Parkinson's disease. 27166283_Overexpression of NR4A3 in adipocytes produces a complex phenotype characterized by impaired glucose metabolism and low serum catecholamines due to enhanced degradation by adipose tissue. 27181368_Results indicate that NOR-1 regulate SMPX in human muscle cells and acts as a muscle regulatory factor to promote myotube differentiation. 27528092_aberrant JAK/STAT3 signaling epigenetically silences a potential tumor suppressor, NR4A3, in gastric cancer, plausibly representing a reliable biomarker for gastric cancer prognosis 27697661_the role of intragenic DNA hypermethylation in reducing the expression of NR4A3 in AML 27891591_NOR1 suppresses cancer stem-like cell properties in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by inhibiting the AKT-GSK-3beta-Wnt/beta-catenin-ALDH1A1 signaling circuit. 28232113_NOR1 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating Notch pathway. 28249774_In the 3 cases of the primary extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma (EMC) of bone we found the most frequent and specific chromosomal translocation t(9:22) EWSR1-NR4A3 of the extraskeletal counterpart. 28249906_Transcript analysis of four different aggressive lymphoma cell lines overexpressing either NR4A3 or NR4A1 revealed that apoptosis was driven similarly by induction of BAK, Puma, BIK, BIM, BID, and Trail. Overall, our results showed that NR4A3 possesses robust tumor suppressor functions of similar impact to NR4A1 in aggressive lymphomas 28637666_NR4A2 and NR4A3 are components of a downstream transcriptional response to PKA activation in the neutrophil, and that they positively regulate neutrophil survival and homeostasis. 28666984_VTN levels were increased in cell supernatants from vascular smooth muscle cells that overexpress NOR-1 28791396_NOR1 activates HSCs and contributes to liver fibrosis in vitro and this effect was achieved through the activation of the Wnt/betacatenin pathway. 28808448_NR4A sub-family of nuclear orphan receptors (Nor-1, Nurr-1 and Nur-77) may have a role in trophoblastic cell differentiation. 29377304_findings indicated that cAMP-PKA up-regulated STAT5B, followed by increase in syncytin2 expression through GCM1 and OVOL1, resulting in cell fusion and hCG production, while cAMP-PKA-up-regulated NR4A3 could decrease syncytin2 expression. 29695901_NOR1 upregulation is associated with hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling in COPD via promoting human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation. 30076719_our study provides the first in vitro evidence highlighting the antiproliferative and antimigratory roles of miR-638 in human Abnormal airway smooth muscle cell (ASMC) remodeling and suggests that targeted overexpression of miR-638 in ASMCs may provide a novel therapeutic strategy for preventing ASM hyperplasia associated with asthma. 30096407_These results indicate that NOR-1 induces NOX1 in human vascular smooth muscle cells and participates in the complex gene networks regulating oxidative stress and redox homeostasis in the vasculature. 30227111_Long non-coding RNA BRE-AS1 represses non-small cell lung cancer cell growth and survival via up-regulating NR4A3 30455429_NR4A3 is a novel target of p53 that contributes to apoptosis 30664630_It has been concluded that NR4A3 is upregulated through enhancer hijacking and has important oncogenic functions in acinic cell carcinomas of the salivary glands. 30696767_results uncover that Nor1 negatively regulates beta-cell mass. Nor1 represents a promising molecular target in diabetes treatment to prevent beta-cell destruction. 31020999_NR4A3 fusion proteins trigger an axon guidance switch that marks the difference between EWSR1 and TAF15 translocated extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcomas cells. 31094928_immunostaining is a highly specific and sensitive marker for acinic cell carcinoma of the salivary glands 31183633_Results indicated that NR4A3 directly activates the expression of GAP43 and induces differentiated phenotypes of NB cells, without affecting the upstream signals regulating GAP43 expression and NB differentiation. 31209222_study demonstrates that miR-665 upregulation is associated with metastasis and poor survival in BC patients, and mechanistically, miR-665 enhances progression of BC via NR4A3/MEK signaling pathway. 31701670_The pro-inflammatory effect of NR4A3 in osteoarthritis. 31936632_Disruption of Beta-Cell Mitochondrial Networks by the Orphan Nuclear Receptor Nor1/Nr4a3. 31985010_NOR-1 is involved in the transcriptional programme leading to Hypertensive cardiac hypertrophy. 32125766_Long non-coding RNA LINC00467 drives hepatocellular carcinoma progression via inhibiting NR4A3. 32241159_The tumor suppressor NOR1 suppresses cell growth, invasiveness, and tumorigenicity in glioma. 32323598_miR-106b-5p induces immune imbalance of Treg/Th17 in immune thrombocytopenic purpura through NR4A3/Foxp3 pathway. 32341238_Nuclear NR4A2 (Nurr1) Immunostaining is a Novel Marker for Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Salivary Glands Lacking the Classic NR4A3 (NOR-1) Upregulation. 32809265_Evaluation of NR4A3 immunohistochemistry (IHC) and fluorescence in situ hybridization and comparison with DOG1 IHC for FNA diagnosis of acinic cell carcinoma. 33163142_SMARCB1 Promotes Ubiquitination and Degradation of NR4A3 via Direct Interaction Driven by ROS in Vascular Endothelial Cell Injury. 33221345_NR4A3 induces endothelial dysfunction through up-regulation of endothelial 1 expression in adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. 33241311_Nor1, a novel cytokine-responsive regulator of pancreatic beta-cell mass and function mediated by disruption of mitochondrial networks. 34248958_Transcriptional Profiling of Monocytes Deficient in Nuclear Orphan Receptors NR4A2 and NR4A3 Reveals Distinct Signalling Roles Related to Antigen Presentation and Viral Response. 34383980_Atypic SUMOylation of Nor1/NR4A3 regulates neural cell viability and redox sensitivity. 34437889_Minireview: What is Known about SUMOylation Among NR4A Family Members? 34565470_NR4A3 and CCL20 clusters dominate the genetic networks in CD146(+) blood cells during acute myocardial infarction in humans. 34657447_Knockdown of long noncoding RNA AC245100.4 inhibits the tumorigenesis of prostate cancer cells via the STAT3/NR4A3 axis. 34768801_NR4A3: A Key Nuclear Receptor in Vascular Biology, Cardiovascular Remodeling, and Beyond. 34873305_Analysis of clinicopathologic features and expression of NR4A3 in sinonasal acinic cell carcinoma. 35230891_MiR-501-5p alleviates cardiac dysfunction in septic patients through targeting NR4A3 to prevent its binding with Bcl-2. 35418692_Matriptase-2/NR4A3 axis switches TGF-beta action toward suppression of prostate cancer cell invasion, tumor growth, and metastasis. 36040481_Functional association of NR4A3 downregulation with impaired differentiation in myeloid leukemogenesis. | ENSMUSG00000028341 | Nr4a3 | 39.455414 | 0.446795649 | -1.162313 | 0.26418943 | 19.648210 | 0.0000093090500840997924799150031738292909722076728940010070800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001252067236311421973352087100295193522470071911811828613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 23.7911680 | 9.5172996 | 53.5682937 | 20.9358995 | |
| ENSG00000119866 | 53335 | BCL11A | protein_coding | Q9H165 | FUNCTION: Transcription factor (PubMed:16704730, PubMed:29606353). Associated with the BAF SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex (PubMed:23644491). Binds to the 5'-TGACCA-3' sequence motif in regulatory regions of target genes, including a distal promoter of the HBG1 hemoglobin subunit gamma-1 gene (PubMed:29606353). Involved in regulation of the developmental switch from gamma- to beta-globin, probably via direct repression of HBG1; hence indirectly repressing fetal hemoglobin (HbF) level (PubMed:29606353, PubMed:26375765). Involved in brain development (PubMed:27453576). May play a role in hematopoiesis (By similarity). Essential factor in lymphopoiesis required for B-cell formation in fetal liver (By similarity). May function as a modulator of the transcriptional repression activity of NR2F2 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QYE3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16704730, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23644491, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29606353, ECO:0000303|PubMed:26375765, ECO:0000303|PubMed:27453576}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Chromosome;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a C2H2 type zinc-finger protein by its similarity to the mouse Bcl11a/Evi9 protein. The corresponding mouse gene is a common site of retroviral integration in myeloid leukemia, and may function as a leukemia disease gene, in part, through its interaction with BCL6. During hematopoietic cell differentiation, this gene is down-regulated. It is possibly involved in lymphoma pathogenesis since translocations associated with B-cell malignancies also deregulates its expression. Multiple transcript variants encoding several different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:53335; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; paraspeckles [GO:0042382]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; SWI/SNF complex [GO:0016514]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; transcription regulatory region nucleic acid binding [GO:0001067]; cellular response to L-glutamate [GO:1905232]; negative regulation of axon extension [GO:0030517]; negative regulation of branching morphogenesis of a nerve [GO:2000173]; negative regulation of collateral sprouting [GO:0048671]; negative regulation of dendrite development [GO:2000171]; negative regulation of dendrite extension [GO:1903860]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; negative regulation of neuron remodeling [GO:1904800]; negative regulation of protein homooligomerization [GO:0032463]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of collateral sprouting [GO:0048672]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein sumoylation [GO:0016925]; regulation of dendrite development [GO:0050773]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 11830502_BCL11A may not be the target of the 2p13 alterations in cHL(clasical Hodgkins lymphoma),rather REL is. 11986957_The t(2;14)(p13;q32.3) involving the BCL11A and IGH genes is associated with a subset of B-CLL/immunocytoma characterized by non-mutated IG genes deriving from pre-germinal center B cells. 15639232_SIRT1 has a role in transcriptional repression mediated by BCL11A in mammalian cells 16704730_The most abundant isoform BCL11A-XL was DNA-sequence-specific transcriptional repressor that associates with itself and with other BCL11A isoforms, as well as with the BCL6 proto-oncogene. 16871282_essential functional role of this repressor of transcription in primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma 17672918_the apparent occurrence of an unusual TG 3' splice site in intron 4 is discussed 17767159_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18245381_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18245381_These results indicate that BCL11A variants, by modulating HbF levels, act as an important ameliorating factor of the beta-thalassemia phenotype, and it is likely they could help ameliorate other hemoglobin disorders. 18667698_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18681895_BCL11A is a SUMOylated protein and recruits SUMO-conjugation enzymes in its nuclear body. 18691915_Study shows that SNPs in BCL11A were associated with HbF containing erythrocyte numbers in Chinese with beta-thalassemia trait, and with HbF levels in Thais with either beta-thalassemia or HbE trait and in African Americans with sickle cell anemia. 18714373_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18948576_deregulated Bcl11a cooperates with Nf1 in leukemogenesis 19020323_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19056937_down-regulation of BCL11A expression in primary adult erythroid cells leads to robust HbF expression; study finds that BCL11A occupies several discrete sites in the beta-globin gene cluster 19153051_BCL11A binds a core motif in the gamma-globin proximal promoter, recruits and interacts with partners to form a repression complex, leading to deacetylation of histones and down-regulation of gamma-globin transcription. 19369625_Chronic lymphocytic leukemia With t(2;14)(p16;q32) involves the BCL11A and IgH genes and is associated with atypical morphologic features and unmutated IgVH genes. 19616629_Data report that Bcl11A downregulates axon branching, and that the expression of DCC and MAP1b, two molecules involved in direction and branching of axon outgrowth, is controlled by Bcl11A-L. 19657335_BCL11A is a critical mediator of species-divergent globin switching 19670153_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19696200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19720844_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19833888_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20018918_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20075150_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20183929_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20395365_transcriptional silencing of gamma-globin genes by BCL11A involves long-range interactions and cooperation with SOX6 20472475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20472475_SNPs in BCL11A and the HBS1L-MYB region did not show statistically significant correlations with HbFlevels.This suggests that the BCL11A and HBS1L-MYB loci have a minor effect on HbF level compared to the XmnI QTL in beta-thalassemia intermedia patients. 20542454_BCL11A is intimately involved in the transcriptional regulation of alpha and beta globins and may also regulate and be regulated by GATA-1 as part of a distinct activator or repressor protein complex. 20575024_characterize the prevalence of REL, BCL11A, and MYCN gains in a consecutive CLL series at the time of diagnosis; (ii) define the prognostic relevance of REL, BCL11A, and MYCN gains in CLL. 20578197_A subset of ALL cases bearing 14q32 LOH showed a down-regulation of miRNA 14q32 clusters linked to the submicroscopic chromosomal deletion. This had an inverse correlation with the expression of their target BCL11a. 20623620_through the interaction with Bcl11A, calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase plays a role in axonogenesis, which may be related to brain anatomical characteristics in humans 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20889853_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21068433_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21157349_BCL11A is a potent silencer of fetal hemoglobin. It controls the beta-globin gene cluster in concert with other factors. 21267535_no convincing associations were established to the surrogate measurements of beta cell function or insulin sensitivity in this Danish population-based study 21326311_A novel intronic SNP, rs7606173, associates with F-cell levels in sickle cell patients (P-value A) was relatively high in patients with HbE/[beta]-thalassemia of Guangxi province of China, accompanying with high level of HbF; polymorphism of rs4671393 possibly prevents severe complications in patients with HbE/[beta]-thalassemia 22271886_Significantly distinct survival curves can be described in beta-thalassemia patients that are attributable to the genetic variants affecting fetal hemoglobin, BCL11A and intergenic HBS1L-MYB loci. 22675500_BCL11A is a novel TLX coregulator that might be involved in TLX-dependent gene regulation in the brain. 22739175_The C and T polymorphisms are found at the rs11886868 locus of the BCL11A gene in beta-thalassemia patients. The C polymorphism may be related to high Hemoblobin F expression in red blood cells. 22936743_Studies indicate that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in regions of BCL11A and HBS1L-MYB intergenic polymorphism are the major modifiers of HbF in African Americans. 23094636_The G>A allele on the rs4671393 locus on chromosome 2 (BCL11A gene), did not show significant association with Hb F levels. 23209159_Regulators, including BCL11A,MYB, and KLF1, hold great promise to develop targeted and more effective approaches for HbF induction 23223429_Simvastatin and tBHQ suppress KLF1 and BCL11A gene expression and additively increase fetal hemoglobin in primary human erythroid cells. 23541515_The influence of the BCL11A polymorphism on the phenotype of patients with beta thalassemia could be affected by the beta globin locus control region and/or the Xmn1-HBG2 genotypic background. 23576758_BCL11A coordinates the hemoglobin switch and fetal hemoglobin silencing by assembling transcriptional corepressor complexes within the beta-globin cluster. 23758992_BCL11A overexpression predicts survival and relapse in non-small cell lung cancer and is modulated by microRNA-30a and gene amplification. 23777413_Data suggest that segregation of BCL11A haplotype 2 indicating an involvement of this locus in Hb F expression. 23975195_BCL11A contains F/YSXXLXXL/Y motifs that mediate highly selective binding to the LBDs of orphan nuclear receptors NR2E1/TLX, NR2E3/PNR and the NR2F/COUP-TF family. These motifs are required for BCL11A/COUP-TFII-mediated repression of foetal globin genes and a lncRNA termed Bgl3. The motifs are conserved in other Nuclear receptor cofactors such as NSD1, constituting a new signature motif related to LXXLL and the CoRNR box. 23975195_Immunohistochemical staining of mouse brain showed strong expression of BCL11A in the cortical regions and also in the pyramidal cell layers in the CA1 and CA3 regions of the hippocampus. 24115442_Genome engineering reveals the enhancer is required in erythroid but not B-lymphoid cells for BCL11A expression. 24502199_Twelve SNPs at the BCL11A gene were shown to modify HbF levels. 24667352_Genetic variants of BCL11A is associated with sickle cell disease. 25042611_HbA2 levels were associated with SNPs in BCL11A, mediated by the association of this locus with gamma-globin gene expression and fetal hemoglobin levels. 25457384_SCF-mediated gamma-globin gene expression in adult human erythroid cells is associated with KLF1, BCL11A and SOX6 down-regulation. 25457385_Genetic variant in the BCL11A (rs1427407), but not HBS1-MYB (rs6934903) loci associate with fetal hemoglobin levels in Indian sickle cell disease patients. 25488618_The study compares polymorphism at BCL11A to HBS1L-MYB loci and explains less of the variance in HbF in patients with sickle cell disease in Cameroon. 25574598_BCL11A has an important role in triple-negative breast cancer and normal mammary epithelial cells 25703683_Common HbF BCL11A enhancer haplotypes in patients with African origin and Arab-Indian sickle cell anemia have similar effects on HbF but they do not explain their differences in HbF. 25938782_the study of these rare patients and orthogonal genetic data demonstrates that BCL11A plays a central role in silencing HbF in humans and implicates BCL11A as an important factor for neurodevelopment 26053062_a successful induction of gamma-globin includes a reduction in BCL11A, KLF1 and TAL1 expression. 26342260_only HbF inducer efficient in rescuing the ability to differentiate along the erythroid program, even in K562 cell clones expressing high levels of BCL11A-XL, suggesting that BCL11A-XL activity is counteracted by mithramycin. 26375765_Extensive genetic analyses have validated BCL11A as a potent repressor of fetal hemoglobin level. Studies of BCL11A exemplify how contextual gene regulation may often be the substrate for trait-associated common genetic variation 26393293_Association has been found between variants at BCL11A erythroid-specific enhancer and fetal hemoglobin levels among sickle cell disease patients in Cameroon. 26707798_These data suggest a possible role for BCL11A expression in acute myeloid leukaemia biology 26816381_this study found that LRF/ZBTB7A transcription factor occupies fetal gamma-globin genes and maintains the nucleosome density necessary for gamma-globin gene silencing in adults, and that LRF confers its repressive activity through a NuRD repressor complex independent of the fetal globin repressor BCL11A. 26849705_The frequency of rs11886868 was determined in Colombian sickle cell anemia patients. It indicated an Amerindian ethnic background. 26888013_Reduced rate of sickle-related complications in Brazilian patients carrying HbF-promoting alleles at the BCL11A and HMIP-2 loci 27009595_this study aimed to find the effect of these genetic modifiers, especially in the XmnI locus, rs11886868, rs766432 (BCL11A), and rs9399137 (HBS1L-MYB), among beta thalassemia (beta-thal) and Hemoglobin E/beta-thal patients in Indonesia. 27077760_The combination of the genotypes GG and CT explains more phenotypic variance than the sum of the two BCL11A SNPs taken individually. 27285855_BCL11A may operate in transformation of CML from chronic to acute phase in some persons 27377501_his study confirms that the T/C variant (rs11886868) of the BCL11A gene causing downregulation of BCL11A gene expression in adult erythroid precursors results in the induction of HbF and ameliorates the severity of a-thalassaemia as well as sickle cell anaemia. 27453576_report of an intellectual disability syndrome caused by de novo heterozygous missense, nonsense, and frameshift mutations in BCL11A, encoding a transcription factor that is a putative member of the BAF swi/snf chromatin-remodeling complex 27573292_our study suggests that FOXQ1 regulates prostate cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis by regulating BCL11A/MDM2 expression and indicates that FOXQ1 may serve as a potential therapeutic target for prostate cancer. 27591578_The BCL11A gene was found to be potentially targeted by 12 MicroRNAs that were up-regulated in Hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin deletion type-2 (HPFH-2) or in Sicilian deltabeta-thalassemia. A down-regulation of BCL11A gene expression in HPFH-2 was verified by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. 27599293_Ubiquitous knockdown of BCL11A in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells impairs hematopoietic reconstitution after transplantation. 27658436_APOL1, alpha-thalassemia, and BCL11A variants as a genetic risk profile for progression of chronic kidney disease in sickle cell anemia 27774950_The BCL11A protein is highly expressed in breast cancer and knock-down of BCL11A promotes the apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 cells. 27838552_both BCL11A and HMIP-2 were associated with increased endogenous levels of HbF. Interestingly, we also found that BCL11A was associated with higher induction of HbF with HU. 28164500_High BCL11A expression level was correlated with lower complete remission rate and shorter overall survival in adult acute myeloid leukemia patients. 28225775_BCL11A rs11886868 and rs4671393 genotype variations and correspondingly high BCL11A plasma levels are related to laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma, besides, differences in plasma levels and genotype distribution may be related to lymph node metastasis status and the stage of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 28332727_Studied association of BCL11A single nucleotide polymorphisms(snps) and HBS1L-MYB Intergenic snps with Hereditary Persistence of Fetal Hemoglobin (HPFH) in a cohort of sickle cell patients. 28361591_the association between modifier loci (beta-globin gene cluster, HBS1L-MYB intergenic region and BCL11A) and Hb F levels in Chinese Zhuang beta-TI patients 28544358_The expression levels of Bcl11a and Mdm2, Pten in B-ALL patients with CR were decreased significantly when compared with the healthy control (P | ENSMUSG00000000861 | Bcl11a | 121.252934 | 0.422394350 | -1.243338 | 0.16222192 | 58.895608 | 0.0000000000000166262912678729197894305424586788684947669027941463681941058894153684377670288085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000007313476800471899091885630459756886898731176316346136445645242929458618164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 69.1687688 | 14.2835118 | 165.2346833 | 33.4780097 | |
| ENSG00000119917 | 3437 | IFIT3 | protein_coding | O14879 | FUNCTION: IFN-induced antiviral protein which acts as an inhibitor of cellular as well as viral processes, cell migration, proliferation, signaling, and viral replication. Enhances MAVS-mediated host antiviral responses by serving as an adapter bridging TBK1 to MAVS which leads to the activation of TBK1 and phosphorylation of IRF3 and phosphorylated IRF3 translocates into nucleus to promote antiviral gene transcription. Exhibits an antiproliferative activity via the up-regulation of cell cycle negative regulators CDKN1A/p21 and CDKN1B/p27. Normally, CDKN1B/p27 turnover is regulated by COPS5, which binds CDKN1B/p27 in the nucleus and exports it to the cytoplasm for ubiquitin-dependent degradation. IFIT3 sequesters COPS5 in the cytoplasm, thereby increasing nuclear CDKN1B/p27 protein levels. Up-regulates CDKN1A/p21 by down-regulating MYC, a repressor of CDKN1A/p21. Can negatively regulate the apoptotic effects of IFIT2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17050680, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20686046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21190939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21642987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21813773}. | 3D-structure;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;Immunity;Innate immunity;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA | Enables identical protein binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of apoptotic process; negative regulation of cell population proliferation; and response to virus. Located in cytosol and mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:3437; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; cellular response to interferon-alpha [GO:0035457]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; response to virus [GO:0009615] | 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17933493_The induction of IFIT4 transcription by IFN-alpha depends upon sequential activation of PKCdelta, JNK and STAT1, and the influence of PKCdelta or JNK on IFN-alpha-mediated induction of IFIT4 is dependent upon the phosphorylation of STAT1 at Ser-727. 18706081_IFIT4 may play roles in promoting monocyte differentiation into dendritic cell-like cells (DCLCs) and in directing DCLCs to modulate T-helper-1 cell differentiation, thus contributing to the autoimmunity and pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. 19351818_Induction of RIG-G by retinoic acid in NB4 cells resulted, to some extent, from an IFNalpha autocrine pathway, a finding that suggests a novel mechanism for the signal cross-talk between IFNalpha and retinoic acid. 20137113_All-trans retinoic acid upregulated RIG-G in NB4 cells by upregulating IRF1, IRF9 and STAT2. 20403236_The complex STAT2/IRF-9 is the key factor mediating the expression of RIG-G gene regulated by IFN-alpha. 20533260_transcription factors for the reporter gene. CONCLUSION: Both ISRE I and ISRE II on the RIG-G promoter are the binding sites for the complex of transcription factors. They are required for RIG-G expression, and ISRE I has a preferential role over ISRE II. 20686046_Identification of alpha interferon-induced genes associated with antiviral activity in Daudi cells and characterization of IFIT3 as a novel antiviral gene. 21056555_concluded that the expression of RIG-G was independent on the classical JAK-STAT pathway, but could be greatly increased by it. 21813773_our study characterizes IFIT3 as an important modulator in innate immunity 22490698_RIG-G gene expression is closely correlated with the cross-talk between all-trans retinoic acid and IFN-alpha-induced signaling pathways in NB4 tumor cells. 23415865_these findings reveal for the first time the negative regulation of Rig-G on SCF-E3 ligase activities through disrupting CSN complex, not only contributing to further investigation on biological functions of Rig-G, but also leading to better understanding of the CSN complex as a potential target in tumor diagnosis and treatment. 24223959_protective roles of IFIT3 following IFN-alpha production in DV infection of human lung epithelial cells 25131332_In cell models of dengue virus 2 infection, authors found that IFITM3 contributed to both the baseline and interferon-induced inhibition of virus entry. 25650658_The transcription factor SOX9, which is linked to regulation of hypoxia-related genes, was identified as a key mediator of upregulation of the oncogene IFIT3 and thereby sustaining a 'pseudoinflammatory' cellular condition in pancreatic tumors. 25905045_Reovirus T3D infection induced STAT-1, ISG-15, IFIT-1, Mx1 and IFIT-3 expression. 26423178_there is a positive feedback loop between phosphorylated STAT1 and ISG56, ISG54 or ISG60. 26686474_results indicated that RIG-G level was high in maturated cells and low in blast cells, and suggested that RIG-G might play a role in the differentiation of bone marrow hemocytes in vivo 26917578_Among the associated variants were two in regions previously unreported for COPD; a low frequency non-synonymous SNP in MOCS3 (rs7269297, pdiscovery=3.08x10(-6), preplication=0.019) and a rare SNP in IFIT3, which emerged in the meta-analysis (rs140549288, pmeta=8.56x10(-6)). 27210312_These findings indicated that hepatitis B virus-induced miR146a attenuates cell-intrinsic anti-viral innate immunity through targeting RIG-I and RIG-G. 27601657_IFNL3 and HLA-DPB1 independently affected viral control at 3- and 6-mo postpartum. Together, these findings support a model where spontaneous control of HCV such as sometimes follows pregnancy is governed by genetic polymorphisms that affect type III IFN signaling and virus-specific cellular immune responses. 27601663_these data suggest that postpartum, the normalization of the physiological rheostat controlling IFN signaling depends on IFNL3 genotype. 27602766_Low RIG-G expression is associated with lung cancer. 27681138_HSV-1 was shown for the first time to evade the antiviral function of IFIT3 via UL41. 28210844_Higher expression of IFIT3 enhances anti-apoptotic activity and chemotherapy resistance of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. High expression of IFIT3 was independently correlated to shorter patients' survival and may serve as a prognostic marker. 28356064_Biomarker expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) of CXCR4, SMAD4, SOX9 and IFIT3 will be prospectively assessed by immunohistochemistry and verified by rt.-PCR from tumor and adjacent healthy pancreatic tissue of surgical specimen. 29554348_IFIT1 and IFIT3 interact through a C-terminal motif. IFIT3 stabilizes IFIT1 protein expression, promotes IFIT1 binding to a cap0 Zika virus reporter mRNA and enhances IFIT1 translation inhibition. 29734133_We provided the evidence that IFIT3 was up-regulated during hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) and knockdown of IFIT3 exerted potent protective effects against hepatic IRI in vitro and in vivo. Our findings not only revealed the mechanism for IFIT3-regulated hepatic IRI, but also proposed potential clinical significance of treatment targeting IFIT3 for patients undergoing liver resection and liver transplantation. 29806091_Levels of IFIT3 were significantly elevated in human systemic lupus erythematosus monocytes, and this was positively correlated with the activity of the cGAS/STING signaling pathway. In vitro, the expression of VACV70-induced IFNbeta was reduced by knockdown of IFIT3, whereas overexpression of IFIT3 produced an opposite effect. Finally, IFIT3 was found to interact with both STING and TANK-binding kinase 1. 30195920_ISG60 constitutes a negative feedback loop in the downstream of TLR3 signaling in brain capillary endothelial cells. 30626937_A statistically positive correlation of p-EGFR(Y1068) expression with IFIT1 and IFIT3 in OSCC tumors. 32641986_Inflammatory IFIT3 renders chemotherapy resistance by regulating post-translational modification of VDAC2 in pancreatic cancer. 32741018_Novel evidence for retinoic acid-induced G (Rig-G) as a tumor suppressor by activating p53 signaling pathway in lung cancer. 33122518_Interferon-Induced Protein With Multiple Tetratricopeptide Repeats 3 Is Associated With Response to Chemotherapy and Recurrence but Not With Survival. 34075171_Interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 3 may be a key factor in primary biliary cholangitis. 34356051_Retinoic Acid-Induced Gene G(RIG-G) as a Novel Monitoring Biomarker in Leukemia and Its Clinical Applications. 34622927_IFIT3 (interferon induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 3) modulates STAT1 expression in small extracellular vesicles. 34724821_Human IFIT3 Protein Induces Interferon Signaling and Inhibits Adenovirus Immediate Early Gene Expression. 34763233_Comprehensive analysis of the prognosis and biological significance for IFIT family in skin cutaneous melanoma. 34884921_Identified Three Interferon Induced Proteins as Novel Biomarkers of Human Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. | ENSMUSG00000074896+ENSMUSG00000062488 | Ifit3+Ifit3b | 45.559011 | 0.493315271 | -1.019418 | 0.22604085 | 20.670688 | 0.0000054544633055295974153209997981051060378376860171556472778320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000772024485249395305518083088003322700387798249721527099609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 31.0694541 | 4.5307754 | 63.2040504 | 8.1712773 |
| ENSG00000119922 | 3433 | IFIT2 | protein_coding | P09913 | FUNCTION: IFN-induced antiviral protein which inhibits expression of viral messenger RNAs lacking 2'-O-methylation of the 5' cap. The ribose 2'-O-methylation would provide a molecular signature to distinguish between self and non-self mRNAs by the host during viral infection. Viruses evolved several ways to evade this restriction system such as encoding their own 2'-O-methylase for their mRNAs or by stealing host cap containing the 2'-O-methylation (cap snatching mechanism). Binds AU-rich viral RNAs, with or without 5' triphosphorylation, RNA-binding is required for antiviral activity. Can promote apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21190939}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Antiviral defense;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Immunity;Innate immunity;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;TPR repeat | Enables RNA binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of protein binding activity; positive regulation of apoptotic process; and response to virus. Located in endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:3433; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; apoptotic mitochondrial changes [GO:0008637]; cellular response to interferon-alpha [GO:0035457]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; response to virus [GO:0009615] | 12708317_The expression of interferon-induced genes IFI-54K and IFI-56K in the infected cells was found to increase 50-100-fold 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16973618_We observed that, although double-stranded RNA or Sendai virus infection induced the two genes with similar kinetics, their induction kinetics in response to interferon-beta were quite different. 17030862_IFIT2/GARG39 was identified as a microtubule-associated protein enriched in the mitotic spindle of mouse NIH3T3 and B16F10 melanoma cells. 18819931_IFN-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 2 inhibits migration activity and increases survival of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 20506645_The expression of OASL and IFIT2 was significantly higher in SLE patients than in controls. 21190939_role of ISG54 in the induction of apoptosis via a mitochondrial pathway shedding new light on the mechanism by which IFN elicits anti-viral and anti-cancer effects 22065572_Inhibitor of kappaB kinase epsilon (IKK(epsilon)), STAT1, and IFIT2 proteins define novel innate immune effector pathway against West Nile virus infection. 22825553_ISG54 binds specifically to some RNAs, such as adenylate uridylate (AU)-rich RNAs, with or without 5' triphosphorylation. 22986528_IFIT2, a protein responsible for interferon stimulation, may prevent oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) metastasis and serve as a valuable prognostic marker. 23867918_Data show that interferon-induced proteins with tetratricopeptide repeats 1 and 2 (IFIT1 and IFIT2) contribute to the regulation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication, likely at both transcriptional and posttranscriptional steps. 25174799_Data shows that IFIT2 expression is downregulated in adenocarcinoma of gastric esophageal junction cells; its ectopic expression leads to cell apoptosis, suggesting its role as a tumor suppressor. 26423178_there is a positive feedback loop between phosphorylated STAT1 and ISG56, ISG54 or ISG60. 27609068_LINC00161 is an essential regulator in cisplatin-induced apoptosis, and the LINC00161-miR-645-IFIT2 signalling axis plays an important role in reducing osteosarcoma chemoresistance. 27893714_Mechanistic investigations reveal that AJUBA specifically binds the FERM domain of JAK1 to dissociate JAK1 from the IFNgamma recepter, resulting in an inhibition of STAT1 phosporylation and concomitantly its nuclear translocation. Clinically, the level of AJUBA in CRC specimens is negatively correlated with the levels of IFIT2 and pSTAT1 28367102_The results of the present study revealed that the inhibition of proteasome activity blocked the degradation of IFIT2 and promoted the aggregation of IFIT2 in the centrosome, which in turn induced cell apoptosis. In short, IFIT2 may be a potential target for cancer therapeutics. 29358655_These studies indicated PLZF inhibited the proliferation and metastasis via regulation of IFIT2. 29554348_IFIT2 and IFIT3 stabilize IFIT1 expression. 30875792_Studied effect of baicalein on gene expression in human breast cancer cell line and found baicalein reduced stem cell-like properties of the cells and induced apoptosis through up-regulation of IFIT2. 32124954_Overexpression of IFIT2 inhibits the proliferation of chronic myeloid leukemia cells by regulating the BCRABL/AKT/mTOR pathway. 32839537_Influenza virus repurposes the antiviral protein IFIT2 to promote translation of viral mRNAs. 33942366_Super-enhancer-associated long noncoding RNA RP11-569A11.1 inhibited cell progression and metastasis by regulating IFIT2 in colorectal cancer. 34215258_PML-II regulates ERK and AKT signal activation and IFNalpha-induced cell death. 34763233_Comprehensive analysis of the prognosis and biological significance for IFIT family in skin cutaneous melanoma. 34884921_Identified Three Interferon Induced Proteins as Novel Biomarkers of Human Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. | ENSMUSG00000045932 | Ifit2 | 13.652793 | 0.380823073 | -1.392807 | 0.42495870 | 11.183196 | 0.0008254145432443158597601851056424493435770273208618164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0064215231540052783096306221466420538490638136863708496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 7.0138738 | 2.3382274 | 18.8115212 | 5.5003468 | |
| ENSG00000120162 | 79817 | MOB3B | protein_coding | Q86TA1 | FUNCTION: Modulates LATS1 expression in the Hippo signaling pathway which plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28792927}. | Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Zinc | The protein encoded by this gene shares similarity with the yeast Mob1 protein. Yeast Mob1 binds Mps1p, a protein kinase essential for spindle pole body duplication and mitotic checkpoint regulation. This gene is located on the opposite strand as the interferon kappa precursor (IFNK) gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:79817; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein kinase activator activity [GO:0030295]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; regulation of hippo signaling [GO:0035330]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20423481_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 26130958_low levels of hMOB3B are closely associated with aggressive clinicopathologic features in patients with prostate cancer. The results suggest that hMOB3B may act as a tumor suppressor in human prostate cancer. | ENSMUSG00000073910 | Mob3b | 22.841390 | 0.305409970 | -1.711181 | 0.53146722 | 10.078140 | 0.0015003874819305806735669772677965738694183528423309326171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0106535127397182557973387417860067216679453849792480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 8.8904310 | 4.0911332 | 29.3898859 | 12.9793994 | |
| ENSG00000120262 | 80129 | CCDC170 | protein_coding | Q8IYT3 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in Golgi-associated microtubules organization and stabilization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28687497}. | Coiled coil;Golgi apparatus;Reference proteome | The function of this gene and its encoded protein is not known. Several genome-wide association studies have implicated the region around this gene to be involved in breast cancer and bone mineral density, but no link to this specific gene has been found. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. | hsa:80129; | ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226] | 20200978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20661439_SNPs associated with breast cancer differ for Asian, European, and African ancestry groups 24481879_Our findings suggest that ESR1 and C6orf97 gene polymorphism is associated with fracture and vertebral fracture risk in Chinese postmenopausal women. 25099679_ESR1-CCDC170 rearrangements are found in an aggressive subset of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers 25338983_Variation in rs3757318 of C6orf97 is associated with breast cancer risk. 25370037_Data suggest that rs2046210 SNPs located in the region of C6ORF97 (CCDC170)-estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) might have substantial roles not only in carcinogenesis but also in progression toward a more aggressive phenotype in breast cancer patients. 26911590_Genetic variation at the WLS and CCDC170/ESR1 loci were found to be significantly associated with bone mineral density 26928228_Expression of ESR1, RMND1 and CCDC170 associated with variants in separate enhancer elements predisposing breast cancer. [meta-analysis] 28687497_Findings demonstrate that CCDC170 plays an essential role in Golgi-associated microtubules organization and stabilization, and implicate a mechanism for how perturbations in the CCDC170 gene may contribute to the hallmark changes in cell polarity and motility seen in breast cancer. 30601066_The study shows that an association of theRMND1/CCDC170-ESR1 single nucleotide polymorphisms can exist with osteopenia, osteoporosis, or fragility fracture. 31246104_COL1A1, CCDC170, and ESR1 single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with distal radius fracture in postmenopausal Mexican women. 32771039_Therapeutic role of recurrent ESR1-CCDC170 gene fusions in breast cancer endocrine resistance. 33291081_CCDC170 affects breast cancer apoptosis through IRE1 pathway. 33785515_Three functional polymorphisms in CCDC170 were associated with osteoporosis phenotype. 35414641_Relationship between rs7586085, GALNT3 and CCDC170 gene polymorphisms and the risk of osteoporosis among the Chinese Han population. | ENSMUSG00000019767 | Ccdc170 | 57.523917 | 3.045950075 | 1.606892 | 0.23301023 | 48.059719 | 0.0000000000041343328433000622549979178433873680227964020339470607723342254757881164550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000001442170768381079133726869001774989823005945765999058494344353675842285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 50.0780525 | 35.9558236 | 16.3574371 | 11.8138746 | |
| ENSG00000120337 | 8995 | TNFSF18 | protein_coding | Q9UNG2 | FUNCTION: Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF18/AITR/GITR. Regulates T-cell responses. Can function as costimulator and lower the threshold for T-cell activation and T-cell proliferation. Important for interactions between activated T-lymphocytes and endothelial cells. Mediates activation of NF-kappa-B. Triggers increased phosphorylation of STAT1 and up-regulates expression of VCAM1 and ICAM1 (PubMed:23892569). Promotes leukocyte adhesion to endothelial cells (PubMed:23892569). Regulates migration of monocytes from the splenic reservoir to sites of inflammation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7TS55, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17449724, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18040044, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23892569}. | 3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Cell membrane;Cytokine;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand family. This cytokine is a ligand for receptor TNFRSF18/AITR/GITR. It has been shown to modulate T lymphocyte survival in peripheral tissues. This cytokine is also found to be expressed in endothelial cells, and is thought to be important for interaction between T lymphocytes and endothelial cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:8995; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily binding [GO:0032813]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of T-helper 17 cell lineage commitment [GO:2000329]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of leukocyte migration [GO:0002687]; positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0010759]; positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090026]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; regulation of dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:2000508]; regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0043254]; regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042129]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell proliferation involved in immune response [GO:0002309]; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033209] | 15326137_Upregulation by proinflammatory cytokines suggests GITRL may play important role in ocular immunity. High level of constitutive GITRL expression on photoreceptor inner segments suggests photoreceptors participate in regulation of ocular inflammation. 16179414_Regulates ossteoclasst genersation and substantiate the major role played by the endothelium in bone physiology. 16397134_Using a GITRL-transfected cell line, we demonstrate that GITRL promotes NK cell cytotoxicity and IFN-gamma production. 16874737_GITRL could be a potential candidate for regulation of the ocular immune privilege and the balance between immune privilege and inflammation 16955181_Since regulatory T-cells are localized in the vicinity of GITRL-expressing cells in atopic dermatitis skin, the GITR/GITRL interaction may serve to perpetuate the inflammation locally. 17360848_Constitutive expression of GITRL by tumor cells diminishes natural killer cell antitumor immunity. 17449724_although huGITRL is not capable of alleviating Treg suppression of responder T cells, huGITRL overexpression on monocyte-derived DC enhances their capacity to induce antigen-specific T cell responses 17602748_These observations raise the possibility that the GITRL-mediated inflammatory activation of macrophages is involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. 17914571_Levels of AITRL were significantly increased in serum of breast cancer patients 18040044_hGITRL ectodomain displays considerable self-association/dissociation in solution with a dynamic equilibrium between trimeric and monomeric forms over the range of protein concentrations studied. 18378892_identify multiple oligomeric species of hGITRL that possess distinct kinetics of ERK activation. 18689545_The strong correlation of tumor incidence and elevated soluble GITRL levels indicates that soluble GITRL is released from cancers in vivo, leading to impaired NK cell immunosurveillance of tumors 18924213_mechanism of IgG4 induction by regulatory cells involves GITR-GITR-L interactions, IL-10 and TGF-beta. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19760754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20228835_The incorporation of an isoleucine zipper motif could markedly improve the costimulation of hsGITRL. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21693309_GITRL expression on Kupffer cells may mediate acute rejection in liver transplantation 21705620_Although GITR transgene costimulation can therapeutically enhance T helper (Th) type 2 cell responses, GITR-GITR ligand interactions are not required for development of Th2-mediated resistance or pathology. 22112394_GITRL upregulation induced by IFN-beta on dendritic cells downregulates CTLA-4 on regulatory T (Treg) cells, facilitating proliferation of anergic Treg cells in multiple sclerosis treatment of multiple sclerosis patients. 22417213_observation suggests a link between cytokine-regulated keratinocyte GITRL expression and its role in inflammatory responses in AD 22649191_Glucocorticoid-induced TNF-related ligand (GITRL) confers pseudoexpression to tumor cells by platelets, which results in GITRL expression by megakaryocytes and their platelet progeny. 23251213_Serum GITRL levels were higher in SLE patients. 23935647_Our findings indicate the possible involvement of GITR-GITRL pathway in the pathogenesis of pSS. 25429429_An increase in GITRL may impair the balance of Th17/Treg, and contribute to the pathopoiesis of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. 26657118_GITRL modulates the activities of p38 MAPK and STAT3 to promote Th17 cell differentiation in autoimmune arthritis. 27098050_GITRL levels are significantly elevated in rheumatoid arthritis serum and synovial fluid and are positively correlated with autoantibody production in rheumatoid arthritis, suggesting a role of GITRL in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. 28524007_Cultured HCN-2 neurons were incubated at different times with GITRL and/or TRAIL, and thereafter nucleic acid and protein expression were measured. HCN-2 cells do not express GITRL mRNA, but the latter is induced after treatment with TRAIL. Cells did not express the GITRL receptor GITR mRNA, neither in control cultures, nor after treatment with TRAIL. TRAIL, when associated to GITRL, exerted additive toxic effects. 30760623_our studies have demonstrated a critical role of GITRL in modulating the suppressive function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells 33188059_Type I interferons drive the maturation of human DC3s with a distinct costimulatory profile characterized by high GITRL. 33654081_Structures of mouse and human GITR-GITRL complexes reveal unique TNF superfamily interactions. | ENSMUSG00000066755 | Tnfsf18 | 28.493873 | 2.803219589 | 1.487085 | 0.33271533 | 20.297631 | 0.0000066282610994908091632733283804501667191289016045629978179931640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000921631374350670348185796121320834117796039208769798278808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 40.8516178 | 4.1306634 | 14.6662809 | 2.0893770 | |
| ENSG00000120885 | 1191 | CLU | protein_coding | P10909 | FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Functions as extracellular chaperone that prevents aggregation of non native proteins (PubMed:11123922, PubMed:19535339). Prevents stress-induced aggregation of blood plasma proteins (PubMed:11123922, PubMed:12176985, PubMed:17260971, PubMed:19996109). Inhibits formation of amyloid fibrils by APP, APOC2, B2M, CALCA, CSN3, SNCA and aggregation-prone LYZ variants (in vitro) (PubMed:12047389, PubMed:17412999, PubMed:17407782). Does not require ATP (PubMed:11123922). Maintains partially unfolded proteins in a state appropriate for subsequent refolding by other chaperones, such as HSPA8/HSC70 (PubMed:11123922). Does not refold proteins by itself (PubMed:11123922). Binding to cell surface receptors triggers internalization of the chaperone-client complex and subsequent lysosomal or proteasomal degradation (PubMed:21505792). Protects cells against apoptosis and against cytolysis by complement (PubMed:2780565). Intracellular forms interact with ubiquitin and SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes and promote the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins (PubMed:20068069). Promotes proteasomal degradation of COMMD1 and IKBKB (PubMed:20068069). Modulates NF-kappa-B transcriptional activity (PubMed:12882985). A mitochondrial form suppresses BAX-dependent release of cytochrome c into the cytoplasm and inhibit apoptosis (PubMed:16113678, PubMed:17689225). Plays a role in the regulation of cell proliferation (PubMed:19137541). An intracellular form suppresses stress-induced apoptosis by stabilizing mitochondrial membrane integrity through interaction with HSPA5 (PubMed:22689054). Secreted form does not affect caspase or BAX-mediated intrinsic apoptosis and TNF-induced NF-kappa-B-activity (PubMed:24073260). Secreted form act as an important modulator during neuronal differentiation through interaction with STMN3 (By similarity). Plays a role in the clearance of immune complexes that arise during cell injury (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P05371, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q06890, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11123922, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12047389, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12176985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12882985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16113678, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17260971, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17407782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17412999, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17689225, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19137541, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19535339, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19996109, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20068069, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21505792, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22689054, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24073260, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2780565}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 6]: Does not affect caspase or BAX-mediated intrinsic apoptosis and TNF-induced NF-kappa-B-activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24073260}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 4]: Does not affect caspase or BAX-mediated intrinsic apoptosis and TNF-induced NF-kappa-B-activity (PubMed:24073260). Promotes cell death through interaction with BCL2L1 that releases and activates BAX (PubMed:21567405). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21567405, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24073260}. | Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Chaperone;Complement pathway;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Membrane;Microsome;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Ubl conjugation | The protein encoded by this gene is a secreted chaperone that can under some stress conditions also be found in the cell cytosol. It has been suggested to be involved in several basic biological events such as cell death, tumor progression, and neurodegenerative disorders. Alternate splicing results in both coding and non-coding variants.[provided by RefSeq, May 2011]. | hsa:1191; | apical dendrite [GO:0097440]; blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; chromaffin granule [GO:0042583]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; neurofibrillary tangle [GO:0097418]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0099020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; platelet alpha granule lumen [GO:0031093]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; spherical high-density lipoprotein particle [GO:0034366]; synapse [GO:0045202]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding [GO:0050750]; misfolded protein binding [GO:0051787]; protein carrier chaperone [GO:0140597]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; tau protein binding [GO:0048156]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; central nervous system myelin maintenance [GO:0032286]; chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly [GO:0051131]; chaperone-mediated protein folding [GO:0061077]; complement activation [GO:0006956]; complement activation, classical pathway [GO:0006958]; immune complex clearance [GO:0002434]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097193]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; microglial cell activation [GO:0001774]; microglial cell proliferation [GO:0061518]; negative regulation of amyloid fibril formation [GO:1905907]; negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation [GO:1902430]; negative regulation of cell death [GO:0060548]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage [GO:1902230]; negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031333]; negative regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090201]; negative regulation of response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:1903573]; positive regulation of amyloid fibril formation [GO:1905908]; positive regulation of amyloid-beta formation [GO:1902004]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001244]; positive regulation of neurofibrillary tangle assembly [GO:1902998]; positive regulation of neuron death [GO:1901216]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; positive regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0048260]; positive regulation of tau-protein kinase activity [GO:1902949]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:2000060]; protein import [GO:0017038]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; protein targeting to lysosome involved in chaperone-mediated autophagy [GO:0061740]; regulation of amyloid-beta clearance [GO:1900221]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of neuron death [GO:1901214]; regulation of neuronal signal transduction [GO:1902847]; release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0001836]; response to misfolded protein [GO:0051788]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; reverse cholesterol transport [GO:0043691] | 10066740_Clusterin is a holdase-type extracellular chaperone 10694874_Clusterin has a chaperone action like that of the small heat shock proteins 11123922_The chaperone action of clusterin is ATP-independent 11714447_Introduction of clusterin gene into human renal cell carcinoma cells enhances their resistance to cytotoxic chemotherapy through inhibition of apoptosis both in vitro and in vivo 11813210_expression increases early after androgen withdrawal in prostate cancer; protects tumor cells from apoptosis induced by medical castration 11892985_Apo J senescence-related overexpression is proposed to have antiapoptotic rather than antiproliferative effects. 11904161_The chaperone action of clusterin targets slowly aggregating proteins 12082621_Clusterin (SGP-2) transient overexpression decreases proliferation rate of SV40-immortalized human prostate epithelial cells by slowing down cell cycle progression. 12172907_clusterin may modify the formation of alpha-synuclein-positive inclusion bodies such as Lewy bodies and GCIs, through a previously proposed chaperone property of clusterin 12176985_Low pH activates the chaperone action of clusterin 12176985_clusterin is activated in reduced pH 12200037_role during cellular senescence and tumorigenesis [review] 12427144_The overall pool of clusterin is reduced in glomerular diseases causing nephrotic syndrome, with hypercholesterolemia appearing as the unifying feature 12429802_Authors conclude that clusterin is a marker of anaplastic large cell lymphoma and that addition of clusterin to antibody panels designed to distinguish systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma from classical Hodgkin's disease is useful. 12551933_synthesis and functional analysis 12679903_Loss of this protein both in serum and tissue correlates with the tumorigenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via proteomics approaches. 12860995_clusterin may act as a negative regulator of MT6-MMP in vivo 12882985_apolipoprotein J has a role in inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling through stabilization of IkappaBs; this activity may result in suppression of tumor cell motility 14618611_Clusterin is downregulated in CaP in comparison with matched benign controls 15033782_Clusterin is downregulated during prostate cancer onset and progression, and its upregulation has inhibited DNA synthesis and cell cycle progression. 15133840_Data suggest that the N-terminal deletion of clusterin may be essential for its alterations of biogenesis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 15158456_clusterin is involved in 15d-PGJ(2)-induced nodule formation and cell differentiation in vascular smooth muscle cells 15247015_although CLU is essential for cellular homeostasis, it may become highly cytotoxic in certain cellular contexts when it accumulates in high amounts intracellularly either by direct synthesis or by uptake from the extracellular milieu 15252304_Clusterin staining supports a diagnosis of follicular dendritic cell tumor and helps classify them. 15304052_platelet ADP receptor P2Y(12) and clusterin are downregulated in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus 15389725_findings suggest that clusterin may contribute to conferring resistance to oxidative stress-mediated cellular injury on prostate cancer cells, especially in the presence of androgen 15492264_Nuclear clusterin function is proapoptotic in colon cancer when induced by APC or chemotherapy in the context of p21 expression. 15499376_Calcium deprivation causes translocation of a 45kDa CLU isoform to the nucleus in human prostate epithelial cells, leading to inhibition of cell proliferation and caspase-cascade-dependent anoikis. 15538973_The Ectopic overexpression of the secreted form of clusterin/apoliporotein J the sensitivity of HaCaT cells to toxic effects of ropivacaine as demonstrated by DNA fragmentation. 15591223_The role of clusterin & its isoforms in SMC behavior is complex & chronologically regulated in response to microenvironmental changes. Proliferative arrest reduces s-CLU; apoptosis increases n-CLU. 15649646_CLU may become highly cytostatic and/or cytotoxic if it accumulates intracellularly in high amounts 15689620_Data show that ionizing radiation causes stress-induced activation of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor-Src-Mek-Erk-Egr-1 signaling that regulates the clusterin pro-survival cascade. 15791650_Clusterin mRNA is increased twofold in early exponential phase of cell proliferation followed by downregulation in the subsequent quiescence phase, whereas it is rapidly increased up to twelvefold upon UV-induced apoptosis. 15809754_Antisense oligonucleotide treatment may improve the outcome of radiation therapy for patients with bladder cancer. 15883054_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15925890_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15925890_The 866C-->T polymorphism might be associated with preeclampsia and essential hypertension. 15929184_overexpression of cytoplasmic clusterin might be involved in the tumorigenesis and/or progression of colorctal cancers 15955107_Clusterin is strongly expressed in melanoma. Downregulation of clusterin reduces drug-resistance, i.e., reduces melanoma cell survival in response to cytotoxic drugs. Reducing clusterin may be novel tool to overcome drug-resistance in melanoma. 16113678_Taken together, our results suggest that the elevated level of clusterin in human cancers may promote oncogenic transformation and tumour progression by interfering with Bax pro-apoptotic activities. 16179938_the importance of CLU in various physiological functions including tumour growth--review 16331665_CLU expression/sub-cellular localization is strictly related to cell fate. 16464517_following exposure to sub-lethal amounts of iron-ascorbate to induce an increase in reactive oxygen species generation and lipid peroxidation, a time-dependent up-regulation of clusterin protein and mRNA levels was observed in neuroblastoma cells 16490286_The results show that clusterin is significantly increased in cerebrospinal fluid from Alzheimer patients as a group, supporting that clusterin might be involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. 16675913_Clusterin and bcl-2 are upregulated in laryngeal carcinomas and their expression is related to invasiveness of these tumors. 16709604_stem cell factor and clusterin may have roles in azoospermia 16709934_clusterin may have a protective effect against cigarette smoke-induced oxidative stress in lung fibroblasts. 16775601_Binding of clusterin to the LDL-R might offer an interpretative key for the pathogenesis of membranous glomerulonephritis in humans 16955214_CLU is actively involved in both replicative senescence and terminal differentiation in different types of human haematopoietic cells. 17048076_This review summarizes our current understanding of the role of clusterin in DNA repair, apoptosis, and cell cycle control and the relevance. 17056579_In rheumatoid arthritis joints, high levels of extracellular CLU and low expression of intracellular CLU may enhance NF-kappaB activation and survival of the synoviocytes. 17080454_low-power 60 GHz radiation does not modify stress-sensitive gene expression of chaperone proteins. 17148459_Clusterin mRNA and protein are shown to increase with androgen treatment in a time- and dose-dependent manner 17203891_CLU immunoreactivity may be helpful as a supplementary criterion to better assess the tumors propensity to relapse in breast carcinoma. 17224269_expression of sCLU modulates growth regulatory effects of 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) in prostate cancer 17260971_Glycosylation is not essential for the chaperone action of clusterin 17260971_deglycosylation of clusterin had little effect on secondary structure content but produced a small increase in solvent-exposed hydrophobicity and enhanced aggregation. These changes were associated with increased binding to a variety of ligands 17322305_Clusterin expression is associated with neuroendocrine differentiation in normal epithelia and that the Clusterin observed in neoplastic cells is de novo synthesized. 17407782_The chaperone action of clusterin targets prefibrillar species to inhibit amyloid formation by lysozyme 17412999_Clusterin is an important element in the control of extracellular protein misfolding and in the formation of neurofibrillary tangles. 17412999_The chaperone action of clusterin can inhibit amyloid formation and toxicity 17420006_Our results indicate that epigenetic factors regulate the clusterin expression of RPE cells and thus might affect the pathogenesis of AMD via the inhibition of angiogenesis and inflammation. 17451556_The extracellular chaperone clusterin appears in the cytosol during endoplasmic stress 17451556_Under certain stress conditions, clusterin can evade the secretion pathway and reach the cytosol, and the retrotranslocation of clusterin is likely to occur through a mechanism similar to the ER-associated protein degradation pathway and involves Golgi. 17512083_Clusterin induces remarkable differentiation of the functional beta cells secreting insulin in response to glucose stimulation. 17534116_The expression and subcellular localization of Clusterin in the nucleus demonstrated the involvement of this protein in the photo-oxidative cell death pathway. 17535098_CLU was identified as a useful tumor marker for the diagnosis of pediatric large cell lymphoma. 17689225_Hyper-expressed form of clusterin localizes to mitochondria, inhibits cytochrome c release, and is inhibited by the proteasome. 17855704_may be a biomarker for longer survival in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer 17872975_Clusterin is constantly associated with altered elastic fibers in aged human skin. Clusterin exerted a chaperone-like activity and effectively inhibited UV-induced aggregation of elastin. 17974975_CLU gene expression might play a crucial role in prostate tumorigenesis by exerting differential biological effects on normal versus tumor cells through differential processing of CLU isoforms in the two cell systems. 18079682_Clusterin shows possible important functions in tumor suppression by the von Hippel-Lindau disease (VHL) gene product. May provide better understanding of retinal hemangioblastoma associated with VHL disease. 18082619_These findings suggest that CLU regulates TGF-beta signaling pathway by modulating the stability of Smad2/3 proteins. 18097679_clusterin is expressed in M cells and follicular dendritic cells at inductive sites of human mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue suggesting a role for this protein in innate immune responses 18239862_Clusterin expression is found nn pituitary adenoma and in non-neoplastic non-neoplastic adenohypophyses. 18378577_Clusterin is markedly elevated in Fuchs' endothelial dystrophy(FED)-affected tissue, pointing to a yet undiscovered form of dysregulation of endothelial cell function involved in FED pathogenesis. 18458059_The interplay between cancer cell-derived clusterin and IGF-1 may dictate the outcome of cell growth and dormancy during tumorigenic progression. 18514801_Data suggest that clusterin expression is related to endometrioid carcinoma of endometrium, in which estrogen is involved in the regulatory network of clusterin. 18542050_TRPM2-mediated Ca2+influx induces chemokine production in monocytes that aggravates inflammatory neutrophil infiltration. 18612545_In atherosclerotic lesions, ApoJ may have protective functions through its capacity to inactivate C5b-9 complement complexes and by reducing the cytotoxic effects of modified LDL on cells that gain contact with the lipoprotein. 18649357_Together with known function of clusterin, the data suggest an epigenetic component in the regulation of clusterin in prostate cancer 18709641_the 4 biomarkers CLU, ITGB3, PRAME and CAPG may be used as prognostic factors for patients with stage III serous ovarian adenocarcinomas. 18712185_ApoJ and leptin may have roles in coronary heart disease 18714397_The chaperone clusterin can protect ovarian cancer cells by sequestering the chemotherapeutic drug paclitaxel 18714397_clusterin is a potential therapeutic target for enhancing chemoresponsiveness in patients with a high-level clusterin expression 18786636_Results identified an interaction between prion protein and clusterin, a chaperone glycoprotein. 18806885_Clusterin is present in ocular anterior segment tissues involved in pseudoexfoliation syndrome. 18806885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18813793_basal clusterin levels are higher in antiestrogen resistant cells; it is up-regulated following antiestrogen treatment; and down-regulation of cytoplasmic clusterin restores sensitivity to toremifene in the antiestrogen-resistant cell line 18842294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19118032_We suggest that elevated sCLU levels may enhance tumorigenesis by interfering with Bax proapoptotic activities and contribute to one of the major characteristics of cancer cells, that is, resistance to apoptosis. 19137541_Results suggest that proteasome inhibition may induce prostate cancer cell death through accumulation of n-clusterin, a potential tumor suppressor factor. 19165232_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19166932_Clusterin-rich cells displayed a spindle-shape morphology while those with low clusterin levels were cuboidal in shape prompted us to investigate if clusterin modulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions. 19177010_Data suggest that Ku70-Bax-clusterin interactions in human colon cancer are modulated by IL-6 that influences Bax-dependent cell death increasing Ku70 binding to Bax and influencing sCLU production that promotes tumor cell survival. 19182256_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19220628_Clusterin expression in cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders and their histologic simulants. 19264665_These data indicated that hepatitis delta virus-induced clusterin protein increases cell survival potential. 19289586_Clusterin expression was not specific for Mycosis fungoides 19344414_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19353783_upregulated after proteasome inhibition due to transactivation by heat-shock factor-1 and due to accumulatioin as a result of reduced proteasomal protein degradation 19357365_Clusterin facilitates exchange of glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-linked SPAM1 between reproductive luminal fluids and mouse and human sperm membranes. 19391138_High clusterin gene expression is associated with disease progression, chemoresistance and metastasis of ovarian cancer. 19413638_Clusterin may protect bile duct epithelium against offensive biliary components or inhibit precipitation of biliary proteins 19446882_A novel heterozygous mutation in the clusterin gene, nucleotide position A1298C (glutamine>proline Q433P), was detected in exon 7 of a child with recurrent hemolytic uremic syndrome. The same mutation was found in the child's two siblings and mother. 19535339_Clusterin forms very large, soluble chaperone-client complexes 19535339_analysis of clusterin-chaperone client protein complexes 19542874_Clusterin is a highly sensitive marker for tenosynovial giant cell tumors 19651157_Reviews the literature linking clusterin to Alzheimer disease (AD). Clusterin can be viewed as a multipotent guardian of brain but is unable to prevent the progressive neuropathology in chronic AD. 19664600_clusterin strongly interacts with wild-type transthyretin (TTR) and TTR variants V30M and L55P under acidic conditions, and blocks the amyloid fibril formation of TTR variants. 19734902_Having removed Single Nucleotide Polymorphism within the APOE, CLU and PICALM loci from the analysis, focused on those that showed the most evidence for association with Alzheimer's disease 19734902_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19734903_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19734903_Two loci gave replicated evidence of association with Alzheimer's disease: one within CLU on chromosome 8 and the other within CR1 on chromosome 1. 19757199_Clusterin may be considered as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for bladder cancer 19793084_Clusterin as a predictor for chemoradiotherapy sensitivity and patient survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 19814590_The secretion of the potential zonal marker clusterin by zonal articular chondrocytes in osteoarthritic and healthy articular cartilage, was characterized. 19878569_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19878774_The chaperone action of clusterin is important in quality control of extracellular protein folding 19879420_This data suggest the importance of epigenetic events in the regulation of CLU in prostate cancer, supporting the idea that prostate cell transformation at early stages requires CLU silencing through chromatin remodeling.[Review] 19879421_CLU expression has contradictory functions, including cell survival, tumor progression, and apoptosis; these ambiguous functions are due to 2 different but related CLU protein forms, a glycosylated and a nonglycosylated form [Review] 19879422_reports the dynamic interaction of the different forms of CLU with their partners DNA-repair protein Ku70 and proapoptotic factor Bax during colon cancer progression, which seems to be a crucial point for the neoplastic cell fate.[Review] 19879423_In early-stage lung cancers CLU represents a positive biomarker correlating with better overall survival.[Review] 19903339_microarray study in sinonasal adenocarcinoma we identified proteins, CLU that is significantly differentially expressed in tumors compared to normal tissue 19903745_CLU acts as a tumor suppressor in the early stages of carcinogenesis, but CLU may also represent a pro-survival stimulus confering increased resistance to anti-cancer drugs or enhancing tumour cell survival in specific niches. Review. 19935703_a role for secreted clusterin as an important extracellular promoter of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition 19940549_Data show that clusterin expression is under epigenetic control via methylation of its promoter. 19996109_Data identified ceruloplasmin, fibrinogen, and albumin as major clients for clusterin. 19996109_The chaperone action of clusterin protects major human plasma proteins from aggregation and precipitation 20007348_Reduction of inducible expression of clusterin results in an increase in tubular cell apoptosis and renders mice prone to ischemia reperfusion injury, implying a protective role of clusterin in kidney injury. 20009887_Overexpression of clusterin is associated with ovarian cancer. 20019877_Clusterin may protect human corneal endothelial cells from oxidative injury-mediated cell death via inhibition of reactive oxygen species production. 20028970_Data demonstrate that it is the presecretory form of CLU that has regulatory activity on NF-kappaB. Results identified the site of psCLU that interacts with IkappaB-alpha, and also showed that this region bears the regulatory activity of psCLU on NF-kappaB. 20057494_Clu showed genome wide significant association with Alzheimer disease. 20058210_clusterin expression could be a new molecular marker to predict response to platinum-based chemotherapy and survival of patients with cervical cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radical hysterectomy. 20068069_Elevated levels of sCLU promote prostate cancer cell survival by facilitating degradation of COMMD1 and I-kappaB, thereby activating the canonical NF-kappaB pathway. 20096688_Chibby and clusterin were co-immunoprecipitated with NBPF1. 20209083_CLU genetic variants may have a role in Alzheimer's disease 20209083_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20353268_Overexpression of cytoplasmic clusterin seems to be related with patient's shorter survival in late stage gastric carcinoma. 20410100_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20410100_SNPs in APOJ show strong statistical evidence of a functional effect on plasma fatty acid distribution. 20460622_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20497247_Clusterin expression may have a role in colonic carcinogenesis 20534741_Data confirmed genetic associations for Alzheimer's disease with APOE, CLU, PICALM and CR1 SNPs. 20534741_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20554627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20554627_These results show near-perfect replication and provide the first additional evidence that CLU is associated with the risk of late onset alzheimer disease. 20570404_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20570404_While no Alzheimer disease association is observed with single nucleotide polymorphisms, a trend of association is seen with Picalm and clusterin single nucleotide polymorphisms. 20599866_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20599866_The minor allele (G) of the rs9331888 polymorphism within CLU was significantly associated with an increased risk of sporadic late-onset Alzheimer's disease in Chinese 20603455_results demonstrate an important role of clusterin in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease (AD) and suggest that alterations in amyloid chaperone proteins may be a biologically relevant peripheral signature of AD 20614220_both cytoplasmic and nuclear immunostaining patterns of clusterin were detected in the tumors of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. 20674675_In this review, clusterin is a major Alzheimer's disease susceptibility gene implicated indirectly in the life cycle of the herpes simplex virus. 20697030_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20697030_This study confirmed in a completely independent data set that CR1, CLU, and PICALM are AD susceptibility loci in European ancestry populations. 20738160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20738160_Polymorphism of the clusterin gene may confer symptomatic specificity in schizophrenia, whereas polymorphism of the clathrin assembly lymphoid myeloid gene does not affect susceptibility to schizophrenia. 20739100_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20842452_The interaction between GOLPH2 and secretory CLU was confirmed intracellularly and extracellularly. 20847305_Clusterin levels in HDL are lower in men with reduced insulin sensitivity, higher body mass index, and an unfavorable lipid profile. Clusterin depletion contributes to the loss of HDL's cardioprotective properties. 20850846_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20850846_The CLU gene was associated with diabetes, probably through an increase in insulin resistance primarily and through an impairment of insulin secretion secondarily 20855565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20873220_Analysis of clusterin gene (CLU/APOJ) polymorphism in Alzheimer's disease patients and in normal cohorts from Russian populations 20873220_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20930273_This study demonistrated that late onset alzheimer's disease linke to 8p21.1 region Including the CLU gene. 21042904_In neuroblastoma, clusterin exerts its anti-apoptotic effects downstream of Ku70 acetylation, likely by directly blocking Bax activation. 21043527_Serum ApoJ levels, determined by a commercial ELISA, were significantly lower in AMI-patients immediately after the event than in controls. In 60% of patients, the lowest ApoJ level was detected within 6 h after the onset of AMI. 21059989_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21059989_clu polymorphisms were associated with late-onset Alzheimer disease in an independent cohort from the National Institute on Aging Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease Family Study 21135756_Results do not support a role for plasma clusterin as an important leptin-binding protein or modulator of leptin action. 21224044_these results suggest that CLU may play a pathogenetic role in transthyretin and Ig light chain amyloidoses and amyloidotic cardiomyopathy. 21240462_Increase in clusterin forms part of the stress response in Hodgkin's lymphoma. 21242307_Clusterin (apolipoprotein J), a molecular chaperone that facilitates degradation of the copper-ATPases ATP7A and ATP7B. 21280673_Results suggest that serum clusterin is not an early, presymptomatic biomarker for Alzheimer's disease. 21300948_This study provides compelling independent evidence that genetic variants in CLU, CR1, and PICALM are genetically associated with risk for AD. 21347408_variants in BIN1, CLU, CR1 or PICALM are associated with changes in the CSF levels of biomarkers 21379329_There was evidence of association for recently-reported late-onset Alzheimer's disease risk loci, including BIN1 and CLU and CUGBP2 with APOE. 21397462_Participants with the clusterin risk genotype have higher brain activity than participants with the protective allele in frontal and posterior cingulate cortex and the hippocampus, particularly during high memory demand. 21422520_The results of this study concluded that the rs11136000 AD-risk variant is associated with low clusterin plasma levels in Alzheimer's disease. 21447104_No association found between CLU gene and Alzheimer's disease in a Japanese population 21460853_these results integrate DNA damage resulting from genetic instability, IR, or chemotherapeutic agents, to ATM activation and abrogation of p53/NF-YA-mediated IGF-1 transcriptional repression, that induces IGF-1-sCLU expression. 21467232_Glycosylated serum Apo-J is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 21467285_data from the general population show that increased plasma clusterin levels are associated with prevalent alzheimer's disease (AD) and are higher in more severe cases of AD 21505792_The chaperone clusterin mediates systemic clearance of misfolded extracellular proteins 21508640_The APOJ single nucleotide polymorphism (1598delT) is associated with risk factors for coronary artery disease in a Chinese population. 21525168_The proteomes of the type-1 diabetic, type-2 diabetic, and non-diabetic obese patients presented elevated amounts of the same set of one molecular form of semenogelin-1, one form of clusterin, and two forms of lactotransferrin. 21527247_these results suggest a molecular basis for the pro-apoptotic function of nCLU by elucidating the residue specific interactions of the BH3 motif in nCLU with anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins. 21543606_Young healthy carriers of the CLU gene risk variant showed a distinct profile of lower white matter integrity that may increase vulnerability to developing Alzheimer disease later in life. 21567405_Nuclear CLU sequesters Bcl-XL via a putative motif in the C-terminal coiled coil (CC2) domain, releasing Bax, and promoting apoptosis. 21573492_nCLU also exerts a strong anti-migratory/anti-invasive activity in prostate cancer cells, by interfering with the cytoskeletal components and by decreasing MMP-2 activity. 21630085_results indicated lower metastatic potential for lung cancer cells with high CLU level 21633299_CLU could be a new molecular marker to predict overall survival of patients with advanced-stage cervical cancer treated with curative intended radiotherapy. 21732348_Results identify clusterin (CLU) as a MDA-7/IL-24 interacting protein in DU-145 cells and investigate the role of MDA-7/IL-24 in regulating CLU expression and mediating the antitumor properties of mda-7/IL-24 in prostate cancer. 21761117_controversial data on CLU function in chemo-response/resistance may be explained by a shift in the pattern of CLU expression and intracellular localization as well when tumor acquires chemoresistance 21824521_Our findings suggest that clusterin is associated with rate of brain atrophy in mild cognitive impairment 21892414_Results suggest a biological mechanism for the genetic association of CLU with Alzheimer's Disease risk and indicate that rs9331888 is one of the functional DNA variants underlying this association. 21899841_Proteomic analysis of intra-arterial thrombus secretions reveals a negative association of clusterin and thrombospondin-1 with abdominal aortic aneurysm. 21900379_We report for the first time that circulating clusterin does not have a day/night variation pattern in healthy young individuals. Clusterin levels are associated with total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol cross-sectionally. 21912625_relationship of Parkinson's disease with SNPs of CLU, CR1 and PICALM 21953030_report abundance levels of CLI in serum samples from patients with advanced breast cancer, colorectal cancer (CRC) and lung cancer compared to healthy controls (age and gender matched) using commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits 21953454_CRM1 protein-mediated regulation of nuclear clusterin (nCLU), an ionizing radiation-stimulated, Bax-dependent pro-death factor 21980627_The overexpression of CLU in various stages of cervical lesions may serve as a potential marker to distinguish cervical neoplasia with borderline morphology features. 21987172_these data indicate that YB-1 transactivation of clusterin in response to stress is a critical mediator of paclitaxel resistance in prostate cancer. 21998749_sCLU at the mature RBCs is an active component being functionally implicated in the signalling mechanisms of cellular senescence and oxidative stress-responses 22012253_Localisation is key for CLU physiology, explaining the wide range of effects in cell survival and transformation. 22013110_Semen clusterin bears a set of complex glycans with high affinity for dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing nonintegrin (DC-SIGN); these glycans mediate the effective binding of semen clusterin to DC-SIGN and interfere with HIV-1 binding to DC-SIGN. 22015308_findings showed evidence of CR1, CLU, and PICALM and late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD) susceptibility in an independent southern Chinese population 22016805_secretory Apolipoprotein J/Clus represents a pro-survival factor acting for the postponement of the untimely clearance of RBCs 22068036_determined that the tumor suppressors CLU, NGFR, and RUNX3 were also directly repressed by EZH2 like CASZ1 in NB cells 22082661_We observed increased clusterin expression in human familial amyloid polyneuropathy nerves. 22122982_The rs11136000 and rs9331888 polymorphisms of the CLU gene are associated with late-onset Alzheimer's disease 22130675_Clusterin and COMMD1 independently regulate degradation of the mammalian copper ATPases ATP7A and ATP7B. 22159129_Healthy carriers of the CLU variant exhibit altered coupling between hippocampus and prefrontal cortex during memory processing. 22166956_CLU downregulation in fibroblast-like synoviocytes alters their aggressiveness in rheumatoid arthritis synovitis. 22179788_Data show that clusterin is able to influence both the aggregation and disaggregation of amyloid-beta(1-40) peptide by sequestration of the amyloid beta oligomers. 22232000_This study showed that overall levels of clusterinmRNA and protein areunchanged in Alzheimer's disease. 22234156_variation in CLU, genes are associated with Fuchs' endothelial dystrophy in Caucasian Australian cases 22236192_study found a 1.9-fold increase in the average levels of serum CLU in colorectal cancer patients compared to healthy donors 22248099_The clusterin gene CLU is a genetic risk association of AD with rare coding CLU variations. 22258514_This study indicates that the rs9331888 AD-risk variant is associated with low blood clusterin levels. 22266332_Data suggest that the effect of sex steroid deprivation appeared specific to clusterin associated with high density lipoproteins (HDL). 22274961_This review discusses the genetic variation and role of the clusterin gene in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. 22296908_Clusterin (rs11136000) was associated with Alzheimer's disease in Chinese Han population. 22391565_Secretory CLU expression was stimulated by insulin-like growth factor-1, but suppressed by p53. 22402018_In conclusion, we confirmed association of CLU, CR1, and PICALM genes with the disease | ENSMUSG00000022037 | Clu | 37.432320 | 2.514025212 | 1.329999 | 0.40308158 | 10.461658 | 0.0012187780882367835535995403972719941521063446998596191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0089586273769081074119791097132292634341865777969360351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 67.3230337 | 20.9550881 | 26.5645965 | 8.2705690 | |
| ENSG00000121068 | 6909 | TBX2 | protein_coding | Q13207 | FUNCTION: Transcription factor which acts as a transcriptional repressor (PubMed:11111039, PubMed:11062467, PubMed:12000749, PubMed:22844464, PubMed:30599067). May also function as a transcriptional activator (By similarity). Binds to the palindromic T site 5'-TTCACACCTAGGTGTGAA-3' DNA sequence, or a half-site, which are present in the regulatory region of several genes (PubMed:11111039, PubMed:12000749, PubMed:22844464, PubMed:30599067). Required for cardiac atrioventricular canal formation (PubMed:29726930). May cooperate with NKX2.5 to negatively modulate expression of NPPA/ANF in the atrioventricular canal (By similarity). May play a role as a positive regulator of TGFB2 expression, perhaps acting in concert with GATA4 in the developing outflow tract myocardium (By similarity). Plays a role in limb pattern formation (PubMed:29726930). Acts as a transcriptional repressor of ADAM10 gene expression, perhaps in concert with histone deacetylase HDAC1 as cofactor (PubMed:30599067). Involved in branching morphogenesis in both developing lungs and adult mammary glands, via negative modulation of target genes; acting redundantly with TBX3 (By similarity). Required, together with TBX3, to maintain cell proliferation in the embryonic lung mesenchyme; perhaps acting downstream of SHH, BMP and TGFbeta signaling (By similarity). Involved in modulating early inner ear development, acting independently of, and also redundantly with TBX3, in different subregions of the developing ear (By similarity). Acts as a negative regulator of PML function in cellular senescence (PubMed:22002537). Acts as a negative regulator of expression of CDKN1A/p21, IL33 and CCN4; repression of CDKN1A is enhanced in response to UV-induced stress, perhaps as a result of phosphorylation by p38 MAPK (By similarity). Negatively modulates expression of CDKN2A/p14ARF and CDH1/E-cadherin (PubMed:11062467, PubMed:12000749, PubMed:22844464). Plays a role in induction of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (PubMed:22844464). Plays a role in melanocyte proliferation, perhaps via regulation of cyclin CCND1 (By similarity). Involved in melanogenesis, acting via negative modulation of expression of DHICA oxidase/TYRP1 and P protein/OCA2 (By similarity). Involved in regulating retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cell proliferation, perhaps via negatively modulating transcription of the transcription factor CEBPD (PubMed:28910203). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q60707, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11062467, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11111039, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12000749, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22002537, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22844464, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28910203, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29726930, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30599067}. | Developmental protein;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation | This gene is a member of a phylogenetically conserved family of genes that share a common DNA-binding domain, the T-box. T-box genes encode transcription factors involved in the regulation of developmental processes. This gene product is the human homolog of mouse Tbx2, and shares strong sequence similarity with Drosophila omb protein. Expression studies indicate that this gene may have a potential role in tumorigenesis as an immortalizing agent. Transcript heterogeneity due to alternative polyadenylation has been noted for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:6909; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; aorta morphogenesis [GO:0035909]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; atrioventricular canal development [GO:0036302]; atrioventricular canal morphogenesis [GO:1905222]; cardiac jelly development [GO:1905072]; cardiac muscle cell myoblast differentiation [GO:0060379]; cardiac muscle tissue development [GO:0048738]; cell fate specification [GO:0001708]; cellular senescence [GO:0090398]; cochlea morphogenesis [GO:0090103]; developmental growth involved in morphogenesis [GO:0060560]; embryonic camera-type eye morphogenesis [GO:0048596]; embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:0042733]; embryonic heart tube development [GO:0035050]; endocardial cushion formation [GO:0003272]; endocardial cushion morphogenesis [GO:0003203]; epithelial tube branching involved in lung morphogenesis [GO:0060441]; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008543]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; mammary placode formation [GO:0060596]; melanocyte proliferation [GO:0097325]; mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in lung development [GO:0060916]; muscle cell fate determination [GO:0007521]; negative regulation of cardiac chamber formation [GO:1901211]; negative regulation of cellular senescence [GO:2000773]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of heart looping [GO:1901208]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neurogenesis [GO:0022008]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003151]; outflow tract septum morphogenesis [GO:0003148]; pharynx development [GO:0060465]; pigment metabolic process involved in pigmentation [GO:0043474]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060045]; positive regulation of cell cycle G1/S phase transition [GO:1902808]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of heart contraction [GO:0008016]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to retinoic acid [GO:0032526]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021]; smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051145]; ureteric peristalsis [GO:0072105] | 12000749_identification of a variant T-site as the essential TBX2/TBX3-binding element in the human p14(ARF) promoter 14595187_upregulation of Tbx2 gene in response to tension downregulates CX43 in cranial sutures 15781639_In human melanoma cells, expression of dnTbx2 leads to severely reduced growth and induction of senescence-associated heterochromatin foci. 16730707_Results are consistent with Tbx2 playing a role in cell cycle progression and organization of subnuclear compartments. 17407139_Tbx2 in fibroblasts reduces expression of the COL1A2 gene 18025091_the ability of Tbx2 to repress the p21 gene is enhanced in response to a stress-induced senescence pathway, which leads to a better understanding of the regulation of the anti-senescence function of Tbx2. 18640248_identify a Sp1 element and a reverse CCAAT box to be essential for basal Tbx2 promoter activity 18829543_Tbx2 and Tbx3 may play a dual role during the radial to vertical growth phase transition by both inhibiting senescence via repression of p21(CIP1) expression, and enhancing melanoma invasiveness by decreasing E-cadherin levels. 19216023_TBX2 is a cell type-dependent survival factor under a p53-negative background. 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19469638_Tbx2 protein might play an important role in the process of the development and metastasis of pancreatic cancers 19633291_Data reveal that TPA activates transcription of TBX2 through activating MSK1, which leads to an increase in phosphorylated histone H3 and the recruitment of Sp1 to the TBX2 gene. 19960541_This review presents a state of the art overview of the role and regulation of Tbx2 in early embryonic development and in cancer[review] 20348948_Data identify a novel mechanism for TBX2-driven oncogenesis and highlight the importance of NDRG1 as a growth control gene in breast tissue. 20502058_We report the first analysis of PSCA, PIWIL1, and TBX2 expression in EAC. Our findings suggest that PSCA and TBX2 might be candidate targets for cancer therapy. 20534814_Rb1 is an important determinant of Tbx2 functional specificity. 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20635360_TBX2 gene duplication is associated with complex heart defect and skeletal malformations. 21271665_Microdeletion of 17q22q23.2 encompassing TBX2 and TBX4 in a patient with congenital microcephaly, thyroid duct cyst, sensorineural hearing loss, and pulmonary hypertension. 22002537_PML and TBX2 act in an autoregulatory loop to control the effective execution of the senescence program. 22284968_TBX2 CPG island methylation predicts progression in bladder cancer. 22844464_an unanticipated link between TBX2 deregulation in cancer and the acquisition of EMT and invasive features of epithelial tumor cells 23020925_The identification of TBX2 as a target for PAX3 provides a key insight into how PAX3 may contribute to melanoma evolution. 23388722_Coimmunoprecipitations and immunofluorescence analyses confirmed the L2-TBX2 interaction and revealed that human papillomavirus 16 L2 also interacts with human TBX3, another member of the T-box family. 23727221_DNA sequence variants within TBX2 gene promoter may contribute to ventricular septal defects ethiology 23959449_TBX2 was a significantly prognostic factor for decreased survival. 24113180_Knocking down TBX2 sensitises the cells to cisplatin by disrupting the ATM-CHK2-p53 signalling pathway. 24309999_The data suggested that the DNA sequence variants within the TBX2 gene promoter was implicated in the indirect inguinal hernia development as a rare cause. 24470334_deregulated TBX2 serves as an oncogene in rhabdomyosarcoma 24742492_High TBX2 expression is associated with breast cancer. 25027744_High TBX2 expression is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 25344916_Our results suggest a conserved role of Tbx2-related proteins in cell invasion and metastasis-related processes 25371204_Data show that the down-regulation of T-box transcription factor TBX2 by transforming growth factor beta I (TGF-beta1) is mediated by T-box transcription factor TBX3. 25394776_this new molecular-grade based on the combination of TBX2 and TBX3 methylation is an excellent marker for predicting progression to muscle-invasive bladder cancer in patients with primary pTaG1/2 bladder cancer. 26686089_TBX2 is a central component of the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway deregulation in RMS cells and that targeting TBX2 in RMS tumors may offer a novel therapeutic approach for RMS 28849151_The results indicated that the expression rates of TBX2 were significantly increased in the prostate cancerous tissues, compared with the healthy tumor adjacent tissue, and TBX2 increased staining was associated with the clinical stage and pathological grade. 29726930_We report four individuals with an overlapping spectrum of craniofacial dysmorphisms, cardiac anomalies, skeletal malformations, immune deficiency, endocrine abnormalities and developmental impairments, reminiscent of DiGeorge syndrome, who are heterozygotes for TBX2 variants. 30223900_Our results indicate that the R608W and R616Q variants of TBX2 as well as the A192T and A562V variants of TBX3 contribute to Conotruncal heart defects (CTDs)etiology; this was the first association of variants of TBX2 and TBX3 to CTDs based on a large population. 30262811_T allele of rs59382073 in TBX2 3'UTR contributes to greater congenital heart defects risk in the Han Chinese population 30451831_TBX2 is a neuroblastoma core regulatory circuitry component enhancing MYCN/FOXM1 reactivation of DREAM targets. 30525309_The minor C allele of rs4455026 in TBX2 promoter region was related with lower congenital heart disease susceptibility in the Han Chinese population via repressing its transcriptional activity. 30599067_transcription factor TBX2 is able to restrain ADAM10 gene expression and that this mechanism might play a role in regulating cellular processes in health, development and disease. 31253870_data demonstrate that TBX2 promotes suppression of normal growth control mechanisms through recruitment of a large repression complex to EGR1-responsive promoters leading to the uncontrolled proliferation of breast cancer cells 32271423_Clinical significance of TBX2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas and its role in cell migration and invasion. 32861705_MicroRNA-7 targets T-Box 2 to inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasiveness in glioblastoma multiforme. 34064060_TBX2, a Novel Regulator of Labour. 35891763_Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Preeclampsia. 36017860_T-Box Transcription Factor 2 Enhances Chemoresistance of Endometrial Cancer by Mediating NRF2 Expression. | ENSMUSG00000000093 | Tbx2 | 84.827236 | 0.464747806 | -1.105480 | 0.16670884 | 45.008805 | 0.0000000000196150490980894979326437315470156455901595826674110867315903306007385253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000006351280249631386077495484186652280333973408232850488275289535522460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 53.6216005 | 8.1915620 | 115.9820952 | 16.5805138 | |
| ENSG00000121858 | 8743 | TNFSF10 | protein_coding | P50591 | FUNCTION: Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF10A/TRAILR1, TNFRSF10B/TRAILR2, TNFRSF10C/TRAILR3, TNFRSF10D/TRAILR4 and possibly also to TNFRSF11B/OPG (PubMed:26457518, PubMed:10549288). Induces apoptosis. Its activity may be modulated by binding to the decoy receptors TNFRSF10C/TRAILR3, TNFRSF10D/TRAILR4 and TNFRSF11B/OPG that cannot induce apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10549288, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26457518}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cell membrane;Cytokine;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc | The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand family. This protein preferentially induces apoptosis in transformed and tumor cells, but does not appear to kill normal cells although it is expressed at a significant level in most normal tissues. This protein binds to several members of TNF receptor superfamily including TNFRSF10A/TRAILR1, TNFRSF10B/TRAILR2, TNFRSF10C/TRAILR3, TNFRSF10D/TRAILR4, and possibly also to TNFRSF11B/OPG. The activity of this protein may be modulated by binding to the decoy receptors TNFRSF10C/TRAILR3, TNFRSF10D/TRAILR4, and TNFRSF11B/OPG that cannot induce apoptosis. The binding of this protein to its receptors has been shown to trigger the activation of MAPK8/JNK, caspase 8, and caspase 3. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. | hsa:8743; | extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; TRAIL binding [GO:0045569]; tumor necrosis factor receptor binding [GO:0005164]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; immune response [GO:0006955]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043280]; positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001238]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090200]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 10542098_crystal structure at 2.2 A resolution of a complex between TRAIL and the extracellular region of DR5 11059770_Apo2 ligand mRNA levels increase following irradiation of human T lineage-derived tumor cells. Recombinant soluble Apo2L enhanced the lethality of therapeutic doses of irradiation, indicating their possible use in combination for clinical therapy. 11095979_The Apo2L gene spans ~ 20 kb and is composed of 5 exons. The 1.2-kb Apo2L promoter region upstream of the translation initiation codon was cloned, its transcription start site defined, and several putative transcription factor binding sites identified. 11466352_TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) enhances T cell proliferation following T cell receptor engagement and signals the augmentation of IFN-gamma secretion via a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway. 11568006_Interferon-alpha and -beta, but not -gamma, induce apoptosis through Apo2 ligand transcriptional induction in multiple myeloma tumor cells and freshly derived primary cells. 11739488_Differential secretion of APO2 ligand microvesicles during activation-induced death of T cells 11781716_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11830480_Up-regulation in highly malignant multiple myeloma plasma cells negatively regulates erythroblast maturation; a major pathogenetic mechanism of anemia in multiple myeloma. 11844843_TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is not constitutively expressed in the human brain, whereas both apoptosis-mediating and apoptosis-blocking TRAIL receptors are found on neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes 11852102_TRAIL/Apo2L-induced apoptosis is mediated by ROS-activated p38 MAP kinase followed by caspase activation in HeLa cells. 11877293_signaling pathway and intracellular regulation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells 11936954_Results suggest that IFN-gamma facilitates TRAIL-induced activation of mitochondria-regulated as well as mitochondria-independent apoptotic pathways in breast tumour cells. 11940602_An inducible pathway for degradation of FLIP protein sensitizes tumor cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis 11956660_Histone deacetylase inhibitors sensitize human colonic adenocarcinoma cell lines to TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis. 11964312_Apo-2L-induced processing of caspase-3,caspase-8, and Bid is significantly increased by overexpression of Smac/DIABLO. 11994437_Although it does not contribute to mechanisms of peripheral T cell tolerance such as clonal anergy or deletion by apoptosis, TRAIL can directly inhibit activation of human T cells via blockade of calcium influx. 12029096_XAF1 augments TRAIL-induced apoptosis 12082620_Stimulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway antagonizes TRAIL-induced apoptosis downstream of BID cleavage in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. 12082629_TRAIL induced translocation of Bax after cleavage of Bid in parental cells but not mitochondrial-DNA-deficient cells. 12097384_APO2L/TRAIL, specifically induced by autologous tumor and up-regulated by IFN-alpha, is a key mediator of tumor-specific CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte-mediated cell death. 12097388_TRAIL/Apo2L in combination with interferon-beta synergistically induces apoptosis and inhibits melanoma cell proliferation in vitro, at least in part by cleavage of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP). 12118245_Data show that transfer of the gene encoding Smac sensitized tumor and malignant glioma cells for apoptosis, and that Smac peptides enhanced the antitumor activity of Apo-2L/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). 12140294_TRAIL gene expression regulation by PI3 kinase, Akt and GSK-3 in tumor cells 12198154_Caspase-10 is recruited to and activated at the native TRAIL death-inducing signalling complex in a FADD-dependent manner. 12351634_TRAIL is a direct target of FKHRL1 12359235_induces apoptosis independently of the mitochondrial apoptosis mediator DAP3 12398939_osteoblasts are resistant to Apo2L/TRAIL-mediated apoptosis 12407100_These results provide new insights into the mechanisms of bile acid cytotoxicity and the proapoptotic effects of cFLIP phosphorylation in TRAIL signaling. 12414956_The human papillomavirus type 16 E5 protein impairs TRAIL- and FasL-mediated apoptosis in HaCaT cells by different mechanisms. 12421926_Plasma cells synthesize TRAIL and are subject to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis, which correlates with inactivation of the CD40-NF-kappa B survival pathway. 12421985_Enhanced expression of TRAIL promotes peripheral blood eosinophil survival in the airways of allergic asthmatics following segmental antigen challenge. 12421989_T cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients kill autologous monocytes through apoptotic pathways involving the ligand TRAIL. 12429913_Trail protein sensitivity and cell cycle phase; TRAIL preferentially induces apoptosis in tumor cells over normal cells. 12439929_soluble TRAIL in the HBV infected people may participate in the liver damage 12445619_The apoptosis-inducing TRAIL gene caused significant changes in the biomechanics properties of Jurkat cells. 12447876_NF-kappaB prevents TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma through a TRAIL-activated TRAF2-NIK-IKK pathway. 12488957_TRAIL death pathway is present and can function in human islet beta cells. 12496482_TRAIL protein binds and induces oligomerization of its cell-membrane death receptors (DR4 and DR5). These trigger the activity of CASP8 and apoptosis through DISC. 12517970_The susceptibility of neutrophils to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis suggests a role for TRAIL in the regulation of inflammation and may provide a mechanism for clearance of neutrophils from sites of inflammation. 12532461_Localization of TRAIL/TRAILR in fetal pancreas. 12556488_c-FLIP(L) and c-FLIP(S) potently control TRAIL responses, both by distinct regulatory features, and further imply that the differentiation state of malignant cells determines their sensitivity to death receptor signals. 12574346_TRAIL is the main effector molecule responsible for the in vitro tumoricidal activity of Newcastle disease virus-stimulated human monocytes. 12576447_high expression of this protein is associated with favorable ovarian cancer survival 12592338_Akt1 may be an important regulator of TRAIL sensitivity in HL60 cells through the activation of NF-kappaB and up-regulation of cFLIP(L) synthesis 12604406_loss of expression of pro-apoptotic proteins (Bax, Bak and Bcl-Xs) in Burkitt's lymphomas resistant to Fas did not compromise sensitivity to TRAIL. 12642868_sensitization hepatoma cells to TRAIL induced apoptosis through DR5 upregulation and NF-kappa B inactivation is sensitized by interferon-alpha 12663665_activation of JNK is required for sensitization of PC3 cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by translation inhibitors in cells that are otherwise TRAIL-resistant. 12707267_TRAIL and JNK1 combine with DNA damage and mediate signals independent of p53 leading to apoptosis 12715915_results suggest involvement in the induction of neuronal apoptosis in HIV-1 infected brain 12738989_bystander effect of the TRAIL gene is mainly mediated by membrane-bound TRAIL on the surface of transduced cells 12761581_TRAIL signaling pathway circumvents caspase-8 activation of Bid upstream of the mitochondria; TRAIL acts in mitochondria via a mechanism that may involve components of the sphingomyelin cycle. 12767990_produced by Tat protein-stimulated monocytes and provides a mechanism by which HIV infection can destroy uninfected CD4-positive t-lymphocytes 12787570_This review focuses on the apoptosis signaling pathways stimulated by Apo2L/TRAIL, summarize what is known to date about the physiological role of this cell death ligand and the potential for its application to cancer therapy. 12808117_likely to be involved in chronic pancreatitis; pancreatic stellate cells may directly contribute to acinar regression by inducing apoptosis of parenchymal cells in a TRAIL-dependent manner 12813457_The data describe the biological significance of TRAIL-mediated activation of NF-kappaB in cancer cells resistant to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis: TRAIL leads to an increase in tumor cell count by a prosurvival and possibly mitogenic function. 12839575_beside its potent pro-apoptotic role, leucine zipper-TRAIL leads to pro-inflammatory responses that are mainly mediated by TRAIL receptor 1 in HaCaT keratinocytes. 12874246_Recombinant human TRAIL can both injure and activate human endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo; compared with TNF, TRAIL is potent at causing injury but less effective at stimulating inflammation. 12907654_Apo2L/TRAIL exhibits enhanced apoptotic activity in prostate carcinoma cells cultured in vitro and xenografted tumors in vivo through differential regulation of Bcl-2 family proteins when combined with the topoisomerase I inhibitor CPT-11 (irinotecan) 12915532_Respiratory syncytial virus-infected cells in vivo are susceptible to killing through the TRAIL pathway. 12915677_osteoprotegerin is abundant in gestational membranes and, in concert with TRAIL decoy receptors, may protect resident cells of membranes against the proapoptotic effects of TRAIL during pregnancy 12920112_results show that protein kinase C activation specifically inhibits the recruitment of TRAIL receptors 1 and 2 complexes, thereby modulating tumor necrosis-related apoptosis-inducing ligand(TRAIL)-induced apoptosis 12927928_TRAIL-induced apoptosis is enhanced by level of HBV replication in human hepatocytes, in part, by HBV-encoded X antigen-dependent upregulation of TRAIL-R1/DR4. 12934102_Apoptosis induced by the combination of Apo2L/TRAIL and PG490 warrants evaluation as a treatment for lung cancer 12969966_biologic activity of on human erythropoiesis 14534533_TRAIL-induced apoptosis of glioma tumors in vivo were studied by real-time imaging. 14601052_Cocotreatment with TRAIL/Apo2L and VP16 provides an attractive approach for selective killing of tumour cells while leaving unaffected normal cells. 14637151_Our data suggest that Akt is an endogenous inhibitor during TRAIL-mediated synovial cell apoptotic pathway. 14645705_sensitization to TRAIL requires p53 14647456_Bak is a regulatory molecule involved in IFNgamma-facilitated TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in thyroid cancer cells 14670183_TRAIL activates a caspase 9/7-dependent pathway in caspase 8/10-defective tumor cell lines 14675194_TRAIL appears to cause apoptosis in dividing, but not differentiating keratinocytes, while internucleosomal DNA fragmentation does not take place. 14691451_MG132 upregulates death receptor-5 and cooperates with APO2L to induce apoptosis in Bax-proficient and -deficient cells. 14715264_Our data suggest a cross-talk between HDAC inhibition and TRAIL that results in modulation of expression of specific apoptotic mediators. 14726404_IFNalpha stimulates the expression of high levels of TRAIL mRNA and the release of elevated amounts of a soluble bioactive form of TRAIL (sTRAIL) in both human neutrophils and monocytes 14729397_Results suggest that human placenta may not only produce TRAIL but also be a TRAIL target organ, and that the TRAIL/TRAIL receptor system could take part in the homeostasis of placenta during gestation. 14742697_Localization of tumour necrosis factor-alpha-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in adult human testes. 15030996_TRAIL expression was down regulated during liver regeneration in organ donors 15033706_Cell-cell-associated and secreted TRAIL contribute to the triggering of Ewing cell apoptosis induced by IFN gamma alone or combinaed with TNF. 15041704_Glucose deprivation enhances TRAIL-induced apoptotic death as well as caspase activation (caspase-3, -9, and -8) in human prostate adenocarcinoma 15064358_OPG blocks endothelial cell apoptosis through binding tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and preventing its interaction with death-inducing TRAIL-receptors. 15077162_Interferon/cytokine combinations are able to induce TRAIL gene expression and TRAIL protein in Ewing tumor cells. 15093732_TRAIL expression and secretion were nalyzed in melanoma cells in culture. The secretion was associated with microvesicles upon melanoma activation with phytohemagglutinins or alpha-MSH. 15094456_TRAIL is present in the brain of Alzheimer's disease patients but absent in the brain of normal patients. TRAIL was localized in AD affected regions, such as cerebral cortex, often in the proximity of Congo-red-positive amyloid plaques. 15137068_Low-dose UV-radiation sensitizes keratinocytes to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. 15201983_8-Cloroadenosine can promote TRAIL killing activity in a hepatoma cell line in a dose- and time-dependent manner in vitro. 15205263_once activated the major cytotoxic effector cells are potentially sensitive to TRAIL but are physiologically protected from its apoptotic action by intracellular level of c-FLIP 15241475_a novel TRAIL-mediated tumor suppressor activity of interferon regulatory factor 1 and suggest a mechanistic basis for the synergistic antitumor activities of certain retinoids and interferons 15251327_TRAIL can induce apoptosis of DR4/DR5-expressing cells and its receptors may participate in renal graft rejection. 15256058_TRAIL may play an unexpected role in promoting angiogenesis in tumor angiogenesis. 15257094_endotoxin increases sTRAIL where the p38 MAP kinase signaling pathway is involved 15285015_Infiltrating lymphocytes were isolated from H pylori-infected gastric mucosa, and expression of TRAIL in T cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. 15286701_New antitumor activity of parthenolide, which can be exploited to reverse resistance of breast cancer cells to TRAIL. 15292354_Enhanced apoptosis adjacent to vascular calcification and concurrent expression of regulators of apoptosis and osteoclastic differentiation, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and OPG. May be involved in pathogenesis of vascular calcification. 15308561_results highlight that MM T cells support OC formation and survival, possibly involving OPG/TRAIL interaction and unbalanced OC expression of TRAIL death and decoy receptors 15326479_TRAIL-induced cell death is magnified by all-trans retinoic acid treatment, independently of telomerase activity on telomeres 15339846_CD40-activated CLL cells also express DR5, a receptor for tumor-necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) that is expressed by CD4+ T-cells 15361826_Triggering triggering the mitochondrial pathway by betulinic acid may enhance TRAIL-based therapy in cancer. 15459016_TRAIL plays important roles in interferon-induced apoptosis. 15459191_cFLIP(L) is not only a central antiapoptotic modulator of TRAIL-mediated apoptosis but also an inhibitor of TRAIL-induced NF-kappaB activation and subsequent proinflammatory target gene expression 15475369_The bility of decoy receptor 3 to promote TRAIL-triggered death may be used to potentiate TRAIL efficacy during treatment tumors overexpressing DcR3. 15498932_TRAIL effects on mitochondrial NF-kappaB-DNA binding 15509531_TRAIL can induce apoptosis in premalignant cells 15511228_IFN-gamma enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through IRF-1 15520016_The DR4-selective Apo2L/TRAIL variants examined in this study showed a markedly reduced ability to trigger apoptosis, whereas the DR5-selective variants had minimally decreased or slightly increased apoptosis-inducing activity 15531913_Rottlerin contribute to amplification of caspase cascades, thereby overcoming resistance of glioma cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. 15539085_TRAIL expression was mediated by increased transcriptional activity of the TRAIL promoter, suggesting lineage-specific regulation of TRAIL during megakaryocyte differentiation 15557763_Fas and TRAIL play an important role in the H. pylori-mediated apoptosis of gastric epithelial cells. 15558024_Amiloride enhances TRAIL-induced cytotoxicity by inhibiting phosphorylation of the PI 3-Kinase-Akt pathway-associated kinases and phosphatases. 15569667_G(1) cell cycle arrest sensitizes breast cancer cells to TRAIL at least in part by reducing levels of the anti-apoptotic protein survivin: ectopic expression of survivin partially suppresses apoptosis induced by TRAIL 15607733_These data suggest that amiloride sensitizes both tumor cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by promoting Akt dephosphorylation and caspase-8 activation via the intracellular acidification. 15615731_Bid mediates apoptotic synergy between TRAIL and DNA damage 15634757_DAP kinase is involved in TRAIL-mediated cell apoptosis and a demethylating agent may have a role in enhancing TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in some NSCLC cells by reactivation of DAP kinase 15637055_removal of N-terminal domains of Bid by caspase-8 and Mcl-1 by caspase-3 enables the maximal mitochondrial perturbation that potentiates TRAIL-induced apoptosis 15653751_Supernatants from T cell blasts, pulse-stimulated with phytohemagglutinin contained TRAIL expressed on microvesicles . 15655781_in patients infected with cagA+/vacAs1+ H. pylori strains, expression of TRAIL and TRAIL-R1 and -R2 was down-regulated; down-regulation may limit apoptosis of gastric epithelial cells & destruction of tissue and may enable H. pylori to maintain its niche 15671071_Results suggest that the intracellular TRAIL mRNA expression in PBMC is up-regulated in MCNS patients during the nephrosis phase. 15681838_TRAIL has a role in the anemia of myelodysplastic syndromes 15688023_Casein kinase II plays a critical antiapoptotic role by conferring resistance to TRAIL in colonic carcinoma. 15757891_RAS-MEK-ERK1/2 signaling pathway can sensitize cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by up-regulating DR4 and DR5 15760909_c-FLIP(L) functions primarily as an inhibitor of death receptor-mediated apoptosis through TRAIL and caspase-8 activation 15767553_Bik and Bim have roles in bortezomib sensitization of cells to killing by death receptor ligand TRAIL 15774464_apoptosis of glioma cells induced by TRAIL is protected from by protein kinase C delta 15792357_hypoxia or low glucose-augmented TRAIL cytotoxicity is mediated through the mitochondria-independent or -dependent pathway 15806163_roles for Bax and Bak in linking the TRAIL death receptor pathway to the mitochondrial apoptosis signaling cascade upon DNA damage by ionizing radiation. 15809718_TRAIL expressed on the surface of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by cytokines or cytostatic drugs might contribute to an alternative mechanism that enables tumors to evade immune surveillance by inducing apoptosis of activated human lymphocytes 15828026_data suggests a role of TRAIL as a regulator of megakaryocytopoiesis 15884050_APO2L/TRAIL plays a role in the regulation of human T cell activation. 15887227_TRAIL is aberrantly expressed in mononuclear leukocytes from patients with B chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 15916713_TRAIL-R4 but not TRAIL-R3 is the decoy receptor which appeared to influence TRAIL sensitivity in breast cancer cells 15962328_We identified the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) as a mediator of TGF-beta-induced apoptosis in hepatoma cells. 15996036_Upregulaationof TRAIL expression may be induced by virus antigen and inflammatory cytokine IFN-gamma in chronic hepatitis B. 16007425_TRAIL does not seem to influence leukocyte and platelet production but has an important relationship to erythropoiesis in healthy adults. 16026644_the effects of TRAIL on apoptosis are associated with changes in mitochondrial functions and expressions of cell cycle regulatory genes in multiple myeloma 16037944_Chemotherapy-resistant tumor cells can be sensitized for TRAIL-induced apoptosis at the death inducing signaing complex by proteasome inhibitor treatment. 16040132_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16040132_The results indicate that the presence of the CC genotype at position 1595 in exon 5 represents a higher risk of MS. 16041267_Pigs expressing biologically active human TRAIL will be used for future xenotransplantation experiments to modulate primate anti-pig cellular immune responses. 16082383_TRAIL expression from a viral vector activated the Caspase-3 enzymatic capacity, and hepatocellular carcinoma cells were sensitive to TRAIL. 16116625_Blocking the proteasome may be a way to sensitize hepatcellular carcinoma cells to TRAIL. 16166346_TRAIL promotes cell migration and invasion via a NF-kappaB-dependent pathway in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines, an observation that has a potential negative implication for TRAIL in cancer therapy. 16174727_HIV-1 induces TRAIL expression on primary CD4+ T cells. 16178278_description of TRAIL (CD253) [review] 16180223_TRAIL receptor 2 is highly expressed on human NPCs derived from fetal cortex, yet TRAIL induces only minimal levels of apoptosis in neural progenitor cells. 16199534_studies suggested that acetylsalicylic acid -promoted Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) cytotoxicity is mediated through down-regulating BCL-2 16206163_jun NH2-terminal kinase pathway is critically involved in human oligodendrocyte death induced by Tumor necrosis-related apoptosis-inducing ligand 16215673_Apo2L/TRAIL, combined with the BH3 mimetic, Bcl-xL inhibitor BH3I-2', induced apoptosis synergistically in prostate cancer cells through activation of Caspase-8 and Bid, resulting in activation of Caspase-3 and PARP cleavage. 16226105_TRAIL apoptotic pathway plays an important role in hepatic cell death during viral infection. 16229016_Nocodazole treatment inhibited TRAIL-increased NOS activity, indicating that, on cultured HUVEC, TRAIL ability to affect NO production by regulating eNOS sub-cellular distribution is mediated by cytoskeleton and Golgi complex modifications. 16245299_these data suggest that TRAIL might act as a paracrine trophic cytokine on intestinal epithelium, promoting intestinal cell differentiation 16288714_systemic upregulation of TRAIL in dilated cardiomyopathy patients and concomitant local upregulation of osteoprotegerin in the myocardium 16289694_In an immortalized human KC cell line (HaCaT cells with both p53 alleles mutated) enhanced apoptotic susceptibility to interferon exposure was also observed and the mechanism for this enhanced apoptosis involved induction of TRAIL 16368536_Apo2L/TRAIL has a role in apoptosis [review] 16382051_bortezomib (Velcade) sensitizes some human tumor cells to Apo2L/TRAIL-mediated apoptosis 16436464_This study identified primary osteoblasts as additional potential targets for myeloma cell-mediated suppression which was partly dependent on the death receptor ligand TRAIL. 16449964_Retinoic acid induction of the TRAIL pathway is also operative in leukemia cells 16455983_Results suggest that TRAIL-mediated mast cell (MC) survival in vivo and, potentially, for down-regulating MC hyperplasia in pathologic conditions 16459719_Gene expression incresed in multiple sclerosis patients treated with interferon-beta. 16478725_Mcl-1 may serve as a direct substrate for TRAIL-activated caspases implying the existence of a novel TRAIL/caspase-8/Mcl-1/Bim communication mechanism between the extrinsic and the intrinsic apoptotic pathways 16514644_complex pattern of synergistic interaction between TRAIL and cisplatin is related to the cleavage of CASP8 and FADD-like apoptosis regulating protein 16518756_significant up-regulation of TRAIL was detected in monocyte-derived macrophages infected with avian influenza viruses A/Hong Kong/483/97 (H5N1/97) or its precursor, A/Quail/Hong Kong/G1/97 16574768_Review. Neutrophils produce in a finely regulated manner TRAIL, a TNF superfamily member involved in apoptosis, tumor cell killing and autoimmunity. 16607283_Decitabine and IFN-gamma at relatively low individual concentrations cooperate to restore caspase-8 expression and sensitize resistant neuroblastoma and medulloblastoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. 16627981_The combined delivery of CYLD and TRAIL may be a new useful strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma or other tumor cells with enhanced NF-kappaB activity. 16645643_Both addition of IGFBP-3 protein to cell cultures or enforced expression of IGFBP-3 in the HT29 colon carcinoma cell line inhibited nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) activation in response to the induction of apoptosis by TRAIL. 16731632_DR5-selective TRAIL variants do not induce apoptosis in DR4-responsive cell lines but show a large increase in biological activity in DR5-responsive cancer cell lines. 16751802_TRAIL strongly induces the expression of the proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 and enhances the invasion of apoptosis-resistant pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells in vitro 16785986_is a mediator of cell death that preferentially targets cancer cells 16807984_IFN-gamma modulates the expression of TRAIL in astrocytes, which may enhance cytotoxic sensitivity of infiltrating immune cells or brain cells other than astrocytes during inflammation of brain 16820090_Apo2L/TRAIL has a role in valproic acid-induced cytotoxicity in cultured thoracic cancer cells through mitochondria-dependent caspase activation 16831934_Persistence of osteoclastogenesis can be related to the formation of the osteoprogerin/TRAIL complex. 16857810_TRAIL has a role in inducing apoptosis in human colorectal adenoma 16863850_TRAIL induces apoptotic cell death in neuroblastoma and survivin inhibits TRAIL induced apoptosis. Neuroblastoma cell sensitivity to TRAIL is governed by the ratio of TRAIL-R to survivin expression. 16887991_Preferentially provokes apoptosis of HIV-1-infected monocyte-derived macrophages, by a mechanism reliant upon the inhibition of Akt-1 phosphorylation. 16941746_upregulation of TRAIL in astroglial cells may abrogate immune cell effector functions 16950202_TRAIL down-regulation of Ste20-related proline-alanine-rich kinase is an important event that enhances its apoptotic effects 16951203_Flavopiridol sensitizes breast cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by facilitating early events in the apoptotic pathway. 17012835_photochemically mediated delivery of TRAIL allows a selective enhancement in cell killing in a colorectal cancer cell line. 17070520_In the present study, we observed strong effects of sodium arsenite treatment on upregulation of TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in human and mouse melanomas. 17079165_a recombinant form of the extracellular domain of the TRAIL (sTRAIL) was expressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) under the control of a T7 promoter. A rapid and simple on-column refolding procedure was developed. 17110373_dissociation of Bad from Bcl-xL and an increase in the intracellular level of Bcl-xL are responsible for development of acquired TRAIL resistance 17187253_Flavopiridol synergizes TRAIL cytotoxicity by downregulation of FLIP(L) and this synergistic effect is Bcl-2 family independent. 17195089_Data show that histone deacetylase inhibition leads to decreased protein kinase casein kinase 2 activity, caspase-2 activation and partial cleavage of caspase-8 that sensitizes the tumor cell to TRAIL. 17278883_These findings suggest that in tumors retaining functional p53 and expressing high levels of Hsp70, TRAIL may be an effective therapy. 17314102_MADD has a role in the control of cancer cell survival/death as a negative regulator of caspase-8 and confers significant resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis 17352408_The effect of hyperinsulinemia on TRAIL expression in diabetic and normal rats and in humans with type 2 diabetes mellitus is reported. 17356300_HIV Tat protein increases Bcl-2 expression in monocytes which inhibited apoptosis induced by TRAIL. 17384675_A mutant of p68 RNA helicase at the phosphorylation sites (Y593/595F) dramatically sensitizes TRAIL-resistant cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis, suggesting a potential therapeutic strategy to overcome TRAIL resistance. 17420249_GAL-3 mediates TRAIL signaling by regulating PTEN in human breast carcinoma cells 17431115_Apo2L/TRAIL, in combination with low-dose CPT-11 or aphidicolin, induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. Combinations with S-phase arrest-inducing drugs may represent promising avenues for its clinical development. 17431792_findings suggest that TRAIL activates apoptosis pathway dependent on Bid, but largely independent of FADD and caspase-8, in U2OS cells 17479107_Fluorocytosine together with TRAIL dramatically decreased tumor growth and eradicated a neuroblastoma tumor. 17495957_Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) cell lines revealed pronounced resistance to death ligands (TRAIL and TNF-alpha) as compared to cell lines of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). 17513605_5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside sensitizes TRAIL- and TNF{alpha}-induced cytotoxicity in colon cancer cells through AMP-activated protein kinase signaling 17525260_Data suggest that interferon-gamma sensitizes resistant Ewing's sarcoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by up-regulation of caspase-8 without altering chemosensitivity. 17540725_Nitric oxide-mediated S-nitrosylation of GAPDH and subsequent nuclear translocation of GAPDH might function as a mediator of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) induced cell death in thyroid cancer cells. 17544413_Wnt3A treatment significantly suppressed TRAIL-induced apoptosis in control hepatic stellate cells versus sFRP1 over-expressing cells. 17548900_The potentiation of TRAIL-induced cell death could be implicated in lung cancer therapy and prevention 17553352_The levels of IFN-gamma, IL-12 and TRAIL in synovium fluid from the patients with RA are higher than those in healthy donors. This result indicates that the pattern of cytokine on course of RA is main of Th1, more typical in synovium fluid than in serum. 17554866_TRAIL could induce endothelial apoptosis and cause regression of hemangiomas. 17558561_We showed that DR5, upregulated by TRAIL, could be the mediator of TRAIL-induced OC apoptosis. intracellular pathway induced by TRAIL in OCs involves caspase-8 and Bid activation. 17571163_ability of TRAIL to modify inflammatory responses and to reduce neuronal cell death in meningitis suggests that it may be used as a novel antiinflammatory agent in invasive infections 17579120_analysis of certain carotenoids that sensitize cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis 17583676_We demonstrated that TRAIL alters gene expression through mRNA splicing and may change proapoptotic potential in response to cytokine stimulation. 17617740_IFNalpha induces TRAIL expression via a STAT-1/IRF-1-dependent mechanism in human bladder cancer cells 17638906_RIP and c-FLIP-mediated assembly of the death-inducing signaling complex in nonrafts is a critical upstream event in TRAIL resistance 17683987_increased expression of TRAIL mRNA in PBMC closely correlates with SLE activity and suggest an important role for TRAIL in the pathogenesis of SLE. 17686764_TRAIL can trigger an apoptotic pathway that involves JNK-dependent activation of Bim, which in turn induces Bax-mediated permeabilization of lysosomes. 17697742_VPA significantly increased sensitivity of leukemic cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and led to downregulation of c-FLIP (L) expression. 17701086_These results establish that unlike HBx, MHBs(t) enhances TRAIL-induced hepatocyte apoptosis through a novel mechanism that involves ERK2. 17702740_Data suggest that OPG can bind both to RANKL and TRAIL and that the affinity of OPG for these two ligands is of a similar order of magnitude. 17703232_Variants of human TRAIL (hTRAIL) and human CD95L (hCD95L), encompassing the TNF homology domain (THD), interact with the corresponding receptors and stimulate CD95 and TRAILR2 signaling after cross-linking. 17765202_the homotrimerization and apoptotic activity of zinc-free TRAIL is enhanced by a more rigid local structure around the zinc-binding region 17767167_New link between death-receptor O-glycosylation and apoptotic signaling provides a potential predictive biomarkers for Apo2L/TRAIL-based cancer therapy. 17803681_data provide a novel link between hypoxia, TRAIL and BRCA1, and suggest that this relationship may be especially relevant to the potential use of TRAIL as a chemotherapeutic agent 17881904_c-Myc activates DR4 transcription through E-box DNA-response elements located in the DR4 promoter, thereby increasing the expression of cell-surface pro-apoptotic death receptors in TRAIL-resistant cell lines 17884184_However, neither sTRAIL nor chemokine levels allowed prediction of one- and two-year clinical treatment response in 30 RRMS | ENSMUSG00000039304 | Tnfsf10 | 55.615731 | 0.476773301 | -1.068625 | 0.23847074 | 20.154389 | 0.0000071436129015521771678685555850840671610058052465319633483886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000986489966732646253368826938512370361422654241323471069335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 35.1278262 | 5.2832708 | 73.8630904 | 10.1839116 | |
| ENSG00000121864 | 51193 | ZNF639 | protein_coding | Q9UID6 | FUNCTION: Binds DNA and may function as a transcriptional repressor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16182284}. | DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a member of the Kruppel-like zinc finger family of proteins. Amplification and overexpression of this gene have been observed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The encoded protein has been shown to bind DNA in a sequence-specific manner and may regulate HIV-1 gene expression. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2014]. | hsa:51193; | nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; negative regulation by host of viral transcription [GO:0043922]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; positive regulation by host of viral transcription [GO:0043923]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; viral entry into host cell [GO:0046718] | 20646234_ZASC1 copy number that increased from primary to recurrent tumor suggested the importance of ZASC1 in tumor progression. The increase of ZASC1 gene copy number in recurrent tumors was associated with the consumption of betel quid in patients. 24204263_ZASC1 as novel regulator of HIV-1 gene expression that functions through the DNA-dependent, RNA-independent recruitment of TAT/P-TEFb to the HIV-1 promoter. | ENSMUSG00000027667 | Zfp639 | 132.148728 | 2.353798593 | 1.234991 | 0.24498967 | 24.867981 | 0.0000006139370814315718657988183923346348080940515501424670219421386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000106021628334133682420746189190019492798455758020281791687011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 142.0502766 | 41.1745863 | 58.7523044 | 17.0862297 | |
| ENSG00000123689 | 50486 | G0S2 | protein_coding | P27469 | FUNCTION: Promotes apoptosis by binding to BCL2, hence preventing the formation of protective BCL2-BAX heterodimers. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19706769}. | Apoptosis;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome | Involved in extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway and positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. Located in mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:50486; | lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001238] | 16086669_A novel putative target gene of PPARalpha, G0S2 (G0/G1 switch gene 2) was identified and characterized. 18636162_G0S2 is an all-trans-retinoic acid target gene 19706769_G0S2 encodes a mitochondrial protein that specifically interacts with Bcl-2 and promotes apoptosis by preventing the formation of protective Bcl-2/Bax heterodimers 19816938_DNA methylation of G0S2 can be an important biomarker for squamous lung cancer. 19878646_mRNA expression of G0S2 was regulated mainly by DNA methylation in squamous lung cancer cell lines. 21613358_findings are compatible with the notion that the ATGL-G0S2 complex is an important long-term regulator of lipolysis under physiological conditions such as fasting in humans 22535977_Reduced mRNA and protein content of Plin and G0S2 and borderline increased ATGL protein in sc adipose tissue from poorly controlled type 2 diabetic subjects. 22716248_Gene expression profiles showed that G0/G1 switch 2 was up-regulated in epidermolysis bullosa subtypes. 22891293_Data indicate that downregulation of G0S2 in adipose tissue could represent one of the underlying causes leading to increased lipolysis in the insulin-resistant state. 23546556_This linked G0S2 subcellular localization to G0S2 transcriptional repression. The potential mechanisms responsible for this G0S2 repression are examined. 23951308_reelin expression is altered by Abeta leading to impaired reelin signaling. 24183236_A new mechanism that controls proliferation in K562 cells, suggesting a possible tumor suppressor function for G0S2 in leukemia cells. 25258314_Data indicate that the peptide corresponding to residues Lys-20 to Ala-52 from G0S2 Inhibits ATGL in the nanomolar range. 25588877_Results indicate that G0S2 acts as a prosurvival molecule in endothelial cells. 26318046_Data indicate that a tumor suppressor mechanism by which G0/G1 switch gene 2 product (G0S2) directly inhibits activity of a key intracellular adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL). 26707160_differences in G0S2 expression may explain depot-specific and obesity-associated differences in lipolysis on the molecular level 27605212_PML/RARalpha synergizes with C/EBPepsilon to reactivate the C/EBPepsilon target G0S2, thereby contributing to All-trans retinoic acid -mediated acute promyelocytic leukemia differentiation and potentially, clinical remission. 28645852_G0S2 functions as a master regulator of tissue-specific balance of TG storage vs. mobilization, partitioning of metabolic fuels between adipose and liver, and the whole-body adaptive energy response. 28910567_ER+ breast cancer cells with restored G0S2 expression had a relative increased sensitivity to tamoxifen 29209111_Palmitate can induce lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells by activating C/EBPbeta-mediated G0S2 expression. 30770352_G0S2 hypermethylation is a hallmark of rapidly recurrent or fatal ACC, amenable to targeted assessment using routine molecular diagnostics. Assessing G0S2 methylation is straightforward, feasible for clinical decision-making, and will enable the direction of efficacious adjuvant therapies for patients with aggressive ACC. 30802154_In addition to its role as a lipolytic inhibitor, G0S2 is capable of directly promoting TG synthesis by acting as a lipid-synthesizing enzyme. 31371451_We conclude that the RNF126/BAG6 complex contributes to G0S2 degradation and that interventions to prevent G0S2 degradation may offer a therapeutic strategy for managing ischemic diseases. 32171335_An epigenome-wide association study of posttraumatic stress disorder in US veterans implicates several new DNA methylation loci. 33545927_Low G0S2 gene expression levels in peripheral blood may be a genetic marker of acute myocardial infarction in patients with stable coronary atherosclerotic disease: A retrospective clinical study. | ENSMUSG00000009633 | G0s2 | 51.043652 | 0.482963455 | -1.050014 | 0.22303694 | 22.489359 | 0.0000021131098226695795349119617184685537836230651009827852249145507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000330258996642481320298728730833204281225334852933883666992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 33.6919175 | 8.4039487 | 70.0813516 | 16.8356335 | |
| ENSG00000124191 | 84969 | TOX2 | protein_coding | Q96NM4 | FUNCTION: Putative transcriptional activator involved in the hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal system. | Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation | Enables transcription coactivator activity. Involved in positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:84969; | nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 14764631_Identification and functional analysis of the rat Gcx1 ortholog. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22496870_A novel aberrantly hypermethylated CpG island in cancer was discovered within the TOX2 promoter. TOX2 was unmethylated in normal cells. Expression of two novel TOX2 transcripts was significantly reduced in primary lung tumors. 25352127_TOX2 plays a crucial role in controlling normal NK cell development by acting upstream of TBX21 transcriptional regulation 28153336_A haplotype block across a 24-kb region within the TOX2 gene reached genome-wide significance in haplotype-block-based regional heritability mapping. Single-SNP- and haplotype-based association tests demonstrated that five of nine genotyped SNPs and two haplotypes within this block were significantly associated with major depressive disorder. 35111387_CD4+ T cells in classical Hodgkin lymphoma express exhaustion associated transcription factors TOX and TOX2: Characterizing CD4+ T cells in Hodgkin lymphoma. | ENSMUSG00000074607 | Tox2 | 185.954156 | 0.481349936 | -1.054842 | 0.13747577 | 58.987846 | 0.0000000000000158648919688321917736193044898387847509678427737611627890146337449550628662109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000007022724963924832161644130446249863198009827369716617795347701758146286010742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 120.7816789 | 15.1778593 | 252.2873283 | 30.5125908 | |
| ENSG00000124225 | 56937 | PMEPA1 | protein_coding | Q969W9 | FUNCTION: Functions as a negative regulator of TGF-beta signaling and thereby probably plays a role in cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, motility, extracellular matrix production and immunosuppression. In the canonical TGF-beta pathway, ZFYVE9/SARA recruits the intracellular signal transducer and transcriptional modulators SMAD2 and SMAD3 to the TGF-beta receptor. Phosphorylated by the receptor, SMAD2 and SMAD3 then form a heteromeric complex with SMAD4 that translocates to the nucleus to regulate transcription. Through interaction with SMAD2 and SMAD3, LDLRAD4 may compete with ZFYVE9 and SMAD4 and prevent propagation of the intracellular signal (PubMed:20129061, PubMed:24627487). Also involved in down-regulation of the androgen receptor (AR), enhancing ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation of AR, probably by recruiting NEDD4 (PubMed:18703514). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18703514, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20129061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24627487}. | Alternative splicing;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal transduction inhibitor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation pathway | This gene encodes a transmembrane protein that contains a Smad interacting motif (SIM). Expression of this gene is induced by androgens and transforming growth factor beta, and the encoded protein suppresses the androgen receptor and transforming growth factor beta signaling pathways though interactions with Smad proteins. Overexpression of this gene may play a role in multiple types of cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. | hsa:56937; | early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; R-SMAD binding [GO:0070412]; WW domain binding [GO:0050699]; androgen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030521]; negative regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0060394]; negative regulation of SMAD protein complex assembly [GO:0010991]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512] | 12670906_Expression of PMEPA1 was well maintained both in colon cancer primary tumors and in colon cancer liver metastases. 12907594_PMEPA1 negatively regulates growth of androgen responsive or refractory prostate cancer cells, and these functions may be mediated through the interaction of PMEPA1 with the NEDD4 protein. 17318295_Differentially expressed genes were identified, including E-cadherin, IL-8 and STAG1/PMEPA1 in an androgen-independent prostate cancer PC3 subclone. 18174752_DNA methylation within the PMEPA1 promoter downstream sequences suggests that methylation of SP1 binding sites may also contribute to the repression of PMEPA1 gene 18703514_decreased PMEPA1 expression frequently noted in prostate cancers may lead to increased AR functions and strengthen the biological role of the NEDD4-binding protein PMEPA1 in prostate cancers 20610632_Results suggest that TMEPAI functions in breast cancer as a molecular switch that converts TGF-beta from a tumor suppressor to a tumor promoter. 23615405_The levels of TMEPAI in lung tumor tissues are very high. 24438557_TMEPAI promotes tumorigenic activities in lung cancer cells. 24694733_Downregulation of PMEPA1 may result in increased androgen receptor protein levels and function in cancer of the prostate cells, contributing to prostate tumorigenesis. 24933703_TMEPAI is translocated on the lysosome and late endosome, and that association with Nedd4 is required for the transport of TMEPAI to the lysosome. 25482449_EGF signaling collaboratively regulates TGF-beta-induced TMEPAI expression. 25883222_Data show that silencing of PMEPA1 protein facilitates the growth of prostate cancer cells and modulates androgen receptor (AR) through NEDD4 ubiquitin protein ligase and PTEN protein. 26215835_binding of SMAD2/3, the intracellular effectors of activin signaling, was significantly enriched at the Pmepa1 gene, which encodes a negative feedback regulator of TGF-beta signaling in cancer cells, and at the Kdm6b gene, which encodes an epigenetic regulator promoting transcriptional plasticity. 26590303_these data elaborated on the diverse activity among TCF/LEF family members with respect to the transcriptional regulation of the TMEPAI gene. 26758191_PMEPA1 was upregulated in breast cancer cell lines as well as in a set of clinical invasive breast ductal carcinomas. Interestingly, depletion of PMEPA1 decreased breast cancer stem cell (CSC)-enriched populations, while ectopic overexpression of PMEPA1 increased breast CSC-enriched populations. 26927372_Data show that over-expressed transmembrane prostate androgen-induced protein 1 (PMEPA1) can promote cell migration and maintain the mesenchymal-like morphology of breast cancer cells. 27035427_the present study suggest that the upregulation of miR19a3p expression levels contributes to tumor progression and that one of its underlying mechanisms involves inhibition of PMEPA1 expression. 27163528_study showed that the inhibition of autophagy induced by the depletion of TMEPAI is involved in regulation of Beclin-1. 27625141_Sp1 up-regulated TMEPAI protein expression, as well as Sp1 promoting TMEPAI-induced cell proliferation. 27697531_these findings indicated that PMEPA1 participates in TGF-beta- and hypoxia-regulated gene expression networks in solid tumors and thereby may contribute to tumor progression. 29467225_This study highlights that TMEPAI decreases c-Maf stability by recruiting the ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 to c-Maf for proteasomal degradation in myeloma cells. 29945215_describe recent progresses in the understanding of how the TMEPAI family physiologically contributes to cellular functions and diseases 30069967_JHY-A007-50 mediates the downregulation of TMEPAI expression. 30873542_observed that knockout (KO) of PMEPA1 in human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 using a CRISPR-Cas9 system resulted in reduction of in vivo tumour growth and lung metastasis but not of in vitro monolayer growth capacity of these KO cell lines 30887697_Prostate transmembrane protein androgen induced 1 (PMEPA1) promotes colorectal cancer metastasis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in vivo and in vitro. 30890370_These data suggest that TMEPAI suppresses Wnt signaling by interfering with beta-catenin stability and nuclear translocation in a TGF-beta signaling-independent manner. 31605013_PMEPA1 isoform a drives progression of glioblastoma by promoting protein degradation of the Hippo pathway kinase LATS1. 32181976_PMEPA1/TMEPAI isoforms function via its PY and Smad-interaction motifs for tumorigenic activities of breast cancer cells. 32842649_PMEPA1 Gene Isoforms: A Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Prostate Cancer. 33831430_Diagnostic and therapeutic values of PMEPA1 and its correlation with tumor immunity in pan-cancer. 33857498_PMEPA1 Stimulates the Proliferation, Colony Formation of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via the MAPK Signaling Pathway. 33896822_PMEPA1 facilitates non-small cell lung cancer progression via activating the JNK signaling pathway. 34254950_Linc00941 regulates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via functioning as a competing endogenous RNA for miR-877-3p to modulate PMEPA1 expression. 34777336_PMEPA1 Is a Prognostic Biomarker That Correlates With Cell Malignancy and the Tumor Microenvironment in Bladder Cancer. 35497877_PMEPA1 Serves as a Prognostic Biomarker and Correlates with Immune Infiltrates in Cervical Cancer. | ENSMUSG00000038400 | Pmepa1 | 43.953684 | 0.319870557 | -1.644440 | 0.61084193 | 6.696583 | 0.0096597856289274228874797145749653282109647989273071289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0481715085124551772866041687848337460309267044067382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 21.0396945 | 10.3695543 | 66.8974364 | 32.3381439 | |
| ENSG00000124731 | 54210 | TREM1 | protein_coding | Q9NP99 | FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Cell surface receptor that plays important roles in innate and adaptive immunity by amplifying inflammatory responses (PubMed:10799849, PubMed:21393102). Upon activation by various ligands such as PGLYRP1, HMGB1 or HSP70, multimerizes and forms a complex with transmembrane adapter TYROBP/DAP12 (PubMed:25595774, PubMed:17568691, PubMed:29568119). In turn, initiates a SYK-mediated cascade of tyrosine phosphorylation, activating multiple downstream mediators such as BTK, MAPK1, MAPK3 or phospholipase C-gamma (PubMed:21659545, PubMed:14656437). This cascade promotes the neutrophil- and macrophage-mediated release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and/or chemokines, as well as their migration and thereby amplifies inflammatory responses that are triggered by bacterial and fungal infections (PubMed:17568691, PubMed:17098818). By also promoting the amplification of inflammatory signals that are initially triggered by Toll-like receptor (TLR) and NOD-like receptor engagement, plays a major role in the pathophysiology of acute and chronic inflammatory diseases of different etiologies including septic shock and atherosclerosis (PubMed:21393102, PubMed:11323674). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10799849, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11323674, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14656437, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17098818, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17568691, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21393102, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21659545, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25595774, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29568119}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Acts as a decoy receptor, counterbalancing TREM1 pro-inflammatory activity through the neutralization of its lignad. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26561551}. | 3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Innate immunity;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a receptor belonging to the Ig superfamily that is expressed on myeloid cells. This protein amplifies neutrophil and monocyte-mediated inflammatory responses triggered by bacterial and fungal infections by stimulating release of pro-inflammatory chemokines and cytokines, as well as increased surface expression of cell activation markers. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Jun 2011]. | hsa:54210; | extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; acute inflammatory response [GO:0002526]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; neutrophil-mediated killing of gram-negative bacterium [GO:0070945] | 12645956_The human TREM gene cluster at 6p21.1 encodes both activating and inhibitory single IgV domain receptors and includes TREM1. 12646648_Activation of TREM-1 on monocytes participates during the early-induced and adaptive immune responses involved in host defense against microbial challenges. 14656437_Crystal structure of the human myeloid cell activating receptor TREM-1 15067076_A new regulatory role is described for TREM-1-mediated signals in the resolution of acute inflammation and the control of neutrophil activity. 15309732_TREM-1 may play an important role in the occurrence and development of acute pancreatitis 15351648_monomeric state of this extracellular ectodomain in solution and, presumably, of the TREM family in general 15585833_TREM-1 is upregulated on monocytes during human endotoxemia together with an increase in soluble TREM-1. 16437719_TREM-1 may play an important role in establishing and amplifying the systemic inflammatory response 16733861_Soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 (sTREM-1) seems to behave as a novel mediator in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in correlation with the degree of the inflammatory reaction of the intestinal mucosa. 17008237_Monocytes contribute to the production of sTREM-1 in the event of septic syndrome. 17202378_Regulation of TREM-1 and the soluble form of TREM-1 expression by prostaglandin E2 may modulate the inflammatory response to microbial pathogens 17277102_NTAL acts as a negative regulator of TNF-alpha and IL-8 production after stimulation via TREM-1 17336301_the effects of aging on TREM-1 engagement in human PMN; respiratory burst, PMN survival, recruitment of TREM-1 in the lipid-rafts, phosphorylation 17505044_sTREM-1 is detectable in exhaled ventilator condensate and may be useful in establishing or excluding the diagnosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia. 17558349_Results show that sTREM-1 and procalcitonin are not specific for infection and can increase markedly in acute inflammation without infection. 17634956_We examined the transcriptional regulation of TREM-1 in macrophages. NF-kappaB and PU.1 are involved in the expression of TREM-1 17659879_prognostic value of serum sTREM-1 levels in patients hospitalized with community acquired pneumonia 17729416_Soluble TREM-1 secreted by the gastric mucosa is an independent mechanism connected to the pathogenesis of peptic ulcer. 17785845_Conclusive evidence favors proteolytic cleavage over alternative splicing as the mechanism responsible for the release of soluble TREM-1 from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated monocytes. 18008257_During melioidosis, TREM-1 expression is differentially regulated on granulocytes and monocytes; measurement of TREM-1 expression on blood granulocytes may not provide adequate information on granulocyte TREM-1 expression at the infection site. 18317529_serum concentrations of sTREM-1 are increased in patients with COPD. Prospective studies are warranted to evaluate the relevance of sTREM-1 as a potential marker of the disease in patients with COPD. 18396215_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18396215_The present findings suggest that the three studied polymorphisms within the TREM-1 gene may not play a major role in the predisposition to severe sepsis in a Chinese Han cohort 18628981_down-regulation of TREM-1 expression in cystic fibrosis patients is at least partly responsible for the endotoxin tolerance state in which their monocytes are locked 18634145_sTREM-1 seems to be a new mediator involved in patients with AS, particularly in the early stages of disease. 18656898_Increased TREM-1 expression on monocytes is associated with both infectious and noninfectious inflammatory processes. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19109693_Results suggest that TREM-1 and sTREM-1 contribute to the development of shock in patients suffering from sepsis. 19230638_upregulation of expression on lamina propria macrophages in patients with inflammatory bowel disease; plasma levels is a prognostic factor for sepsis 19251433_sTREM-1 may not have a role in infection in patients with secondary peritonitis 19396532_TREM-1 protein expression levels were up-regulated in sepsis patients with acute cholangitis 19479878_TREM-1 ligation contributes to the pathology of autoimmune arthritis. 19484952_Serum sTREM-1 correlates closely with injury severity score, TNF-alpha and onset of sepsis. 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19591072_propose that triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1(sTREM-1) play a role in the innate immune response against intra-amniotic infection 19596984_TREM-1 was up-regulation in infected lungs and human plasma together with augmented alveolar macrophage responsiveness toward Streptococcus pneumoniae 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19917159_Serum sTREM-1 (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 ) levels were significantly higher in the infection group than in the flare group of febrile systemic lupus erythematosus patients 19923060_The expression of human TREM-1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells is up-regulated in the early stage of acute obstructive suppurative cholangitis. 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20156945_Serum sTREM-1 levels were elevated in diffuse systemic sclerosis patients and correlated with severity of pulmonary fibrosis, suggesting that serum sTREM-1 is a novel serological marker for the disease severity of systemic sclerosis. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20375613_we provide new insights into the mechanisms how TREM-1 and TLR interact creating synergistic activation in polymorphonuclear neutrophils 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20640189_Trem1 expression is increased in the inner zone of amyloid plaques using a transgenic animal model of Alzheimer's disease. 21148811_TREM-1 is expressed on mature dendritic cells infiltrating the inflamed hypoxic joints of children affected by juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 21306476_sTREM-1 concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid fluid are of potential prognostic value in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia. 21393102_These data are in line with the TLR4-TREM1 co-localization in human neutrophils. 21421043_TREM-1 gene expression was increased in the monocytes of schizophrenic and bipolar patients & tended to be increased in the monocytes of major depressive disorder patients. 21555403_this study provides the fi rst evidence that TREM-1 functions as an in fl ammatory ampli fi er in P. aeruginosa keratitis by modulating TLR signaling and Th1/Th2 responses. 21701149_study shows an increase in sTREM-1 in patients with COPD compared to smokers but not in acute exacerbation-COPD compared to stable COPD. Viral exacerbations showed significantly lower sTREM-1 levels than non-viral exacerbations. 21763322_TREM-1 SNPs may play a significant role in the development of intestinal Behcet's disease and may have modest effects on disease severity. 21855288_Although serum levels of sTREM-1 are increased early upon advent of severe sepsis/shock, gene expression of TREM-1 on monocytes in severe sepsis/shock is not increased. 21910175_High sTREM-1 is associated with intestinal Behcet's disease. 21942576_Data show that kinetics of sTREM-1 differs among patients undergoing hemiarthroplasty of the hip and those undergoing total hip arthroplasty. 21967868_the putative periodontal pathogen P. gingivalis can positively regulate the expression of the TREM-1/DAP12 pathway in monocytic cells. 21976106_Data demonstrate that sTREM-1 is elevated in high-risk patients with febrile neutropenia and is potentially useful to predict their clinical course, either together with, or as an alternative to procalcitonin. 22179409_Serum and amniotic fluid sTREM-1 levels may emerge as early biological indicators for predicting PROM complicated with subclinical chorioamnionitis. 22417086_levels of sTREM-1 were significantly higher in patients with epatocellular carcinoma (HCC) than those with benign liver tumors; peritumoral density of TREM-1 was shown to be an independent prognosis predictor; observations suggest that TREM-1 is related to the aggressive tumor behavior and has potential value as a prognostic factor for HCC 22422501_Patients with rheumatoid arthritis had higher plasma sTREM-1 levels than controls, and plasma sTREM-1 levels were correlated with disease activity, suggesting that plasma sTREM-1 could play a role in the inflammatory process associated with TNF-alpha. 22459945_the sustained TREM-1 expression at the cell surface suffices to block the progress of a refractory state in human monocytes 22642593_Our finding that TREM-1 controls the production of interleukin-8 and TNF-alpha in U937 foam cells defines a potentially critical role of TREM-1 in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis 22721842_In ulcerative colitis, sTREM-1 level was correlated most closely with the endoscopic disease activity among serum biomarkers, but was not superior to the clinical activity index. 22798017_dynamic change in serum sTREM- 1 may be a more accurate parameter for the assessment of sepsis prognosis; there is no association between variations rs2234246 and rs2234237 in the TREM-1 gene and susceptibility to sepsis; TREM-1 rs2234237 polymorphism is associated with increased 28-day mortality in sepsis 22829716_Elevated plasma levels of sTREM-1 reflect the severity, state of exacerbation, presence of respiratory tract obstruction in allergic asthma bronchiale patients. 22996209_Gene expression in 23 patients (12 with pneumonia and 11 w/sepsis) were analyzed using quantitative real time pcr. The mRNA levels of TLR2 (20/23 cases) and CD14 (18/23 cases) were upregulated in the PMNs of patients when compared with healthy subjects. 23046618_Patients with sepsis had increased soluble TREM-1 and decreased TREM-1 expression on neutrophils compared to systemic inflammatory response syndrome patients. 23364598_Activation of TREM-1 protected monocytic cells from apoptosis through activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homologue pathways and MCL1 23414215_Patients with E. coli sepsis are characterized by an association of Trem-1 expression on blood neutrophils with cytokine inducibility. 23436478_TREM-1 induction by the hypoxic microenvironment represents a mechanism of regulation of Th1-cell trafficking and activation by iDCs differentiated at pathologic sites. 23468854_sTREM-1 concentrations in maternal serum were elevated during spontaneous term and preterm labor and sTREM-1 levels were significantly higher in preterm labor. 23571837_Data indicate a positive correlation between serum levels of soluble TREM-1 (sTREM-1) and disease severity in infected patients as well as in experimentally infected mice. 23734253_Studies indicate that bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) sTREM-1 is a useful biomarker of bacterial lung infections in in intensive care unit (ICU) patients. 23861562_Serum sTREM-1 may have a role in myocardial dysfunction in patients with severe sepsis 23880194_We found an increased oxidative stress as well as an increased expression of TREM-1 and serum levels of sTREM-1 in patients with critical limb ischemia. 24012914_Studied sTREM-1, procalcitonin and C-reactive protein in postmortem serum in a series of sepsis-related fatalities and control individuals who underwent medico-legal investigations. 24012964_upregulated by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in human monocytes/macrophages 24026310_Knockdown of TREM-1 by RNA interference inhibits cell differention but has no effect on cell-cell fusion. 24261769_The serum level of sTREM-1 may be a useful marker of disease activity in relapsing polychondritis. 24281714_signaling contributes to the regulation of innate inflammatory responses 24289157_Soluble TREM-1 levels in serum were useful for the diagnosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia after cardiac surgery. 24290866_Elevated sTREM-1 could be considered an early marker for neonatal sepsis that reflects sepsis severity and poor prognosis. 24447863_gene expression is modulated in the process of dengue infection 24465168_The gene expression levels of TREM1 in PMNs isolated from patients with bacterial infections may be used as a surrogate biomarker for determining the severity. 24605677_Level of sTREM-1 in blood sera of patients with severe thermic injury could be proposed as an additional laboratory marker of burn wound mixed microbial infection. 24661408_Soluble TREM-1 is an accurate marker of Lower respiratory tract infections. The overall diagnostic value of sTREM-1 for community acquired and hospital-acquired Lower respiratory tract infections is similar. 24672147_sTREM-1 and procalcitonin have roles in sepsis and may predict sepsis mortality 24702227_elevated in cholesteatoma 24842612_TREM-1 is induced in tumor associated macrophages by cyclo-oxygenase pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer 24924298_Biofilm-challenged MM6 cells exhibited higher TREM-1 expression. 24954324_Unlike CRP levels and ESR, serum sTREM-1 levels were not correlated with endoscopic activity in patients with intestinal Behcet's disease. 25128583_Data indicate that single nucleotide polymorphisms of Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells-1 (TREM-1) were significantly associated with elevated risk of coronary artery disease (CAD). 25213166_study found no association between the other investigated SNPs within TREM-1 gene and infective endocarditis risk 25242387_plays critical roles in fungal infection of corneal epithelial cells 25294884_Soluble TREM-1, a member of the immunoglobulin super-family, is upregulated when neutrophils are exposed to bacteria. 25319790_Soluble TREM-1 can serve as a biomarker for diagnosing sepsis and assessing disease severity. 25448705_25(OH)2D3-induced expression of TREM-1 was inhibited by rapamycin, a specific inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway, indicating the involvement of mTOR. 25461656_In neonates with late-onset neonatal sepsis, soluble TREM-1 has the potential to provide an excellent predictive value for septic shock/death. 25465376_High TREM-1 expression correlated significantly with increased recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. 25532536_A reciprocal decrease of the pro-inflammatory surface receptor TREM-1 linked with sepsis-induced immunosuppression may be part of the explanation 25545807_Variants within the TREM locus are associated with pathological features of AD and aging-related cognitive decline. 25595774_The role for PGLYRP1 as a TREM-1 activator provides a new mechanism by which bacteria can trigger myeloid cells, linking two known, but previously unrelated, pathways in innate immunity. 25642940_isolated PMNs have an increased proportion of both TREM1 and DAP12 compared to normal healthy control 25840803_Data indicate that plasma concentration of soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 (sTREM-1) predicts death at 2 years after myocardial infarction. 25944130_Plasma and urine TREM-1 levels can be used as diagnostic biomarkers for acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with sepsis. 26184544_Report altered TREM-1/TREM-2 ratio in cutaneous melanoma. 26281323_TREM-1 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily released from phagocytic cells in the presence of bacterial and fungal infections. 26320130_TREM-1 is induced by MSU and is associated with the inflammation of human acute gouty arthritis. 26384438_study to determine soluble TREM-1 and TREM-2 levels in serum, and membrane-bound TREM-1 and TREM-2 on peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with pulmonary TB 26397033_LPS-induced TREM-1 transcription. 26495896_Soluble TREM-1 level is significantly increased in hemodialysis patients as are other pro-inflammatory markers. 26506490_This study shows increased expression of TREM-1 in monocytes from patients with advanced cervical cancer. 26852644_TREM-1 expression is decreased during the generation of human osteoclast precursors 26877157_study found that soluble TREM-1 is increased and correlates with the clinical and laboratory findings in Crimean Congo Haemorrhagic Fever, a viral infection characterized by activation of inflammation. 26963514_TREM-1 and Dectin-1 function concurrently in the corneal innate immune response by regulating inflammatory cytokine expression in fungal keratitis. 27017522_Increased expression of TREM-1 in S compared to AS patients involving TNFa, MMP-1 and MMP-9 suggest a potential role of TREM-1 in plaque destabilization 27096761_The study simultaneously evaluated both PCT and soluble TREM-1 along with CRP in febrile patients with autoimmune diseases. 27238916_sTREM1 was increased in septic patients with myocardial depression compared to those without myocardial depression. 27244892_low expression level of TREM-1 might be a characteristic for tumor-associated macrophages in lung cancer 27319606_Plasma levels of sTREM-1 were found to identify patients with septic shock more effectively than procalcitonin and C-reactive protein. Moreover, sTREM-1 was identified to be an early predictor for survival in patients with septic shock. 27324541_TREM-1 activation may be involved in the development of Kawasaki disease. 27409178_TREM-1 may have a role in pathology of craniopharyngioma and Rathke's cleft cyst 27448788_The results demonstrate that both commensal and pathogenic oral bacteria activate the TREM-1 pathway, resulting in a proinflammatory TREM-1 activity-dependent increase in proinflammatory cytokine production. 27521929_In the premature rupture of membranes group,the NF-kappaB p65 and sTREM-1 levels in maternal blood were significantly higher in women with chorioamnionitis than women without chorioamnionitis (P<.05 findings suggest that there are no differences in soluble trem-1 levels gingival crevicular fluid between healthy and periodontally diseased elderly adults serum level significantly associated with the presence severity of coronary artery disease restrains inflammatory reaction endothelial cells study shows higher plasma systemic lupus erythematosus egyptian patients provided evidence rs6910730g an intronic variant trem1 reduced ability human monocytes for abeta phagocytosis this reduction was likely attributed to a decreased monocytic expression. rs2234237t allele appears be risk factor development severe malaria. may play important role cascade after subarachnoid hemorrhage act as monitoring biomarker core temperature saps ii value were only independent predictors death adjustment potential confounders sepsis admitted intensive care. provides new insights into possible mechanism hif-1alpha psoriasis. links dyslipidemia inflammation lipid deposition atherosclerosis. hmgb1 rage shoulder tendon: dual mechanisms based on coincidence glenohumeral arthritis indicates children community-acquired pneumonia strem-1 midregional-proanp midregional-proadm blood have poor abilities differentiate bacterial from viral diseases or identify cases. seem newly diagnosed type diabetes than their siblings statistically significant concluded both released during response periodontal tissues they can promote process which leads tissue destruction. interventions by means lp17 lr12 fusion protein did not ameliorate ir-induced injury. renal transplant cohort donor recipient gene p.thr25ser dgf nor biopsy-proven rejection death-censored graft failure. we conclude does major experimental ir kidney transplantation plays critical osteoarthritis il1b induced chondrocyte injury through regulation nf-kappab signaling novel modulatory pathogenesis sle. production is useful diagnostic marker molecular target combination therapy lupus. found biopsies subjects obesity. greater expression activity underlying pathophysiology obesity comorbidities. data show macrophages infected immunodeficiency virus-1 increased trem-1. parallel direct exposure virus-1-related proteins tat gp120 induces confers anti-apoptotic attributes. showed detectable samples urinary tract infection non-uti groups detected uti but tend neutrophils cytokine bacteria minor t rs2234246 term1 discovery population explaining its variance mrna. bronchoalveolar lavage triggering receptor expressed myeloid cells-1 do discriminate mild-to-moderate asthma chronic obstructive pulmonary contrast interleukin ratio measured balf effectively differentiated these two diseases. mediating platelet activation. il-8 pct crp febrile neutropenia autologous stem cell predictive in-stent restenosis mediator cellular migration proliferation vascular smooth muscle murine colorectal tumors. review summarizes studies association trem-2 malignant tumors medical field provide ideas correlation periodontitis oral cavity cancer strem1 cytokines gcf decrease introduction treatment underlines importance periodontitis. present highlights urine late-onset sepsis. diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome positively correlates abdominal pain initiated trem-1-associated macrophage activation indicating existence subclinical d-ibs. tlr4 surface observed maternal cord monocyte confirming proinflammatory profiles preterm birth chorioamnionitis. might infection-related birth. become prediction neonatal however variation used threshold values ranged pg methodological across limit our clinical practice. circulating independently predict all-cause mortality adverse cardiac events acute myocardial infarction. neutrophilic pathway suppressed eosinophilic rhinosinusitis nasal polyps showing mrna dna hypomethylation ad methylation rates promoter. support liver hepatic fibrogenesis master regulator kupffer escalates responses activates stellate reveals promotion fibrosis. pro-inflammatory via regulating nf-small ka cyrillicb nuclear translocation mycoplasma pneumoniae-infected a549 lung epithelial cells. expressions behcet those group difference reach statistical significance. has been realized tnf-alpha macrophages. inhibit transition m1 phenotype stat-1 pathway. elevated thrombotic primary anti-phospholipid syndrome. concentrations correlated total tau alzheimer patients. subsequent subgroup analysis indicated more pronounced dementia. identified low specific anti-tnf endoscopic remission. results aid selection biologic-naive tumor-associated hepatocellular carcinoma advanced stages slamf7 up-regulation occur metastatic stage iv tissues. hiv hcv-mediated due enhanced erk1 indicate rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts upregulating suggesting therapy. modulation axis peri-implant familial mediterranean fever case amyloidosis demonstrated positive state progress diabetic nephropathy played high-glucose- transformation. here discussed trems especially bridging processes intestinal neurodegenerative disorders. biomarkers: pentraxin-3 pro-adrenomedullin early diagnosis onset impairs thrombin generation. influencing brain amyloid mild cognitive impairment disease. suggested could accelerate monosodium urate inflammation. inhibition strategy alleviating gouty receptors salmonella typhi cirp endogenous ligand fuel key driving enterovirus a71 infection. presepsin prognostic markers related aa-amyloidosis. non-bacterial infections. overweight patients: cells-1. other biomarkers cholangitis. cd14 sarcoidosis hypersensitivity pneumonitis context immune response. score il-6 sirs children. help survival high-grade glioma post-stroke depressive symptoms peripheral glial cell-derived neurotrophic proadrenomedullin andtriggering pyelonephritis. exacerbates neuroinflammatory nlrp3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis hemorrhage. signalling promotes trem-1-mediated prostate line invasion. integrating immune-related signature improve prognosis carcinoma. trem2 liver-related upregulated participated progression nf-kb promoted apoptosis inhibited autophagy lps-treated hk-2 effect idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. regulates antifungal invasive aspergillosis. arthritis. inhibits invasion polarization. organ injuries cardiogenic shock: cardshock study. outcome. maxillary sinusitis. outcomes covid-19. relationship course covid-19 pneumonia. genetic determinants cardiovascular prospective infarction fast-mi amplifies trophoblastic activating preeclampsia. modulate subtype microglia formation neutrophil extracellular traps interaction syk mediate immunogenic cells: focus microsatellite stability. fosters immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment papillary thyroid cancer.> | ENSMUSG00000042265 | Trem1 | 84.097522 | 0.492550510 | -1.021656 | 0.20605272 | 24.531494 | 0.0000007310511016645525582210063571253488845513857086189091205596923828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000124101247695191265320389245596643945646064821630716323852539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 66.2827335 | 15.3231631 | 135.2913918 | 30.5054330 | |
| ENSG00000124782 | 6239 | RREB1 | protein_coding | Q92766 | FUNCTION: Transcription factor that binds specifically to the RAS-responsive elements (RRE) of gene promoters (PubMed:9305772, PubMed:15067362, PubMed:8816445, PubMed:10390538, PubMed:17550981). Represses the angiotensinogen gene (PubMed:15067362). Negatively regulates the transcriptional activity of AR (PubMed:17550981). Potentiates the transcriptional activity of NEUROD1 (PubMed:12482979). Promotes brown adipocyte differentiation (By similarity). May be involved in Ras/Raf-mediated cell differentiation by enhancing calcitonin expression (PubMed:8816445). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3UH06, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10390538, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12482979, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15067362, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17550981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8816445, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9305772}. | Activator;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | The protein encoded by this gene is a zinc finger transcription factor that binds to RAS-responsive elements (RREs) of gene promoters. It has been shown that the calcitonin gene promoter contains an RRE and that the encoded protein binds there and increases expression of calcitonin, which may be involved in Ras/Raf-mediated cell differentiation. Multiple transcript variants encoding several different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2009]. | hsa:6239; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation [GO:0090336]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010634]; positive regulation of lamellipodium morphogenesis [GO:2000394]; positive regulation of mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0033601]; positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900026]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells [GO:1903691]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] | 12700664_The p16 promoter can be downregulated by transfected human RREB, in a Ras- or Mek-dependent manner, and that the BALB/c promoter is more sensitive than DBA/2 to regulation by RREB, a ras-responsive transcriptional element with zinc-finger binding motifs. 15067362_Finb functions as a sequence-specific transcriptional repressor of the hANG gene 18394891_essential to reduce cell-cell adhesion when epithelial cells within an interconnected group undergo dynamic changes in cell shape 19558368_Findings provide evidence that RREB-1 participates in modulating p53 transcription in response to DNA damage. 19802870_Ras pathway and activation of RREB-1 are involved in hZIP1 down-regulation and may play a role in the decrease of the transporter expression in prostate cancer. 19890057_This demonstration is the first of a repressor factor of HLA-G transcriptional activity taking part in HLA-G repression by epigenetic mechanisms. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20884846_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21159816_KRAS and RREB1 are targets of miR-143/miR-145, revealing a feed-forward mechanism that potentiates Ras signaling 21360563_RREB-1 overexpression results in down-regulation of hZIP1 and contributes to the loss of hZIP1 expression and zinc in prostate cancer. 21613827_Data show that the combination of concurrent zinc, ZIP3, and RREB-1 changes represent early events in the development of adenocarcinoma. 21703425_RREB1 transcription factor splice variants are associated with urologic cancer. 21792086_Data indicate the upregulation of RREB1, PDE6B, and CD209 suggests that these proteins might play important roles in the differentiation of primitive gut tube cells from embryonic stem cells (hESCs) and in primitive gut tube development into pancreas. 22427155_These results support a concept that downregulation of RREB-1 causes downregulation of ZIP3, which results in decreased zinc in pancreatic premalignant and carcinoma cells 22751122_RREB1 is overexpressed in colorectal adenocarcinoma tumors. RREB1 repressed miR-143/145 modulates KRAS signaling. 24348900_Data show the transcriptional activation of the cholecystokinin gene by DJ-1 through interaction of DJ-1 with RREB1 and the effect of DJ-1 on the cholecystokinin level. 24418439_Thus HNT and c are functional homologs at the level of DNA binding, transcriptional regulation and developmental control 25027322_RREB1 is a novel candidate gene for type 2 diabetes associated end-stage kidney disease. 25050557_The pathway of RREB1/ZIP3/Zinc and its downregulation during oncogenesis exist to prevent the accumulation of cytotoxic levels of zinc during the development and progression of the malignant cells in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. 26608785_Histone modifier genes (JMJD1C, RREB1, MINA, KDM7A) alter conotruncal heart phenotypes in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. 27185405_RREB1 and CCND1 gains are common in nail apparatus melanoma 28341660_RREB1 cooperates with noncoding RNA linc-ADAMTS5 to inhibit ADAMTS5 expression, thereby affecting degeneration of the extracellular matrix (ECM) of the intervertebral disc. 29099273_Of the 465,447 CpG sites analyzed, 12 showed differential methylation (false discovery rate | ENSMUSG00000039087 | Rreb1 | 465.791323 | 0.187160521 | -2.417652 | 0.79897036 | 8.012058 | 0.0046466900565775137027513252974131319206207990646362304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0270149212433110005870950942608033074066042900085449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 167.2717426 | 82.1436170 | 909.2463364 | 446.5183584 | |
| ENSG00000125730 | 718 | C3 | protein_coding | P01024 | FUNCTION: C3 plays a central role in the activation of the complement system. Its processing by C3 convertase is the central reaction in both classical and alternative complement pathways. After activation C3b can bind covalently, via its reactive thioester, to cell surface carbohydrates or immune aggregates.; FUNCTION: Derived from proteolytic degradation of complement C3, C3a anaphylatoxin is a mediator of local inflammatory process. In chronic inflammation, acts as a chemoattractant for neutrophils (By similarity). It induces the contraction of smooth muscle, increases vascular permeability and causes histamine release from mast cells and basophilic leukocytes. {ECO:0000250}.; FUNCTION: [C3-beta-c]: Acts as a chemoattractant for neutrophils in chronic inflammation. {ECO:0000250}.; FUNCTION: [Acylation stimulating protein]: Adipogenic hormone that stimulates triglyceride (TG) synthesis and glucose transport in adipocytes, regulating fat storage and playing a role in postprandial TG clearance. Appears to stimulate TG synthesis via activation of the PLC, MAPK and AKT signaling pathways. Ligand for C5AR2. Promotes the phosphorylation, ARRB2-mediated internalization and recycling of C5AR2 (PubMed:8376604, PubMed:2909530, PubMed:9059512, PubMed:10432298, PubMed:15833747, PubMed:16333141, PubMed:19615750). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10432298, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15833747, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16333141, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19615750, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2909530, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8376604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9059512}. | 3D-structure;Age-related macular degeneration;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Complement alternate pathway;Complement pathway;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Fatty acid metabolism;Glycoprotein;Hemolytic uremic syndrome;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Lipid metabolism;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Thioester bond | Complement component C3 plays a central role in the activation of complement system. Its activation is required for both classical and alternative complement activation pathways. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate alpha and beta subunits that form the mature protein, which is then further processed to generate numerous peptide products. The C3a peptide, also known as the C3a anaphylatoxin, modulates inflammation and possesses antimicrobial activity. Mutations in this gene are associated with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome and age-related macular degeneration in human patients. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. | hsa:718; | azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; serine-type endopeptidase complex [GO:1905370]; C5L2 anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor binding [GO:0031715]; endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004866]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; amyloid-beta clearance [GO:0097242]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway involved in cell-cell signaling [GO:1905114]; complement activation [GO:0006956]; complement activation, alternative pathway [GO:0006957]; complement activation, classical pathway [GO:0006958]; complement-dependent cytotoxicity [GO:0097278]; complement-mediated synapse pruning [GO:0150062]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; neuron remodeling [GO:0016322]; opsonization [GO:0008228]; oviduct epithelium development [GO:0035846]; positive regulation of activation of membrane attack complex [GO:0001970]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of apoptotic cell clearance [GO:2000427]; positive regulation of apoptotic process in another organism [GO:0044533]; positive regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045745]; positive regulation of glucose transmembrane transport [GO:0010828]; positive regulation of immune response [GO:0050778]; positive regulation of lipid storage [GO:0010884]; positive regulation of opsonization [GO:1903028]; positive regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050766]; positive regulation of phagocytosis, engulfment [GO:0060100]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0048260]; positive regulation of type IIa hypersensitivity [GO:0001798]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010575]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of complement activation [GO:0030449]; regulation of complement activation, alternative pathway [GO:0030451]; regulation of triglyceride biosynthetic process [GO:0010866]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; vertebrate eye-specific patterning [GO:0150064] | 11785295_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11803045_Allelic distribution of complement components BF, C4A, C4B, and C3 in Psoriasis vulgaris. 11854358_complement interaction with trypanosomatid promastigotes in normal human serum 11979403_genes of C3, hormone-sensitive lipase, and PPARgamma may exert a modifying effect on lipid and glucose metabolism in familial combined hyperlipidemia 12006395_The postprandial plasma C3 response is impaired in familial combined hyperlipidemia patients, probably as a result of a delayed response by C3 (the precursor for the biologically active acylation-stimulating protein) acting on free fatty acid metabolism. 12511407_results indicate that normal human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells express functional C3aR and that the C3aR-C3a axis sensitizes the responses of these cells to SDF-1 12679444_changes in acylation-stimulating protein and adiponectin are predictive of decreased apolipoprotein B and improved insulin action after gastric bypass surgery 12761187_The physiological interaction between glycyrrhizin (GL) and serum C3, and the inhibitory effects of GL, & glycyrrhetinic acid on the phosphorylation of C3 by casein kinase 2 12816955_C3bi binds to integrin alpha M beta 2 12893820_C4b and C3b do not undergo the same conformational changes upon binding to the C4BP mutants as during the interaction with the wild type C4BP, which then results in an observed loss of the cofactor activity 12942785_The analysis involved the data on nine polymorphic codominant loci: HP, GC, TF, PI, PGM1, GLO1, C3, ACP1, and ESD. The loci were selected by significance of differences in genotype frequencies between tuberculosis patients and healthy controls 12967641_IL-1alpha, IFN-gamma, and the combination of IL-1beta with IL-6 or IFN-gamma specifically enhanced C3 secretion by HepG2 cells 14527961_upon physiological inactivation, C3b2-IgG complexes retain dimeric inactivated C3b and C3dg, which allows bivalent binding to the corresponding complement receptors 14563826_ASP significantly predicted postprandial plasma triglyceride and NEFA clearance and, based on lower ASP, women may be more ASP sensitive than men 14639503_A premature termination codon in the C3 gene results in a lack of the protein in serum, correlating with acceleration of C3 mRNA decay in fibroblasts consistent with a nonsense-codon-mediated decay process. 14662858_Expressed in a bacterial system, a recombinant C3 segment of C345C module has substantial beta-sheet structure and internal disulfide bonds but does not inhibit complement hemolytic activity, and does not bind C6 or C7. 15033778_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15090635_findings show a significant genetic contribution to variation in circulating levels of acylation-stimulating protein and an interesting pattern of genetic correlation (i.e., pleiotropy) with other risk factors associated with the metabolic syndrome 15187133_electrostatic calculations provide global and site-specific explanations of the physical causes that underlie the ionic strength dependence of C3d-CR2 association 15241561_HGF and IL-1ra adhesion-dependent release from human blood granulocytes and monocytes involves plasma IgG, complement C3 and beta2 integrin 15278436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15381670_MT1-MMP cleaves complement C3b 15383607_Transgenic mice expressing C3a/glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the brain progress to severe experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis during the chronic phase of the disease, with significant mortality compared with nontransgenic littermates. 15489226_thermodynamic analysis of interaction of C3 with its inhibitor, compstatin 15550543_A peptide (C3a) derived from the complement C3 protein has antimicrobial activity against E. coli, P. aeruginosa, E. faecalis, and C. albicans. 15590640_complement C3 expression is regulated by the bile acid receptor FXR 15648851_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15713467_characterized the interaction between the first two short consensus repeats (SCR1-2) of complement receptor type 2 (CR2, CD21) and C3d 15713468_the open V-shaped structures formed by CR2 SCR 1-2, both when free and when bound to C3d, are optimal for the formation of a tight two-domain interaction with its ligand C3d 15749882_mapped the regions of C3 involved in conformational transition when hydrolyzed to C3(H2O) 15810889_iC3b interferes with monocyte-derived dendritic cell differentiation and IL-12 and IL-10 production is mediated via an ERK MAPK-dependent mechanism 15833747_determination of C5L2 as its receptor and the receptor's role in mediating acylation stimulating protein triglyceride stimulation 15872081_C3 secretion induced by CD40L may represent a mechanism of amplification of tubulointerstitial damage associated with lymphocyte infiltration. 16148107_Moraxella catarrhalis UspA1/A2 exert their actions by absorbing and neutralizing C3 from serum and restrain complement activation 16148115_C3a increased the binding affinity of CXCL12 to human CXCR4(+)/C3aR(-), REH pro-B cells, which is compatible with a direct interaction between C3a and CXCL12 16177781_crystal structures of native C3 and its final major proteolytic fragment C3c 16301317_properdin has a role in the assembly of the alternative pathway C3 convertases of complement 16339538_streptavidin-C3dg enhancement of BCR-induced [Ca2+]i responses required CD21 and CD19 expression and resulted in significantly enhanced CD19 and Lyn phosphorylation, with enhanced Lyn/CD19 associations 16355111_C3 gene is a priority candidate controlling risk for asthma and allergic disease in the Barbados population of African descent. 16355111_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16449793_data cast new light on the mechanism of complement-mediated tissue injury in nonimmunological disorders 16516157_The differential expression of the complement proteins provides potentially useful biomarkers as well as evidence for the involvement of inflammatory processes in the pathogenesis of ALS and PD. 16570073_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16627066_Complement C3a is continuously elevated in deep second-degree burned wounds in patients older than 60 years. (complement 3a) 16670774_Mannan-binding lectin activates C3 and the alternative complement pathway without involvement of C2 16809564_South Asians have elevated C3 & CRP levels; results suggest they have a greater level of chronic subclinical inflammation independent of family history of stroke; C3 is more likely to cluster with features of insulin resistance syndrome compared with CRP 16823297_C3a is acutely elevated after human ischemic stroke, C5a shows delayed elevations 7 to 14 days after cerebral ischemia, and sC5b-9 is acutely depressed after stroke. (Complement 3a, c5a, and C5b-9) 16889542_C3d was somewhat more predictive of margination than C4d in ABO-incompatible 16893076_Results describe three distinct profiles of serum complement C4 proteins in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients, and show tight associations of complement C4 and C3 protein levels in SLE but not in healthy subjects. 17051160_crystal structure of C3b; structural data indicate that the large conformational changes in the proteolytic activation and regulation of C3 take place mainly in the first conversion step, from C3 to C3b 17060630_C3 split products inactivated C3b (iC3b) and C3a were elevated in serum, overlying ARPE-19 cells that had accumulated A2E and were irradiated to induce A2E photooxidation 17172439_Studies on two products of nucleophile addition to C3 reveal a structural intermediate in activation, and a final product, in which the anaphylatoxin domain has undergone a remarkable movement through the macroglobulin ring 17322907_data indicate that C5L2 can function as a positive modulator for both C5a- and C3a-anaphylatoxin-induced responses 17372315_Increased plasma ASP levels at late gestation may further contribute to the hyperlipidemic state, shifting energy in the form of triglycerides to the rapidly growing fetus. 17482181_Impairment of the mechanisms involved in the regulation of activation of complement system factor C3c fragment may be important in the pathogenesis of endometriosis and endometriosis-associated infertility. 17498719_in stenotic aortic valves, complement is activated leading to generation of the anaphylatoxin C3a 17502296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17520688_These results indicate that C3 causes mesangial cells to convert to the synthetic phenotype and stimulates growth of mesangial cells, suggesting that C3 may play an important role in phenotypic regulation of mesangial cells in renal diseases. 17634448_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17634448_The common functional polymorphism rs2230199 (Arg80Gly) in the C3 gene, corresponding to the electrophoretic variants C3S (slow) and C3F (fast), was strongly associated with age-related macular degeneration in both English group and the Scottish group 17684013_compstatin sterically hinders the access of the substrate C3 to the convertase complexes, thus blocking complement activation and amplification 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17762737_inflammatory processes involving C3a may contribute to delayed morbidity and mortality after aneurysmal rupture 17767156_Identification of a nonsynonymous coding change in complement factor 3 that is strongly associated with risk of age-related macular degeneration in a large case-control sample. 17984207_The binding of complement components C4b and C3b to the proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis is reported. 18039528_C3a and C5a can bring about eosinophil extravasation and increase in vascular permeability that facilitates eosinophil accumulation at sites of allergic inflammation. 18039777_Human oviduct possesses C3 convertase activity converting C3 to C3b, and Crry of the preimplantation embryos may be involved in the production of embryotrophic iC3b on the surface of the embryos. 18054386_The dominant types of C1q complexes that circulate in vivo are C1q-C3d and C1q-C4d complexes. 18061265_These results provide evidence for a novel role of C3 as a critical cofactor in human dendritic cell differentiation and maturation. 18174230_C3 gene is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus and decreased serum level of C3 arre correlated with this allele. 18174230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18206145_Levels are increased in young women with polycystic ovary syndrome. 18247123_morphine modulates IL-1beta-mediated C3 expression in astrocytic cells. 18253759_Results demonstrate alterations in C3 and ASP that may contribute to or compensate for dyslipidemia in pediatric proteinuric renal disease. 18325906_Variation in C3 is associated with increased risk for age-related macular degeneration, with the R102G polymorphism showing the strongest evidence for the functional variant in our dataset. 18356838_Maternal hypertriglyceridemia is associated with increased fetal ASP production, thus enhancing fetal fat storage independent of maternal glucose variations in nondiabetic women. 18383369_Non-nuclear antibodies and C3 and C4 cluster within the families of SLE probands, suggesting that specific autoantibody formation is partly genetically determined, even if the total genetic effect in unaffected relatives is insufficient to cause disease 18434316_Sbi helps mediate bacterial evasion of human complement C3 via a novel mechanism, namely futile fluid-phase consumption 18456336_Hydrogen/deuterium exchange coupled with mass spectrometry (HDX-MS) is utilized to investigate relative changes in the solution-phase structures of C3 and C3b. 18562232_study concluded that hyperglycaemia &/or hyperinsulinaemi per se regulated concentration & expression of leptin, adiponectin & acylation-stimulating protein in healthy lean young men, suggesting contribution to dysregulation of these hormones in diabetes 18562603_C3 plays a beneficial role in plaque clearance and neuronal health as well as in modulation of the microglia phenotype in a complement C3-deficient amyloid precursor protein transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. 18566738_Linkage disequilibrium block 4 spanning exons 24-41 of the C3 gene confers susceptibility to adult bronchial asthma, with mechanisms relevant to the effector phase of allergic inflammation in Japan. 18566738_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18572187_Report method for enzyme-independent, orientation-selective conjugation of whole human complement C3 to protein surfaces. 18585783_A novel role for C3 that broadens its capacity to modulate acquired immune response. 18596911_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18631248_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18631248_Polymorphisms within the C3 gene are associated with specific IgE levels to common allergens and super-antigens among atopic dermatitis patients 18671285_findings show sex steroids, particularly estradiol, and preimplantation embryos regulate the expression pattern of C3 in the oviduct; data support a physiological role of C3 in preimplantation embryo development 18682851_C4BP binds to jeopardized cardiomyocytes early after acute myocardial infarct and co-localizes to other well known markers such as complemenb 3b. 18694577_C3a is a highly sensitive early indicator of ischemia-reperfusion damage. 18702682_results suggest that an elevated ASP response during the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp is associated with metabolic disturbances in overweight and obese postmenopausal women 18755462_Complement C3 and C-reactive protein have a role in myocardial infarction 18760301_functionally important structural differences between CVF and C3 are located in the very C-terminal region of both homologous proteins, and that small substitutions in human C3 with homologous CVF sequence result in C3 derivatives with CVF-like functions. 18796626_study reports mutations in C3 in association with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS); 9 novel mutations in 14 aHUS patients with a persistently low serum C3 level are described 18802120_Association of important functional defects of dendritic cells, acquisition of B cell memory, and regulatory T cells with C3 deficiency strongly supports a major role for C3 in bridging innate and adaptive immunity in humans. 18805911_Changes in plasma adipokine ASP in early obesity are associated with blood lipid and glucose modifications, family environment, and distinct metabolic syndrome risk factors. 18854167_analysis of denaturation and unfolding of human anaphylatoxin C3a 18936151_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18974840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19005416_Significantly more transcripts encoding alternative pathway components factor B, C3 and properdin, and C3a receptor and C5a receptor were detected in grade 3 versus grade 0 or 1 biopsies of human cardiac allografts. 19015224_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19015224_Study provides insights into the genetic pathogenesis of AMD, and C3 has been shown as one of the five genes independently involved in progression from intermediate disease to advanced disease in which blindness is frequent. 19017934_members of the Staphylococcus aureus extracellular fibrinogen-binding protein family inhibit the interaction of C3d with complement receptor 2 19022911_during the menstrual cycle of normal women, the ASP levels coincidentally fluctuate with the progesterone levels, possibly reflecting cooperation between them in fat storage enhancement 19028820_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19028829_hypercomplementemia in anti-AQP4 antibody-positive patients may reflect a systemic inflammatory reaction at relapse in multiple sclerosis 19048105_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19112495_Sbi is a multifunctional bacterial protein, which binds host complement components Factor H and C3 as well as IgG and beta(2)-glycoprotein I and interferes with innate immune recognition. 19117936_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19131662_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19164292_C3dp1 interacts at the same CR2 site as C3d 19168221_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19168221_Our study showed a significant association between variants in the C3 gene and age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and further highlights the crucial role of the complement pathway in the etiology of AMD. 19179465_Binding of C3 by paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) red blood cells may constitute an additional disease mechanism in PNH, strongly enhanced by eculizumab treatment and producing a variable degree of extravascular hemolysis 19196712_Data demonstrate the structural basis for complement inhibition by a C3b-selective antibody and provides insights into the molecular mechanisms of alternative pathway complement activation. 19202148_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19225544_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19234341_Nonsynonymous coding single nucleotide polymorphisms (nsSNPs) in C3 increased the risk of developing AMD 1.8-fold for 1 risk allele or 2.4-fold for two risk alleles and were preferentially associated with advanced age-related macular degeneration. 19234341_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19246358_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19246358_The hazard ratios for allograft survival in the SS recipient and FS or FF donor group as compared with the other three groups were not significant 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19259132_Data show that SNPs, and haplotypes risk trends were consistent with those seen in other population studies for CFH, C3, C2, and CFB. 19259132_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19263529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19265162_In mesenchymal stem cells both C3a and C5a cause prolonged and robust extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 and proto-oncogene protein c-akt (Akt) kinase phosphorylation. 19328844_C3 serves as an opsonin for B. anthracis spores resulting in enhanced phagocytosis by human macrophages. 19336475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19344414_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19387462_In an extended cohort of 585 systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) families the association between C3 variants and SLE was assessed by transmission disequilibrium test. SNP rs3745568 was associated with SLE(P=0.0046), but not with serum C3. 19387462_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19399715_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19407382_hanging-drop vapor-diffusion technique was used to crystallize human C3b in the presence of a recombinant form of staphylococcal complement-inhibitor protein 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19454698_found four atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome-linked CFH mutations that decreased binding to C3b and/or to heparin, and five aHUS-associated mutants with increased affinity for either or both ligands. 19457998_Paramyxoviruses simian virus 5 and mumps virus recruit host cell surface complement inhibitors, CD46, into progeny virions to limit C3-mediated neutralization. 19503104_Results offer general models for complement regulation and provide structural explanations for disease-related mutations in the genes encoding both FH and C3b. 19505474_The authors conclude that the physiological interaction between FH and C3d is not a simple 1:1 binding stoichiometry between the two proteins that is often assumed. 19549636_protective effect of the fH-Ile(62) variant is due to its better capacity to bind C3b, inhibit proconvertase formation and catalyze inactivation of fluid-phase and surface-bound C3b. 19559392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19590060_Case Report: A large family with a gain-of-function mutation of complement C3 predisposing to atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, microhematuria, hypertension and chronic renal failure. 19661236_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19665237_produced by trophoblast cells, may be regulated by IFNgamma 19670317_Serum levels of complement C3 correlates with the level of severity of generalized myasthenia gravis. 19680263_Factor H-monomeric C reactive protein complexes enhance C3b inactivation both in the fluid phase and on the surface of damaged cells and inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. 19694644_plasma C3a levels can be used as diagnostic test for endometriosis 19703145_serum C3 levels are not affected in pre-eclamptic patients 19767107_Recombinant C3adesArg/acylation stimulating protein (ASP) is highly bioactive: a critical evaluation of C5L2 binding and 3T3-L1 adipocyte activation. 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19797206_The findings indicate that age-related maculopathy (AMD) progression is differentially affected by genotypic variants. 19823576_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19823576_variants at CFH, C3, and ARMS2 confer significant risks for geographic atrophy due to age-related macular degeneration 19825847_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19828715_Complement component 3 polymorphisms interact with polyunsaturated fatty acids to modulate risk of metabolic syndrome. 19828715_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19843088_Robust generation of both C3a and C5a by either the alternative pathway or classical pathway alone were observed with both mouse and human sera, after adherent IgG-induced complement activation. 19850835_noncoding variant rs1410996 of the CFH gene moderately increased the risk of exudative AMD in a Chinese population. The C3 variants were rare and not associated with exudative AMD in this Chinese cohort. 19861685_Association of factor H autoantibodies with deletions of CFHR1, CFHR3, CFHR4, and with mutations in CFH, CFI, CD46, and C3 in patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. 19899988_The G allele of C3 IVS2 rs2250656 may be a significantly protective factor for neovascular AMD in the Chinese population. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913840_Complement C3 is part of the metabolic syndrome X cluster and confers coronary heart disease risk, additively to metabolic syndrome X components and C-reactive protein, in a population in which metabolic syndrome X prevails. 19939777_Diagnosis of hereditary deficiency of the third complement component (C3) with compound heterozygous mutation of the gene. 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20089077_The increased mucosal mRNA expressions of complement C3 and interleukin-17 in inflammatory bowel disease. 20091675_analysis of the physicochemical properties underlying C3d-CR2 association 20104494_donor and recipient C3 genotypes are not associated with liver transplantation outcomes 20105190_Exaggerated weight gain during childhood, but not foetal growth, contributes to alterations in ASP metabolism, which may be associated with impaired FFA uptake and delayed triglycerides clearance. 20105310_taken together, the profile of C5L2 receptor, ASP gene expression and metabolic factors in adipose tissue from morbidly obese high ASP and triglyceride subjects (HAT) suggests a compensatory response associated with the increased plasma ASP and TG 20109314_sinus mucosa expression is increased in chronic rhinosinusitis patients 20139276_Data show that C1q, C4, C3, and C9 bind to thrombin receptor-activating peptide-activated platelets in lepirudin-anticoagulated platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and whole blood. 20139773_early marker for pancreatic adenocarcinoma 20157618_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20157618_This study confirmed the association between Complement Component 3 (C3) and late-stage age-related macular degeneration. 20173020_Many children with Prader-Willi syndrome had dyslipidemia and high acylation-stimulating protein levels. 20188594_Complement C3d activation may play a role in the pathogenesis of coronary artery vasculopathy. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20238042_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20378178_Data show that FH Q1139 in domain 19 and R1203 in domain 20 are directly involved in binding to the C3d part of C3b and therefore both the domains are involved in the interaction with C3d and C3b. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20381870_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20385819_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20395963_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20453728_This study showed that resistant arterial hypertension is characterized by higher levels of complement C3a and complement C3b and a negative correlation between circulating C3a and endothelial progenitor cells. 20498262_Secretome analysis and protease inhibitor studies identified the secreted alkaline protease Alp1 as the central molecule responsible for the cleavage of human complement proteins C3, C4, and C5. 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20513133_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20513133_Study identified novel mutations in CFH, CFHR5, CFI, CFB and C3 in American patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. 20523265_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20523265_This study showed that CFH was more likely to be age-related macular(AMD) susceptibility gene, and none of the other C2, CFB, and C3 genes were associated with AMD in a white population. 20576771_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20603037_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20644161_Data show that the fungus secretes a potent complement inhibitor, pH-regulated Ag 1 (Pra1), which in the direct surrounding of the pathogen binds to fluid-phase C3 and blocks cleavage of C3 to C3a and C3b. 20664795_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20664795_This study shows C3 to be a moderate susceptibility gene for exudative age-related macular degeneration in the French population. 20706769_Data suggest that compared to high sensitive C-reactive protein, serum C3 might be a better inflammatory marker of insulin resistance in the non-diabetic Chinese population. 20807366_We present three boys with acquired partial lipodystrophy having C(3) hypocomplementemia 20817881_Through direct interaction, C3a and CpGA synergize to increase IFN-alpha production in a RAGE-dependent manner and stimulate an innate immune response. 20837143_Studies indicate that mutations or polymorphisms in complement genes C3 and factor B are genetic risk factors contributing hemolytic uremic syndrome. 20841369_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20841369_polymorphisms are strong independent predictors of neurocognitive dysfunction following carotid endarterectomy 20852386_findings expose structural requirements in C3 that are critical for recognition of the substrate C3 by the alternative pathway C3-convertase 20862287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20862287_Polymorphism in the promoter of the complement C3 participates in the genetic susceptibility to temporal lobe epilepsy and febrile seizures. 20888482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20926033_The results indicate higher C3 levels in hypothyroid patients. 20926148_Human plasma complement C3 is associated with prevalent coronary heart disease, but only in heavy smokers, and this association is independent of important metabolic cardiovascular risk factors. 20951140_Molecular modeling approaches used to investigate disparities between the biochemical data and the X-ray structure of the CR2-C3d cocrystal result in highest-scoring solutions in which CR2 SCR1-2 is docked within the concave surface of C3d. 21055811_The structure of the complement-binding domain of Staphylococcus aureus protein Sbi (Sbi-IV) in complex with ligand C3d is presented. 21085669_Data indicate that the deposition of both C4 and C3 showed a significant positive correlation with the serum concentration of Ficolin-3. 21163532_These studies show that the acquisition of fH to the S. aureus surface inhibits complement-mediated opsonization via disruption of the alternative pathway convertase. 21173647_Elevated C3a as early as the first trimester of pregnancy is an independent predictive factor for adverse pregnancy outcomes. 21205667_crystal structure of C3bB at 4 A and complex with factor D at 3.5 A; data show how factor B binding to C3b forms open 'activation' state of C3bB; Factor D binds open conformation of factor B through a site distant from the catalytic center 21270401_Binding of C3 is related to bacterial ubiquitous surface protein (Usp)A expression of Moraxella catarrhalis in clinical isolates and correlates with serum resistance. Most of the UspA-expressing M. catarrhalis interacts with C3. 21270401_The binding of complement C3d to ubiquitous surface protein A (UspA) is an efficient strategy of Moraxella catarrhalis to block complement activation and to inhibit C3a-mediated inflammation. 21308746_Results suggest that the p38alpha, MAPK, and MKK6 play prominent roles in IL-1beta and C/EBP-beta-mediated C3 gene expression in astrocytes. 21402993_CFH confers more risk to the bilaterality of geographic atrophy, whereas HTRA1/LOC387715 contributes more to the bilaterality of choroidal neovascularization. C3 confers more risk for geographic atrophy 21404895_sPLA2-IIA, CRP, and C3d are significantly more activated in atherosclerotic aortic valves compared to degeneratively changed aortic valves. 21414106_In this sample of patients with ischemic stroke, genetic variation in complement C3 is associated with ischemic stroke. 21415311_studies implicate alternative pathway dysregulation in a spectrum of rare renal diseases that includes GN-C3 and dense deposit disease 21435440_Complement 3 and factor h in human cerebrospinal fluid have roles in Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and multiple-system atrophy 21462136_Results suggest that C3 gene could be associated with adult asthma of Han population in southern China. 21464960_PLG-bound spores were capable of exhibiting anti-opsonic properties by cleaving C3b molecules in vitro and in rabbit bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. 21501302_This study demonstrated that hereditary C3 deficiency in the patient is caused by novel compound heterozygous | ENSMUSG00000024164 | C3 | 549.124816 | 0.494819945 | -1.015024 | 0.22384615 | 20.059000 | 0.0000075089297519619857367153756277922127537749474868178367614746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001031777105800041848242959430237419837794732302427291870117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 371.7745927 | 53.8830768 | 752.7978162 | 107.8799861 | |
| ENSG00000125863 | 8195 | MKKS | protein_coding | Q9NPJ1 | FUNCTION: Probable molecular chaperone that assists the folding of proteins upon ATP hydrolysis (PubMed:20080638). Plays a role in the assembly of BBSome, a complex involved in ciliogenesis regulating transports vesicles to the cilia (PubMed:20080638). May play a role in protein processing in limb, cardiac and reproductive system development. May play a role in cytokinesis (PubMed:28753627). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20080638, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28753627}. | ATP-binding;Bardet-Biedl syndrome;Chaperone;Ciliopathy;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Obesity;Reference proteome;Sensory transduction;Vision | This gene encodes a protein which shares sequence similarity with other members of the type II chaperonin family. The encoded protein is a centrosome-shuttling protein and plays an important role in cytokinesis. This protein also interacts with other type II chaperonin members to form a complex known as the BBSome, which involves ciliary membrane biogenesis. This protein is encoded by a downstream open reading frame (dORF). Several upstream open reading frames (uORFs) have been identified, which repress the translation of the dORF, and two of which can encode small mitochondrial membrane proteins. Mutations in this gene have been observed in patients with Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 6, also known as McKusick-Kaufman syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2013]. | hsa:8195; | centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; kinociliary basal body [GO:1902636]; motile cilium [GO:0031514]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; artery smooth muscle contraction [GO:0014824]; brain morphogenesis [GO:0048854]; cartilage development [GO:0051216]; cerebral cortex development [GO:0021987]; chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly [GO:0051131]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; convergent extension involved in gastrulation [GO:0060027]; detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound [GO:0050910]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; developmental process [GO:0032502]; face development [GO:0060324]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; gonad development [GO:0008406]; heart development [GO:0007507]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; hippocampus development [GO:0021766]; intracellular transport [GO:0046907]; melanosome transport [GO:0032402]; negative regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030837]; negative regulation of appetite by leptin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038108]; negative regulation of blood pressure [GO:0045776]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0034260]; non-motile cilium assembly [GO:1905515]; photoreceptor cell maintenance [GO:0045494]; pigment granule aggregation in cell center [GO:0051877]; positive regulation of multicellular organism growth [GO:0040018]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; regulation of cilium beat frequency involved in ciliary motility [GO:0060296]; regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051492]; sensory perception of smell [GO:0007608]; social behavior [GO:0035176]; spermatid development [GO:0007286]; striatum development [GO:0021756]; vasodilation [GO:0042311]; visual perception [GO:0007601] | 11567139_Unaffected individuals in 2 pedigrees had 2 but not all 3 mutations that affecteds had which suggests that Bardet-Biedle syndrome might not be a single-gene recessive disease but a complex trait requiring three mutant alleles to manifest the phenotype. 12837689_The presence of three mutant alleles in the BBS family correlates with a more severe Bardet-Biedl phenotype. 15483080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15731008_MKKS/BBS6 is a novel centrosomal component required for cytokinesis 17003356_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18094050_These results indicate that the MKKS mutants have an abnormal conformation and that chaperone-dependent degradation mediated by CHIP is a key feature of McKusick-Kaufman syndrome/Bardet-Biedl syndrome diseases. 18813213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18813213_results suggest that genetic variation in the MKKS gene may play a role in the development of obesity and the metabolic syndrome. 19077438_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19247371_genetic variations at MKKS gene influence the risk of metabolic syndrome 19876004_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20472660_Using sequence analysis, the role of BBS6, 10 and 12 was assessed in a Bardet-Biedl syndrome patient population comprising 93 cases from 74 families. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20801516_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 23432027_Novel mutation (c.1272+1G>A) in BBS6 found in Tunisian families with Bardet-Biedl syndrome. 23671934_Three uORFs (uMKKS0, uMKKS1 and uMKKS2) are reported, and they can repress the translation of the downstream MKKS ORF. uMKKS1 and uMKKS2 are highly conserved in mammals and they encode two different mitochondrial membrane proteins respectively. 23716571_Findings indicate that Bbs proteins play a central role in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton and control the cilia length through alteration of RhoA levels. 24400638_we report here, for the first time, in Indian population, a novel, different profile of mutations in BBS genes (BBS3, BBS9, BBS10 and BBS2) compared to worldwide (BBS1 and 10) reports. 26900326_We identified a novel H395R substitution in MKKS/BBS6 that results in a unique phenotype of only retinitis pigmentosa and polydactyly. 28624958_found compound heterozygous variants (c.1192C>T, p.Q398* and c.1175C>T, p.T392M) in MKKS in both the siblings, and these were likely to be pathogenic variants 28761321_Two novel mutations and three previously reported variants, identified in the present study, further extend the body of evidence implicating BBS6, BBS7, BBS8, and BBS10 in causing Bardet-Biedl Syndrome. 29232001_Novel sequence variants in the MKKS gene cause Bardet-Biedl syndrome in two consanguineous families with intra- and inter-familial variable phenotypes. 31989739_Novel mutation in MKKS/BBS6 linked with arRP and polydactyly in a family of North Indian origin. 33741323_Apparent but unconfirmed digenism in an Iranian consanguineous family with syndromic Retinal Disease. | ENSMUSG00000027274 | Mkks | 129.806061 | 0.150992333 | -2.727453 | 0.96253145 | 7.026793 | 0.0080299012381314302522206105550139909610152244567871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0419655355652382433540026340779149904847145080566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 22.4308012 | 20.0120926 | 131.6087554 | 117.4105939 | |
| ENSG00000125954 | 100529261 | CHURC1-FNTB | protein_coding | B4DL54 | FUNCTION: Essential subunit of the farnesyltransferase complex. Catalyzes the transfer of a farnesyl moiety from farnesyl diphosphate to a cysteine at the fourth position from the C-terminus of several proteins having the C-terminal sequence Cys-aliphatic-aliphatic-X. {ECO:0000256|RuleBase:RU365056}. | Metal-binding;Prenyltransferase;Reference proteome;Transferase;Zinc | This locus represents naturally occurring read-through transcription between the neighboring CHURC1 (churchill domain containing 1) and FNTB (farnesyltransferase, CAAX box, beta) on chromosome 14. The read-through transcript produces a fusion protein that shares sequence identity with each individual gene product. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. | protein farnesyltransferase complex [GO:0005965]; protein farnesyltransferase activity [GO:0004660]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; protein farnesylation [GO:0018343] | 56.978867 | 2.276505807 | 1.186821 | 0.39549524 | 8.763905 | 0.0030725050027095414731381772810436814324930310249328613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0192210196681131782747709024761206819675862789154052734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 95.2925110 | 47.1699109 | 40.2627779 | 19.9596527 | |||||
| ENSG00000126353 | 1236 | CCR7 | protein_coding | P32248 | FUNCTION: Receptor for the MIP-3-beta chemokine. Probable mediator of EBV effects on B-lymphocytes or of normal lymphocyte functions. | 3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor family. This receptor was identified as a gene induced by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and is thought to be a mediator of EBV effects on B lymphocytes. This receptor is expressed in various lymphoid tissues and activates B and T lymphocytes. It has been shown to control the migration of memory T cells to inflamed tissues, as well as stimulate dendritic cell maturation. The chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 19 (CCL19/ECL) has been reported to be a specific ligand of this receptor. Signals mediated by this receptor regulate T cell homeostasis in lymph nodes, and may also function in the activation and polarization of T cells, and in chronic inflammation pathogenesis. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. | hsa:1236; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; C-C chemokine binding [GO:0019957]; C-C chemokine receptor activity [GO:0016493]; C-C motif chemokine 19 receptor activity [GO:0038117]; C-C motif chemokine 21 receptor activity [GO:0038121]; chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 19 binding [GO:0035757]; chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 21 binding [GO:0035758]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cellular response to cytokine stimulus [GO:0071345]; dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:0002407]; establishment of T cell polarity [GO:0001768]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; homeostasis of number of cells [GO:0048872]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; lymphocyte migration into lymph node [GO:0097022]; mature conventional dendritic cell differentiation [GO:0097029]; myeloid dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:0002408]; negative regulation of dendritic cell apoptotic process [GO:2000669]; negative regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032695]; negative thymic T cell selection [GO:0045060]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of cell motility [GO:2000147]; positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001954]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of dendritic cell antigen processing and presentation [GO:0002606]; positive regulation of dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:2000510]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of filopodium assembly [GO:0051491]; positive regulation of glycoprotein biosynthetic process involved in immunological synapse formation [GO:2000526]; positive regulation of humoral immune response [GO:0002922]; positive regulation of hypersensitivity [GO:0002885]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of immunological synapse formation [GO:2000522]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090023]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043552]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of pseudopodium assembly [GO:0031274]; positive regulation of T cell costimulation [GO:2000525]; positive regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050862]; regulation of dendritic cell dendrite assembly [GO:2000547]; regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032651]; regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032649]; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051209]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to nitric oxide [GO:0071731]; response to prostaglandin E [GO:0034695]; ruffle organization [GO:0031529] | 11830455_Up-regulation OF CCR7 in classical but not in lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin disease correlates with distinct dissemination of neoplastic cells in lymphoid organs 11929789_important for migration of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells into lymph nodes 12070001_Few NKT cells express lymphoid tissue-homing chemokine receptors (CCR7 and CXCR5). A population with homing potential for lymph nodes (L selectin(+) CCR7(+)) exists only within a small subset of CD4 NKT cells. 12149218_PGE2 enhanced the expression of the CCL19/CCL21 receptor CCR7 on the cell surface of monocyte-derived dendritic cells 12486098_Data show that interaction between iC3b-opsonized apoptotic cells and immature dendritic cells down-regulated the expression of CD86 and up-regulated expression of CC chemokine receptor 7. 12642342_Coincident expression of CCR6 and CCR7 by pathologic Langerhans cells in Langerhans cell histiocytosis may contribute to their accumulation in nonlymphoid organs such as skin and bone 12673677_Overexpression of CCR7 mRNA in nonsmall cell lung cancer is associated with development of lymph node metastasis 12799021_A striking pattern of early inducible CCR7 expression was seen preferentially on primary T(H)1 cell lines, as compared to T(H)2 cells, and was dependent on the strength and duration of the T cell receptor signal. 14990723_cytomegalovirus infection inhibits dendritic cell migration by impairment of the chemokine receptor switch at the level of the expression of CCR7 molecules 15034011_Premature expression of CCR7 repositions CD4+CD8+ double-positive cells into the thymic medulla of transgenic mice. This repositioning of the thymocytes is accompanied by impairment of their development. 15040017_The expression of VEGF-C and CCR7 is related to lymph node metastasis of gastric carcinoma and both of them may become new targets for the treatment of gastric carcinoma. 15059845_CCR7 induces antiapoptotic signaling in mature DCs 15073111_CCR7 has a role in cell migration induced by CCL21 chemokine in malignant melanoma 15122702_Study of expression of CCR7 and its ligands on dendritic and T cell populations in inflamed central nervous system lesions of multiple sclerosis patients gives insight into pathways for immune cell trafficking and surveillance. 15247147_IL-6 led to inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) binding activity, regulating CCR7 transcription 15265234_A dose-dependent, mesangioproliferative and antiapoptotic effect of SLC/CCL21 was seen via activation of the chemokine receptor CCR7, constitutively expressed on MC. This suggests involvement in renal inflammation, regeneration and glomerular homeostasis. 15284247_specific CC chemokine receptor 7 residues have roles in receptor activation 15304089_MAPK are necessary for haptens to induce CCR7 expression. 15569314_Activation of CCR7 on mesangial cells by SLC/CCL21 enhances the degree and firmness of cell adhesion and increases cell spreading and the formation of cell-cell contacts 15674360_The CC chemokine receptor 7 consists with the known defect in adhesion and migration of CML cells. 15743472_CCR7 may have a role in the synovial recruitment of memory T cells in juvenile idiopathic arthritis, irrespective of the pattern of lymphoid organisation. 15753377_Epigenetic up-regulation of C-C chemokine receptor 7 expression is associated with melanoma 15778365_CCR7 activates two independent signaling modules, one involving G(i) and a hierarchy of MAPK family members and another involving Rho/Pyk2/cofilin, which control, respectively, chemotaxis and the migratory speed of DCs. 15867478_High expressions of CCR7 is associated with differentiated and intestinal-type gastric cancers 15950936_The selective expression of CCR7 in JDM may open new perspectives in the understanding of the pathogenesis of inflammatory myopathies, offering a new tool for the differential diagnosis of these disorders. 16115904_Results suggest that the chemokine receptor CCR7 is a novel biomarker that can predict lymph node metastases in breast cancer. 16223574_we investigated the expression of CC chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7) in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas 16225771_Data show that CXCL13 and CCL19 together by means of activation of CXCR5 and CCR7 up-regulated PEG10 expression and function in leukemic B cells. 16272303_functional and lineage relationships of three distinct memory CD4 subpopulations distinguished by their expression of the cysteine chemokine receptor CCR7 and the TNFR family member CD27 16278374_Chemokine receptor 7 is a new player in regulating apoptosis of CD8+ T cells in cancer patients [editorial] 16278415_CCR7 absence on the majority of CD8(+) T cells in the peripheral circulation of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck contributes to apoptosis 16494043_CXCR4 and CCR7 are highly expressed in laryngeal carcinoma. Expression was associated with tumor grade, clinical stage and neck lymph node metastasis. 16500130_The maturation, in vitro migration and cytokine production of human DC after stimulation with live H. pylori is reported. 16690519_CD62L and CCR7, as well as dendritic cells, are reduced in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma 16786131_expression of CCR7 promotes intrahepatic and lymphatic human hepatocellular carcinoma dissemination 16802356_In systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients, significant increases of CCR7-, CD27- and CCR7-, CD27+ and a reduction of CCR7+, CD27+ CD4 memory T cells were found. 16857986_CD45RA+ CCR7- CD8+ T cells are resting memory cells that, upon antigenic stimulation and then proliferate, lose CD45RA, and transiently acquire CCR7. 16887149_The CCL19,CCL21/CCR7 chemokine system is expressed in inflamed muscles of polymyositis and may be involved in the pathomechanism of polymyositis. 17006331_Rapamycin selectively up-regulates CCR7 and enhances the migration of differentiated dendritic cells to regional lymph nodes. 17032700_Significantly higher CCR7 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis in human cervical cancer 17178876_CCR7 may be regulated by the breast tumor microenvironment and further support the use of endothelin receptor antagonists in the treatment of invasive and metastatic breast cancer. 17440035_Borrelia garinii blocks the up-regulation of CCR7 and CD38, important molecules in DC migration to lymph nodes, thus affecting further immune responses in Lyme borreliosis infection. 17587445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17587445_variants of CCR7 gene occur at an extremely low frequency in the German population and that neither Sjogren's syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, nor systemic sclerosis are associated with these variants 17687340_High levels of CCR7 expression predicted a poor prognosis. 17890452_role for MMP-9 and CCR7 in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression 18065728_We have identified a new three-gene classifier that is independent of and improves on stage to stratify early-stage NSCLC patients with significantly different prognoses. 18166500_This study showed that memory Tregs contain high proportions of inflammatory chemokine-expressing cells and comprise two populations that differ in the expression of the lymphoid chemokine receptor CCR7. 18235009_CXCR4 and CCR7 provide directional migration of uveal melanoma cells toward the liver, the most common site for the formation of uveal melanoma metastases. 18319253_CCR7 and the EP2/EP4 receptor signaling pathway are down-stream targets for COX-2 to enhance the migration of breast cancer cells toward LECs and to promote lymphatic invasion 18437055_CCR7 plays a critical role in mediating chemotactic and invasive responses in colon cancer 18497951_Expression of CCR7 was significantly associated with lymph node metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma 18544997_The survival impact of CCR7 expression on resectable pancreatic cancer may be associated with lymphatic spread. 18623114_results indicate in CRC frequent alternative splicing or post-transcriptional mRNA modification resulting in a CCR7 molecule lacking an intact signal peptide prohibiting membrane translocation 18664492_A CCR7 mutant lacking virtually the complete C-terminus readily bound CCL19 and was internalized, but was unable to activate the G protein and to transmit signals required for cell migration. 18696160_High CCR7 expression is associated with extrathyroidal extension, angiolymphatic invasion, and lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. 18802075_Independent of arrestin 2 or arrestin 3 expression, CCR7/CCL21 internalize. 19068542_Patients with psoriasis vulgaris have a skewed distribution of T lymphocytes, with an increased level of CCR7-positive T lymphocytes compared to healthy controls. No CCR7 expression is observed in the skin of healthy individuals. 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19087620_CCR7 may play an important role in the development and lymph node metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 19136936_A novel property of the chemokine receptors CCR7 in inhibiting detachment-induced cell death-anoikis, which is believed to be one of the major blocks in the metastatic spread of various neoplasms. 19196101_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19287948_CCR7 expression might play an important role in establishing LN metastases in patients with esophageal SCC 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19513547_CCR7 and CXCR4 expression predicts lymph node status including micrometastasis in gastric cancer. 19536265_Ccr7 gene expression is controlled by the activity of the T-ALL oncogene Notch1 and is expressed in human tumours carrying Notch1-activating mutations 19536742_Low-expression frequency for the chemokine receptor CCR7 is associated with mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. 19540558_macrophages may participate in lymphangiogenesis in diffuse alveolar damage, which is facilitated by CCL19 and CCR7. 19585516_Alloimmune-induced APOBEC3G was found to be significantly increased in CD45RA(-), CCR5(+) and CD45RA(-)CCR7(-) subsets of effector memory T cells. 19615795_Results show interaction between CCR7 and its ligand CCL19 induces phosphorylation of mTOR and its target p70s6k. This phosphorylation is abolished by inhibition of CCR7 and PI3K/Akt, indicating that mTOR is involved in the CCR7-PI3K cascade. 19731977_Our data support the notion that CCR3, CCR7, and CXCR4 are increasingly expressed in tumor cells from PTC and that CXCR4 expression in PTC could be a potential marker for enhanced tumor aggressiveness. 19749090_Analysis of NK-cell clones revealed that alloreactive (KIR-ligand mismatched) but not autologous NK cells acquire CCR7. 19862774_Data revealed that DV infection enhances DC migration by inducing CCR7 expression, and that blocking COX-2 or MAPK activity suppresses DV-induced DC migration. 20029460_demonstrated that hypoxia induces T-cell apoptosis by the A(2)R signaling pathway partly by suppressing CCR7. 20036791_CCR7 gene plays role in lymph nodes and distant metastases in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20150960_SSTR5 and CCR7 have a role in Crohn's disease pathogenesis 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20439195_We studied a unique cohort of 21 primary lung cancers with matched adrenal metastases for the expression of CX3CR1, CXCR4, CCR6, and CCR7 20651394_VEGF-C and -D and CCR7 may play critical roles in lymphatic invasion in primary tumors. 20811680_our data indicate that CCR7 regulate cell adhesion and migration via beta1 integrin in metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck 20855251_The expressions of CCR5 and CCR7 on dendritic cells may correlate to the disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis. 20889506_the CCR7/CCL21 signaling pathway leading to T lymphocyte migration on fibronectin is a beta1 integrin-dependent pathway involving transient ERK1/2 phosphorylation, which is modulated by PLCgamma1 20889923_Studies indicate that improved prevention of graft-versus-host disease might be achieved by redirecting to lymph nodes adoptively transferred, alloreactive NK cells by inducing CCR7-uptake in vitro. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21071608_Human beta-defensin 3 represents a novel NF-kappaB-regulated mediator of CCR7 expression and anti-apoptotic pathways. 21081040_CCR7 induces lymph node metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer via upregulating MMP-9 expression. 21092675_The relative expression levels of CCR6 and CCR7 mRNA in tumor tissues with lymphatic metastases were significantly lower than those without lymph node metastases. 21165563_NF-kappaB is activated by CCR7 via PI3K/Akt/mTOR; this signal pathway plays an important role in regulating the cell survival and prognosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. 21165582_CCL19-induced chemokine receptor 7 activates the phosphoinositide-3 kinase-mediated invasive pathway through Cdc42 in metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. 21261017_CCR6 and CCR7 are expressed in metastatic lymph nodes and PBMC, and might play a role in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma development. 21347514_chemokine receptor 7 regulates cell adhesion and migration via integrin alpha v beta 3 in metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck 21464944_These results suggest a new combinatorial guiding mechanism by CCL19 and CCL21 for the migration and trafficking of CCR7 expressing leukocytes. 21548969_High CCR7 expression in T-NHL cells is significantly associated with lymphatic and distant dissemination as well as with tumor cell migration and invasion in vitro. 21594558_The chemotactic interaction between CCR7 and its ligand, CCL21, may be a critical event during progression in pancreatic cancer 21624121_In our series, unlike what was previously published, CCR7 was exclusively expressed on stromal cells and was not associated with survival. 21680174_RNAi-mediated silencing of VEGF-C inhibits non-small cell lung cancer progression by simultaneously down-regulating the CXCR4, CCR7, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3-dependent axes-induced ERK, p38 and AKT signalling pathways. 21698152_results suggest that CCL21/CCR7 contributes to the time-dependent proliferation of human NSCLC cells by upregulating cyclin A, cyclin B1, and CDK1 potentially via the ERK pathway 21731495_in contrast to HPIV3 and IAV, HMPV and HRSV did not efficiently decrease CCR1, 2, and 5 expression, and did not efficiently increase CCR7 expression. 21735098_PKCalpha is involved in the CCR7/NF-kappaB autocrine signaling loop in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck. 21739164_A(2A) adenosine receptor activation not only modulates CCR7 expression in both normal and inflammatory environments but also regulates macrophage migration to CCR7-specific chemoattractants. 21739671_Studies indicate that the mechanisms that regulate the retention of tissue-resident memory T cells include TGF-beta-mediated induction of CD103 and downregulation of CCR7. 21953548_The autoantigen DNA topoisomerase I interacts with chemokine receptor 7 and exerts cytokine-like effects on dermal fibroblasts. 22020953_Moderate-to-strong immunohistochemical CCR7 expression, found in 58 of 121 well-characterized human PDACs, correlated with high rates of lymph vessel invasion 22043010_we characterize a cross-talk between the TCR and CCR7 and provide mechanistic evidence that the activation status of T cells controls lymphocyte motility 22158872_an important biological role for inflammatory NF-kappaB and AP1 in the regulation of CCR7 expression in metastatic SCCHN. 22163030_Statins promote the beneficial remodeling of plaques in diseased mouse arteries through the stimulation of the CCR7 / CD68 emigration pathway in macrophages 22221265_Chemical shift mapping indicates that the CCR7 N-terminus binds to the N-loop and third beta-strand of CCL21's chemokine domain. 22251626_let-7a suppressed breast cancer cell migration and invasion by downregulating CCR7 expression. 22334704_the first report to link the two signaling events that control migration through the lymph nodes: CCR7 mediates entry into the lymph nodes and EDG-1 signaling controls their subsequent exit. 22350183_CCR7 overexpression correlated with expression of metallothionein, while CCR10 was associated with cerebral metastases. CCR7 and CCR10 overexpressions were associated with a worse outcome independent of Breslow's tumor thickness and Clark level. 22438908_CCL21/CCR7 prevents apoptosis by upregulating the expression of bcl-2 and by downregulating the expression of bax and caspase-3 potentially via the ERK pathway in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines 22498742_the use of trogocytosis as a tool to transiently express the chemokine receptor CCR7 on expanded human NK cells with the aim to enhance their homing to lymph nodes. 22533989_CCR7 seems to influence distinct immunological events during inflammatory responses in the central nervous system, including immune-cell entry and migration, and neuroglial interactions. 22619482_oxLDL induces an in vitro downregulation of CCR7 and CCL21, which may play a role in the reduction of dendritic cell migration from the plaques 22634622_Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) constitutively migrate into the splenic white pulp in a manner dependent on chemokine receptors CCR7 and CXCR4. 22659045_RhoA/ROCK pathway is essential for PGE2-mediated CCR7-dependent monocyte migration. 22718198_The results demonstrated that COX-2 up-regulates CCR7 expression via AKT-mediated phosphorylation and activation of Sp1 and that this pathway is highly activated in metastatic breast cancer. 22797918_The lack of CCR7 ubiquitylation profoundly impairs immune cell migration. 22821963_In a series of experiments, the yield of cultured CD8+CCR7+ T cells by the end of a 6-day induction period varies widely; loss of CD8+CCR7+ regulatory T (Treg) cells in the elderly may be of relevance in the aging immune system. 22923218_data suggest that CCR7 via Pyk2 and cofilin regulates the chemotaxis and migration ability of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck cells 22990666_A combination of Leishmania-reactive CCR7- T(effector memory) cells and Leishmania-reactive CCR7+ T(central memory) cells are identified in patients with a history of cutaneous leishmaniasis which may play a protective role against Leishmania infection. 23028633_a rise of CD56(bright) NK cells in HIV-infected individuals, which lack CCR7-expression and strongly correlate with HIV viral load 23290307_beta-arrestin 2 and CCR7 and PI3K phosphorylation have a role in bisoprolol reversed epinephrine-mediated inhibition of cell migration, in dendritic cells loaded with cholesterol 23363813_The CD8(+)CCR7(+) T-cell frequency in HNSCC patients' blood tested at diagnosis can discriminate them from normal controls and predicts disease recurrence 23449735_Human eosinophils express CCR7 and have multipotent responses to the known ligands of CCR7. 23469143_ChemR23 forms homomers, and provide data suggesting that ChemR23 also forms heteromers with the chemokine receptors CCR7 and CXCR4. 23498789_Results suggest that the CCL21/CCR7 signaling pathway is involved in renal fibrosis in kidney transplant patients. 23519840_Overexpression of CCR7 protein is associated with lymph node metastasis of gastric carcinoma. 23747721_The CCR7+CD45RA-CD27+CD28+ central memory subset is significantly decreased in the peripheral blood CD4+ T cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. 23888080_In the cord blood of children with respiratory syncytial virus disease there was downregulation of interleukin 7 receptor and chemokine receptor 7, and in the severe disease subcategory, downregulation of Toll-like receptor 4. 23922113_High CCR7 mRNA expressions indicated better prognoses than those of the groups with low CCR7 mRNA expressions. 23939705_Transwell assays revealed that VEGF-C receptor, VEGFR-3, as well as chemokine CCL21 receptor, CC chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7), were responsible for the migration of PC3 cells toward hypoxia preconditioned MSCs 24040244_High CCR7 expression in gastric cancer cells was significantly associated with poor overall survival and lymph node metastasis. 24052640_data suggest that CCR7 plays a role in uveal melanoma metastasis and is associated with poor survival. 24111618_CCR7 ligands CCL19 and CCL21 contribute to the accumulation of dendritic cells and alveolar macrophages in the inflamed lungs of patients with eosinophilic pneumonia. 24136650_This is the first report demonstrating the dissociation of CCR7 and MMP-9 expression in phenotypically mature CD83(+) dendritic cells by cervical cancer cells 24138884_Circulating precursor cd4+ T cells expressing CCR7(low)PD-1(high) CXCR5+ indicate T-helper cell activity and promote antibody responses upon antigen re-exposure. 24311382_In human histological sections of chronic thrombosed femoral veins, CCR7(+) cells were present in the fibrotic areas. 24411580_CCR7 is more likely to be expressed in mycosis fungoides skin lesions with subcutaneous involvement. Activation of CCR7 promotes migration of MyLa cells (MF cell line) through the mTOR pathway. 24595810_results indicate a regulatory influence of MR signaling on human T-cell migration and suggest a role for endogenous aldosterone in the redistribution of T-cell subsets to lymph nodes, involving CD62L, CCR7, and CXCR4. 24673602_The TRIMEL induces a phenotypic maturation and increases the expression of surface CCR7 on melanoma patient-derived DCs, and also on the monocytic/macrophage cell line THP-1. 24725321_The involvement of dendritic cells and their expression of CCR7 in corneal and ocular surface diseases such as in ocular allergy, dry eye disease, immune rejection and more, are also reviewed here. 24766770_These results demonstrated the significant clinicopathological relationship and functional causality between CCR7 expression and lymph node metastasis in ESCC patients. 24856897_Except for an increase in the number of C-C chemokine receptor 7-expressing DC from MS patients, no major differences were found between groups in the expression of maturation-associated membrane markers 24910430_Downmodulation of CCR7 did not involve degradation or endocytosis and was strictly dependent on Vpu expression. 24912620_Data indicated that CCR7 regulates cell chemotaxis and migration via MMP-9 in metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck. 24990231_Monocyte adhesion to HUVEC cells was induced by CCR7. CCR7 rs588019 was associated with coronary artery disease in a Chinese Han population. 25142946_Studied expression of CCR7 and EMT markers in the primary breast carcinoma tissues from patients who underwent radical mastectomy. and investigated whether CCL21/CCR7 induces EMT process during mediating cancer cell invasion or migration in vitro. 25168373_CCR7 can constitutively express in epithelial ovarian carcinomas and be induced rapidly in response to hypoxia, which indeed participates in EMT development and prompts the cell migration and invasion. 25255875_Suggest that CCRL1 impairs chemotactic events associated with CCR7 in the progression and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 25270024_Therefore, our study demonstrates that MAPK members (ERK1/2 and JNK) play a key role in CCR7 regulating SCCHN metastasis. 25318003_High expression of CCR-7 is associated with atherosclerotic arteries. 25327843_Our findings show that the molecular cues secreted by TALs alone or in combination with CCR7 may emerge as future therapeutic targets for lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients. 25405202_JAk2/STAT3 plays a key role in CCR7 regulatingSquamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck metastasis. 25425646_CCR7 can also promote survival of mDCs through a novel MEK1/2-ERK1/2-AMPK signaling axis. 25434638_CCR7 via RhoA/ROCK-Pyk2 cofilin pathway promotes invasion and migration of metastatic SCCHN cells 25556164_CCL21/CCR7 pathway activates signallings to up-regulate Slug pathway, leading to the occurrence of epithelial-mesenchymal transition process in human chondrosarcoma 25557171_Data indicate that inhibition of TGF-beta-activated protein kinase 1 (TAK1) reduces chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 7 (CCR7) expression. 25572817_our study suggested that CCR7 promotes Snail expression to induce the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, resulting in cell cycle progression, migration, and invasion in gastric cancer 25614627_Data indicate that coupling selectivity of chemokine receptors CCR2, CCR5, and CCR7 with G protein subtypes was measured and compared. 25636509_CrkL regulates CCL19 and CCR7-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via ERK signaling pathway in epithelial ovarian carcinoma patients. 25733353_Data show the effect of C-terminus mutation of CC chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7) on lymphocyte migration. 25744065_These results reveal that CCR7 and VEGF-C display a significant crosstalk and suggest a novel role of the CCL21/CCR7 chemokine axis in the promotion of breast cancer-induced lymphangiogenesis. 25961063_in given donor/recipient pairs, KIR2DS4 expression may contribute to potentiating natural killer cell function by increasing both the cytotoxicity and the expression of CCR7 on their surface. 25961925_Blockade of CCR7, or treatment with a p38 MAP kinase inhibitor, reduced lymphatic dissemination of epithelial-mesenchymal transition cells. 26115234_The solution structure of CCL19 is reported. It contains a canonical chemokine domain. Chemical shift mapping shows the N-termini of PSGL-1 and CCR7 have overlapping binding sites for CCL19 and binding is competitive. 26176983_the CCR7 axis mediates TGF-beta1-induced EMT via crosstalk with NF-kappaB signaling, facilitating lymph node metastasis and poorer overall survival in patients with gastric cancer 26179425_High CCR7 expression was associated with colorectal cancer metastasis. 26219899_CCR7 pathway up-regulates Twist expression via ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling to manage the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma 26231034_findings indicated that circulating memory Tfh cells, especially CCR7+ICOS+ memory Tfh cells, may be associated with the relapse of MS and may serve as a new therapeutic target 26282174_Recycling accounts, to a major extent, for the high levels of surface CXCR4/CCR7 on CLL cells. Increased CCR4/CCR7 is detectable not only in circulating leukemic cells, but also in secondary lymphoid organs of CLL patients with lymphoadenopathy. 26352169_Pyk2 is a key downstream signaling molecules of CCR7 in SCCHN, which promotes SCCHN tumorigenesis and progression. 26352871_Membrane associated PGES1dependent release of PGE2 is ccompanied by elevated CCR7 expression in colon cancer cells. 26616645_This study showed that CCR7 are overexpressed in CD4(-) CD8(-) thymocytes of myasthenia gravis patients. 26667143_Our findings suggested that MUC1 plays an important role in CCL21-CCR7-induced lymphatic metastasis and may serve as a therapeutic target in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma . 26722441_The present study demonstrated that down-regulation of CCR7 reduced proliferation, cell cycle, cell migration and invasion in prostate cancer cells 26819318_leukocyte subsets express distinct patterns of CCR7 sialylation that contribute to receptor signaling and fine-tuning chemotactic responses. 26884842_CCL21/CCR7 induce VEGF-D up-regulation and promote lymphangiogenesis via ERK/Akt pathway in lung cancer. 26923638_Constitutively expressed Siglec-9 inhibits LPS-induced CCR7, but enhances IL-4-induced CD200R expression in human macrophages. 26936935_tumor microenvironment stimulation down-regulated the migration of CCR7-expressing tumor cells toward CCL21 and inhibited the formation of directional protrusions toward CCL21 in a novel 3-dimensional hydrogel system. 26984468_High CCR7 expression is associated with gastric cancer. 27009073_Results indicated that CCR7 is overexpressed in gallbladder cancer tissues and its expression correlates with staging and lymph node metastasis. 27317472_we conclude that CCR7 gene locus harbours a polymorphism that modifies risk of MI in patients with Coronary artery disease (CAD). Replication of this association could be sought in a prospective cohort of initially healthy individuals 27421624_this study shows that plasmacytoid dendritic cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients have high expression levels of CCR7 27424807_CCR7 expression levels in human tumors correlate with signatures of CD141(+) DC, intratumoral T cells, and better clinical outcomes. 27505247_specific role for CCL21/CCR7 in promoting EMT and metastasis in CD133+ pancreatic cancer stem-like cells 27574129_CCL21/CCR7 interaction contributes to the time-dependent proliferation of PTC cells by upregulating cyclin A, cyclin B1 and cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) expression via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway associated with iodine. 27666723_This study suggests that NRP1 expression and LVD are independent factors that are likely to predict the risk of LN metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)of the tongue, whereas the expression of VEGFC, VEGFR3, CCR7, and SEMA3E are nonindependent predictive factors 27916085_Down-regulating CCR7 expression in MG63 cells could apparently inhibit cell proliferation, migration and invasion abilities of MG63 cells, and also induce cell apoptosis. 28011488_High CXCR4 expression in primary breast tumors (PTs) was found to be associated with luminal A type tumor, suggesting more favorable outcome. In contrast, CCR7 and FOXP3 expressions in PTs represented luminal B tumors, pointing to more aggressive tumor behavior. Maspin expression did not differ between luminal types. 28035134_These results suggest that upregulation of rat CCR7 expression does not change the phenotype, differentiation, or proliferation capacity of human adipose-derived stem cells (hASCs), but does enable efficient migration of hASCs to rat secondary lymphoid organs. 28112745_the acute GvHD (aGvHD) patients received higher percentage of CD4+CCR7+ T-cells in donor T-cells, whereas chronic GvHD (cGvHD) patients were transplanted with higher percentages of CD8+CCR7+ T-cells. Functional experiments demonstrated that CCR7+ T-cells exhibited higher potential for activation than CCR7- T-cells did. 28114889_High tumoral CCR7 expression correlated with potential lymphatic involvement and poor prognosis of metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. 28339080_Results show that upregulation of CCR7 promotes cell proliferation and inflammation in A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells. However, silencing of CCR7 via siRNA treatment promotes cell apoptosis and suppresses the inflammatory response and TGF-beta1-induced EMT, which may be associated with NF-kappaB signaling. 28378417_Study provide evidence that CCR7 mediates EMT progress via AKT pathway, which indicates that CCR7 has a key role in breast cancer progression. 28416768_CCL21/CCR7 interaction was shown to allow NK cell adhesion to endothelial cells (ECs) and its reduction by hypoxia. 28421995_Report an increased percentage of peripheral CCR7 T cells accompanied by endothelial dysfunction in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. 28487957_these results demonstrated that CCL21/CCR7 may activate EMT in lung cancer cells via the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. 28534984_High CCR7 expression is associated with urinary bladder cancer metastasis. 28535405_CXCR4, CCR7, VEGF-C and VEGF-D expression might have synergistic effects on the lymph node metastasis in patients with cervical cancer. 28729639_The research findings demonstrate for the first time that the chemokines CCL19, CCL21 and CCR7 play important roles in bone destruction by increasing osteoclast migration and resorption activity, and that has been linked to rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. 28767178_protein expression elevated in synovial tissue from osteoarthritis patients 28817313_that CCR7 mediates TGF-beta1-induced MMP2/9 expression through NF-kappaB signaling 28819198_Study indicates that chemokine receptor CCR7 (CCR7) homodimerization critically regulates CCR7 ligand-dependent cell migration and intracellular signalin | ENSMUSG00000037944 | Ccr7 | 321.574617 | 0.322195729 | -1.633991 | 0.10213213 | 261.332891 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000878983066008700247329242823600872030721593879320639733360341701959495364655833706904217465320974113955935955166123680668346508348567135 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000211986467712581022490134029587302873275250620961167761410674675460482764620014838547331274536597076100320546580748046052646255750404930 | Yes | No | 150.5930039 | 55.3494476 | 469.5566158 | 171.7859939 | |
| ENSG00000126709 | 2537 | IFI6 | protein_coding | P09912 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in apoptosis, negatively regulating the intrinsinc apoptotic signaling pathway and TNFSF10-induced apoptosis (PubMed:15685448, PubMed:17823654, PubMed:26244642). However, it has also been shown to have a pro-apoptotic activity (PubMed:27673746). Has an antiviral activity towards hepatitis C virus/HCV by inhibiting the EGFR signaling pathway, which activation is required for entry of the virus into cells (PubMed:25757571). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15685448, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17823654, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25757571, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26244642, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27673746}. | Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;Apoptosis;Immunity;Innate immunity;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene was first identified as one of the many genes induced by interferon. The encoded protein may play a critical role in the regulation of apoptosis. A minisatellite that consists of 26 repeats of a 12 nucleotide repeating element resembling the mammalian splice donor consensus sequence begins near the end of the second exon. Alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different isoforms by using the two downstream repeat units as splice donor sites have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:2537; | mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097190]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; immune response [GO:0006955]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097193]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043154]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:2001240]; negative regulation of mitochondrial depolarization [GO:0051902]; reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:0072593]; regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0042058]; release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0001836] | 15685448_G1P3 protein may have function as a cell survival protein by inhibiting mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis 17823654_IFN-alpha2b induced the expression of G1P3 and antagonized the TRAIL induced apoptosis in myeloma suggesting that either the deregulated or the induced expression of G1P3 could lead to apoptosis resistance in tumor cells. 18838000_Respiratory syncytial virus upregulated the mRNA expression of chemokines CC and CXC and interfered with type alpha/beta interferon-inducible gene expression by upregulation of MG11 and downregulation of G1P3. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20377629_PRINS regulates G1P3, a gene with anti-apoptotic effects in keratinocytes. siRNA-mediated inhibition of PRINS gene resulted in altered cell morphology and gene expression alterations. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21996729_Here we elucidate G1P3, a survival protein induced by interferons (IFNs), as a target of estrogen signaling and a contributor to poor outcomes in estrogen receptor-positive (ER(+)) breast cancer. 25757571_IFI6 inhibits HCV entry by impairing EGFR mediated CD81/CLDN1 interactions. This may be relevant to other virus entry processes employing EGFR. 26105982_In conclusion, over-expression of IFI6 promotes hepatitis C virus RNA replication and rescues the interferon alpha-mediated anti-hepatitis C virus activity. 27422384_In insulitic islets from living patients with recent-onset T1D, most of the overexpressed ISGs, including GBP1, TLR3, OAS1, EIF2AK2, HLA-E, IFI6, and STAT1, showed higher expression in the islet core compared with the peri-islet area containing the surrounding immune cells 28159892_Data suggest that p7 is a critical immune evasion protein that suppresses the antiviral interferon function by counteracting the function of IFI6-16. 29899394_Consequent to its localisation on inner-mitochondrial membrane, mtROS were higher in G1P3-expressing cells (MCF-7G1P3). This study identified that G1P3-induced mtROS have a direct role in migratory structure formation and nuclear gene expression to promote breast cancer cell metastasis. 29899394_G1P3-induced mtROS have a direct role in migratory structure formation and nuclear gene expression to promote breast cancer cell metastasis. Therefore, interrupting mitochondrial functions of G1P3 may improve clinical outcomes in breast cancer patients 30224801_Flavivirus replication at the ER is targeted by the interferon (IFN) response. Interferon alpha inducible protein 6 (IFI6) is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-localized integral membrane effector that is stabilized through interactions with the ER-resident heat shock protein 70 chaperone BiP. IFI6 prophylactically protects uninfected cells by preventing the formation of virus-induced ER membrane invaginations. 32727517_IFI6 depletion inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through reactive oxygen species accumulation via mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress. 33059972_Interferon-alpha inducible protein 6 (IFI6) confers protection against ionizing radiation in skin cells. 33539340_ATF3 downmodulates its new targets IFI6 and IFI27 to suppress the growth and migration of tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells. 33868257_The Functional and Antiviral Activity of Interferon Alpha-Inducible IFI6 Against Hepatitis B Virus Replication and Gene Expression. 35883685_IDO1, FAT10, IFI6, and GILT Are Involved in the Antiretroviral Activity of gamma-Interferon and IDO1 Restricts Retrovirus Infection by Autophagy Enhancement. | 1858.313206 | 0.349269691 | -1.517587 | 0.03824919 | 1627.206088 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 966.9330990 | 28.9605744 | 2781.3620017 | 74.3572853 | |||
| ENSG00000127586 | 63922 | CHTF18 | protein_coding | Q8WVB6 | FUNCTION: Chromosome cohesion factor involved in sister chromatid cohesion and fidelity of chromosome transmission. Component of one of the cell nuclear antigen loader complexes, CTF18-replication factor C (CTF18-RFC), which consists of CTF18, CTF8, DCC1, RFC2, RFC3, RFC4 and RFC5. The CTF18-RFC complex binds to single-stranded and primed DNAs and has weak ATPase activity that is stimulated by the presence of primed DNA, replication protein A (RPA) and by proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). The CTF18-RFC complex catalyzes the ATP-dependent loading of PCNA onto primed and gapped DNA. Interacts with and stimulates DNA polymerase POLH. During DNA repair synthesis, involved in loading DNA polymerase POLE at the sites of local damage (PubMed:20227374). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12766176, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12930902, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17545166, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20227374}. | Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell cycle;DNA replication;DNA-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a protein which is a component of a replication factor C (RFC) complex, which loads proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) on to DNA during the S phase of cell cycle. The encoded protein may interact with other proteins, including RFC complex 3, to form a clamp loader complex that plays a role in sister chromatid cohesion during metaphase-anaphase transition. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. | hsa:63922; | Ctf18 RFC-like complex [GO:0031390]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; DNA duplex unwinding [GO:0032508]; DNA replication [GO:0006260]; positive regulation of DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity [GO:1900264] | 12171929_identification as proliferating cell nuclear antigen-binding protein 12766176_hCTF18, hCTF8, and hDCC1 interact with each other as well as with the p38 subunit of RFC 12930902_The alternative Ctf18-Dcc1-Ctf8-replication factor C complex required for sister chromatid cohesion loads proliferating cell nuclear antigen onto DNA. 17545166_Ctf18-RFC interacts physically with pol eta, which allows DNA replication forks to overcome interference by various template structures, including damaged DNA and DNA-protein complexes that maintain chromosome cohesion 18499658_hChlR1 has a role in the establishment of sister chromatid cohesion, with Ctf18-RFC and Fen1 20826785_Stable interaction between the human proliferating cell nuclear antigen loader complex Ctf18-replication factor C (RFC) and DNA polymerase {epsilon} is mediated by the cohesion-specific subunits, Ctf18, Dcc1, and Ctf8. 23755103_This is the first report of somatic mutations within ESCO1 and CHTF18 in endometrial tumors and of MRE11A mutations in microsatellite-stable endometrial tumors. 27175616_CTF18 forms a complex with RPA when replication stress is elicited by hydroxyurea treatment or UV exposure during S phase. The interaction kinetics between CTF18 and RPA is positively associated with the phosphorylation status of Chk1. 28199690_Human CTF18-RFC clamp-loader complexed with non-synthesising POLE efficiently loads the PCNA sliding clamp. | ENSMUSG00000019214 | Chtf18 | 185.639686 | 0.447787376 | -1.159114 | 0.29023166 | 15.540993 | 0.0000807353716465841183885440712764136605983367189764976501464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0008555502868124384430181805782922310754656791687011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 105.0880223 | 20.1720883 | 236.2785946 | 44.9109999 | |
| ENSG00000128342 | 3976 | LIF | protein_coding | P15018 | FUNCTION: LIF has the capacity to induce terminal differentiation in leukemic cells. Its activities include the induction of hematopoietic differentiation in normal and myeloid leukemia cells, the induction of neuronal cell differentiation, and the stimulation of acute-phase protein synthesis in hepatocytes. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Pharmaceutical;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | The protein encoded by this gene is a pleiotropic cytokine with roles in several different systems. It is involved in the induction of hematopoietic differentiation in normal and myeloid leukemia cells, induction of neuronal cell differentiation, regulator of mesenchymal to epithelial conversion during kidney development, and may also have a role in immune tolerance at the maternal-fetal interface. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. | hsa:3976; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; leukemia inhibitory factor receptor binding [GO:0005146]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; blood vessel remodeling [GO:0001974]; decidualization [GO:0046697]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048144]; immune response [GO:0006955]; leukemia inhibitory factor signaling pathway [GO:0048861]; lung alveolus development [GO:0048286]; lung lobe morphogenesis [GO:0060463]; lung vasculature development [GO:0060426]; macrophage differentiation [GO:0030225]; meiotic nuclear division [GO:0140013]; muscle organ morphogenesis [GO:0048644]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of hormone secretion [GO:0046888]; negative regulation of meiotic nuclear division [GO:0045835]; neuron development [GO:0048666]; positive regulation of astrocyte differentiation [GO:0048711]; positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033630]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of histone H3-K27 acetylation [GO:1901676]; positive regulation of macrophage differentiation [GO:0045651]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of mesenchymal to epithelial transition involved in metanephros morphogenesis [GO:0072108]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0033141]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus [GO:1900182]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045595]; regulation of metanephric nephron tubule epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0072307]; regulation of RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:1903025]; somatic stem cell population maintenance [GO:0035019]; spongiotrophoblast differentiation [GO:0060708]; stem cell differentiation [GO:0048863]; trophoblast giant cell differentiation [GO:0060707]; tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0007260] | 11448119_LIF stimulates proliferation of rat pituitary tumor cells in culture, inhibits secretion of prolactin and growth hormone and induces tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT3 in the cells. 11587067_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11587067_The entire structure of the LIF gene of 48 alleles in the Japanese population was sequenced. 11811789_Oncostatin M and leukemia inhibitory factor regulate the growth of normal human breast epithelial cells 11855863_LIF does not activate STAT3, ERK, or gp130 receptor in human N tera-2/D1 EC cells. The suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS-1) is constitutively expressed, suggesting that LIF signal transduction is inhibited by elevated levels of SOCS-1 expression. 12153570_experimental N-Myc overexpression results in down-regulation of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), a modulator of endothelial cell proliferation 12218157_LIF stimulates (45)Ca release and enhances expression of receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL) and osteoprotegerin in neonatal mouse calvarial cultures, but has no effect on the expression of RANK. 12574225_role for LIF in loss of autocrine prolactin suppression contributing to unrestrained prolactinomas prolactin secretion. 12579339_LIF regulates cell survival of normal human endometrial stromal cells dose-dependently. 12707269_Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), cardiotrophin-1, and oncostatin M share structural binding determinants in the immunoglobulin-like domain of LIF receptor 12764151_LIF has a role in src family kinase-independent signal transduction and gene induction 12807438_Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) increased overall expansion of human neural precursor cells grown in culture; Following LIF withdrawal, 200 genes showed significant decreases 14557674_binding of ETS transcription factors to the ETS binding sites in the human LIF promoter is critical for its inducibility in response to T cell activators and play an important functional role within the endocrine-immune network. 14647442_role in hepatocyte growth factor expression 14687743_Decreased concentartion of LIF in infertile women do not seem to have a genetic basis due to the low frequency of LIF gene alterations. 14715713_Constitutive expression of cytokines in brain induces changes in gene expression characteristic of chronic inflammation leading to either temporal weight reduction (CNTF) or severe cachexia (leukemia inhibitory factor). 15044601_immunocytochemical staining and mRNA expression of LIF and its receptor are consistent with the concept that LIF might be involved in growth initiation of primordial follicles through its receptor 15180980_At early human post-implantation stage, LIF is produced from decidua and chorionic villi and may exert its action on trophoblasts. Anembryonic pregnancy cannot be accounted for by defective expression of either LIF or LIF-Rbeta in most circumstances. 15341921_Both IL-6 and LIF can be very efficiently induced by IL-1beta in articular chondrocytes in vitro, more so in osteosarthritis than in normal cells. 15342941_LIFRbeta and the signaling subunit gp130 are expressed in hESCs and human LIF can induce STAT3 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation in hESCs. 15543003_LCH represents a cytokine-driven condition partially mediated by TNF, IL-11, and LIF. These three cytokines are all osteoclastogenic, suggesting a pathogenetic pathway for the osteolytic lesions in LCH. 15670782_These results indicated that LIF induced multi-lineage differentiation of adult stem-like cells in kidney via cadherin 16. 15731310_role of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and its receptors in human embryo implantation 15837065_demonstrate using RNAi that Stat3 activation is necessary in the invasive phenotype of trophoblast cells and can be controlled via Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) 15905624_different members of the TGF-beta superfamily may also contribute in the reproductive process by enhancing endometrial proimplantatory LIF secretion and reducing proinflammatory IL-6 release by endometrial epithelium 16263181_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16295654_LIF plays an essential role in the preimplantation embryo development and the blastocyst implantation and its gene mutations in women contribute to the implantation failure and subsequent infertility. 16341766_Leukemia inhibitory factor concentration in follicular fluid is not a useful marker for the prediction of number and quality of embryos, or implantation and pregnancy rates. 16489116_Data show that increased leukemia inhibitory factor secretion enhances airway reactivity and intracellular calcium signaling. 16545901_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16545901_results suggest that the LIF gene mutations affect fertility 16648972_Since we demonstrated that not only SDF-1, but also HGF and LIF are upregulated in damaged tissues, we postulate that CXCR4+ c-Met+ LIF-R+ TCSC could be mobilized from the BM into the PB, where they play a role in tissue repair/regeneration. 16759928_Down-regulation of PRB in the endometrium is concomitant with the presence of glycodelin in the endometrium, suggesting interaction. 16949591_Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 may prevent leukemia inhibitory factor signaling in human embryonic stem cells. 17000646_There is no receptivity defect with regard to LIF and IL-11 secretions by eutopic endometrium in infertile women with endometriosis. 17054938_Ciliary neurotrophic factor/LIF signaling pathway acts via regulation of nitric oxide production to modulate developmental programmed cell death of postmitotic rod precursor cells. 17332938_The regulation of LIF and its receptor (LIFR) expression in pancreatic carcinoma cells were studied. 17652170_provides a structural template to understand the formation and orientation of the high-affinity signaling complex between LIF, LIF receptor, and gp130 17671691_interleukin-8 (CXCL-8) is induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and leukemia inhibitory factor in pancreatic carcinoma cells 17681328_Endometrial integrin beta3 and LIF expressions in the peri-implantation phase were significantly lower in stimulated cycles (including both moderate and high responders) compared to natural controls. 17702963_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17848619_LIF and IL6 skew monocyte differentiation into tumor-associated macrophage (TAM)-like cells by enabling monocytes to consume monocyte-CSF. Depletion of LIF, IL-6, and M-CSF in ovarian cancer ascites suppressed TAM-like cell induction 17966612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17966612_the LIF gene mutation, the heterozygote G to A transition on the position 3400, affects fertility but the infertility treatment can succeed. 17979974_Increased expression of some IL-6 cytokine family members (oncostatin M, gp130, CT-1, LIF) in cutaneous inflammation might contribute to the promotion of hair loss. 18042242_Increased LIF expression in peri-infarcted regions and sequestration from the peripheral circulation in acute stroke patients are characteristic of the pathobiological response to ischaemia and tissue damage. 18047677_Present predominantly in glandular epithelium. 18048043_higher levels found in the placentas of pre-eclamptic compared with normotensive women 18258286_Immunohistochemical labeling of LIF in the fallopian tube was found to be increased in ectopic pregnancies compared to non-pregnant and healthy pregnant controls 18298054_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18298054_The antiphospolipid antibodies (aPLs) are elevated in infertile women with LIF gene mutations. 18317962_secretion of OSM and LIF by both epithelial and stromal (paracrine manner) cells seems to promote tumor growth in human breast carcinoma 18468598_Leukemia inhibitory factor may be one of the reasons that cause patients with salpingitis to be more susceptible to tubal pregnancy and might be involved in the implantation process of tubal pregnancy. 18492704_LIF can regulate extravillous trophoblast invasion, suggesting an important role in early placental development. 18540977_Overexpression may be a potential molecular marker for predicting poor prognosis in patients with epithelial ovarian carcinoma. 18637760_LIF secretion is a predictor and indicator of early progenitor status in adult bone marrow stromal cells. 18639869_Results describe the role of leukemia inhibitory factor in human mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression. 18684446_Unexplained infertility in some women might be explained by disturbances in the LIF pathway in midsecretory-phase endometrium. 18953658_A potential role for LIF in the melanoma-induced bone metastasis possibly through the stimulation of osteoclastogenesis is suggested. 19011087_In silico models predicted that five of the up-regulated miRNAs targeted leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) expression 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19213836_IL-11 and LIF regulated endometrial epithelial cell adhesion, suggesting that targeting IL-11 and LIF may be useful in regulating fertility by either enhancing or blocking implantation. 19251277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19251277_results indicate that LIF 3' UTR StuI polymorphism is not associated with multiple sclerosis, however we cannot exclude the hypothesis that other polymorphic alleles of LIF could be implicated in MS susceptibility 19255255_hCG-mediated LIF expression in the endometrium is dependent on prior induction of PROK1. 19342253_Results indicate that leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and Oncostatin M increase the expression of MMP-1, MMP-3, and TIMP-1 several fold, and that their expression is reduced to basal levels in the presence of the LIF antagonist MH35-BD. 19361790_Leukemia inhibitory factor is dysregulated in the endometrium and uterine flushing fluid of women with adenomyosis during the implantation window. 19374770_LIF has a role in the optimization of the endometrium for embryo implantation. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19470478_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19495417_N-Myc regulates expression of pluripotency genes in neuroblastoma including lif, klf2, klf4, and lin28b 19541590_The key features of leukaemia inhibitory factor cytokine, its numerous physiological effects the most recent data are presented. Review. 19545488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19545488_The results suggest that in LIF gene mutation-positive women the idiopathic infertility and endometriosis have a negative impact on the outcome of IVF treatment. 19548631_The levels of E-selectin, ICAM-1, IL-11, IRF-1, IL-6, IL-1beta and LIF genes expression in the B. pseudomallei-infected cells were 1.5-5 times lower than in the B. thailandensis-infected cells. 19550366_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19647472_Studies indicate potential of LIF/IL11 as contraceptive targets and therapeutic agents for infertility. 19704963_The expression of mRNA isoforms for leukemia-inhibitory factor changes with embryonic and neonatal development, changes reflect a decrease in stimulatory influences on the expression and number of LIF-producing circulating cells 19751193_Studies indicate that leptin, CNTF, LIF and IL-6 present similar three-dimensional fold structure, interact with related class-I receptors and activate similar intracellular pathways. 19879916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20074285_LIF protein is expressed in Alzheimer's and Parkinson diseases. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20396801_Results describe the effects of 6-h marathon ultra-race on the levels of IL-6, leukemia inhibiting factor (LIF), and stem cell growth factor (SCF) in athletes. 20570039_Suggest that growth inhibition and activation of the autocrine/paracrine signaling through LIF/JAK/STAT may be a common response to Ras/Raf activation in different medullary thyroid carcinoma types. 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20597819_Wharton's jelly - and adipose tissue-mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCc) were more potent than BMbone marrow-MSCs in suppressing lymphocyte responses, and they mediated this effect by secreting high levels of leukemia inhibitory factor. 20618183_Patients with recurrent spontaneous abortion not only displayed a decrease in LIF expression but also had a reduced frequency of endometrial infiltrated CD4+ LIF+ cells in comparison with fertile women. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20851233_OPN, IL-6 and LIF may have critical roles in human pregnancy maintenance. 21129244_TGFbeta1, TNFalpha and LIF expressions showed increased level in the untreated patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia. 21155043_Serum concentrations of IL-6 family cytokines, including IL-6, IL-11, and LIF, were significantly elevated in patients with RA compared to those of healthy controls. 21178106_The cytokine LIF promotes trafficking of T-type calcium channel subunits in human HEK293 cells via transient activation of JAK- and ERK-kinase signaling pathways. 21191816_The epigenetic up-regulation of the LIF gene likely play an important role in the development of breast cancer. 21527666_LIF is a contraction-induced myokine, potentially acting in an autocrine or paracrine fashion to promote skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation. 21570299_LIF could be significantly involved in the pathophysiology of Multiple sclerosis 21613225_Extensive mannose phosphorylation on leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) controls its extracellular levels by multiple mechanisms. 21726338_MiR-141 has been significantly downregulated by more than 50% after leukemia inhibitory factor stimulation 21745467_stimulation with alpha(1)-adrenoceptor may enhance DNA synthesis and proliferation of mouse iPS cells cultured with LIF via augmentation of both the MEK/MAPK and the PI3K/Akt pathways 21966484_Study demonstrated that LIF was an important regulator of decidualization in humans and mice. 21987111_Endometrial HOXA11 and LIF mRNA expression levels (normalized to beta-actin expression) were significantly decreased in endometrium of infertile patients with endometriosis compared with healthy fertile controls 22142941_Addition of IL-4 or IL-13 had no effect on IL-6 expression, but significantly inhibited LIF and IL-11 mRNA and protein stimulated by IL-1beta and TNF-alpha. 22252755_No correlation was found between pinopodes development stage and LIF expressions in endometrium. 22285730_LIF expression might be regulated by microRNA-199a 22323722_LIF delivery can be harnessed to enhance the generation of oligodendrocytes that express myelin proteins and reform the nodes of Ranvier in the context of chronic demyelination in the adult mouse hippocampus. 22341639_LIF mRNA expression was significantly decreased in abnormal uterine cavities during the midsecretory phase, indicating that endometrial cavity defects are a possible cause of poor reproductive outcomes. 22436290_plasma concentrations is a predictive marker of in vitro fertilization outcome 22520363_LIF was expressed in endometrium of fertile women but significantly decreased in infertile women. Infertile women secreted significantly less LIF molecules in uterine flushing compared with fertile women. 22537815_there is an altered expression of LIF and IL-15 in the endometrium of women with recurrent implantation failure 22649064_Although leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and LIF receptors were increased in muscle tissue and myoblasts from diabetic patients, LIF signaling and LIF-induced cell proliferation were impaired in diabetic myoblasts. 22698642_Expression of LIF and integrin-beta3 (ITGB3) in the peri-implantation endometrium does not change in women with unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss. 22712053_Data show that LIF through STAT3 negatively regulates Th2 differentiation. 22720020_findings suggest that our LIF-dependent human iPSCs could provide a novel model to investigate the role of cytokine signaling in cellular reprogramming 22835519_LIF combined with VEGF can maintain the preliminary, progenitor phenotype of EPCs and alleviate cell differentiation by upregulating KLF4, which may provide new insights into transcriptional regulation in endothelial progenitor cells 22905257_Acyloxy nitroso compounds inhibit LIF signaling in endothelial cells and cardiac myocytes, showing that STAT3 signaling is redox-sensitive 23122949_Identification of novel molecules associated with a LIF-mediated increase in trophoblastic cell invasion may facilitate our understanding of implantation biology. 23541977_study found lower expression of LIF in the edndometrium in unexplained infertile women with multiple implantation failures compared to fertile women; data suggest that the initial lower expression of LIF in proliferative phase may be one of the causes for multiple failure of implantation 23628981_novel expression and purification protocol for the production of recombinant hLIF 23687977_Data show that the expressions of ER-alpha, PR, LIF, VEGF, iNOS and CB1 in fallopian tube and chorionic villi of tubal pregnancy were not altered by exposure to levonorgestrel emergency contraception. 23729555_Data from 3-year-old girl and other reported cases support model in which abundance of LIF in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia results in leukemic infiltration of central nervous system and development of Cushing syndrome. [CASE STUDY; REVIEW] 23831429_In summary, we can show that LIF is an important factor in melanoma progression. 23876532_Polyethylene glycated leukemia inhibitory factor antagonist inhibits human blastocyst implantation and triggers apoptosis by down-regulating embryonic AKT1. 23963683_Results show that endogenous levels of Pkig reciprocally regulate osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation and that this reciprocal regulation is mediated in part by LIF. 24074901_Data suggest LIF/LIF receptor (alpha subunit) signal transduction facilitates blastocyst implantation or development of tubal pregnancy by stimulating blastocyst adhesion and outgrowth/proliferation of placenta or Fallopian tube epithelial cells. 24270418_NPC patients had increased serum levels of LIF. Higher LIF levels correlated with local tumor recurrence. Xenograft mouse studies showed that LIF critically contributes to NPC tumor growth & radioresistance. 24310780_Addition of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) neutralizing antibodies inhibited oligodendrocyte differentiation, indicating a crucial role of TNFR2-induced astrocyte derived LIF for oligodendrocyte maturation 24664722_This mini review will summarize the findings that are related to LIF signaling and discuss the neuroprotective effects of LIF in different models. 24690239_The use of LIF in combination with alphanubeta3 integrin as biomarkers appears to be superior to integrin testing alone when evaluating endometrial receptivity, primarily because of its earlier pattern of expression during the secretory phase. 24857661_LIF mediates fibroblast activation to promote invasive tumor microenvironment. 25128195_An increased mRNA expression of PROK1 and LIF could be one of the several abnormalities characterizing the endometrium in women recurrent pregnancy loss. 25179300_Data indicate that NanoLuc-fusion strategy provided an efficient approach for preparation of recombinant leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) protein 25277705_Expression of LIF protects the lung from lung injury and enhanced pathology during respiratory syncytial virus infection. 25323535_LIF has a role in negatively regulating tumour-suppressor p53 through Stat3/ID1/MDM2 in colorectal cancers 25514345_LIF downregulates the autoimmune response by enhancing Treg numbers. 25790555_Studied the association of tubal pregnancy with leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR) expression in oviduct tissues. 25879318_LIF structure, signaling pathway, and primary roles in the development and function of an organism are reviewed--{REVIEW} 25885043_LIF/p21 signaling cascade as a novel tumor suppressive-like pathway in melanoma, acting downstream of TGFbeta to regulate cell cycle arrest and cell death, further highlight new potential therapeutic strategies for the treatment of cutaneous melanoma 26187859_Despite common signal transduction mechanisms (JAK/STAT, MAPK and PI3K) LIF can have paradoxically opposite effects in different cell types including stimulating or inhibiting each of cell proliferation, differentiation and survival. 26271643_LIF was frequently overexpressed in osteosarcoma, which could promote the growth and invasion through activating the STAT3 pathway. 26296968_Data show that leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) signaling promote chemoresistance in cholangiocarcinoma by up-regulating myeloid cell factor-1 (Mcl-1) via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/c-akt protein (AKT)-dependent pathway. 26615902_LIF SNP T/G (rs929271) seems to be a susceptibility biomarker capable of predicting implantation efficiency and pregnancy outcomes. 26716902_Overexpression of LIF promotes Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and results in cancer. 26723254_Taken together, we firstly demonstrate that LIF enhances the adhesion of trophoblastic cells to endometrial cells by up-regulating expression of integrin heterodimer alphaVbeta3 and alphaVbeta5. 26776907_Women with dormant genital tuberculosis were found to have decreased endometrial LIF-STAT3 signaling. 26817395_Cytokines of the LIF/CNTF family and metabolism 26817565_This review discusses the role of LIF and the recent analysis of its action on the uterine LE in regulating endometrial receptivity and implantation. 26984928_Although further studies would be required to deconvolute the targets involved in LIF induction and to confirm activity of hits in more disease-relevant assays, our results have demonstrated the potential of the phenotypic approach to identify specific and chemically tractable small molecules that trigger the production of LIF in relevant cell lines 27082016_Endometrial expression of LIF and LIFR is significantly reduced in the epithelial cells of infertile women. 27304912_Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) - STAT3 transcription factor (STAT3) signaling pathway is systemically dysregulated in in the endometrium of patients with recurrent/repeated implantation failure (RIFE). 28064096_In summary, this study has shown that LIF is implicated in the HG-mediated inhibition of osteoblast differentiation, via promoting STAT3/SOCS3 signaling. This study may provide insights into the signal pathway of HG-induced bone loss or delayed injured joint healing. 28246407_These findings implicate ZEB1 as a stem cell regulator in glioma via LIF repression which when deleted leads to increased stemness, tumorigenicity and shortened patient survival. 28247842_The expression of LIF was associated with tumor size and a poorer overall survival. Microarray and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction assessments suggest that LIF can facilitate tumor-promoting inflammation. Results indicate that LIF plays a role in maintaining cancer stem cells in chordomas. 28391028_findings illustrate that DeltaNp63alpha can inhibit the levels of LIF mRNA by direct transcription regulation and decrease LIF mRNA stability by suppressing the expression of Lnc-LIF-AS. An inverse interaction of LIF and DeltaNp63alpha expression was as well validated in clinical samples of cervical cancer, and high level of LIF in cervical cancers was related with poor patient survival. 28432985_study indicated impaired LIF expression levels only in women with unexplained infertility, while LIF-R expression was impaired in all sub-groups of infertile women. 28466814_SNP 3951C/T of LIF may not be associated with in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer outcome in Iranian population. 28512205_Data suggest a 216-nucleotide proximal cis-element in LIF mRNA exhibits mRNA destabilizing potential; on exposure to carcinogen PMA (phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate), this cis-element exhibits mRNA stabilizing activity. PMA induces nucleo-cytoplasmic translocation of both nucleolin and PCBP1, 2 trans-acting factors that bind to and stabilize LIF mRNA. [LIF = leukemia inhibitory factor; PCBP1 = poly(rC) binding protein 1] 28577574_ATF3 plays a significant role in regulating human endometrial receptivity and embryo attachment in vitro via up-regulation of leukemia inhibitory factor. 28729093_These results demonstrate the involvement of PIM kinases in LIF-induced regulation in different trophoblastic cell lines which may indicate similar functions in primary cells. 28755912_This report describes the involvement of proteins responsible for cell growth and progression and defines the LIF-mediated novel autocrine-paracrine signaling loop for cell growth arrest. 29038846_Decreased serum LIF levels may be associated with vasculopathy in systemic sclerosis (SSc) and that Fli1 deficiency may contribute to the inhibition of LIF-dependent biological effects on SSc endothelial cells by suppressing the expression of LIF, LIF receptor, and gp130. 29063331_The endometrial expression of LIF and CD34 in the pathogenesis of non-developing pregnancy can be used for evaluating the pregnancy prognosis in women of young and old reproductive age. 29269518_In serum from human PDAC patients, authors found that LIF titers positively correlated with intratumoral nerve density. 29393372_This study uses LIF to activate the PI3K/ AKT signal and induce the anti-inflammatory effect during the neuron differentiation from human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural precursor cells. 29397316_The findings indicate that low LIF concentrations in serum and follicular fluid may contribute to disordered folliculogenesis in polycystic ovary syndrome. 29605252_miR-181c-3p and -5p promotes high-glucose-induced dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by regulating leukemia inhibitory factor 30213486_Differential expression of LIF and IGF-1 in molar trophoblasts and chorionic villi might have a role in regulation of trophoblasts in complete moles. Decreased expression of glandular IGF-1 and decidual LIF might be related to the decidual changes during trophoblastic proliferation and invasion of decidua in complete HMs. 30242886_Low LIF expression is associated with myoma uteri. 30305729_Ruxolitinib-treated tumors in both the immunocompromised and immunocompetent animal models demonstrate decreased phospho-STAT3, indicating on-target activity. In conclusion, CA-MSC activate ovarian cancer cell STAT3 signaling via IL6 and LIF and increase tumor cell stemness. 30383471_Interplay Between Helicobacter pylori Infection, Interleukin-11, and Leukemia Inhibitory Factor in Gastric Cancer Among Egyptian Patients 30565675_Leukemia inhibitory factor inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by inducing G1-phase arrest. 30611552_The association between ESR1 and LIF polymorphisms can help in the prediction of recurrent implantation failure. 30664218_Although rhLIF had no effect on proliferation, it inhibited apoptosis of degenerated nucleus pulposus cells in a concentrationdependent manner. LIF was upregulated during the process of intervertebral disc degeneration, and may promote the expression of extracellular matrix components. 30996350_findings reveal a function of LIF in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis, and suggest its translational potential as an attractive therapeutic target and circulating marker; studies underscore how a better understanding of cell-cell communication within the tumour microenvironment can suggest novel strategies for cancer therapy 31296870_Study shows that LIF expression is induced specifically by oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDAC) and that LIF depletion by genetic means or by neutralizing antibodies prevents engraftment in pancreatic xenograft models. The related cytokine IL-6 cannot substitute for LIF, suggesting that LIF mediates KRAS-driven malignancies through a non-STAT-signaling pathway. 31586768_Identification of miRNAs and associated pathways regulated by Leukemia Inhibitory Factor in trophoblastic cell lines. 31615908_Epigenetic Profiling Identifies LIF as a Super-enhancer-Controlled Regulator of Stem Cell-like Properties in Osteosarcoma. 31854204_Study in eight datasets from four public databases revealed that LIF was highly expressed while LIFR was lowly expressed in pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAAD) tissues compared with adjacent or normal tissues. High LIF expression was associated with shorter overall survival whereas high LIFR expression was associated with longer overall survival confirming significance LIF and LIFR as biomarkers in PAAD. 31916327_EC yes-associated protein (YAP) is not only a critical coactivator of Hippo signalling in retinal vessel development but also plays an essential role in retinal astrocyte maturation by regulating LIF production. 32045772_Examined whether and how LIF regulates the behavior of macrophages and trophoblast cells in response to pro-inflammatory stress factors. We found that LIF modulated the activating effects of interferon-gamma and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in macrophages and trophoblast cells. 32324266_Impact of IFN-beta and LIF overexpression on human adipose-derived stem cells properties. 32504404_Polymorphism in the 3'-UTR of LIF but Not in the ATF6B Gene Associates with Schizophrenia Susceptibility: a Case-Control Study and In Silico Analyses. 32540613_LIF in embryo culture medium is a predictive marker for clinical pregnancy following IVF-ET of patients with fallopian tube obstruction. 32827446_Leukemia inhibitory factor promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via the LIFR-Hippo-YAP pathway. 32914874_Leukemia inhibitory factor is a novel biomarker to predict lymph node and distant metastasis in pancreatic cancer. 33004621_Autocrine Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Promotes Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression via Src Family Kinase-Dependent Yes-Associated Protein Activation. 33410420_Leukemia inhibitory factor: A main controller of breast cancer. 33555431_The expression and significance of leukemia inhibitory factor, interleukin-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor in Chinese patients with endometriosis. 33914392_Association of novel stop-gained leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene (rs121912501) variant, leukaemia inhibitory factor and ovarian steroids with unexplained infertility among Pakistani women. 33931487_Mutant KRAS Downregulates the Receptor for Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) to Enhance a Signature of Glycolysis in Pancreatic Cancer and Lung Cancer. 34074039_Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Conditioned Medium Promotes Endogenous Leukemia Inhibitory Factor to Attenuate Endotoxin-Induced Acute Lung Injury. 34265288_Tumor-derived LIF promotes chemoresistance via activating tumor-associated macrophages in gastric cancers. 34392367_Myeloid cell-mediated targeting of LIF to dystrophic muscle causes transient increases in muscle fiber lesions by disrupting the recruitment and dispersion of macrophages in muscle. 34416362_Plasma proteomics identifies leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) as a novel predictive biomarker of immune-checkpoint blockade resistance. 34815524_PCK1 regulates neuroendocrine differentiation in a positive feedback loop of LIF/ZBTB46 signalling in castration-resistant prostate cancer. 35012573_Endometrial injury concurrent with hysteroscopy increases the expression of Leukaemia inhibitory factor: a preliminary study. 35680099_The Pleiotropic role, functions and targeted therapies of LIF/LIFR axis in cancer: Old spectacles with new insights. | ENSMUSG00000034394 | Lif | 34.394716 | 0.304748546 | -1.714309 | 0.28173549 | 38.842449 | 0.0000000004594275724248638516531211816324711469383679229849803959950804710388183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000124544048121685963006471191383793539753099821609794162213802337646484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 16.0215424 | 4.6582985 | 52.7581042 | 14.2024622 | |
| ENSG00000128594 | 64101 | LRRC4 | protein_coding | Q9HBW1 | FUNCTION: Synaptic adhesion protein. Regulates the formation of exitatory synapses through the recruitment of pre-and-postsynaptic proteins. Organize the lamina/pathway-specific differentiation of dendrites. Plays an important role for auditory synaptic responses. Involved in the suppression of glioma (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | 3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene is significantly downregulated in primary brain tumors. The exact function of the protein encoded by this gene is unknown. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:64101; | dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; excitatory synapse [GO:0060076]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density membrane [GO:0098839]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; excitatory synapse assembly [GO:1904861]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; postsynaptic density protein 95 clustering [GO:0097119]; synaptic membrane adhesion [GO:0099560] | 15967442_LRRC4 may play an important role in maintaining normal function and suppressing tumorigenesis in the central nervous system. 16188120_LRRC4 gene might be involved in tumor suppression by restraining DNA synthesis and nucleoli organizer regions-associated proteins. 16215635_these studies represent the first cDNA array analysis of the effects of LRRC4 on the involvement of different neurobiological genes in U251MG glioblastoma cells and provide new insights into the function of LRRC4 in glioma 16723503_LRRC4 plays a major role in suppressing U251 cell proliferation by regulating the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/Akt/NF-kappaBp65, STAT3, and JNK2/c-Jun pathways. 16941076_LRRC4 may be a negative regulator of the RPTP-zeta receptor, and contribute to suppressing the invasion ability of gliomas cells 17541939_LRRC4 inhibits glioblastoma cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis by downgrading pleiotropic cytokine responses. 18976507_Methylation-mediated inactivation of LRRC4 is a frequent and glioma-specific event. 21435336_As a glioma suppressor, LRRC4 inhibits the endogenous expression of small regulatory microRNA hsa-miR-381 and decreases cell proliferation and tumor growth in cultured glioma cells. 21809374_Potentially, modulation of LRRC4 or STMN1 expression may be useful for design of new therapies for the intervention of glioma 22834685_LRRC4 inhibited the miR-185 pathway function in glioma 24404152_Disturbing miR-182 and -381 inhibits BRD7 transcription and glioma growth by directly targeting LRRC4. 24563334_polymorphisms and haplotypes in the LRRC4 may have a role in pituitary adenoma in a Chinese population 27612424_Results show a strong negative correlation between the expression of miR-381 and LRRC4 in osteosarcoma (OS) tissues, indicating LRRC4 as a direct target gene of miR-381. 27884160_Following EGF stimuli, the D domain of LRRC4 anchors ERK1/2 in the cytoplasm and abrogates ERK1/2 activation and nuclear translocation. 30790560_High LRRC4 expression is associated with Liposarcoma . 32372061_Leucine-rich repeat containing 4 act as an autophagy inhibitor that restores sensitivity of glioblastoma to temozolomide. | ENSMUSG00000049939 | Lrrc4 | 51.716173 | 2.642541156 | 1.401926 | 0.25640166 | 29.995039 | 0.0000000433153066022631160720590454051709405902670368959661573171615600585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000009056719114386494912951296176739646170972264371812343597412109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 70.2886586 | 9.5257598 | 26.6521333 | 4.1532981 | |
| ENSG00000128965 | 79094 | CHAC1 | protein_coding | Q9BUX1 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the cleavage of glutathione into 5-oxo-L-proline and a Cys-Gly dipeptide. Acts specifically on glutathione, but not on other gamma-glutamyl peptides (PubMed:27913623). Glutathione depletion is an important factor for apoptosis initiation and execution. Acts as a pro-apoptotic component of the unfolded protein response pathway by mediating the pro-apoptotic effects of the ATF4-ATF3-DDIT3/CHOP cascade (PubMed:19109178). Negative regulator of Notch signaling pathway involved in embryonic neurogenesis: acts by inhibiting Notch cleavage by furin, maintaining Notch in an immature inactive form, thereby promoting neurogenesis in embryos (PubMed:22445366). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19109178, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22445366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27913623}. | Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Golgi apparatus;Lyase;Neurogenesis;Notch signaling pathway;Reference proteome;Unfolded protein response | This gene encodes a member of the gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase family of proteins. The encoded protein has been shown to promote neuronal differentiation by deglycination of the Notch receptor, which prevents receptor maturation and inhibits Notch signaling. This protein may also play a role in the unfolded protein response, and in regulation of glutathione levels and oxidative balance in the cell. Elevated expression of this gene may indicate increased risk of cancer recurrence among breast and ovarian cancer patients. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. | hsa:79094; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase activity [GO:0003839]; glutathione specific gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase activity [GO:0061928]; Notch binding [GO:0005112]; glutathione biosynthetic process [GO:0006750]; glutathione catabolic process [GO:0006751]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0070059]; negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045746]; negative regulation of protein processing [GO:0010955]; neurogenesis [GO:0022008]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986] | 22108517_High CHAC1 mRNA expression could be an independent indicator for elevated risk of cancer recurrence in breast and ovarian cancer 23342279_nisin exerts these effects on HNSCC, in part, through CHAC1, a proapoptotic cation transport regulator, and through a concomitant CHAC1-independent influx of extracellular calcium 24767995_Botch regulates Notch signaling through deglycination and identify a posttranslational modification of Notch that plays an important role in neurogenesis. 25931127_Human CHAC1 Protein Degrades Glutathione, and mRNA Induction Is Regulated by the Transcription Factors ATF4 and ATF3 and a Bipartite ATF/CRE Regulatory Element. 27986595_Temozolomide (TMZ)-mediated gene expression profiles and networks are involved in inducing glioblastoma cell death. Increased CHAC1 and reduced Notch3 levels are both also significantly involved in TMZ-mediated cytotoxicity. The TMZ-regulated CHAC1 pathway inhibits Notch3 activation, resulting in attenuation of Notch3-mediated signaling pathways. 29054545_The data revealed that CHAC2 prevented CHAC1-mediated GSH degradation, which suggests that CHAC2 competes with CHAC1 to maintain GSH homeostasis. 30555487_results suggest that CHAC1 is involved in the regulation of inflammation in bronchial cells during Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection and may explain the excessive inflammation present in the respiratory tracts of patients with cystic fibrosis. 31111570_Significant CHAC1 overexpression was detected in H. pylori-infected parietal cells that expressed the human proton pump/H,K-ATPase alpha subunit. 32949369_Transcriptomic analysis of the effect of (E)-3-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(2-methoxyphenyl) prop-2-en-1-one (DPP23) on reactive oxygen species generation in MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells. 33728749_Ferroptosis-related gene CHAC1 is a valid indicator for the poor prognosis of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. 35930144_High levels of unfolded protein response component CHAC1 associates with cancer progression signatures in malignant breast cancer tissues. | ENSMUSG00000027313 | Chac1 | 21.749740 | 0.498049584 | -1.005639 | 0.35527709 | 8.118947 | 0.0043805001096093518220264684259745990857481956481933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0257455611484099233798872319312067702412605285644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 14.7183583 | 4.3330005 | 29.6272680 | 8.1730687 | |
| ENSG00000130368 | 4142 | MAS1 | protein_coding | P04201 | FUNCTION: Receptor for angiotensin 1-7 (By similarity). Acts specifically as a functional antagonist of AGTR1 (angiotensin-2 type 1 receptor), although it up-regulates AGTR1 receptor levels. Positive regulation of AGTR1 levels occurs through activation of the G-proteins GNA11 and GNAQ, and stimulation of the protein kinase C signaling cascade. The antagonist effect on AGTR1 function is probably due to AGTR1 being physically altered by MAS1. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15809376, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16611642}. | Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Proto-oncogene;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a class I seven-transmembrane G-protein-coupled receptor. The encoded protein is a receptor for angiotensin-(1-7) and preferentially couples to the Gq protein, activating the phospholipase C signaling pathway. The encoded protein may play a role in multiple processes including hypotension, smooth muscle relaxation and cardioprotection by mediating the effects of angiotensin-(1-7). [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]. | hsa:4142; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; angiotensin receptor activity [GO:0001595]; angiotensin type II receptor activity [GO:0004945]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; peptide binding [GO:0042277]; activation of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activity [GO:0007250]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; hippocampus development [GO:0021766]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA replication [GO:0045740]; positive regulation of inositol phosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0060732]; protein kinase C signaling [GO:0070528]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; response to activity [GO:0014823]; response to gonadotropin [GO:0034698]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] | 16611642_the ability of MAS to up-regulate AT(1) receptor levels reflects the constitutive capacity of MAS to activate Galpha(q)/Galpha(11) and hence stimulate PKC-dependent phosphorylation of the AT(1) receptor 18636314_Mas, MrgD, and MRG mediated Ang IV-stimulated AA release that was highest for Mas. While Ang III activated Mas and MrgX2, Ang II stimulated AA release via Mas and MRG. 19164480_The vasoactive peptide angiotensin-(1-7), its receptor Mas and the angiotensin-converting enzyme type 2 are expressed in the human endometrium. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19461648_the Mas oncogene acts as a receptor for Angiotensin (1-7)--REVIEW 20361351_The immunolocalization of Ang-(1-7) and its receptor Mas in testes of fertile and infertile men suggests that this system may be altered when spermatogenesis is severely impaired. 20592051_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20674894_Angiotensin-(1-7), its receptor Mas, and ACE2 are expressed in the human ovary 21316680_Report expression (pro)renin receptors and angiotensin converting enzyme 2/angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas receptor axis in human aortic valve stenosis. 22003054_Activation of Mas during myocardial infarction contributes to ischemia-reperfusion injury and suggest that inhibition of Mas-G(q) signaling may provide a new therapeutic strategy directed at cardioprotection. 22048948_MasR was significantly upregulated in colon adenocarcinoma compared with non-neoplastic colon mucosa, which showed little or no expression of it. ACE gene expression and enzymatic activity were also increased in the tumors. 23459756_Mas appears to be a critical component required for NO-mediated vasodilatation induced by renin angiotensin system-dependent and RAS-independent agonists and therefore arises as a key pharmacological target to modulate endothelial function 23488800_Data suggest that angiotensin converting enzyme 2/angiotensin II-(1-7)/MAS1 axis regulates leukocyte recruitment/activation, cell proliferation, and inflammation/fibrosis; main topic here is kidney/inflammatory renal disease. [REVIEW] 23592774_Control of adipogenesis by the autocrine interplays between angiotensin 1-7/Mas receptor and angiotensin II/AT1 receptor signaling pathways. 24128372_A proximal promoter construct for the MAS gene was repressed by the SOX [SRY (sex-determining region on the Y chromosome) box] proteins SRY, SOX2, SOX3 and SOX14, of which SRY is known to interact with the KRAB domain. 24168260_Up-regulation of the ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas axis protected against pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the MAPK/NF-kappaB pathway. 25068582_Data show that MAS receptor exhibited constitutive activity that was inhibited by the non-peptide inverse agonist. 26080617_MAS1 might act as an inhibitory regulator of breast cancer. 26225830_Ang-(1-7) downregulated AT1R mRNA, upregulated mRNA levels of Ang II type 2 receptor (AT2R) and Mas receptor (MasR) and p38-MAPK phosphorylation and suppressed H22 cell-endothelial cell communication 26883384_These results indicated that angiotensin-(1-7)/ACE2/Mas axis may reduce liver lipid accumulation partly by regulating lipid-metabolizing genes through ATP/P2 receptor/CaM signaling pathway. 26995300_Here, we review the role and effects of ACE2, ACE2 activators, Ang-(1-7) and synthetic Mas receptor agonists in the control of inflammation and fibrosis in cardiovascular and renal diseases and as counter-regulators of the ACE-Ang II-AT1 axis. 27063099_Downregulation of ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas axis stimulates breast cancer metastasis through the activation of store-operated calcium entry and PAK1/NF-kappaB/Snail1 pathways. 28599664_High levels of MAS is associated with angiogenesis in bladder cancer. 28747140_These findings suggest that mitochondrial assembly receptor signaling may be a promising novel target for oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. 29052864_These findings suggest a critical role for MasR in cardiomyocyte survival. 29351514_ANG-(1-7) acts on the receptor MAS to influence a range of mechanisms in the heart, kidney, brain, and other tissues. [review] 29982252_High MAS1 expression in the endometrium might promote the initiation of endometriosis via migration of proliferative tissue. 30055537_We have hypothesized the mechanism that reverses the downregulation of the ACE2-angiotensin 1-7/Mas receptor axis path and the upregulation of angiotensin receptor type 1-mediated signaling. Thus, we posit that ACE2, Ang-(1-7), and the Mas receptor could be novel therapeutic targets for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia . 30581499_MAS1 expression in the left atrium in mitral regurgitation patients significantly differed from those in aortic valve disease patients and normal controls. 31642813_The production of ANG 1-7 was significantly lower in breast cancer cells, whereas the expression of MAS receptor was higher than that in the control breast tissue cells. This finding suggests that substances with MAS receptor agonist activity could be useful in the treatment of breast cancer. 31843339_Ang-(1-7) stimulates beige markers and thermogenesis via the Mas receptor. 32599080_Angiotensin- and angiotensin-(1-7) imbalance affects comorbidity of depression and coronary heart disease. 32764118_Oestrogen-mediated upregulation of the Mas receptor contributes to sex differences in acute lung injury and lung vascular barrier regulation. 32777324_Impact of angiotensin II type 1 and G-protein-coupled Mas receptor expression on the pulmonary performance of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 32875393_Localization of angiotensin-(1-7) and Mas receptor in the rat ovary throughout the estrous cycle. 33511992_ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas1 axis and the vascular system: vasoprotection to COVID-19-associated vascular disease. 34124808_Human placenta mesenchymal stem cell protection in ischemic stroke is angiotensin converting enzyme-2 and masR receptor-dependent. 35328506_Neuroinflammation and COVID-19 Ischemic Stroke Recovery-Evolving Evidence for the Mediating Roles of the ACE2/Angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas Receptor Axis and NLRP3 Inflammasome. 35363333_The function of the ACE2/Ang(1-7)/Mas receptor axis of the renin-angiotensin system in myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. 36148474_Sex Difference in MasR Expression and Functions in the Renal System. | ENSMUSG00000068037 | Mas1 | 177.383307 | 0.251767718 | -1.989835 | 0.12804172 | 258.562657 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003530416021680969180824202060130999125701302779809114595088561676410501905869420785108985845999733656272460908406879655770748225641199609 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000837007784936837304253481804744624620606679765726343760679122388092812878191136509070109998679359307313956006111633605499755637768502620 | Yes | No | 71.9949064 | 15.9320450 | 287.3109062 | 61.6807801 | |
| ENSG00000130477 | 23025 | UNC13A | protein_coding | Q9UPW8 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in vesicle maturation during exocytosis as a target of the diacylglycerol second messenger pathway. Involved in neurotransmitter release by acting in synaptic vesicle priming prior to vesicle fusion and participates in the activity-dependent refilling of readily releasable vesicle pool (RRP). Essential for synaptic vesicle maturation in most excitatory/glutamatergic but not inhibitory/GABA-mediated synapses. Facilitates neuronal dense core vesicles fusion as well as controls the location and efficiency of their synaptic release (By similarity). Also involved in secretory granule priming in insulin secretion. Plays a role in dendrite formation by melanocytes (PubMed:23999003). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q4KUS2, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62768, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23999003}. | Calcium;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;Exocytosis;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a member of the UNC13 family. UNC13 proteins bind to phorbol esters and diacylglycerol and play important roles in neurotransmitter release at synapses. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in this gene may be associated with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. | hsa:23025; | neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; presynaptic active zone cytoplasmic component [GO:0098831]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; terminal bouton [GO:0043195]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; diacylglycerol binding [GO:0019992]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; syntaxin-1 binding [GO:0017075]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; dense core granule priming [GO:0061789]; neuromuscular junction development [GO:0007528]; neuronal dense core vesicle exocytosis [GO:0099011]; neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0007269]; positive regulation of dendrite extension [GO:1903861]; presynaptic dense core vesicle exocytosis [GO:0099525]; regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0051966]; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0035249]; synaptic vesicle docking [GO:0016081]; synaptic vesicle maturation [GO:0016188]; synaptic vesicle priming [GO:0016082] | 19734901_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19734901_rs12608932 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism is located at 19p13.3 and maps to a haplotype block within the boundaries of UNC13A, which regulates the release of neurotransmitters such as glutamate at neuromuscular synapses. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20385924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20385924_Results do not provide evidence of an association between a variant in the UNC13A gene and susceptibility to sporadic Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in a French homogeneous population. 22118904_Our results further corroborate the role of UNC13A in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pathogenesis. 22248876_Here, we report that, like Rab3A, RIM and Munc13 are present in human sperm and that they play a functional role in acrosomal exocytosis before the acrosomal calcium efflux 22921269_This study demonistrated that UNC13A influences survival in Italian amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. 23801330_CAPS1 binds to the full-length of cytoplasmic syntaxin-1 with preference to its 'open' conformation, whereas Munc13-1 binds to the first 80 N-terminal residues of syntaxin-1. 23830992_Munc13-1, on account of its role in both insulin and neurotransmitter exocytosis and through its binding properties, may be an important factor contributing to the development or progression of diabetic neuropathy. 24931836_UNC13A provides a novel link between amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia and identifies changes in neurotransmitter release and synaptic function as a converging mechanism in the pathogenesis of ALS and FTD-TDP. 26162714_UNC13A rs12608932 is a risk factor for ALS and a modifying factor for survival and disease progression rate in a Spanish cohort. 27584932_This study demonstrated that the population specific rare variants of UNC13A may modulate survival in ALS in United kingdom. 28192369_Synaptic UNC13A protein variant causes increased neurotransmission and dyskinetic movement disorder 30368160_Its polymorphism contributes to frontotemporal disease in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 31201598_rs12608932(C) is associated with increased ALS susceptibility, especially in Caucasian and European subjects, and that the CC genotype of rs12608932 is associated with reduced ALS patient survival. 32627229_The Distinct Traits of the UNC13A Polymorphism in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. 33818064_Probing the Diacylglycerol Binding Site of Presynaptic Munc13-1. 35197626_TDP-43 represses cryptic exon inclusion in the FTD-ALS gene UNC13A. 35197628_TDP-43 loss and ALS-risk SNPs drive mis-splicing and depletion of UNC13A. | ENSMUSG00000034799 | Unc13a | 23.287767 | 0.340888494 | -1.552628 | 0.39298585 | 15.406157 | 0.0000867053015976275187918706488510167673666728660464286804199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0009126434393085531681516497926054398703854531049728393554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 12.3525107 | 4.3235835 | 36.2528882 | 12.5820672 | |
| ENSG00000130590 | 140700 | SAMD10 | protein_coding | Q9BYL1 | Reference proteome | Predicted to be involved in transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. Predicted to be active in cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:140700; | cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] | ENSMUSG00000038605 | Samd10 | 14.336074 | 0.401618643 | -1.316102 | 0.47126922 | 7.834656 | 0.0051253907350862935518587271133128524525091052055358886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0292270548725589371374944391845929203554987907409667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 7.8595496 | 2.3885612 | 19.4351848 | 5.2841948 | |||
| ENSG00000130714 | 10585 | POMT1 | protein_coding | Q9Y6A1 | FUNCTION: Transfers mannosyl residues to the hydroxyl group of serine or threonine residues. Coexpression of both POMT1 and POMT2 is necessary for enzyme activity, expression of either POMT1 or POMT2 alone is insufficient (PubMed:12369018, PubMed:14699049, PubMed:28512129). Essentially dedicated to O-mannosylation of alpha-DAG1 and few other proteins but not of cadherins and protocaherins (PubMed:28512129). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12369018, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14699049, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28512129}. | Alternative splicing;Congenital muscular dystrophy;Disease variant;Dystroglycanopathy;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Lissencephaly;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. | The protein encoded by this gene is an O-mannosyltransferase that requires interaction with the product of the POMT2 gene for enzymatic function. The encoded protein is found in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. Defects in this gene are a cause of Walker-Warburg syndrome (WWS) and limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2K (LGMD2K). Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. | hsa:10585; | acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0016529]; dolichyl-phosphate-mannose-protein mannosyltransferase activity [GO:0004169]; mannosyltransferase activity [GO:0000030]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; positive regulation of protein O-linked glycosylation [GO:1904100]; protein O-linked glycosylation [GO:0006493]; protein O-linked mannosylation [GO:0035269] | 12369018_Mutations in the O-mannosyltransferase gene POMT1 give rise to the severe neuronal migration disorder Walker-Warburg syndrome 12757935_Extracellular matrix and nuclear abnormalities in skeletal muscle of a patient with Walker-Warburg syndrome caused by POMT1 mutation. 14699049_active enzyme complex of POMT1 and POMT2 suggests that the regulation of protein O-mannosylation is complex and appears to be required for normal structure and function of alpha-dystroglycan in muscle and brain 15037715_The authors report on a patient with Walker-Warburg syndrome and a novel POMT1 mutation. The patient expressed alpha-dystroglycan core protein, but fully glycosylated alpha-DG antibody epitopes were absent, associated with loss of laminin-binding activity 15522202_Results indicate that mutations in the protein O-mannosyltransferase 1 gene result in a defect of protein O-mannosylation in Walker-Warburg syndrome patients. 15792865_the phenotype of glycosylation disorders linked to POMT1 mutations. Furthermore, the A200P mutation is part of a conserved core haplotype, indicating an ancestral founder mutation. 16698797_human protein O-mannosyltransferases 1 and 2 form heterocomplexes which possess protein O-mannosyltransferase activity 16887026_Several mutations were found in the Protein O-Mannosyltransferase 1 and 2 (POMT1 and POMT2) genes, and one mutation was found in each of the fukutin and fukutin-related protein (FKRP) genes. 17079174_An inverse Alu-repeated DNA element within exon 3 is associated with Walker Warburg syndrome in French Caucasian families. 17869517_In conclusion, the lymphoblast-based enzymatic assay is a sensitive and useful method (i) to select patients harbouring POMGNT1, POMT1 or POMT2 mutations; (ii) to assess the pathogenicity of new or already described mutations. 17878207_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18513969_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18513969_Thirteen CMD patients showed mutations in POMT1, But normal brain MRI associated with mental retardation and microcephaly. mutations in POMT1 (six out of 13). 18647264_We conclude that a significant increase of POMT1 missense mutations may indicate a functional role in neoplastic conditions in individual glioneuronal and glial brain tumors. 19299310_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19519795_A double homozygous mutation in the POMT1 gene in two unrelated Gypsy families, is reported. 19639522_pyramidal neurons frequently displayed abnormal (oblique, horizontal, or inverted) orientation in a 2.5-month-old infant with Walker-Warburg syndrome homozygotic for a novel POMT1 gene mutation 19880378_the N-glycosylation of POMT1 and POMT2 is required for maintaining the conformation as well as the activity of the POMT1-POMT2 complex. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20816175_the function of the gene products is only known for POMT1, POMT2, and POMGnT1, all responsible for the O-mannosylglycan biosynthesis 21782786_the effects of replacing Arg(64), Glu(78) and Arg(138)residues in human POMT1 and POMT2 with Ala on complex formation and enzymatic activity were studied. 22549409_Three patients with heterozygous POMT1 mutations showed left ventricular (LV) dilation and/or decrease in myocardial contractile force. 24491487_report of 2 male siblings and an unrelated female with early onset muscular dystrophy and intellectual disability with minimal structural brain anomalies and no ocular abnormalities; a novel missense mutation (c.1958C>T; p.Pro653Leu) was identified 26245304_Inhibition of POMT1/2 in human mesencyhmal stem cells , resulted in complete abolishment of chondrogenesis and alterations of adipogenic and osteogenic potential together with a lethal effect during myogenic induction. 27193224_Our results suggest that POMT activity is inversely proportional to clinical severity, and demonstrate that skin fibroblasts can be used for differential diagnosis of patients with alpha-dystroglycanopathies. We have provided clinical, histological, enzymatic and genetic evidence of POMT1 involvement in five unrelated Chinese patients. 27358400_results demonstrate functional and biochemical similarities between POMT1 and its orthologue from bakers' yeast Pmt4. 28157257_These findings may expand phenotype and mutation spectrum of the POMT1 gene. Clinical diagnosis supplemented with molecular screening may result in more accurate diagnoses of, prognoses for, and improved genetic counselling for this disease 28512129_O-mannosylation of cadherins and protocadherins does not require POMT1 and/or POMT2 in contrast to alpha-dystroglycan, and moreover, the O-Man glycans on cadherins are not elongated. 29419866_The child was found to carry a heterozygous missense mutation c.1939G>A (p.Ala647Thr) in exon 19 of the protein-O-mannosyltransferase 1 (POMT1) gene inherited from the mother and a heterozygous frameshift mutation c.2141delG (p.Trp714Ter) in exon 20 inherited from the father. 30454682_In this review, we highlight the present knowledge of the identified disease-associated POMT1 gene mutations and genetic animal models related to the POMT1 gene. 33863907_Enhanced influenza A H1N1 T cell epitope recognition and cross-reactivity to protein-O-mannosyltransferase 1 in Pandemrix-associated narcolepsy type 1. 34565739_POMT1 and POMT2 gene mutations result in 2 cases of alpha-dystroglycanopathy.', trans 'POMT1POMT22alpha-. | ENSMUSG00000039254 | Pomt1 | 219.291915 | 2.123803011 | 1.086650 | 0.38036748 | 7.948835 | 0.0048118340882278322345744214771912083961069583892822265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0277444085845552010360925976328871911391615867614746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 281.1049125 | 127.9742784 | 128.0221592 | 58.2486252 |
| ENSG00000131203 | 3620 | IDO1 | protein_coding | P14902 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the first and rate limiting step of the catabolism of the essential amino acid tryptophan along the kynurenine pathway (PubMed:17671174). Involved in the peripheral immune tolerance, contributing to maintain homeostasis by preventing autoimmunity or immunopathology that would result from uncontrolled and overreacting immune responses (PubMed:25691885). Tryptophan shortage inhibits T lymphocytes division and accumulation of tryptophan catabolites induces T-cell apoptosis and differentiation of regulatory T-cells (PubMed:25691885). Acts as a suppressor of anti-tumor immunity (PubMed:23103127, PubMed:25157255, PubMed:14502282, PubMed:25691885). Limits the growth of intracellular pathogens by depriving tryptophan (PubMed:25691885). Protects the fetus from maternal immune rejection (PubMed:25691885). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14502282, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17671174, ECO:0000303|PubMed:23103127, ECO:0000303|PubMed:25157255, ECO:0000303|PubMed:25691885}. | 3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Dioxygenase;Direct protein sequencing;Heme;Immunity;Iron;Metal-binding;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Tryptophan catabolism | PATHWAY: Amino-acid degradation; L-tryptophan degradation via kynurenine pathway; L-kynurenine from L-tryptophan: step 1/2. | This gene encodes indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) - a heme enzyme that catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in tryptophan catabolism to N-formyl-kynurenine. This enzyme acts on multiple tryptophan substrates including D-tryptophan, L-tryptophan, 5-hydroxy-tryptophan, tryptamine, and serotonin. This enzyme is thought to play a role in a variety of pathophysiological processes such as antimicrobial and antitumor defense, neuropathology, immunoregulation, and antioxidant activity. Through its expression in dendritic cells, monocytes, and macrophages this enzyme modulates T-cell behavior by its peri-cellular catabolization of the essential amino acid tryptophan.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. | hsa:3620; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; smooth muscle contractile fiber [GO:0030485]; stereocilium bundle [GO:0032421]; electron transfer activity [GO:0009055]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity [GO:0033754]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase activity [GO:0004833]; 'de novo' NAD biosynthetic process from tryptophan [GO:0034354]; female pregnancy [GO:0007565]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; kynurenic acid biosynthetic process [GO:0034276]; multicellular organismal response to stress [GO:0033555]; negative regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032693]; negative regulation of T cell apoptotic process [GO:0070233]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; positive regulation of chronic inflammatory response [GO:0002678]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of T cell apoptotic process [GO:0070234]; positive regulation of T cell tolerance induction [GO:0002666]; positive regulation of type 2 immune response [GO:0002830]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; swimming behavior [GO:0036269]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098]; tryptophan catabolic process [GO:0006569]; tryptophan catabolic process to kynurenine [GO:0019441] | 11867636_heme environment--structural properties and substrate-ligand interactions 11987129_Data show that overexpression of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase is present in Crohn's disease as well as in ulcerative colitis, but nit in diverticulitis, as compared to normal mucosa. 12186837_inhibition of allogeneic T cell proliferation by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-expressing dendritic cells: mediation of suppression by tryptophan metabolites 12228717_describe a subset of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells that use IDO to inhibit T cell proliferation in vitro 12471139_Induction of IDO in airway epithelial-like tumor cells by exposure to IFN-gamma for 24 hr markedly amplifies IL-6 and IL-8 responses via depletion of tryptophan from the culture medium. 12766158_Asp274 and his346 are essential for heme binding and catalytic function of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 12938169_Data show that indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-expressing fibroblasts embedded within collagen gel suppress the proliferation of allogenic immune cells, while they still remain viable in a tryptophan-deficient culture environment. 12963490_one important consequence of increasing IDO activity in astroglial cells during inflammation is to maintain NAD levels through de novo synthesis from tryptophan. 13678429_characterization of regulatory sequences involved in the synergistic transcriptional activation of the indoleamine dioxygenase gene by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. 14502282_Data show that most human tumors constitutively express indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), and that expression of IDO by immunogenic mouse tumor cells prevents their rejection by preimmunized mice. 14871294_indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is necessary for cytolytic activity of natural killer cells. 14969766_Downregulation of MHC class I expression by Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase(IDO) might be one of the mechanisms through which IDO mediates local immunosuppression. 15001472_Bone marrow stromal cells express IDO protein and exhibit functional IDO activity upon stimulation with IFN-gamma. 15070879_despite suppression by progesterone, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression in endometrial stromal cells may increase during decidualization due to stimulation by interferon-gamma secreted by infiltrating leukocytes. 15102781_RT4 cells were able to inhibit the growth of Staphylococcus aureus in an IDO-mediated fashion, and this bacteriostatic effect was abolished by endogenously produced NO. 15245429_stimulation with interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) induces the expression of functionally active IDO in highly purified human epidermal Langerhans cells 15254595_Data suggest that indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated suppression by plasmacytoid dendritic cells in tumor-draining lymph nodes creates a local microenvironment that is potently suppressive of host antitumor T cell responses. 15374002_HSV-2 antiviral effect of type II interferon and TNF-alpha is dependent on IDO activation. 15528322_IDO induction in eosinophils is a potential mechanism in the regulation of T helper type 2 (Th2) cell polarization. 15711557_Findings indicate that attenuated Bin1 causes elevation of IDO and immune escape of cancers in mice. Additionally, small molecule inhibitors of IDO reverse the effects of Bin1 loss and leverage the efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs in cancer. 15919929_IFN-gamma-induced enzyme IDO plays an important antiviral role in Measles Virus infections of epithelial, endothelial, and astroglial cells. 15947091_indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase (IDO) activity is induced in a two-step process during dendritic cell maturation 15950064_the function of IDO and kynurenine hydroxylase may change from a role in immunosuppression at the maternal-fetal interface in early pregnancy, to one associated with regulation of fetoplacental blood flow or placental metabolism in late gestation 15967116_Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is expressed not by tumor cells, but by normal cells infiltrating the peritumoral stroma 16135011_A high T-helper type 1 (Th1)/Th2 cell ratio is more likely to cause loss of an allogeneic embryo in early pregnancy than is the loss of putative protection by reduced uterine levels of IDO. 16176799_In this review, the unique catalytic properties of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase are described, and the recent findings regarding the dioxygenase-initiated tryptophan metabolism are summarized. 16319139_HO-1/IDO cross-regulation modulates apoptosis and proliferation in rat and human breast cancer cells 16406698_examine the arguments for and against a function of IDO-expressing human dendritic cells (DCs) and conclude that proof for an immunoregulatory role in vivo is still lacking 16421220_CTLA-4 on regulatory T cells up-regulates IDO expression on decidual and peripheral blood dendritic cells and monocytes by the induction of IFN-gamma production. 16477023_X-ray crystal structure of human IDO, complexed with the ligand inhibitor 4-phenylimidazole and cyanide was reported. 16489067_IDO significantly contributes to disease progression and overall survival in patients with colorectal cancer. 16511306_purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray study of human IDO 16513157_Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase may have a role in the decline of T cell responses in immunosenescence 16686756_The variable expression of IDO in different endothelial cells is important not only in understanding the role of endothelial cells in the regulation of graft rejection, but also as a potential therapeutic strategy. 16834326_These data provide the first glimpse of the possible regulatory mechanism of hIDO by NO and suggest that the NO-dependent regulation can be modulated by cellular factors, such as the NO abundance, pH, redox environment, and L-Trp availability. 16842443_reduced IDO activity found in the macrophages of patients with hepatitis C virus infection suggest the infection may hamper macrophage functions 17015408_Sleeping beuaty-bsed human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase represents a new strategy for treating lung transplantation-associated chronic complications in rats. 17038913_Recombinant antithymocyte globulin inhibits maturation of immature dendritic cells and llows the generation of dendritic cells expressing indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. 17170728_Acute myelocytic leukemia cells expresse INDO mRNA, but not IDO protein when exposed to optimal concentrations of IFN-gamma. 17182891_hCG can upregulate human trophoblast indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase, which probably plays a key role at maternal fetal interface in preventing fetal rejection. 17192467_IDO activation may protect islet cells from cytotoxic damage by interferon gamma. 17202379_TNF-alpha enhanced TLR ligand-induced IL-8 production in human gingival fibroblasts 17229698_Induction of IDO may dampen T-cell reactivity to viral antigens in chronic hepatitis C virus infection 17294609_change in the clinical course of multiple sclerosis observed in pregnancy may be related to the estrogen-dendritic cell-IDO axis 17318080_CD123/CCR6 dendritic cells (DCs) do not constitutively express IDO and 'induced' IDO DCs 17321596_From the expression pattern we conclude that IDO may play a central role in human pregnancies for the establishment of maternal tolerance of fetal antigens 17393386_Review discusses the immunoregulatory pathway of tryptophan catabolism initiated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) as a bidirectional feedback loop that could be part of an integrated response for preventing excessive inflammation and autoimmunity. 17433037_IDO expression at the invasive front of cancer cells and APC, and the localization of Foxp3(+) Treg cells in front of cancer tissues, may create a network between IDO and Treg for the 17535808_NO inhibits rhIDO activity reversibly by binding to the active site heme to trap the enzyme as an inactive nitrosyl-Fe(II) enzyme adduct with Trp bound and O2 displaced 17605849_Human acute monocyte leukemia and acute lymphocyte leukemia express indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase. 17626075_poly(I:C)induction of IDO was mediated in part by IFN-beta but not IFN-gamma, and both NF-kappaB and interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) were required. 17674321_The levels of intralesional expression of mRNA of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interferon, interleukin-10, RANTES, and indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase in Mediterranean spotted fever are reported; levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase are also reported. 17711549_Transfected into rats, reduces vascular permeability and leukocyte extravasation, and consequently improves graft function and histologic appearance. 17911610_Interferon gamma-inducible expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase by human vascular smooth muscle cells inhibits allogeneic T cell activation, proliferation, and accumulation in vitro and in vivo. 17951526_indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and prostaglandin E2 represent key mediators of the Mesenchymal stem cells-induced inhibition of NK cells 18008147_The finding of this study revealed that the proliferation of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells are suppressed in response to tryptophan deficient environment caused by IDO expression and it is more so for CD8+ T than CD4+ T cells. 18036645_The present study has demonstrated for the first time that baseline IDO enzymatic activity in induced sputum from asthmatic patients is very low compared with that seen in nonasthmatic control subjects and is inversely related to sputum eosinophilia. 18045970_Any possible antitumor effects of dextro-1-methyl tryptophan cannot be attributed to abrogation of IDO activity in dendritic cells. 18055547_Type I IFN-mediated skin disorders, such as lichen planus , strongly express IDO in lesional skin. 18176870_We submit that an impaired IDO induction characterizes PBC (primary biliary cirrhosis)and might represent a contributing factor in disease pathogenesis in association with several specific defects in the target tissue 18205804_it is suggested that tryptophan depletion via IFN-gamma-mediated IDO induction is a major antibacterial, antiparasitic, antiviral and immunoregulatory mechanism in human lung cells. 18274832_are differences and similarities between biochemical behaviour and structural features of recombinant human IDO and recombinant mouse IDO 18299324_Cytochrome b(5) rather than O(2)(*-) plays a major role in the activation of IDO in human cells. 18332894_transgenic expression of IDO in xenografts contributes to prolonged graft survival 18370410_reveal significant differences between the IDO and tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO) enzymes, and the implications of these results are discussed in terms of our current understanding of IDO and TDO catalysis 18438685_IDO may be a novel favorable prognostic indicator and candidate adjuvant therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. 18622801_IDO is a sensitive marker of atherosclerosis--or the inflammatory response associated with it--but does not have an independent role in the pathogenesis of this disease. 18639339_In patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the serum kynurenine/tryptophan ratio (Kyn/Trp) was raised, suggesting a higher IDO activity than in healthy people 18660700_considerable potential for immunoregulation and antigen-specific tolerance induction in transplantation 18776940_differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells into Tregs with suppressive function was primarily dependent on plasmacytoid dendritic cell expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 18802343_increased activity is associated with asymptomatic atopy during seasonal allergen exposure 18832696_IDO pathway is essential for PDC-driven Treg generation from CD4(+)CD25(-) T cells and implicate the generation of kynurenine pathway metabolites as the critical mediator of this process. 19004406_Hydatidiform moles express IDO, but the majority of gestational trophoblastic tumors do not express this enzyme, suggesting that IDO-mediated immunoregulation is unlikely to be a major component of the malignant phenotype in these tumors. 19010841_IDO overexpression in human cancer cells contributes to tumor progression in vivo with suppression of NK cells 19050070_determined INDO mRNA expression in leukemic blasts of 286 patients with acute myeloid leukemia by gene-expression profiling; high INDO expression is a strong negative independent predicting variable for overall and relapse-free survival 19058839_House dust mite-sensitive DCs exposed to Der p 1 downregulated IDO activity and tipped the T(H)1/T(H)2 cytokine balance toward IL-4, resulting in sustainable IDO suppression. 19074858_IDO is critically involved in tumor resistance to repeated treatments with IFNgamma-NGR, likely causing excessive stimulation of tryptophan catabolism and inhibiting antitumor immune mechanisms 19106591_significance of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) in recurrent breast cancer patients during chemotherapy 19155537_IDO activity and serum levels of tryptophan catabolites of the kynurenine pathway increase with chronic kidney disease (CKD) severity. In CKD, induction of IDO may primarily be a consequence of chronic inflammation. 19168733_Role in the suppressive activity of intralesional Treg cells during acute and chronic cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania guyanensis. 19264674_Our results demonstrate that IDO plays an important role in the antiviral effect of IFN-gamma against DENV infection in vitro and suggest that it has a role in the immune response to DENV infections in vivo. 19306922_Elevation of intracellular iron levels during stimulation with IFNgamma impeded IFNgamma-induced IDO mRNA and protein expression. 19353519_Induction of IDO1 by TLR involved an autocrine interferon (IFN)-beta signaling loop, which was dependent on protein kinase R 19363598_Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-expression in antigen-presenting cells (APCs) may control autoimmune responses by depleting the available tryptophan, whereas tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase (TTS) may counteract this effect 19434461_Imaging correlates of differential expression of IDO1 in brain neoplasms are reported. 19448397_These data support the notion that metastatic malignant melanoma cells select for expression of IDO to evade immunologic detection. 19465693_priming of resting T cells with autologous, IDO-expressing, mature moDCs results in up to 10-fold expansion of CD4(+)CD25(bright)Foxp3(+)CD127(neg) Tregs. 19487045_These results suggest that increased IDO activity is involved in disease progression of lung cancer, possibly through its immunosuppressive effect. 19489917_INDO showed significant associations with Aspirin-intolerant asthma. 19514129_Identification of genetic variants in the human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO1) gene, which have altered enzyme activity 19564344_impaired cytotoxic function seen in the IDO-treated CD8(+) T cells was accompanied by defects in production of granule cytotoxic proteins, including perforin and granzyme A and B 19597340_rhIDO significantly inhibited IL-2 expression in CHO cells. It decreased proliferative response & increased apoptosis in human T cells. IDO suppressed Vav1 mRNA & protein production in T cells. IDO inhibited TCR-activation-induced Vav1 phosphorylation. 19604093_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19604349_Foxp3 and IDO expression is associated with sentinel lymph node metastases in breast cancer 19693771_These results suggest that the activation of NF-kappaB through the PI3K-PKC-reactive oxygen species and PI3K-Akt pathways is required for the Hb-induced IDO expression in bone marrow dendritic cells. 19695096_Data show that high density indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)+ cells exist in tumor-draining lymph nodes and that IDO is down-regulated in lymph nodes with metastases, implying that IDO in tumor and immune cells functions differently. 19737010_Presented is evidence supporting the presence of an inhibitory substrate binding site in IDO that is capable of binding the substrates (L-Trp and 1-methyl-L-tryptophan), an effector (3-indole ethanol), and an uncompetitive inhibitor (Mitomycin C). 19740345_Inhibition of IDO expression with both classes of siRNAs inhibited dendritic cells immunosuppressive function on T-cell proliferation 19783182_Plasma IDO activity does not reflect the degree of lung graft acceptance, but instead is correlated with the degree of chronic inflammation. 19815714_Results suggest that functional thymic indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-positive eosinophils during human infant life may have an immunomodulatory role in Th2 immune responses. 19828629_IDO1-mediated tryptophan depletion induces transcriptional repressor B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein-1 (BLIMP-1) in U937 cells. 19829303_IDO positive plasmacytoid dendritic cells are the classical BDCA2 positive cells in melanoma lymph nodes 19844741_increased IDO expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas is from a mixed cellular source (both cancer cells and noncancerous cells) 19929471_Dendritic cells polarizing culture conditions increased expression of IDO protein and IDO enzyme activity. 19933867_Activated T cells can induce functional IDO expression in breast and kidney tumor cell lines. IDO is expressed in the majority of breast and kidney carcinoma samples, with infiltration of activated T helper type 1-polarized T cells in human tumors. 20128646_The expression of IDO may in part explain retinal pigment epithelial mediated immune suppression effects. 20192952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20192952_Variation 'c.-147_150delGAAA' in the 5'-untranslated region of the IDO1 gene does not appear to be a primary cause of pre-eclampsia. 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20361220_subtle differences between the TDO and IDO reactions 20386557_mediates immunosuppressive properties of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells 20484731_Postulate that induction of IDO may represent a critical initiating event that results in inversion of the T(H)17/T(reg) balance and in the consequent maintenance of a chronic inflammatory state in progressive HIV disease. 20522587_Human IDO transfected into composite three-dimensional islet grafts in mice, prolongs the islet allograft. 20570568_In human chronic granulomatous disease (CGD)IDO metabolic activity is intact. Reactive oxygen intermediates apparently are dispensable for IDO activity. Thus, hyperinflammation in human CGD cannot be attributed to disabled IDO activation. 20635895_Studies suggest that increased IDO activity may play an activating role in the autoimmune response. 20648630_Data suggest that high expression of protein IMPACT homolog in non-immune cells acts as a protective mechanism against indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-induced GCN2 activation, making them resistant to the amino acid-deprived environment caused by IDO. 20663292_Data show elevated levels of 3-HK modifications and the upstream, rate-limiting enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO-1) in Alzheimer's diseased brains when compared to controls. 20689575_Psychological stress stimulates cytokine-driven IDO1 activation and Trp depletion which seems to have a central role for developing stress-induced immunosuppression and behavioral alteration. 20801903_Data identify indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated catabolism as a tolerogenic mechanism exerted by leukemic dendritic cells and have clinical implications for the use of these cells for active immunotherapy of leukemia. 20938662_Data suggest that indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) activity might play a role in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and cells that express IDO appear important for determining outcomes after R-CHOP treatment. 21028817_Binding of CO to l-Trp-bound IDO causes a significant change in the electronic and RR spectra of the heme, indicating that the pi* orbitals of the carbon atom of CO interact with pi orbitals of Fe and the porphyrin 21030093_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21030093_study concludes that there is no association between INDO polymorphisms and susceptibility of Iranian women to recurrent spontaneous abortion 21094802_Patients receiving belatacept showed greater amounts of peripheral blood CD16+/IDO+ cells and Tregs on graft biopsies than those under cyclosporine treatment. 21118329_[review] Induction of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase and quinolinic acid mediates seizure activity in multiple sclerosis at least in part via an increase in interferon (IFN)gamma. 21176371_Thymosin alpha1 can up-regulate the expression of ido mRNA in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from children with aplastic anemia. 21292009_Compared to healthy volunteers, IDO concentration was twice as high in hemodialysis patients, which contributed to inadequate immune response to HBV vaccination. 21324164_Data suggest an inflammatory response characterized by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activation may be relevant to the development of post-stroke cognitive impairment. 21328335_Loss of indoleamine 23-dioxygenase is associated with basal-like breast carcinoma. 21355883_High IDO Dioxygenase is associated with acute graft-versus-host disease. 21359206_IFN-gamma inhibited proliferation and altered human and mouse MSC neural, adipocytic and osteocytic differentiation via the activation of IDO. 21361337_Studies indicate that the heme dioxygenases are differentiated by their ability to catalyze the oxidation of l-tryptophan to N-formylkynurenine. 21461563_The intensity of IDO immunostaining was lower in the preeclamptic placentae than in the normal controls, and was related to the clinical severity of the preeclampsia. 21461581_IDO plays a key role in gastric cancer immune suppression, possibly by inhibiting T cell-mediated cytotoxicity and proliferation in vitro. 21487895_These results suggest that the activity of IDO enzyme is insufficient in immune thrombocytopenia patients. 21501890_in infectious, but also in noninfectious human cutaneous granulomas the large myeloid CD11c(+)S100(+)CD68(-) dendritic cells and the CD68(+) macrophages express IDO. 21502325_analysis of ferryl derivatives of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 21517752_This article reviews the interplay between indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 in chronic inflammation and cancer. 21517753_This review offers a survey of preclinical literature suggesting that IDO functions as a modifier of inflammatory states rather than simply as a suppressor of immune function. 21517755_The paper suggests that IDO may represent an important regulatory checkpoint influencing Regulatory T cells activity: both by stabilizing and augmenting the suppressive phenotype, and by preventing reprogramming into non-suppressive helper-like cells. 21517756_IDO is widely expressed in human tissues and cell subsets, including dendritic cells, where it modulates their function by increasing tolerogenic capacities. 21517757_As it is comprehensively reviewed, IDO competence in human dendritic cells, in general, is induced by molecules such as interferon-gamma, which otherwise initiate immunity. 21575365_Treatment with thymosin alpha1 downregulated TLR9 expression but upregulated IDO expression in a concentration- and time-dependent manner in aplastic anemia mesenchymal stem cells. 21592112_data suggest that M. leprae chronic infection activates the suppressive molecule IDO which, in turn, contributes to the specific immunosuppression observed in lepromatous leprosy 21600662_In women, IDO activity moderated the association between depressive symptoms and carotid intimamedia thickness (IMT), so that a longitudinal association between depressive symptoms and IMT was found only in combination with high IDO activity 21616522_indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression seems to be an independent prognostic factor in patients with vulvar squamous cell carcinoma . 21617756_It is possible that the substitution c.422+90G-->A; rs4613984 in an intron downstream to exon 4 of indoleamine 2, 3- dioxygenase (IDO) may be related with cataract formation among the aged. 21690092_trace amounts of peroxide previously proposed to occur in NADH solutions as well as solid NADH activate IDO and lead to aerobic formation of superoxide and the reactive dioxygen adduct of the enzyme. 21691274_The findings in Caucasians further support the notion that IDO has an important role in cytokine-induced behavioral changes. 21692032_IDO expression in lower lip squamous cell carcinoma may aid immune escape and chronic inflammation to promote cancer progression. 21693183_Our results suggest no influence of the variants in the IDO gene and the diagnosis of interferon-alpha-related depression in the Brazilian population. 21712776_Somatization is characterized by increased IDO activity 21742973_the ability of IDO-expressing tumor cells to thrive in a tryptophan-depleted microenvironment by expressing a novel, highly tryptophan-specific transporter, which is resistant to inhibition by most other amino acids 21755000_A gradient of vascular endothelial IDO1 expression is present at both sides of the feto-maternal interface. 21823214_High Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase-1 is associated with Crohn's disease. 21835147_The proportion of CD4(+)IDO(+) T cells was significantly higher in patients with moderate GVHD. 21835273_Purification and kinetic characterization of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenases 1 and 2 (IDO1 and IDO2) and discovery of selective IDO1 inhibitors. 21892828_The data suggest that IDO uses a ring-opening mechanism during N-formylkynurenine formation, rather than Criegee or dioxetane mechanisms as previously proposed. 21952237_ligation of TLR-3 by poly(I:C) induces IDO expression in human first-trimester trophoblasts via an IFN-beta-dependent pathway 21980470_identification of a variable number of tandem repeats polymorphism in IDO1 promoter and characterization of LEF-1 response elements 22013481_high expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma correlates with impaired overall survival time 22039265_Data suggest a strong association of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) activity with the severity and outcome of clinical graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). 22069308_a novel role for interleukin-27 (IL-27) as mediator of intestinal epithelial barrier protection mediated via DMBT1 and IDO1 22093628_Expression of IDO is associated with clinical stage, lymph node metastasis, and microvessel density in breast cancer. 22110525_upregulated expression in primary breast cancer correlates with increase of infiltrated regulatory T cells and lymph node metastasis 22112045_Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression and serum kynurenine concentrations in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 22184722_T cells isolated from the hepatocellular carcinoma tissues expressed significantly more CD69 molecules than did those on paired circulating and nontumor-infiltrating T cells; these tumor-derived CD69(+) T cells could induce considerable IDO in monocytes 22202241_expression of IDO did not correlate to histologic classification, tumor size, lymphatic invasion, venous invasion and lymph nodes metastasis, but it was correlated to clinical stage 22301793_although IDO is not required by MDM for the clearance of established viral infection, the spread of flavivirus infection is limited by IDO expressed in uninfected, neighboring cells. 22424783_zebularine plus interferon gamma induce IDO1 gene expression related to demethylation events in the IDO1 promoter region and to up-regulation of expression of transcription factors 22519828_results show that cholera toxin per se does not induce the expression of functional IDO protein 22526360_The expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in dendritic cells of immune thrombocytopenia patients was significantly decreased. 22592557_IDO1 activation represents a local compensatory mechanism to limit obesity-induced inflammation and hypertension. 22638210_IDO1 is possibly involved in endometriosis pathogenesis via promoting COX-2 and MMP-9 expression and regulation of endometrial stromal cells biological characteristics 22690871_The cystine/glutamate antiporter regulates the functional expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in human dendritic cells. 22722711_Data indicate that indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is expressed in primary MMCs to a low degree and is unlikely to play a direct major role in vivo in dampening antitumor immunity. 22751107_observed elevated plasma IDO activity in patients with both pain and depression 22828446_High IDO expression is associated with acute graft-versus-host disease. 22860140_Activation of IDO1 appeared to be a defensive mechanism downstream of IFN-gamma that limited intracellular expansion of Orientia tsutsugamushi via tryptophan depletion. 22891315_IDO inserts oxygen into indole in a reaction that is mechanistically analogous to the 'peroxide shunt' pathway of cytochrome P450. 22913669_Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and prostaglandin E-2 are key modulators involved in the mesoangioblast suppression of T-cell proliferation. 22923135_IDO downregulation enhanced the sensitivity of cervical cancer cells to natural killer cells in vitro and promoted NK cell accumulation in the tumor stroma in vivo. 22929065_Data suggest that IDO activity may be a risk factor for future depression especially in women. IDO-induced alterations in serotonergic function may offer one biologic explanation to the well-established associations between inflammation and depression. 22932670_A critical role for IDO-mediated immunosuppression in glioma. 22936460_The upregulation of IDO1 in peripheral blood dendritic cells after maturation was significantly reduced in immune thrombocytopenia. 23090116_Systemic delivery of Salmonella typhimurium transformed with IDO shRNA enhances intratumoral vector colonization and suppresses tumor growth. 23109825_Downregulation of CD4 expression by IDO was significantly attenuated by the addition of tryptophan or IDO inhibitor in the infected C8166 cells. 23179760_Tumoral indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase express-ion predicts poor outcome in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 23200754_Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase gene polymorphisms correlate with CD8+ Treg impairment in systemic sclerosis. 23209301_IDO has a novel function of catalyzing physiological peroxidase reactions. 23232072_These data suggest that IDO1 expression may contribute to immune suppression in patients with multiple myeloma and possibly other hepatocyte growth factor-producing cancers. 23289444_IDO plays an important role in the pregnancy-specific immune tolerance, and might be a contributing factor in the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia. 23344392_Indoleamine 2-3 dioxygenase (IDO1) is expressed in breast cancer tissue, as shown by immunohistochemistry. Expression is lower in ER- breast tumors with greater neoangiogenesis. 23358471_Freshly-resected meningiomas expressed both LAT1, the tryptophan transporter system and IDO, demonstrating an active kynurenine pathway. Dissociated meningioma cells lost IDO expression. 23411497_Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-1 (IDO1) enhances survival and invasiveness of endometrial stromal cells via the activation of JNK signaling pathway. 23413147_decrease in activity could constitute a relevant biomarker for the restoration of the immune response during visceral leishmaniasis 23426156_IDO is expressed more strongly in both primary and secondary glioblastoma tissue than low-grade glioma and may affect clinical outcome 23440412_Myeloid-derived suppressor cells suppress antitumor immune responses through IDO expression and correlate with lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer. 23620105_the data provide proof-of-principle that immunisation with indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase -silenced DC vaccine is safe and effective in inducing antitumour immunity. 23651343_Indoleamine2,3-dioxygenase and tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase may play critical roles in the immune pathogenesis of chronic kidney disease. 23669411_In human colon cancer cells, blockade of IDO1 activity reduced nuclear and activated b-catenin, transcription of its target genes (cyclin D1 and Axin2), and, ultimately, proliferation. 23682557_Results show that expressions of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) mRNA and protein were coincidentally higher in non-Hodgkin lymphoma tissues. 23751345_study reports on the contribution of all the individual cysteine residues towards the overall catalytic properties, secondary structure, heme environment and stability of IDO1 23752227_The immunosuppressive role of IDO is to target immune checkpoints | ENSMUSG00000031551 | Ido1 | 49.503881 | 0.324841403 | -1.622193 | 0.26730022 | 37.333462 | 0.0000000009956156600915199069905913480875263299463284738521906547248363494873046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000259825967413436192052612563494970454591737052396638318896293640136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 22.3150616 | 5.5724097 | 68.9079773 | 16.0383725 |
| ENSG00000131355 | 84658 | ADGRE3 | protein_coding | Q9BY15 | FUNCTION: Orphan receptor that may play a role myeloid-myeloid interactions during immune and inflammatory responses. A ligand for the soluble form of this receptor is present at the surface of monocytes-derived macrophages and activated neutrophils. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11279179}. | Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a member of the class B seven-span transmembrane (TM7) receptor family expressed predominantly by cells of the immune system. Family members are characterized by an extended extracellular region with a variable number of N-terminal epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domains coupled to a TM7 domain via a mucin-like spacer domain. This gene is closely linked to the gene encoding egf-like molecule containing mucin-like hormone receptor 2 on chromosome 19. This protein may play a role in myeloid-myeloid interactions during immune and inflammatory responses. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014]. | hsa:84658; | extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule membrane [GO:0101003]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186] | 17108056_The expression of EGF-TM7 receptors on myeloid cells is differentially regulated. EMR3 is the first family member found mainly on granulocytes. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20625511_Additional transcription changes likely associated with Th2-like eosinophilic inflammation were prominent and included increased EMR1&3. 20827226_Given the poor survival associated with high levels of EMR-3 expression in glioma patients, impetus is provided to explore EMR-3 as a potential therapeutic target. 34755660_[Peripheral blood EMR3 gene methylation level is correlated with breast cancer in Chinese women]. | 17.235353 | 0.473570323 | -1.078349 | 0.41612647 | 6.784511 | 0.0091952201778465036258181086736840370576828718185424804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0462671726070924063667355596862762467935681343078613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 10.5143436 | 4.2210385 | 22.2144041 | 8.4775487 | |||
| ENSG00000131370 | 9467 | SH3BP5 | protein_coding | O60239 | FUNCTION: Functions as guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) with specificity for RAB11A and RAB25 (PubMed:26506309, PubMed:30217979). Inhibits the auto- and transphosphorylation activity of BTK. Plays a negative regulatory role in BTK-related cytoplasmic signaling in B-cells. May be involved in BCR-induced apoptotic cell death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10339589, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26506309, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30217979, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9571151}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3-binding | Enables guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity and protein kinase inhibitor activity. Acts upstream of or within intracellular signal transduction. Located in cytoplasmic vesicle membrane and nuclear body. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:9467; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; protein kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0004860]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0061099]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 15158451_mitochondrial protein Sab is phosphorylated by stress-activated protein kinase 3 23861391_SH3BP5 binds to JNK and directly inhibits JNK through its two putative mitogen-activated protein kinase interaction motifs (KIMs). 25666017_The interplay of p-JNK with mitochondrial Sab leads to impaired respiration, ROS production, sustained JNK activation, and apoptosis. 26745340_REI/SH3BP5 protein family is conserved in evolution and is a group of new guanine nucleotide exchange factors for Rab11. 27184832_SH3BP5, LMO3, and SNAP25 were expressed in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells and associated with clinical features. 30322886_SH3 domain binding protein 5 (Sab) expression is reduced in ovarian cancer (OC), suggesting that Sab may be a prognostic biomarker to discern personalized treatments for OC patients. 31546831_Study found that expression of SH3BP5 was enhanced in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells and was negatively correlated with patients survival. Elevated expression of SH3BP5 was an independent prognostic factor for AML patients. Furthermore, SH3BP5-mediated activation of JNK-BAD signaling contributes to the survival of AML cells. 32066809_trans-Fatty acids facilitate DNA damage-induced apoptosis through the mitochondrial JNK-Sab-ROS positive feedback loop. 34128958_Tankyrase regulates epithelial lumen formation via suppression of Rab11 GEFs. 34783986_Novel blood-based hypomethylation of SH3BP5 is associated with very early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000021892 | Sh3bp5 | 281.536036 | 0.461063693 | -1.116962 | 0.09766629 | 132.742246 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000010294628158568756704381147462603766489657889249125044657671571440895896480000883902589103868763231730554252862930297851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000000000000001125009833453591874356802373847136813005819847719074955655102804267887059365589597081935835376498289406299591064453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 186.3106225 | 20.6306491 | 404.7125604 | 43.2418360 | |
| ENSG00000132274 | 10346 | TRIM22 | protein_coding | Q8IYM9 | FUNCTION: Interferon-induced antiviral protein involved in cell innate immunity. The antiviral activity could in part be mediated by TRIM22-dependent ubiquitination of viral proteins. Plays a role in restricting the replication of HIV-1, encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV). Acts as a transcriptional repressor of HBV core promoter. May have E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18389079, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18656448, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19218198, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19585648}. | Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Host-virus interaction;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the tripartite motif (TRIM) family. The TRIM motif includes three zinc-binding domains, a RING, a B-box type 1 and a B-box type 2, and a coiled-coil region. This protein localizes to the cytoplasm and its expression is induced by interferon. The protein is involved in innate immunity against different DNA and RNA viruses. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2021]. | hsa:10346; | Cajal body [GO:0015030]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; immune response [GO:0006955]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; protein polyubiquitination [GO:0000209]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of protein localization [GO:0032880]; regulation of viral entry into host cell [GO:0046596]; response to virus [GO:0009615] | 15064739_May be involved in proliferation and/or differentiation of leukemic cells. 16926043_Overexpression of Staf50 inhibited the HIV-1 infection between 50% and 90% in 293 T CD4/CCR5 as well as in monocyte-derived macrophages. 17970695_These data suggest a more complex role for TRIM22 during T lymphocyte activation than merely as an antiproliferative factor. 18389079_TRIM22 inhibits HIV-1 particle production by interfering with the trafficking of Gag to the plasma membrane and is a key player in the antiviral activity of the Type I interferon response to HIV-1. 18656448_A novel property of TRIM22, E3 ubiquitin ligase activity, was demonstrated. 19212762_Study shows that human and rhesus TRIM22 localise to different subcellular compartments and that this difference can be assigned to the positively selected B30.2 domain. 19218198_TRIM22 is an E3 Ubiquitin ligase whose expression leads to antiviral effects towards Encephalomyocarditis virus infections in HeLa cells. [TRIM22] 19481078_Deletion of putative nuclear localization signal abolished TRIM22 localization and nuclear body (NB) formation, the B30.2/SplA and ryanodine receptor (SPRY) domain, and residues 491-494 specifically are essential for nuclear localization and NB formation. 19585648_TRIM22-mediated anti-hepatitis B virus activity dependent on the nuclear-located RING domain 19902255_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19943174_REVIEW: current knowledge on the anti-retroviral effects of TRIM5 alpha and TRIM22 20001730_Specific polymorphisms in tripartite motif22 (TRIM22) genes were significantly associated with rubella vaccine humoral immunity 20006605_endogenous TRIM22 is localized to both nucleus and cytosol in primary human mononuclear cells, as well as in the human osteosarcoma cell line U2OS 20980524_These data suggest concordance between type 1 IFN and TRIM22 in PBMCs and that TRIM22 likely acts as an antiviral effector in HIV-1 infection. 21345949_Nuclear TRIM22 significantly impairs HIV-1 replication, likely by interfering with Tat- and NF-kappaB-independent long-terminal-repeat-driven transcription. 21651891_These data suggested that TRIM22 was a positive regulator of NF-kappaB-mediated transcription. 21683060_BRG1-mediated chromatin remodeling is critical for the IFN-gamma-inducibility of TRIM22 gene. 22509910_TRIM22 to repress protein translation preferably of some specific mRNAs. TRIM22 represses translation by inhibiting the binding of eIF4E to eIF4G, suggesting a mechanism for regulation of protein translation 23408607_Restriction of influenza A virus replication was accounted for by the interaction between TRIM22 and the viral nucleoprotein (NP), resulting in its polyubiquitination and degradation in a proteasome-dependent manner 23670564_p300 contributed to both IFN-gamma- and IRF-1-mediated TRIM22 transcription independent of its histone acetyltransferase activity, however, it was required for the recruitment of RNA polymerase II to TRIM22 promoter region. 23818111_These data indicate that overexpression of TRIM22 may negatively regulate the TRAF6-stimulated NF-kappaB pathway by interacting with and degrading TAB2. 23921607_TRIM22 genetic diversity affects HIV-1 replication in vitro and it is a potentially novel determinant of HIV-1 disease severity 24066097_Data report that markers in two TRIMs, TRIM5 and TRIM22 and a marker in BST2, associated statistically with the risk of getting MS. 24183724_this study shows that TRIM22 is greatly under-expressed in breast cancer. p53 dysfunction may be one of the mechanisms for TRIM22 down-regulation. 24478420_TRIM5alpha and TRIM22 have differential transcriptional regulation and distinct anti-HIV roles according to infection phase. 24863734_our data characterize the extensive genetic variation in TRIM22 and identify rs1063303:G>C as a highly prevalent SNP that influences its function. 24889558_Upregulation of TRIM22 may be associated with responsiveness to Peg-IFNalpha-2a/RBV combination therapy in hepatitis C. 24983760_A number of putative structural and functional residues, including several sites that undergo post-translational modification, were also identified in TRIM22. 25510414_TRIM22 could interact with IkappaB kinase (IKK)alpha but not IKKbeta and could increase the level and phosphorylation of IKKalpha through its really interesting new gene (RING) and spla-ryanodine receptor (SPRY) domains. 25683609_Interferon-alpha-induced TRIM22 interrupts hepatitis c virus replication by ubiquitinating NS5A. 26237181_regulation of FoxO4 protein expression and cell survival by TRIM22 controls TLR3-mediated IFN type I gene induction, preventing excessive antiviral response through dsRNA-induced apoptosis. 26271984_Data show that capsid protein p24-DsRed-Monomer was co-localized with tripartite motif containing 22 (TRIM22)-EGFP in HEK293T cells. 26316153_propose that TRIM22 is a direct target gene of PR and that it can mediate progesterone actions in uterine cells 26683615_Demonstrated that TRIM22 acts as a negative regulator of HIV-1 replication via inhibition of basal Sp1-driven proviral transcription. 26836588_Infant with severe IBD characterized by granulomatous colitis and severe perianal disease, we identified a homozygous variant of TRIM22 that affects the ability of its product to regulate NOD2. 27590274_TRIM5 and TRIM22 single nucleotide polymorphisms are associated to increased odds of significant liver fibrosis and sustained virological response after pegIFNalpha/RBV therapy in human immunodeficiency virus/hepatitis C virus coinfected patients. 27704462_Wthis study identified a genetic variation (rs7935564 G allele) in TRIM22 gene, which encodes TRIM22 protein acting like a HIV restriction factor, as being associated with good response to dendritic cell-based immunotherapy 28079123_Upregulation of TRIM22 triggers the expression and oligomerization of Bak and subsequently leads to cytochrome c release in a caspase-9- and caspase-3-dependent manner. Both the RING domain and the SPRY domain of the TRIM22 molecule are associated with its pro-apoptotic function. 28341749_Suppression of interferon-mediated anti-HBV response by single CpG methylation in the 5'-UTR of TRIM22. 28782753_trim22 is a broad and multifunctional host anti-viral factor induced by interferons. 29650252_TRIM22 may act as epigenetic inhibitor of HIV-1 transcription by preventing the binding of the host cell transcription factor Sp1 to the viral promoter. 29749134_miR-215 facilitated HCV replication via inactivation of the NF-kappaB pathway by inhibiting TRIM22, providing a novel potential target for HCV infection. 29762880_Loss of TRIM22 suppresses the progression and invasion of CML through regulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. 30011088_Results suggest that TRIM22-augmented autophagy prevents intracellular Mtb to evade autophagic clearance, thereby inhibiting the persistence of Mtb infections. 31136823_TRIM22 is a novel determinant of HIV-1 latency, at least in T cell lines. 31863490_Downregulation of TRIM22 in patients who failed to attain rapid virus clearance. 32319602_TRIM22 inhibits endometrial cancer progression through the NOD2/NFkappaB signaling pathway and confers a favorable prognosis. 32803897_TRIM22 inhibits respiratory syncytial virus replication by targeting JAK-STAT1/2 signaling. 33299853_Long Noncoding RNA LINC01207 Promotes Colon Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Regulating miR-3125/TRIM22 Axis. 34558381_Knockdown of Tripartite motif-containing 22 (TRIM22)relieved the apoptosis of lens epithelial cells by suppressing the expression of TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6). 34621686_Constitutive TRIM22 Expression in the Respiratory Tract Confers a Pre-Existing Defence Against Influenza A Virus Infection. 34870928_TRIM22 genotype is not associated with markers of disease progression in children with HIV-1 infection. 35636015_TRIM22 inhibits osteosarcoma progression through destabilizing NRF2 and thus activation of ROS/AMPK/mTOR/autophagy signaling. 35674157_Role of TRIM22 in ulcerative colitis and its underlying mechanisms. 35946462_FOXC1mediated TRIM22 regulates the excessive proliferation and inflammation of fibroblastlike synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis via NFkappaB signaling pathway. 36028902_On the relationship between tripartite motif-containing 22 single-nucleotide polymorphisms and COVID-19 infection severity. 36170453_TRIM22 actives PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway to promote psoriasis through enhancing cell proliferation and inflammation and inhibiting autophagy. | ENSMUSG00000071089 | Trim75 | 62.307521 | 0.439931754 | -1.184648 | 0.38093223 | 9.313775 | 0.0022743739511772251976617909008382412139326333999633789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0150705555798517406435044208024010004010051488876342773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 37.8885401 | 10.3123988 | 87.1243935 | 22.8987847 |
| ENSG00000132361 | 23277 | CLUH | protein_coding | O75153 | FUNCTION: mRNA-binding protein involved in proper cytoplasmic distribution of mitochondria. Specifically binds mRNAs of nuclear-encoded mitochondrial proteins in the cytoplasm and regulates transport or translation of these transcripts close to mitochondria, playing a role in mitochondrial biogenesis. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03013, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25349259}. | Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;TPR repeat | Enables mRNA binding activity. Involved in intracellular distribution of mitochondria. Located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:23277; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; intracellular distribution of mitochondria [GO:0048312]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005] | 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 27573102_Here, the authors show that CLUH, a host protein whose cellular function is not well established, plays a key role in the subnuclear transport of influenza virus nucleoprotein. 28424233_CLUH couples mitochondrial distribution to the energetic and metabolic status. 32149416_CLUH granules coordinate translation of mitochondrial proteins with mTORC1 signaling and mitophagy. | ENSMUSG00000020741 | Cluh | 302.486068 | 0.493236140 | -1.019650 | 0.28635005 | 12.346965 | 0.0004417039257514248956799918222060341577162034809589385986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0037697098922580426182127322221049325889907777309417724609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 199.0354170 | 36.9276569 | 403.4143738 | 74.6336898 | |
| ENSG00000132530 | 54739 | XAF1 | protein_coding | Q6GPH4 | FUNCTION: Seems to function as a negative regulator of members of the IAP (inhibitor of apoptosis protein) family. Inhibits anti-caspase activity of BIRC4. Induces cleavage and inactivation of BIRC4 independent of caspase activation. Mediates TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis and is involved in apoptosis in trophoblast cells. May inhibit BIRC4 indirectly by activating the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. After translocation to mitochondria, promotes translocation of BAX to mitochondria and cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Seems to promote the redistribution of BIRC4 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, probably independent of BIRC4 inactivation which seems to occur in the cytoplasm. The BIRC4-XAF1 complex mediates down-regulation of BIRC5/survivin; the process requires the E3 ligase activity of BIRC4. Seems to be involved in cellular sensitivity to the proapoptotic actions of TRAIL. May be a tumor suppressor by mediating apoptosis resistance of cancer cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11175744, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12029096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16432762, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17329253, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17613533}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Tumor suppressor;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a protein which binds to and counteracts the inhibitory effect of a member of the IAP (inhibitor of apoptosis) protein family. IAP proteins bind to and inhibit caspases which are activated during apoptosis. The proportion of IAPs and proteins which interfere with their activity, such as the encoded protein, affect the progress of the apoptosis signaling pathway. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. | hsa:54739; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; response to interferon-beta [GO:0035456] | 12029096_XAF1 augments TRAIL-induced apoptosis 14612497_Epigenetic silencing of XAF1 by aberrant promoter methylation may contribute to the malignant progression of human gastric tumors. 15610524_XAF1 expression in melanoma tissues was significantly reduced compared with benign melanocytic nevi 16303760_endogenous stress pressure in cancer cells sustained the high level expression of HSF1 and subsequently suppressed XAF1 expression, implicating the synergized effect of two anti-apoptotic protein families in cytoprotection under stress circumstances 16343440_The ratio of XAF1(A) and XAF1C mRNA expression differs amongst the cell lines tested, suggesting differential mRNA stabilities and/or the existence of tissue- or cell type-specific splicing regulation. 16353137_alternative splicing of XAF1 mRNA leads to formation of truncated XAF1 protein, which likely affects its functional interaction with XIAP, and consequently, contributes to pathogenesis of prostate cancers by disrupting balance of apoptosis machinery 16459719_Gene expression incresed in multiple sclerosis patients treated with interferon-beta. 16801630_siRNA to XAF1 inhibited IFN-induced apoptosis; conversely, overexpression of XAF1 overcame resistance to apoptosis induction by IFN-beta. 16909101_Epigenetic alteration of XAF1 is frequent in human urogenital cancers and may contribute to the malignant progression of tumors by rendering tumor cells a survival advantage partially through the attenuated p53 response. 17087954_Down-regulation of XAF1 in association with hypermethylation was detected in 3 of 4 human gastric cancer cell lines and 6 of 8 colon cancer cell lines. 17331366_In cancerization of oral mucosa, XIAP protein could play an important antiapoptotic role by overexpression, while XAF1 protein does not appear to antagonize effectively the role of XIAP. 17376236_Our study provides evidence that XAF1 is a crucial interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) mediator of IFN-induced sensitization to TRAIL in cancer. 17449173_Low XAF1 mRNA expression levels relate to an unfavorable clinical course in renal cell carcinoma. 17471152_An increased expression ratio of XIAP to XAF1 in combination with a disturbed expression of the XAF1 splice variants could be shown in gastric adenocarcinomas. 17570219_Genetic and epigenetic alteration of XAF1 is a common event in colorectal tumorigenesis and contributes to the malignant tumor progression by providing survival advantages for tumor cells under various stress conditions. 17613533_XAF1 mediates Survivin down-regulation through a complex containing XIAP, supporting dual roles for XAF1 in apoptosis 17884799_The high expression of HSF1 in gastro-intestinal cancer is associated with suppressed expression of XAF1. 18035482_Induction of XAF1 by IFNbeta was mediated by the transcription regulator Stat1 through the ISRE site within the promoter region of XAF1 gene in colon cancer. 18192275_Interferon gamma induces XAF1 and Noxa expression and potentiates apoptosis by STAT3 activation 18250043_INFalpha and 5-AZA-CdR can induce Xaf1 mRNA expressions in HL-60 and K562 cells. 18362468_CBP is a novel binding partner of XAF1, and the interaction between XAF1 and CBP and their functional consequence were mediated by adaptor-related protein complex 1. 18555708_XAF1 may have a role as a tumor suppressor gene in advanced bladder cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy 18830757_Promoter hypermethylation and down regulation of XAF1 is associated with liver tumor recurrence after liver transplantation. 18979398_These data suggest that a down-regulation of Smac/DIABLO and HtrA2 is implicated in the development and progression of TGCT, whereas overexpression of XAF1 in TGCT might contribute to their extraordinary sensitivity to chemotherapy. 19056926_JNK1 stimulated and mediated the effects of IFN and TNF-alpha on XAF1 expression through transcriptional regulation by induction of IRF-1. 19358264_results document that the restoration of XAF1 inhibits gastric tumorigenesis and tumor growth and that XAF1 is a promising candidate for cancer gene therapy. 19397802_imbalance in XIAP/XAF1 mRNA expression levels correlated to overall patient survival, and that high XIAP immunoreactivity was a poor prognostic factor. 19549372_5-AZA treatment can induce the expression of XAF1 mRNA and protein in myeloma. 19628579_XAF1 as a novel cell cycle regulator through modulating G(2)/M checkpoint and interaction with checkpoint kinase 1 in gastrointestinal cancer. 19664236_XIAP associated factor-1 (XAF1) is downregulated during progression of clear-cell renal cancer 19731821_5-azacytidine treatment led to XAF1 promoter CpG islands hypomethylation and showed anti-myeloma activity in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. 19847196_The expression levels of the pro-apoptotic XAF-1 gene modulate the cytotoxic response to Nutlin-3 in B chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 19922503_XAF1 is a valuable prognostic marker in pancreatic cancer and could be a potential candidate for cancer gene therapy. 20198350_Demonstrate that p53 could suppress the transcription of XAF1 through interaction with a high affinity responsive element (-95 to -86 nt) within XAF1 promoter in gastrointestinal cancer cells. 21143993_XAF1 down-regulation may contribute to the prostate cancer development 21678496_These findings suggest that a potential novel feedback loop exists between XAF1 and wild-type p53 22088514_The levels of XAF1 protein and mRNA in cancer tissues were significantly lower than those in cancer adjacent and normal lung tissues. 22719195_XAF1 is frequently methylated in esophageal cancer, and XAF1 expression is regulated by promoter region hypermethylation. 22759793_XAF1 may be involved in ovarian cancer development and up-regulation of XAF1 may confer sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin-mediated apoptosis. 22811387_The search of XIAP binding region within XAF1 revealed a modest affinity XIAP(RING) binding site is located at the C-terminal portion of XAF1.We also mapped the interaction sites for XAF1(RBD) on XIAP(RING) by using NMR. 22944270_Promoter methylation of the XAF1 gene plays an important role in the carcinogenesis and progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma. 23207547_the role of XAF1 in promoting apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells after DENV2 infection. 23645777_Missense polymorphisms in XIAP-associated factor-1 is associated with papillary thyroid cancer. 23826230_Dysfunction of XAF1 is frequent and is regulated through XAF1 promoter hypermethylation in gastric cancer. Circulating methylated XAF1 DNA was associated with tumor burden and malignant progression, which may be a valuable biomarker for diagnosis of gastric cancer, predicting patients' prognosis and monitoring tumor recurrence after surgery treatment. 24249729_Transcriptionally active p73 induces translocation of XAF-1 during apoptosis caused by melphalan. XAF-1 directly interacts with Puma and promotes Bax translocation during melphalan-induced apoptosis. 24663488_XAF1 as a possible sarcoidosis risk gene 25216542_Our study identified a novel splice variant of XAF1 in cancer cells 25313037_XAF1 stimulates HIPK2-mediated Ser-46 phosphorylation of p53 and XAF1 also steps up the termination of p53-mediated cell-cycle arrest by activating ZNF313. 25367849_Up-regulation of XAF1 distinctly increased apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells administered cisplatin. 25539606_Restored XAF1 expression inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549. Furthermore, XAF1 may activate associated apoptotic signaling pathways in A549 cell line. 25824780_Underexpression of XAF1 confers cisplatin-resistance in ovarian carcinoma. 26643258_SHC1 regulates the alternative splicing of XAF1 in extracellular matrix-detachment induced autophagy to coordinate with the anoikic cell death. 27048285_Data show that X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) mRNA and protein expression increased, whereas XIAP-associated factor 1 (XAF1) mRNA and protein expression decreased with the growth of radiation dose and exposure time. 27097110_XAF1 may be a candidate tumor suppressor in neuroblastoma 27121136_the present study was the first to construct an adenovirus which coexpressed XAF1 and TNFalpha in the same open reading frame and expressed them proportionally. As AdXAF1&TNFalpha inhibited HCC cells with enhanced efficiency, it may be applicable for the treatment of HCC. 27121748_Taken together, our results suggest that ROS generation might be a predisposing event in berberine-induced mitochondrial apoptosis in EBV-transformed B cells through the upregulation of XAF1 and GADD45alpha expression by MAPK and functional p53. 27349281_Expression of XAF1 and TAp73 was also upregulated in casticin-treated T24 cells. 27768232_XAF1 acts as a feedback regulator of the TNF receptor signaling pathway to suppress NF-kappaB activation 28034876_human genome-wide gene expression profile assay was used to screen the targets of miR-3131. The overexpressed miR-3131 could lead to a significant decrease of DTHD1 and XAF1 mRNA level. 28122345_XAF1 promoter hypomethylation is associated with high-grade gliomas. 28507149_this study uncovers an important role for XAF1-MT2A antagonism as a linchpin to govern cell fate under various stressful conditions including heavy metal exposure. 28534973_XAF1 expression was associated with VM in ovarian cancer, suggesting a potential role of XAF1 in the formation of VM in EOC. 28560416_XAF1 expression was markedly altered in non-small cell lung cancer tumor samples when compared to that found in normal lung tissues. 30042418_XAF1 enhances IRF-1-mediated transcription of proapoptotic genes via the XAF1-IRF-1 complex formation on these target promoters. XAF1 inhibits NF-kappaB-mediated tumor cell malignancy by reinforcing IRF-1 binding to a subset of coregulated promoters. 30551877_Results support a model in which YY1 is able to silence tumor suppressor genes such as XAF1 through HDAC1 in prostate cancer. 31081052_Results found that XAF1 transcription levels are downregulated in colorectal neoplasm cells by TGFB1 which activates RAS-ERK signaling. 31575897_Paradoxical epigenetic regulation of XAF1 mediates plasticity towards adaptive resistance evolution in MGMT-methylated glioblastoma. 34134965_[Effect of stable overexpression of XAF1 gene on biological characteristics of ovarian cancer A2780 cells]. 35430604_XAF1 destabilizes estrogen receptor alpha through the assembly of a BRCA1-mediated destruction complex and promotes estrogen-induced apoptosis. 36132546_IRF9 and XAF1 as Diagnostic Markers of Primary Sjogren Syndrome. | ENSMUSG00000040483 | Xaf1 | 69.773756 | 0.477778236 | -1.065587 | 0.28357410 | 13.841287 | 0.0001989169441518385162033510926704593657632358372211456298828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0018876867128873250911702541543490951880812644958496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 46.3763013 | 7.7190677 | 98.9210804 | 15.2251985 | |
| ENSG00000132688 | 10763 | NES | protein_coding | P48681 | FUNCTION: Required for brain and eye development. Promotes the disassembly of phosphorylated vimentin intermediate filaments (IF) during mitosis and may play a role in the trafficking and distribution of IF proteins and other cellular factors to daughter cells during progenitor cell division. Required for survival, renewal and mitogen-stimulated proliferation of neural progenitor cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Acetylation;Coiled coil;Developmental protein;Intermediate filament;Isopeptide bond;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes a member of the intermediate filament protein family and is expressed primarily in nerve cells. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. | hsa:10763; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; intermediate filament [GO:0005882]; intermediate filament cytoskeleton [GO:0045111]; CCR5 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031730]; intermediate filament binding [GO:0019215]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cell projection morphogenesis [GO:0048858]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; embryonic camera-type eye development [GO:0031076]; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000086]; negative regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0043086]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091]; neuron apoptotic process [GO:0051402]; positive regulation of intermediate filament depolymerization [GO:0030844]; positive regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation [GO:2000179]; stem cell proliferation [GO:0072089] | 12101039_Nestin-containing neurons occurred in hippocampus, septum, diagonal band, amygdala and basal nucleus of Meynert. Nestin-containing astrocytes occurred in the subependymal zone and dentate gyrus. 12172785_The tissue distribution of nestin has been studied in the muscularis propria of normal gastrointestinal autopsy material. 12187925_Beta-cell differentiation during human development does not rely on nestin-positive precursors 12786777_Nestin-immunoreactive cells colocalized with vimentin throughout the retina. Colocalized with mitotic Ki67 immunoreactive cells. 14625035_Demonstration of strong expression of nestin in Purkinje cells in pathologically advanced Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease correlates with the process that Purkinje cells undergo to promote survival. 15088413_detection of nestin-positive keratinocytes in the basal layer of cultured epidermis 15117961_nestin may be one mediator of N-myc-associated tumor aggressiveness of human neuroblastoma 15176089_In transgenic mice, nestin transgene expression in the olfactory bulb is limited to periglomerular neurons and is absent from granule cells, suggesting that this nestin promoter construct differentiates between the two interneuronal populations. 15502861_Nestin expression in tumor endothelium is enhanced by the first intron. 15526158_nestin has a role in multi-potentiality and regenerative potential [review] 15684833_nestin expression is recognized under all conditions of vascular development 16136494_Nestin is constantly expressed in situ in the cortex of normal human adrenal glands; a positive nestin immunoreaction could be useful in differential diagnosis of clear cell tumors in adrenal glands. 16186627_Data evaluate and compare the bcl2, bax, and nestin patterns in the frontal cortices of Alzheimer and multiple-infarct dementia patients, and in normal aging. 16275024_These results show that the pattern of nestin expression is related to the differentiation of epidermal stem cells. 16487364_Moderate to strong expression of nestin was observed in all tumors. 16538520_Nestin expression in adenomas cannot be viewed as a biologically relevant marker of cell proliferation and as a prognostic indicator in pituitary neoplasms. 16616189_Purkinje cells were immunoreactive with nestin regardless of the severity of degenerative cerebellar cortex. 16713999_cultured pancreatic islets contain nestin and Isl-1 positive mesenchymal stem cells with multipotential developmental capacity 16736556_Nestin-positive pancrease stem cells are in the stroma of human embryonic pancrease. 16826367_In a series of 40 surgical specimens, including gliomas, vascular malformations, abscesses and angiomas, nestin was poorly expressed in mature astrocytes and more expressed in developing reactive astrocytes, mainly in the cytoplasm. 16874866_The putative pancreatic stem cells expressed pdx-1 and nestin. 17036052_nestin is a survival determinant whose action is based upon a novel mode of Cdk5 regulation, affecting the targeting, activity, and turnover of the Cdk5/p35 signaling complex 17210924_Nestin is expressed in the human kidney from the first steps of glomerulogenesis within podocytes, mesangial, and endothelial cells. 17255215_The expression of nestin in the podocytes of normal and diseased kidneys of adolesscent and adult patients is reported. 17273760_nestin has a role in neovasculaturization in colorectal cancer 17300669_Nestin is more sensitive for malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) than other neural markers, and immunostains for nestin in combination with other markers could be useful in the diagnosis of MPNST. 17537965_Transgenic mice in which the nestin neural enhancer drives expression of a green fluorescent protein reporter show that the regulation in Schwann cells is transcriptional. 17652163_The nestin(-) vimentin(+) fibroblasts may represent a novel type of multipotent adult stem cells in human dermis. 17784648_Nestin is expressed in podocytes of mature human glomerular tissues in quiescent states. 17784840_The extent of nestin-positive neuronal cells correlated with the appearance of tyrosine hydroxylase positive neurons. 17909025_Results specify a function for Nestin in cell motility and identify a novel pathway for prostate cancer metastasis. 17984177_enhanced expression of nestin in the injured myocardium might reflect spontaneous regenerative processes supposedly based on the differentiation of resident cardiac stem cells into diverse cardiac cell types. 18265627_Nestin is expressed in proliferating and metabolically active cells, such as endothelium, independent of developmental and neoplastic processes. 18546018_Nestin plays a crucial role in remodeling the cytoskeleton of cells in the human postinfarcted myocardium. 18618166_Dental follicle cells expressed the stem cell marker nestin in both serum-free and serum-containing cell culture media. 18724036_Nestin gene variants are associated with early-onset CHD. 18724036_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18724228_Cyclosporin A induced renal injury recruits nestin-expressing cells to injured areas. 18799194_Nestin expression in pancreatic cancer cells may contribute to nerve and stromal invasion in this malignancy 18923447_SOX9 and SOX10 but not BRN2 seem to be required for nestin expression in human melanoma. 18925963_expression is detected in osteosarcomas 18998057_higher expression of nestin in the non-specific form of Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors suggests that the non-specific form has an earlier developmental origin than the simple or complex forms. 19012049_candidate for stem cell marker and renewal factor in nasal mucosa, may contribute to tissue homeostasis and differentiation in the epithelium and submucosal glands of normal nasal mucosa, and may play a role in proliferation of nasal polyps 19170896_Findings indicate that transplantation of embryonic neural stem cells into adult rat peri-infarction zone may be performed as early as 24 hours after cerebral ischemia. 19268442_nestin mRNA is a differentiation marker, and its expression does not relate to malignant characteristics in thyroid tumors 19294612_Expression of nestin mRNA could be detected in adrenocortical tumors, independently of their grade of dedifferentiation. 19417621_marker of Wilms tumor in or around the kidney 19473053_Increased expression of nastin is associated with astrocytoma pathogenesis and progression. 19554024_nestin expression at the gene and protein levels in human scalp skin is restricted to the periappendage mesenchyme and can be stimulated by leptin 19562035_expression of nestin is a major determinant in suppression of anti-proliferative activity of GR in undifferentiated tissue and facilitates activation of this growth control in a precise tissue and differentiation dependent manner 19578047_Our results support the combined role of WT1 and nestin in glial tumorigenesis and progression. 19704967_Nestin is present in podocytes of the renal corpuscle in rats and humans. Specific differences manifested in more intensive and widespread expression of nestin by endothelial cells of blood vessels in human kidney. 19845757_nestin was significantly associated with presence of ulceration in primary tumors in melanoma. 19864043_nestin functions as a stem cell marker of the follicular mesenchyme and has a major regulatory role in dermal homeostasis, cutaneous neovasculogenesis, and tumor stroma development 19956860_nestin has a role in progression of human melanoma 20017104_These observations emphasize an essential role of nestin for the process of regeneration, and also highlight this factor as a candidate marker for sustentacular cells in the human olfactory epithelium. 20044038_We suggest that some nestin-positive cells might be capable to differentiate into neurons during the earliest stages of development 20132963_nestin expressed in most tumor cells of non-small cell lung cancer tissue and had a direct linkage to lymph node metastasis and tumor-induced lymphangiogenesis, independent of COX-2 signal pathway. 20337823_In all 15 trichoblastomas, the stromal cells expressed nestin with variable positive reactions, except for superficial trichoblastomas within nevus sebaceous lesions, in which stromal cells were constantly positive for nestin 20426902_Compared with the controls, the number of nestin-positive cells is increased in the subgranular zone of the hippocampus dentate gyrus and in the subventricular zone following cerebral ischemia. 20518888_Nestin-positive myofibroblast may represent a relatively immature subpopulation of cells with multipotentiality. 20520523_We found a significant population of nestin-positive progenitor cells in neurofibromas from patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. 20536663_marker of HMB-45-negative melanoma cells in the dermal parts of patients with nodular melanoma 20649878_Nestin expression is associated with tubulointerstitial injury and predicts renal prognosis in IgA nephropathy. 20669222_nestin plays a crucial role in development of glioblastoma and may potentially be targeted for treatment of the disease. 20700038_Report expression of stem-cell markers cytokeratin 15 and nestin in primary adnexal neoplasms. 20943257_The distribution pattern of nestin in normal meningeal and tumor cells indicates that nestin might characterize immature cells. 21151388_Nestin may be the most specific marker for stemness in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma by immunohistochemial staining. 21251041_Expression of embryonic stem cell markers SOX2 and nestin in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and dermatofibroma. 21276080_Nestin-positive cells are found as frequently as balloon cells and are associated with abnormal reconstitution of the cortex in epileptic patients. 21323603_Nestin and Sox-2 immunoreactivity was significantly associated with astrocytic glioma tumor cell proliferation and nestin expression was independently associated with poor patient survival. 21340483_we perform the first study of the intracellular distribution of nestin in cell lines derived from neurogenic tumors 21440298_High nestin expression is associated with plasma cells of multiple myeloma. 21490921_Data demonstrate that Class III cells are mature neurons in the adult brain that express nestin. 21503585_nestin plays important roles in cell growth, migration, invasion and adhesion to extra-cellular matrices in glioma cells 21524985_These results suggest that the nestin-positive cells play an important role not only in the hair follicle pluripotent stem cells but also in the dermal papilla in the regenerating hair follicle. 21527990_eGFP-positive cells in the subventricular zone express multiple phenotype markers and neuroblast-specific molecules suggesting the transgene is expressed through the lineage. 21672338_The presence of nestin protein parallels the biological behaviour of osteochondromas and is restricted to prehypertrophic and hypertrophic chondrocytes. 21915031_We sought to determine if ezrin, KBA.62, p-Akt, CD166, and nestin, may be helpful in distinguishing melanoma from nevi and atypical melanocytic lesions 21985235_Smooth muscle cells expressing nestin and Nkx6.1 are the main cell population derived from culturing human spinal cord cells in adherent conditions with serum. 22113177_In epithelioid mesotheliomas, 13% of cells expressed nestin, 39% EMA and 7% mesothelin 22135720_nestin and CD44 are significantly expressed in a subset of gastric adenocarcinoma 22156015_The co-expression of CD133 and nestin as well as results of the functional assays suggest a possible presence of cancer cells with a stem-like phenotype in rhabdomyosarcoma. 22178090_Both CD133-positive and nestin-positive blood vessels have an important role in maintaining the structure of the glioma stem cell niche. 22187705_An intimate link of nestin to a biological process of pancreatic cancer was confirmed. The expression of nestin did not prove to be a valuable prognostic factor. 22207173_Oct-4 and Nestin were important regulators of the development of breast cancer. 22246533_Nestin is a potential novel therapeutic target in pancreatic cancers to inhibit tumor angiogenesis. 22296500_High expression level of nestin is associated with chemotherapy-resistance in serous ovarian cancer. 22297445_Nestin was detectable in tumoral cells and in endothelial cells of blood microvessels, and it is significantly expressed in triple-negative and in inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) subgroups of T4 breast tumours 22344865_Despite significantly shorter survival rates observed in patients with high levels of nestin expression assessed by immunofluorescence, nestin does not seem to represent a powerful prognostic marker that would be superior to conventional methods. 22350668_Our results suggest that: (1) nestin is a useful marker for diagnosis of high-grade gliomas, (2) nestin is helpful in diagnosis of schwannomas, and (3) nestin expression is related to poor prognosis in high-grade gliomas. 22395498_nestin and caveolin-1 could have a role in GISTs, together with CD117 and CD34 22568867_In summary, our data implicate nestin as a useful novel marker for intracranial ependymoma risk stratification easily implementable in routine diagnostics. 22572237_The present study suggests that nestin expression seems to be a prognostic indicator of a poorer survival probability in patients with resected LCNEC, although its prognostic significance still requires confirmation with larger patient populations. 22580387_Nestin was not localized in the squamous epithelium in normal cervical tissues, but it was weakly expressed in the basal squamous epithelium in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 22649953_Nestin expression was higher in tumor tissues of renal cell carcinoma, than normal tissues (p | ENSMUSG00000004891 | Nes | 495.392789 | 2.290831229 | 1.195871 | 0.09729552 | 150.163025 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000001597079520872663013951788702108124019790122385468969279605730230066876619836100553529925757598184610230873659020289778709411621093750000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000201260795837538822638597139058892933895134359206507949197570483684412553086291146483503139430482065108662936836481094360351562500000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 696.2928799 | 37.8309061 | 305.3641358 | 17.7472486 | |
| ENSG00000133019 | 1131 | CHRM3 | protein_coding | P20309 | FUNCTION: The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Primary transducing effect is Pi turnover. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7565628}. | 3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Synapse;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The muscarinic cholinergic receptors belong to a larger family of G protein-coupled receptors. The functional diversity of these receptors is defined by the binding of acetylcholine and includes cellular responses such as adenylate cyclase inhibition, phosphoinositide degeneration, and potassium channel mediation. Muscarinic receptors influence many effects of acetylcholine in the central and peripheral nervous system. The muscarinic cholinergic receptor 3 controls smooth muscle contraction and its stimulation causes secretion of glandular tissue. Alternative promoter use and alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that have different tissue specificities. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. | hsa:1131; | basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; synapse [GO:0045202]; acetylcholine binding [GO:0042166]; G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor activity [GO:0016907]; G protein-coupled serotonin receptor activity [GO:0004993]; neurotransmitter receptor activity [GO:0030594]; phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C activity [GO:0004435]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0095500]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007197]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007213]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger [GO:0007187]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of smooth muscle contraction [GO:0045987]; protein modification process [GO:0036211]; regulation of ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0032412]; regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle contraction [GO:0003056]; saliva secretion [GO:0046541]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; smooth muscle contraction [GO:0006939] | 11856737_potential role of endogenous GRK6 in the regulation of M(3) mACh receptor 11877431_Stimulation of phospholipase C-epsilon by the M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediated by cyclic AMP and the GTPase Rap2B 12126481_We show that activation of these receptors leads to divergent growth responses: M(2) AChR activation causes an increase in DNA synthesis, whereas M(3) AChR activation causes a dramatic decrease in DNA synthesis. 12194018_both G(q) and G(11) are involved in mediating the action of the M(3) receptor on cytosolic Ca(2+) in HT29 cells 12381439_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12642833_Single nucleotide polymorphisms not more frequent in asthma. No nonrandom transmission of short tandem repeat polymorphism haplotypes in asthma. Nonrandom transmission of haplotypes in skin test reactivity to cockroach allergens. 12649280_the conserved poly-basic region in the C-terminal tail of the M3 muscarinic receptor contributes to the ability to mediate protection against apoptotic cell death 12799371_the M3 receptor displays a major ARF1-dependent route of phospholipase D1 activation with an additional ARF6-dependent pathway to PLD1 or PLD2 14573754_M3 mAChR desensitization is mediated by GRK6 in human SH-SY5Y cells, and receptor desensitization of phospholipase C signaling can be monitored in 'real-time' in single, living cells. 14977875_The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3 is a mediator of bradycardia and bronchoconstriction due to vagal innervation. 15263021_M3 up-regulates 'sedentary' integrins alpha2beta1 and alpha3beta1. Inhibition of migration by M3 was mediated through Ca2+-dependent guanylyl cyclase-cyclic GMP-protein kinase G signaling pathway. 15280370_M1- and M3- but not M2- or M4-AchR signals activate HIF-1 by both stabilization and synthesis of HIF-1alpha and by inducing the transcriptional activity of HIF-1alpha. 15383626_(HEK) 293 cells expressing recombinant Galpha(q/11)-coupled muscarinic M3 receptors showed transient coexpression of RGS proteins 15725576_demonstration of the antigenicity of a novel peptide fragment of the human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor 3 in primary Sjogren's syndrome 15769745_binding of beta-arrestin-1 to muscarinic M(3) receptors requires paired stimulation of two receptor components within the same receptor dimer 16113538_characterization of the muscarinic receptor in the spontaneously immortalized human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT and its role in cell migration 16368694_Data demonstrate that M(1), M(2), and M(3) muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChR)can form homo- and heterodimers in living cells, and suggest that heterodimerization plays a role in the mechanism of mAChR long term regulation. 17005862_The muscarinic Ca2+ signaling pathway is not necessarily affected by depolarization and suggest that the M3 receptor itself is not sensitive to voltage. 17130513_C allele as associated with a reduced acute insulin response and modestly associated with increased risk of early-onset type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians. 17130513_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17192665_affects endocrine and exocrine hormone and salivary secretion 17335853_Resuts show that urothelium carries multiple cholinergic receptor subtypes, with predominant expression of M2R, M3R and alpha7-nAChR and suggest that this layer-specific distribution serves to stratify cholinergic regulation of urothelial function. 17373692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17513382_alphaM3 belongs to a complex and diverse set of synchronously moving parts that change structure relatively late in the channel-opening process. 17637176_M3R was involved in the up-regulation of H1R by activating H1R gene transcription through a PKC-dependent process 17851256_Poly I:C caused increased M3R in airway smooth muscle cells by interacting with TLR3. 17890325_These results indicate caveolae and caveolin-1 facilitate [Ca(2+)](i) mobilization leading to ASM contraction induced by submaximal concentrations of acetylcholine. 17951979_the M(3)/M(5) subtypes appear to be the major contributor, leading to intracellular calcium mobilization from the internal store via an IP(3)-dependent pathway in the undifferentiated retinoblastoma cells. 18070938_M3 employs two distinct mechanisms of chemical imitation to potently sequester chemokines, thereby inhibiting chemokine receptor binding events as well as the formation of chemotactic gradients necessary for directed leukocyte trafficking 18249005_Neither the linear M3R peptide nor M3R transfectants represent suitable tools for discrimination of pathogenic from natural autoantibodies in Sjogren's syndrome. 18272392_The observed effect of tau protein on neurons (in neuroblastomas and primary cultures of hippocampal and cortical neurons) is through M1 and M3 muscarinic receptors. 18348264_The results demonstrate that multiple muscarinic receptor subtypes regulate mTOR, and that both MAPK-dependent and -independent mechanisms may mediate the response in a cell context-specific manner. 18385290_Results demonstrate that the actions of pilocarpine and carbachol in salivary cells are mediated through two distinct signaling mechanisms via M3/M1 receptors. 18422974_Muscarinic receptor M3 expression is associated with invasive migration of melanomas. 18524769_airway M(2)Rs inhibit BK channels by a dual, Gbetagamma-mediated mechanism, a direct membrane-delimited interaction, and the activation of the phospholipase C/protein kinase C pathway 18563417_M2 and M3 receptors are upregulated in a time-dependent and pressure-dependent fashion after as little as a 24 h exposure to increased hydrostatic pressure in bladder 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19033440_the beta2 adrenergic and M3 muscarinic receptors, enter cells constitutively by clathrin-independent endocytosis and colocalize with markers of this endosomal pathway on recycling tubular endosomes subsequently recycle back to the plasma membrane 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19156168_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19182865_The DEP domain of RGS7 can directly bind to the third intracellular loop of the M3R and attenuate receptor-induced Ca2+ mobilization in a M3 subtype-selective manner. 19183167_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19460789_muscarinic M3 receptor stimulation augments cigarette smoke extract-induced IL-8 (but not IL-6) production by airway smooth muscle 19575010_Data show that NALCN and M3R belong to the same protein complex, involving the intracellular I-II loop of NALCN and the intracellular i3 loop of M3R. 19626040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19648965_M(3)-muscarinic receptor can regulate the apoptotic properties of a chemotherapeutic DNA-damaging agent by regulating the expression, subcellular trafficking and modification of p53 in a manner that is, in part, dependent on the cell type. 19668880_The protein and gene expression of the M3 receptor in the prostatic carcinoma group were higher than that of benign prostatic hyperplasia group and normal prostate group. 19669628_Data show that exon-acquisition and alternative splicing events of CHRM3 genes were occurred through the continuous integration of transposable elements following conservation. 19751772_m3 receptor-expressing HeLa cells are a valuable system for studying IP(3) receptor ERAD, and suggest that the SPFH1/2 complex is a factor that selectively mediates the ERAD of activated IP(3) receptors. 19874574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19927300_Muscarinic cholinoceptor activation by pilocarpine triggers apoptosis in human skin fibroblast cells. 19951374_The results showed that microbial products up regulate the expression of M3 receptor in nasal mucosal immune cells that further increases the production of OX40L in nasal DCs and drives the production of TNF-alpha in nasal mucosa. 20146726_Distribution of M3 receptors in human colon. 20332620_The results of co-immunoprecipitation of different scaffold and kinase proteins, provide experimental evidence for the role for the third cytoplasmic loop of the human M(3) muscarinic receptor in G-protein activation and multiprotein complex formation. 20395537_Use muscarinic antagonists to demonstrate that muscarinic M3 receptors mediate the excitatory effects of acetylcholine on small intestinal and colonic transit in humans. 20489201_the capacity of the human M(3) muscarinic acetylcholine receptor to exist as dimeric/oligomeric complexes at the surface of cells 20519144_M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtype as being primarily responsible for these transcription factor responses after stimulation with carbachol through activation of the ERK1/2 pathway 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20613776_skin of patients with cholinergic urticaria CHRM3 lack of expression is divided into anhidrotic and wheal occuring hypohidrotic areas 21041608_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21118716_WNK4 kinase negatively regulates the anterograde trafficking of MR through kinase-independent mechanism. 21224444_Data show that the crosstalk between ORs and the M3-R suggests that the functional coupling of ORs and the M3-R is required for robust OR activation. 21245133_Complex regulation of the TRPM8 cold receptor channel: role of arachidonic acid release following M3 muscarinic receptor stimulation. 21450750_In contrast to other genes reported to be associated with primary SJogren syndrome, like STAT4 and IRF5, CHRM3 has not been reported to be associated with other autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis. 21685385_Structural basis of M3 muscarinic receptor dimer/oligomer formation. 21798865_The data provide experimental evidence of the critical role that N-glycan chains play in determining muscarinic receptor distribution, localization, as well as 21873996_The M3R C terminus is sufficient, and a six-amino-acid polybasic sequence distal to helix 8 ((565)KKKRRK(570)) is necessary for preassembly with G(q). 21877253_Autoantibodies against the second extra-cellular loop of M3R could be involved in salivary dysfunction in patients with Sjogren's syndrome. 21940308_CHRM3 polymorphisms are likely associated with disease duration in IBS. CHRM3 polymorphisms could be associated with IBS. 22077972_Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3(1q41-q44) homozygous frameshift mutation in familial congenital bladder malformation associated with a prune-belly-like syndrome, defining an isolated gene defect underlying this sometimes devastating disease. 22137887_Incubation of hSMG cells with pSS IgG (1mg/ml) significantly decreased M3R expression levels at the membrane. 22178951_The Asn-7.49 is important for the interaction between M(3)R and ARF1 and also for the formation of the ARF/Rho/beta gamma signaling complex, a complex that might determine the rapid activation and desensitization of PLD.(muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3) 22192964_The results of the study suggest that the differential expression of the ADRB2 and CHRM3 genes in bronchial mucosa is associated with asthma and COPD clinical subtypes. 22410194_Data suggest that M3 muscarinic receptor and Kir6.1 colocalize to detrusor caveolae; studies include tissue from both male and female subjects. 22466417_Mutation of this region in the M3-MR altered receptor coupling to G protein. 22500107_The study reports the results of a combined computational and site mutagenesis study designed to provide new insights into the orthosteric binding site of the human M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. 22510450_The anti-M3RP205-220 antibody was detected in most patients with Sjogren syndrome. 22511543_Its cytoprotective effect was decreased by a M3R antagonist. 22564786_The Asn-514-Tyr point mutation produces constitutive activation of muscarinic M3-AChR by decreasing the rate of receptor deactivation, while having minimal effect on receptor activation. 22610841_Exposure to the cholinergic agonist carbachol induced a concentration-dependent increase in cell proliferation rate. This effect was mainly mediated by the receptor subtypes M3 and M2. 22691178_The acetylcholine M3 receptor was slightly decreased as compared to control in overactive bladder. 22893470_The expression of mAChR M3 is influenced by the extent of differentiation, distant metastasis and the site of cholangiocarcinoma. It also plays a key role in the proliferation and metastasis of cholangiocarcinoma. 22899762_CHRM3 and M(3) were suggested to play important roles in the pathogenesis of myopia and in the arrested progression of myopia by atropine. 22949513_Generalized epilepsies implicates susceptibility genes: CHRM3 at 1q43, VRK2 at 2p16.1, ZEB2 at 2q22.3, SCN1A at 2q24.3 and PNPO at 17q21.32. 23142559_Overall, the results of the present study suggest that TNF--alpha causes (1) the release of ACh from A549 cells, (2) the decrease in cholinesterase activity, and (3) the upregulation of M3R expression facilitating the autocrine effects of ACh on M3R. 23227858_Results suggest a major role of M(3) muscarinic receptors mediating the human gallbladder contraction through voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels and Rho kinase. 23382834_Our findings clearly indicate that binding of anti-M3R autoantibodies to the receptor, which was verified by immunoprecipitation, suppresses AQP5 trafficking to the membrane and contribute to impaired fluid secretion in SjS. 23521066_CHMR3 at the plasma membrane exists as stable dimeric complexes, a large fraction of which interact dynamically to form tetramers without the presence of trimers, pentamers or higher-order oligomers 23760269_Data indicate that carbachol (Cch) activates cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) through the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3 (M3R). 23786223_M3-mediated contractions in the M2KO strain were decreased 54% by the protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor chelerythrine. 23838802_Data indicate that high M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (M3 receptor) expression correlates with poor survival in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, indicating that M3 receptor may be a novel antineoplastic target. 24334576_The presence of muscarinic M3 receptor (HM3) autoantibodies may be related to the underlying disease mechanism in idiopathic generalized anhidrosis patients. 24393526_M3R preserves the endothelial barrier function through a mechanism potentially maintaining PTP1B activity, keeping the adherens junction proteins (AJPs) dephosphorylation. 24419413_Overexpression of muscarinic receptor 3 promotes metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer. 24430298_CHRM2 but not CHRM1 or CHRM3 polymorphisms are associated with asthma susceptibility in Mexican patients. 24522860_HM3-mediated IL8 expression through PKC-NFkappaB signaling pathways 24596086_the M3 muscarinic receptor maximizes the efficiency of PLCbeta3 signaling beyond its canonical role as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Galpha. 24697698_The M3 receptor facilitates interaction of the VE-cadherin-based adherens junctional complex and the actin-based cytoskeleton by maintaining Rac1 activity, which regulates the interaction between IQGAP1/Rac1 and IQGAP1/beta-catenin. 24821386_changes in membrane cholesterol concentration differentially impact preferential and non-preferential M1 and M3 receptor signaling 25316767_Results uncovered that Gaq binding to GRK2 enhances the recruitment of GRK2 to M3-ACh receptors. 25375131_Cigarette smoking may contribute to this imbalance by affecting the polarization and survival of Th/Tregs through the up-regulation of MR3 and MR5. 25769304_an incorrect organizational structure of many mutants of hM3R provides the molecular basis for why they are poorly expressed and fail to be effectively trafficked to the cell surface. 25916507_Suggest Gbeta4gamma1 as a modulator of M3 muscarinic receptor signaling. 25964092_ACh-induced activation of EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway and subsequent IL-8 upregulation may be one of the important mechanisms of M3R function 26066647_M3 AChR or AMP-activated protein kinase Small Interfering RNA abrogated the ACh-elicited the attenuation of Endoplasmic reticulum stress in endothelial cells, indicating that the salutary effects of ACh were likely mediated by M3 AChR-AMPK signaling. 26071486_Blockading CHRM3 by shRNA or treatment with darifenacin inhibited prostate cancer growth. 26346168_our findings support an oncogenic role for the M3 receptor in gastric cancer 26692031_Report using biosensing techniques to monitor dynamic changes of inositol lipid pools in living cells reveals a PKC-dependent PtdIns4P increase upon EGF and M3 receptor activation. 26901532_results suggest that the autoantibodies against peptides of the second extracellular loop of M3R are not pathogenic in vivo and they are not suitable as biomarkers for pSS diagnosis 26956674_These findings indicate that M3 mAChR may be important therapeutic target for obstructive airway diseases, as it regulates the effects of the epithelial-derived chemokines on ASM cell migration, which results in lung remodeling. 26959877_The CHRM3 gene plays a role in abnormal thalamo-orbital frontal cortex functional connectivity in first-episode treatment-naive patients with schizophrenia. 27221048_This study presents the endocytic pathways of internalization for muscarinic type 3 receptor and flotillin-1/2 in salivary gland epithelial cells. knockdown of flot-1 or -2 by flotillin-specific siRNA prevented internalization and reduced the endocytic efficiency of muscarinic type 3 receptor. 27460476_this study shows that anti-M3R is significantly elevated in Sjogren's syndrome plasma in comparison with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and healthy controls 27803431_M3-mAChR activation leads to enhancement of hsp expression via PKC-dependent phosphorylation of HSF1, thereby stabilizing the mutant hERG-FLAG protein. Thus, M3-mAChR activators may have a therapeutic value for patients with LQT2. 27923235_There were no significant associations between CHRM3 SNPs and autonomic nervous system activity in patients with schizophrenia on high-dose antipsychotics. 28008134_Interacting post-muscarinic receptor signaling pathways potentiate MMP1 expression and invasion of human colon cancer cells. 28053981_To our knowledge, this is the first genetic association study that reveals the genetic contribution of CHRM3 gene in bladder cancer etiology. 28276525_Regulation of molecular clock oscillations and phagocytic activity via muscarinic Ca(2+) signaling in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. 28411124_Morphine-induced MOP receptor endocytosis is facilitated by concurrent M3 activation.M3 and MOP assemble in receptor heterocomplexes mainly located at the plasma membrane.M3-MOP receptor pharmacological interaction is independent of heterocomplex formation.M3 and MOP receptor heteromers disrupt upon both receptor endocytosis. 28412413_These results indicate that not H1 but M3 receptor-induced activation of p38 MAPK might contribute to the maintenance of epithelial barrier function through down-regulation of TNF-alpha signalling and activation of EGFR. 28416748_M3R expression plays an important role in early progression and invasion of colon neoplasia but is less important once tumors have spread. 29864421_M3R activation-induced GRK2 recruitment is Ggamma subtype dependent in which Gbetagamma dimers with low cell membrane-affinity Ggamma9 exhibited a two-fold higher GRK2-recruitment compared to high affinity Ggamma3 expressing cells. 29935595_The CHRM3 polymorphism and the Apfel score independently predict PONV susceptibility. Dexamethasone/acustimulation should be considered in patients with low Apfel score but at high genetic risk 29959237_Genetic M3R ablation in human cells results in improved remyelination and is mediated by acceleration of oligodendrocyte commitment from oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. 29959979_the M3 receptor is the dominant muscarinic receptor in the human adrenal cortex. 30483762_The findings of the present study suggest that miR30e inhibited the adhesion, migration, invasion and cell cycle entry of Prostate cancer (PCa) cells by suppressing the activation of the MAPK signaling pathway and inhibiting CHRM3 expression. Thus, miR30e may serve as a candidate target for the treatment of PCa. 31441039_A homozygous missense variant in CHRM3 associated with familial urinary bladder disease. 31445019_M3R has protective effects against hepatocyte lipid accumulation by activating AMPK pathway. 31584702_Muscarinic receptor M3 contributes to vascular and neural growth factor up-regulation in severe asthma. 31740666_A regulatory variant of CHRM3 is associated with cannabis-induced hallucinations in European Americans. 32205868_Muscarinic receptors promote castration-resistant growth of prostate cancer through a FAK-YAP signaling axis. 32614803_M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-reactive Th17 cells in primary Sjogren's syndrome. 34935917_Methylation-reprogrammed CHRM3 results in vascular dysfunction in the human umbilical vein following IVF-ETdagger. 35673819_Expression of M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in gastric cancer. 35967390_Impaired sweating in patients with cholinergic urticaria is linked to low expression of acetylcholine receptor CHRM3 and acetylcholine esterase in sweat glands. | ENSMUSG00000046159 | Chrm3 | 323.400315 | 2.899390811 | 1.535750 | 0.16361547 | 85.762354 | 0.0000000000000000000202912606362345080201168436238672577169921197132046057414953010855640513909747824072837829589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000014630626483487026529699461723008360450365819790296195365697506929336668690666556358337402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 441.3464228 | 39.6414543 | 153.0328546 | 14.4309335 | |
| ENSG00000133106 | 94240 | EPSTI1 | protein_coding | Q96J88 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in M1 macrophage polarization and is required for the proper regulation of gene expression during M1 versus M2 macrophage differentiation (By similarity). Might play a role in RELA/p65 and STAT1 phosphorylation and nuclear localization upon activation of macrophages (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VDI1}. | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome | The protein encoded by this gene has been shown to promote tumor invasion and metastasis in some invasive cancer cells when overexpressed. Expression of this gene has been shown to be upregulated by direct binding of the Kruppel like factor 8 protein to promoter sequences. The translated protein interacts with the amino terminal region of the valosin containing protein gene product, resulting in the nuclear translocation of the nuclear factor kappa B subunit 1 gene product, and activation of target genes. Overexpression of this gene has been observed in some breast cancers and in some individuals with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. | hsa:94240; | 20133812_These observations implicate EPSTI1 as a hitherto unappreciated regulator of tumor cell properties. 24096480_A novel KLF8 to EPSTI1 to VCP to NF-kappaB signaling mechanism potentially critical for breast cancer invasion and metastasis. 30083277_circEPSTI1,a significantly upregulated circRNA, which is derived from the EPSTI1 (epithelial stromal interaction 1) gene locus, is an independent prognostic marker for triple-negative breast cancer patient survival. 30887698_Data show that showed that circular RNAs (circEPSTI1) and EPSTI1 (epithelial stromal interaction 1) could directly bind to miR-942. 31702512_circEPSTI1 Acts as a ceRNA to Regulate the Progression of Osteosarcoma. 32114510_Elevated EPSTI1 expression in primary Sjogren's syndrome B cells promoted TLR9 signalling activation and contributed to the abnormal B cell activation, which was promoted by facilitating p65 phosphorylation and activation of NF-kappaB signalling via promoting IkappaBalpha degradation. 32769326_Role of epithelial - Stromal interaction protein-1 expression in breast cancer. 32826876_The circEPSTI1/mir-942-5p/LTBP2 axis regulates the progression of OSCC in the background of OSF via EMT and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. 34738627_Contrasting functions of the epithelialstromal interaction 1 gene, in human oral and lung squamous cell cancers. 35527663_Knockdown of EPSTI1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury through regulation of NF-kappaB signaling in a cellular pneumonia model. 36330510_EPSTI1 as an immune biomarker predicts the prognosis of patients with stage III colon cancer. | ENSMUSG00000022014 | Epsti1 | 54.843762 | 0.359683261 | -1.475201 | 0.23134397 | 41.797442 | 0.0000000001012357871422972653651296764182787504132710054705057700630277395248413085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000030193735406107762453245561888549516882385148619505343958735466003417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 33.2509769 | 6.5841980 | 92.9015341 | 16.7725661 | ||
| ENSG00000133250 | 84330 | ZNF414 | protein_coding | Q96IQ9 | FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. | Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nucleus. Predicted to be part of chromatin. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:84330; | nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872] | 27664836_KPNA7 binding and nuclear transfer was validated for two proteins, MVP and ZNF414. MVP and ZNF414 have a key role in the regulation of pancreatic cancer cell growth. | ENSMUSG00000073423 | Zfp414 | 56.189633 | 0.369584327 | -1.436025 | 0.41674921 | 11.388938 | 0.0007388275438800179055476302636407126556150615215301513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0058753380806103976119469933792061056010425090789794921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 30.7317393 | 7.8851749 | 83.4161474 | 21.0301320 | |
| ENSG00000133561 | 474344 | GIMAP6 | protein_coding | Q6P9H5 | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;GTP-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a member of the GTPases of immunity-associated proteins (GIMAP) family. GIMAP proteins contain GTP-binding and coiled-coil motifs, and may play roles in the regulation of cell survival. Decreased expression of this gene may play a role in non-small cell lung cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene, which is found in a cluster with seven additional GIMAP genes on the long arm of chromosome 7. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. | hsa:474344; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; GTP binding [GO:0005525] | 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27667392_These data,demonstrating the downregulation of the mRNA and protein expression levels of GIMAP5 and GIMAP6 in the tumor tissues and blood of patients with Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) , suggested the involvement of GIMAP5 and GIMAP6 in the pathogenesis of HCC, and indicate their possible use as diagnostic markers for HCC. 28381553_GIMAP6 plays a role in modulating immune function and that it does this by controlling cell death and the activation of T cells. 33328581_A human case of GIMAP6 deficiency: a novel primary immune deficiency. 35551368_GIMAP6 regulates autophagy, immune competence, and inflammation in mice and humans. | ENSMUSG00000047867 | Gimap6 | 141.249717 | 2.164600357 | 1.114101 | 0.15335836 | 52.895061 | 0.0000000000003518532203835207572947793697294690065408701018512260816351044923067092895507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000134841721828073655477616473479395735931424260556354965956415981054306030273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 194.0885589 | 13.9426734 | 90.0801385 | 7.2313432 | ||
| ENSG00000133574 | 55303 | GIMAP4 | protein_coding | Q9NUV9 | FUNCTION: During thymocyte development, may play a role in the regulation of apoptosis (By similarity). GTPase which exhibits a higher affinity for GDP than for GTP. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99JY3}. | 3D-structure;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;GTP-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a protein belonging to the GTP-binding superfamily and to the immuno-associated nucleotide (IAN) subfamily of nucleotide-binding proteins. The encoded protein of this gene may be negatively regulated by T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia 1 (TAL1). In humans, the IAN subfamily genes are located in a cluster at 7q36.1. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:55303; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; GTP binding [GO:0005525] | 11964296_molecular and genetic properties; expression in resting T- and B-cells and decreased expression during lymphocyte activation 18701445_GIMAP1 and GIMAP4 genes are up-regulated by IL-12 and other Th1 differentiation-inducing cytokines in cells induced to differentiate toward Th1 lineage and down-regulated by IL-4 in cells induced to Th2. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23041938_Genome-wide association study identifies GIMAP as a novel susceptibility locus for Behcet's disease 25287446_GIMAP4 regulates secretion of cytokines in early differentiating human CD4(+) T helper lymphocytes and in particular the secretion of interferon-gamma also affecting its downstream targets. 36246963_Prognostic Value of GIMAP4 and Its Role in Promoting Immune Cell Infiltration into Tumor Microenvironment of Lung Adenocarcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000054435 | Gimap4 | 20.886146 | 2.029233298 | 1.020935 | 0.36117570 | 8.036126 | 0.0045853492145701453541750680642508086748421192169189453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0267249436722529973287088012057211017236113548278808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 28.7131697 | 4.1540739 | 14.1732705 | 2.4448493 | |
| ENSG00000133816 | 9645 | MICAL2 | protein_coding | O94851 | FUNCTION: Methionine monooxygenase that promotes depolymerization of F-actin by mediating oxidation of residues 'Met-44' and 'Met-47' on actin to form methionine-sulfoxide, resulting in actin filament disassembly and preventing repolymerization (PubMed:24440334, PubMed:29343822). Regulates the disassembly of branched actin networks also by oxidizing ARP3B-containing ARP2/3 complexes leading to ARP3B dissociation from the network (PubMed:34106209). Acts as a key regulator of the SRF signaling pathway elicited by nerve growth factor and serum: mediates oxidation and subsequent depolymerization of nuclear actin, leading to increase MKL1/MRTF-A presence in the nucleus and promote SRF:MKL1/MRTF-A-dependent gene transcription. Does not activate SRF:MKL1/MRTF-A through RhoA (PubMed:24440334). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24440334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29343822, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34106209}. | 3D-structure;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;FAD;Flavoprotein;LIM domain;Metal-binding;Monooxygenase;NADP;Nucleus;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc | The protein encoded by this gene is a monooxygenase that enhances depolymerization of F-actin and is therefore involved in cytoskeletal dynamics. The encoded protein is a regulator of the SRF signaling pathway. Increased expression of this gene has been associated with cancer progression and metastasis. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. | hsa:9645; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; FAD binding [GO:0071949]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; mitogen-activated protein kinase binding [GO:0051019]; NAD(P)H oxidase H2O2-forming activity [GO:0016174]; NADPH:sulfur oxidoreductase activity [GO:0043914]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen, NAD(P)H as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen [GO:0016709]; actin filament depolymerization [GO:0030042]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; heart development [GO:0007507]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; sulfur oxidation [GO:0019417] | 16675569_MICAL2-PV is likely to be involved in cancer progression of prostate cancer and could be a candidate as a novel molecular marker and/or target for treatment of prostate cancers. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22331357_although MICAL1 is auto-inhibited by its C-terminal coiled-coil region, MICAL2 remains constitutively active and affects stress fibers, suggesting differential but complementary roles for MICAL1 and MICAL2 in actin microfilament regulation 24440334_These data show that SRF/MRTF-A signaling is regulated by MICAL-2-dependent redox regulation of nuclear actin. 26689989_Data suggest that MICAL2 protein might be an important regulator of epithelial to mesenchymal transition and therefore a promising target for anti-metastatic therapy. 28719045_MICAL2 is a major regulator of breast cancer cell migration 30853343_In pulmonary artery hypertension miR-205-5p suppressed pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation by targeting MICAL2, which activated ERK1/2 signaling. 31004710_MICAL2 expression in endothelial cells participates to inflammation-induced neo-angiogenesis and that MICAL2 inhibition should be tested in cancer- and noncancer-associated neo-angiogenesis, where chronic inflammation represents a relevant pathophysiological mechanism. 32360180_MICAL2 is a novel nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein promoting cancer invasion and growth of lung adenocarcinoma. 34096155_MICAL2PV suppresses the formation of tunneling nanotubes and modulates mitochondrial trafficking. 34106209_MICAL2 enhances branched actin network disassembly by oxidizing Arp3B-containing Arp2/3 complexes. 34650666_MICAL2 Contributes to Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation by Promoting YAP Dephosphorylation and Nuclear Translocation. 36064550_MICAL2 contributes to gastric cancer cell migration via Cdc42-dependent activation of E-cadherin/beta-catenin signaling pathway. | ENSMUSG00000038244 | Mical2 | 578.051678 | 0.432505936 | -1.209208 | 0.24911223 | 22.902702 | 0.0000017041212193787775867941320165344087911307724425569176673889160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000271185979711835522620953092820528240736166480928659439086914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 322.5164845 | 94.1861937 | 751.3318255 | 219.5231525 | |
| ENSG00000134107 | 8553 | BHLHE40 | protein_coding | O14503 | FUNCTION: Transcriptional repressor involved in the regulation of the circadian rhythm by negatively regulating the activity of the clock genes and clock-controlled genes (PubMed:12397359, PubMed:18411297). Acts as the negative limb of a novel autoregulatory feedback loop (DEC loop) which differs from the one formed by the PER and CRY transcriptional repressors (PER/CRY loop) (PubMed:14672706). Both these loops are interlocked as it represses the expression of PER1/2 and in turn is repressed by PER1/2 and CRY1/2 (PubMed:15193144). Represses the activity of the circadian transcriptional activator: CLOCK-BMAL1|BMAL2 heterodimer by competing for the binding to E-box elements (5'-CACGTG-3') found within the promoters of its target genes (PubMed:15560782). Negatively regulates its own expression and the expression of DBP and BHLHE41/DEC2 (PubMed:14672706). Acts as a corepressor of RXR and the RXR-LXR heterodimers and represses the ligand-induced RXRA and NR1H3/LXRA transactivation activity (PubMed:19786558). May be involved in the regulation of chondrocyte differentiation via the cAMP pathway (PubMed:19786558). Represses the transcription of NR0B2 and attentuates the transactivation of NR0B2 by the CLOCK-BMAL1 complex (PubMed:28797635). Drives the circadian rhythm of blood pressure through transcriptional repression of ATP1B1 in the cardiovascular system (PubMed:30012868). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12397359, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14672706, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15193144, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15560782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18411297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19786558, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28797635, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30012868}. | Biological rhythms;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes a basic helix-loop-helix protein expressed in various tissues. The encoded protein can interact with ARNTL or compete for E-box binding sites in the promoter of PER1 and repress CLOCK/ARNTL's transactivation of PER1. This gene is believed to be involved in the control of circadian rhythm and cell differentiation. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2014]. | hsa:8553; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; bHLH transcription factor binding [GO:0043425]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; E-box binding [GO:0070888]; MRF binding [GO:0043426]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; circadian rhythm [GO:0007623]; entrainment of circadian clock by photoperiod [GO:0043153]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of circadian rhythm [GO:0042752]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 11688991_hypoxia-induced gene in pancreatic cancer cell lines 12119049_DEC1-mediated anti-apoptosis is achieved by blocking apoptotic pathways initiated via the mitochondria. The results functionally distinguish DEC1 from other bHLH proteins and directly link this factor to oncogenesis. 12354771_DEC1 and DEC2 may play a crucial role in the adaptation to hypoxia 12384505_DEC1 is the first transcription factor that can promote both chondrogenic differentiation and terminal differentiation 12397359_Dec1 and Dec2 are regulators of the mammalian molecular clock, and form a fifth clock-gene family. 12624110_DEC1-mediated repression on the expression of DEC2 provides an important mechanism that these transcription factors regulate the cellular function of members within the same class 15560782_Findings suggest that the basic region of DEC1 participates in the transcriptional regulation through a protein-protein interaction with BMAL1 and DNA binding to the E-box. 15719173_STRA13 interacts with the cell cycle-associated transcription factor MSP58. 15994878_STRA13 was expressed in epithelial cells of normal and neoplastic tissues mostly in the nucleus. Intense cytoplasmic STRA13 immunoreactivity was characteristic of myoepithelial and differentiated squamous epithelial cells and their neoplastic counterparts 16136500_DEC1 expression is found in the majority of 1p-aberrant oligodendroglial neoplasms; its immunohistochemical detection does not correlate with tisue hypoxia in this type of primary brain tumor. 16462771_DEC1 selectively increases the expression of survivin among antiapoptotic proteins. 16487626_These findings suggest that Dec1 modulates osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by inducing the expression of several, but not all, bone-related genes. 16878149_link between HIF-1 and STAT1 reveals a previously unknown role of STRA13 in hypoxia and carcinogenesis 17376295_differentiated embryo-chondrocyte expressed gene 1 downregulates hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha at both mRNA and protein levels at hypoxia in lung adenocarcinoma cells 18025081_DEC1 is induced by the p53 family and DNA damage in a p53-dependent manner. p53 family proteins bind to, and activate, the promoter of the DEC1 gene. 18228528_A multi-locus interaction between rs6442925 in the 5' upstream of BHLHB2, rs1534891 in CSNK1E, and rs534654 near the 3' end of the CLOCK gene, however, is significantly associated with bipolar disorder 18228528_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18345027_MLH1 is transcriptionally repressed by the hypoxia-inducible transcription factors, DEC1 and DEC2. 18411297_DEC1, along with DEC2, plays a role in the finer regulation and robustness of the molecular clock CLOCK/BMAL1 19590847_Identificaiton of BHLHB2 as a potential novel mediator of insulin transcriptional action in human skeletal muscle. 19624270_The hypoxia-regulated transcription factor DEC1 and its expression in gastric cancer are reported. 19693801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20072116_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20174623_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20863812_Hypoxia-inducible BHLHB2 expression is a novel independent prognostic marker in pancreatic cancer patients and indicates increased chemosensitivity towards gemcitabine. 21317427_Study conclude that DeltaNp63 is a novel target of DEC1 and HDAC2 and modulates the efficacy of HDAC inhibitors in growth suppression and keratinocyte differentiation. 21327324_DEC1 has pro-apoptotic effects on the paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. 21528084_DEC1 is expressed in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes and because nuclear DEC1 expression is decreased with decreasing differentiation status ofhepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), nuclear DEC1 might be a marker of HCC differentiation 21779800_DEC1 expression is correlated with HIF-1alpha protein in gastric cancer cell line. 21829689_findings suggested that posttranslational modification of DEC1 in the form of SUMOylation may serve as a key factor that regulates the function of DEC1 in vivo 21867633_Expression of BHLHB2 is inhibited by PML-RARalpha through binding to its promoter in acute promyeloid leukemia. 22644784_IL-1beta can induce DEC1 and HIF-1alpha protein levels in gingival epithelial cells. We also demonstrate that the increase in DEC1 protein subsequently is followed by Akt phosphorylation. 22678901_Marginal zone B cells activated by hepatitis C virus undergo functional exhaustion associated with BCR signaling defects and overexpression of a key antiproliferative gene, and may subsequently become terminally spent CD21(low) B cells. 22723347_DEC1 controls the response of p53-dependent cell survival vs. cell death to a stress signal through MIC-1 22728071_findings suggest that the repression of CYP3A4 by IL-6 is achieved through increasing the DEC1 expression in human hepatocytes, the increased DEC1 binds to the CCCTGC sequence in the promoter of CYP3A4 to form CCCTGC-DEC1 complex 22825629_These findings suggest that DEC1 plays an important role in the regulation of these EMT-related factors in pancreatic cancer. 22844531_DEC1 overexpression in precursor lesions of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is a protective mechanism 22905217_SUMO modification of Stra13 is required for repression of cyclin D1 expression and cellular growth arrest 23220548_Staircase-style fluctuations in the BHLHE40 mRNA accumulation relate to the short half-life of the gene's mRNA of 0.9h. 23423709_Loss of DEC1 may promote tumor progression in non-small-cell lung cancer through upregulation of cyclin D1 23426649_Studied DEC1 & claudin-1 in invasive breast ductal carcinomas;found DEC1 elevated in invasive breast ductal carcinoma. DEC1 knockdown led to the enhanced expression of claudin-1 at both the mRNA and protein levels in breast cancer cell lines. 23445622_DEC1 level was positively correlated with HIF-1alpha and Ki67 expression in gastric cancer. 23578198_Sunitinib treatment performance could be attributable to TIS, depending on p53/Dec1 activation. 24100543_The efficacy of inhibiting HIF-1alpha and DEC1 expression as a possible treatment for HCC should be assessed in clinical trials. 24397494_Study demonstrates that DEC1 is involved in osteogenesis. 24404147_DEC1 coordinates with HDAC8 to differentially regulate TAp73 and DeltaNp73 expression. 24758579_The expression of DEC1 was associated with the incidence of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) and there was a negative correlation between the expression of DEC1 and the prognosis of OSCC. 25202122_USP17 binds and deubiquitylates DEC1, markedly extending its half-life. Subsequently, during checkpoint recovery, DEC1 proteolysis is reestablished through betaTrCP-dependent ubiquitylation. 25876658_DEC1 has a pro-apoptotic effect on human esophageal cancer TE 10 cells of well-differentiated type. 26340669_decreases of CES and CYP3A4 expression and enzymatic activities induced by Fluoxetine are through decreasing PXR and increasing DEC1 in HepG2 cells 26391953_BHLHE40/41 are promising markers to predict the aggressiveness of each Endometrial Neoplasm case and that molecular targeting strategies involving BHLHE40/41 and SP1 may effectively regulate Endometrial Neoplasm progression. 26967308_BHLHE40 was identified as a viable candidate for which a droplet digital PCR assay for demethylation was developed. The assay revealed high demethylation in activated NK cells and low demethylation in naive NK, T- and B-cells. We conclude the NK cell methylome is plastic with potential for remodeling. 26967585_STRA13 may be essential for the progression of atopic dermatitis by interacting with hsa-miR-148b and hsamiR- 152. 27591677_High BHLHE40 expression is associated with glioblastomas. 27765932_Cisplatin-induced synthetic lethality to arginine-starvation therapy by transcriptional suppression of ASS1 is regulated by DEC1, HIF-1alpha, and c-Myc transcription network and is independent of ASS1 promoter DNA methylation. 27840944_Dec1 is a prognostic factor for the clinical outcome and a predictive factor for the response to TMZ chemotherapy in patients with glioma 28794399_DEC1 is involved in hypoxia-induced EMT processes via negatively regulating E-cadherin expression in HepG2 cells. 28797635_This study was performed to test the hypothesis that the SHP gene is a target gene of DEC1. Cotransfection demonstrated that DEC1 repressed the SHP promoter and attenuated the transactivation of the classic circadian activator complex of Clock/Bmal1. 29601939_The expression of transcription factor BHLHE40 DEC1/STRA13) is induced in human naive and memory resting B cells by activation through the B-cell receptor (BCR) or Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9). DEC1/STRA13 is upregulated in human anergic CD21(low) B cells clonally expanded in patients with HCV-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia, which fail to proliferate in response to BCR or TLR9 ligation. 29704436_BHLHE40 suppressed CLDN1 transcription by preventing the interaction between SP1 and a specific motif within the promoter region of CLDN1. 30002194_Study reveals sCLU as a novel target of DEC1 (BHLHE40) which modulates the sensitivity of the DNA damage response. DEC1 and sCLU are frequently overexpressed in breast cancer. 30158530_DEC1 expression is a specific feature of tumor cells, that this transcription factor is significantly over-expressed in all major thyroid cancer histotypes and that its expression correlated with NOTCH1 in these tumors. 30285805_Gene expression analysis suggests a role of basic helix-loop-helix protein 40 (BHLHE40) in transcriptional activation of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (HBEGF). 30442142_The involvement of DEC1 provides new insight into the positive or negative functional roles of p53 in the metformin-induced cytotoxicity in tumor cells. 31914631_BHLHE40 upregulation in gastric epithelial cells increases CXCL12 production through interaction with p-STAT3 in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis 32483833_LncRNA-ES3 inhibition by Bhlhe40 is involved in high glucose-induced calcification/senescence of vascular smooth muscle cells. 32522343_DEC1 directly interacts with estrogen receptor (ER) alpha to suppress proliferation of ER-positive breast cancer cells. 32579212_BHLHE40 plays a pathological role in pre-eclampsia through upregulating SNX16 by transcriptional inhibition of miR-196a-5p. 32885250_Systematic screening of CTCF binding partners identifies that BHLHE40 regulates CTCF genome-wide distribution and long-range chromatin interactions. 33176151_TFEB Transcriptional Responses Reveal Negative Feedback by BHLHE40 and BHLHE41. 33507476_Loss of Dec1 prevents autophagy in inflamed periodontal ligament fibroblast. 34045534_Identification of BHLHE40 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells as a novel biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 34215553_Role of differentiated embryo-chondrocyte expressed gene 1 (DEC1) in immunity. 34481230_Hypoxia-induced DEC1 mediates trophoblast cell proliferation and migration via HIF1alpha signaling pathway. 34638690_The Potential Roles of Dec1 and Dec2 in Periodontal Inflammation. 34758708_DEC1 negatively regulates CYP2B6 expression by binding to the CYP2B6 promoter region ascribed to IL-6-induced downregulation of CYP2B6 expression in HeLa cells. 34758939_Differentiated embryo chondrocyte 1, induced by hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha, promotes cell migration in oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. 35217585_REL and BHLHE40 Variants Are Associated with IL-12 and IL-10 Responses and Tuberculosis Risk. 35334277_Differentiated embryonic chondrocyte expressed gene-1 (DEC1) enhances the development of colorectal cancer with an involvement of the STAT3 signaling. 35689549_Upregulation of INHBA mediated by the transcription factor BHLHE40 promotes colon cancer cell proliferation and migration. 36053880_Overexpression of DEC1 in the epithelium of OSF promotes mesenchymal transition via activating FAK/Akt signal axis. | ENSMUSG00000030103 | Bhlhe40 | 837.896948 | 0.481560106 | -1.054212 | 0.06765221 | 243.061588 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008455903471617487480073116334894924335228934142450802340771221833450710676947397030819438507372868536920868387287613016130041935354783120410 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001714219967550512968382130422299106304188240189024285565207402403579723680252141701361278057233847290075806663464253846939054275546904931860 | Yes | No | 533.0089396 | 45.5742232 | 1111.9544717 | 93.2711240 | |
| ENSG00000134256 | 9398 | CD101 | protein_coding | Q93033 | FUNCTION: Plays a role as inhibitor of T-cells proliferation induced by CD3. Inhibits expression of IL2RA on activated T-cells and secretion of IL2. Inhibits tyrosine kinases that are required for IL2 production and cellular proliferation. Inhibits phospholipase C-gamma-1/PLCG1 phosphorylation and subsequent CD3-induced changes in intracellular free calcium. Prevents nuclear translocation of nuclear factor of activated T-cell to the nucleus. Plays a role in the inhibition of T-cell proliferation via IL10 secretion by cutaneous dendritic cells. May be a marker of CD4(+) CD56(+) leukemic tumor cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11093127, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15737213, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7722299, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9233604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9389317, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9647226}. | Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Predicted to enable hydrolase activity, acting on carbon-nitrogen (but not peptide) bonds, in cyclic amides. Predicted to be involved in cell surface receptor signaling pathway. Predicted to act upstream of or within positive regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:9398; | extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; hydrolase activity, acting on carbon-nitrogen (but not peptide) bonds, in cyclic amides [GO:0016812]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; positive regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation [GO:0002763] | 19898481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21159825_Results suggest a possible role for CD101 expression and function in the control of certain manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis pathology. 21467233_Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in CD101 gene may be associated with pancreatic cancer. 25421756_Low expression of CD39(+) /CD45RA(+) on regulatory T cells (Treg ) cells in type 1 diabetic children in contrast to high expression of CD101(+) /CD129(+) on Treg cells in children with coeliac disease. 26813346_In patients with intestinal bowel disease, a reduced CD101 expression on peripheral and intestinal monocytes and CD4-positive Tcells correlated with enhanced IL-17 production and disease activity. 27888582_Study shows nucleotide substitutions in CD101, the human homolog of a diabetes susceptibility gene in non-obese diabetic mouse, in patients with type 1 diabetes. The results raise the possibility that CD101 is a susceptibility gene for type 1 diabetes. 29108000_variants in CD101 and UBE2V1 associated with increased risk of sexually acquired HIV-1 32976203_Brief Report: Bacterial Vaginosis and Risk of HIV Infection in the Context of CD101 Gene Variation. 34195685_CD101 genetic variants modify regulatory and conventional T cell phenotypes and functions. | ENSMUSG00000086564 | Cd101 | 76.209557 | 0.434460353 | -1.202704 | 0.25889863 | 21.218939 | 0.0000040969602245515671415897196450117689892067573964595794677734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000602610721567059079060123261140091699417098425328731536865234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 47.1742758 | 10.9727220 | 107.4342037 | 24.6283190 | |
| ENSG00000134321 | 91543 | RSAD2 | protein_coding | Q8WXG1 | FUNCTION: Interferon-inducible antiviral protein which plays a major role in the cell antiviral state induced by type I and type II interferon (PubMed:31812350). Catalyzes the conversion of cytidine triphosphate (CTP) to 3'-deoxy-3',4'-didehydro-CTP (ddhCTP) via a SAM-dependent radical mechanism (PubMed:29925952, PubMed:30872404). In turn, ddhCTP acts as a chain terminator for the RNA-dependent RNA polymerases from multiple viruses and directly inhibits viral replication (PubMed:29925952). Therefore, inhibits a wide range of DNA and RNA viruses, including human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), west Nile virus (WNV), dengue virus, sindbis virus, influenza A virus, sendai virus, vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), zika virus, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) (PubMed:29925952, PubMed:30587778, PubMed:31921110, PubMed:30934824). Promotes also TLR7 and TLR9-dependent production of IFN-beta production in plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) by facilitating 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitination of IRAK1 by TRAF6 (PubMed:30872404). Plays a role in CD4+ T-cells activation and differentiation. Facilitates T-cell receptor (TCR)-mediated GATA3 activation and optimal T-helper 2 (Th2) cytokine production by modulating NFKB1 and JUNB activities. Can inhibit secretion of soluble proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11752458, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16108059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16982913, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17686841, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18005719, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19074433, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29925952, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30587778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30872404, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30934824, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31812350, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31921110}. | 4Fe-4S;Acetylation;Antiviral defense;Atherosclerosis;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Innate immunity;Iron;Iron-sulfur;Isopeptide bond;Lipid droplet;Lyase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Ubl conjugation | The protein encoded by this gene is an interferon-inducible antiviral protein that belongs to the S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) superfamily of enzymes. The protein plays a role in cellular antiviral response and innate immune signaling. Antiviral effects result from inhibition of viral RNA replication, interference in the secretory pathway, binding to viral proteins and dysregulation of cellular lipid metabolism. The protein has been found to inhibit both DNA and RNA viruses, including influenza virus, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) and Zika virus. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2020]. | hsa:91543; | endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding [GO:0051539]; lyase activity [GO:0016829]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation [GO:0035710]; CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation [GO:0043367]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050709]; negative regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045071]; positive regulation of immune response [GO:0050778]; positive regulation of T-helper 2 cell cytokine production [GO:2000553]; positive regulation of toll-like receptor 7 signaling pathway [GO:0034157]; positive regulation of toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway [GO:0034165]; response to virus [GO:0009615] | 15890971_Viperin is expressed in atherosclerosis and induced in vascular cells by inflammatory stimuli and cytomegalovirus infection 16108059_ISG (interferon-stmiulated genese) viperin has anti-Hepatitis c virus activity in vitro; we postulate that viperin, and other ISGs, acts to limit HCV replication. 16849320_Results identify Viperin as a tightly regulated ISGF3 target gene, which is counter-regulated by PRDI-BF1. 17626075_poly(I:C) upregulated TLR3, thereby augmenting the primary (IFN-beta) and secondary (IDO and viperin) response genes 18005724_Overexpression of farnesyl diphosphate synthase reverses viperin-mediated inhibition of virus production and restores normal membrane fluidity. 18077728_This work, for the first time, provides strong evidence suggesting that viperin is a putative radical S-adenosyl-l-methionine (SAM) enzyme. 18768981_The results suggest that even though viperin gene expression is highly induced by Japanese encephalitis virus, it is negatively regulated at the protein level to counteract its antiviral effect. 19074433_The N-terminal amphipathic alpha-helix of viperin mediates localization to the cytosolic face of the endoplasmic reticulum and inhibits protein secretion 19920176_Viperin inhibits hepatitis C virus (HCV) by localizing to lipid droplets using a domain and mechanism similar to that used by HCV itself. 20026307_the first experimental evidence confirming that viperin is indeed a radical SAM enzyme provided. 20176015_Incubation of reduced viperin with SAM results in reductive cleavage of SAM to produce 5'-deoxyadenosine (5'-dAdo), a reaction characteristic of the radical SAM superfamily. 20534863_IFITM2 and IFITM3, disrupted early steps (entry and/or uncoating) of the viral infection, viperin, ISG20, and double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase, inhibited steps in west nile virus and dengue virus viral proteins and/or RNA biosynthesis. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21053045_Data idenified two cleavage sites for RNase MRP/RNase P in the coding sequence of viperin mRNA. 21527675_study shows human cytomegalovirus (HCMV)-induced viperin disrupts cellular metabolism to enhance infectious process; viperin interaction with vMIA resulted in viperin relocalization from endoplasmic reticulum to mitochondria 21957124_Viperin inhibits hepatitis C virus replication by interfering with binding of NS5A to host protein VAP-33. 22045669_We propose that viperin interacts with NS5A and the host factor, VAP-A, to limit hepatitis C virus replication at the replication complex. 22182524_Viperin is now known to act in different ways in the inhibition of the replication of different viruses that employ different mechanisms and organelles in their replication cycle. [Review] 22363738_Viperin is an alpha-beta protein containing iron-sulfur cluster at the center pocket. 22377585_Viperin restrict influenza H1N1 virus replication in vitro. 22896602_The restriction of Bunyamwera virus replication mediated by interferon is an accumulated effect of at least three interferon-stimulated genes viperin, MTAP44 and PKR. 23018837_inhibits replication of respiratory syncytial virus 23160199_viperin is a critical antiviral host protein that controls chikungunya virus infection. 23638199_Viperin is induced following dengue virus type-2 (DENV-2) infection and has anti-viral actions requiring the C-terminal end of viperin. 23935494_The data indicate that viperin is the major effector underlying the ability of HCMV to regulate cellular lipid metabolism. 24245804_These data suggest that viperin requires CIAO1 for [4Fe-4S] cluster assembly, and acts through an enzymatic, Fe-S cluster- and SAM-dependent mechanism to inhibit viral RNA synthesis. 25433308_data suggested that viperin impaired respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) transmission by inhibiting virus filament formation, providing a basis for its anti-virus activity in RSV-infected cells 25814471_Viperin was localized in trophoblast cells. HCMV IE1 mRNA expression was significantly inhibited by viperin RNA interference. 25997337_Viperin inhibits viral replication by interactiing with host cell proteins and viral proteins. [review] 27943419_Exposure to hepatitis B virus up-regulates viperin expression in vivo and in vitro in placental trophoblast, and lack of this up-regulation is associated with intrauterine transmission of hepatitis B virus. 28242342_Study demonstrated that viperin expression was significantly down-regulated in the epidermis of wart patient's samples compared to normal samples. In cell culture viperin expression was reversed by E7-specific siRNA. HPV-2 E7 dampens viperin expression to evade antiviral activity in persistent infections. 28615450_Data suggest that CIA2B and MMS19 physically interact with C-terminus of viperin/RSAD2; CIAO1 appears to function as primary viperin-interacting protein; CIA2A binds to N-terminus of viperin in CIAO1-, CIA2B-, and MMS19-independent fashion. (CIA2B = metallochaperone CIA2B/FAM96B; MMS19 = transcription factor MMS19; CIAO1 = cytosolic iron-sulfur assembly component 1; CIA2A = metallochaperone CIA2A/Fam96a) 28667332_These results suggest that ZIKV can attenuate ISG expression to avoid the cellular antiviral innate response, thus allowing the virus to replicate unchecked. Moreover, we have identified that the ISG viperin has significant anti-ZIKV activity. 28708394_Data suggest that human viperin exerts 'ancient radical' SAM-dependent activity in invading bacteria such as Escherichia coli; here, expression of recombinant viperin induces dramatically elongated morphology of 'host'/pathogen cells. (SAM = S-adenosylmethionine) 29046456_Study shows that viperin induces capsid particle release by interacting and inhibiting the function of the cellular protein GBF1. 29202415_Viperin N-terminal is necessary for the interaction with Junin viral nucleoprotein. 29251770_Study reports the identification of geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) and farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), two terpene intermediates in the mevalonate pathway, as substrates of human viperin. 29263272_RSAD2 and AIM2 Modulate Coxsackievirus A16 and Enterovirus A71 Replication in Neuronal Cells in Different Ways That May Be Associated with Their 5' Nontranslated Regions. 29321318_viperin also reduced the stability of several other viral proteins in a NS3-dependent manner, suggesting a central role of NS3 in viperin's antiflavivirus activity. 30059238_Viperin is antivirally active against many different viruses from different families and has been shown to inhibit several flaviviruses. Authors summarize the current knowledge about viperin and its role in antiflavivirus defense. [Review] 30684519_In this study, the authors report that Radical S-adenosyl methionine domain containing 2 (RSAD2) restricts measles virus infection at the stage of virus release in infected 293T cells. 30718282_Viperin (also known as radical SAM domain-containing 2 (RSAD2)) is expressed in differentiating chondrocytic cells and regulates their protein secretion and the outcome of chondrogenic differentiation by influencing transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta)/SMAD family 2/3 (SMAD2/3) activity via C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10). 30872404_conclude that the synergistic activation of viperin and IRAK1 provides a mechanism that couples innate immune signaling with the production of the antiviral nucleotide ddhCTP 30934824_Lys358 was a key amino-acid in viperin antiviral properties against Zika virus. 31225658_Weighted gene correlation network analysis identifies RSAD2, HERC5, and CCL8 as prognostic candidates for breast cancer. 31489375_A pivotal role of viperin in catalyzing the methionine oxidation of helicases. 31517388_Viperin inhibits classical swine fever virus replication by interacting with viral nonstructural 5A protein. 31666594_The interferon stimulated gene viperin, restricts Shigella. flexneri in vitro. 31980458_Targeting viperin to the mitochondrion inhibits the thiolase activity of the trifunctional enzyme complex. 32061099_Viperin, through its radical-SAM activity, depletes cellular nucleotide pools and interferes with mitochondrial metabolism to inhibit viral replication. 32232843_ddhCTP produced by the radical-SAM activity of RSAD2 (viperin) inhibits the NAD(+) -dependent activity of enzymes to modulate metabolism. 32546482_Viperin: An ancient radical SAM enzyme finds its place in modern cellular metabolism and innate immunity. 32937646_Prokaryotic viperins produce diverse antiviral molecules. 33512636_Knockdown of RSAD2 attenuates B cell hyperactivity in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome (pSS) via suppressing NF-kappab signaling pathway. 34029588_The antiviral enzyme viperin inhibits cholesterol biosynthesis. 34108265_Viperin interacts with PEX19 to mediate peroxisomal augmentation of the innate antiviral response. 34372530_Viperin, an IFN-Stimulated Protein, Delays Rotavirus Release by Inhibiting Non-Structural Protein 4 (NSP4)-Induced Intrinsic Apoptosis. | ENSMUSG00000020641 | Rsad2 | 59.031859 | 0.232778395 | -2.102971 | 0.23618096 | 83.944876 | 0.0000000000000000000508764729341555470599461642814359160302958976581826018624823970704085240868153050541877746582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000035761814241355164384814895871508258641126618994202958357053745430675917305052280426025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 21.5974420 | 3.7679346 | 93.1946996 | 13.5656495 | |
| ENSG00000134326 | 129607 | CMPK2 | protein_coding | Q5EBM0 | FUNCTION: May participate in dUTP and dCTP synthesis in mitochondria. Is able to phosphorylate dUMP, dCMP, CMP, UMP and monophosphates of the pyrimidine nucleoside analogs ddC, dFdC, araC, BVDU and FdUrd with ATP as phosphate donor. Efficacy is highest for dUMP followed by dCMP; CMP and UMP are poor substrates. May be involved in mtDNA depletion caused by long term treatment with ddC or other pyrimidine analogs. Also displays broad nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17999954, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23416111}. | Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Coiled coil;Kinase;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Pyrimidine biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transit peptide | This gene encodes one of the enzymes in the nucleotide synthesis salvage pathway that may participate in terminal differentiation of monocytic cells. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. | hsa:129607; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; CMP kinase activity [GO:0036430]; cytidylate kinase activity [GO:0004127]; dCMP kinase activity [GO:0036431]; nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity [GO:0004550]; thymidylate kinase activity [GO:0004798]; UMP kinase activity [GO:0033862]; uridylate kinase activity [GO:0009041]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; dTDP biosynthetic process [GO:0006233]; dTTP biosynthetic process [GO:0006235]; dUDP biosynthetic process [GO:0006227]; nucleoside diphosphate phosphorylation [GO:0006165]; nucleoside triphosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0009142] | 17999954_a human mitochondrial UMP-CMP kinase (UMP-CMPK, cytidylate kinase; EC 2.7.4.14), designated as UMP-CMP kinase 2 (UMP-CMPK2), is identified. 18498354_Upregulated in monocyte/macrophage differentiating cells, suggesting coordinated regulation with the terminal differentiation program. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 33874983_Mitochondrial protein CMPK2 regulates IFN alpha-enhanced foam cell formation, potentially contributing to premature atherosclerosis in SLE. | ENSMUSG00000020638 | Cmpk2 | 31.155367 | 0.458690870 | -1.124406 | 0.30143638 | 14.125149 | 0.0001710416378362845262785241207126318840892054140567779541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0016523000207554889001010378635214692621957510709762573242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 17.9395331 | 5.7440747 | 39.2174114 | 12.0291683 | |
| ENSG00000134815_ENSG00000134830 | 96.807764 | 0.023236867 | -5.427441 | 1.12184389 | 15.626113 | 0.0000771813653265666514734569259026386589539470151066780090332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0008253921545779926462194087122270502732135355472564697265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 6.9825811 | 5.2805650 | 148.0618409 | 105.6149798 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000134815_ENSG00000288827 | 25.863338 | 0.004038498 | -7.951965 | 1.25496550 | 42.484479 | 0.0000000000712453520503266684038425319124422478711533557316215592436492443084716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000021478016906895893001181143864251887887206748928292654454708099365234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 0.1763081 | 0.2576937 | 45.0321252 | 48.7972108 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000135074 | 8728 | ADAM19 | protein_coding | Q9H013 | FUNCTION: Participates in the proteolytic processing of beta-type neuregulin isoforms which are involved in neurogenesis and synaptogenesis, suggesting a regulatory role in glial cell. Also cleaves alpha-2 macroglobulin. May be involved in osteoblast differentiation and/or osteoblast activity in bone (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;SH3-binding;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc;Zymogen | This gene encodes a member of the ADAM (a disintegrin and metalloprotease domain) family. Members of this family are membrane-anchored proteins structurally related to snake venom disintegrins and have been implicated in a variety of biological processes involving cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, including fertilization, muscle development, and neurogenesis. This member is a type I transmembrane protein and serves as a marker for dendritic cell differentiation. It has been demonstrated to be an active metalloproteinase, which may be involved in normal physiological processes such as cell migration, cell adhesion, cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, and signal transduction. It is proposed to play a role in pathological processes, such as cancer, inflammatory diseases, renal diseases, and Alzheimer's disease. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. | hsa:8728; | collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metalloendopeptidase activity involved in amyloid precursor protein catabolic process [GO:1902945]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; amyloid precursor protein catabolic process [GO:0042987]; membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0006509]; placenta development [GO:0001890]; positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin [GO:2000049]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; protein processing [GO:0016485] | 12006600_activation by furin via one of two consecutive recognition sites 12393862_investigation of proteolytic activity 12463424_yeast two-hybrid screen performed in fetal brain cDNA library isolated four proteins that interact with the cytoplasmic tail of ADAM19 15242783_A new autolytic processing site at Lys543-Val544 was identified in soluble mutants of ADAM19 when these cysteine residues were individually mutated to serine residues. 15896713_ChIP assays demonstrated high levels of acetylated histone H3 in the promoter region of the MADDAM gene in TSA-treated THP-1 cells/dendritic cells compared to macrophages, indicating an important role of histone acetylation in regulating the MADDAM gene. 16827870_ADAM19 may have a modulatory role in the dysfunctional renal allograft state 17112471_results suggest that ADAM19 has a constitutive alpha-secretase activity for amyloid precursor protein 18458692_ADAM19 correlates with the progress and prognosis of endometrial carcinoma. 18714391_we suggest that epigenetic dysregulation of ADAM19 may contribute to the neoplastic process in ovarian cancer. 19079262_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19727588_ADAM19 may participate in the coordinated regulation of human trophoblast cell behaviors during the process of placentation. 20010835_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20460109_These findings suggest that ADAM19 autolysis is activated by lipopolysaccharide and that ADAM19 promotes the secretion of CRIP2. 21239057_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in ADAM19 gene is associated with lymphoma. 21270819_Prorenin receptor is mainly localized in the subcellular organelles, such as the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, and the prorenin receptor is cleaved by ADAM19 in the Golgi, resulting in two fragments. 23429442_ADAM19 was upregulated in patients with ulcerative colitis and, to a lesser extent, in patients with Crohn's disease compared with normal controls. In contrast, ADAM9 and ADAM10 expression did not differ between patients with IBD and controls. 24951661_ADAM19 rs1422795 and HTR4 rs11168048 are associated with pulmonary function. 25114068_four suggestive loci (PAX3, CCRN4L, PIGQ, and ADAM19)determinants of disease progression in Alzheimer's disease. 25475731_MiR-153 has a role in inhibiting migration and invasion of human non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting ADAM19 25799050_miR-30c inhibited colon cancer cells via targeting ADAM19. 26823772_these findings suggested that miR-145 functions as a tumor suppressor in RB by directly targeting ADAM19 in retinoblastoma cells 26912236_ADAM19 is a protective factor for human prostate cancer. Further, this study suggests that upregulation of ADAM19 expression could be of therapeutic potential in human prostate cancer. 27078193_3 SNPs (rs4329505 and rs4845626 in interleukin 6 receptor [IL6R] and rs1422794 in a disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain 19 [ADAM19]) were associated with a lower risk of suffering the most severe stages of the disease. 31352763_MiR-874-3p suppresses cell proliferation and invasion by targeting ADAM19 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 31675985_ADAM19 hypermethylation was associated with more advanced gastric neoplasm (GC) as stage IV. 32844346_Circular RNA has_circ_0000034 accelerates retinoblastoma advancement through the miR-361-3p/ADAM19 axis. 32960074_Comparison of ADAM19 and CUEDC2 expression in EHCC and their clinicopathological significance. 33548228_The elevated transcription of ADAM19 by the oncohistone H2BE76K contributes to oncogenic properties in breast cancer. 33775119_MicroRNA-874-3p/ADAM (A Disintegrin and Metalloprotease) 19 Mediates Macrophage Activation and Renal Fibrosis After Acute Kidney Injury. 34927445_Synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-320c enhances chondrogenesis by targeting ADAM19. 35902972_Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-335-5p attenuates the inflammation and tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation of renal tubular epithelial cells by reducing ADAM19 protein levels. | 120.353586 | 0.419663281 | -1.252696 | 0.16752085 | 56.355990 | 0.0000000000000604687841084576062155402779028173394500027260090035952089237980544567108154296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000025324471620033084920197728932844083936902490616915883947513066232204437255859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 73.0748403 | 8.0677631 | 175.2509341 | 17.2260969 | |||
| ENSG00000135114 | 8638 | OASL | protein_coding | Q15646 | FUNCTION: Does not have 2'-5'-OAS activity, but can bind double-stranded RNA. Displays antiviral activity against encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) via an alternative antiviral pathway independent of RNase L. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18931074, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20074559, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9826176}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;Immunity;Innate immunity;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding | Enables DNA binding activity and double-stranded RNA binding activity. Involved in several processes, including interleukin-27-mediated signaling pathway; negative regulation of viral genome replication; and positive regulation of RIG-I signaling pathway. Located in cytosol; nucleolus; and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:8638; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; nuclear thyroid hormone receptor binding [GO:0046966]; nucleotidyltransferase activity [GO:0016779]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; interleukin-27-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070106]; negative regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045071]; positive regulation of RIG-I signaling pathway [GO:1900246]; regulation of ribonuclease activity [GO:0060700]; response to virus [GO:0009615] | 14728690_interaction with methyl CpG-binding protein 1 was confirmed in vitro and in vivo and was mapped to the ubiquitin-like domain of p59 OASL 16235172_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18571276_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18931074_Proof that OASL is an antiviral protein that works through a novel mechanism distinct from other OASL proteins in other vertebrate species. 19203244_The pronounced difference in gene regulation between the OASL gene agrees with a functional difference between these genes, which must exist as a consequence of the lack of the 2-5A synthetase activity of the OASL protein. 19559055_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20074559_OASLa, a major isoform of OASL induced in human liver, may mediate anti-HCV activity through two different domains. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20506645_The expression of OASL and IFIT2 was significantly higher in SLE patients than in controls. 20588308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20889853_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21050126_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21943158_variants in LPL, OASL and TOMM40/APOE-C1-C2-C4 genes are associated with multiple cardiovascular-related traits 23306614_we propose that VSV treatment combined with the selective regulation of genes such as STAT1 and OASL2 will improve therapeutic outcomes for CUG2-overexpressing tumors 24328427_Primary mononuclear cells from patients with systemic sclerosis have increased basal levels of OASL and OAS2 genes. 24931123_these findings show a mechanism by which human OASL contributes to host antiviral responses by enhancing RIG-I activation. 26178980_OASL acts as a cellular antiviral protein and RSV NS1 suppresses this function to evade cellular innate immunity and allow virus growth. 27190175_These data uncover a promycobacterial role for STING-dependent OASL production during Mycobacterium leprae infection that directs the host immune response toward a niche that permits survival of the pathogen. 30635239_these resulta define distinct mechanisms by which OASL differentially regulates host IFN responses during RNA and DNA virus infection and identify OASL as a negative-feedback regulator of cGAS 31855809_OASL regulates pro-inflammatory mediators such as cytokines and chemokines which suppress intracellular mycobacterial growth and survival. | ENSMUSG00000041827 | Oasl1 | 19.179693 | 0.220905743 | -2.178497 | 0.42261425 | 28.412817 | 0.0000000980142789624907867170494927752666391995717276586219668388366699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000019310193438412974637223475798952776472106052096933126449584960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 6.6931633 | 2.0861958 | 30.5449161 | 7.7193938 | |
| ENSG00000135253 | 375616 | KCP | protein_coding | Q6ZWJ8 | FUNCTION: Enhances bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling in a paracrine manner. In contrast, it inhibits both the activin-A and TGFB1-mediated signaling pathways (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal | Predicted to act upstream of or within hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation and positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway. Predicted to be located in extracellular space. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:375616; | extracellular space [GO:0005615]; BMP binding [GO:0036122]; BMP receptor binding [GO:0070700]; positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030513] | 30144436_The KCP was closely associated with heart failure. The regulation of BMP2/7 and TGF-beta1 expression may be the possible mechanisms. | ENSMUSG00000059022 | Kcp | 72.972795 | 0.321007830 | -1.639320 | 0.21544715 | 58.328725 | 0.0000000000000221782102162465559169679562892527192938111387648936201344440632965415716171264648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000009693296546793912905176840780695146843667225899920936171838548034429550170898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 37.4005406 | 5.3991081 | 117.2795334 | 15.2449256 | |
| ENSG00000135454 | 2583 | B4GALNT1 | protein_coding | Q00973 | FUNCTION: Involved in the biosynthesis of gangliosides GM2, GD2, GT2 and GA2 from GM3, GD3, GT3 and GA3, respectively. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1601877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7487055, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7890749}. | Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Sphingolipid metabolism;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | PATHWAY: Sphingolipid metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1601877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7487055, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7890749}. | GM2 and GD2 gangliosides are sialic acid-containing glycosphingolipids. GalNAc-T is the enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of G(M2) and G(D2) glycosphingolipids. GalNAc-T catalyzes the transfer of GalNAc into G(M3) and G(D3) by a beta-1,4 linkage, resulting in the synthesis of G(M2) and G(D2), respectively. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2013]. | hsa:2583; | Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; (N-acetylneuraminyl)-galactosylglucosylceramide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0003947]; acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008376]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; ganglioside biosynthetic process [GO:0001574]; glycosphingolipid metabolic process [GO:0006687]; lipid glycosylation [GO:0030259]; lipid storage [GO:0019915]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] | 17119850_The expression of three messengers coding for SAT-1, SAT-2 and GalNAcT-1 in human samples of intestinal cancer and some cell lines (breast cancer and melanomas), was evaluated. 19318031_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19318031_Transmission disequilibrium test and case-control analysis did not detect an association of B4GALNT1 gene with T1DM. 19457569_GD2/GM2 is not a reliable biomarker in small cell lung carcinoma 21135695_Molecular upstaging of GalNAc-T using rt-pcr was correlated with prognosis in melanoma patients 23721779_Minimally disseminated disease in high risk retinoblastoma patients was detected using reverse transcriptase PCR for GD2 synthase mRNA in CSF. 24103911_The resukts of this study identified mutations in B4GALNT1 (GM2 synthase), encoding the enzyme that catalyzes the second step in complex ganglioside biosynthesis, as the cause of this neurodegenerative phenotype. 24283893_Novel B4GALNT1 mutations reported in two families with hereditary spastic paraplegia. 28698248_Data suggest that ganglioside glycosyltransferases ST3GAL5, ST8SIA1, and B4GALNT1 are S-acylated at conserved cysteine residues located close to cytoplasmic border of their transmembrane domains; ST3Gal-II is acylated at conserved cysteine residue in N-terminal cytoplasmic tail; for B4GALNT1 and ST3Gal-II, dimer formation controls their S-acylation status. 29983310_Since the nineties, mice lacking genes for single glycosyltransferases involved in ganglioside biosynthesis, including ST3GAL5 and B4GALNT1, were created and studied. The resulting phenotypes were frequently mild or very mild, so double knock-out animals were created to effectively study the function of gangliosides 30463940_Sp1 or HDAC1 knock down increased GM2-synthase transcription, and butyrate-mediated activation of GM2-synthase mRNA expression in SK-RC-45 cells was accompanied by Sp1 and HDAC1 loss from the +38/+187 region. Taken together, we have identified an epigenetic mechanism for the de-repression of the GM2-synthase gene in RCC. 30521973_Study analyzed enzyme activity and intracellular localization of the products of mutant cDNAs from eleven cases of hereditary spastic paraplegia with mutation in the coding region of B4GALNT1, and noted a lack of enzyme activity in a majority of them except two family cases. Then compared profiles of clinical findings of patients with hereditary spastic paraplegia and abnormal phenotypes of B4galnt-KO mice. 31075227_Data suggest that GD2 synthase (GD2) can well be considered as a diagnostic and prognostic marker in breast cancer. 31491435_High B4GALNT1 expression is associated with clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis. 31988291_B4GALNT1 enhanced tumorigenesis via induction of angiogenesis,ganglioside GM2/GD2 and cell motility. 33367717_B4GALNT1 promotes progression and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma through JNK/c-Jun/Slug pathway. 34907737_Does GD2 synthase (GD2S) detect cancer stem cells in blood samples of breast carcinomas? 35775650_Functional validation of novel variants in B4GALNT1 associated with early-onset complex hereditary spastic paraplegia with impaired ganglioside synthesis. | ENSMUSG00000006731 | B4galnt1 | 52.500410 | 0.454454956 | -1.137791 | 0.27134965 | 17.511452 | 0.0000285582383242905493605633820974887271404440980404615402221679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0003391108978609305669646434289177250320790335536003112792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 33.7959192 | 6.8832002 | 74.6390374 | 14.3903265 |
| ENSG00000135547 | 23493 | HEY2 | protein_coding | Q9UBP5 | FUNCTION: Downstream effector of Notch signaling which may be required for cardiovascular development. Transcriptional repressor which binds preferentially to the canonical E box sequence 5'-CACGTG-3'. Represses transcription by the cardiac transcriptional activators GATA4 and GATA6. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10692439, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11095750, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15485867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16293227}. | Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Notch signaling pathway;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation | This gene encodes a member of the hairy and enhancer of split-related (HESR) family of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)-type transcription factors. The encoded protein forms homo- or hetero-dimers that localize to the nucleus and interact with a histone deacetylase complex to repress transcription. Expression of this gene is induced by the Notch signal transduction pathway. Two similar and redundant genes in mouse are required for embryonic cardiovascular development, and are also implicated in neurogenesis and somitogenesis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found, but their biological validity has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:23493; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription repressor complex [GO:0017053]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; anterior/posterior axis specification [GO:0009948]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; aortic valve morphogenesis [GO:0003180]; arterial endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0060842]; ascending aorta morphogenesis [GO:0035910]; atrial septum morphogenesis [GO:0060413]; cardiac conduction system development [GO:0003161]; cardiac epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0060317]; cardiac left ventricle morphogenesis [GO:0003214]; cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010659]; cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060038]; cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress [GO:0014898]; cardiac right ventricle morphogenesis [GO:0003215]; cardiac septum morphogenesis [GO:0060411]; cardiac vascular smooth muscle cell development [GO:0060948]; cardiac ventricle morphogenesis [GO:0003208]; cell fate commitment [GO:0045165]; circulatory system development [GO:0072359]; cochlea development [GO:0090102]; coronary vasculature morphogenesis [GO:0060977]; dorsal aorta morphogenesis [GO:0035912]; endocardial cushion to mesenchymal transition involved in heart valve formation [GO:0003199]; epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation [GO:0003198]; heart trabecula formation [GO:0060347]; labyrinthine layer blood vessel development [GO:0060716]; mesenchymal cell development [GO:0014031]; muscular septum morphogenesis [GO:0003150]; negative regulation of biomineral tissue development [GO:0070168]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010667]; negative regulation of cardiac vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:2000723]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045746]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of transcription by transcription factor localization [GO:0010621]; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter involved in smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:2000820]; negative regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0060633]; negative regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding [GO:2000678]; Notch signaling involved in heart development [GO:0061314]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003151]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060045]; positive regulation of heart rate [GO:0010460]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein-DNA complex assembly [GO:0065004]; pulmonary artery morphogenesis [GO:0061156]; pulmonary valve morphogenesis [GO:0003184]; regulation of inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0045607]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of vasculogenesis [GO:2001212]; smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051145]; tricuspid valve formation [GO:0003195]; tricuspid valve morphogenesis [GO:0003186]; umbilical cord morphogenesis [GO:0036304]; vascular associated smooth muscle cell development [GO:0097084]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570]; ventricular cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0055015]; ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0060412]; ventricular trabecula myocardium morphogenesis [GO:0003222] | 12535671_These results indicate that the molecular association between HES1-, HEY2- and SIRT1-related proteins is conserved among metazoans, from Drosophila to human, and suggest that the Sir2-bHLH interaction also plays important roles in human cells. 15389319_To clarify the role of HEY2 in human CHD and AGS, we screened by direct sequencing 23 children with CHD and 38 patients diagnosed with AGS. Mutation of HEY2 is not a major contributing factor. 15643620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15680351_A similar gene in mouse regulates cardiovascular development 16151017_HERP1 may play a role in promoting the phenotypic modulation of vascular smooth muscle cells during vascular injury and atherosclerotic process by interfering with SRF binding to CArG-box 16293227_CHF1/Hey2 may affect smooth-muscle cell phenotype through an important transcriptional mechanism 16329098_This result suggests a possible role of HEY2 in the regulation of ventricular septation in humans. 18239137_Present a novel mechanism by which a balance between Notch-1/-2/-4 signaling, via CBF-1, and HRT-1/-2 activity determines the expression of smooth muscle differentiation markers including actin. 18266235_The absence of mutations in NOTCH2 and Hey2 its downstream target in the heart does not exclude the possibility that other genes in this pathway might be implicated in the diverse phenotypes observed in Alagille syndrome 21290414_In this study, we analyzed the effects of HESR1, -2, and -3 on DAT1 expression in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells 21362320_Through activating the Dll4-Notch-Hey2 signaling pathway, HGF indirectly promotes the proliferation and migration ability of cells, so that offspring artery branches are formed. 22310065_Report down-regulation of Notch signaling components NOTCH3 and HEY2 in abdominal aortic aneurysms. 23744056_Hey2 and COUP-TFII have an important role in arteriovenous differentiation of human endothelial cells. 23872634_Common variants at SCN5A-SCN10A and HEY2 are associated with Brugada syndrome, a rare disease with high risk of sudden cardiac death 24108462_Data indicate that culture abrogated differential gene expression in part due to gradual loss of canonical Notch activity and HEY2 expression. 24366871_a new HRD1-associated membrane protein named HERP2, which is homologous to the previously identified HRD1 partner HERP1. Despite sequence homology, HERP2 is constitutively expressed in cells, whereas HERP1 is highly induced by ER stress. 25361534_Overexpression of HEY1 and HEY2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is correlated to different indices of poor prognosis, and it is extrapolated that such overexpression is important in progression and development of ESCC tumorigenesis. 25799559_bone morphogenic proteins within the serum of cell culture medium are potent inducers of endothelial Hey1 and Hey2 gene expression within the first few hours after medium change 25832314_Individuals with HEY2 duplications should be screened for congenital heart defects. 26729854_HEY2 CC genotype may be a favorable prognostic marker for BrS, protectively acting to prevent ventricular fibrillation presumably by regulating the repolarization current. 27191260_HEY2 as a promising biomarker for unfavorable outcomes and a novel therapeutic target for the clinical management of HCC 28637782_Genetic variation of HEY2 is associated with Brugada syndrome through alteration of ion channel expression in the cardiac ventricular wall. 28694461_We also highlighted that Hey2 is involved in radiation-induced EndoMT and that Hey2 invalidation reduces EndoMT and tissue damage. 29636455_The findings identify HEY2 as a novel component of the NKX2-5 cardiac transcriptional network. 30125982_These results provide evidence that miR-146a and Hey2 form a mutual negative feedback regulatory loop to regulate the inflammatory response in chronic apical periodontitis. 30257372_we confirmed that lncRNA PRNCR1 upregulates HEY2 to promote tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer by competitively binding miR-448. 31255287_Attenuation of PRRX2 and HEY2 enables efficient conversion of adult human skin fibroblasts to neurons. 31565805_microRNA-599 promotes apoptosis and represses proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells via downregulation of Hey2-depentent Notch signaling pathway. 32712748_TWIST1 correlates with Notch signaling pathway to develop esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 32820247_Germline variants in HEY2 functional domains lead to congenital heart defects and thoracic aortic aneurysms. 32997309_Notch-HEY2 signaling pathway contributes to the differentiation of CD34(+) hematopoietic-like stem cells from adult peripheral blood insulin-producing cells after the treatment with platelet-derived mitochondria. | ENSMUSG00000019789 | Hey2 | 27.164376 | 2.703275242 | 1.434708 | 0.38614207 | 13.757389 | 0.0002080010613284861563550276475353939531487412750720977783203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0019594475016923864306439551086214123643003404140472412109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 39.5361459 | 5.5881248 | 14.7347228 | 2.5369106 | |
| ENSG00000135636 | 8291 | DYSF | protein_coding | O75923 | FUNCTION: Key calcium ion sensor involved in the Ca(2+)-triggered synaptic vesicle-plasma membrane fusion. Plays a role in the sarcolemma repair mechanism of both skeletal muscle and cardiomyocytes that permits rapid resealing of membranes disrupted by mechanical stress (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | 3D-structure;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the ferlin family and is a skeletal muscle protein found associated with the sarcolemma. It is involved in muscle contraction and contains C2 domains that play a role in calcium-mediated membrane fusion events, suggesting that it may be involved in membrane regeneration and repair. In addition, the protein encoded by this gene binds caveolin-3, a skeletal muscle membrane protein which is important in the formation of caveolae. Specific mutations in this gene have been shown to cause autosomal recessive limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2B (LGMD2B) as well as Miyoshi myopathy. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2008]. | hsa:8291; | centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; T-tubule [GO:0030315]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; macrophage activation involved in immune response [GO:0002281]; membrane fusion [GO:0061025]; monocyte activation involved in immune response [GO:0002280]; negative regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050765]; plasma membrane organization [GO:0007009]; plasma membrane repair [GO:0001778]; T-tubule organization [GO:0033292]; vesicle fusion [GO:0006906] | 12836053_The dysferlin gene, a strong candidate gene responsible for two other distal myopathies in the same region, is located centromeric to PAC3-H52 and can thereby formally be excluded as cause for Welander distal myopathy 14506716_Isolated calf atrophy and weakness with onset after age 30, and associated with serum CK levels that are only moderately elevated, represents a distinct myopathy phenotype. 14512171_In muscular dystrophy with dysferlinopathy, the inflammatory response is triggered by altered expression of dysferlin and is involved in muscle degeneration. 14749532_the importance of dysferlin-caveolin 3 relationship for skeletal muscle integrity 15221058_If, in particular, a dysferlinopathy is supposed, the underlying mutation should be identified to confirm the diagnosis and as a basis for current and future therapeutic interventions. 15318348_Dysferlin and its differentially spliced isoforms play different roles in myogenic cell differentiation, hence dysferlin function in peripheral nerve might be accomplished by this novel spliced variant isoform. 15469449_This study identified 11 different mutations, including eight missense and three deletion mutations. Nine of them were novel mutations. 15477515_Miyoshi distal myopathy in these 2 Chinese families demonstrated a homogenous phenotype and compound heterozygous mutations. Among the 4 mutations, 3 were novel mutations that, to our knowledge, have not been reported previously. 15535137_Dysferlin expression when satellite cells are activated confirm the involvement of dysferlin in human muscle regeneration/repair and its possible role in fusion events during muscle development. 15835269_Data show that affixin is a dysferlin binding protein that colocalizes with dysferlin at the sarcolemma of normal skeletal muscle. 16010686_LGMD2B mutational analysis in Miyoshi myopathy, and atypical dysferlinopathies 16087766_The new R1905X dysferlin founder mutation produced the 3 possible dysferlinopathy phenotypes without intrafamilial heterogeneity. 16100712_annexin A1 and A2 may have roles in dysferlin deficiency and in muscular dystrophies 16606933_Two severely affected sisters sith limb-girdle muscular dystrophy were homozygous for a dysferlin null mutation. 16608842_there is a functional link between dysferlin and myogenin in the differentiation of skeletal muscle 16797397_dysferlin is present in glomeruli and may be associated with glomerular permeabi 16862423_membrane attack complex deposits and a pro-inflammatory milieu in the absence of interleukin-10 expression may contribute to progressive muscle damage in dysferlinopathies 16896923_DYSF_v1 retains phylogenic conservancy and shows similar expression pattern as the currently known human dysferlin. 16934466_While the quantity of beta-sarcoglycan was nearly normal in the limb girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD)2E carrier, the levels of dysferlin protein were reduced to 50% of controls in the carriers of LGMD2B. 16996541_Thus, alteration of structurally important residues in dysferlin could lead to improper folding and degradation of the mutant protein. 17287450_The diagnosis of symptomatic carriers of dysferlin mutations should be considered when a pathologic pattern of dysferlin protein is observed. 17363620_dysferlin is not expressed at the plasmalemma of myotubes but mostly localizes to the T-tubule network. However, dysferlin translocated to the site of injury and toward the plasma membrane in a Ca2+-dependent fashion in response to a wounding assay 17554076_A proteomics screen of human placental microvillous syncytiotrophoblasts (STBs) revealed the expression of dysferlin (DYSF), a plasma membrane repair protein associated with certain muscular dystrophies. 17698709_Phenotypic study in 40 patients with dysferlin gene mutations 17825554_Genomic analysis of the dysferlin coding sequence performed in patients from Caucasus Jews, who lacked muscle dysferlin, revealed a homozygous frameshift mutation predicting a truncated dysferlin and a complete loss of functional protein. 17828519_These data suggest that disturbances in dysferlin as well as Z-line proteins and transcription factors particularly under mechanical stress cause cardiomyopathy. 17868276_study reports a novel pair of heterozygous mutations in the 3'-splicing site of exon 26 and the translation site of exon 28 of the dysferlin gene in two siblings 17897828_Cytoplasmic localization of dysferlin correlates with fiber regeneration in a subset of muscular dystrophy patients. We also identified patients with forms of LGMD and with abnormal dysferlin localization that doesn't correlate with fiber regeneration. 18276788_Dysferlin deficiency enhances monocyte phagocytosis. 18294055_missense mutation c.4253G>A on the DYSF gene in a Mexican family from an endogamic population 18306167_Mutations located between exons 7 and 16, corresponding to the predicted second and third C2 domain of dysferlin, are amyloidogenic. 18396043_A case represents the eldest age of onset of dysferlinopathy reported so far and widens the clinical spectrum of this disease. 18495154_solution structure of the inner DysF domain of the dysferlin paralogue myoferlin, which has a unique fold held together by stacking of arginine and tryptophans, mutations that lead to clinical disease in dysferlin 18641458_AQP4 expression was analyzed in muscle biopsies from patients affected by Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophies. 18832576_Rab27A/Slp2a expression in limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2B muscle provides a compensatory vesicular trafficking pathway that is able to repair membrane damage in the absence of dysferlin. 18853459_The mutational spectrum significantly shows a higher proportion of nonsense mutations in DYSf gene, but a lower proportion of deleterious missense changes as compared to previous series . 19084402_We report two patients with a new phenotype of dysferlinopathy presenting as congenital muscular disease. Muscle biopsy showed mild dystrophic features and the absence of dysferlin. 19221801_study identified alternative splicing involving novel dysferlin exons 5a & 40a, in addition to previously reported exon 17; differences in frequencies of dysferlin transcripts in skeletal muscle & blood were characterized 19228595_In trophoblastic cells, there was a positive correlation between cell fusion and increased dysferlin expression. 19253956_Dysferlin's C2A domain was able to bind to phosphoinositides in a Ca(2+)-dependent fashion. 19286669_dysferlin-deficient patients show an increase in immature muscle fibres. 19309282_In two Chilean patients with dysferlinopathy, two new mutations were found: homozygous c.1948delC (p.Leu650TyrfsX6) in a male patient; the heterozygous mutation c.1276G>A (p.Gly426Arg) in a female patient in association with c.2858dupT (p.Phe954ValfsX2). 19326120_All of the mutations associated with amyloid were located in the N-terminal region of dysferlin, and dysferlin clearly proved to be a component of the amyloid deposits. 19380584_Molecular complex formed by MG53, dysferlin, and Cav3 is essential for repair of muscle membrane damage in muscular dystrophy. 19493611_Mutation analysis of DYSF revealed novel compound heterozygous mutations in two related Miyoshi myopathy patients 19545895_role for DYSF in the stability of the apical syncytiotrophoblast plasma membrane may account for the increased shedding of microparticles from this membrane in preeclampsia 19594366_We report for the first time the characterization of disease-causing exonic rearrangements in the large-sized gene encoding dysferlin. 19834057_Data show that restoration of dysferlin in skeletal muscle fibers is sufficient to rescue Dysf-deficient mice, although its mild overexpression does not appear to functionally enhance membrane repair in other models of muscular dystrophy. 19929428_No disease-causing mutation was identified in alternative exons 1 of DYSF-v1, exon 5a, and exon 40a, demonstrating a low frequency of disease-causing mutations in these exons. 20082313_Dysferlin is necessary for correct T-tubule formation, and dysferlin-deficient skeletal muscle is characterized by abnormally configured T-tubules. 20373350_Expression levels of dysferlin are important for appropriate function without deleterious or cytotoxic effects. Future endeavors in gene replacement for correction of dysferlinopathy should be tailored to take account of this. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20413686_Data show that components of the inflammasome pathway are specifically up-regulated and activated in dysferlin-deficient but not in dystrophin-deficient and normal muscle, and suggest that muscle cells can actively participate in inflammasome formation. 20535123_Dysferlin exon skipping mutation (c.5492G>A) with a founder effect reveals further alternative splicing involving exons 49-51 in muscle disorders. 20544924_Six subjects had atypical calf enlargement, and 3 of these exhibited a paradoxical pattern of dysferlin expression 20558759_Nonsense suppression drug, ataluren (PTC124), is able to induce read-through of the premature stop codon in a patient with a R1905X mutation in dysferlin and produce sufficient functional dysferlin to rescue myotube membrane blebbing. 20574037_Splitting dysferlin myopathy into separate phenotypes does not reveal significant differences in terms of rate of progression, prognosis, genotype, or MRI pattern 20595382_dysferlin and syntaxin-4 similarly transit a common endosomal pathway in skeletal muscle cells. 20618995_B cell depletion with rituximab/dysferlin monoclonal antibody has been proved useful in the treatment of two patients affected by muscular dystrophy. There may be a possible role for B cells in the immune system involvement of this muscle disorder. 20724702_loss of dysferlin in endothelial cells resulted in deficient adhesion followed by growth arrest an impaired angiogenic response 21119217_Dysferlin function in intracellular vesicles and its implication in muscle membrane resealing. 21173544_A simple and rapid screening method to detect hot spot mutations in the dysferlin gene is essential for the diagnosis of dysferlinopathy. 21280221_A new computational method establishes an increase in the mean average prediction precision for dysferlin protein partners, which is important for new targeted therapies. 21412170_MG53, annexin A1, and dysferlin localize to the t-tubule network and show enriched labeling at longitudinal tubules of the t-system in overstretch 21522182_This study presents the first direct and conclusive evidence that an amount of Dysferlin =20% is pathogenic and always caused by primary dysferlin gene mutations. 21556485_Studies indicate that dysferlinopathies are autosomal recessive disorders caused by mutations in the dysferlin (DYSF) gene, encoding the dysferlin protein. 21658164_A novel mutation in exon 47 (c.5289G>C) of the dysferlin gene in the heterozygous state, causing an amino acid change (p.Glu1763Asp), was detected in 2 patients 22037454_these data further support the claims that dysferlin not only mediates membrane repair but also trafficking of client proteins, ultimately, help bridging dysferlinopathies to aberrant membrane signaling. 22043020_Data suggest dysferlin has an important function in the internal membrane systems of skeletal muscle, involved in calcium homeostasis and excitation-contraction coupling. 22110769_C2 domains mediate high affinity self-association of dysferlin in a parallel homodimer 22194990_The aim of the study was to determine whether dysferlin expression in peripheral blood monocytes correlates with that in skeletal muscle. 22297152_In Koreans with dysferlinopathy, DYSF mutations appeared to cluster in the N-terminal region. 22720081_provide proof of principle that AAV5 mediated delivery of dysferlin is a highly promising strategy for treatment of dysferlinopathies and has far-reaching implications for the therapeutic delivery of other large genes 23185377_Dysferlin-peptides reallocate mutated dysferlin thereby restoring function 23243261_we observed 40 Japanese patients in 36 families with limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2B in whom dysferlin mutations were confirmed 23254335_We described 8 Chinese patients with dysferlinopathy 23516275_Dysferlin is subject to enzymatic cleavage releasing a synaptotagmin-like fragment with a specialized protein- or phospholipid-binding role for muscle membrane repair. 23519732_study reported 4 novel mutations and 2 cases of dysferlinopathy in which patients exhibited a reduction of sarcolemmal dysferlin in conjunction with cytoplasmic retention 23558685_dysferlin is involved in regulating cellular interactions and has a role in inflammatory cells 23792176_a direct interaction of dysferlin with Trim72/MG53, AHNAK, cytoplasmic dynein, myomesin-2 and calsequestrin-1, but not with caveolin-3 or dystrophin, is reported. 23859474_Data indicate that dysferlin, otoferlin, and myoferlin do not merely passively adsorb to membranes but actively sculpt lipid bilayers. 24091414_our results identify dysferlin as a newly identified binding partner of AbetaPP 24239457_Alternate splicing of the dysferlin C2A domain confers Ca(2+)-dependent and Ca(2+)-independent binding for membrane repair. 24438169_The crystal structure of the human dysferlin inner DysF domain shows that most of the pathogenic mutations are part of aromatic/arginine stacks that hold the domain in a folded conformation. 24454878_distinct membrane protein signature specific to patients with Diamond-Blackfan Anemia 24461013_all dysferlin domains bind Ca(2+) albeit with varying affinity and stoichiometry 24488599_Our results suggest that dysferlin protein levels of =10% in PBMCs, are highly indicative of primary dysferlinopathies 24685690_These novel observations of conspicuous intermyofibrillar lipid and progressive adipocyte replacement in dysferlin-deficient muscles. 24687993_The tricomplex Fam65b-HDAC6-dysferlin is transient. 24838345_Dysferlin carrier frequency and the number of affected individuals at risk for dysferlinopathy could be higher than previously estimated. 24902367_These data suggest that although dysferlin is not an integral part of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex, its expression is altered in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. 24967968_results provide the mechanism for dysferlin-mediated repair of skeletal muscle sarcolemma and identify ASM as a potential therapy for dysferlinopathy 25312915_minigene strategy is an efficient tool for the detection of splicing defects in dysferlinopathies, which could allow for a better comprehension of splicing defects due to mutations and could improve prediction tools evaluating splicing defects 25591676_Our study underlines clinical heterogeneity and a high proportion of novel mutations for dysferlin in Chinese patients affected with dysferlinopathy. 25904108_By targeting DYSF premRNA introns harbouring differentially defined 3' splice sites (3' SS), we found that target introns encoding weakly defined 3' SSs were trans-spliced successfully in vitro in human myoblasts also in vivo in skeletal muscle of mice. 26077327_We conclude that two independent mutations in ALMS1 and DYSF cause CRD and muscular dystrophy in the studied consanguineous Israeli Arab family. 26671124_This study demonstrated that novel mutation of DYSF in patient with Dysferlinopathy in Iran. 26806107_These differences in the structural dynamics of the predicted binding site suggest that mutation R959W alters recognition dynamics of the inner DysF domain. 26911292_This study showed that 4 patients with Inflammatory Myopathy associated with DYSF mutation. 27226605_results support a function for dysferlin as a calcium-sensing SNARE effector for membrane fusion events 27229680_Human deltoid muscle biopsies of 5 Chilean dysferlinopathy patients exhibited the presence of muscular connexins (Cx40.1, Cx43 and Cx45). 27349407_This review suggested that the functions of dysferlin in vesicle trafficking and membrane remodeling in skeletal muscle. 27641898_arginine-rich motif crucial for phosphatidylserine accumulation in sarcolemma repair 27647186_DYSF mutations in Chinese patients clustered in the N-terminal region of the gene. Exonic rearrangements were found in 23% of patients with only one pathogenic mutation identified by Sanger sequencing or NGS. The novel mutations found in this study greatly expanded the mutational spectrum of dysferlinopathy. 27666772_Immunofluorescence demonstrated that the percentage of complex I- and complex IV-deficient fibres was higher in patients with DYSF mutations than in age-matched controls. No clonally expanded mtDNA deletions were detected using long-range PCR in any of the analysed muscle fibres. Complex I and complex IV deficiency is higher in patients than age matched controls but patients do not have rearrangements of the mtDNA. 28005267_DYSF expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 28104817_dysferlin has membrane tubulating capacity and that it shapes the T-tubule system. 28523511_As muscular biopsy showed inflammatory infiltrates, polymyositis was suspected and immunosuppressive treatment was initiated. However, clinical improvement could not be achieved. Gene sequencing of the DYSF-gene showed a previously unreported homozygous mutation. 28904177_Data suggest that dysferlin exhibits modular architecture of 4 tertiary domains: 1) C2A, readily removed as solo domain; 2) midregion C2B-C2C-Fer-DysF, excised as intact module with several dynamic folding options; 3) C-terminal four-C2 domain module; 4) calpain-2-cleaved mini-dysferlinC72, particularly resistant to proteolysis. Missense variant L344P in muscular dystrophy patient largely escapes proteasomal surveillance. 29209666_A novel duplication of 22 bases (c.897_918dup; p.Gly307Leufs5X) in the DYSF gene was identified in a family suffering from Miyoshi myopathy 29480214_This review detailed the different partners and function of dysferlin and positions the sarcolemma repair in normal and pathological conditions. [Review] 29484758_MiRNA target prediction software, TargetScan, revealed dysferlin (DYSF) and protein kinase cAMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha (PRKACA), as target genes of miR-92a-1-5p. 29879922_DYSF mutation is associated with Neuromuscular Disease. 30026467_Results show that, in addition to clinically-defined dysferlin FerA mutations, is a novel four-helix bundle fold with its own Ca(2+)-dependent phospholipid-binding activity which interaction with the membrane is enhanced by the presence of Ca(2+). 30098242_two compound heterozygous mutations of the DYSF gene probably underlie the limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2B in the two pedigrees 31004665_The initial C2 domains of dysferlin and myoferlin are 57% similar (42% identical). Unlike dysferlin C2A, myoferlin binds two Ca2+ with equivalent affinity. Unlike dysferlin C2A, the membrane binding loop 1 of myoferlin C2A is relatively rigid. 31019989_Deep intronic mutations of dysferlin can be a common underlying cause of dysferlinopathy 31693312_In patients with limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2B, two new mutations were found in DYSF. A nonsense mutation c.2419C > T, which eliminates downstream part of the protein, and a novel one c. (1,053 + 1_1,054-1)_(1,397 + 1_1,398-1)del causing deletion of the DNA from exon 12 to exon 15. Two unrelated families are from the same ethnicity and share the same mutation and haplotype patterns, suggesting a founder mutation. 31770675_Radiological findings in siblings with dysferlin mutation with diverse phenotype. 31861684_Results support a role of dysferlin in actin cytoskeleton dynamics in muscle cells and suggest that this mechanism could be deregulated in dysferlinopathy. 31873062_Antisense-Mediated Skipping of Dysferlin Exons in Control and Dysferlinopathy Patient-Derived Cells. 32087766_AMPK Complex Activation Promotes Sarcolemmal Repair in Dysferlinopathy. 32400077_The genetic profile of dysferlinopathy in a cohort of 209 cases: Genotype-phenotype relationship and a hotspot on the inner DysF domain. 32666437_Novel splicing dysferlin mutation causing myopathy with intra-familial heterogeneity. 33215690_Null variants in DYSF result in earlier symptom onset. 33927379_Retrospective analysis and reclassification of DYSF variants in a large French series of dysferlinopathy patients. 33987686_Frequent DYSF rare variants/mutations in 152 Han Chinese samples with ovarian endometriosis. 34559919_Molecular landscape of DYSF mutations in dysferlinopathy: From a Chinese multicenter analysis to a worldwide perspective. 35460889_DYSF promotes monocyte activation in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease as a DNA methylation-driven gene. 35962550_Identification of a novel heterozygous DYSF variant in a large family with a dominantly-inherited dysferlinopathy. | ENSMUSG00000033788 | Dysf | 34.418345 | 2.095941940 | 1.067599 | 0.34846953 | 9.330193 | 0.0022540861366645917329698534103954443708062171936035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0149858160074450141169277728181441489141434431076049804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 45.9010764 | 5.5852179 | 21.7549819 | 3.4458712 | |
| ENSG00000135678 | 1368 | CPM | protein_coding | P14384 | FUNCTION: Specifically removes C-terminal basic residues (Arg or Lys) from peptides and proteins. It is believed to play important roles in the control of peptide hormone and growth factor activity at the cell surface, and in the membrane-localized degradation of extracellular proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12457462}. | 3D-structure;Carboxypeptidase;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Hydrolase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal;Zinc | The protein encoded by this gene is a membrane-bound arginine/lysine carboxypeptidase. Its expression is associated with monocyte to macrophage differentiation. This encoded protein contains hydrophobic regions at the amino and carboxy termini and has 6 potential asparagine-linked glycosylation sites. The active site residues of carboxypeptidases A and B are conserved in this protein. Three alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:1368; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; carboxypeptidase activity [GO:0004180]; metallocarboxypeptidase activity [GO:0004181]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; peptide metabolic process [GO:0006518]; protein processing [GO:0016485] | 11891060_Multiple transcription start sites in two regions ~30 kb apart are flanked by two unique functional promoters. Five major types of transcripts resulting from multiple transcription start sites and alternate splicing in the 5-prime region were identified. 12457462_CPM is membrane-bound via attachment of glycosylphosphatidylinositol at Ser406. Glu264 is a critical catalytic residue, whereas Glu260 affects stability and substrate kinetics. 15066430_Results report the crystallization of human carboxypeptidase M and its 3.0 angstrom crystal structure. 18187413_Carboxypeptidase M and kinin B1 receptors interact to facilitate efficient b1 signaling from B2 agonists 18292211_Cleavage of the C-terminal lysine residue of SDF-1alpha by CPM leads to attenuated chemotactic responses. 19820690_CPM amplification could be used as an alternative diagnostic tool for the diagnosis of well-differentiated liposarcoma/atypical lipomatous tumors. 20673876_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21454694_CPM and B1Rs on cell membranes form a critical complex that potentiates B1R signaling. 22157720_novel marker and cellular player in lipid uptake and/or metabolism of activated macrophages by promoting foam cell formation 23172796_Carboxypeptidase M expression is lost in human renal cell carcinoma tumor cells, whereas it is abundant in tumor-associated foam cells and neovasculature. 24108126_CPM binding to extracellular loop 2 of the B1R results in positive allosteric modulation of B1R signaling, and disruption of this interaction could provide a novel therapeutic approach to reduce pathological B1R signaling. 28186967_Low CPM expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 30674606_The rs12812500 variant of the CPM gene may increase silicosis susceptibility by affecting the expression of CPM, which may contribute to silicosis susceptibility with biological plausibility. 31218444_Our work shows for the first time that the interaction between CPM and kinin B1 receptor alters not only B1R pharmacology, but also modulates enzyme expression and activity. | ENSMUSG00000020183 | Cpm | 607.345893 | 0.254174548 | -1.976109 | 0.68101620 | 7.777886 | 0.0052889661945169624129858831906858540605753660202026367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0300008350076655591620600205260416259989142417907714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 202.7078022 | 136.6801096 | 786.2885972 | 529.9490331 | |
| ENSG00000136122 | 79866 | BORA | protein_coding | Q6PGQ7 | FUNCTION: Required for the activation of AURKA at the onset of mitosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16890155}. | Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Mitosis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | BORA is an activator of the protein kinase Aurora A (AURKA; MIM 603072), which is required for centrosome maturation, spindle assembly, and asymmetric protein localization during mitosis (Hutterer et al., 2006 [PubMed 16890155]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:79866; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; meiotic spindle [GO:0072687]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; activation of protein kinase activity [GO:0032147]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell division [GO:0051301]; regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0007088]; regulation of mitotic spindle organization [GO:0060236]; regulation of protein localization [GO:0032880] | 18378770_Study concludes that tight regulation of the Bora protein by its synthesis and degradation is critical for cell cycle progression. 18521620_Plk1 controls Aurora A localization and function by regulating cellular levels of hBora. 18566290_study reports that the synergistic action of Bora & the kinase Aurora A controls G2-M transition; Bora accumulates in G2 phase & promotes Aur-A-mediated activation of Polo-like kinase 1, leading to activation of cyclin-dependent kinase 1 & mitotic entry 19487276_Recent advances in the understanding of the functional crosstalk between Plk1 and Aurora-A before and during mitosis. 20923822_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23592782_Following UV irradiation, ataxia telangiectasia-mutated- and Rad3-related protein phosphorylates Bora at Thr-501. The phosphorylated Thr-501 is subsequently recognized by the E3 ubiquitin ligase SCF-beta-TRCP, which targets Bora for degradation. 23970419_Pin1 acts as a negative regulator of the G2/M transition by interacting with the Aurora-A-Bora complex. 24338364_Activation of Plk1 by Aurora-A may function as a bistable switch 25742493_Bora was found to play a significant role in radiosensitivity through the regulation of MDC1 and DNA repair. 27068477_These results reveal a crucial and conserved role of phosphorylation of the N terminus of Bora for Plk1 activation and mitotic entry. 27831827_the mechanism of Plk1 activation and the potential role of Bora phosphorylation by Cdk1, is reported. 28402276_our findings demonstrated that Bora was overexpressed and served as an independent biomarker for poor prognosis in multiple adenocarcinomas. 33771996_Bora phosphorylation substitutes in trans for T-loop phosphorylation in Aurora A to promote mitotic entry. 34287649_Aurora A kinase activation: Different means to different ends. | ENSMUSG00000022070 | Bora | 133.423704 | 2.228803235 | 1.156269 | 0.33828452 | 11.311695 | 0.0007702043254424113284672959167664885171689093112945556640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0060458014053246062965984997106261289445683360099792480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 142.4154003 | 82.6538222 | 63.8495307 | 37.0827018 | |
| ENSG00000136244 | 3569 | IL6 | protein_coding | P05231 | FUNCTION: Cytokine with a wide variety of biological functions in immunity, tissue regeneration, and metabolism. Binds to IL6R, then the complex associates to the signaling subunit IL6ST/gp130 to trigger the intracellular IL6-signaling pathway (Probable). The interaction with the membrane-bound IL6R and IL6ST stimulates 'classic signaling', whereas the binding of IL6 and soluble IL6R to IL6ST stimulates 'trans-signaling'. Alternatively, 'cluster signaling' occurs when membrane-bound IL6:IL6R complexes on transmitter cells activate IL6ST receptors on neighboring receiver cells (Probable). {ECO:0000305|PubMed:30995492}.; FUNCTION: IL6 is a potent inducer of the acute phase response. Rapid production of IL6 contributes to host defense during infection and tissue injury, but excessive IL6 synthesis is involved in disease pathology. In the innate immune response, is synthesized by myeloid cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells, upon recognition of pathogens through toll-like receptors (TLRs) at the site of infection or tissue injury (Probable). In the adaptive immune response, is required for the differentiation of B cells into immunoglobulin-secreting cells. Plays a major role in the differentiation of CD4(+) T cell subsets. Essential factor for the development of T follicular helper (Tfh) cells that are required for the induction of germinal-center formation. Required to drive naive CD4(+) T cells to the Th17 lineage. Also required for proliferation of myeloma cells and the survival of plasmablast cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P08505, ECO:0000305|PubMed:30995492}.; FUNCTION: Acts as an essential factor in bone homeostasis and on vessels directly or indirectly by induction of VEGF, resulting in increased angiogenesis activity and vascular permeability (PubMed:17075861, PubMed:12794819). Induces, through 'trans-signaling' and synergistically with IL1B and TNF, the production of VEGF (PubMed:12794819). Involved in metabolic controls, is discharged into the bloodstream after muscle contraction increasing lipolysis and improving insulin resistance (PubMed:20823453). 'Trans-signaling' in central nervous system also regulates energy and glucose homeostasis (By similarity). Mediates, through GLP-1, crosstalk between insulin-sensitive tissues, intestinal L cells and pancreatic islets to adapt to changes in insulin demand (By similarity). Also acts as a myokine (Probable). Plays a protective role during liver injury, being required for maintenance of tissue regeneration (By similarity). Also has a pivotal role in iron metabolism by regulating HAMP/hepcidin expression upon inflammation or bacterial infection (PubMed:15124018). Through activation of IL6ST-YAP-NOTCH pathway, induces inflammation-induced epithelial regeneration (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P08505, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12794819, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15124018, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17075861, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20823453, ECO:0000305|PubMed:30995492}. | 3D-structure;Acute phase;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | This gene encodes a cytokine that functions in inflammation and the maturation of B cells. In addition, the encoded protein has been shown to be an endogenous pyrogen capable of inducing fever in people with autoimmune diseases or infections. The protein is primarily produced at sites of acute and chronic inflammation, where it is secreted into the serum and induces a transcriptional inflammatory response through interleukin 6 receptor, alpha. The functioning of this gene is implicated in a wide variety of inflammation-associated disease states, including suspectibility to diabetes mellitus and systemic juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Elevated levels of the encoded protein have been found in virus infections, including COVID-19 (disease caused by SARS-CoV-2). [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. | hsa:3569; | endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; interleukin-6 receptor complex [GO:0005896]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; interleukin-6 receptor binding [GO:0005138]; acute-phase response [GO:0006953]; cellular response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0070301]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; endocrine pancreas development [GO:0031018]; germinal center B cell differentiation [GO:0002314]; glucagon secretion [GO:0070091]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; hepatic immune response [GO:0002384]; hepatocyte proliferation [GO:0072574]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; interleukin-6-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070102]; liver regeneration [GO:0097421]; maintenance of blood-brain barrier [GO:0035633]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045779]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032682]; negative regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032966]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599]; negative regulation of interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway [GO:2000660]; negative regulation of lipid storage [GO:0010888]; negative regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050768]; negative regulation of primary miRNA processing [GO:2000635]; neuron cellular homeostasis [GO:0070050]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; neutrophil apoptotic process [GO:0001781]; neutrophil mediated immunity [GO:0002446]; platelet activation [GO:0030168]; positive regulation of acute inflammatory response [GO:0002675]; positive regulation of apoptotic DNA fragmentation [GO:1902512]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of B cell activation [GO:0050871]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900017]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0090091]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of glial cell proliferation [GO:0060252]; positive regulation of immunoglobulin production [GO:0002639]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032733]; positive regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032740]; positive regulation of interleukin-21 production [GO:0032745]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of leukocyte adhesion to vascular endothelial cell [GO:1904996]; positive regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002690]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of neuroinflammatory response [GO:0150078]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of platelet aggregation [GO:1901731]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via STAT [GO:1904894]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of T-helper 2 cell cytokine production [GO:2000553]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of type B pancreatic cell apoptotic process [GO:2000676]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010575]; regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045765]; regulation of astrocyte activation [GO:0061888]; regulation of glucagon secretion [GO:0070092]; regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0050796]; regulation of microglial cell activation [GO:1903978]; regulation of neuroinflammatory response [GO:0150077]; regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010574]; response to activity [GO:0014823]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384]; response to peptidoglycan [GO:0032494]; T follicular helper cell differentiation [GO:0061470]; T-helper 17 cell lineage commitment [GO:0072540]; vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010573] | 11028446_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11040178_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11054276_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11072134_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11072751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11116068_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11145851_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11167813_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11196676_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11196678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11199329_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11204808_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11212160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11224491_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11233912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11266856_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11266927_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11266928_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11267084_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11282548_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11312376_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11315919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11316066_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11342474_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11354638_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11355017_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11371414_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11391238_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11397324_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11404167_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11448119_IL-6 stimulates proliferation of rat pituitary tumor cells in culture, inhibits secretion of prolactin and growth hormone and induces tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT3 in the cells. 11485024_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11500818_Individuals genetically predisposed to produce high levels of IL-6 during aging are disadvantaged for longevity. 11520812_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11544427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11544434_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11544437_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11557672_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11574109_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11640949_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11687509_Data demonstrate that exercise activates transcription of the IL-6 gene in working skeletal muscle, a response that is dramatically enhanced when glycogen levels are low. 11692078_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11703956_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11713964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11716039_Interleukin-6 stimulates thyrotropin receptor expression in human orbital preadipocyte fibroblasts from patients with Graves' ophthalmopathy 11728144_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11733366_Interleukin (IL)-6 protein concentrations are increased approximately 18-fold in clinically localized prostate cancers when compared to normal prostate tissue. 11751408_Autocrine production of interleukin 6 causes multidrug resistance in breast cancer cells. 11758653_Levels of IL-6 were significantly higher in patients with dyslipidemia as compared with the healthy controls 11774563_Interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha and interferon gamma serum levels in patients with anorexia nervosa. 11777983_Pancreatic periacinar myofibroblasts secrete a large amount of IL-6 in response to proinflammatory cytokines IL-17, IL-1 beta, and TNF-alpha. 11781191_detection in pericardial fluid in coronary pathologies 11788581_Function and molecular modeling of the interaction between human interleukin 6 and its HNK-1 oligosaccharide ligands 11792588_Expression of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-6 receptor mRNA in human bone samples from pre- and postmenopausal women. 11794009_biosynthesis induced by tnf-alpha or interleukin 1 beta in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes increases with cell passage 11801594_Heat shock factor 1 represses transcription of the IL-1beta gene through physical interaction with the nuclear factor of interleukin 6 11818668_Il-6 and oncostatin M act synergistically to promote growth in a new human myeloma cell line. 11820460_Certoparin but not UFH led to a dose-dependent increase in IL-6 from non-stimulated PBMC. 11847482_NADH significantly stimulated the dose-dependent release of IL-6 from peripheral blood leukocytes.The biological relevance of these data is discussed in the context of the recent use of NADH for the treatment of several neurodegenerative disorders. 11849463_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11853279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11855786_Increased plasma levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 are observed in beta-thalassaemia major patients and may be relevant in the pathophysiology of beta-thalassaemia 11858187_In dengue shock syndrome pts, IL-6 was significantly associated with both activation markers of coagulation (F1+2; p A and -174 G-->C polymorphisms in the promoter of the IL-6 gene are associated with hyperandrogenism. 11895465_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11902285_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11906646_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11914754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11914754_polymorphism -174G/C does not contribute substantially to hyperlipidaemia and Type II diabetes mellitus in Japanese men 11918227_results suggest that IL-6 is a mediator of the effects of Crohn's serum on in vitro mineralization and may be a contributing factor to the osteopenia associated with Crohn's disease 11919083_TNF-alpha induced IL-6 gene expression in airway smooth muscle (ASM) cells via a nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB-dependent pathway 11922913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11949822_Fas engagement increases expression of interleukin-6 in human glioma cells. 11950481_process of cervical dilatation during parturition at term is associated with an increased expression of interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 mRNA in the lower uterine segment 11950697_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11956023_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11959895_Reproductive hormone-induced, STAT3-mediated interleukin 6 action in normal and malignant human ovarian surface epithelial cells. 11960393_Secretion levels of sIL-2R, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, and TNF-alpha, but not IL-4 and IL-12, are elevated in activated T-cells in large granular lymphocytic leukemia associated with autoimmune disorders. 11961304_the effects of high glucose in concert with AGII on IL-6 production in human mesangial cells and the modulation by blocking AGII 11966578_determine the cellular contents and concentrations of interleukin 6 (IL-6), interleukin 8 (IL-8) and tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) in fluids of patients with spermatocele or epididymal cyst 11981433_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11983287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11984595_expressed in multiple sclerosis brain lesions 11988246_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11988625_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11990931_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11992567_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11992567_findings suggest that the IL-6prom G allele which may affect plasma IL-6 concentration might be a risk factor for sporadic AD in Japanese 12012622_high concentrations of IL-6 in the mid-secretory phase, the putative implantation window, and a further increase in the late secretory phase, the premenstrual period, support a role of IL-6 in the regulation of endometrial functions 12027404_IL-6 has a role in contributing directly to paclitaxel and doxorubicin resistance in U-2OS through a non-MDR-1 pathway. 12031914_secretion from acute myelogenous leukemia blasts was up-regulated by leptin 12032172_IL-6 induced activation of full-length LCAT promoter activity. A minimal IL-6 response element mapped within the distal promoter and was sufficient to mediate the IL-6 response 12036196_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12036196_These results suggest that polymorphism of the IL-6 gene may be a useful marker for reduced bone mineral density. 12038454_VEGF and IL-6 were both independent prognostic factors for overall survival of aggressive lymphoma 12047360_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12050565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12051396_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12067898_Interleukin-6 production is induced in smooth muscle cells by monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 via differential activation of nuclear factor-kappa B. 12070032_The role of interleukin-6 in the development of functionally defective dendritic cells in multiple myeloma.IL-6 inhibited the colony growth of CD34(+)DC progenitors and switched the commitment of CD34(+) cells from DCs to monocytic cells. 12080442_IL-6 is produced by human adipocytes and is a potential marker of adipocyte differentiation; it is a hormonally regulated cytokine, suppressed by glucocorticoids, and stimulated by catecholamines and insulin in physiological concentrations 12082590_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12086705_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12089714_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12091348_identification of the positive role of IL-6 in the secretolytin release from monocytes in vitro 12095061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12096924_Glutamine decreases rhis and interleukin-8 but not nitric oxide and prostaglandins e(2) production by human gut in-vitro. 12096927_Endotoxin-stimulated production is increased in short-term cultures of whole blood from healthy term neonates. 12107724_Impaired glucose tolerance is associated with increased serum concentrations. 12110411_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12114287_The loss of response to IL-6 is an important step in the process of adrenal tumorigenesis. IL-6 stimulates cortisol secretion from adrenal cells. IL-6 mRNA is upregulated in adrenal adenomas from Cushing syndrome patients. 12117737_Simvastatin reduces expression of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 in circulating monocytes from hypercholesterolemic patients. 12117921_role of p38 map kinase, NF-kappaB, and protein kinase c in IL-6 mRNA expression by human peripheral blood leukocytes, monocytes, and neutrophils in response to Anaplasma phagocytophila 12117953_Acanthamoeba castellanii by release of ADP and other metabolites lead to human monocytic cell death through apoptosis and stimulate the secretion of IL-6 12121679_IL-6 gene region may contribute to susceptibility to HTLV-I associated myelopathy 12121679_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12133353_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12140751_Inheritance of the G/G genotype of both IL-1B and IL-6 was a particularly strong predictor for the development of recurrent aphthous stomatitis. 12140751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12149213_IL-7 may function to regulate the milieu of the microenvironment by modulating IL-6 secretion by the IL-7R-expressing stromal elements 12150965_regulation of synthesis by isoflavones during osteoblast cell differentiation via an estrogen-receptor-dependent pathway 12151314_These results suggest that hepatocyte growth factor and interleukin-6 upregulate each other's receptors, and thus cooperatively enhance tissue invasion. 12164325_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12165085_Normal and SV40 transfected human peritoneal mesothelial cells produce IL-6 and IL-8: implication for gynaecological disease. 12176919_activation of the hIL-6 gene by HHV-8/KSHV. role of hIL-6 in the development of Kaposi sarcoma. 12183057_activation of the ERK pathway is involved in the induction of IL-6 mRNA stabilization by IL-17 plus TNF-alpha. 12185451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12185451_the IL-6 G(-174)C polymorphism is not associated with the risk of CAD or MI and does not contribute to cardiovascular risk stratification. 12187073_The endogenous levels of TPO, IL-6 and IL-8 are elevated in the thrombocytopenic patients with AML and MDS. 12198224_an independent predictor of mortality in patients starting dialysis treatment 12200114_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12202945_IL-6 levels were not correlated with seminal parameters. IL-6 and TNF-alpha may be involved in male fertility. 12214260_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12215823_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12217290_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12218157_IL-6 in combination with its recombinant receptor enhances the expression of receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL) and osteoprotegerin in neonatal mouse calvarial bone cultures, while decreasing RANK expression. 12219016_Interleukin-10 activates the transcription factor C/EBP and the interleukin-6 gene promoter in human intestinal epithelial cells. 12220549_Review. We review the evidence for the involvement of IL-6 in the pathophysiology of autoimmune diseases and chronic inflammatory proliferative diseases (CIPD) and discuss the possible molecular mechanisms of its involvement 12226829_role in human herpesvirus-8 replication 12232842_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12235153_antagonism by a homodimeric form of recombinant interleukin-6 12239630_human IL6 expression mediates elements of the systemic inflammatory response in pancreatic tumor cell lines 12240899_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12297113_IL-6 expression is modulated by hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women 12297725_Interleukin-6 down-regulates TFF expression in human stomach neoplasm cells cultivated in vitro. 12352619_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12359225_results strongly suggest that the IL-6-induced tyrosine-phosphorylation and activation of STAT3 were suppressed by overexpression of the nuclear isoform of TC-PTP in 293T cells 12359431_Rta expression during lytic reactivation of HHV-8 would lead to expression of some cellular genes, including IL-6, whereas activation of NF-kappa B could inhibit some responses to transcription activator, Rta 12370360_results indicate that mouse IL-19 may play some important roles in inflammatory responses because it up-regulates IL-6 and TNF-alpha and induces apoptosis [IL-19] 12370503_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12371985_Carriers of the -174C-allele (genotype GC/CC) had an inferior three-year graft survival (71/104 = 68.3%; P = 0.0059) with a 3.7-fold increased relative risk of graft loss compared to carriers of the -174GG-genotype (48/54 = 88.9%). 12371985_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12372336_Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells do not differentiate into the osteogenic lineage until Gp130 is activated by soluble IL-6 receptors and IL-6. 12382118_IL-6 production induced by hydrostatic pressure stresses was dependent on the PKC signaling pathway. 12383455_results suggest that tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 are involved in endotoxin-induced anorexia in humans 12391243_Release of IL-6 from oncostatin M-stimulated peritoneal mesothelial cells is dose- and time-dependent and contributes to the control of leukocyte recruitment by the soluble IL-6 receptor. 12392859_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12393446_IFN-gamma shifts monocyte differentiation to macrophages rather than DCs through autocrine M-CSF and IL-6 production. 12393542_Inhibition of p38 MAPK inhibits IL-6 and VEGF secretion in bone marrow stromal cells triggered by adherence of multiple myeloma cells. 12393699_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12394188_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12413693_cystatins SA1 and SA2 adhere to human fibroblasts and that the event results in tyrosine phosphorylation and upregulation of the release of IL-6 mediated enhancement of NF-kappa B activity. 12419823_results show for the first time that interleukin-6 (IL), in the presence of its soluble receptor (sIL-6R), induces activation of JAK1, JAK2, and STAT1/STAT3 proteins in bovine articular chondrocytes 12430875_growth mechanism of human myeloma cells by interleukin-6 12431817_a multifunctional cytokine which causes contrasting effects in prostate cancer cells; may have an important role in progression of prostate cancer towards resistance to endocrine therapy [review] 12445202_in basal cell carcinoma cells, the upregulation of the anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 protein by interleukin-6 is mainly through the Janus tyrosine kinase/phosphotidyl inositol 3-kinase/Akt, but not the STAT3 pathway. 12445803_soluble proteins of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-6 receptor subunit gp80 (sIL-6R gp80), as markers of multiple sclerosis 12451269_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12451269_The presence of high-expression polymorphisms at position -174 of the IL-6 gene significantly increases the risk for bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome development after lung transplantation. 12453469_IL6 regulates growth-related gene espression in murine myeloma cells 12468916_levels in children with acute and chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and their relationship with mega-dose methylprednisolone therapy 12472176_IL-18 is a promising candidate for the enhanced secretion of IL-6 by human neutrophils. 12482836_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12482836_The IL-6 -174G>C polymorphism combined with IL-6 plasma levels may chronically predispose an individual to develop atherosclerosis. 12483530_role in inducing N-ras and K-ras in myeloma cells 12491092_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12493411_An examination of quantitative gene expression of this protein in the renal artery wall of chronically rejected human renal allografts. 12495721_IL-6: a regulator of the transition from neutrophil to monocyte recruitment during inflammation(review) 12507818_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12509497_IL-6 may be linked to the regulation of glucose homeostasis during exercise. The observation of a relationship between IL-6 release and muscle glycogen store both at rest and after exercise suggests that IL-6 may act as a carbohydrate sensor. 12517591_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12517591_The interleukin-6 promoter polymorphism -174 G/C does not contribute significantly to overall disease susceptibility but does predispose the carrier to distinct endometriosis with chocolate cysts 12517814_Paracrine interactions of basic fibroblast growth factor and interleukin-6 in multiple myeloma 12519862_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12519862_describe two functional polymorphisms in the IL-6 gene regulatory region associated with IL-6 activity in postmenopausal women both systemically (C-reactive protein) and locally in bone 12526950_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12540635_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12540635_The promoter polymorphism of this gene affects energy expenditure and insulin sensitivity. 12553555_only in a subset of both benign and malignant thyroid nodules the interleukin-6/interleukin-6 receptor signal could be induced by the CD30 ligand/CD30 12554901_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12558814_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12559950_data demonstrated that Hsp90 may function as a stabilizer of an IL-6-mediated signal-transducing molecule, STAT3, by directly interacting with STAT3 12560330_IL-6 mediates insulin resistance with SOCS-3 in the liver 12560873_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12560873_in men, the IL6 -174G/C polymorphism is associated with some indices of body composition and parameters of glucose and insulin homeostasis 12571160_Although known to alter IL-6 expression, the IL-6 polymorphism investigated was not associated with idiopathic recurrent miscarriage and alterations in IL-6 serum levels in a Middle-European Caucasian population. 12571160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12574550_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12584029_Recombinant human IL-6 induces from peripheral blood mononuclear cells the formation of osteoclastic cells, which are positive for tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase, vitronectin receptor, and calcitonin receptor and capable of lacunar resorption. 12585340_IL-6 secreted during an aseptic inflammatory state, such as sustaining head trauma with SIADH, is quantitatively correlated to AVP, indicating that this cytokine is directly and/or indirectly involved in the pathogenesis of SIADH. 12589429_found that the G/C polymorphism in the IL6 promoter region is associated with development of type-2 diabetes mellitus in Native Americans and Caucasians; Pima Indians have a higher frequency of the GG genotype than Caucasians 12590978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12591385_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12592380_Inhibition of IL-6+IL-6 soluble receptor-stimulated aromatase activity by the IL-6 antagonist, Sant 7, in breast tissue-derived fibroblasts 12594059_Bradykinin induces IL-6 production in human airway smooth muscle cells. 12595908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12606524_combined elevation of interleukin-1beta and interleukin-6, rather than the isolated elevation of interleukin-6 alone, independently increases the risk of type 2 diabetes 12615367_IL-6 and GM-CSF may be involved in the autoimmune mechanism of non-segmental vitiligo. 12618859_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12626585_STAT3 activation induced by IL-6 in primary human macrophages is affected differentially compared to STAT3 activation by IL-10, by mechanisms that suppress the Jak1/STAT3 pathway, despite the ability of the two cytokines to signal via similar pathways. 12629515_We conclude that IL-6 may promote cervical tumorigenesis by activating VEGF-mediated angiogenesis via a STAT3 pathway. 12633940_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12634650_Interleukin-6 levels were elevated 5-fold in preeclamptic plasma. Human umbilical vein endothelial cell interleukin-6 production was increased 25% by preeclamptic plasma. plasma. 12637697_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12637697_Synergistic effect of -174 G/C polymorphism of the interleukin-6 gene promoter and a polymorphism of the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 gene in Italian patients with history of ischemic stroke. 12647840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12651071_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12653788_The significant correlation of IL-6 and fructose levels indicates that the seminal vesicles take part in the production of seminal IL-6. 12657090_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12660820_lack of role in expression of Mcl-1 in multiple myeloma 12660878_This study provides further evidence that IL-6, leptin, and adiponectin are associated with impaired fibrinolysis in overweight hypertensive humans. 12663465_data suggest a transcriptional mechanism leading to decreased adiponectin plasma levels in obese women and demonstrate that low levels of adiponectin are associated with higher levels of C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 12664314_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12668153_the thermotolerant effect of IL-6 is independent of the heat shock response 12668157_IL-6 release from human adipocytes is stimulated in the autocrine/paracrine system by IL-1beta 12681965_IL-6 precludes the negative effects induced by IL-3 on cord blood CD34+ cell expansion and telomerase activity. 12694213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12713584_interleukin-6 stimulates mast cell adhesion to extracellular matrix and thus allows for the accumulation of the cells at tissue sites by enhancing integrin expression 12714254_MTmRNA is high in lymphocytes from elderly people coupled with high IL-6, low zinc ion bioavailability, decreased NK cell activity and impaired capacity of PARP-1 in base excision DNA-repair. 12714267_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12714267_reduction in the frequency of GG homozygotes in the octo/nonagenarian age group and a higher serum IL-6 level associated with CC homozygotes with reciprocal changes for the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. 12716337_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12719374_higher IL6 promoter activity may confer risk to type 1 diabetes mellitus in very young females 12720537_IL-8 increased by 30% after weight loss. IL-8 and IL-6 correlated with measures of insulin resistance, and changes in IL-6 but not IL-8 were correlated with improvement in insulin sensitivity after weight loss. 12727482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12727794_parallel expression with cyclooxygenase-2, interleukin-1beta, and NF-kappaB in colorectal cancer 12727841_Constitutive activation of nuclear factor kappaB p50/p65 and Fra-1 and JunD is essential for deregulated interleukin 6 expression in prostate cancer. 12727948_combination of low insulin-like growth factor-I and high interleukin-6 levels confers a high risk for progressive disability and death in older women 12727959_in healthy adults, age-related alterations in nocturnal wake time and daytime sleepiness are associated with elevations of both plasma interleukin-6 and cortisol concentrations, but REM sleep decline with age is associated with cortisol increases 12736743_A disease-modifying effect of IL-6 C allele could not be demonstrated in multiple sclerosis patients of German Caucasian descent. 12736743_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12737276_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12742994_Giant cell arteritis patients with ischemic complications have lower tissue expression and circulating levels of IL-6 than patients with no ischemic events; IL-6 effects on vascular wall components may be protective 12743452_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12745542_intestinal epithelial and smooth muscle cells demonstrate the ability to release significant amounts of IL-6.Human intestinal parenchymal cells, influenced by paracrine mediators might contribute to the systemic inflammatory response by producing IL-6. 12746914_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12748876_might also be valuable biochemical marker in the evaluation of oocyte maturation 12754410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12754410_there appeared to be no significant associations between IL6 promoter variants and disease outcome in chronic hepatitis B 12756345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12757654_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12760309_The level of IL-6 secretion in the gastric cancer cell lines correlated with the level of soluble IL-6R secretion, and was significantly higher ( | ENSMUSG00000025746 | Il6 | 32.751522 | 0.116553449 | -3.100936 | 0.37120687 | 83.160450 | 0.0000000000000000000756563587997444269084740263371317697557883829125095721465643627823283168254420161247253417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000052077636808145040193776089739902111908103822347847026985601104343004408292472362518310546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 6.4698371 | 5.2998596 | 55.6516041 | 43.9248945 | |
| ENSG00000136305 | 27141 | CIDEB | protein_coding | Q9UHD4 | FUNCTION: Activates apoptosis.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Involved in Hepatatis C virus (HCV) assembly and required for HCV entry into hepatocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27282740}. | 3D-structure;Apoptosis;Host-virus interaction;Reference proteome | Enables identical protein binding activity. Involved in activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity; positive regulation of cell death; and positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria. Acts upstream of or within apoptotic process. Located in cytosol and perinuclear region of cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:27141; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0097202]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; bile acid signaling pathway [GO:0038183]; execution phase of apoptosis [GO:0097194]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage [GO:0008630]; positive regulation of cell death [GO:0010942]; positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090200]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; response to nutrient levels [GO:0031667] | 16248853_A novel mechanism for the cell-specific transcription of the human CIDE-B gene, which involves epigenetic and genetic control at separate respective promoters is reported. 19064571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20551328_PGC-1alpha plays an important role in partitioning cytoplasmic TG toward the VLDL secretory compartments and promoting VLDL secretion via transcriptional induction of CideB. 23475172_CIDE proteins expression correlate with tumor and survival characteristics in patients with renal cell carcinoma. 24161736_this work highlights CIDEB's role in lipid droplet (LD) fusion, and presents a new model system to study the PGC-1alpha/CIDEB pathway's role in LD dynamics and the VLDL pathway. 24829338_Authors found CIDEB to be an essential cofactor for hepatitis C virus entry into hepatocytes. 24831470_these data revealed that Cideb plays an important role in controlling intestinal chylomicron lipidation. 24980280_CIDEB can act as an anti-HCV host factor and contribute to altered triglyceride homeostasis. 26865724_CIDEB downregulation may contribute to HCV-induced hepatic steatosis 27213693_this study shows that C5a signaling induces apoptosis in brain vascular endothelial cells in experimental lupus through activation of CIDEB 27282740_CIDEB interacts with the HCV NS5A protein, and the N terminus of CIDEB and the domain I of NS5A are involved in this interaction. 28719542_High Cideb expression is associated with Ulcerative Colitis. 31097771_The Differential Expression of Cide Family Members is Associated with Nafld Progression from Steatosis to Steatohepatitis. 35475772_Association of CIDEB gene promoter methylation with overweight or obesity in adults. 35939579_Germline Mutations in CIDEB and Protection against Liver Disease. | ENSMUSG00000022219 | Cideb | 37.917107 | 0.270108941 | -1.888387 | 0.65959420 | 7.536031 | 0.0060477120229154449418396133353326149517670273780822753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0335031270402143532827210492541780695319175720214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 20.1995194 | 8.7979469 | 76.1714095 | 33.0971995 | |
| ENSG00000136688 | 56300 | IL36G | protein_coding | Q9NZH8 | FUNCTION: Cytokine that binds to and signals through the IL1RL2/IL-36R receptor which in turn activates NF-kappa-B and MAPK signaling pathways in target cells. Part of the IL-36 signaling system that is thought to be present in epithelial barriers and to take part in local inflammatory response; similar to the IL-1 system with which it shares the coreceptor IL1RAP. Seems to be involved in skin inflammatory response by acting on keratinocytes, dendritic cells and indirectly on T-cells to drive tissue infiltration, cell maturation and cell proliferation. In cultured keratinocytes induces the expression of macrophage, T-cell, and neutrophil chemokines, such as CCL3, CCL4, CCL5, CCL2, CCL17, CCL22, CL20, CCL5, CCL2, CCL17, CCL22, CXCL8, CCL20 and CXCL1; also stimulates its own expression and that of the prototypic cutaneous pro-inflammatory parameters TNF-alpha, S100A7/psoriasin and inducible NOS. May play a role in pro-inflammatory responses during particular neutrophilic airway inflammation: activates mitogen-activated protein kinases and NF-kappa B in primary lung fibroblasts, and stimulates the expression of IL-8 and CXCL3 and Th17 chemokine CCL20 in lung fibroblasts. May be involved in the innate immune response to fungal pathogens, such as Aspergillus fumigatus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11466363, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20870894, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21965679, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23095752, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23147407, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24829417}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytokine;Cytoplasm;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Reference proteome;Secreted | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the interleukin 1 cytokine family. The activity of this cytokine is mediated by interleukin 1 receptor-like 2 (IL1RL2/IL1R-rp2), and is specifically inhibited by interleukin 1 family, member 5 (IL1F5/IL-1 delta). Interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1, beta (IL1B) are reported to stimulate the expression of this cytokine in keratinocytes. The expression of this cytokine in keratinocytes can also be induced by a contact hypersensitivity reaction or herpes simplex virus infection. This gene and eight other interleukin 1 family genes form a cytokine gene cluster on chromosome 2. [provided by RefSeq, May 2019]. | hsa:56300; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; interleukin-1 receptor binding [GO:0005149]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002437]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628] | 14734551_IL-1F6 and IL-1F8, in addition to IL-1F9, activate the pathway leading to NF-kappaB in an IL-1Rrp2-dependent manner in Jurkat cells 15331687_This is the first report of IL-1 genotype association with the inflammation of skeletal muscle following acute resistance exercise that may potentially affect the adaptations to chronic resistance exercise. 15701729_This report demonstrates expression of IL1F9 by bronchial epithelial cells induced by pro-inflammatory stimuli, suggesting a function of this molecule in airway inflammation. 18484691_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20141484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20870894_Regulation and function of the IL-1 family cytokine IL-1F9 in human bronchial epithelial cells. 21242515_Expression of IL-1F9 is increased in human plaque psoriasis skin and is overexpressed in a transgenic mouse psoriasis model. 21965679_Interleukin-36 (IL-36) ligands require processing for full agonist (IL-36alpha, IL-36beta, and IL-36gamma) or antagonist (IL-36Ra) activity 22318382_This is the first report of extracellular release of endogenous IL-36gamma through pyroptosis suggesting a function of IL-36gamma as an alarmin. 23095752_Data presented herein shed further light on involvement of T-bet in innate immunity and suggest that IL-36gamma, besides IFNgamma, may contribute to functions of this transcription factor in immunopathology. 24829417_IL-36 promotes myeloid cell infiltration, activation, and inflammatory activity in skin 24950037_Decreased Langerhans cell responses to IL36G: altered innate immunity in patients with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis 25305315_CAMP induces IL-36gamma expression leading to initiation of skin inflammation and occasional exacerbations of psoriasis. 25525775_IL-36gamma is a valuable biomarker in psoriasis patients, both for diagnostic purposes and measurement of disease activity during the clinical course 25897967_IL36G was identified as strong regulators of skin pathology in both lesional and non-lesional skin samples. 26321222_IL-36gamma expression inversely correlated with the progression of human melanoma and lung cancer. 26516833_Study shows that plasma concentrations of IL-36alpha and IL-36gamma are overexpressed in active systemic lupus erythematosus patients and that IL-36alpha has a substantial pro-inflammatory effect through regulation of IL-6 and CXCL8 production. 26524325_IL-36gamma is significantly more strongly expressed in the epidermis of patients with psoriasis-based erythroderma than in other inflammatory skin diseases. 26562662_Findings indicate that Interleukin (IL)-1beta-induced interleukin 36 gamma (IL-36gamma) expression is mediated by the activation of transcriptional factors, NF-kappaB p65 and AP-1 (c-jun). 26819203_IRF6 is likely to promote inflammation to P. gingivalis through its regulation of IL-36gamma. 27183581_Autocrine and Paracrine Regulation of Keratinocyte Proliferation through a Novel Nrf2-IL-36gamma Pathway 27389350_Here the authors show that Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection of macrophages induces IL-36gamma production in a 2-stage-regulated fashion. 27673278_IL-36gamma-stimulated endothelial cells secrete the proinflammatory chemokines IL-8, CCL2 and CCL20. 27853811_IL-36gamma, a member of the IL-1 superfamily, is involved in host defense and contributes to proinflammatory responses and development of inflammatory diseases. 28176791_enhanced expression of IL-36gamma was observed in plasma and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome because of bacterial pneumonia 28289191_Cathepsin S was identified as the major IL-36gamma-activating protease expressed in epithelial cells. 28774595_skin injury increases IL-36gamma via the activation of TLR3-SLUG-VDR axis and IL-36gamma induces REG3A to promote wound healing 28811383_With a focus on the skin as a target for microbial and viral invasion, the current knowledge of IL-36: IL-36alpha, IL-36beta and IL-36gamma, functions is reviewed. One physiological function of the IL-36smay be to counteract microbial immune evasion. [Review] 28869889_IL-36-mediated IL-6 and CXCL8 production in human lung fibroblasts and bronchial epithelial cells may be involved in pulmonary inflammation especially caused by bacterial or viral infections. 28924372_IL-36gamma inhibits differentiation and induces inflammation of keratinocyte via Wnt signaling pathway in psoriasis. 29274415_Increased production and activation of IL-36gamma may act on neutrophils and further exaggerate neutrophilic inflammation in CRS. 29474749_this study not only advances our understanding of how IL-36 cytokines may control mucosal inflammation, but also establishes EGFR signaling as a potentially important modulator of IL-36 cytokine function 29571080_serum IL-36gamma levels were higher in active systemic lupus erythematosus patients and correlated with disease activity and arthritis 29782895_The results presented here confirm that IL-36gamma is a robust, specific, and reliable biomarker for psoriatic inflammation that outperforms previously reported biomarkers and is likely to withstand all challenges in real-life primary and secondary dermatologic care. 29914927_The expression of IL-36gamma by oral epithelial cells in response to P. gingivalis might enable the subsequent autocrine stimulation of PGLYRP2 expression. Our data identify how IL-36gamma may promote oral mucosal homeostasis by regulating PGLYRP2 expression. 30118914_data indicate that IL-36gamma may participate as a key player in host defense mechanisms against invading pathogens in the female reproductive tract. 30315348_Interleukin 36 gamma (IL-36gamma) is detected in the immune and vascular compartments in the tumor microenvironment. 30395846_IL-36gamma secretion by monocytes/macrophages and keratinocytes in response to culprit drug exposure likely plays a key role in the pathogenesis of AGEP. 30614571_IL-17A synergistically enhances TLR3-mediated IL-36gamma production by keratinocytes 30634937_Polymorphisms in IL36G gene are associated with plaque psoriasis. IL36G has previously demonstrated markedly increased levels in plaque psoriasis patients and is linked to IL-23/IL-17 axis critical in psoriasis pathology. 30831444_High expression of IL-36gamma exaggerates eosinophilic inflammation in allergic rhinitis by promoting the survival, adhesion, and activation of eosinophils. 30856602_IL-36gamma regulates mediators of tissue homeostasis in epithelial cells. 31235551_our findings reveal a novel activity for IL-36gamma as an inducer of autophagy, which represents a critical inflammatory cytokine that control the outcome of M. tuberculosis infection in human macrophages. 31430658_Increased expression of interleukin 36 in chronic rhinosinusitis and its contribution to chemokine secretion and increased epithelial permeability. 31586390_Interleukin-36gamma Is Elevated in Cervicovaginal Epithelial Cells in Women With Bacterial Vaginosis and In Vitro After Infection With Microbes Associated With Bacterial Vaginosis. 31736959_Biology of IL-36 Signaling and Its Role in Systemic Inflammatory Diseases. 31805013_IL-36gamma drives skin toxicity induced by EGFR/MEK inhibition and commensal Cutibacterium acnes. 31848404_IL-36gamma is a pivotal inflammatory player in periodontitis-associated bone loss. 32013927_IL-36 s in the colorectal cancer: is interleukin 36 good or bad for the development of colorectal cancer? 32351508_IL36 Cooperates With Anti-CTLA-4 mAbs to Facilitate Antitumor Immune Responses. 32447345_Cytokine IL-36gamma improves CAR T-cell functionality and induces endogenous antitumor response. 32814555_Increased serum IL-36gamma levels are associated with disease severity in myasthenia gravis patients. 33034926_Serum IL-36 cytokines levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with obesity, insulin resistance, and inflammation. 33188781_Cigarette Smoke Underlies the Pathogenesis of Palmoplantar Pustulosis via an IL-17A-Induced Production of IL-36gamma in Tonsillar Epithelial Cells. 33193319_High Expression of IL-36gamma in Influenza Patients Regulates Interferon Signaling Pathway and Causes Programmed Cell Death During Influenza Virus Infection. 33491092_IkBzeta is a Key Regulator of Tumour Necrosis Factor-a and Interleukin-17A-mediated Induction of Interleukin-36g in Human Keratinocytes. 33593161_Elevated urinary IL-36gamma in patients with active lupus nephritis and response to treatment. 33675789_IL-36 and IL-17A Cooperatively Induce a Psoriasis-Like Gene Expression Response in Human Keratinocytes. 34289144_IL-36alpha and IL-36gamma expressions in the differential diagnosis of palmoplantar psoriasis and palmoplantar eczema: A retrospective histopathologic and immunohistochemical study. 34369094_IL-36gamma and IL-36Ra Reciprocally Regulate NSCLC Progression by Modulating GSH Homeostasis and Oxidative Stress-Induced Cell Death. 34376113_Downregulation of interleukin 36gamma and its cleaver cathepsin G following treatment with narrow-band ultraviolet B phototherapy in psoriasis vulgaris. 35222417_Increased Levels of Interleukin-36 in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Fuel Adipose Tissue Inflammation by Inducing Its Own Expression and Release by Adipocytes and Macrophages. 35325069_IL-36gamma in enthesitis-related juvenile idiopathic arthritis and its association with disease activity. 35698471_IL-36 is Closely Related to Neutrophilic Inflammation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 35862195_Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 is a psoriasis-susceptibility locus that is negatively related to IL36G. 35903102_IL-36 Cytokines: Their Roles in Asthma and Potential as a Therapeutic. 36040155_Treponema denticola Induces Interleukin-36gamma Expression in Human Oral Gingival Keratinocytes via the Parallel Activation of NF-kappaB and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways. 36172384_L36G is associated with cutaneous antiviral competence in psoriasis. | ENSMUSG00000044103 | Il36g | 11.722915 | 0.157180887 | -2.669502 | 0.58157820 | 25.161856 | 0.0000005271457307425196438490830851131274670251514180563390254974365234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000092402437113112345445182713166154542250296799466013908386230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 3.4954874 | 3.1117795 | 21.9828056 | 17.9292363 | |
| ENSG00000136689 | 3557 | IL1RN | protein_coding | P18510 | FUNCTION: Anti-inflammatory antagonist of interleukin-1 family of proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1beta/IL1B and interleukin-1alpha/IL1A. Protects from immune dysregulation and uncontrolled systemic inflammation triggered by IL1 for a range of innate stimulatory agents such as pathogens. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P25085, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7775431}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Pharmaceutical;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the interleukin 1 cytokine family. This protein inhibits the activities of interleukin 1, alpha (IL1A) and interleukin 1, beta (IL1B), and modulates a variety of interleukin 1 related immune and inflammatory responses, particularly in the acute phase of infection and inflammation. This gene and five other closely related cytokine genes form a gene cluster spanning approximately 400 kb on chromosome 2. A polymorphism of this gene is reported to be associated with increased risk of osteoporotic fractures and gastric cancer. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. | hsa:3557; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; interleukin-1 receptor antagonist activity [GO:0005152]; interleukin-1 receptor binding [GO:0005149]; interleukin-1 type I receptor antagonist activity [GO:0045352]; interleukin-1 type II receptor antagonist activity [GO:0045353]; interleukin-1, type I receptor binding [GO:0005150]; interleukin-1, type II receptor binding [GO:0005151]; acute-phase response [GO:0006953]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002437]; insulin secretion [GO:0030073]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; negative regulation of heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034115]; negative regulation of interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway [GO:2000660]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384] | 11023482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11027520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11033452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11045853_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11127488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11138328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11171832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11233912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11247888_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11264025_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11423389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11448121_The serum level of IL-1Ra is higher in cicatricial pemphigoid patients in prolonged clinical remission and following intravenous immunogloglobulin therapy, when compared to the pre-IVIg treatment level. 11531943_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11600466_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11606494_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11606496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11640949_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11641511_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11665981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11686217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11686217_There were no significant differences in the distributions of the IL-1RN and IL-1B genotpes, allele frequencies or halotypes. 11762793_There is an association between urolithiasis and polymorphism in the IL-1Ra gene. 11770040_Septic shock whole-blood leukocytes and neutrophils (PMNs) selectively maintained production of sIL-1RA after treatment with LPS. 11784248_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11793861_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11803448_Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) gene VNTR polymorphism was studied in children with DSM-IV ADHD and their parents to determine the role of brain cytokine activity in the etiopathogenesis of ADHD. 11816697_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11840488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11840488_Slight association of mutations with hypertension. 11841485_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11841485_results suggest that polymorphisms within IL1RN and IL1L1 themselves or a gene in linkage disequilibrium with IL1RN and IL1L1 predispose to the more severe forms of alopecia areata 11841553_A borderline association was observed between il-1rn and patchy alopecia areata. 11846196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11858187_In dengue shock syndrome pts, IL-1Ra was significantly associated with F1+2, TATc (p T and IL1RA VNTR polymorphisms do not play a crucial role in susceptibility or resistance to cerebral malaria. 16098232_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16100774_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16106254_Association seen between common haplotype in the IL1RN gene and prostate cancer in Swedish population; supports role of inflammation in prostate cancer development 16106254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16109659_IL-1Ra gene polymorphism was found in patients diagnosed with crohn disease living in India. 16109659_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16114018_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16115908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16126303_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16126303_results indicate that individuals homozygous for the IL1RN*1 allele and carrying the IL1B-31T allele had increased risk of non-small cell lung cancer; findings support the significance of IL1 gene cluster polymorphisms and risk of lung cancer 16128937_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16142351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16142351_an IL-1Ra polymorphism has a role in colorectal carcinogenesis 16159520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16164697_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16172101_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16174285_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16183821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16195370_IL-1Ra, Bcl-2, and iNOS are upregulated and counter the proinflammatory and proapoptotic effects of ischemia-reperfusion 16200608_IL1RN has a role in determining susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in the Spanish population. 16200608_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16202742_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16217062_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16226351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16244470_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16246569_Exerts intracellular functions regulating effect of N-terminal IL-1alpha propiece on movement of ECV304 tumor cells. 16263000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16268484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16284368_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16284379_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16301842_Increased levels of cord IL-1ra levels are associated with neonatal morbidity and adverse outcome in preterm infants 16318998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16319982_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16361275_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16361815_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16362796_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16369899_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16389181_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16403098_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16405550_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16409203_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16414081_substance P, epinephrine, and norepinephrine are not involved in mediating peripheral inflammation following psychosocial stress, at least with respect to interleukin-1 receptor antagonist 16423338_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16423338_results suggest that IL-1RN2 allele positivity is associated with periodontal disease in a Turkish population 16436009_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16454826_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16454826_The | ENSMUSG00000026981 | Il1rn | 1261.984467 | 0.400008369 | -1.321898 | 0.04583482 | 851.687174 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003124435 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002081171 | Yes | No | 721.0261023 | 38.8087407 | 1811.0729815 | 93.5827182 | |
| ENSG00000136717 | 274 | BIN1 | protein_coding | O00499 | FUNCTION: Is a key player in the control of plasma membrane curvature, membrane shaping and membrane remodeling. Required in muscle cells for the formation of T-tubules, tubular invaginations of the plasma membrane that function in depolarization-contraction coupling (PubMed:24755653). Is a negative regulator of endocytosis (By similarity). Is also involved in the regulation of intracellular vesicles sorting, modulation of BACE1 trafficking and the control of amyloid-beta production (PubMed:27179792). In neuronal circuits, endocytosis regulation may influence the internalization of PHF-tau aggregates (By similarity). May be involved in the regulation of MYC activity and the control cell proliferation (PubMed:8782822). Has actin bundling activity and stabilizes actin filaments against depolymerization in vitro (PubMed:28893863). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O08839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24755653, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27179792, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28893863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8782822}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Endocytosis;Endosome;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain | This gene encodes several isoforms of a nucleocytoplasmic adaptor protein, one of which was initially identified as a MYC-interacting protein with features of a tumor suppressor. Isoforms that are expressed in the central nervous system may be involved in synaptic vesicle endocytosis and may interact with dynamin, synaptojanin, endophilin, and clathrin. Isoforms that are expressed in muscle and ubiquitously expressed isoforms localize to the cytoplasm and nucleus and activate a caspase-independent apoptotic process. Studies in mouse suggest that this gene plays an important role in cardiac muscle development. Alternate splicing of the gene results in several transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Aberrant splice variants expressed in tumor cell lines have also been described. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. | hsa:274; | actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; axon [GO:0030424]; axon initial segment [GO:0043194]; axon terminus [GO:0043679]; cerebellar mossy fiber [GO:0044300]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0098850]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; I band [GO:0031674]; lipid tube [GO:0060987]; membrane [GO:0016020]; node of Ranvier [GO:0033268]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; RNA polymerase II transcription repressor complex [GO:0090571]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; T-tubule [GO:0030315]; varicosity [GO:0043196]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; aspartic-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0019828]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; clathrin binding [GO:0030276]; GTPase binding [GO:0051020]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; RNA polymerase binding [GO:0070063]; tau protein binding [GO:0048156]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; endosome to lysosome transport [GO:0008333]; lipid tube assembly [GO:0060988]; negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation [GO:1902430]; negative regulation of aspartic-type endopeptidase activity involved in amyloid precursor protein catabolic process [GO:1902960]; negative regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel [GO:1904878]; negative regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1901380]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:1903946]; nucleus localization [GO:0051647]; nucleus organization [GO:0006997]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of astrocyte differentiation [GO:0048711]; positive regulation of endocytosis [GO:0045807]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; regulation of cell cycle process [GO:0010564]; regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction [GO:0086091]; regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045664]; synaptic vesicle endocytosis [GO:0048488]; T-tubule organization [GO:0033292] | 8782822_A nucleocytosolic myc-interacting isoform of Bin1 has properties of a tumor suppressor. 9395479_Several tissue-specific splice isoforms of the human Bin1 gene are found only in brain or muscle. 9418903_Bin1 plays a crucial role in terminal differentiation of myoblasts; associated with induction of a muscle-specific splice isoform and subcellular relocalization. 10449755_Missplicing of a brain-specific exon of Bin1 in human melanoma is sufficient to abolish tumor suppressor properties; ectopic WT Bin1 activates PCD in malignant but not normal melanocytes. 10652430_There is frequent downregulation of Bin1 in malignant breast cells; ectopic Bin1 activates PCD in cells lacking expression. 10738240_There is frequent loss or downregulation of Bin1 in metastatic prostate cancer. 12183633_findings support a role of the bilayer-deforming properties of amphiphysin at T-tubules and, more generally, a physiological role of amphiphysin in membrane deformation 12532338_Results document the extent of expression of nuclear Bin1 isoforms, which exhibit cancer suppression and proapoptotic activity in human cells. 12668730_Sorting nexin 4 and amphiphysin 2 have roles in endocytosis and intracellular trafficking 12773571_Studies in mouse indicate that Bin1 is dispensable for endocytosis but essential for appropriate cardiac development. 14704274_role in activating various target genes after induction with the microtubule disrupting agent T113242 15483625_Phosphoinositides regulate BIN1 SH3 domain binding. 15992821_tumor-specific isoforms of Bin1 are precluded from interaction with c-Myc through an intramolecular polyproline-SH3 domain interaction. Furthermore, c-Myc/Bin1 interaction can be inhibited by phosphorylation of c-Myc at Ser62. 16516635_combination of gene dosages of MYCN and Survivin and the expression level of BIN1 using the quantitative polymerase chain reaction method was significantly correlated with the clinical stage and the patients' outcome in neuroblastoma 17059209_Crystal structure shows that both the quaternary and tertiary architectures of the homodimeric Bin1 BAR domain are built upon 'knobs-into-holes' packing of side chains, and this packing governs the curvature of a putative membrane-engaging concave face. 17210688_Mammary specific deletion of the Bin1 gene cooperates with ras activation to drive mammary tumor progression. The findings establish a role for Bin1 as a negative modifier of oncogenicity and progression in breast cancer. 17218774_Bin1 gene encodes a protein that suppresses neoplastic cell transformation.Bin1 may be a clinical prognostic marker in breast cancer. 17218774_Immunohistochemical losses of nuclear Bin1 proteins in cases of human breast cancer were associated with increased progression status and poor prognosis. 17611416_hob1+, the fission yeast homolog of Bin1, supports a mechanism of Rad6/Set1-dependent transcriptional repression that may relate to cancer suppression by Bin1. 17671430_potential relevance of Bin1-Ku interaction to cancer are discussed in light of these findings 17676042_Mutations in amphiphysin 2 (BIN1) disrupt its membrane tubulation properties and its interaction with dynamin 2, and cause autosomal recessive centronuclear myopathy 17676042_Results suggest that mutations in BIN1 cause centronuclear myopathy by interfering with remodeling of T tubules and/or endocytic membranes, and that the interaction between BIN1 and DNM2 is necessary for normal muscle function and positioning of nuclei. 17699764_Mosaic knockout mice lacking Bin1 exhibit lung and liver cancer, increased inflammation or premalignant lesions in prostate, and more progressive colon cancer. Thus, Bin1 suppresses inflammation and cancer during aging. 18154705_Mutated in recessive centronuclear myopathies. 18348166_Results suggest that Bin1 gene suppression caused by oncogenic E1A via Rb/E2F1 inactivation is an essential step in cell cycle progression promoted by c-Myc, and subsequently, E1A transformation. 18658220_findings support models for membrane curving by BAR domains in which helix-0 increases the binding affinity to the membrane and enhances curvature generation 18817572_REVIEW : BIN1 mutations and centronuclear myopathy 19004523_Amphiphysin 2/BIN1 participates in the tubulation of traffic intermediates and intracellular organelles first via its intrinsic tubulating potential and second via its ability to bind CLIP-170 and microtubules. 19418541_Bin1 appears to function as a metastasis suppressor and chemosensitizer in neuroblastoma. 19629135_BIN1 is transcriptionally activated by E2F1 and mediates E2F1-induced apoptosis in response to DNA damage. 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19915558_show a requirement for human BIN1 (also known as Amphiphysin 2) in EHD1-regulated endocytic recycling. 20140253_Characterization of amphiphysin 2 membrane tubules in cultured cells with correlative light-electron microscopy 20142620_BIN1 sequencing revealed a homozygous missense mutation in a patient with recessive centronuclear myopathy 20169111_Data have identified that membrane-associated BIN1 not only induces membrane curvature but can direct specific antegrade delivery of microtubule-transported membrane proteins. 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20460622_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20558387_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20558387_This study shown that established and candidate AD genes have a role in 6 neuroimaging traits linked to AD. 2 promising genes from Alzheimer disease GWASs, CNTN5 and BIN1, are associated with these neuroimaging measures. 20927630_This study proposed that aberrant BIN1 localization and defects in triad structure are part of a common pathogenetic mechanism shared between the three forms of centronuclear myopathies. 21059989_BIN1 polymorphisms were associated with late-onset Alzheimer disease in an independent cohort from the National Institute on Aging Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease Family Study 21059989_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21129173_We present the first clinical description of intrafamilal variability in two first-degree cousins with a novel BIN1 stop mutation. 21220176_we confirmed that BIN1 is a genetic determinants of Alzheimer disease. 21321396_Logistic regression analysis successfully replicates the association of BIN1 (rs744373) with late-onset Alzheimer's disease, with an odds ratio comparable to that previously reported. 21347408_variants in BIN1, CLU, CR1 or PICALM are associated with changes in the CSF levels of biomarkers 21379329_There was evidence of association for recently-reported late-onset Alzheimer's disease risk loci, including BIN1 and CLU and CUGBP2 with APOE. 21447796_A model has been proposed in which increased abundance of c-MYC indirectly leads to decreased BIN1 expression, in turn leading to increased PARP activity and resistance to DNA-damaging agents. 21623381_alternative splicing associated with T tubule alterations and muscle weakness in myotonic dystrophy 21678469_Results suggest that the coiled-coil BIN1 BAR peptide encodes a novel BIN1 MID domain, through which BIN1 acts as a MYC-independent cancer suppressor. 21984944_Study showing the importance of Bin1 in the maintenance of intact t-tubule structure and ([Ca(2)]i) homeostasis in adult skeletal muscle could provide insight on the potential role of Bin1 in skeletal muscle contractility and pathology of myopathy. 22281836_BIN1 expression is significantly decreased in surgically excised hepatocellular carcinoma patient specimens as well as in HCC cell lines and decreased BIN1 expression correlates with the degree of differentiation of HCC and predicts poor prognosis. 22539578_The SNP genotype pattern at the BIN1 gene is associated with episodic memory. 22544318_The re-expression of BIN1 specifically compromises the proliferation of SNF5-deficient rhabdoid tumors cell lines. 22976291_Findings suggest that RIN1 orchestrates RAB5 activation, ABL kinase activation and BIN1 recruitment to determine EGFR fate. 23202439_We identified rare small events overlapping CR1 and BIN1 in Alzheimer's disease and normal controls with opposite copy number variation dosage. 23399914_BIN1 expression is increased in Alzheimer Disease brains when compared with controls. 23570733_To our knowledge, this is the first study to show significant association between rs744373 polymorphism and AD in East Asian population. 23754947_Our data demonstrate that the alteration of the muscle-specific function of BIN1 is a common pathomechanism for centronuclear myopathy, myotonic dystrophy, and IMGD. 23803295_The resukts of this study highlight the possible use of plasma BIN1 as a biomarker for AD diagnosis. 23871436_REVIEW--BIN1: form, function, and Alzheimer's disease 24205320_BIN1 is decreased in sporadic but not familial Alzheimer's disease or in aging 24582639_It is the most important genetic susceptibility locus in late-onset Alzheimer's disease. 24590001_BIN1 downregulation is linked to cancer progression and also correlates with ventricular cardiomyopathy and arrhythmia preceding heart failure. Increased BIN1 expression is linked to increased susceptibility for late-onset Alzheimer's disease. [review] 24616074_The study compares the binding dynamics and affinities of the relevant regions for binding of c-Myc and NS5A to Bin1 SH3. The result gives further insights into the potential role of NS5A in Bin1-mediated apoptosis. 24660791_physical activity attenuated the effects of genetic risk (ie. the constellation of PICALM, BIN1, and CLU polymorphisms) on episodic memory 24755653_Two mutants of BIN1 showed impaired membrane tubulation both in vivo and in vitro, and displayed characteristically different behaviors. 25022885_BIN1 rs744373 polymorphism is significantly associated with late onset Alzheimer disease. 25024306_Results suggest that BIN1 is likely involved in Alzheimer's disease as a modulator of neurofibrillary tangle pathology, and that this role may extend to other human diseases that feature tau pathology 25051234_These findings suggest that an intracellular form CLU and BIN1 interaction might impact Tau function in neurons and uncover potential new mechanisms underlying the etiology of Tau pathology in in Alzheimer's disease. 25129075_Our analyses suggest that these DNA methylation changes may have a role in the onset of Alzheimer disease given that we observed them in presymptomatic subjects and that six of the validated genes connect to a known susceptibility gene network. 25257171_The release of BIN1 from hypo-poly(ADP-ribosyl)ated E2F1 is a mechanism by which serum starvation promotes E2F1-induced apoptosis. 25260562_specific amphiphysin 2 mutations can cause either recessive or dominant centronuclear myopathy and that both disorders involve different pathomechanisms 25262827_These results support a role for N-WASP in amphiphysin-2-dependent nuclear positioning and triad organization and in centronuclear myopathy and myotonic dystrophy pathophysiology. 25350771_These results suggest an autoinhibition model for BIN1 that involves a synergistic regulation by membrane composition and protein-protein interactions. 25365775_Brain DNA methylation in BIN1 was associated with pathological Alzheimer disease. 25461955_The study is the first to confirm the association of the variant rs7561528 adjacent to Bin1 with Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease in a Han Chinese Population. 25487648_BIN1/M-Amphiphysin2 has a role in inducing clustering of phosphoinositides to recruit its downstream partner dynamin 25578476_Reduced BIN1 expression is associated with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. 25630570_This study findings demonstrate that rs744373 itself or a variation in linkage disequilibrium may provide a neurogenetic mechanism for BIN.1 25683635_Results show low expression of Bin1, along with high expression of IDO, are predictor for poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell cancer and thereby could be used to establish new therapeutic strategies. 25957634_This study demonistrated that BIN1 mutation releated to Centronuclear myopathy. 26194865_analysis of a novel deregulated mechanism in chronic myeloid leukemia patients, indicating BIN1 and RIN1 as players in the maintenance of the abnormal RTK signaling in this hematological disease 26195312_In vitro studies in human Caco-2 cells showed that Bin1 antibody altered the expression of tight junction proteins and improved barrier function. 26233692_Alterations in the BIN1 locus, previously associated with Alzheimer disease, may modify the age of onset of GBA-associated Parkinson. 26733302_no association was found for either polymorphism, suggesting that these genes are not implicated in the aetiology of Alzheimer's disease in all populations. 26738348_The frequencies of BIN1 alleles were similar in both control and Alzheimer patients showing o no association. 26833786_Data demonstrate that EHBP1L1 links Rab8 and the Bin1-dynamin complex, which generates membrane curvature and excises the vesicle at the endocytic recycling compartment for apical transport. 26846281_the association between the rs744373 polymorphism of BIN1 protein and late-onset Alzheimer's disease in East Asian, American, and European populations (Meta-Analysis) 26947052_findings support a contribution of BIN1 to individual differences in episodic memory performance among Type 2 Diabetes patients. 27003210_This study supported that BIN1 contributes to the risk of Alzheimer's disease by altering neural degeneration (abnormal tau, brain atrophy and glucose metabolism) but not Abeta pathology 27179792_the depletion of BIN1 increases cellular BACE1 levels through impaired endosomal trafficking and reduces BACE1 lysosomal degradation, resulting in increased Ab production. Our findings provide a mechanistic role of BIN1 in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease (AD), as a novel genetic regulator of BACE1 levels and Ab production 27268056_data show that the previously described consensus sequence PXRPXR for amphiphysin SH3 ligands is inaccurate and instead define it as an extended Class II binding motif PXXPXRpXR, where additional positive charges between the two constant arginine residues can give rise to extraordinary high SH3 binding affinity. 27346750_BIN1 protein expression in cerebral cortex was related to disease progression in Alzheimer's Disease patients. 27538496_propose that efforts to define how genetic variants in BIN1 elevate the risk for Alzheimer's disease would behoove to consider BIN1 function in the context of its main expression in mature oligodendrocytes 27773727_BIN1 is involved with late onset Alzheimer's disease. [review] 27854204_Italian family with centronuclear myopathy, carrying a novel pathogenic mutation of BIN1 gene in heterozygous state, consistent with autosomal dominant inheritance. 28152502_Low Bin1 expression is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 28302384_bridging integrator 1 Gene rs7561528 polymorphism contributes to Alzheimer's disease susceptibility in East Asian and Caucasian populations 28714960_Findings indicated that BIN1 restoration in NSCLC could reverse PD-L1-mediated immune escape by inactivating the c-MYC and EGFR/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. 28755476_The results emphasize an additional level of complexity in the regulation of the interaction between BIN1 and Tau dependent on the BIN1 isoforms. 28806752_Data (including data from studies using transgenic mice) suggest that the process leading to microparticle release from cardiac myocytes involves recruitment of CHMP4B protein to the forming microparticle membrane which also contains cBIN1; plasma cBIN1 is reduced in patients with heart failure as compared to control subjects. (CHMP4B = charged multivesicular body protein 4B; cBIN1 = cardiac bridging integrator 1) 28893863_The findings reveal the ability of Bin1 to modify actin dynamics and provide a possible mechanistic connection between Bin1 and tau-induced pathobiological changes of the actin cytoskeleton. 29504051_Meta-analysis validated the association of late onset Alzheimer disease with BIN1 (rs744373) variants. 29764032_incidence of amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) in Tujia region of Enshi may be related to the rs744373 polymorphic site of BIN1 gene, ApoEepsilon2 is the protective factor and ApoEepsilon4 is the risk factor for aMCI in Tujia region of Enshi 29950440_A BIN1 founder Roma mutation associated with a highly specific phenotype, was identified as the cause of centronuclear myopathy in Spain. 30253944_propose that under conditions of oxidative stress given by the internalization of oxLDL, macrophages employ the formation of the amphiphysin 2(Bin1)/c-Myc complex as a control mechanism to initially avoid the process of cell death 30260023_the findings of the study indicated that miR-211 mediated BIN1 downregulation had crucial significances in Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), suggesting the miR-211 might be a novel potential therapeutic target for the OSCC treatment. 30353632_By studying the role of BIN1 during the differentiation of hESC-CMs, we show that BIN1 is also important for CaV 1.2 channel clustering, junctional SR organization, and the establishment of excitation-contraction coupling 30733337_study unveils an E2F1-specific signaling circuit that constitutively activates ATM and provokes cisplatin resistance in BIN1-deficient cancer cells and further reveals that gammaH2AX emergence may not always reflect DSBs if BIN1 is absent. 30885349_this study shows that high BIN1 expression has a favorable prognosis in malignant pleural mesothelioma and is associated with tumor infiltrating lymphocytes 30967682_A novel role for the late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD)-associated protein Bin1 in regulating postsynaptic trafficking and glutamatergic signaling. 30992433_BIN1 rs744373 SNP is associated with increased tau but not beta-amyloid pathology, suggesting that alterations in BIN1 may contribute to memory deficits via increased tau pathology 31263146_BIN1 favors the spreading of Tau via extracellular vesicles. 31335457_we found that hypomethylation levels at specific CpGs in BIN1, rather than in the whole open sea region, elevated the risk for late onset Alzheimer's Disease (LOAD). We also found that hypomethylation at specific CpGs (26, 44, and 87) increased the risks for LOAD. 31478261_SRSF1-dependent alternative splicing attenuates BIN1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. 31815296_Splicing Regulator p54(nrb) /Non-POU Domain-Containing Octamer-Binding Protein Enhances Carcinogenesis Through Oncogenic Isoform Switch of MYC Box-Dependent Interacting Protein 1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 31874619_large-scale meta-analysis highlighted the significant association between BIN1 rs744373 polymorphism and AD risk in Caucasian populations but not in the East Asian populations[meta-analysis] 31884801_MiR-744 mediates the Oxaliplatin chemoresistance in colorectal cancer through inhibiting BIN1. 32568785_Alzheimer Gene BIN1 may Simultaneously Influence Dementia Risk and Androgen Deprivation Therapy Dosage in Prostate Cancer. 32719966_The Mechanistic Role of Bridging Integrator 1 (BIN1) in Alzheimer's Disease. 32727516_BIN1 protein isoforms are differentially expressed in astrocytes, neurons, and microglia: neuronal and astrocyte BIN1 are implicated in tau pathology. 32842621_Microglia Implicated in Tauopathy in the Striatum of Neurodegenerative Disease Patients from Genotype to Phenotype. 33516273_Convergent lines of evidence support BIN1 as a risk gene of Alzheimer's disease. 33531457_Association between methylation of BIN1 promoter in peripheral blood and preclinical Alzheimer's disease. 34060233_The BIN1 rs744373 Alzheimer's disease risk SNP is associated with faster Abeta-associated tau accumulation and cognitive decline. 34072165_Genetic Predisposition to Alzheimer's Disease Is Associated with Enlargement of Perivascular Spaces in Centrum Semiovale Region. 34375641_Alzheimer's disease BIN1 coding variants increase intracellular Abeta levels by interfering with BACE1 recycling. 34982487_Enrichment of rare variants of BIN1 but not APOE genes in Chinese patients with Parkinson's disease. 35217605_BIN1 modulation in vivo rescues dynamin-related myopathy. 35241726_The neuronal-specific isoform of BIN1 regulates beta-secretase cleavage of APP and Abeta generation in a RIN3-dependent manner. 35269588_Epigenetic Studies in the Male APP/BIN1/COPS5 Triple-Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease. 35526014_BIN1 is a key regulator of proinflammatory and neurodegeneration-related activation in microglia. 35546756_Link of BIN1, CLU, and IDE Gene Polymorphisms with the Susceptibility of Alzheimer's Disease: Evidence from a Meta-analysis. 35871342_Bridging Integrator 1 (BIN1, rs6733839) and Sex Are Moderators of Vascular Health Predictions of Memory Aging Trajectories. 36280690_Genetic polymorphism in BIN1 rather than APOE is associated with poor recognition memory among men without dementia. | ENSMUSG00000024381 | Bin1 | 64.801120 | 2.375328636 | 1.248127 | 0.20975514 | 35.725039 | 0.0000000022722466637046420036450177306914383068559004641429055482149124145507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000568590095382835941341361700538531431803335181029979139566421508789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 92.8456545 | 8.6842754 | 39.2631837 | 4.2724750 | |
| ENSG00000136869 | 7099 | TLR4 | protein_coding | O00206 | FUNCTION: Cooperates with LY96 and CD14 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (PubMed:27022195). Acts via MYD88, TIRAP and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response (PubMed:9237759, PubMed:10835634, PubMed:27022195,PubMed:21393102). Also involved in LPS-independent inflammatory responses triggered by free fatty acids, such as palmitate, and Ni(2+). Responses triggered by Ni(2+) require non-conserved histidines and are, therefore, species-specific (PubMed:20711192). Both M.tuberculosis HSP70 (dnaK) and HSP65 (groEL-2) act via this protein to stimulate NF-kappa-B expression (PubMed:15809303). In complex with TLR6, promotes sterile inflammation in monocytes/macrophages in response to oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) or amyloid-beta 42. In this context, the initial signal is provided by oxLDL- or amyloid-beta 42-binding to CD36. This event induces the formation of a heterodimer of TLR4 and TLR6, which is rapidly internalized and triggers inflammatory response, leading to the NF-kappa-B-dependent production of CXCL1, CXCL2 and CCL9 cytokines, via MYD88 signaling pathway, and CCL5 cytokine, via TICAM1 signaling pathway, as well as IL1B secretion. Binds electronegative LDL (LDL(-)) and mediates the cytokine release induced by LDL(-) (PubMed:23880187). Stimulation of monocytes in vitro with M.tuberculosis PstS1 induces p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 activation primarily via TLR2, but also partially via this receptor (PubMed:16622205, PubMed:10835634, PubMed:15809303, PubMed:17478729, PubMed:20037584, PubMed:20711192, PubMed:23880187, PubMed:27022195, PubMed:9237759). Activated by the signaling pathway regulator NMI which acts as damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) in response to cell injury or pathogen invasion, therefore promoting nuclear factor NF-kappa-B activation (PubMed:29038465). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10835634, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15809303, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16622205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17478729, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20037584, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20711192, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23880187, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27022195, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29038465, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9237759}. | 3D-structure;Age-related macular degeneration;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;NAD;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family which plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. TLRs are highly conserved from Drosophila to humans and share structural and functional similarities. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns that are expressed on infectious agents, and mediate the production of cytokines necessary for the development of effective immunity. The various TLRs exhibit different patterns of expression. In silico studies have found a particularly strong binding of surface TLR4 with the spike protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19). This receptor has also been implicated in signal transduction events induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) found in most gram-negative bacteria. Mutations in this gene have been associated with differences in LPS responsiveness, and with susceptibility to age-related macular degeneration. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. | hsa:7099; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; lipopolysaccharide receptor complex [GO:0046696]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; phagocytic cup [GO:0001891]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; lipopolysaccharide binding [GO:0001530]; lipopolysaccharide immune receptor activity [GO:0001875]; NAD(P)+ nucleosidase activity [GO:0050135]; NAD+ nucleotidase, cyclic ADP-ribose generating [GO:0061809]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; astrocyte development [GO:0014002]; B cell proliferation involved in immune response [GO:0002322]; cellular response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904646]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to lipoteichoic acid [GO:0071223]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular response to oxidised low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus [GO:0140052]; cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor stimulus [GO:0036120]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; detection of fungus [GO:0016046]; detection of lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032497]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; I-kappaB phosphorylation [GO:0007252]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; intestinal epithelial structure maintenance [GO:0060729]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; macrophage activation [GO:0042116]; MHC class II biosynthetic process [GO:0045342]; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002755]; negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120163]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032700]; negative regulation of interleukin-23 production [GO:0032707]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045671]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; negative regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032689]; nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0006809]; nitric oxide production involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002537]; nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 1 signaling pathway [GO:0070427]; nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 signaling pathway [GO:0070431]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; positive regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030890]; positive regulation of cellular response to macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus [GO:1903974]; positive regulation of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 production [GO:2000343]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900017]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interferon-alpha production [GO:0032727]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 production [GO:0032732]; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032733]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of macrophage activation [GO:0043032]; positive regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0060907]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of matrix metallopeptidase secretion [GO:1904466]; positive regulation of MHC class II biosynthetic process [GO:0045348]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase biosynthetic process [GO:0051770]; positive regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly [GO:1900227]; positive regulation of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 1 signaling pathway [GO:0070430]; positive regulation of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 signaling pathway [GO:0070434]; positive regulation of oxidative stress-induced neuron death [GO:1903223]; positive regulation of platelet activation [GO:0010572]; positive regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process [GO:1903428]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014911]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; regulation of dendritic cell cytokine production [GO:0002730]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; T-helper 1 type immune response [GO:0042088]; toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway [GO:0034142]; toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002224]; TRIF-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0035666]; wound healing involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002246] | 11466383_Intestinal epithelial cells express very low levels of Toll-like receptor-4 by a mechanism which protects them against dysregulated proinflammatory signaling in response to Gram-negative commensal bacteria and their products. 11477091_A TLR4 agonist specifically promoted the production of the Th1-inducing cytokine interleukin (IL) 12 p70 and the chemokine interferon-gamma inducible protein (IP)-10. 11494169_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11529488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11688988_downregulation on gingival fibroblasts by Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide 11728442_LPS may activate a mammalian serine protease, which generates a product required for TLR4 signalling 11835533_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11836257_identification of role in novel signal transduction pathway utilized by exracellular HSP70 11841848_regulation of TLR4 surface expression in human peripheral blood monocytes and B cells by interleukin-2 (IL-2) and IL-4 11842086_stimulation of signal pathway by HSP70 11877429_signaling events by TLR2 and TLR4 agonists are similar but there are distinct differences in the responses elicited by two bacterial products 11893689_sequence polymorphism in the gene causes an endotoxin-hyporesponsive phenotype in humans 11923281_expression regulated by immune-mediated signals in intestinal epithelial cells 11932926_The extracellular, but not cytoplasmic domain of TLR1 inhibits Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in endothelial cells. TLR1 might restrain the dangerous innate response to LPS by binding to TLR4 and preventing the formation of active signaling complexes. 11932927_Though TLR4 binds bacterial lipopolysaccharides, it had no role in binding non-lipopolysaccharide components from C. pneumoniae. 11964313_interferon-gamma augmented mRNA and surface expression of TLR4 in monocytes and macrophages 12089142_involvement in cell activation by mannuronic acid polymers 12117914_bacterium-induced CXCL10 secretion by osteoblast can be mediated in part through toll-like receptor 4 12124407_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12124407_The Asp299Gly TLR4 polymorphism is associated with a decreased risk of atherosclerosis. 12165534_Hypoxia decreases TLR4 expression in endothelial cells and this change is mediated by mitochondrial ROS leading to attenuation of AP-1 transcriptional activity. 12174084_Data show that the TLR4-mediated LPS response in bladder epithelial cells also uses the co-receptor CD14 for efficient LPS signalling. 12193670_According to the present results an allelic variation in the TLR4 receptor was associated with increased risk of premature birth. 12193670_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12270725_Susceptibility of human dendritic cells (DCs) to measles virus (MV) depends on their activation stages in conjunction with the level of CDw150: role of Toll stimulators in DC maturation and MV amplification 12324469_Lipopolysaccharide rapidly traffics to and from the Golgi apparatus with the toll-like receptor 4-MD-2-CD14 complex 12324481_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12391239_Although expression levels of TLR4 mRNA and protein are normal in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-tolerant monocytes, association of TLR4 with MyD88 is inhibited by LPS restimulation. 12397216_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12397216_We conclude that the CARD15 mutation and hyporesponsive TLR4 allele do not contribute to ethnic variation in the incidence of PPROM. 12402214_role of polymorphism in susceptibility to Candida albicans infection 12404174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12406828_Polymorphisms in toll-like receptor 4 are not associated with asthma or atopy-related phenotypes. 12438323_lipopolysaccharide may induce proliferation of periodontal epithelial cells by upregulating keratinocyte growth factor 1 expression via the CD14 and Toll-like receptor signaling pathway 12477953_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12495941_LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation and IL-8 gene expression use a signaling pathway requiring protein tyrosine kinase and that such regulation may occur through tyrosine phosphorylation of TLR4. 12525572_TLR2 and TLR4 mRNA were significantly up-regulated by IL-10 in monocyte cells that were adherent compared to those nonadherent. 12552467_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12588460_participates in the innate immune response to stimulation by bacterial products in periodontal tissues 12591474_Expressed in immortalized human liver cell lines 12592402_These data indicate that Toll-like receptor 4 modulation of polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) surface chemokine receptor expression is a critical determinant of PMN migration. 12594207_innate immune recognition of LTA via LBP, CD14, and TLR-2 represents an important mechanism in the pathogenesis of systemic complications in the course of infectious diseases brought about by Gram-positive pathogens. while TLR-4 and MD-2 are not involved. 12599057_findings indicate that, although the gastric epithelium is important in directing the immune response against H. pylori infections, the response is independent of TLR4 12622779_Mutations in the gene for toll-like receptor 4 and multiple sclerosis 12622779_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12630564_Review. TLR4 signaling is intimately involved in anti-cancer immunity induced by immunopotentiators. Our clinical examination in oral cancer patients also suggests the requirement of both TLR4 and MD-2 in the OK-432-induced anti-cancer host response. 12717385_human activated hepatic stellate cells utilize components of TLR4 signal transduction cascade to stimulate NF-kappaB and JNK and up-regulate chemokines and adhesion molecules. 12724322_TLR4 activation of NFkappaB requires Bruton's tyrosine kinase 12730365_Assay of locus-specific genetic load implicates mutations in this receptor in meningococcal susceptibility. 12734376_First comparative investigation in highly purified, monocyte-depleted neutrophil populations shows a distinct and separate role for TLR4, compared with TLR2, in neutrophil responses and neutrophil survival. 12738639_TLR4 is able to undergo multiple glycosylations without MD-2 but that the specific glycosylation essential for cell surface expression requires the presence of MD-2. 12742999_Among symptomatic men with documented coronary artery disease, the TLR4 Asp299Gly polymorphism was associated with the risk of cardiovascular events; carriers of the allele had significantly more benefit from pravastatin 12742999_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12773175_Polymorphism is associated with systemic inflammatory response syndrome. 12773319_TLR4 polymorphism contributes to the development acute rejection after lung transplantation. 12777373_TLR4 has a role in inducing IL8 transcription in a pathway involving oxidized 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine 12782302_TLR4 has a role in upregulating IL-8 through neutrophil elastase 12796470_Data show that monocytes from individuals heterozygous for both mutations in the toll-like receptor 4 gene exhibit no deficit in recognition of lipopolysaccharides from different species of bacteria. 12810071_Data show that Toll-like receptors TLR2 and TLR4 were expressed on dendritic cells, whereas only TLR2 was weakly detected on Langerhans cells. 12832426_there may be a resistive exercise training-induced reduction in TLR4/CD14 expression in older women. 12846053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12846053_TLR-4 polymorphism does not appear to influence susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. 12855579_a functional Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) was expressed on human mast cells when it was up-regulated by interferon gamma (IFN-gamma). 12865424_saturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids reciprocally modulate the activation of TLR4 and its downstream signaling pathways involving MyD88/IRAK/TRAF6 and PI3K/AKT. 12874320_signaling pathways involved in NF-kappa B activation by TLR4 signaling in microvascular endothelial cells 12897738_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12897738_The TLR4 gene G299/I399 polymorphisms were associated with a modified response to endotoxin in asthma 12923493_Down-regulation of TLR-4 by TNF-alpha is associated with LPS hyporeactivity for NF-kappaB formation, whereas upregulation of TLR-4 via IL-6 can increase the responsiveness of mononuclear phagocytes 12942028_Results show that the surface receptors TLR2/4 and CD14 are essential for in vitro cellular activation induced by Neisseria meningitidis lipopolysaccharide-containing outer membrane vesicles and purified lipopolysaccharides. 12957699_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12957699_The findings of this study do not support the hypothesis that the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) Asp299Gly polymorphism influences predisposition to and progression of coronary artery disease. 12960171_Toll-like receptor-4 aggregation and signal transduction are affected by lipopolysaccharide binding to MD-2 12964127_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12964127_data demonstrate that the heterozygous Asp299Gly polymorphism does not exhibit a functional defect in cytokine release after the stimulation of blood monocytes 14517278_LPS-TLR4 signaling to IRF-3/7 and NF-kappaB involves the toll adapters TRAM and TRIF. 14519765_lipopolysaccharide-TLR4-mediated activation of IFN-beta requires the adapter complex of TICAM-2 and TICAM-1 14551607_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14557267_TLR4-mediated activation of the interferon-sensitive response element has an absolute requirement for NFKBp65, whereas the TLR3-induced ISRE response is NFKB-independent 14563652_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14563652_The Asp299Gly polymorphism provides evidence of an association of the TLR4 receptor and acute coronary syndromes. 14565959_TLR4 has a role in an LPS-induced inflammatory response as demonstrated by increased mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase activity, IL-8 production, and tumor necrosis factor alpha production 14578307_The endotoxin receptor TLR4 polymorphism is not associated with diabetes or components of the metabolic syndrome 14597728_When the effect of lipopolysaccharide contamination is abrogated, Hsp65 is unable to activate TLR4 in the presence of CD14 and MD2. 14600154_TLR4 is a key element in the response of pulmonary epithelial cells to Gram-negative bacteria. The intracellular localization of TLR4 in lung epithelia plays an important role in the prevention of the development of chronic inflammatory disease. 14610481_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14610481_The single-nucleotide polymorphisms at position +896 or +1196 in the TLR-4 gene is associated with systemic inflammatory hyporesponsiveness to inhaled lipopolysaccharide. 14638766_P. gingivalis LPS-dependent antagonism of E. coli LPS in human endothelial cells likely involves the ability of P. gingivalis LPS to directly compete with E. coli LPS at the TLR4 signaling complex. 14651524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14693986_Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile genotypes of the TLR4 gene are associated with reduced prevalence of diabetic neuropathy in type 2, but not in type 1, diabetes. 14693986_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14699116_TLR4 intracellular domains have an important role in receptor dimerization 14706103_downregulated by Ehrlichia chaffeensis infection in monocytes 14709406_expression of CCL21, and TLRs 2 and 4 is predominantly induced in the peripheral lymphatic endothelium of the small intestinal microcirculation 14715415_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14735148_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14738464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14739370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14764071_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14764599_TLR4 has a role in hyaluronan-stimulated endothelial recognition of injury 14987294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15007351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15016407_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15016407_in this model of natural LPS release, the variation between individuals in TNF-alpha release can only modestly be determined by genetic background (tumor necrosis factor -alpha promoter, Nod2 and TLR4) of the individual 15022344_Association between rheumatoid arthritis disease susceptibility and functional TLR-4 variant. TLR-4 polymorphism also associated with disease activity at baseline but not with disease severity or outcome. 15039334_Reactive oxygen species regulate immune signaling through TLR4 via their effects on NF-kappa B activation 15041961_Expression of toll-like receptor 4 and immune response in innate immunity may be altered after surgical insults. 15044215_primary ATII cells express mRNA and protein for both TLR-2 and TLR-4, which can be modulated by incubation with lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor 15069085_Involvement of CD14/TLR4, CR3, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in the degradation of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase in response to LPS. 15081257_Comparison of the genotypes of 242 patients with Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) and 210 healthy subjects shows that polymorphisms in Toll-like receptor 4 do not confer susceptibility to GBS and are not associated with Campylobacter jejuni infection. 15081257_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15087412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15132988_TLR4 is not only located intracellularly but also functions intracellularly in human coronary artery & umbilical vein endothelial cells, thus internalization of LPS is required for its activation. 15138173_TLR4 mediates antitumor immunity induced by the plant-derived (Aeginetia indica L) protein AILb-A. 15143473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15148609_upregulation of TLR expression during differentiation in keratinocytes could be a part of the differentiation process of keratinocytes and could have biological significance in protecting skin against microbes. 15155619_detected in epithelial cells lining the entire urinary tract and in the renal tubular epithelium in response to Escherichia coli infections 15175334_Toll-like receptor 4 is activated by MD-2 and lipopolysaccharide in inflammation 15175649_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15187145_activation of Rac1 leads to HIV-LTR trans-activation, mediated through TIRAP. Rac1 and TIRAP are important in TLR4 activation of HIV replication 15190267_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15194649_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15207785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15225640_Hepatocytes utilize components of TLR4 signal transduction pathways in response to lipopolysaccharide. 15247281_inhibition of TLR4-mediated activation of NF-kappa B by MalE190A 15258789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15258789_The Asp299Gly TLR4-allele might have a protective role in carotid atherosclerosis, but not in cerebral ischemia. 15273551_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15277575_TLR4 of retinal pigment epithelial cells participates in transmembrane signaling events that contribute to the recognition and clearance of effete photoreceptor outer segments, a process central to the maintenance of normal vision. 15292002_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15302104_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15305230_Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) was expressed in the human adrenocortical cell line NCI-H295. Immunohistochemical analysis of normal human adrenal glands revealed TLR4 expression in the adrenal cortex, but not in the adrenal medulla. 15321997_The presence of multiple lipid A species in Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide contributes to cell activation through both TLR2 and TLR4. 15337750_Results show that the N-terminal region of toll-like receptor 4 is essential for association with MD-2, which is required for the cell surface expression and hence the responsiveness to lipopolysaccharide. 15341923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15351720_pancreatic elastase-induced proinflammatory effects are mediated by TLR4 and NF-kappaB in human myeloid cells 15356101_Direct interaction of TLR4 with NADPH oxidase 4/NOX4 is involved in lipopolysaccharide-mediated generation of reactive oxygen species and NF-kappa B activation in HEK293T cells. 15356557_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15356557_The TLR4 (Asp299Gly) polymorphism was associated with a 4-fold higher prevalence of asthma in school-aged children (adjusted odds ratio 4.5, 95% CI 1.1-17.4)and decreased LPS-induced IL-12(p70) and IL-10 responses. 15358455_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15358455_The TLR4 896 A > G polymorphism contributes to inter-individual differences in the vaginal immune defense against G. vaginalis and anaerobic Gram-negative rods. 15367917_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15373967_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15385480_TLRs are differentially expressed in distinct compartments of the female reproductive tract 15452251_Coxsackievirus B4 triggers cytokine production through a TLR4-dependent pathway in pancreatic cells. 15456896_The mutants of TLR4 did not inhibit H. pylori-induced COX-2 promoter activity. in gastric mucosa. 15489631_the endotoxin tolerance seen in patients with sepsis does not depend solely on TLR-2 or TLR-4 expression 15509550_interleukin-1beta has roles in direct and toll-like receptor 4-mediated neutrophil activation and survival 15516360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15520404_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15525557_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15528333_TLR4 antibody blockage in human macrophages demonstrates that TLR4 is a putative receptor of extract of Ganoderma lucidum (Reishi) polysaccharides and mediates the consequent immunomodulating events associated with IL-1 gene expression. 15547160_Prevalence of the TLR4 genotype may have an association with acute myocardial infarction and with longevity. 15557191_The extracellular TLR4-MD-2 complex, but not TLR4 alone, can bind lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Extracellular TLR4 domain (residues Glu24-Lys631) enables MD-2 binding and LPS recognition to TLR4. 15576653_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15576653_The Toll-like receptor 4 Asp299Gly gene polymorphism was not associated with risk of incident myocardial infarction or stroke in a large prospective study of US men. 15591473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15610077_blockage of TLR-4 activation by EGCG resulted in inactivation of extracellular signal response kinase 1/2 and of nuclear factor-kappaB, the downstream molecules of TLR-4 signaling induced by H. pylori 15614130_Neutrophil elastase, MIP-2, and TLR-4 have roles in progression of human sepsis and murine peritonitis 15623538_TGF-beta1 can specifically interfere with TLR2, -4, or -5 ligand-induced responses involving the adaptor molecule MyD88 (myeloid differentiation factor 88) but not the TRAM/TRIF signaling pathway 15632890_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15632890_The TLR4 299Gly allele was associated with reduced CRP levels and, in parallel, a decreased risk of angiographic CAD and clinical diabetes 15644417_Pattern recognition of bacterial superantigens by MHC class II receptors may exacerbate the proinflammatory response of monocytes to Gram-negative infection or endotoxin by up-regulation of TLR4. 15647432_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15650037_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15655821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15655821_co-existence of a mutation in either the TLR4 or CD14 gene, and in NOD2/CARD15 is associated with an increased susceptibility to developing Crohn disease compared to ulcerative colitis 15661045_evidence that HPV-VLP signal dendritic cells through a pathway involving proteoglycan receptors, TLR4 and NF-kappaB 15665723_the function of CaMK II is essential for PAF-induced macrophage priming, while CaMK IV is not specific for priming by PAF and appears to have a direct link in TLR4-mediated events 15670831_CXCR4 could exert local control of TLR4 and suggest the possibility of new therapeutic approaches to suppression of TLR4 function 15694388_These results clearly demonstrate that the amino-terminal TLR4 region of Glu(24)-Pro(34) is critical for MD-2 binding and LPS signaling. 15695310_TLR4 may play an important role in modulation of immunological tolerance in the lower parts of the female reproductive tract, and in host defence against ascending infection. 15696495_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15696495_Sampling analysis in Han population of Chongqing showed that the two highly distributed SNPs of TLR4 were common in Chinese population and could be used for genetic marker of TLR4 gene. 15699327_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15699327_TLR4 SNPs are associated with resistance to Legionnaires' disease. 15728517_Engagement of TLR4 mediates deactivation of human monocytes in the presence of tumor cells, an effect apparently involved in IL-1 receptor associated kinase-M (IRAK-M) up-regulation. 15752733_We further confirmed that the No. 9 peptide could bind to TLR4 extracellular domain, but the No. 24 peptide could not, suggesting that two peptides were identified as antagonists of TLR4, which inhibited the effects of endotoxin in vitro. 15760452_lipopolysaccharides from some Helicobacter pylori strains are able to antagonize TLR4 15760459_BCG induced transcription and secretion of the chemokine CXCL8, by signalling through Toll-like receptors TLR2 and TLR4, in conjunction with myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88)in neutrophils 15770725_Although the frequency of TLR4 D299G polymorphism was not different from controls, NOD2/TLR4 mutation carriers tended to present at earlier age. 15770725_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15778388_Mastoparan, a G protein agonist peptide,preferentially targets the TLR4 pathway over the TLR2 pathway, confirming the importance of heterotrimeric G proteins in TLR4-mediated responses 15790341_The TLR4 expression was analyzed after the stimulation of JAR cells with different TLR ligands. 15796767_Data suggest that, during Gram-negative bacteria-induced infections or inflammatory processes, LPS could affect pituitary tumour pathophysiology and progression in the subset of Tlr4-expressing pituitary adenomas. 15809303_HSP65 and HSP70 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis signal via TLR4 in human cells 15829498_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15829498_examination of a variant as candidate gene for age related macular degeneration susceptibility 15843568_TLR4 signaling effects the induction of cell death by secreted Helicobacter pylori antigen HP0175 in human gastric epithelial cell line AGS. 15845500_activation of TLR4-MyD88-dependent and -independent signaling pathways by endotoxins determined by structure of the endotoxin 15852007_RP105 regulated TLR4 signaling in dendritic cells 15863460_TLR4 signaling promotes a proinflammatory phenotype in vascular smooth muscle cells 15864121_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15864121_variation in the TLR4 gene contributes to inter-individual variability in susceptibility to coronary ischaemic events, and TLR4 genotype and statin treatment may have a synergistic effect 15866212_expression down-regulated in Helicobacter pylori infected monocytes by clarithromycin 15866876_SIGIRR inhibits IL-1R and TLR4-mediated signaling through different mechanisms 15875057_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15879290_minimized expression of TLR4 contributes to the susceptibility of very low birth weight infants to infections with Gram-negative bacteria due to the lack of cytokines to boost initial immune response 15882292_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15883205_unstable angina and myocardial infarction are associated with enhanced expression and signaling events downstream of hTLR4 in circulating monocytes 15905704_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15905704_TLR4 is associated with both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis; Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile variants do not show an association with Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, or inflammatory bowel disease and are likely not the causal polymorphisms 15910421_results indicate that Entamoeba histolytica lipopeptidophosphoglycan initiates an innate immune response by interacting with TLR2 and TLR4 15910856_Data possibly implicate TLR4 as an important genetic factor for stroke in ethnic Chinese populations despite the rarity of the Asp299Gly polymorphism 15910856_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15919371_phenomenon as shown by experiments using different toll-like receptor-agonists in interleukin 10(-/-) macrophages 15927851_first study to demonstrate that even homozygosity for the Asp299Gly mutation does not confer hyporesponsiveness to stimulation with TLR4 stimuli 15932772_An Asp299Gly polymorphism in the TLR-4 receptor has no clinical relevance in multiple sclerosis patients with different TLR-4 genotypes. 15932772_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15953129_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15972671_TLR3 and TLR4 signal primarily through NF-kappaB to enhance transcription of pIgR mRNA. 15973118_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15973118_TLR4 Asp299Gly polymorphism seems to be a minor risk factor for CD in the population studied. TLR4 and CARD15/NOD2 mutations may contribute to the development of distinct CD phenotypes. 16002719_Diminished expression and function of TLR4 is a likely consequence of chronic filarial antigen stimulation and could serve as a novel mechanism underlying the dysfunctional immune response in lymphatic filariasis 16006099_Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is expressed in bile duct epithelial cells and periportal hepatocytes in primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) livers, suggesting the possible involvement of bacterial pathogens and TLR4 in the inflammatory processes of PBC. 16010583_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16019531_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16019531_a functional Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphism may have a role in susceptibility to gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma 16044857_first study describing TLR expression on tumor cells of gastric carcinoma and its precursor lesions 16051275_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16085746_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16107886_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16135957_signaling pathways activated by LPS and its receptor TLR4 and TNFalpha have roles in septic shock [review] 16142747_Finds that TLR-4 polymorphisms influence regulators of the inflammation induced by endotoxin in organic dusts 16142747_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16146574_The up-regulation of Toll-like receptors 2, 3 and 4 in the nasal mucosa of patients with symptomatic allergic rhinitis supports the idea of a role for Toll-like receptors in allergic airway inflammation. 16157088_TLR-4 protein expression is increased in interstitial trophoblasts of paitents with preeclampsia. 16157451_Our data further support a role for innate immunity in neurodegeneration and give the first evidence that the TLR4 Asp299Gly variant may be protective toward the development of LOAD. 16202743_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16213463_Our results suggest that overexpression of TLR2 and TLR4 in CHO cells sensitizes the cells to serum deprivation-induced apoptosis and that the mechanisms are involved in the death receptor-mediated signaling pathway. 16215326_In females the TLR4 and IL4 genes show an epistatic effect on the risk of asthma. 16215326_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16219107_This data defines an additional role for TLR4 in the host defense in the lung. 16219455_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16239565_the synergistic effect of LPS and PepG on cytokine release is preceded by a reciprocal upregulation of TLR2 and TLR4 by both Staphylococcus aureus cell wall components 16239841_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16246938_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16266379_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16266379_Polymorphisms in the TLR4 gene may be associated with milder forms of disease in atopic asthmatics in the Turkish children studied. 16266460_TLR4/NF-kappaB plays an important role in monocyte-endothelium adhesion partly through upregulation of LOX-1, ICAM-1 and E-selection expression. 16267105_first direct evidence that HMGB1 can interact with both TLR2 and TLR4 and also supply an explanation for the ability of HMGB1 to induce cellular activation and generate inflammatory responses that are similar to those initiated by LPS 16270639_TLR2 and TLR4 agonists have a significant role in diseases such as atherosclerosis and DIC, but our research suggests that this is through a mechanism other than direct platelet activation or by modification of platelet responses to other agonists. 16290232_Maternal allergy status may affect allergic risk in offspring through a decreased expression of fetal TLR4. 16301860_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 16304445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16338228_A PRotein Associated with Tlr4 (PRAT4B), regulates cell surface expression of TLR4. PRAT4B has a signal peptide followed by a mature peptide. PRAT4B is associated with the hypoglycosylated, immature form of TLR4 but not with MD-2 or TLR2. 16338476_the subcellular localization of TLR-4 in term placenta is preferentially in the maternal facing plasma membrane compared to basal membrane . 16343635_A study evaluating the role of polymorphic alleles of TLR4 gene in susceptibility to brucellosis is presented. 16343635_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16357190_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16357190_Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in toll-like receptor 4 is associated with prostate cancer 16371473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16371473_TLR4-mediated responses to malaria in vivo and TLR-4 polymorphisms are associated with disease manifestation. 16385250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16388712_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16393227_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16395111_Observational study of gene-disease associatio | ENSMUSG00000039005 | Tlr4 | 226.107431 | 2.547383555 | 1.349016 | 0.15043196 | 79.680795 | 0.0000000000000000004400574689712044017058391151019579631700876167388781362577176992090244311839342117309570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000284977957220796607033313833339312991679539077347071973633774177869781851768493652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 320.7723583 | 27.1717360 | 126.6592497 | 11.5267680 | |
| ENSG00000137177 | 63971 | KIF13A | protein_coding | Q9H1H9 | FUNCTION: Plus end-directed microtubule-dependent motor protein involved in intracellular transport and regulating various processes such as mannose-6-phosphate receptor (M6PR) transport to the plasma membrane, endosomal sorting during melanosome biogenesis and cytokinesis. Mediates the transport of M6PR-containing vesicles from trans-Golgi network to the plasma membrane via direct interaction with the AP-1 complex. During melanosome maturation, required for delivering melanogenic enzymes from recycling endosomes to nascent melanosomes by creating peripheral recycling endosomal subdomains in melanocytes. Also required for the abcission step in cytokinesis: mediates translocation of ZFYVE26, and possibly TTC19, to the midbody during cytokinesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19841138, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20208530}. | Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell cycle;Cell division;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Microtubule;Motor protein;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport | This gene encodes a member of the kinesin family of microtubule-based motor proteins that function in the positioning of endosomes. This family member can direct mannose-6-phosphate receptor-containing vesicles from the trans-Golgi network to the plasma membrane, and it is necessary for the steady-state distribution of late endosomes/lysosomes. It is also required for the translocation of FYVE-CENT and TTC19 from the centrosome to the midbody during cytokinesis, and it plays a role in melanosome maturation. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. | hsa:63971; | centrosome [GO:0005813]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; kinesin complex [GO:0005871]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; midbody [GO:0030496]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; microtubule motor activity [GO:0003777]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell division [GO:0051301]; endosome to lysosome transport [GO:0008333]; Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport [GO:0043001]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; melanosome organization [GO:0032438]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018]; plus-end-directed vesicle transport along microtubule [GO:0072383]; regulation of cytokinesis [GO:0032465]; vesicle cargo loading [GO:0035459] | 11106728_Functionally characterizes the homologous mouse protein. 19328558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19841138_show that the clathrin adaptor AP-1 and the kinesin motor KIF13A together create peripheral recycling endosomal subdomains in melanocytes required for cargo delivery to maturing melanosomes. 20208530_PtdIns(3)P production is essential for proper cytokinesis. PtdIns(3)P-binding centrosomal protein FYVE-CENT and TTC19 control cytokinesis through their translocation from the centrosome to the midbody mediated by the kinesin protein KIF13A. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21873978_the kinesin-13 MCAK has an unconventional ATPase cycle adapted for microtubule depolymerization 24462287_KIF13A interacts and cooperates with RAB11 to generate endosomal tubules. 24859087_kjh kiiou ouiy 8yt 8iy 7i9y 29061883_that KIF13A plays an important role in the transport of influenza A viral ribonucleoproteins 29980677_the crystal structure of a catalytically active kinesin-13 monomer (Kif2A) in complex with two bent alphabeta-tubulin heterodimers in a head-to-tail array, providing a view of these interactions, is reported. 30049714_KIF13A-mediated endosomal trafficking modulates RhoB plasma membrane localization to control membrane blebbing and blebby amoeboid migration. 31469403_Identification of novel splicing patterns and differential gene expression in RE+/FECD- samples provides new insights and more relevant gene targets that may be protective against FECD disease in vulnerable patients with TCF4 CTG TNR expansions. 33526817_Postzygotic inactivating mutation of KIF13A located at chromosome 6p22.3 in a patient with a novel mosaic neuroectodermal syndrome. 35122963_Coordination of two kinesin superfamily motor proteins, KIF3A and KIF13A, is essential for pericellular matrix degradation by membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) in cancer cells. | ENSMUSG00000021375 | Kif13a | 48.400331 | 10.967279772 | 3.455134 | 0.83919066 | 14.187419 | 0.0001654731684734627122999178761020289130101446062326431274414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0016051585857189988853360729237351733900140970945358276367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 63.3232992 | 38.3720514 | 5.4492454 | 3.2918868 | |
| ENSG00000137203 | 7020 | TFAP2A | protein_coding | P05549 | FUNCTION: Sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that interacts with inducible viral and cellular enhancer elements to regulate transcription of selected genes. AP-2 factors bind to the consensus sequence 5'-GCCNNNGGC-3' and activate genes involved in a large spectrum of important biological functions including proper eye, face, body wall, limb and neural tube development. They also suppress a number of genes including MCAM/MUC18, C/EBP alpha and MYC. AP-2-alpha is the only AP-2 protein required for early morphogenesis of the lens vesicle. Together with the CITED2 coactivator, stimulates the PITX2 P1 promoter transcription activation. Associates with chromatin to the PITX2 P1 promoter region. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11694877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12586840}. | Activator;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation | The protein encoded by this gene is a transcription factor that binds the consensus sequence 5'-GCCNNNGGC-3'. The encoded protein functions as either a homodimer or as a heterodimer with similar family members. This protein activates the transcription of some genes while inhibiting the transcription of others. Defects in this gene are a cause of branchiooculofacial syndrome (BOFS). Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2009]. | hsa:7020; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; nuclear receptor corepressor activity [GO:0140536]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; anatomical structure development [GO:0048856]; bone morphogenesis [GO:0060349]; cellular response to iron ion [GO:0071281]; embryonic cranial skeleton morphogenesis [GO:0048701]; embryonic forelimb morphogenesis [GO:0035115]; eyelid development in camera-type eye [GO:0061029]; inner ear morphogenesis [GO:0042472]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000378]; negative regulation of transcription by competitive promoter binding [GO:0010944]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; oculomotor nerve formation [GO:0021623]; optic cup structural organization [GO:0003409]; optic vesicle morphogenesis [GO:0003404]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043525]; positive regulation of tooth mineralization [GO:0070172]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045595]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; retina layer formation [GO:0010842]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; trigeminal nerve development [GO:0021559] | 9632747_AP-2 interacts with Rb which enhances its activity on the E-cadherin promoter 12145340_Transcription of cholesterol side-chain cleavage cytochrome P450 in the placenta: activating protein-2 assumes the role of steroidogenic factor-1 by binding to an overlapping promoter element. 12203368_Mutation analyses of the N-terminus region showed that activation and squelching were intricately linked; suggesting that squelching causes transformation and that the factors that are sequestered at this region are critical in tumorigenesis. 12226108_Results indicate that the tumor suppressor activity of AP2alpha is mediated through a direct interaction with p53. 12228234_AP2 regulates human reduced folate carrier gene expression 12358602_findings underline an essential role of AP-2/Sp1 recognition sites in UVB-mediated VEGF expression by the keratinocyte-derived cell line HaCaT 12475396_Alterations in the binding activity of AP-2 transcription factor to the sodium/iodide symporter (NIS) promoter results at least in part in reduced expression and transport of NIS in thyroid tumors. 12843180_AP-2alpha gene expression in the placenta is enhanced by a cis-acting element at nucleotides -1279 to -1139 that contains a critical Ets1-binding site. 12960147_neither clathrin nor AP-2 is essential for the internalization of epidermal growth factor 12975361_analysis of the PAR-1 promoter regions bp -365 to -329 and bp -206 to -180 demonstrated that Sp1 was predominantly bound to the PAR-1 promoter in metastatic cells, whereas AP-2 was bound to the PAR-1 promoter in nonmetastatic cells. 14517991_Gene expression regulation, developmental, and enhancer elements (genetics) associated with AP2-alpha were identified. 14551210_AP-2alpha inhibits the growth of cells by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis 14744778_Molecular events resulting from loss of AP-2 in the prostate epithelium has implications for the understanding and prevention of the onset of prostate cancer. 14752511_AP-2alpha as a novel cardiac regulator implicated in the activation of apoptosis in idiopathic-dilated cardiomyopathy 15039486_AP-2alpha plays a critical role for induction & repression of genes that comprise postsyncytialization gene expression programs of trophoblast differentiation & maturation. It is not required for cytotrophoblast cell fusion or syncytin expression. 15331612_AP-2alpha binds directly to APC, stabilizes APC/beta-catenin interaction in the nucleus, attenuates beta-catenin/TCF4 interaction, and inhibits TOPflash reporter activity in human colorectal cancer cells 15498833_c-Src has a role in regulating the dissociation of AP-2 from agonist-occupied AT1R and beta-arrestin during the clathrin-mediated internalization of receptors 15569994_Expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in breast cancer seems to be partly related to expression of AP-2 and HER2 15671555_AP-2alpha may have a direct role in glioma tumorigenicity 15864740_USF1 and USF2 mRNA levels were reduced in non-small cell lung carcinomas; AP2-alpha levels were elevated; regression analysis demonstrated that reduced USF2 mRNA & increased AP2-alpha mRNA levels were predictive of downregulated PIGR mRNA expression 15870067_YY1 cooperates with AP-2 to stimulate ERBB2 promoter activity through the AP-2 binding sites 15930016_AP-2alpha associates with the Fmr1 promoter in vivo and selectively regulates Fmr1 transcription during embryonic development 16108032_unusual stability is main mechanism that raises levels of AP-2 proteins; defective ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal-degradation pathway is possibly prime cause that affects the HER-2/neu gene and culminates in breast cancer 16260418_AP-2alpha and Sp1 are strong transcriptional regulators of KiSS-1 16361535_The AP-1 site in the u-PAR promoter seems to be a less tumor-specific regulator than the Sp1 and AP-2 alpha. 16502414_Transgenic expression of Tcfap2a in the developing frontal nasal process and limb bud mesenchyme is mediated by a highly conserved element of this tissue specific enhancer. 16533807_AP-2alpha induces apoptosis by down-regulating Bcl-2 and utilizing a bax/cytochrome c/Apaf1/caspase 9-dependent mitochondrial pathway 16636674_AP-2alpha and AP-2gamma interact with p53 both physically and functionally. 16707488_PIPKIgamma661 enzyme is involved in the AP2-mediated endocytosis of transferrin. 16867219_expression of either AP-2gamma or AP-2alpha induces p21 and inhibits breast carcinoma cell growth 16946713_Loss of AP-2 is a crucial event in the progression of human melanoma and contributes to the acquisition of the metastatic phenotype via upregulation of PAR-1. 17097614_These findings suggest that GPx-1 inhibits UVA-induced AP-2alpha expression by suppressing the accumulation of H(2)O(2). 17224907_data provide evidence that AP-2alpha acts as a tumor suppressor gene in colon cancer 17318229_Activating protein transcription factor 2 (AP2)alpha forms a complex with NPM during retinoic-acid-induced cell differentiation. 17355223_Data suggest that activator protein 2alpha and peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor alpha may be especially involved in the ozone-inducible up-regulation mechanism of bombesin receptor subtype 3 expression. 17513613_Rad51 has a role in chemoresistance in human soft tissue sarcoma cells along with p53 and activator protein 2 transcriptional regulation 17556657_Doxazosin inhibits AP2alpha activity independent of alpha(1)-adrenoceptor blockade and increases the ABCA1 expression and HDL biogenesis 17621592_AP-2alpha is an important in vivo negative regulator of MUC4 expression in human pancreatic tissue 17651731_Role for the transcription factor AP-2alpha in the regulation of APP gene expression in human keratinocytes. 17695722_AP-2alpha transcription factor regulates tumor cell migration and apoptosis 17719138_Data indicated that the synergistic activation of the human AM gene promoter by Sp1 and AP-2alpha may be mediated by the binding of Sp1 to the promoter region and the interaction with AP-2alpha, which binds to the promoter region. 18036196_The G/G genotype of MAPK8 SNP-1066 did not affect T2DM susceptibility despite specific binding of AP2alpha. 18042070_AP2 transcription factors may play decisive pacemaker roles in initiating and coordinating budding and branching processes during formation of the fetal breast anlage. 18275040_analysis of TBX20 in human hearts and its regulation by TFAP2 18316341_AP-2alpha transcription factor is required for the ganglioside GM3-stimulated transcriptional regulation of the PTEN gene 18358093_TFAP2 is involved in doxazosin-induced HeLa cell apoptosis. 18423521_BOFS is caused by mutations involving TFAP2A. 18443366_AP-2alpha regulates specific genes involved in cell cycle, cell death, adhesion, and migration 18515748_After high glucose stimulation, AhR was found in complex with Egr-1 & activator protein-2. The activity of the DNA-binding complex was regulated by glucose (a physiological stimulus) via activation of hexosamine pathway & intracellular glycosylation. 18620802_TFAP2a was strongly expressed in 4 of 6 neuroblastoma cell lines, and TFAP2a siRNA mediated knock down in SH-EP cells reduced proliferation and induced a more differentiated phenotype associated with an increase in the expression of the marker neurotensin 18639284_TFAP2A is hypermethylated in renal cell carcinoma. 18836445_These findings place IRF6 and AP-2alpha in the same developmental pathway and identify a high-frequency variant in a regulatory element contributing substantially to a common, complex disorder. 18955504_Binding elements for ETS and transcription factor AP-2 (TFAP2) were significantly enriched in Smad2/3 binding sites, and knockdown of either ETS1 or TFAP2A resulted in overall alteration of TGF-beta-induced transcription. 19074833_the high level of MnSOD observed in aggressive cancer cells may be due, in part, to the absence of AP-2 transcriptional repression 19089912_AP2alpha suppresses C/EBPalpha promoter activity and protein expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 19115315_indicate the novel function of KCTD1 as the transcriptional repressor for AP-2 family, especially for AP-2alpha 19154347_binding of SP1 to the proximal promoter region stimulated the promoter activity and endogenous KCTD10 expression, whereas binding of AP-2alpha to this region showed opposite effects. 19206157_A complex TFAP2A allele is associated with branchio-oculo-facial syndrome and inner ear malformation in a deaf child. 19228880_The GSTM1 variant allele modifies DNA binding to the AP-2alpha transcription factor, resulting in reduced promoter activity and mRNA expression. This low-activity allele is associated with reduced breast cancer risk. 19351721_Data show that the AP-2 complex is involved in the internalization of activated epidermal growth factor receptor from the cell surface. 19363595_c-FLIPL inhibits Bax activation via modulating PKC expression at the transcriptional level involving AP-2 during gp120 treatment 19376641_these studies support a tumor suppressor role for AP-2alpha in the gastrointestinal tract 19411194_Data suggest that AP-2 overexpression stimulates PA activity by a mechanism involving derepression rather than activation, possibly by neutralizing an inhibitory effect of endogenous AP-2 or AP-2-like factors. 19443578_The present data suggest that AP-2 may suppress trophoblast migration and invasion, thus leading to a shallow placentation in preeclampsia. 19578371_Data show that AP-2alpha was identified as a repressive target of BCOR, and BCOR mutation resulted in abnormal activation of AP-2alpha. 19654299_Nicotine increases PPARbeta/delta gene expression through alpha7 nAChR-mediated activation of PI3K/mTOR signals that inhibit AP-2alpha protein expression and DNA binding activity to the PPARbeta/delta gene promoter. 19672266_AP-2alpha overexpression could be exploited to decrease in vivo tumour growth of pancreatic cancer cells and to increase their sensitivity to gemcitabine. 19685247_study reveals that TFAP2A is critical to eye, brain, and craniofacial development in humans in the context of classical branchio-oculo-facial syndrome (BOFS), and may also play a role in isolated eye anomalies 19742317_AP-2alpha induces epigenetic silencing of tumor suppressive genes and microsatellite instability in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma 19763255_temporal regulation of EGFR endocytosis is achieved by auto-regulatory PLD1 which senses the receptor activation and triggers the translocation of AP2 near to the activated receptor 20145123_HLJ1 switches the role of NPM1, which can act as tumor suppressor or oncogene, by modulating the oligomerization of NPM1 via HLJ1-NPM1 heterodimer formation and recruiting AP-2alpha to the MMP-2 promoter. 20358615_This study represents the second group of branchio-oculo-facial syndrome patients with molecular confirmation, expanding the phenotype and spectrum of mutations in TFAP2A and limiting it to a restricted part of the gene. 20376207_WAFL may play an important role in endocytosis and subsequent membrane trafficking by interacting with AP2 through KIAA0196 and KIAA1033 20564234_Data confirmed an essential role for AP2 alpha in MUC8 gene expression. 20607706_Loss of TFAP2A is associated with retinoblastoma. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20635357_Mutations in TFAP2A is associated with Branchio-Oculo-Facial syndrome. 20731749_Data demonstrate a cross-talk between IGF-1R and AT-1R in AT-II and IGF-1-induced Cx43 expression in SV SMCs involving Erk 1/2 and downstream activation of the AP-1 transcription factor. 20805990_Loss of AP-2alpha expression in metastatic melanoma occurs via a dual mechanism involving binding of CREB to the AP-2alpha promoter and CREB-induced overexpression of E2F-1. 20808827_two transcription factors, SRF and TFAP2, as well as an intronic element encompassing EGR3-like sequence, that work together to regulate expression of the FXN gene 20932315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21084835_TFAP2A binds to two regions of the promoter of CDKN1A and alters with time post-induction, with the proximal, p53-independent site becoming more important at later stages of p21cip induction. 21204207_We have identified a hotspot region in the highly conserved exons 4 and 5 of TFAP2A that harbors missense mutations in 27/30 (90%) families with members affected by branchio-oculo-facial syndrome. 21250552_descriptions of the new mutations in the TFAP2A gene in our 2 new patients with BOF syndrome 21303946_Data show that AP-2alpha expression positively affects human trophoblast invasion under EGF-stimulated conditions, likely by inducing critical invasion-promoting genes such MMP-2, urokinase plasminogen activator, and CG. 21375726_findings suggest that TFAP2A isoforms may be differentially regulated during breast tumourigenesis and this, coupled with differences in their transcriptional activity, may impact on tumour responses to tamoxifen therapy 21654541_Multiple isoforms of AP-2alpha are highly expressed in pancreatic cancer cell lines including a new isoform, AP-2alpha variant 6, which seems to be pancreatic cancer specific and is deprived of transcriptional activity. 21659426_AP2 regulates the inhibin alpha subunit gene expression during trophoblast differentiation and may be a key regulator of syncytialization 21683068_this study provides further evidence regarding the role of IRF6 variations in non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate (NSCLP) development and finds no significant association between TFAP2A and NSCLP in this northern Chinese population. 21728810_Patients with Branchio-Oculo-Facial Syndrome (BOFS) and predominant ocular phenotypes can be diagnosed by upper lip examination. TFAP2A analysis provides diagnostic confirmation and improves genetic counselling. 21777522_These data suggest a novel cellular function of CK-2 as a transcriptional co-activator of AP-2alpha. 21781438_Evidence of association was obtained with both single marker and haplotype analyses, thus providing a support for TFAP2A in non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate aetiology 21829699_defined a physical interaction between Aurora-A and AP-2alpha, and such interaction might bridge the suppressive effect of Aurora-A on AP-2alpha protein stability 21850486_Bcl-2 gene transcription is regulated by Ap2alpha-Rb complex binding to the Bcl-2 promoter. 21876733_A protein-binding microarrays-based study of human healthy and breast tumor tissue extracts allowed the identification of previously unknown AP2alpha target genes. 21940908_findings provide a better understanding of the epigenetic mechanisms that are involved in the loss of AP-2alpha protein in prostate cancer cells which lead to decreased cellular zinc uptake-a sine qua non of prostate cancer development 21966377_Data suggest that AP-2alpha plays an important role in tumor progression and that reduced AP-2alpha expression independently predicts an unfavorable prognosis in gastric adenocarcinoma patients. 21979958_AP-2alpha regulation of CHRNA7 mRNA expression in multiple tissues during development 22191992_A mutation in the TFAP2A gene associated with Branchio-Oculo-Facial syndrome (heterozygous H384Y in exon 7) was found in both the proband and her mother. 22359570_a robust transcriptional CTNNAL1 up-regulation occurs during acute ozone-induced stress and is mediated at least in part by ozone-induced recruitments of LEF-1 and AP-2alpha to the human CTNNAL1 promoter. 22484487_fcho1 morphant phenotype is distinct from severe embryonic defects apparent when AP-2 is depleted 22575257_The different pattern of activator protein-2alpha expression in mild and severe preeclampsia clearly suggests that these conditions may have 2 independent pathogenic mechanisms. 23036739_ESDN and AP-2g expression is lower in thick melanomas, it is associated with unfavourable histo-pathological parameters (increased vascularity, vascular invasion and mitoses) and correlates with a shorter DFS like for AP-2a. 23151229_Molecular modeling of the HIV-1 Nef C-terminal flexible loop in complex with AP2 suggests that M168L170 occupies a pocket in the AP2 sigma2 subunit. 23275444_The new HIF2alpha partners microphthalmia-associated transcription factor, SOX10, and AP2alpha, which are master actors of melanoma development, were confirmed via co-immunoprecipitation experiments. 23382213_results indicate that Kctd15 acts in the embryo at least in part by specifically binding to the activation domain of AP-2alpha, thereby blocking the function of this critical factor in the neural crest induction hierarchy. 23578821_Result suggests that the individual TFAP2A Branchio-Oculo-Facial Syndrome mutations can generate null alleles. These mutations combined with a role for AP-2alpha in epigenetic events, may influence the resultant pathology and the phenotypic variability. 23660297_Hoxa7, Hoxa9 and Hox cofactor Meis1 were identified as AP-2alpha target genes, which are involved in myeloid leukemogenesis. 23660954_The present study examined the expression of AP-2alpha, TIMP-2, MMP-2, MMP-9, and E-cadherin in severe preeclamptic placentas and normal placentas. 23680675_These data define a mechanism through which AP-2alpha acetylation and increased promoter access induce the expression of the TLR2 gene. 23764310_TFAP2C repressed CD44 expression in basal-derived breast cancer. 24335623_TFAP2A regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth and survival through the modulation of the HIF-1alpha-mediated VEGF/PEDF signaling pathway. 24450359_AP2-mediated receptor internalization can be dissociated from AP2-mediated chemotaxis 24641171_High-confidence AP2alpha-binding peaks were detected in the regulatory regions of many target genes involved in the development of facial tissues including MSX1, IRF6, TBX22, and MAFB. In addition, we uncovered multiple single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) disrupting a conserved AP2alpha consensus sequence. 24753151_AP-2alpha continues to be required after lens vesicle separation to maintain a normal lens epithelial cell phenotype and overall lens integrity and to ensure correct fiber cell differentiation. 25050743_Cigarette smoke condensate decreased AP-2alpha expression by suppressing its transcription in human lung cancer cell lines, particularly in p53-deficient NCI-H1299 cells. 25063728_During pregnancy, regulation of hCG beta subunit genes expression correlates with both methylation of their promoters and TFAP2A expression level. 25358080_INHA gene expression is upregulated by cAMP via CRE in human trophoblasts, and TFAP2 regulates this expression by interacting with CRE. 25590586_Direct sequencing of the coding region of the TFAP2A gene revealed missense mutations in four branchio-oculo-facial syndrome patients; one patient was observed to have a previously described mutation (p.Arg251Gly), while three patients from two families were found to have novel mutations: p.Arg213Ser and p.Val210Asp. 25625848_Human melanomas display higher than normal CpG DNA methylation at the TFAP2A promoter.Aberrant CpG DNA methylation as an epigenetic mark associated with TFAP2A silencing in human melanoma. 25651508_ETS1 induction of syncytiotrophoblast marker genes likely results in part from transactivation by activator protein-2alpha. 25669978_Results indicate that AP-2alpha activates COX-2 expression to promote NPC growth. 25674231_The AP-2alpha transcription factor may play an important role in suppressing glioma progression. 25953442_TFAP2A might play a role in the development of Ovarian Cancer, and may be a therapeutic target in OC. 26073327_Hepatitis B virus X protein is able to elevate the expression of SPHK1 in hepatoma cells by upregulating transcription factor AP2 alpha. 26780928_AP-2alpha expression has a role in human hepatocellular cancer by regulating signaling to affect cell growth and migration 26819314_role in the expression of Latent membrane protein 1 27499261_AP-2a is an important transcription factor of DEK expression, which is correlated with the methylation level of the DEK core promoter in hepatocellular carcinoma . 27663566_We identified two SLN genes (PIGR and TFAP2A) that provided high prognostic accuracy in SLN-positive melanoma patients (AUC = 0.864). These two SLN genes, along with clinicopathological features, can differentiate the high- and low-risk groups in node-positive melanoma patients 27866707_the atrial fibrillation (AF)-associated SNP rs2595104 altered PITX2c expression via interaction with TFAP2a; such a pathway could ultimately contribute to AF susceptibility at the PITX2 locus associated with AF 27933721_The data suggest that IRF6, TFAP2A, and GRHL3, among others, are shared in neural tube and orofacial development. 28031466_dimerization-defective mutant of Nef failed to interact with either CD4 or AP-2 in the BiFC assay, indicating that Nef quaternary structure is required for CD4 and AP-2 recruitment as well as CD4 down-regulation 28085512_TFII-I factors and the neural crest master regulator AP2alpha associate with the promoters of key genes important in the development of facial and dental structures. Mutations in TFAP2A cause branchio-oculo-facial syndrome. 28249010_Data show that TFAP2A binds many of the same regulatory elements as MITF in melanocytes. 28439677_our results indicate that AP-2alpha can reverse the Multidrug resistance (MDR) of gastric cancer cells, which may be realized by inhibiting the Notch signaling pathway. 28749936_We identified miR-1254 as a negative regulator inhibiting HO-1 translation by directly targeting HO-1 3'UTR via its seed region, and suppressing HO-1 transcription via non-seed region-dependent inhibition of transcriptional factor AP-2 alpha (TFAP2A), a transcriptional activator of HO-1. 28932319_Results show that gout-associated increased NRBP1 expression is regulated through methylation-dependent TFAP2A binding to the B1 region, which might be involved in the pathogenesis of gout. 30256193_In the present paper, we report that Wnt-induced lipid droplet biogenesis does not depend on the canonical TCF/LEF transcription factors. Instead, we find that TFAP2 family members mediate the pro-lipid droplet signal induced by Wnt3a, leading to the notion that the TFAP2 transcription factor may function as a 'master' regulator of lipid droplet biogenesis. 30443989_AP2a may regulate the osteogenic differentiation in an indirect way through competing with RUNX2 to relieve the RUNX2 activity which inhibited by YAP, and also in a direct way via inhibiting the BARX1 in mesenchymal stem cells. 30700826_Synergistic activation of the NEU4 promoter by p73 and AP2 in colon cancer cells. 30824562_Molecular network of transcription factor AP-2 alpha (AP-2alpha) and transcription factor AP-2 gamma (AP-2gamma) and other molecules may clarify the atypical molecular mechanisms occurring during carcinogenesis [Review]. 31020390_A functional indel polymorphism rs34396413 in TFAP2A intron-5 significantly increases female encephalocele risk in Han Chinese population. 31146003_study presents the first description that TFAP2A and ETS family signaling networks are involved in the androgen-mediated transcriptional regulation of NR4A1, which contributes to the understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved in the TFAP2A-NR4A1 and ETS-NR4A1 signaling networks in PCOS. 31337972_TFAP2A induced KRT16 overexpression promotes tumorigenicity in lung adenocarcinoma via epithelial-mesenchymal transition 31490282_We report an unusual phenotype of TFAP2A mutation in a child and mother with BOFS, with predominantly ocular anomalies. We would recommend screening for mutations in TFAP2A to be included in work up of patients with microphthalmia. 31534499_The miR-26a/AP-2alpha/Nanog signaling axis mediates stem cell self-renewal and temozolomide resistance in glioma. 31701656_MicroRNA-576-5p enhances the invasion ability of trophoblast cells in preeclampsia by targeting TFAP2A. 31915245_The motif EXEXXXL in the cytosolic tail of the secretory human proprotein convertase PC7 regulates its trafficking and cleavage activity. 32015686_TFAP2A Induced ITPKA Serves as an Oncogene and Interacts with DBN1 in Lung Adenocarcinoma. 32362655_Integrated single-cell and bulk gene expression and ATAC-seq reveals heterogeneity and early changes in pathways associated with resistance to cetuximab in HNSCC-sensitive cell lines. 32432738_TFAP2A is a novel regulator that modulates ferroptosis in gallbladder carcinoma cells via the Nrf2 signalling axis. 32462520_Comprehensive analysis of the expression and prognosis for TFAP2 in human lung carcinoma. 32467991_Transcription factor AP2alpha negatively regulates thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression in respiratory syncytial virus infection. 32474464_MiR-204-5p/TFAP2A feedback loop positively regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT process in cervical cancer. 33000225_KCTD1 mutants in scalpearnipple syndrome and AP2alpha P59A in Char syndrome reciprocally abrogate their interactions, but can regulate Wnt/betacatenin signaling. 33038379_Role of AP-2alpha/TGF-beta1/Smad3 axis in rats with intervertebral disc degeneration. 33170430_Silencing of lncRNA DLEU1 inhibits tumorigenesis of ovarian cancer via regulating miR-429/TFAP2A axis. 33213447_Functional genomics of AP-2alpha and AP-2gamma in cancers: in silico study. 33580997_TFAP2A-induced SLC2A1-AS1 promotes cancer cell proliferation. 33609534_Involvement of TFAP2A in the activation of GSDMD gene promoter in hyperoxia-induced ALI. 33742988_Polymorphism of rs6426749 at 1p36.12 is associated with the risk of osteoarthritis in Taiwanese female population. 33753551_AP-2alpha Regulates S-Phase and Is a Marker for Sensitivity to PI3K Inhibitor Buparlisib in Colon Cancer. 33824285_TFAP2A potentiates lung adenocarcinoma metastasis by a novel miR-16 family/TFAP2A/PSG9/TGF-beta signaling pathway. 34193219_A positive feedback loop between Periostin and TGFbeta1 induces and maintains the stemness of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via AP-2alpha activation. 34210752_AP-2alpha-Mediated Activation of E2F and EZH2 Drives Melanoma Metastasis. 34310873_Family based and case-control designs reveal an association of TFAP2A in nonsyndromic cleft lip only among Vietnamese population. 36123698_Transcription factor AP2 enhances malignancy of non-small cell lung cancer through upregulation of USP22 gene expression. | ENSMUSG00000021359 | Tfap2a | 50.051129 | 0.415024763 | -1.268731 | 0.28694184 | 19.317487 | 0.0000110687962784690140647693434861054129214608110487461090087890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001452442048247885256900824302306318713817745447158813476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 28.2221290 | 5.2795893 | 67.9735006 | 12.0061428 | |
| ENSG00000137474 | 4647 | MYO7A | protein_coding | Q13402 | FUNCTION: Myosins are actin-based motor molecules with ATPase activity. Unconventional myosins serve in intracellular movements. Their highly divergent tails bind to membranous compartments, which are then moved relative to actin filaments. In the retina, plays an important role in the renewal of the outer photoreceptor disks. Plays an important role in the distribution and migration of retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) melanosomes and phagosomes, and in the regulation of opsin transport in retinal photoreceptors. In the inner ear, plays an important role in differentiation, morphogenesis and organization of cochlear hair cell bundles. Involved in hair-cell vesicle trafficking of aminoglycosides, which are known to induce ototoxicity (By similarity). Motor protein that is a part of the functional network formed by USH1C, USH1G, CDH23 and MYO7A that mediates mechanotransduction in cochlear hair cells. Required for normal hearing. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19643958, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21493626, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21687988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21709241}. | 3D-structure;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Calmodulin-binding;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Deafness;Disease variant;Hearing;Leber congenital amaurosis;Motor protein;Myosin;Non-syndromic deafness;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Retinitis pigmentosa;SH3 domain;Synapse;Usher syndrome | This gene is a member of the myosin gene family. Myosins are mechanochemical proteins characterized by the presence of a motor domain, an actin-binding domain, a neck domain that interacts with other proteins, and a tail domain that serves as an anchor. This gene encodes an unconventional myosin with a very short tail. Defects in this gene are associated with the mouse shaker-1 phenotype and the human Usher syndrome 1B which are characterized by deafness, reduced vestibular function, and (in human) retinal degeneration. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:4647; | actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; microvillus [GO:0005902]; myosin complex [GO:0016459]; photoreceptor connecting cilium [GO:0032391]; photoreceptor inner segment [GO:0001917]; photoreceptor outer segment [GO:0001750]; stereocilium [GO:0032420]; stereocilium base [GO:0120044]; synapse [GO:0045202]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; microfilament motor activity [GO:0000146]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; spectrin binding [GO:0030507]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; actin filament-based movement [GO:0030048]; auditory receptor cell stereocilium organization [GO:0060088]; equilibrioception [GO:0050957]; eye photoreceptor cell development [GO:0042462]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; lysosome organization [GO:0007040]; mechanoreceptor differentiation [GO:0042490]; phagolysosome assembly [GO:0001845]; pigment granule transport [GO:0051904]; post-embryonic animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0048563]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; sensory organ development [GO:0007423]; sensory perception of light stimulus [GO:0050953]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; vesicle transport along actin filament [GO:0030050]; visual perception [GO:0007601] | 12485990_the shaping of the hair bundle relies on a functional unit composed of myosin VIIa, harmonin b and cadherin 23 that is essential to ensure the cohesion of the stereocilia 15180257_Expressed in retina. Domain structure. Carrier proteins determine cellular function. 15300860_A new heterozygous missense mutation (c.2557C>T; p.R853C) was found in autosomal dominant non-syndromic hearing loss that changes an invariant residue of the fifth IQ motif, a putative calmodulin (CaM) binding domain. 15606003_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15660226_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15823922_Mutations in MYO7A is associated with Usher syndrome 15965244_MYO7A is the gene associated with the Usher syndromes. 16001398_Myosin-VIIa is associated with cathepsin D- and Rab7-positive lysosomes. Association of myosin-VIIa with lysosomes was Rab7 independent. These studies suggest that myosin-VIIa is a lysosome motor. 16449806_A genome-wide scan found linkage to locus DFNA11. Sequencing of the MYO7A gene in the linked region identified a new missense mutation resulting in an Ala230Val change in the motor domain of the myosin VIIA, causing a dominant form of deafness. 16470552_there is an absence of hot spot mutations in the MYO7A gene and this gene plays a major role in Usher syndrome 17093394_Three new pathological mutations causing either premature termination of translation or replacement of an evolutionary conserved MYO7A amino acid. 17361009_19 different mutations were identified, 13 of which were novel. These variants include two nonsense mutations, one putative splice site mutation, one insertion and five deletions in coding sequence and 10 missense mutations. 17702415_Significant linkage in DFNA11 markers was found in hereditary deafness. 17960123_Missense change p.Y1719C. Homozygous c.1687G>A mutation in last nucleotide of exon 14, predicted to result in aberrant splicing and may lead to loss of MYO7A transcript. P.Y1719C is not disease-causing. Frequent polymorphism in the Moroccan population. 18181211_p.E1716del causes a less severe phenotype (DFNB2) than the USH1B-associated alleles because the resulting protein retains some degree of normal function. 18323324_Molecular genetic analysis was performed in 11 patients and pathogenic mutations were identified in all cases: (mutation in myosin 7A gene in 5 cases). Two new mutations in the MYO7A gene never reported before were found. 18463160_Humans with PCDH15 (USH1F), USH2A or GPR98 (USH2C) had a similar retinal phenotype to MYO7A 18700726_the mutations responsible for USH1B cause the complete loss of the actin-activated ATPase activity or the reduction of duty ratio of myosin VIIa. 19074810_Patients with MYO7A-USH1B can have regions of structurally and functionally normal retina with definable transitions to severe laminopathy and visual loss. 19299023_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19320733_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19320733_There is an association with the variant S1666C (rs2276288) in the MYO7A gene and the risk of developing malignant melanoma. 19324852_The data indicate that melanosomes in the retinal pigment epithelium and choroid are the dominant source of NIR-autofluorescence from the posterior region of the eye with ushers syndrome due to MYO7A mutation. 19375528_Molecular screening of deafness in Algeria: high genetic heterogeneity involving DFNB1, DFNB2, DFNB12, and DFNB23. 19683999_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20132242_Variable hearing impairment in a DFNB2 family with a novel MYO7A missense mutation 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20801516_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20844544_Five mutations (three in MYO7A and two in CDH23) were identified in four of five unrelated patients with Usher syndrome type 1. 21031134_The molecular determinant of a mild form of retinopathy in association with a subtle splicing modulation of MYO7A mRNA, was investigated. 21150918_Novel missense mutations in MYO7A underlying postlingual high- or low-frequency non-syndromic hearing impairment in two large families. 21378158_a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) T/C at position -4128 in the wild-type MYO7A promoter allele that sorts with the degree of hearing loss severity in the pedigree 21482763_association of myosin VIIA monomers with membrane via the MyRip/Rab27a complex facilitates the cargo-transporting activity of myosin VIIA, which is achieved by cluster formation on the membrane 21687988_The results suggested that in a cellular environment, compartment-specific fluctuations in free Mg2+ ions can mediate the conditional switching of myosin-7a between cargo moving and tension bearing modes. 21873662_The authors speculate that null MYO7A alleles could be associated with milder dysfunction and fewer photoreceptor structural losses at ages when other genotypes show more severe phenotypes. 21901789_in a set of consanguineous patient families with Leber congenital amaurosis study identified five putative disease-causing mutations, including four novel alleles, in six families; These five mutations are located in four genes, ALMS1, IQCB1, CNGA3, and MYO7A 22219650_Pathogenic mutations in MYO7A, USH1C, and USH1G have been found in four consanguineous Israeli Arab families with Usher syndrome type 1. 22681893_Possible digenism could not be excluded in two families segregating genomic variations in both MYO7A and USH2A, and two families with CLRN1 and USH2A. 22690115_A previously reported mutation (c.52C>T; p.Q18X) in the myosin VIIA (MYO7A) gene was found in the homozygous state in the affected siblings. 23344065_Our results show that MYO7A therapy with AAV2 or AAV5 single vectors is efficacious; however, the dual AAV2 approach proved to be less effective. 23383098_A new missense mutation (Arg668His) in the motor head domain of myosin VIIA in a family with autosomal dominant hearing impairment (DFNA11). 23559863_Two novel mutations, c.3742G>A (p.E1248K) and c.6051+1G>A (donor splice site mutation in intron 44), of MYO7A in a Chinese non-consanguineous family with Usher syndrome type 1, were identified. 23770805_Hearing loss was found to co-segregate with locus-specific STR markers for MYO7A in 32 Pakistani families. 23991031_Data show that AAV-mediated hMYO7A gene transfer to the mice sh1(-/-) retina is effective. 24022220_Data indicate that that CIB2 localizes to stereocilia and interacts with the USH proteins myosin VIIa and whirlin, suggesting CIB2 is a Ca2+-buffering protein essential for calcium homeostasis in the mechanosensory stereocilia of inner ear hair cells. 24194196_The MYO7A gene is responsible for two distinct diseases and gives evidence that the p.P1887L mutation in a homozygous state may be responsible for nonsyndromic hearing loss. 24199935_MYO7A-related ocular disease is variable. Central vision typically remains preserved at least until the third decade of life, with 50% of affected individuals reaching legal blindness by 40 years of age. 24275721_new variants in genes such as MYO7A is associated with nonsyndromic deafness and vestibular dysfunction 24831256_Clinical phenotypes of Usher syndrome associated with MYO7A mutations. 25080338_concluded that the USH1 in this family was caused by compound heterozygous mutations in MYO7A 25558175_Ten variants in the MYO7A gene and 34 variants in the USH2A gene were detected in Italian patients with Usher syndrome at a high detection rate. 26001786_Electron microscopy revealed that myosin VIIA is a monomer in which the tail domain bends back toward the head-neck domain to form a compact structure. This compact structure is extended at high ionic strength or in the presence of Ca(2+). 26469752_c.6377delC mutation in significant proportion of Usher syndrome in indigenous South Africans 26864046_We suggest that this new mutation named c.6079_6081del (p.H2027del) is the main cause of deaf-blindness found in this family clinically diagnosed as USH1B. 26960254_MYO7A binds to and impinges on CASPASE-8, revealing a new regulatory axis affecting RIPK1>CASPASE-8 signaling. Results expose a conserved role for unconventional myosins in transducing caspase-dependent regulation of kinases. 26968074_The novel compound heterozygous mutations (c.3671C>A and c.390_391insC) in MYO7A gene identified in this study were responsible for the autosomal recessive sensorineural hearing loss of this Chinese family 27013738_The genetic correction of MYO7A mutation resulted in morphologic and functional recovery of hair cell-like cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells from a deaf patient. 27083884_This study showed that Mendelian sensorineural hearing loss exhibits vestibular dysfunction, including DFNA9, DFNA11, DFNA15 and DFNA28. 27409480_In USH1B-MYO7A, constriction rate of EZ extent depends on the initial eccentricity of the transition. Ellipsoid zone edges in the macula correspond to large local changes in cone vision, but extramacular EZ edges show more pronounced losses on rod-based vision tests. 27440999_We found a remarkable genetic heterogeneity in the studied families with USH1 with a variety of mutations, among which three were novel. These novel mutations will be included in the NADf mutation screening chip that will allow a higher diagnosis efficiency of this extremely genetically heterogeneous disease. 27729122_An unreported splice site mutation c.3924+1G > C compound with c.6028G > A in the MYO7A gene were detected to cosegregate with Usher syndrome type 2 in a Han Chinese family. 27743438_There are more than 39 deafness genes reported to cause non-syndromic hereditary hearing loss (HHL) in Iran, of which the most prevalent causative genes include GJB2, SLC26A4, MYO15A, and MYO7A. In addition, we highlight some of the more common genetic causes of syndromic HHL in Iran. [review] 27828912_Patients carrying mutations in MYO7A had a younger age of onset of hearing and visual impairments than those carrying mutations in USH2A, leading to an earlier diagnosis of the disease in the former patients. 28262393_Results show the structures of Myo7a IQ5-SAH (single a helix) lever arm extension in complex with apo- and Ca2+-CaM, respectively, reveal that the motor contains an extended and rigid lever arm at low Ca2+ concentration conditions. Increased cellular Ca2+ concentration induces conformational flexibility of the motor and thus regulates its activity. 28472130_report the results of genetic analyses performed on Moroccan families with autosomal recessive non syndromic hearing loss that identified two families with compound heterozygous MYO7A mutations 28507101_myosin VIIa movement appears to be suitable for translocating USH1 proteins on stereocilia actin bundles in inner-ear hair cells 28660889_Crystall structure shows the interactions between Myo7a protein domains and their partners, harmonin and SANS/ANKS4B. 28688563_novel mutation c.3847_3848insTCTG (p. N1285LfsX24) in compound heterozygosity with c.2239_2240delAG in the MYO7A gene is the main cause of USH1 in the proband 28731162_These findings broaden the phenotype spectrum of the MYO7A gene, and may facilitate understanding of the molecular pathogenesis of the disease, and genetic counseling for the family. 29142287_Likely causative mutations were found in all patients: 25 pathogenic variants, 18 previously reported and 7 novel, were identified in three genes (USH2A, MYO7A, ADGRV1). All USH1 presented biallelic MYO7A mutations, one USH2 exhibited ADGRV1 mutations, whereas 16 USH2 displayed USH2A mutations 29287847_a novel stop gained variant c.4513G > T (p.Glu1505Ter) in MYO7A was found in an Iranian pedigree with two affected members with USH type 1 29287864_Two pathogenic variations (c.849+2T>C and c.5994G>A) in MYO7A were successfully identified and individually separated from parents 29361540_We found that silencing Myo7a by means of RNAi inhibited melanoma cell growth through upregulation of cell cycle regulator p21 (also known as CDKN1A) and suppressed melanoma cell migration and invasion through downregulation of RhoGDI2 (also known as ARHGDIB) 29400105_pathogenic mutation c.2011G>A identified in Chinese family with autosomal dominant hearing loss 29490346_We report here novel homozygous mutations in various genes causing USH, extending the spectrum of causative mutations. We also prove combined sequencing techniques as useful tools to identify novel disease-causing mutations. To the best of our knowledge, this is the largest report of a genetic analysis of Israeli and Palestinian families (n = 74) with different USH subtypes. 29605349_This study extends the spectrum of known MYO7A mutations and proves next generation sequencing as a valuable tool in molecular diagnosis of Usher syndrome. 30358468_The Russian USH cohort shows both novel and known USH mutations. Clinically the prevalence of USH2 is low (39.28%) and the frequency of MYO7A mutations responsible for USH1B is very high (63.63%, N = 7/11) compared to other cohorts. These seven patients carrying MYO7A mutations are preliminarily eligible for the UshStat(R) gene therapy. 30826590_In summary, four novel mutations were identified in MYO7A gene by using next-generation sequencing. Of these mutations, MYO7A c.2187 + 2_+8 delTGAGCAC and c.2138 T > C (p.L728P) were associated with nonsyndromic hearing loss, while MYO7A p.Tyr560Ser and p.Ala2039Pro were related to the Usher syndrome 1B. 31266775_Characterisation of microvascular abnormalities using OCT angiography in patients with biallelic variants in USH2A and MYO7A. 31320737_Retinal findings in pediatric patients with Usher syndrome Type 1 due to mutations in MYO7A gene. 31479088_PHENOTYPIC CHARACTERISTICS OF ROD-CONE DYSTROPHY ASSOCIATED WITH MYO7A MUTATIONS IN A LARGE FRENCH COHORT. 31598937_The compound heterozygous mutations of the MYO7A gene probably underlies the non-syndromic autosomal recessive deafness disease in this family. 31644917_Myosin VII, USH1C, and ANKS4B or USH1G Together Form Condensed Molecular Assembly via Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation. 31997689_Investigation of MYO15A and MYO7A Mutations in Iranian Patients with Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss. 32097363_Clinical Profiles of DFNA11 at Diverse Stages of Development and Aging in a Large Family Identified by Linkage Analysis. 32428919_The p.R206C Mutation in MYO7A Leads to Autosomal Dominant Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss. 33576163_Genotype-phenotype correlation in patients with Usher syndrome and pathogenic variants in MYO7A: implications for future clinical trials. 33671976_Spectrum of MYO7A Mutations in an Indigenous South African Population Further Elucidates the Nonsyndromic Autosomal Recessive Phenotype of DFNB2 to Include Both Homozygous and Compound Heterozygous Mutations. 33976695_Next-Generation Sequencing Identifies Pathogenic Variants in HGF, POU3F4, TECTA, and MYO7A in Consanguineous Pakistani Deaf Families. 34391192_Rare coding variants involving MYO7A and other genes encoding stereocilia link proteins in familial meniere disease. 34948090_The Study of a 231 French Patient Cohort Significantly Extends the Mutational Spectrum of the Two Major Usher Genes MYO7A and USH2A. | ENSMUSG00000030761 | Myo7a | 75.239356 | 0.158967772 | -2.653194 | 0.48631947 | 26.779065 | 0.0000002280950368348700341187841036591499310759445506846532225608825683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000042036803362927040010350171472808256112330127507448196411132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 22.8746939 | 7.5480354 | 143.8532223 | 45.7805169 | |
| ENSG00000137673 | 4316 | MMP7 | protein_coding | P09237 | FUNCTION: Degrades casein, gelatins of types I, III, IV, and V, and fibronectin. Activates procollagenase. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2550050}. | 3D-structure;Calcium;Collagen degradation;Direct protein sequencing;Extracellular matrix;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen | This gene encodes a member of the peptidase M10 family of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Proteins in this family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protease. This secreted protease breaks down proteoglycans, fibronectin, elastin and casein and differs from most MMP family members in that it lacks a conserved C-terminal hemopexin domain. The enzyme is involved in wound healing, and studies in mice suggest that it regulates the activity of defensins in intestinal mucosa. The gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes on chromosome 11. This gene exhibits elevated expression levels in multiple human cancers. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. | hsa:4316; | extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0006509]; membrane protein intracellular domain proteolysis [GO:0031293]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] | 11701474_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11801551_MMP-7 activity is upregulated in colorectal cancer liver metastases 11925859_plays an important role not only in tumor metastasis but in micrometastasis to lymph node 11927011_Overexpression of MMP-7 is associated with invasiveness in gastric carcinoma 11983918_Gene expression analysis reveals matrilysin as a key regulator of pulmonary fibrosis in mice and humans. 12005165_Immunoelectron microscopy revealed that matrix metalloproteinase-7 was expressed within basal laminar deposits and amorphous materials around the retinal pigment epithelial cells in age-related macular degeneration. 12034345_destruction of the surrounding matrix by endometriosis might be caused by various MMPs, which are mainly produced in stromal cells. 12112311_study of expression in ulcerative colitis related tumorigenesis 12464266_Cleavage of FasL by MMP-7 occurs at the leucine residues in sequence 'ELAELR' within the region between the transmembrane and trimerization domains. When this site is unavailable, a 'SL,' is cleaved. MMP-7 differentially processes murine and human FasL 12579270_increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-7 is associated with high grade transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder may be associated with tumor invasion and metastasis 12684625_Increased expression of MMP-7 in high grade renal cell carcinoma might be associated with tumor invasion and metastasis 12759241_In alveolar-like epithelial cells, transfection of activated matrilysin resulted in shedding of E-cadherin and accelerated cell migration. In vivo, matrilysin co-localized with E-cadherin at the basolateral surfaces of migrating tracheal epithelium. 12759346_findings suggest that local pericellular production of hypochlorous acid by phagocytes is a physiological mechanism for governing matrix metalloproteinase-7 activity during inflammation 12808021_MMP-7 is induced in human gastric epithelial cells infected with Helicobacter pylori; it has a role in epithelial cell migration 12958188_src oncogene signaling involves synergistic cooperation between the AP-1 and LEF-1 transcription factors in activation of the matrilysin promoter in colon cancer cells. 12963695_Data show that matrilysin confers macrophages with their most potent matrix metalloproteinase-dependent elastolytic system. 14516315_Down-regulated PTEN expression and up-regulated MMP-7 expression were greatly implicated in tumorigenesis and progression of gastric carcinoma. 14744783_May contribute to the tumorigenesis of MMP-7-producing IGF-IR-expressing tumors in the primary site and to organ-specific metastasis in a paracrine manner 15040016_Heparanase, CD44v6 and nm23 may play important roles in the invasive infiltration and lymph node metastasis in gastric carcinomas. 15102692_matrix metalloproteinase-7 has a role in progression of pancreatic cancer 15149334_matrilysin may have a role in renal tubular injury and progression of tubulointerstitial fibrosis, and Wnt4 may regulate matrilysin expression in the kidney 15239678_the importance of MMP7 as a predictor of secondary Extramammary Paget's disease or the putative origin of Paget's cells from the dermal adenocarcinoma cells of apocrine duct origin 15375490_Overexpression of MMP-7 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer 15523695_These results indicate MMP-7 is overexpressed in malignant ovarian epithelium and suggest MMP-7 may facilitate tumor cell invasion in vivo partly through the induction of progelatinase activation. 15618645_alcohols are considered to bind the hydrophobic S1' subsite most plausibly, and the size of the pocket was estimated to be large enough to accommodate the length of 1-butanol (4-carbon chain) and the bulk of tertiary alcohols 15652345_pattern of secretion in polarized MDCK cells expressing stably transfected human MMP-7 15696117_Results imply that MMP-7 is a major MMP associated with the tissue remodeling during the progression of liver fibrosis in biliary atresia. 15725655_We assessed mRNA expression of MMPs in six human colorectal cancer cell lines and found a considerable level of MMP-7 expression in HT-29 cells. 15800927_results suggest E1A-F is overexpressed in early stages of human CRC development and may be an important factor in the overexpression of COX-2 and MMP-7 15809719_Activation of MMP-7 protein closely involved in disruption of tight junction structure and consequent induction of cell dissociation as well as invasion in pancreatic cancer 15860507_Some green tea catechins induce pro-MMP-7 production via O2- production and the activation of JNK1/2. 15866216_expression up-regulated in Helicobacter species-infected colon and bile duct epithelial cells and hepatocytes. 15930031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15930031_Polymorphism might be a candidate marker for predicting individuals who are at higher risk to certain tumors but might not be used to predict potential of lymphatic metastasis in various cancers. 15979995_sFasL and matrilysin are expressed in seminal plasma and have a role in regulation of the function of the Fas system 16097959_MMP7 immunoreactivity was present in only polymyositis not dermatomyositis 16115946_Study suggests that targeting matrilysin may have important therapeutic implications. 16142384_Increased expression of MMP-7 in high grade uterine endometrial carcinoma (UEC) may be associated with tumor invasion and metastasis, and MMP-7 could serve as a prognostic maker in UEC. 16248458_In chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps tissues the expression of TGF-beta1, MMP-7, MMP-9, TIMP-1 protein was significant increased compared to controls. 16278009_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16286510_shed syndecan-1 or MMP7-syndecan-1 complexes may have roles in tumor progression 16356191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16405530_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16455621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16455621_The 181A/G polymorphism in MMP7 has a potential to be a susceptibility factor for endometriosis and adenomyosis. 16474169_Fas downregulation and a consequential increased resistance to FasL-triggered apoptosis resulting from upregulated MMP-7 in colorectal cancer cells could be a key mechanism for their escape from the immune surveillance 16474379_Data suggest that tissue expression of MMP-7 could be a useful marker to predict the progression and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 16476739_it is likely that binding of matrilysin to cholesterol sulfate facilitates the matrilysin-catalyzed modulation of cell surface proteins, thus inducing the cancer cell aggregation 16494848_FGF-2-induced MMP7 expression in endothelium depends on AP-1 and FGF-2 signaling to AP-1 involves a Stat1/3-dependent pathway. 16804904_intense MMP-7 signal in tumor cells is an independent prognostic factor predicting better survival in epithelial ovarian cancer 16940985_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16956593_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16956593_The present result, for the first time, suggested that the MMP-7-181A/G polymorphism might be associated with the susceptibility to adult astrocytoma. 17009118_Matrix metalloproteinase-7 overexpression is thought to be an early event in the colonic adenoma-carcinoma pathway. 17009258_These data demonstrate that CD151 is overexpressed in osteoarthritic cartilage and suggest that CD151 plays a role in the pericellular activation of proMMP-7, leading to cartilage destruction and/or chondrocyte cloning. 17029196_Data show that MMP7 may be relevant with carcinogenesis, development and metastasis of adenoid cystic carcinoma, and different metastasis potential may result from different subtype of MMPs gene family. 17038551_Estrogen modulates tight junctional resistance through estrogen receptor-alpha-mediated remodeling of occludin 17114341_MMP-7 secretion/activation may represent a new mechanism that facilitates ovarian cancer invasion. 17125518_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17129995_A significant increase in the proportion of MMP 7 immunopositive cells was seen in the nucleus pulposus of discs classified as showing intermediate levels of degeneration and a further increase was seen in discs with severe degeneration. 17145820_MMP-7 influences tumor progression by regulating invasion and angiogenesis. Multivariate analysis showed that MMP-7 status of cancer tissues was strong predictor of poor prognosis. MMP-7 targeting treatment may be a potential target against human RCC. 17145868_Data show that MMP7 and LN5 are coexpressed in colonic carcinoma cells HT29 cells. 17153464_Our results suggested the importance of MMP-7 and MT1-MMP in the peritoneal metastases of gastric cancer. 17209789_MMP-7 is associated with the innate host defense in periodontal tissues. 17219436_MMP-7 has a role in invasiveness of glioma 17310281_MMP-7-selective targeting to the plasma membrane of epithelial cells promotes its activity by conferring resistance to TIMP-2. 17373931_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17396032_incubation with HGF mediated the release of MMP-7, resulting in extracellular cleavage of E-cadherin from stomach cancer cells 17487834_MMP-7 is an independent prognostic factor for survival in advanced colorectal cancer. In our sample, the risk of death associated to MMP-7 increase is much higher than the risk of death associated to lactate dehydrogenase elevation 17502620_reveal the MMP7-activated photodynamic therapy efficacy of this photodynamic molecular beacons 17507989_The expression of MMP7 was specifically enhanced at the bronchiolo-alveolar duct junction and suggests that MMP7 plays a key role during the bronchioalveolar remodeling. 17554258_Diminished expression of MMP-7 may play a role in fibronectin accumulation in the diabetic kidney in response to advanced glycation end products and/or TGF-beta. 17564313_Expression of MMP7 was evaluated in hepatocellular carcinoma and surrounding non-tumor tissue. 17607721_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17671679_VEGF, MMP2, 7 and 9, and COX-2 expression is related to progression of advanced uterine cervical cancer in young women 17672933_MMP-7 -181A/G polymorphism may influence the susceptibility to astrocytoma. 17672933_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17695544_MMP-7 gene expression is associated with increased risk only for early stages of oral cancer. 17718429_MMP-7 expression in human rectal cancer increases significantly and plays a key role in the invasion and metastasis of human rectal cancer. 17728005_Wnt1 may play a critical role in regulating the intratumoral MMP-7 expression 18006768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18023162_MMP-7 is involved in tumor angiogenesis, thereby contributing to malignant growth and hence associated with decreased survival 18036564_evidence that matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) interacts with anionic, cationic and neutral lipid membranes, although it interacts strongest with anionic membranes. 18179407_the significantly increased expression of MMP7 in primary CNS lymphoma (PCNSL), suggest the involvement of this MMP in the characteristic infiltration pattern of PCNSL. 18202161_Circulating Pro-MMP-7 is associated with IgG specific to pro-MMP-7 in patients with renal cell carcinomas 18214300_Immunoassays showed significantly elevated content of matrix metalloproteinase 7 in tumors compared to adjacent histologically unchanged mucosa of patients with colorectal cancer. 18308831_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18329694_Expression of MMP-7 in cholangiocarcinoma is an unfavorable postoperative prognostic factor of cholangiocarcinoma arising from the large bile ducts. Underexpression of MMPs in papillary cholangiocarcinoma might be associated with a favorable prognosis. 18340552_matrilysin may be multiple, multifarious, and multifaceted functions contributing to early tumor growth 18364512_reduced extracellular proteolytic activity of certain matrix metalloproteinases-for example, MMP-7-is associated with accelerated aging and senescence in normal HMECs. 18385523_TIMP-1 interacts with matrix metalloproteinases and regulates matrilysin activity during airway epithelial repair. 18411043_HER2-dependent transcriptional upregulation and protein secretion of MMP-7 are mediated by activated STAT3. 18422740_Increased plasma MMP-7 is associated with metastatic disease in patients with renal cell carcinomas 18447576_MMP7 and MMP1, are overexpressed in the lung microenvironment and distinguish idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis from other chronic lung diseases. Additionally, increased MMP7 concentration may be indicative of asymptomatic ILD and reflect disease progression. 18448157_Individuals with MMP-7 -181GG genotype are at significantly higher risk of cervical cancer. 18448157_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18485588_HLE may be a natural inactivator of MMP-7 which can counteract MMP-7-induced apoptosis resistance. 18500535_MMP7 may contribute to the process by which intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) of the pancreas advances from adenoma to carcinoma and to subsequent invasion of tumor cells in IPMN. 18511876_E1AF mRNA overexpression correlated well with matrilysin expression in rectal cancers. 18548257_MMP7 may act as a downstream mediator of FVIIa/TF signal transduction to facilitate the development of metastasis in colon cancer. 18600430_HRG-beta-induced MMP-7 expression was regulated by HER2-mediated AP-1 activation in MCF-7 cells. 18636198_Higher matrix metallopeptidase 7 is associated with colorectal cancer. 18644839_MMP-7 cleaves the NR1 subunit of the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor to generate an N-terminal fragment of approximately 65 kDa 18648013_Results from our study suggest that common MMP-7 genetic polymorphisms may contribute to breast cancer susceptibility 18653469_p120 and Kaiso regulate Helicobacter pylori-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase-7 18674869_beta-catenin expression was significantly related to E-cadherin and MMP-7 expression 18695873_activin A may modulate the expression of MMP-7 via AP-1 18713744_MMP7 and MMP9-mediated cleavage of EphB2 is induced by receptor-ligand interactions at the cell surface and that this event triggers cell-repulsive responses 18715618_The matrix metalloproteinase-7 gene may be up-regulated by mutated or continuously elevated beta-catenin protein in sporadic desmoid tumors. 18721140_It is supposed that the cleavage of cell surface annexin II by matrilysin contributes to tumor invasion and metastasis by enhancing tPA-mediated pericellular proteolysis by cancer cells. 18768525_Functional polymorphisms in the promoter of MMP-7 do not significantly confer susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma in a southern Chinese population. 18768525_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18798254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18798254_common MMP-7 genetic polymorphisms may have roles in survival among Chinese women with breast cancer 18805052_Gene expression revealed up-regulation of pro-angiogenic (PGF), anti-apoptotics (BAG-1, BCL-2), heart development (TNNT2, TNNC1) and extracellular matrix remodelling (MMP-2, MMP-7) genes in SM. 18823373_the expression level of MMP-7 in tumor cells is predictive of response to chemotherapy and outcome in patients with advanced NSCLC receiving platinum-based chemotherapy. 18931651_metalloproteinase-7 expression was associated with more aggressive buccal squamous cell carcinomas 18955490_Identification of amino acid residues of matrix metalloproteinase-7 essential for binding to cholesterol sulfate. 18958543_In Japan, carriage of the MMP-7-181 G allele and of the CMA/B A allele were each associated with an increased risk for H. pylori-related noncardia gastric cancer development. 18958543_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18974372_VEGF escapes the sequestration by endothelial sVEGFR-1 and promotes angiogenesis in the presence of MMP-7. 19000448_High concentration of tamoxifen can inhibit the proliferation of ERbeta-positive HT-29 cells, and effectively bind with ERbeta to down-regulate MMP-7 expression. 19016757_MMP7 gene expression was significantly higher in colorectal cancer patients than in healthy volunteers. 19020757_Serous and mucinous ovarian tumors express different profiles of MMP-7. 19022775_RECK is cleaved by MMP-2 and MMP-7 and competitively inhibits MMP-7-catalyzed cleavage of fibronectin 19094228_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19121849_metastasis and survival of patients with bladder cancer are mediated, at least in part, by matrix metalloproteinase-7 19132754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19173304_cleavage of CLEC3A by MMP-7 weakens the stable adhesion of 19181662_Differential Processing of {alpha}- and {beta}-Defensin Precursors by Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7). 19221016_These findings indicate that MMP7-catalyzed release of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor mediates acetylcholine induced transactivation of epithelial growth factor receptors and consequent proliferation of colon cancer cells 19231585_Hyaluronan synthase (HAS2 and HAS3) and hyaluronan may mediate cellular invasion via changes in MMP-7 expression in SW620 colon carcinoma cells. 19266094_MMP7 is related to the acquisition of oxaliplatin-resistance and its inhibition restores drug sensitivity by increasing Fas receptor. 19303106_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19317620_Helicobacter pylori CagA-positive patients carrying MMP-7 -181 G allele had a higher risk for lymphoid follicle formation. 19317620_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19329997_MMP7 coordinates allergic lung inflammation by activating interleukin 25 while simultaneously inhibiting retinoid-dependent development of regulatory T cells. 19360357_Three-dimensional culture using a radial flow bioreactor induces matrix metalloprotease 7-mediated EMT-like process in tumor cells via TGFbeta1/Smad pathway. 19420105_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19421758_Elevated expressions of MMP7, TROP2, and survivin are associated with survival, disease recurrence, and liver metastasis of colon cancer. 19435861_none of 30 haplotype tagging polymorphisms in MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-7 were found to be significantly associated with endometrial cancer risk. 19465902_Hepatocellular adenoma was characterized by the complete absence of matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression 19505922_The fecal RNA test using COX-2 and MMP-7 mRNAs improved the sensitivity to detect colorectal cancer without decreasing the specificity 19586554_SFRP5 is downregulated and inversely correlated with MMP-7 and MT1-MMP in gastric cancer 19596921_Significantly higher expression of MMP-7 and MMP-9 in tumor tissue than in the surrounding tissue or in benign lung disease tissue supports the notion of an important role of these metalloproteinases in the growth of lung carcinoma 19608871_matrilysin-1 may play an important role in the bronchiolization of alveoli by promoting proliferation, migration, and attenuation of apoptosis involving multiple genes in the MAP kinase pathway. 19634113_E-cadherin and metalloproteinase-1 and -7 polymorphisms have roles in colorectal cancer 19634113_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19643940_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19643940_SNPs in MMP1, MMP2, MMP7 and MMP12 have roles in response to chemotherapy in lung cancer 19654318_These observations demonstrate that sulfated GAGs regulate matrilysin activation from promatrilysin and its activity against specific substrates. 19676133_A novel nonsynonymous variant of matrix metalloproteinase-7 confers risk of liver cirrhosis. 19676133_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19679556_The selective inhibition of MMP-7 in the tumor-bone microenvironment may be of benefit for the treatment of lytic breast-to-bone metastases. 19682489_Cellular senescence of human mammary epithelial cells (HMEC) is associated with an altered MMP-7/HB-EGF signaling and increased formation of elastin-like structures. 19690403_increased expression in interstitial pneumonia 19690958_Concomitant elevations of MMP-3 and MMP-7 serum levels in the H. pylori-infected gastric cancer patients could serve as potential biomarkers to correlate with poor survival. 19701966_Results suggest that laminin (LN)gamma2 and LNbeta3, in conjunction with MMP7, play a key role in the progression of biliary tract cancer. 19724852_positive expression of both CD44v6 and MMP-7, and negative expression of nuclear Cdx2 may serve as powerful predictors of lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer 19728912_MMP-7 and survivin are related to the generation of colon cancer, and are independent factors for prognosis of colon cancer. 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19785773_endocrine therapy is an efficient therapy for inhibiting ERbeta-positive colon cancer cell proliferation and migration via down-regulation of MMP7. 19787626_Immunoexpression of metalloproteinase-7 does not correlate with recurrence, mortality, relapse-free survival, survival, degree of cell differentiation, or staging of colorectal cancer. 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19929564_MMP-7 is associated with the prognosis of patients with acinic cell and mucoepidermoid carcinoma. 20007614_MMP-7 protein expression in epithelial cells was significantly higher in red peritoneal lesions compared with that of deep infiltrating endometriosis, ovarian endometriosis and black peritoneal lesions, in all phases of the menstrual cycle. 20040080_although the level of MMP7 secretion was the highest in the secretory phase the difference from the proliferative phase did not reach statistical significance 20096949_we have identified novel relationships between serum MMP-7 and diabetic complications specifically in renal disease and in diastolic dysfunction. 20113256_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20113256_The MMP-7 -181 A/G genotype is a potential factor for susceptibility to endometrial cancer. 20132413_Data show that genes overexpressed in ovarian/peritoneal carcinoma including MMP7. 20139113_MMP-7 is involved in the cleavage of N-cadherin and modulates vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis, and may contribute to atherosclerotic plaque development and rupture. 20146992_Increased circulating MMP-7 might indicate enhanced adipocyte differentiation in subjects who had undergone bariatric surgery. 20156184_MMP-7 was used for the screening secretory metalloproteinase inhibitors in conditioned media of human cancer cell cultures. Human epidermoid carcinoma conditioned media demonstrated the most intense band in reverse-zymography and in Western blotting. 20180812_MMP-7 is a promising marker to detect present and to predict future metastasis in bladder cancer 20192597_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20219015_MMP-10 and -7 abundance increased, accompanied by decreased TIMP-4 in dilated cardiomyopathy failing hearts compared with non-failing hearts. 20230842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20300917_MMP-7 overexpression is associated with lymph node and distant metastases as well as with prognosis of gastric cancer 20347338_Genetic polymorphisms of MMP7 predispose to development of bronchiolitis obliterans (BOS). Patients carrying these risk alleles express lower levels of MMP-7, which may contribute to aberrant tissue repair and culminate in development of BOS. 20347338_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20359117_The positive rates of Ang-2 and MMP-7 were significantly higher in laryngeal carcinoma tissue than those in adjacent non-cancerous tissue. Patients with positive expression of Ang-2 had worse overall survival. 20360147_MMP7 -181 AG and GG genotype carriers had an increased gastric cancer risk 20360147_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20372795_MMP-7 and SGCE are distinctive molecular factors in sporadic colorectal cancers from the mutator phenotype pathway 20375326_Increased expression of MMP7 was the only consistent differentially regulated gene in the conjunctival samples of trichiasis subjects. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20473942_Elevated serum matrix metalloproteinase 7 levels are associated with metastatic prostate cancer. 20484597_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20491537_role of these proteins in the process of invasion and metastasis cannot be ruled out since their presence is more marked along the tumor invasion front compared to more central areas of squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue 20584750_Enhanced expression of MMP-7 is associated with progression from non-dysplastic Barrett's oesophagus to adenocarcinoma. 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20605361_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20605361_The A/G genotype had a significant association with recurrence-free survival in postprostatectomy patients & the frequency of the risk-reducing genotype A/A was 74% whereas that of the risk-enhancing genotypes A/G & G/G were 20% & 6% 20605794_Cholesterol sulfate alters substrate preference of matrix metalloproteinase-7 and promotes degradations of pericellular laminin-332 and fibronectin. 20624652_chronic disordered epithelial expression of MMP-7 in patients with asthma might increase mFasL cleavage and contribute to airway epithelial damage and inflammation. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20662554_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20662554_investigation of the association of single-nucleotide polymorphism at MMP-1 16071G/2G, MMP-7 181A/G, and MMP-9 279R/Q genes with colorectal cancer in the southwest Chinese Han population 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20680712_High MMP7 expression was confirmed to be an independent prognostic factor of colon cancer 20707923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20730428_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20736794_Tissue present at the site of hypertrophic nonunions commonly expresses significantly higher levels of MMP-7 and MMP-12 in relation to mineralized fracture callus. 20813660_PKD3 may contribute to the malignant progression of prostate cancer cells through negative regulation of MMP-7 expression. 20826916_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20826916_study provided new support for the association of MMP1-1607 and MMP7-181 in bladder cancer development, the tumorigenic effect of which was observed to be more enhanced in case of tobacco exposure 20827277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20853162_NGAL may be considered a novel stress protein, whereas MMP-7, MMP-9, and TIMP-1 may be regarded as indicators of stress response in the pediatric population on chronic dialysis 20872971_Serum values of MMP7 and CA19-9 appear to be useful biomarkers for differentiating cholangiocarcinoma from benign biliary tract obstructive diseases. 20939893_Up-regulation of MMP-7 expression through beta2-AR-mediated signaling pathway is involved in invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer. 20979817_In the serum of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, the level of MMP-1 was lower but the level of MMP-7 higher than in patients with sarcoidosis. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21116502_The concentration of MMP-7 was maximum in the blood of patients with tumor invasion in lymph vessels. These data suggest MMP-7 as a possible serological marker of gastric cancer. 21165404_We revealed a positive correlation between serum levels of MMP-7 in patients with primary ovarian cancer and the size of the primary tumor 21255765_direct association observed between morphological scores of malignancy and MMP immunoreactivity, with the association being significant for MMP-7. present results demonstrate important role of MMPs in development of SCCs of lower lip and tongue. 21302026_There is marked relationship between matrix metalloproteinase 7 and brain atrophy in HIV infection. 21315773_These results suggest that the induction of MMP-7 by Tax is regulated by JunD and that MMP-7 could facilitate visceral invasion in adult T-cell leukemia . 21336735_There was significant difference in IL-8 -251TT and MMP-7 -181GG genotypes between the cervical cancer group and the lymph node metastasis group. Individuals with IL-8 T or MMP-7 G carriers were at significantly higher risk of cervical cancer. 21455340_MMP-7 may have a role in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 21481787_demonstrate that serum MMP7 level in human patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma correlated with metastatic disease and survival 21516345_The aim of this study was to evaluate serum concentrations of sFas, sFasL, and their potential regulators (MMP-2, MMP-7, MMP-9, TIMP-1, TIMP-2), in children and young adults chronically dialyzed. 21517234_Homozygous variant GG genotype of MMP-7 (-181A>G) polymorphism was associated with a more than two fold increased risk of gastric cancer. 21593056_These results suggest thatactive-site tyrosyl residue, Tyr219 of the matrix metalloproteinase 7 is not critical for catalytic activity, but is involved in the broad pH-dependence of the activity. 21707759_The median MMP-7 serum level of systemic sclerosis patients with lung fibrosis (LF) was significantly higher compared with those without LF. 21722074_MMP7 -181A/G polymorphism is associated with the development of vulnerable carotid plaques 21764478_High levels of MMP-7 in tumor cells and high levels of MMP-9 in tumor associated stroma were independent positive prognostic factors in NSCLC patients. 21787888_Thermodynamic analysis of ionizable groups involved in the catalytic mechanism of human matrix metalloproteinase 7. 21814482_The increased MMP-7 expression due to H2O2 treatment of SW620 cells was mediated by activation of MAP kinases in an AP-1-dependent manner. Dimerumic acid inhibits AP-1-mediated MMP-7 gene transcription. 21858178_Data show that decidualization was associated with increased expression of 428 genes including SCARA5 (181-fold), DKK1 (71-fold) and PROK1 (32-fold), and decreased expression of 230 genes including MMP-7 (35-fold) and SFRP4 (21-fold). 21901248_fibulin-3 negatively modulates the invasiveness of lung cancer cells via regulation of MMP-7 and MMP-2 and its expression is regulated by hypermethylation of the promoter region 21912055_MMP-7 (-181A>G) GG carriers are at a higher risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Kashmir valley. 21935919_plasma HYP, collagen I and MMP-7 may be useful as novel predictive markers of opisthorchiasis-related BBD, and HYP may be used as a diagnostic marker for CCA 21981819_Antisense oligonucleotide targeting matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) changes the ultrastructure of human A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells, inhibiting proliferation and invasion. 21999204_correlation between MSLN and MMP-7 in the progression of ovarian cancer, and the mechanism of MSLN in enhancing ovarian cancer invasion 22024063_Overexpression of MMP-7 generally indicated a higher metastatic potential and inferior overall survival of adenocarcinoma of colon and rectum. 2204255 | ENSMUSG00000018623 | Mmp7 | 37.077081 | 0.464633400 | -1.105835 | 0.27078914 | 16.917849 | 0.0000390328238355865773261989259967918997062952257692813873291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0004449805540441606325520462750233718907111324369907379150390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 24.3428779 | 7.2718449 | 52.7193289 | 15.1304983 | |
| ENSG00000137745 | 4322 | MMP13 | protein_coding | P45452 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in the degradation of extracellular matrix proteins including fibrillar collagen, fibronectin, TNC and ACAN. Cleaves triple helical collagens, including type I, type II and type III collagen, but has the highest activity with soluble type II collagen. Can also degrade collagen type IV, type XIV and type X. May also function by activating or degrading key regulatory proteins, such as TGFB1 and CCN2. Plays a role in wound healing, tissue remodeling, cartilage degradation, bone development, bone mineralization and ossification. Required for normal embryonic bone development and ossification. Plays a role in the healing of bone fractures via endochondral ossification. Plays a role in wound healing, probably by a mechanism that involves proteolytic activation of TGFB1 and degradation of CCN2. Plays a role in keratinocyte migration during wound healing. May play a role in cell migration and in tumor cell invasion. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16167086, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17623656, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19422229, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19615667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20726512, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22689580, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23810497, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8207000, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8576151, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8603731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8663255, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9065415}. | 3D-structure;Calcium;Collagen degradation;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen | This gene encodes a member of the peptidase M10 family of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Proteins in this family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protease. This protease cleaves type II collagen more efficiently than types I and III. It may be involved in articular cartilage turnover and cartilage pathophysiology associated with osteoarthritis. Mutations in this gene are associated with metaphyseal anadysplasia. This gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes on chromosome 11. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. | hsa:4322; | extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; bone mineralization [GO:0030282]; bone morphogenesis [GO:0060349]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; endochondral ossification [GO:0001958]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; growth plate cartilage development [GO:0003417]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904645] | 11883937_AGRE site plays a rate-limiting role in human collagenase-3 production. 11903048_Investigation of the role of Endo180/urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor-associated protein as a collagenase 3 (matrix metalloproteinase 13) receptor 12009331_involvement of MAPKs, AP-1 and NF-kappa B transcription factors in the IL-1 induction of MMPs in chondrocytes 12009332_Reduction of cytokine-induced expression and activity of MMP-1 and MMP-13 by mechanical strain in MH7A rheumatoid synovial cells 12139441_REVIEW: The structure, regulation, and function of human matrix metalloproteinase-13 12192005_Data show that keratinocytes use an alternative plasminogen and matrix metalloproteinase-13-dependent pathway for dissolution of collagen fibrils. 12270924_induction by transforming growth factor-beta via activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway 12392760_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12392760_Two new MMP13 promoter polymorphisms. Genotype for one MMP13 polymorphism associated with fibrous plaque in black males. MMP13 expressed in all layers of aorta. Polymorphism a functional variant. Genetic risk factor for extent of fibrous plaque. 12426321_translational repression by an alternatively spliced form of T-cell-restricted intracellular antigen-related protein 12734180_MMP13 expression is regulated by IGF-1 and OP-1 12878172_induction of the MMP-13 gene by TNF-alpha is mediated by ERK, p38, and JNK MAP kinases as well as AP-1 and NF-kappaB transcription factors 12974393_Together with other prognostic markers, determination of MMP-13 in ascitic fluid may help to identify patients at risk for early death and help to individualize adjuvant therapy 14558091_catabolic role of ET-1 in osteoarthritis cartilage via MMP-1 and MMP-13 up-regulation. 15067375_MMP-13, uPA, and PAI-1 antigen levels were determined in the synovium of patients with osteoarthritis 15551360_MMP13 is upregulated in breast cancer 15640153_MMP-1 and MMP-3 secretion by gastric epithelial cells are differentially regulated by E prostaglandins and MAPKs 15654517_gene expression regulation in Lyme disease 15693018_regulation of the PLC pathway through the PTH1R is increased by elevating expression of G(11)alpha in osteoblastic cells leading to increased PTH stimulation of MMP-13 expression by increased stimulation of AP-1 factors c-jun and c-fos. 15763932_study showed a marked expression of MMP-13 in dental pulp tissue of both sound and carious teeth 15944607_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15947272_MMP-9 and MMP-13 are involved in stroke progression and the neuroinflammatory response 16024014_Down-regulated by integrin alphavbeta6, not essential for the degradation of type I collagen by oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. 16144844_GADD45beta plays an essential role during chondrocyte terminal differentiation and mediates MMP-13 gene expression 16331612_activation of MMP-13 as well as MMP-9 induced by H-Ras is involved in angiogenesis and with farnesyl transferase inhibitors, in part, exerts their anticancer effects 16356191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16398406_MMP-13 appears to be a factor associated with tumor aggressiveness in cutaneous malignant melanoma 16507124_MMP-13 can degrade members from two classes of small leucine-rich repeat proteoglycans. Site at which biglycan is cleaved by MMP-13. MMP-13 induced SLRP degradation may represent early event affecting collagen network by exposing MMP-13 cleavage site. 16648633_the involvement of p38 MAP kinase in the hyaluronan oligosaccharide induction of MMP-13 16877349_The expression of matrix-modeling genes in chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis (cIMF) is not influenced by the JAK2 mutation status but is predominantly related to the stage of disease. 16917496_a novel role for human MMP-13 in regulating dermal fibroblast survival, proliferation, and interaction in 3D collagen. 16948116_Since both S100A4 and RAGE are up-regulated in osteoarthritis cartilage, this signaling pathway could contribute to cartilage degradation in this disease. 16984617_TUNEL-positive cells and MMP-3- and -13-expressing cells were distributed in the degenerative articular cartilage and reparative fibrocartilage tissue in osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) of the elbow. 17009260_Premature induction of hypertrophy-related molecules (type X collagen and matrix metalloproteinase 13) occurred before production of type II collagen and was followed by up-regulation of alkaline phosphatase activity. 17033924_No convincing evidence was found to support the association of MMP13 SNPs with increased breast cancer risk or survival. 17033924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17076612_activity in gingival crevicular fluid samples was significantly increased in active sites from progressive periodontal disease, supporting its role in the alveolar bone loss 17116693_These results identify an unexpectedly broad involvement for p8 in key cellular events linked to cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and cardiac fibroblast matrix metalloproteases production, both of which occur in heart failure. 17138534_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17138534_Thus, in the region of Hebei Province where there is a high incidence of GCA and ESCC, the MMP-13 A-77G SNP may not be associated with cancer susceptibility. 17151781_nicotine stimulates bone matrix turnover by increasing production of tPA and MMP-1, 2, 3, and 13, thereby tipping the balance between bone matrix formation and resorption toward the latter process 17196980_We have solved the 2.0 A crystal structure of the complex between the catalytic domain of human MMP-13 (cdMMP-13) and bovine TIMP-2. 17208315_oncostatin M-stimulated ADAMTS-4 and MMP-13 expression is mediated by extracellular signal-regulated kinases, Janus kinase 3/STAT1/3 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and by cross talk between these pathways 17311929_deregulation of cross-talk between mitogen-activated protein kinases and protein kinase Cdelta signaling may contribute to the etiology of osteoarthritis in human patients 17373717_CpG-ODN-treatment also increased MMP-13 activity and neutralizing anti-MMP-13 antibody prevented CpG-ODN-induced invasion in TLR9(+) CaP cells. 17373931_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17395008_Increased production of reactive oxygen species but not nitric oxide as secondary messengers in the chondrocyte fibronectin fragment signaling pathway leads to increased production of MMPs, including MMP-13. 17495113_MMP-13 is involved in osteogenic differentiation. 17607721_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17623656_a matrix metalloprotease-13 inhibitor reduces cartilage damage in vivo without joint fibroplasia side effects 17626252_Nucleolin interacts with the AP-1 site within the promoter sequence of the metalloproteinase-13 gene. 17697361_TauCl differentially inhibits the expression of MMP-1 and MMP-13 in human synoviocytes 17724016_BFGF activates the MAPK and NFkappaB pathways that converge on ELK1 to control production of MMP13 by articular chondrocytes. 17786186_MMP-13 may serve as a marker for progression of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. 17822788_Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1) as a new repressor of MMP-13 transactivation. 17853491_Fibroblasts of the interface from aseptically loosened endoprostheses selectively express MMP-13 17876296_ROCK-II is a critical mediator of colon cancer cell invasion through its modulation of MMP-2 and -13 at the site of invadopodia but regulates proliferation in non-malignant intestinal cells. 17905570_MyD88, IRAK1 and TRAF6 proteins are crucial early mediators for the IL-1-induced MMP-13 regulation through MAPK pathways and AP-1 activity. 18006768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18091353_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18091353_the MMP-13 gene, at least in part, contributes to the development of coroonary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease 18225566_MMP-13 gene expression-related polymorphism is associated with risk for the highly aggressive form of oral cancer; the high expression A allele of the -77A/G polymorphism seems to be a prognostic factor for tumor progression 18225566_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18262231_MMP-13 is involved in disc histopathology, and that disc cells actively participate in the synthesis of extracellular matrix-degrading proteinases 18289056_This review highlights MMP-13, expressed by chondrocytes and synovial cells in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis and thought to play a critical role in cartilage destruction. 18289383_Chondrocytes were found to express IL-7 receptors and to respond to IL-7 stimulation with increased production of matrix metalloproteinase-13. 18308831_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18308831_potential role for MMP12 -82 A/G and MMP13 -77 A/G combined polymorphisms in superficial endometriosis. As no association was found with deep infiltrating endometriosis, these polymorphisms might protect from a more in-depth penetration of tissues. 18366705_MMP8, but not MMP1 or MMP13, may affect the metastatic behaviour of breast cancer cells through protection against lymph node metastasis 18373849_MMP-13 may be particularly useful as a prognostic marker when evaluated along with Her-2/neu and lymph node status. 18487224_CXCL12 enhances Laryngeal and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma cell invasiont through paracrine-activated CXCR4, triggering MMP-13 upregulation. 18528653_increases in IL-6, MMP-13, and RANKL (receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand)expression in osteoarthritis (OA) subchondral bone osteocytes suggest that in subchondral bone OA progression involves abnormal osseous tissue remodeling 18593949_SRC-3/AIB1 directly regulates transcription of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-13 through its coactivation of AP-1 and PEA3. 18709334_MMP-13 is over-expressed in renal cell carcinoma bone metastasis and is induced by TGF-beta1. 18753468_MMP-13 and thioredoxin-like 2 in lungs increased in patients with COPD. MMP-13 was mainly expressed in the alveolar macrophages and type II pneumocytes 18755271_MMP-1 and -13 differentially regulate osteoblastic markers and their combined suppression is important for the elaboration of an osteoblastic phenotype in periodontal ligament cells 18971037_The structural changes in the venous wall in addition to the increased expression of MMP-2, MMP-9 and MMP-13 in venous aneurysms suggests a possible causal role for these MMPs in their pathogenesis. 18985055_Nuclear extracts from cells confirmed upregulation of active MMP-13 after oxygen and glucose deprivation 18987329_Active MMP13 is suppressed in vivo and in vitro by estradiol and progesterone, suggesting a protective effect against vaginal supportive tissue deterioration. 19038372_BMP-2 enhanced the invasiveness of chondrosarcoma cells by increasing MMP-13 expression through the PI3K, Akt, c-Fos/c-Jun and AP-1 signal transduction pathway. 19094243_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19180518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19185056_Data show that both AF-1 and AF-2 domains of estrogen receptor alpha are required for regulation of MMP-13 promoter activity. 19248099_C/EBPbeta directly binds to the MMP-13 promoter region and stimulates the expression of MMP-13 in chondrocytes in inflammatory arthritis. 19248107_Activated protein C resulted in MMP-13 activation in cartilage cultures, and it was associated with increased MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity. 19248116_IL-7 stimulates chondrocyte secretion of S100A4 via activation of JAK/STAT signaling, and then S100A4 acts in an autocrine manner to stimulate MMP-13 production via RAGE. 19258954_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258954_the A/A genotype of MMP-13-77A/G polymorphism was associated with special pathological subtype and clinical stage in epithelial ovarian cancer at least in Chinese women. 19296842_15-lipoxygenases may have chondroprotective properties by reducing MMP-1 and MMP-13 expression. 19301259_Connective tissue growth factor enhances the migration of chondrosarcoma cells by increasing MMP-13 expression through the alphavbeta3 integrin, FAK, ERK, and NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. 19333684_mRNA expression and protein production of IL-6, IL-8, and MMP-13, which are involved in the progression of osteoarthritis, were increased in the osteophytes 19415460_DDR2-mediated MMP-13 induction by collagen matrix in synovial fibroblasts of RA contributed to articular cartilage destruction 19422937_Runx2 may play a crucial role in cytokine-mediated MMP-13 expression in Giant Cell Tumor of bone stromal cells. 19442604_Primary cultures stromal cells from giant cell tumour of bone produce MMP-1 and MMP-13. Immunohistochemistry confirmed the presence of MMP-1 and MMP-13 in paraffin-embedded GCT tissue samples. 19453573_Data suggest that the -77A/G and 11A/12A polymorphisms of MMP-13 gene are not associated with susceptibility to severe, generalized CP in a Turkish population. It seems that -77G allele carriage may not influence the outcome of periodontal therapy. 19494318_age-related shift in ALK1/ALK5 ratio in murine cartilage and a strong correlation between ALK1 and MMP-13 expression in human cartilage 19551542_The migration of bone marrow (BM) mesenchymal stromal cells was the result of the variable level of MMP/TIMP in response to inflammatory stimuli. 19561643_Results indicate that Wnt5a/Ror2 signaling involves the activation of a SFK, leading to MMP-13 expression, and that constitutively active Wnt5a/Ror2 signaling confers invasive properties on osteosarcoma cells in a cell-autonomous manner. 19562509_Functional polymorphisms in matrix metalloproteinases might play roles in developing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and gastric cardia adenocarcinoma in high incidence region of North China. 19562509_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19564415_FOXO3a promotes invasive migration by inducing the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) and MMP-13. 19615667_Mutation in MMP13 determines the mode of inheritance and the clinical spectrum of metaphyseal anadysplasia. 19779140_Nitric oxide may regulate the development of abdominal aortic aneurysms in part by inducing the expression of EMMPRIN and modulating the activity of MMP-13 in murine and human aneurysms. 19784544_Elevated HDAC7 expression in human osteoarthritis may contribute to cartilage degradation via promoting MMP-13 gene expression. 19787229_High MMP13 is associated with breast cancer. 19821768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19883500_Adiponectin may play a significant role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis by stimulating the production of VEGF and MMP-1 and MMP-13 19902888_Membrane type-1 metalloproteinase mediates nitric oxide-induced activation of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in chondrocytes (chondrocarcoma cell line sw1353) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948051_Regulation of the IGFBP-5 and MMP-13 genes by the microRNAs miR-140 and miR-27a in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. 20043086_overexpression of ErbB2 promotes invasive and migratory abilities of H-Ras-activated MCF10A human breast epithelial cells through upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-13 and urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA). 20067416_Taken together, these studies demonstrate a new level of transcriptional regulation of MMP-13 expression by the c-maf. 20097749_HDAC4 represses matrix metalloproteinase-13 transcription in osteoblastic cells, and parathyroid hormone controls this repression 20131257_miR-27b may play a role in regulating the expression of MMP-13 in human chondrocytes 20175118_Thrombin enhances the migration of chondrosarcoma cells by increasing MMP-2 and MMP-13 expression through the PAR/PLC/PKCalpha/c-Src/NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. 20196777_there is an association among RUNX-2, SOX-9 and FGF-23 in relation to MMP-13 expression in osteoarthritic chondrocytes 20376807_Individuals with MMP-12 -82A/G and MMP-13 -77A/A might have higher risk of overall or special histological type of epithelial ovarian carcinoma development. 20376807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20463008_These data identify atypical PKC isozymes as STAT and ERK activators that mediate c-fos and collagenase expression. 20484597_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20506238_MMP-13 loss leads to a breakdown in primary human articular chondrocyte differentiation by altering the expression of multiple regulatory factors. 20573369_Inhibition of MMP-13 reduces resorptive activity of the cells indicating that MMP-13 likely plays an important role giant cell tumor of bone. 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20615395_These results indicate that Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) enhances migration of glioma cells through the increase of MMP-13 production and is mainly regulated by the MEK/ERK and JNK, c-Jun and AP-1 pathways. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20667128_data show for the first time that growth stimuli are mediated via MMP13 in melanocytes and melanoma, suggesting an autocrine MMP13-driven loop 20672350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20683000_MMP-13 expression levels were higher in tumour tissue with liver metastasis than in that without liver metastasis. It is concluded that MMP-13 gene expression is a useful predictor of liver metastasis in patients with CRC. 20685652_Nuclear S100A4 was bound to the promoter region of MMP-13 in IL-1beta-treated cells. 20706991_Hyaluronan inhibits IL-1beta-induced MMP-13 and p-p38 in a concentration-dependent manner in arthritic chondrocytes, via CD44. 20827277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20857147_MMP-9 and -13 mRNA levels are significantly elevated in patients with chronic pain, indicating their possible synergistic effect in intervertebral disc herniation. 20878060_the highly invasive potential of cancer stem cells depends on MMP-13 enzymatic activity, thus MMP-13 might be a potential therapeutic target for glioblastomas. 20878116_that MMP13 is a secreted protein with a significant correlation to development of postoperative relapse; hence it could be a potential prognostic marker for colorectal cancer patients 20936527_RT-PCR performed on samples of whole umbilical cord confirmed the transcriptional expression for the genes encoding all the six matrix metalloproteinases investigated, while in HUVEC only the expression of MMP-2, 3, 9, 10 and 13 mRNAs was detected. 20948207_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21039987_over-expression of Nedd4L might lead to gallbladder cancer invasion by regulating the transcription of the MMP-1 and MMP-13 genes. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21107991_polymorphism of the -77 MMP-13 promoter region acts as a surrogate marker of anti-CCP antibody production in HLA-DRB1*SE allele-negative patients, which may reflect rheumatoid arthritis severity 21142220_Results describe the conserved water molecular dynamics of catalytic and structural Zn(+2) ions in matrix metalloproteinase 13 21187486_Cells expressed PTHrP and that this factor stimulated MMP-13 expression, metastatic bone destruction may result from a PTHrP autocrine loop involving a PKC-ERK1/2 signaling pathway. 21191416_Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 is controlled by IL-13 via PI3K/Akt3 and PKC-delta in normal human dermal fibroblasts. 21205837_These results strongly suggest the underlying mechanism of CXCR4 promoting Tca8113 migration and invasion by regulating MMP-9 and MMP-13 expression perhaps via activation of the ERK signaling pathway. 21211511_the implication of H-Ras and NADPH oxidase-generated superoxide production in MMP-13 gene regulation by IL-1beta and TNF-alpha 21278254_IL-6 and IL-6 receptor interaction enhances migration of chondrosarcoma through an increase in MMP-13 production. 21339746_findings indicate that MUC1 contributes to ESCC metastasis by stimulating MMP13 expression, suggesting MUC1 as a novel diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target in ESCC 21344378_CCN3 enhances the migration of chondrosarcoma cells by increasing MMP-13 expression through the alphavbeta3/alphavbeta5 integrin receptor, FAK, PI3K, Akt, p65, and NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. 21344384_15-deoxy-Delta(12,14)-prostaglandin-J2 and ciglitazone attenuated TNF-alpha-induced MMP-13 expression in synovial fibroblasts primarily through the modulation of NF-kappaB signaling pathways. 21437966_Autologous protein solution inhibits MMP-13 production by IL-1beta and TNFalpha-stimulated human articular chondrocytes. 21508380_Induction of MMP-13 expression is associated with bone-metastasizing breast cancer. 21539914_MMP-1 and MMP-13 differential regulation of osteoblastic markers in MG63 cells likely results from their modulation of divergent signaling pathways involved in osteoblastic differentiation 21720458_Short-term, high-dose rosuvastatin therapy has no effect on matrix metalloproteinase-13 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 levels in hypercholesterolemic patients. 21849805_Forced MMP-13 expression effectively accelerated recovery from liver cirrhosis 21881840_MMP-9, MMP-13 and TIMP-1 expression may serve as a prognostic marker for early tumor invasiveness. Moreover, up-regulation of TIMP-1 in tumor and/or surrounding stromal cells may indicate an increased risk for BCC recurrence. 21913037_MMP-9 and uPA might be involved in the activation of pro-MMP-13 through unknown mechanisms in arthritic diseases. 21938739_Oct-3/4 enhanced degradation of surrounding extracellular matrix by increasing MMP-13 expression and altering integrin signaling 21959927_ET-1 activated FAK/PI3K/AKT/mTOR, which in turn activated IKK and NF-kappaB, resulting in increased MMP-13 expression and migration in human chondrosarcoma cells. 22006368_The results suggest that the main proteolytic cascade, MMP-2/MMP-13/MT1-MMP is involved in osteoblast differentiation through mechanical forces. 22032644_within the inflammatory bone microenvironment MMP-13 production was up-regulated in breast tumour cells leading to increased pre-osteoclast differentiation and their subsequent activation 22084953_Nuclear expression of MMP-13, but not cytoplasmic expression of MMP-2, -8, and -9, was associated with invasion depth and tumor size. Furthermore, high nuclear MMP-13 expression was predictive of poor outcome 22095691_findings show that C/EBPbeta and RUNX2, with MMP-13 as the target and HIF-2alpha as the inducer, control cartilage degradation 22102411_a conserved region at 20 kb upstream from the MMP-13 TSS includes a distal transcriptional response element of MMP-13, which contributes to MMP-13 gene expression. 22128168_Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling might also be required for expression of MMP-13 gene during the development of the cartilaginous tissue. 22153941_analysis of non-zinc binding inhibitors of MMP13 22158614_a novel role for ELF3 as a procatabolic factor that may contribute to cartilage remodeling and degradation by regulating MMP13 gene transcription. 22273691_Expression of miRNA-140 and MMP-13 was induced by IL-1beta 22327326_Increased expression of MMP-13 and MT1-MMP in the tumor portion of hyperostosis of meningiomas might contribute to the initiation of osteolysis. 22488635_expression by tumor cells associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer 22505473_identified CREB as the regulating factor able to only bind to the MMP13 promoter when the -104 CpG is demethylated 22573319_The minimum collagen type III sequence necessary for cleavage by MMP1 and MMP13 was 5 GXY triplets, including 4 residues before and 11 residues after the cleavage site (P4-P11'). 22590832_Data show that angiotensin II through activation of AT1 receptors can stimulate the expression of MMP-2, MMP-13 and VEGF, but not MMP-13, in B16F10 melanoma cells. 22610965_demonstrate that beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation leads to MMP-13 transactivation of protease-activated receptor 1 in both cardiac fibroblasts and cardiomyocytes 22710194_Genetic variations in MMP13 may contribute to individual differences in caries susceptibility. Our findings reinforce that susceptibility to caries results from gene-environment interactions. 22710868_T allele of MMP-13 intron polymorphism rs640198 is associated with the severity of coronary artery disease. 22722466_MMP-13 is expressed by tumor epithelial cells, stromal and inflammatory cells of nonmelanoma skin cancer in xeroderma pigmentosum and non-xeroderma pigmentosum. 22782903_a novel molecular mechanism by which MMP13 is up-regulated in cSCCs and indicate that miR-125b plays a tumor suppressive role in cSCC. 22869368_Osterix regulates calcification and degradation of chondrogenic matrices through matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) expression in association with transcription factor Runx2 during endochondral ossification 22950625_MMP-13 was correlated with progression and metastasis of colorectal cancer. 22992737_MMP-13 may directly and indirectly promote tumor angiogenesis 23132541_Report elevated expression of MMP-13 in osteroarthritic cartilage. 23162804_The present results suggest that the S100A4 gene may control the invasive potential of human breast cancer cells by modulating MMP-13 levels, thus regulating metastasis and angiogenesis in breast tumors. 23334990_Our data add to the understanding of MMP13 regulation, which is essential before such mechanisms can be exploited to alleviate the cartilage destruction associated with osteoarthritis. 23417678_methylation of different CpG sites in the proximal promoters of the human MMP13 and IL1B genes modulates their transcription by distinct mechanisms 23465389_Decreases in the MMP-2 (-735) polymorphism GG genotype and increases in the MMP-13 (A77G) polymorphism AG and GG genotypes increase the risk for lung cancer. 23467939_MMP-13 is associated with thyroid tumour invasion and metastasis. 23665089_Nonmucinous carcinomas showed higher MMP-13 expression compared with mucinous carcinomas. 23732700_MicroRNA-143 inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase 13 in prostate cancer. 23762330_This is the first report elucidating a feedback regulation between miR-127 and the TGFbeta/c-Jun cascade in hepatocellular carcinoma migration via MMP13. 23847446_provide the first evidence to demonstrate that 1,25-(OH)2D3 activates MMP13 expression through p38 pathway in chondrocytes 23898086_The present study evaluated the association between these single nucleotide polymorphisms in MMP12 and MMp13 in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) patients and healthy controls. 23913860_Crystal structure of peptide-MMP-13 interactions have led authors to propose how triple helical collagen strands fit into the active site cleft of the collagenase. 24008762_MMP13 expression alone is sufficient to overcome the SENP2-induced inhibition of cell migration and invasion. 24023851_presence of MMP-13 seems to limit the overall extent of ECM deposition in lung fibrosis 24180431_activity in chondrocytes reduced by moderate fluid flow shear stress 24351915_genotype distribution of MMP13 differed significantly between the group with unilateral tooth agenesis and the controls 24360951_miR-126-5p was significantly downregulated in stromal cells of Giant cell tumor and affect osteoclast (OC) differentiation and bone resorption by repressing MMP-13 expression at the post-transcriptional level. 24398989_All these data proved the utility of CXCR4, MMP-13 and beta-catenin immunohistochemical investigation in basal cell carcinoma. 24563279_In colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence, MMP- 13 overexpression occurred early in the adenoma stage and persisted after malignant transformation. 24599080_Data indicate that osthole-directed migration activity involves down-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-13 and cell motility dependent focal adhesion kinase (FAK) in migration-prone glioma cells. 24610617_Suggest elevated level of preoperative MMP-13 was found to associate with tumor progression and poor survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 24615104_The results showed that MMP7-181A/G and MMP13-77A/G variants were associated with Colorectal cancer 24648384_MMP13 mutations are the cause of recessive metaphyseal dysplasia, Spahr type. 24704999_These in vivo findings suggest a role for metalloproteinase-13 in the development and progression of adult human dental tissue disorders. 24781753_Nonsense mutation in exon 2 of MMP13 was described in two brothers who presented with short stature and mixed epiphyseal and metaphyseal dysplasia. 24974940_Collagenase-3 may play a role in the conversion of a periapical granuloma with epithelium to radicular cyst 25006778_Elevated levels of MMP-13 may play a role in the pathogenesis of chronic periodontitis. There is a direct correlation of increased expression of MMP-13 with various clinical and histologic parameters in disease severity 25166220_MMP-13 overexpression or exogenous MMP-13 reduces anoikis by more effectively shedding NG2. 25401159_High level of protein expression of MMP13 was significantly associated with poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 25433723_in degenerative intervertebral discs, IL1b upregulates NFkB, MMP13 and ADAMTS4 25527274_Pit-1 regulates MMP-1 and MMP-13, and that inhibition of MMP-13 blocked invasiveness to lung in Pit-1-overexpressed breast cancer cells. 25562781_During the Barrett's pathogenesis process, MMP activity is increased early on in the inflamed esophagus and remains high in metaplasia and esophageal adenocarcinoma. However, there is a switch of MMP13 to MMP9 expression once neoplasia develops. 25607396_The expression of MMP-7, -8, -9 and -13 in the gingiva of the young patients with aggressive periodontitis and type 1 diabetes mellitus was positive in all studied cases. 25609201_Clusterin is an independent predictive factor for prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and it facilitates metastasis through EIF3I/Akt/MMP13 signaling. 25726157_MMP13 expression positively related to the lymph node and distal metastasis, tumor stage and relapse of colorectal cancer 25742789_Up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase 13 is associated with colitis-associated cancer. 25749207_MMP-13 was associated with metastasis and poor survival in 79 patients with melanoma. MMP-13 expression was inversely correlated with vasculogenic mimicry. MMP-13 cleaves laminin-5 gamma 2 to accelerate metastasis. 25772251_Expression levels of miR-125b were negatively correlated with metastatic potential of NSCLC tumors, which may function through regulation of MMP-13. 25835975_Together, these data suggest that GRh2 may suppress GBM migration through inhibiting Akt-mediated MMP13 activation. 25846944_IL-32 stimulation promotes the invasion and motility of osteosarcoma cells, possibly via the activation of AKT and the upregulation of MMP-13 expression. 25863779_MMP-13 can be useful to confirm the diagnosis of alcoholic liver cirrhosis, but levels of MMP-1 are not significantly increased in patients with liver cirrhosis compared to controls. 25880591_This study demonstrates that stromal as well as tumor derived MMP13 contribute to tumor cell extravasation and establishment of metastases in the liver microenvironment. 25948792_High expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 is associated with pancreatic cancer. 25966777_Both VEGF-C and MMP13 are significantly upregulated in Multiple Myeloma with lymph-node metastases. 25976617_our resu | ENSMUSG00000050578 | Mmp13 | 104.192784 | 2.060342366 | 1.042884 | 0.15476605 | 45.895278 | 0.0000000000124746309651267094899311293015211460875890647770347641198895871639251708984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000004105767951533939079030975846787204427967843400892888894304633140563964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 141.9939271 | 21.8766287 | 69.1902941 | 11.0380338 | |
| ENSG00000137766 | 440279 | UNC13C | protein_coding | Q8NB66 | FUNCTION: May play a role in vesicle maturation during exocytosis as a target of the diacylglycerol second messenger pathway. May be involved in the regulation of synaptic transmission at parallel fiber - Purkinje cell synapses (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Calcium;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Exocytosis;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Predicted to enable calmodulin binding activity and syntaxin-1 binding activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including glutamatergic synaptic transmission; regulated exocytosis; and synaptic vesicle maturation. Predicted to be located in presynaptic active zone. Predicted to be active in several cellular components, including axon terminus; parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse; and presynaptic active zone cytoplasmic component. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:440279; | calyx of Held [GO:0044305]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse [GO:0098688]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; presynaptic active zone cytoplasmic component [GO:0098831]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; terminal bouton [GO:0043195]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; diacylglycerol binding [GO:0019992]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; syntaxin-1 binding [GO:0017075]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; dense core granule priming [GO:0061789]; negative regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0031914]; neuromuscular junction development [GO:0007528]; presynaptic dense core vesicle exocytosis [GO:0099525]; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0035249]; synaptic vesicle docking [GO:0016081]; synaptic vesicle maturation [GO:0016188]; synaptic vesicle priming [GO:0016082] | 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 33715625_Circ-KIAA0907 inhibits the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the miR-96-5p/UNC13C axis. | ENSMUSG00000062151 | Unc13c | 44.233775 | 0.164786211 | -2.601333 | 0.62797856 | 15.025631 | 0.0001060608611049673445864485743506122616963693872094154357910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0010878268877656293092681671907939744414761662483215332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 11.2673452 | 7.6263947 | 70.4899792 | 47.5349326 | |
| ENSG00000137812 | 57082 | KNL1 | protein_coding | Q8NG31 | FUNCTION: Performs two crucial functions during mitosis: it is essential for spindle-assembly checkpoint signaling and for correct chromosome alignment. Required for attachment of the kinetochores to the spindle microtubules. Directly links BUB1 and BUB1B to kinetochores. Part of the MIS12 complex, which may be fundamental for kinetochore formation and proper chromosome segregation during mitosis. Acts in coordination with CENPK to recruit the NDC80 complex to the outer kinetochore. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15502821, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17981135, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18045986}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Centromere;Chromosomal rearrangement;Chromosome;Chromosome partition;Coiled coil;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Kinetochore;Mitosis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Primary microcephaly;Reference proteome;Repeat | The protein encoded by this gene is a component of the multiprotein assembly that is required for creation of kinetochore-microtubule attachments and chromosome segregation. The encoded protein functions as a scaffold for proteins that influence the spindle assembly checkpoint during the eukaryotic cell cycle and it interacts with at least five different kinetochore proteins and two checkpoint kinases. In adults, this gene is predominantly expressed in normal testes, various cancer cell lines and primary tumors from other tissues and is ubiquitously expressed in fetal tissues. This gene was originally identified as a fusion partner with the mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL) gene in t(11;15)(q23;q14). Mutations in this gene cause autosomal recessive primary microcephaly-4 (MCPH4). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Additional splice variants have been described but their biological validity has not been confirmed. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]. | hsa:57082; | acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; kinetochore [GO:0000776]; NMS complex [GO:0031617]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; acrosome assembly [GO:0001675]; attachment of spindle microtubules to kinetochore [GO:0008608]; cell division [GO:0051301]; protein localization to kinetochore [GO:0034501] | 12087463_a new cancer/testis gene frequently expressed in lung cancer of smokers 12618768_AF15q14 seems identical to an mRNA previously found to be expressed in melanoma rendered nontumorigenic by microcell-mediated introduction of normal chromosome 6, suggesting the gene may function normally to suppress cell growth and/or enhance maturation. 17981135_Blinkin may be the center of the network for generating kinetochore-based checkpoint signaling 18045986_the vertebrate KNL1 counterpart is essential for chromosome segregation and is required to localize a subset of outer kinetochore proteins. 18771174_c-Abl and D40 interact with the tumor suppressor pRb protein and subsequently can lead to regulation of the cell proliferation. 20231380_phosphorylation of KNL1 by Aurora B disrupts the KNL1-PP1 interaction 21199919_h-KNL1 functions to connect Bub1 and BubR1 with the hMis12, Ndc80, and Zwint-1 complexes. 21272090_Expression levels of D40 mRNA and proteins decrease according to the degree of spermatogenesis impairment in male infertile patients. 22000412_we identify the Blinkin motif critical for interaction with BUBR1, define the stoichiometry and affinity of the interaction, and present a 2.2 Angstrom resolution crystal structure of the complex 22983954_Data provide strong evidence for CASC5 as a novel MCPH gene, and underscore the role of kinetochore integrity in proper volumetric development of the human brain. 24344183_KNL1 contains an extensive array of short linear sequence modules that encompass TxxOmega and MELT motifs and that can independently localize BUB1. 24344188_KNL1 is a requirement for Aurora B activity at kinetochores and for wild-type kinetochore-MT attachment dynamics. 24361068_In cells depleted of endogenous Knl1, kinetochore-targeted Knl1(1-250) suffices to restore spindle assembly checkpoint and chromosome alignment 24363448_Protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) binding to KNL1 during prometaphase reduces the levels of Bub proteins at kinetochores to approximately the level recruited by four active MELT repeats. 25246613_PP2A-B56 is a key phosphatase for the removal of the Mps1-mediated Knl1 phosphorylations necessary for Bub1/BubR1 recruitment in mammalian cells. 25601404_Mechanisms of mitosis-specific assembly of the checkpoint platform Knl1/MIS12/NDC80 at human kinetochores. 25661489_Data show sequential multisite regulation of the microtubule-associated protein KNL1-kinase-adaptor complex BUB1/BUB3 interaction. 26348410_Targeted Knockdown of the Kinetochore Protein D40/Knl-1 Inhibits Human Cancer in a p53 Status-Independent Manner 26621532_We propose that CASC5 has a key role for the correct functioning of DNA damage response proteins, and a defect in this connection might affect upstream and downstream DNA damage response events as response to increased genotoxic stress. 26626498_Involvement of CASC5 in autosomal recessive microcephaly and a founder effect of the c.6125G>A mutation. 27878434_CASC5 may contribute to the morphological and structural changes of the human brain during recent evolution. The observed between-population divergence of CASC5 variants was driven by natural selection that tends to favor a larger gray matter volume in East Asians. 28072388_Therefore, Mps1 promotes checkpoint activation through sequentially phosphorylating Knl1, Bub1, and Mad1. This sequential multi-target phosphorylation cascade makes the checkpoint highly responsive to Mps1 and to kinetochore-microtubule attachment. 28901661_Mutations in the CASC5 gene were found to encode a kinetochore protein essential for mitotic cell division and to cause autosomal recessive primary microcephaly 4. (Review) 30100357_Data show how KNL1 binds both PP1 and microtubules. Unexpectedly, PP1 and microtubules bind KNL1 via overlapping binding sites. Co-sedimentation assays unequivocally demonstrated that microtubules and PP1 binding to KNL1 is mutually exclusive, with preferential formation of the KNL1:PP1 holoenzyme in the presence of PP1. 30304678_KNL1 mutation is associated with Microcephaly. 30655516_Study demonstrates that KNL1 acts as a receptor of linear ubiquitin chains to anchor CENP-E at attached kinetochores. Thus, linear ubiquitin chains constitute a critical mechanism for chromosome congression and alignment by coupling the dynamic kinetochore microtubule motor CENP-E to the static one, the KMN network. 31315522_KNL1 protein expression was also significantly associated with poorer survival. Moreover, there was a significant correlation between KNL1 and BUB1 in colorectal cancer tissues. KNL1 plays an effective role in decreasing apoptosis and promoting the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells, suggesting that its inhibition may represent a promising therapeutic approach in patients with colorectal cancer. 32283571_CASC5 is a potential tumour driving gene in lung adenocarcinoma. 32795273_LINC02418 promotes malignant behaviors in lung adenocarcinoma cells by sponging miR-4677-3p to upregulate KNL1 expression. 33566033_[CASC5 Gene Expression Changes Correlate with Targeted Mutations in Leukemia]. | ENSMUSG00000027326 | Knl1 | 244.936974 | 2.032250727 | 1.023078 | 0.28043435 | 12.993694 | 0.0003125418146774916472452332527609542012214660644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0027899393131517249977413541728310519829392433166503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 341.4434398 | 80.1046298 | 167.6908942 | 39.3655837 | |
| ENSG00000137936 | 8412 | BCAR3 | protein_coding | O75815 | FUNCTION: Acts as an adapter protein downstream of several growth factor receptors to promote cell proliferation, migration, and redistribution of actin fibers (PubMed:24216110). Specifically involved in INS/insulin signaling pathway by mediating MAPK1/ERK2-MAPK3/ERK1 activation and DNA synthesis (PubMed:24216110). Promotes insulin-mediated membrane ruffling (By similarity). In response to vasoconstrictor peptide EDN1, involved in the activation of RAP1 downstream of PTK2B via interaction with phosphorylated BCAR1 (PubMed:19086031). Inhibits cell migration and invasion via regulation of TGFB-mediated matrix digestion, actin filament rearrangement, and inhibition of invadopodia activity (By similarity). May inhibit TGFB-SMAD signaling, via facilitating BCAR1 and SMAD2 and/or SMAD3 interaction (By similarity). Regulates EGF-induced DNA synthesis (PubMed:18722344). Required for the maintenance of ocular lens morphology and structural integrity, potentially via regulation of focal adhesion complex signaling (By similarity). Acts upstream of PTPRA to regulate the localization of BCAR1 and PTPRA to focal adhesions, via regulation of SRC-mediated phosphorylation of PTPRA (By similarity). Positively regulates integrin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of BCAR1 (By similarity). Acts as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for small GTPases RALA, RAP1A and RRAS (By similarity). However, in a contrasting study, lacks GEF activity towards RAP1 (PubMed:22081014). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:D3ZAZ5, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QZK2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18722344, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19086031, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22081014, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24216110}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cytoplasm;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain | Breast tumors are initially dependent on estrogens for growth and progression and can be inhibited by anti-estrogens such as tamoxifen. However, breast cancers progress to become anti-estrogen resistant. Breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance gene 3 was identified in the search for genes involved in the development of estrogen resistance. The gene encodes a component of intracellular signal transduction that causes estrogen-independent proliferation in human breast cancer cells. The protein contains a putative src homology 2 (SH2) domain, a hall mark of cellular tyrosine kinase signaling molecules, and is partly homologous to the cell division cycle protein CDC48. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]. | hsa:8412; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; membrane [GO:0016020]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784]; endothelin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0086100]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; lens morphogenesis in camera-type eye [GO:0002089]; positive regulation of DNA replication [GO:0045740]; positive regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045742]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0007264] | 15671247_AND-34 activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and induces anti-estrogen resistance in a SH2 and GDP exchange factor-like domain-dependent manner 17270363_BCAR3 and NSP1 are more highly expressed than SH2D3C (SHEP1) in breast cancer cells, and the expression patterns suggest differential roles for the three genes during breast cancer progression. 17427198_BCAR3 induces anti-estrogen resistance in breast tumor cell lines by altering cell-cell/cell-matrix interactions and cyclin D1 promoter activity. 17616674_the spatial and temporal regulation of BCAR3/p130(Cas) interactions within the cell is important for controlling breast cancer cell motility 18722344_BCAR3 protein, through its SH2 domain, is involved in the signaling pathways of EGF leading to cell cycle progression; BCAR3 itself is part of a mitogenic signaling pathway. 19454314_The expression of breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance 3 results in basal serine phosphorylation of Crk-Associated Substrate Protein that normally occurs during adhesion of breast cancer cells to fibronectin. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19940159_the c-Src/Cas/BCAR3 signaling axis is a prominent regulator of c-Src activity, which in turn controls cell behaviors that lead to aggressive and invasive breast tumor phenotypes 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21262352_BCAR3-p130Cas complex formation is not required for BCAR3-mediated anti-estrogen resistance, Rac activation or discohesion of epithelial breast cancer cells 22711540_BCAR3 expression may regulate Src signaling in a BCAR3-p130(cas) complex-dependent fashion by altering the ability of the Src SH3 domain to bind the p130(cas) SBD 23388341_The high expressions of Mig-7 and MMP-2 in gastric carcinoma tissues may have a synergistic promoting effect on VM formation. VM is closely associated with the invasion, metastasis and poor prognosis of gastric carcinoma. 23762409_BCAR3 promotes cell motility by regulating actin cytoskeletal and adhesion remodeling in invasive breast cancer cells. 24216110_Taken together, these results demonstrated that BCAR3 plays an important role in the signaling pathways of insulin leading to cell cycle progression and cytoskeleton reorganization, but not GLUT4 translocation. 24584939_BCAR1 and BCAR3 scaffolding proteins have roles in cell signaling and antiestrogen resistance 25499443_BCAR3 acts as a putative suppressor of breast cancer progression by inhibiting the prometastatic TGFbeta/Smad signaling pathway in invasive breast tumors. 25817040_BCAR3 is an essential interactor and mediator of HEF1-induced migration. 27050277_Inhibiting MIG-7 by RNA interference in grafted EOC cells retarded tumor growth, angiogenesis and improved host survival, and suppressing MIG-7 expression with a small molecule inhibitor D-39 identified from the mitigated EOC growth and invasion and specifically abrogated the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. 28616909_MIG7 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue is high and correlated positively with vasculogenic mimicry formation, invasion and metastasis. 29192416_MIG-7 mRNA expression may serve as an additional molecular marker of vasculogenic mimicry in ovarian malignancies. 29251318_Study provides evidence that MIG7 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissue is correlated positively with vasculogenic mimicry (VM) formation and MIG7 expression in different HCC cell lines is coincident with their VM formation, invasion and metastasis. 29750896_MIG-7 serves as an independent unfavorable prognostic indicator in osteosarcoma patients and MIG-7 is an important mediator of osteosarcoma Vascular Mimicry formation. 30563570_high expression level of BCAR3 predicted better prognosis of multiple myeloma patients. 31140421_Silencing of Mig-7 gene inhibits vasculogenic mimicry formation and invasion of U251 cells possibly by suppressing MEK/ERK signaling, suggesting the important role of Mig-7 gene in vasculogenic mimicry formation and invasion of human glioma cells 31233772_miR-126-5p negatively regulated BCAR3 expression in eutopic endometriosis, enhanced the migration and invasion of endometrial cells, and promoted the occurrence of endometriosis. 31688418_this study indicates that the expression of Mig-7 in gliomas is positively correlated with vasculogenic mimicry formation and is related to the glioma pathological grade 34169835_A Cas-BCAR3 co-regulatory circuit controls lamellipodia dynamics. 35031902_Comprehensive immunohistochemical analysis of RET, BCAR1, and BCAR3 expression in patients with Luminal A and B breast cancer subtypes. | ENSMUSG00000028121 | Bcar3 | 39.091677 | 0.345522721 | -1.533148 | 0.31099613 | 23.817451 | 0.0000010591780938037914949507046352694672464167524594813585281372070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000173894168733890113289798640128225315493182279169559478759765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 21.5721248 | 3.7893875 | 62.3521839 | 10.6077988 | |
| ENSG00000137959 | 10964 | IFI44L | protein_coding | Q53G44 | FUNCTION: Type I interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) that plays a critical role in antiviral and antibacterial activity (PubMed:34722780). During bacterial infection, promotes macrophage differentiation and facilitates inflammatory cytokine secretion (PubMed:34722780). Plays a role in the control of respiratory syncytial virus/RSV infection, reducing the ability of the virus to replicate (PubMed:32611756). Exhibits a low antiviral activity against hepatitis C virus (PubMed:21478870). Acts also as a feedback regulator of IFN responses by negatively regulating IKBKB and IKBKE kinase activities through interaction with FKBP5 (PubMed:31434731). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21478870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31434731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32611756, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34722780}. | Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome | Predicted to enable GTP binding activity. Involved in defense response to virus. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:10964; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; immune response [GO:0006955] | 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24755989_LMKB is the first protein identified to date that interacts with this portion of Ge-1. LMKB was expressed in human B and T lymphocyte cell lines; depletion of LMKB increased expression of IFI44L. 28289848_study reveals common CD46 and IFI44L SNPs associated with measles-specific humoral immunity, and highlights the importance of alternative splicing/virus cellular receptor isoform usage as a mechanism explaining inter-individual variation in immune response after live measles vaccine 29848298_Study demonstrated for the first time that IFI44L is a novel tumor suppressor to affect cancer stemness, metastasis, and drug resistance via regulating Met/Src signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma and can be serve as an important prognostic marker. 31018104_miR-628-5p promotes growth and migration of osteosarcoma by targeting IFI44L. 31409879_A qPCR expression assay of IFI44L gene differentiates viral from bacterial infections in febrile children. 32561935_Associations Between IFI44L Gene Variants and Rates of Respiratory Tract Infections During Early Childhood. 32611756_Interferon-Induced Protein 44 and Interferon-Induced Protein 44-Like Restrict Replication of Respiratory Syncytial Virus. 33159419_IFI44L expression is regulated by IRF-1 and HIV-1. 33494515_Targeted Profiling of Immunological Genes during Norovirus Replication in Human Intestinal Enteroids. 34516357_Integrated weighted gene co-expression network analysis uncovers STAT1(signal transducer and activator of transcription 1) and IFI44L (interferon-induced protein 44-like) as key genes in pulmonary arterial hypertension. 34722780_IFI44L as a Forward Regulator Enhancing Host Antituberculosis Responses. 34884921_Identified Three Interferon Induced Proteins as Novel Biomarkers of Human Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. 34903206_The prognostic and clinical significance of IFI44L aberrant downregulation in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. 35059970_Differentially methylation of IFI44L gene promoter in Iranian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. 35592687_Epigenetic Regulation of IFI44L Expression in Monocytes Affects the Functions of Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. | ENSMUSG00000039146 | Ifi44l | 50.429503 | 0.136921872 | -2.868575 | 0.29036450 | 109.640628 | 0.0000000000000000000000001174680854128631542910847113772851494018355690951262204114212973736367309762762545233272248879075050354003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000000000106697634984099334675977757129875233818354961428341246222971209784563528799594678275752812623977661132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 12.0443185 | 3.8928902 | 88.3285481 | 25.6738197 | |
| ENSG00000137965 | 10561 | IFI44 | protein_coding | Q8TCB0 | FUNCTION: This protein aggregates to form microtubular structures. {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome | Predicted to be involved in immune response. Predicted to act upstream of or within response to bacterium. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:10561; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; immune response [GO:0006955]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617]; response to virus [GO:0009615] | 16886895_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17784819_Binds and depletes intracellular GTP, abolishing extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling and resulting finally in cell cycle arrest. 18953482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22896602_The restriction of Bunyamwera virus replication mediated by interferon is an accumulated effect of at least three interferon-stimulated genes viperin, MTAP44 and PKR. 25776761_IFI44 localizes to nuclei and suppresses HIV-1 LTR promoter. 31455651_The data indicate that binding of IFI44 to FKBP5 decreased the phosphorylation of IRF-3 and IkappaBalpha mediated by IKKepsilon and IKKbeta, respectively, providing a likely explanation for the function of IFI44 in negatively modulating IFN responses. 32611756_Interferon-Induced Protein 44 and Interferon-Induced Protein 44-Like Restrict Replication of Respiratory Syncytial Virus. 36189314_IFI44 is an immune evasion biomarker for SARS-CoV-2 and Staphylococcus aureus infection in patients with RA. | ENSMUSG00000028037 | Ifi44 | 73.805777 | 0.353214422 | -1.501384 | 0.24911758 | 35.873675 | 0.0000000021053415753278213715457595656566774922069384956557769328355789184570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000529667589131035381438719861039998715313004140625707805156707763671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 36.2641467 | 7.9049791 | 102.5967192 | 21.2243990 | |
| ENSG00000138185 | 953 | ENTPD1 | protein_coding | P49961 | FUNCTION: In the nervous system, could hydrolyze ATP and other nucleotides to regulate purinergic neurotransmission. Could also be implicated in the prevention of platelet aggregation by hydrolyzing platelet-activating ADP to AMP. Hydrolyzes ATP and ADP equally well. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8955160}. | Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Calcium;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Hydrolase;Lipoprotein;Magnesium;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Nucleotide-binding;Palmitate;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is a plasma membrane protein that hydrolyzes extracellular ATP and ADP to AMP. Inhibition of this protein's activity may confer anticancer benefits. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015]. | hsa:953; | extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; GDP phosphatase activity [GO:0004382]; nucleoside diphosphate phosphatase activity [GO:0017110]; UDP phosphatase activity [GO:0045134]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; nucleoside diphosphate catabolic process [GO:0009134] | 11897808_NTPDase/E-ATPDase activity was demonstrated on cryosections of human pancreas.Significantly diminished activity of NTPDase1 in the tissues surrounding the ducts was detected 12067895_Thrombin-induced deactivation of CD39 in endothelial cells is reversed by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and preservation of ATP and ADP metabolism. 12234494_Roles of Asp54 and Asp213 in Ca2+ utilization by soluble enzymes 12482826_Depolarization causes the endothelial production of superoxide, which inhibits the activity of endothelial NTPDase-1 and enhances platelet aggregation. 12623446_Correlation was observed between ATP hydrolysis and triglycerides in patients with chronic heart disease, suggesting a relationship between ATP diphosphohydrolase and thrombogenesis. 15146241_hCD39 transgenic mice exhibit impaired platelet aggregation, prolonged bleeding times, and resistance to systemic thromboembolism 15496502_capacity of NTPDase1 to hydrolyze both nucleoside triphosphates and diphosphates. 15590415_The NTPDase1/CD39 is the dominant ecto-nucleotidase of vascular and placental trophoblastic tissues and appears to modulate the functional expression of type-2 purinergic (P2) G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). 15772061_After exercise, all subjects showed a significant reduction of CD39 expression in platelet and an increase of CD39 expression in B lymphocytes. 15890655_there is a functional link between the localization of CD39 in cholesterol-rich domains of the membrane and its role in thromboregulation 16011960_leukocyte NTPDase1 provides means of dephosphorylating ATP which enables ATP-induced platelet aggregation via conversion to ADP, but also converts ADP to AMP and adenosine. 16028070_Changes in the expression of NTPDase1 and caveolins seem to be independent of human cardiovascular disease 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16478441_CD39 associations with RanBPM have the potential to regulate NTPDase catalytic activity. This intermolecular interaction may have important implications for the regulation of extracellular nucleotide-mediated signalling. 16920697_Distinct roles for CD39 and P2-purinergic signaling in both tissue remodeling and fibrogenesis with respect to human pancreatic diseases. 17374358_Composition of the active site of wild-type CD39 appears optimized for ADPase function in the context of the transmembrane domains. 17449799_Patients with the remitting/relapsing form of multiple sclerosis have strikingly reduced numbers of CD39(+) Treg cells in the blood 17560607_Data show that host-derived CD39 is acquired by both laboratory-adapted and clinical variants of HIV-1 produced in cellular reservoirs of the virus. 18485080_the effect of overexpressed CD39/NTPDase-1 in injured aorta 18600538_Prolonged exposure to endogenous ATP related to decreased NTPDase1/CD39 activity leads to P2-purinoceptor desensitization in impotent men 18713747_E-NTPDase1 plays an important role in regulating neutrophil chemotaxis by facilitating the hydrolysis of extracellular ATP 18812468_a novel Sp1-dependent regulatory pathway for CD39 indicate the likelihood that CD39 is central to protective responses to hypoxia/ischemia 18979366_stable oxidants present in diluted aqueous cigarette smoke extract (aCSE) are responsible for platelet NTPDase inhibition induced by aCSE. 19095759_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19095759_Studies in human cell lines and in vivo mouse data support a potential role for ENTPD1 genetic variation in susceptibility to type 2 diabetes. 19450601_Isolation of functional human regulatory T cells (Treg) from the peripheral blood based on the CD39 expression. 19877008_report that the ectoenzyme CD39/NTPDase1 helps to delineate a novel population of human 'inducer' CD4+ T cells (Tind) that significantly increases the proliferation and cytokine production of responder T cells in a dose-dependent manner. 19914228_The NTPDase activity and expression were increased in lymphocytes from RRMS patients when compared with the control group. 20190036_Cystic fibrosis epithelia exhibit >50% lower NTPDase1 activity, protein, and mRNA levels than normal epithelia, whereas these parameters are threefold higher for NTPDase3. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20487644_CD39(+);Fxop3(+);Treg subset may play an essential role in immune regulation of Treg, and CD39 can be used as a surface marker to identify the functional Treg cells. 20498355_Increased expression of CD39 is restricted to the CD4-expressing T cell population from the inflamed joint in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 20638239_reduced expression by CD8-positive Treg populations from primary biliary cirrhosis patients 20936356_CD39 is expressed at high levels in clinical inflammatory bowel disease tissues. 20977632_We conclude that the ectonucleotidase CD39 is a useful and dynamic lymphocytes surface marker that can be used to identify different peripheral blood T cell-populations to allow tracking of these in health and disease, as in renal allograft rejection. 21492831_In type 2 diabetes (T2D) patients, the percentages of CD39+ cells and CD39+CD19+ cells were significantly associated with HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose levels. Enhanced CD39 enzyme activity and low serum levels of IL-17 were detected in T2D patients. 21638125_the ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73 and ADORA2A appear as possible targets for novel treatments in ovarian cancer 21663645_CD39(+)Tregs inhibit generation and differentiation of Th17 cells via a latency-associated peptide-dependent mechanism in malignant pleural effusion. 21670316_Extracellular nucleotides, whose levels are tightly controlled by endogenously expressed NTPDase1, induce interleukin (IL)-8 production by human neutrophils. 21677139_Exosomes from diverse cancer cell types exhibit potent ATP and 5'AMP phosphohydrolytic activity, partly attributed to exosomally expressed CD39 and CD73, which contribute to extracellular adenosine production. 21763644_Data indicate that CD39-expressing T(regs) comprised 37+/-13% of the T(reg) population in healthy controls and 36+/-21% in lupus subjects. 21939667_transgenic ENTPDase-1 expression preferentially conveys myocardial protection from ischemic injury via adenosine A(2B) receptor engagement 22184407_Data show that the alterations in the CD39/CD73 adenosinergic machinery and loss of function in ADA-deficient Tregs provide insights into a predisposition to autoimmunity and the underlying mechanisms causing defective peripheral tolerance in ADA-SCID. 22349724_CD39(+) may also serve as a future target for the development of novel therapies with immune-modulating antitumor agents in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 22489829_These findings not only suggest that CD39 Treg cells may be involved in hepatitis B virus disease progression but also identify CD39 Tregs as a dynamic immune regulatory cell population that may represent a new target of immunomodulatory therapeutic interventions. 22613024_Ectonucleotide triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-1 (CD39) mediates resistance to occlusive arterial thrombus formation after vascular injury. 22622462_heightened nucleotide scavenging by increased levels of CD39 altered the release of endogenous argipressin in response to dehydration 22637533_identified hitherto unrecognized soluble forms of AK1 and NTPDase1/CD39 that contribute in the active cycling between the principal platelet-recruiting agent ADP and other circulating nucleotides 22684996_hCD39 expressed by circulating leukocytes and intrinsic renal cells limits innate AN injury. 22792409_We demonstrate for the first time increased CD39 expression and function on circulating microparticles in patients with IPAH. 22802412_a chronic increase of epithelial CD39 expression and activity promotes airway inflammation in response to bacterial challenge 22846899_The expression of ENTPD1 and ecto-adenosine deaminase in lymphocytes of Chagase disease patients are reported. 23359087_CD39 counteraction inhibits the suppression activity of CD8+ Treg (both from peripheral blood and tumor microenvironment) suggesting that CD39-mediated inhibition constitutes a prevalent hallmark of their function 23606272_These data identify CD39 as a novel marker of human regulatory CD8(+) T cells and indicate that CD39 is functionally involved in suppression by CD8(+) Treg cells 23737488_The data indicates that glioma-derived CD73 contributes to local adenosine-mediated immunosuppression in synergy with CD39 from infiltrating CD4(+)CD39(+) T lymphocytes in human malignant gliomas. 23941770_The present findings suggest the existence of an endogenous anti-tissue destructive mechanism in gingival tissue via the CD39-adenosinergic axis. 24043462_Our data suggests that human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells can effectively suppress immune responses of the Th17 cells via the CD39-CD73-mediated adenosine-producing pathway 24684231_our data indicate that T-cell CD39 expression may identify subsets of patients with B-CLL with an unfavorable clinical outcome. 24707115_ecto-nucleotidases CD39 and CD73 are expressed in human endometrial tumors 24752698_data show that Ag-specific CD4(+) CD25(+) CD134(+) CD39(+) T cells are highly enriched for Treg cells, form a large component of recall responses and maintain a Treg-cell-like phenotype upon in vitro expansion. 24970562_Results show the interplay between promoter SNPs of CD39 and FAM134B results in an intercellular epistasis which influences the risk of a complex inflammatory disease. 24990235_FOXP3(+) CD39(+) Treg cells are enriched at the site of inflammation, do not produce proinflammatory cytokines, and are good suppressors of many effector T-cell functions including production of IFN-gamma, TNF, and IL-17F but do not limit IL-17A secretion 25034034_Data show that Rubus leave extracts significantly increased CD39 antigen NTPDase 1 ecto-ATP diphosphohydrolase 1 (CD39/NTPDase-1) expressions and decreased ATPDase activities. 25172498_CD39 and CD161 modulate human Th17 responses in CD through alterations in purinergic nucleotide-mediated responses and ASM catalytic bioactivity, respectively. 25318477_by regulating ATP availability at the cardiac mast cell surface surface, CD39 modulates local renin release and thus, renin-angiotensin system activation, ultimately exerting a cardioprotective effect 25407137_Blackcurrant leaf extract increases endothelial cell NOS and CD39 levels in a concentration dependent manner. 25421756_Low expression of CD39(+) /CD45RA(+) on regulatory T cells (Treg ) cells in type 1 diabetic children in contrast to high expression of CD101(+) /CD129(+) on Treg cells in children with coeliac disease. 25640206_this study demonstrates that the expression of CD39 in Tregs is primarily genetically driven, and this may determine interindividual differences in the control of inflammatory responses. 25820525_apelin, a known regulator of pulmonary vascular homeostasis, can potentiate the activity of CD39 both in vitro and in vivo 25877509_The Na-K-2Cl cotransporter was downregulated by high-sodium diet in wild-type mice, but it increased in transgenic mice overexpressing human CD39 26018728_Despite the increased level of NTPDase1 and NTPDase3 mRNA expression in chondrogenically induced MSCs, their activity toward ATP remains quite low. 26059452_We suggest modulation of human Th17 responsiveness by CD39 and CD161 and describe novel molecular mechanisms integrating elements of both extracellular nucleotide and sphingolipid homeostasis--{REVIEW} 26113408_the current study revealed that malignant epithelial cells of human rectal adenocarcinoma strongly express CD39 that may play a potential role in the tumor invasion and metastasis. 26121751_these data establish CD39 as a regionalized regulator of atherogenesis that is driven by shear stress. 26226423_role of CD73 and CD39 ectonucleotidases in T cell differentiation 26307000_The altered function and expression of P2X7 and ART1 in the human CD39+ Treg or CD39- Treg cells could participate in the resistance against cell death induced by ATP or NAD. 26386144_the expression of CD39 on Treg cells and also in CD4(+)IL-17(+) cells from T2D patients is related to hyperglycemia as well as to overweight and obesity and therefore may participate as a modulator of the effector capacity of Th17 cells. 26541524_Pulmonary CD39 expression and activity are increased in COPD. Following acute cigarette smoke exposure CD39 was upregulated in BALF cells in smokers. 26549640_Findings provide insights into Tc1-mediated IFNgamma responses and ROS generation and link these pathways to CD39/adenosine-mediated effects in immunological disease. 26832412_Increased inducibility of CD39 after activation may contribute to the impaired vaccine response with age. 27044834_This study aimed to investigate the activities of purinergic system ecto-enzymes present on the platelet surface as well as CD39 and CD73 expressions on platelets of sickle cell anemia treated patients. 27210814_Data show that Th17(CD39+) cells are markedly diminished and fail to generate AMP/adenosine, thereby limiting control of both target cell proliferation and IL-17 production in juvenile autoimmune liver disease (AILD). 27346340_Phosphoantigens (pAgs) induced expression of the ecto-ATPase CD39, which, however, not only hydrolyzed ATP but also abrogated the gammadelta T cell receptor (TCR) agonistic activity of self and microbial pAgs. 27417582_Ablation of CD73 minimally effects in vivo thrombosis, but increased CD39 expression on hematopoietic-derived cells, especially monocytes, attenuates in vivo arterial thrombosis. 27430193_this study shows that T-cell expression of CD39 was higher in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients than stable COPD patients or healthy controls 27830476_The peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from the transgenic pigs were more resistant to lysis by pooled complement-preserved normal human serum than that from wild type (WT) pig. Accordingly, GGTA1 mutated piglets expressing hCD39 will provide a new organ source for xenotransplantation research 27899277_concluded that CD39 and CD73 are molecular targets for the development of drugs for ALF patients care 27906627_Oxidized low density lipoproteins modulate CD39 and CD73 activity in the endothelium. 28198766_Transgenic expression of human CD39 is associated with increased renal fibrosis after ischemia in mice. 28302652_These studies showed that the G allele of rs3176891 marks a haplotype associated with increased clotting and platelet aggregation attributable to a promoter variant associated with increased transcription, expression, and activity of NTPDase1. 28377485_CD39 overexpression protects against cerebral ischemia in a transgenic mouse model. 28389406_this paper shows that simultaneous overexpression of human E5NT and ENTPD1 protects porcine endothelial cells against H2O2-induced oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in vitro 28509416_CD39, CD43, CD81, and CD95 expressions appear to be helpful to distinguish CD10(+) BCL. 28916770_While in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic auto-antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) patients (n = 29) CD26 was increased on CD4(+) lymphocytes, CD39 and CD73 were generally reduced on patients' T-cells. 29103803_this paper shows that CD39 activity is protective in a mouse model of antiphospholipid antibody-induced miscarriages 29172836_expression in primary lesions and metastatic lymph nodes seems to identify patients at high risk in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck 29426578_this study shows that TGF-beta signaling defect is linked to low CD39 expression on regulatory T cells and methotrexate resistance in rheumatoid arthritis 29524036_monocyte-derived macrophages from ankylosing spondylitis patients expressed reduced levels of CD39 mRNA compared to those from healthy controls 29742141_ur results demonstrate that CD39 is upregulated on conventional CD4+ and CD8+ T cells at sites of acute infection and inflammation, and that CD39 dampens responses to bacterial infection. 29807526_CD39 expression and activity is attenuated in lung tissue of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. 30006565_Co-expression of CD39 and CD103 identifies tumor-reactive CD8 T cells in human solid tumors. 30056298_Changes in the local expression and activity of CD39 and CD73 in calcified valves suggest their potential role in calcific aortic valve disease. 30155690_We found an altered Th17/Treg balance in patients with complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) as a consequence of decreased pro-inflammatory Th17 cells. We suggest that the decrease in Th17 cells is regulated by an increase of CD39+ Tregs and a decreased expression of miR-206 in CD4+ cells. The alteration of CD39 and miR-206 expression may be a possible mechanism to control the inflammatory process in CRPS. 30318734_Low CD39 expression is associated with defective suppressive function of regulatory T cells in type 1 diabetes. 30336122_CD39 expression on CD4+ Tcells and del 6q act as prognostic markers in CLL. Blocking or inhibition of CD39 may be a target for new immune therapy for CLL. 30409763_The ENTPD1 and ecto-adenosine deaminase (E-ADA )perform key functions in the modulation of the immune and inflammatory response in Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). 30663116_Physical fitness modulates the expression of CD39 and CD73 on CD4(+) CD25(-) and CD4(+) CD25(+) T cells following high intensity interval exercise. 31428081_Mass Cytometry Discovers Two Discrete Subsets of CD39(-)Treg Which Discriminate MGUS From Multiple Myeloma. 31652269_Monitoring and characterizing soluble and membrane-bound ectonucleotidases CD73 and CD39. 31868071_High-Throughput Screening Assays for Cancer Immunotherapy Targets: Ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73. 32181525_A single-nucleotide polymorphism in the human ENTPD1 gene encoding CD39 is associated with worsened graft-versus-host disease in a humanized mouse model. 32248630_Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1 and 5'-nucleotidase ecto gene polymorphisms and acute cellular rejection after liver transplantation. 32304668_CD39 Produced from Human GMSCs Regulates the Balance of Osteoclasts and Osteoblasts through the Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway in Osteoporosis. 32319705_The TGF-b/SOX4 axis and ROS-driven autophagy co-mediate CD39 expression in regulatory T-cells. 32446352_Human platelets express functional ectonucleotidases that restrict platelet activation signaling. 32452837_Ecto-NTPDase CD39 is a negative checkpoint that inhibits follicular helper cell generation. 32483858_Genetically driven CD39 expression shapes human tumor-infiltrating CD8(+) T-cell functions. 32707842_Defining the CD39/CD73 Axis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The CD73(-) Phenotype Identifies Polyfunctional Cytotoxic Lymphocytes. 32759363_CD39 Identifies the CD4(+) Tumor-Specific T-cell Population in Human Cancer. 33208731_Endogenous antisense RNA curbs CD39 expression in Crohn's disease. 33675538_Expression quantitative trait loci of genes predicting outcome are associated with survival of multiple myeloma patients. 33771085_Description of clinical features and genetic analysis of one ultra-rare (SPG64) and two common forms (SPG5A and SPG15) of hereditary spastic paraplegia families. 33848530_ENTPD1 (CD39) Expression Inhibits UVR-Induced DNA Damage Repair through Purinergic Signaling and Is Associated with Metastasis in Human Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 34265363_Regulation of immune responses through CD39 and CD73 in cancer: Novel checkpoints. 34360833_CD39 Regulation and Functions in T Cells. 34465393_Favorable function of Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1 high expression in thyroid carcinoma. 34741235_Is the regulation by miRNAs of NTPDase1 and ecto-5'-nucleotidase genes involved with the different profiles of breast cancer subtypes? 35032133_Assessment of CD39 expression in regulatory T-cell subsets by disease severity in adult and juvenile COVID-19 cases. 35173744_Role of CD39 in COVID-19 Severity: Dysregulation of Purinergic Signaling and Thromboinflammation. 35199627_Variability in CD39 and CD73 protein levels in uveal melanoma patients. 35326415_Tissue-Specific Expression of TIGIT, PD-1, TIM-3, and CD39 by gammadelta T Cells in Ovarian Cancer. 35471564_Biallelic Variants in the Ectonucleotidase ENTPD1 Cause a Complex Neurodevelopmental Disorder with Intellectual Disability, Distinct White Matter Abnormalities, and Spastic Paraplegia. 35533722_Genetically Driven CD39 Expression Affects Sezary Cell Viability and IL-2 Production and Detects Two Patient Subsets with Distinct Prognosis. 35738329_Exhaustion of CD39-Expressing CD8(+) T Cells in Crohn's Disease Is Linked to Clinical Outcome. 36048381_Evaluation of CD39, CD73, HIF-1alpha, and their related miRNAs expression in decidua of preeclampsia cases compared to healthy pregnant women. 36240436_Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-1 (CD39) impacts TGF-beta1 responses: insights into cardiac fibrosis and function following myocardial infarction. | ENSMUSG00000048120 | Entpd1 | 211.390165 | 0.391160596 | -1.354167 | 0.31648720 | 17.693165 | 0.0000259557522294374255864436024099362043671135324984788894653320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0003140735832053379722461627920893079135566949844360351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 141.0066335 | 63.3475350 | 358.8933909 | 160.8056853 | |
| ENSG00000138378 | 6775 | STAT4 | protein_coding | Q14765 | FUNCTION: Transcriptional regulator mainly expressed in hematopoietic cells that plays a critical role in cellular growth, differentiation and immune response (PubMed:8943379, PubMed:10961885). Plays a key role in the differentiation of T-helper 1 cells and the production of interferon-gamma (PubMed:12213961, PubMed:35614130). Participates also in multiple neutrophil functions including chemotaxis and production of the neutrophil extracellular traps (By similarity). After IL12 binding to its receptor IL12RB2, STAT4 interacts with the intracellular domain of IL12RB2 and becomes tyrosine phosphorylated (PubMed:7638186, PubMed:10415122). Phosphorylated STAT4 then homodimerizes and migrates to the nucleus where it can recognize STAT target sequences present in IL12 responsive genes. Although IL12 appears to be the predominant activating signal, STAT4 can also be phosphorylated and activated in response to IFN-gamma stimulation via JAK1 and TYK2 and in response to different interleukins including IL23, IL2 and IL35 (PubMed:11114383,PubMed:34508746). Transcription activation of IFN-gamma gene is mediated by interaction with JUN that forms a complex that efficiently interacts with the AP-1-related sequence of the IFN-gamma promoter (By similarity). In response to IFN-alpha/beta signaling, acts as a transcriptional repressor and suppresses IL5 and IL13 mRNA expression during response to T-cell receptor (TCR) activation (PubMed:26990433). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P42228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10415122, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10961885, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11114383, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12213961, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26990433, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34508746, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35614130, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7638186, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8943379}. | Acetylation;Activator;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;Systemic lupus erythematosus;Transcription;Transcription regulation | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the STAT family of transcription factors. In response to cytokines and growth factors, STAT family members are phosphorylated by the receptor associated kinases, and then form homo- or heterodimers that translocate to the cell nucleus where they act as transcription activators. This protein is essential for mediating responses to IL12 in lymphocytes, and regulating the differentiation of T helper cells. Mutations in this gene may be associated with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode the same protein. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. | hsa:6775; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; defense response [GO:0006952]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0007259]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to peptide hormone [GO:0043434] | 12372421_STAT4 regulates IL-12-induced expression of the perforin gene in NK cells 12496413_Active STAT4, essential for IL-12-mediated Th1 differentiation, is readily detectable in biopsies from Peyer's patches and ileal mucosa, and STAT4-DNA binding activity is demonstrable by electrophoretic mobility-shift assay of lamina propria lymphocytes. 12615922_STAT4 is constitutively activated in Crohn's patients but not in healthy volunteers 12716907_STAT4 is repressed by PIASx 12805384_requires the N-terminal domain for efficient phosphorylation 15087447_STAT4 signaling in human vascular endothelial cells is activated by interferon alpha but not by IL-12 15637551_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15744455_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16081070_The STAT4 is transactivated by Ikaros (Ik) and Ik binding elements were revealed in its promoter. 16301617_identify and characterize the transcriptional regulatory elements in the promoter region of the human STAT4 gene. 17046972_these results indicate that STAT-4 can be finely tuned along with DC maturation through NF-kappaB activation and that its induction may be involved in preparing the DC to be receptive to the cytokine environment present in lymphoid organs. 17095088_IFNAR2 cytoplasmic domain serves to link STAT4 to the IFNAR as a pre-assembled complex that facilitates cytokine-driven STAT4 activation. 17532201_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17532201_STAT-4 T90089C polymorphism might be the genetic factor for the risk of asthma in the Chinese population 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17804842_A haplotype of STAT4 is associated with increased risk for both rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, suggesting a shared pathway for these illnesses. 17804842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17932559_A haplotype of the STAT4 gene shows consistent association with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility across Whites and Asians. 18204446_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18273036_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18273036_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the STAT4 gene are associated with primary Sjogren's syndrome. 18432273_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18432273_STAT4 but not TRAF1/C5 variants influence the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus in Colombians. 18434327_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18434327_STAT4 and the TRAF1/C5 loci are associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. 18516230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18516230_STAT4 contributes to the phenotypic heterogeneity of systemic lupus erythematosus, predisposing specifically to more severe disease. 18576330_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18576330_We conclude that STAT4 is associated with RA and SLE in the Japanese. 18576336_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18576336_Our findings indicate an association between the STAT4 polymorphism rs7574865 and RA in 3 different populations, from Spain, Sweden, and The Netherlands, thereby confirming previous data. 18579578_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18579578_The SNP rs7582694 in STAT4 displayed a increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus with two independent risk alleles of the IRF5. 18625278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18625278_study concludes that mutant alleles or genotypes of both TRAF1 and STAT4 polymorphisms are associated with the development of Rheumatoid arthritis in our population. 18703106_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18703106_in a genetically homogeneous population, the STAT4 rs7574865 G/T polymorphism, which has been shown to be associated with several autoimmune diseases, is associated with susceptibility to type 1 diabetes (T1D) 18759272_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18759272_The association of STAT4 polymorphism rs7574865 with RA was validated in patients of Spanish origin and described for the first time in both clinical forms of inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and type 1 diabetes mellitus. 18802110_T helper (Th) type 1 cells expressing transgenic STAT4 beta (an isoform lacking the C-terminal transactivation domain) secrete significantly more tumor necrosis factor-alpha upon T cell receptor stimulation than transgenic STAT4alpha-expressing Th1 cells. 18803832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18803832_The same STAT4 risk allele is associated with SLE in Caucasian and Japanese populations. 19019891_Data confirm STAT4 as a susceptibility gene for systemic lupus erythematosus and suggest the presence of at least two functional variants affecting levels of STAT4 and also indicate that the genes STAT4 and IRF5 act additively to increase the risk for SLE 19019891_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19092842_Additive effects of the major risk alleles of IRF5 and STAT4 in primary Sjogren's syndrome are reported. 19092842_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19109131_The risk allele of STAT4 is associated with increased sensitivity to IFN-alpha signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus. 19110536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19120275_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19120275_The age at diagnosis is lowest in the patients carrying the homozygotes of a minor allele, middle in the heterozygotes, and highest in the homozygotes of a major allele, suggesting the dosage effects of risk alleles on the age of onset of disease. 19225526_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19225526_Our data confirmed association of STAT4 (rs7574865, odds ratio (OR) =1.71, P=3.55 x 10(-23)) and BLK (rs13277113, OR=0.77, P=1.34 x 10(-5)) with SLE 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19282076_Genetic polymorphisms in the Jak-Stat signaling pathway are associated with an increased risk of new cardiovascular events in incident dialysis patients. 19282076_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19286670_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19286670_STAT4 influences the genetic predisposition to systemic sclerosis phenotype. 19332627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19332627_Our results do not support a major role of the STAT4 rs7574865 gene polymorphism in susceptibility to or clinical manifestations of giant cell arteritis. 19333953_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19333953_STAT4 is likely to be a crucial component in systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis in multiple racial groups 19359411_STAT4 is required for optimal human Th1 lineage development 19362457_Focusing on how STAT4 work in concert with other transcription factors will hopefully provide a better mechanistic understanding of the pathogenesis of various autoimmune diseases. 19371230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19371230_STAT4 is not associated with type 2 diabetes in the genetically homogeneous population of Crete. 19404967_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19404967_Our results replicate and firmly establish the association of STAT4 and CTLA4 with RA and provide highly suggestive evidence for IL2/IL21 loci as a risk factor for RA. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19479340_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19479340_The results of this meta-analysis demonstrated that STAT4 rs7574865 single nucleotide polymorphism is significantly associated with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. 19500629_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19500629_single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with psoriasis in population of Crete, Greece 19565500_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19565500_There are associations between juvenile idiopathic arthritis and variants in the TNFAIP3, STAT4, and C12orf30 regions that have previously shown associations with other autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. 19588142_Meta-analysis confirms that the STAT4 rs7574865 polymorphism is associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in different ethnic groups. 19588142_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19605742_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19605742_results show, for the first time, the positive correlation between the T allele of STAT4 rs7574865 and antiphospholipid syndrome. 19605749_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19605749_STAT4 appears to be a common susceptibility gene to Systemic Sclerosis in Caucasian and Asian populations. 19644876_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19644876_STAT4 and BLK displayed a strong genetic association with primary antiphospholipid syndrome. 19644887_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19644887_Our results establish STAT4 rs7574865 as a new systemic sclerosis genetic susceptibility factor. 19674979_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19684152_A lack of significant associations of STAT4 with smoking in systemic lupus erythematosus was observed. 19684152_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19710469_STAT4 binding to target genes, while critical, is not the only determinant for STAT4-dependent gene programming during Th1 differentiation 19717398_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19717398_The main association signal for STAT4 with systemic lupus erythematosus previously reported in Caucasians is the same in the Finnish population and this is the first study that confirms the association of STAT4 with SLE in a family cohort. 19737838_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19741008_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19762360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19762360_There was no association with ischemic heart disease or venous thromboembolism and the presence of two or more antiphospholipid antibodies was associated with the risk allele (OR(c)=1.6, 95% CI 1.2 to 2.0). 19838193_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19877059_BANK1 is a new systemic sclerosis genetic susceptibility factor. BANK1, IRF5, and STAT4 act with additive effects. 19877059_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19950257_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19950257_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in TBX21 and STAT4 contribute uniquely and interactively to SSc susceptibility. 20045654_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20045654_Polymorphisms of STAT1 and STAT4 are associated with increased susceptibility, pathological advancement, and development of proteinuria in childhood IgA nephropathy. 20049410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20131273_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20153791_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20153791_Our data suggest that the rs7574865 STAT4 single nucleotide polymorphism is a genetic susceptibility variant for ulcerative colitis but not Crohn's disease in the Spanish population. 20169389_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20169389_results support STAT4 rs7574865 polymorphism as a susceptibility factor for systemic lupus erythematosus in populations of European and Asian origin. results also suggest that STAT4 rs7601754 polymorphism might be associated with SLE risk. 20176035_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20176035_Our data demonstrated that the STAT4 genetic variants could predispose an individual to inflammatory bowl disease and its extra-intestinal ailments in Koreans 20219786_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20233754_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237121_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237121_the association of rs7574865 with susceptibility to RA has been replicated in all populations studied, including those of Asian and European descent but this finding was not reproduced in African Americans. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20353580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20360187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20360187_These data reinforce the influence of STAT4 gene on primary Sjogren's Syndrome and as a general autoimmune gene. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20383147_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20438790_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438790_The STAT4 TT genotype of rs7574865 may be a susceptible factor for Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome in a Chinese Han population, and the GG genotype of this SNP may confer susceptibility in male Behcet's disease patients. 20439292_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20444755_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20453440_studies found that IRF5, STAT4 and BLK are associated not only with systemic lupus erythematosus, but also rheumatoid arthritis and systemic sclerosis [review] 20454450_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20454450_STAT4 SNP rs7574865 is a disease-modifying gene variant in colonic CD. 20479942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20498205_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20535138_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20535138_STAT4 is a confirmed genetic risk factor for Sjogren's syndrome and could be involved in type 1 interferon pathway signaling. 20584675_HLA-DR4, PAD4 and STAT4 are overexpressed in rheumatoid arthritis and may be involved in the pathogenesis of RA. 20716621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20797713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20822712_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20822712_Our results do not show that the PTPN22, STAT4 and TRAF1/C5 gene polymorphisms may confer a direct risk of cardiovascular disease disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. 20848568_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20861858_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20881011_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20962850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21163111_The TT genotype and T allele in STAT4 rs7574869 are susceptibility factors for systemic lupus erythematosus, especially for male SLE patients. 21167895_Study found a strong association of SNP rs7574865 of STAT4 with the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus in a northern Han Chinese population 21237270_gene polymorphism is assiciated with acute renal allograft rejection in the Chinese population 21258797_Demonstrate that STAT4 rs7582694 SNP was significantly associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in female Chinese population. 21418779_results support involvement of the STAT4 gene in the genetic susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis but not to autoimmune thyroid diseases in the Tunisian population 21543583_prolonged IL-12 stimulation of NK cells specifically decreases the level of activated STAT4 protein 21683716_These findings strongly suggest that STAT4 genetic polymorphisms are associated with rheumatoid arthritis in Northwestern Chinese Han population 21740896_data provide a new information that the STAT4 (rs3024912 and rs3024908) polymorphisms may be the underlying cause of membranous glomerulonephritis, and these polymorphisms revealed by this study warrant further investigation 22069275_according to the age of onset, the minor alleles of all four single-nucleotide polymorphisms of STAT4 and the same haplotypes showed significant association with the susceptibility of T1D in the early-onset subgroup 22077060_Data indicate that STAT4 might be the molecular target of miR-132, miR-212, and miR-200a. 22133489_Results indicate that single nucleotide polymorphisms in TBX21 and STAT4 might contribute to susceptibility to aplastic anemia (AA) in the Chinese population. 22402141_This is the first study to show a positive association between a STAT4 polymorphism and polymyositis/dermatomyositis 22483685_Our results indicate that the interaction of specific IL17A, interleukin 23 receptor, and STAT4 modulate susceptibility to intestinal Behcet's disease in the Korean population 22569826_These data demonstrated that the DNA methylation status of STAT4 is associated with genetic polymorphisms, providing insights into the interactions between genetic and epigenetic aberrances in STAT4 and inflammatory bowel diseases. 22714917_This meta-analysis demonstrates that the STAT4 rs7574865 T allele confers susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. 22718836_STAT4 regulates antiviral gamma interferon responses and recurrent disease during herpes simplex virus 2 infection. 22729903_Our studies confirmed an association of the STAT4 C (rs7582694) variant with the development of SLE and occurrence of some clinical manifestations of the disease. 22730365_By participating in transcription complex with other co-factors, IRF5 and STAT4 harbour the potential of regulating a large number of target genes, which may contribute to their strong association with systemic lupus erythematosus 22753649_The findings suggest that variants in the STAT4 gene may contribute differentially to susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in seropositive and in seronegative patients. 22937072_patients with early arthritis who are homozygous for the T allele of rs7574865 in STAT4 may develop a more severe form of the disease with increased disease activity and disability. 23001997_STAT4 is a novel locus underlying Behcet's disease in Han Chinese. 23064011_Investigation into the signaling mechanism suggested that phosphorylation of STAT-4 in response to IL-12 was sustained for a longer duration in aged CD4+ T cells as compared to CD4+ T cells from young subjects 23202532_STAT-4-T-allele is identified as fibrogenic factor and seems to have a negative impact on HCV-induced fibrosis development 23242368_Genetic variants in STAT4 and HLA-DQ genes confer risk of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. 23295549_Studies indicate that genetic single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) rs7574865 in STAT4 gene might be associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) susceptibility. 23360093_the STAT4 gene may play an important role in facilitating susceptibility to Type 1 diabetes in this Han Chinese population. 23628400_STAT4 polymorphisms are associated with autoimmune diseases which are characterized by a systemic pathology and anti-dsDNA antibody. 23727609_STAT4 rs7574865 G/T polymorphism was associated with the risk of RA. 23748017_Studied HBV patients of chronic hepatitis B carriers, liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma and found the STAT4 variant (rs7574865) was marginally associated with HCC susceptibility in CHB carriers in allelic and recessive genetic models. 23755762_STAT4 SNPs may play an important role in genetic susceptibility to systemic sclerosis in a Chinese population. 23773642_STAT4 rs7574865 is significantly associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in northern Chinese Han subpopulations. 23912645_STAT4 rs7574865 is associated with Systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility in the Iranian population and this single nucleotide polymorphism might be a factor in the pathogenesis of Systemic lupus erythematosus. 23990947_STAT4 SNP rs7574865 is a disease-susceptible gene variant in type-1 autoimmune hepatitis in Japan 24014567_A redundant interaction between IRF5 and STAT4 polymorphisms was found in susceptibility to the type I interferon pathway-associated rheumatic autoimmune diseases, systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. 24312163_No evidence of association between common autoimmunity STAT4 and IL23R risk polymorphisms and non-anterior uveitis. 24321062_STAT4 and STAT6 involve in the regulation of Th1/Th2 cell 24386384_genetic variations in STAT4 predispose to lupus nephritis and a worse outcome with severe renal insufficiency. 24610875_The G allele of rs897200 was associated with lower STAT4 expression. 24614117_Significant association with alleles of two STAT4 markers and nominal association of Autoimmune Addison's disease with alleles at GATA3, is reported. 24632671_The observations suggested that C8orf13-BLK, in combination with STAT4, plays a pivotal role in creating genetic susceptibility to polymyositis/dermatomyositis in Japanese individuals. 24648611_STAT4 is involved in primary biliary cirrhosis susceptibility and may play a role in anti-nuclear antibody status in the Japanese population. 24697319_The gene interactions of the rs7574865 SNP with SNPS in IRF5, ETS1 and IKZF1 in Han Chinese SLE patients were defined. The T allele is a risk factor. 24751105_Review/Meta-analysis: STAT4 rs7574865 polymorphism confers susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in major ethnic groups. 24844303_STAT4 plays a crucial role in the function of innate and adaptive immune cells; dysregulated expression and aberrant activation of STAT4 is observed in many human autoimmune conditions. 24979672_Rheumatoid arthritis cases showed a significantly higher frequency of the STAT4 T allele carriage (GT+TT genotypes) compared to controls. 25019342_STAT4 rs7574865/rs10181656 polymorphisms increase the risk of autoimmune thyroid diseases in a Chinese population. 25041342_STAT4 rs7574865 seems to be Tibetan specific in hepatitis B virus natural clearance. 25178516_STAT4 rs7574865 polymorphism may be associated with significantly reduced risk of HBV-induced HCC in Asian 25179669_indicates that the 4 rs7574865 G/T polymorphism was significantly associated with a decreased rheumatoid arthritis like this risk in an Asian population 25351936_we can conclude that STAT4-rs7574865 polymorphism is clearly associated with the risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in the Western Algerian population 25365208_STAT4 rs7574865 seemed not to correlate with hepatitis B virus infection susceptibility or natural clearance; its role in hepatocellular carcinoma development seemed ambiguous 25369137_Evidence of a higher risk to develop pericarditis with STAT4 genotypes, and an association between HCP5 rs3099844 and anti-Ro/SSA antibodies in Italian systemic lupus erythematosus patients. 25486484_Loss of STAT4 expression and associated switch to Th2 phenotype during Mycosis Fungoides progression may be driven via aberrant histone acetylation and/or upregulation of oncogenic miR-155 microRNA. 25665738_This work reported the association of 14q32.11 (EFCAB11) with Hepatocellular carcinoma in Chinese Han population and revealed the genetic interaction between STAT4 (2q32.2-q32.3) and EFCAB11 (14q32.11) in Hepatocellular carcinoma. 25771902_that STAT1, JAK2, and NFkappaB, together with STAT4, contribute to the development of cell-mediated immunity 25781893_STAT4 rs7574865 G/T and PTPN22 rs2488457 G/C polymorphisms as susceptibility factors for JIA 25829184_STAT4 minor allele may be associated with the spontaneous clearance of HBV, whereas the major allele may be associated with the progress of the HBV-related liver disease. 25852285_STAT4 may inhibit HCC development by modulating HCC cell proliferation. 25864744_Increased expression of STAT4 is positively correlated with the depth of invasion in colorectal cancer patients. 25913043_our replication study showed that the rs7574865 in STAT4 and rs9275319 in HLA-DQ were not associated with CHB-related HCC in a Korean population. 25963842_gene polymorphisms along with Ptpn22 polymorphism confers susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in all major ethnic groups. [meta-analysis] 26066297_There is a significant association between STAT4 rs7574865 polymorphism and IBD susceptibility in overall population. 26097239_CCR1, KLRC4, IL12A-AS1, STAT4, and ERAP1 are bona fide susceptibility genes for Behcet's disease. 26538132_Five SNPs (rs7574865 in STAT4, rs9267673 near C2, rs2647073 and rs3997872 near HLA-DRB1 and rs9275319 near HLA-DQ), were found to be significantly associated with the risk of HBV-related LC. 26569609_the presence of the rs7574865 T allele enhances STAT4 mRNA transcription and protein expression 26704347_STAT4 protein genetic variation is a prognostic factor predicting the treatment with interferon-alpha therapy in chronic hepatitis B. 26712637_The results demonstrated that STAT4 rs7574865 and IRF5 rs2004640G/T substitution are associated with a susceptibility to systemic sclerosis. 26745093_SNP rs7574865 in STAT4 might contribute to progression to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 26765219_IL13 AA of rs20541 and STAT4 TT of rs925847 are potential genomic biomarkers for predicting lower pulmonary function. The administration of high-dose ICSs to asthmatic patients with genetic variants of IL13 AA may inhibit the advancement of airway remodelling. The genetic variants of STAT4 TT did not respond to high-dose ICSs. 26782418_Our findings indicate that although STAT4 and IFIH1 SNPs are not associated with T1D in a Brazilian population, they might play a role in susceptibility to T1D on a larger worldwide scale 26990433_This is the first demonstration of STAT4 acting as a transcriptional repressor in response to IFN-alpha/beta signaling and highlights the unique activity of this cytokine to acutely block the expression of an inflammatory cytokine in human T cells. 27178308_STAT4 rs7574865G/T polymorphism is associated with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus in Mexican women 27234231_STAT4 rs7574865 polymorphism has a role in rheumatoid arthritis and disease activity, but not in anti-CCP antibody levels in a Mexican population 27235632_Our results for the first time showed a significant association between STAT4 rs7582694 alleles and genotypes and susceptibility to endometriosis in a population. 27342690_A higher risk to develop RA was observed for rs7574865 in the STAT-4 gene, while the rs1800872 in the IL-10 gene showed a protective effect. 27394003_this study shows that STAT4 gene polymorphisms are associated with ankylosing spondylitis in Southwest China 27444301_findings demonstrate that variants in STAT4 play a critical role in HBV infection and clearance in the Chinese Han population. 27494881_STAT4 is a novel transcriptional regulator of p66Shc in normal and chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells 27960128_this study shows that STAT4 single nucleotide polymorphism affects clinical outcomes of pediatric acute leukemia patients after hematopoietic stem cell transplant 28107378_reported that SNPs in STAT4, PTPN2, PSORS1C1, and TRAF3IP2 are associated with response to TNF-i treatment in RA patients; however, these findings should be validated in a larger population 28114283_Results found that activated STAT4 was overexpressed in epithelial cells of ovarian cancer and provide evidence that it promotes ovarian cancer metastasis via tumor-derived Wnt7a-induced activation of cancer-associated fibroblasts. 28145159_STAT4_rs7574865 TT was associated with the presence of actively inflamed joints and extra-articular damage in patients with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. 28395724_STAT4 rs7574865 gene polymorphism is associated with the susceptibility of primary biliary cirrhosis in the Han population of Jiangsu province. 28400678_results show specific and dominant contribution of STAT4 in the hematopoietic compartment to metabolic health and inflammation in diet-induced obesity. 28420002_rs744166GG in STAT3 and rs7574865TT in STAT4 had higher frequencies in the case than the control group, suggesting these 2 genotypes increase the susceptibility to psoriasis ( p | ENSMUSG00000062939 | Stat4 | 12.048855 | 0.250826955 | -1.995236 | 0.47837150 | 18.437301 | 0.0000175587038024810403267356173628854776325169950723648071289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0002194916432431678128718577358569064017501659691333770751953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 3.6330200 | 1.6316761 | 14.5406542 | 5.8854526 | |
| ENSG00000138411 | 57520 | HECW2 | protein_coding | Q9P2P5 | FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that mediates ubiquitination of TP73. Acts to stabilize TP73 and enhance activation of transcription by TP73 (PubMed:12890487). Involved in the regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition (PubMed:24163370). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12890487, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24163370}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. | This gene encodes a member of a family of E3 ubiquitin ligases which plays an important role in the proliferation, migration and differentiation of neural crest cells as a regulator of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF)/Ret signaling. This gene also plays an important role in angiogenesis through stabilization of endothelial cell-to-cell junctions as a regulator of angiomotin-like 1 stability. The encoded protein contains an N-terminal calcium/lipid-binding (C2) domain involved in membrane targeting, two-four WW domains responsible for cellular localization and substrate recognition, and a C-terminal homologous with E6-associated protein C-terminus (HECT) catalytic domain. Naturally occurring mutations in this gene are associated with neurodevelopmental delay, hypotonia, and epilepsy. The decreased expression of this gene in the aganglionic colon is associated with Hirschsprung's disease. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2017]. | hsa:57520; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitotic spindle [GO:0072686]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; negative regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:2000650]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein polyubiquitination [GO:0000209]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048814]; regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition [GO:0030071] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24163370_NEDL2 is a novel substrate of APC/C-Cdh1 as cells exit mitosis and functions as a regulator of the metaphase to anaphase transition 25156441_Low HECW2 expression is associated with cervical cancer. 27334371_This work lends further support to previously identified candidate gene HECW2 as a novel candidate gene in intellectual disability and epilepsy. In 39 patient-parent trios, 29 de novo mutations in coding sequence were identified. 27389779_HECW2 is an ubiquitin ligase that stabilises p73, a crucial mediator of neurodevelopment and neurogenesis. This study implicates pathogenic genetic variants in HECW2 as potential causes of neurodevelopmental disorders in humans. 27498087_HECW2, a novel EC ubiquitin E3 ligase, plays a critical role in stabilizing endothelial cell-to-cell junctions by regulating AMOT-like 1 (AMOTL1) stability. 29753763_Results show that HECW2 interacts with two lamin A-binding proteins: proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), via a canonical PCNA-interacting protein (PIP) motif, and lamin B1. HECW2 mediates their ubiquitination and targets them for proteasomal degradation. 30208514_Ectopic expression of HECW2 causes the ubiquitination of HP1alpha and beta, thereby targeting them for proteasomal degradation. 33205896_Association of HECW2 variants with developmental and epileptic encephalopathy and knockdown of zebrafish hecw2a. 34047014_HECW2-related disorder in four Japanese patients. 34321324_Delineating the genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of HECW2-related neurodevelopmental disorders. 34327820_A novel likely pathogenic heterozygous HECW2 missense variant in a family with variable expressivity of neurodevelopmental delay, hypotonia, and epileptiform EEG patterns. 34767155_Circ_0057583 facilitates brain microvascular endothelial cell injury through modulating miR-204-5p/NR4A1 axis. | ENSMUSG00000042807 | Hecw2 | 64.692127 | 0.456337016 | -1.131828 | 0.33027758 | 11.452051 | 0.0007141511669890559382833927770661830436438322067260742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0057050522694705391515967995985647576162591576576232910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 35.5577593 | 10.8207893 | 77.7399615 | 23.0157002 |
| ENSG00000138646 | 51191 | HERC5 | protein_coding | Q9UII4 | FUNCTION: Major E3 ligase for ISG15 conjugation. Acts as a positive regulator of innate antiviral response in cells induced by interferon. Functions as part of the ISGylation machinery that recognizes target proteins in a broad and relatively non-specific manner. Catalyzes ISGylation of IRF3 which results in sustained activation, it attenuates IRF3-PIN1 interaction, which antagonizes IRF3 ubiquitination and degradation, and boosts the antiviral response. Catalyzes ISGylation of influenza A viral NS1 which attenuates virulence; ISGylated NS1 fails to form homodimers and thus to interact with its RNA targets. Catalyzes ISGylation of papillomavirus type 16 L1 protein which results in dominant-negative effect on virus infectivity. Physically associated with polyribosomes, broadly modifies newly synthesized proteins in a cotranslational manner. In an interferon-stimulated cell, newly translated viral proteins are primary targets of ISG15. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16407192, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16815975, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16884686, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20133869, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20308324, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20385878, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20542004}. | Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;Immunity;Innate immunity;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway | This gene is a member of the HERC family of ubiquitin ligases and encodes a protein with a HECT domain and five RCC1 repeats. Pro-inflammatory cytokines upregulate expression of this gene in endothelial cells. The protein localizes to the cytoplasm and perinuclear region and functions as an interferon-induced E3 protein ligase that mediates ISGylation of protein targets. The protein also acts as a modulator of the antiviral immune response. The gene lies in a cluster of HERC family genes on chromosome 4. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2021]. | hsa:51191; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; ISG15 transferase activity [GO:0042296]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; ISG15-protein conjugation [GO:0032020]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0000079]; regulation of defense response to virus [GO:0050688]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] | 15331633_Data show that HERC5, a functionally active HECT ubiquitin ligase, exhibits a tightly controlled cytosolic level under inflammatory conditions in endothelial cells. 16815975_HERC5/Ceb1 is involved in the conjugation of ISG15 to cellular proteins. 16884686_these results suggest that Herc5 functions as a general E3 ligase for protein ISGylation. 17471231_Overexpression of cyclin E is associated with neuroendocrine lung tumors 20308324_This study characterizes HERC5 as a positive regulator of innate antiviral responses, and show that it sustains IRF3 activation via a novel posttranslational modification, ISG15-ylation. 22093708_The E3 ligase activity of HERC5 was required for blocking HIV-1 Gag particle production and correlated with the post-translational modification of Gag with ISG15. 23538710_Data indicate that income was inversely related to smoking behavior, and paternally derived CEB1 mutations were dose dependently increased when the father smoked in the 6 mo before pregnancy, 0.21 vs. 0.05 in smoking and nonsmoking fathers, respectively. 24693865_Authors identified a second distinct mechanism by which HERC5 inhibits HIV-1 replication and demonstrate that HERC5 is evolving under strong positive selection. 24742225_The study reports on the NMR solution structure of a G-quadruplex formed by the CEB1 DNA G-rich fragment d(AGGGGGGAGGGAGGGTGG), harboring several G-tracts including one with six continuous guanines. 25353388_Results show that HERC5 gene may be involved in regulating the spread of non-small cell lung cancer tumors where the methylation of its promoter is correlated with number increase of disseminated tumor cells and metastases as well as survival decreased. 26355087_vIRF1 association with HERC5 altered ISG15 modification of cellular proteins, and knockdown of ISG15 augmented reactivation of KSHV from latency. 26361997_The inhibitory effect of ISG15 on HCV RNA replication does not require its conjugation to substrates by HERC5. 26653219_HERC5 plays a crucial role in HCC immune evasion and has clinical relevance as a reproducible prognostic marker for risk of tumor recurrence and survival in patients. 27534820_Results show that HERC5 mediates covalent ISG15 conjugation to parkin in mammalian cells and that ISG15 is conjugated to the Lys349 and Lys369 residues of parkin. 28737979_A synonymous mutation at rs6857425 (T-C) was present in the same region among all study groups (T-C), irrespective of their HIV status. 29669830_Low HERC5 expression is associated with HIV infections. 31225658_Weighted gene correlation network analysis identifies RSAD2, HERC5, and CCL8 as prognostic candidates for breast cancer. 34147029_Downregulation of HERC5 E3 ligase attenuates the ubiquitination of CtBP1 to inhibit apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. 34661519_HERC5 E3 ligase mediates ISGylation of hepatitis B virus X protein to promote viral replication. 35671810_HERC5/IFI16/p53 signaling mediates breast cancer cell proliferation and migration. | 13.840986 | 0.432722275 | -1.208487 | 0.45282045 | 7.205966 | 0.0072661620833574880676253293643185315886512398719787597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0385727040690719349957937822637177305296063423156738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 7.8735398 | 2.4873067 | 18.5928085 | 4.9506990 | |||
| ENSG00000138759 | 80144 | FRAS1 | protein_coding | Q86XX4 | FUNCTION: Involved in extracellular matrix organization (By similarity). Required for the regulation of epidermal-basement membrane adhesion responsible for proper organogenesis during embryonic development (By similarity). Involved in brain organization and function (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80T14}. | Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes an extracellular matrix protein that appears to function in the regulation of epidermal-basement membrane adhesion and organogenesis during development. Mutations in this gene cause Fraser syndrome, a multisystem malformation that can include craniofacial, urogenital and respiratory system abnormalities. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. | hsa:80144; | basement membrane [GO:0005604]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; cell communication [GO:0007154]; embryonic limb morphogenesis [GO:0030326]; metanephros morphogenesis [GO:0003338]; morphogenesis of an epithelium [GO:0002009]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021]; skin development [GO:0043588] | 12766769_Locus FS1 at chromosome 4q21 is associated with Fraser syndrome. Mutation analysis identified five frameshift mutations in FRAS1, which encodes one member of a family of novel proteins related to an extracellular matrix (ECM) protein found in sea urchin. 17654118_In this review, recent studies support direct interactions between Fras1 and Frem proteins and shed new light on their role in the regulation of epidermal-basement membrane adhesion and organogenesis during development. 18155042_Supramodular nature of GRIP1 revealed by the structure of its PDZ12 tandem in complex with the carboxhyl tail of Fras1. 18671281_11 new mutations in FRAS1 were identified in families with Fraser syndrome. 20602751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21900877_Heterozygous missense mutations in FRAS1 cause non-syndromic congenital abnormalities of the kidney and urinary tract in humans. 22029163_molecular, clinical findings of 4 fetuses with Fraser syndrome from 2 families; in family one, found nonsense mutation (c.3730C>T, p.R1244X) previously described; in family 2 found a novel nonsense mutation previously not known (c.370C>T, p.R124X) 22283518_Analysis of FRAS1 and STRA6 mutations in the same family with eye anomalies. 23473829_First case of a family with two patients affected by Fraser syndrome due to a deletion of 64 kb (deletion 4q21.21) and an additional novel frameshift mutation in exon 66 of the FRAS1 gene. 24700879_In 15 of 590 families, we identified recessive mutations in the genes FRAS1, FREM2, GRIP1, FREM1, ITGA8, and GREM1, all of which function in the interaction of the ureteric bud and the metanephric mesenchyme. 29618029_Based on these data, we conclude that deficiency of FREM2, and possibly FRAS1, are associated with an increased risk of developing Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) and that loss of the FREM1/FREM2/FRAS1 complex, or its function, leads to anterior sac CDH development through its effects on mesothelial fold progression 31597194_Fraser extracellular matrix complex subunit 1 promotes liver metastasis of gastric cancer. 31999076_Two unrelated families with variable expression of Fraser syndrome due to the same pathogenic variant in the FRAS1 gene. 32643034_Novel loss of function variants in FRAS1 AND FREM2 underlie renal agenesis in consanguineous families. 33956343_A polymorphism in the promoter of FRAS1 is a candidate SNP associated with metastatic prostate cancer. | ENSMUSG00000034687 | Fras1 | 21.102632 | 4.890978325 | 2.290123 | 0.46016901 | 25.183170 | 0.0000005213518221216387337640409127548224432757706381380558013916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000091501496710633412745702561230665139646589523181319236755371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 35.2019800 | 4.9676302 | 7.2449050 | 1.5599862 | |
| ENSG00000138794 | 839 | CASP6 | protein_coding | P55212 | FUNCTION: Cysteine protease that plays essential roles in programmed cell death, axonal degeneration, development and innate immunity (PubMed:8663580, PubMed:19133298, PubMed:22858542, PubMed:27032039, PubMed:28864531, PubMed:30420425, PubMed:32298652). Acts as a non-canonical executioner caspase during apoptosis: localizes in the nucleus and cleaves the nuclear structural protein NUMA1 and lamin A/LMNA thereby inducing nuclear shrinkage and fragmentation (PubMed:8663580, PubMed:9463409, PubMed:11953316, PubMed:17401638). Lamin-A/LMNA cleavage is required for chromatin condensation and nuclear disassembly during apoptotic execution (PubMed:11953316). Acts as a regulator of liver damage by promoting hepatocyte apoptosis: in absence of phosphorylation by AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), catalyzes cleavage of BID, leading to cytochrome c release, thereby participating in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (PubMed:32029622). Cleaves PARK7/DJ-1 in cells undergoing apoptosis (By similarity). Involved in intrinsic apoptosis by mediating cleavage of RIPK1 (PubMed:22858542). Furthermore, cleaves many transcription factors such as NF-kappa-B and cAMP response element-binding protein/CREBBP (PubMed:10559921, PubMed:14657026). Cleaves phospholipid scramblase proteins XKR4 and XKR9 (By similarity). In addition to apoptosis, involved in different forms of programmed cell death (PubMed:32298652). Plays an essential role in defense against viruses by acting as a central mediator of the ZBP1-mediated pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis), independently of its cysteine protease activity (PubMed:32298652). PANoptosis is a unique inflammatory programmed cell death, which provides a molecular scaffold that allows the interactions and activation of machinery required for inflammasome/pyroptosis, apoptosis and necroptosis (PubMed:32298652). Mechanistically, interacts with RIPK3 and enhances the interaction between RIPK3 and ZBP1, leading to ZBP1-mediated inflammasome activation and cell death (PubMed:32298652). Plays an essential role in axon degeneration during axon pruning which is the remodeling of axons during neurogenesis but not apoptosis (By similarity). Regulates B-cell programs both during early development and after antigen stimulation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O08738, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10559921, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11953316, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14657026, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17401638, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19133298, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22858542, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27032039, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28864531, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30420425, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32029622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32298652, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8663580, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9463409}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Proteolytically cleaves the N protein of coronoviruses such as MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV (PubMed:35922005, PubMed:18155731). The cleavage of MERS-CoV N-protein leads to two fragments and modulates coronavirus replication by regulating IFN signaling. The two fragments produced by the cleavage interact with IRF3 inhibiting its nuclear translocation after activation and reduce the expression of IFNB and IFN-stimulated genes (PubMed:35922005). The same mechanism seems to be used by other coronaviruses such as SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 to enhance their replication (PubMed:35922005). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18155731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35922005}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Autocatalytic cleavage;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Lipoprotein;Nucleus;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Thiol protease;Zymogen | This gene encodes a member of the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family of enzymes. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes which undergo proteolytic processing at conserved aspartic acid residues to produce two subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme. This protein is processed by caspases 7, 8 and 10, and is thought to function as a downstream enzyme in the caspase activation cascade. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants that encode different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2015]. | hsa:839; | caspase complex [GO:0008303]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004197]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0097153]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in execution phase of apoptosis [GO:0097200]; cysteine-type peptidase activity [GO:0008234]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0097202]; activation of innate immune response [GO:0002218]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to staurosporine [GO:0072734]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; hepatocyte apoptotic process [GO:0097284]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator [GO:0072332]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of necroptotic process [GO:0060545]; protein autoprocessing [GO:0016540]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; pyroptosis [GO:0070269]; regulation of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1901028] | 12089322_identified executioner caspase-6 as a transcriptional target of p53. The mechanism involves DNA binding by p53 to the third intron of the caspase-6 gene and transactivation. 12145703_Pro-CASP6 was the only proenzyme whose localization was limited to the cytosol in U937 cells during TPA-induced differentiation. 15273717_ARK5 negatively regulates procaspase-6 by phosphorylation at Ser257, leading to resistance to the FasL/Fas system. 15280469_induced and utilized by human Astrovirus Yuc8 to promote processing of the capsid precursor and dissemination of the viral particles in CAC0-2 cells. 15321985_programmed cell death was executed by caspase 6 in Streptococcus pneumoniae infected lung epithelium 15356202_CASP-6 cleaves the N terminus of tau in vitro at D13, a semicanonical and hitherto undescribed caspase cleavage site in tau. This suggests a role for caspase-6 & N-terminal truncation of tau during neurofibrillary tangle & Alzheimer's disease progression. 15511269_caspase-2, -6 and -7 expression in gastric cancer cells is decreased compared to in normal gastric mucosal cells 15654952_caspase 6 cleaves periplakin at an unconventional recognition site, amino acid sequence TVAD 16123779_results show that Csp-1 is an upstream positive regulator of Csp-6-mediated cell death in primary human neurons; also results suggest that the activation of Csp-1 must be accompanied by an apoptotic insult to induce Csp-6-mediated cell death 16135563_results suggest that splitting of BL41-E95-A cells induces de novo synthesis of a protein involved in the activation of casp-6 and casp-8, which cleaves 5-LO. 16518869_caspase-6 and its cleavage of lamin A are critical in apoptotic signaling triggered by resveratrol in the colon carcinoma cells, which can be activated in the absence of Bax or p53 16948818_data indicate that the CASP6 gene is occasionally mutated in gastric and colorectal carcinomas; also, the data suggest the possibility that deficiency of caspase-6 expression might contribute to the pathogenesis of gastric cancers 16977583_Caspase-6 was overexpressed in 52.9% of the 210 cases studied, showing predominantly cyoplasmic with some nuclear staining. 17392160_Active caspase-6 could be an early instigator of neuronal dysfunction. 18155731_The experiments revealed that N induces the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, resulting in processing of N at residues 400 and 403 by caspase-6 and/or caspase-3. 18497562_Resveratrol displays converse dose-related effects on fluorouracil-evoked colon cancer cell apoptosis: the role of CASP6 is reported. 18762957_Expression of caspase 6 and caspase 14 genes were different between normal skin of keloid-prone individuals and normal skin of keloid-resistant patients. 18820706_Caspase 6 cleaves cyclin B1 during mitotic catastrophe. Mitotic & apoptotic functions may be linked by caspase-dependent processing of mitotic activators. 18946722_Report co-localization of hyperphosphorylated tau and caspases 3/6 in the brainstem of Alzheimer's disease patients. 19022247_During hypoxia in tube-forming endothelial cells, caspase-7 is responsible for chromatin condensation and nuclear fragmentation while caspase-6 is responsible for DNA ladder formation. 19052714_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19219602_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19269008_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19414860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19694615_The crystal structure of caspase-6, a selective effector of axonal degeneration. 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19897582_p53 activation enhances XIAP inhibition-induced cell death by promoting mitochondrial release of second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases (SMAC) and by inducing the expression of caspase-6. 19915487_Casp-6 is activated in familial forms of Alzheimer disease, as previously observed in sporadic forms. 20332099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20402676_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20427671_results show that p97 is cleaved by Casp6 in Alzheimer's disease and suggest p97 cleavage as an important mechanism for ubiquitin proteasome system impairment 20437871_Data showed that prostate cancer and PIN cells display higher expression of the proapoptotic proteins caspase-6 and BNIP3 than normal cells. 20606168_The NPM mutant specifically inhibits the activities of the cell-death proteases, caspase-6 and -8, through direct interaction with their cleaved, active forms, but not the immature procaspases. 20661084_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20682790_These results imply that pro-Casp6b could negatively regulate pro-Casp6a activation in neurons and prevent Casp6a-mediated axonal degeneration. 20702410_a central and so far underappreciated role of caspase-8 dimerization/dissociation in avoiding unwanted cell death by lethal amplification of caspase responses via the caspase-8, -3, -6 loop. 20855536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20890311_CASP6 can be activated and regulated through intramolecular self-cleavage. 21098228_Intact IRAK-M is strongly expressed in resting alveolar macrophages but is cleaved in patients with pneumonia via neutrophil-mediated induction of CASP-6 activity. 21111746_These data suggest that caspase-6 undergoes a significant conformational change upon substrate binding, adopting a structure that is more like canonical caspases. 21317160_Data suggest that Casp4, Casp 6 and TNFSF10 are differentially expressed in potentially fertile and subfertile men and represent useful biomarkers for predicting male fertility in combination with P1 and P2. 21621544_New crystal form of apo-caspase-6 is presented in canonical conformation by identifying the previous apostructure as a hydrogen-ion concentration (pH)-inactivated form of caspase-6. 21936563_Caspase-6 cleaves human TERT at residues E129 and D637 as part of the apoptosis pathway in cultured cells. 22433863_Results showed the inhibition mechanism of CASP6 phosphorylation and laid the foundation for a new strategy of rational CASP6 drug design. 22683611_peptide binds at a tetramerization interface that is uniquely present in zymogen caspase-6, rather than binding into the active site, and acts via a new allosteric mechanism that promotes caspase tetramerization 22858542_Results demonstrate that in the absence of caspase 6 activity, intrinsic triggers of apoptosis induce the receptor-interacting-kinase-1-dependent production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. 22891250_binding of zinc at the exosite is the primary route of inhibition, potentially locking caspase-6 into the inactive helical conformation. 23402898_Caspase 6 activity in entorhinal cortex identifies aged individuals at risk for developing Alzheimer's disease. 24058506_Significant associations have been found between CpG sites and patient sex, including DNA methylation in CASP6, a gene that may respond to estradiol treatment, and in HSD17B12, which encodes a sex steroid hormone. 24070868_p53 activity is an important upstream regulator of caspase-6 activity in Huntington's disease. 24265764_Caspase-6 is likely important in most tissues during early development but is less involved in adult tissues 24363090_Caspase-6 plays a role in activating caspase-3 in Tau truncation. 24419379_In this study, the crystal structure of a full-length CASP6 zymogen mutant, proCASP6H121A, was solved. 24727569_axon regeneration promoted by suppression of CASP2 and CASP6 is CNTF-dependent and mediated through the JAK/STAT signalling pathway 24810717_unmodified STAT1 is cleaved at multiple sites by caspase-3 and caspase-6 in malignant undifferentiated hematopoietic cells 26505998_The ability of sox11 to reduce effector caspase activity was also reflected in its capacity to reduce cell death following toxic insult. Interestingly, other sox proteins also had the ability to reduce caspase-6 activity but to a lesser extent than sox11 26908611_Results identified novel members of the CASP6 interactome and demonstrate that a number of them are involved in key signaling pathways observed in neurodegenerative diseases. 27633091_Following specific binding to and internalization into HER2-overexpressing tumor cells, the e23sFv-Fdt-casp6 protein induced tumor cell apoptosis and inhibited the proliferation of HER2-overexpressing A172 and U251MG cells in vitro, but not in U87MG cells with undetectable HER2 27931265_Results support the possibility that the Casp6 activity in the anterior olfactory nucleus of the olfactory bulb reflects degeneration in the entorhinal cortex and suggest that Casp6 activity in the olfactory bulb could represent degeneration associated with cognitive decline and early Alzheimer disease. 28154009_Caspase-6 undergoes helix-strand transition upon substrate binding. Caspase-6 shows distinctive conformational dynamics in its 130's region Local pKa Values of Key Amino Acid Residues within the 130's Region Vary between the Unliganded (Helical) and the VEID-bound (Strand) States of Caspase-6 . 28659495_SMSr is a novel and specific substrate of caspase-6, a non-conventional effector caspase implicated in Huntington's and Alzheimer's diseases. 28726391_These data suggest that caspase-6 deactivating mutations may contribute to multifactorial carcinogenic transformations. 28864531_The prodomain region was found to be intrinsically disordered independent of the activation state of caspase-6; however, its complete removal resulted in the protection of the adjacent 26-32 region, suggesting that this region may play a regulatory role. The molecular details of caspase-6 dynamics in solution provide a comprehensive scaffold for strategic design of therapeutic approaches for neurodegenerative disorders. 29535332_Results show that two Casp6 variants, Casp6-G66R and Casp6-R65W, have less self-processing and exogenous proteolytic activity than Casp6-WT and reveal a novel regulatory area of Casp6 activity. Furthermore, the existence of these Casp6 variants suggests that full Casp6 activity may be dispensable in humans. 30420425_have identified an exosite on caspase-6 that is critical for protein substrate recognition and turnover and therefore highly relevant for diseases such as cancer in which caspase-6-mediated apoptosis is often disrupted, and in neurodegeneration in which caspase-6 plays a central role. 30940883_Identification of Allosteric Inhibitors against Active Caspase-6. 33649324_Caspase-6-cleaved Tau fails to induce Tau hyperphosphorylation and aggregation, neurodegeneration, glial inflammation, and cognitive deficits. 34135352_Rare CASP6N73T variant associated with hippocampal volume exhibits decreased proteolytic activity, synaptic transmission defect, and neurodegeneration. | ENSMUSG00000027997 | Casp6 | 26.148119 | 2.624992665 | 1.392313 | 0.51575033 | 7.036338 | 0.0079872192751092620233155372488909051753580570220947265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0417976891957457380444296290988859254866838455200195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 35.3159847 | 12.0306860 | 13.4969976 | 4.7017368 | |
| ENSG00000139160 | 254013 | ETFBKMT | protein_coding | Q8IXQ9 | FUNCTION: Protein-lysine methyltransferase that selectively trimethylates the flavoprotein ETFB in mitochondria (PubMed:25023281, PubMed:25416781). Thereby, may negatively regulate the function of ETFB in electron transfer from Acyl-CoA dehydrogenases to the main respiratory chain (PubMed:25416781). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25023281, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25416781}. | Cytoplasm;Methyltransferase;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transit peptide | Enables heat shock protein binding activity and protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity. Involved in negative regulation of electron transfer activity; negative regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation using acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; and peptidyl-lysine trimethylation. Located in mitochondrial matrix. Part of protein-containing complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:254013; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; heat shock protein binding [GO:0031072]; protein methyltransferase activity [GO:0008276]; protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0016279]; negative regulation of electron transfer activity [GO:1904733]; negative regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation using acyl-CoA dehydrogenase [GO:1904736]; peptidyl-lysine methylation [GO:0018022]; peptidyl-lysine trimethylation [GO:0018023]; protein methylation [GO:0006479] | 22948820_The METTL20 protein is here suggested to be a protein methyltransferase, as it is shown to belong to a family of 10 human methyltransferases, some of which are shown to have lysine specific protein methyltransferase activity. 25023281_Tagged METTL20 expressed in HEK293T cells specifically associates with the ETF and promotes the trimethylation of ETFbeta lysine residues 199 and 202 25416781_Human METTL20 is a mitochondrial lysine methyltransferase that targets ETFbeta and modulates its activity. 29352221_These results further indicate that METTL20-mediated protein methylation is not essential in humans but more likely modulates energy production during fasting or under other metabolic conditions where beta-oxidation is up-regulated. | ENSMUSG00000039958 | Etfbkmt | 17.775906 | 2.348837454 | 1.231947 | 0.46270428 | 6.841919 | 0.0089043142512983085301581098747192299924790859222412109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0452592833383578252437473565805703401565551757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 24.3606867 | 5.5515283 | 11.0219247 | 2.5369890 | |
| ENSG00000140563 | 55784 | MCTP2 | protein_coding | Q6DN12 | FUNCTION: Might play a role in the development of cardiac outflow tract. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23773997}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Developmental protein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Enables calcium ion binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of neurotransmitter secretion. Located in cytosol and nucleoplasm. Is integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:55784; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; regulation of neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0046928] | 15528213_MCTPs are evolutionarily conserved C2 domain proteins that are unusual in that the C2 domains are anchored in the membrane by two closely spaced transmembrane regions and represent Ca(2+)-binding but not phospholipid-binding modules 18367154_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19223264_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19223264_The present study suggested that MCPT2 gene as aputative susceptibility gene for schizophrenia of Scandinavian origin. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23773997_Results identify MCTP2 as a novel genetic cause of coarctation of the aorta and related cardiac malformations. 33198772_Circular RNA MCTP2 inhibits cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer by miR-99a-5p-mediated induction of MTMR3 expression. 33826368_Multiple C2 domain-containing transmembrane proteins promote lipid droplet biogenesis and growth at specialized endoplasmic reticulum subdomains. | ENSMUSG00000032776 | Mctp2 | 73.108134 | 0.374756125 | -1.415976 | 0.20760176 | 46.858683 | 0.0000000000076294306779677953172639396885148425995343268724013796600047498941421508789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000002571577742732855736362872643756488991173547731250437209382653236389160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 30.0755325 | 10.4693675 | 80.4468958 | 27.5637698 | |
| ENSG00000140950 | 57707 | MEAK7 | protein_coding | Q6P9B6 | FUNCTION: Activates an alternative mTOR signaling through RPS6KB2 activation and EIF4EBP1 repression to regulate cell proliferation and migration (PubMed:29750193). Recruits MTOR at the lysosome, essential for MTOR signaling at the lysosome (PubMed:29750193). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29750193}. | 3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Lipoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Myristate;Reference proteome | Involved in several processes, including TOR signaling; positive regulation of protein localization to lysosome; and response to insulin. Located in cytosol; lysosomal membrane; and nuclear lumen. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:57707; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced neuron death [GO:1903204]; positive regulation of protein localization to lysosome [GO:0150032]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; response to amino acid [GO:0043200]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; response to nutrient levels [GO:0031667]; TOR signaling [GO:0031929] | 34468015_miR325p suppresses the proliferation and migration of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells by targeting TLDC1. 35672408_Molecular basis of mEAK7-mediated human V-ATPase regulation. 35994636_Identification of mEAK-7 as a human V-ATPase regulator via cryo-EM data mining. | ENSMUSG00000034105 | Meak7 | 148.443715 | 0.207412272 | -2.269427 | 0.49000303 | 19.059707 | 0.0000126691674257778333915125043573901564286643406376242637634277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001639373857093250064220768535960814915597438812255859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 48.2969626 | 28.6667184 | 242.2407815 | 143.8303169 | |
| ENSG00000143971 | 54465 | ETAA1 | protein_coding | Q9NY74 | FUNCTION: Replication stress response protein that accumulates at DNA damage sites and promotes replication fork progression and integrity (PubMed:27601467, PubMed:27723720, PubMed:27723717). Recruited to stalled replication forks via interaction with the RPA complex and directly stimulates ATR kinase activity independently of TOPBP1 (PubMed:27723720, PubMed:27723717). Probably only regulates a subset of ATR targets (PubMed:27723720, PubMed:27723717). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27601467, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27723717, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27723720}. | Coiled coil;DNA damage;DNA repair;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation | Enables protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity. Involved in several processes, including positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity; regulation of DNA damage checkpoint; and replication fork processing. Located in cytosol; nuclear replication fork; and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:54465; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear replication fork [GO:0043596]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity [GO:0043539]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071902]; regulation of DNA damage checkpoint [GO:2000001]; replication fork processing [GO:0031297] | 16003559_results suggest that ETAA16 may function as a tumour-specific cell surface antigen in Ewing's family of tumors 27601467_results reveal that ETAA1 is a novel RPA-interacting protein that promotes restart of stalled replication forks. 27723717_that parallel TopBP1- and ETAA1-mediated pathways underlie ATR activation and that their combined action is essential for coping with replication stress 27723720_ETAA1 acts as a direct ATR serine-threonine kinase protein activator 27818175_These our data suggest that ETAA1 is a new ATR activator involved in replication checkpoint control. 30755469_ETAA1 regulates mitotic ATR signaling and is required for proper chromosome alignment during metaphase and for a fully functional spindle assembly checkpoint response. 30940728_ETAA1 and TOPBP1 contain a predicted coiled-coil motif that is required for ATR activation in vitro and in cells. Mutation of the predicted coiled coils does not alter AAD oligomerization but does impair binding of the AADs to ATR. 31615875_ETAA1 may have an important role in protecting against genome instability arising from incompletely duplicated DNA via regulatory control of its ATR-stimulating potential 33636182_ATR activation is regulated by dimerization of ATR activating proteins. | ENSMUSG00000016984 | Etaa1 | 132.904074 | 5.036986003 | 2.332561 | 0.53895620 | 16.644095 | 0.0000450904510049417162325519070620316597342025488615036010742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0005060755691898210714696482170893432339653372764587402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 145.1894688 | 114.4084322 | 27.5460059 | 21.7162788 | |
| ENSG00000144161 | 84524 | ZC3H8 | protein_coding | Q8N5P1 | FUNCTION: Acts as a transcriptional repressor of the GATA3 promoter. Sequence-specific DNA-binding factor that binds to the 5'-AGGTCTC-3' sequence within the negative cis-acting element intronic regulatory region (IRR) of the GATA3 gene (By similarity). Component of the little elongation complex (LEC), a complex required to regulate small nuclear RNA (snRNA) gene transcription by RNA polymerase II and III (PubMed:23932780). Induces thymocyte apoptosis when overexpressed, which may indicate a role in regulation of thymocyte homeostasis. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12077251, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12153508, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23932780}. | Apoptosis;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;RNA-binding;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Enables RNA binding activity. Involved in several processes, including positive regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process; regulation of transcription, DNA-templated; and snRNA transcription. Located in Cajal body; histone locus body; and transcriptionally active chromatin. Part of transcription elongation factor complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:84524; | Cajal body [GO:0015030]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; euchromatin [GO:0000791]; histone locus body [GO:0035363]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription elongation factor complex [GO:0008023]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA polymerase II intronic transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0001162]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033085]; positive regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process [GO:0070245]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0045945]; response to antibiotic [GO:0046677]; snRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0042795]; snRNA transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0042796]; T cell homeostasis [GO:0043029] | Mouse_homologues 12077251_Fliz1 binds specifically to a negative cis-acting element in the intronic regulatory region of GATA-3 and, when overexpressed, can function as a transcriptional repressor of the GATA-3 promoter in vitro and in vivo. 30041613_Using RNA silencing to decrease expression of ZC3H8 in a mouse tumor cell line in vitro, then studied phenotype and cell behavior of the tumor cell line, and further studied ability of those cells to form tumors in mice in vivo. | ENSMUSG00000027387 | Zc3h8 | 72.796439 | 2.195755310 | 1.134717 | 0.35947394 | 9.691542 | 0.0018511808326042661441285241963328189740423113107681274414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0127244803373309459809670229901712446007877588272094726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 109.5299895 | 26.2088804 | 49.8748880 | 12.0029638 | |
| ENSG00000144339 | 23671 | TMEFF2 | protein_coding | Q9UIK5 | FUNCTION: May be a survival factor for hippocampal and mesencephalic neurons. The shedded form up-regulates cancer cell proliferation, probably by promoting ERK1/2 phosphorylation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10903839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17942404}. | Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a member of the tomoregulin family of transmembrane proteins. This protein has been shown to function as both an oncogene and a tumor suppressor depending on the cellular context and may regulate prostate cancer cell invasion. Multiple soluble forms of this protein have been identified that arise from both an alternative splice variant and ectodomain shedding. Additionally, this gene has been found to be hypermethylated in multiple cancer types. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2015]. | hsa:23671; | basement membrane [GO:0005604]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of integrin biosynthetic process [GO:0045720]; negative regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051497]; substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:0034446]; tissue development [GO:0009888]; wound healing, spreading of cells [GO:0044319] | 12384516_Hypermethylation of HPP1 is associated with hMLH1 hypermethylation in gastric adenocarcinomas. 12460892_Aberrant methylation of the HPP1 gene is a relative common early event in ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal carcinoma. 12729735_inverse correlation between TMEFF2 and c-Myc expression 15068392_Analysis of DNA from peripheral blood revealed that TPEF methylation was detectable in colorectal tumor patients and patients with early or pre-neoplastic lesions, but not in healthy volunteers. 15824739_Hypermethylation of p16, RUNX3, and HPP1 in Barreett exophagus may represent independent risk factors for the progression of Barrett esophagus to esophageal cancer. 16439095_A secreted form of TMEFF2 is expressed from TMEFF2 locus and may functionally interact with full-length TMEFF2, or its binding partners, and may also influence current immune-based treatment strategies 16619216_Hypermethylation of HPP1 is associated with primary adenocarcinomas of the small bowel 17352030_Methylation testing of fecal DNA using a panel of epigenetic markers (methylated SFRP2, HPP1 and MGMT) may be a simple and promising non-invasive screening method for colorectal carcinoma and precancerous lesions. 17942404_TMEFF2 contributes to cell proliferation in an ADAM17-dependent autocrine fashion in cells expressing this protein 18059030_data provides evidence to support the role of HPP1 as a tumor suppressor gene; activation of the STAT1 pathway likely represents the principal mediator of HPP1's tumor suppressive properties 18070176_Methylated PAX6- or TPEF-promoters could represent biomarkers for bladder cancer. 18799374_Distinct TPEF/HPP1 (transmembrane protein containing epidermal growth factor) gene methylation patterns in gastric cancer indicate a field effect in gastric carcinogenesis. 19040536_promoter of TPEF gene is frequently hpermethylated, and associated with loss of TPEF mRNA expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19288010_Methylation of CLDN6, FBN2, RBP1, RBP4, TFPI2, and TMEFF2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20975101_GDF15, HSPA2, TMEFF2, and VIM were identified as epigenetic biomarkers for Bladder cancer. 21393249_the tumor suppressor activity of TMEFF2 requires the cytoplasmic/transmembrane portion of the protein and correlates with its ability to bind to SARDH and to modulate the level of sarcosine. 21559523_TMEFF2 can function to regulate PDGF signaling; it is hypermethylated and downregulated in glioma and several other cancers 22238370_Several genes expressed at exceptionally high levels were identified associated with early oocyte development, TMEFF2, the Rho-GTPase-activating protein oligophrenin 1 (OPHN1) and the mitochondrial-encoded ATPase6 (ATP6). 22532293_Methylation of TMEFF2 gene is associated with colorectal neoplasia in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's colitis. 22814847_Findings suggest that methylation-associated down-regulation of TMEFF2 gene may be involved in lung tumorigenesis and TMEFF2 methylation can serve as a specific blood-based biomarker for NSCLC. 23405127_Androgen signaling promotes eIF2alpha phosphorylation and subsequent translation of TMEFF2 via a mechanism that requires uORFs in the 5'-UTR of TMEFF2. 23824605_TMEFF2 and SARDH cooperate to modulate one-carbon metabolism and invasion of prostate cancer cells. 24919179_c-Myc contributes to the epigenetic regulation of HPP1 via the dominant recruitment of HDAC3. 24987055_TMEFF2 acts as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer through direct interaction with SHP-1 and can be a potential biomarker of carcinogenesis. 25573902_TMEFF2 regulates the non-canonical activin/BMP4 signaling, PI3K, and Ras/ERK1/2 pathways. 26402097_Results suggest that TMEFF2 is a brain-enriched endogenous modulator of Abeta neurotoxicity and an enhancer of alpha-secretase processing of AbetaPP 28128743_TMEFF2 methylation is associated with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 28762604_Differential TMEFF2 processing from a single transmembrane protein may be a general mechanism to modulate transmembrane protein levels and domains, dependent on the repertoire of ADAMs or TTSPs expressed by the target cell. 30614793_Our data show that candidate TSG genes QKI and TMEFF2 harbor mutational ITH as well as the frameshift mutations in GC and CRC with MSI-H. From this observation, frameshift mutations of QKI and TMEFF2 may play a role in tumorigenesis through their TSG inactivation in GC and CRC. 31044775_TMEFF2 expression was down-regulated in pancreatic cancer tissue compared with normal pancreas. In human pancreatic cancer cell lines, overexpression of TMEFF2 suppressed cell proliferation and enhanced apoptosis, suppressed the expression of p-STAT3, MCL1, VEGF and increased the expression of the tyrosine-specific protein phosphatase, SHP-1. 31060542_Study identifies a panel of 11 TMEFF2 regulated cell cycle related genes (TMCC11), provides evidence that the TMCC11 gene signature is a robust independent prognostic marker for prostate cancer (PCa), and suggests the possibility that low TMEFF2 expression marks a distinct subclass of PCa. 31610211_TMEFF2 plays an important role in the initiation, development, and malignant behavior of endometrial carcinoma (EC) and can be a potential target for early diagnosis and treatment in EC 32009129_MiR-323-3p Targeting Transmembrane Protein with EGF-Like and 2 Follistatin Domain (TMEFF2) Inhibits Human Lung Cancer A549 Cell Apoptosis by Regulation of AKT and ERK Signaling Pathways. 32450419_HPP1 Ectodomain Shedding is Mediated by ADAM17 and is Necessary for Tumor Suppression in Colon Cancer. 32497621_Roles of a TMPO-AS1/microRNA-200c/TMEFF2 ceRNA network in the malignant behaviors and 5-FU resistance of ovarian cancer cells. 32559621_Long non-coding RNA LINC01963 inhibits progression of pancreatic carcinoma by targeting miR-641/TMEFF2. 34339705_Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of TMEFF2, SMOC-2, and SOX17 expression in endometrial carcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000026109 | Tmeff2 | 12.263127 | 3.257305959 | 1.703679 | 0.56024101 | 9.310158 | 0.0022788685047045605623627917424300903803668916225433349609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0150931878048330466585147391356258594896644353866577148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 18.8433940 | 5.3664899 | 5.8030078 | 1.9310076 | |
| ENSG00000145147 | 9353 | SLIT2 | protein_coding | O94813 | FUNCTION: Thought to act as molecular guidance cue in cellular migration, and function appears to be mediated by interaction with roundabout homolog receptors. During neural development involved in axonal navigation at the ventral midline of the neural tube and projection of axons to different regions. SLIT1 and SLIT2 seem to be essential for midline guidance in the forebrain by acting as repulsive signal preventing inappropriate midline crossing by axons projecting from the olfactory bulb. In spinal cord development may play a role in guiding commissural axons once they reached the floor plate by modulating the response to netrin. In vitro, silences the attractive effect of NTN1 but not its growth-stimulatory effect and silencing requires the formation of a ROBO1-DCC complex. May be implicated in spinal cord midline post-crossing axon repulsion. In vitro, only commissural axons that crossed the midline responded to SLIT2. In the developing visual system appears to function as repellent for retinal ganglion axons by providing a repulsion that directs these axons along their appropriate paths prior to, and after passage through, the optic chiasm. In vitro, collapses and repels retinal ganglion cell growth cones. Seems to play a role in branching and arborization of CNS sensory axons, and in neuronal cell migration. In vitro, Slit homolog 2 protein N-product, but not Slit homolog 2 protein C-product, repels olfactory bulb (OB) but not dorsal root ganglia (DRG) axons, induces OB growth cones collapse and induces branching of DRG axons. Seems to be involved in regulating leukocyte migration. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10102268, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10864954, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10975526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11239147, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11309622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11404413}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chemotaxis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Heparin-binding;Leucine-rich repeat;Neurogenesis;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal | This gene encodes a member of the slit family of secreted glycoproteins, which are ligands for the Robo family of immunoglobulin receptors. Slit proteins play highly conserved roles in axon guidance and neuronal migration and may also have functions during other cell migration processes including leukocyte migration. Members of the slit family are characterized by an N-terminal signal peptide, four leucine-rich repeats, nine epidermal growth factor repeats, and a C-terminal cysteine knot. Proteolytic processing of this protein gives rise to an N-terminal fragment that contains the four leucine-rich repeats and five epidermal growth factor repeats and a C-terminal fragment that contains four epidermal growth factor repeats and the cysteine knot. Both full length and cleaved proteins are secreted extracellularly and can function in axon repulsion as well as other specific processes. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. | hsa:9353; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; GTPase inhibitor activity [GO:0005095]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; laminin-1 binding [GO:0043237]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; proteoglycan binding [GO:0043394]; Roundabout binding [GO:0048495]; aortic valve morphogenesis [GO:0003180]; apoptotic process involved in luteolysis [GO:0061364]; axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048846]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube [GO:0048754]; cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002042]; cellular response to heparin [GO:0071504]; cellular response to hormone stimulus [GO:0032870]; chemorepulsion involved in postnatal olfactory bulb interneuron migration [GO:0021836]; corticospinal neuron axon guidance through spinal cord [GO:0021972]; induction of negative chemotaxis [GO:0050929]; motor neuron axon guidance [GO:0008045]; negative chemotaxis [GO:0050919]; negative regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030837]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0090288]; negative regulation of chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070100]; negative regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010596]; negative regulation of lamellipodium assembly [GO:0010593]; negative regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002689]; negative regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090027]; negative regulation of mononuclear cell migration [GO:0071676]; negative regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090024]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; negative regulation of retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:0090260]; negative regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051058]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell chemotaxis [GO:0071672]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014912]; negative regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043116]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of axonogenesis [GO:0050772]; pulmonary valve morphogenesis [GO:0003184]; response to cortisol [GO:0051414]; retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:0031290]; Roundabout signaling pathway [GO:0035385]; ureteric bud development [GO:0001657]; ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0060412] | 12141424_Analysis of alternative splicing and conserved domains in human and mouse slit genes 12384551_SLIT2, a human homologue of the Drosophila Slit2 gene, has tumor suppressor activity and is frequently inactivated in lung and breast cancers. 12615722_SLIT2 is an excellent candidate tumor suppressor gene for colorectal cancer. 12881718_Our data indicate that SLIT2 is frequently inactivated by promoter region CpG island hypermethylation in gliomas and may be a good candidate for a glioma tumour suppressor gene (TSG) located at 4p15.2. 14645233_effect of Slit (=Slit-2) on the metastatic properties of breast cancer cells 16162649_evidence showing that Slit1 and Slit2 proteins are selective inhibitors and repellents for dorsally projecting, but not for ventrally projecting, cranial motor axons 16439689_Slit2 inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell migration by suppressing small GTPase Rac1 activation. 16636676_Both medulloblastoma and glioma tumors express Robo1 and Slit2, but only medulloblastoma invasion is inhibited by recombinant Slit2 protein. 16840550_Slit-2 inhibited neurite outgrowth in stem cell cultures. 17268810_Slit2 induces targeted migration and may play a role in brain metastasis of breast cancer cells. 17448996_long-range Ca(2+) signaling coordinates the Slit-2-induced changes in motility at two distant parts of migrating neurons by regulating RhoA distribution 17496152_SLIT2 mRNA decreases with vascular function decline in pulmonary fibrosis. 17609981_Inactivation of SLIT2-ROBO1 signaling pathway may have an important role in uterine cervical carcinoma development. 17848514_the crystal structures of the second LRR domain of human Slit2 and the minimal complex between these proteins (Slit2 D2-Robo1 Ig1). 17903301_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17968499_a chemorepulsive effect mediated by interaction of Slit2 and Robo1 participates in glioma cell guidance in the brain. 18611862_Slit-2-overexpressing breast cancer cells exhibit tumor suppressor capabilities through the novel mechanism of beta-catenin modulation. 18829537_Slits are negative regulators of Sdf1 and Cxcr4 in breast cancer cells. 19033678_Slit2 plays a role in regulating in vitro osteoblast differentiation. 19048120_Slit2 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis of fibrosarcoma and squamous cell carcinoma and its effect on cell cycle and apoptosis signal pathways is an important mechanism for Slit2-mediated tumor suppression 19100240_These results suggest that epigenetic inactivation of SLIT2 in hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC) may be important in the development and progression of HCC. 19350278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19350278_gene variants in SLIT2 are rare causes of VUR in humans. Our results provide further evidence for the genetic heterogeneity of this disorder 19351956_HDAC5 represses angiogenic genes, such as FGF2 and Slit2, which causally contribute to capillary-like sprouting of endothelial cells. 19498462_Fourth Slit2 domain heparan sulphate binding contributes to a Slit-Robo signalling mechanism more intricate than previously thought. 19550140_The SLIT2 5' CpG island is methylated in chronic and acute lymphocytic leukemia. 19706539_Data uncover a previously unknown function of USP33 and reveal a new player in Slit-Robo signaling in cancer cell migration. 19759280_Slit2 potently inhibits chemotaxis but not random motion of circulating neutrophils 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19855388_data reveal that a Slit2-Robo4-paxillin-GIT1 network inhibits the cellular protrusive activity underlying neovascularization and vascular leak, and identify a new therapeutic target for ameliorating diseases involving the vascular system 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20008733_Downregulation of Slit2 expression is associated with gliomas. 20029409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20029409_This study suggested that the importance of axonal guidance genes(SLIT2) in shaping an individual's vulnerability to suicidality, likely in the direction of the aggression/impulsivity endophenotype. 20068157_Findings indicate that SLIT2 suppresses lung cancer progression, defining it as a novel 'theranostic' factor with potential as a therapeutic target and prognostic predictor in lung cancer. 20153733_These results suggest that Slit2 may play an important role in the pathogenesis of temporal lobe epilepsy 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20375003_Activating with the soluble ligand Slit an endothelium-specific, Robo4-dependent signaling pathway that strengthens the vascular barrier, diminishing deleterious aspects of the host's response to the pathogen-induced cytokine storm. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20438712_these findings reveal that through interacting with Robo1, Slit2 is a novel and potent lymphangiogenic factor and contributes to tumor lymphatic metastasis. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20944010_the newly identified Slit2 gradient at the bronchus-alveoli axis induces attractive PI3K signaling in eosinophils and repulsive srGAP1 signaling in neutrophils through differential srGAP1 expression during lung inflammation. 21264840_Because slit2-DeltaE15 splice variant is present in low invasive cancer cells and nontumor lung tissues, loss of this splice variant is an important event in tumor progression and invasion 21283129_Colorectal carcinoma cells secrete Slit2 for signaling through Robo1 expressed on these same cells. 21349947_Findings establish the critical role of the neuronal differentiation factor NeuroD1 in neuroblastoma as well as its functional relationship with the neuronal repellent factor Slit2. 21385904_Data show that epigenetic silencing of SLIT2 promoter was discovered as an underlying mechanism by which miR-218 is suppressed in NPC. 21465248_three major members (Slit2/3 and Robo1) of Slit/Robo family are widely expressed in the human normal and malignant ovarian tissues; but Slit/Robo signaling may not play an important role in regulating human ovarian cancer cell proliferation and migration 21627385_SLIT2 is epigenetically silenced in ovarian cancers. 21686327_SLIT-ROBO signaling potentially contributes to the development of diabetic retinopathy. 21857494_studies demonstrate a novel role for Slit2/Robo1 axis in HIV replication and may contribute to the understanding of HIV-1 pathogenesis 21894562_Slit2 promoter hypermethylation appears to be responsible for functionally silencing Slit2 expression 21986575_Over-expression of human Slit2 in transgenic mouse significantly increased brain vessel density and the permeability of brain vessels to large molecules. 22011669_We confirmed that the expression of SLIT2 in squamous cell carcinoma is regulated by DNA methylation of its specific promoter region. 22198087_New insights into the role of Slit proteins during the angiogenic process that relies on the directional migration not only of endothelial cells but also of pericytes. 22241990_targeting Slit2/Robo4 signaling may protect the integrity of the lymphatic barrier and limit the dissemination of HIV in the host. 22315090_Promoter methylation status analysis of hereditary breast tumors revealed high methylation frequencies for the three genes (67% RASSF1A, 80% SLIT2, and 72% WIF1). 22532293_Methylation of SLIT2 gene is associated with colorectal neoplasia in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's colitis. 22613430_aberrant methylation of the SLIT2 promoter was present in ovarian tissue from 29/36 (80.6%) ovarian cancer patients, but not in the 25 healthy controls; hypermethylation of the SLIT2 promoter may be a relatively early event in ovarian cancer 22719878_data suggests the importance of abrogation of SLIT2-ROBO1 and SLIT2-ROBO2 interactions in the initiation and progression of CACX and also for early diagnosis and prognosis of the disease 22826604_we report that the tumorigenic potential of breast cancer cells is determined by an interaction between the Robo1 receptor and its ligand Slit2 22865890_The cell motility modulator Slit2 is a potent inhibitor of platelet function. 22875847_Slit2 overexpression increases the lesion size in endometriosis and increases microvessel density. 22898079_Silencing of miRNA-218 promotes migration and invasion of breast cancer via Slit2-Robo1 pathway 23119100_Data indicate that slit2N alters the localization and binding of Robo1 to WASp and LSP1 in HIV-1-gp120-treated immature dendritic cells (iDCs). 23294842_N-terminal of Slit2 inhibits HIV-1 replication by regulating the actin cytoskeleton 23314850_SLIT2 suppresses colon tumor metastasis, and it exerts its suppressive activity against colorectal cancer metastasis by restraining AKT-GSK3beta signaling. 23381221_hypomethylation of LINE-1 and hypermethylation of SLIT2, MAL and IGFBP7 were frequently detected in NSCLCs and associated with various clinical features. 23671423_Loss of expression of SLIT2 by promoter hypermethylation and loss of heterozygosity events is significantly associated with serrated adenoma development 23694962_Hypermethylation of SLIT2 is associated with colorectal cancer. 23702092_Slit2 inhibits Andes virus and Hantaan virus induced permeability and adherens junctions disassembly of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells by interactions with Robo4 23933755_Slit2 was highly expressed in gastric cancer patients with less advanced clinicopathological features. Slit2 levels were correlated with beta-catenin level and subcellular localization. 24272999_Slit2-Robo4 is a key regulator of endothelial inflammation, and its dysregulation during endotoxemia is a novel mechanism for LPS-induced vascular pathogenesis. 24287947_Slit2 is downregulated in renal cell carcinoma and may have a role as a tumor suppressor 24297051_Slit2 knockdown promotes gastric cancer growth and metastasis through activation of the AKT/betacatenin-mediated signaling pathway. 24448236_An N-terminal SLIT2 cleavage fragment stimulated such migration. 24673457_Biological activity of Slit2 and its binding to Robo1 have no affect on the dimer formation of Robo1. 24777535_In this review, we summarize recent findings demonstrating that the neuronal guidance cues, Slit and Roundabout (Robo), prevent the migration of multiple leukocyte subsets towards diverse inflammatory chemoattractants. 24840330_Results suggest that Slit2 might be involved in skin tumorigenesis. 24981056_Data show that ubiquitin specific peptidase 33 (USP33) mediates nerve tissue proteins Slit-Robo signaling in lung cancer cell migration. 25114073_These findings of this study demonstrated that Slit2 overexpression may be responsible for AD-like alterations and the increased BBB permeability in these mice 25130654_Slit2 is decreased in human myometrium after labor and knock-down studies describe an anti-inflammatory effect of Slit2 in myometrial cells. 25329354_reduced expression in obese placenta and in primary trophoblast cells treated with pro-inflammatory mediators IL-1beta, TNF-alpha and LPS 25333347_PDGFD, CDH1 and SLIT2 are upregulated in low grade meningiomas and schwannomas compared with healthy tissue. 25465073_Inactivation of SLIT2 and/or ROBO1 is one of the early events in development of dysplastic lesions of head and neck and has prognostic importance. 25489114_data may explain why fibrocytes are rarely observed in healthy tissues, may suggest that the relative levels of Slit2 present in healthy tissue and at sites of fibrosis may have significant effect on decision of monocytes to differentiate into fibrocytes 25490006_Results provide novel evidence that low expression of SLIT2 correlates with poor prognosis and promotes metastasis in ESCC, which may be regulated by the Cdc42-mediated pathways. 25590802_SLIT2 expression and cancer-associated fibroblasts are correlated with neural remodeling. 25605242_Slit2/Robo1 signaling promotes intestinal tumorigenesis through Src-mediated activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 25786906_Data indicate that SLIT2, miR-218-1, RET/PLAG1 and SLIT2/ROBO1 pathway involved in Hirschsprung's disease. 26002231_VEGFR2 activation was not affected by Slit2, but eNOS phosphorylation was diminished 26021305_Slit2-exon 15 splicing variants have different roles in angiogenesis and HUVEC permeability 26026792_Mutations of the SLIT2-ROBO2 pathway genes SLIT2 and SRGAP1 confer risk for congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract 26264936_Significantly increased serum Slit2 levels and hepatic expression of Slit2 and Robo1 were observed in patients with liver fibrosis. 26282852_temporary up-regulation in remodeling vessel and down-regulation in remodeled vessel of polygonal-shape extravillous trophoblast cells occurred in tubal pregnancies 26400100_our findings indicated that Slit2/Robo1 axis possibly be regarded as a significant clinical parameter for predicting brain metastasis in breast cancer patients. 26456684_expression of the evolutionarily conserved slit2 Gene Promoter Requires Sp1 26542734_Overexpression of Slit2 induces its tumor suppressive effects in Breast cancer. 26713366_These results suggest that Slit2/Robo1 binding exerts an effect on cell migration, which is negatively regulated by Robo4, and Robo1 may function by interacting with CdGAP in HUVECs. 26745454_human placental multipotent mesenchymal stromal cell express Slit2 and both Robo1 and Robo4 are present in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 26935705_Study shows that Slit2 mRNA and protein levels were significantly reduced in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) specimens and implicates Slit2 functions as a negative regulator in the development and progression of PTC. 27176045_We postulate that Robo1 promotes tumor invasion partly by the upregulation of MMP2 after activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Notably, Slit2 knockdown caused the upregulation of Robo1 expression both at the mRNA and protein levels. Thus, the stimulatory effects of Slit2 knockdown on tumor progression can be ascribed, at least in part, to the upregulation of Robo1 and its positive role in tumor progression. 27431199_Slit2-Robo1 signaling promoted the adhesion, invasion and migration of tongue carcinoma cells by upregulating the expression levels of MMP2 and MMP9 and, downregulating the expression of E-cadherin. 27659325_Results indicate the importance of SLIT2-ROBO1-CDC42 signaling pathway in predicting tumor progression. 27888432_findings suggest that AK3 and SLIT2 may be potential candidates involved in genetic susceptibility to colorectal cancer 27916173_Low Slit2 expression is associated with glioma. 28402926_Curcumin up-regulates Slit-2 and down-regulates the expression of CXCR4, SDF-1, MMP2 and MMP9 in Ishikawa, Hec- 1B and primary human endometrial carcinoma cells. 28406573_The findings indicate that the migration of human neural progenitor cells from the fetal subventricular zone to the olfactory bulb is partially regulated by the Slit2-Robo1 axis. 28485101_SLIT2/ROBO1 signalling may regulate trophoblast differentiation and invasion causing restricting beta human chorionic gonadotrophin (beta-hCG) production, shallow trophoblast invasion and inhibiting placental angiogenesis in missed and threatened miscarriage during the first trimester. 28973045_The alteration of Slit2 and Robo1 expression in the retinas of diabetic rats and patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy suggests a role for the Slit-Robo signal in the various stages diabetic retinopathy. 29107007_Elevated SLIT2 promoter methylation contributed to the risk of NPC. 29299781_findings indicate that in a diabetic-like environment, in addition to mesangial cells, autocrine activation of Slit2/Robo1 signaling of HRGECs may contribute to angiogenesis of HRGECs through PI3K/Akt/VEGF pathway. 29317497_an interaction between the BMP2-Gremlin and SLIT2 pathways in human kidney cells 29523788_SLIT2 and ROBO1promotes proliferation, inhibits apoptosis, and contributes to the Warburg effect in osteosarcoma. 29610848_The novel CAPN5 mutation (p.R289W) is responsible for the present autosomal dominant neovascular inflammatory vitreoretinopathy (ADNIV) family. The mutant CAPN5 stimulated secretion and cleavage of SLIT2 fragments that may act as a bystander to regulate abnormal RPE cell proliferation for ADNIV. 29752312_TSH induces Slit2 levels in GD-OF by enhancing both Slit2 gene transcription and mRNA stability. 30510066_this study shows that different isoforms of the neuronal guidance molecule Slit2 directly cause chemoattraction or chemorepulsion of human neutrophils 30648543_Study demonstrated a role for Slit2 as a tumor suppressor of papillary thyroid cancer (PTC). Slit2 suppressed thyroid cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Loss of Slit2 expression was associated with poor prognostic factors, such as lymphovascular invasion, cervical LN metastasis, distant metastasis, advanced stage, and recurrence in PTC. 30739251_Low Expression and Promoter Hypermethylation of the Tumour Suppressor SLIT2 is Associated with Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. 30842157_SLIT2 induced motility and a SLIT2 gradient induced chemotaxis of breast cancer cells, which was amplified by heparin. ROBO1 was abundantly expressed in BMs of breast and colon cancer as well as in PM of ovarian cancer. Together, this suggests that ROBO-expressing tumor cells are attracted to the brain and peritoneum by SLIT2-mediated chemotaxis. 30896071_Our study reveals the inhibitory function of Slit-Robo signalling in gastric cancer (GC) and uncovers a role of USP33 in suppressing cancer cell migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by enhancing Slit2-Robo1 signalling. USP33 represents a feasible choice as a prognostic biomarker for GC. 31194736_SLIT2-ROBO1 signaling was linked with regulation of genes involved in inflammation, pregnancy-specific beta-1-glycoprotein genes, decidualization and fetal growth. We propose that this receptor-ligand couple is a component of the signaling network that promotes Spontaneous preterm birth (SPTB). 31393085_The mRNA levels of SLIT2 and ROBO1 were higher in the basal plate of SPTB placentas when compared to those of infants born at term or from elective preterm deliveries 31571851_The gene SLIT2 was decreased in patients with COPD and this decreases was significantly negatively correlated with the disease stages of COPD 31791578_Engagement of Robo1 by Slit2 induces formation of a trimeric complex consisting of Src-Robo1-E-cadherin for E-cadherin phosphorylation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 32086386_Slit2 May Underlie Divergent Induction by Thyrotropin of IL-23 and IL-12 in Human Fibrocytes. 32213157_A Study Based on the Correlation Between Slit2/Robo1 Signaling Pathway Proteins and Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis. 32738556_TUG1 Represses Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Inflammatory Response by Regulating miR-27a-3p/SLIT2 in Lipopolysaccharide-Treated Vascular Endothelial Cells. 32999457_Tumoural activation of TLR3-SLIT2 axis in endothelium drives metastasis. 33028376_Overexpression of Slit2 decreases neuronal excitotoxicity, accelerates glymphatic clearance, and improves cognition in a multiple microinfarcts model. 33068960_Role of Slit2 upregulation in recurrent miscarriage through regulation of stromal decidualization. 33079290_Slit2 is a potential biomarker for renal impairment in systemic lupus erythematosus. 33236535_Crosstalk between the activated Slit2-Robo1 pathway and TGF-beta1 signalling promotes cardiac fibrosis. 33275139_Placental multipotent mesenchymal stromal cell-derived Slit2 may regulate macrophage motility during placental infection. 33318575_Structural insights and evaluation of the potential impact of missense variants on the interactions of SLIT2 with ROBO1/4 in cancer progression. 33481259_Exome sequencing identifies SLIT2 variants in primary CNS lymphoma. 33574432_The neurorepellent, Slit2, prevents macrophage lipid loading by inhibiting CD36-dependent binding and internalization of oxidized low-density lipoprotein. 34400395_Slit2 Inhibits Breast Cancer Metastasis by Activating M1-Like Phagocytic and Antifibrotic Macrophages. 34414975_Expression of the axon guidance factor Slit2 and its receptor Robo1 in patients with Hirschsprung disease: An observational study. 34490644_Ductular reaction promotes intrahepatic angiogenesis through Slit2-Roundabout 1 signaling. 34543483_Genomic evolution and the impact of SLIT2 mutation in relapsed intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 34777365_Slit2-Mediated Metabolic Reprogramming in Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages Enhances Antitumor Immunity. 35426130_Slit guidance ligand 2 promotes the inflammatory response of periodontitis through activation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. 35813663_The Role of Slit-2 in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Its Effect on Pregnancy Outcome. 36250924_RNA m6A reader IGF2BP3 promotes metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer via SLIT2 repression. 36411451_SLIT2 promoter hypermethylation predicts disease progression in chronic myeloid leukemia. | ENSMUSG00000031558 | Slit2 | 104.763030 | 2.948869115 | 1.560162 | 0.46283162 | 10.858865 | 0.0009832394462770568770160206639729949529282748699188232421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0074747572687627571175195129171697772108018398284912109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 145.5293002 | 59.0592973 | 49.2552595 | 20.1131729 | |
| ENSG00000145331 | 93587 | TRMT10A | protein_coding | Q8TBZ6 | FUNCTION: S-adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent guanine N(1)-methyltransferase that catalyzes the formation of N(1)-methylguanine at position 9 (m1G9) in tRNAs (PubMed:23042678, PubMed:25053765). Probably not able to catalyze formation of N(1)-methyladenine at position 9 (m1A9) in tRNAs (PubMed:23042678). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23042678, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25053765}. | 3D-structure;Coiled coil;Diabetes mellitus;Disease variant;Dwarfism;Intellectual disability;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase | This gene encodes a protein that belongs to the tRNA (Guanine-1)-methyltransferase family. A similar gene in yeast modifies several different tRNA species. Mutations in this gene are associated with microcephaly, short stature, and impaired glucose metabolism. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2014]. | hsa:93587; | actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; tRNA (guanine(9)-N(1))-methyltransferase activity [GO:0052905]; tRNA (guanine-N1-)-methyltransferase activity [GO:0009019]; tRNA binding [GO:0000049]; tRNA methylation [GO:0030488]; tRNA N1-guanine methylation [GO:0002939] | 24204302_This is the first study describing the impact of TRMT10A deficiency in mammals, highlighting a role in the pathogenesis of microcephaly and early onset diabetes. 25053765_TRMT10A dysfunction is associated with abnormalities in glucose homeostasis, short stature and microcephaly. 26297882_Homozygous deletion of TRMT10A is associated with a syndrome of failure to thrive, delayed puberty, intellectual disability and diabetes mellitus. 26526202_A homozygous G to T transition in exon 2 of gene TRMT10A at nucleotide position 79 of the coding sequence was identified in a family with young-adult onset diabetes with intellectual disability, microcephaly and epilepsy. 30247717_tRNA guanosine 9 hypomethylation leads to tRNAGln fragmentation and that 5'-tRNAGln fragments mediate TRMT10A deficiency-induced beta-cell death. This study unmasks tRNA hypomethylation and fragmentation as a hitherto unknown mechanism of pancreatic beta-cell demise relevant to monogenic and polygenic forms of diabetes. 31292261_demonstrate that human TRMT10A (hTRMT10A) and human TRMT10B (hTRMT10B) are not biochemically redundant 32213595_transcripts with increased m(6)A upon TRMT10A ablation contain an overrepresentation of m(1)G9-containing tRNAs codons read by tRNA(Gln(TTG)), tRNA(Arg(CCG)), and tRNA(Thr(CGT)) These findings collectively reveal the presence of coordinated mRNA and tRNA methylations and demonstrate a mechanism for regulating gene expression through the interactions between mRNA and tRNA modifying enzymes. 32392304_Functional characterization of the human tRNA methyltransferases TRMT10A and TRMT10B. | ENSMUSG00000004127 | Trmt10a | 52.291033 | 2.252874885 | 1.171767 | 0.42488513 | 7.390787 | 0.0065558791099258606482891309497063048183917999267578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0355854237445257792771258209540974348783493041992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 72.1915821 | 27.5807197 | 31.8370261 | 12.2614759 | |
| ENSG00000145723 | 54826 | GIN1 | protein_coding | Q9NXP7 | Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | Predicted to enable nucleic acid binding activity. Predicted to be involved in DNA integration. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:54826; | nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; DNA integration [GO:0015074] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) | ENSMUSG00000026333 | Gin1 | 34.001157 | 2.377943121 | 1.249714 | 0.34955872 | 12.507329 | 0.0004053586660396178036926129184536193861276842653751373291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0034884362790488900388230497640051908092573285102844238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 42.8192613 | 9.7626470 | 18.0177367 | 4.2197339 | ||
| ENSG00000145743 | 64839 | FBXL17 | protein_coding | Q9UF56 | FUNCTION: Substrate-recognition component of the SCF(FBXL17) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, a key component of a quality control pathway required to ensure functional dimerization of BTB domain-containing proteins (dimerization quality control, DQC) (PubMed:30190310). FBXL17 specifically recognizes and binds a conserved degron of non-consecutive residues present at the interface of BTB dimers of aberrant composition: aberrant BTB dimer are then ubiquitinated by the SCF(FBXL17) complex and degraded by the proteasome (PubMed:30190310). The ability of the SCF(FBXL17) complex to eliminate compromised BTB dimers is required for the differentiation and survival of neural crest and neuronal cells (By similarity). The SCF(FBXL17) complex mediates ubiquitination and degradation of BACH1 (PubMed:24035498, PubMed:30190310). The SCF(FBXL17) complex is also involved in the regulation of the hedgehog/smoothened (Hh) signaling pathway by mediating the ubiquitination and degradation of SUFU, allowing the release of GLI1 from SUFU for proper Hh signal transduction (PubMed:27234298). The SCF(FBXL17) complex mediates ubiquitination and degradation of PRMT1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:B1H1X1, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QZN1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24035498, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27234298, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30190310}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation pathway | Members of the F-box protein family, such as FBXL17, are characterized by an approximately 40-amino acid F-box motif. SCF complexes, formed by SKP1 (MIM 601434), cullin (see CUL1; MIM 603134), and F-box proteins, act as protein-ubiquitin ligases. F-box proteins interact with SKP1 through the F box, and they interact with ubiquitination targets through other protein interaction domains (Jin et al., 2004 [PubMed 15520277]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:64839; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; SCF ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0019005]; entrainment of circadian clock by photoperiod [GO:0043153]; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000086]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neural crest cell differentiation [GO:0014033]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein polyubiquitination [GO:0000209]; protein quality control for misfolded or incompletely synthesized proteins [GO:0006515]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0008589]; SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0031146] | 18820369_F-box protein 17 (FBXL17) can serve as a therapeutic target and surrogate marker for breast cancer therapy. 20200978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24035498_Identify a role for SCF(FBXL17) in controlling the threshold for NRF2-dependent gene activation via BACH1 repressor turnover. 27234298_In summary, these findings reveal Fbxl17 as a novel regulator of the Hedgehog signaling pathway and highlight the perturbation of the Fbxl17-Sufu axis in the pathogenesis of medulloblastoma. 31560077_Rearrangements of Fbxl17 in breast cancer affect its ability to bind substrates and to assemble as part of a functional SCF ubiquitin ligase complex. 32814905_Structural basis for dimerization quality control. | ENSMUSG00000023965 | Fbxl17 | 140.301713 | 2.157384822 | 1.109284 | 0.26194629 | 17.554931 | 0.0000279125994325062155355411663837372771013178862631320953369140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0003334256540238232039558008423796309216413646936416625976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 175.8783717 | 52.9278735 | 79.3817793 | 23.9275471 | |
| ENSG00000146067 | 54540 | FAM193B | protein_coding | Q96PV7 | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | Located in cytoplasm; nuclear speck; and nucleolus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | Mouse_homologues mmu:212483; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634] | 21177767_Expression of full length IRIZIO cDNA also cooperated with PAX3-FOXO1 in the transformation of Arf-/- myoblasts. Given that IRIZIO is expressed at increased levels in rhabdomyosarcoma, it might contribute to rhabdomyosarcomagenesis in humans. 26188516_Identification of FAM193b as KCTD5 interaction partner. Formation of trimeric complexes of KCTD5/cullin3 with MCM7, ZNF711 and FAM193B. 34518442_The ceRNA PVT1 inhibits proliferation of ccRCC cells by sponging miR-328-3p to elevate FAM193B expression. | ENSMUSG00000021495 | Fam193b | 159.419459 | 0.491358411 | -1.025152 | 0.28291849 | 12.817575 | 0.0003433784750179480764649408985889067480457015335559844970703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0030380633197666399511471801986317586852237582206726074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 92.3049242 | 16.8482788 | 186.4263986 | 33.5548470 | ||
| ENSG00000146070 | 7941 | PLA2G7 | protein_coding | Q13093 | FUNCTION: Lipoprotein-associated calcium-independent phospholipase A2 involved in phospholipid catabolism during inflammatory and oxidative stress response (PubMed:7700381, PubMed:8624782, PubMed:2040620, PubMed:16371369, PubMed:17090529, PubMed:10066756). At the lipid-aqueous interface, hydrolyzes the ester bond of fatty acyl group attached at sn-2 position of phospholipids (phospholipase A2 activity) (PubMed:2040620, PubMed:10504265). Specifically targets phospholipids with a short-chain fatty acyl group at sn-2 position (PubMed:2040620). Can hydrolyze phospholipids with long fatty acyl chains, only if they carry oxidized functional groups (PubMed:2040620, PubMed:8624782). Hydrolyzes and inactivates platelet-activating factor (PAF, 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine), a potent pro-inflammatory signaling lipid that acts through PTAFR on various innate immune cells (PubMed:10504265, PubMed:10066756, PubMed:7592717, PubMed:11590221, PubMed:7700381, PubMed:18434304, PubMed:16371369, PubMed:8675689, PubMed:8624782). Hydrolyzes oxidatively truncated phospholipids carrying an aldehyde group at omega position, preventing their accumulation in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles and uncontrolled pro-inflammatory effects (PubMed:2040620, PubMed:7700381). As part of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles, can hydrolyze phospholipids having long-chain fatty acyl hydroperoxides at sn-2 position and protect against potential accumulation of these oxylipins in the vascular wall (PubMed:17090529). Catalyzes the release from membrane phospholipids of F2-isoprostanes, lipid biomarkers of cellular oxidative damage (PubMed:16371369). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10066756, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10504265, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11590221, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16371369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17090529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18434304, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2040620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7592717, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7700381, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8624782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8675689}. | 3D-structure;Asthma;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;HDL;Hydrolase;LDL;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Phospholipid degradation;Phospholipid metabolism;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | The protein encoded by this gene is a secreted enzyme that catalyzes the degradation of platelet-activating factor to biologically inactive products. Defects in this gene are a cause of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase deficiency. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2009]. | hsa:7941; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; high-density lipoprotein particle [GO:0034364]; low-density lipoprotein particle [GO:0034362]; 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase activity [GO:0003847]; calcium-independent phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0047499]; hydrolase activity, acting on ester bonds [GO:0016788]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; lipid oxidation [GO:0034440]; low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling [GO:0034374]; peptide hormone processing [GO:0016486]; phosphatidylcholine catabolic process [GO:0034638]; plasma lipoprotein particle oxidation [GO:0034441]; platelet activating factor catabolic process [GO:0062234]; platelet activating factor metabolic process [GO:0046469]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090026] | 11248283_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11369691_Overexpression of hPLA2G7 by adenoviral gene transfer in mice diminished the neointima formation (restenosis) induced by a wire-guided denudation of endothelium of the common left carotid and spontaneous atherosclerosis in aortic roots. 11501940_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11807372_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11807372_The genetic mutation of plasma PAF-AH gene appear to be an independent risk factor for AAA (abdominal aortic aneurysm) 11810302_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11850055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11861667_the ratio of HDL-associated PAF-AH-total plasma enzyme activity may be useful as a potential marker of atherogenicity in subjects with primary hypercholesterolemia. 12068200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12428682_electrotransfer of the human plasma PAF-AH gene to skeletal muscle reduces the extent of atherosclerosis in apoE(-/-) mice 12466264_role as oxidized phospholipid hydrolase of high density lipoprotein particles 12548211_colony-stimulating factors may modulate the local concentration of platelet-activating factor in the decidua via their inhibitory or stimulatory effect on the secretion of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase 12590019_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12649088_Human plasma PAF-AH exerts an antiatherogenic effect by binding to all the lipoproteins and thereby protecting them from oxidation, producing less proatherogenic lipoproteins and preserving HDL functions. 12801611_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12801611_This genotype is not major determinant of population genetic risk of coronary heart disease(CHD), but association of this genotype with low levels of Lp-PLA(2) strongly support pro-inflammatory causative, and not consequential, role of Lp-PLA(2) in CHD. 14671207_Platelet-activating factor inhibits PAF-AH secretion by decidual macrophages.Inhibitory action is mediated by signal transduction involving intracellular calcium and protein kinase C. 15081260_The PAF-AH gene missense mutation has no relation to either susceptibility or severity of conventional multiple sclerosis, yet its activity is down-regulated, and it may confer the severity of female opticospinal-MS. 15115767_Ala379 substitution to Val in PLA2G7 was less frequent in CAD patients than in controls, was associated with a lower risk of future CAD and showed higher plasma activity, thus Val379 may be protective against development of CAD. 15115767_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15148590_mutations InsA191 and I317N impair function of the Lp-PLA2 gene in lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 deficiency patients 15215249_the mechanism by which LPS modulates expression of PAF AH at the transcriptional level 15318030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15364890_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15956136_OxLDL accumulates in arteries in nonhyperlipidemic transgenic animals within 1 week after injury and local expression of human PAFAH reduces this accumulation and exerts antiinflammatory, antithrombotic, and antiproliferative effects 16086290_The findings show that the 994(G--> T) mutation of plasma PAF-AH gene may be an independent risk for atherosclerotic cerebral infarction, but not for lacunar infarction. 16223884_lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) activity, but not the enzyme mass, is a marker of small, dense LDL in human plasma 16308493_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16371369_PAF acetylhydrolases play key roles in the hydrolysis of F2-isoprostanes esterified on phospholipids in vivo 16438975_Lp-PLA2 activity and PLA2G7 A379V genotype were related to mediators of atherosclerosis in a diabetic study. 16530769_Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) (Lp-PLA(2))is strongly correlated with several cardiovascular risk factors. 16787988_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17090529_PON1 is neither a PLOOH peroxidase nor hydrolase and that the phospholipase A(2)-like activity previously attributed to PON1 in natural enzyme preparations was actually due to novel PLOOH hydrolytic activity of contaminating PAF-AH 17092424_COX-2 and PAF-AH play a role in the occurrence of MODS 17160904_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17174223_Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 A379V variant is associated with body composition changes in response to exercise training. 17174223_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17251670_The distribution of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH) was associated with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) and may be a marker of inflammation in patients with paroxysmal AF. 17502572_Early coronary atherosclerosis in humans is characterized by local production of Lp-PLA2. Local coronary production of lysophosphatidylcholine, the active product of Lp-PLA2, is associated with endothelial dysfunction. 17509958_The increased values of VEGF, PLA2-LDL and P-selectin in patients with long standing pulmonary hypertension are related to severe endothelial dysfunction and may have prognostic values. 17587752_LDL-C level showed a significant interaction with the G994T genotype in Japanese 17908960_inactivation of PAF, produced by TEC, by the overexpression of plasma PAF-AH affects survival, migration, and the angiogenic response of TEC both in vitro and in vivo 17981297_PAF-AcH could play an anti-inflammatory role by reducing the concentration of PAF. 18001304_We described two new highly polymorphic markers located 31 bp downstream of the last nucleotide of exon 12 in the 3' UTR region of the gene PLA2G7 18061193_Race and sex independently influence Lp-PLA2 activity and mass 18094516_Lp-PLA2 may have different mechanisms of action among American and Japanese men. Lp-PLA2 levels can not explain the observed CAC differences between the two populations. 18165686_Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry identifies substrates and products of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 in oxidized human low density lipoprotein 18201705_Elevated levels of Lp-PLA(2)(lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2) activity and mass, respectively, were in this study, independently of established risk factors related to the incidence of ischemic stroke 18204052_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18204052_PLA2G7 represents an important, potentially functional candidate in the pathophysiology of coronary artery disease based on replicated associations using two independent datasets and multiple statistical approaches. 18259035_Lp-PLA(2) was associated with incident ischemic stroke independently of C-reactive protein and traditional cardiovascular risk factors among nonusers of hormone therapy with highest risk in those who had both high C-reactive protein and high Lp-PLA(2) 18356547_These findings strongly support a role for Lp-PLA2 in the pathophysiology and clinical presentation of cerebrovascular disease. 18383322_association of Lp-PLA(2) levels with arterial disease events implies a role for this enzyme in atherogenesis, our findings suggest that it is not prothrombotic. 18408575_Lp-PLA2 is independently associated with progression of cardiac allograft vasculopathy and predicts a higher incidence of cardiovascular events and cardiovascular death in transplant patients 18431085_The aim of the present study was to evaluate the contribution of the PAFAH gene Arg92His, Ile198Thr and Ala379Val polymorphisms to resistance toward developing cardiovascular events in healthy Sicilian octogenarians. 18434304_mouse and human PAF-AHs associate with human HDL particles of different density 18587071_In atherogenic aortas, an imbalance between PAF-AH and transacetylase activity, as well as lyso-PAF accumulation, may lead to unregulated PAF formation and to progression of atherosclerosis 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18779277_Association of elevated Lp-PLA(2) activity with coronary disease risk in relation to oxidant stress supports a proatherogenic role of Lp-PLA(2). 18784071_crystal structure is also presented of PAF acetylhydrolase reacted with the organophosphate compound paraoxon via its active site Ser273 18789441_Plasma lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 has a role in heart failure 18832472_If Lp-PLA(2) independently influences clinical events, it does so by promoting atherosclerotic plaque instability rather than by stimulating atherogenesis. 18930040_Results describe the correlations between the plasma levels of adiponectin and two markers of inflammation: lipoprotein associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) and myeloperoxidase (MPO). 18983494_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19034521_An independent association of increased plasma Lp-PLA(2) activity with coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction existed in this Chinese Han Population. 19034521_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19069165_plasma PAF-AH deficiency may be considered as a genetic risk factor for stroke. (review) 19135199_Cardiovascular risk factors and genetic variation contribute to variability in Lp-PLA(2) activity and mass. 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19272461_The potential role of Lp-PLA2 associated with different lipoprotein classes in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease, is discussed. 19336475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19359705_the relationship between Lp-PLA(2) and oxLDL in the atherosclerotic plaque 19373214_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19373214_The 994T allele increased the plasma oxLDL/LDL ratio in a recessive manner, whereas 994T had a codominant effect on the Lp-PLA(2) activity. 19500354_Lp-PLA2 may compensate for the adiposity-associated increases in inflammatory and oxidative burden, in men. 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19583678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19596311_PAF acetylhydrolase activity and distribution in women with polycystic ovaries could contribute to the low-grade chronic inflammation and increased risk of atherosclerosis in these patients 19644070_Lp-PLA2 mass levels decrease modestly, whereas hsCRP and Lp-PLA2 activity appear stable over time. Acutely after stroke and MI, hsCRP increases whereas Lp-PLA2 mass and activity levels decrease. 19763134_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19763134_data suggest an ethnic difference and the possible involvement of genetic polymorphisms of PLA2G7 in the prevalence of carotid atherosclerosis in the hypertensive Japanese, especially in men 19804884_Lp-PLA(2) mass and activity were associated with incident CVD events in older adults in CHS. Lp-PLA(2) and CRP were independent and additive in prediction of events. 19850020_The alterations in lipoprotein profile, CETP, PON 1 and LpPLA(2) activities described in the present study indicate that non-treated iron deficiency anaemia might represent a proatherogenic state. 19886071_Patients with ischemic stroke and severe inflammatory reaction presented Lp-PLA2 (lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 ) with high levels more frequently than the healthy controls 19892409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19892409_PLA2G7 may influence the clinical manifestation of schizophrenia. 19910444_oxLDL, and more specifically its unhydrolyzed oxidized phospholipids, can up-regulate lp-PLA2 expression in monocytes through the PI3K and p38 MAPK pathway 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20067121_Patients with polycystic ovary syndrome have similar total plasma PAF-AH activity as healthy women. 20080080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20080080_recessive effects of Lp-PLA(2) V279F on LDL-cholesterol and significant correlations between Lp-PLA(2) activity and LDL-cholesterol, 8-epi-PGF(2alpha) and fibrinogen support a pro-oxidative or pro-atherogenic role for this enzyme 20185515_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20185811_Levels of Lp-PLA(2) activity were significantly associated with incident CHD among men and women with type 2 diabetes, independent of traditional and inflammatory risk factors. 20200624_of 33 studies that met inclusion criteria, 30 showed a significant association between Lp-PLA2 and cardiovascular events; available body of evidence suggests that Lp-PLA2 is a reliable marker of risk for cardiovascular events [systematic review] 20331434_Studies designed to evaluate the ability of precursor forms of PAF-AH to mature to fully active proteins indicated that the N-terminal end of human and mouse PAF-AH played important and opposite roles in this process. 20367923_The elevated L-PAF-AH activity may be associated with insulin resistance in polycystic ovary syndrome patients. 20442857_analyses demonstrate that genetic polymorphisms may contribute to inter-individual variation in Lp-PLA(2) activity and mass. 20444451_Lp-PLA(2) activity is associated with allele-specific apo(a) levels, but this association differs across African American-Caucasian ethnicity 20479152_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20479152_Unlike Lp-PLA2 activity, PLA2G7 variants associated with modest effects on Lp-PLA2 activity were not associated with cardiovascular risk markers, coronary atheroma, or coronary heart disease. 20507838_The oxidative modification of low density lipoproteins and the higher activity of PAF-AH are related with the low Mg status. 20625038_patients with beta-thalassemia exhibit high plasma Lp-PLA(2) levels 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634581_Genetic deficiency of Lp-PLA2 activity is not associated with a reduced risk of AD in the Japanese population. 20634581_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20926117_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20926117_Variants of PLA2G7 gene have been reported to be associated with coronary heart disease (CHD) 21107710_The V279F polymorphism in LP-PLA2 gene may contribute to coronary heart disease development. 21155029_Taiwanese female vegetarians have lower serum Lp-PLA2 activity. 21176638_LPS significantly upregulated Lp-PLA(2) in macrophages, and simvastatin suppressed this upregulation by inhibiting the p38MAPK pathway. 21247435_lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity was significantly increased in Metabolic Syndrome subgroups when compared with controls, and was higher in patients with carotid plaques than those without plaques 21281786_The PLA2G7, HPGD, EPHX2, and CYP4F8 genes are highly expressed in prostate cancer. 21316774_Of the inflammation markers, Lp-PLA2 levels are significantly higher in patients with good coronary collateral (CC) development than with poor CC in patients with isolated left coronary artery disease. 21432021_Data show that the proinflammatory mediators, lipopolysaccharide and platelet-activating factor, increased levels of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase mRNA via distinct signaling pathways. 21476960_Multiple regression analysis showed that apo B was significantly associated with LP-PLA2 adjusted for age, Body mass index, triglycerides and LDL-C (R2=0.32). 21490708_Natural deficiency in Lp-PLA activity due to carriage of PLA2G7 279F allele protects from CAD in Korean men. 21553808_Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) interacts with phospholipid vesicles via a surface-disposed hydrophobic alpha-helix 21606947_Lp-PLA2 activity was significantly lower in rare non-synonymous single-nucleotide polymorphisms carriers compared with non-carriers and seven variants had enzyme activities consistent with a null allele. 21616491_analysis of genetic and environmental regulation of inflammatory CVD biomarkers Lp-PLA2 and IgM anti-PC 21620406_Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 may have a role in symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic disease 21708876_Lp-PLA(2) is not associated with endothelial dysfunction, suggesting its role in atherosclerosis development is primarily related to other factors. 21714927_Whites have the highest Lp-PLA mass and activity levels, followed by Hispanics and Asians, and then African-Americans; in age- and sex-adjusted analyses, these differences are significant for each non-White race when compared to Whites. 21834908_We conclude that there is significant association between the rs16874954 mutation and CAD in the Chinese Han population. 21880383_subjects carrying the Ala/Val genotype are less likely to have essential hypertension, while hypertensive patients carrying the Ala/Val genotype have elevated fibrinogen levels 21882811_both the myristoyl group and the hydrophobic patch are essential for proper trafficking of the enzyme to the membranes following oxidative stress 21933589_Plasma Lp-PLA(2) activity is associated with plaque rupture in patients with CAD, independently of traditional CAD risk factors, hs-CRP level and IVUS parameters. 21942556_Data indicate that LpPLA2 seems to be a biomarker constantly correlated with heart failure, regardless of etiology. 22024276_Circulating Lp-PLA2 levels are associated with coronary plaque regression determined by intravascular ultrasonography in patients with acute coronary syndrome. 22028154_Serum level of Lp-PLA is associated with both eccentricity index and fibrous cap thickness in both UA and SA groups. Elevated levels of circulating Lp-PLA might to be a strong risk factor and more serious for unstable angina than stable angina. 22139405_Serum platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase levels were increased in patients with systemic sclerosis and associated with a lower frequency of pitting scars/digital ulcers and arthritis/ arthralgias. 22153151_Lp-PLA2 mass may add relevant information regarding early arterial recanalization in intravenous tissue-type plasminogen activator treated stroke patients. 22164942_Lipoprotein associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) is an inflammatory biomarker which provides information on plaque inflammation and stability; it is expressed in macrophages and foam cells in rupture-prone atherosclerotic plaque. 22178747_Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) activity is associated with large-artery atherosclerotic etiology and recurrent stroke in transient ischemic attack patients. 22197603_apoE-containing HDL has a relatively high PAF-AH activity in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. 22202492_PLA2G7 is a cancer-selective biomarker in 50 % of prostate cancers and associates with aggressive disease. 22246459_Lp-PLA2 mass is altered in multiple scelrosis patients compared to healthy controls 22300679_Lp-PLA(2) and PCSK9 levels were both correlated positively with LDL cholesterol and non-high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and Lp-PLA(2) was inversely related to PCSK9. 22338104_In this population-based cohort enriched with dysmetabolic phenotypes, LpPLA(2) mass and activity showed divergent associations with cardiovascular diseases. 22340269_Common genetic variation in PLA2G7 is associated with subclinical coronary atherosclerosis. 22359537_The lack of relation between circulating Lp-PLA(2) activity and Lp-PLA(2) activity in PBMCs was found in postmenopausal women with high ox-LDL 22447189_Elevated Lp-PLA(2) mRNA expression is associated with acute ischemic stroke. 22499993_The associations among Lp-PLA2, lysophosphatidylcholine, and proinflammatory cytokines in human plaques suggest that lysoPCs play a key role in plaque inflammation and vulnerability. 22632920_The presence of the apo E4 isoform was associated with a higher level of Lp-PLA(2) index, a marker of vascular inflammation, synergistically increasing cardiovascular risk. 22665167_associations between Lp-PLA(2) and vascular disease 22755553_It was concluded that Lp-PLA2 may be a new useful biomarker to evaluate clinical or subclinical activity of the disease besides CRP and ESR 22784637_variability of Lp-PLA(2) across gender, ethnicity, and levels of circulating lipids and markers of systemic inflammation are more consistent and appear not to vary importantly across categories defined by CVD or its risk factors. 22797139_The neonates of women with severe preeclampsia had significantly higher plasma PAF-AH levels. 22859728_In the WHI-OS Lp-PLA2 mass, but not activity, was independently associated with CVD. However, model fit did not significantly improve with Lp-PLA2 mass, and assay calibration remains a clinical concern 22898284_Val279Phe SNPs in the 9th exon of PAF-AH may be associated with intracranial hemorrhage in preterm infants. 23083783_Total plasma Lp-PLA(2) is a predictor of cardiac death, while HDL-Lp-PLA(2) is associated with lower risk for cardiac death in patients with stable CAD 23089713_aortic valve stenosis (AVS) is characterized by increased plasma Lp-PLA2 levels associated with the severity of AVS 23089916_the interaction between recombinant human Lp-PLA(2) and human HDL 23103135_Lp-PLA2 levels are significantly associated with coronary heart disease. 23118945_High Lp-PLA2 activity implies a worse prognosis at long term follow up in high-risk Caucasian patients referred for coronary angiography. 23140470_Our results demonstrated dynamic alterations in Lp-PLA2 levels during the early stages of ACS and, therefore, indirectly support the hypothesis of an active role for Lp-PLA2 in the pathogenesis of ACS. 23361301_PLA2G7 expression is elevated in colon tumors compared with normal tissues. 23413990_Lp-PLA2 activity changes in obesity and it shows important associations with markers of cardiovascular risk. 23439604_Darapladib produced sustained inhibition of Lp-PLA2 activity in Japanese dyslipidemic patients with/without the V279F SNP of Lp-PLA2. 23546765_Prediabetes patients have significantly decreased high-density lipoprotein-LP-PLA2 activity compared with subjects with glucose levels Phe Polymorphism of Lp-PLA2 may lead to decrease the enzymatic activity via changes of folding kinetics and recognition to its substrate. 26642708_circulating CETP and Lp-PLA2 might partly play a role in the atherogenic disturbances in patients with iron deficiency anemia through increased susceptibility to lipid peroxidation 26775119_Lp-PLA2 activity in Japanese men aged 50-79 years was associated significantly and positively with IMT and plaque in the carotid artery but Mendelian randomization did not support that Lp-PLA2 is a causative factor for subclinical atherosclerosis. 26791069_A V279F loss-of-function variant in the PLA2G7 gene resulting in 50% lower activity for each copy of the variant, is common in East Asians and associated with risk of Vascular diseases. 26801405_Increased plasma Lp-PLA2 activity portends increased risk of resistant hypertension. 26828804_no relationship with either proinflammatory cytokines or neopterin identified in Alzheimer disease 26848158_Higher Lp-PLA2 mass and activity were associated with development of both incident clinical peripheral arterial disease and low ankle brachial index. 27097870_results do not support added value of Lp-PLA2 for predicting cardiovascular events or mortality among CHD patients beyond traditional risk factor 27206945_LpPLA2 is found in both LDL and HDL and is distributed differently in men with T1D without any relationship to CAC score progression 27301456_Lifelong lower Lp-PLA2 activity was not associated with major risks of vascular or non-vascular diseases in Chinese adults. 27392709_Taken together, these results revealed that Lp-PLA2 silencing protected against ox-LDL-induced oxidative stress and cell apoptosis via Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in human THP1 macrophages. 27450918_PLA2G7 gene expression was co-regulated by 17-beta-estradiol and promoter methylation. 27461004_Data show that all the six inflammation-related CpG-SNPs genotypes including IL1B rs16944, IL1R2 rs2071008, PLA2G7 rs9395208, FAM5C rs12732361, CD40 rs1800686, and CD36 rs2065666 were associated with coronary heart disease (CHD), suggesting an important role of inflammation in the risk of CHD. 27487154_phospholipase A2 Group 7 (PLA2G7), to be important in regulating tumor cell migration and a novel tumor-promoting factor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 27614353_Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 as a new marker to determine cardiovascular risk in hypercholesterolemic dyslipidaemic children 27641736_A considerable portion of Chinese ischemic stroke patients are insensitive to aspirin treatment, which may be correlated with the MDR1 C3435T, TBXA2R (rs1131882), and PLA2G7 (rs1051931-rs7756935) polymorphisms. 27710915_High Lp-PLA2 expression is associated with type 1 diabetes. 27776715_Elevated mass and activity of Lp-PLA2 related to inflammation and atherosclerosis may take part in the development of kidney injury and atherosclerosis in patients with chronic kidney disease. 27905470_A PLA2G | ENSMUSG00000023913 | Pla2g7 | 28.541452 | 0.472385390 | -1.081964 | 0.29050906 | 14.138843 | 0.0001698011057807009805634829158194065712450537830591201782226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0016448600191554330410270701179342722753062844276428222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 18.5674164 | 4.8280259 | 39.5514883 | 9.6047490 | |
| ENSG00000146192 | 221472 | FGD2 | protein_coding | Q7Z6J4 | FUNCTION: Activates CDC42, a member of the Ras-like family of Rho- and Rac proteins, by exchanging bound GDP for free GTP. Activates JNK1 via CDC42 but not RAC1. Binds to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate, phosphatidylinositol 5-monophosphate, phosphatidylinositol 4-monophosphate and phosphatidylinositol 3-monophosphate (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Endosome;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to a family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) which control cytoskeleton-dependent membrane rearrangements by activating the cell division cycle 42 (CDC42) protein. This gene is expressed in B lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. The encoded protein may play a role in leukocyte signaling and vesicle trafficking in antigen-presenting cells in the immune system. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. | hsa:221472; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate binding [GO:1901981]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; filopodium assembly [GO:0046847]; positive regulation of JUN kinase activity [GO:0043507]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056] | 18838382_FGD2 has a role in leukocyte signaling and vesicle trafficking in cells specialized to present antigen in the immune system 32681954_Characterization of guanine nucleotide exchange activity of DH domain of human FGD2. | ENSMUSG00000024013 | Fgd2 | 41.895893 | 0.436459823 | -1.196079 | 0.24286842 | 24.750367 | 0.0000006525636369172534831918316457211037828756161616183817386627197265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000111589977422965062930004451202670168186159571632742881774902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 25.5993991 | 4.4442712 | 58.9788999 | 9.1134738 | |
| ENSG00000146281 | 135293 | PM20D2 | protein_coding | Q8IYS1 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the peptide bond hydrolysis in dipeptides having basic amino acids lysine, ornithine or arginine at C-terminus. Postulated to function in a metabolite repair mechanism by eliminating alternate dipeptide by-products formed during carnosine synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24891507}. | Carboxypeptidase;Hydrolase;Protease;Reference proteome | Enables dipeptidase activity and identical protein binding activity. Acts upstream of or within proteolysis and regulation of cellular protein metabolic process. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:135293; | nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; carboxypeptidase activity [GO:0004180]; dipeptidase activity [GO:0016805]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of cellular protein metabolic process [GO:0032268] | 24891507_PM20D2 hydrolyzed beta-alanyl-lysine, beta-alanyl-ornithine, gamma-aminobutyryl-lysine, and gamma-aminobutyryl-ornithine as its best substrates. | ENSMUSG00000054659 | Pm20d2 | 130.890572 | 0.204640645 | -2.288835 | 0.51776717 | 16.244215 | 0.0000556793398998639378692614154697793082959833554923534393310546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0006108569462896445241215093169273586681811138987541198730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 48.7937474 | 19.7199436 | 223.9289911 | 90.5257713 | |
| ENSG00000147364 | 26260 | FBXO25 | protein_coding | Q8TCJ0 | FUNCTION: Substrate-recognition component of the SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein)-type E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. May play a role in accumulation of expanded polyglutamine (polyQ) protein huntingtin (HTT) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Direct protein sequencing;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation pathway | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. | This gene encodes a member of the F-box protein family which is characterized by an approximately 40 amino acid motif, the F-box. The F-box proteins constitute one of the four subunits of ubiquitin protein ligase complex called SCFs (SKP1-cullin-F-box), which function in phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination. The F-box proteins are divided into 3 classes: Fbws containing WD-40 domains, Fbls containing leucine-rich repeats, and Fbxs containing either different protein-protein interaction modules or no recognizable motifs. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the Fbxs class. Three alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:26260; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; SCF ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0019005]; ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000151]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] | 16278047_investigated hFBX25's genomic organization and established hFBX25 as an FBP by verifying its interaction with Skp1 and Cul1 18287534_The cellular distribution of FBXO25 and its colocalization with some nuclear proteins is investigated by using immunochemical and biochemical approaches. 20473970_Beta-actin, physically interacts through its N-terminus with FBXO25 and is enriched in the FBXO25 nuclear compartments. 21596019_Altogether, Fbxo25 acts as an ubiquitin E3 ligase to target cardiac transcription factors including Nkx2-5, Isl1, and Hand1, indicating that cardiac protein homeostasis through Fbxo25 has a pivotal impact on cardiac development. 23940030_FBXO25 mediates ELK-1 degradation through the ubiquitin proteasome system and thereby plays a role in regulating the activation of ELK-1 pathway in response to mitogens 25419709_FBXO25 functions as a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor in mantle cell lymphoma. 27596142_High FBXO25 expression is associated with non-small-cell lung cancer. 28389297_Taken together we show that FBXO25 functions as a negative regulator of MAPK signaling though the reduction of ERK1/2 activation. 31827076_LncRNA ODIR1 inhibits osteogenic differentiation of hUC-MSCs through the FBXO25/H2BK120ub/H3K4me3/OSX axis. 31849056_From man to fly - convergent evidence links FBXO25 to ADHD and comorbid psychiatric phenotypes. 32335130_FBXO25 Promotes Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth and Metastasis through Cyclin D1. 33428929_ELK-1 ubiquitination status and transcriptional activity are modulated independently of F-Box protein FBXO25. | ENSMUSG00000038365 | Fbxo25 | 117.593051 | 2.859935352 | 1.515983 | 0.44516861 | 10.773374 | 0.0010297065858165380981825709483246100717224180698394775390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0077647092843136037570994645307109749410301446914672851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 180.6804560 | 50.7463276 | 63.1514386 | 17.7753677 |
| ENSG00000148143 | 58499 | ZNF462 | protein_coding | Q96JM2 | FUNCTION: Zinc finger nuclear factor involved in transcription by regulating chromatin structure and organization (PubMed:20219459, PubMed:21570965). Involved in the pluripotency and differentiation of embryonic stem cells by regulating SOX2, POU5F1/OCT4, and NANOG (PubMed:21570965). By binding PBX1, prevents the heterodimerization of PBX1 and HOXA9 and their binding to DNA (By similarity). Regulates neuronal development and neural cell differentiation (PubMed:21570965). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:B1AWL2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20219459, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21570965}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Glycoprotein;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to C2H2-type zinc finger family of proteins. It contains multiple C2H2-type zinc fingers and may be involved in transcriptional regulation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. | hsa:58499; | nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; negative regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043392]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468] | 18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20080650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22826440_Zinc finger protein 462 (ZNF462) is the first human O-GlcNAc-6-phosphate modified protein. 28513610_Loss of function variants in ZNF462 were identified in patients with ptosis, metopic ridging, craniosynostosis, dysgenesis of the corpus callosum, and developmental delay. 29427787_In the current study we describe a patient with a syndromic form of autism spectrum disorder and intellectual disability characterized by metopic craniosynostosis, ptosis and corpus callosum dysgenesis most likely caused by ZNF462 haploinsufficiency. The possible contribution of the disruption of KLF12 by one of the translocation breakpoints remains unclear. 31361404_a multiple congenital anomaly syndrome associated with haploinsufficiency of ZNF462 that has distinct clinical characteristics and facial features, is reported. | ENSMUSG00000060206 | Zfp462 | 90.354111 | 0.304627967 | -1.714880 | 0.51452763 | 10.497972 | 0.0011950562989848788515712119107092803460545837879180908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0088120440222459062856730227508705866057425737380981445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 33.6694083 | 11.4809529 | 110.6724637 | 37.5192821 | |
| ENSG00000148297_ENSG00000148296 | 7.417504 | 75.308170537 | 6.234734 | 1.28482965 | 25.147118 | 0.0000005311897027178162826598789049425963781914106220938265323638916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000092994762973927585461998007732020710136566776782274246215820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 12.3244178 | 13.9016487 | 0.1641898 | 0.2453160 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000148677 | 27063 | ANKRD1 | protein_coding | Q15327 | FUNCTION: May play an important role in endothelial cell activation. May act as a nuclear transcription factor that negatively regulates the expression of cardiac genes. Induction seems to be correlated with apoptotic cell death in hepatoma cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15805281, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7730328}. | ANK repeat;Coiled coil;Disease variant;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat | The protein encoded by this gene is localized to the nucleus of endothelial cells and is induced by IL-1 and TNF-alpha stimulation. Studies in rat cardiomyocytes suggest that this gene functions as a transcription factor. Interactions between this protein and the sarcomeric proteins myopalladin and titin suggest that it may also be involved in the myofibrillar stretch-sensor system. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:27063; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; I band [GO:0031674]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; R-SMAD binding [GO:0070412]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; titin binding [GO:0031432]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis [GO:0055008]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus [GO:0071560]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466]; negative regulation of DNA biosynthetic process [GO:2000279]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:0043517]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; protein kinase C signaling [GO:0070528]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to muscle stretch [GO:0035994]; sarcomere organization [GO:0045214]; skeletal muscle cell differentiation [GO:0035914] | 12054667_Cardiac ankyrin repeat protein, a negative regulator of cardiac gene expression, is augmented in human heart failure. 12524226_CARP expression is observed by in situ hybridization in endothelial cells lining human atherosclerotic plaques, whereas lesion macrophages are devoid of CARP; it is induced by activin A in cultured intimal smooth muscle cells. 12679596_These findings suggest that type-specific expression patterns of ARPP and CARP are altered in skeletal muscles of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 15698842_endogenous ANKRD1 and calsequestrin are co-enriched in piglet cardiac Purkinje cells 16450059_CARP interacts with itself and desmin. CARP, ankrd2, and DARP contain potential coiled-coil dimerization motifs within their unique aminoterminal domains that mediate the formation of homo-dimers. 17239933_CARP was expressed in renal podocytes at a high level in 10 of 13 cases of crescentic glomerulonephritis, 7 of 19 cases of diabetic nephropathy, and 12 of 20 cases of lupus nephritis. 18273862_cloned both translocation breakpoints and mapped the ANKRD1 gene, encoding a cardiac transcriptional regulator, 130 kb proximally to the breakpoint on chromosome 10, in total anomalous pulmonary venous return, a congenital heart defect 18656235_Our results indicate that CARP is a sensitive and specific marker for rhabdomyosarcoma and that it will be useful for the differential diagnosis of rhabdomyosarcoma. 18980987_We suggest that CDH1 cytoplasmic immunolocalization as a result of increased IGF-II levels identifies those nonmuscle invasive presentations most likely to recur 19359327_Augmented CARP expression may be a common molecular event in failing hearts regardless of cardiomyopathic aetiology. 19525294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19525294_On the basis of genetic and functional analysis of CARP mutations, ANKRD1 has been identified as a new gene associated with dilated cardiomyopathy, accounting for approximately 2% of the 231 cases studied. 19589340_Data show that ANKRD1 is a short-lived protein whose levels are tightly regulated by the 26S proteasome. 19608030_ANKRD1 is a novel DCM gene, with mutations present in 1.9% of DCM patients. The ANKRD1 mutations may cause DCM 19608030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19608031_CARP abnormalities may be involved in the pathogenesis of HCM. 19608031_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20164196_CD45 lateral mobility is regulated by the spectrin-ankyrin cytoskeleton of T cells 20599664_p53 operates as an upstream effector of Ankrd1/CARP, by up regulating the proximal ANKRD1 promoter 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20860623_CARP and its regulator calpain 3 appear to occupy a central position in the important cell fate-governing NF-kappaB pathway in skeletal muscle 22085644_Ankrd1 and desmin may play important roles in airway smooth muscle cell homeostasis. 22185618_Although analyzed in a limited number of patients, there is a considerable body of evidence that MARP proteins could be suitable candidates for prognostic and diagnostic biomarkers. 22892129_the 26S proteasome is the dominant regulator of Ankrd1/CARP degradation, and that Ankrd1/CARP half-life is significantly longer in cardiomyocytes (h) than endothelial cells (min). 23572067_Report impact of ANKRD1 mutations associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy on contraction parameters of engineered heart tissue. 24531715_ANKRD1 has a significant role in the regulation of apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells 25125175_Report structure activity relationships for ANKRD1. 25585647_To the Ankrd1, it is not responsive to the cardiotoxic drug Doxorubicin, suggesting that different mechanisms govern their expression in cardiac cells. 25961010_The association of ANKRD1 with antiapoptotic response suggests its role as myocyte survival factor during late stage heart disease, warranting further studies on ANKRD1 during end-stage heart failure. 26860204_These data suggest that hepatitis C virus coopts ANKRD1 for its own propagation and up-regulation of ANKRD1 may contribute to hepatitis C virus-mediated liver pathogenesis. 27143260_review of CARP, including its discovery, structure, and the role it plays in cardiac development and heart diseases [review] 29371118_ANKRD1 expression is reduced in patients with eczema herpeticum and might contribute to its pathogenesis 30291293_ANKRD1 overexpression associated with the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and anti-apoptosis involved in resistance to second-and third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. 30659708_To identify the p.S187F mutant of ANKRD1, which is associated with cardiac septal defects. 30814490_Data show that RREB1-induced upregulation of AGAP2-AS1 regulates cell proliferation and migration in PC partly through suppressing ANKRD1 and ANGPTL4 by recruiting EZH2. 31688894_Myocardial overexpression of ANKRD1 causes sinus venosus defects and progressive diastolic dysfunction. 33647290_Molecular Characterisation of Titin N2A and Its Binding of CARP Reveals a Titin/Actin Cross-linking Mechanism. 34152365_Muscle ankyrin repeat protein 1 (MARP1) locks titin to the sarcomeric thin filament and is a passive force regulator. 34583851_LncRNA RGMB-AS1 up-regulates ANKRD1 Through Competitively Sponging miR-3614-5p to Promote OSA Cell Proliferation and Invasion. 34918678_ANKRD1 and SPP1 as diagnostic markers and correlated with immune infiltration in biliary atresia. | ENSMUSG00000024803 | Ankrd1 | 12.772418 | 0.377917407 | -1.403857 | 0.46219625 | 9.479313 | 0.0020780177915804090051088426349679139093495905399322509765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0140489670703850960675751480266626458615064620971679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 6.9937975 | 4.8052341 | 18.5830337 | 12.3452102 | |
| ENSG00000148824 | 92170 | MTG1 | protein_coding | Q9BT17 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in the regulation of the mitochondrial ribosome assembly and of translational activity. Displays mitochondrial GTPase activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23396448}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;GTP-binding;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Translation regulation | Enables GTPase activity. Involved in regulation of mitochondrial translation and regulation of respiratory system process. Located in mitochondrial inner membrane and mitochondrial ribosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:92170; | mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrial ribosome [GO:0005761]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; mitochondrial translation [GO:0032543]; regulation of mitochondrial translation [GO:0070129]; regulation of respiratory system process [GO:0044065]; translation [GO:0006412] | 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23396448_The results suggested that Mtg1 functions with the large subunit of the mitochondrial ribosome, and are involved in both the translation and assembly of respiratory complexes. 30085276_MTG1 establishes a quality control checkpoint in mitoribosome assembly. In conclusion, MTG1 controls mitochondrial translation by coupling mtLSU assembly with intersubunit bridge formation using the intrinsic GEF activity acquired by the mtSSU through mS27, a unique occurrence in translational systems. 30707992_dampening oxidative stress with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) lowered hypertrophy in MTG1 KO to WT levels. Collectively, our data indicate that MTG1 protects against pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction by preserving mitochondrial function and reducing oxidative stress and downstream TAK1 stress signaling. 34385605_Potential pathogenetic link between angiomyofibroblastoma and superficial myofibroblastoma in the female lower genital tract based on a novel MTG1-CYP2E1 fusion. 36177509_Vulvar angiomyofibroblastoma is molecularly defined by recurrent MTG1-CYP2E1 fusions. | ENSMUSG00000039018 | Mtg1 | 80.088021 | 0.362240803 | -1.464979 | 0.24589967 | 34.793302 | 0.0000000036663273357981001606813401135463725832863701725727878510951995849609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000893459699880554409789793022383941334396695310715585947036743164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 34.0822477 | 6.2893560 | 94.4335420 | 17.1849459 | |
| ENSG00000149564_ENSG00000019102 | 107.206815 | 2.048429735 | 1.034518 | 0.15712876 | 43.722241 | 0.0000000000378446433720977638328179323054506867987645257755957572953775525093078613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000011711744944444767351293275304234542399939300594269298017024993896484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 145.8011073 | 8.0816915 | 71.4960386 | 4.9099915 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000151012 | 23657 | SLC7A11 | protein_coding | Q9UPY5 | FUNCTION: Sodium-independent, high-affinity exchange of anionic amino acids with high specificity for anionic form of cystine and glutamate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15151999}. | 3D-structure;Amino-acid transport;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | This gene encodes a member of a heteromeric, sodium-independent, anionic amino acid transport system that is highly specific for cysteine and glutamate. In this system, designated Xc(-), the anionic form of cysteine is transported in exchange for glutamate. This protein has been identified as the predominant mediator of Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus fusion and entry permissiveness into cells. Also, increased expression of this gene in primary gliomas (compared to normal brain tissue) was associated with increased glutamate secretion via the XCT channels, resulting in neuronal cell death. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. | hsa:23657; | apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; astrocyte projection [GO:0097449]; brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; rough endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005791]; cystine:glutamate antiporter activity [GO:0015327]; L-amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015179]; adult behavior [GO:0030534]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; dipeptide import across plasma membrane [GO:0140206]; glutamate homeostasis [GO:0090461]; glutathione metabolic process [GO:0006749]; glutathione transmembrane transport [GO:0034775]; L-glutamate import across plasma membrane [GO:0098712]; lens fiber cell differentiation [GO:0070306]; limb development [GO:0060173]; lung alveolus development [GO:0048286]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced neuron death [GO:1903204]; platelet aggregation [GO:0070527]; regulation of AMPA glutamate receptor clustering [GO:1904717]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of cysteine metabolic process [GO:1901494]; regulation of glutamate metabolic process [GO:2000211]; regulation of glutathione biosynthetic process [GO:1903786]; regulation of melanin biosynthetic process [GO:0048021]; regulation of neutrophil apoptotic process [GO:0033029]; regulation of protein transport [GO:0051223]; regulation of synapse organization [GO:0050807]; response to nicotine [GO:0035094]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; response to redox state [GO:0051775]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; striatum development [GO:0021756]; ventricular system development [GO:0021591]; visual learning [GO:0008542] | 14722095_Cys(327) is a functionally important residue accessible to the aqueous extracellular environment and is structurally linked to the permeation pathway and/or the substrate binding site 15151999_topological model for xCT of 12 transmembrane domains with the N and C termini located inside the cell 15326101_Expression of Tat led to decrease in glutathione and increase in gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. The transport function of xc-was upregulated and was accompanied by increases in mRNAs for xCT and 4F2hc and in corresponding protein levels. 16574866_xCT was identified as the receptor mediating KSHV cell fusion; KSHV target cell permissiveness correlated closely with endogenous expression of xCT messenger RNA and protein in diverse cell types 18054200_These results suggest that reduced calcium signaling impairs AP-1 activation and that xCT expression may directly affect cell proliferation. 18287333_Induction of xCT led to glutamate-inhibitable cystine uptake and an increased rate of cysteine release from cells; overexpression of xCT in smooth muscle cells or endothelial cells led to glutamate-inhibitable cysteine release. 18469825_Small interfering RNA-mediated xCT silencing in gliomas inhibits neurodegeneration and alleviates brain edema. 18648370_The results suggest that the x(c)(-) transporter by enhancing glutathione biosynthesis plays a major role in pancreatic cancer growth, therapy resistance and represents a potential therapeutic target for the disease. 18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19015640_Caveolin-1 was upregulated and beta-catenin was recruited to the plasma membrane when xCT was deficient, which were followed by the inhibition of beta-catenin transcriptional activity. 19017641_long term activation of the phospho-eIF2alpha/ATF4/xCT signaling module by the specific eIF2alpha phosphatase inhibitor, salubrinal, induces resistance against oxidative glutamate toxicity in the hippocampal cell line HT22 and primary cortical neurons 19207949_Expression of xCT is significantly reduced in low-grade oligodendroglial tumours harbouring LOH1p 20007406_x(c)(-) transporter provides a useful target for glioma therapy. 20053169_Review discusses system xc- function in vitro and in vivo, its role as an ambivalent drug target, and the relevance of oxytosis mediated by inhibition of xCT for identification of neuroprotective proteins and signaling pathways. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20733204_The cystine/glutamate antiporter demonstrates its major role of cystine and glutamate transport while modulating intracellular glutathione content and efflux in dendritic cells during cell differentiation and cross-presentation in a transgenic system. 21369940_The pathways modify system activity beyond the level of xCT transcription, including regulation on the level of membrane trafficking and substrate availability, especially the regulation by glutamate transport through excitatory amino acid transporters. 21510944_Data show that SLC7A11 is the direct target of miR-26b and its expression is remarkably increased in both breast cancer cell lines and clinical samples. 21555518_SLC7A11 is a functional target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq and knockdown analysis in HEK 293 cells. 21639880_Results reveal that increased expression of the cystine/glutamate antiporter system xCT in multiple sclerosis provides a link between inflammation and excitotoxicity in demyelinating diseases. 21689549_Both IGF-1 and TGF-beta stimulated system xc-mediated cystine uptake in dental pulp cells. 23096413_These findings suggest that xCT is an independent predictive factor in glioblastomas 23771433_These observations suggest that the expression of xCT in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells might affect the G1/S checkpoint and impact on the prognosis of ESCC patients 24094812_the xCT antiporter, which is expressed on one-third of triple-negative breast tumors in this study, may have a role in glutamine updake and dependence 24516043_Our findings indicate that miRNA-27a negatively regulates SLC7A11 in cisplatin-resistant bladder cancer, and shows promise as a marker for patients likely to benefit from cisplatin-based chemotherapy 24686172_IGF-I regulates cystine uptake and cellular redox status by activating the expression and function of xCT in estrogen receptor-positive (ER(+)) breast cancer cells by a mechanism that relies on the IGF receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1). 25002527_Results show that Nrf2 and ATF4 were upregulated by proteasome inhibition and cooperatively enhance human xCT gene expression upon proteasome inhibition. 25399695_Data indicate that cystine-glutamate exchange transporter protein SLC7A11 mRNA is regulated by cellular stress and nonsense-mediated RNA decay (NMD). 25860939_We discovered that many genes involved in oxidative stress/antioxidant defense system, apoptosis/anti-apoptosis/cell death, and cellular response to unfolded proteins/topologically incorrect proteins are potentially regulated by xCT. 26019222_increased SLC7A11 expression predicted shorter malignant glioma patient survival. 26252954_the rate of cystine uptake was significantly faster than the rate of glutamate release in human glioma cells. 26254540_Sulfasalazine, a relatively non-toxic drug that targets cystine transporter, may, in combination with CDDP, be an effective therapy for colorectal cancer. 26540405_Study demonstrated that the mRNA expression levels of the two system xc- subunits, SLC7A11 and SLC3A2, in peripheral white blood cells are lowered in patients with schizophrenia than healthy individuals 26729415_Although LCN2 increased intracellular iron concentrations, LCN2-induced GSH may catalyze and override oxidative stress via CD44 and xCT, and subsequently enhance the survival of clear cell carcinoma tumor cells in oxidative stress-rich environment. 26865117_The most frequent SLC7A7 mutation in Japanese LPI patients is p.R410*, which is a founder effect mutation in northern Japan. 26930718_MUC1-C binds directly with CD44v and in turn promotes stability of xCT in the cell membrane 26980765_High SLC7A11 expression is associated with glioma. 27129162_Authors found that the xCT expression was increased in peripheral blood monocyte of active tuberculosis. xCT expression in macrophage was induced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) through TLR2/Akt- and p38-dependent signaling pathway. 27279909_Mechanistically, CD44v interacts with and stabilizes xCT and thereby promotes the uptake of cysteine for glutathione synthesis and stimulates side-population cell enrichment. 27658422_Results suggest that expression of SLC7A11 in the context of glioma contributes to tumorigenesis, tumor progression, and resistance to standard chemotherapy. 27705786_simultaneous mutations at all four acetylation sites completely abolish its ability to regulate metabolic targets, such as TIGAR and SLC7A11. Moreover, p53(4KR) is still capable of inducing the p53-Mdm2 feedback loop, but p53-dependent ferroptotic responses are markedly abrogated 28057599_Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of xCT potentiated the cytotoxic effects of aspirin plus sorafenib; this effect was diminished by xCT overexpression. Low-dose aspirin plus sorafenib enhanced the cytotoxicity of cisplatin in resistant HNC cells through xCT inhibition and oxidant and DNA damage. 28081640_While the transsulfuration pathway plays a primary role in supplying Cys to the redox system in the liver, xCT is induced in cases of emergencies, by compensating for Cys supply systems. 28202313_As targets of oncogenes with intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity, STAT3 and STAT5 become constitutively active in hematologic neoplasms and solid tumors, promoting cell proliferation and survival and modulating redox homeostasis via regulation xCT expression. (Review) 28348409_accumulated mutant-p53 protein suppresses the expression of SLC7A11, a component of the cystine/glutamate antiporter, system xC(-), through binding to the master antioxidant transcription factor NRF2. 28429737_In some breast cancer cells, xCT antiporter expression is upregulated through the antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2 and contributes to their requirement for glucose as a carbon source. 28553953_ATF4 expression fosters the malignancy of primary brain tumors and increases proliferation and tumor angiogenesis; experiments revealed that ATF4-dependent tumor promoting effects are mediated by transcriptional targeting the glutamate antiporter xCT 28610554_overexpression of SLC7A11 in the context of glioblastoma multiforme may contribute to tumor progression. 28627030_miR-375 served as a tumor suppressor via regulating SLC7A11. 28630042_Data suggest that glucose starvation of various neoplasm cell lines induces SLC7A11 expression; SLC7A11 overexpression decreases intracellular glutamate, an alternative source of metabolic energy; provision of alpha-ketoglutarate, a key downstream metabolite of glutamate, restores survival in SLC7A11-overexpressing neoplasm cell lines under glucose starvation. 28630426_the over-expression of SLC7A11, or supplementation with sufficiently cystine, or treatment with N-acetylcysteine significantly decreased P-gp expression and activity. It was suggested that ROS and SLC7A11/cystine were the two relevant factors responsible for the expression and function of P-gp, and that SLC7A11 might be a potential target modulating ADR resistance. 28648777_Identify mTORC2 as a critical regulator of amino acid metabolism in cancer via phosphorylation of the cystine-glutamate antiporter xCT. mTORC2 phosphorylates serine 26 at the cytosolic N terminus of xCT, inhibiting its activity. 28974116_Aberrant neuronal or neuroendocrine system may be involved in the suppressed reproductive performance in xCT deficient male mice. 28985506_ARF inhibits tumor growth by suppressing the ability of NRF2 to transcriptionally activate its target genes, including SLC7A11, a component of the cystine/glutamate antiporter that regulates reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced ferroptosis. 29048627_these observations suggest that SLC7A11 may be a vital biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) and targeting SLC7A11 appears to be a potentially significant method for LSCC treatment. 29259101_Oncogenic PIK3CA alters methionine and cysteine utilization, partly by inhibiting xCT to contribute to the methionine dependency phenotype in human breast cancer cells. 29385995_CD44v9 in tumor specimens has potential as a novel indicator for identifying a cisplatin-chemoresistant population among urothelial cancer patients. CD44v8-10 contributes to reactive oxygen species defenses, which are involved in chemoresistance, by promoting the function of xCT, which adjusts the synthesis of glutathione. 29404978_In a multivariate analysis, high xCT expression and WHO tumor grade but not IDH1 R132H mutation, were significantly associated with epileptic seizures at diagnosis. 29441937_the level of antisense SLC7A11 was markedly reduced in epithelial ovarian cancer tissues and cell lines compared with those of normal control; reduction of antisense SLC7A11 level prompted ovarian cancer cell migration mainly by suppressing the expression of SLC7A11 29528250_High expression of cystine-glutamate antiporter SLC7A11 is associated with advanced pathological stages of liver carcinoma. SLC7A11 overexpression is a novel biomarker and a potential unfavorable prognostic factor as well as a potential therapeutic target for liver carcinoma. 29761734_System xC(-)-mediated TrkA activation therefore presents a promising target for therapeutic intervention in cancer pain treatment. 29764521_Studies indicate that SLC7A11 plays critical roles in glutamine metabolism and regulates the glucose and glutamine dependency of cancer cells. 29789716_Smoking could induce the expression of xCT (SLC7A11) in oral cancer cells. 30298963_Results showed that xCT-mediated glutamate release promotes glioma cell migration via N-methyl-d- aspartate- sensitive glutamate receptor signaling. 30448176_CD44v overexpression is not involved in cancer stem cell properties but increases xCT expression, which leads to the acquisition of Cisplatin-resistance. 30760873_mTOR-dependent upregulation of xCT blocks melanin synthesis and promotes tumorigenesis. 30799686_This study demonstrated that xCT knockdown in human breast cancer cells delays onset of cancer-induced bone pain. 31071489_Study have shown that a response to reactive oxygen species and up-regulation of xCT activity is crucial for reprogramming of zymogenic chief cells into pasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia. 31152846_The cystine/glutamate antiporter xCT is a key regulator of EphA2 S897 phosphorylation under glucose-limited conditions. 31419780_The expression of SLC7A11, but not of the other genes, was significantly higher in melanoma patients than in healthy individuals. 31692172_Identification of drugs for combination with xCT inhibitors that are able to overcome resistance to xCT-targeted therapy . 31705320_Cystine and glutamate bind xCT with favorable binding energies. 31874110_Suppression of the SLC7A11/glutathione axis causes synthetic lethality in KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. 31931281_xCT (SLC7A11) expression confers intrinsic resistance to physical plasma treatment in tumor cells. 32109492_MiR-139-5p/SLC7A11 inhibits the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of pancreatic carcinoma via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 32144264_Study identified two previously unreported epigenome-wide significant associations with Parkinson's disease (PD), including cg06690548 on chromosome 4 and demonstrated that cg06690548 hypermethylation in PD is associated with down-regulation of the SLC7A11 gene and show this is consistent with an environmental exposure, as opposed to medications or genetic factors with effects on DNA methylation or gene expression. 32231310_The results identify a coupling between SLC7A11-associated cystine metabolism and the pentose phosphate pathway, and uncover an accompanying metabolic vulnerability for therapeutic targeting in SLC7A11-high cancers. 32265299_High cell density increases glioblastoma cell viability under glucose deprivation via degradation of the cystine/glutamate transporter xCT (SLC7A11). 32321821_Allelic-Specific Regulation of xCT Expression Increases Susceptibility to Tuberculosis by Modulating microRNA-mRNA Interactions. 32471991_TGF-beta1-mediated repression of SLC7A11 drives vulnerability to GPX4 inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 32532810_Immunotargeting of the xCT Cystine/Glutamate Antiporter Potentiates the Efficacy of HER2-Targeted Immunotherapies in Breast Cancer. 32818320_Loss of the cystine/glutamate antiporter in melanoma abrogates tumor metastasis and markedly increases survival rates of mice. 33000412_Cystine transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: ferroptosis, nutrient dependency, and cancer therapy. 33016372_Consensus mutagenesis approach improves the thermal stability of system xc (-) transporter, xCT, and enables cryo-EM analyses. 33019976_SLC7A11 as a biomarker and therapeutic target in HPV-positive head and neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 33285240_Epidermal growth factor promotes glioblastoma cell death under glucose deprivation via upregulation of xCT (SLC7A11). 33358859_RNA binding protein DAZAP1 promotes HCC progression and regulates ferroptosis by interacting with SLC7A11 mRNA. 33531365_Autophagy is required for proper cysteine homeostasis in pancreatic cancer through regulation of SLC7A11. 33629335_Insights into the novel function of system Xc- in regulated cell death. 33689883_KDM4A-mediated histone demethylation of SLC7A11 inhibits cell ferroptosis in osteosarcoma. 33722571_PARP inhibition promotes ferroptosis via repressing SLC7A11 and synergizes with ferroptosis inducers in BRCA-proficient ovarian cancer. 33744468_Inhibition of xCT suppresses the efficacy of anti-PD-1/L1 melanoma treatment through exosomal PD-L1-induced macrophage M2 polarization. 33878705_Endogenous hydrogen sulfide regulates xCT stability through persulfidation of OTUB1 at cysteine 91 in colon cancer cells. 33980655_Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Determine Response to SLC7A11 Inhibition. 34004141_Signals of pseudo-starvation unveil the amino acid transporter SLC7A11 as key determinant in the control of Treg cell proliferative potential. 34074015_Mutant p53 Mediates Sensitivity to Cancer Treatment Agents in Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma Associated with MicroRNA and SLC7A11 Expression. 34091991_Amino acid transporters as emerging therapeutic targets in cancer. 34283663_The Knockdown of ETV4 Inhibits the Papillary Thyroid Cancer Development by Promoting Ferroptosis Upon SLC7A11 Downregulation. 34288020_IL-1beta-Induced Elevation of Solute Carrier Family 7 Member 11 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis Through Up-regulating Programmed Death Ligand 1 and Colony-Stimulating Factor 1. 34427100_SLC7A11 negatively associates with mismatch repair gene expression and endows glioblastoma cells sensitive to radiation under low glucose conditions. 34445395_Glutathione and Related Molecules in Parkinsonism. 34446045_SLC7A11 regulated by NRF2 modulates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma radiosensitivity by inhibiting ferroptosis. 34571083_SLC7A11/ xCT is a target of miR-5096 and its restoration partially rescues miR-5096-mediated ferroptosis and anti-tumor effects in human breast cancer cells. 34609072_Hypoxia blocks ferroptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma via suppression of METTL14 triggered YTHDF2-dependent silencing of SLC7A11. 34609966_RBMS1 regulates lung cancer ferroptosis through translational control of SLC7A11. 34857913_Epigenome-wide association study of alcohol consumption in N = 8161 individuals and relevance to alcohol use disorder pathophysiology: identification of the cystine/glutamate transporter SLC7A11 as a top target. 34927544_The ubiquitin hydrolase OTUB1 promotes glioma cell stemness via suppressing ferroptosis through stabilizing SLC7A11 protein. 35064112_RNA binding protein NKAP protects glioblastoma cells from ferroptosis by promoting SLC7A11 mRNA splicing in an m(6)A-dependent manner. 35245456_Kynurenine importation by SLC7A11 propagates anti-ferroptotic signaling. 35311457_Long non-coding RNA ADAMTS9-AS1 attenuates ferroptosis by Targeting microRNA-587/solute carrier family 7 member 11 axis in epithelial ovarian cancer. 35325354_Novel insights into the SLC7A11-mediated ferroptosis signaling pathways in preeclampsia patients: identifying pannexin 1 and toll-like receptor 4 as innovative prospective diagnostic biomarkers. 35367340_Functional role of the SLC7A11-AS1/xCT axis in the development of gastric cancer cisplatin-resistance by a GSH-dependent mechanism. 35440604_xCT contributes to colorectal cancer tumorigenesis through upregulation of the MELK oncogene and activation of the AKT/mTOR cascade. 35509981_A Comprehensive Prognostic and Immune Analysis of Ferroptosis-Related Genes Identifies SLC7A11 as a Novel Prognostic Biomarker in Lung Adenocarcinoma. 35522946_The N6-methyladenosine modification enhances ferroptosis resistance through inhibiting SLC7A11 mRNA deadenylation in hepatoblastoma. 35707044_lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 Facilitates Tumorigenesis and Ferroptosis Resistance through SLC7A11 by IGF2BP2 Pathway in Melanoma. 35757509_SLC7A11/GPX4 Inactivation-Mediated Ferroptosis Contributes to the Pathogenesis of Triptolide-Induced Cardiotoxicity. 35867762_Hypersensitivity to ferroptosis in chromophobe RCC is mediated by a glutathione metabolic dependency and cystine import via solute carrier family 7 member 11. 36046690_MITD1 Deficiency Suppresses Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Growth and Migration by Inducing Ferroptosis through the TAZ/SLC7A11 Pathway. 36084707_The amino acid transporter SLC7A11-mediated crosstalk implicated in cancer therapy and the tumor microenvironment. 36147463_PHGDH Inhibits Ferroptosis and Promotes Malignant Progression by Upregulating SLC7A11 in Bladder Cancer. 36164726_Circular RNA hsa_circ_0018189 drives non-small cell lung cancer growth by sequestering miR-656-3p and enhancing xCT expression. 36216119_lncRNA BBOX1-AS1 silencing inhibits esophageal squamous cell cancer progression by promoting ferroptosis via miR-513a-3p/SLC7A11 axis. 36439690_Hypoxia Enhances Glioma Resistance to Sulfasalazine-Induced Ferroptosis by Upregulating SLC7A11 via PI3K/AKT/HIF-1alpha Axis. | ENSMUSG00000027737 | Slc7a11 | 1146.831085 | 0.479037193 | -1.061790 | 0.05529531 | 369.932503 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001935932763966067916149493991039036150444326369633080323087791736151226912843667720996773751041388049934405554027 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000615450625053576373496968988633333453990166112052105738417650196165300642303072078501164020644585332995821087870 | Yes | No | 700.3481455 | 87.9478280 | 1467.1583444 | 183.1491895 | |
| ENSG00000151474 | 55691 | FRMD4A | protein_coding | Q9P2Q2 | FUNCTION: Scaffolding protein that regulates epithelial cell polarity by connecting ARF6 activation with the PAR3 complex (By similarity). Plays a redundant role with FRMD4B in epithelial polarization (By similarity). May regulate MAPT secretion by activating ARF6-signaling (PubMed:27044754). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BIE6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27044754}. | Cell junction;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Intellectual disability;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tight junction | This gene encodes a FERM domain-containing protein that regulates epithelial cell polarity. It connects ADP ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6) with the Par protein complex, which regulates the remodeling of adherens junctions and linear actin cable formation during epithelial cell polarization. Polymorphisms in this gene are associated with Alzheimer's disease, and also with nicotine dependence. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. | hsa:55691; | adherens junction [GO:0005912]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; establishment of epithelial cell polarity [GO:0090162]; negative regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050709]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714] | 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22006218_A single nucleotide polymorphism in the FERM domain containing 4A protein is associated with nicotine dependence. 22430674_data suggest that FRMD4A could be a relevant candidate gene for AD risk. 22564525_findings suggest FRMD4A as a novel candidate therapeutic target in HNSCC based on the key role in metastatic growth we have identified 25388005_novel microcephaly, intellectual disability and dysmorphism syndrome is associated with a mutation in FRMD4A. 27044754_FRMD4A RNAi or inhibition of cytohesins strongly upregulated secretion of endogenous tau. These results suggest that FRMD4A, a genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer's disease, regulates tau secretion by activating cytohesin-Arf6 signaling. 27666346_Findings suggest that FRMD4A expression correlates with the development of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. 35312514_Polymorphisms in the FRMD4A Gene Are Associated With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Susceptibility in a Latin American Population.', trans 'Polimorfismos en el gen FRMD4A se asocian a riesgo de enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva cronica en poblacion latinoamericana. | ENSMUSG00000026657 | Frmd4a | 222.980810 | 3.849393875 | 1.944631 | 0.39724855 | 22.177694 | 0.0000024854466349498152375754270876351270658233261201530694961547851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000382890171031696212896981712514588025442208163440227508544921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 330.2347796 | 197.5050681 | 81.4160962 | 48.7137650 | |
| ENSG00000151617 | 1909 | EDNRA | protein_coding | P25101 | FUNCTION: Receptor for endothelin-1. Mediates its action by association with G proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. The rank order of binding affinities for ET-A is: ET1 > ET2 >> ET3. | Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Hypotrichosis;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes the receptor for endothelin-1, a peptide that plays a role in potent and long-lasting vasoconstriction. This receptor associates with guanine-nucleotide-binding (G) proteins, and this coupling activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Polymorphisms in this gene have been linked to migraine headache resistance. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. | hsa:1909; | plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; endothelin receptor activity [GO:0004962]; phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C activity [GO:0004435]; activation of adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0007190]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007193]; aorta development [GO:0035904]; artery smooth muscle contraction [GO:0014824]; atrial cardiac muscle tissue development [GO:0003228]; axon extension [GO:0048675]; axonogenesis involved in innervation [GO:0060385]; blood vessel remodeling [GO:0001974]; branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0001569]; calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070588]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cardiac chamber formation [GO:0003207]; cardiac neural crest cell migration involved in outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003253]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular response to follicle-stimulating hormone stimulus [GO:0071372]; cellular response to human chorionic gonadotropin stimulus [GO:0044751]; cellular response to luteinizing hormone stimulus [GO:0071373]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; cranial skeletal system development [GO:1904888]; developmental pigmentation [GO:0048066]; embryonic heart tube development [GO:0035050]; embryonic skeletal system development [GO:0048706]; endothelin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0086100]; endothelin receptor signaling pathway involved in heart process [GO:0086101]; enteric nervous system development [GO:0048484]; establishment of endothelial barrier [GO:0061028]; face development [GO:0060324]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; glomerular endothelium development [GO:0072011]; glomerular filtration [GO:0003094]; heparin metabolic process [GO:0030202]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; left ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis [GO:0003220]; meiotic cell cycle process involved in oocyte maturation [GO:1903537]; mesenchymal cell apoptotic process [GO:0097152]; middle ear morphogenesis [GO:0042474]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; multicellular organism aging [GO:0010259]; neural crest cell fate commitment [GO:0014034]; neuromuscular process [GO:0050905]; neuron remodeling [GO:0016322]; noradrenergic neuron differentiation [GO:0003357]; norepinephrine metabolic process [GO:0042415]; pharyngeal arch artery morphogenesis [GO:0061626]; podocyte apoptotic process [GO:1903210]; podocyte differentiation [GO:0072112]; positive regulation of cation channel activity [GO:2001259]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; protein kinase A signaling [GO:0010737]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; protein transmembrane transport [GO:0071806]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of glucose transmembrane transport [GO:0010827]; regulation of heart rate [GO:0002027]; regulation of protein localization to cell leading edge [GO:1905871]; renal albumin absorption [GO:0097018]; renal sodium ion absorption [GO:0070294]; respiratory gaseous exchange by respiratory system [GO:0007585]; response to acetylcholine [GO:1905144]; response to amphetamine [GO:0001975]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to wounding [GO:0009611]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway involved in axon guidance [GO:1902287]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; smooth muscle contraction [GO:0006939]; sodium ion homeostasis [GO:0055078]; sympathetic nervous system development [GO:0048485]; sympathetic neuron axon guidance [GO:0097492]; thyroid gland development [GO:0030878]; vascular associated smooth muscle cell development [GO:0097084]; vasoconstriction [GO:0042310] | 11376172_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11601839_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11601839_The endothelin system plays a role in the complex pathophysiology of idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. 11930911_The vasoconstrictor effect of endothelin-1 in small resistance arteries of normotensive subjects and, in part, also in hypertensive patients is mediated by ET(A) receptors, while ET(B) receptors play a minor role, if any 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12544508_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12595285_endothelin-1 increased diastolic distensibility of acutely loaded myocardium and this effect was mediated by endothelin (A) receptors and Na(+)/H(+) exchanger activation 12629276_In autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease, neo-expression of ETA receptors has been found overlying glomeruli and cysts and markedly increased in medium-sized renal arteries. 12768436_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12875994_Data show that in a human Kaposi sarcoma cell line, blockade of endothelin receptors A and B blocked the endothelin-1-induced increase in secretion and activation of matrix-metalloproteinases. 14519635_ET(A)R expression in breast cancer corrrelated with favorable prognosis. 14616768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14636059_It is clear from the present data for lung fibroblasts that for both stimulated and unstimulated states of ETA receptors, there exist multiple covalent forms differing in the number and location of sites of posttranslational modifications. 14729387_Endothelin ETA receptor mRNA levels are significantly higher in arteries from patients with ischemic heart disease as compared to congestive heart failure and controls. 15041798_there is an increased microvessel density (MVD) in metastatic bone lesions from different primary tumors, and ETA and ET1 are upregulated in metastatic bone lesions 15047866_ET-1 induces collagen matrix contraction through the ETA, but not the ETB, receptor 15073116_increased ET-1, ET(A)R, and ET(B)R expression are associated with increased VEGF expression and higher vascularity of breast carcinomas and could be involved in the regulation of angiogenesis in breast cancer 15139053_Endothelin receptor type A was significantly down-regulated in papillary renal tumor specimens 15187089_endothelin A receptor regulates cell migration through the Cdc42-dependent c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and is mediated by Nck1 15213100_ET-1/ETA/ETB autocrine/paracrine loops on DCs appear to be essential for the normal maturation and function of human dendritic cells 15713850_Recycling of ET(A) receptor is mediated by a motif with the structural characteristics of an internal PDZ ligand. This structural motif may represent a more general principle of endocytic sorting of G protein-coupled receptors. 15838262_Examine therapeutic targeting of the endothelin-A receptor in human ovarian carcinoma. Report that efficacy of cytotoxic agents is markedly enhanced by co-administration with atrasentan. 15838285_Compared kidney endothelin-A and endothelin-B receptor distribution visualized by radioligand binding versus immunocytochemical localization using subtype selective antisera. 15838315_Results suggest that [F]-SB209670 binds rapidly and primarily to endothelin-A receptors in the heart. 15838329_Report pharmacological characterization of YM598, a selective endothelin-A receptor antagonist. 15838364_Targeting the endothelin-A receptor, but not the endothelin-B receptor, may be a valid tool in the therapy of cervical carcinoma. 15838366_Report the effects of the selective ET(A) receptor antagonist, sitaxsentan sodium, in a patient population with pulmonary arterial hypertension that meets traditional inclusion criteria of previous pulmonary arterial hypertension trials 15838367_Endothelin-A receptor antagonism promotes decreased vasodilation but has no differential effect on coronary artery compliance in hypertensive patients. 15988412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15988412_The polymorphism of EDNRA/C+70G may be related to NTG (normal tension glaucoma) risk factors. 16002759_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16002759_Polymorphisms in the ET-1 gene (K198N), the ET receptor type A (ETA), (-231G>A and +1222C>T), and the ET type B (ETB) receptor (G57S and L277L) do not play a role in cerebral small-vessel disease 16149067_in human lung fibroblasts ET-1 exerts a profibrogenic action via an ET(A) receptor-dependent, MAPK-mediated induction of IL-11 release and cell proliferation 16208144_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16531800_Observations strongly suggest that the expression of ETA receptor is enhanced in neointimal smooth muscle cells at early stages after percutaneous coronary intervention injury in human coronary arteries. 16567585_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16582543_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16618267_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16648553_Integrin-linked kinase functions as a downstream mediator of the ET-1/ET(A)R axis to potentiate aggressive cellular behavior in ovarian cancer cells. 16816835_Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis revealed mRNA the ETA receptor subtype in the human trigeminal ganglion. Immunocytochemistry revealed numerous cell bodies containing ETA proteins. 16879994_endothelin receptor type A(ETR-A) is selectively up-regulated in placental tissue of delayed miscarriages as compared to normal pregnancies 16947775_Associations between endothelin receptors A and B in aystemic ssclerosis subsets supports the role of endothelin and its receptors in the pathogenesis of this disease. 16947775_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16962346_ET receptors in pigment cells of vertebrate species were identified by RT-PCR assays, and the differential expression of the various subtypes in each species was compared by quantitative PCR. 16971893_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16971893_Polymorphism of EDNRA:c.*1222C > T was significantly associated with normal tension glaucoma. AA genotype of EDNRA:c.-231G > A polymorphism was associated with lower baseline intraocular pressure than in GG+GA genotype group. 16984730_Endothelin receptor A has a role in progression of prostate cancer 17016617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17122448_ET-1 mediates the increased vascular tone of extremely inactive legs of SCI individuals by increased activation of ET(A)-receptors 17198909_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17198909_association of genetic variation with aortic pressure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy 17203161_analysis of Endothelin-1, ETAR and ETBR expression in different histologic subtypes of renal cell carcinoma 17353514_Endogenous endothelin, predominantly via ET(A) receptor stimulation, contributes to basal constrictor tone and endothelial dysfunction, whereas ET(B) activation mediates vasodilation in human coronaries. 17437213_No association between the -231 G > A polymorphism in the EDNRA gene and preeclampsia as well as any correlation with the main clinical features of the disorder were found. 17437213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17468950_Hypoxia-induced breast carcinoma invasiveness was reduced by ETRA antagonist atrasentan. 17470272_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17525706_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17575543_neutrophils taken from healthy donors damage the endothelium by a mechanism dependent on ETs acting via ET(A) receptor, whereas neutrophils from acute pancreatitis patients cause more severe damage that is not dependent on ETs 17616673_Endothelin receptor type B counteracts tenascin-C-induced endothelin receptor type A-dependent focal adhesion and actin stress fiber disorganization 17616694_endothelin A receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor are targeted by the combination of ZD4054 and gefitinib in ovarian carcinoma 17706018_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17706018_The CC genotype could be protective in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease females. This genotype was described to be associated with lower pulse pressure. 18172451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18212505_endogenous ET-1 is involved in the regulation of microvascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes and microangiopathy 18326801_Activation of ET(A) localized in T tubules was associated with a strong positive iontropic effect, whereas the activation of ET(A) in surface sarcolemma was not. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18678984_These results suggest that possible coupling of NHE with NCX via Na+ transport is involved in ET(A)R-mediated sustained [Ca2+]i increase. 18756291_review of heterodimerization involving the ETA receptor and renal endothelin ETB-dopamine D(3) receptor interactions at the cellular level that appear to have functional consequences in vivo 18945538_Lack of ET(A)R expression may be an independent negative marker for recurrence-free survival in bladder cancer. 19217622_Endothelin-1 activates ETA receptors on human vascular smooth muscle cells to yield proteoglycans with increased binding to LDL 19225824_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19367425_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19460784_NF-kappaB, endothelin-1, and ET-1 receptor A (ETAR) have roles in pulmonary vascular dysfunction in end-stage cystic fibrosis 19479828_ET-1-dependent vasoconstrictor tone is increased predominantly in the subgroup of SSc patients with dcSSc, in whom acute blockade of ETA receptors was able to improve impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilator function. 19558538_No significant association was detected between migraine with aura end-diagnosis and three migraine trait components and 32 single nucleotide polymorphisms in endothelin-1 and its receptors EDNRA and EDNRB 19558538_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19575782_Endothelin-1 acts primarily via the ETA receptors to induce phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in human aortic smooth muscle cells. 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19593212_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19626996_Expression levels of ET-1, ET(A)R and ET(B)R were not associated with r-AFS staging of endometriosis. 19653178_Systemic hypertension is associated with increased ET-1 and ET(A) receptor mRNA expression;insulin-dependent diabetes down-regulates ET(A) receptors in the internal mammary artery in patients with coronary artery disease undergoing bypass grafting 19898645_Selective endothelin A-receptor blockade attenuates coronary microvascular dysfunction after coronary stenting in patients with type 2 diabetes. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20028935_A significant association between EDNRA 3'-untranslated region (UTR) variant rs5335 and pulmonary function, was demonstrated. 20034471_these results suggest that the amount of Jab1 bound to ETR regulates the degradation rate of ET(A)R and ET(B)R by modulating ubiquitination of these receptors, leading to changes in ET(A)R and ET(B)R levels. 20043107_Both ET(A)R and ET(B)R are present in lung carcinomas but at different levels, according to the histological type of tumor. 20083432_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20083432_SNPs as susceptibility factors for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome 20100616_Endothelin receptor type A polymorphism rs 5335 may be associated with congenital bilateral absence of vas deferens penetrance. 20100616_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20150570_Our data demonstrate that the level of circulating ET-1 is regulated by ETA receptor-mediated negative feedback. 20346360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20371740_Expression of ETA receptor in normal endometrium and decidua is regulated by homeobox protein A10 (HOXA10). 20401344_The results suggested that during the luteal phase, ET(A) and ET(B) receptors participate in contractile effects of endothelins on isthmic segment of fallopian tubes, probably regulating the length of time the oocyte remains in the ampulla 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20538960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20725140_Similar to ETB receptors, ETA receptors are also present in human aortic vascular endothelial cells (hVECs). ETA, but not ETB receptors mediate the effect of ET-1 on total intracellular Ca2+ of hVECs. 20963824_Study of a novel enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) reporter (Ednra) transgenic mouse line enables visualization of placode-derived inner ear sensory cell lineage. 20964792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20964792_Our results show additional findings for a role of endothelin receptor type A as a susceptibility factor for migraine without aura 21057729_Studies indicate that understanding the mechanisms of how cigarette smoke causes up-regulation of endothelin receptors in the vasculature and airways may provide new strategies for treatment of cigarette smoke-associated cardiovascular and lung diseases. 21220476_Data show that blockade of ET(A)R-driven EMT can overcome chemoresistance and inhibit tumor progression, improving the outcome of EOC patients' treatment. 21356562_The mRNA expressions of endothelin A and B receptors and endothelin-1 are significantly increased in failed Fontan patients. 21418087_Renal medullary endothelin-1/endothelin receptor second messenger signaling regulates sodium/water balance via control of natriuresis and renin-angiotensin system; both endothelin 1 receptor and endothelin 2 receptor are involved. [REVIEW] 21424380_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in EDNRA gene is associated with breast cancer. 21453125_the role of EDNRA -231 G>A and APOE HhaI polymorphism for a possible association with migraine 21487064_Data show that EDNRA/H323H polymorphism is a novel and independent prognostic marker, which may help identify patient subgroups at high risk for poor disease outcome. 21498912_Increased expression of ET-1, ETRA/B, and activation of signaling pathways were observed in the pulmonary arteries and arterioles of irreversible pulmonary arterial hypertension patients associated with congenital heart defects. 21515378_ET1 induced calcium responses are only mediated by endothelin A receptors, possibly due to sub-threshold endothelin B receptor expression. 21601190_Immunohistochemical evaluation of spermatic and control vein samples from 55 patients with varicocele showed overexpression of ET-1 and its receptors ETA and ETB in varicose veins. 21773759_Findings suggest a potential link between specific genotypes in the ednra gene and susceptibility to pulmonary arterial hypertension. 22106312_Results demonstrated significant association of IA with rs6841581 on chromosome 4q31.23, immediately 5' of the endothelin receptor type A with P = 2.2 x 10(-8) [odds ratio (OR) = 1.22, PPA = 0.986]. 22129540_four TRPC isoforms, TRPC3, TRPC5, TRPC6, and TRPC7, can function as endothelin type A receptor-operated Ca2+ channels. 22286173_SNP, rs6842241, near EDNRA at chromosome 4q31.22 (combined P-value = 9.58 x 10(-9); odds ratio = 1.25), was found to be significantly associated with intracranial aneurysm 22365955_ETB receptors predominated in normal human liver and displayed the highest ratio (ETB:ETA 63:47) compared with other peripheral tissues; liver ETB expression was upregulated in cirrhosis (ETB:ETA 83:17) 22480520_endothelin A receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling converge on beta-catenin to promote ovarian cancer metastasis 22510270_Data show that optical imaging with a fluorescent ET(A)R tracer allows the noninvasive imaging of tumor-associated ET(A)R expression in vivo. 22561246_Expressed recombinant ET(A) as a fusion protein with phi6 p9 envelope protein. The purified protein showed specific binding to ET-1 and the alpha subunit of G(q) protein. 22580289_Early onset preeclampsia (PE)(=GW34) with or without fetal growth restriction is associated with increased mRNA expression of the ET/ETR system, while in late onset PE and gestational diabetes, the opposite effect was observed 22688668_Both endothelin A and B receptors were reduced in pulmonary arterial hypertension, particularly type B, and type B signaling through protein kinases was markedly reduced in vascular smooth cells with a mutation in bone morphogenetic protein receptor 2. 22997346_We used this sample of 250 surgical patients to describe the distribution of ET-1, ETA and ETB polymorphisms in the aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage population. 23058564_A significant difference existed between migraineurs & controls with AA genotype vs. AG+GG. Pooled relative risk with fixed effect was 4.04. This meta-analysis suggests a significant association between EDNRA -231G>A polymorphism and migraine. 23217151_Genetic deletion of a nephron-specific endothelin A receptor causes very modest fluid retention that does not alter arterial pressure, nor doea it play a major role in regulating sodium excretion or systemic hemodynamics. 23233754_Right ventricular hypertrophy myocardial endothelin type A receptor level is increased compared to nonhypertrophied right ventricular endothelin receptor level. 23384184_EDNRA mRNA expression was increased in reflux esophagitis and Barrett's esophagus compared to controls. 23436727_C-terminus of ETA/ETB receptors regulate endothelin-1 signal transmission. 23515723_The presence ETr-A and ETr-B in rheumatic mitral valves suggests its interaction with the system of c endothelins, particularly ETr-B detected in a greater proportion, which could explain the lack of expression of endothelin in rheumatic mitral valve. 23683481_the positive correlation between ET-1 and ETAR in lesional compared with perilesional normal epidermis suggest an important role of this receptor in vitiligo. 23754170_Mutation of EDNRA is involved in ACTH-independent macronodular adrenal hyperplasia. 23818293_ETAR overexpression promoted colon cancer liver metastases. 23987636_ETAR and CXCR4 expression levels are potential prognostic biomarkers in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. 24064210_Desensitization and internalization of endothelin receptor A: impact of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2)-mediated phosphorylation. 24291390_no association between Graves' disease and genetic polymorphism 24332749_In thyroid cancer, endothelin 1 and endothelin receptor A are associated with growth in advanced stages and lymph node metastases, likely through known angiogenic linkages. 24570333_Polymorphisms of EDNRA have been associated with the development of group I pulmonary hypertension, dilated cardiomyopathy and essential hypertension 24582810_The aim was to quantify the density of ETA and ETB receptors in cardiopulmonary tissue from pulmonary arterial hypertension patients and the monocrotaline (MCT) rat. 24612997_findings suggest a role for agonistic autoantibodies-induced activation of immune cells mediated by the AT1R and the ETAR in the pathogenesis or even the onset of systemic sclerosis 24627317_Report serum levels ETAR autoantibodies in peripheral arterial disease. 24633486_effect of SNP polymorphisms of EDN1, EDNRA, and EDNRB gene on ischemic stroke 24815860_no significant association between EDNRA (C+70G, G-231A) allele and Hashimoto's thyroiditis in Turkish population; this polymorphism relates to decreased risk for early disease onset 24856242_Data suggest that subjects with metabolic syndrome in association with overweight/obesity exhibit higher vasoconstrictor tone than normal weight subjects; enhanced vasoconstrictor activity is mediated via endothelin-1/endothelin A receptor signaling. 24958810_genetic association study in population in India: Data suggest that (in addition to mutations in cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator) an SNP in EDNRA (rs5335) is associated with congenital absence of vas deferens in population studied. 25048859_role of ET-1/ETR-A signalling in Gd-induced fibrosis and calcification in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis 25056169_Suggest a functional link between endothelin receptor autoantibody formation and down-regulated midkine serum levels, that may be relevant in the pathogenesis of clinically relevant peripheral artery occlusive disease. 25194819_These results indicate a novel function for Galphas signaling in ET-1/ETAR-mediated ovarian cancer oncogenesis. 25225183_significant single nucleotide polymorphism associations with birth weight near coding regions for two genes involved in oxygen sensing and vascular control, PRKAA1 and EDNRA, respectively, were identified. 25377471_our findings reveal the existence of a novel mechanism by which ETAR/beta-arr1 signaling is integrated with the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway to sustain chemoresistance in epithelial ovarian cancer, and they offer a solid rationale for clinical evaluation 25381251_Data show that upon endothelin-1 (ET-1) stimulation, ET type A receptor (ETAR) is recycled back to plasma membrane, whereas ET type B receptor (ETAR) is targeted to lysosome for degradation. 25424718_Genebased analyses revealed associations of the EDNRA gene with longitudinal Blood Pressure phenotypes, associations with essential hypertension, Blood Pressure salt sensitivity, preeclampsia, or preclinical stages of atherosclerosis. 25772936_Mutations in the endothelin receptor type A cause mandibulofacial dysostosis with alopecia. 25801761_Plasma proET-1 levels increase in CKD and may be useful biomarkers of renal injury. Increases in response to endothelin A antagonism may reflect EDN1 upregulation, which may partly explain fluid retention with these agents. 25946671_Endothelin receptor A was detected in all patients with squamous cell carcinoma and psoriasis, with a higher frequency and grade of expression than controls and basal cell carcinoma. 26176954_Ednra, encoding Endothelin receptor A (ETA)-the target of Endothelin 1 (ET-1)-was significantly increased in Systemic Capillary Leak Syndrome blood-outgrowth endothelial cells compared to healthy controls. 26357964_Data show that macitentan interferes with the profibrotic action of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta), blocking the endothelin receptor type A (ET-1 receptor) portion of the ET-1/TGF-beta receptor complex. 26522724_Data show that endothelin A receptor drives invadopodia function by direct interaction of beta-arrestin-1 (beta-arr1) with Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 11 protein (PDZ-RhoGEF). 26675258_High ETAR expression is associated with ovarian carcinoma. 26773103_Patients with lung fibrosis and patients with high modified Rodnan skin score showed a reduced endothelin 1 Type A receptor (ETAR)/ETBR ratio. 26874031_presence of ET-1 receptors in the chronic thrombus in proximal CTEPH suggests ET-1 could act not only on the distal vasculopathy in the unobstructed vessels but may also stimulate smooth muscle cell proliferation within chronic clot 27072656_Data show that auriculo-condylar syndrome (ACS)-associated mutations in G protein subunit alpha i3 (GNAI3) produce dominant-negative Galpha(i3) mutant proteins that couple to endothelin type A receptor (ET(A)R). 27367030_endothelin-A receptor-activated ABCB1 expression has a role in nintedanib resistance in FGFR1-driven small cell lung cancer 27422754_Data suggest that TNFalpha (tumor necrosis factor-alpha) induces proliferation of airway smooth muscle cells via ET1 (endothelin-1), GM-CSF (granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor), and IL6 (interleukin 6) signaling; ET1 induces cell proliferation via ETAR (endothelin receptor type A); ETBR (endothelin receptor type B) is up-regulated by TNFalpha and appears to mediate ET1 effects on cell proliferation. 27777505_Polymorphic variants of endothelin EDN (K198N) and endothelin receptor type A genes EDN RA (C1222T, C70G, G231A) affected ET plasma concentrations. There was no association between the plasma endothelin levels and the risk factors for normal tension glaucoma. 27876299_The interaction between stages of essential hypertension and risk factors with the polymorphism H323H of the receptor gene A ET-1 (ETRA) was analyzed. For the H323H polymorphism, images showed a higher frequency of dilations of left auricular and auricular fibrillation (P=.03) in the T/T carrier. A higher frequency of cardiomegaly was detected in C/C patients. The T/T genotype may indicate worse outcome. 27899487_Increased circulating Edn1 and expression of Ednra in endothelial cells are characteristic of diabetic kidney disease. 28095606_ETA and ETB receptors are present in human haemorrhoids with ETB receptors predominating 28249901_ETAR stimulation acted via downstream G-protein Galphaq/11 and Rho GTPase to suppress the Hippo pathway, thus leading to YAP/TAZ activation, which was required for ETAR-induced tumorigenesis. Overall, these results indicate a critical role of the YAP/TAZ axis in ETAR signaling 28548598_Common endothelin SNPs were found to be associated with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH) and its sequelae. The T allele of the END1 T/G SNP (rs1800541) was associated with aSAH. The G allele of the EDNRA G/C SNP (rs5335) was associated with clinical vasospasm. 28606962_In control arteries, ETAR was expressed by vascular smooth muscle cells in the media whereas ETBR was hardly detected. In giant cell arteritis, both ETAR and ETBR receptors were expressed by alphaSMA-positive cells at the intima-media border. Endothelial cells and inflammatory cells also expressed both ET receptors. 28732172_Endothelin-1 possesses an anti-apoptotic effect in vascular endothelial cells and this effect is mediated, to a great extent, via the activation of EDNRB, with a minor contribution via activation of EDNRA. 29064794_There is no association between the C+70G polymorphism of the EDNRA gene and the development of ischemic atherothrombotic stroke. 29097630_Subjects with either TC or CC genotypes at rs5333 exhibited significantly greater increases in brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity with age 29272493_High ETAR expression is associated with Colitis-Associated colon Cancer. 29286062_miR200c regulates the proliferation, apoptosis and invasion of gastric carcinoma cells through the downregulation of EDNRA expression. 29696364_Presence of SST5, CXCR4 and ETA on tumor cells and of SST3, CXCR4 and ETA on microvessels gradually increased from grade II to grade IV tumors. 29849817_No link between EDNRA rs5335 and large artery stroke risk in a Ukrainian population was found. 29999581_fluctuations in ovarian hormones modulate ETBR and ETAR responses in young women. 30384975_our results suggest a role for Ednra in Hoxa9/Meis1-driven leukemogenesis. 30411193_The GG genotype of EDNRA + 70 SNP was associated with threefold increased papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) risk (p = 0.01), and the combined CG + GG genotype was 2.48 fold higher among PTC patients compared to controls. The variant EDNRA - 231 allele was overrepresented in PTC patients according to controls (p = 0.05). 30672385_The ENDRA rs5333 gene polymorphism may be associated with genetic predisposition to steroid resistance in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome Egyptian children 30937921_The findings suggest that ETAR expression, as detected by Immunohistochemical staining, could be useful as a molecular marker to predict prognosis for gastric cancer patients. 31106465_Endothelins and their receptors in embryo implantation. 31150867_These findings support the important role of EDNRA and EDNRB polymorphisms in intracerebral hemorrhage, and suggest that they do not interact with blood pressure levels on altering intracerebral hemorrhage risk. 31295611_In this systematic review, the genetic variant of EDNRA, rs6841581, was significantly associated with increased risk of intracranial aneurysm. 31661578_Effects of genotype on TENS effectiveness in controlling knee pain in persons with mild to moderate osteoarthritis. 31705661_The role of endothelin A receptors in peripheral vascular control at rest and during exercise in patients with hypertension. 32133772_Loss-of-function of Endothelin receptor type A results in Oro-Oto-Cardiac syndrome. 32431219_Homology modeling, molecular dynamics and virtual screening of endothelin-A receptor for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. 32496159_Diabetes-related sex differences in the brain endothelin system following ischemia in vivo and in human brain endothelial cells in vitro. 32744876_Endothelin receptor heteromerization inhibits beta-arrestin function in HEK293 cells. 34165174_Endothelin-1 induces changes in the expression levels of steroidogenic enzymes and increases androgen receptor and testosterone production in the PC3 prostate cancer cell line. 34757123_Non-HLA antibodies targeting angiotensin II Type 1 receptor and endothelin-1 Type A receptors induce endothelial injury via beta2-arrestin link to mTOR pathway. 35043642_Association of polymorphisms in endothelin-1 and endothelin receptor a genes with vasovagal syncope. 36179900_Gender differences in genotypic distribution of endothelin-1 gene and endothelin receptor A gene in pulmonary hypertension associated with rheumatic mitral valve disease. 36384316_Endothelin A receptors contribute to senescence of brain microvascular endothelial cells. 36430296_High Glucose-Induced Cardiomyocyte Damage Involves Interplay between Endothelin ET-1/ETA/ETB Receptor and mTOR Pathway. | ENSMUSG00000031616 | Ednra | 46.713396 | 2.034865050 | 1.024933 | 0.23459569 | 19.243050 | 0.0000115088610631858025417240815047037472140800673514604568481445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001505949004226782197545658759096909307118039578199386596679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 61.8412644 | 7.4274588 | 30.5577276 | 4.1136731 | |
| ENSG00000151651 | 101 | ADAM8 | protein_coding | P78325 | FUNCTION: Possible involvement in extravasation of leukocytes. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc | This gene encodes a member of the ADAM (a disintegrin and metalloprotease domain) family. Members of this family are membrane-anchored proteins structurally related to snake venom disintegrins, and have been implicated in a variety of biological processes involving cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, including fertilization, muscle development, and neurogenesis. The protein encoded by this gene may be involved in cell adhesion during neurodegeneration, and it is thought to be a target for allergic respiratory diseases, including asthma. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2009]. | hsa:101; | alpha9-beta1 integrin-ADAM8 complex [GO:0071133]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dense core granule membrane [GO:0032127]; ficolin-1-rich granule membrane [GO:0101003]; phagolysosome [GO:0032010]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; podosome [GO:0002102]; specific granule [GO:0042581]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; tertiary granule [GO:0070820]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; leukocyte migration involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002523]; lymphocyte chemotaxis [GO:0048247]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; positive regulation of acute inflammatory response [GO:0002675]; positive regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045780]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of cellular extravasation [GO:0002693]; positive regulation of eosinophil migration [GO:2000418]; positive regulation of fibronectin-dependent thymocyte migration [GO:2000415]; positive regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045089]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0051044]; positive regulation of neutrophil extravasation [GO:2000391]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of protein processing [GO:0010954]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; positive regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033089]; positive regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process [GO:0070245]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily member 11 production [GO:2000309]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022407] | 15623614_Overexpression of ADAM8 is associated with lung cancer progression 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17339047_ADAM8 may contribute to the airway remodeling process that occurs with asthma progression. 17548643_All these data support a potential relevant role for ADAM-8 in the function of neutrophils during inflammatory response. 17979891_ADAM8 is overexpressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, influences cancer cell invasiveness and correlates with reduced survival. 18566576_ADAM8 may have a role as a hypoxia-dependent protein in the pathogenesis and evolution of pancreatic cancer 18682798_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18691140_ADAM8 might be a therapeutic target for allergic respiratory diseases. 18710625_ADAM8 and EGFR are overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer. 18811590_Autoactivation of ADAM8: a novel pre-processing step is required for catalytic activity. 19284887_ADAM8 is up-regulated upon formation of multinuclear giant cells after HPIV2 induction. 19397475_The structure, function & expression of ADAM8 and its role in asthma are reviewed. Review. 19469654_Increasing trend for ADAM8 expression is associated with early to advanced stages of myelodysplastic syndrome. 19575316_ADAM8 is a promising candidate to be involved in atherosclerosis, and its 2662 T/G allelic variant significantly associates with advanced atherosclerotic lesion areas and myocardial infarction. 19714641_ADAM-8 as a fibronectinase in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. 19766586_the effects of pH on substrate cleavage by ADAM8 beyond autocatalysis 20453887_expression of truncated forms of ADAM8 by the lung cancer cells may result in the specific upregulation of their invasive and osteoclastogenic activities in the bone microenvironment 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21077325_It regulates onset of blood circulation. (review) 21640993_variation in the ADAM8 gene may affect serum sADAM8 concentrations and the risk of myocardial infarction 21679521_increased expression in allergic rhinitis 21728902_gene expressions for ADAM8 and ADAM15 were notably lower in ascending aorta as compared with aortic dissection 21983884_These findings suggest for the first time that ADAM8 is frequently overexpressed in human gliomas and is closely associated with poor clinical outcome. 22215309_Upregulation of a disintegrin and metalloprotease 8 influences tumor metastasis with osteosarcoma. 22229154_ADAM8 is both associated with PSGL-1 through the ezrin-radixin-moesin actin-binding proteins and able to cause the proteolytic cleavage of this adhesion receptor. 22878099_ADAM8 was highly expressed in 54.3% of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. ADAM8 expression was closely associated with tumor size, histological differentiation, recurrence, metastasis, and stage. High levels of ADAM8 resulted in poor prognosis. 22941466_High expression of ADAM8 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 22959284_ADAM8 mRNA & protein were highly expressed in medulloblastoma tissues when compared with normal cerebellum. This correlated with advanced stage, aggressive type, undifferentiated tumor & decreased survival. 22965687_We used immunohistochemistry to compare ADAM8 protein expression in HCC and normal liver tissues and further analyze the ADAM8 protein expression in 105 HCC cases. Studied knocked down expression of ADAM8 in HepG2 cells. 23670189_ADAM8 was robustly expressed by airway granulocytes in lung sections from human asthma patients 24147597_ADAM8 expression is increased in both severe asthma and COPD and associated with sputum total cell count and neutrophils. ADAM8 may facilitate neutrophil migration to the airways in severe asthma and COPD. 24247244_Data show that Cu2+-generated reactive oxygen species (ROS), human ADAM8, ADAM10, and ADAM17 are all capable of cleaving mouse PrP (MoPrP). 24375628_ADAM8 is abundantly expressed in breast tumors and derived metastases compared to normal tissue. 24526468_High ADAM8 expression is associated with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. 25010013_Data indicate that fibronectin fragments (FN-fs) are present in adult ntervertebral disc (IVD) from adult subjects, and ADAM-8, known to cleave FN, is present at the pericellular matrix of disc cells. 25098630_Results show that ADAM8 is overexpressed in colorectal cancer and promotes cell growth. 25336660_N-glycosylation is essential for processing, localization, stability, and activity of ADAM8. 25481287_ADAM8 and endostatin play a role in osteosarcoma progression. 25629724_ADAM8 expression is associated with increased migration and invasiveness of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. 25825051_ADAM8 causes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma cells by enhancing pAkt/PI3K, pERK1/2, and cleavage of CD44 and HGF R/c-met 26024798_ADAM8 promotes GC cell proliferation and invasion, and its expression is positively correlated with poor survival, indicating that it might be a promising target in GC therapy 27039296_miR-720 is elevated in serum of patients with ADAM8-high TNBC and, in a group with other miRNAs downstream of ADAM8, holds promise as a biomarker for early detection of or treatment response of ADAM8-positive triple-negative breast cancer 28596294_ADAM8 on leukocytes holds a proinflammatory function in acute lung inflammation by promoting alveolar leukocyte recruitment. 28986926_Authors conclude that ADAM8 promotes early metastatic processes such as transendothelial migration by upregulation of MMP-9 and shedding of PSGL-1 from breast cancer cells. 29429960_ADAM8 is a marker of residual CML cells. 29750543_ADAMs binds to integrins to regulate cell adhesion and migration. 30861616_Study in human pancreatic cancer cells demonstrated that ADAM8 was a direct target of miR-328. Knockdown of miR-328 or ADAM8 led to significantly decreased cell growth and viability. 31305294_ADAM8 promotes chondrosarcoma cell migration and invasion by activating the NF-kappaB/MMP-13 signaling axis. 31347325_Blood ADAM 8 is a promising biomarker for early detection of gastric cancer. 32954649_A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 8 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote the invasion of colon cancer cells via TGF-beta/Smad2/3 signalling pathway. 33314720_Expression levels of the metalloproteinase ADAM8 critically regulate proliferation, migration and malignant signalling events in hepatoma cells. 33544472_ADAM8 affects glioblastoma progression by regulating osteopontin-mediated angiogenesis. 33846772_TrkB/C-induced HOXC6 activation enhances the ADAM8-mediated metastasis of chemoresistant colon cancer cells. 35103068_Three Potential Tumor Markers Promote Metastasis and Recurrence of Colorectal Cancer by Regulating the Inflammatory Response: ADAM8, LYN, and S100A9. 35216088_ADAM8-Dependent Extracellular Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment Involves Regulated Release of Lipocalin 2 and MMP-9. | ENSMUSG00000025473 | Adam8 | 64.361704 | 0.499021343 | -1.002827 | 0.32291967 | 9.451749 | 0.0021094780160659408127510339170385122997686266899108886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0142279265262121919904947375812298560049384832382202148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 39.6848047 | 8.4867169 | 80.0448383 | 16.6212840 | |
| ENSG00000152192 | 5457 | POU4F1 | protein_coding | Q01851 | FUNCTION: Multifunctional transcription factor with different regions mediating its different effects. Acts by binding (via its C-terminal domain) to sequences related to the consensus octamer motif 5'-ATGCAAAT-3' in the regulatory regions of its target genes. Regulates the expression of specific genes involved in differentiation and survival within a subset of neuronal lineages. It has been shown that activation of some of these genes requires its N-terminal domain, maybe through a neuronal-specific cofactor. Ativates BCL2 expression and protects neuronal cells from apoptosis (via the N-terminal domain). Induces neuronal process outgrowth and the coordinate expression of genes encoding synaptic proteins. Exerts its major developmental effects in somatosensory neurons and in brainstem nuclei involved in motor control. Stimulates the binding affinity of the nuclear estrogene receptor ESR1 to DNA estrogen response element (ERE), and hence modulates ESR1-induced transcriptional activity. May positively regulate POU4F2 and POU4F3. Regulates dorsal root ganglion sensory neuron specification and axonal projection into the spinal cord. Plays a role in TNFSF11-mediated terminal osteoclast differentiation. Negatively regulates its own expression interacting directly with a highly conserved autoregulatory domain surrounding the transcription initiation site. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P17208}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Able to act as transcription factor, cannot regulate the expression of the same subset of genes than isoform 1. Does not have antiapoptotic effect on neuronal cells. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P17208}. | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Intellectual disability;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation | This gene encodes a member of the POU-IV class of neural transcription factors. This protein is expressed in a subset of retinal ganglion cells and may be involved in the developing sensory nervous system. This protein may also promote the growth of cervical tumors. A translocation of this gene is associated with some adult acute myeloid leukemias. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. | hsa:5457; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; GTPase binding [GO:0051020]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; single-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003697]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; cell migration in hindbrain [GO:0021535]; cellular response to cytokine stimulus [GO:0071345]; cellular response to estradiol stimulus [GO:0071392]; central nervous system neuron differentiation [GO:0021953]; habenula development [GO:0021986]; heart development [GO:0007507]; innervation [GO:0060384]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator [GO:0072332]; mesoderm development [GO:0007498]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of programmed cell death [GO:0043069]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuron apoptotic process [GO:0051402]; neuron fate specification [GO:0048665]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; peripheral nervous system neuron development [GO:0048935]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043525]; positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045672]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding [GO:2000679]; proprioception involved in equilibrioception [GO:0051355]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051090]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; sensory system development [GO:0048880]; suckling behavior [GO:0001967]; synapse assembly [GO:0007416]; trigeminal nerve development [GO:0021559]; ventricular compact myocardium morphogenesis [GO:0003223] | 12427558_genomic organization of the Brn-3a locus and the mechanisms that control the expression of two different proteins from one genomic locus 12893201_Measurement of Brn-3a levels in smears can be used to detect a significant proportion of cervical lesions that were missed by Pap smear. 12911730_These results indicate that Brn-3a could play an important role in the near future in improving cervical cancer screening. 15021903_oncogenic rearrangement of EWS to produce EWS/Fli-1 may enhance the antiapoptotic effect of Brn-3a and inhibit its ability to promote neuronal differentiation. 15272315_Hsp27 expression and cell survival are regulated by the POU transcription factor Brn3a 16247485_Brn-3a has a role in differential regulation of different human papilloma virus variants 16276351_Upregulation of Brn-3a is associated with prostate cancer 20348952_Ewing sarcoma induce expression of neuronal markers such as BRN3A showing that the function of those same markers may be restricted or controlled in an sarcoma-dependent manner. 20376082_Dysregulation of POU4F1 is associated with t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia. 21928122_BRN3A possesses anti-apoptotic property, and considering the above results, it may be regarded as the key component in promoting tumorigenic growth in the uterine cervical cells. 22064348_PoU4F1 is highly expressed in t(8;21) samples, with AML/ETO appearning to promote some BRN3A expression 22930747_Data indicate that median methylation levels of BCAN, HOXD1, KCTD8, KLF11, NXPH1, POU4F1, SIM1, and TCF7L1 were >/=30% higher than in normal samples, representing potential biomarkers for tumor diagnosis. 23666755_Brn3a cooperates with activated RAS/RAF signalling by reducing oncogene-induced senescence in melanocytic tumourigenesis. 27863625_We report a case of a nine-year-old male who presented with facial nerve stimulation four years after cochlear implantation. A dilated internal auditory meatus was revealed. Genetic analysis demonstrated X-linked deafness type 2 (DFNX2) caused by a novel c.769C T nucleotide change in the POU domain, class 3, transcription factor 4 gene 30488195_Papillary thyroid carcinoma was characterized by high expression of ESR2 and AR, which was associated with expression and content of nuclear factors Brn-3A and TRIM16. 32474599_Brn3a/Pou4f1 Functions as a Tumor Suppressor by Targeting c-MET/STAT3 Signaling in Thyroid Cancer. 32532957_POU4F1 promotes the resistance of melanoma to BRAF inhibitors through MEK/ERK pathway activation and MITF up-regulation. 32597291_No association between POU4F1, POU4F2, ISL1 polymorphisms and normal-tension glaucoma. 32988584_POU4F1 confers trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer through regulating ERK1/2 signaling pathway. 33783914_Haploinsufficiency of POU4F1 causes an ataxia syndrome with hypotonia and intention tremor. 35055045_HDAC2 Is Involved in the Regulation of BRN3A in Melanocytes and Melanoma. | ENSMUSG00000048349 | Pou4f1 | 10.419260 | 2.598853099 | 1.377875 | 0.49363206 | 7.979194 | 0.0047317991706965238304927190426951710833236575126647949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0274185612260575695131592510733753442764282226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 14.9525409 | 4.3189377 | 5.7716205 | 1.9099882 | |
| ENSG00000152409 | 133746 | JMY | protein_coding | Q8N9B5 | FUNCTION: Acts both as a nuclear p53/TP53-cofactor and a cytoplasmic regulator of actin dynamics depending on conditions (PubMed:30420355). In nucleus, acts as a cofactor that increases p53/TP53 response via its interaction with p300/EP300. Increases p53/TP53-dependent transcription and apoptosis, suggesting an important role in p53/TP53 stress response such as DNA damage. In cytoplasm, acts as a nucleation-promoting factor for both branched and unbranched actin filaments (PubMed:30420355). Activates the Arp2/3 complex to induce branched actin filament networks. Also catalyzes actin polymerization in the absence of Arp2/3, creating unbranched filaments (PubMed:30420355). Contributes to cell motility by controlling actin dynamics. May promote the rapid formation of a branched actin network by first nucleating new mother filaments and then activating Arp2/3 to branch off these filaments. Upon nutrient stress, directly recruited by MAP1LC3B to the phagophore membrane surfaces to promote actin assembly during autophagy (PubMed:30420355). The p53/TP53-cofactor and actin activator activities are regulated via its subcellular location (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QXM1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30420355}. | Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Cytoskeleton;DNA damage;DNA repair;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation | Predicted to enable Arp2/3 complex binding activity and transcription coactivator activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including actin nucleation; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator; and regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Located in cell leading edge. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:133746; | autophagosome membrane [GO:0000421]; cell leading edge [GO:0031252]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; Arp2/3 complex binding [GO:0071933]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; 'de novo' actin filament nucleation [GO:0070060]; actin polymerization-dependent cell motility [GO:0070358]; Arp2/3 complex-mediated actin nucleation [GO:0034314]; cellular response to starvation [GO:0009267]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator [GO:0072332]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 18398821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19287377_JMY represents a new class of multifunctional actin assembly factor whose activity is regulated, at least in part, by sequestration in the nucleus. 19897726_Data demonstrate a pathway that links the cytoskeleton with the p53 response, and further suggest that the ability of JMY to regulate actin and cadherin is instrumental in coordinating cell motility with the p53 response. 21625218_results establish the interplay between JMY and HIF-1alpha as a new mechanism that controls cell motility under hypoxic stress 21965285_JMY is expressed at high levels in brain tissue, and in various cell lines JMY is predominantly cytoplasmic, with a minor fraction in the nucleus. 22262458_actin assembly regulates nuclear import of JMY in response to DNA damage. 23758122_JMY is related to the severity of AS in Chinese Han patients. 24069348_JARID1A, JMY, and PTGER4 polymorphisms are related to ankylosing spondylitis in Chinese Han patients. 25280461_JMY was expressed in normal tissues and heterogeneously in different tumor types, with close correlation between cytoplasmic and nuclear expression. 26223951_In autophagosomes, the integrity of the WH2 domains allows JMY to promote actin nucleation, which is required for efficient autophagosome formation. 30420355_LC3 and STRAP regulate actin filament assembly by JMY during autophagosome formation. 32363797_Role of Junction-Mediating and Regulatory Protein in the Pathogenesis of Glucocorticoid-Induced Endothelial Cell Lesions. 33872315_The actin nucleation factors JMY and WHAMM enable a rapid Arp2/3 complex-mediated intrinsic pathway of apoptosis. | ENSMUSG00000021690 | Jmy | 143.392747 | 4.788078897 | 2.259447 | 0.82622514 | 6.802255 | 0.0091042809828341050848443671839049784466624259948730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0459086814664323925039290941185754491016268730163574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 177.2329009 | 78.4774027 | 36.2590085 | 16.1311414 | |
| ENSG00000153162 | 654 | BMP6 | protein_coding | P22004 | FUNCTION: Growth factor of the TGF-beta superfamily that plays essential roles in many developmental processes including cartilage and bone formation (PubMed:31019025). Also plays an important role in the regulation of iron metabolism by acting as a ligand for hemojuvelin/HJV (By similarity). Initiates the canonical BMP signaling cascade by associating with type I receptor ACVR1 and type II receptor ACVR2B (PubMed:18070108). In turn, ACVR1 propagates signal by phosphorylating SMAD1/5/8 that travel to the nucleus and act as activators and repressors of transcription of target. Can also signal through non-canonical pathway such as TAZ-Hippo signaling cascade to modulate VEGF signaling by regulating VEGFR2 expression (PubMed:33021694). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P20722, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18070108, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31019025, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33021694}. | 3D-structure;Chondrogenesis;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Cytokine;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Osteogenesis;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | This gene encodes a secreted ligand of the TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) superfamily of proteins. Ligands of this family bind various TGF-beta receptors leading to recruitment and activation of SMAD family transcription factors that regulate gene expression. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate each subunit of the disulfide-linked homodimer. This protein regulates a wide range of biological processes including iron homeostasis, fat and bone development, and ovulation. Differential expression of this gene may be associated with progression of breast and prostate cancer. Mutations in this gene may be associated with iron overload in human patients. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. | hsa:654; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; BMP receptor binding [GO:0070700]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cartilage development [GO:0051216]; cellular iron ion homeostasis [GO:0006879]; cellular response to BMP stimulus [GO:0071773]; cellular response to iron ion [GO:0071281]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; endochondral ossification [GO:0001958]; eye development [GO:0001654]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; male genitalia development [GO:0030539]; multicellular organismal iron ion homeostasis [GO:0060586]; negative regulation of adherens junction organization [GO:1903392]; negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin [GO:2000048]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of aldosterone biosynthetic process [GO:0032349]; positive regulation of aldosterone secretion [GO:2000860]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0032332]; positive regulation of endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0045603]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031666]; positive regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045666]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; positive regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060391]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043117]; response to activity [GO:0014823]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384]; response to magnesium ion [GO:0032026]; response to retinoic acid [GO:0032526]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395]; type B pancreatic cell development [GO:0003323] | 13130469_the presence of BMP-6 in adult human articular cartilage indicates a functional role for this growth factor in the maintenance of joint integrity. 14558086_BMP-2 and BMP-6 are expressed in arthritic synovium and are strongly up-regulated by proinflammatory cytokines. 15186723_results revealed a novel potent effect of PTH and vitamin D(3) plus BMPs in inducing bone development by human mesenchymal stem cells 15516325_BMP-6 increases the levels of osteopontin, BMP-2, alkaline phosphatase and core binding factor alpha 1 mRNAs in human periodontal (HPL) ligament cells. 15548695_Recombinant noggin inhibited the function of BMP-6, suggesting a negative feedback regulation of BMP activity and indicating a strategy for the development of a novel therapeutic target in treatment of osteosclerotic bone metastases of prostate cancer 15784727_several single nucleotide polymorphisms in bone morphogenic protein 6, annexin A2, and klotho were associated with sickle cell osteonecrosis 15861517_To analyze the expression of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) in prostate and breast cancers with established metastasis in bone 15877825_In mature human B cells, BMP-6 inhibited cell growth, and rapidly induced phosphorylation of Smad1/5/8 followed by an upregulation of Id1. 16527843_endogenous BMP-6 system plays critical roles in aldosterone production between Ang II and K through ERK signaling pathway. 16547600_Excess numbers of BMP6-deficient myofibroblast progenitor cells may favour adverse tissue remodelling in patients with diabetes. 16604289_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16886151_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17238135_a distinct BMP and TGFbeta-receptor repertoire may explain the reduced chondrogenic capacity of adipose tissue stromal cells in vitro 17262821_strong BMP staining is seen in maturing chondrocytes, and thus may play a role in chondrocyte differentiation and/or apoptosis; BMP release by osteoclasts may promote osteoblastic differentiation at sites of bone remodeling 17574840_BMP-6 promoter methylation status is correlated with estrogen receptor status in breast cancer 17575215_BMP-6 promoter methylation may be a potential new biomarker of risk prediction in DLBCL. 17577985_Data show that pcDNA-BMP2/6 produced more rhBMP6 than pcDNA-BMP6. 17879955_BMP6 induced cell cycle arrest in estrogen-insensitive breast cancer cells. BMP6 inhibits stress-induced apoptosis via both Smad and p38 signal pathways. 17899540_A functional bone morphogenetic protein 6 (BMP-6) signalling pathway is present in adult pre-T-leukemia lymphoma cell line Jurkat TAg. 17924656_presents the crystal structure of BMP-6 18070108_The crystal structure of human BMP-6 was determined to a resolution of 2.1 A. 18187665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18308844_Affects aldosterone breakthrough induced by long-term treatment with agtr1 stimulated aldosterone production by adrenocortical cells. 18326817_BMP-2, BMP-4, and BMP-6 are endogenous ligands for Hemojuvelin in hepatoma-derived cell lines, and all 3 of these ligands are expressed in human liver 18349123_Expression of BMP1, BMP6, BMP7, and BMP-receptor 2 was significantly increased in advanced stages of myelofibrosis compared and enhanced levels of BMP6 expression were already evident in prefibrotic stages of primary myelofibrosis. 18436533_BMP-2/4 and BMP-6/7 differentially utilize cell surface receptors to induce osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells 18632632_Wnt3a and Wnt5a have roles in inducing BMP-4 and 6 expression in prostate cancer osteoblast differentiation 18683889_BMP signaling plays a role in the induction of an osteoblastic phenotype in human dermal fibroblasts in response to vitamin D(3) stimulation 18688853_BMP-6 promoter methylation is likely to be a common epigenetic event at later stages of ATL and that the methylation profiles may be useful for the staging of ATL as well as for evaluation of the individual risk of developing the disease. 18805502_significant role of BMP-6 in inhibiting MDA-MB-231 migration through decreasing deltaEF1 expression which subsequently relieves deltaEF1-mediated invasion. 18931653_the potential use of bone-morphogenetic protein-6, noggin and sclerostin expression together as a prognostic predictor for metastatic progression of prostate cancer. 18949431_BMP3b and BMP6 genes were suppressed by DNA methylation and methylation of BMP3b is significantly frequent in Japanese malignant pleural mesotheliomas (MPMs), suggesting its pathogenic role and the ethnic difference in MPMs. 19075223_S1P induces osteoblast precursor recruitment and promotes mature cell survival. Wnt10b and BMP6 also were significantly increased in mature osteoclasts, whereas sclerostin levels decreased during differentiation. 19093115_study confirmed association of a single SNP, BMP6-3 (rs3812163), suggesting a potential role for BMP6 in the development of sickle avascular necrosis in sickle cell disease patients. 19245827_attenuates oxidant injury in kidney cells via Smad-dependent HO-1 induction 19252488_Mtations in BMP6 mayause iron overload in humans with severe juvenile hemochromatosia. 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19308091_Bone morphogenetic protein-6 may function as an anti-metastasis factor by a mechanism involving transcriptional repression of microRNA-21 in breast cancer. 19539911_BMP-6 is an important mediator to support healthy follicle growth in the human ovary. 19543302_Data show that bone morphogenetic protein 6 ameliorates TGF-beta1-induced changes in HK-2 cells. 19694819_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19718049_A high BMP6 expression in primary myeloma cell samples delineates significantly superior overall survival for patients undergoing high-dose chemotherapy 19765379_regulates hepcidin an iron metabolism in humans 20016212_Malignant human clear cell renal carcinoma tissue had significantly higher BMP-6 mRNA expression than healthy tissue 20048150_Using BMP-6/7 chimeras, we identified lysine 60 as a key residue conferring noggin resistance within the BMP-6 protein. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20401668_Results suggest that PTHrP (ParaThyroid Hormone-related Protein) acts upstream of BMP-6, and exerts its antimitogenic effect by reducing BMP-6 mRNA expression through PKA signaling pathway in breast cancer cells. 20460105_BMP6, Smad1, Smad2 mRNA and protein expression were significantly higher in during sickle-cell pathology with orthopedic complications. 20530805_c/hemojuvelin is a broad spectrum bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) antagonist and inhibits both BMP2- and BMP6-mediated signaling and gene expression 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20567515_conclude that BMP-2/6 is more potent than BMP-2 or BMP-6 for inducing differentiation of human embryonic stem cells, and it can be used as a more powerful substitute of these BMPs in in vitro differentiation guidance 20573596_the cBMP6 mRNA and H3K27me3 levels revealed significant differences between patients with local local advanced, or metastatic disease 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20605837_AGTR1 gene deletion is associated with congenital anomalies of the kidneys and urinary tract. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20844121_Ass-associated increases in BMP6 expression in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease may have deleterious effects on neurogenesis in the hippocampus. 21136273_a novel role of BMP-6/HO-1 cascade to relieve breast cancer metastasis by regulating the secretion of growth factors in tumor microenvironment. 21374653_BMP-6 secreted by prostate cancer cells induces IL-6 expression in macrophages; IL-6, in turn, stimulates the neuroendocrine differentiation of prostate cancer cells. 21622652_BMP6 and iron not only induce hepcidin expression but also induce TMPRSS6, a negative regulator of hepcidin expression 21898381_BMP-6 mainly inhibited plasmablast differentiation, and BMP-7 mainly induced apoptosis in human memory B cells 22086350_The methylation of BMP6 was correlated with decreased levels of mRNA transcripts. 22305102_Growth differentiation factor 3 is induced by bone morphogenetic protein 6 (BMP-6) and BMP-7 and increases luteinizing hormone receptor messenger RNA expression in human granulosa cells. 22364398_investigated role of BMP6 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) development and progression;high BMP6 activity, defined by strong BMP6 expression with weak noggin or SOST expression, was associated with shorter survival in esophageal SCC patients; results suggest BMP6, noggin and SOST could be used in combination as a prognostic indicator in cancer progression 22641693_BMP4 and BMP6, from two different BMP subclasses, and their antagonists noggin and sclerostin were variably expressed in melanocytes and keratinocytes in human skin 22792339_Estrogen is involved in hepcidin expression via a GPR30-BMP6-dependent mechanism 23674072_BMP6 plays a critical role in breast cancer cell aberrant proliferation and chemoresistance and may serve as a novel diagnostic biomarker or therapeutic target for breast cancer. 23799295_Marker gene screening for human mesenchymal stem cells in early osteogenic response to bone morphogenetic protein 6 with DNA microarray. 23853066_determined whether BMP-2, -6, and -7 differentially regulate the proliferation, mineralization, and mRNA expression of bone/mineralized tissue associated genes of human periodontal ligament stem cells obtained from periodontal ligament tissue 24012720_High BMP6 expression is associated with breast cancer. 24185914_Prostate cancer-derived BMP-6 stimulates tumor-associated macrophages to produce IL-1a through a crosstalk between Smad1 and NF-kB1; IL-1a, in turn, promotes angiogenesis and prostate cancer growth. 24263212_the patients carried genotype TA of rs 267196 and genotype AG of rs267201 present a high risk factor for developing osteonecrosis RR=1.317 and RR=1.3 respectively 24406789_BMP-6 attracted neutrophils and controlled the regulation of the neutrophils in the ovary. 24498236_The BMP-6 staining intensity was downregulated. 24518599_WNT5A derived from bone stromal cells induced the expression of BMP-6 by CaP cells; BMP-6 in turn stimulated cellular proliferation of CaP cells. 24658703_these data highlight a therapeutically innovative role for BMP6 by providing a means to enhance the amount of myogenic lineage derived brown fat. 24875397_There were no correlations between iron parameters and the expression of the BMP-6 in granulosa cells from polycycstic ovary syndrome patients. 24890613_Data indicated that hypermethylation modifications contributed to the regulation of BMP6 and induced an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition phenotype of breast cancer during the acquisition of drug resistance. 25011936_In vitro analysis revealed that recombinant BMP6 inhibited the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and reduced proinflammatory and profibrogenic gene expression in already activated HSCs 25121767_demonstrate that BMP6 is associated with radiographic severity in AS, supporting the role wingless-type like/BMP pathway on radiographic progression in AS 25227796_CpG island methylation of BMP6 is found in high frequency in CRC and this epigenetic event is associated with suppressed protein expression in the tumor tissue. 25753222_These observations imply that crosstalk between the VEGF and BMP-6 signaling pathways enhances osteogenic differentiation of MSCs. 26410368_BMP6 and oxidized low-density lipoprotein independently and synergistically induced osteogenic differentiation and mineralization in vascular endothelial cells. 26475719_the combined delivery of VEGF and BMP-6 to the bone defect significantly enhanced bone repair through the enhancement of angiogenesis and the differentiation of endogenously recruited MSCs into the bone repair site. 26582087_Identify 3 heterozygous missense mutations in BMP6 in patients with unexplained iron overload. These mutations lead to loss of signaling to SMAD proteins and reduced hepcidin production. 26598555_BMP-dependent physical interaction of VE-cadherin with the BMP receptor ALK2 (BMPRI) and BMPRII, resulting in stabilization of the BMP receptor complex and, thereby, the support of BMP6-Smad signaling. 26751737_These observations suggest a novel role of BMP-6 in the inhibition of breast cancer metastasis by regulating secretion of MMPs(MMP-1) in the tumor microenvironment. 26779985_BMP-6 upregulates somatostatin receptor actions, leading to reduction of GnRH-induced secretion of luteinizing hormone. 26855134_These results demonstrated that Hcy up-regulated hepcidin expression through the BMP6/SMAD pathway, suggesting a novel mechanism underlying the hyperhomocysteinemia-associated perturbation of iron homeostasis. 27051019_study shows that patients with CRA had high expression of BMP6 and hepcidin and low expression of s-HJV. BMP6 was found to be negatively correlated with s-HJV; both regulate hepcidin expression and play important roles in the development of anemia. 27592865_Plasma BMP6 was significantly increased in chronic heart failure patients. 27959431_Further investigation on clinical ESCC samples and non-tumorous adjacent tissue found that tumors with triple-positive BMP6, ALK2 and BMPRII had deeper growth than tumors with only BMP6 expression 28335084_Our results independently add further evidence to the role of BMP6 mutations as likely contributing factors to late-onset moderate IO unrelated to mutations in the established five HH genes. 28434979_Synergistic effects of BMP-2, BMP-6 or BMP-7 with human plasma fibronectin onto hydroxyapatite coatings. 28523310_Study demonstrated that the mesenchymal epithelial/myoepithelial potential of transdifferentiation of the luminal cells that make up the proliferative units is certified by the immunohistochemical expression of some BMP6 purely mesenchymal protein cells. 28733457_both bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2) and BMP6 are proangiogenic in vitro and ex vivo and that the BMP type I receptors, activin receptor-like kinase 3 (ALK3) and ALK2, play crucial and distinct roles in this process. 29767257_The present study demonstrated that BMP6 may protect retinal pigment epithelial cells from oxidative stress injury to a certain extent, which may be associated with alterations in the MAPK signaling pathway. 30171260_This study elucidates a novel role of BMP6-induced modulation of the tumor microenvironment. 30230035_All these data suggest that BMP6 decrease KC proliferation and promote KC differentiation. Together, these findings raise the possibility that BMP6 acts as the HIF-1alpha target, mediating the effects of HIF-1alpha on hyperproliferation and abnormal differentiation. 30510168_Hepatitis C virus (HCV) blunted induction of hepcidin expression by hepatic bone morphogenetic protein BMP6. In HCV patients, disruption of the BMP6/hepcidin axis and genetic variation associated with the BMP/SMAD pathway predicts the outcome of infection. BMP6 enhances the transcriptional and antiviral response to type I interferon (IFN), but BMP6 also potently blocks HCV replication independently of IFN. 30542109_BMP-6 is downregulated in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 30633987_The results demonstrate that BMP6 increases the production of TGF-beta1 by up-regulating the expression of furin in human granulosa cells via an ALK2/ALK3-mediated SMAD1/5/8-SMAD4 signaling pathway. 30878675_Study detected that BMP6 is significantly increased in skin-derived fibroblasts of patients with localized scleroderma. Moreover, it was shown that BMP6 significantly impacts proliferation, migration, cytoskeletal organization, and collagen expression, as well as activity of the major pro-fibrogenic transcription factor AP-1 in dermal fibroblasts. 30982140_Identification of Pathogenic Genes and Transcription Factors in Osteosarcoma. 31276102_Nrf2 controls iron homeostasis in haemochromatosis and thalassaemia via Bmp6 and hepcidin. 31434001_demonstrate that ALK2 and ALK3 BMP type I receptors are involved in BMP6-induced suppressive effects on Cx43 expression 31495245_Bone morphogenetic protein 6 expression in cumulus cells is negatively associated with oocyte maturation. 32059748_miR-765 inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targeting BMP6 via regulating the BMP6/Smad1/5/9 signaling pathway. 32076051_Inhibition of bone morphogenetic protein 6 receptors ameliorates Sjogren's syndrome in mice. 32464486_Novel mutations in the bone morphogenetic protein 6 gene in patients with iron overload and non-homozygous genotype for the HFE p.Cys282Tyr mutation. 32524577_BMP-6 and SMAD4 gene expression is altered in cumulus cells from women with endometriosis-associated infertility. 32641001_Association analysis of polymorphisms rs12997 in ACVR1 and rs1043784 in BMP6 genes involved in bone morphogenic protein signaling pathway in primary angle-closure and pseudoexfoliation glaucoma patients of Saudi origin. 32845956_BMP6 Regulates Corneal Epithelial Cell Stratification by Coordinating Their Proliferation and Differentiation and Is Upregulated in Pterygium. 32854680_Synergistic interaction of hTGF-beta3 with hBMP-6 promotes articular cartilage formation in chitosan scaffolds with hADSCs: implications for regenerative medicine. 33232799_BMP6 binding to heparin and heparan sulfate is mediated by N-terminal and C-terminal clustered basic residues. 33332786_Genome-wide Association Analysis Across 16,956 Patients Identifies a Novel Genetic Association Between BMP6, NIPAL1, CNGA1 and Spondylosis. 34037557_Novel BMP6 gene mutation in patient with iron overload. 34314740_BMP6 increases CD68 expression by up-regulating CTGF expression in human granulosa-lutein cells. 34611951_Runx3 regulates iron metabolism via modulation of BMP signalling. 34740612_Bone morphogenetic protein 6-mediated crosstalk between endothelial cells and hepatocytes recapitulates the iron-sensing pathway in vitro. 34933731_The effect of cellular and physiological indicators on gender determination. 35033126_Immunohistochemical analysis revealed the expression of bone morphogenetic proteins-4, 6, 7, and 9 in human induced membrane samples treated with the Masquelet technique. 35694925_Blood BMP6 Associated with Cognitive Performance and Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosis: A Longitudinal Study of Elders. 36153321_RNF4~RGMb~BMP6 axis required for osteogenic differentiation and cancer cell survival. | ENSMUSG00000039004 | Bmp6 | 39.338395 | 0.402557295 | -1.312734 | 0.25076625 | 28.207970 | 0.0000001089550263406132300332475760368255990329089399892836809158325195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000021256107509797738701275322814598922605000552721321582794189453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 22.2500168 | 4.9523883 | 55.6088953 | 11.4278450 | |
| ENSG00000153234 | 4929 | NR4A2 | protein_coding | P43354 | FUNCTION: Transcriptional regulator which is important for the differentiation and maintenance of meso-diencephalic dopaminergic (mdDA) neurons during development. It is crucial for expression of a set of genes such as SLC6A3, SLC18A2, TH and DRD2 which are essential for development of mdDA neurons (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17184956}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a member of the steroid-thyroid hormone-retinoid receptor superfamily. The encoded protein may act as a transcription factor. Mutations in this gene have been associated with disorders related to dopaminergic dysfunction, including Parkinson disease, schizophernia, and manic depression. Misregulation of this gene may be associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described, but their biological validity has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:4929; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; nuclear glucocorticoid receptor binding [GO:0035259]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; nuclear retinoid X receptor binding [GO:0046965]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; adult locomotory behavior [GO:0008344]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cellular response to corticotropin-releasing hormone stimulus [GO:0071376]; cellular response to extracellular stimulus [GO:0031668]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; central nervous system neuron differentiation [GO:0021953]; central nervous system projection neuron axonogenesis [GO:0021952]; DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006351]; dopamine biosynthetic process [GO:0042416]; dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:0071542]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; general adaptation syndrome [GO:0051866]; habenula development [GO:0021986]; midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:1904948]; negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001234]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuron apoptotic process [GO:0051402]; neuron maturation [GO:0042551]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; positive regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0043085]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; regulation of dopamine metabolic process [GO:0042053]; regulation of respiratory gaseous exchange [GO:0043576]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to amphetamine [GO:0001975]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] | 11803525_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11803525_The result suggests that the c.-469delG and possibly other variants of the NR4A2 gene may be of relevance to the complex factors involved in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. 11840500_may contribute to susceptibility to alcoholism. 11884470_NURR1 induction by proinflammatory mediators represents a point of convergence of at least two distinct signaling pathways, suggesting an important common role for this transcription factor in mediating multiple inflammatory signals. 11914402_A homozygous polymorphism has been found in intron 6 of Nurr1 gene, which was significantly higher in Parkinson's subjects compared to control. 11914402_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11959923_Decreased expression of the transcription factor NURR1 in dopamine neurons of cocaine abusers 12496759_Mutations in NR4A2 associated with familial Parkinson disease 12496759_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12564761_Nurr1, NGFI-B and NOR-1 mRNA are expressed constitutively in various human neural and non-neural cell lines, and their levels are up-regulated in human neurons by activation of protein kinase A or protein kinase C pathway. 12627459_Data do not support the notion that the NR4A2 gene plays a major role in risk for schizophrenia among Japanese individuals. 12627459_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12694388_Nurr1 may play a direct role for specification of DA neurotransmitter identity by activating TH gene transcription in a cell context-dependent manner 12756136_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12756136_The common heterozygous NI6P is associated with an increased risk of Parkinson disease and an association of borderline significance was found for the homozygous NI6P and diffuse Lewy body disease. 12774125_crystal structure of the orphan receptor Nurr1 at 2.2 A resolution; structure-activity relationship 12815740_NURR1 promoter polymorphisms were studied in Parkinson's disease (PD), schizophrenia (SZ), and personality traits and found unlikely to be involved in conferring susceptibility for SZ or PD. 12815740_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12827450_Point mutations in exon 1 are not major cause of familial Parkinson disease 12852843_NURR1 is a nuclear receptor which can assume an active conformation in the absence of a ligand agonist. 12875905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14525795_The genes identified here are novel candidates as key early mediators of VEGF-induced endothelial functions. 14988426_Nurr1 activates the OPN promoter directly in osteoblastic cells and may have a role in the regulation of bone homeostasis 15018843_NR4A2 (A NEWLY DISCOVERED MUTANT GENE)IS A MEMBER OF A NUCLEAR RECEPTOR SUPERFAMILY REQUIRED FOR THE DIFFERENTIATION AND MAINTENANCE OF NIGRAL DOPAMINERGIC NEURONS. LOCATION 2Q22-23(P.81) 15184637_To evaluate the role of NR4A2 in PD, exon 1 was analyzed in 108 families with apparent autosomal dominant PD. None of the previously described mutations were found by sequence analysis of the 481 bp fragment of exon 1; no new sequence variants were found. 15197702_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15197702_Polymorphic variant within intron 6 of the Nurr1 gene was reported to be associated with familial Parkinson disease. 15211629_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15211629_search for all known mutations in 176 Caucasian Portuguese and 82 Caucasian Brazilian subjects with lifetime diagnosis of schizophrenia failed to identify any of the described mutations in patients or controls 15276233_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15292355_Expression of Nurr1 and NGFI-B plays an important role in human adrenal cortex and its neoplasms, including possible regulation of steroidogenesis. 15390059_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15450088_Virtually all striatal cells that stain for tyrosine hydroxylase also express Nurr1, confirming the existence of dopaminergic neurons intrinsic to the human striatum. 15486232_Causal relationship between the rapid decline of aromatase mRNA and induction of orphan nuclear receptors NURR1 and NGFI-B expression, which concomitantly occur upon LH surge at the later stages of ovarian follicular development. 15548686_down-regulation of NR4A2 as well as NR4A1 promoted intrinsic apoptosis 15635645_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15635701_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15964844_NR4A nuclear receptors NR4A1, NR4A2, NR4A3 are potential transcriptional mediators of inflammatory signals in activated macrophages 16293616_NR4A2 can stimulate progression of colorectal cancer downstream from cyclooxygenase 2-derived PGE2. 16320253_In Parkinsons, Nurr1 was decreased in nigral neurons containing alpha-synuclein-immunoreactive inclusions. In Alzheimer's, Nurr1 was decreased in neurons containing neurofibrillary tangles. In PSP, Nurr1 was also decreased. 16477036_Nurr1 and Pitx3 cooperatively promote terminal maturation to the midbrain dopamine neuron phenotype in murine and human ES cell cultures. 16532445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16873729_Nur77, Nurr1, and NOR-1 are expressed in human atherosclerotic lesion macrophages and reduce human macrophage lipid loading and inflammatory responses, providing further evidence for a protective role of these factors in atherogenesis. 16977628_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17032747_Insights into the mechanisms of transcription via the Nurr1 LBD identifies an alternative co-activator-binding surface that is unique to the NR4A family of NRs. 17283078_Nurr1 has a protective function in cartilage homeostasis by selectively repressing matrix metalloproteinase gene expression during inflammation. 17427185_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17427185_This study examines whether BDNF V66M (c.196 G --> A) or NR4A2 IVS6 +18insG polymorphism is associated with the risk of Taiwanese Parkinson's disease and the age of onset using a case-control study. 17574328_These results suggest that the suppression of aromatase activity and its transcription level by MEHP exposure to NCI-H295R cells was regulated through the rapid and transient expression of Nur77 gene. 17671512_aberrant expression and distribution of NURR1 in psoriasis 17681692_Nurr1 phosphorylation by ERK2 may play a role in regulating the TH expression. 17728669_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18057194_Significant alteration of mRNA expression of Nurr1, a transcription factor that regulates dopamine transporter expression, is confined to the paranigral nucleus. 18195715_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18242186_Rat and mouse species-dependent differences of Nurr1 and Ngn2 actions in dopamine neuron differentiation. 18292087_These data identify the NR4A receptor family as potential mediators of an MC1R-coordinated DNA damage response to ultraviolet rays exposure in melanocytic cells. 18463503_decreased expression of Nurr1, which has been found in Parkinson's disease patients with Nurr1 mutations, was shown to transcriptionally increase alpha-synuclein expression 18577687_The induction of nur77 expression by n-butylenephthalide as pharmaceuticals on hepatocellular carcinoma cell therapy is reported. 18583979_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18684475_NURR1 gene expression were associated with significantly increased risk for PD in women, in patients 60 years old or older, and in patients of Caucasian origin. 18937842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19065535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19065535_association between the polymorphisms of [c.-2922(C)2-3 and IVS6+ 18insG] in the NURR1 gene and Parkinson's disease (PD) in a Han population from Sichuan province 19074857_the orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1 has a role in inhibiting bladder cancer growth 19156841_Associations for NR4A2 were found with both HDL levels and blood pressure, and it remains to be investigated which pathophysiological mechanisms pertain to NR4A2 function in cardiovascular disease. 19156841_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19224617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19224617_This study found that no associations were seen for NR4A2 in Australia patient with Parkinson's disease 19352218_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19429166_the c.-309C>T mutation reduces NR4A2 expression resulting in the downregulation of genes involved in the development and maintenance of the nervous system and synaptic transmission 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19494806_In this study, the NR4A2 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms rs834829 is in association with increased Fagerstrom Test for Nicotine Dependence scores among both treatment-seeking and community smokers. 19494806_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19549529_Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors down-regulate osteopontin and Nr4A2-new therapeutic targets for colorectal cancers. 19569046_NR4A2 was significantly down-regulated in synchronous liver metastasis compared with the paired gastric cancer. 19570744_Activation of thromboxane A(2) receptors induces orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1 expression and stimulates cell proliferation in human lung cancer cells. 19671681_Nurr1 promotes cell survival through its interacting with and repressing p53. 19692620_Nr4a2 is critically involved in the specification of amacrine cell subtype identity. 19732956_an important role for NR4A2 in modulating IL-8 expression and reveal novel transcriptional responses to TNF-alpha in human inflammatory joint disease. 19861119_FABP5 could be a regulated target of Nurr1. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20016108_Study of conditional gene ablation in trangenic mice shows that disrupted function of Nurr1 and other developmental transcription factors may contribute to neurodegenerative disease. 20049900_We show here that Foxa2, a forkhead transcription factor whose role in midbrain DA neuron development was recently revealed, synergistically cooperates with Nurr1 to induce a DA phenotype, midbrain-specific gene expression, and neuronal maturation. 20421523_Nurr1 haplotypes are associated with human restenosis risk, and Nurr1 is expressed in human in-stent restenosis 20560679_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20659174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20829434_Results propose a MIF-NURR1 signaling axis as a regulator of the glucocorticoid sensitivity of MKP1. 21299892_NR4A2 was found to have bimodal expression in human skeletal muscle tissue. 21480782_Nur77 and Nurr1 promote fetal bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells migration. 21621845_stimulation of peripheral blood mast cells caused a robust upregulation of NR4A2 and, in particular, NR4A3, while NR4A1 expression was only moderately affected 21757690_NR4A2 plays a key role as a transcriptional integration point between the eicosanoid and fatty acid metabolic pathways 21826669_we have identified a molecular signature associated with potential cancer stem cells and showed for the first time the existence of a functional relationship between CD133, endothelin-1 and NR4A2 expression in colon cancer cells. 21936000_Moracenin D protected against dopamine-induced cell death by up-regulation of nurr1 and down-regulation of alpha-synuclein mRNA levels. 21979916_NR4A functions directly at DNA repair sites by a process that requires phosphorylation by DNA-PK 22024154_Data suggest that DJ-1 upregulates tyrosine hydroxylase expression by activating its transcription factor Nurr1 via the ERK1/2 pathway. 22066143_Forced expression of retinoic X receptor (RXR)alpha with Nurr1 remarkably reduces Nurr1 activity in tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive dopaminergic neuronal stem cells, significantly down-regulating TH promoter activity. 22143616_Data show altered adipose tissue expression of the NURR1 stress-responsive nuclear receptor in obesity, suggesting it may modulate pathogenic potential in humans. 22230598_Association of nuclear receptor related 1 protein (Nurr1) haplotypes to the restenosis/re-occlusion rate after femoropopliteal percutaneous transluminal angioplasty was investigated. 22275273_NR4A2 is a downstream mediator of TNFalpha signaling in synovial tissue. NR4A2 transcriptional activity contributes to the hyperplastic and invasive phenotype of synoviocytes that leads to cartilage destruction. 22294735_Recessive genotypes of rs1150143, rs1150144, rs834830, and rs707132 were associated with a worse sustained attention task performance in schizophrenic males, but not females. Males with the GGGTG haplotype had poorer performance. 22309633_This study provided that NURR1 and PITX3 gene expression is decreased in the peripheral blood lymphocytes of Chinese patients with Parkinson's disease patients. 22514272_INFS/Nurr1 nuclear partnership provides a novel mechanism for TH gene regulation in mDA neurons and a potential therapeutic target in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders. 22764233_alpha-Synuclein-mediated suppression of transgenic Nurr1 protein overexpression contributes to the vulnerability of midbrain dopaminergic neurons in a model of Parkinson's disease pathogenesis. 22789442_Pin1 enhances the transcriptional activity of all three NR4A nuclear receptors and increases protein stability of Nur77 through inhibition of its ubiquitination. 22800541_analysis of Nurr1 gene expression in electrically-stimulated human MSCs and the induction of neurogenesis 22827504_Collectively, our results suggest that NR4A2 may be a susceptibility gene for Parkinson's disease in the Chinese population 23066323_Nur-related receptor 1 gene polymorphisms are implicated in alcohol dependence in Mexican Americans 23283970_Nurr1 shuttling between the cytosol and nucleus is controlled by specific nuclear import and export signals 23358114_PIASgamma fully represses Nurr1 transactivation through a direct interaction, independently of its E3-ligase activity 23416839_in human melanoma HMV-II cells both CRF and Ucn1 regulate TRP1 gene expression via Nurr-1/Nur77 production, independent of pro-opiomelanocortin or alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone stimulation. 23517088_NURR1 function presents a dichotomy in breast cancer etiology, in which NURR1 expression is associated with normal breast epithelial differentiation and efficacy of systemic cancer therapy. 23679312_High nurr1 is associated with progression of prostate cancer 23803035_High cytoplasmic expression of NR4A2 is a potential unfavorable prognostic factor for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 23809767_High expression of NR4A2 in CRC cells confers chemo-resistance, attenuates chemotherapeutics-induced apoptosis, and predicts unfavorable prognosis of colon cancer patients. 23821160_High NR4A2 expression in gastric cancer cells confers chemoresistance, attenuates 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis, and predicts an unfavorable survival, especially for those who received chemotherapy. 23933487_Bioinformatic and deletion studies identified a 5' region of the TSP-1 promoter repressed by NR4A2 and proangiogenic transcription factors, including NF-kappaB and Ets1/2. 23950896_Data indicate that expression of Nurr1 was significantly induced by 1,1-bis(3'-indolyl)-1-(p-chlorophenyl methane) (DIM-D). 23977047_Nurr1 overexpression significantly increased the SIRT1 occupancy of the consensus elements for Nurr1 binding hTH promoter region. 24005216_NR4A nuclear receptors are involved in negative selection of thymocytes, Treg differentiation and the development of Ly6C monocytes. Nur77 and Nurr1 attenuate atherosclerosis in mice whereas NOR-1 aggravates vascular lesion formation. 24086717_NR4A2 is regulated by gastrin and influences cellular responses of gastric adenocarcinoma cells. 24172139_our data demonstrate that key midbrain dopamine regulators (Nurr1, Pitx3, and Lmx1a) play overlapping as well as distinct roles during neurogenesis and neurotransmitter phenotype determination of mDA neurons 24223135_A novel role for the NR4A2 nuclear receptors as direct facilitators of nucleotide excision repair. 24685177_The current review describes the role of two such factors, Nurr1 and engrailed, in differentiation, maturation, and in normal physiological functions including acquisition of neurotransmitter identity. 24852325_The results of this study suggest a protective and anti-inflammatory role of NR4A2 and TNFAIP3, both being under-regulated in monocytes and CD4 + T cells of MS patients 25089663_In this review, a concise overview of the current understanding of the important metabolic roles governed by NR4A members NR4A1, NR4A2 and NR4A3 including their participation in a number of diseases shall be provided 25092869_The AngII-NGFIB/NURR1 pathway controls HSD3B1 expression. 25199433_gestational diabetes mellitus, but not pre-existing maternal obesity, associated with increased placental expression 25503547_NURR1 upregulation by tissue-type plasminogen activator during ischemic stroke is associated with endothelial dysfunction and inflammation. 25752609_Because the phosphorylation site mutants of NR4A2 cannot rescue the cell death-promoting activity, ASK1-p38 pathway-dependent phosphorylation and subsequent cytoplasmic translocation of NR4A2 may be required for oxidative stress-induced cell death. 25809189_A2M is expressed in the vasculature and NR4A receptors modulate VSMC MMP2/9 activity by several mechanisms including the up-regulation of A2M. 25917081_NR4A2 is a key factor in multiple diseases, such as inflammation, cancer and cardiovascular diseases. 25953901_Thus our data identify a previously unknown role for Nr4a2 in the regulation of macrophage polarization. 25982322_The results failed to reveal significant link between NR4A2 polymorphism and schizophrenia risk. [META-ANALYSIS] 26022133_The immunohistochemical, qRT-PCR and western blot analyses revealed that Nurr1 expression was increased in gastric cancer tissues compared with normal gastric tissue. 26148973_Data show that some rexinoids display selective coactivator (CoA) recruitment by the retinoid X receptors (RXRs) homodimer and by the heterodimers nuclear receptor Nur77/RXR and Nurr1/RXR. 26239742_decreased expression levels of Nurr1 were associated with chronic inflammation and insulin resistance in patients with T2D. 26678495_NURR1 is an essential transcription factor for the differentiation, maturation, and maintenance of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. 27036119_Our results suggest that NLK inhibits transcriptional activation of Nurr1 gene by impeding CBP's role as a co-activator of NF-kappaB and CREB in prostate cancer. 27121375_miR-34 was identified as a direct negative regulator of NR4A2. A novel regulatory network linking p53, miR-34, and NR4A2 was revealed, in which p53 can overcome its inhibition by endogenous NR4A2 through upregulating miR-34. 27128111_show that unsaturated fatty acids also interact with the Nurr1 LBD, and solution NMR spectroscopy reveals the binding epitope of DHA at its putative ligand-binding pocket 27159982_Study found a marked down-regulated gene expression of the NR4A subfamily (NR4A1, NR4A2, and NR4A3) obtained from Parkinson's disease patients, but only a NR4A1 decrease in Alzheimer's disease patients compared to healthy controls. This study reports that the entire NR4A subfamily and not only NR4A2 could be systemically involved in Parkinson's disease. 27553040_Nurr1 was induced during intestinal regeneration after I/R injury. Nurr1 promoted proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells after H/R injury. Nurr1 inhibited p21 expression in a p53-independent manner. Nurr1 inhibited p21 gene transcription by binding to p21 promoter directly. 27667480_In the PPI network, genes may be involved in Down syndrome (DS) by interacting with others, including nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 2 (NR4A2)early growth response (EGR)2 and NR4A2EGR3. Therefore, RUNX1, NR4A2, EGR2, EGR3 and ID4 may be key genes associated with the pathogenesis of DS. 27940361_Nurr1 overexpression exerts neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory roles via down-regulating CCL2 in both in vivo and in vitro Parkinson's disease models, contributing to developing mechanism-based and neuroprotective strategies against PD 28423575_Findings support that Notch1/NR4A2 co-regulate HCC cell functions by playing oncogenic roles and regulating the associated downstream signaling pathways. 28544326_Our findings of a de novo deletion of NR4A2 in an individual with mild intellectual disability and prominent speech and language impairment provides further evidence for NR4A2 haploinsufficiency being causative for neurodevelopmental and particularly language phenotypes 28607006_Data expand the understanding of the mechanism by which the NR4A2 nuclear receptor can facilitate DNA DSB repair. 28621822_this study shows over-expression of NR4A2 mRNA in peripheral CD4+ T cells of Sjogren's syndrome patients 28637666_NR4A2 and NR4A3 are components of a downstream transcriptional response to PKA activation in the neutrophil, and that they positively regulate neutrophil survival and homeostasis. 28716280_An association was identified in a Mexican population between genotype and mRNA expression levels of NR4A2 in patients with Parkinson's disease. 28808448_NR4A sub-family of nuclear orphan receptors (Nor-1, Nurr-1 and Nur-77) may have a role in trophoblastic cell differentiation. 29540663_Nurr1 regulated intestinal epithelial development and barrier function after intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. 29738496_PARP1 inhibitor also suppressed the aldosterone secretion in response to the angiotensin II. Together, these results suggest PARP1 is a prime coregulator for Nurr1. 29770430_We report 3 additional patients with a de novo deletion encompassing NR4A2: 2 patients have deletions encompassing only NR4A2 gene and 1 patient has a deletion including NR4A2 and the first exon of GPD2 30106181_Mechanistically, NR4A1 and NR4A2 synergistically activate the CTNNB1 gene promoter . Knocking down CTNNB1 or NR4A1 in AML-MSC-co-cultured-CD34(+) cells increased leukaemia-reactive T-effector cells production and rescued anti-leukaemia immunity. 30121937_Promoter-activity assays confirmed that exposure of cells to full-length Nurr1 fusion protein activated not only its cognate human tyrosine hydroxylase promoter but also the corresponding mouse sequence, although at a reduced efficiency. 30515963_Nurr1 critically regulates Alzheimer's disease-related pathophysiology. 30817108_peripheral Nurr1 was significantly decreased in Parkinson disease patients compared with healthy controls. 31704909_investigation showed low expression levels of FoxM1, Nurr1, and Ki-67 in the intestinal epithelium of patients with intestinal ischemic injury. FoxM1 acts as a critical regulator of intestinal regeneration after I/R injury by directly promoting the transcription of Nurr1. 31723028_analysis of the molecular basis for the binding of the NR4A2 protein dimers to Nur-responsive DNA elements 31811028_we provide in silico and experimental evidence for a role of the TFs NURR1 and ERR1 in modulating the expression pattern of genes coexpressed with DRD2 in human prefrontal cortex. 31922365_Loss-of-Function Mutations in NR4A2 Cause Dopa-Responsive Dystonia Parkinsonism. 32114387_Orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1 promotes Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric carcinogenesis by directly enhancing CDK4 expression. 32188741_The transcription factor Nurr1 is upregulated in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients and SOD1-G93A mice. 32341238_Nuclear NR4A2 (Nurr1) Immunostaining is a Novel Marker for Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Salivary Glands Lacking the Classic NR4A3 (NOR-1) Upregulation. 32366965_De novo variants of NR4A2 are associated with neurodevelopmental disorder and epilepsy. 32461025_Dysfunctional Nurr1 promotes high glucose-induced Muller cell activation by up-regulating the NF-kappaB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis. 32522891_Genome-Wide Analysis Identifies NURR1-Controlled Network of New Synapse Formation and Cell Cycle Arrest in Human Neural Stem Cells. 32553196_De Novo Variants in CNOT1, a Central Component of the CCR4-NOT Complex Involved in Gene Expression and RNA and Protein Stability, Cause Neurodevelopmental Delay. 32612143_Nurr1 performs its anti-inflammatory function by regulating RasGRP1 expression in neuro-inflammation. 33010383_HPV-induced Nurr1 promotes cancer aggressiveness, self-renewal, and radioresistance via ERK and AKT signaling in cervical cancer. 33188139_CD28 Costimulatory Domain-Targeted Mutations Enhance Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell Function. 33563249_Working memory deficits in schizophrenia are associated with the rs34884856 variant and expression levels of the NR4A2 gene in a sample Mexican population: a case control study. 34248958_Transcriptional Profiling of Monocytes Deficient in Nuclear Orphan Receptors NR4A2 and NR4A3 Reveals Distinct Signalling Roles Related to Antigen Presentation and Viral Response. 34437889_Minireview: What is Known about SUMOylation Among NR4A Family Members? 34667209_NR4A2 expression is not altered in placentas from cases of growth restriction or preeclampsia, but is reduced in hypoxic cytotrophoblast. 34672863_Exosomal lncRNA Nuclear Paraspeckle Assembly Transcript 1 (NEAT1)contributes to the progression of allergic rhinitis via modulating microRNA-511/Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 4 Group A Member 2 (NR4A2) axis. 35272569_Structural, molecular hybridization and network based identification of miR-373-3p and miR-520e-3p as regulators of NR4A2 human gene involved in neurodegeneration. 35296964_A Proposed TUSC7/miR-211/Nurr1 ceRNET Might Potentially be Disturbed by a cer-SNP rs2615499 in Breast Cancer. 35409005_Transcriptional Regulation of the Synaptic Vesicle Protein Synaptogyrin-3 (SYNGR3) Gene: The Effects of NURR1 on Its Expression. 35761385_The role of NURR1 in metabolic abnormalities of Parkinson's disease. 35797416_Recruitment of the CoREST transcription repressor complexes by Nerve Growth factor IB-like receptor (Nurr1/NR4A2) mediates silencing of HIV in microglial cells. 35867766_NURR1 expression regulates retinal pigment epithelial-mesenchymal transition and age-related macular degeneration phenotypes. | ENSMUSG00000026826 | Nr4a2 | 18.695494 | 0.397086291 | -1.332476 | 0.44981708 | 8.707552 | 0.0031689451685613955790599138850893723429180681705474853515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0197360663481018702714031576306297210976481437683105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 11.1469811 | 4.3492702 | 28.2710790 | 10.1790230 | |
| ENSG00000153982 | 284161 | GDPD1 | protein_coding | Q8N9F7 | FUNCTION: Hydrolyzes lysoglycerophospholipids to produce lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and the corresponding amines (PubMed:27637550, PubMed:25596343). Shows a preference for 1-O-alkyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (lyso-PAF), lysophosphatidylethanolamine (lyso-PE) and lysophosphatidylcholine (lyso-PC) (PubMed:27637550, PubMed:25596343). May be involved in bioactive N-acylethanolamine biosynthesis from both N-acyl-lysoplasmenylethanolamin (N-acyl-lysoPlsEt) and N-acyl-lysophosphatidylethanolamin (N-acyl-lysoPE) (PubMed:27637550, PubMed:25596343). In addition, hydrolyzes glycerophospho-N-acylethanolamine to N-acylethanolamine (PubMed:27637550). Does not display glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase activity, since it cannot hydrolyze either glycerophosphoinositol or glycerophosphocholine (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9CRY7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25596343, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27637550}. | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a member of the glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase family of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of deacylated glycerophospholipids to glycerol phosphate and alcohol. The encoded protein is localized to the cytoplasm and concentrates near the perinuclear region. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. | hsa:284161; | endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; lysophospholipase activity [GO:0004622]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phosphoric diester hydrolase activity [GO:0008081]; glycerophospholipid catabolic process [GO:0046475]; N-acylethanolamine metabolic process [GO:0070291] | 14612981_A novel splice variant of the gene is mainly expressed in human ovary and small intestine. 18991142_3-D model provides the structural information; subcellular localization is in the cytoplasm; over-expression of GDE4 did not induce neurite formation or change cell morphology 33022222_Structural Variants Create New Topological-Associated Domains and Ectopic Retinal Enhancer-Gene Contact in Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa. 34673020_Development of a selective fluorescence-based enzyme assay for glycerophosphodiesterase family members GDE4 and GDE7. | ENSMUSG00000061666 | Gdpd1 | 39.914964 | 2.032956819 | 1.023580 | 0.25022701 | 16.762566 | 0.0000423607923737418098301260593885331218189094215631484985351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0004782427471540762176603622801707160760997794568538665771484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 49.9422037 | 5.7450211 | 24.7106961 | 3.1310070 | |
| ENSG00000153993 | 223117 | SEMA3D | protein_coding | O95025 | FUNCTION: Induces the collapse and paralysis of neuronal growth cones. Could potentially act as repulsive cues toward specific neuronal populations. Binds to neuropilin (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Neurogenesis;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | This gene encodes a member of the semaphorin III family of secreted signaling proteins that are involved in axon guidance during neuronal development. The encoded protein contains an N-terminal Sema domain, an immunoglobulin like domain and a C-terminal basic domain. The protein encoded by this gene binds neuropilin and plays an important role in cardiovascular development. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. | hsa:223117; | extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; chemorepellent activity [GO:0045499]; semaphorin receptor binding [GO:0030215]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; negative chemotaxis [GO:0050919]; negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048843]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway [GO:0071526] | 18818766_Sema3D inhibits tumor development from MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435 cancer cells. It inhibits tumor angiogenesis in all of the formed tumors. 19054571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20684831_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20684831_This study provided strong evidence that SEMA3D confers susceptibility to schizophrenia, which could contribute to the neurodevelopmental impairments in the disorder. 23372769_in this study we have analyzed three aminoacidic substitutions, A131T-SEMA3A, S598G-SEMA3A and E198K-SEMA3D. These variants result in an increase of SEMA proteins levels in the HSCR colon tissue. 23685842_In the absence of Sema3d, endothelial tubes form in a region that is normally avascular 24825896_Semaphorin 3d requires neuropilin 1 or PI3K/Akt, whereas semaphorin 3e requires plexin D1 in directing endothelial motility. 25839327_Functional loss of semaphorin 3C and/or semaphorin 3D and their epistatic interaction with ret are critical to Hirschsprung disease liability. 26073756_CTNNA3 and SEMA3D: Promising loci for asthma exacerbation identified through multiple genome-wide association studies 26286962_Data show significant increases in semaphorin3C, 3D and their receptor neuropilin-2 in degenerate samples which were shown to contain nerves and blood vessels, compared to non-degenerate samples without nerves and blood vessels. 27876815_Novel mutation in SEMA3D segregates with the complete phenotype with variable expressivity in two pedigrees with autosomal dominant familial Meniere's disease. 28320475_Low SEMA3D expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 29074988_SEMA3D mRNA is expressed mainly in the cytoplasm of the endometrial cancer cells. 35190928_Semaphorin 3D inhibits proliferation and migration of papillary thyroid carcinoma by regulating MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. | ENSMUSG00000040254 | Sema3d | 95.256868 | 2.247848960 | 1.168545 | 0.18896579 | 38.329723 | 0.0000000005974566264474441477404423922101771304848938370923860929906368255615234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000158882572067430595470639544336891035847258990543195977807044982910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 133.4556749 | 11.6792846 | 59.6867792 | 5.8938847 | |
| ENSG00000154358 | 84033 | OBSCN | protein_coding | Q5VST9 | FUNCTION: Structural component of striated muscles which plays a role in myofibrillogenesis. Probably involved in the assembly of myosin into sarcomeric A bands in striated muscle (PubMed:11448995, PubMed:16205939). Has serine/threonine protein kinase activity and phosphorylates N-cadherin CDH2 and sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit ATP1B1 (By similarity). Binds (via the PH domain) strongly to phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4)P2) and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2), and to a lesser extent to phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns(3)P), phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns(4)P), phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate (PtdIns(5)P) and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P3) (PubMed:28826662). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A2AAJ9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11448995, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16205939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28826662}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Calmodulin-binding;Cell membrane;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Lipid-binding;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Muscle protein;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;SH3 domain;Transferase | The obscurin gene spans more than 150 kb, contains over 80 exons and encodes a protein of approximately 720 kDa. The encoded protein contains 68 Ig domains, 2 fibronectin domains, 1 calcium/calmodulin-binding domain, 1 RhoGEF domain with an associated PH domain, and 2 serine-threonine kinase domains. This protein belongs to the family of giant sacromeric signaling proteins that includes titin and nebulin, and may have a role in the organization of myofibrils during assembly and may mediate interactions between the sarcoplasmic reticulum and myofibrils. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:84033; | cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; M band [GO:0031430]; myofibril [GO:0030016]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; ankyrin binding [GO:0030506]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding [GO:0005547]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding [GO:0043325]; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding [GO:0032266]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding [GO:0070273]; phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate binding [GO:0010314]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; structural constituent of muscle [GO:0008307]; titin binding [GO:0031432]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; protein localization to M-band [GO:0036309]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; sarcomere organization [GO:0045214] | 12631729_Results suggest that obscurin binds small ankyrin 1, and document a specific and direct interaction between proteins of the sarcomere and the sarcoplasmic reticulum. 16625316_The complete gene giant muscle protein obscurin was analysed. The fusion of the conventional obscurin A, containing only the GEF domain, and obscurin B, fusing into the 3' kinase exons, was experimentally confirmed and analysed. 17360660_OBSCN and C9orf65 comprise a highly accurate two-gene classifier for differentiating gastrointestinal stromal tumors and leiomyosarcomas. 17716621_Studies suggest that the obscurin abnormality may be involved in the pathogenesis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 17720975_Structural and mutational studies of the binding region on small Ank1 for obscurin suggest that it consists of two ankyrin repeats with very similar structures. 18350308_Obscurin was never lacking in myofibrillar alterations, but was either preserved at the M-band level or diffusely spread over the sarcomeres. 19258391_These findings reveal a novel signaling pathway in human skeletal muscle that involves obscurin and the Rho GTPase TC10 and implicate this pathway in new sarcomere formation. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20489725_Results describe the molecular basis for the head-to-tail interaction of the carboxyl terminus of titin and the amino-terminus of obscurin-like-1 by X-ray crystallography. 22251166_OBSCN polymorphisms, in particular, highly conserved nonsynonymous Leu2116Phe variant, might contribute to aspirin hypersensitivity in asthmatics 22441987_Nontumorigenic MCF10A breast epithelial cells stably transduced with shRNAs targeting giant obscurins exhibited increased viability ( approximately 30%) and reduced apoptosis ( approximately 20%) following exposure to the DNA-damaging agent etoposide. 22573887_Obscurin and KCTD6 regulate cullin-dependent small ankyrin-1 (sAnk1.5) protein turnover 25261370_Loss of the obscurin-RhoGEF downregulates RhoA signaling and increases microtentacle formation and attachment of breast epithelial cells. 25381817_Findings indicate that loss of giant obscurins from breast epithelium results in disruption of the cell-cell contacts and acquisition of a mesenchymal phenotype that leads to enhanced tumorigenesis, migration and invasiveness in vitro and in vivo. 25490259_this study presents here the X-ray structure of the human titin:obscurin M10:O1 complex extending our previous work on the M10:OL1 interaction. 26147384_Gene-based association analyses shows nominal significant association with multifocal fibromuscular dysplasia for obscurin. 26406308_OBSCN mutations may result in the development of a familial dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) phenotype via haploinsufficiency. These mutations should be considered as a significant causal factor of DCM, alone or in concert with other mutations. 27323778_demonstrate that loss of giant obscurins from breast epithelial cells is associated with significantly increased phosphorylation and subsequent activation of the PI3K signaling cascade 27855815_association of frameshift and splicing variants, all clustering to the C terminus of the same isoform group, with occurrence of rare left ventricular noncompaction phenotype 27989621_Crystal structure of the obscurin(-like-1):myomesin complex reveals a trans-complementation mechanism whereby an incomplete immunoglobulin-like domain assimilates an isoform-specific myomesin interdomain sequence. 29073160_suggest that the combination of the OBSCN p.Arg4444Trp variant and of the FLNC c.5161delG mutation, can cooperatively affect myofibril stability and increase the penetrance of muscular dystrophy in the French family 30666746_This study finds in all cases tested that tandem obscurin Ig domains interact at the poles of each domain and tend to stay relatively extended in solution. NMR, SAXS, and MD simulations reveal that while tandem domains are elongated, they also bend and flex significantly. 33042279_Intracellular calcium current disorder and disease phenotype in OBSCN mutant iPSC-based cardiomyocytes in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. 33438037_When is an obscurin variant pathogenic? The impact of Arg4344Gln and Arg4444Trp variants on protein-protein interactions and protein stability. 34601892_Truncating Variants in OBSCN Gene Associated With Disease-Onset and Outcomes of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. 34826548_Giant obscurin regulates migration and metastasis via RhoA-dependent cytoskeletal remodeling in pancreatic cancer. 34957489_Bi-allelic loss-of-function OBSCN variants predispose individuals to severe recurrent rhabdomyolysis. | ENSMUSG00000061462 | Obscn | 70.546941 | 0.311068717 | -1.684695 | 0.53929538 | 9.129609 | 0.0025150548428496031193313253737642298801802098751068115234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0163925857839228097945216688913205871358513832092285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 29.1733351 | 10.6205499 | 94.5227321 | 34.2044445 | |
| ENSG00000154529 | 728577 | CNTNAP3B | protein_coding | Q96NU0 | Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Predicted to be involved in cell adhesion. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:728577; | membrane [GO:0016020]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155] | Mouse_homologues 26389685_The findings of this study suggest that Caspr3 may play an important role in basal ganglia development during early postnatal stages. 26807827_Our findings suggest that reduced activation of neural cells in the dorsal striatum in Caspr3-KO mice leads to a decline in motor learning in the accelerated rotarod task. 31150793_These evidences elucidate the pivotal role of CNTNAP3 in synapse development and social behaviors, providing mechanistic insights into autism spectrum disorders 34143959_In trans neuregulin3-Caspr3 interaction controls DA axonal bassoon cluster development. | ENSMUSG00000033063 | Cntnap3 | 57.899290 | 3.696833891 | 1.886290 | 0.66532868 | 7.489522 | 0.0062059023568274600604621760169266053708270192146301269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0342303478577691278061934099241625517606735229492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 39.7829274 | 22.3106617 | 10.9221481 | 6.1720820 | ||
| ENSG00000154645 | 140578 | CHODL | protein_coding | Q9H9P2 | FUNCTION: May play a role in the development of the nervous system such as in neurite outgrowth and elongation. May be involved in motor axon growth and guidance. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q568T5, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9CXM0}. | Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Lectin;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a type I membrane protein with a carbohydrate recognition domain characteristic of C-type lectins in its extracellular portion. In other proteins, this domain is involved in endocytosis of glycoproteins and exogenous sugar-bearing pathogens. This protein localizes predominantly to the perinuclear region. Several transcript variants encoding a few different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. | hsa:140578; | centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of axonogenesis [GO:0050772] | 12079284_cloning and characterization; localized at chromosome 21q21 12621022_study describes the molecular characterization of novel members of the chondrolectin family associated with T cell maturation and a subcellular localization of chondrolectin f isoform in the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi apparatus 17606388_CHODLDeltaE/CHODLfDeltaE protein variant localizes in the late endoplasmic reticulum and is detected in spleen and tonsils; the isoform seems to be differentially expressed in thymocytes and lymphocytes. 22016508_Data indicate that chondrolectin (CHODL) is likely to be a prognostic biomarker in the clinic and targeting CHODL might be a strategy for the development of anticancer drugs. | ENSMUSG00000022860 | Chodl | 19.173536 | 2.983248206 | 1.576884 | 0.39311112 | 16.452015 | 0.0000498971214475809146139673178055318203405477106571197509765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0005534979657484233057235245567540005140472203493118286132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 28.9348978 | 5.9633711 | 9.7621703 | 2.3739973 | |
| ENSG00000156265 | 56911 | MAP3K7CL | protein_coding | P57077 | Alternative splicing;Reference proteome | Located in cytosol and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:56911; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634] | 32401115_Genome-wide identification of lncRNAs and mRNAs differentially expressed in human vascular smooth muscle cells stimulated by high phosphorus. | 89.381976 | 3.020095080 | 1.594594 | 0.18532683 | 75.439481 | 0.0000000000000000037678026002230766657278157857133769365759737260022314148111277631869597826153039932250976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000002311579946136859492182943095951568339607529536678526271842315509275067597627639770507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 134.7115338 | 8.4054531 | 44.7767654 | 3.8448853 | ||||
| ENSG00000156500 | 159091 | PABIR3 | protein_coding | Q6P4D5 | Alternative splicing;Reference proteome | Predicted to enable protein serine/threonine phosphatase inhibitor activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of catalytic activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:159091; | protein serine/threonine phosphatase inhibitor activity [GO:0004865] | ENSMUSG00000036013 | Fam122c | 78.109178 | 0.064742739 | -3.949138 | 0.62217371 | 32.571727 | 0.0000000114873730961869492129265920427050318153305852320045232772827148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000002604301051368930912137866686556497697324630280490964651107788085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 12.3606524 | 5.6893968 | 187.8532760 | 86.5506685 | |||
| ENSG00000156509 | 286151 | FBXO43 | protein_coding | Q4G163 | FUNCTION: Required to establish and maintain the arrest of oocytes at the second meiotic metaphase until fertilization. Acts by inhibiting the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) ubiquitin ligase. Probably recognizes and binds to some phosphorylated proteins and promotes their ubiquitination and degradation (PubMed:34052850, PubMed:34595750). Plays a vital role in modulating the ubiquitilation of CCNB1 and CDK1 during gametogenesis. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CDI2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34052850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34595750}. | Disease variant;Meiosis;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. | Members of the F-box protein family, such as FBXO43, are characterized by an approximately 40-amino acid F-box motif. SCF complexes, formed by SKP1 (MIM 601434), cullin (see CUL1; MIM 603134), and F-box proteins, act as protein-ubiquitin ligases. F-box proteins interact with SKP1 through the F box, and they interact with ubiquitination targets through other protein interaction domains (Jin et al., 2004 [PubMed 15520277]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:286151; | nucleus [GO:0005634]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051321]; negative regulation of cell cycle process [GO:0010948]; negative regulation of meiotic nuclear division [GO:0045835]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0007088] | 18550795_Cdc2 and Mos regulate Emi2 stability to promote the meiosis I-meiosis II transition 30878252_The mutation in FBXO43 is a causative factor of male infertility and teratozoospermia. 32253818_EMI2 expression as a poor prognostic factor in patients with breast cancer. 34052850_FBXO43 variants in patients with female infertility characterized by early embryonic arrest. 34595750_A homozygous loss-of-function mutation in FBXO43 causes human non-obstructive azoospermia. 34645483_Downregulation of the FBXO43 gene inhibits tumor growth in human breast cancer by limiting its interaction with PCNA. | ENSMUSG00000048230 | Fbxo43 | 51.956951 | 0.043875724 | -4.510433 | 1.25647970 | 9.348571 | 0.0022315938787613983154689556442917819367721676826477050781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0148787107607790472507680590297240996733307838439941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 4.2943585 | 4.8428053 | 99.5695444 | 111.4887081 |
| ENSG00000156886 | 3681 | ITGAD | protein_coding | Q13349 | FUNCTION: Integrin alpha-D/beta-2 is a receptor for ICAM3 and VCAM1. May play a role in the atherosclerotic process such as clearing lipoproteins from plaques and in phagocytosis of blood-borne pathogens, particulate matter, and senescent erythrocytes from the blood. | Calcium;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Integrin;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene belongs to the beta-2 integrin family of membrane glycoproteins, which are are composed of non-covalently linked alpha and beta subunits to form a heterodimer. It encodes the alpha subunit of the cell surface heterodimers and is involved in the activation and adhesion functions of leukocytes. The gene is located about 11kb downstream of the integrin subunit alpha X gene, another member of the integrin family. It is expressed in the tissue and circulating myeloid leukocytes. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. | hsa:3681; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; integrin complex [GO:0008305]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033627]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034113]; immune response [GO:0006955]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229] | 15561714_a longer isoform of gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor 4 (GKLF) we term GKLFa interacts with the CD11d promoter 19571252_multiple CD11d domains play a role in controlling intracellular location and association with CD18. 21508205_CD11d expression increased in the subcutaneous white adipose tissue of obese adult women; this appears to be a common feature of obesity. 21712539_the cross-talk between neutrophils and NK cells is mediated by ICAM-3 and CD11d/CD18, respectively. 23414334_The effects of anti-CD11d treatment improves functional recovery in a rat model of repeated concussion. 25415295_alpha(D)beta(2) is a major member of the integrin repertoire of both circulating and tissue myeloid leukocytes in humans 27881604_These results expand the potential for CD11d to regulate lymphocyte migration and tissue retention, and illuminate the possibility of a previously unconsidered role for CD11d in leukocyte biology and disease. 28500072_findings suggest that CD11d/CD18 upregulation on proinflammatory macrophages may represent a common mechanism for macrophage retention at inflammatory sites, thereby promoting chronic inflammation and disease development. 35038314_LINC02190 inhibits the embryo-endometrial attachment by decreasing ITGAD expression. | ENSMUSG00000070369 | Itgad | 52.025121 | 21.994200477 | 4.459051 | 0.83761946 | 22.051898 | 0.0000026537712787137896912640841473596253763389540836215019226074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000407027989546584312947549721961593149899272248148918151855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 106.9640830 | 67.7753374 | 4.6494476 | 2.9636999 | |
| ENSG00000157110 | 11030 | RBPMS | protein_coding | Q93062 | FUNCTION: Acts as a coactivator of transcriptional activity. Required to increase TGFB1/Smad-mediated transactivation. Acts through SMAD2, SMAD3 and SMAD4 to increase transcriptional activity. Increases phosphorylation of SMAD2 and SMAD3 on their C-terminal SSXS motif, possibly through recruitment of TGFBR1. Promotes the nuclear accumulation of SMAD2, SMAD3 and SMAD4 proteins (PubMed:26347403). Binds to poly(A) RNA (PubMed:17099224, PubMed:26347403). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17099224, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26347403}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;Transcription;Transcription regulation | This gene encodes a member of the RNA recognition motif family of RNA-binding proteins. The RNA recognition motif is between 80-100 amino acids in length and family members contain one to four copies of the motif. The RNA recognition motif consists of two short stretches of conserved sequence, as well as a few highly conserved hydrophobic residues. The encoded protein has a single, putative RNA recognition motif in its N-terminus. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2013]. | hsa:11030; | cytoplasmic stress granule [GO:0010494]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; P-body [GO:0000932]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; poly(A) binding [GO:0008143]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060391]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979]; RNA processing [GO:0006396] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25281386_RBPMS1 is a critical repressor of AP-1 signaling and RBPMS1 activation may be a useful strategy for cancer treatment. 27166999_Data indicate RNA Binding Protein with Multiple Splicing (RBPMS), Regulator of Chromosome Condensation and POZ Domain Containing Protein 1 (RCBTB1), and Zinc Finger protein 608 (ZNF608) as miR-21-3p target genes. 27273514_ERG is recruited to mRNAs via interaction with the RNA-binding protein RBPMS, and it promotes mRNA decay by binding CNOT2, a component of the CCR4-NOT deadenylation complex. 27592836_Study indicates that the RNA binding increases the stability of RNA-recognition motif (RRM) in RBPMS domain, but residue mutations of RRM domain induce the fluctuation of complex systems through weakening of hydrogen bonds, conformational change or loss of binding affinity. 28003515_Conserved binding of GCAC motifs by MEC-8, couch potato, and the RBPMS protein family has been reported. 28017375_observation of a strong in vivo erythropoietic effect for RBPMS but not for GTF2E2, supporting the statistical fine-mapping at this locus and demonstrating that RBPMS is a regulator of erythropoiesis 29423656_The possible involvement of the GC box 1 at position - 54 in transcriptional regulation of Rbpms was corroborated by EMSA, which showed formation of a DNA-protein complex in the presence of the oligonucleotide corresponding to this Sp1-binding site. 29542167_the key role of miR-21-3p in CRC 29743723_RBPMS silencing confers resistance to MM cells. 35008958_Reduced RBPMS Levels Promote Cell Proliferation and Decrease Cisplatin Sensitivity in Ovarian Cancer Cells. 36423381_Loss of RBPMS in ovarian cancer compromises the efficacy of EGFR inhibitor gefitinib through activating HER2/AKT/mTOR/P70S6K signaling. | ENSMUSG00000031586 | Rbpms | 32.287638 | 5.727860496 | 2.517996 | 0.74277847 | 10.113788 | 0.0014716420859558262262956063182173238601535558700561523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0104759946556489055846661528903496218845248222351074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 32.5077025 | 16.7569150 | 5.7523992 | 2.9697352 | |
| ENSG00000157570 | 90139 | TSPAN18 | protein_coding | Q96SJ8 | Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be integral component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:90139; | plasma membrane [GO:0005886] | 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23505562_These results confirm the significant association, in Han Chinese populations, of increased SCZ risk and the variant of the TSPAN18 gene containing the 'A' allele of SNP rs835784. 26016498_Meta-analysis results show no significant association between TSPAN18 gene and schizophrenia in the Han Chinese population indicating the gene is unlikely to be a major susceptibility gene for schizophrenia in this population. 27208512_The frequency of rs11038167 minor allele (A) was significantly higher only in female patients with thought disorder. Our result suggested that the TSPAN18 gene may be involved in the development of psychotic symptoms and contribute to clinical heterogeneity of schizophrenia. 27312590_Our results showed that two SNPs (rs11038167 and rs11038172) at TSPAN18, reported as genome-wide significant SCZ risk variants in Han Chinese, were entirely monomorphic in Europeans, indicating a deep between-population divergence at this gene locus. 30573509_The findings identify Tspan18 as a novel regulator of endothelial cell Orai1/Ca2+ signaling and von Willebrand factor release in response to inflammatory stimuli. 32447449_Tspan18 is a novel regulator of thrombo-inflammation. | ENSMUSG00000027217 | Tspan18 | 52.736010 | 0.492591284 | -1.021537 | 0.29182944 | 12.138558 | 0.0004938995653411600711413242947855906095355749130249023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0041418867625852198027791573053946194704622030258178710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 35.5800804 | 7.7943409 | 71.9350980 | 14.9789125 | ||
| ENSG00000157601 | 4599 | MX1 | protein_coding | P20591 | FUNCTION: Interferon-induced dynamin-like GTPase with antiviral activity against a wide range of RNA viruses and some DNA viruses. Its target viruses include negative-stranded RNA viruses and HBV through binding and inactivation of their ribonucleocapsid. May also antagonize reoviridae and asfarviridae replication. Inhibits thogoto virus (THOV) replication by preventing the nuclear import of viral nucleocapsids. Inhibits La Crosse virus (LACV) replication by sequestering viral nucleoprotein in perinuclear complexes, preventing genome amplification, budding, and egress. Inhibits influenza A virus (IAV) replication by decreasing or delaying NP synthesis and by blocking endocytic traffic of incoming virus particles. Enhances ER stress-mediated cell death after influenza virus infection. May regulate the calcium channel activity of TRPCs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11880649, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14687945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14752052, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15047845, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15355513, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15757897, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16202617, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16413306, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17374778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18668195, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19109387, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21900240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21992152}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;GTP-binding;Immunity;Innate immunity;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA | This gene encodes a guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-metabolizing protein that participates in the cellular antiviral response. The encoded protein is induced by type I and type II interferons and antagonizes the replication process of several different RNA and DNA viruses. There is a related gene located adjacent to this gene on chromosome 21, and there are multiple pseudogenes located in a cluster on chromosome 4. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]. | hsa:4599; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; antiviral innate immune response [GO:0140374]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; defense response [GO:0006952]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; interleukin-27-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070106]; negative regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045071]; response to type I interferon [GO:0034340]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 10971132_The MxA promoter nt -88 G/T SNP may be useful to predict the response of chronic hepatitis C patients to interferon therapy. 11805446_The MxA promoter with haplotype -88T/-123A confers greater expression of MxA in vitro, as well as a better treatment outcome for chronic hepatitis C patients treated with interferon in vivo, as compared to the MxA promoter with haplotype -88G/-123C. 11847228_Self-assembly of human MxA GTPase into highly ordered dynamin-like oligomers 11911186_MxA promoted cell death induced by apoptotic stimuli as well as influenza virus infection 11916975_The antiviral dynamin family member, MxA, tubulates lipids and localizes to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum 12447867_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12595530_Lipopolysaccharide stimulates p38-dependent induction of antiviral genes , such as myxovirus resistance-1 (MX1) in neutrophils independently of paracrine factors. 12867637_down regulated by HBV preC/C proteins interacting directly with the MxA promoter, as shown by electrophoretic mobility shift 12944978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12944978_Polymorphisms in the MxA gene is associated with outcome of hepatitis C virus infection 14687945_the reduction of Dugbe(DUGV) viral antigen expression and N protein accumulation, together with the decrease in viral genomic RNA and the decrease in viral titre in the presence of MxA, suggest a role for MxA in the inhibition of DUGV replication 14752052_nuclear MxA suppresses the influenza virus transcription by interacting not only with RNA polymerase subunit PB2 but also with influenza NP 14872030_MxA promoter -88 G/T SNP may confer host genetic susceptibility to SSPE in Japanese individuals. The MxA protein promotes the establishment of persistent measles virus infection of neural cells. 14872030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15047845_MxA, by interacting with a component of the nucleocapsid, prevents replication of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus viral RNA and thereby inhibits the production of new infectious virus particles. 15063762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15117331_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15117331_SNP of the MxA gene is one of the important host factors that independently influences the response to IFN in patients with chronic HCV infection, especially those with a low viral load. 15135736_not responsible for the strong inhibitory effect of interferon-beta against SARS-CoV in cell culture 15163707_induced 16 hr after HUVEC ( human umbilical vein endothelial cells) infection with Tula virus ; in contrast, Hantaan virus-infected HUVECs showed no expression of MxA until 48 h postinfection. 15221897_HCV core protein clearly inhibited the nuclear import of MxA protein expression 15602733_Upregulation in epithelial cells in response to andes virus infection. 15757897_MxA is a new regulatory protein involved in Ca2+ signaling 15766558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15766558_polymorphisms of two interferon-inducible genes 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase 1 and MxA might affect susceptibility to the disease and progression of severe acute respiratory syndrome at each level 15850793_IL-28A and IL-29 induced mRNA expression of the antiviral proteins 2',5'-OAS and MxA was abolished by overexpression of SOCS-1 16168514_MxA reduces Hepatitis B virus expression augments the antiviral activity interferon alpha against HBV. 16390004_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16390004_mxA promoter-88G/T SNP might be confered to host genetic susceptibility to SARS in Chinese Han population. 16459719_MxA was the most sensitive gene to detect decreased bioavailability due to betaferon theapy in multiple sclerosis. 16595158_Pretreatment of Huh-7 cells with 0.5-1 mM H2O2 resulted in the suppression of the IFN-alpha-induced antiviral protein MxA and of IRF-9 mRNA expression. 16704297_In the case of cell death after in vitro influenza viral infection, both C-terminal and N-terminal regions of MxA were shown to be involved in cell death promotion. 16769349_Immunostaining for Mx proteins was positive in the hepatocytes of all newborns with biliary atresia. Intrahepatic bile ducts were positive in all but one. 16792864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16824203_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16824203_Polymorphisms within the MxA gene are associated with susceptibility to severe acute respiratory syndrome. 16843495_A significantly higher frequency of the haplotype with -88T and -123A, which correlates with over-expression of MxA, was observed in MS. SNPs on MxA promoter region may play an important role in the pathophysiology of MS. 16894313_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16978069_Results demonstrate that MxA is an interferon-induced antiviral effector protein that resembles the constitutively expressed large GTPase family members in its capacity to localize to and reorganize intracellular membranes. 17075576_MxA mRNA expression was also significantly higher in early stage of biliary atresia (BA) and in choledochal cyst than in late stage of BA 17126411_No significant association was found between the MXA genotype and promoter region single nucleotide polymorphisms (rs2071430 and rs17000900) and the gene expression responses, clinical and MRI phenotypes in IFN-beta treated multiple sclerosis patients. 17126411_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17177148_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17307214_the effects of MxA on the replication cycle of parainfluenza virus type 5 17374778_MxA targets two double-stranded RNA viruses, Infectious bursal disease virus and a mammalian reovirus 17407708_Chronic hepatitis B patients with GT genotype at MxA promoter -88 responded well to IFN treatment. 17845304_A highly significant difference in the distribution of MxA -88 G/T was observed between those with persistent and self-limiting HBV infections. 17845304_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17947524_Pretreatment of A549 cells with IFN-alpha lead to increased expression of MxA, which contributed to inhibition of WNV(KUN) replication and secretion. 18549400_significantly higher levels of MxA in stable patients with primary progressive multiple sclerosis treated with interferon beta compared with progressing patients 18668195_GTPase activity is not essential for MxA protein to inhibit HBV replication. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18782441_HIV replication unresponsive to antiretroviral treatment in perinatal-infected patients with advanced disease and plasmacytoid dendritic cell depletion may lead to interferon-alpha expression and subsequent induction of MxA mRNA 18843779_induction of MxA expression in some patients with systemic sclerosis, correlating with the presence of ischemic ulcers and other signs of worse disease, suggests a potential role of Type I IFN in the pathogenesis of this disease and/or its complications 19109387_MxA protein inhibits African swine fever virus replication and reduces ASFV late protein synthesis. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19177264_The expression of MxA protein in arteries from patients with polymyalgia rheumatica and temporal arteritis shows that non-inflamed and inflamed vessel walls are influenced by IFN-I. 19236454_In MS, Mx proteins are detectable in plaques suggesting endogenous synthesis of type I IFNs as part of the acute inflammatory process. 19297326_MxA inhibits tumor cell motility and invasion. 19434718_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19462904_The expression levels of both MX1 and OAS1 in systemic lupus erythematosus patients are up-regulated. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19625466_This study shows that hepatitis delta virus p24 and p27 proteins inhibit HBV replication by trans-repressing its enhancers and by trans-activating the IFN-alpha-inducible MxA gene. 19635103_MxA expression in hepatocytes was independently associated with allograft rejection and donor's age. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19744071_The haplotype of the MxA gene promoter is associated with hepatitis B virus infection in a Chinese population. 19817957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20019841_Data sghow a higher frequency of CRABP2 and MX1 hypermethylation in primary HNSCC when compared with lymphocytes from healthy individuals. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20309637_These findings indicate that the expression of MxA, 2',5'-OAS and PKR are up-regulate by PI3K-AKT signal pathway, and Raf-MEK-ERK signal pathway has a negative regulatory effect on the expression of MxA and no significant effect on 2',5'-OAS and PKR. 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20428112_the crystal structure of the stalk of human MxA, which folds into a four-helical bundle; this structure tightly oligomerizes in the crystal in a criss-cross pattern involving three distinct interfaces and one loop 20462354_data suggest -123C>A plays a more important role in modulating basal MxA expression, thus contributing significantly to innate immune response against viral infections that suppress endogenous IFN-alpha & -beta induction such as SARS coronavirus 20494980_The MX1 promoter is activated by serum depletion according to promoter reporter assays in HEK 293 cells. 20588308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20603636_human MxA gene encodes two MxA isoforms, which are expressed differentially depending on whether the stimulus is IFN-alpha or HSV-1. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20921509_Low levels of MxA mRNA were associated with the occurrence of relapses (p = 0.002) and contrast-enhancing lesions (CELs) on baseline MRI 20959021_The inhibitory effect on MxA gene transcription by the wild-type or mutated hepatitis B virus core proteins (L60V, S87G and I97L) has no impact on inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by interferon-alpha in Huh7 cells. 21166595_The structural and functional data suggest that MxA targets the nucleoprotein of MxA-sensitive viruses. [Review] 21859714_Mx proteins exert their antiviral activity against IAV by interfering with the function of the RNA helicases UAP56 and URH49 21900240_the oligomeric structures formed by MxA critically differ from those of dynamin. 21935451_SNPs in IRF3 (OR 0.54, p = 0.035) and MX1, (OR 0.19, p = 0.014) were associated with symptomatic WNV infection. 21962493_demonstrated that the intra- and intermolecular domain interplay between the bundle signaling element and stalk was essential for oligomerization and the antiviral function of MxA 21992152_The MxA-enhanced ER stress signaling is a part of the antiviral activity of MxA by accelerating cell death. 22340769_In HCV-infected patients the peripheral blood mononuclear cells from premenopausal women showed the highest MxA gene expression compared to both postmenopausal females and males before and after IFN stimulation. 22507598_study demonstrates the expression of type 1 IFN-related protein MxA and plasmacytoid plasmacytoid dendritic cells in lesional but not in non-lesional biopsies of morphea 22531919_a novel pathway of human MxA induction, which is initiated by an endogenous antimicrobial peptide, namely alpha-defensin. 22714910_Four new polymorphisms in the human MxA gene were identified. 22950423_This is the first study showing the significant association of MxA SNPs and predisposition of AD, modulation of AAO in AD, and rate of cognitive decline. 22985419_these results show that allelic diversity in the MxA gene proximal promoter significantly alter the tight regulation of antiviral MxA protein expression by type-I and type-III interferons. 22998463_myxovirus resistance protein A expression is increased in thyroid tissue in the early stages of Hashimoto's thyroiditis 23015724_findings support a model in which Mx1 interacts with the influenza ribonucleoprotein complex and interferes with its assembly by disturbing the PB2-NP interaction 23084925_Single amino acid changes in the L4 loop are necessary and sufficient to explain dramatic differences in species-specific antiviral activity of primate MxA proteins against the orthomyxoviruses Thogoto virus and influenza A virus. 23115279_The authors show that silencing of myxovirus resistant 1 (MX1), a known interferon-induced antiviral gene, is responsible for HRP4 cells, another subclone of Huh-7 cells, being permissive for hepatitis C virus replication. 23152507_Taken together, these results demonstrate that MxA mediates control of influenza virus replication in primate cells treated with IFN-alpha. 23160781_Our results suggest that MxA observed in respiratory viral infections is possibly dominated by the MxA transcript and partly influenced by relevant 5' SNPs. 23232524_The MxA-88T/-123A gene variants indirectly increase the risk for heptaitis C virus infection. 23274784_IL-17A but not IL-22 suppresses the replication of hepatitis B virus by inducing the expression of MxA and OAS. 23438650_Studied the association of the functional polymorphism rs2071430 in MxA with prostate cancer.A significant association was observed between rs2071430 genotype GG and prostate cancer. Individuals with the GG genotype have increased risk of prostate cancer. 23529855_protein expression is inhibited by hepatitis C virus 23831963_MxA protein levels in whole blood and monocytes correlated with primary Sjogren's syndrome disease activity and IFN type I bioactivity. 23848523_It describes the standardized cellular myxovirus resistance protein A (MxA) protein measurement-based assay for detection of IFN-beta NAbs and its use for the validation of assays used for the quantitative determination of such antibodies. 24032645_Upregulation of MxA expression during the early stages of Graves disease, and the correlation between the number of PDCs and MxA+ leucocytes, suggests that activated PDCs secrete type I IFNs at the lesion site, possibly in response to viral infection. 24049170_Interferon-induced MxA protein inhibits influenza A virus infection by retaining the incoming viral genome in the cytoplasm. 24085612_polymorphisms in the MxA promoter may play a role in mediating the susceptibility to enterovirus 71 infection in Chinese population 24212839_Hepatitis C genotype 1 patients who were responders to interferon-based therapy had a high frequency of multiple protective polymorphisms in the myxovirus resistance protein, osteopontin and suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 genes. 24314641_MxA protein sequestered the West Nile virus capsid protein in cytoplasmic tubular structures and resulted in reduced titers of secreted virus particles. 24421397_Data indicate susceptibility genes including myxovirus (influenza virus) resistance 1 (MX1) for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) disease severity and risk. 24438589_Plasmacytoid dendritic cells in the infiltrate of progressive vitiligo produce MxA. Strong MxA expression was seen in perilesional skin near remaining melanocytes, surrounded by a prominent T-cell infiltrate, but it was not detectable in lesional skin. 24448803_Structural requirements for the antiviral activity of the human MxA protein against Thogoto and influenza A virus. 24553842_These studies disclosed that antiviral IFN-induced MxA and APOBEC3G/3F mRNA levels were increased after IL-32gamma treatment of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. 24674141_antiviral innate immunity may be involved in mesangial cells (MCs) of lupus nephritis patients, which results in the expression of Mx1 in MCs. 24733382_These data warrant the quantification of MxA mRNA as a primary tool for a routine monitoring of IFNbeta therapy. 24771638_MX1 may have a role in lymph node metastasis in colorectal carcinoma 24899177_The L4 loop of the stalk domain of MX1 is a critical determinant. 25056900_Varicella-zoster virus inhibits the nuclear translocation of phosphorylated-STAT1 and antiviral MX1 protein expression in human brain vascular adventitial fibroblasts. 25239021_heterozygosity for both -88G/T and -123C/A polymorphisms of the MxA gene is important host factor that influence the response to IFN therapy in patients with chronic HCV infection. 25295396_Transient dimerization of human MxA promotes GTP hydrolysis.The GTPase domains of Mx proteins dimerize transiently to facilitate catalysis. 25327819_MxA expression is inversely correlated with prostate cancer. Down-regulation of MxA in LNCaP cells by DHT suggests that MxA could play a significant role in disease progression. 25384438_upregulated in the skin of Lichen planus patients 25396411_Baseline MxA mRNA levels may be useful for predicting whether multiple sclerosis patients will respond or not to interferon-beta treatment. 25447205_MxA interacts with Ubc9 and SUMO1 in a yeast two-hybrid system. 25542463_Blood MxA protein levels are increased in young children with symptomatic respiratory virus infections, including rhinovirus infections. MxA is an informative general marker for the most common acute virus infections. 25829498_study highlights the role of nucleotide binding and hydrolysis for the intracellular dynamics of MxA during its antiviral action. 25868067_polymorphism at position -88 in the MxA promoter region might be a potential biomarker to predict HCV progression toward end-stage fibrosis and response to IFN-based therapy in chronic hepatitis C patients. 25905045_Reovirus T3D infection induced STAT-1, ISG-15, IFIT-1, Mx1, and IFIT-3 expression. 26175399_E2F1 transcripts and miR-17-5p were significantly downregulated while c-Myc and MxA transcripts were significantly upregulated in SLE. 26507657_data suggest that, during infection, a fraction of MxA disassembles into dimers that bind to NP synthesized following primary transcription in the cytoplasm, thereby preventing viral replication 26815367_A significant association was observed between MX1 -88G/T SNP and susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus 26857498_This study demonstrated that MxA mRNA expression of interferon beta response in multiple sclerosis patients. 27075916_Study shows different levels of expression of MxA in each breast cancer subtype and its close relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. MxA protein expression was higher in triple-negative breast cancer and correlated with a higher histologic grade. 27456948_High expression of MxA in tumor cells was associated with high levels of TILs in HER2-positive breast cancers. Additionally, a high level of TILs was a prognostic factor for breast cancer, whereas the level of MxA expression had no prognostic value. 27458866_Here, the authors show that for North African patients with chronic hepatitis, MX1 gene variation at position -123 may influence the outcome of hepatitis B virus infection but not hepatitis B virus infection. 27875556_the data identify MxA as a novel stimulator of BMP4 and BMP9 transcriptional signaling, and suggest it to be a candidate IFN-alpha-inducible mechanism that might have a protective role against development of pulmonary arterial hypertension and other vascular diseases. 28039312_This study provides Class II evidence that immunohistochemistry-detected sarcoplasmic MxA expression accurately identifies patients with dermatomyositis (DM): sarcoplasmic MxA expression detected by immunohistochemistry is a more sensitive marker of DM than the conventional hallmarks 28139728_Mx1 and OAS1-2 polymorphisms were associated with the severity of liver disease in HIV/HCV-coinfected patients, suggesting a significant role in the progression of hepatic fibrosis. 28386647_Study demonstrated associations between rs464138 AA genotype in MxA gene and IFNbeta responsiveness in multiple sclerosis patients. However, the allele and genotype frequencies of other SNPs were not significantly different among patient subtypes or between patients and controls. Besides, results demonstrated that CGC, ATA, and AGA (-123, -88, +20) haplotypes were significantly associated with IFNbeta response in MS pa... 28548099_MxA conformational dynamics through GTP hydrolysis revealed by single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer. 28561372_findings indicated that MxA over-expression inhibited HCV replication and potentiated the IFNalpha-mediated anti-HCV activity; MxA stimulated the production of IFNalpha, IFNbeta, and enhanced IFNalpha-induced activation of Jak-STAT signaling pathway; concluded that MxA is a positive regulator of type I IFN signaling in HCV infection 28727764_studied the susceptibility of Vaccinia virus and Cowpox viruses to MxA antiviral action, and concluded that these viruses are not affected by the antiviral action of MxA 28744639_Relative expression of OAS1 and Mx1 in patients with recurrent forms of Herpes simplex both during the acute stage and clinical remission did not differ significantly from that in healthy people after stimulation with IFN-alpha2b. 29271328_IL28B and MxA gene genotypes were detected among 231 chronic hepatitis C (CHC) carriers, 428 subjects with hepatitis C virus spontaneous clearance and 662 CHC patients with pegylated IFN-alpha and ribavirin (pegIFN-alpha/RBV) treatment. 29330299_naturally occurring mutations in the human MX1 gene can influence MxA function 29417241_MxA inhibits hepatitis C virus replication through JAK-STAT pathway activation. 29530483_Integrin alpha5beta6 down-regulation causes a significant increase in donor cancer cells, and their exosomes, of two molecules that have a tumor suppressive role, STAT1 and MX1. 29770465_Expression of myxovirus-resistance protein A: a possible marker of muscle disease activity and autoantibody specificities in juvenile dermatomyositis. 30555157_Overexpression of IFNAR1, MX1 and signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (Stat1) indicated the endogenous IFNa activation in tumour microenvironment, which correlated with immunosuppression status in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC) patients 30667074_Distinguishing pustular psoriasis and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis on the basis of plasmacytoid dendritic cells and MxA protein. 30945621_MxA efficiently blocks viral replication in vitro as well as in MxA transgenic mice. 31444947_Intrahepatic immune changes after hepatitis c virus eradication by direct-acting antiviral therapy. 31484749_New data correct a long-standing misinterpretation in the MxA literature and provide evidence for membraneless MxA biomolecular condensates in the uninfected cell cytoplasm. 31574080_Rapidly evolving MxA residues yield super-restrictor antiviral proteins. 32209695_A MicroRNA Network Controls Legionella pneumophila Replication in Human Macrophages via LGALS8 and MX1. 32350677_Myxovirus resistance 1 (MX1) is an independent predictor of poor outcome in invasive breast cancer. 32554437_TLR Stimulation Produces IFN-beta as the Primary Driver of IFN Signaling in Nonlymphoid Primary Human Cells. 32640729_Myxovirus Resistance Protein 1 (MX1), a Novel HO-1 Interactor, Tilts the Balance of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress towards Pro-Death Events in Prostate Cancer. 32740454_Genetic Susceptibility to Life-threatening Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Previously Healthy Infants. 32907985_Subcellular Localization of MxB Determines Its Antiviral Potential against Influenza A Virus. 33933170_The transcriptome profile of human trisomy 21 blood cells. 34382080_Myxovirus resistance protein 1-expressing fatal myocarditis in a patient with anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis. 34413236_Rare variant MX1 alleles increase human susceptibility to zoonotic H7N9 influenza virus. 35080443_Myxovirus Resistance Protein A as a Marker of Viral Cause of Illness in Children Hospitalized with an Acute Infection. 36250826_Evaluation of MX1 Gene Promoter Methylation in Different Severities of COVID-19 Considering Patient Gender. | ENSMUSG00000000386+ENSMUSG00000023341 | Mx1+Mx2 | 145.375232 | 0.236356285 | -2.080965 | 0.17742995 | 138.162882 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000671378365008511078253321860223519731230190389501741444339034181448233821616431305900202231029538779694121330976486206054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000076977381719172565848755745387298837835751748544281667782603860144233652803051008023382806300105585251003503799438476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 56.0101740 | 8.8049896 | 236.8258774 | 34.6250261 |
| ENSG00000157613 | 90993 | CREB3L1 | protein_coding | Q96BA8 | FUNCTION: Transcription factor involved in unfolded protein response (UPR). Binds the DNA consensus sequence 5'-GTGXGCXGC-3' (PubMed:21767813). In the absence of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, inserted into ER membranes, with N-terminal DNA-binding and transcription activation domains oriented toward the cytosolic face of the membrane. In response to ER stress, transported to the Golgi, where it is cleaved in a site-specific manner by resident proteases S1P/MBTPS1 and S2P/MBTPS2. The released N-terminal cytosolic domain is translocated to the nucleus to effect transcription of specific target genes. Plays a critical role in bone formation through the transcription of COL1A1, and possibly COL1A2, and the secretion of bone matrix proteins. Directly binds to the UPR element (UPRE)-like sequence in an osteoblast-specific COL1A1 promoter region and induces its transcription. Does not regulate COL1A1 in other tissues, such as skin (By similarity). Required to protect astrocytes from ER stress-induced cell death. In astrocytes, binds to the cAMP response element (CRE) of the BiP/HSPA5 promoter and participate in its transcriptional activation (By similarity). Required for TGFB1 to activate genes involved in the assembly of collagen extracellular matrix (PubMed:25310401). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z125, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12054625, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21767813, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25310401}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) May play a role in limiting virus spread by inhibiting proliferation of virus-infected cells. Upon infection with diverse DNA and RNA viruses, inhibits cell-cycle progression by binding to promoters and activating transcription of genes encoding cell-cycle inhibitors, such as p21/CDKN1A (PubMed:21767813). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21767813}. | Activator;Alternative splicing;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Nucleus;Osteogenesis imperfecta;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation;Unfolded protein response | The protein encoded by this gene is normally found in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). However, upon stress to the ER, the encoded protein is cleaved and the released cytoplasmic transcription factor domain translocates to the nucleus. There it activates the transcription of target genes by binding to box-B elements. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2013]. | hsa:90993; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cAMP response element binding [GO:0035497]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; SMAD binding [GO:0046332]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response [GO:0030968]; extracellular matrix constituent secretion [GO:0070278]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1902236]; negative regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0040037]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903671]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:1990440]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 12054625_a transcriptional activator of CREB/ATF family with a transmembrane domain 17721195_Presence of FUS/CREB3L2 and FUS/CREB3L1 in low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma and sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma suggests these neoplasms may be related. 21041443_The human Creb3L1 can activate SPCG transcription in a heterologous system(Drosophila embryos), which suggests a general and direct role for this family of bZip transcription factors in mediating high-level secretory capacity. 21536545_FUS-CREB3L2/L1-positive sarcomas show a specific gene expression profile with upregulation of CD24 and FOXL1. 21767813_CREB3L1 may play an important role in limiting virus spread by inhibiting proliferation of virus-infected cells. 21767813_Upon infection with diverse DNA and RNA viruses, CREB3L1 was proteolytically cleaved, allowing its NH(2) terminus to enter the nucleus and induce multiple genes encoding inhibitors of the cell cycle to block cell proliferation of infected cells. 21987447_Rapid amplification of cDNA ends revealed exon 6 of the cAMP-responsive element binding protein 3-like 1 gene (CREB3L1) fused in-frame to the EWSR1 exon 11. 22705851_OASIS is notably unstable proteins that are easily degraded via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway under normal conditions. 23256041_CREB3L1 expression may be a useful biomarker in identifying cancer cells sensitive to doxorubicin. 23335989_OASIS is important for the ER stress response and maintenance of some extracellular matrix proteins in human glioma cells. 23383089_a novel regulatory mechanism for VEGFA transcription by OASIS in human retinal pigment epithelial cells 23588368_We report 2 cases of Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma serendipitously found to harbor a novel alternative EWSR1-CREB3L1 gene fusion. 23955342_Fbxw7 controls osteogenesis and chondrogenesis by targeting OASIS and BBF2H7, respectively, for degradation. 24126059_CREB3L1 plays an important role in suppressing tumorigenesis and that loss of expression is required for the development of a metastatic phenotype. 24242870_Temporally regulates the differentiation from neural precursor cells into astrocytes [review] 24441665_EWSR1-CREB3L1 gene fusions are predominant over FUS and CREB3L2 rearrangements in pure sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma. 24896634_Case Report: low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma of the kidney found to harbor the EWSR1-CREB3L1 gene fusion. 25310401_Cleavage of CREB3L1 releases its NH2-terminal domain from membranes, allowing it to enter the nucleus where it binds to Smad4 to activate transcription of genes encoding proteins required for assembly of collagen-containing extracellular matrix. 25353281_Case Reports: genetically confirmed primary renal sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma with EWSR1-CREB3L1 gene fusion. 25625847_CREB3L1 mRNA expression is downregulated in human bladder cancer.CREB3L1 is epigenetically silenced in human bladder cancer facilitating tumor cell spreading and migration in vitro. 26110425_CREB3L1 was expressed in 19% of RCC, which is generally resistant to doxorubicin, but in 70% of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma that is sensitive to doxorubicin. 26810754_Our data further strengthens the role for CREB3L1 as a metastasis suppressor in breast cancer and demonstrates that epigenetic silencing is a major regulator of the loss of CREB3L1 expression 26917262_The results suggest that CREB3L1 is required for decidualization in mice and humans and may be linked to the pathogenesis of endometriosis in a progesterone-dependent manner. 27121396_These findings indicate that the miR-146a-CREB3L1-FGFBP1 signaling axis plays an important role in the regulation of angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 27499293_Ceramide inverts the membrane orientation of TMS4SF20, creating a form of TM4SF20 that stimulates the cleavage of CREB3L1. 28750683_Identification of novel prostate cancer drivers, ERF, CREB3L1, and POU2F2, using RegNetDriver, a framework for integration of genetic and epigenetic alterations with tissue-specific regulatory network. 28817112_ConclusionThis report confirms that CREB3L1 is an OI-related gene and suggests the pathogenic mechanism of CREB3L1-associated OI involves the altered regulation of proteins involved in cellular secretion. 29093023_Our findings support a model in which CREB3L1 acts as a downstream effector of TSH to regulate the expression of cargo proteins, and simultaneously increases the synthesis of transport factors and the expansion of the Golgi to synchronize the rise in cargo load with the amplified capacity of the secretory pathway 29531016_There was a relationship between the expression levels of both proteins and survival time. CREB3L1 and PTN expression levels serve as biomarkers with utility in grading gliomas. Absence of CREB3L1 and presence of PTN in brain glioma cells correlate with survival time of the glioma patients. 30103710_These results suggest that CREB3L1 expression level may be used as a biomarker to identify TNBC patients who are more likely to benefit from doxorubicin-based chemotherapy. 30657919_Here, we presenta Turkish family, in which molecular analysis of the proband revealeda previously unreported homozygous missense variant(c.911C>T,p.(Ala304Val))of the CREB3L1 31207160_Study reports a novel homozygous CREB3L1 mutation in a large Indonesian family with osteogenesis imperfecta (OI); the homozygous affected members have survived to adulthood and they present a more severe phenotype than previously reported, expanding the clinical spectrum of OI for this gene. 32234057_Mutations in COL1A1/A2 and CREB3L1 are associated with oligodontia in osteogenesis imperfecta. 33150680_Transcription factor old astrocyte specifically induced substance is a novel regulator of kidney fibrosis. 34990868_A group of sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcomas with low-level amplified EWSR1-CREB3L1 fusion gene in children. 35689957_Clinical and biological relevance of CREB3L1 in Philadelphia chromosome-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms. 35802566_Reduced CREB3L1 expression in triple negative and luminal a breast cancer cells contributes to enhanced cell migration, anchorage-independent growth and metastasis. 36192735_CREB3L1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma by remodeling the tumor microenvironment. | ENSMUSG00000027230 | Creb3l1 | 75.749263 | 0.495827617 | -1.012089 | 0.19293483 | 27.637906 | 0.0000001462838152209285649956740059385307262118658400140702724456787109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000027953797914075804131840089633564971904888807330280542373657226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 48.8419943 | 8.5119561 | 98.8950667 | 16.5826930 | |
| ENSG00000157873 | 8764 | TNFRSF14 | protein_coding | Q92956 | FUNCTION: Receptor for four distinct ligands: The TNF superfamily members TNFSF14/LIGHT and homotrimeric LTA/lymphotoxin-alpha and the immunoglobulin superfamily members BTLA and CD160, altogether defining a complex stimulatory and inhibitory signaling network (PubMed:9462508, PubMed:10754304, PubMed:18193050, PubMed:23761635). Signals via the TRAF2-TRAF3 E3 ligase pathway to promote immune cell survival and differentiation (PubMed:19915044, PubMed:9153189, PubMed:9162022). Participates in bidirectional cell-cell contact signaling between antigen presenting cells and lymphocytes. In response to ligation of TNFSF14/LIGHT, delivers costimulatory signals to T cells, promoting cell proliferation and effector functions (PubMed:10754304). Interacts with CD160 on NK cells, enhancing IFNG production and anti-tumor immune response (PubMed:23761635). In the context of bacterial infection, acts as a signaling receptor on epithelial cells for CD160 from intraepithelial lymphocytes, triggering the production of antimicrobial proteins and pro-inflammatory cytokines (By similarity). Upon binding to CD160 on activated CD4+ T cells, down-regulates CD28 costimulatory signaling, restricting memory and alloantigen-specific immune response (PubMed:18193050). May interact in cis (on the same cell) or in trans (on other cells) with BTLA (PubMed:19915044) (By similarity). In cis interactions, appears to play an immune regulatory role inhibiting in trans interactions in naive T cells to maintain a resting state. In trans interactions, can predominate during adaptive immune response to provide survival signals to effector T cells (PubMed:19915044) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80WM9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10754304, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18193050, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19915044, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23761635, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9153189, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9162022, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9462508}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Herpes simplex virus 1/HHV-1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11511370, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9696799}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Herpes simplex virus 2/HHV-2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11511370, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9696799}. | 3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Innate immunity;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA | This gene encodes a member of the TNF (tumor necrosis factor) receptor superfamily. The encoded protein functions in signal transduction pathways that activate inflammatory and inhibitory T-cell immune response. It binds herpes simplex virus (HSV) viral envelope glycoprotein D (gD), mediating its entry into cells. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. | hsa:8764; | external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; tumor necrosis factor receptor activity [GO:0005031]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; immune response [GO:0006955]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of adaptive immune memory response [GO:1905675]; negative regulation of alpha-beta T cell proliferation [GO:0046642]; positive regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response [GO:0002720]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of T cell migration [GO:2000406]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295] | 11742858_Data suggest involvement of TNF superfamily receptor members and ligands in human atherosclerosis. TNFRSF14 (HVEM, TR2, LIGHTR)analysis, found this receptor in regions rich in CD68-positive macrophage-derived foam cells and HLA-DR-positive cells. 11976496_Crystallization and preliminary diffraction studies of the ectodomain of the envelope glycoprotein D from herpes simplex virus 1 alone and in complex with the ectodomain of the human receptor HveA 12466117_Data show that mRNA encoding LIGHT and its receptors [HVEM, LTbetaR, and TR6 (DcR3)] are present in placentas and cytotrophoblast cells at term. 12915568_association of HVEM and nectin-1 with lipid rafts during herpes simplex virus entry 14749527_sHVEM levels were elevated in sera of patients with allergic asthma, atopic dermatitis and rheumatoid arthritis 15110526_both nectin 1 and HVEM receptors play a role during HSV infection in vivo and both are highly efficient even at low levels of expression 15301860_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15568026_HVEM binds to B T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA), an Ig family member, which inhibits T cell proliferation. 15647361_Binding of HVEM to BTLA attenuates T cell activation, identifying HVEM/BTLA as a coinhibitory receptor pair. 15767456_in cells a complex forms through physical associations of HVEM, HSV-1 gD, and at least gH 15917993_both LTbetaR and HVEM can discriminatively mediate the expression of different genes in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells, including LIGHT, a proinflammatory cytokine 16131544_distinct herpesviruses target the HVEM-BTLA cosignaling pathway, suggesting the importance of this pathway in regulating T cell activation during host defenses. 16169851_2.8-A crystal structure of the BTLA-HVEM complex shows that BTLA binds the N-terminal cysteine-rich domain of HVEM and employs a unique binding surface 16797773_Real-time RT-PCR confirmed up-regulation of IL-8, osteopontin, and TNFRSF14 and down-regulation of SAMeS and CD209 in AH. 17010447_HVEM, a membrane-bound receptor that protects against apoptosis, was expressed only on syncytiotrophoblast 17405920_HSV-1-gD-HveA interaction initiates a signal transduction pathway leading to NF-kappaB activation 17947707_Ca(2+)is a downstream mediator of the LIGHT/HVEM interaction in monocytes 18193050_CD160 serves as a negative regulator of CD4+ T cell activation through its interaction with HVEM. 18502984_Expression of entry receptors nectin-1 and HVEM prevent entry of HSV-1 into human conjunctival epithelium. 18671825_These results establish that HVEM is involved in NF-kappaB activation by herpes simplex virus 1 glycoprotein D. 18794853_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18987746_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19023130_LIGHT-mediated upregulation of PAR-2 in endothelial cells is mediated through the HVEM receptor, involving Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathways. 19110536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19332782_HVEM-B and T lymphocyte attenuator bidirectional signaling may serve as a critical cell-survival system for lymphoid and epithelial cells 19473566_tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 14 (TNFRSF14) and signal regulatory protein, gamma (SIRPG) appear to contribute to gender difference in incidence of systemic lupus erythematosus. 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19680232_Results provide evidence of an existing relationship between HVEM and obesity, which suggest that this TNF superfamily receptor could be involved in the pathogenesis of obesity and inflammation-related activity. 19701890_unknown killing effect of LIGHT through HVEM on a lymphoid malignancy is described. 19762537_results suggest that down-regulation of the BTLA-HVEM pathway may be involved in germinal center B-cell activation. 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19915044_the HVEM-BTLA cis-complex competitively inhibits HVEM activation by ligands expressed in the surrounding microenvironment, thus helping maintain T cells in the naive state. 20066438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20187130_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20187130_We have identified and replicated a novel gene-gene interaction between 2 polymorphisms of TNFRSF members in Spanish patients with RA, based on the hypothesis of shared pathogenic pathways in complex diseases. 20233754_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20439292_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20884631_Findings identify TNFRSF14 as a candidate gene associated with a subset of FL, based on frequent occurrence of acquired mutations and their correlation with inferior clinical outcomes. 20884631_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20962851_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20962851_Polymorphisms were associated with MS predisposition, with stronger effect in patients with HHV6 active replication-TNFRSF6B-rs4809330(*)A: P=0.028, OR=1.13; TNFRSF14-rs6684865(*)A: overall P=0.0008, OR=1.2. 21533159_data show that HVEM stimulatory signals promote experimental colitis driven by innate or adaptive immune cells 21920726_HVEM-BTLA cis complex provides intrinsic regulation in T cells serving as an interference mechanism silencing signals coming from the microenvironment. 21941365_TNFRSF14 appears to be a serious candidate gene that might contribute to follicular lymphoma development. 21959263_The results of a mutagenesis study of HVEM suggest that the CD160 binding region on HVEM was slightly different from, but overlapped with, the BTLA binding site. 22113134_Results indicate that mHVEM on leukocytes and sHVEM in sera may contribute to the development and/or progression of gastric cancer. 22179929_study described the expression and spatial distribution of HVEM and BTLA in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissues, and results indicated that HVEM/BTLA may be involved in regulating the progress of joint inflammation 22239829_These results suggest that the C-terminal portion of the soluble HVEM ectodomain inhibits herpes simplex virus type 1 gD activation and that this effect is neutralized in the full-length form of HVEM in normal infection. 22459947_These findings support role for BTLA and/or HVEM as potential, novel diagnostic markers of innate immune response/status and as therapeutic targets of sepsis. 22634623_HVEM-B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) interactions impair minor histocompatibility antigen (MiHA)-specific T cell functionality, providing a rationale for interfering with BTLA signaling in post-stem cell transplantation. 23375291_BTLA and HVEM may have roles in graft rejection after kidney transplantation 23445872_Sequencing of TNFRSF14 located in the minimal region of loss in 1p36.32 showed nine mutations in pediatric follicular lymphoma. 23470321_Studies indicate co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory receptors B7-1, B7-2, CD28 and TNFRSF14 have a pivotal role in T cell biology, as they determine the functional outcome of T cell receptor (TCR) signalling. 23761635_HVEM functions as a regulator of immune function that activates NK cells via CD160 and limits lymphocyte-induced inflammation via association with B and T lymphocyte attenuator 23976978_HVEM gene polymorphisms are associated with sporadic breast cancer in Chinese women. 24249528_HVEM plays a critical role in both tumor progression and the evasion of host antitumor immune responses, possibly through direct and indirect mechanisms. 24314649_The conformation of the N-terminus of herpes simplex virus gD is induced by direct binding to HVEM and nectin-1. 24980868_Relative expression of HVEM and LTbetaR modulates canonical NF-kappaB and pro-apoptotic signals stimulated by LIGHT. 25468715_Data indicate that tumour-expressing herpes virus entry mediator (HVEMplays a critical role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), suggesting targeting HVEM may be a promising therapeutic strategy for HCC. 25750286_HVEM may play a critical role in tumor progression and immune evasion 26202493_Study report the crystal structure of unbound HVEM, which further contributes to the understanding of the molecular mechanisms controlling recognition between HVEM and its ligands. 26650888_In eight cases (42%) we observed recurrent copy number loss of chr1:2,352,236-4,574,271, a region containing the candidate tumor suppressor TNFRSF14. 26965583_Report a variant of t(14;18) negative nodal diffuse follicular lymphoma with CD23 expression, 1p36/TNFRSF14 abnormalities, and STAT6 mutations. 27103745_The increased immune-stimulatory capacity of lymphoma B cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations had clinical relevance, associating with higher incidence of acute GVHD in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. 27257180_genetic landscape of Pediatric-type follicular lymphoma suggests that TNFRSF14 mutations accompanied by copy-number neutral loss of heterozygosity of the 1p36 locus in over 70% of mutated cases, as additional selection mechanism, might play a key role in the pathogenesis of this disease. 27297871_These results suggest that TNFRSF14 mutations point towards a diagnosis of follicular lymphomas , and can be used in the sometimes difficult distinction between marginal zone lymphomas and follicular lymphomas 27458100_the overexpression of HVEM in ovarian cancer cells may suppress the proliferation and immune function of T cells, thus leading to the development of ovarian cancer. The current study partially explains the immune escape mechanism of ovarian cancer cells. 27987232_Roles of HVEM are likely to be immunosuppressive rather than activating tumor immunity and it in peripheral blood is a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. 28365939_HVEM is highly expressed in ovarian serous adenocarcinoma tissues and correlated with the patient clinicopathological features. 28470686_Low HVEM expression is associated with pancreatic and ampullary cancer. 28533310_TNFRSF14 and MAP2K1 mutations are the most frequent genetic alterations found in pediatric-type follicular lymphoma (PTFL) and occur independently in most cases, suggesting that both mutations might play an important role in PTFL lymphomagenesis. 28612127_High HVEM Expression is Associated with Cancer Progression in Breast Cancer. 28671524_Transgenic mice expressing HVEMIg showed a complete resistance to the lethal infection even with 300 MLD50 (survival rate of 100 %). 28809154_HIV-1 produced from CD4+ T cells bears HSV-2 receptor HVEM and can bind to and enter HSV-2-infected epithelial cells depending on HVEM-gD interaction and the presence of gB/gH/gL. 29061848_Data suggest that both HVEM and UL144 bind a common epitope of BTLA, whether engaged in trans or in cis; these studies were conducted in cell lines representing B-lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, and natural killer cells. (HVEM = human herpes virus entry mediator; UL144 = membrane glycoprotein UL144 of Human herpesvirus 5; BTLA = human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator) 29339444_LIGHT signaling through HVEM in epidermal keratinocytes directly induced proliferation and periostin expression, and both keratinocyte-specific deletion of HVEM or antibody blocking of LIGHT-HVEM interactions after disease onset prevented expression of periostin and limited atopic dermatitis symptoms. 29858685_Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphomas with concomitant 1p36 deletion and TNFRSF14 mutations frequently express high levels of EZH2 protein. 30066919_TNFRSF14 may serve a tumor suppressive role in bladder cancer by inducing apoptosis and suppressing proliferation, and act as a novel prognostic biomarker for bladder cancer. 30116751_our data suggested that the BTLA/HVEM pathway contributes to peripheral T cell suppression in hepatocellular carcinoma patients 30429008_HVEM was found to have a significant negative correlation with PD-L1 expression. 30508197_These data provide the first evidence of overexpression of LIGHT and its receptors HVEM and LT beta receptor in systemic sclerosis and suggest that the LIGHT axis might contribute to the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. 30770415_we have shown that soluble Fc-disabled HVEM-(Fc*) augments NK cell activation, IFN-gamma production, and cytotoxicity of NK cells without inducing NK cell fratricide by promoting cross-talk between NK cells and monocytes without Fc receptor-induced effects 30918139_the BTLA-TNFRSF14 immune modulation pathway seems to play a role in the pathobiology and prognosis of FL. 30984188_BTLA/HVEM Signaling: Milestones in Research and Role in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. 30987862_Our data highlights the importance of HVEM in the development of GBM and as a potential molecular target in combination with current immune checkpoint blockades for treatment of GBM. 31313042_High TNFRSF14 expression is associated with Colorectal Liver Metastasis. 31522034_HVEM expression on CD3+ cells increases after trauma. Patients developing secondary infections have less circulating HVEM+CD3+. This implies HVEM signaling in lymphocytes plays a role in maintaining host defense to infection in after trauma. 32027253_expression of BTLA and its ligand HVEM, the proportion of T lymphocytes and the expression of BTLA on the surface of gammadelta T cells in patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia are reduced 32312328_HVEM/HIF-1alpha promoted proliferation and inhibited apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells under hypoxic microenvironment conditions. 32454905_The Analysis of PTPN6 for Bladder Cancer: An Exploratory Study Based on TCGA. 32795404_Redesigning HVEM Interface for Selective Binding to LIGHT, BTLA, and CD160. 33238640_Fragments of gD Protein as Inhibitors of BTLA/HVEM Complex Formation-Design, Synthesis, and Cellular Studies. 34478526_Frequent mutated B2M, EZH2, IRF8, and TNFRSF14 in primary bone diffuse large B-cell lymphoma reflect a GCB phenotype. 34709351_HVEM structures and mutants reveal distinct functions of binding to LIGHT and BTLA/CD160. 35196150_Clinical Significance of BTLA and HVEM Expression on Circulating CD4(+) T and CD8(+) T Cells in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. 35537322_The role of the BTLA-HVEM complex in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. 36081508_BTLA inhibition has a dominant role in the cis-complex of BTLA and HVEM. | ENSMUSG00000022074+ENSMUSG00000042333 | Tnfrsf10b+Tnfrsf14 | 465.665504 | 0.446379240 | -1.163658 | 0.08851926 | 173.437797 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000013132885858859692313833096855027047229642908684509793040640051920396848663228366178973575317811936416078494316295177668507676571607589721679687500000000000 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000001996769645584015031574353563767135511527199465782773703915105390701969146837103066058077849455722543869917728898144559934735298156738281250000000000000000 | Yes | No | 296.9343032 | 20.3567350 | 668.2977687 | 43.0607055 |
| ENSG00000158301 | 114928 | GPRASP2 | protein_coding | Q96D09 | FUNCTION: May play a role in regulation of a variety of G-protein coupled receptors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15086532}. | Deafness;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of a family that regulates the activity of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). The encoded protein has been shown to be capable of interacting with several GPCRs, including the M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor and the calcitonin receptor. Several transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. | hsa:100528062;hsa:114928; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; G protein-coupled receptor binding [GO:0001664]; hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis [GO:0061484] | 16835690_that huntingtin protein and GASP2 form a complex in cotransfected mammalian cells 20479760_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 28096187_A missense variation of GPRASP2 was first identified to be implicated in X-linked SHL. 28849214_Dynamic expression analysis of armc10, the homologous gene of human GPRASP2, in zebrafish embryos, has been reported. | ENSMUSG00000072966 | Gprasp2 | 8.529735 | 0.060784514 | -4.040152 | 1.04733046 | 15.947061 | 0.0000651388349967467255793862612733846617629751563072204589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0007046883402432275534180150522445273963967338204383850097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 0.9862194 | 0.8975759 | 14.9873678 | 10.6239743 | |
| ENSG00000158747 | 4681 | NBL1 | protein_coding | P41271 | FUNCTION: Possible candidate as a tumor suppressor gene of neuroblastoma. May play an important role in preventing cells from entering the final stage (G1/S) of the transformation process. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Tumor suppressor | This gene product is the founding member of the evolutionarily conserved CAN (Cerberus and DAN) family of proteins, which contain a domain resembling the CTCK (C-terminal cystine knot-like) motif found in a number of signaling molecules. These proteins are secreted, and act as BMP (bone morphogenetic protein) antagonists by binding to BMPs and preventing them from interacting with their receptors. They may thus play an important role during growth and development. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified for this gene. Read-through transcripts between this locus and the upstream mitochondrial inner membrane organizing system 1 gene (GeneID 440574) have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. | hsa:100532736;hsa:4681; | extracellular space [GO:0005615]; BMP binding [GO:0036122]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; morphogen activity [GO:0016015]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; determination of dorsal identity [GO:0048263]; negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030514]; negative regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090027]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812]; positive regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045666]; sequestering of BMP from receptor via BMP binding [GO:0038098]; sequestering of BMP in extracellular matrix [GO:0035582] | 12150978_expression dependent on p73 during cisplatin-induced cell death and osteoblast differentiation 15528323_Data demonstrate for the first time that Dan physically and functionally interacts with Slit proteins to act as a negative regulator for monocyte chemotaxis. 19995712_This study was to establish if NBL1 was a molecular marker for pancreatic cancer. 21743959_CDKN2A, GATA3, CREBBP, ITGA2, NBL1 and TGM4 were down-regulated in the prostate carcinoma glands compared to the corresponding normal glands 22948749_NBL1 is a secreted protein that is highly restricted to the prostate. Underexpression of NBL1 correlated with prostate cancer progression. 24810382_The DAN family proteins with regards to BMP inhibition and also highlights their emerging roles in the modulation of Wnt and VEGF signaling pathways. 25561725_inhibition toward BMP2 and BMP7, but not GDF5. Although NBL1(S67Y) was able to antagonize BMP7 as effectively as PRDC, NBL1(S67Y) was still 32-fold weaker than PRDC against BMP2. 27524626_The structure of Grem2-GDF5 complex has revealed a number of key findings for DAN-family mediated BMP2 inhibition. 35947673_Neuroblastoma suppressor of tumorigenicity 1 is a circulating protein associated with progression to end-stage kidney disease in diabetes. | ENSMUSG00000041120 | Nbl1 | 13.512270 | 0.256151148 | -1.964933 | 0.57241230 | 12.209420 | 0.0004754881991452146808296852498187945457175374031066894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0040042919504173768441290803821175359189510345458984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 5.3264208 | 2.7500975 | 18.2040939 | 8.6986878 | |
| ENSG00000158859 | 9507 | ADAMTS4 | protein_coding | O75173 | FUNCTION: Cleaves aggrecan, a cartilage proteoglycan, and may be involved in its turnover. May play an important role in the destruction of aggrecan in arthritic diseases. Could also be a critical factor in the exacerbation of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer disease. Cleaves aggrecan at the '392-Glu-|-Ala-393' site. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen | This gene encodes a member of the ADAMTS (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs) protein family. Members of this family share several distinct protein modules, including a propeptide region, a metalloproteinase domain, a disintegrin-like domain, and a thrombospondin type 1 (TS) motif. Individual members of this family differ in the number of C-terminal TS motifs, and some have unique C-terminal domains. The enzyme encoded by this gene lacks a C-terminal TS motif. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protease. This protease is responsible for the degradation of aggrecan, a major proteoglycan of cartilage, and brevican, a brain-specific extracellular matrix protein. The expression of this gene is upregulated in arthritic disease and this may contribute to disease progression through the degradation of aggrecan. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes an isoform that is proteolytically processed. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. | hsa:9507; | collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501] | 11796708_activation of proteolytic activity by C-terminal truncation 11801682_Aggrecanase-1 is expressed by fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients and is induced by cytokines, especially TGF-beta. 11831030_extracellular matrix degrading enzyme 11854269_has a specific cleavage site at the matrix metalloproteinase site in its interglobular domain 11956193_Inhibition of ADAM-TS4 and ADAM-TS5 prevents aggrecan degradation in osteoarthritic cartilage. 12202483_Autocatalytic cleavage reveals multiple glycosaminoglycan-binding sites 12646579_ADAMTS-2 metalloproteinase is shown to cleave procollagen III N-propeptides as effectively as those of procollagens I and II 14561220_Multiple forms of ADAMTS4 protein characterized by Western analysis in human brain tissue lead to the conclusion that the 'aggrecanase' group of the ADAMTS family (ADAMTS 1, 4, 5 and 9) is responsible for turnover of versican V2 in the adult brain. 14662755_ADAMTS-4 lacking the spacer domain has promiscuous substrate specificity considerably different from that previously reported for aggrecan core protein 14701864_ADAMTS-4 activation involves the coordinated activity of both glycosylphosphatidyl inositol-anchored MT4-MMP and the proteoglycan form of syndecan-1 on the cell surface 14715656_ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 are inhibited by alpha2-macroglobulin 14744861_pro-ADAMTS4 is cleaved by proprotein convertase furin in the trans-Golgi network 15161923_the aggrecanase activity of ADAMTS4 is inhibited by fibronectin through interaction with their C-terminal domains 16003758_ADAMTS4 and 5 are upregulated on proliferating glioblastoma cells, and these proteases may contribute to their invasive potential 16099106_Taken together, these data suggest that aggrecanase-1 and alpha1-antitrypsin bind in vivo, although the physiological significance of the interaction between aggrecanase-1 and alpha1-antitrypsin remains unclear. 16677612_The ADAMTS-4 promoter would serve as a valuable mechanistic tool to better understand the regulation of ADAMTS-4 expression by signaling pathways that modulate cartilage matrix breakdown. 16723216_analysis of osteoarthritic synovium using primers designed to amplify across the exon 8/9 junction resulted in amplification of the expected product and a smaller product missing 161 bp from the 5' end of exon 9, the result of alternative splicing 16741450_Macrophages infiltrating granulation and adjacent disc tissues express ADAMTS-4, suggesting its involvement in herniated disc regression. 16771712_The inhibition of ADAMTS-2 by TIMP-3 alone out of 4 TIMP proteins is reported. 17009305_The induction of ADAMTS-4 by B burgdorferi results in the cleavage of aggrecan, which may be an important first step that leads to permanent degradation of cartilage. 17095512_analysis of aggrecanase (ADAMTS-4) conformation, affinity and sequence specificity 17208315_oncostatin M-stimulated ADAMTS-4 and matrix metallopeptidase 13 expression is mediated by extracellular signal-regulated kinases, Janus kinase 3/STAT1/3 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and by cross talk between these pathways 17265492_Our data suggest that both ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5 contribute to the structural damage that characterizes human osteoarthritis. 17295438_Inhibition of NF0kappaB results in the decreased expression of several destructive metalloproteinases and also the ADAMTS4 aggrecanase 17311924_recombinant ADAMTS-4 effectively cleaved intact matrilin-3 at the predicted motif at Glu435/Ala436 generating two species of 45 and 5 kDa 17430884_ADAMTS-5 is a major aggrecanase in cartilage metabolism and pathology, with aggrecanase activity at least 1,000-fold greater than that of ADAMTS-4 under physiological conditions 17470431_TIMP-3 inhibition of ADAMTS-4 is modulated by interactions between aggrecan and the C-terminal domain of ADAMTS-4 17606262_ADAMTS-4 and -8 are inflammatory regulated enzymes expressed in macrophage-rich areas of atherosclerotic plaques. 17978660_In both nucleus pulposis and anulus fibrosus, ADAMTS4 was higher in discs with a higher level of degeneration. Aggrecan fragmentation profile analysis showed the involvement of aggrecanases and other proteases during disc degeneration. 18039650_after stimulation, the protease activity of PC5A is enhanced, as evidenced by the cleavage of the PC5A substrates Lefty, ADAMTS-4, endothelial lipase, and PCSK9. 18042673_Crystal structures of the two most active human aggrecanase isoforms, ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5, each in complex with bound inhiitor. 18050214_PKCzeta is involved in regulation of IL-1beta-induced NF-kappaB signaling in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes, which regulates downstream expression of ADAMTS-4 and NOS2 via NF-kappaB. 18156631_the catalytic domain of ADAMTS-5 has higher intrinsic catalytic ability than that of ADAMTS-4 18221525_Human ADAMTS-4 was expressed in rodent pyramidal neurons and neuropil of stratum oriens and the lacunosum moleculare. 18387286_Both ADAMTS-4 mRNA and protein processing may be differentially regulated in normal and damaged tendons. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18671934_PACE4 is a proprotein convertase responsible for activation of aggrecanases in osteoarthritic and cytokine-stimulated cartilage; posttranslational activation of ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5 in the extracellular milieu of cartilage results in aggrecan degradation 18941754_Expression of ADAMTS4 by chondrocytes in the surface zone of human osteoarthritic cartilage is regulated by epigenetic DNA de-de-methylation. 19054571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19342688_findings suggest that Ras, ROS along with MyD88, IRAK1, or TRAF6 synergistically mediate ADAMTS-4 regulation by IL1-beta 19643179_The C-terminal domains of ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5 affect the structure around the active site, favouring interaction with TIMP-3. 19944557_Plasma ADAMTS4 was measured in stable-effort angina pectoris, acute coronary syndrome & controls. The pattern of its release was clearly different in various forms of ACS. It showed a weak correlation with high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. 20625753_Patients with acute coronary syndrome showed increased ADAMTS4 expression, which may aggravate the development of atherosclerosis and instability of atherosclerotic plaques. 20664926_ADAMTS4 expression was found to be regulated by EWS-FLI1 fusion gene-dependent manner. ADAMTS4 protein was highly expressed in tumor samples of the patients with EWS by using immunohistochemistry. 20857147_Multiple matrix metalloproteinases and ADAMTS-4 are involved in the natural history of interverteral lumbar disc herniation. 21334453_effect of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) on ADAMTS-4 expression in macrophages along with the regulatory mechanisms underlying its actions 21345877_ADAMTS-4 is present in human coronary atherosclerotic plaques. 21664283_results suggest that during the acute phase after knee injury there is an increased aggrecanase activity against both the interglobular domain (IGD) and the CS2 cleavage sites of joint cartilage aggrecan 21946608_Serum ADAMTS4 levels are associated with the presence and the severity of coronary artery disease. 22065068_Sp1 transcription factor partly mediates IL-1 induction of ADAMTS-4. 22324945_Suggest IL-6 may participate in cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis as an inducer of ADAMTS-4 expression from synoviocytes. 22562232_Data show that the expression of ADAMTS4, 9, 16 and was up-regulated during chondrogenesis, ADAMTS1 and 5 were down-regulated. 22670872_Data suggest that cleavage of aggrecan by matrix metalloproteinases in knee cartilage from injured or osteoarthritic subjects is low compared with cleavage by aggrecanase-1 (at least early in osteoarthritis, as suggested by other evidence). 22735305_study showed that ADAMTS-1, -4, -5 and TIMP3 were expressed at differential levels in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines 23082219_The serine protease tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and two matrix metalloproteinases, ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5, were identified as Reelin cleaving enzymes. 23137648_Citrullinated fibronectin is less effective in inhibiting the proteolytic activity of ADAMTS4 and may contribute to the destruction of joint cartilage in rheumatoid arthritis. 23295731_Cartilage affected by varying degrees of osteoarthritis stained strongly for active ADAMTS-4 where surface fibrillation and clustered chondrocytes were observed. 23319426_AMTS4 has roles in melanoma growth and angiogenesis 23406982_Our results indicate that miR-125b plays an important role in regulating the expression of ADAMTS-4 in human chondrocytes 23438438_The purpose of the present study was to investigate the precise molecular mechanisms of high molecular weight hyaluronic acid on ADAMTS4 expression induced by IL- 1b in vitro. 23859810_We have demonstrated that the expression of ADAMTS-1, -4 and -5 is induced during the differentiation of monocytes into macrophages. 23897278_ADAMTS-4_v1 is expressed as a protein in vivo in human osteoarthritis synovium, functions as an aggrecanase, and cleaves other proteoglycan substrates. 24051360_ADAMTS-4 and its substrate biglycan are involved in tubulogenesis by endothelial cells 24126638_This is the first evidence of crosstalk between TNF-alpha and ADAMTS-4 in relation to osteoarthritis cartilage degradation. 24474687_This study highlights that the affinity between a ligand and LRP1 dictates the rate of internalization and suggests that LRP1 is a major traffic controller of the two aggrecanases, especially under inflammatory conditions, where the protein levels of ADAMTS-4 increase, but those of ADAMTS-5 do not. 24732836_We conclude that the upregulation of TNF-alpha and ADAMTS-5, but not ADAMTS-4, may play an important role in degenerative cartilage endplate-induced low back pain. 24786121_The restricted expression of ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5 and their increased expression in gestational trophoblastic diseases suggest that these 2 ADAMTS subtypes are associated with human placentation and the development of gestational trophoblastic diseases. 25225099_ADAMTS4 is largely associated with synapses, and is the main brevican-processing protease. 25433723_in degenerative intervertebral discs, IL1b upregulates NFkB, MMP13 and ADAMTS4 25477257_Evaluate ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5 immunohistochemical expression in human TMJ discs from patients affected by internal derangement. 25501175_ADAMTS-4 is a potential biomarker and an early diagnostic indicator of knee osteoarthritis. 25592103_ADAMTS4 may be responsible for the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. ADAMTS4 serum levels were also higher in diabetic cases. There is an association between ADAMTS4 and TGFb1 serum levels in the progression of atherosclerosis in coronary artery disease. 25707877_A positive feedback loop involving sSema4D/IL-6 and TNFalpha/ADAMTS-4 may contribute to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. 25709087_CCN1 suppresses ADAMTS-4 activity and that CCN1 overexpression is directly correlated with chondrocyte cloning in osteoarthritis cartilage. The TGFbeta/CCN1 axis plays a role in chondrocyte cluster formation through inhibition of ADAMTS-4. 26152337_Results show that ADAMTS4 mRNA is the target of mir-1268a and its expression might be modified by MIR-1268a rs28599926 polymorphism in hepatocellular carcinoma. 26495885_The SNP rs4233367 in the exon of ADAMTS-4 gene may be associated with lumbar disc degeneration. 26612259_These data demonstrate that the antibody is specific to ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 and inhibits their aggrecanase activity at molecular and cellular levels. 26916548_progesterone acts via the progesterone receptor to modulate ADAMTS 1 and 4 levels in ovarian cancer cell lines. 27182768_ADAMTS4 may have a role in the pathogenesis by causing increased oxidative and inflammatory environment in preterm premature rupture of membranes . 27401455_HipHop-based pharmacophore modeling and virtual screening of the Maybridge database to identify novel ADAMTS-4 inhibitors. These novel lead compounds act as potent and specific inhibitors for the ADAMTS-4 enzyme and could have therapeutic potential in the treatment of OA. 27706574_we investigated whether important polymorphisms in the ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 genes affect osteoarthritis (OA) susceptibility. ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 genotypes were determined using the ABI Prism StepOnePlus Real-Time system. Our findings suggest that the ADAMTS4 (rs4233367 and rs11807350) and ADAMTS5 (rs226794 and rs2830585) variants examined may not contribute to susceptibility to knee OA in the Turkish population. 28005267_ADAMTS4 expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 28081267_Single Nucleotide Variants of Candidate Genes in Aggrecan Metabolic Pathway Are Associated with Lumbar Disc Degeneration and Modic Changes 28099917_Using in vitro approaches and cultured breast cancer cell lines authors demonstrate that Fibulin-2 is a better substrate for ADAMTS-5 than it is for ADAMTS-4. Fibulin-2 degradation is associated to an enhancement of the invasive potential of T47D, MCF-7 and SK-BR-3 cells. 28323982_ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS15 were upregulated in symptomatic uterine leiomyomas. 28829887_ADAMTS-4 protein expression increased in cartilage tissue from spinal tuberculosis patients. 28888475_methylation status of the ADAMTS4 gene is altered in patellar tendinopathy 28955046_Study showed significant ADAMTS-4 expression in aortic tissues from patients with sporadic ascending thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection, particularly in smooth muscle cells. 29135310_ADAMTS 1, 4, 12, and 13 levels in the maternal and cord blood were lower in the preeclampsia group than in the control group. ADAMTS 1, 4, and 12 levels in placental tissues were higher in the preeclampsia group. 29153440_ADAMTS4 expression was upregulated during carotid atherosclerotic plaque development. Serum levels of ADAMTS4 were associated with increased plaque vulnerability in both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients with carotid artery stenosis. 29694979_ADAMTS4 was associated macrophages infiltration and polarization in the tumor microenvironment of CRC and ADAMTS4 knockdown had no inhibitory implications on cell proliferation and invasion in vitro, but significantly attenuated tumor growth in vivo. 30016600_High ADAMTS4 expression is associated with osteoarthritic cartilage deterioration. 30187439_The lower levels of ADAMTS4 in the primary ovarian insufficiency group, when compared with the idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism patients pointed out that even limited hormone secretion and ovulation in the POI group, may have protective effect on cardiovascular system. The higher levels of ADAMTS4 and lipid accumulation in the IHH group demonstrated the increased risk of these patients for cardiovascular disease. 30369484_Since only two of the collected studies referred to ADAMTS4, we did not perform meta-analysis for these comparisons. Taken together, rs226794 and rs2830585 in ADAMTS5 gene were not associated with musculoskeletal degenerative diseases in overall population, but there seemed to be an ethnicity-dependent effect of rs2830585 in the risk of musculoskeletal degenerative diseases 30426203_ADAMTS4 was exclusively expressed in oligodendrocytes 30730845_significantly higher second-trimester amniotic fluid levels in pregnant women with spontaneous preterm birth 31663692_Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the coding region of a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 4 and hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective case-control study. 31734379_ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 may be considered as new molecular therapeutic targets for cartilage damages with Kashin-Beck Disease. 32067610_Expression Levels of A Disintegrin-like Metalloproteinase with Thrombospondin Motifs-4 and -5 (ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5) in Inflamed and Healthy Gingival Tissues. 32490633_The utility of synovial fluid levels of ADAMTS9 and ADAMTS4 in predicting treatment responses to intraarticular steroid injections in patients with knee osteoarthritis 33116313_Exuberant fibroblast activity compromises lung function via ADAMTS4. 33350314_Interrelationship of Osteopontin, MMP-9 and ADAMTS4 in Patients With Osteoarthritis Undergoing Total Joint Arthroplasty. 33358865_Requirement for C-mannosylation to be secreted and activated a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 4 (ADAMTS4). 33444494_ADAMTS proteoglycanases downregulation with impaired oocyte quality in PCOS. 34718343_Synergistic upregulation of ADAMTS4 (aggrecanase-1) by cytokines and its suppression in knee osteoarthritic synovial fibroblasts. 35051931_The Role of ADAMTS-4 in Atherosclerosis and Vessel Wall Abnormalities. 35701493_Identification of Adamts4 as a novel adult cardiac injury biomarker with therapeutic implications in patients with cardiac injuries. | ENSMUSG00000006403 | Adamts4 | 99.874679 | 2.147843947 | 1.102889 | 0.25443135 | 18.472368 | 0.0000172385595694370814779609185629638545833586249500513076782226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0002158755338024045706147441281430587878276128321886062622070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 142.9752125 | 34.8648670 | 66.8893249 | 16.4777219 | |
| ENSG00000160145 | 8997 | KALRN | protein_coding | O60229 | FUNCTION: Promotes the exchange of GDP by GTP. Activates specific Rho GTPase family members, thereby inducing various signaling mechanisms that regulate neuronal shape, growth, and plasticity, through their effects on the actin cytoskeleton. Induces lamellipodia independent of its GEF activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10023074}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disulfide bond;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;SH3 domain;Transferase | Huntington's disease (HD), a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by loss of striatal neurons, is caused by an expansion of a polyglutamine tract in the HD protein huntingtin. This gene encodes a protein that interacts with the huntingtin-associated protein 1, which is a huntingtin binding protein that may function in vesicle trafficking. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. | hsa:8997; | actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; ephrin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048013]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] | 14742910_we have identified multiple transcriptional start sites in rats and humans. These multiple transcriptional start sites result in full-length Kalirin transcripts possessing different 5' ends encoding proteins with differing amino termini 15950621_Kalirin GEF1 domain induces lamellipodia through activation of Pak, where Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activity is not required. 17357071_Three SNPs from the kalirin (KALRN) gene are associated with early-onset coronary artery disease. 17640372_ARF6 recruits KALRN to the cell membrane facilitating Rac activation. 17851188_Our observation is the first to relate kalirin to Alzheimer's disease. Kalirin was consistently under-expressed in Alzheimer's disease hippocampus. 18199770_Kalirin-7 is an essential component of both shaft and spine excitatory synapses in hippocampal interneurons. 18839057_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18953434_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19706030_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20080650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20107840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20107840_Two SNPs in the KALRN gene region (rs17286604 and rs11712619)constitute risk factors for ischemic stroke. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20604901_SNX1 and SNX2 interact with Kalirin-7. Overexpression of SNX1 or SNX2 and Kalirin-7 partially redistributes both SNXs to the plasma membrane, and results in RhoG-dependent lamellipodia formation. 20730383_Studies indicate that Kalirin-7 plays a key role in excitatory synapse formation and function. 21041834_Missense mutations in KALRN may be genetic risk factors for schizophrenia. 21041834_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21664346_KALRN gene variation is not associated with overall ischemic stroke 22120753_We found Kalirin-9 expression to be paradoxically increased in schizophrenia 22194219_Neuronal guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) kalirin is emerging as a key regulator of structural and functional plasticity at dendritic spines. 22429885_The kalirin expression were reduced in Alzheimer disease with psychosis. 22458949_In both anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), study found a reduction of Duo expression and PAK1 phosphorylation in schizophrenia. Cdc42 protein expression was decreased in ACC but not in DLPFC 22720673_The age-at-onset of Huntington disease (HD) is not associated with eleven SNPs, including SNP rs10934657 in the kalirin gene in 680 European HD patients. 25224588_A sequence variant in human KALRN impairs protein ability to activate Rac1 and coincides with reduced cortical thickness. 25316661_consider the GG genotype and the G allele of rs9289231 polymorphism of KALRN to be genetic risk factors for CAD in an Iranian population, especially in early-stage atherosclerotic vascular disease 25917671_4 KALRN gene SNPs were studied in Han ischemic stroke patients. rs11712619 seemed associated with lacunar stroke until risk factors were considered. re6438833 was significantly associated with ischemic and lacunar stroke. 27218147_GG genotype and the G allele of the rs9289231 polymorphism of KALRN and the rs224766 polymorphism of ADIPOQ genes may be considered genetic risk factors for Iranian type 2 diabetic patients with coronary artery disease. 27421267_DNA sequencing provided evidence linking KALRN to monogenic intellectual disability in two patients. 28152519_Data suggest protein levels of kalirin and CHD7 in circulating extracellular vesicles (EVs) as endothelial dysfunction markers to monitor vascular condition in hypertensive patients with albuminuria. 28706949_The GG genotype and G allele of SNP rs7620580 were associated with a risk for ischemic stroke with an adjusted OR of 3.195 and an OR of 1.446, respectively. Haplotype analysis revealed that A-T-G,G-T-A, and A-T-A haplotypes were associated with ischemic stroke. Our results provide evidence that kalirin gene variations were associated with ischemic stroke in the Chinese Han population. 29241584_The data of this study reveal a novel mechanism for disease-associated single nucleotide variants of KALARN and provide a platform for modeling morphological changes in mental disorders. 29554915_Combination of polymorphisms in the NOD2, IL17RA, EPHA2 and KALRN genes could play a significant role in the development of sarcoidosis by maintaining a chronic pro-inflammatory status in macrophages 29789657_The interaction of kalirin with the C-terminal region of Htt influences the function of kalirin and modulates the cytotoxicity induced by C-terminal Htt. 30232674_SNPs of the KALRN gene are associated with intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis in the northern Chinese population. 31801062_Synaptic Kalirin-7 and Trio Interactomes Reveal a GEF Protein-Dependent Neuroligin-1 Mechanism of Action. 33037113_KALRN mutations promote antitumor immunity and immunotherapy response in cancer. 33658318_Kalirin-RAC controls nucleokinetic migration in ADRN-type neuroblastoma. | ENSMUSG00000061751 | Kalrn | 19.390694 | 4.640964670 | 2.214425 | 0.58349526 | 13.472819 | 0.0002420443408327709305244423987346635840367525815963745117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0022355093521293856531628740924588782945647835731506347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 33.2261554 | 7.1915040 | 6.4520102 | 1.7139131 | |
| ENSG00000160229 | 7617 | ZNF66 | protein_coding | Q6ZN08 | FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. {ECO:0000250}. | DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Predicted to be located in nucleus. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | Mouse_homologues | nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) | ENSMUSG00000058246 | Gm10037 | 94.977254 | 2.531998018 | 1.340276 | 0.45024703 | 8.530790 | 0.0034918805332104694248707144055288154049776494503021240234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0213948422683083866457920407810888718813657760620117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 89.2071768 | 35.9676435 | 35.3306615 | 14.2466744 | |
| ENSG00000160654 | 917 | CD3G | protein_coding | P09693 | FUNCTION: Part of the TCR-CD3 complex present on T-lymphocyte cell surface that plays an essential role in adaptive immune response. When antigen presenting cells (APCs) activate T-cell receptor (TCR), TCR-mediated signals are transmitted across the cell membrane by the CD3 chains CD3D, CD3E, CD3G and CD3Z. All CD3 chains contain immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) in their cytoplasmic domain. Upon TCR engagement, these motifs become phosphorylated by Src family protein tyrosine kinases LCK and FYN, resulting in the activation of downstream signaling pathways (PubMed:2470098). In addition to this role of signal transduction in T-cell activation, CD3G plays an essential role in the dynamic regulation of TCR expression at the cell surface (PubMed:8187769). Indeed, constitutive TCR cycling is dependent on the di-leucine-based (diL) receptor-sorting motif present in CD3G. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2470098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8187769, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8636209}. | 3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is the CD3-gamma polypeptide, which together with CD3-epsilon, -delta and -zeta, and the T-cell receptor alpha/beta and gamma/delta heterodimers, forms the T-cell receptor-CD3 complex. This complex plays an important role in coupling antigen recognition to several intracellular signal-transduction pathways. The genes encoding the epsilon, gamma and delta polypeptides are located in the same cluster on chromosome 11. Defects in this gene are associated with T cell immunodeficiency. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:917; | alpha-beta T cell receptor complex [GO:0042105]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; gamma-delta T cell receptor complex [GO:0042106]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; signaling receptor complex adaptor activity [GO:0030159]; T cell receptor binding [GO:0042608]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; alpha-beta T cell activation [GO:0046631]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; establishment or maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0007163]; gamma-delta T cell activation [GO:0046629]; positive thymic T cell selection [GO:0045059]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of lymphocyte apoptotic process [GO:0070228]; T cell activation [GO:0042110]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] | 1709425_Protein level controlled by OTHER KINASES PROTEINS 12374807_human CD3gamma has specific NFAT binding motifs that differentially bind NFATc1, NFATc2, and NF-kappa B p50 12410792_CD3 epsilon undergoes a conformational change after dimerization with CD3 gamma or CD3 delta 12794121_CD3 gamma contributes to, but is not absolutely required for, the regulation of T cell receptor trafficking in resting and antigen-stimulated mature T lymphocytes. 15459203_there is one molecule each of CD3delta and CD3gamma in the surface TCR/CD3 complex 15778375_significant rigidity was observed in use of the (D/E)xxxL(L/I) motif in CD3gamma, due to an absolute requirement for the position of this signal in the context of the TCR complex and for a highly conserved lysine residue, K128, not present in CD3delta 15879122_The CD3 gamma gene promoter is lymphoid specific, initiates transcription from multiple start sites and contains two core promoters capable of recruiting the general transcription machinery through specificity protein binding motifs. 16888097_CD3delta and CD3gamma play a different role in humans and mice in pre-TCR and TCR function during alphabeta T-cell development 16916653_Several amino acids are essential for an optimal association between CD3gamma and CD3 and the assembly of a cell-surface expressed TCR-CD3deltagammazeta2 complex. 17023417_analysis of TCRalpha-CD3deltaepsilon and TCRbeta-CD3gammaepsilon dimers and the role of the membrane-proximal tetracysteine motif 17176095_The CD3 gamma immune recognition receptor cytoplasmic domain binds to acidic and mixed phospholipid vesicles with a binding strength that correlates with the protein net charge and the presence of clustered basic amino acid residues. 17822534_HTLV-I infection initiates a process leading to a complete loss of CD3 membrane expression by an epigenetic mechanism which continues along time, despite an early silencing of the viral genome. 17923503_In CD3gamma-deficient patients there can be substitution of CD3gamma by the CD3delta chain and which can then support gammadelta T cell development. 18815285_(Pre)malignant transformation in refractory celiac disease type II correlates with defective synthesis or defective association of the TCR chains, resulting in loss of surface TCR-CD3 expression 19056690_Stage-dependent molecular changes in Notch signaling that are critical for normal human T-cell development. 19536290_human eosinophils express a functional gammadeltaTCR/CD3 with similar, but not identical, characteristics to gammadeltaTCR from gammadeltaT cells 19724882_Data show CD3 epsilon pairs with CD3 gamma or with CD3 delta, forming CD3 epsilon gamma and CD3 epsilon delta heterodimers, which provide insight into our understanding of the molecular assembly of the CD3 molecular complex. 19860678_In this review, some of the genetic and epigenetic factors that determine the correct assembly and structure of the TCR/CD3 complex are summarized--REVIEW 19898481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20478055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20511557_When compared with other human T cell subsets, T cell receptor/CD3-activated Vgamma9Vdelta2-expressing T cells display an unusually delayed and sustained intracellular calcium mobilization, dramatically quickened and shortened on costimulation by NKG2D. 20660709_CD3gamma and CD3delta evolved from a common precursor gene to optimize major histocompatibility antigen (MHC)-triggered alphabeta T cell receptor activation. 21669053_Data show that the expression pattern of the four CD3 chains was epsilon>zeta>delta>gamma in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from MM, while a gamma>epsilon>zeta>delta expression pattern was found in healthy controls. 21669059_Study characterized the expression pattern of CD3-gamma, -delta, -epsilon and -zeta chain genes from placenta, which contributes to further understanding of the features of T-cell immune status in placenta. 21670311_A combination of trastuzumab antibody and phosphoantigen-stimulated gammadelta T-lymphocytes increases the efficacy of trastuzumab alone against HER-2-positive breast carcinoma cell lines in vivo and mammary carcinoma xenografts in mice. 21764047_Data show that TCRzeta phosphorylation signal pathways were affected in CD3gamma(-/-) primary and HVS-transformed T cells. 21984702_A transgenic T cell receptor gammadelta-low expressing subset of T cells accumulates in mouse epidermis after IL-23 injections. 22401598_Altered expression of the TCR signaling related genes CD3 and FcepsilonRIgamma in patients with aplastic anemia. 22482414_Data show that the expressions of CD3, CD4 were significantly associated with overall survival(OS) of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. 22731821_roles of CD3G polymorphisms in predisposition for HCC 23336327_The surface TCR expression of primary alphabeta and gammadelta T cells from healthy donors carrying a single null or leaky mutation in CD3G (gamma+/-) or CD3D (delta+/-, delta+/leaky) with that of normal controls, were compared. 23348211_In conclusion, TCR-gamma expression seems to be rare and is confined to cytotoxic primary cutaneous T-cell lymphomas 23590417_deficiency results in autoimmunity 24794251_Data indicate that the high CD68/CD3 ratio identifies a bad prognosis group among muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma (UC). cases. 24910257_The results suggest that CD3G should be studied as a candidate gene for autoimmunity and that CD3gamma deficiency should be considered among other primary immunodeficiencies with predominantly autoimmune manifestations. 24966976_Case Report: T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with t(7;14)(p15;q32) [TCRgamma-TCL1A translocation] confirmed by FISH. 25113399_Low cord blood Foxp3/CD3gamma mRNA ratios are highly predictive for early allergy development. 25760691_HER2/CD3 BsAb efficiently inhibited the growth of breast cancer tissue by activating and inducing the proliferation of tumor tissue infiltrating lymphocytes. 25920998_The study identifies an important role of the CD3gamma dileucine motif in T-cell development most probably mediated by its fine-tuning of pre-TCR and TCR expression, down-regulation and signaling. 25957593_CD3 showed a positive correlation with tryptase and microvascular density, while multiple regression analysis efficaciously predicted microvascular density depending on CD3 and tryptase as predictors, supporting a complex interplay between these cells in sustaining tumor angiogenesis in Diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients. 26109064_The docking site for CD3 subunits on the T Cell receptor beta chain has been identified by solution NMR. 29653965_These data demonstrate that the T-cell repertoire of patients with CD3G mutations is characterized by a molecular signature that may contribute to the increased rate of autoimmunity associated with this condition. | ENSMUSG00000002033 | Cd3g | 33.897032 | 2.994833821 | 1.582476 | 0.27258607 | 34.963390 | 0.0000000033596297985305788308346767030666477071854103542136726900935173034667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000823021044165424524578534041727162495760694582713767886161804199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 47.0742343 | 9.1425998 | 15.7989750 | 3.4318507 | |
| ENSG00000160932 | 4061 | LY6E | protein_coding | Q16553 | FUNCTION: GPI-anchored cell surface protein that regulates T-lymphocytes proliferation, differentiation, and activation. Regulates the T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling by interacting with component CD3Z/CD247 at the plasma membrane, leading to CD3Z/CD247 phosphorylation modulation (By similarity). Restricts the entry of human coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, by interfering with spike protein-mediated membrane fusion (PubMed:32641482). Also plays an essential role in placenta formation by acting as the main receptor for syncytin-A (SynA). Therefore, participates in the normal fusion of syncytiotrophoblast layer I (SynT-I) and in the proper morphogenesis of both fetal and maternal vasculatures within the placenta. May also act as a modulator of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) activity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q64253, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32641482}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Promotes entry, likely through an enhanced virus-cell fusion process, of various viruses including HIV-1, West Nile virus, dengue virus and Zika virus (PubMed:28130445). In contrast, the paramyxovirus PIV5, which enters at the plasma membrane, does not require LY6E (PubMed:28130445, PubMed:29610346). Mechanistically, adopts a microtubule-like organization upon viral infection and enhances viral uncoating after endosomal escape (PubMed:28130445, PubMed:30190477). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28130445, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29610346, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30190477}. | Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Host-virus interaction;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal | This gene belongs to the human Ly6 gene family and encodes a glycosylphosphatidyl-inositol (GPI)-anchored cell surface protein. The protein plays an important role in T cell physiology, oncogenesis and immunological regulation. The protein is also involved in modulation of viral infection by coronaviruses, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2021]. | hsa:4061; | extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; acetylcholine receptor inhibitor activity [GO:0030550]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; negative regulation of viral entry into host cell [GO:0046597] | 18755862_Increased expression of the type I interferon-inducible gene, lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus E, in peripheral blood cells is predictive of lupus activity in a large cohort of Chinese lupus patients. 18990604_Two SCA3 and one SCA2 cases have been identified which show autosomal dominant inheritance in Parkinson disease. 19672991_This study suggested that a mutation in SCA2 or SCA3/MJD may be one of the genetic causes of Parkinson's disease in china. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25225669_the LY6E pathway in monocytes represents one of negative feedback mechanisms that counterbalance monocyte activation which may serve as a potential target for immune intervention. 25344775_LY6E level of gene expression may serve as good biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus diagnosis. 27197181_LY6E overexpression is associated with Breast Cancer Progression, Immune Escape, and Drug Resistance. 27589564_High LY6E expression is associated with breast cancer. 28130445_LY6E is a positive modulator of HIV-1 infection in primary human peripheral blood mononuclear cells, immortalized CD4+ T lymphoid cells, and macrophages. HIV Long Terminal Repeat-driven HIV-1 gene expression is also enhanced by LY6E, suggesting additional roles of LY6E in HIV-1 replication. 29448250_LY6E knockdown by targeted-siRNA inhibited gastric cancer cell survival and proliferation and induced G1-S cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer cells 30190477_LY6E belongs to a growing class of interferon-inducible factors that broadly enhance viral infectivity in an interferon-independent manner. 30674630_LY6E downregulates the cell surface receptor CD4. 32694157_A Phase I Study of DLYE5953A, an Anti-LY6E Antibody Covalently Linked to Monomethyl Auristatin E, in Patients with Refractory Solid Tumors. 32839948_Protein LY6E as a candidate for mediating transport of adeno-associated virus across the human blood-brain barrier. 34994389_alpha5-nAChR associated with Ly6E modulates cell migration via TGF-beta1/Smad signaling in non-small cell lung cancer. 35310607_Multidimension Analysis of the Prognostic Value, Immune Regulatory Function, and ceRNA Network of LY6E in Individuals with Colorectal Cancer. 36165190_LY6E protein facilitates adeno-associated virus crossing in a biomimetic chip model of the human blood-brain barrier. | ENSMUSG00000022587 | Ly6e | 474.417574 | 0.418785331 | -1.255717 | 0.07955871 | 252.402467 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000077748159635095350214250979319593032879899168434592797579215610622570411989393372290383022139009361438551265906016235545251071574463555322 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000016992832140245526528940976534667079852932136568566333883509890592376795422134941911436778742978364462584506809314173335654251136181381535 | Yes | No | 284.4246307 | 14.0503647 | 682.3167398 | 29.5723193 | |
| ENSG00000161640 | 114132 | SIGLEC11 | protein_coding | Q96RL6 | FUNCTION: Putative adhesion molecule that mediates sialic-acid dependent binding to cells. Preferentially binds to alpha-2,8-linked sialic acid. The sialic acid recognition site may be masked by cis interactions with sialic acids on the same cell surface. In the immune response, may act as an inhibitory receptor upon ligand induced tyrosine phosphorylation by recruiting cytoplasmic phosphatase(s) via their SH2 domain(s) that block signal transduction through dephosphorylation of signaling molecules. | Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Lectin;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a member of the sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin family. These cell surface lectins are characterized by structural motifs in the immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains and sialic acid recognition sites in the first Ig V set domain. This family member mediates anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive signaling. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. | hsa:114132; | plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; sialic acid binding [GO:0033691]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155] | 11986327_cloning and characterization; a recently evolved signaling that can interact with SHP-1 and SHP-2 and is expressed by tissue macrophages including brain microglia 16151003_expressed in human but not in chimpanzee brain microglia; findings indicate that human SIGLEC11 emerged through human-specific gene conversion by an adjacent pseudogene 18629938_SIGLEC16 encodes a DAP12-associated receptor expressed in macrophages that evolved from its inhibitory counterpart SIGLEC11 and has functional and non-functional alleles in humans. 20203208_Siglec-11 ectopically expressed on murine microglia interacts with PSA on neurons, reduces LPS-induced gene transcription of proinflammatory mediators, impairs phagocytosis and alleviates microglial neurotoxicity. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21467073_The results indicate potential roles for Siglec-11 in ovarian physiology and human evolution. 28100677_The authors demonstrated that the human-specific pathogen Escherichia coli K1 uses its polysialic acid capsule as a molecular mimic to engage Siglec-11 and escape killing. In contrast, engagement of the activating counterpart Siglec-16 increases elimination of bacteria. 32845322_Human-specific microglial Siglec-11 transcript variant has the potential to affect polysialic acid-mediated brain functions at a distance. | ENSMUSG00000030468 | Siglecg | 26.419551 | 2.069083705 | 1.048992 | 0.33772470 | 9.635514 | 0.0019085075298903610152567722479943768121302127838134765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0130543781555532371202454910985579772386699914932250976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 36.1300221 | 5.3005485 | 17.6188509 | 2.8964408 | |
| ENSG00000161647 | 4356 | MPP3 | protein_coding | Q13368 | Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain | This gene product is a member of a family of membrane-associated proteins termed MAGUKs (membrane-associated guanylate kinase homologs). MAGUKs interact with the cytoskeleton and regulate cell proliferation, signaling pathways, and intracellular junctions. This protein contains a conserved sequence, called the SH3 (src homology 3) motif, found in several other proteins that associate with the cytoskeleton and are suspected to play important roles in signal transduction. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified. One transcript variant is experimentally supported, but it doesn't encode a protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:4356; | cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165] | 13679854_MPP3, a human homologue of a Drosophila tumor suppressor gene (Discs large), associates with TSCL1, a tumor suppressor gene. 16519681_These data implicate a role for MPP3 in photoreceptor polarity and, by association with MPP5, pinpoint MPP3 as a functional candidate gene for inherited retinopathies. 17669239_TSLC1 strongly inhibits the growth of HepG2 cells in vitro and induces apoptosis. 23011156_Data suggested that epigenetic inactivation of MPP3 frequently occurred during the development of colorectal cancer and might also be a potential biomarker for molecular classification of colorectal cancer patients. 24503895_MPP3 and Dlg, membrane-associated guanylate kinase homologs (MAGuK) proteins, connect CADM1 with p85 of PI3K by forming a multi-protein complex at the periphery of cells. 24513266_MPP3 plays an important role in hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by promoting cell migration and invasion via up-regulating MMP1 25780926_a central role of CADM1 in stabilizing the complex with 4.1B and MPP3 | ENSMUSG00000052373 | Mpp3 | 30.184945 | 0.344739679 | -1.536421 | 0.57650932 | 6.650872 | 0.0099107334243480216945387795135502528864890336990356445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0491426228783339719141665113966155331581830978393554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 13.8868476 | 5.6767622 | 40.5311635 | 16.4745355 | ||
| ENSG00000161835 | 160622 | TAMALIN | protein_coding | Q7Z6J2 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in intracellular trafficking and contributes to the macromolecular organization of group 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) at synapses. {ECO:0000250}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Reference proteome;Synapse | This gene encodes a protein that functions as a molecular scaffold, linking receptors, including group 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors, to neuronal proteins. The encoded protein contains conserved domains, including a leucine zipper sequence, PDZ domain and a C-terminal PDZ-binding motif. Alternately spliced transcript variants have been observed for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2012]. | hsa:160622; | glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; regulation of neurotransmitter receptor transport, endosome to postsynaptic membrane [GO:0099152]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 17396155_The crystal structures of the autoinhibitory PDZ domain of Tamalin has implications for the regulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor trafficking. 20016009_protein-protein interaction mediated by ARNO coiled-coil domain required for ARNO induced motility; coiled-coil domain promotes assembly of multiprotein complex containing ARNO and Dock180; assembly of complex requires coiled-coil domain, GRASP and IPCEF 22523075_the structural basis of the phosphoinhibition of GRASP-mediated membrane tethering and provide a mechanism for its allosteric regulation. 22931251_GRASP regulates the non-clathrin/Arf6-dependent, plasma membrane recycling and signalling pathways. 23441967_GRASP bridges the guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) that activate Arf and Rac, thereby promoting Arf-to-Rac signaling By binding to both cytohesin 2/ARNO and Dock180. 24505136_myristoylated GRASP promoted tethering and exhibited a unique membrane complex. Thus, myristoylation restricts the membrane orientation of the GRASP domain favoring interactions in trans for membrane tethering. 26048293_Schizophrenia subjects compared to controls showed a marked increase in CA1 hippocampal Norbin, and Tamalin proteins (47% and 34% respectively), which are endogenous regulators of mGluR5 signalling and trafficking 32376687_The post-synaptic scaffolding protein tamalin regulates ligand-mediated trafficking of metabotropic glutamate receptors. | ENSMUSG00000000531 | Tamalin | 9.648599 | 0.383372984 | -1.383179 | 0.52314487 | 7.139685 | 0.0075396380841834236691267889796108647715300321578979492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0398430137973395312456226236008660634979605674743652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 4.9786634 | 4.1117007 | 13.0223390 | 10.4794476 | |
| ENSG00000162591 | 1953 | MEGF6 | protein_coding | O75095 | Alternative splicing;Calcium;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal | Predicted to enable calcium ion binding activity. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:1953; | extracellular region [GO:0005576]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509] | 29719292_MEGF6 accelerated Colorectal Cancer cell growth and inhibited apoptosis, and promoted Colorectal Cancer metastasis by inducing the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. 33026655_A role for the MEGF6 gene in predisposition to osteoporosis. | ENSMUSG00000057751 | Megf6 | 191.673077 | 0.279283623 | -1.840197 | 0.58261043 | 8.870309 | 0.0028984610924569663079064518740324274403974413871765136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0183538586515563824363983513876519282348453998565673828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 75.9922179 | 22.0694126 | 272.4577600 | 78.7406274 | ||
| ENSG00000163395 | 91156 | IGFN1 | protein_coding | Q86VF2 | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Immunoglobulin domain;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat | Predicted to be involved in homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules; retina layer formation; and synapse assembly. Predicted to be located in Z disc and nucleus. Predicted to be active in synapse. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:91156; | nucleus [GO:0005634]; synapse [GO:0045202]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; retina layer formation [GO:0010842]; synapse assembly [GO:0007416] | 18756455_a model in which this increased expression of IGFN1 serves to down-regulate protein synthesis via interaction with eEF1A during denervation. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 29323771_A novel variant, c.6196A>G in the IGFN1 gene, was significantly associated with only Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (combined p = 7.1 x 10(-11) , odds ratio = 9.44), but not with neovascular age-related macular degeneration(combined p = 0.683, odds ratio = 1.30). 30335789_Study results in UOK146 renal cell carcinoma cell line provide evidence of novel splicing in intron 15 of IGFN1 leading to the formation of two more alternative spliced isoforms. Potential G-quadruplex forming sequence (PQS) in this intron forms a stable G-quadruplex which is involved in the alternative splicing and regulates splicing efficiency. | ENSMUSG00000051985 | Igfn1 | 8.708441 | 0.084497813 | -3.564942 | 0.75152372 | 28.362723 | 0.0000001005835889135273731440534290826338548185958643443882465362548828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000019733004792740824563169240585258634723686554934829473495483398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 1.4271794 | 0.8163690 | 17.1873299 | 6.7201189 | ||
| ENSG00000163406 | 6565 | SLC15A2 | protein_coding | Q16348 | FUNCTION: Proton-coupled amino-acid transporter that transports oligopeptides of 2 to 4 amino acids with a preference for dipeptides (PubMed:7756356, PubMed:18367661). Transports the dipeptide-like aminopeptidase inhibitor bestatin (By similarity). Can also transport the aminocephalosporin antibiotic cefadroxil (By similarity). Also able to transport carnosine (PubMed:31073693). Involved in innate immunity by promoting the detection of microbial pathogens by NOD-like receptors (NLRs) (By similarity). Probably acts by mediating transport of bacterial peptidoglycans across the plasma membrane: catalyzes the transport of certain bacterial peptidoglycans, such as muramyl dipeptide (MDP), the NOD2 ligand (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P46029, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63424, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ES07, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18367661, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31073693, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7756356}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Membrane;Peptide transport;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | The mammalian kidney expresses a proton-coupled peptide transporter that is responsible for the absorption of small peptides, as well as beta-lactam antibiotics and other peptide-like drugs, from the tubular filtrate. This transporter, SLC15A2, belongs to the same gene family as SLC15A1 (MIM 600544), the proton-coupled peptide transporter found in the small intestine (Liu et al, 1995 [PubMed 7756356]).[supplied by OMIM, Feb 2011]. | hsa:6565; | apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; dipeptide transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0071916]; peptide:proton symporter activity [GO:0015333]; dipeptide import across plasma membrane [GO:0140206]; dipeptide transport [GO:0042938]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; peptidoglycan transport [GO:0015835]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; regulation of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing signaling pathway [GO:0070424]; renal absorption [GO:0070293]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104]; xenobiotic detoxification by transmembrane export across the plasma membrane [GO:1990961]; xenobiotic transport [GO:0042908] | 11944083_the two identified aminoterminal regions in mammalian peptide carriers play an important role in determining the substrate affinity and also other characteristic features of the two transporter subtypes. 12579467_expression, localization and functional aspects of this protein in the normal respiratory tract and in cystic fibrosis 15020234_Amino acid substitution at Arg57 in PEPT2 causes a complete loss of transport function. 15282265_polymorphisms in the gene encoding hPEPT2 can alter substrate transport and therefore could affect drug disposition in vivo 15626774_expression and function of the peptide transporter PepT2 (SLC15A2) in differentiated primary cultures of upper airway lung epithelia 15981923_functionalities of PEPT1 and PEPT2 were largely conserved in terms of glycylsarcosine uptake kinetics and inhibitor specificity 16738539_PEPT2-PDZK1 interaction thus plays a physiologically important role in both oligopeptide handling as well as peptide-like drug transport in the human kidney 18367661_does not operate as a cotransporter in tissues where there is little or no pH gradient, such as choroid plexus, lung, or mammary gland 18474668_PEPT2 plays a vital role in microbial recognition by nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptor proteins 18668438_PEPT2 to be the dominant transporter for the reabsorption of di- and tripeptides and its pharmacological substrates in the organism, and for the removal of these substrates from the cerebrospinal fluid 18713951_there are no major differences in the substrate recognition pattern of hPEPT1 and rPEPT2 with regard to the ACE inhibitors tested. 18762712_the expression/activity of PEPT2 may be a critical factor in the modulation of opioidergic neurotransmission in vivo. 18766334_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18766334_PEPT2 polymorphism distributions differ significantly between Chinese, Malay and Asian Indian populations. Cephalexin pharmacokinetics were not different between Chinese and Asian Indians. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19246733_hPEPT1 and hPEPT2 are unlikely to contribute to clinically important drug interactions in humans. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19723536_Higher blood lead burden in children with the PEPT2*2 mutation may suggest that this common genetic variant is a biomarker of increased vulnerability to the neurotoxic effects of lowest level lead exposure. 19723536_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19898482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20067523_anserine is recognized by the proton-coupled peptide transporters PEPT1 and PEPT2 with medium affinity. Anserine is able to displace other substrates from the transport process. 20173083_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20406817_Data identify Drosophila Yin and PEPT2 as evolutionarily conserved phagosome-associated transporters. 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20868728_PepT2-mRNA is expressed in U373-MG and glial cells but showed no regulation of PepT2-mRNA expression in both cell types. 21327641_ALAD2 and hPEPT2*2 polymorphisms may exaggerate Pb blood burden in boys. 21366347_PEPT1,PEPT2, PHT1, and PHT2 are expressed in human nasal epithelium. 22950754_LNCaP expresses high levels of PEPT2 and PHT1. 23934551_JAK3 is a powerful regulator of the peptide transporters PEPT1 and PEPT2. 25514583_This study showed that ALAD2 and hPEPT2*2 may be valuable markers of risk, and indicate novel mechanisms of lead-induced neurotoxicity 25531100_OSR1 has the capacity to downregulate the peptide transporters PEPT1 and PEPT2 by decreasing the carrier protein abundance in the cell membrane 25965825_In vitro study displayed different response to sorafenib depending on the genotype of SLC15A2. 26168863_PEPT2 is functionally expressed in H441 cells, making the cell line a good in vitro model to study PEPT2 function and its regulation in human distal lung. 27216463_PEPT2 is expressed in keratinocytes and involved in skin oligopeptide uptake. 29234073_Two novel genes, SLC15A2 (rs1143671 and rs1143672) and SLCO1B3 (rs4149117 and rs7311358), are associated with the warfarin maintenance dose in a Chinese population. 31073693_The transporters PEPT2, PHT1, and PHT2 are responsible for the uptake of carnosine into glioblastoma cells and full function of all three transporters is required for maximum uptake. 31757425_Alternate expression of PEPT1 and PEPT2 in epidermal differentiation is required for NOD2 immune responses by bacteria-derived muramyl dipeptide. | ENSMUSG00000022899 | Slc15a2 | 29.406515 | 0.405795458 | -1.301175 | 0.47409803 | 7.293712 | 0.0069196377825296289526546544834673113655298948287963867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0371276920989737080347481423814315348863601684570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 18.3506587 | 5.1388314 | 44.8934469 | 12.5607241 | |
| ENSG00000163605_ENSG00000255423 | 66.199917 | 2.178906453 | 1.123604 | 0.41502598 | 7.163587 | 0.0074398260641408871240987110695641604252159595489501953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0394496918063694940181918013877293560653924942016601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 79.4234202 | 24.2600063 | 35.1310977 | 10.9382785 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000163617 | 57577 | CCDC191 | protein_coding | Q8NCU4 | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome | hsa:57577; | ENSMUSG00000022701 | Ccdc191 | 34.476381 | 0.216397546 | -2.208244 | 0.76805838 | 7.535154 | 0.0060506555335021645902759956925365258939564228057861328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0335061637381742979946430693871661787852644920349121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 15.6894234 | 7.9265857 | 71.4013334 | 35.8076322 | |||||
| ENSG00000163739 | 2919 | CXCL1 | protein_coding | P09341 | FUNCTION: Has chemotactic activity for neutrophils. May play a role in inflammation and exerts its effects on endothelial cells in an autocrine fashion. In vitro, the processed forms GRO-alpha(4-73), GRO-alpha(5-73) and GRO-alpha(6-73) show a 30-fold higher chemotactic activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10095777}. | 3D-structure;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Growth factor;Inflammatory response;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | This antimicrobial gene encodes a member of the CXC subfamily of chemokines. The encoded protein is a secreted growth factor that signals through the G-protein coupled receptor, CXC receptor 2. This protein plays a role in inflammation and as a chemoattractant for neutrophils. Aberrant expression of this protein is associated with the growth and progression of certain tumors. A naturally occurring processed form of this protein has increased chemotactic activity. Alternate splicing results in coding and non-coding variants of this gene. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome 4. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. | hsa:2919; | extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; CXCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0045236]; enzyme activator activity [GO:0008047]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 11816717_GRO-alpha levels in blood, quantities released from platelets ex vivo, and quantities released from SFFLRN stimulated platelets ex vivo were compared for preeclamptic and normal pregnancies. 12012624_may play a role in the pathogenesis of endometriosis, possibly by chemoattraction and activation of neutrophils present in higher numbers in the peritoneal fluid of women with endometriosis 12388718_mediates angiogenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma 12734381_Eosinophils produce large amounts of the CXC chemokine GRO-alpha, which may be important during resolution of inflammation and may explain the interaction between eosinophils and certain tumors. 12744776_The role of GROa in cultured nasal epithelial cells was studied for its ability to synthesize and deliver neutrophil chemotactic factors following TNF-alpha induction. 12949249_This protein displays antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus. 14530367_Recombinant GROalpha induces articular chondrocyte hypertrophy and calcification through p38 MAP kinase and transglutaminase 2. 15218300_expression of GRO-1 in 9 oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell lines and 94 OSCC specimens; findings suggest a possible relationship between the expression level of GRO-1 and tumor progression 15492419_This suggests that GRO-alpha plays a role in the infiltration of neutrophils into the lesional skin and in bulla formation in linear IgA bullous dermatosis. 15843053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15994316_KC (CXCL1) mRNA is regulated by functionally independent AU-rich sequence motifs 16086366_We propose that the concurrence of CXCR2 on oligodendrocytes and induced CXCL1 on hypertrophic astrocytes in MS provides a novel mechanism for recruitment of oligodendrocytes to areas of damage, an essential prerequisite for lesion repair. 16098041_endothelin-1 (ET-1) induces CXCL1 and CXCL8 secretion in three human melanoma cell lines 16567391_CXCL1 released from prostaglandin E2-treated carcinoma cells induces microvascular endothelial cell migration and tube formation in vitro. 16617094_IL-1beta- and TNF-alpha-stimulated expression of GRO-alpha from airway smooth muscle is regulated by independent pathways involving NF-kappaB activation and ERK and JNK pathways 16941962_GRO-1 can promote tumor growth and metastasis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 17022986_LDL lipoprotein subunit L5 induces human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) to express GRO-alpha. 17060621_Gro-1 may be a therapeutic target as well as a diagnostic marker in ovarian cancer 17062666_Coexpression of fibulin-1 with GROalpha abrogates key aspects of the transformed phenotype, including colonic tumor formation in a murine xenograft model. 17096385_GROalpha led to p38 MAPK activation in chondrocytes cultured in micromass but not as a high-density monolayer. This caused the downstream triggering of chondrocyte hypertrophy and apoptosis/anoikis following concurrence of matrix degrading activity. 17456471_CX3CR1 and CX3CL1 mediate heterotypic anchorage of foam cells to coronary artery smooth muscle cells in the context of atherosclerosis 17466952_Inhibition of ERK decreased expression of Groa. 17581194_PAR-2 plays a role in serine protease-mediated regulation of IL-8 and GRO-alpha in nasal epithelial cells and may be involved in the pathophysiology of rhinosinusitis. 17703315_During treatment of ulceretive colitis with corticosteroids CXCL1/CXCL9 were decreased. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17999991_rease of CXCL1 and -2 mediated by Curcumin is involved in the inhibition of metastasis in breast cancer cells. 18056965_GRO-alpha may be a novel diagnostic marker for age-related pathology, including cancer. 18065201_The production of GRO-alpha, IL-6 and IL-8 was shown to account for the ability of the HeLa cell culture medium to stimulate the migration of monocytes/macrophages, suggesting a key role for p38 MAPK and ERK1/ERK2. 18211687_In addition to transcriptional up regulation of CXCL1, these primary cells exhibited the greatest IL-8 secretion and cell damage in response to stimulation with an acapsular strain of C. neoformans. 18276907_GROalpha could be involved in atherogenesis and plaque destabilization, potentially contributing to inflammation, matrix degradation, and lipid accumulation within the atherosclerotic lesion. 18283335_CXCL1 secreted by endothelial cells induces tumor cell invasion 18451219_results suggest that CXCL1 modulates the invasive abilities of bladder cancer cells and this chemokine may be a potential candidate of urinary biomarker for invasive bladder cancer and a possible therapeutic target for preventing tumor invasion 19103522_observed that CCL4, CXCL1 and CXCL8 secretion, following PROK1 induction 19176759_Vascular endothelial growth factor induces protein kinase D-dependent production of proinflammatory cytokine GRO-alpha in endothelial cells. 19258312_a novel mechanism by which mutant p53 acquires its gain of function via transactivating the GRO1 gene in cancer cells. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19430878_Data show that oral fibroblasts respond to LPS stimulation by increasing GROalpha production via the transcription factor NF-kappaB, suggesting that this mechanism may be involved in development of periodontal inflammation. 19435811_Results indicate that EGR-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB mediate GRO/CXCR2 proliferative signaling in esophageal cancer and may represent potential target molecules for therapeutic intervention. 19549892_Data show that expression of CXCL1 and its receptor, CXCR2, are elevated in cancer tissue compared with normal endometrium. 19780053_The expression levels of four of the up-regulated genes, CXCL1, SPARC, SPP1 and SULF, were significantly higher in the cancerous tissue compared with the normal tissue (fold change 3.4-8.9). 19838218_Data show that the knockdown of Ron in PC-3 or DU145 cells results in a significant decrease in angiogenic chemokine production and is associated with a decreased activation of NF-kappaB. 19906815_Lysophosphatidic acid mediates trophoblast cells to produce GRO-alpha, IL-8, and MCP-1 via LPA1 receptors and nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent signal pathways. 20042592_CXCL1 transgene mRNA stabilization is dependent on AUUUA-containing sequence motifs that are recognized by the RNA binding protein tristetraprolin. 20195728_PGI(2) analogues enhanced LPS-induced GRO-alpha expression via the IP receptor-cAMP and p38-MAPK pathways in human dendritic cells. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20495539_Aberrant expression of selectin E, CXCL1, and CXCL13 occurs in chronic endometritis. 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20621720_We conclude that primary human thymic epithelial cells produce GRO-alpha and that its expression is regulated primarily by autocrine IL-6 and IL-6-activated Jak2 signaling. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20685145_Our findings suggest up-regulation of GRO-alpha and down-regulation of RANTES at the onset of a septic episode in premature and term neonates. 20702723_CXCL1 functions through CXCR2 to transactivate theefgr by proteolytic cleavage of HB-EGF, leading to activation of MAPK signaling and increased proliferation of epithelial ovarian cancer cells. 20731665_Within gastric cancer patients, CXCL1 serum levels increased according to tumor stage and lymph node metastasis. 21042742_GRO-alpha may play a pivotal role in the invasion of human colorectal cancer. 21075844_Serglycin is a major proteoglycan in polarized human endothelial cells and is implicated in the secretion of the chemokine GROalpha/CXCL1. 21220697_Chemokines CCL2, CCL8, CXCL1, and CXCL2 rank highest among signaling and inflammatory genes significantly enriched in human antigen R (HuR) ribonucleoprotein from stimulated airway epithelial cells compared to controls. 21257927_Fas induces KC release by a mechanism requiring MyD88, mitogen-activated protein kinases, and likely activator protein-1 21343381_Cancer cells expressing CXCL1 stably exhibited an increase in their migration and invasion ability, whereas CXCL1 or CXCR2 depletion significantly reduced the migration and invasion ability of each cell line. 21396766_GROalpha regulates human embryonic stem cell self-renewal or adoption of a neuronal fate 21531038_GRO-alpha and IP-10 are the predominant CXC chemokines involved in neutrophil and activated T lymphocyte chemoattraction in endogenous uveitis, particularly in Behcet's disease 21820916_IL-8 and GRO-alpha were measured by enzyme immunoassay in the first 48 h. After multiple regression analysis only absence of preeclampsia was associated with high IL-8 levels 21928244_Serum CCL18 and CXCL1 are potentially useful as novel circulating tumor markers for the differential diagnosis between ovarian cancer and benign ovarian masses. 21994122_CD133(+) liver tumor-initiating cells promote tumor angiogenesis, growth, and self-renewal through neurotensin/interleukin-8/CXCL1 signaling. 22030312_The induction of IL-6, CXCL1 and CXCL8 upon the interaction of bronchial epithelial cells with mast cells was mediated by MAPKs and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. 22069268_elevated serum CXCL1, indicating a predisposition to autoimmunity, is a good marker of T1DM risk 22125641_Data show that tumour conditioned media obtained from cultured colorectal tumour explant tissue contained high levels of the chemokines CCL2, CXCL1, CXCL5 in addition to VEGF. 22129625_Down-regulation of CXCL1 resulted in a nearly complete prevention of tumor growth. 22173151_CXCL1 rs4074 A allele as a genetic risk factor for cirrhosis progression in hepatitis C. 22183310_CCL2-CCR2 and CX3CL1-CX3CR1 signaling are involved in age related macular degeneration. 22251138_Vitamin D3 oppositely regulated the expression of Growth-related oncogene-alpha in THP-1 cells in vitro and human primary monocytes ex vivo via different intracellular signal pathways. 22615136_Suppression of CXCL1 and CXCL2 by siRNA or by progesterone and calcitriol inhibits endometrial and ovarian tumor cell invasiveness. 22732298_Seminal plasma rapidly enhanced the expression of the angiogenic chemokines, interleukin (IL)-8 and growth regulated oncogene alpha (GRO) in HeLa cells. 22770218_Study uncovered a paracrine network, with the chemokines CXCL1 and 2 at its core, that mediates lung metastasis and chemoresistance in breast cancer. 22902060_IL-17A produced by neutrophils stimulates Gro-alpha secretion from endometrial stromal cells, thereby recruiting more neutrophils and inducing perpetuating inflammation in endometriosis. 22975476_CXCL1 was elevated in acute lymphoblastic leukemia and decreased after bone marrow transplantation. 23027620_CXCL1/GROalpha increases cell migration and invasion of prostate cancer by decreasing fibulin-1 expression through NF-kappaB/HDAC1 epigenetic regulation. 23043537_Upregulation of IL-6, IL-8 and CXCL-1 production in dermal fibroblasts by normal/malignant epithelial cells in vitro: Immunohistochemical and transcriptomic analyses. 23052840_The silencing of the pro-angiogenic chemokine GRO-alpha is proportionally correlated with decreased expression of CXCR2 in pro-inflammatory cytokine-stimulated SGEC indicating the GRO-alpha/CXCR2 complex as a novel therapeutic target for Sjogren's syndrome. 23198952_The CXCL1 gene and particularly T allele of rs3117604 was associated with ischemic stroke. 23207068_Cowpox virus but not Vaccinia virus induces secretion of CXCL1, IL-8 and IL-6 and chemotaxis of monocytes in vitro. 23225384_This study demonistrated that CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, CXCL8, and CXCL11, absent from normal muscle fibers, were induced in DMD myofibers. 23269549_Data indicate that in NIH3T3 cells expressing unsulfated vGPCR mutant (yydd-vGN) but not vGPCR (wt-vGN) could significantly inhibit the tumor growth triggered by hGRO-alpha. 23334998_When expressed, CXCL1 is limited to small areas with faint staining and PCa progression does not rely on CXCL1 expression. 23389772_findings of the current study suggest a broad involvement of the chemokine GRO-alpha/CXCR2 system in Sjogren's syndrome pathogenesis that is mediated by the involvement of ADAM17 23444042_A novel miRNA, miR-7641, significantly suppressed CXCL1 expression in embryonic stem cells. 23479735_Chemokine CXCL1 dimer is a potent agonist for the CXCR2 receptor. 23502337_decreased serum levels in patients with alopecia areata 23505918_Elevated levels of CXCL1 and CXCL10 could possibly be used as a marker of inflammation and angiogenesis/angiostasis in type 2 diabetes 23519936_sequence-linked, post-transcriptional activities provide substantial mechanistic diversity in the control of GRO family chemokine gene expression. 23554905_Neutrophil priming led to the rapid expression of a common set of transcripts for cytokines, chemokines and cell surface receptors (CXCL1, CXCL2, IL1A, IL1B, IL1RA, ICAM1). 23567329_CXCL1 mRNA expression was significantly higher in the lymphocytes of Thromboangiitis obliterans patients than control subjects. 23665907_VEGF markedly induces CXCL1 release in A549 lung epithelial cells. 23732813_expressed and secreted from endothelial cells 23815949_this is the largest study describing increased CXCL1 protein expression in more aggressive phenotypes in human bladder cancer 23890481_Normal keratinocytes and cancer cells can stimulate the CXCL-1 secretion from normal dermal fibroblasts and stromal fibroblasts from squamous cell carcinoma. 23953856_CXCL1 is a target for the embryos' secretion product IL-1beta in decidualised endometrial stromal cells during the peri-implantation period. 23967336_CXCL1 expressed by monocytes and CXCR2 on HBMEC is involved in monocytes migrating from blood to brain in AD patients 24023680_IgA1 complexes from IgA nephropathy patients could up-regulate the secretion of CXCL1 and TGF-beta1 in mesangial cells. 24250750_Expression of the CXCL8, CXCL6 and CXCL1 genes are under the primary control of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its receptor. 24260493_The rs4074 single nucleotide polymorphism within the CXCL1 gene is associated with increased CXCL1 blood levels and increased risk for development of cirrhosis in alcoholics. 24273934_IL-1alpha regulated its sub-network genes including CXCL1, CXCL10, and ICAM1 mRNA levels in time dependent but not in concentration dependent manner 24487964_TNF-alpha stimulates CXCL1 release from human endothelial cells through JNK-mediated CXCL1 mRNA expression and p38 MAPK- and PI-3K-mediated CXCL1 secretory processes. 24581860_Four genes showed increased expression in the epithelium of OLP patients: CD14, CXCL1, IL8, and TLR1, and at least two of these proteins, TLR1 and CXCL1, were expressed at substantial levels in oral keratinocytes. 24588865_CXCL1 is a negative regulator of mast cell chemotaxis to airway smooth muscle cell products in vitro. 24600982_findings of this study demonstrated that serum concentrations of CXCL1 and CXCL12 were elevated in SCD patients when compared with controls 24619879_Increased CXCL1/CXCL8 instigated polymorphonuclear leukocyte adhesion to cerebral microvascular endothelial cells, possibly contributing to Diabetic ketoacidosis-associated intracranial vascular complications. 24981451_CXCL1 inhibits airway smooth muscle cell migration via activation of the ERK-1/2 MAP kinase pathway. 24999605_High CXCL1 stromal protein expression is highly specific for the tumorous transition in cases of sporadic colorectal neoplasias. 25135733_The present study showed that nasal fibroblasts can produce GRO-alpha and IL-8, and their production is remarkably enhanced by IL-17 stimulation, thereby clarifying the mechanism of the IL-17 mediated neutrophil infiltration in nasal polyps. 25175281_CXCL1 expression was a negative prognostic factor. 25301363_The released CXCL1 enhanced monocyte migration. 25344051_Elevated CXCL1 expression in breast cancer stroma predicts poor prognosis and is inversely associated with expression of TGF-beta signaling proteins. 25349304_miR141-CXCL1-CXCR2 signaling-induced Treg recruitment regulates metastases and survival of non-small cell lung cancer. 25383568_In CSF, CXCL1 is up-regulated in opioid-tolerant patients (and rodents). 25393692_SF of BC OA displayed significantly higher concentrations for a number of proinflammatory cytokines [CXCL1, eotaxin, interferon (IFN)-gamma, interleukin (IL)-7, IL-8, IL-9, IL-12]. 25471749_Intense glomerular CXCL1 expression was observed in biopsy specimens from patients with lupus nephritis 25641338_CXCL1 increases local tumor growth through activation of VEGF signaling. 25766782_There was a significant positive correlation between CXCL-1 levels in the vitreous and the extent of the retinal detachment. 25802102_CXCL1 and CXCL2 chemokines stimulate osteoclast differentiation in vitro 25816025_urinary CXCL1 as a new non-invasive predictor of IgAN progression 25930080_CXCL1 expression was highly upregulated in patients with alcoholic hepatitis. 26104296_High CXCL1 expression is a poor prognostic biomarker in metastatic colorectal cancer. 26252654_TGF-beta negatively regulates CXCL1 expression in CAFs through Smad2/3 binding to the promoter, and through suppression of HGF/c-Met autocrine signaling 26341115_increased amounts released by neutrophils from fibromyalgia patients 26345899_Polymorphisms in the promoter regions of the CXCL1 and CXCL2 genes contribute to increased risk of alopecia areata in the Korean population 26349659_The novel findings reveal the critical role of NLRP12-IL-17A-CXCL1 axis in host defense by modulating neutrophil recruitment against Klebsiella pneumoniae. 26397389_BBP also stimulated the production of CXCL1/GROalpha by TADCs, which increased the angiogenesis of breast cancer in a mouse model 26406865_Urine CXCL1 is a promising, non-invasive molecular marker for tumor detection and outcome prediction in patients with bladder cancer . 26499374_these findings suggest that CXCL1 plays critical roles in the growth and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma 26503598_CXCR2-CXCL1 axis is correlated with neutrophil infiltration and predicts a poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma 26721883_hCXCL1-GAG interactions provide stringent control over regulating chemokine levels and receptor accessibility and activation, and that chemotactic gradients mediate cellular trafficking to the target site. 27049944_work shows parallel networks of necroptosis-induced CXCL1 and Mincle signalling that promote macrophage-induced adaptive immune suppression and thereby enable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression 27092462_Results suggest that CXCL1 is a key molecular link between senescence of stromal fibroblasts and tumor growth. 27190986_the serum levels of the soluble factors sCD40L and CXCL1 are not associated with endometriosis and are not suitable as biomarkers for disease diagnosis. 27241286_Adipose stromal cells recruitment to tumours, driven by CXCL1 and CXCL8, promotes prostate cancer progression. 27297392_Increased IL-8 and CXCL1 transcription in T84 and THP-1 cells compared to that in wild-type EPEC. 27446967_These results demonstrate that tumor-derived CXCL1 contributes to TANs infiltration in lung cancer which promotes tumor growth. 27472713_Elevated expression of GRO-alpha in cytoplasm of cancer cells (hazard ratio [HR] = 5.730, P = 0.007) and stroma (HR = 3.120, P = 0.022) were independent prognostic factors of pancreatic cancer. T classification (HR = 2.130, P = 0.023), lymphatic metastasis (HR = 4.211, P = 0.009) and TNM classification (HR = 0.481, P = 0.031) were also prognostic predictors in PC patients. 27542259_we identified the microRNA miR-200a as a putative post-transcriptional regulator of CXCL1 in hepatocellular carcinoma 27577959_IL-8, but not the CXCL1 circuit, is critical for the regulation of thyroid cancer stem cells. 27665197_this study shows that CXCL1 is expressed in epithelium of the endometrium with adenomyosis and demonstrate that VEGF is capable of inducing CXCL1 expression 27690238_CXCL1 signaling in the tumor microenvironment is highly responsible for repeated intravesical recurrence, disease progression, and drug resistance through enhanced invasion ability. In conclusion, disrupting CXCL1 signaling to dysregulate this chemokine is a promising therapeutic approach for human UCB. 27748927_Silencing of the CXCL1 gene inhibits HGC803 cell migration and invasion. The positive expression of CXCL1 is correlated with poor survival of gastric cancer patients and CXCL1 is an independent prognostic factor for gastric cancer. 27799352_These findings support a role for CXCL1 and IL-8 in cystic fibrosis lung disease severity and identify STAT3 as a modulating pathway. 27832972_CXCL1 secreted by tumor-associated lymphatic endothelial cells promotes lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer through integrin beta1/FAK/AKT signaling pathway. 27958346_the plasma concentrations of CXCL1 indicated the disease activity and prognosis in interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features (IPAF). Thus, the CXCL1/CXCR2 axis appears to be involved in the progression of IPAF. 28176455_The results of the transwell chemotaxis assay also supported the above results. Our data suggest that APN can promote h-JBMMSC chemotaxis by up-regulating CXCL1 and CXCL8 28375674_GROalpha high in the tumor microenvironment can be used as potential indicators for the progression of non-small cell lung cancer 28381820_S100A9 and S100A12 may have a role in the pathogenesis of pneumonia: S100A9 and CXCL1 may contribute solely in mild pneumonia, and CCL5 and CXCL11 may contribute in severe pneumonia. 28455419_Study provides the first evidence that primary malignant cell-secreted VEGFA stimulates tumor-associated macrophages to produce CXCL1, which recruits CXCR2-positive MDSCs to form a premetastatic niche to promote liver metastases. 28514506_CXCL1/8 secreted by adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells could promote breast cancer angiogenesis. 28518141_This study highlighted CAF-secreted CXCL1 as an attractive target to reverse tumor radioresistance. 28560447_GROA overexpression is associated with invasion in triple negative breast cancer. 28575019_The expressions of CXCL1 in cancer cells and CXCR2 in stromal cells are useful prognostic factors for gastric cancer patients 28637660_Taken together, the present study indicates that IL-33 localized in the human atherosclerotic plaque increases GRO-alpha mRNA expression and protein secretion via activation of ERK1/2, JNK, and NF-kappaB in HUVECs, suggesting that IL-33 plays an important role in the pathophysiology and development of atherosclerosis. 28831670_Thrombocytosis was more prevalent in patients with inflammatory breast cancer (IBC)than in those with non-IBC and it was associated with poor prognosis. GRO and TGF-beta were associated with thrombocytosis in IBC 28859336_This study describe elevated levels of CXCL1 and it receptor in the Solid Component and Cyst Fluid of Human Adamantinomatous Craniopharyngioma, relative to other pediatric brain tumors and normal cerebral tissue. 28870907_the presence of elevated circulating levels of VEGF and CXCL1 are predictive of liver and lung metastasis, respectively of colorectal cancer. 28960786_These results suggest that secretion of the myokine CXCL1 is stimulated by saturated fatty acids and that CXCL1 promotes myogenesis from satellite cells to maintain skeletal muscle homeostasis. 29283424_miR-204 inhibits cell proliferation in gastric cancer by targeting CKS1B, CXCL1 and GPRC5A. 29360827_study demonstrates that CXCL1 can transform NOFs into senescent CAFs via an autocrine mechanism 29369549_Association of polymorphic markers of chemokine genes, their receptors, and CD14 gene with coronary atherosclerosis 29438938_CXCL1, which is produced by breast cancer cells, can promote cancer growth and development 29507619_Both GRO-alpha and IL-8 can activate TAK1/NFkappaB signaling via the CXCR2 receptor. 29520695_These results show that AKIP1 is crucial in cervical cancer angiogenesis and growth by elevating the levels of the NF-kappaB-dependent chemokines CXCL1, CXCL2, and CXCL8. 29784873_By inducing glycolysis, CXCL1 plays a crucial role in both cancer progression and metastasis in colorectal cancer patients. 30015110_CXCL1 gene expression was associated with the negative syndrome in non-deficit schizophrenia patients, while no association in deficit schizophrenia was observed. 30035347_GRO-alpha from OSF-associated fibroblasts paracrinally promotes oral malignant transformation and significantly contributes to OSCC development. 30115896_CXCL1 displays a specific microRNA (miR) upregulated by the prototypical colon cancer onco-miR miR-105. 30158589_TAMs/CXCL1 promotes breast cancer metastasis via NF-kappaB/SOX4 activation, and CXCL1-based therapy might become a novel strategy for breast cancer metastasis prevention. 30201019_The chemokine Gro1 induced in response to inflammation triggers senescence and arrests development of new neurons in the hippocampus and that the magnitude of this response is sex-dependent. 30230320_Distinct Differences in Structural States of Conserved Histidines in Two Related Proteins: NMR Studies of the Chemokines CXCL1 and CXCL8 in the Free Form and Macromolecular Complexes. 30259595_Results show that the expression of CXCL1 and CXCL2 in tumor cells and tumor-infiltrated CD11b+ myeloid cells is critically involved in the promotion of the generation of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (mo-MDSC) from bone marrow cells. CXCL1 and CXCL2 were found to specifically promote the expansion of mo-MDSC rather than granulocytic MDSC (G-MDSC). 30489503_The rs1429638 polymorphism in the CXCL1 gene and the rs2297630 polymorphism in the CXCL12 gene were associated with altered susceptibility to sepsis and might be used as important genetic markers to assess the risks of sepsis in trauma patients. 30514120_Among 29 immune and inflammatory proteins, CXCL1, CD84 and TNFRSF10A were associated with early post-acute coronary syndrome (ACS) after initial ACS-admission 30669188_CXCL1 and CSF3 levels are controlled by MAFF in myometrial cells. 30676127_Sputum CXCL1 levels in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease andasthma-COPD overlap patients were higher than in interstitial pneumonia 30705034_High CXCL1 expression is associated with Colorectal Cancer Progression. 30802327_CXCL1-dependent neutrophil transendothelial migration was not associated with neutrophil microtubule polymerization. 30809313_Taken together, these results argue that CXCL1 plays an important role in sustaining the growth of bladder and prostate tumors via up-regulation of IL6 and down-regulation of TIMP4. 30967059_Adiponectin treatment of ovarian cancer cells induces angiogenesis via CXC chemokine ligand 1 independently of vascular endothelial growth factor. These findings suggest that adiponectin may serve as a novel therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. 31147602_MicroRNAs (miRNAs) profiling of the EVs and the transfection experiment suggested that several miRNAs played a role in the induction of chemokines such as CXCL1 and CXCL8 in fibroblasts 31239384_vCXCL-1 increases mouse cytomegalovirus dissemination kinetics for both primary and secondary dissemination. We confirm the hypothesis that vCXCL-1 is a Human cytomegalovirus virulence factor 31322183_Findings revealed that the expression levels of CXCL1 were upregulated in ERnegative breast cancer. It was demonstrated that CXCL1 can stimulate tumor cell invasion via the ERK1/2/MMP2/9 pathway axis. 31387444_Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of CXCL1 in cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. 31500632_CXCL1-LCN2 axis is a key contributor to prostate cancer cells migration 31617252_A-kinase interacting protein 1 might serve as a novel biomarker for worse prognosis through the interaction of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1/chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 in acute myeloid leukemia. 31722447_CXCL1 is upregulated during the development of ileus resulting in decreased intestinal contractile activity. 32132577_Oxidative stress enhanced the transforming growth factor-beta2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through chemokine ligand 1 on ARPE-19 cell. 32187449_Elevation of CXCL1 indicates poor prognosis and radioresistance by inducing mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma. 32326946_Associations of CXCL1 gene 5'UTR variations with ovarian cancer. 32694172_Fusobacterium nucleatum host-cell binding and invasion induces IL-8 and CXCL1 secretion that drives colorectal cancer cell migration. 32782028_Tumor-suppressor miRNA-27b-5p regulates the growth and metastatic behaviors of ovarian carcinoma cells by targeting CXCL1. 32910411_Epithelial-stromal communication via CXCL1-CXCR2 interaction stimulates growth of ovarian cancer cells through p38 activation. 32968020_14-3-3zeta-TRAF5 axis governs interleukin-17A signaling. 33223508_Histone methyltransferase SETD2 inhibits tumor growth via suppressing CXCL1-mediated activation of cell cycle in lung adenocarcinoma. 33571109_Regulation of tumor immune suppression and cancer cell survival by CXCL1/2 elevation in glioblastoma multiforme. 33579221_A 4-gene signature predicts prognosis of uterine serous carcinoma. 33867350_MicroRNA-532-5p protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by directly targeting CXCL1. 33959656_CXCL1 Clone Evolution Induced by the HDAC Inhibitor Belinostat Might Be a Favorable Prognostic Indicator in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. 34049975_Apolipoprotein E Promotes Immune Suppression in Pancreatic Cancer through NF-kappaB-Mediated Production of CXCL1. 34269159_Expression levels of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligands CXCL1 and CXCL3 as prognostic biomarkers in rectal adenocarcinoma: evidence from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) analyses. 34403447_CXCL1: A new diagnostic biomarker for human tuberculosis discovered using Diversity Outbred mice. 34461944_Aiduqing formula inhibits breast cancer metastasis by suppressing TAM/CXCL1-induced Treg differentiation and infiltration. 34465514_Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote myeloid-derived suppressor cell enrichment by secreting CXCL1 to prevent graft-versus-host disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. 34860147_MicroRNA miR-145-5p regulates cell proliferation and cell migration in colon cancer by inhibiting chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 and integrin alpha2. 34961474_Chemokine CXCL1 as a potential marker of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. 35173310_EMT-mediated regulation of CXCL1/5 for resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer. 35421427_Mechanotransduction-induced glycolysis epigenetically regulates a CXCL1-dominant angiocrine signaling program in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo. 35481427_Adipose tissue from subjects with type 2 diabetes exhibits impaired capillary formation in response to GROalpha: involvement of MMPs-2 and -9. 35764974_High expression level of CXCL1/GROalpha is linked to advanced stage and worse survival in uterine cervical cancer and facilitates tumor cell malignant processes. 35864308_ROS-activated CXCR2(+) neutrophils recruited by CXCL1 delay denervated skeletal muscle atrophy and undergo P53-mediated apoptosis. 35958781_Expression and Prognostic Role of CXCL1 Gene in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma. 36434686_CXCL1 promotes colon cancer progression through activation of NF-kappaB/P300 signaling pathway. | 186.980277 | 0.487889069 | -1.035375 | 0.12442785 | 69.810841 | 0.0000000000000000652731530554042729474212993901884177335810590259851382555211785074789077043533325195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000036965217204007895078765111959282635671218599643372826335507852490991353988647460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 122.5708633 | 23.8206322 | 252.5205765 | 48.3371759 | |||
| ENSG00000164125 | 51313 | GASK1B | protein_coding | Q6UWH4 | Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Located in Golgi apparatus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:51313; | Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139] | 29217529_Data show that matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP-1) as a critical downstream target of golgi associated kinase 1B (FAM198B) and implicate FAM198B as a potential tumor suppressor and to be a prognostic marker in lung adenocarcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000027955 | Gask1b | 20.071327 | 0.322546992 | -1.632419 | 0.40380527 | 16.561779 | 0.0000470905800967758025876719329971820116043090820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0005248629756125099046076831754703562182839959859848022460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 9.4369504 | 4.0140713 | 29.3498276 | 11.8460630 | ||
| ENSG00000165300 | 26050 | SLITRK5 | protein_coding | O94991 | FUNCTION: Suppresses neurite outgrowth. {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Members of the SLITRK family, such as SLITRK5, are integral membrane proteins with 2 N-terminal leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domains similar to those of SLIT proteins (see SLIT1; MIM 603742). Most SLITRKs, including SLITRK5, also have C-terminal regions that share homology with neurotrophin receptors (see NTRK1; MIM 191315). SLITRKs are expressed predominantly in neural tissues and have neurite-modulating activity (Aruga et al., 2003 [PubMed 14557068]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:26050; | plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; synapse [GO:0045202]; adult behavior [GO:0030534]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; circulatory system development [GO:0072359]; dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048813]; grooming behavior [GO:0007625]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; regulation of presynapse assembly [GO:1905606]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; skin development [GO:0043588]; striatum development [GO:0021756] | 25426764_This study did not find any evidence supporting the association of Tourette syndrome and SLITRK5. 28085938_Mutation in SLITRK5 gene is Associated with Obsessive Compulsive Disorder 34326333_SLITRK5 is a negative regulator of hedgehog signaling in osteoblasts. 35579188_MUC21 controls melanoma progression via regulating SLITRK5 and hedgehog signaling pathway. 35872846_The Role of SliTrk5 in Central Nervous System. | ENSMUSG00000033214 | Slitrk5 | 73.547963 | 2.090042605 | 1.063532 | 0.21527213 | 24.295397 | 0.0000008263630517580468942654575194295407669642372638918459415435791015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000138433130155587558429404818061136950291256653144955635070800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 91.6354222 | 7.9753648 | 44.2242527 | 4.2142938 | |
| ENSG00000165698 | 11092 | SPACA9 | protein_coding | Q96E40 | Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cilium;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Cytoskeleton;Flagellum;Nucleus;Reference proteome | Predicted to enable calcium-dependent protein binding activity. Located in cytoplasmic microtubule. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:11092; | acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; ciliary base [GO:0097546]; cytoplasmic microtubule [GO:0005881]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; sperm flagellum [GO:0036126]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306] | 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 36191189_SPACA9 is a lumenal protein of human ciliary singlet and doublet microtubules. | ENSMUSG00000026809 | Spaca9 | 51.906170 | 19.773890482 | 4.305525 | 0.78898955 | 23.460698 | 0.0000012749178971285167936923401338367156654385325964540243148803710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000206168225954146738982970116227377843642898369580507278442382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 124.6762123 | 82.4420139 | 6.0323148 | 3.9739048 | ||
| ENSG00000166068 | 161742 | SPRED1 | protein_coding | Q7Z699 | FUNCTION: Tyrosine kinase substrate that inhibits growth-factor-mediated activation of MAP kinase (By similarity). Negatively regulates hematopoiesis of bone marrow (By similarity). Inhibits fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-induced retinal lens fiber differentiation, probably by inhibiting FGF-mediated phosphorylation of ERK1/2 (By similarity). Attenuates actin stress fiber formation via inhibition of TESK1-mediated phosphorylation of cofilin (PubMed:18216281). Inhibits TGFB-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lens epithelial cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q924S8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18216281}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleus;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Sprouty family of proteins and is phosphorylated by tyrosine kinase in response to several growth factors. The encoded protein can act as a homodimer or as a heterodimer with SPRED2 to regulate activation of the MAP kinase cascade. Defects in this gene are a cause of neurofibromatosis type 1-like syndrome (NFLS). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:161742; | caveola [GO:0005901]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0030291]; stem cell factor receptor binding [GO:0005173]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090051]; negative regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010719]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of lens fiber cell differentiation [GO:1902747]; negative regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043409]; negative regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0010801]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; positive regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:0043517]; regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043408]; regulation of protein deacetylation [GO:0090311]; vasculogenesis involved in coronary vascular morphogenesis [GO:0060979] | 15683364_We show here that Spred-1 and Spred-2 appear to have distinct mechanisms whereby they induce their effects, as the Sprouty domain of Spred-1 is not required to block MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) activation, while that of Spred-2 is required. 16652141_reduction of Spred expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the causes of the acquisition of malignant features. Thus, Spred could be not only a novel prognostic factor but also a new therapeutic target for human HCC 17672918_the apparent occurrence of an unusual TG 3' splice site in intron 1 is discussed 17704776_Studies show that the clinical features of the reported disorder resemble those of neurofibromatosis type 1 provide the first report of mutations of SPRED1 (SPROUTY)/SPRED family of genes) in human disease. 18216281_enhanced TESK1 activity results in increased stress fibers (via phospho-cofilin), but this can be blocked by elevating Spred1 19120036_Linkage analysis of SPRED1 excluded its involvement in Cafe-au-lait spots in a patient with a severe form of Noonan syndrome. 19366998_SPRED1 mutations occurred with a prevalence of 0.5% in NF1 patients and in 5% of NF1 patients displaying an NF1-like phenotype. 19443465_Unrelated mild NF1 patients were screened for mutations of the SPRED1-3 and the SPRY1-4 genes. SPRED1 mutations were identified in 6 cases. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19920235_A high SPRED1 mutation detection rate was found in NF1 mutation-negative families with an autosomal dominant phenotype of CALMs (cafe au lait macules)with or without freckling and no other NF1 features. 19920235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20179001_The frequency of SPRED1 mutations in patients meeting diagnostic criteria for neurofibromatosis 1 in a hospital-based clinic is 1% to 2%. The likelihood an individual is harboring a SPRED1 mutation increases with age. 20339110_no evidence of leukemogenic SPRED1 involement in juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21364986_Sprouty and Spred proteins are negative regulators of the ERK/Elk-1 pathway activation induced not only by growth-factors, but also by reactive lipidic mediators. 21531714_SPRED1 is a likely substrate of SHP2, whose tyrosine dephosphorylation is required to attenuate the inhibitory action of SPRED1 in the Ras/ERK pathway. 21616146_Interaction of FGFRL1 with Spred1 increases the proportion of the receptor at the plasma membrane. 21649642_a cohort of 115 NF1-like patients were screened for SPRED1 gene mutations and six mutations were identified. 12 potentially pathogenic SPRED1 mutations have been detected in 200 such NF1-like patients 22751498_show that neurofibromin, the NF1 gene product, is a Spred1-interacting protein that is necessary for Spred1's inhibitory function 22753041_Sixty-three mutations and deletions are definitely pathogenic or most likely pathogenic, eight SPRED1 mutations are probably benign rare variants, and 17 SPRED1 missense mutations are still unclassified. Review. 23016555_Based on our current understanding of KIT and SPRED1 protein interactions, we propose that cafe-au-lait macules and freckling may be seen in some patients with piebaldism and does not necessarily represent coexistence of neurofibromatosis type 1. 23811937_Data indicate that upregulated miR-126 upon coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) infection targets SPRED1, LRP6, and WRCH1 genes, mediating cross-talk between ERK1/2 and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways, and thus promoting viral replication. 23823658_Older age and deletions of IKZF1 and SPRED1 were also associated with poor overall survival of pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 24014835_Microrna-126 was transported into recipient human coronary artery endothelial cells by endothelial microparticles and functionally regulated the target protein sprouty-related, EVH1 domain-containing protein 1 (SPRED1). 24334617_SPRED1 seems to play an important role in recruiting neurofibromin to the plasma membrane. (Review) 24469042_SPRED1 decreased expression correlated with genetic features of AML. Our study reveals a new mechanism which contributes to deregulate RAS MAPK pathway in the vast majority of paediatric AMLs 25202123_Antisense-mediated knockdown (anti-miR) revealed that miR-206/21 coordinately promote RAS-ERK signaling and the corresponding cell phenotypes by inhibiting translation of the pathway suppressors RASA1 and SPRED1. 25981987_This study constitutes the first report from Japan of Legius syndrome occurring in siblings. Mutation analysis showed a mutation of c.349C>T resulting in p.Arg117* in exon 4. 26075267_Cosuppression of Sprouty and Sprouty-related negative regulators of FGF signalling in prostate cancer 26635368_Data suggest SPRED1 EVH1 domain interacts with NF1 GRD domain [N-term. 16AA/C-term. 20AA of GTPase-activating protein-related domain]; SPRED1 EVH1 and NF1 GRD mutations observed in Legius syndrome reduce binding affinity between EVH1/GRD domains. 27203443_Results provide genetic evidence that miR-126, through its target gene Spred-1, plays a critical role in the development of retinal vascular layers. 27313208_The EVH1 domain of Spred1 binds to the noncatalytic portion of the GAP-related domain of neurofibromin. 27748283_PURA may be a potential target of miR-144 and observed downregulation of PURA may be caused by increased expression of miR-144. The other predicted target of miR-144 SPRED1, was found to be downregulated in 69 per cent EC tissues as compared to matched distant non-malignant tissues. 28150585_In one case we identified a nonsense mutation c.46C>T (p.Arg16*) in exon 2 of SPRED1 gene, confirming diagnosis of Legius syndrome. This mutation was reported previously. 29685157_SPRED1 is down-regulated by E2 and negatively correlated to ER status in BC cells. SPRED1 was a new direct target of miR-196a which participated in miR-196a-promoted BC development and was suppressed by ligand-activated ER-alpha signal pathway. 30385465_this study establishes SPRED1 as a major tumor suppressor gene in mucosal melanoma. 30745814_Aberrant methylation statuses of the SPRED1 promoter regions are associated with the downregulation of gene transcription in acute myeloid leukemia. 31401120_These data provide structural insight into the interaction of Spred1 and neurofibromin. 32575496_Simultaneous Detection of NF1, SPRED1, LZTR1, and NF2 Gene Mutations by Targeted NGS in an Italian Cohort of Suspected NF1 Patients. 32773772_Constitutional mismatch repair deficiency is the diagnosis in 0.41% of pathogenic NF1/SPRED1 variant negative children suspected of sporadic neurofibromatosis type 1. 33073945_A Study on the Expression of SPRED1 and PBRM1 (Baf180) and their Clinical Significances in Patients with Gastric Cancer. 33078527_Moyamoya syndrome in a child with Legius syndrome: Introducing a cerebral vasculopathy to the SPRED1 phenotype? 33306107_SPRED1 deletion confers resistance to MAPK inhibition in melanoma. | ENSMUSG00000027351 | Spred1 | 297.475484 | 2.122695335 | 1.085897 | 0.14774447 | 53.314181 | 0.0000000000002842471701835501032160414071040458510656982749065235793750616721808910369873046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000110139873034002750076816649431570970668614606324808846693485975265502929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 421.4988001 | 33.1499064 | 199.0437361 | 16.3707007 | |
| ENSG00000166104 | transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene | 37.245226 | 0.422985585 | -1.241320 | 0.28975249 | 18.623418 | 0.0000159252226099019653299867366191833184529969003051519393920898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0002005400526956699314932303090941445589123759418725967407226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 28.5700236 | 8.5018279 | 68.9549087 | 19.6461790 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000166396 | 8710 | SERPINB7 | protein_coding | O75635 | FUNCTION: Might function as an inhibitor of Lys-specific proteases. Might influence the maturation of megakaryocytes via its action as a serpin. | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Palmoplantar keratoderma;Phosphoprotein;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Serine protease inhibitor | This gene encodes a member of a family of proteins which function as protease inhibitors. Expression of this gene is upregulated in IgA nephropathy and mutations have been found to cause palmoplantar keratoderma, Nagashima type. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2014]. | hsa:8710; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; negative regulation of endopeptidase activity [GO:0010951]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of glomerular mesangial cell proliferation [GO:0072126]; positive regulation of platelet-derived growth factor production [GO:0090362]; positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta1 production [GO:0032914] | 12386281_Mesangial cell-predominant gene, megsin. Genetic manipulation of megsin engenders two elementary mesangial lesions, mesangial expansion and an increase in the number of mesangial cells. 12397041_One positive regulatory motif, an incomplete activator protein-1 binding motif (CTGATTCAC) within the -120 to -112 region. This cis-acting element in the 5'-flanking region of megsin is involved in the activation of the megsin gene in mesangial cells. 15213261_Megsin has a role in susceptibility to immunoglobulin A nephropathy 15788472_in transgenic rats, overexpression of human megsin, a recently discovered serpin located in the kidney, produces renal and pancreatic lesions characteristic of serpinopathies 16431886_In this Chinese population, the 2093C-2180T haplotype at the 3'UTR of MEGSIN gene is associated with more severe forms of IgA nephropathy, and more rapid disease progression 16431886_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16550745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16550745_The polymorphism of megsin A23167G is associated with susceptibility and progression of IgA nephropathy in Chinese population. GG genotype is associated with severe histological lesions and progression of the disease. 16796905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18471408_A267G in 5'-untranslated region within the exon of megsin may be one of the substantial genetic basis for differentiating 'deficiency of liver yin and kidney yin' syndrome and 'deficiency of qi and yin' syndrome in primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy. 18471408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18498720_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18498720_study found out that the megsin TT haplotype (defined as T-2093, T-2180 alleles) could play a protective role in the progression of IgA nephropathy 18580857_recombinant megsin did not affect the mRNA expressions of TGF- and PAI-1, and did not modify the enzymatic activity of PAI-1 18793525_Megsin 2093T-2180C haplotype at the 3' untranslated region is associated with poor renal survival in Korean IgA nephropathy patients. 18793525_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24207119_All of the identified mutants are predicted to cause premature termination upstream of the reactive site, which inhibits the proteases, suggesting a complete loss of the protease inhibitory activity of SERPINB7 in palmoplantar keratosis skin. 24514002_study reports on seven unrelated Chinese patients with Nagashima-Type Palmoplantar Keratosis with four underlying SERPINB7 mutations, of which one is a recurrent variant (c.796C>T) 24575807_megsin 2093C/T C allele may be genetic marker for IgA nephropathy susceptibility [review] 24773080_These data clearly provide further evidence that NPPK is caused by loss-of-function mutations in SERPINB7. 24954659_The mean concentration of serpin B7 at 28-32 weeks was 1.5-fold higher in women with subsequent preterm deliveries compared to controls. 25007157_Megsin 2093C/T TT genotype, and C25663G G allele and GG genotype were associated with the risk of IgAN in Asian population 25940237_Results show splice variants from the two recurrent splice-site mutations in SERPINB7, provide evidence for the pathogenicity of the mutations and suggest an in-frame deletion of exon 3 may cause NPPK and that the CD-loop could affect SERPINB7 function 26763456_Recessive missense mutation of SERPINB7 gene was found in Japanese families diagnosed with palmoplantar keratosis. 26871801_These results indicate that megsin gene variants may play a role in the severity, development, and/or progression of IgAN in Northwest Chinese population 27666198_Direct sequencing of SERPINB7 revealed five homozygous founder mutations (c.796C>T) and four compound heterozygous mutations in nine patients, including one novel mutation (c.122_127delTGGTCC). 27786350_Case Report: striate palmoplantar keratoderma showing transgrediens in a patient with heterozygote nonsense mutations in DSG1 and SERPINB7. 28211129_SERPINB7 mutations are related strictly to the PPKN phenotype. Our study indicates that screening for SERPINB7 mutations is useful to distinguish PPKN from other PPK types and from non-PPK keratinizing diseases with palmoplantar skin lesions. 29106929_mutant SERPINB7 mRNAs harboring r.796c>u were degraded by nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Furthermore, the truncated SERPINB7 protein was degraded via a proteasome-mediated pathway 30592269_SERPINB7 may be a valuable candidate for further studies. In the present study, a method for identifying novel key pathogenic skinspecific molecules is presented, which may be used for investigating and treating psoriasis. 31706940_Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis in Finland caused by a SERPINB7 founder mutation. 32406097_SERPINB7 novel mutation in Chinese patients with Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis and cases associated with atopic dermatitis. 34334259_Updated allele frequencies of SERPINB7 founder mutations in Asian patients with Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis/keratoderma. 34379845_Acral peeling in Nagashima type palmo-plantar keratosis patients reveals the role of serine protease inhibitor B 7 in keratinocyte adhesion. 34454985_Uniting biobank resources reveals novel genetic pathways modulating susceptibility for atopic dermatitis. 35178744_Two novel mutations of SERPINB7 in eight cases of Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis in the Chinese population. 35864103_SerpinB7 deficiency contributes to development of psoriasis via calcium-mediated keratinocyte differentiation dysfunction. | ENSMUSG00000067001 | Serpinb7 | 110.622965 | 0.230192814 | -2.119085 | 0.17815665 | 148.830440 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000003123232157682687299511528111232886385369817493881197773432840505603025704934307770120290904947157883952968404628336429595947265625000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000386617446209428582953303892147322086639782184667065146479876821727003668667293958399744369103245844598859548568725585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 43.1332475 | 17.5196762 | 188.2401644 | 75.1787059 | |
| ENSG00000166523 | 26253 | CLEC4E | protein_coding | Q9ULY5 | FUNCTION: Calcium-dependent lectin that acts as a pattern recognition receptor (PRR) of the innate immune system: recognizes damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) of abnormal self and pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) of bacteria and fungi (PubMed:18509109, PubMed:23602766). The PAMPs notably include mycobacterial trehalose 6,6'-dimycolate (TDM), a cell wall glycolipid with potent adjuvant immunomodulatory functions (PubMed:23602766, PubMed:24101491). Interacts with signaling adapter Fc receptor gamma chain/FCER1G to form a functional complex in myeloid cells (By similarity). Binding of mycobacterial trehalose 6,6'-dimycolate (TDM) to this receptor complex leads to phosphorylation of the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) of FCER1G, triggering activation of SYK, CARD9 and NF-kappa-B, consequently driving maturation of antigen-presenting cells and shaping antigen-specific priming of T-cells toward effector T-helper 1 and T-helper 17 cell subtypes (By similarity). Also recognizes alpha-mannose residues on pathogenic fungi of the genus Malassezia and mediates macrophage activation (By similarity). Through recognition of DAMPs released upon nonhomeostatic cell death, enables immune sensing of damaged self and promotes inflammatory cell infiltration into the damaged tissue (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R0Q8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18509109, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23602766, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24101491}. | 3D-structure;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Lectin;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a member of the C-type lectin/C-type lectin-like domain (CTL/CTLD) superfamily. Members of this family share a common protein fold and have diverse functions, such as cell adhesion, cell-cell signalling, glycoprotein turnover, and roles in inflammation and immune response. The encoded type II transmembrane protein is a downstream target of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), beta (CEBPB) and may play a role in inflammation. Alternative splice variants have been described but their full-length sequence has not been determined. This gene is closely linked to other CTL/CTLD superfamily members on chromosome 12p13 in the natural killer gene complex region. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:26253; | cell projection [GO:0042995]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; membrane [GO:0016020]; phagocytic cup [GO:0001891]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; glycolipid binding [GO:0051861]; pattern recognition receptor activity [GO:0038187]; antifungal innate immune response [GO:0061760]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038094]; immune response [GO:0006955]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002221]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; T cell differentiation involved in immune response [GO:0002292] | 18509109_Several functional states mediating the interaction of Mincle and yeast at the surface of the macrophage. 19120481_important for the initiation of an innate immune response to Candida albicans 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20608913_progenitor-derived mast cells expressed the macrophage-inducible C-type lectin receptor Mincle, and exposure of these cells to M. sympodialis induced up-regulation of the mRNA expression of Mincle 21282371_Our data suggest that Mincle is induced in adipose tissue macrophages in obesity at least partly through the saturated fatty acid/TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway, thereby suggesting its pathophysiologic role in obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation. 22479529_silencing of renal DNaseI gene expression initiates a cascade of inflammatory signals including activation of Toll like receptors and Clec4e, leading to progression of both murine and human lupus nephritis 22641025_Data indicate an unusual pattern of reciprocal expression of Mincle on peripheral blood monocytes or neutrophils. 22698596_Mincle is a potentially critical player in human B cell responses. 22932191_Macrophage-inducible C-type lectin is associated with anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies-positive rheumatoid arthritis in men. 24101491_Results show the molecular mechanism of glycolipid recognition through C-type lectin receptors, which may provide clues to rational design for effective adjuvants. 24721577_mincle is a fungal receptor that can suppress antifungal immunity and, as such, is a potential therapeutic target. 24733387_These results demonstrated that GroMM is a unique ligand for human Mincle that is not recognized by mouse Mincle. 25111533_our findings identify mincle as a contributor to the inflammatory response after traumatic brain injury 26202982_Data indicate that MINCLE receptor is able to mediate the response to trehalose-6,6-dimycolate (TDM) dependent on SYK kinase and CARD9 protein. 26296894_results suggest that cholesterol crystals are an endogenous ligand for hMincle and that they activate innate immune responses 26456705_Induction of Mincle by Helicobacter pylori and consequent anti-inflammatory signaling denote a bacterial survival strategy. 27363694_No association was detected with any of the SNPs analysed and susceptibility to tuberculosis. 27587433_a nonredundant role for Clec4e in coordinating major biological pathways involved in atherosclerosis 27714279_Mincle has the ability to survey mycolate-derived glycolipids from actinomycetes, distinguishing non-pathogenic (e.g. Rhodococcus spp.) and pathogenic (e.g. Mycobacterium tuberculosis) species on the basis of alpha-chain length. 27793997_combination adjuvant systems demonstrate markedly different immune activation with age, with combined DC activation via Macrophage-inducible C-type lectin and TLR7/8 representing a novel approach to enhance the efficacy of early-life vaccines. 27923071_We here show that Mincle gene expression was induced in alveolar macrophages and neutrophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids of mice and patients with pneumococcal pneumonia 28005267_CLEC4E expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 28141595_The expression of Mincle increases significantly during the early period of Aspergillus fumigatus infection, while expression of eight corresponding cytokines changes. Mincle, as a pattern recognition receptor, may play a role in the early innate immune response of the corneal resistance against fungus. 30793298_Spontaneous labour is associated with up-regulated Mincle expression in the myometrium and fetal membranes. Mincle expression was also increased in fetal membranes and myometrium in the presence of pro-labour mediators. 31075410_variations at rs10841845 and rs10841847 of CLEC4E gene are associated with increased individual protection against Pulmonary tuberculosis 31852849_Molecular mechanism of obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation; the role of Mincle in adipose tissue fibrosis and ectopic lipid accumulation. 32152942_overview of the accumulated knowledge of the multi-task danger receptor Mincle from its discovery to the latest findings 32971250_CLEC4E (Mincle) genetic variation associates with pulmonary tuberculosis in Guinea-Bissau (West Africa). 34376176_A case-control study on correlation between the single nucleotide polymorphism of CLEC4E and the susceptibility to tuberculosis among Han people in Western China. | ENSMUSG00000030142 | Clec4e | 18.417520 | 0.386734138 | -1.370586 | 0.40697953 | 11.332986 | 0.0007614238675089080293084675687964590906631201505661010742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0059925812756551604526533694183854095172137022018432617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 9.3408675 | 7.7257111 | 24.2852552 | 19.6771835 | |
| ENSG00000166548 | 7084 | TK2 | protein_coding | O00142 | FUNCTION: Phosphorylates thymidine, deoxycytidine, and deoxyuridine in the mitochondrial matrix (PubMed:9989599, PubMed:11687801). In non-replicating cells, where cytosolic dNTP synthesis is down-regulated, mtDNA synthesis depends solely on TK2 and DGUOK (PubMed:9989599). Widely used as target of antiviral and chemotherapeutic agents (PubMed:9989599). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11687801, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9989599}. | Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;DNA synthesis;Kinase;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Primary mitochondrial disease;Progressive external ophthalmoplegia;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transit peptide | This gene encodes a deoxyribonucleoside kinase that specifically phosphorylates thymidine, deoxycytidine, and deoxyuridine. The encoded enzyme localizes to the mitochondria and is required for mitochondrial DNA synthesis. Mutations in this gene are associated with a myopathic form of mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms, some of which lack transit peptide, so are not localized to mitochondria. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2012]. | hsa:7084; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; deoxycytidine kinase activity [GO:0004137]; deoxynucleoside kinase activity [GO:0019136]; nucleoside kinase activity [GO:0019206]; thymidine kinase activity [GO:0004797]; deoxycytidine metabolic process [GO:0046092]; DNA biosynthetic process [GO:0071897]; nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process [GO:0006139]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; pyrimidine nucleoside salvage [GO:0043097]; thymidine metabolic process [GO:0046104] | 12391347_TK2 mutations have been identified in four patients from two families with myopathic mitochondrial DNA depletion and spinal muscular atrophy. 12493767_human thymidine kinase 2 has a role in mitochondrial DNA depletion myopathy as demonstrated by kinetic analysis 12682338_TK2 deficiency associated with myopathy and apparent reversion of mtDNA depletion noted in a 14-year-old patient in whom pathogenic mutations were identified in the TK2 gene 12873860_exon 5 is a 'hot spot' for TK2 mutations in patients with myopathic mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome 14659972_Long-term treatment of H9 human lymphoid cells in the presence of dideoxycytidine down-regulated TK2 gene expression and reduced the expression and activity of TK in resistant cells. 16969512_an increase in activity of dCK, TK1 and 2 might be involved in an adaptive response of cultured human squamous lung carcinoma cells to radiation by facilitation of DNA repair 17065084_import of cytosolic dNTPs in mitochondria of proliferating cells can compensate a TK2 induced imbalance of the mitochondrial dNTP pool 17468435_Using (124)I-FIAU, (18)F-FIAU, or (18)F-FEAU, it should be possible to image DeltahTK2 reporter gene expression with PET in preclinical and clinical studies. 17913703_activity of TK2 is curbed by thymidine phosphorylase, which degrades thymidine in the cytoplasm, thus limiting the availability of thymidine for phosphorylation by TK2 in mitochondria 18021809_A 12-year-old patient with mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) depletion syndrome due to TK2 gene mutations has been evaluated serially over the last 10 years. We observed progressive muscle atrophy with selective loss of type 2 muscle fibers. 18265975_FMAU is preferably phosphorylated by TK2 and can track TK2 activity and mitochondrial mass in cellular stress. FMAU may provide an early marker of treatment effects. 18446447_Mutations in TK2, necessary for mtDNA biogenesis, increased risk for defective mtDNA replication, leading to LV hypertrophy. 18508266_Novel mutations(p.Q87X and p.N100S) in the TK2 gene associated with fatal mitochondrial DNA depletion myopathy. 19154348_Normal fibroblasts apparently contain more TK2 than needed to maintain dTTP during quiescence, which would explain why TK2-mutated fibroblasts do not manifest mtDNA depletion despite their reduced TK2 activity. 19265691_Gene mutations in TK2 resulting in MDS syndrome was studied. 19736010_Sequence analysis of the TK2 gene revealed two novel heterozygous mutations: the frame shift mutation, c.255_c.258delAGAA, and the heterozygous missense mutation, c.515G>A, (p.R172Q). 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21382338_TK2-deficient cells showed severe mtDNA depletion. 21937588_R225W and T230A mutation of TK2 leads to a significant reduction activity in autosomal recessive progressive external ophthalmoplegia patients. 22661713_Results strongly suggest that oxidative damage-induced S-glutathionylation and degradation of TK2 have significant impact on mitochondrial DNA precursor synthesis. 23932787_Clinically, hypotonia and proximal muscle weakness are the major phenotypes present in all subjects. In summary, our study expands the molecular and clinical spectrum associated with TK2 deficiency. 24198295_Thymidine kinase-2 mutations causing mtDNA deletions are linked to a case of late-onset respiratory failure. 24455740_We suggest that a chip including DPYD, TYMS, TYMP, TK1, and TK2 genes is a potential tool to predict response in LARC following fluoropyrimidine-based CCRT. 24940680_thymidine kinase 2 but not deoxyguanosine kinase is up-regulated during the stationary growth phase of cultured cells 25215937_Data indicate that the thymidine kinase 2 enzyme kinetics of thymidine (dT) phosphorylation exhibits negative cooperativity, but deoxycytidine (dC) phosphorylation follows hyperbolic Michaelis-Menten kinetics. 25948719_Severe deficiency of thymidine kinase 2 was associated with patients with mild forms of myopathy. 28729369_We confirm the pathogenicity of the rare mitochondrial m.8340G>A variant the basis of single-fibre segregation studies and its association with an expanded clinical phenotype. Our case expands the phenotypic spectrum of diseases associated with mitochondrial tRNA point mutations, highlighting the importance of considering a mitochondrial diagnosis. 29602790_In TK2 deficiency, age at onset, rate of weakness progression and POS are important variables that define three clinical subtypes. Nervous system involvement often complicates the clinical course of the infantile-onset form while extraocular muscle and facial involvement are characteristic of the late-onset form. 29735374_Thymidine Kinase 2 mutation is associated with myopathic form of mitochondrial DNA maintenance defect. 34758700_Mutational analyses of human thymidine kinase 2 reveal key residues in ATP-Mg(2+) binding and catalysis. 35907766_Metrics of progression and prognosis in untreated adults with thymidine kinase 2 deficiency: An observational study. | ENSMUSG00000035824 | Tk2 | 249.942515 | 2.937839333 | 1.554755 | 0.52312349 | 8.405959 | 0.0037399301261887593454680267512912905658595263957977294921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0226468149805750494640843584193135029636323451995849609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 349.3104127 | 190.7789233 | 116.6927151 | 63.7500678 | |
| ENSG00000167103 | 138429 | PIP5KL1 | protein_coding | Q5T9C9 | FUNCTION: May act as a scaffold to localize and regulate type I PI(4)P 5-kinases to specific compartments within the cell, where they generate PI(4,5)P2 for actin nucleation, signaling and scaffold protein recruitment and conversion to PI(3,4,5)P3. {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transferase | PIP5KL1 is a phosphoinositide kinase-like protein that lacks intrinsic lipid kinase activity but associates with type I PIPKs (see PIP5K1A; MIM 603275) and may play a role in localization of PIPK activity (Chang et al., 2004 [PubMed 14701839]).[supplied by OMIM, Jun 2009]. | hsa:138429; | cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; 1-phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase activity [GO:0016308]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0010917]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0046854]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065] | 14701839_PIPKH acts as a scaffold to localize and regulate type I PI(4)P 5-kinases and the synthesis of PI(3,4,5)P(3) 19680787_These studies indicate a functional negative correlation between elevated levels of PIP5KL1 and the development of human gastric cancer. 31616009_Enforced expression of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase homolog alters PtdIns(4,5)P2 distribution and the localization of small G-proteins. | ENSMUSG00000046854 | Pip5kl1 | 50.378002 | 0.152388903 | -2.714170 | 0.85321087 | 8.689346 | 0.0032007545876770477494277500341013364959508180618286132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0198987356321895757227391499100122018717229366302490234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 13.2606425 | 7.8108508 | 86.6183028 | 50.4785438 | |
| ENSG00000167123 | 51148 | CERCAM | protein_coding | Q5T4B2 | FUNCTION: Probable cell adhesion protein involved in leukocyte transmigration across the blood-brain barrier. Does not express any beta-galactosyltransferase activity in vitro. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10608765, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19075007}. | Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal | Enables identical protein binding activity. Acts upstream of or within cell adhesion. Predicted to be located in endoplasmic reticulum lumen. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:51148; | endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; leukocyte cell-cell adhesion [GO:0007159] | 34105305_The oncogenic role of the cerebral endothelial cell adhesion molecule (CERCAM) in bladder cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. | ENSMUSG00000039787 | Cercam | 49.372032 | 0.266665126 | -1.906899 | 0.34934262 | 28.930590 | 0.0000000750187867017815764277471673668329366080342879286035895347595214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000015055420206377628587730106365927262856985180405899882316589355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 16.8360543 | 4.2843647 | 63.7227100 | 15.3622756 | |
| ENSG00000167244 | 3481 | IGF2 | protein_coding | P01344 | FUNCTION: The insulin-like growth factors possess growth-promoting activity (By similarity). Major fetal growth hormone in mammals. Plays a key role in regulating fetoplacental development. IGF2 is influenced by placental lactogen. Also involved in tissue differentiation. In adults, involved in glucose metabolism in adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and liver (Probable). Acts as a ligand for integrin which is required for IGF2 signaling (PubMed:28873464). Positively regulates myogenic transcription factor MYOD1 function by facilitating the recruitment of transcriptional coactivators, thereby controlling muscle terminal differentiation (By similarity). Inhibits myoblast differentiation and modulates metabolism via increasing the mitochondrial respiration rate (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P09535, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28873464, ECO:0000305|PubMed:24593700}.; FUNCTION: Preptin undergoes glucose-mediated co-secretion with insulin, and acts as physiological amplifier of glucose-mediated insulin secretion. Exhibits osteogenic properties by increasing osteoblast mitogenic activity through phosphoactivation of MAPK1 and MAPK3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16912056}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Carbohydrate metabolism;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Glucose metabolism;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Hormone;Mitogen;Osteogenesis;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | This gene encodes a member of the insulin family of polypeptide growth factors, which are involved in development and growth. It is an imprinted gene, expressed only from the paternal allele, and epigenetic changes at this locus are associated with Wilms tumour, Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, rhabdomyosarcoma, and Silver-Russell syndrome. A read-through INS-IGF2 gene exists, whose 5' region overlaps the INS gene and the 3' region overlaps this gene. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2010]. | hsa:3481; | extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; platelet alpha granule lumen [GO:0031093]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; hormone activity [GO:0005179]; insulin receptor binding [GO:0005158]; insulin-like growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005159]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity [GO:0043539]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activator activity [GO:0030297]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; embryonic placenta development [GO:0001892]; embryonic placenta morphogenesis [GO:0060669]; exocrine pancreas development [GO:0031017]; glucose metabolic process [GO:0006006]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; insulin receptor signaling pathway via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase [GO:0038028]; insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048009]; negative regulation of muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051148]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation [GO:0042104]; positive regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0043085]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of glycogen (starch) synthase activity [GO:2000467]; positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0045725]; positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046628]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0045840]; positive regulation of multicellular organism growth [GO:0040018]; positive regulation of organ growth [GO:0046622]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue growth [GO:0048633]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation [GO:1905564]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of gene expression by genomic imprinting [GO:0006349]; regulation of histone modification [GO:0031056]; regulation of muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051147]; spongiotrophoblast cell proliferation [GO:0060720]; striated muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051146] | 8385745_IGF2 gene is imprinted, with expression from only the paternal allele. 11448941_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11793026_Insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2 ) gene variant is associated with overfeeding-induced metabolic changes. Insulin sensitivity decreased . 11811790_Contribution of residues A54 and L55 of the human insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II) A domain to Type 2 IGF receptor binding specificity 11849996_These data indicate that the translational machinery encounters major parts of IGF II-leader 1. 11889182_Association of H19 promoter methylation with the expression of IGF-II gene in adrenocortical tumors. 11903044_Human insulin-like growth factor II leader 2 mediates internal initiation of translation 11937266_Loss of genomic imprinting of IGF2 is strongly associated with cellular proliferation in normal hematopoietic cells. 11969341_altered IGF-II and IGFBP-1 expression at the fetomaternal interface may be important in the pathophysiology of pre-eclampsia 12005306_cDNA probes were used to analyze the gene expression of IGF-II 6 in luteinized granulosa cells from different-sized follicles after ovarian hyperstimulation. 12006706_determination of blood levels in adult patients with severe liver disease before and after orthotopic liver transplantation 12032304_igf2 expression regulates hemangioma growth and involution 12075589_Caucasians with the IGF2 A/A genotype exhibit higher fat mass than G/G individuals 12075589_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12125963_Brain tumor invasiveness in degrees from respect of the arachnoid membrane progressing to frank brain invasion correlated with increases in IGF-II and IGFBP-6 expression. 12127559_Autocrine production of IGF-I and IGF-II may via IGF-IR play a significant role in the growth and megakaryocytic differentiation of K562 cells. 12243757_Data suggest a causal relation between telomere shortening and reduced expression of KGF and IGF-II in human fibroblasts. 12270940_The dependence of the methylation of a region of this gene depends on the primary methylation imprint about 90 kilobases away. 12388463_Glucose transporter gene expression in the jejunum in response to insulin-like growth factors in rat pups 12446294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12519841_data demonstrate for the first time that serum levels of IGFs (including free fractions) and IGFBPs are not increased in euthyroid Graves' patients with active thyroid eye disease 12532445_IGF-II was expressed in human hepatoma cell lines. 12548223_effect of relaxin on cellular proliferation in WISH cells is likely through the transcriptional up-regulation of IGF-II 12558805_mitogenic effects on Malassez cells in the normal periodontal ligament 12579496_Overexpression of IGF2 was found to play an important role in carcinogenesis of colorectal cancer. 12605037_Alterations in the IFGII imprinted region occur in juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. 12610512_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12637750_investigated the utility of loss of IGF2 imprinting as a marker of colorectal cancer risk 12700030_IGF2 is maternally imprinted thus is expressed only through the paternal allele, also IGF2 is over expressed in ovarian tumors. 12702581_Human insulin-like growth factor II gene (IGF2) is overexpressed, and its imprinting is disrupted in many tumors, including Wilms' tumor. 12719950_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12727212_Data suggest that insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II) is complexed in vivo with intact insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBP-2) and with processed IGFBP-2 fragments, which do not impair the activity of IGF-II on cell survival. 12732844_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12765950_circulating IGF-II levels may play a role in body weight regulation and development of obesity in men and women with normal glucose tolerance 12782403_p53mt249 stimulates IGF-II dependent IGF-IR signaling by upregulating the expression of both ligand (IGF-II) and receptor (IGF-IR) through an autocrine and/or paracrine loop 12804776_PTEN modulates IGF2-mediated signaling. The phosphoprotein phosphatase activity of PTEN downregulates IGF-2 expression in hepatoma cells. 12881524_214 transcripts were similarly regulated by insulin and IGF-II through Insulin Receptor A, whereas 45 genes were differentially transcribed 13679437_IGF2, a potent growth factor, may play a role in the development or progression of clear cell sarcoma of the kidney. 14614750_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14645199_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14645508_AT-rich DNA sequences located in the vicinity of previously characterized differentially methylated regions (DMRs) of the imprinted Igf2 gene are conserved between mouse and human. 14695992_PLAG1 regulates promoter P3-dependent transcription of IGF2 in hepatoblastomas. 14710345_Serum IGF-I shows positive correlations with myoblast retrieval in control patients that is lost in malignancy. 14749262_Both first- and second-phase insulin secretion were not significantly different between the various IGF-I or IGF-II genotypes. 14749262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14749349_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14764950_In human fetuses, IGF-I and IGF-II levels increase longitudinally throughout pregnancy. 14996863_Our findings support the hypothesis that LOI of IGF-II is an epigenetic trait polymorphic in the population and suggest that LOI of IGF-II may play a role in colorectal cancer. 15003992_Fibroblast proliferation, differentiation into myofibroblasts, & increased collagen synthesis are regulated via a CTGF-dependent pathway in concert with either EGF or IGF-2. 15140223_IGF-II:VN and IGF-I:IGFBP-5:VN complexes may be useful in situations where enhanced keratinocyte cell migration and proliferation is required, such as in wound healing and skin regeneration. 15163116_IGF-II gene APA I polymorphism can not serve as a candidate gene marker for screening rheumatoid arthritis patients in Taiwan. 15181035_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15191555_IGF-II enhances the expression of VEGF in HaCaT cells by increasing HIF-1alpha levels. 15205474_The C and D domains of IGF-II promote higher affinity binding to the IR-A than the equivalent domains of IGF-I. 15217931_free IGF-II but not IGF-I may have a role in progression of breast cancer 15298990_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15298990_variation within IGF2, a gene known to influence developing muscle, affects muscle mass and muscle function in later life. 15355996_CRD-BP has a dominant role in proliferation of human K562 cells by an IGF-II-dependent mechanism independent of its ability to serve as a c-myc mRNA masking protein 15471867_novel mechanism for IGF2 imprinting regulation, that is, the reduction of CTCF expression in the control of IGF2 imprinting 15528386_IGF-2 may play a role in the selective recruitment of basophils in vivo. 15621215_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15642732_plasminogen binds with high affinity to IGF-II and IGF-binding protein-3 15645136_there is a disturbed regulation of the IGF-2/H19 locus in myeloid leukemias which is not caused by loss of imprinting 15701574_mature IGF-II is more effective in down-regulating the IGF-IR than pIGF-II 15706404_Here, using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and immunohistochemistry, we show that IGF2 is highly expressed in both proliferating and involuting phase hemangioma, but is not detectable in other vascular lesions. 15731405_humans with loss of imprinting (LOI) of the IGF2 gene show a shift in differentiation in the normal colonic mucosa 15769738_observed, subsequent to knocking down CRD-BP/IMP1, decreased c-myc expression, increased IGF-II mRNA levels, and reduced cell proliferation rates 15797461_The IGF2(67 amino acids) is single-chain polypeptides structurally similar to proinsulin. 15799974_there is no finite M6P/IGF2R dimerization domain, but interactions between dimer partners occur all along the extracytoplasmic region of the receptor 15809062_PTEN may inhibit antiapoptotic IGF actions not only by blocking the IGF-IGFR-induced Akt activity, but also by regulating expression of components of the IGF system, in particular, upregulation of IGFBP-3 15935984_IGF-II plays a role in colonic carcinogenesis from ulcerative colitis by interacting with interleukin 5. 15954927_In sedentary, clinically stable maintenance hemodialysis patients as compared to sedentary normal individuals, the mRNA levels for IGF-IEa, IGF-II, and the IGF-I receptor are decreased in vastus lateralis muscle 15956340_C-domain of IGFBP-2 plays a key role in binding regions of IGF-I and -II that are also involved in binding to the type-1 IGF receptor 15970649_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15987847_IGF II is an early indicators of fetal growth as measured in seconsd semestser amniotic fluid. 16018936_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16037384_Resveratrol regulates IGF-II and IGF-II mediates RSV effect on cell survival and growth in breast cancer cells. 16102992_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16102992_Polymorphisms of the IGF2 gene is associated with predisposition to high body mass index and obesity 16115888_PAPP-A increased the proliferation and differentiation of myoblasts, its myogenic effect is governed by its proteolytic activity, and it promotes skeletal myogenesis by increasing the amount of free IGFs. 16166779_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16247461_SYT-SSX1 induces insulin-like growth factor II expression in fibroblast cells. 16251897_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16330588_A highly significant association was observed between the IGF2 ApaI G allele and scores on the Eating Attitudes Test overall and each of its subscales 16330588_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16344718_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16489075_IGF-II expression was found to be higher in tumors with poor prognosis. 16518847_Association of 11q loss, trisomy 12, and possible 16q loss with loss of imprinting of insulin-like growth factor-II in Wilms tumor 16525660_Results suggest that loss of imprinting (LOI)of IGF2 in colorectal carcinoma and LOI in the background mucosa play important roles in carcinogenesis. 16603642_Elevated IGF2 expression is a frequent event in serous ovarian cancer and this occurs in the absence of IGF2 loss of imprinting. 16612114_Interplay between placental and fetal Igf2 regulates both placental growth and nutrient transporter abundance. 16716263_IGF-I and -II are chemotactic factors for mesenchymal progenitor cells; IGFBP-5 both modulates the IGF-I effect and directly stimulates migration of human mesenchymal progenitor cells 16750516_IGF2 polymorphisms were found to be strongly associated with the clearance of hepatitis B virus (HBV) or the occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic HBV infection 16750516_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16857788_analysis of hypomethylated P4 promoter induction of expression of the insulin-like growth factor-II gene in hepatocellular carcinoma in a Chinese population 16868148_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16888814_IGFs co-activate proliferative and apoptotic pathways in LIM 1215 cells, which may contribute to increased cell turnover. 16926156_heterotrimeric G protein-dependent ERK1/2 activation is mediated by IGF-1 and IGF-2 by transactivating sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors 16935391_High plasma levels of IGF-1, IGF-2, and IGFBP-3 were associated with good prognosis in patients with advanced NSCLC. 17029194_The risk of IGF-II gene imprinting loss is higher in female twins and has no relationship with assisted reproductive technology and zygosity. 17072986_IGF-II was shown to be a growth factor of hepatoblastoma via IGF-I receptor and PI3 kinase which were good candidates for target of molecular therapy 17285535_In newborns of Chinese Han population, 21.6% showed IGF2 loss of imprinting (LOI) in cord blood, and IGF2 LOI may have some influences on fetal growth. Paternal age is associated with LOI. 17289909_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17294726_IGF2 gain of imprinting and H19 loss of imprinting are common in hepatocellular carcinoma. 17310846_IGF2 may participate in carcinogenesis of esophageal cancer through its over-expression. IGF2 loss of imprinting. 17325026_Implication of IGF2 duplication in overgrowth and Wilms'tumorigenesis. 17339271_Variation in DNA methylation of the IGF2/H19 locus is mainly determined by heritable factors and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in cis, rather than the cumulative effect of environmental and stochastic factors occurring with age. 17341887_The results provide further evidence that IGFBP-2 and IGF-II in breast milk are relevant factors for the early development of preterm infants. 17360667_IGF2-PIK3R3 signaling axis is involved in promoting the growth of a subclass of highly aggressive human glioblastomas that lack EGF receptor amplification. 17369847_IGF-II and IGFBP-2 differentially regulate PTEN in human breast cancer cells 17407457_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17407457_There was a significant difference in birth weight standard deviation scores among the three neonatal +3123/Apal genotypes of the insulin-like growth factor 2 gene, indicating that the IGF2 gene variant is associated with fetal growth. 17440932_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17475626_novel binding surface on IGF-II critical for IGF2R binding 17488802_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17488802_We did not confirm the previously reported associations between IGF2 polymorphisms and body mass index, but common variation in the IGF2 gene may be associated with adult height 17556377_These results demonstrate that the InsR regulates choriocarcinoma cell invasion through activation by IGF-II. 17560154_Severely deficient in a case of insulin-resistance syndrome (Rabson-Mendenhall type). 17569086_methylation varies among three IGF-II promoters in ovarian cancer and that this variation seems to have biologic implications as it relates to clinical features and prognosis of the disease. 17591929_A panel of markers including at least RUNX3, CACNA1G, IGF2, and MLH1 can serve as a sensitive and specific marker panel for CIMP(Cpg island methylator phenotype)-high. 17620336_that endogenous IGF-1 and IGF-2 receptors can independently initiate ERK1/2 signaling and point to a potential physiologic role for IGF-2 receptors in the cellular response to IGF-2 17635080_IGF-II metabolism may play a role in atherogenesis in in schizophrenic Arab subjects 17639583_Duplication of the paternal IGF2 allele in trisomy 11 and elevated expression levels of IGF2 mRNA is associated with congenital mesoblastic nephroma 17640993_Different members of Rho GTPase family regulate IGF-II-mediated EVT cell migration differentially, depending upon whether it signals through IGF1R or in an IGF1R-independent manner. 17667841_Demonstrate significant relationship between paternally transmitted haplotypes at INS-IGF2 locus and newborn IGF-II levels, but no association with maternally transmitted haplotypes. 17700581_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17786320_Upregulation of IGF-2 expression is associated with oral cancer. 17919721_Intrauterine growth restricted (IUGR) pregnancies are associated with normal value of IGF2 mRNA. 17972051_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18006818_analysis of IGF2 and H19 loss of imprinting in bladder cancer 18022169_Endometrial IGF-I and -II are differentially regulated during decidualization and by human chorionic gonadotropin. 18035699_IGF-II may represent an excellent target for interferon gamma-treatment and specific siRNA-mediated therapeutic intervention in human hepatoma. 18085551_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18085551_common genetic variants in the IGF2-INS-TH cluster modify susceptibility to idiopathic Parkinson's disease 18159214_In 30% of patients, differentially methylated IGF2/H19 imprinting center region (ICR1) on chromosome 11p15 was found to be hypomethylated, as determined by Southern blot analysis of an HpaII restriction site close to third CTCF-binding site within ICR1 18199734_Genetic variants in the IGF-II genes is not associated with breast cancer 18245780_Methylation-imprinting defects at the IGF2-H19 locus can result from inherited mutations of the imprinting center and have high recurrence risk or arise independently from the sequence context and generally not transmitted to the progeny. 18259111_Higher early levels of the human milk IGF system might contribute to maturation of the infant gut. 18287964_IGF-2 mRNA was expressed in congenital hemangiomas at a level comparable with that detected in common infantile hemangioma over 4 y of age. 18297687_Data show that vitamin C suppresses proliferation of the human melanoma cell line SK-MEL2 via the down-regulation of IGF-II production and IGF-IR expression, which is followed by the activation of p38 MAPK and the inhibition of COX-2 expression. 18308616_IGF2 is epigenetically regulated and has roles in development and disease [review] 18349294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18350600_Review of the insulin-like growth factor-II signaling pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. 18358696_Of the informative human hepatocellular carcinoma samples 47.06% (8 of 17) demonstrated a gain of imprinting of IGF2, and 21.74% (5 of 23) of the informative HCC samples demonstrated a loss of imprinting of H19. 18372285_IGF2 helps predict disease outcome in GIST patients. 18428028_IGF-II differentially regulated the intracellular translocation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-X(L), a critical process in breast cancer progression to hormone-independence 18464243_three WT1 subtypes were correlated with WT1, IGF2, and CTNNB1 genetics 18467708_increased local IGF-II expression in SSc-associated pulmonary fibrosis both in vitro and in vivo as well as IGF-II-induced ECM production through both phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase- and Jun N-terminal kinase-dependent pathways. 18481170_IGF-I, IGF-II and IGFBP-3 mRNA expression and tissue levels of IGF peptides are regulated by different mechanisms 18520331_Propose that IGF-II, mainly through the insulin receptor is involved in functional leydig cell differentiation. 18524796_Markedly elevated IGF-II and IGFBP-2 serum levels in patients with non-seminomatous germ cell cancer, showing a significant decrease after successful therapy and an increase in recurrent disease. 18537183_Activation of IGF-II/IGF-IR signaling is likely a progression switch selected by function that promotes tumor cell dissemination and aggressive tumor behavior. 18541649_Results indicate that IGF2 promoter proximal sequence hypomethylation is highly prevalent in cancer and detected more frequently than loss of imprinting. 18562769_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18573128_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18573128_The presence of IGF-2 ApaI polymorphism in partners of recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA) women could affect IGF-2 level of expression in placenta and embryo and represent a risk factor for RSA susceptibility. 18604514_Results decribethe loss IGF2/H19 imprinting,loss of heterozygosity of IGF2R and CTCF, and incidental H. pylori infections in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 18607558_Data suggest a positive role of the IGF2 expression level, as reflected by the methylation index, in the determination of body and placental growth in epimutation-positive patients, except for the brain where IGF2 is expressed biallelically. 18611974_IGF-II transcripts were overexpressed in both pediatric adrenocortical carcinomas and adenomas. 18616667_Competitive equilibrium binding assays revealed significantly reduced specific binding to the insulin, IGF-I, and IGF-II and their receptors in both the anterior cingulate and vermis of alcoholic human brains. 18619647_Our findings indicate that colorectal cancers with demethylation of the insulin-like growth factor II gene are distinct from normal imprinting tumors, both in clinical and genetic features. 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18701505_Loss of insulin-like growth factor 2 imprinting is associated with the development of prostate cancer 18719053_Women with localized, early-stage breast cancer show elevated circulating free IGF1 and IGF2, reduced total IGF2 and alterations in IGFBPs 18728168_A break point 184 kb upstream of the paternally derived IGF2 gene resulted in reduced expression in some mesoderm-derived adult tissues causing intrauterine growth retardation, short stature, lactation failure, and insulin resistance. 18772331_Neuraminidase caused the desialylation of both PDGF and IGF-1 receptors and diminished the intracellular signals induced by the mitogenic ligands PDGF-BB and IGF-2. 18786438_IGF2 was overexpressed in childhood adrenocortical tumors with maternal, but not paternal, allele loss of heterozygosity at 11p15. It did not relate to clinical outcome. 18788888_Expression of the IGF2 ligand is associated with translocation-negative tumors and may serve as a diagnostic aid in distinguishing rhabdomyosarcoma subtypes. 18794369_Data identify a novel transcriptional activity at both the human and the mouse H19/IGF2 imprinted loci. 18803353_hypomethylation at the Igf2 locus in the liver could be predictive for the occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis C virus cirrhosis 18832656_locally generated IGF2 at either ischemic or tumor sites may contribute to postnatal vasculogenesis by augmenting the recruitment of endothelial progenitor cells 18931647_Report overexpression of IGF2 in pancreatic islets of nesidioblastosis patients. 18955703_In humans, low birth weight correlates with hypomethylation of the IGF2 promoter. 18980977_We suggest that CDH1 cytoplasmic immunolocalization as a result of increased IGF-II levels identifies those nonmuscle invasive presentations most likely to recur 19034281_we found 12 childhood hematoblasoma tumours (22%) with LOH in IGDF2, 9 (17%) with loss of imprinting (LOI) and 33 (61%) with retention of imprinting (ROI). 19064563_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19066168_findings demonstrate that hypomethylation of H19 or IGF2 alone appears to be sufficient to cause Silver-Russell syndrome(SRS); germ cell mosaicism & vertical transmission from an affected father to his child shows a recurrence risk for epimutations in SRS 19121847_Insulin-like growth factor-II and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 may be novel prognostic markers in metastatic ovarian carcinoma. 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19127217_Effects of different CMV-heat-inactivation-methods on IGF-2 in human breast milk. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19207313_Serum levels of IGF-1, IGF-2, ALS, and IGFBP-3 were reduced in children with congenital disorders of glycosylation. 19208780_The function of the Gly1619Arg non-synonymous amino acid modification of domain 11, was evaluated. 19218281_Significantly higher IGF2 expression is associated with adrenocortical carcinomas compared to adrenocortical adenomas. 19242102_Loss of genomic imprinting of the IGF2 gene in PBL appears to be a stable epigenetic phenomenon in most colorectal cancer patients and may be a risk factor for colorectal cancer predisposition 19259766_Increased high-molecular-weight insulin-like growth factor II is associated with giant phyllodes tumor of the breast with hypoglycemia. 19276395_We identified pro-IGF-IIE[68-88] as a marker that may be used in the surveillance of GIST. 19293570_methylation defects at the IGF2-H19 locus can result from inherited mutations of the imprinting center and have high recurrence risk or arise independently from the sequence context and not transmitted to the progeny 19317253_IGF-II (insulin-like growth factors-2) can enhance KCC1 (KC1 co-transport-1) gene expression in cervical cancer cells through signal transduction pathways 19333718_data demonstrated that preptin is involved in bone anabolism mediated by ERK/CTGF in human osteoblasts and may contribute to the preservation of bone mass observed in hyperinsulinemic states, such as obesity 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19365888_Tissue markers of hypoglycemia: insulin growth factor-II and E-domain of proinsulin growth factor-II expression in solitary fibrous tumor of the pleura.(Case Report) 19367319_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19390492_Data suggest that inheriting the IGF2 CTG haplotype from a paternal allele results in reduced feto-placental growth, but it is not associated with the methylation status of IGF2/H19. 19390492_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19407853_IGF2 protein expression among mesenchymal tumors is largely consistent with gene expression studies and suggests a potential for molecular therapy targeting the IGF signaling pathway system in these neoplasms. 19417744_IGF-1 was significantly positively associated with birth weight and birth length in Boston, but not Shanghai. In contrast, stronger positive, though statistically non-significant, associations of IGF-2 with birth size were only evident in Shanghai 19421925_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19421925_The combined analyses of both polymorphism revealed that the genotypes IGF-2 (GG)/ PON-1 (TT) and IGF-2 (AA)/ PON-1 (TT) were more frequent in the PCOS group, whereas the genotype IGF-2 (AA)/ PON-1 (CC) did not occur in the PCOS group at all. 19427670_hypomethylation of the IGF2-P3 promoter correlates with expression of P3 transcripts in osteosarcoma. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19499149_data indicated that Hcy could induce hypomethylation of the sixth CTCF-binding sites upstream of H19, which is an important regulating area for the imprinting expression of IGF2 and H19 19502451_Methylation of IGF2 might be a useful biomarker for classification and staging of pancreatic endocrine tumors. 19513555_Report aberrant epigenetic modifications in the CTCF binding domain of the IGF2/H19 gene in prostate cancer compared with benign prostate hyperplasia. 19546867_In the parent-of-origin specific association analysis, in which only the paternally inherited allele was incorporated, the 1156T>C single nucleotide polymorphism showed significant association with IGF-binding protein 1 levels 19546867_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19549920_This study population does not support the hypothesis that colon cancer can be predicted from the different degrees of methylation in the IGFII gene from lymphocyte DNA. 19560381_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19584898_The DNA methylation status of 47 CpGs located in differentially methylated regions (DMRs), IGF2 gene and in the 3rd and 6th CTCF-binding sites of the H19 DMR in human sperm from men with normal semen and infertile patients, was analysed. 19586133_The results suggest that upregulation of the IGF pathway in pediatric undifferentiated soft tissue sarcomas is a critical early event in the development of sarcomas. 19588890_the presence of IGF-2 in the nucleus of cells cultured from human fetal thymus and its association with the insulin-linked polymorphic region in the chromatin of these cells 19598235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19672298_combination of SDF-1, PTN, IGF2, and EFNB1 mimics the DA phenotype-inducing property of SDIA and was sufficient to promote differentiation of hESC to functional midbrain DA neurons 19689072_The loss of imprinting of IGF-2 could be involved in the development of breast cancer. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19713175_results indicate that the levels of placental insulin-like growth factor 2 and insulin-like growth factor I receptor may be involved in the development of macrosomia 19724140_Preliminary X-ray analysis of the complexes between a Fab and two forms of human insulin-like growth factor II at 2.2 A resolution, is reported. 19737423_IGF2 loss of imprinting is present in high frequency in Chinese gastric cancer patients, especially those with gastric corpus cancer. 19749460_The expression of factor IGF-II and its receptor, IGF-1R was significantly higher in breast carcinoma having Loss of Heterozygosity at WT1 locus. 19767753_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19769965_M6P/IGF2R is involved in the regulation of CREG-mediated IGF-II endocytosis 19786462_Body mass index contributes to racial differences in IGF2 19843644_analysis of the loss of imprinting of the insulin-like growth factor II (IGF2) gene in esophageal normal and adenocarcinoma tissues 19876004_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19919531_These results suggest that positive feedback regulation of bFGF and IGFs leads to proliferation of UCB-MSCs. 19924280_Periconceptional folic acid use is associated with epigenetic changes in IGF2 in the child that may affect intrauterine programming of growth and development with consequences for health and disease throughout life 19938957_Serum IGF-II levels, which appeared to be negatively correlated with elevated E2, decreased in polycystic ovary syndrome patients early after hMG & hCG administration when monitored for 24 h, while no such changes were observed in IGF-I & IL-6. 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19950580_Expression profiles of human VIGILIN, H19, and IGF2 mRNA increased with cell-cycle prograssion. 19953105_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19956766_cohesin has a critical role in maintaining CTCF-mediated chromatin conformation at the at the IGF2-H19 locus locus and disruption of this conformation coincides with changes in IGF2 expression. 19956846_frequent combined aberrant methylation of the IGF2-H19 locus and LINE1 in the vast majority of ovarian carcinoma samples suggests that these changes are important events in tumorigenesis 19957330_results suggest that IGF2 participates in colorectal neoplasms tumorigenesis through 2 different forms of aberrant gene expression 19962924_Mature IGF-II prevents the formation of 'big' IGF-II/IGFBP-2 complex in the circulation of healthy human controls. 20007505_Analysis of the IGF2 imprinting control region uncovers new genetic defects, including mutations of OCT-binding sequences, in patients with 11p15 fetal growth disorders 20010889_DNA methylation at IGF2 is significantly correlated with brain weight 20027339_FGF-2 levels were detected in patients with tumors of different histological structure. 20042264_expression level of imprinted gene IGF2 in the endometrium of women with unexplained infertility was increased compared with controls. 20057340_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20057340_There is a signi | ENSMUSG00000048583 | Igf2 | 30.377112 | 0.305778637 | -1.709440 | 0.30227393 | 33.913742 | 0.0000000057610347038552023798871632028709838246882668499893043190240859985351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000001370499208121200232863087656656753132722315058344975113868713378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 13.4626074 | 10.7682614 | 44.2019608 | 34.7717542 | |
| ENSG00000167680 | 10501 | SEMA6B | protein_coding | Q9H3T3 | FUNCTION: Functions as a cell surface repellent for mossy fibers of developping neurons in the hippocampus where it plays a role in axon guidance. May function through the PLXNA4 receptor expressed by mossy cell axons. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O54951}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for P.sordellii toxin TcsL in the in the vascular endothelium. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32302524, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32589945}. | Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Epilepsy;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Neurodegeneration;Neurogenesis;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a member of the semaphorin family, a group of proteins characterized by the presence of a conserved semaphorin (sema) domain. Whereas some semaphorins are transmembrane proteins, others are secreted. Semaphorins play a major role in axon guidance. The protein encoded by this gene may be involved in both peripheral and central nervous system development. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:10501; | extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; chemorepellent activity [GO:0045499]; semaphorin receptor binding [GO:0030215]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; hippocampus development [GO:0021766]; negative chemotaxis [GO:0050919]; negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048843]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway [GO:0071526] | 15177567_Gene SEMA6B is strongly down regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. 23665584_states a clear relation among breast cancer and SEMA6B expression; moreover we describe for the first time the SEMA6Ba protein and report here the analysis of SEMA6Ba RNA messenger, the protein expression and the cellular localization 23781008_Semaphorin 6B is related to tumour differentiation and metastasis in vivo, and tumour cell migration, adhesion and invasion in vitro. 32169168_Heterozygous truncating variants in the NMD(+) region of SEMA6B are observed in general populations. 32302524_Genome-Wide CRISPR Screen Identifies Semaphorin 6A and 6B as Receptors for Paeniclostridium sordellii Toxin TcsL. 33125690_Aberrant expression of semaphorin 6B affects cell phenotypes in thyroid carcinoma by activating the Notch signalling pathway. 34110594_A Frameshift Variant in the SEMA6B Gene Causes Global Developmental Delay and Febrile Seizures. 35604360_SEMA6B variants cause intellectual disability and alter dendritic spine density and axon guidance. | ENSMUSG00000001227 | Sema6b | 14.557017 | 0.393080182 | -1.347104 | 0.50614566 | 6.930960 | 0.0084716221427758638812255398420347773935645818710327148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0435986205052055833530921802321245195344090461730957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 6.5215092 | 3.0642601 | 16.3537415 | 7.0802568 | |
| ENSG00000168237_ENSG00000114841 | 22.822365 | 18.869962874 | 4.238020 | 0.76830374 | 26.544007 | 0.0000002576025941589074210598365403251941430085025785956531763076782226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000047102550158101916813946016815428663448983570560812950134277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 52.6700934 | 83.4515015 | 2.6335382 | 4.4294421 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000169245 | 3627 | CXCL10 | protein_coding | P02778 | FUNCTION: Pro-inflammatory cytokine that is involved in a wide variety of processes such as chemotaxis, differentiation, and activation of peripheral immune cells, regulation of cell growth, apoptosis and modulation of angiostatic effects (PubMed:7540647, PubMed:11157474, PubMed:22652417). Plays thereby an important role during viral infections by stimulating the activation and migration of immune cells to the infected sites (By similarity). Mechanistically, binding of CXCL10 to the CXCR3 receptor activates G protein-mediated signaling and results in downstream activation of phospholipase C-dependent pathway, an increase in intracellular calcium production and actin reorganization (PubMed:12750173, PubMed:19151743). In turn, recruitment of activated Th1 lymphocytes occurs at sites of inflammation (PubMed:12750173, PubMed:12663757). Activation of the CXCL10/CXCR3 axis also plays an important role in neurons in response to brain injury for activating microglia, the resident macrophage population of the central nervous system, and directing them to the lesion site. This recruitment is an essential element for neuronal reorganization (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P17515, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11157474, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12663757, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12750173, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19151743, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22652417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7540647}. | 3D-structure;Chemotaxis;Citrullination;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Inflammatory response;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | This antimicrobial gene encodes a chemokine of the CXC subfamily and ligand for the receptor CXCR3. Binding of this protein to CXCR3 results in pleiotropic effects, including stimulation of monocytes, natural killer and T-cell migration, and modulation of adhesion molecule expression. This gene may also be a key regulator of the 'cytokine storm' immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2020]. | hsa:3627; | external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulator activity [GO:0008603]; chemoattractant activity [GO:0042056]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; CXCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0045236]; CXCR3 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0048248]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; antiviral innate immune response [GO:0140374]; blood circulation [GO:0008015]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to heat [GO:0034605]; cellular response to interleukin-17 [GO:0097398]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; endothelial cell activation [GO:0042118]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045662]; negative regulation of myoblast fusion [GO:1901740]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090026]; positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051281]; positive regulation of T cell migration [GO:2000406]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of endothelial tube morphogenesis [GO:1901509]; regulation of T cell chemotaxis [GO:0010819]; response to auditory stimulus [GO:0010996]; response to cold [GO:0009409]; response to gamma radiation [GO:0010332]; response to vitamin D [GO:0033280]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell chemotaxis [GO:0010818] | 11418676_In a mouse model, this protein is expressed as a marker of hepatic inflammation and injury, suggesting a role in liver repair and regeneration. 11818520_Production by endometrial stromal cells is regulated by inflammatory mediators; Level may regulate leukocyte trafficking in the endometrium 11897701_synthesis was detected in human Leydig cells exposed to the Sendai virus, but not in human total germ cells 12016104_These findings suggest that the CXCR3/CXCL10 axis may be involved in the T cell recruitment that occurs in peripheral airways of smokers with COPD and that these T cells may have a type-1 profile. 12117914_bacterium-induced CXCL10(IP-10) secretion by osteoblast can be mediated in part through toll-like receptor 4 12117926_Leishmania promastigotes release a granulocyte chemotactic factor and inhibit gamma-interferon-inducible protein 10 production by neutrophil granulocyte 12162873_The IFN-gamma-inducible IP-10 protein was induced in human brain microvascular endothelial cells and astrocytes only after inflammatory stimuli. 12173928_The structure of IP-10 has been solved by NMR spectroscopy and the surface of IP-10 that interacts with the N-terminus of the receptor CXCR3 has been defined. 12189440_circulating IP-10 concentrations is increased in patients with Type I diabetes, but only during the early and subclinical stage of the disease. 12270371_Gene expression is predictive for the individual response of children with chronic allograft nephropathy to mycophenolate mofetil. 12356205_Increased levels of CXCL10 in cerebrospinal fluid were found in a subgroup of MS patients. 12384933_IFNgamma stimulates the production of IP-10 and Mig in the SS ductal epithelium, and that IP-10 and Mig are involved in the accumulation of T cell infiltrates in the SS salivary gland. 12393716_complex gene expression regulation for IP-10 in peripheral blood t lymphocytes, involving both calcineurin-dependent and -independent pathways, is demonstrated 12441140_release is evoked by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma in HaCaT cell line by interleukin-4 12584353_highly expressed by mumps virus-infected Leydig cells and ribavirin does not block IP-10 production 12603854_17beta-estradiol inhibited interferon-gamma-induced interferon-induced protein of 10 kDa secretion, mRNA expression, and promoter activity in keratinocytes; effects may be mediated by cell surface receptors 12663757_infection with cytomegalovirus was found to elicit the production of CXCL10 from primary microglial cells but not from astrocytes; CXCL10 production was regulated by human and viral interleukin-10 12667820_This chemokine receptor stimulates HIV-1 replication. 12668159_IP-10 expression and secretion in human monocytic cells is selectively induced by leptin 12718750_Regulation of interferon-inducible cytokine IP-10 expression in rheumatoid arthritis. 12794718_expression in serum and liver highest in chronic hepatitis C and correlates with accumulation of Il-18 and INFgamma mRNA in chronic hepatitis C, but not in hepatitis B nor in nonviral liver disorders 12819030_Data suggest that in oral lichen planus, the presence of CCL5 and CXCL10 in the cytolytic granules of tissue-infiltrating CD8(+)T cells expressing CCR5 and CXCR3 reveals a potential self-recruiting mechanism involving activated effector cytotoxic T cells 12819903_Cannot be related to islet autoimmune processes in IDDM. 12847282_A higher amount of IP-10 mRNA is expressed after exposure of keratinocytes to interferon-gamma, leading to migration of T cells from the dermis to the epidermis and representing a second step of chemotaxis following T cell recruitment from blood. 12884299_CCR3 functional responses are regulated by both CXCR3 and its ligands CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11. 12946268_Constitutive NF-kappaB activity is required for the induced gene expression of CXCL10 in tumour cell lines in response to IFNgamma. 12949249_CXCL10 displays antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus. 14507644_Peak of expression of CXCL9 and CXCL10 occurred 4 days before CD8+ T cells infiltrated infected tissues. CXCL9 and CXCL10 may play role early during immune response against rickettsial infections. 14550288_MIG and IP-10 are cleaved by gelatinase B and neutrophil collagenase 14578618_In restinosis, increased plasma concentrations of IP10 were accompanied by a compensatory decrease in the CXCR3 expression on lymphocytes, but not monocytes, suggesting that a high plasma concentration of IP10 strongly induces monocytes signaling. 14600836_both at molecular and protein levels CXCL10 and CXCL12 significantly increased only when cells were differentiated on calcium phosphate-coated slides 14739277_furin is a novel chemokine-modifying enzyme in vitro and most probably also in vivo, generating a C-terminally truncated CXCL10, which fully retains its (inverse) agonistic properties. 15063730_Nitric oxide suppressed IP-10 expression. 15081247_Chronic production of CXCL10 does not alter synaptic plasticity in CXCL10 transgenic (TG)mouse hippocampal slices. By contrast, exogenous recombinant CXCL10 significantly inhibits long-term potentiation in slices from normal C57Bl/6J and CXCL10 TG mice. 15081261_The chemokine CXCL10, usually associated with Th1 cells, is elevated in serum of patients with acute Syndenham's chorea. 15150261_CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11 functions are mediated by intracellular domains of CXCR3 15307834_Pretransplant serum CXCL10 levels might represent a clinically useful parameter to identify subjects who are at high risk of severe rejection and graft failure. 15644410_TRAIL pretreatment of endothelial cells down-modulated mRNA steady-state levels of several TNF-alpha-induced chemokines, and it abrogated the TNF-alpha-mediated up-regulation of CCL8 and CXCL10, modulating leukocyte/endothelial cell adhesion 15725351_These data indicate that IFN-gamma mediates the recruitment of lymphocytes into the lung via production of the chemokine CXCL10, resulting in Tc1-cell alveolitis and granuloma formation. 15745922_increased CXCL10 especially in hypothyroid patients with a more aggressive disorder, and normal CCL2 serum levels in autoimmune thyroiditis 15814716_recruitment might enhance the sequestration of T cells in infected lymphoid organs and the spread of infection between cells, contributing to the immunopathology of AIDS 15843529_IP-10/CXCR3 signaling is associated with the pathogenesis of human myasthenia gravis. 15879427_These results suggest that inhibition of the CXCL10/CXCR3 axis offers a novel target for the treatment of asthma. 15880073_Pretransplant serum CXCL10 levels greater than 150 pg/mL confer an increased risk of early, severe, acute rejection. 15885315_CXCL10 creates a chemokine gradient between the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum and recruits CXCR3-expressing memory CD4+ T-cells into the CSF of neuroborreliosis patients. 15919935_expression induced in macrophages by SARS-CoV infection 15944327_Elevated bronchial mucosal expression of IP-10/CXCL10 is implicated in asthma pathogenesis; its action is partly through selective development and retention, or recruitment of T helper type 2, not Th1, receptor-bearing cells. 15988033_IP10 inhibits viral replication through the induction of host cell death via a p53-mediated apoptotic pathway. 16181055_Increase in serum CXCL10 with advancing age. 16195357_IP-10 was increased in lung tissue from patients who died of SARS 16200621_Increased expression of the interferon-induced angiostatic ELR- CXC chemokines is a feature of juvenile DM that parallels the degree of vasculopathy in patients with the disease. 16210647_This CXCR3 ligand has the ability to activate biochemical (e.g., PtdIns 3-kinase and MAP kinase activation) and functional events in intestinal myofibroblasts. 16243485_Increased plasma IP-10 levels in daughters and sisters of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) patients demonstrates involvement of IP-10 interaction with its receptor CXCR3 as a familial risk factor for PBC. 16490936_Poly IC enhanced the expression of IP-10 mRNA and protein in concentration- and time-dependent manners. Overexpression of RIG-I or IRF-3 potentiated the poly-IC-induced upregulation of IP-10. 16507178_High levels of CXCL10 are present in synovial fluid of children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 16581825_Furthermore, hyaluronan, by inducing IL-8 and IP-10 by distinct pathways, provides a unique target for differential regulation of key inflammatory chemokines. 16645011_Increased sCXCL10 is not associated with Hyper or Hypo per se, but is specifically sustained by the autoimmune inflammatory event occurring in both Graves disease and autoimmune thyroiditis 16709871_CXCL10 is up-regulated in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid taken from human lungs 24 h after lung transplantation. 16733654_Results suggest that MCP-1/CCL2 and IP-10/CXCL10 produced by astrocytes may activate astrocytes in an autocrine or paracrine manner and direct reactive gliosis followed by migration and activation of microglia/macrophages in demyelinating lesions. 16825597_Elevated systemic levels of the chemokines MCP-1, IL-8, and IP-10 precede coronary heart disease but do not represent independent risk factors. 16864907_M. bovis BCG-infected human epithelial cells can have an active role in a local inflammatory immune response via the secretion of IL-4, CXCL-8 and CXCL-10, which can be selectively regulated by Th2-derived cytokines 16867276_The histone H4 deacetylation at the ISRE site is related to the activation of IP-10 by IFN-gamma. 16920957_inhibitory effect of CXCL10/IP-10 on the binding of dengue virus to cells may represent a novel contribution of this chemokine to the host defense against viral infection 16931519_IP-10 mRNA is stabilized by RNA-binding proteins in monocytes treated with S100b 16934957_These results indicated that CXCL10 inhibited LNCaP cell proliferation and decreased PSA production by up-regulation of CXCR3 receptor. CXCL10 may be potentially useful in the treatment of prostate cancer. 16969644_Uregulation of IP-10 during infection of the islets in vivo is the first step towards destructive insulitis. 17018607_Activation of Ras plays a critical role in modulating the expression of both CXCL10 and CXCR3-B, which may have important consequences in the development of breast tumors through cancer cell proliferation. 17052298_IP-10 may play an important role in regulating lymphocytes into the lung and ENA-78 may be associated with lung parenchymal disease in pulmonary sarcoidosis. 17052299_The early induction of IP-10 and IL-2, as well as the subsequent over-production of IL-6 and lack of IL-10 production, probably contribute to the main immuno-pathological processes involved in lung injury in SARS. 17085967_Activation of CXCL10 transcription in response to interferon gamma was paralleled by a decrease in histone H4 acetylation and an increase in recruitment of the STAT1 complex to the CXCL10 interferon-stimulated response element locus. 17211148_Preterm infants have the ability to induce a robust chemokine and cytokine response during sepsis, and IP-10 is a sensitive early marker of infection. 17244787_The reduction of CXCL10 levels after 131I treatment in Graves disease shows that the thyroid gland itself is the main source of circulating CXCL10. 17250724_GGTT haplotype of CXCL10 gene is not susceptibility factor for development of multiple sclerosis(MS), but is probably to influence the course of MS, possibly contributing to slow down disease progression. 17250724_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17255201_prolactin may enhance IFN-gamma-induced CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11 production in keratinocytes 17364892_A study of CXCL10 transport across vascular endothelial cells was done. 17467667_PA increase in IP-10 gene expression (and 2- to 4-fold increases in IL-8, MCP-1, COX-2, and MIG). PA also induced an approximately 2-fold increase (pT, P=.007; 1642 C 17957030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17963704_The serum IP-10 level was increased in AMI, and a higher level of serum IP-10 before PCI may be informative regarding infarct size. 17996064_IP-10 expression in epithelial cell/PBMC co-cultures is regulated by multiple factors, such as intercellular interactions in addition to IFN-gamma and IL-12 levels. 18037659_CXCL10 was detected in macrophages, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts in inflamed dental pulp. 18046562_In colonic epithelial cells, depending on the cellular context and utilizing the NF-kappaB pathway, IL-1beta alone and/or in synergism with IFN-gamma may play a major role in the induction of CXCL10. 18085351_Serum IP-10 levels reflected ulcerative colitis disease activity, and the source of IP-10 was granulocytes and monocytes. 18234638_Chemokine IP-10 may play an important role in trafficking inflammatory cells to the local focus in the liver and induce the development of the chronicity of hepatitis B 18259970_Cytokine treatment (TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IFN-gamma) increased IP-10 and IL-8 protein and mRNA levels. Fluticasone (0.1 nM to 1 microM) increased IP-10 but reduced IL-8 protein release without changing IP-10 mRNA levels assessed by real time RT-PCR. 18275857_DP8 cleavage of the N-terminal two residues of IP10 (CXCL10), ITAC (CXCL11) and SDF-1 (CXCL12), is reported. 18281042_Low serum and peritoneal fluid concentration of interferon-gamma-induced protein-10 (CXCL10) in women with endometriosis. 18282714_Data demonstrate high serum levels of CXCL10 in mixed cryoglobulinemia (MC) and that CXCL10 in MC+autoimmune thyroiditis patients are significantly higher compared to MC patients. 18325387_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18325387_Polymorphism G-210A in the promoter of CXCL10 gene could be a part of the genetic variation underlying the susceptibility of individuals to disease progression of chronic hepatitis B infection. 18379127_CXCL-10 could play an important role in the intra-thyroid angiogenesis modulation, explaining, at least partiality, color Doppler ultrasound findings typical of thyroid autoimmune diseases. 18415893_CXCL10 levels were lower in patients with Graves' disease, but the difference was statistically significant only when compared with patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. 18424889_Significantly decreased interferon-gamma-inducible protein 10 expression is associated with angiogenesis in uterine endometrial cancers 18538864_expression of chemokine receptor/ligand pairs such as CXCR3/CXCL10 have an important role in the proliferation of glioma cells 18645041_These data provide new structure-function dimensions for chemokines in leukocyte mobilization, disclosing an anti-inflammatory role for PAD. 18647352_Candida albicans-derived PGE(2) may impair IFN-gamma-induced IP-10 expression in human keratinocytes and may play a role in the pathogenesis of cutaneous candidiasis. 18682747_IP-10 and il-2 are expressed in high levels in children with tuberculosis and may be used as a diagnostic tool. 18684849_IP-10 and MCP-2 are expressed in tuberculosis patients 18702954_High CXCL10 and CCL2 serum levels in patients with mixed cryoglobulinemia and chronic hepatitis c(MC); CXCL10 in MC + autoimmune thyroiditis is significantly higher than that in MC. 18729739_IFN-alpha2b possibly controls chemotaxis by regulating the interaction between CXCL10 and CXCR3A 18798334_CXCL10 play an important role in the development of necroinflammation and fibrosis in the liver. 18855195_study demonstrates higher serum levels of CXCL10 & CCL2 in patients with psoriatic arthritis without autoimmune thyroiditis than controls; serum CXCL10 levels in psoriatic arthritis patients are significantly higher in presence of autoimmune thyroiditis 18973545_production might be important for the regulation of T-helper 1 cell infiltration in periodontally diseased tissue 18985732_findings demonstrate a synergistic induction of CXCL10 mRNA and protein in astrocytes exposed to HIV-1 and the proinflammatory cytokines 18986693_NO inhibits HRV-16-induced production of CXCL10 by inhibiting viral activation of nuclear factor kappaB and of IRFs, including IRF-1, through a cGMP-independent pathway 19031697_NS1 protein of H5N1 down-regulates the expression level of IP-10. 19065267_Like IFNgamma, IP-10 also does not distinguish between active tuberculosis (TB) and latent TB infection. 19070948_A second phase of injury observed in patients with acute kidney injury may involve IP-10 recruitment of inflammatory cells. 19088500_Report downmodulatory effect of the antihistaminic drug bepotastine on CXCL10 expression in human keratinocytes. 19105984_increased expression are in rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus rythematosus, Sjogren syndrome, systemic sclerosis, and idiopathic inflammatory myopathy 19134328_The interactions between CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL12 expressed in decidua and villi and CXCR3, CXCR4 expressed in CD(56)(+) decidua NK cells may influence the CD(56)(+)NK cell recruitment at the maternal-fetal interface. 19155980_Measurement of pretransplant CXCL10 serum levels could be a clinically useful tool for predicting cardiac acute rejection, especially in the early posttransplant period. 19175890_Development of allergic disease is associated with a more marked Th2-like deviation already at birth, shown as increased levels of cord blood IgE and MDC (CCL22) and higher ratios of MDC (CCL22) to IP-10 (CXCL10) and I-TAC (CXCL11). 19181310_The functional association between PI3K/Akt and NF-kB demonstrates another mechanism in the regulation of M. bovis BCG-induced CXCL10 in A549 cells. 19187771_CXCL10 protein may serve as a marker for beta cell destruction and a potential mechanism for the switch from proliferation into apoptosis in insulin-secreting cells. 19195322_Pretreatment IP-10 levels correlated with HCV viral load, ALT levels, hepatic inflammation and fibrosis. 19203362_transcript levels of CXCL8, CXCL10, calgranulin B and CXCL2 are correlated to ulcerative colitis severity 19223260_The results indicate that the GBP1, STAT1 and CXCL10 may be novel risk genes for the differentiation of PBM at the monocyte stage. 19258635_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19274094_SpeB destroys most of the signaling and antibacterial properties of chemokines expressed by an inflamed epithelium. 19281798_Results from gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry using recombinant CCL2 and CXCL10, incubated with either MMP-2 or -9, indicate that both chemokines are cleaved by the enzymes. 19327225_patients with Psoriatic arthritis had high circulating levels of CXCL10 (chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 10) and CCL2(chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2) compared with controls 19342252_Results suggest upregulated monocytic expression of CXCL-10 as an important molecular mechanism that contributes to increased IL-6 and inflammation activation in frail older adults. 19342664_activation of MEK1 selectively down-regulates human rhinovirus-16-induced expression of CXCL10 via modulation of IFN regulatory factor-1 interactions with the gene promoter in human airway epithelial cells 19410617_Although data did not find an association of the CXCL9 and CXCL10 polymorphisms with type 1 diabetes in the German population, it cannot discard their role in other populations or other autoimmune diseases. 19410617_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19441886_higher circulating levels in patients with hepatitis C virus chronic infection 19447045_Down-regulation of TLR2 and TLR4 abrogates hyperglycemia-induced IP-10 release via NF-kappaB inhibition 19459809_urinary CXCL9 and CXCL10 concentrations demonstrated a close correlation with the extent of subclinical tubulitis, while no such distinction was seen for urinary CXCL4, CXCL11, CCL2 and tubular injury markers. 19472212_Report essential involvement of cross-talk between IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha in CXCL10 production in human THP-1 monocytes. 19479051_The combined actions of HIV-1 Tat and the pro-inflammatory cytokines, IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha, result in the induction of CXCL10 at both the RNA and protein level. 19506876_There was a remarkably high proportion of proangiogenic factors, in particular IP10, ENA-78, and IL-8 accounting for a genetically determined susceptibility to reactive arthritis at the host cell level. 19508602_IL-1beta, TNF and IP-10 in the cerebrospinal fluid and serum are not altered in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension compared to controls. 19523460_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19523460_Single nucleotide polymorphism of CXCL10 might account for susceptibility to tuberculosis. 19558503_We identify IFI27, CCL2 and CXCL10 as sensitive biomarkers for the response of multiple sclerosis patients to IFN-beta. 19565490_There are disease-specific associations between anti-Jo-1 antibody-positive interstitial lung disease and serum levels of CRP as well as the interferon-gamma-inducible chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10. 19590927_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19639049_Significantly lower serum concentration of CXCL-9, CXCL-10, CCL-17, and IL-18 and higher concentration of CXCL-12 and CCL-27 were found in atopic dermatitis patients under 10 years old when compared to Control. 19641142_Enterovirus infection of the pancreas initiates coexpression of interferon-gamma and CXCL10 in beta-cells in type 1 diabetes. 19694638_neutrophils and T cells release differential levels of interferon-gamma-induced protein-10 and IL-8 in response to stimulation with peritoneal fluid obtained from patients with endometriosis 19756997_Endocrine disrupting chemicals suppressed CCL22 and IP-10 levels in cultured monocytes via, at least in part, the MKK1/2-ERK MAPK pathway and histone H4 acetylation. 19800124_The three-dimensional structure of CXCL9 and CXCR3, and, successively, of the CXCL9/CXCR3 complex were modelled in comparison to CXCL10/CXCR3 and CXCL11/CXCR3 complexes. 19817957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19821051_Detection of CXCL10, as a prognostic marker for stage II and III colorectal cancer patients, may contribute to predicting clinical outcome. 19827943_elevated levels of CXCL10 (chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 10) are detected in the Cerebrospinal fluid of patients with late stage African trypanosomiasis 19880820_Human rhinovirus-16-induced CXCL10 production is dependent upon IRF-1. 19887486_IP-10 may play an important role in cell invasion in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma through an autocrine mechanism 19901067_These results suggest that, following L. braziliensis infection, the production of multiple inflammatory mediators, such as CXCL10, by the host may contribute to disease severity by increasing cellular recruitment. 19918044_Results describe the serum levels of IL-1beta, IFN-gamma, and CXCL10 in a series of patients with hepatitis C-related mixed cryoglobulinemia and correlate these measurements with clinical disease features. 19939453_TNFSF14 enhanced IFN-gamma-induced secretion of CXCL10 and CXCL11 from human gingival fibroblasts. 19969087_Data show that Cxcl10 is expressed by a subset of cells within the subventricular zone, constituting a primary chemo-attractant signal for activated T cells in both experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice and in healthy human brain. 20041963_CXCL10 induces cell death in human cultured pancreatic cells leading to apoptosis and DNA fragmentation via CXCR3 signalling 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20059481_Insulitic lesions were characterized by presence of beta cells, elevated levels of the chemokine CXCL10 and infiltration of lymphocytes expressing the corresponding chemokine receptor CXCR3 in all pancreatic lesions of type 1 diabetes patients 20137269_The -1596T allele of IP-10 may be a beneficial factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 20137825_CXCL-9 and CXCL-10 play a major role in the development of hepatic flares. Their differential expression in acute versus chronic patients suggests the presence of different mechanisms that govern liver injury during acute and chronic hepatitis B. 20144041_Serum chemokine (C-X-C motif ) ligand 10 levels are elevated in patients with Graves' disease in long-term remission 20153790_elevated plasma levels in patients with autoimmune thrombocytopenia 20164184_novel molecular mechanism of HBV infection inducing IP-10 expression, which involves viral protein HBx affecting NF-kappaB pathway, leading to transactivation of the IP-10 promoter 20186422_CXCL10 appears to be a new promising noninvasive biomarker for pulmonary arterial hypertension. 20186843_In patients with chronic hepatitis C, low levels of intrahepatic and systemic IP-10 predict a favorable first-phase decline of HCV RNA during therapy with pegylated interferon and ribavirin for genotypes of HCV. 20187787_CXCL10 polymorphism can predict severity of Graves disease. 20187787_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20299237_The effect of IFNalpha, IFNbeta and IFNgamma on the secretion of the Th1 chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10, in primary cultures of human thyroid follicular cells and to assess the effect of PPARgamma activation on CXCL9 and CXCL10 secretion, were tested. 20302596_elocalcitol and BXL-01-0029 could decrease the expression of CXCL10 in activated renal tubular cells in vitro and thus be useful in kidney allograft rejection treatment. 20404089_These findings strongly suggest that epigenetic dysregulation involving interactions between histone deacetylation and hypermethylation is responsible for targeted repression of IP-10 in fibrotic lung disease. 20473322_Autophagic responses play a role in influenza virus-induced CXCL10 and interferon-alpha expression in primary human blood macrophages. 20485145_CXCL10 over-expression, the distinct gene signature of acute-phase graft injury and tumor invasiveness in small-for-size liver grafts, may contribute to early tumor recurrence after liver transplantation 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20523065_Serum levels of ECP, IL-5, -6, -8 and -10, G-CSF, MCP-1, IL-1 ra and IP-10 were significantly elevated in acute compared with stable childhhood asthma. 20525556_The levels of IP-10 and IP-10 mRNA in the peripheral blood of patients with cirrhosis increase, are closely correlated with the load of HBV DNA in serum, and play a key role in the progression of post-hepatitic cirrhosis. 20592450_Decreased IP-10 levels are associated with viral clearance following therapy in patients with hepatitis C virus. 20626297_predominant expression in the brain during chronic infection with Toxoplasma gondii is dependent on interferon-gamma 20648615_in this study the mean CXCL10 serum levels were not elevated in patients with type 1 diabetes neither in patients with proven enterovirus infection. 20680966_Data show that oncostatin M stimulation induced CXCL10 and ICAM-1 expression in human gingival fibroblasts stimulated with IL-1beta. 20833730_TNFalpha and IFNgamma synergistically enhance transcriptional activation of CXCL10 in human airway smooth muscle cells via STAT-1, NF-kappaB, and the transcriptional coactivator CREB-binding protein. 20856926_CXCL10 inhibits endothelial cell proliferation independently of CXCR3. 20929277_increased serum levels in cryoglobulinemic patients with hepatitis C virus chronic infection 20943047_Our study identifies IP-10 and interleukin 5 as proteins differentiating complicated and uncomplicated plaques from human carotid arteries 20948191_microRNA-155 negatively regulates the expression of transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase-1-binding protein 2 and downstream IFN-gamma-inducible protein of 10 kDa as a negative feedback system (IP-10). 20980518_This study identifies VZV-induced CXCL10 as a potential driver of T lymphocyte recruitment into dorsal root ganglion during herpes zoster. 21045270_Low plasma levels of CXCL10 may reflect successful control of non-tuberculosis mycobacteria lung disease with or without therapy 21054674_Viral persistence was associated with elevated IL-10 mRNA and inducible protein-10 gene expression. 21062959_in this study, we could demonstrate that the NF-kappaB pathway is essential for the regulation of IP-10 in primary human 21099280_Toll like receptor 4 as the receptor for CXCL10 and as new pathway for the induction of beta-cell apoptosis. 21106778_A time- and dose-dependent increase in IP-10 is found upon activation of viral receptors expressed on mesothelial cells, which provides novel evidence for a link between viral infections and inflammation of serous membranes. 21167783_Mycobacterium tuberculosis increases IP-10 and MIG protein despite inhibition of IP-10 and MIG transcription. 21183794_CXCL10 in the plasma of patients chronically infected with HCV exists in an antagonist form, due to in situ amino-terminal truncation of the protein. 21191639_CXCL10 and CXCL13 Expression were highly up-regulated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in acute rejection and poor response to anti-rejection therapy. 21219680_IP-10 may be used for detecting latent tuberculosis infection and as a potential biomarker to identify active TB in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving anti-TNF-alpha treatment. 21254158_When IL28B genotype is combined with pretreatment serum IP-10 measurement, the predictive value for discrimination between sustained virological response and nonresponse is significantly improved, especially in non-CC genotypes. 21270681_Chemokine CXCL10, in particular, effectively recruits isolated annulus fibrosis cells in the process of herniated disc tissue repair and homeostasis. 21303425_Suggest that the renal TWEAK/Fn14 and IP-10/CXCR3 axis may contribute to the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. 21303517_These results show that while the expression of MIG/CXCL9 and IP-10/CXCL10 are elevated in Systemic sclerosis (SSc) serum, the expression of CXCR3 is downregulated on SSc dermal Endothelial cells. 21390311_Concomitant assessment of pretreatment IP-10 and IL28B-related SNPs augments the prediction of the first phase decline in HCV RNA, RVR, and final therapeutic outcome. 21454254_In hepatitis C virus-associated glomerulonephritis a significant upregulation of both interferon-gamma-inducible protein and TNF-alpha is mediated specifically by the viral receptor Toll-like receptor 3 21457060_from a number of neuromuscular manifestations, only the existence of carpal tunnel syndrome correlated with significantly higher CXCL10 levels 21475065_Letter: Pret | ENSMUSG00000034855 | Cxcl10 | 33.983682 | 0.207526623 | -2.268632 | 0.31729279 | 55.043787 | 0.0000000000001178743341047394189498690661059109736615111568847069634102808777242898941040039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000047930993763287641610600466347294707023657389655113547632936388254165649414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 11.9543911 | 4.0060360 | 57.9559275 | 17.6669822 | |
| ENSG00000169248 | 6373 | CXCL11 | protein_coding | O14625 | FUNCTION: Chemotactic for interleukin-activated T-cells but not unstimulated T-cells, neutrophils or monocytes. Induces calcium release in activated T-cells. Binds to CXCR3. May play an important role in CNS diseases which involve T-cell recruitment. May play a role in skin immune responses. | 3D-structure;Chemotaxis;Citrullination;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Inflammatory response;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | Chemokines are a group of small (approximately 8 to 14 kD), mostly basic, structurally related molecules that regulate cell trafficking of various types of leukocytes through interactions with a subset of 7-transmembrane, G protein-coupled receptors. Chemokines also play fundamental roles in the development, homeostasis, and function of the immune system, and they have effects on cells of the central nervous system as well as on endothelial cells involved in angiogenesis or angiostasis. Chemokines are divided into 2 major subfamilies, CXC and CC. This antimicrobial gene is a CXC member of the chemokine superfamily. Its encoded protein induces a chemotactic response in activated T-cells and is the dominant ligand for CXC receptor-3. The gene encoding this protein contains 4 exons and at least three polyadenylation signals which might reflect cell-specific regulation of expression. IFN-gamma is a potent inducer of transcription of this gene. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2014]. | hsa:6373; | extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; CXCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0045236]; CXCR3 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0048248]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051281]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell chemotaxis [GO:0010818] | 11559369_chemotactic activity for CXCR3-expressing cells; substrate for dipeptidylpeptidase IV 12055261_I-TAC is a highly potent chemoattractant of normal blood CD4 and CD8 T cell transendothelial migration and a major mediator of blood memory T lymphocyte migration to inflammation. 12162873_The IFN-gamma-inducible T cell alpha-chemoattractant was induced in human brain microvascular endothelial cells and astrocytes only after inflammatory stimuli. 12169689_These data suggest that IFN-beta acts through PI3K to enhance the transactivation competence of NF-kappa B complexes through phosphorylation of p65 within the TAD of beta-R1. 12695288_Levels of ITAC/CXCL11 were found elevated in patients with severe transplantation coronary artery disease (TCAD) compared with long-term survivors of transplantation without TCAD and healthy volunteers who had not undergone transplantation 12787142_increased calpain activity in undifferentiated keratinocytes. inhibited calpain activity in fibroblasts. redifferentiated basal keratinocytes limit fibroblast repopulation of dermis of healed wounds while promoting re-epithelialization. 12847282_A higher amount of I-TAC mRNA is expressed after exposure of keratinocytes to interferon-gamma, leading to migration of T cells from the dermis to the epidermis and representing a second step of chemotaxis following T cell recruitment from blood. 12884299_CXCR3 ligands inhibit CCR3-mediated functional responses of both human eosinophils and CCR3 transfectants induced by all three eotaxins, with CXCL11 being the most efficacious antagonist. 12949249_CXCL11 displays antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus. 15122750_I-TAC, one of the most potent chemoattractants for activated T cells, is produced by hepatocytes in the HCV-infected liver and plays an important role in T cell recruitment and ultimately the pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis C 15150261_CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11 functions are mediated by intracellular domains of CXCR3 15308116_ductal epithelial cells produce I-TAC proteins in response to stimulation with IFNgamma secreted by lymphocytes 15653416_novel I-TAC -599del5 promoter polymorphism is a functional variant in the presence of replicating HCV and may predispose to HCV disease susceptibility. 15814716_recruitment might enhance the sequestration of T cells in infected lymphoid organs and the spread of infection between cells, contributing to the immunopathology of AIDS 15885315_CXCL11 creates a chemokine gradient between the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum and recruits CXCR3-expressing memory CD4+ T-cells into the CSF of neuroborreliosis patients. 16081539_autocrine-acting CXCL11 mediates, at least in part, the regulations of osteoclastogenesis by type I interferons 16200621_Increased expression of the interferon-induced angiostatic ELR- CXC chemokines is a feature of juvenile DM that parallels the degree of vasculopathy in patients with the disease 16210647_This CSCR3 ligand has the ability to activate biochemical (e.g., PtdIns and MAP kinase activation) and functional events (actin reorganization) in intestinal myofibroblasts. 16358960_Increased I-TAC levels in blood and cerebrospinal fluid is associated with Lyme borreliosis 16368892_CXCL11-dependent CXCR3 internalization and cell migration are regulated by the CXCR3 membrane proximal carboxyl terminus, whereas adhesion is regulated by the 3i loop S245. 17142784_IFN-gamma promotes implantation by stimulating EEC to produce CXCL11, which induces migration of trophoblast cells and T cells, proliferation of ESC, and apoptosis of EEC. 17255201_prolactin may enhance IFN-gamma-induced CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11 production in keratinocytes 17363734_CD13 rapidly processed CXCL11, but not CXCL8, to generate truncated CXCL11 forms that had reduced binding, signaling, and chemotactic properties for lymphocytes and CXCR3- or CXCR7-transfected cells. 18209084_Egression of human T cells across the bronchial epithelium is a multistep process, driven in part by a polarized transepithelial gradient of CXCL11 that is up-regulated in patients with chronic obstructive airways disease. 18258269_Data show that RIG-I mRNA and protein are expressed in HeLa cells stimulated with IFN-gamma, and that RNA interference against RIG-I results in the suppression of IFN-gamma-induced CXCL11 expression. 18275857_DP8 cleavage of the N-terminal two residues of IP10 (CXCL10), ITAC (CXCL11) and SDF-1 (CXCL12), is reported. 18316607_CXCL-11 is targeted by ebv-mir-BHRF1-3 in primary lymphomas 18411283_potential new roles in down-regulating Th1 lymphocyte chemoattraction through MMP processing of CXCL11. 18515987_There are elevated concentrations of the chemokines MDC, eotaxin, I-TAC, and MCP-1 in malignant pleural effusions. 18645041_These data provide new structure-function dimensions for chemokines in leukocyte mobilization, disclosing an anti-inflammatory role for PAD. 18669615_IP-9 is a key ligand in the CXCR3 signaling system for wound repair 19175890_Development of allergic disease is associated with a more marked Th2-like deviation already at birth, shown as increased levels of cord blood IgE and MDC (CCL22) and higher ratios of MDC (CCL22) to IP-10 (CXCL10) and I-TAC (CXCL11). 19274094_SpeB destroys most of the signaling and antibacterial properties of chemokines expressed by an inflamed epithelium. 19800124_The three-dimensional structure of CXCL9 and CXCR3, and, successively, of the CXCL9/CXCR3 complex were modelled in comparison to CXCL10/CXCR3 and CXCL11/CXCR3 complexes. 19875106_Studies indicate that I-TAC-targeted intervening strategies would have potential application for the alleviation of acute transplant rejection. 19939453_TNFSF14 enhanced IFN-gamma-induced secretion of CXCL10 and CXCL11 from human gingival fibroblasts. 20036838_Studies indicate that CXCR7 is an interceptor for CXCL12 and CXCL11. 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20529825_The expression and function of CXCR3 and CXCR7 receptors in cervical carcinoma, rhabdomyosarcoma and glioblastoma cell lines, was evaluated. 20810571_A potent dose-dependent inhibition by PPARalpha-agonists was observed on the cytokines-stimulated secretion of CXCL11 in Graves disease and in primary thyrroid culture. 20848514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21438871_involved in microbial-induced intestinal inflammation and Th17 cell development in ulcerative colitis 21442287_positive ratios of CXCR7, CXCL12 and CXCL11 in oral leukoplakia and oral squamous cell carcinoma tissues respectively, were significantly higher than that in normal epithelia 21470996_We first show that circulating CXCL9 and CXCL11 are increased in patients with thyroiditis and hypothyroidism and are related to each other. 21645215_CXCR3 ligands, CXCL9,10,11, are differentially expressed during chronic liver diseases across different disease stages and aetiologies. 21724697_A strong relationship between circulating IFN-gamma and CXCL11 is shown, supporting the role of a T helper (Th)1 cell immune response in the pathogenesis of mixed cryoglobulinemia and hepatitis C. 21962843_Elevated plasma levels of interferon-gamma and Cys-X-Cys chemokine receptor 3-binding chemokine CXCL11 are present in patients with thoracic aortic aneurysms. 22008312_CXCL10, CXCL11, CXCL12 and CXCL13 chemokines are biomarkers in serum and cerebrospinal fluid in patients with tick borne encephalitis 22160826_Our study first demonstrates higher serum levels of CXCL11 chemokine in patients with mixed cryoglobulinemia than in hepatitis C virus-positive patients, and in particular in the presence of autoimmune thyroiditis. 22168752_circulating CXCL11, together with CXCL10, is increased in patients with thyroiditis and hypothyroidism, and is related to CXCL10 levels. 22367045_Expression of CXCL9, -10, and -11 chemokines and their receptor CXCR3 increases in the aqueous humor of patients with herpetic endotheliitis. 22691213_Elevated BALF concentrations of CXCL11 in systemic sclerosis patients who do not developed lung fibrosis suggest that determination of CXCL11 in BALF could serve as a prognostic factor for pulmonary function decline. 23012327_In chronic graft-vs-host disease, increased levels of the Th1-associated chemokines CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11 led to recruitment of CXCR3+ T cells from the peripheral blood into affected tissues. 23158864_There was no difference in expression of I-TAC between immune thrombocytopenic purpura patients and healthy controls. 23225384_This study demonistrated that CXCL11, absent from normal muscle fibers, were induced in DMD myofibers. and up regulattion on blood vessel endothelium of DMD patients. 23527708_Our study demonstrates in mixed cryoglobulinemia and hepatitis C vs controls: (i)high serum CXCL9 and CXCL11, significantly associated with the presence of active vasculitis; (ii) a strong relationship between circulating CXCL9 and CXCL11 23559389_Th1 chemokines CXCL11 and CXCL10 may be involved in the pathogenesis of mixed cryoglobulinemia; IL-6 and CCL2 may be involved in regulating their elevation 23600831_CXCR3 ligands CXCL10, CXCL9 and CXCL11 were measured in 245 children with opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome and 81 controls. 23985752_The expression of MIF mRNA was compared with VEGF mRNA expression and with mRNA expression of other chemokines related to neo-angiogenesis, such as CXCL12, CXCL11, CXCL8 and CXCR4, in human endometrial cancer tissue and normal endometrium. 24063316_CXCL11 was mildlylavage fluid during diffuse alveolar damage, but not during acute rejection or lymphocytic bronchiolitis. Elevated CXCL11 was associated with increased risk of chronic allograft dysfunction. 24104601_Although TARC and I-TAC may not directly regulate pruritus in atopic dermatitis patients, these chemokines are very sensitive disease markers of AD. 24526602_The chemokine CXCL11 is produced by mesenchymal stem cells and interacts with CXCR3. 25251331_High CXCL11 expression is associated with acute cellular rejection. 25559603_The homozygosity for the CXCL9 rs10336 (T), CXCL10 rs3921 (G), and CXCL11 rs4619915 (A) alleles is associated with the higher likelihood of significant liver fibrosis in HIV-infected patients coinfected with hepatitis C virus genotype 1. 25605062_Cyclic stretch significantly induced ESC secretion of CXCL8 and CXCL1 and neutrophil chemotaxis. Stretch also increased MMP-1, MMP-2, and MMP-3 activity, activin A secretion, and activity in ESC. 25713416_These findings functionally integrate K17, hnRNP K, and gene expression along with RSK and CXCR3 signaling in a keratinocyte-autonomous axis and provide a potential basis for their implication in tumorigenesis 25741937_In contrast to elevated 1st trimester levels of IP-10 previously found in the maternal serum of women who later developed preeclampsia, this study found lower umbilical cord IP-10 and ITAC plasma levels in near-term gestations with established severe preeclampsia. 25810367_Developmental expression patterns of chemokines CXCL11, CXCL12 and their receptor CXCR7 in testes 25858769_Common variants of CXCR3 and its ligands CXCL10 and CXCL11 are associated with vascular permeability of dengue infection in peninsular Malaysia. 25890876_Resveratrol substantially inhibited the proinflammatory cytokines-induced CXCL11 production while partially blocking nuclear factor-kappaB activation. 26212075_CXCL11 levels are mainly increased in patients with non-alcoholic cirrhosis and high portal pressure. Moreover, levels of CXCL11 might predict long-time survival of cirrhotic patients undergoing TIPS. 26275808_higher concentration is associated with neutrophils accumulation in the alveolar space of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus patients with pulmonary fibrosis 26506526_congruent with the concept that inflammation plays a key role in the pathogenesis of LV dysfunction, MIG, IP10 and I-TAC add diagnostic accuracy over and beyond NT-pro BNP. 26910919_High CXCL11 expression is associated with clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. 27014863_CCL5 and CXCL11 expression were also induced in response to the activation of the PKC pathway, and gene silencing experiments indicated that their inducible expression was dependent on RIPK4 and IRF6. Moreover, gene reporter assays suggested that RIPK4 induces CCL5 and CXCL11 expression by stimulating the transactivation of their promoters by IRF6. 27034164_Neuroendocrine-like cells promote the chemotaxis activity of tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) via CXCL10 and CXCL11. 27356947_The homozygous variant CXCL11 AA genotype (rs6817952) is associated with an increased risk of contact allergy. 27522581_this study shows that melanoma peptides vaccination and intratumoral administration of IFNgamma increases production of CXCL11 in patient tumors 27567247_CXCL8/11 may promote the disease progression of osteoarthritis (OA), and may also serve as new therapeutic targets for treatment of OA. 27759557_BK polyomavirus infection can induce CXCL11 gene expression in kidney transplant patients. 28363904_this study shows that oxidative signaling inhibits T lymphocyte chemotaxis to the inflammatory chemokine CXCL11 28381820_S100A9 and S100A12 may have a role in the pathogenesis of pneumonia: S100A9 and CXCL1 may contribute solely in mild pneumonia, and CCL5 and CXCL11 may contribute in severe pneumonia. 28472186_data suggest that STAT2 plays a role in the psoriasis pathogenesis by regulating the expression of CXCL11 and CCL5, and thereby attracting IFNgamma-producing immune cells to the skin 28488542_Downregulation of CXC chemokine ligand 11 can inhibit tumor angiogenesis, suggesting that anti-CXC chemokine ligand 11 therapy may offer an alternative treatment strategy for TWIST1-positive ovarian cancer 28693588_CXCL11 production in cerebrospinal fluid was found in herpes simplex meningitis, but not in herpes simplex encephalitis. 29542173_Finding demonstrated that miR-206 negatively regulated PCa cell proliferation and migration, and arrested cell cycle by targeting CXCL11 as a tumor suppressor in prostate cancer. 29795466_Studied role of chemokines (including C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 11 [CXCL11] and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 [CXCL10] in the CXCR3 axis with regards to angiogenesis in adipose tissue of morbidly obese patients. 29901202_V2O5 induction of CXCL8 and CXCL11 chemokines may lead to the appearance and perpetuation of an inflammatory reaction into the dermal tissue. Further studies are required to evaluate dermal integrity and manifestations in subjects occupationally exposed, or living in polluted areas. 30051594_These findings identify a feed-forward mechanism that sustains activation of the CXCR7/CXCL11 axis under ERalpha control to induce the epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathway and metastatic behavior of ovarian cancer cells. 30771435_Study confirmed that CXCL11 expression was significantly upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) alpha2delta1+ tumor-initiating cells (TICs) and that it played a crucial role in the acquirement and subsequent maintenance of self-renewal and tumorigenic abilities of HCC alpha2delta1+ TICs through the CXCR3/ERK1/2 signaling axis via autocrine signaling. 30826602_serum CXCL11 and CXCL12 levels were elevated in cirrhotic patients 31437604_CXCL11 promotes tumor progression by the biased use of the chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CXCR7. 31836011_The combination of CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11 levels during primary HIV infection predicts HIV disease progression. 32659248_Endothelial cells under therapy-induced senescence secrete CXCL11, which increases aggressiveness of breast cancer cells. 32971208_Mechanisms underlying the production of chemokine CXCL11 in the reaction of renal tubular epithelial cells with CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells. 33187013_The CXCL11-CXCR3A axis influences the infiltration of CD274 and IDO1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 33441425_The intratumoral CXCR3 chemokine system is predictive of chemotherapy response in human bladder cancer. 33502606_Identification of CXCL11 as part of chemokine network controlling skeletal muscle development. 33707417_Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived CXCL11 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and tumor metastasis through the circUBAP2/miR-4756/IFIT1/3 axis. 34101271_Childhood CCL18, CXCL10 and CXCL11 levels differentially relate to and predict allergy development. 34205098_The Pro-Inflammatory Chemokines CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11 Are Upregulated Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection in an AKT-Dependent Manner. 34534571_Association of chemokines IP-10/CXCL10 and I-TAC/CXCL11 with insulin resistance and enhance leukocyte endothelial arrest in obesity. 34655278_Colon cancer cells secreted CXCL11 via RBP-Jkappa to facilitated tumour-associated macrophage-induced cancer metastasis. 35381326_Epigenetic activation of RBM15 promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma growth, metastasis and macrophage infiltration by regulating the m6A modification of CXCL11. 35390315_RAMP2-AS1 inhibits CXCL11 expression to suppress malignant phenotype of breast cancer by recruiting DNMT1 and DNMT3B. 35935945_CXCL11 Correlates with Immune Infiltration and Impacts Patient Immunotherapy Efficacy: A Pan-Cancer Analysis. | 7.050470 | 0.221499150 | -2.174627 | 0.70135355 | 10.149083 | 0.0014437304144061904095236448242189908341970294713973999023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0103140454732961149575398707156637101434171199798583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 2.5565243 | 1.8186586 | 11.5586368 | 7.3616073 | |||
| ENSG00000169403 | 5724 | PTAFR | protein_coding | P25105 | FUNCTION: Receptor for platelet activating factor, a chemotactic phospholipid mediator that possesses potent inflammatory, smooth-muscle contractile and hypotensive activity. Seems to mediate its action via a G protein that activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1281995, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1374385, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1656963, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1657923}. | Cell membrane;Chemotaxis;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a seven-transmembrane G-protein-coupled receptor for platelet-activating factor (PAF) that localizes to lipid rafts and/or caveolae in the cell membrane. PAF (1-0-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine) is a phospholipid that plays a significant role in oncogenic transformation, tumor growth, angiogenesis, metastasis, and pro-inflammatory processes. Binding of PAF to the PAF-receptor (PAFR) stimulates numerous signal transduction pathways including phospholipase C, D, A2, mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), and the phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Following PAFR activation, cells become rapidly desensitized and this refractory state is dependent on PAFR phosphorylation, internalization, and down-regulation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. | hsa:5724; | membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; G protein-coupled purinergic nucleotide receptor activity [GO:0045028]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; lipopolysaccharide binding [GO:0001530]; lipopolysaccharide immune receptor activity [GO:0001875]; mitogen-activated protein kinase binding [GO:0051019]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; platelet activating factor receptor activity [GO:0004992]; cellular response to 2-O-acetyl-1-O-hexadecyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine [GO:1904317]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; cellular response to fatty acid [GO:0071398]; cellular response to gravity [GO:0071258]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; inositol trisphosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0032959]; negative regulation of blood pressure [GO:0045776]; parturition [GO:0007567]; phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling [GO:0048015]; positive regulation of cellular extravasation [GO:0002693]; positive regulation of gastro-intestinal system smooth muscle contraction [GO:1904306]; positive regulation of inositol phosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0060732]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of leukocyte tethering or rolling [GO:1903238]; positive regulation of maternal process involved in parturition [GO:1904303]; positive regulation of neutrophil degranulation [GO:0043315]; positive regulation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0010863]; positive regulation of sensory perception of pain [GO:1904058]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of transcytosis [GO:1904300]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of voltage-gated chloride channel activity [GO:1902943]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to dexamethasone [GO:0071548]; response to symbiotic bacterium [GO:0009609]; transcytosis [GO:0045056] | 11861812_activates the extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase and induces proliferation of epidermal cells 11928813_Neuroblastoma clone cells show an inverse relationship between invasiveness and differentiative capacity and by the expression of specific cell surface PAF receptors. 12467527_PAF receptor transcripts in five human cancer cell lines derived from the breast (BT20, SKBR3 and T47D cells), the pancreas (Miapaca cells) and the bladder (5,637 cells) confirm the existence of a splice variant of the PAF-R transcript 2. 12601006_a novel pathway whereby the epidermal PAF-R can augment chemotherapy-induced apoptotic effects through an NF-kappaB-dependent process 12713583_the epidermal platelet-activating factor receptor augments staphylococcal alpha-toxin signaling 12756251_platelet-activating factor receptor is desensitized and internalized by coumermycin-gyrase B-induced dimerization 14500680_The C-terminal tail of the PAFR is of critical importance for platelet-activating factor-induced Janus kinase 2 activation. 14500726_PAFR degradation can occur via both the proteasome and lysosomal pathways and ligand-stimulated degradation is ubiquitin-dependent 14617636_platelet-activating factor receptor-mediated signaling has a critical role in differentiated endothelial cell functions, including cell migration and proteolytic activation of MMP2 15115767_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15149885_investigated whether the increase of uPA monocyte expression and chemokine releases induced by oxidised low density lipoproteins involved proinflammatory phospholipid products having platelet-activating factor-like activity via the PAFR pathway 15160913_Analysis of 102 B-CLL patients revealed dramatic differences for their membrane PAF-R expression, a result that might be related to their plasma IL-4 levels. 15748960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15748960_the PAFR gene missense mutation has a relation to the susceptibility for multiple sclerosis . 16115894_UVB photo-oxidizes cellular phospholipids, creating PAF analogs that stimulate the PAF receptor to induce further PAF synthesis and apoptosis 16306050_PAF induced CREB and ATF-1 phosphorylation via a PAFR-mediated signal transduction mechanism that required pertussis toxin-insensitive Galphaq protein and adenylate cyclase activity and was antagonized by a cAMP-dependent PKA and p38 MAPK inhibitors. 16793019_presence of functional PAF-R in arterial spindle-shaped smooth muscle cells of synthetic phenotype may be important for their migration from the media into the intima and atherosclerotic plaques formation 16837045_The functional PAF-R are present in blast cells of patients with acute leukemia; a result that could be of physiologic importance regarding the important effect of PAF on leukocytes maturation and functions. 16984258_These studies suggest that SZ95 sebocytes express functional PAF-Rs and PAF-Rs are involved in regulating the expression of inflammatory mediators, including COX-2, PGE(2) and IL-8. 17928889_epidermal PAF-R can modulate UVB-mediated early gene expression 18187960_a lower expression of PAFR in HCC correlated with both poor differentiation and portal venous invasion. 18632638_analysis of PAFR activation and pleiotropic effects on tyrosine phospho-EGFR/Src/FAK/paxillin in ovarian cancer 19474802_cis-urocanic acid stimulates mediator production by a pathway that is independent of these serotonin 2A and PAF receptors in human keratinocytes 19620302_PAFR is localized in lipid rafts and/or caveolae, a position that is important for proper coupling to downstream signaling elements. 19703903_analysis of the cross-talk between protease-activated receptor 1 and platelet-activating factor receptor regulates melanoma cell adhesion molecule (MCAM/MUC18) expression and melanoma metastasis 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20007715_conserved proline in TM6 is crucial for intracellular trafficking of PAFR. 20032301_Results reveal that some strains of Gram-positive bacteria exploit hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha-regulated platelet-activating factor receptor as a means for translocation through intestinal epithelial cells. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20392487_role in activation of mast cells by PAF. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20637897_The expression of PAF receptor (PAF-R) in early endothelial progenitor cell and the release of PAF under stimulation with factors involved in endothelial dysfunction, were investigated. 21063106_Platelet-activating factor plays a pivotal role in the oxLDL-induced recruitment of hBMSCs through mechanisms involving platelet-activating factor receptor dependent activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases. 21247619_Urban particulate matter (PM) increases adhesion of S. pneumoniae to human airway epithelial cells. PM-stimulated adhesion is mediated by oxidative stress and PAFR. 21615674_Pneumococcal ligands keratin 10, laminin receptor and platelet-activating factor receptor are elevated in aged lungs and contribute to the enhanced susceptibility to pneumonia. 21658861_An implication of platelet-activating factor receptor A224D mutation in the susceptibility to relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis in Tunisian population. 22570511_PAFR may have a role in tumor response mechanisms, such as stress responses caused by chemotherapeutic agents 22577252_recognition of apoptotic cells by phagocytes leads to activation of PAFR pathways, resulting in a microenvironment response favorable to melanoma growth 22595142_Eosinophils use their platelet-activating factor receptors (PAFRs) to interact directly with Staphylococcus aureus. 23070058_Data suggest that expression of PAFR and SIRT1 (sirtuin 1) is down-regulated in endothelial progenitor cells of type 2 diabetic patients with poor glycaemic control compared to those with good glycaemic control. 23911710_Inhibition of platelet aggregation by lipoteichoic acid was blocked using a monoclonal anti-PafR antibody and Ginkgolide B,a well-defined PafR antagonist, demonstrating that the LTA inhibitory signal occurs via PafR. 24062612_oxLDL induces alternative macrophage activation by mechanisms involving CD36 and PAFR 24130805_oxLDL induces the recruitment of PAFR and CD36 into the same lipid rafts, which is important for oxLDL uptake and IL-10 production 24289152_Data suggest PAF/PAF receptor signaling exerts proinflammatory effect on neutrophil via down-regulation of LXRa (liver X receptor alpha) and target genes (ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABC) A1, ABC G1, sterol response element binding protein 1c). 24824933_patients presenting elevated PAFR expression had significantly longer survival times compared to those with low PAFR expression (log-rank test, p | ENSMUSG00000056529 | Ptafr | 52.619819 | 0.365898044 | -1.450486 | 0.23394262 | 39.280168 | 0.0000000003671515526740078409954808439394444846692877604255045298486948013305664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000100700312133412190992991393483774187345147765881847590208053588867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 28.0195921 | 7.4031064 | 76.8523284 | 19.4088782 | |
| ENSG00000169964 | 131616 | TMEM42 | protein_coding | Q69YG0 | Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:131616; | membrane [GO:0016020] | ENSMUSG00000066233 | Tmem42 | 50.593428 | 2.673721915 | 1.418849 | 0.44504364 | 9.763608 | 0.0017800022088922339523475724121226448914967477321624755859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0122956399496220083328301697633833100553601980209350585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 71.6385683 | 25.5860206 | 26.7243144 | 9.5000724 | |||
| ENSG00000170054 | 327657 | SERPINA9 | protein_coding | Q86WD7 | FUNCTION: Protease inhibitor that inhibits trypsin and trypsin-like serine proteases (in vitro). Inhibits plasmin and thrombin with lower efficiency (in vitro). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17447896}. | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine protease inhibitor;Signal | Enables serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of endopeptidase activity. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and membrane. Predicted to be active in extracellular space. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:327657; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; negative regulation of endopeptidase activity [GO:0010951] | 12819018_Results report the cloning of germinal center B-cell expressed transcripts 1 and 2 (GCET1 and 2), and show that both are expressed in follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with germinal center B-cell differentiation. 17447896_The cloning, expression and molecular characterization of recombinant serpina9 (centerin) are reported. 17898315_Gcet-1 protein expression is restricted to a subset of germinal center B cells, establishing the existence of a distinct heterogeneity among normal and neoplastic germinal center B cells 17975119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18550480_Immunohistochemical expression of centerin further defines the germinal center cell origin of a subgroup of lymphomas. 18799872_serpinA9 was associated with stroke in both whites and blacks 19023099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25203428_Diagnostic Utility of the Germinal Center-associated Markers GCET1, HGAL, and LMO2 in Hematolymphoid Neoplasms. | ENSMUSG00000058260 | Serpina9 | 15.557513 | 0.257122290 | -1.959473 | 0.41730105 | 23.786457 | 0.0000010763714104721143823169531711370083826295740436762571334838867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000176509768929471697084584297376963490933121647685766220092773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 6.2353339 | 5.1583864 | 24.3163513 | 19.4586604 | |
| ENSG00000170190 | 9121 | SLC16A5 | protein_coding | O15375 | FUNCTION: Proton-linked monocarboxylate transporter. Catalyzes the rapid transport across the plasma membrane of many monocarboxylates such as lactate, pyruvate, branched-chain oxo acids derived from leucine, valine and isoleucine, and the ketone bodies acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetate (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Membrane;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | This gene encodes a member of the monocarboxylate transporter family and the major facilitator superfamily. The encoded protein is localized to the cell membrane and acts as a proton-linked transporter of bumetanide. Transport by the encoded protein is inhibited by four loop diuretics, nateglinide, thiazides, probenecid, and glibenclamide. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2012]. | hsa:9121; | membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; monocarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008028]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; monocarboxylic acid transport [GO:0015718] | 22911660_We demonstrated that SLC16A5 and ZNF206 displayed altered methylation patterns in the neuroblastoma genome 28448657_Identify a novel association between protein-coding variation in SLC16A5 and cisplatin-induced ototoxic effects in testicular cancer patients. 34549875_Solute carrier family 16 member 5 downregulation and its methylation might serve as a prognostic indicator of prostate cancer. | ENSMUSG00000045775 | Slc16a5 | 18.484372 | 2.120662052 | 1.084515 | 0.35573043 | 9.346237 | 0.0022344374976777489801016418624612924759276211261749267578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0148905725190644853267452063505515980068594217300415039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 25.1626078 | 4.1836127 | 11.9914368 | 2.2577165 | |
| ENSG00000170745 | 3790 | KCNS3 | protein_coding | Q9BQ31 | FUNCTION: Potassium channel subunit that does not form functional channels by itself. Can form functional heterotetrameric channels with KCNB1; modulates the delayed rectifier voltage-gated potassium channel activation and deactivation rates of KCNB1 (PubMed:10484328). Heterotetrameric channel activity formed with KCNB1 show increased current amplitude with the threshold for action potential activation shifted towards more negative values in hypoxic-treated pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O88759, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10484328}. | Cell membrane;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Potassium;Potassium channel;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel | Voltage-gated potassium channels form the largest and most diversified class of ion channels and are present in both excitable and nonexcitable cells. Their main functions are associated with the regulation of the resting membrane potential and the control of the shape and frequency of action potentials. The alpha subunits are of 2 types: those that are functional by themselves and those that are electrically silent but capable of modulating the activity of specific functional alpha subunits. The protein encoded by this gene is not functional by itself but can form heteromultimers with member 1 and with member 2 (and possibly other members) of the Shab-related subfamily of potassium voltage-gated channel proteins. This gene belongs to the S subfamily of the potassium channel family. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]. | hsa:3790; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; voltage-gated potassium channel complex [GO:0008076]; delayed rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:0005251]; potassium channel regulator activity [GO:0015459]; voltage-gated potassium channel activity [GO:0005249]; potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071805]; potassium ion transport [GO:0006813]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765] | 15714333_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15714333_Our findings suggest that SNPs located at the 3' downstream region of KCNS3 have a significant role in the etiology of AHR. 15827117_formation of heteromeric Kv2.1/Kv9.3 channels of fixed stoichiometry consisting of three Kv2.1 subunits and one Kv9.3 subunit 18676988_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20876197_There is evidence of heteromultimeric Kv2.1/Kv9.3 channel expression in control of middle cerebral arterial diameter. 22422395_stromatoxin-1 -sensitive KV2-containing channels are expressed in detrusor smooth muscle (DSM); they control DSM excitability, intracellular Ca2+ levels, and myogenic and nerve-evoked contractions 22943705_study concluded that potassium voltage-gated channel K(V)9.3 is localised to human placental vascular tissues and syncytiotrophoblast 24170294_By in situ hybridization, KCNS3 mRNA levels were 23% lower in schizophrenia subjects than in controls. At the cellular level, both KCNS3 mRNA-expressing neuron density and KCNS3 mRNA level per neuron were significantly lower. 34352340_Association analysis and polygenic risk score evaluation of 38 GWAS-identified Loci in a Chinese population with Parkinson's disease. | ENSMUSG00000043673 | Kcns3 | 41.214198 | 2.073612073 | 1.052146 | 0.24236213 | 19.076313 | 0.0000125594049611975739049862105245480847770522814244031906127929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001628183100993805935453873079410413993173278868198394775390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 55.7314196 | 6.6543934 | 26.9934777 | 3.6894845 | |
| ENSG00000170989 | 1901 | S1PR1 | protein_coding | P21453 | FUNCTION: G-protein coupled receptor for the bioactive lysosphingolipid sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) that seems to be coupled to the G(i) subclass of heteromeric G proteins. Signaling leads to the activation of RAC1, SRC, PTK2/FAK1 and MAP kinases. Plays an important role in cell migration, probably via its role in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and the formation of lamellipodia in response to stimuli that increase the activity of the sphingosine kinase SPHK1. Required for normal chemotaxis toward sphingosine 1-phosphate. Required for normal embryonic heart development and normal cardiac morphogenesis. Plays an important role in the regulation of sprouting angiogenesis and vascular maturation. Inhibits sprouting angiogenesis to prevent excessive sprouting during blood vessel development. Required for normal egress of mature T-cells from the thymus into the blood stream and into peripheral lymphoid organs. Plays a role in the migration of osteoclast precursor cells, the regulation of bone mineralization and bone homeostasis (By similarity). Plays a role in responses to oxidized 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine by pulmonary endothelial cells and in the protection against ventilator-induced lung injury. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10982820, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11230698, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11583630, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11604399, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19286607, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22344443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8626678, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9488656}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Angiogenesis;Cell membrane;Chemotaxis;Disulfide bond;Endosome;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is structurally similar to G protein-coupled receptors and is highly expressed in endothelial cells. It binds the ligand sphingosine-1-phosphate with high affinity and high specificity, and suggested to be involved in the processes that regulate the differentiation of endothelial cells. Activation of this receptor induces cell-cell adhesion. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. | hsa:1901; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endosome [GO:0005768]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; G protein-coupled receptor binding [GO:0001664]; sphingolipid binding [GO:0046625]; sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor activity [GO:0038036]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007193]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; blood vessel maturation [GO:0001955]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cardiac muscle tissue growth involved in heart morphogenesis [GO:0003245]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0045446]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; heart trabecula morphogenesis [GO:0061384]; lamellipodium assembly [GO:0030032]; leukocyte chemotaxis [GO:0030595]; negative regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051497]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway [GO:0051482]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050927]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030500]; regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045124]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of metabolic process [GO:0019222]; sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor signaling pathway [GO:0003376]; T cell migration [GO:0072678]; transmission of nerve impulse [GO:0019226] | 11032855_in mouse, this protein is essential for vascular maturation 11741892_phosphorylation of the sphingosine 1-phosphate (SSP) receptor 'endothelial differentiation gene 1' (EDG1 or S1P(1)) receptor is increased in response to either SSP or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) exposure but not lysophosphatidic acid 11915345_functions as an intracellular signaling molecule and angiogenesis factor 11915348_activates Rho family G proteins and cell motility 12742228_S1P(1) inhibits Ca(2+) signalling most likely via G(i) proteins and classical PKC isoforms. Co-expression of S1P(1) with S1P(3), but not S1P(2), reversed the inhibitory effect of S1P(1), furthermore suggesting a specific interplay of S1P receptor subtypes 14500646_S1P1 receptors expressed in mouse Th1 cells mediate suppression of T cell proliferation and cytokine production. 14988150_Immunosuppressant FTY720 activates sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors that affect responsiveness of lymphocytes to chemokines such as stromal cell-derived factor 1. 15626732_cross-communication between the prototypical barrier-protective S1P and barrier-disruptive PAR1 pathway 15699128_Persistent expression of S1P1 receptor by lymphocytes of S1P1 receptor-transgenic mice suppresses delayed-type hypersensitivity and results in production of significantly more IgE antibody (Ab) and less IgG2 Ab than in wild-type mice. 15710622_endothelial protein C receptor ligation and sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor transactivation results in endothelial cell cytoskeletal rearrangement and barrier protection through activated protein C 15728452_Signaling by S1P1 receptor-transgenic mice affects systemic trafficking of peripheral T cells and primary immune responses; levels of S1P1 receptor expression represent an important mechanism of immune regulation. 16148028_Tyrosine sulfation of S1P1 may be a major controller of S1P effects on T cell traffic 16195373_S1P-induced recruitment of S1P1 to CEM fractions promotes PI3 kinase-mediated Tiam1/Rac1 activation required for alpha-actinin-1/4-regulated cortical actin rearrangement and EC barrier enhancement 16319133_The constitutively active endogenous S1P1 receptor enhances PDGF-induced cell migration. 16926156_heterotrimeric G protein-dependent ERK1/2 activation is mediated by IGF-1 and IGF-2 by transactivating sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors 16963454_Transactivation of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors is essential for vascular barrier regulation 17237497_FTY720-P targets the S1P1 receptor to the ubiquitinylation and proteasomal degradation pathway 17331465_Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced inflammatory response genes expression is mediated through S1P(1) and S1P(3) 17918267_FTY720 induces time-dependent modulation of S1P receptors on human OPCs with consequent functional responses that are directly relevant for the remyelination process. 17975119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18172456_S1P(1) receptor, without stimulating [Ca(2+)](i) increases, mediates chemotaxis of keratinocytes 18247041_S1P-mediated signaling via the S1P1/Gi/Rho GTPases pathway activates integrin alpha v beta 3, which is indispensable for S1P-stimulated chemotactic response of ECs. 18541717_S1P promotes lymphangiogenesis by stimulating S1P1/G(i)/phospholipase C/Ca(2+) signaling pathways. 18606817_HDL has endothelial barrier promoting activities, which are attributable to its S1P component and signaling through the S1P1/Akt pathway. 18644866_Datas suggest that filamin A links sphingosine kinase 1 and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 to locally influence the dynamics of actin cytoskeletal structures at lamellipodia to promote cell movement. 18658144_Plays essential roles in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis by modulating fibroblast-like synoviocyte migration, cytokine/chemokine production, and cell survival. 18713968_FOXO1 controls the expression of L-selectin and EDG1 and EDG6, receptors that regulate lymphocyte trafficking 18760838_S1P(1) acts as an inhibitor of CXCR4-dependent migration of hematopoietic cells to sites of SDF-1 production. 18773427_subconfluent pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells express predominantly S1P2 and S1P3 receptors; S1P1 receptor mRNA levels are significantly up-regulated following bFGF treatment 18849324_the crucial role of activation of the SPHK1S1PS1P1 signaling pathway in response to inflammatory mediators in endothelial cells in regulating endothelial barrier homeostasis. 18936953_plasma membrane S1P(1) receptors are rapidly internalized and subsequently translocated to nuclear compartment upon S1P stimulation; nuclear S1P(1) is able to regulate the transcription of Cyr61 and CTGF 19023099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19150609_S1PR1 has an important role in disease-related angiogenesis, especially in the processes of migration/invasion and tube formation. 19158154_Data suggest that human antibodies to the amino terminus of the type 1 sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor suppress T-cell trafficking sufficiently to impair host defense and provide therapeutic immunosuppression. 19286607_Akt-mediated transactivation of the S1P1 receptor in caveolin-enriched microdomains regulates endothelial barrier enhancement by oxidized phospholipids. 19633297_IGFBP-3 in MCF-10A cells requires SphK1 activity and S1P1/S1P3, suggesting that S1P, the product of SphK activity and ligand for S1P1 and S1P3 19778812_The activation of S1PR results in increased chemotactic response of CD34(+) hematopoietic stem cells to SDF-1. 19810093_downregulation of S1P(1) expression enhances the malignancy of glioblastoma by increasing cell proliferation and correlates with the shorter survival of patients with glioblastoma. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20036214_S1P(1) signaling linked to cell migration is facilitated by a functional interaction with P-Rex1 via a mechanism that involves the maintenance of S1P(1) receptors at the cell membrane. 20081804_Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 immunohistochemistry may be useful in the histological diagnosis of mantle cell lymphoma with formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded sections. 20348395_Protein S controls hypoxic/ischemic blood-brain barrier disruption through the TAM receptor Tyro3 and sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor1. 20416181_Mobilization with rhG-CSF obviously down-regulates the expression of S1P1 in CD4+ T cells. 20501673_Data hypothesize that VEGFR-2 forms a signaling complex with S1P(1) and and protein kinase C-alpha , evoking bidirectional signaling regulating both ERK1/2 phosphorylation and haptotaxis of ML-1 cells. 20566754_S1PR1 is localized in astrocytes, and its expression level may change during the processes that occur after brain damage. 20592280_In four-and-a-half LIM domain protein (FHL)2-deficient bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDC), repression of S1PR1 is lost, leading to its overexpression. Signaling via S1PR1 is responsible for increased migratory phenotype of FHL2-deficient BMDCs. 20624651_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20624651_strong support for a role for S1PR1 gene variants in asthma susceptibility and severity. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20648639_this study demonstrated that reactive astrocytes in MS lesions and cultured under proinflammatory conditions strongly enhance expression of S1P receptors 1 and 3. 20889557_These results support a model in which the interaction between sphingosine kinase 1, sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors 1 and/or 3, and ERK-1/2 might drive breast cancer progression 20951945_Analysis using clinical biopsy specimens revealed autophagy and increased levels of BCL2, S1P1, and ICAM1 in human T-lymphoblastic lymphoma compared with T-lymphoblastic leukemia. 21145832_SphK/S1P/S1PRs signaling axis plays an important role in liver fibrosis and is involved in the directed migration of hepatic myofibroblasts into the damaged areas. 21613209_Purification and identification of activating enzymes of CS-0777, a selective sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 modulator, in erythrocytes. 21660960_These data have identified an additional function regulated by S1P/S1PR1,3 axis involving migration and fibrogenic activation of hepatic stellate cells. 21719706_FTY720 (Gilenya) phosphate selectivity of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor subtype 1 (S1P1) G protein-coupled receptor requires motifs in intracellular loop 1 and transmembrane domain 2 22100314_5- and 6-subtituted benzothiazoles with improved physicochemical properties are potent S1P agonists with in vivo lymphocyte-depleting activity 22104144_analysis of quinolinone-based agonists of S1P 22326262_These findings suggest that S1P/S1P1 signaling may play an important role in RANKL expression by MH7A cells and CD4(+) T cells. 22334704_the first report to link the two signaling events that control migration through the lymph nodes: CCR7 mediates entry into the lymph nodes and EDG-1 signaling controls their subsequent exit. 22422617_Data suggest that S1PR1 transactivation is dependent on sphingosine kinase 1, is upstream of MAP kinase signaling system, and is required for LDL-regulated expression of connective tissue growth factor in mesangial cells. 22547907_abdominal aortic aneurysms have down-regulation of the S1P2 protein with simultaneous up-regulation of the S1P3 protein, but not S1P1 22595806_However, growing evidence strongly suggests that the assessment of Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1/3 (S1P1/3) own advantages over present measurements in predicting the risk of developing diabetic cardiovascular diseases. 22623751_the structure of S1P highlighted key interactions associated with the binding of S1P and agonists and suggested that the ligand may gain access to the binding pocket by lateral diffusion within the plasma membrane. 22624714_Demonstrate that S1PR1-STAT3 signalling enables myeloid cells to intravasate, prime the distant organ microenvironment and mediate sustained proliferation and survival of their own and other stromal cells at future metastatic sites. 22745305_Persistent activated STAT3 colocalizes with elevated expression of S1PR1, a G-protein-coupled receptor for sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), in the tumor cells of the activated B cell-like subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 22837470_Report role for S1PR1 in regulation venous endothelial barrier function. 22889737_S1P receptors S1P1,2,3 are expressed in human anaplastic thyroid cancer C643 and THJ-16T cells at both mRNA and protein levels 22898216_Sphingosine-1-phosphate modulates expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human articular chondrocytes. 22975327_The S1PR1 signaling inhibits angiogenic sprouting and enhances cell-to-cell adhesion. 23033271_S1P1 expression is controlled by the pro-oxidant activity of p66Shc and is impaired in B-CLL patients with unfavorable prognosis. 23135269_cell surface levels of S1P1 and levels of S1P1 in caveolin-enriched microdomains were higher after treatment with HDL-S1P as compared with albumin-S1P. 23192342_PI3K-C2alpha plays the crucial role in S1P(1) internalization into the intracellular vesicular compartment, Rac1 activation on endosomes, and thereby migration through regulating vesicular trafficking in ECs 23212923_S1PR1 and ITGB4 transactivation are rate-limiting events in the transduction of HGF signals via a dynamic c-Met complex resulting in enhanced EC barrier integrity 23300082_Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptors 1 and 2 coordinately induce mesenchymal cell migration through S1P activation of complementary kinase pathways 23419711_subset of classical Hodgkin lymphoma cases (7/57; 12%) shows strong, membranous staining for S1PR1 in Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg cells 23466305_key role of Sphk1, S1PR1 and S1PR3 in angiogenesis underlying the liver fibrosis process 23538947_binding of sphingosine-1-phosphate to sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 activates multiple Rho GTPases-dependent pathways that coordinate with PI3K pathway for secretion of IL-6 in BeWo cells. 23551178_The data demonstrates that S1P1 expression is differentially modulated in grey matter and white matter lesions in multiple sclerosis. 23558074_S1P1 overexpression or ERp29 absence is related to the carcinogenesis and progression, and may be potential biomarkers for early detection of gallbladder adenocarcinoma. 23934754_S1PR1 expression on macrophages might, therefore, be relevant for restoring tissue homeostasis during the resolution of inflammation. 24038457_we provide evidences that S1PR1/3, but not S1PR2, negatively regulate the expression of collagen in hMSCs using cellular and molecular approaches in vitro 24076635_Impaired S1P1 phosphorylation enhances TH17 polarization and exacerbates autoimmune neuroinflammation. 24131465_Data indicate that in cultured endothelial cell (umbilical vein endothelial cells) showed a co-localization of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor S1P(1) and proteinase activated receptor-2 PAR2. 24239722_The role of protein kinase C (PKC) isozymes in phorbol myristate acetate (PMA)-induced sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor 1 (S1P1) phosphorylation was studied. 24263101_pro-survival/anti-apoptotic signalling from S1P1 is intimately linked to its ability to promote the accumulation of pro-survival protein Mcl-1 and downregulation of pro-apoptotic BH3-only protein Bim via distinct signalling pathways. 24420784_Our data demonstrate that neuronal cell death evoked by ceramide is regulated by PARP/PAR/AIF and by S1P receptor signalling. 24456642_study demonstrates loss of S1P and sphingosine kinase activity early in AD pathogenesis, and prior to AD diagnosis. Our findings establish a rationale for further exploring S1P receptor pharmacology in the context of AD therapy. 24520353_Edg-1 is a potential target gene of RTEF-1 and is involved in RTEF-1-induced angiogenesis in endothelial cells. 24630990_Study demonstrates a stark contrast between the consequences of S1PR1 signaling in Treg cells in the periphery versus tumors. 24631531_miR-363 is a negative regulator of S1PR1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 24679343_Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors control B-cell migration through signaling components associated with primary immunodeficiencies, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and multiple sclerosis. 24728592_Three-dimensional structure of the S1P1 receptor has been determined by X-ray crystallography and the specifics of the sphingosine 1 phosphate ligand binding pocket mapped. [review] 24780445_Data indicate that the internalization of S1P1 receptor was induced by Syl930-P, the active phosphorylated form of selective S1P1 receptor agonist Syl930. 24903384_Data show that sphingosine kinase SphK1 and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptors S1P1, S1P2, S1P3, and S1P5 were expressed from primary, up to recurrent and secondary glioblastomas, with sphingosine kinase SphK2 levels were highest in primary tumors. 24972972_Aberrant S1PR1 expression in colorectal cancer was associated with metachronous liver metastasis and worse survival outcome 25127862_the regulated expression of S1PR1 might modulate the egress of the leukemic clone from lymphoid tissues to peripheral blood. 25188412_Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes extravillous trophoblast cell invasion by activating MEK/ERK/MMP-2 signaling pathways via S1P/S1PR1 axis activation. 25251470_S1PR1 was a target of miR-125b-1-3p in the placenta. Overexpression of S1PR1 could reverse the inhibitory effect of miR-125b-1-3p on the invasion of trophoblast cells. Abnormal expression of miR-125b-1-3p might contribute to the etiology of preeclampsia. 25287214_Ponesimod, a selective S1P1 receptor modulator, causes small, dose-dependent QT prolongation. 25293589_Data suggest an SNP in S1PR1 (rs41287280) is associated with protection against coronary artery disease; some SNPs in S1PR1 have the effect that endocytosis is resistant to S1PR1 antagonists (fingolimod) or S1PR1 agonists (sphingosine 1-phosphate). 25330249_The role of sphingosine-1-phosphate in the production of immature double-negative thymocytes in experimental and chronic Chagas disease is reported. 25498971_S1P1 is widely expressed across tissues and, when activated, has broad functions in the immune, vascular and nervous systems. [Review] 25557733_Activation of the S1PR1-PLC-IP3 R-Ca(2+) -Rac1 pathway governs the low-dose S1P-enhanced endothelial barrier integrity. 25588843_rapid reduction of endothelial cell surface expression of S1PR1 subsequent to Y143 phosphorylation is a crucial mechanism of modulating S1PR1 signaling, and hence the endothelial barrier repair function of S1P. 25632006_Expression of functional S1PR1 is reduced by B cell receptor signaling and increased by inhibition of PIK3CD but not SYK or BTK in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. 25673082_both S1PR1 and S1PR2 play a pivotal role in hyperglycemia-induced EC dysfunction and endothelial injury by reducing and enhancing the production of oxidative stress. 25872153_S1P interacts with its receptors on neutrophils, resulting in NADPH oxidase activation by the PI3K-Akt cell signaling pathway and induction of the neutrophil respiratory burst. 26197437_S1P receptor modulation reduces leukocyte migration across the endothelial barrier 26238015_S1PR1 expression was associated with unfavourable clinicopathological features and the expression of several anti-apoptosis/proliferation-related markers in urothelial carcinoma. 26268607_the ability of ApoM(+)HDL to act as a biased agonist on S1P1 inhibits vascular inflammation, which may partially explain the cardiovascular protective functions of HDL. 26282174_Within lymphoid follicles, the S1P1 distribution pattern is complementary to that of CCR7/CXCR4, with strong immunoreactivity tightly restricted to mantle zone B cells. This may play a role in B-cell migration toward the S1p-enriched follicle center. 26321412_Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced IL-8 gene expression is mainly regulated via S1PR(1), and its secretion is regulated through S1PR(2) receptor subtype. 26493335_SGPL1 ratio correlated with increased cellular sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), and S1P correlated with drug resistance (IC50). 26787880_multiple lines of evidence demonstrate that S1PR1 signaling sets the sensitivity of pDC amplification of IFN responses, thereby blunting pathogenic immune responses 26824863_The results indicate that sphingosine 1-phosphate is involved in the migration of precursor T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia-lymphoma blasts in vitro, which is dependent on S1P1 expression. 27056271_Mature human thymocytes rely on S1P-R1 to migrate toward S1P. Taken in the context of murine work demonstrating that S1P is required for thymocyte egress to the periphery. 27061580_The present high prevalence of S1PR1 overexpression warrants the consideration of testicular diffuse large B-cell lymphoma as a distinct disease subtype and suggests the potential of the S1P/S1PR1 axis as a therapeutic target. 27282481_The S1P1,3 activation results in Akt phosphorylation and subsequent activation of eNOS via phosphorylation at serine(1177) and dephosphorylation at threonine(495). 27494562_this review discusses sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor as a novel therapeutic target in ulcerative colitis 27572094_S1PR1 inhibits the apoptosis of human myeloid leukemia cells and promotes their proliferation. 27785703_These results suggest that S1P signaling plays a role in cell proliferation and drug resistance in multiple myeloma, and targeting this pathway will provide a new therapeutic direction for multiple myelomamanagement. 27879252_ApoM-bound sphingosine-1-phosphate regulates adhesion molecule abundance, leukocyte-endothelial adhesion, and endothelial barrier function via sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor1. 27881715_Model recombinant HDL (rHDL) particles formed in vitro with S1P incorporated into the particle initiated the internalization of S1PR1, whereas rHDL without supplemented S1P did not, suggesting that S1P transported in HDL can selectively activate S1PR1. 27974574_These findings are consistent with a model in which signalling via S1P and S1PR1 are integral components in the response of lymphatic endothelial cells to the stimulus provided by fluid flow. 28167760_Astrocytic S1PR controls astrocyte neurotoxicity and monocyte recruitment and activation. 28179022_HDL-associated ApoM is anti-apoptotic by delivering sphingosine 1-phosphate to S1P1 and S1P3 receptors on vascular endothelium. 28206609_High S1PR1 expression is associated with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. 28300069_Extracellular alpha-synuclein induces sphingosine S1P1R uncoupled from inhibitory G-protein leaving beta-arrestin signal intact. 28343295_S1P1 has a pathogenic role in transient focal cerebral ischemia and is associated with microglial activation in ischemic brain 28370663_a lipid molecule repeatedly entered the receptor between the extracellular ends of TM1 and TM7, providing important insights into the pathway of ligand entry into the S1PR1 . 28399143_Activated S1PR1 signaling regulates the production of cellular adhesion molecules by inhibiting NF- kappaB activation via a beta-arrestin2-dependent manner 28466272_the Blood-brain barrier protection effect of bFGF is at least partially through rescuing the oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation-induced downregulation of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1PR1) protein. 28492873_Blocking of S1PR activity and inhibition of S1P synthesis led to decreased expression of fibrosis and tissue remodeling-related proteins in primary cultures of orbital fibroblasts derived from patients with GO. 28716816_Elevated S1PR1 expression and STAT3 activation are also observed in human NB cells with acquired resistance to etoposide. We show in vitro and in human NB xenograft models that treatment with FTY720, an FDA-approved drug and antagonist of S1PR1, dramatically sensitizes drug-resistant cells to etoposide. 28878352_Knockdown of BATF3 in HL cell lines revealed that BATF3 contributed to the transcriptional programme of primary HRS cells, including the upregulation of S1PR1. 28982858_S1PR1/3 silencing alters proliferation, adhesion, viability and lateral motility in estrogen receptor-negative MCF-7 and estrogen receptor-positive MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. 28986246_Low S1PR1 expression is associated with Coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis. 29134505_Upregulated S1PR1 expression in human and mouse atherosclerotic plaques was successfully identified. 29549086_dysfunctional/diminished S1PR1 contributes to the retention of malignant cells in the surrounding tissue, constituting a minimal residual disease reservoir that later may give rise to a relapse. In DLBCL, mutations of S1PR1 have not yet been reported, but lack of membrane expression of S1PR1 in DLBCL at early stages (Ann Arbor I+II) correlates to superior outcome 29632069_S1P1R regulates vesicular trafficking, and its expulsion involved alpha-Syn binding to membrane-surface gangliosides 29734379_We conclude that S1P attenuates the invasion of C643 cells by activating S1P2 and the Rho-ROCK pathway, by decreasing calpain activity, and by decreasing the expression, secretion and activity of MMP2 and, to a lesser extent, MMP9. Our results thus unveil a novel function for the S1P2 receptor in attenuating thyroid cancer cell invasion. 29750961_These results demonstrated that ApoM protein mass were clearly higher in the NSCLC tissues than in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tissues. Overexpression of ApoM could promote NSCLC cell proliferation and invasion in vitro and tumor growth in vivo, which might be via upregulating S1PR1 and activating the ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. 29781582_Findings indicate that S1P1 signaling in endothelial cells modulates vascular responses to immune complex deposition. 29804740_S1PR1-positive smooth muscle cells use S1PR1 to recognize the sphingosine-1-phosphate gradient from tissue (low) to plasma (high) and so migrate out of the media toward the intima of the injured internal mammary artery. 29901713_Data suggest that sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1) exhibits a inhibitory effect on kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury-inducedepithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in the kidney by affecting the PI3K/Akt pathway. 30304001_Overexpression of S1PR1 decreased p65 phosphorylation and translocation into the nucleus. Furthermore, we demonstrated that S1PR1 stimulation inhibited Akt-mTOR signaling, which might contribute to activation of autophagy in HPMECs. Thus, our study provides knowledge crucial to better understanding novel mechanisms underlying the S1PR1-mediated attenuation of cytokine amplification in the pulmonary system during influenza 30316864_S1PR1-STAT3 signaling may participate drug resistance in gastric cancer (GC), thus could serve as a drug target to increase the efficacy of GC treatment. 30453284_Overexpression of S1PR1 promoted subcutaneous xenograft growth and pulmonary metastases and enhanced expression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition markers. 30476824_this study shows that sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes inflammation-induced tube formation by human lymphatic endothelial cells via the S1PR1/NF-kappaB pathway 30712233_High expression of S1PR1 is associated with bladder transitional cell carcinoma. 30718502_S1P1 activated the TGF-beta signaling pathway, leading to the secretion of TGF-beta and IL-10 from BC cells. Findings suggest that S1P1 induces tumor-derived Treg expansion in a cell-specific manner. 30814488_Results show that S1PR1 regulated RhoA activation to accelerate VE-cadherin phosphorylation (Y731), leading to increased EDV and reduced VM in breast cancer. 30877143_T cell S1PR1 and S1PR4, and lymphatic endothelial cell (LEC) S1PR2, were required for migration across LECs and into lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes. S1PR1 and S1PR4 differentially regulated T cell motility and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) binding. S1PR2 regulated LEC layer structure, permeability, and expression of the junction molecules VE-cadherin, occludin, and zonulin-1 through the ERK pathway. 30963819_Sphk1/S1P/S1PR1 Signaling is Involved in the Development of Autoimmune Thyroiditis in Patients and NOD.H-2(h4) Mice. 31293578_S1P-S1PR1 Signaling: the ''Sphinx'' in Osteoimmunology. 31438989_High S1PR1 expression is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 32006593_Transcription factor STAT1 could bind to upstream region of -29 bp to -12 bp of the S1PR1 promoter and stimulate the expression of S1PR1. 32045395_S1PR1-Associated Molecular Signature Predicts Survival in Patients with Sepsis. 32155312_Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptors: Promising drug targets for treating bone-related diseases. 32424937_Coinhibition of S1PR1 and GP130 by siRNA-loaded alginate-conjugated trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles robustly blocks development of cancer cells. 32487716_A G protein-biased S1P1 agonist, SAR247799, protects endothelial cells without affecting lymphocyte numbers. 32544090_S1PR1 regulates the quiescence of lymphatic vessels by inhibiting laminar shear stress-dependent VEGF-C signaling. 32799825_Prognostic value of S1PR1 and its correlation with immune infiltrates in breast and lung cancers. 32801704_Nanoparticle BAF312@CaP-NP Overcomes Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor-1-Mediated Chemoresistance Through Inhibiting S1PR1/P-STAT3 Axis in Ovarian Carcinoma. 32810927_A label-free impedance assay in endothelial cells differentiates the activation and desensitization properties of clinical S1P1 agonists. 32907751_Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors are dysregulated in endometriosis: possible implication in transforming growth factor beta-induced fibrosis. 33000224_miR181b5p inhibits trophoblast cell migration and invasion through targeting S1PR1 in multiple abnormal trophoblast invasionrelated events. 33307511_Sphingosine-1-phosphate Receptor-1 Promotes Vascular Invasion and EMT in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 33574820_Deletion of Mir223 Exacerbates Lupus Nephritis by Targeting S1pr1 in Fas(lpr/lpr) Mice. 33685344_FAM19A5/S1PR1 signaling pathway regulates the viability and proliferation of mantle cell lymphoma. 33788630_Ozanimod, an S1PR1 ligand, attenuates hypoxia plus glucose deprivation-induced autophagic flux and phenotypic switching in human brain VSM cells. 33797381_SphK1 Promotes Cancer Progression through Activating JAK/STAT Pathway and Up-Regulating S1PR1 Expression in Colon Cancer Cells. 34301921_SMYD3 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by methylating S1PR1 promoters. 34407633_Apolipoprotein M and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 1 Promote the Transendothelial Transport of High-Density Lipoprotein. 34535564_Deconstructing the Pharmacological Contribution of Sphingosine-1 Phosphate Receptors to Mouse Models of Multiple Sclerosis Using the Species Selectivity of Ozanimod, a Dual Modulator of Human Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor Subtypes 1 and 5. 34652421_Tyrosine phosphorylation of S1PR1 leads to chaperone BiP-mediated import to the endoplasmic reticulum. 34751249_S1P Signaling Pathways in Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes. 35136060_Differential activation mechanisms of lipid GPCRs by lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate. 35412894_Structural insights into sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor activation. 36068200_S1PR1 induces metabolic reprogramming of ceramide in vascular endothelial cells, affecting hepatocellular carcinoma angiogenesis and progression. 36209115_New mechanism for mesenchymal stem cell microvesicle to restore lung permeability: intracellular S1P signaling pathway independent of S1P receptor-1. 36394527_Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulation improves neurogenesis and functional recovery after stroke. | ENSMUSG00000045092 | S1pr1 | 12.500720 | 2.614767182 | 1.386682 | 0.46342696 | 9.082292 | 0.0025809641762470267832563219911889973445795476436614990234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0167373791828203111187178819818655028939247131347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 19.0157444 | 3.8127494 | 7.1815064 | 1.9008343 | |
| ENSG00000171115_ENSG00000242258 | 72.682047 | 0.374055734 | -1.418675 | 0.48967803 | 8.094649 | 0.0044396123787563291501756523871335957664996385574340820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0260055686574721632575712959578595473431050777435302734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 44.5304677 | 31.0338851 | 118.8216807 | 82.2962269 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000171757 | 151827 | LRRC34 | protein_coding | Q8IZ02 | FUNCTION: Highly expressed in stem cells where it may be involved in regulation of pluripotency. In embryonic stem cells (ESCs), important for normal expression of the pluripotency regulators POU5F1/OCT4 and KLF4. Also important for expression of the ectodermal marker gene NES and the endodermal marker gene GATA4. Promotes stem cell proliferation in vitro. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9DAM1}. | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;Leucine-rich repeat;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat | Predicted to be involved in cell differentiation. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and nucleolus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:151827; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24991885_LRRC34 is a novel nucleolar protein that is predominantly expressed in pluripotent stem cells. 32051256_Variants in LRRC34 reveal distinct mechanisms for predisposition to papillary thyroid carcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000027702 | Lrrc34 | 19.080721 | 3.287535518 | 1.717006 | 0.40302704 | 17.785212 | 0.0000247297820105450577858781369133822636285913176834583282470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0003000175115034729028673510242697375360876321792602539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 30.1928190 | 9.5481576 | 8.9295523 | 2.8830713 | |
| ENSG00000171951 | 7857 | SCG2 | protein_coding | P13521 | FUNCTION: Neuroendocrine protein of the granin family that regulates the biogenesis of secretory granules. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19357184}. | Calcium;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Glycoprotein;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Sulfation | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the chromogranin/secretogranin family of neuroendocrine secretory proteins. Studies in rodents suggest that the full-length protein, secretogranin II, is involved in the packaging or sorting of peptide hormones and neuropeptides into secretory vesicles. The full-length protein is cleaved to produce the active peptide secretoneurin, which exerts chemotaxic effects on specific cell types, and EM66, whose function is unknown. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:7857; | endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; neuronal dense core vesicle [GO:0098992]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; chemoattractant activity [GO:0042056]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; endothelial cell migration [GO:0043542]; eosinophil chemotaxis [GO:0048245]; induction of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050930]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process [GO:2000352]; negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001937]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; positive chemotaxis [GO:0050918]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; protein secretion [GO:0009306] | 11853870_Transendothelial migration of leukocytes and signalling mechanisms in response to the neuropeptide secretoneurin. 12788858_secretogranin II-derived peptide EM66 generated in human tumoral chromaffin tissue; significant difference in EM66 concentrations between benign and malignant pheochromocytomas 15572199_the high concentration of secretoneurin in the aqueous humor indicates a significant role of this peptide 17584765_a variant of Secretogranin II has a role in regulation by PHOX2 transcription factors and in hypertension 18239671_Results suggest that secretogranin II represents a key AP-1-regulated protein that counteracts nitric oxide toxicity and mediates neuronal differentiation of neuroblastoma cells. 18448176_Increased concentrations of SgII, especially the N-terminal part of secretoneurin could be measured in plasma from patients with endocrine pancreatic tumours. 18549351_Suppression of Pdcd4 resulted in an increased release of CgA and Sg II and was accompanied by an up-regulation of intracellular PC1. 18721831_semiquantitative immunocytochemistry for secretogranin II in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 20550951_More SgII immunoreactive cells were observed in phaeochromocytomas. 21046454_This short review deals with investigations in neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) with antibodies against defined epitopes of chromogranins (Cgs) A and B and secretogranins (Sgs) II and III. 21803620_Manserin may serve as a marker of prostate cancer progression. 22217803_Data describe the gene expression and protein production of SgII in normal adrenal glands and pheochromocytomas with the goal to examine the molecular mechanisms leading to the marked variations in the expression of EM66 in tumoral chromaffin tissue. 22655045_Circulating Levels of SgII are Increased in Patients with chronic, stable heart failure. 23081990_In vivo secretoneurin improves left ventricular function, inhibits remodeling, and reduces scar formation; in the infarct border zone, secretoneurin induces coronary angiogenesis. 23423580_CgA, CgB, and secretoneurin are detectable in feces, and collagenous colitis patients express higher values than patients with inflammatory bowel disease and controls. In treatment, fecal secretoneurin decreased to control levels in collagenous colitis. 23918206_Topical secretoneurin gene therapy accelerates diabetic wound healing by interaction between heparan-sulfate proteoglycans and basic FGF. 24556756_SN induces MUC5AC hypersecretion in a dose- and time-dependent manner; moreover, the MUC5AC over synthesis induced by SN is strongly associated with the enhanced binding of EGF to NRP1 25307750_present data show that SgII is highly expressed in advanced prostate cancer and may contribute to the neuroendocrine differentiation by promoting the formation of secretory granules and the proliferation of PCa cells. 26378181_Differential Reovirus-Specific and Herpesvirus-Specific Activator Protein 1 Activation of Secretogranin II Leads to Altered Virus Secretion. 30887724_serum levels of CgA, CgB, and SgII were determined in Parkinson's disease patients and assessed their association with disease severity. 34160138_Secretogranin II impairs tumor growth and angiogenesis by promoting degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in colorectal cancer. 34815513_Nanoplasmonic immunosensor for the detection of SCG2, a candidate serum biomarker for the early diagnosis of neurodevelopmental disorder. 35341274_AGTR1, PLTP, and SCG2 associated with immune genes and immune cell infiltration in calcific aortic valve stenosis: analysis from integrated bioinformatics and machine learning. 35844556_SCG2: A Prognostic Marker That Pinpoints Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy in Colorectal Cancer. | ENSMUSG00000050711 | Scg2 | 35.354135 | 0.374064145 | -1.418642 | 0.27596079 | 27.233472 | 0.0000001803099534169075978185035717682449529775112750940024852752685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000033945836182983895327113996187584632480138679966330528259277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 19.4337667 | 3.6150848 | 51.9689541 | 8.2919580 | |
| ENSG00000172339 | 199857 | ALG14 | protein_coding | Q96F25 | FUNCTION: Involved in protein N-glycosylation. May play a role in the second step of the dolichol-linked oligosaccharide pathway. May anchor the catalytic subunit ALG13 to the ER. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16100110}. | Congenital myasthenic syndrome;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Epilepsy;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene is a member of the glycosyltransferase 1 family. The encoded protein and ALG13 are thought to be subunits of UDP-GlcNAc transferase, which catalyzes the first two committed steps in endoplasmic reticulum N-linked glycosylation. Mutations in this gene have been linked to congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMSWTA). Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2015]. | hsa:199857; | endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transferase complex [GO:0043541]; dolichol-linked oligosaccharide biosynthetic process [GO:0006488] | 16100110_ALG13 and ALG14 form a functional endoplasmic reticulum UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transferase 23404334_We identify ALG14 and ALG2 as novel genes in which mutations cause a congenital myasthenic syndrome 28733338_New ALG14 congenital disorder of glycosylation with early and lethal neurodegeneration with myasthenic and myopathic features. 30221345_We highlight the findings in two affected siblings with splice altering variants in ALG14 and propose a new clinical entity, which includes severe intellectual disability, epilepsy, behavioral problems and mild dysmorphic features, caused by biallelic variants in ALG14. 33751823_A novel ALG14 missense variant in an alive child with myopathy, epilepsy, and progressive cerebral atrophy. | ENSMUSG00000039887 | Alg14 | 86.628044 | 0.486272877 | -1.040162 | 0.36236840 | 8.046383 | 0.0045594589822543938814614072896347352070733904838562011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0266073059006151288463648540982831036671996116638183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 57.0075662 | 17.4893310 | 118.2638705 | 36.2572794 | |
| ENSG00000172380 | 55970 | GNG12 | protein_coding | Q9UBI6 | FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as a modulator or transducer in various transmembrane signaling systems. The beta and gamma chains are required for the GTPase activity, for replacement of GDP by GTP, and for G protein-effector interaction. | Acetylation;Cell membrane;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Reference proteome;Transducer | Enables PDZ domain binding activity. Predicted to be involved in G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:55970; | extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; heterotrimeric G-protein complex [GO:0005834]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G-protein beta-subunit binding [GO:0031681]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 31262328_Results showed some evidence of differentially methylated cg25189904 in GNG12 gene mediating the effect of exposure to maternal smoking on schizophrenia-related outcomes. 31898405_GNG12 regulates PD-L1 expression by activating NF-kappaB signaling in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 34691083_Low GNG12 Expression Predicts Adverse Outcomes: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Osteosarcoma. | ENSMUSG00000036402 | Gng12 | 145.204949 | 2.434619600 | 1.283696 | 0.36559915 | 11.930925 | 0.0005520974485875449139574144830078239465365186333656311035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0045750824116365983521004245915264618815854191780090332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 218.8806514 | 51.9617963 | 90.3529222 | 21.5955120 | |
| ENSG00000172399 | 51778 | MYOZ2 | protein_coding | Q9NPC6 | FUNCTION: Myozenins may serve as intracellular binding proteins involved in linking Z line proteins such as alpha-actinin, gamma-filamin, TCAP/telethonin, LDB3/ZASP and localizing calcineurin signaling to the sarcomere. Plays an important role in the modulation of calcineurin signaling. May play a role in myofibrillogenesis. | Cardiomyopathy;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to a family of sarcomeric proteins that bind to calcineurin, a phosphatase involved in calcium-dependent signal transduction in diverse cell types. These family members tether calcineurin to alpha-actinin at the z-line of the sarcomere of cardiac and skeletal muscle cells, and thus they are important for calcineurin signaling. Mutations in this gene cause cardiomyopathy familial hypertrophic type 16, a hereditary heart disorder. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. | hsa:51778; | actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; sarcomere [GO:0030017]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; FATZ binding [GO:0051373]; protein phosphatase 2B binding [GO:0030346]; telethonin binding [GO:0031433]; negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade [GO:0070885]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; sarcomere organization [GO:0045214]; skeletal muscle fiber adaptation [GO:0043503]; skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0007519] | 17347475_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17347475_Two missense mutations, S48P substitution and I246M affecting highly conserved amino acids were linked to hereditary Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy characterized by early onset of symptoms, pronounced cardiac hypertrophy, and cardiac arrhythmias. 17434779_Mutations in MYOZ1 and MYOZ2 are at least very rare events as an underlying disease mechanism for idiopathic or familial DCM 18591919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19472918_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20332099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22987565_The cardiac phenotype in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy caused by MYOZ2 mutations might be independent of calcineurin activity in the heart. 28296734_may play a modifying role in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy by affecting the penetrance or degree of performance of the MYH7 gene 30280773_Study found that MYOZ2 can be used as prognostic factor for gastric cancer. MYOZ2 is highly expressed in gastric cancer (GC) tissues, and its expression is associated with lymph node metastasis, TNM staging and poor patients survival. These results suggest that MYOZ2 gene may play an important role in the occurrence and development of gastric cancer. | ENSMUSG00000028116 | Myoz2 | 12.868473 | 3.090918933 | 1.628036 | 0.45256065 | 13.381404 | 0.0002541314012924934806481047644410864450037479400634765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0023233921838427440582919292211272477288730442523956298828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 19.9031211 | 3.4117624 | 6.4555959 | 1.5142178 | |
| ENSG00000172803 | 254122 | SNX32 | protein_coding | Q86XE0 | FUNCTION: May be involved in several stages of intracellular trafficking. {ECO:0000250}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport | Predicted to enable phosphatidylinositol binding activity. Predicted to be involved in retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi. Predicted to be located in cytosol. Predicted to be active in endosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:254122; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; endosome [GO:0005768]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016241]; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi [GO:0042147] | ENSMUSG00000056185 | Snx32 | 34.107178 | 0.469914750 | -1.089529 | 0.31148784 | 12.248521 | 0.0004656270609495324007930106002817183252773247659206390380859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0039331478322209264056330546566186967538669705390930175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 22.3715541 | 4.5604095 | 47.6845918 | 9.0722533 | ||
| ENSG00000173083 | 10855 | HPSE | protein_coding | Q9Y251 | FUNCTION: Endoglycosidase that cleaves heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) into heparan sulfate side chains and core proteoglycans. Participates in extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation and remodeling. Selectively cleaves the linkage between a glucuronic acid unit and an N-sulfo glucosamine unit carrying either a 3-O-sulfo or a 6-O-sulfo group. Can also cleave the linkage between a glucuronic acid unit and an N-sulfo glucosamine unit carrying a 2-O-sulfo group, but not linkages between a glucuronic acid unit and a 2-O-sulfated iduronic acid moiety. It is essentially inactive at neutral pH but becomes active under acidic conditions such as during tumor invasion and in inflammatory processes. Facilitates cell migration associated with metastasis, wound healing and inflammation. Enhances shedding of syndecans, and increases endothelial invasion and angiogenesis in myelomas. Acts as procoagulant by increasing the generation of activation factor X in the presence of tissue factor and activation factor VII. Increases cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix (ECM), independent of its enzymatic activity. Induces AKT1/PKB phosphorylation via lipid rafts increasing cell mobility and invasion. Heparin increases this AKT1/PKB activation. Regulates osteogenesis. Enhances angiogenesis through up-regulation of SRC-mediated activation of VEGF. Implicated in hair follicle inner root sheath differentiation and hair homeostasis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12213822, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12773484, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15044433, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16452201, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18557927, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18798279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19244131, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20097882, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20181948, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20309870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20561914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21131364}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lysosome;Magnesium;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | Heparan sulfate proteoglycans are major components of the basement membrane and extracellular matrix. The protein encoded by this gene is an enzyme that cleaves heparan sulfate proteoglycans to permit cell movement through remodeling of the extracellular matrix. In addition, this cleavage can release bioactive molecules from the extracellular matrix. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. | hsa:10855; | autophagosome [GO:0005776]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; heparanase complex [GO:1904974]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; beta-glucuronidase activity [GO:0004566]; heparanase activity [GO:0030305]; syndecan binding [GO:0045545]; angiogenesis involved in wound healing [GO:0060055]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; establishment of endothelial barrier [GO:0061028]; Factor XII activation [GO:0002542]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan catabolic process [GO:0030200]; heparin metabolic process [GO:0030202]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of blood coagulation [GO:0030194]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001954]; positive regulation of extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0090091]; positive regulation of hair follicle development [GO:0051798]; positive regulation of osteoblast proliferation [GO:0033690]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900026]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010575]; protein transmembrane transport [GO:0071806]; proteoglycan metabolic process [GO:0006029]; regulation of hair follicle development [GO:0051797]; response to organic substance [GO:0010033]; vascular wound healing [GO:0061042] | 11759110_Erythromycin and clarithromycin modulation of growth factor-induced expression of heparanase mRNA on human lung cancer cells in vitro. 11798780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11973358_Activation, processing and trafficking of extracellular heparanase by primary human fibroblasts. 12027584_REVIEW: Heparinase: involvement in cancer metastasis, angiogenesis and normal development 12029075_Results indicate consistent expression of heparanase in normal and abnormal placenta, in small fetal vessels and in a variety of trophoblast subpopulations with different invasive potentials. 12065771_It was concluded that heparanase might play an important role in the development of invasion and metastasis of the gastric cancer. 12097647_Cell surface expression and secretion markedly promote tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. 12213822_structural recognition plays critical roles in tumor metastasis; specificity of the purified recombinant human heparanase 12219030_Heparanase-1 expression is associated with the metastatic potential of breast cancer 12509917_Heparanase participates in the structure damage and remodeling of abdominal aorta at matrix level, which contributes to abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) formation. 12679316_reduced heparanase mRNA expression may result in abnormal cell growth and correlate with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression 12824922_Expression correlates with tumor invasiveness patterns in human oral squamous cell carcinoma xenografts in SCID mice. 12837765_Intracellular processing of the heparin proteoglycan polysaccharide chains is catalyzed by heparanase. 12904690_results suggest that the expression of heparanase may influence different malignant behaviors in endometrial cancer 12927802_heterodimer formation is necessary and sufficient for heparanase enzymatic activity in mammalian cells 14522979_heparanase gene transcription is regulated in activated T cells by early growth response 1 14558943_NF-kappaB is an essential factor in the regulatory mechanisms of heparanase gene transcription. 14573609_glycosylation affected the kinetics of endoplasmic reticulum-to-Golgi transport and of secretion of the enzyme 14633698_Heparanase activates signal transduction pathways and, depending on its expression levels, may modulate tumor progression in glioma cells. 14676122_Increased HPR1 expression is associated with thyroid tumor malignancy and may significantly contribute to thyroid tumor metastases 14769819_characterization of the hpa-tg mice emphasizes the involvement of heparanase and heparan sulfate in processes such as embryonic implantation, food consumption, tissue remodeling, and vascularization 14967027_Tobacco etch virus protease cleavage sites of heparanase are engineered to provide evidence that proteolytic processing at both junctions between residues 109 and 110 and 157 and 158 leads to activation of the 65 kDa heparanase precursor. 14989983_Heparanase gene expression may play some roles in the pathogenesis of endometriosis, and it may participate the regulation of menstrual cycle and may be an important target of the trentment for endometriosis. 15034597_heparanase is translocated into the cell nucleus where it may degrade the nuclear heparan sulfate and thereby affect nuclear functions that are thought to be regulated by heparan sulfate 15040016_Heparanase, CD44v6 and nm23 may play important roles in the invasive infiltration and lymph node metastasis in gastric carcinomas. 15100255_In sites relatively remote from inflammatory foci, within blood vessels and extravascular tissues, heparanase can act as a T cell cytokine that is involved in regulating cell activation and behavior. 15109255_Inflammatory cytokines and fatty acids regulate endothelial cell heparanase expression. 15144715_Heparanase mRNA may be important to the loss of glomerular negative charge in GBM and lead to proteinuria in steroid responsive nephrotic syndrome. 15292202_Heparan sulfate is not only a substrate for, but also a regulator of, heparanase. 15334672_Point mutation may be one of the causes for enhanced heparanase mRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. 15368349_one of the roles CREB plays in the acquisition of melanoma cells metastatic phenotype is affecting HPSE-1 activity 15471949_Heparanase is a critical determinant of myeloma dissemination and growth in vivo. 15610235_dysregulated heparanase expression may play a significant role in the pathogenesis of steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome, possibly through an abnormality in post-translational control of latent heparanase activation 15625607_Expression of heparanase was significantly more frequent in tumors of higher TNM stage, higher Dukes stage, higher vascular infiltration, higher lymph vessel infiltration and poor survival. 15645118_HPSE-1 likely plays important roles in regulating the in vivo growth and progression of melanoma 15659389_Results suggest that proheparanase processing at site 2 is brought about by cathepsin L-like proteases. 15682491_NF-kappaB RelA (p65) activation was related with increased heparanase gene expression and correlated with poor clinicopathological characteristics in gastric cancers. 15728796_Heparanase plays a role in ovarian tissue remodeling during folliculogenesis and corpus luteum formation and regression. 15737842_HPR1 was expressed at a significantly higher frequency in the invasive comedo and DCIS with microinvasion subtypes than in the noninvasive subtypes. HPR1 expression was inversely associated with HS deposition in the extracellular basement membrane. 15760902_identified three potential heparin binding domains and provided evidence that one of these is mapped at the N terminus of the 50-kDa active heparanase subunit 15983219_Loss of heparan sulfsate in the glomerular basement membrane in diabetic nephropathy is attributable to accelerated heparan sulfate degradation by increased HPR1 expression. 16007175_expression during the pathogenesis of bladder cancer is due to promoter hypomethylation and transcription factor EGR1 16093249_EGR1 regulates heparanase transcription in tumor cells and importantly, can have a repressive or activating role depending on the tumor type 16097072_The expression of heparanase mRNA in an esophageal cancer cell line can be inhibited by antisense oligonucleotides, which can inhibit metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma or other tumors by inhibiting the expression of heparanase. 16112651_In summary, we have characterized a link between leukomogenic factors and the downregulation of heparanase in myeloid leukemic cells. 16217746_results emphasize the significance and clarify the involvement of heparanase in primary breast cancer progression by generating a supportive microenvironment that promotes tumor growth, angiogenesis and survival 16288472_Brain-metastatic melanoma cells (B16B15b) showed augmenting levels of HPSE-1 protein expression in a time-dependent manner. Secondly, B16B15b cells pre-treated with HPSE-1 showed a significant increase in the number of cells that invaded into the brain . 16391819_heparanase may play a novel role for cyclooxygenase 2 mediated tumor angiogenesis in breast-cancer progression 16429446_HPSE-1 activity may represent a physiological mechanism involved in neural cellular differentiation 16514606_proteoglycans tonically suppress osteoblast function and that this inhibition is alleviated by heparan sulfate degradation with heparanase 16709798_Heparanase is a key enzyme in dendritic cell transmigration through the extracellular matrix. 16759020_Hypoxia plays an important role in the augmentation of the heparanase expression and the invasiveness of human laryngeal carcinomas. 16790442_Heparanase resides in and accumulates in the lysosomal compartment, where it may participate in normal turnover of heparan sulfate. The secreted enzyme facilitates cell invasion associated with cancer metastasis, angiogenesis, and inflammation. 16826429_Expressions of p75(NTR) and HPSE-1 correlated with each other in medulloblastoma. 16855356_REVIEW of heparanase involvement in cancer metastasis and angiogenesis 16867222_heparanase modifies FGF2 binding, signaling, and angiogenesis in metastatic melanoma cells 16890383_This hypothesis indicates a possible novel function of heparanase and its link to HIF1alpha and Cox-2, and therefore this function would give us a clue about potential new strategies for cancer therapy. 16982797_HPSE 'off/on switch': Lacritin targets the deglycanated core protein of SDC1 and not HS chains or SDC2 or SDC4. Binding requires partial or complete removal of HS chains by endogenous HPSE. This limits lacritin activity to HPSE release sites. 17051139_HPSE is involved in the pathogenesis of proteinuria in overt diabetic nephropathy by degradation of heparan sulfates 17095861_4 Israeli Jewish populations (Ashkenazi, North African, Mediterranean and Near Eastern) were examined for 7 HPSE gene SNPs. Four out of 7 SNPs (rs4693608, db11099592, rs4364254, db6856901) were found to be polymorphic. 17095861_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17141400_The higher expression of Hpa and Ang-2 in ectopic and eutopic endometrium may play an important role in the pathogenesis and development of endometriosis. 17208203_Splice 5 escaped proteolytic cleavage, was devoid of HS degradation activity and exhibited diffused rather than granular cellular localization. 17217623_Nuclear localization of heparanase predicts a favorable outcome in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. 17261577_heparanase-1 expression and heparan sulphate proteoglycan degradation are induced by estradiol in human endometrium 17284253_we speculate that nuclear translocation of enzymatically active heparanase may be involved in cellular differentiation. 17339423_Heparanase influences expression and shedding of syndecan-1 17419711_The CGC HSPE-1 haplotype associates with stage in ovarian cancer. This haplotype may affect splicing of the HSPE-1 gene, as in silico it alters the presence of a splicing motif. 17437011_The combined effects of heparanase and HSULF could account for the lack of biologically active HS in tumour cells rather than deficiencies in the biosynthetic enzymes. 17467664_Genetic downregulation of the expression of heparanase may serve as an efficient cancer therapeutic for human HCC. 17481627_There is no significant difference in heparanase-1 expression in the eutopic endometrium from women with or without endometriosis. 17519955_This review focuses on the role of heparanase in heparan sulfate degradation in proteinuric diseases and the possibility/feasibility of heparanase inhibitors 17524042_High expression of heparanase, combined with NF-kappaB p65, may contribute to the highly invasive and metastatic behavior of gallbladder carcinoma. 17611567_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17611567_certain HPSE gene SNPs may contribute to basal heparanase gene expression; alterations in this gene are an important determinant in the pathogenesis of ALL, AML and MM 17634531_Heparanase induction by estrogen receptors represents an important pathway in breast tumorigenesis and may be responsib, for failure of tamoxifen therapy in some patients. 17715045_Heparanase and NF-kappaB p65 proteins were found in 30 (62.5%) and 22 (45.9%) tumor specimens, respectively, a rate significantly higher than that in the adjacent tissues. 17989358_HPSE plays a role in extracellular matrix remodeling and in increasing heparin-binding growth factor release during embryo implantation. 18064313_Heparanase pro-enzyme reverses the anti-coagulant activity of unfractionated heparin on the coagulation pathway and on thrombin activity. Heparanase pro-enzyme abrogated the factor X inhibitory activity of low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH). 18167611_Accumulating evidence suggests that small inhibitory genetic molecules targeting heparanase are of value for control and treatment of human malignancies. 18212251_Heparanase directly contributes to prostate tumor growth in bone and its ability to metastasize to distant organs. 18217145_Heparanase facilitates blood coagulation by dissociation of TFPI from the vascular surface shortly after local elevation of heparanase levels, and subsequent induction of TF expression. 18246800_The high expression of HPA mRNA and HIF-1alpha protein is correlated with carcinogenesis, progression, invasion and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 18288398_The coexpression of heparanase and vascular endothelial growth factor in atypical melanocytes and melanoma cells suggests their function in cell migration and invasion. 18305555_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18329709_Trophoblast heparanase is not required for invasion in vitro. Its abundant expression suggests another role during pregnancy, perhaps in controlling the availability of ECM-bound growth factors or acting as a transcription factor. 18357711_The expression of HPSE is significantly increased in squamous carcinomas of head and neck, and is directly related to the clinical stage and lymph node metastasis. 18390199_Hpa may up-regulate the expression of C-erbB-2 in invasive ductal breast carcinoma. 18450756_Cathepsin L has a role in processing and activation of proheparanase through multiple cleavages of a linker segment 18487013_heparanase overexpression can facilitate tumor invasion and accelerate bone destruction caused by prostate cancer bone metastasis. 18512775_Heparanase (HPSE) activity was dramatically higher in Synovial fluid (SF) and Synovial tissue (ST)of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients than in SF and ST from Osteoarthritis patients and asymptomatic donors;HPSE RNA was upregulated in ST of RA patients 18545691_pro-adhesive properties of heparanase are mediated by its interaction with cell surface HS proteoglycans, and utilized the KKDC peptide to examine this possibility 18557927_Heparanase 1 is a key actor of inner root sheath differentiation and hair homeostasis. 18609704_Strong heparanase expression is related with the degradation of basement membrane which allows or accelerates tumor invasion and metastasis. 18618498_findings suggest that heparanase expression and cellular localization are decisive for lung cancer patients' prognosis, most likely because of heparanase-mediated tumor cell dissemination by blood and lymph vessels. 18646256_Overexpressed heparanase and its splice variant localize to the endoplasmic reticulum independent of glycosylation in COS-7 cells. 18647407_Results indicate that heparanase has pleiotropic effects on tumor cells. 18662687_The hydrophobic C-terminus region of heparanase is a determinant for its intracellular trafficking to the Golgi apparatus, followed by secretion, activation, and tumor cell migration. 18704599_Heparanase seems to be significantly associated with lymph node metastasis as well as dedifferentiation. We assume that HPSE plays a crucial role for the aggressiveness of pancreatic cancer. 18773863_The overexpression of heparanase may play an important role in hepatocarcinogenesis, progression, and metastases of hepatocellular carcinoma. 18798279_heparanase plays a unique dual role in tumor metastasis, facilitating tumor cell invasiveness and inducing VEGF C expression, thereby increasing the density of lymphatic vessels that mobilize metastatic cells 18809970_heparanase plays an important role in invasion and metastasis in renal cell carcinoma 18812315_heparanase acts as a master regulator of the aggressive tumor phenotype by up-regulating protease expression and activity within the tumor microenvironment 19096032_role for heparanase in the regulation of arterial structure, mechanics, and repair 19157148_The expression of heparanase was associated with invasion, metastasis and prognosis of nasopharyngeal cancer. 19180921_Hypoxia promotes the expression of HPA and the invasiveness of SKOV3 cells through the HIF-1alpha pathway. 19305494_Results show that heparanase alters the level of nuclear syndecan-1. 19401035_mRNA and protein are detected in inflammatory sinus mucosa and nasal polyps but not in normal sinus mucosa 19406828_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19406828_The current study indicates that rs4693608 and rs4364254 SNPs are involved in the regulation of heparanase expression and provides the basis for further studies on the association between HPSE gene SNPs and disease outcome. 19437318_Changes in plasma HP levels correlated with response to treatment for children diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma 19452723_The expressions of HGF and Hpa in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma are higher than that in nonmalignant tissues, and correlate with lymph node metastasis, clinical stages and pathological grading. 19715595_HPSE gene expression is involved in rhabdomyosarcoma tumor invasion. 19749739_Heparanase expression is already induced in Barrett's epithelium without dysplasia, and is further increased during progression through distinct pathological stages, namely, low-grade dysplasia, high-grade dysplasia, and adenocarcinoma. 19802384_syndecan-1 and FGF-2, but not FGFR-1 share a common transport route and co-localize with heparanase in the nucleus, and this transport is mediated by the RMKKK motif in syndecan-1 19835469_Glioma tissues contain increased levels of heparanase 19916174_heparanase has a role in invasiveness, metastasis and angiogenesis, but not proliferation of human gastric cancer cells 19955948_The gene expression of heparanase in cervical cancer enhances growth, invasion, and angiogenesis of the tumor. 19956890_up-regulation of Hpa by hypoxia is NF-kappaB-dependent in MIA PaCa-2 cells 20007507_T5 is a novel functional splice variant of human heparanase endowed with protumorigenic characteristics 20075159_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20075159_The present study indicates a highly significant correlation of HPSE gene single-nucleotide polymorphisms rs4693608 and rs4364254 and their combination with the risk of developing acute graft-versus-host disease. 20097882_pathway driven by heparanase expression in myeloma cells: elevated levels of VEGF and shed syndecan-1 form matrix-anchored complexes that together activate integrin and VEGF receptors on adjacent endothelial cells thereby stimulating tumor angiogenesis 20164500_Altogether, these findings support the notion that HPSE is a critical downstream target of HER2 mechanisms driving BMBC and is potentially relevant for BMBC therapeutic interventions. 20193112_Decreased expression of Syndecan-1 mRNA and the increased expression of HPA-1 mRNA can promote the invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer. 20309870_HPSE expresses and functions in human osteoblasts. It may mediate osteoblastogenesis through regulation of osteogenic gene expression and histone H3 modification. 20339231_may facilitate the function of heparan sulfate-binding growth factors that elicit an angiogenic response and favor osteoclastogenesis in ameloblastomas 20388348_HPSE, HIF-1alpha and VEGF play a role in tumor angiogenesis and promote malignant progress of retinoblastoma. 20403028_results indicate that aberrant expression of EGR1 in gastric cancer is associated with tumor invasion and metastasis, and heparanase transcription 20434010_The results support the notion that heparanase is a modulator of blood coagulation, and suggest a novel mechanism by which heparanase regulates tissue factor and TFPI levels in endothelial and cancer cells. 20578081_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20578081_Single nucleotide polymorphisms of the HPSE gene is associated with gastric cancer. 20619346_Recent progress in heparanase research emphasizing the molecular mechanisms that govern its pro-tumorigenic and pro-adhesive properties. 20634491_heparanase is a potential modulator of blood hemostasis, and suggest a novel mechanism by which heparanase increases the generation of activated factor X in the presence of tissue factor and activated factor VII. 20653782_Preferential up-regulation of heparanase and cyclooxygenase-2 in carcinogenesis of Barrett's oesophagus and intestinal-type gastric carcinoma. 20660327_Serum heparanase and vascular endothelial growth factor were identified as independent predictive factors for hepatocellular carcinoma 20798248_The results suggest that loss of the adenine (A)/uracil (U)-rich consensus element is an important regulatory mechanism contributing to heparanase induction in human cancer. 21029368_Heparanase expression is induced in Ewing's sarcoma. 21076620_Data show that BRAF knockdown led to suppression of the expression of the GABPbeta, which involved in regulating HPR1 promoter activity. 21131364_a novel mechanism driving the HGF pathway whereby heparanase stimulates an increase in both HGF expression and syndecan-1 shedding to enhance HGF signaling. 21153652_Heparanase expression was found to be insignificant among the various stages in the endometrial pathway to cancer. 21257720_SST0001, a chemically modified heparin, inhibits myeloma growth and angiogenesis via disruption of the heparanase/syndecan-1 axis 21364956_Heparanase levels are elevated in the urine and plasma of type 2 diabetes patients and associate with blood glucose levels. 21385059_Overexpression of heparanase influenced expression of most genes involved in heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthesis, albeit to a different degree in the cortex and thalamus of the transgenic mice. 21415391_findings uncover a new level of regulation governing sVEGF-R1 retention versus release and suggest that manipulations of the heparin/heparanase system could be harnessed for reducing unwarranted release of sVEGF-R1 in pathologies such as preeclampsia 21424539_HPR1 production is increased in endothelial cells from rat models of diabetes, and in macrophages in atherosclerotic lesions of diabetic and nondiabetic patients. Increased HPR1 production may contribute to pathogenesis and progression of atherosclerosis. 21461610_Advanced glycation end-products induce heparanase expression in endothelial cells 21464728_Heparanase expression was present in 57 (67.8%) of the 84 endometrial carcinomas, and was significantly associated with the endometrioid histotype 21483695_Over-expression of heparanase demonstrates the importance of heparan sulfate proteoglycans for the uptake of intestinal derived lipoproteins and its role in the formation of fatty streaks 21490396_heparanase generates a vicious cycle that powers colitis and the associated tumorigenesis: heparanase, acting synergistically with the intestinal flora, stimulates macrophage activation 21505182_Multiple antigenic peptides of human heparanase elicit a much more potent immune response against tumors 21600934_analyzed the involvement of heparanase, a heparan sulfate glycosidase, in the homeostasis of proximal tubular epithelial cells in the diabetic milieu 21671176_Targeted silencing of heparanase gene by siRNA could dramatically inhibit the invasiveness and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells. 21706269_Study found positive staining for HPA-1 in 15% of adrenocortical adenomas and 91.67% of human adrenocortical carcinomas. 21757697_Heparanase-mediated loss of nuclear syndecan-1 enhances histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity to promote expression of genes that drive an aggressive tumor phenotype 21780097_Molecular model of human heparanase with proposed binding mode of a heparan sulfate oligosaccharide and catalytic amino acids. 21965756_Elevated serum CL, Hpa, and MMP-9 levels are correlated with malignant invasion and progression in ovarian cancer. 22001963_heparanase expression is associated with histone modifications and promoter DNA methylation plays a role in the control of gene silencing in glioblastoma 22005029_Hyperpigmentation in human solar lentigo is promoted by heparanase-induced loss of heparan sulfate chains at the dermal-epidermal junction. 22009724_heparanase enhances pituitary cell viability and proliferation and may thus contribute to pituitary tumor development and progression. 22020734_Findings indicate the prominent presence of heparanase in the epithelial component of radicular cysts versus sparse or no expression in periapical granulomas. 22102278_Heparanase and syndecan-1 interplay orchestrates fibroblast growth factor-2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular cells. 22133010_heparanase over-expression is associated with clear cell renal cell cancer. 22194600_Heparanase enhances the phosphorylation of STAT3 and STAT5b but not STAT5a in head and neck cancers. 22227299_study demonstrates a role for heparanase in modulation of acute localized inflammation and mast cell activity, accordingly affecting inflammatory pain 22260074_Heparanase can induce angiogenesis to promote tumor growth by releasing bFGF and VEGF in nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. 22276173_SNPs in HPSE play an important role in gastric cancer progression and survival, and perhaps may be a molecular marker for prognosis and treatment values. 22331282_Role for heparanase in sustaining immune cell-epithelial crosstalk that underlies intestinal inflammation and the associated cancer. Review. 22363633_These results suggest that small RNAs targeting transcription start site can induce transcriptional gene silencing of heparanase via interference with transcription initiation. 22488243_the expression levels of HPSE and miR-1258 in NSCLC tissue are closely related. In HPSE-positive samples, the expression levels of miR-1258 were relatively low; in HPSE-negative samples, the expression levels of miR-1258 were relatively high. 22575501_Heparanase and COX-2 might play complementary roles in the stepwise progression of oral epithelial dysplasia to carcinoma. 22682139_Taking into account the pro-metastatic and pro-angiogenic functions of heparanase, with over-expression in human malignancies and abundance in platelets and placenta. 22692572_data indicate that intact heparan sulfate chains are required to mediate neuroinflammatory responses, and point to heparanase as a modulator of this process, with potential implications for Alzheimer's disease 22719918_demonstrated that artificial miRNAs against HPSE might serve as an alterative mean of therapy to low HPSE expression and to block the adhesion, invasion, and metastasis of melanoma cells 22952874_The results in this study demonstrate that genetic alteration and reduction of HPSE expression are associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 22956610_Heparanase is upregulated and associated with the VEGF expression in hypoxia-induced retinal diseases. 23028487_Elevated urine heparanase levels are associated with proteinuria and decreased renal allograft function. 23048032_Heparanase enhances the insulin receptor signaling pathway to activate extracellular signal-regulated kinase in multiple myeloma 23162016_Heparanase activates macrophages, resulting in marked induction of cytokine expression associated with plaque progression toward vulnerability. 23241438_heparanase plays essential roles in regulating the invasion, proliferation, and angiogenesis of A549 cells 23251556_T5, a novel splice variant of heparanase, is a functional, pro-tumorigenic entity. 23288725_These results suggest that heparanase participates in tumor growth of cervical cancer by influencing the proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells 23313782_study did not find any significant difference in heparanase promoter methylation between colon carcinoma and normal colonic mucosa, suggesting that heparanase overexpression in colon carcinoma is mediated by other mechanisms 23370684_Data indicate that the overexpression of HPSE1 and HPSE2 in the intervertebral degenerated discs suggests a role for these factors in mediating extracellular matrix remodeling in degenerative discs during disease development. 23415719_MiR-1258 may play an important role in breast cancer development and progression by regulating the expression of HPSE, and they might be potential prognostic biomarkers for breast cancer. 23430739_Heparanase regulates secretion, composition, and function of tumor cell-derived exosomes 23499526_Heparanase is critically involeved in inflammation, diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. (Review) 23499527_Heparanase mediates unexpected intracellular effects on T cell differentiation and insulin-producing beta cell survival in T cell-dependent autoimmune Type 1 diabetes mellitus. (Review) 23499528_Induction of heparanase prior to the appearance of malignancy was reported in essentially all inflammatory conditions. (Review) 23499529_The plastic substrate specificity suggests a complex role of heparanase in regulating the structures of heparan sulfate in matrix biology. (Review) 23499530_Heparanase is up-regulated in atherosclerosis and other vessel wall pathologies. (Review) 23504321_Targeting of heparanase-modified syndecan-1 by prosecretory mitogen lacritin requires conserved core GAGAL plus heparan and chondroitin sulfate as a novel hybrid binding site that enhances selectivity. 23504323_Characterization of heparanase-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT activation and its integrin dependence. 23511033_Elevation of serum heparanase is associated with Crohn's disease. 23649655_CCL19/CCR7 may upregulate the expression of heparanase via Sp1 and contribute to the invasion of A549 cells. 23704979_The prognostic role of FLT1/VEGFR1, heparanase and epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression in patients with resected cholangiocarcinoma, was investigated. 23771368_The relative Heparanase mRNA expression level in hepatocellular carcinoma was lower than that in noncancerous tissue. 23794232_Heparanase is frequently expressed in oral mucosal melanoma. 23907942_The study suggest that one of the causes of unexplained miscarriages may result from the impaired expression of heparanase and heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. 23982701_role of HPSE in tumor invasion and metastasis in ovarian cancer and concluded that either the expression of HPSE in cancer and/or the serum concentration of HPSE may be a useful biomarker for the evaluation of surgery effects and prognosis prediction. 23984412_the function of heparan sulfate proteoglycans and heparanase in breast cancer behavior and progression, is discussed. 24169805_Involvement of heparanase in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and a role for the enzyme in facilitating abnormal interactions between immune and epithelial cell subsets of the affected skin. 24189015_results revealed that dialysis treatments induce change in the transcriptomic pattern of biosynthetic proteoglycans in PBMCs with an up-regulation of HPSE. 24286246_HPV16 oncogene E6 is capable of inducing overexpression of heparanase in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 24291708_this study describes (1)H NMR spectroscopic studies of the hydrolysis of the pentasaccharide substrate fondaparinux by heparanase, and provide conclusive evidence that heparanase hydrolyses its substrate with retention of configuration and is thus established as a retaining glycosidase 24319286_the importance of rs4693608 SNP for HPSE gene expression in activated MNCs, indicating a role in allogeneic stem cell transplantation, including postconditioning, engraftment, and GVHD. 24465803_Heparanase potentiates the bioactivity of resistin in its standard bioassay. 24632672_DNA methylation play the regulation role in heparanase gene in different stages of breast cancer 24699306_We found that heparanase induction is associated with decreased levels of CXCL10, suggesting that this chemokine exerts tumor-suppressor properties in myeloma. 24740543_Together, these data indicate a role for heparanase in inflammatory cell trafficking in vivo that appears to require enzymatic activity. 24747732_Heparanase was localized to the cytoplasm and nucleus of tumor cells and to cells within the microenvironment in different types of lung cancer. 24753252_Because HS with unsubstituted glucosamine residues accumulates in heparanase-expressing breast cancer cells, we assumed that these HS structures are resistant to heparanase and can therefore be utilized as a heparanase inhibitor. 24766948_High heparanase expression is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma. 24861922_serum levels of HPSE were significantly higher in breast cancer patients than in benign breast disease and in healthy controls. 24862152_Taking into account the prometastatic, pro-angiogenic and pro-coagulant functions of heparanase, ove | ENSMUSG00000035273 | Hpse | 107.238522 | 2.041624881 | 1.029718 | 0.18050828 | 32.422408 | 0.0000000124047786939125146676578633668855400351560547278495505452156066894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000002803199424401425784457767519108895015733651234768331050872802734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 143.8566577 | 12.7928631 | 70.5600714 | 6.7917191 | |
| ENSG00000173918 | 114897 | C1QTNF1 | protein_coding | Q9BXJ1 | Alternative splicing;Collagen;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | Enables collagen binding activity. Involved in several processes, including negative regulation of platelet aggregation; positive regulation of aldosterone secretion; and positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration. Located in extracellular space. Is integral component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:114897; | collagen trimer [GO:0005581]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; negative regulation of platelet activation [GO:0010544]; negative regulation of platelet aggregation [GO:0090331]; positive regulation of aldosterone secretion [GO:2000860]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; regulation of glucose metabolic process [GO:0010906] | 12409230_molecular cloning, gene expression, and subcellular localization of GIP 16386877_The review describes the potential role of C1qTNF1 as an intracellular regulator of signal transduction 16806199_These findings indicate that CTRP1 expression may be associated with a low-grade chronic inflammation status in adipose tissues. 18171693_CTRP1 enhances the production of aldosterone. CTRP1 was highly expressed in obese subjects as well as up-regulated in hypertensive patients, CTRP1 may be a newly identified molecular link between obesity and hypertension. 18783346_CTRP1 may be considered a novel adipokine, providing an important framework to further address the physiological functions and mechanisms of the action of this family of secreted glycoproteins in normal and disease states. 18842294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23000311_CTRP1 level was significantly higher in subjects with metabolic syndrome compared to healthy subjects. 24827430_CTRP1 is a novel adipokine associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in humans. 24945145_The levels of circulating CTRP1 are associated with coronary artery disease in men. 24965225_Increased plasma CTRP1 was independently associated with type 2 diabetes. Profiling of plasma adipokines such as CTRP1 is particularly important to obtain a greater understanding of their contribution to the type 2 diabetic state. 25635749_The variation of plasma CTRP-1 and IL-6 concentrations may play an important role in reflecting the degree of inflammation in CHD and the severity of coronary arterial atherosclerosis. 25767880_the strong association of CTRP1 with insulin resistance in NAFLD 27169633_Increased serum CTRP 1 levels were closely associated with the prevalence and severity of CAD, it might be regarded as a marker for myocardial infarction. 27175610_CTRP1 has a role in linking dysregulation of lipid metabolism and inflammatory responses in macrophages 28207876_High serum CTRP1 level is associated with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. 28625919_In cultured endothelial cells, treatment of CTRP1 led to increased permeability to fluorescent-labelled dextran and apparent formation of paracellular holes as observed after disturbed flow exposure, which was evidently reduced in the presence of a CTRP1-specific neutralizing antibody. 29360808_CTRP1 may participate in the process of vasculitis and blood coagulation during the acute phase of Kawasaki Disease 29953821_A single bout of high-intensity interval exercise may stimulate CTRP1 and CTRP9 secretions in healthy men. 30103635_serum levels significantly elevated in both early-onset and late-onset pre-eclampsia 31081425_High serum CTRP1 levels are associated with coronary artery disease. 31183364_These findings suggest that CTRP1 potentially indicates poor prognosis in Glioblastoma (GBM) and promotes the progression of human GBM. 31965030_Implications of C1q/TNF-related protein superfamily in patients with coronary artery disease. 32081468_Hypomethylation of C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein-1 promoter region in whole blood and risks for coronary artery aneurysms in Kawasaki disease. 32383048_Methylation of CpG sites in C1QTNF1 (C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 1) differs by gender in acute coronary syndrome in Han population: a case-control study. 32569781_C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein-1 attenuates microglia autophagy and inflammatory response by regulating the Akt/mTOR pathway. 33060724_CTRP-1 levels are related to insulin resistance in pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus. 34288211_CTRP1 decreases ABCA1 expression and promotes lipid accumulation through the miR-424-5p/FoxO1 pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. 34840267_C1q Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Protein 1: A Promising Therapeutic Target for Atherosclerosis. 35172300_Novel Adipokines CTRP1, CTRP9, and FGF21 in Pediatric Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. 35202556_C1q/TNF-related protein-1: Potential biomarker for early diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder. 36195912_CTRP1 prevents high fat diet-induced obesity and improves glucose homeostasis in obese and STZ-induced diabetic mice. | ENSMUSG00000017446 | C1qtnf1 | 73.221720 | 0.310045502 | -1.689448 | 0.24032873 | 49.344162 | 0.0000000000021477269804964552761328495834891751494269418465421495056943967938423156738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000768347954045637269880949677784427297860814221053260553162544965744018554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 35.9340429 | 28.4110616 | 116.4611253 | 91.5992651 | ||
| ENSG00000174837 | 2015 | ADGRE1 | protein_coding | Q14246 | FUNCTION: Orphan receptor involved in cell adhesion and probably in cell-cell interactions specifically involving cells of the immune system. May play a role in regulatory T-cells (Treg) development. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61549}. | Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a protein that has a domain resembling seven transmembrane G protein-coupled hormone receptors (7TM receptors) at its C-terminus. The N-terminus of the encoded protein has six EGF-like modules, separated from the transmembrane segments by a serine/threonine-rich domain, a feature reminiscent of mucin-like, single-span, integral membrane glycoproteins with adhesive properties. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. | hsa:2015; | external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186] | 17823986_Highly specific marker for eosinophils. 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20625511_Additional transcription changes likely associated with Th2-like eosinophilic inflammation were prominent and included increased EMR1&3. 28005267_EMR1 expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 34486997_The myeloid cell biomarker EMR1 is ectopically expressed in colon cancer. | ENSMUSG00000004730 | Adgre1 | 13.418052 | 0.344105879 | -1.539076 | 0.48560364 | 10.213873 | 0.0013938813985801294312305564915277500404044985771179199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0100244796932333415928617625922925071790814399719238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 6.7811310 | 2.9653420 | 19.9604503 | 8.0466883 | |
| ENSG00000174945 | 155185 | AMZ1 | protein_coding | Q400G9 | FUNCTION: Probable zinc metalloprotease. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8TXW1}. | Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Zinc | Predicted to enable metal ion binding activity and metallopeptidase activity. Predicted to be involved in proteolysis. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:155185; | metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] | ENSMUSG00000050022 | Amz1 | 23.660327 | 0.419221755 | -1.254215 | 0.34068792 | 13.686421 | 0.0002160107446109575690153248306302202763617970049381256103515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0020211092278381768104489335513562764390371739864349365234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 13.8635356 | 4.3536075 | 33.2748984 | 10.0039549 | ||
| ENSG00000176049 | 9832 | JAKMIP2 | protein_coding | Q96AA8 | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Golgi apparatus;Reference proteome | The protein encoded by this gene is reported to be a component of the Golgi matrix. It may act as a golgin protein by negatively regulating transit of secretory cargo and by acting as a structural scaffold of the Golgi. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2012]. | hsa:9832; | Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017] | 17572408_NECC 1 & 2 proteins primarily expressed in (neuro)endocrine tissues in vertebrates thus supporting a role for these proteins in the regulated secretory pathway. 19845895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 30796769_individuals with SNP62 (rs12653715 G/C) who were GG homozygous had a significantly increased risk of Graves' disease. The transmission disequilibrium test (TDT) indicated that SNP62 (rs12653715) and SNP63 (rs12653081) loci in the Janus kinase and microtubule interacting protein 2 (JAKMIP2) gene showed dominant transmission from heterozygous parents to the affected offspring. | ENSMUSG00000024502 | Jakmip2 | 34.153305 | 0.489397132 | -1.030922 | 0.30277326 | 11.540113 | 0.0006811048230500928992933729055891944881295785307884216308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0054880727331939518215397910694264282938092947006225585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 20.3049372 | 8.8259091 | 41.6480279 | 17.8395455 | ||
| ENSG00000176155 | 284001 | CCDC57 | protein_coding | Q2TAC2 | FUNCTION: Pleiotropic regulator of centriole duplication, mitosis, and ciliogenesis. Critical interface between centrosome and microtubule-mediated cellular processes. Centriole duplication protein required for recruitment of CEP63, CEP152, and PLK4 to the centrosome. Independent of its centrosomal targeting, localizes to and interacts with microtubules and regulates microtubule nucleation, stability, and mitotic progression. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32402286}. | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Reference proteome | Involved in several processes, including G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle; cilium assembly; and microtubule cytoskeleton organization. Located in centriolar satellite; centriole; and spindle microtubule. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:284001; | centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; centriole [GO:0005814]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; spindle microtubule [GO:0005876]; centriole replication [GO:0007099]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000086]; microtubule nucleation [GO:0007020]; positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0045931] | 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 32402286_CCDC57 Cooperates with Microtubules and Microcephaly Protein CEP63 and Regulates Centriole Duplication and Mitotic Progression. | ENSMUSG00000048445 | Ccdc57 | 268.240197 | 2.833733121 | 1.502704 | 0.54589520 | 7.255678 | 0.0070677195469672684374762283709969779010862112045288085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0377383307915071311566812539695092709735035896301269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 444.4473026 | 122.7343214 | 158.0058325 | 43.4556563 | |
| ENSG00000176681 | 9884 | LRRC37A | protein_coding | A6NMS7 | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA | Glycoprotein;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA | Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:9884; | membrane [GO:0016020] | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA | ENSMUSG00000034239+ENSMUSG00000078632 | Gm884+Lrrc37a | 27.361825 | 0.373745345 | -1.419872 | 0.53403459 | 6.828255 | 0.0089726892615312418138850958371222077403217554092407226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0455110202285590043080887312498816754668951034545898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 13.6920795 | 4.2742009 | 33.7233370 | 9.9213225 |
| ENSG00000177943 | 158056 | MAMDC4 | protein_coding | Q6UXC1 | FUNCTION: Probably involved in the sorting and selective transport of receptors and ligands across polarized epithelia. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63191}. | Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | Predicted to be involved in protein transport. Predicted to be located in membrane. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:158056; | Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; protein transport [GO:0015031] | 7829488_PMID:7829488 describes studies in rat, however, the human MAMDC4 gene product appears to be a homolog of rat apical early endosomal glycoprotein. 25956157_Results suggest that it is the presence of rare syntenic SEC16A and MAMDC4 deletions that increases susceptibility to axial spondyloarthritis in family members who carry the HLA-B*27 allele. 27821716_Expression is localized to the apical surface of the neonatal enterocyte and decreases over time in association with bacterial colonization of the intestine | ENSMUSG00000026941 | Mamdc4 | 42.575640 | 0.371056105 | -1.430291 | 0.28747477 | 24.543051 | 0.0000007266791912776078185396853512112436135339521570131182670593261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000123508973603781031634250495154780935536109609529376029968261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 21.4589616 | 10.1867876 | 50.8362072 | 23.7726570 | |
| ENSG00000178685 | 84875 | PARP10 | protein_coding | Q53GL7 | FUNCTION: ADP-ribosyltransferase that mediates mono-ADP-ribosylation of glutamate and aspartate residues on target proteins (PubMed:18851833, PubMed:23332125, PubMed:23474714, PubMed:25043379). In contrast to PARP1 and PARP2, it is not able to mediate poly-ADP-ribosylation (PubMed:18851833). Catalyzes mono-ADP-ribosylation of GSK3B, leading to negatively regulate GSK3B kinase activity (PubMed:23332125). Involved in translesion DNA synthesis in response to DNA damage via its interaction with PCNA (PubMed:24695737). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18851833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23332125, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23474714, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24695737, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25043379}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;ADP-ribosylation;Cytoplasm;DNA damage;DNA repair;Glycosyltransferase;NAD;Nucleotidyltransferase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase | Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs), such as PARP10, regulate gene transcription by altering chromatin organization by adding ADP-ribose to histones. PARPs can also function as transcriptional cofactors (Yu et al., 2005 [PubMed 15674325]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:84875; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding [GO:0070530]; NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase activity [GO:0003950]; NAD+- protein-lysine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity [GO:0140804]; NAD+-protein ADP-ribosyltransferase activity [GO:1990404]; nucleotidyltransferase activity [GO:0016779]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; NAD biosynthesis via nicotinamide riboside salvage pathway [GO:0034356]; negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048147]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; negative regulation of protein K63-linked ubiquitination [GO:1900045]; protein auto-ADP-ribosylation [GO:0070213]; protein poly-ADP-ribosylation [GO:0070212]; translesion synthesis [GO:0019985]; viral protein processing [GO:0019082] | 15674325_novel PARP enzyme involved in the control of cell proliferation 16455663_Overexpression of PARP10 results in loss of cell viability, although down-expression by short hairpin RNA leads to delayed G1 progression and concomitant cell death. 18851833_alternative catalytic mechanism for PARP10 compared to PARP1 in which the acidic target residue of the substrate functionally substitutes for the catalytic glutamate by using substrate-assisted catalysis to transfer ADP-ribose 22176891_study results show that the interaction between PARP10 and NS1 of H5N1 avian influenza virus can change cell cycle, and PARP10 can affect virus replication 24695737_PARP10 binding to PCNA is required for translesion DNA synthesis. 24878761_ARTD10 plays roles in immunity, metabolism ,apoptosis and DNA damage repair. [review] 29293500_PARP10 expression decreased upon fasting, a condition that is characterized by increases in mitochondrial biogenesis. Finally, lower PARP10 expression is associated with increased fatty acid oxidation 29515234_Study shows that PARP10 is downregulated in intrahepatic metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Further results provide evidence that deficiency of PARP10 markedly increased the migration and invasion of tumor cells through regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and that PARP10 expression inhibited tumor metastasis in vivo. 30032250_PARP10 promotes cellular proliferation, and its overexpression alleviates cellular sensitivity to replication stress and fosters the restart of stalled replication forks. In mouse xenograft studies, PARP10 loss reduces the tumorigenesis activity of HeLa cells. Its overexpression results in tumor formation by non-transformed RPE-1 cells. PARP10 may promote cellular transformation by alleviating replication stress. 32060423_PLK1/NF-kappaB feedforward circuit antagonizes the mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of PARP10 and facilitates HCC progression. 32392194_[PARP10 Influences the Proliferation of Colorectal Carcinoma Cells, a Preliminary Study]. 33059680_The mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase ARTD10 regulates the voltage-gated K(+) channel Kv1.1 through protein kinase C delta. | ENSMUSG00000063268 | Parp10 | 563.626725 | 0.492152874 | -1.022822 | 0.09891388 | 106.127435 | 0.0000000000000000000000006914271788414110513178193550142985695920700771054027301557204398304440351452626600803341716527938842773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000000000604480211102103607665677236327628427383392960178416762916558989740534180157283117296174168586730957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 368.8739219 | 22.1232022 | 752.8180024 | 43.0592225 | |
| ENSG00000179388 | 1960 | EGR3 | protein_coding | Q06889 | FUNCTION: Probable transcription factor involved in muscle spindle development. | Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a transcriptional regulator that belongs to the EGR family of C2H2-type zinc-finger proteins. It is an immediate-early growth response gene which is induced by mitogenic stimulation. The protein encoded by this gene participates in the transcriptional regulation of genes in controling biological rhythm. It may also play a role in a wide variety of processes including muscle development, lymphocyte development, endothelial cell growth and migration, and neuronal development. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. | hsa:1960; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; synapse [GO:0045202]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002042]; cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus [GO:0044344]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; circadian rhythm [GO:0007623]; endothelial cell chemotaxis [GO:0035767]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; neuromuscular synaptic transmission [GO:0007274]; peripheral nervous system development [GO:0007422]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033089]; regulation of gamma-delta T cell differentiation [GO:0045586]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 11909874_HIV Tat binds Egr proteins and enhances Egr-dependent transactivation of the Fas ligand promoter 14525795_Vascularendothelial growth factor induces expression of NR4A nuclear receptors and Egr3 via KDR and KDR-mediated signaling mechanisms. 15171706_data suggest that Egr3 is a target for the estrogen receptor alpha 15173177_Egr-2 and Egr-3 transcription is enhanced by Hepatitis B virus X protein, which induces fasL gene expression 17360599_These findings support the previous genetic association of altered calcineurin signaling with schizophrenia pathogenesis and identify EGR3 as a compelling susceptibility gene. 18059339_findings indicate that Egr3 has an essential downstream role in VEGF-mediated endothelial functions leading to angiogenesis and may have particular relevance for adult angiogenic processes involved in vascular repair and neovascular disease 19124717_Enforced expression of Egr3 transgene, from the CD2 antigen promoter, facilitates development of RAG2-deficient double-negative (DN) stage 3 thymocytes to the DN4 stage and subsequently to the double-positive stage of development. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19822898_Data show that VEGFR1 promoter binding sites for ELF-1, CREB and EGR-1/3 play a positive role in gene transcription in endothelial cells. 19839995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19965691_Egr-3 is a critical determinant of VEGF signaling in activated endothelial cells 20144677_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20379146_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20506119_Results suggest that in many cells of neuroectodermal and epithelial origin EGR1, EGR2, and EGR3 activate NAB2 transcription which is in turn repressed by NAB2, thus establishing a negative feedback loop. 20537399_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20537399_This study demoistrated that ERG3 are not genetic risk factors for schizophrenia in japanese. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20687139_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20687139_SNP rs35201266 in intron 1 of the EGR3 gene showed a significant association with schizophrenia 21421043_EGR3 bound to the TREM-1 promoter. 22276163_Study supports the association of EGR3 with schizophrenia in Han Chinese sample. 22370066_EGR3, a gene that translates environmental stimuli into long-term changes in the brain, may be associated with risk for child bipolar disorder 1. 22425949_EGR3 gene may play an important role in schizophrenia susceptibility 23342084_Egr3 mRNA expression reveals that Egr3 mRNA expression is increased in tumor cells of non-relapsed samples compared to normal prostate cells, but is significantly lower in relapsed samples compared to non-relapse. 23460371_Decreased EGR3 expression might play a critical role in the differentiation, proliferation, metastasis and progression of gastric cancer cells. 23485457_EGR2 and EGR3 are regulated by NFkappaB and MAPK signalling pathways downstream of TNFalpha stimulation in breast adipose fibroblasts, and this in turn is upstream of CYP19A1 transcription via PI.4 23904169_Our results suggest that Egr-3 is a transcription factor associated with TGF-beta1 expression and in vivo regulatory activity 23906810_These results provide the first evidence that Egr-3, is up-regulated in scleroderma and is necessary and sufficient for profibrotic responses. 23935197_These data suggest that type I IFN stimulation induces a rapid recruitment of a repressive Egr3/Nab1 complex that silences transcription from the ifngr1 promoter. 23962955_Genetic variation in EGR3 may affect prefrontal function through neurodevelopment 24886494_Data shows association of Egr3 genetic polymorphisms and coronary artery disease in the Uygur and Han of China 25633035_EGR3 promotes excessive production of IL6 and IL8 observed during the progression of prostate cancer. 26474411_These findings support previously reported associations between EGR3 and schizophrenia. 27667480_In the PPI network, genes may be involved in Down syndrome (DS) by interacting with others, including nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 2 (NR4A2)early growth response (EGR)2 and NR4A2EGR3. Therefore, RUNX1, NR4A2, EGR2, EGR3 and ID4 may be key genes associated with the pathogenesis of DS. 27856665_Egr2 and Egr3 have emerged as regulatory molecules that suppress excessive immune responses. Mice deficient for Egr2 and Egr3 develop a lupus-like disease with dysregulated activation of effector T cells. Egr2 and Egr3 confer suppressive activity to CD4(+) T cells and regulate the production of inhibitory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-beta1. 28070994_miR-718 acts as a tumor suppressive microRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating the expression of EGR3, which may provide a new diagnostic marker and treatment target for HCC 28098878_EGR3 contributes to cell growth inhibition via upregulation of FasL in Hepatocellular carcinoma. 28847731_KSRP decreased EGR3 mRNA stability in an ARE-independent manner. 31081063_Study demonstrated that EGR3 expression was enhanced in prostate cancer (PC) tissues. EGR3 was proposed as a possible target of miR335, and was negatively regulated by miR335. Silencing EGR3 suppressed the viability and angiogenesis of PC cell line. 32138690_Silencing of miRNA-210 inhibits the progression of liver cancer and Hepatitis B virus-associated liver cancer via up-regulating EGR3. 32518380_Expression and prognostic value of the transcription factors EGR1 and EGR3 in gliomas. 33113163_Schizophrenia risk candidate EGR3 is a novel transcriptional regulator of RELN and regulates neurite outgrowth via the Reelin signal pathway in vitro. 33485349_HELQ and EGR3 expression correlate with IGHV mutation status and prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 34243729_XIST promotes apoptosis and the inflammatory response in CSE-stimulated cells via the miR-200c-3p/EGR3 axis. | ENSMUSG00000033730 | Egr3 | 93.923192 | 0.491517422 | -1.024686 | 0.16408000 | 39.554002 | 0.0000000003191118759723654152779455609053281539555513290906674228608608245849609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000089096545331366211704517319943698316908609058373258449137210845947265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 63.9925389 | 19.2593526 | 130.8073349 | 38.8278603 | |
| ENSG00000179528 | 85474 | LBX2 | protein_coding | Q6XYB7 | FUNCTION: Transcription factor. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q804R0}. | Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation | Enables sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including muscle cell differentiation; positive regulation of convergent extension involved in gastrulation; and positive regulation of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Predicted to be part of chromatin. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:85474; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; muscle cell differentiation [GO:0042692]; positive regulation of convergent extension involved in gastrulation [GO:1904105]; positive regulation of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:2000052]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 29669692_LBX2 was identified as a pathogenic gene in Chinese patients with atrial septal defect. 32559617_LncRNA LBX2-AS1 facilitates abdominal aortic aneurysm through miR-4685-5p/LBX2 feedback loop. 32567804_Identification of LBX2 as a novel causal gene of lung adenocarcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000034968 | Lbx2 | 16.279471 | 0.238470717 | -2.068116 | 0.47114612 | 19.069374 | 0.0000126051536902955827021584334080017697488074190914630889892578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001632600831665320434329252696770140573789831250905990600585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 6.4495684 | 2.0686406 | 27.2364219 | 7.9864878 | |
| ENSG00000179532 | 144132 | DNHD1 | protein_coding | Q96M86 | FUNCTION: Essential for the normal assembly and function of sperm flagella axonemes. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:34932939}. | Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cilium;Coiled coil;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Flagellum;Reference proteome | Predicted to enable dynein intermediate chain binding activity; dynein light intermediate chain binding activity; and minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity. Predicted to be involved in cilium movement. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:144132; | dynein complex [GO:0030286]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; inner dynein arm [GO:0036156]; sperm flagellum [GO:0036126]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; dynein intermediate chain binding [GO:0045505]; dynein light intermediate chain binding [GO:0051959]; minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity [GO:0008569]; cilium movement [GO:0003341]; flagellated sperm motility [GO:0030317]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018]; sperm flagellum assembly [GO:0120316] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 34932939_Bi-allelic variants in DNHD1 cause flagellar axoneme defects and asthenoteratozoospermia in humans and mice. | ENSMUSG00000030882 | Dnhd1 | 65.738012 | 0.385107445 | -1.376667 | 0.34218799 | 15.694302 | 0.0000744481203888839096743240686393505711748730391263961791992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0007979925731798529452143409201880785985849797725677490234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 31.9224287 | 6.5690037 | 83.5505429 | 16.6548211 | |
| ENSG00000179813 | 144809 | FAM216B | protein_coding | Q8N7L0 | Reference proteome | hsa:144809; | ENSMUSG00000045655 | Fam216b | 28.695912 | 0.357013857 | -1.485948 | 0.34510326 | 18.797816 | 0.0000145333477405823531546959215265957254814566113054752349853515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001849794979028807821817143031140062703343573957681655883789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 15.2591324 | 7.9808993 | 42.9023624 | 21.8747306 | |||||
| ENSG00000180008 | 122809 | SOCS4 | protein_coding | Q8WXH5 | FUNCTION: SOCS family proteins form part of a classical negative feedback system that regulates cytokine signal transduction. Substrate-recognition component of a SCF-like ECS (Elongin BC-CUL2/5-SOCS-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins. Inhibits EGF signaling by mediating the degradation of the Tyr-phosphorylated EGF receptor/EGFR. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15590694, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17997974}. | 3D-structure;Growth regulation;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;Signal transduction inhibitor;Ubl conjugation pathway | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. | The protein encoded by this gene contains a SH2 domain and a SOCS BOX domain. The protein thus belongs to the suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS), also known as STAT-induced STAT inhibitor (SSI), protein family. SOCS family members are known to be cytokine-inducible negative regulators of cytokine signaling. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:122809; | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex [GO:0005942]; 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase regulator activity [GO:0046935]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of epidermal growth factor-activated receptor activity [GO:0007175]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0046854]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] | 15590694_the expression of SOCS5 and its closest homolog SOCS4 is elevated in cells following treatment with EGF, similar to several negative feedback regulators of EGFR whose expression is up-regulated upon receptor activation. 17997974_The structure of the SOCS4-ElonginC-ElonginB complex reveals a distinct SOCS structural class. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20433750_Higher mRNA expression levels of SOCS1, 3, 4 and 7 are significantly associated with earlier tumour stage and better clinical outcome in human breast cancer. 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20486857_These data suggest that miRNAs play an important role in the regulation of cytokine-inducible Src homology and SOCS expression in epithelial cells in response to C. parvum infection. 22127425_The expression of SOCS4 seems to be controlled epigenetically and is often weakly expressed in gastric cancer tissue and cell lines. SOCS4 methylation status could be a predictor of gastric cancer prognosis. 22423360_Identified is a conserved region of about 70 residues in the N-terminal domains of SOCS4 and 5 that is predicted to be more ordered than the surrounding sequence. 25286386_This study showed that increased protein levels of SOCS-4 and SOCS-7 in Alzheimer's disease brains. 25639832_SOCS4 is a known inhibitor of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor signalling, and functional studies demonstrated specific upregulation of EGF-dependent immune stimulation in affected family members. 26437444_miR-25 promotes the migration and invasion of thyroid cancer cells by directly binding to the 3'-UTR of SOCS4 that leads to the inhibition of SOCS4. 27635428_Significantly higher levels of suppressor of cytokine signalling proteins SOCS3 and SOCS4 in non-healing chronic wounds compared to the healing/healed chronic wounds were observed at the transcript level. 28751715_In vitro significance of SOCS-3 and SOCS-4 and potential mechanistic links to wound healing have been presented. 31200002_Mechanistic investigations demonstrated that TUSC7 can interact with miR-616 and decrease its expression, thereby upregulating the expression of miR-616's targets SOCS4 (SOCS5). 31398463_SOCS4 expression was lower in T-cell-mediated kidney allograft rejection group compared with non-rejected individuals 32819588_Exosome-mediated miR-9-5p promotes proliferation and migration of renal cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo by targeting SOCS4. | ENSMUSG00000048379 | Socs4 | 398.288169 | 2.427924735 | 1.279724 | 0.48232870 | 6.805803 | 0.0090862072452748705170266774189258285332471132278442382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0458954620855956049729762469269189750775694847106933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 484.1098312 | 218.2532064 | 197.0390206 | 88.8810658 |
| ENSG00000180616 | 6752 | SSTR2 | protein_coding | P30874 | FUNCTION: Receptor for somatostatin-14 and -28. This receptor is coupled via pertussis toxin sensitive G proteins to inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. In addition it stimulates phosphotyrosine phosphatase and PLC via pertussis toxin insensitive as well as sensitive G proteins. Inhibits calcium entry by suppressing voltage-dependent calcium channels. Acts as the functionally dominant somatostatin receptor in pancreatic alpha- and beta-cells where it mediates the inhibitory effect of somatostatin-14 on hormone secretion. Inhibits cell growth through enhancement of MAPK1 and MAPK2 phosphorylation and subsequent up-regulation of CDKN1B. Stimulates neuronal migration and axon outgrowth and may participate in neuron development and maturation during brain development. Mediates negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling through PTPN6. Inactivates SSTR3 receptor function following heterodimerization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15231824, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18653781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19434240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22495673, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22932785}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Somatostatin acts at many sites to inhibit the release of many hormones and other secretory proteins. The biologic effects of somatostatin are probably mediated by a family of G protein-coupled receptors that are expressed in a tissue-specific manner. SSTR2 is a member of the superfamily of receptors having seven transmembrane segments and is expressed in highest levels in cerebrum and kidney. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:6752; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; neuropeptide binding [GO:0042923]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; peptide binding [GO:0042277]; somatostatin receptor activity [GO:0004994]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007193]; cellular response to estradiol stimulus [GO:0071392]; cellular response to glucocorticoid stimulus [GO:0071385]; cerebellum development [GO:0021549]; forebrain development [GO:0030900]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger [GO:0007187]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; neuropeptide signaling pathway [GO:0007218]; peristalsis [GO:0030432]; regulation of muscle contraction [GO:0006937]; response to starvation [GO:0042594]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] | 11753241_SSTR transcripts are expressed and functional in retroorbital fibroblasts. SSTR1 is expressed in Grave's disease and octreotide inhibits retroorbital cell growth, explaining the SRIH therapeutic effect. 11839658_Quantitative evaluation of somatostatin receptor subtype 2 expression in sporadic colorectal tumor and in the corresponding normal mucosa 11920268_Somatostatin modulates G-CSF-induced but not interleukin-3-induced proliferative responses in myeloid 32D cells via activation of somatostatin receptor subtype 2. 12021920_SSTRs 1-5 are heterogeneously expressed in gastroenteropancreatic endocrine tumors 12210479_expression of SSTR2 transcripts up-regulated in prostatic carcinoma cells; SSTR2 agonists may have role in treatment of prostate cancer 12414882_somatostatin receptor transcripts were found in lymphocytes both from Graves' ophthalmopathy retroorbital tissues and blood samples, with levels of expression of SST1, -2, and -4 mRNA higher than those of the SST3 and -5 transcripts 12474541_localization and expression in human prostatic tissue and prostate cancer cell lines 12490654_sensitizes human pancreatic cancer cells to death ligand-induced apoptosis 12675130_Presence and intracellular localization of the spliced variant SSR2(a) and its endogenous ligand SS in the cultured human neuroblastoma (NB) cell line, SH-SY5Y. 12684217_study demonstrates for the first time a selective and inducible expression of the recently discovered cortistatin, as well as somatostatin receptor 2, in human monocyte-derived cells 14572771_Expression of somatostatin receptor 2 by human pancreatic cancer causes significant slowing of tumor growth by a mechanism independent of exogenous somatostatin 14576502_Activation of SSTR 2 by SSTR 2 agonist significantly suppressed insulin secretion. 14602773_Sst2 and sst5 were expressed in 70%, sst1 in 50%, and sst3 and sst4 subtypes only in 15-20% of insulinomas 14671213_The receptor from somatostatinoma was completely phosphorylated. Only unphosphorylated sst2A was present in human tumors not exposed to autocrine stimulation. 14695784_SST2R gene together with p53 and ras genes may participate in pancreatic cancerous angiogenesis. 14760765_Expression of reintroduced human SSTR2 gene exerts its antiangiogenic effects by down-regulating expressions of factors involved in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis, suggesting SSTR2 gene transfer as new strategy of gene therapy for pancreatic cancer. 15118275_The degree (or level) of sst2 and sst5 expression is critical for the ultimate GH response of somatotropinomas to endogenous SRIF tone and exogenous SRIF analogue therapy. 15153427_Epithelial sst2A cells, identified as neuroendocrine, gastrin-producing cells, were found in large numbers in the antrum and the duodenum, but not in the gastric corpus. 15205362_SSTR2 provides an anti-angiogenic effect on pancreatic cancer xenografts, susgesting gene transfer as a promising strategy of gene therapy for pancreatic cancer. 15231824_human somatostatin receptor 2 dimers have a role in receptor trafficking 15257106_Expression of the SSTR2 gene in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells induces apoptosis, which may be mediated via down-regulation of Bcl-2 & up-regulation of Bax (alteration of Bcl-2/Bax ratio) & inhibits tumor angiogenesis, inhibiting of tumor growth. 15754023_gene transfer into pancreatic neoplasm cells resulted in no apoptosis, but a significant cell proliferation inhibition 15914528_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15914528_SSTR2 and SSTR5 variants seem to have a minor role in determining the responsiveness to somatostatin analogs in acromegaly 16115892_activation of the IKK/NFkappaB signaling cascade by SSTR2 requires a complicated network consisting of Galpha(14), protein kinase C, CamkII, ERK, and c-Src 16214911_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16254490_In the temporal lobe epilepsy, dentate gyrus, sst2 receptor mRNA expression was strongly increased in the granule cell layer, sst2 receptor-binding sites and immunoreactivity was preserved in the inner but decreased in the outer molecular layer. 16601140_the subtype 2 receptor-mediated antiproliferative effect of SRIH on TT cell proliferation may be exerted through a decrease in cyclin D1 and cdk4 levels 16606630_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16645635_Sst2 sensitized NIH3T3 cells to TNFalpha-induced apoptosis, enhanced TNFalpha-mediated activation of NF-kappaB, resulting in JNK inhibition and subsequent executioner caspase activation and cell death. 16917505_Physical interaction between a sst2 and p85, revealing a novel mechanism for negative regulation by ligand-activated GPCR of PI3K-dependent survival pathways, which may be an important molecular target for antineoplastic therapy. 16954443_Cytostatic action exerted by SSTR2 analogs might account for the tumor shrinkage observed in acromegalic patients treated with long-acting somatostatin analogs. 16996150_results show that Somatostatin receptor 2 is predominantly expressed on thyroid tissue and is a valid target for treatment of thyroid tumours 17546456_We conclude that the somatostatin receptor plays a role in the total renal uptake of radiolabelled somatostatin analogues. 17603546_Somatostatin caused rapid sst(2a) receptor phosphorylation and desensitization of epithelial antisecretory responses. 17678886_17q gain and promoter polymorphisms can play a role into the regulation of sst2 expression in neuroblastomas 17706924_The functional interactions between human somatostatin receptor 2 (hSSTR2) and human dopamine receptor 2 (hD2R) in both co-transfected CHO-K1 or HEK-293 cells as well as in cultured neuronal cells which express both the receptors endogenously. 17848636_Analysis of orbital tissues reveals upregulation of SSTR1 and -2 in a group of Graves' ophthalmopathy (GO) patients. Adipogenesis, a process occurring in GO orbits, provides one possible explanation for some of the observed increase. 18196892_Sst(2) is the best target for visualization of neuroendocrine tumors(NE) tumors, whereas noradrenaline transporter is only a useful target in a subpopulation of NE tumors. 18234910_This study was undertaken to investigate molecular mechanism of transcriptional regulation of the human sst2 gene, for which an additional exon (exon 1) in the 5'-untranslated region was recently found. 18292657_sst2 was expressed in 67% of the patients with HCC 18325993_Existence of a novel upstream promoter for the hSSTR2 gene that is regulated by epigenetic modifications, suggesting for complex control of the hSSTR2 transcription. 18599562_SSTR2 is the predominant mediator of functional ocular antiangiogenic effects. 18617261_Somatostatin regulates early trophoblast functions mainly through an interaction with SSTR2. 18653781_Data show that human somatostatin receptors (SSTR)2 and SSTR5 heterodimerize, and that selective activation of SSTR2 and not SSTR5, or their costimulation, modulates the association. 18682975_SSTR2 is not suited as prognostic marker or therapeutic target in uveal melanoma 18695896_High somatostatin receptor 2 expression is associated with neo-angiogenesis and high grade meningiomas. 18697876_Rabbit monoclonal antibody UMB-1 may prove of great value in the assessment of sst2A status in human neuroendocrine tumors during routine histopathological examination. 18808065_sst2 mRNA and receptor levels were significantly higher in the meningothelial subtype than in the fibroblastic subtype of meningiomas 18852217_Results show that glucocorticoids selectively downregulate somatostatin type 2, but not dopamine D2 and only to a minor degree sst5 receptors in human neuro-endocrine BON and TT cells. 18936524_Immunohistochemistry stufy of SSTR2 in prostate tissue from patients with bladder outlet obstruction showed that the majority of cells showed a weak intensity. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19106227_An autocrine and paracrine role of SST in the lacrimal system and at the ocular surface and a role of SST in corneal immunology. 19148511_SSTR2 could be a promising candidate for gene therapy for SSTR2-positive and SSTR2-negative tumors 19318729_Both SSTR1 and 2 mRNA levels in SCA were greater than Cushing disease, while SSTR1 mRNA levels, but not SSTR2, in silent corticotroph adenoma were also greater than non-functioning pituitary tumor. 19324939_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19324939_Variants in SSTR2 may influence pathways of insulin sensitivity to modulate glucose homeostasis. 19330452_SSTR2 had higher expression in patients that had normalized GH and IGF-I. There was a positive correlation between the percentage of tumor reduction by octreotide-lar and SSTR2 expression. 19389921_Site specificity of agonist and second messenger-activated kinases for somatostatin receptor subtype 2A (Sst2A) phosphorylation. 19423539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19434240_Somatostatin sst2A receptor participates in the development and maturation of specific neuronal populations during rat and human brain ontogenesis. 19575008_Data suggest that enhanced SSTR2 expression plays an antiproliferative role in MCF-7 cells through inducing apoptosis and G(1)/S cell cycle arrest, and by decreasing EGFR expression, thereby counteracting the growth-stimulating effect of EGF. 19671855_hSSTr2 restoration mediated by oncolytic adenovirus enhances TRAIL-induced antitumor efficacy against pancreatic cancer. 19748526_heterodimerisation between hSSTR2 and hSSTR5 is potentiated in the absence of receptor-stimulation 19759190_Overexpression of SSTR type 2A was associated with metastatic carcinoids in pulmonary neuroendocrine tumours. 19805200_The upregulation of both sst2 and TSP-1 tumor suppressors may function as an early negative feedback to restrain pancreatic carcinogenesis. 19885591_down-regulation of MDR genes MDR1, MRP2, and LRP is responsible for the improvement in the chemotherapeutic sensitivity of hSSTR2-expressing pancreatic cancer cells 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20182388_Studies show that this study may be the basis for further functional studies to evaluate the role of somatostatin receptors sst1 to sst5 in the diabetic state. 20228164_sst(2) receptors can be internalized in sst(2)-expressing neuroendocrine tumors in patients under octreotide therapy. 20233796_Data indicate that OcF showing high-affinity binding to the sstr2. 20422506_The association between SST immunostaining and tracer uptake in [(111)In]-DTPA octreotide (DTPAOC) scintigraphy and [(68)Ga]-DOTA-D-Phe(1)-Tyr(3)-octreotide (DOTATOC) positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT). 20450431_SSTR2 expression is inhomogeneous in thyroid disease, with the highest density detected in cold thyroid nodules 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634197_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20717067_Data show that the mRNA levels of SSTR1, SSTR2, SSTR3, and SSTR5 were high in PET compared with AC, whereas the expression of SSTR4 was low in PET and AC. 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20810604_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20942237_Lower expression of SSTR2 and activation of STAT3 in olfactory neuroblastoma cells might contribute to the development of ONB. 20948194_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20948194_polymorphism in the SSTR2 gene is associated with obesity, food intake and nutrient intake in the Mediterranean population 21215273_Mean cortical SSTR2 mRNA levels were significantly (19%) lower in the subjects with schizophrenia compared to controls. 21287294_The co-expression of sstrs and D2R in a significant number of the studied cases offers a potential therapeutic alternative for gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. 21330405_pasireotide activates the somatostatin receptor 2 via a molecular switch that is structurally and functionally distinct from that turned on during octreotide-driven sst(2A) activation 21383526_differential gene expression profiles revealed more abundant mRNA expression in ectopic ACTH syndrome than in Cushing disease of SSTR-2 21503779_mRNA levels of SSTR2a, SSTR3 and SSTR5 in neuroendocrine lung cancer affected patients, were determined. 21667819_we investigated expression of SSTR2 and SSTR5 in the human thoracic duct 22213295_High somatostatin receptor 2 is associated with gastric adenocarcinoma. 22419713_Determination of the expression of SSTR2 in an attempt to establish correlations and/or associations with clinical characteristics of patients with nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas. 22472799_Low somatostatin receptor subtype 2, but not dopamine receptor subtype 2 expression is associated with the lack of biochemical response of somatotropinomas to treatment with somatostatin analogs 22495673_Data show that the aspartic acid changes at position 89 to either Ala, Leu, or Arg generated mutant somatostatin receptor subtype 2 (SSTR2) with varying expression profiles and a complete inability to bind somatostatin-14 (SST). 22592599_Results suggest that targeting adenoviral vectors to sstr2A could provide a new strategy for the efficient transfer of genes to glioblastoma cells. 22640914_Report down-regulation of SSTR-2 expression in operable hepatocellular carcinomas. 22932785_Data suggest that somatostatin-14 inhibits secretion from alpha and beta pancreatic cells by activating GIRK (G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channel) and inhibiting exocytosis; these effects are mediated by SSTR2 in both cell types. 23677175_The analyses of this study demonstrated specific upregulation of sst 2 mRNA in medulloblastoma 23794313_Somatostatin receptor-2 positivity, either focal or diffuse, does not seem to predict prognosis in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. 23828624_We genotyped two single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes of importance for respiratory control: P2RY1 (adenosine diphosphate/adenosine triphosphate receptor) and SSTR2 (somatostatin receptor). 24060005_Because of its diffuse strong expression and widespread availability, immunohistochemistry for SSTR2A is useful to confirm the diagnosis of phosphaturic mesenchymal tumors in an appropriate setting particularly if material is limited. 24098585_ZAC1 and SSTR2 are down-regulated in non-functioning pituitary adenomas but not in somatotropinomas. 24182563_We studied the expression of SSTR(2A) and SSTR(5) with new procedures in 108 pituitary tumors 24189142_Whereas sst2 receptors might play a primary role in the differentiation and regulation of TSH, LH, and FSH cells, sst5 receptors appear to be mainly involved in GH regulation from birth onward 24565507_SSTR2 is overexpressed in gastric and duodenal neuroendocrine tumors 24565897_agonist-selective sst2 receptor internalization is regulated by multi-site phosphorylation of its carboxyl-terminal tail. 24828612_Filamin A is involved in SST2 stabilization and signaling in tumoral somatotrophs, playing both a structural and functional role. 24967740_SSTR 5 was shown to be the main receptor subtype in the analysed differentiated or anaplastic thyroid malignancies, whereas SSTR 2 was found only in a small percentage. 25008035_SSTR2 expression was tested in GH-secreting adenomas from 60 patients with acromegaly who had undergone pituitary surgery, 36 of whom had received octreotide with varying levels of response. Its expression was not correlated with baseline or post-octreotide GH or IGF-1 levels or tumor volume. 25010045_SSTR2 expression seems an important factor in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer 25554089_SSTR2A and SSTR3 are more likely to be expressed in SDH-deficient pheochromocytomas/paragangliomas compared with tumors demonstrating normal SDHB staining pattern. 25591947_Somatostatin type 2 receptor, a clinically crucial molecular target, shows variable and unpredictable expression in neuroendocrine neoplasms irrespective of tumor grade. 25635370_Relationships between SSTR2A and breast or prostate cancer showed low concordance between CpGs methylation grade and cancer. 25676386_This study indicated that SSTR2 may be associated with the selective vulnerability of the noradrenergic system in Alzheimer's disease. 25765179_Somatostatin receptors were expressed in a high proportion of merkel cell carcinomas, although expression was heterogeneous between tumours and was not associated with disease severity. 25808161_Data indicate that somatostatin receptor scintigraphy (SRS) and immunohistochemical results for somatostatin and dopamine receptors sstr2, sstr3, sstr5 and D2R were compared in neuroendocrine neoplasms tissues. 25872131_In pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, the primary tumor and metastases differ significantly in their SSTR2A expression. 25872132_Study demonstrates the first evidence of SST2R expression and somatostatin receptor scintigraphy positivity in pancreatic serous cystadenomas. 25879040_e hSSTr2 gene can act as not only a reporter gene for in vivo imaging, but also a therapeutic gene for local radionuclide therapy. 25890201_Low SSTR2 expression is associated with pancreatic cancer. 25906124_although the limited number of cases with adequate term follow-up, SSTR-2A expression could be a prognostic factor and somatostatin analogs therapeutic candidate for SmCCs of the bladder as these tumors show high percentage of SSTR-2A expression 25925002_SSTR2 and SSTR5 protein levels were induced as compared to any agent alone. 25962406_An immunohistochemical investigation of the expression of somatostatin receptor subtypes 26036598_mir-185 regulates the expression of SSTR2 in GH-secreting pituitary adenoma. The staining intensity of SSTR2 is stronger in adenoma samples than controls. 26095613_sST2 is proposed as a biomarker for progressive vascular fibrosis, and the involvement of sST2 in the pathogenesis of limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis may be exploited therapeutically. 26158180_The expression of VEGF and SSTR2 were associated with progression and prognosis of gastric cancer. 26211366_VPA was observed to stimulate the expression of somatostatin receptor type 2 (SSTR2). 26238605_SSTR2 gene expression was dysregulated in the anterior cingulate of bipolar patients. 26259237_there is an elevation in CXCR4 and a decrease in SSTR2A expression with increasing malignancy in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms 26339384_CD56 marker is a useful alternative that is comparable to SSTR2A for the diagnosis of phosphaturic mesenchymal tumors. 26391562_Results show that histological subtyping of pituitary tumor correlated with SSTR2, E cadherin and p27kip protein levels and these may serve as useful biomarkers for prognosis. 26474434_Data showed that the distribution of somatostatin receptor (SSTR) subtypes among the 199 pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs) was: SSTR2 (54.8%), SSTR1 (53.3%), SSTR4 (51.8%), SSTR5 (33.7%), and SSTR3 (28.6%). 26531719_Combination treatment increased both SSTR2 and SSTR5 mRNA and protein levels in DU-145 cells. The data suggest that this combination therapy may be a good candidate for patients with advanced metastatic Prostate cancer (PCa) do not respond to androgen deprivation. 26733502_Filamin-A is required to mediate SSTR2 effects in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours 26796520_SSTR2 promoter hypermethylation might be associated with the risk and progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma in males. 26978232_The number of SSTR-2-expressing cells was significantly smaller in the patients with Crohn's disease than that in those with the unchanged mucosa and in those with indeterminate (unclassified) colitis. 27402219_expression of MDM2, somatostatin receptor 2A, and PD-L1 in follicular dendritic cell sarcoma 27455094_The results of this study showed the SSTR2 expression was lower in patients pretreated with LA-SSA/PEGV compared to the drug-naive acromegalic patients. 28120505_This study investigated the presence of progenitor/stem cells in non-functioning pituitary tumors (NFPTs) and tested the efficacy of dopamine receptor type 2 (DRD2) and somatostatin receptor type 2 (SSTR2) agonists to inhibit in vitro proliferation 28467778_SSTR2A expression is infrequent in astrocytomas and negative in the majority of glioblastomas where it is of no prognostic significance. In contrast, oligodendrogliomas show intense membranous and cytoplasmic SSTR2A expression. 28782576_SSTR2 was significantly hypermethylated in colorectal cancer tissues when compared with adjacent normal colorectal tissues. 29807052_Olfactory neuroblastoma demonstrate high SSTR2a expression regardless of their differentiation. 30128959_SSTR2A expression is correlated with longer OS in medullary thyroid carcinoma, especially for stage IV patients, suggesting that SSTR2A expression might be a useful prognostic factor in medullary thyroid carcinoma. 30152518_SSTR2 is a poor prognostic biomarker in SCLC and potential future therapeutic signaling target. 30193580_In this cohort showed that most IDH-wild type gliomas did not express SSTR2A protein and a significant overexpression of SSTR2A protein was observed in the IDH-mutant gliomas 30334904_Patients with neuroblastoma, including relapsed or progressive disease, showed SSTR2 expression at diagnosis 30531706_This study indicates a down-regulation of SSTR2 expression as small intestinal neuroendocrine tumors progress through the intestinal wall, which might signify underlying biological processes of importance for SI-NET invasion behavior. 30585825_SSTR2a may be helpful to distinguish follicular dendritic cell sarcomas from inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell sarcomas ... and may be a potential therapeutic target for treatment of follicular dendritic cell sarcomas 30609928_study suggests that SSTR2 might play a critical role in the aetiopathogenesis of periodontitis 30822353_Reaults indicate that endosomal trafficking of somatostatin receptor 2 (SSTR2) is dependent on numerous regulatory mechanisms controlled by its C terminus and the retromer machinery. 31208995_Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules cells closely resemble SSTR2a-positive meningothelial cells. 32328798_Expression of potential therapeutic target SSTR2a in primary and metastatic non-keratinizing nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 32576907_Enhancing the anti-tumour activity of (177)Lu-DOTA-octreotate radionuclide therapy in somatostatin receptor-2 expressing tumour models by targeting PARP. 33132215_SSTR2a is constantly expressed in lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma with squamous differentiation other than that with glandular differentiation. 33313679_The PDZ Domain Protein SYNJ2BP Regulates GRK-Dependent Sst2A Phosphorylation and Downstream MAPK Signaling. 33402692_Somatostatin receptor 2 expression in nasopharyngeal cancer is induced by Epstein Barr virus infection: impact on prognosis, imaging and therapy. 33491286_Predictive and prognostic significance of tumour subtype, SSTR1-5 and e-cadherin expression in a well-defined cohort of patients with acromegaly. 33598797_The potential of somatostatin receptor 2 as a novel therapeutic target in salivary gland malignant tumors. 33828200_Understanding the influence of lipid bilayers and ligand molecules in determining the conformational dynamics of somatostatin receptor 2. 33886620_Octreotide inhibits secretion of IGF-1 from orbital fibroblasts in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy via inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway. 34040115_A potential role for somatostatin signaling in regulating retinal neurogenesis. 34320691_The prognostic significance of neuroendocrine markers and somatostatin receptor 2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 34601710_The immunohistochemical expression of SSTR2A is an independent prognostic factor in meningioma. 35184184_Diagnostic Utility of Somatostatin Receptor 2A Immunohistochemistry for Tumor-induced Osteomalacia. 35264912_Somatostatin Receptor 2: A Potential Predictive Biomarker for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment. | ENSMUSG00000047904 | Sstr2 | 67.847392 | 0.484816246 | -1.044490 | 0.22329262 | 21.962517 | 0.0000027802766732590818220087480749924679912510327994823455810546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000423643900931895786999420439045138664369005709886550903320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 42.9372109 | 8.8827468 | 89.0760025 | 17.7262141 | |
| ENSG00000180953 | 400410 | ST20 | lncRNA | Q9HBF5 | FUNCTION: May act as a tumor suppressor. Promotes apoptosis of cancer cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11857354}. | Reference proteome;Tumor suppressor | Enables cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process. Involved in several processes, including apoptotic signaling pathway; cellular response to UV-C; and positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0008656]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097190]; cellular response to UV-C [GO:0071494]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; positive regulation of apoptotic DNA fragmentation [GO:1902512] | 89.065083 | 0.171538421 | -2.543396 | 0.21041489 | 144.256300 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000031228780264035479474929264483747664274527798735251301982970669128654040383351074897360505344678927031054627150297164916992187500000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000003798505898550680825105137877835953786817305464426070855178587887270580240733433845419508845253631079685874283313751220703125000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 28.0524410 | 9.1324916 | 165.0967920 | 52.9573287 | |||||
| ENSG00000181577 | 221416 | C6orf223 | lncRNA | 78.534005 | 0.306648958 | -1.705340 | 0.19314455 | 81.083338 | 0.0000000000000000002163967705143115737478838711934344497587997575041530648465304409455711720511317253112792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000143457726348539828502739576033730615288089345490084303147426680880016647279262542724609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 36.9884430 | 12.2991121 | 121.1297013 | 39.2662673 | ||||||||||
| ENSG00000181634 | 9966 | TNFSF15 | protein_coding | O95150 | FUNCTION: Receptor for TNFRSF25 and TNFRSF6B. Mediates activation of NF-kappa-B. Inhibits vascular endothelial growth and angiogenesis (in vitro). Promotes activation of caspases and apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10597252, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11911831, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11923219, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9872942}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand family. This protein is abundantly expressed in endothelial cells, but is not expressed in either B or T cells. The expression of this protein is inducible by TNF and IL-1 alpha. This cytokine is a ligand for receptor TNFRSF25 and decoy receptor TNFRSF21/DR6. It can activate NF-kappaB and MAP kinases, and acts as an autocrine factor to induce apoptosis in endothelial cells. This cytokine is also found to inhibit endothelial cell proliferation, and thus may function as an angiogenesis inhibitor. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. | hsa:9966; | extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; tumor necrosis factor receptor binding [GO:0005164]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; activation of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activity [GO:0007250]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; immune response [GO:0006955]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 11739281_Vascular endothelial growth inhibitor is an endothelial cell-specific gene and inhibitor of endothelial cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and tumor growth; mediates G1 arrest in G0/G1 cells responding to growth stimuli, and apoptosis in cell division 12882979_TL1A-induced NF-kappaB activation and c-IAP2 production prevent DR3-mediated apoptosis 14568967_TL1A mRNA and protein expression is up-regulated in inflammatory bowel disease, particularly in involved areas of Crohn's disease (CD) in gut mucosa cell types other than endothelial, including lamina propria lymphocytes as well as tissue macrophages. 15207783_Expression of TL1A and its receptor DR3 by lamina propria mononuclear cells (LPMC) could have significant influence on the severity of mucosal inflammation. 15760679_TL1A and DR3 is involved in atherosclerosis via the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines/chemokines 16061878_VEGI is an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis 16221758_Genetic variations in the TNFSF15 gene contribute to the susceptibility to inflammatory bowel diseases in Japanese and European populations. 16221758_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16604264_It can be concluded that VEGI72-251 is able to increase the level of human IL-2 production by the activation of T lymphocytes 16966713_a significant association between TNFSF15 and Crohn's disease 17030188_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17371957_The induction of TL1A on APCs via specific pathway stimulation suggests a role for TL1A in Th1 responses to pathogens, and in CD. 17513783_Mononuclear phagocytes are a major source of TL1A in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), as revealed by their strong TL1A expression in either synovial fluids or synovial tissue of rheumatoid factor (RF)-seropositive RA patients, but not RF-negative/RA patients. 17663424_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17663424_TNFSF15 is an ethnic-specific IBD susceptibility gene. Five SNPs that comprise the 2 common haplotypes were genotyped in 599 Caucasian patients with Crohn's dis, 382 Caucasian patients with ulcerative colitis, and 230 controls. 17935696_TL1A forms a homotrimer with each monomer assuming a jellyroll beta-sandwich fold. The CD loop in TL1A is the longest among the TNF ligand members with known structure and the AA' loop in TL1A is the second longest after that in TRAIL. 18287561_TL1A may contribute to renal inflammation and injury through DR3-mediated activation of NF-kappaB and caspase-3 18338776_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18338776_Variants in TNFSF15 contribute to overall CD susceptibility in European populations, although to a lesser extent than that seen in the Japanese. 18422820_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18422820_TNFSF15 genotypes play an important role in the pathogenesis of Crohn's disease in Koreans. 18757243_TL1A may serve as an inflammatory marker in rheumatoid arthritis. Interactions between TL1A and its receptors may be important in the pathogenesis of rheumatois arthritis. 19124533_The allelic expression imbalance of TNFSF15 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells was examined to reveal the effects of the single nucleotide polymorphisms on the transcriptional activity of TNFSF15. 19174806_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19174806_confirms that TNFSF15 or a closely linked gene is involved in the genetic predisposition to CD 19251437_sodium butyrate has different effects on lung vascular TNFSF15 (TL1A) expression in pulmonary artery and microvascular endothelial cells 19262684_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19262684_TL1A gene variation exacerbates induction of TL1A in response to FcgammaR stimulation in Jewish CD patients and this may lead to chronic intestinal inflammation via overwhelming T cell responses 19422935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19522538_Results provide insights into the structure and function of TL1A and provide the basis for the rational manipulation of its interactions with cognate receptors. 19543369_A haplotype strongly associated with predisposition to spondyloarthritis is located near to TNFSF15. 19760754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19786547_these data suggest that TL1A secretion in lymphoid organs might contribute to rheumatoid arthritis initiation by promoting autoantibody production. 19815424_Data suggest that lipopolysaccharide induces TL1A expression through the transcriptional activation via a NF-kappa B pathway. 19839006_Our findings suggest a role for TL1A in pro-inflammatory APC-T cell interactions 19885571_VEGI functions as a negative regulator for aggressiveness during the development and progression of prostate cancer. 20018961_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20125169_critically involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis 20150621_VEGI functions as a negative regulator of aggressiveness during development and progression of bladder cancer. 20176734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20349123_TL1A increased cytotoxicity of IL-12/IL-18-activated NK cells against target cells dependent on NK activation for lysis and could function in vivo as a key co-activator of NK cytotoxicity. 20367632_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20410491_TL1A promotes foam cell formation in human macrophages in vitro by increasing low density lipoprotein uptake, by enhancing intracellular total and esterified cholesterol levels and reducing cholesterol efflux. 20473688_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20675196_The TL1A/DcR3 ligand/receptor pair is upregulated in active ulcerative colitis. 20848476_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20863486_TL1A can regulate the inflammatory processes through modulation of the betaig-h3 expression through two separate pathways, one through PKC and PI3K and the other through ERK, which culminates at NF-kappaB activation. 20886065_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21072187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21153332_role in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis 21153333_role of TNFRSF25:TNFSF15 in disease and health 21217782_studies for the first time establish the regulatory axis of AMPK-LITAF-TNFSF15 and also suggest that LITAF may function as a tumor suppressor 21228792_neither TNFSF15 nor IL23R variants contribute to ulcerative colitis susceptibility in Koreans 21300286_Decoy Receptor 3 (DcR3)neutralizes three different TNF ligands: FasL, LIGHT, and TL1A. Crystal structure of DcR3 reported here provides a mechanistic basis for the broadened specificity required to support the decoy function of DcR3. 21368235_Substance P- and hemokinin-1-stimulated monocytes potentiate T helper type (Th)17 cell generation in vitro through IL-1beta, IL-23, and tumor necrosis factor-like (TNF)1A expression. 21537832_DcR3 may act as an inducer, and membrane-bound TL1A may act as a receptor in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. 21636646_susceptibility gene for irritable bowel syndrome and irritable bowel syndrome constipation 21672030_in active psoriasis, we observed abundant immunostaining for TL1A and significant upregulation of its receptors DR3 and DcR3 21730793_the TNFSF15 genotype is positively associated with isolated colonic (L2) Crohn disease. 22210436_Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) produced by cancer cells and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) produced mainly by tumor-infiltrating macrophages and regulatory T cells effectively inhibits TNFSF15 production by endothelial cells. 22641456_Protein expression of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-like ligand 1A (TL1A) and death-domain receptor (DR)3 is upregulated in the aged bladder tissues. 22684480_Polymorphisms in TNFSF15 were associated with irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea. 23000144_Two significant susceptibility loci, TNFSF15 (rs4979462) and POU2AF1 (rs4938534) (combined odds ratio [OR] = 1.56, p = 2.84 x 10(-14) for rs4979462. 23204549_TL1A is up-regulated in ankylosing spondylitis (AS), associates with disease activity and is influenced by anti-TNF treatment, suggesting that TL1A may be of pathogenic and potentially of therapeutic importance in AS patients. 23250276_increased expressiojn in gut tissue , but not in the peripheral blood, from inflammatory bowel disease patients 23382586_VEGI192 and VEGI174 expression is markedly decreased in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma and are linked to pathological grade and stage. 23404494_attenuated S. typhimurium carrying the dual function plasmid VEGI151/survivin cannot only be specifically enriched in the tumor tissue, but also showed a synergistic antitumor effect in vivo. 23545578_this suggests that VEGI functions mainly through inhibition of angiogenesis and is a negative regulator of aggressiveness during the development and progression of renal cell carcinoma . 23598291_Circulating levels of TL1A correlate with the progression of atheromatous lesions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis 23642711_Response elements regulating TNFSF15 in primary human myeloid cells, were analyzed. 24005100_It has been identified as a new disease susceptibility gene among Japanese. Though different from Europeans, it is indicated that a T lymphocyte differentiation route (Th1/Th17) shares a common disease developing process. [Review] 24016146_may play an important role in the pathogenesis of primary biliary cirrhosis 24023314_VEGI, possibly via DR3, suppresses the aggressive nature of pituitary tumours and its expression level is closely linked to the invasion and destruction of the suprasellar and sella regions 24141405_Tumor-infiltrating natural killer and CD4(+) T cells under the influence of cancer cells significantly increase the production of IFNgamma, which in turn inhibits TNFSF15 expression in vascular endothelial cells. 24220298_Our data demonstrate a key role for TL1A in promoting ILC2s at mucosal barriers. 24269700_genetic polymorphism is associated with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis in Hungarians 24384427_ADAMTS 8, CCL23, and TNFSF15 are implicated in anti-angiogenic activities 24783249_Combining the genetic marker TNFSF15 with ASCA IgA increased the power of predicting stenosis/perforating phenotype in Crohn's disease patients with TNFSF15 but not with a NOD2 genetic background 24814505_The SNP rs7848647 associated with the TNFSF15 gene is associated with surgical diverticulitis. 24832108_These results suggested that TL1A could promote Th17 differentiation in rheumatoid arthritis via the activation of RORc, and this effect may be mediated by the binding of TL1A with DR3. 24835165_TNFSF15 SNPs, rs6478108 and rs4574921, may be independent genetic predictive factors for the development of stricture/non-perianal penetrating complications and perianal fistula, respectively. 25028192_This meta-analysis indicated that most of the seven TNFSF15 polymorphisms (except for rs4263839) were risk factors contributed to CD and UC susceptibility. The differences in ethnicity did not influence the risk obviously. 25148371_TL1A increases expression of CD25, LFA-1, CD134 and CD154, and induces IL-22 and GM-CSF production from effector CD4 T-cells 25197060_Mechanisms mediating TNFSF15:DR3 contributions to pattern recognition receptor outcomes included TACE-induced TNFSF15 cleavage to soluble TNFSF15; soluble TNFSF15 then led to TRADD/FADD/MALT-1- and caspase-8-mediated autocrine IL-1 secretion. 25200589_Soluble TL1A synergized with IL-23 to stimulate peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with psoriasis vulgaris to produce IL-17. 25251497_Results show that subjects with TNFSF15 -358CC genotype were at higher risks for developing gastric adenocarcinoma in the Helicobacter pylori infected group. 25399326_DR3 is expressed in some interstitial vascular endothelial cells (EC) in human kidney in situ; these EC also respond to its ligand TL1A by activating NF-kappaB. 25501099_associations exist between TNFSF15 gene polymorphisms and IBD (both CD and UC) in the Indian population 25647275_study has defined the increased serum and SF samples levels of TL1A and DcR3 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA); findings support the hypothesis that TL1A and DcR3 may contribute to the pathogenesis of RA 25664710_This is the first report of the association between early Crohn's disease and the TNFSF15 single nucleotide polymorphisms. 25778932_This study indicates that the HDAC inhibitor may be exploited as a therapeutic strategy modulating the soluble VEGI/DR3 pathway in osteosarcoma patients 25899471_Human primary biliary cirrhosis-susceptible allele of rs4979462 enhances TNFSF15 expression by binding NF-1. 25908025_TL1A blood levels are elevated in psoriasis patients; TL1A expression is higher in psoriatic lesions than in normal skin 25929716_Plasma levels of TL1A were significantly higher in newly diagnosed SLE patients compared with controls, and were positively associated with SLE disease activity index. 25998826_There were significant associations of rs3810936, rs6478108, rs6478109, rs7848647 with CD in Korean pediatric patients (P = 6.5x10(-8), P = 1.3x10(-8), P = 3.7x10(-8), P = 2.9x10(-8), respectively). 26046454_Addition of TL1A to IL-1beta + IL-23 also augmented ILC3 proliferation 26072972_The data indicate that TL1A may contribute to pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases via local but not systemic induction of IL-17A but not IL-4, IL-13 or IFN-gamma. 26200500_This study shows an association between TNFSF15-rs3810936 and AAU and suggests that the TL1A/DR3 pathway may be implicated in the pathogenesis of this disease. 26393680_Higher TL1A levels were associated with early stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 26509650_TL1A-induced cell death is directly mediated through DR3. 26768609_(188)Re-NGR-VEGI has the potential as a theranostic agent. 26810853_Biologics beyond TNF-alpha inhibitors and the effect of targeting the homologues TL1A-DR3 pathway in chronic inflammatory disorders. 26823868_Rs3810936 of TNFSF15 were related to the risk of ankylosing spondylitis 26945876_Patients with mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) exhibited higher VEGI levels than those with moderate and severe TBI. 27081759_the blocking of tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 (TNFR2) decreased TL1A-stimulated IL-6 production by rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. 27188743_miRNA-31 can directly bind to the 3-UTR of TNFSF15, thereafter negatively regulating its expression in Caco2 cells. 27507062_Results provide evidence that variance within TNFSF15 has the potential to affect cytokine expression across a range of tissues and thereby contribute to protection from infectious diseases such as leprosy, while increasing the risk of immune-mediated diseases including Crohn's disease and primary biliary cholangitis. 27665176_These results raise the possibility for involvement of TL1A/DR3/DR3-mediated mechanisms in epithelial-mesenchymal interactions and the development of inflammation-induced intestinal fibrosis in Crohn's disease. 27733581_TL1A differentially induces expression of TH17 effector cytokines IL-17, -9, and -22 and provides a potential target for therapeutic intervention in TH17-driven chronic inflammatory diseases. 28062298_the DR3/TL1A pathway directly enhances human OC formation and resorptive activity, controlling expression and activation of CCL3 and MMP-9. 28197769_results support an idea that the genetic susceptibility of TNFSF15 to CD may be confounded, in part, by the increase of Prevotella 28337757_Data suggest that human regulatory T-lymphocytes express DR3 and demonstrate DR3/TL1A-mediated activation of signaling via MAP kinases and NFkappaB. (DR3 = death receptor 3; TL1A/TNFSF15 = tumor necrosis factor [ligand] superfamily, member 15) 28362712_The expression of VEGI and E-cadherin was significantly lower in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) tissues compared with normal kidney tissues (P | ENSMUSG00000050395 | Tnfsf15 | 286.767602 | 0.231563730 | -2.110519 | 0.70504561 | 7.092743 | 0.0077396707377245608366900242458541470114141702651977539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0407308180132773395287770767936308402568101882934570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 104.1167682 | 38.9012933 | 459.9748906 | 171.1248905 | |
| ENSG00000181804 | 285195 | SLC9A9 | protein_coding | Q8IVB4 | FUNCTION: May act in electroneutral exchange of protons for Na(+) across membranes. Involved in the effusion of Golgi luminal H(+) in exchange for cytosolic cations. Involved in organelle ion homeostasis by contributing to the maintenance of the unique acidic pH values of the Golgi and post-Golgi compartments in the cell. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15522866}. | Antiport;Autism;Autism spectrum disorder;Chromosomal rearrangement;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sodium;Sodium transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | This gene encodes a sodium/proton exchanger that is a member of the solute carrier 9 protein family. The encoded protein localizes the to the late recycling endosomes and may play an important role in maintaining cation homeostasis. Mutations in this gene are associated with autism susceptibility 16 and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. | hsa:285195; | late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; potassium:proton antiporter activity [GO:0015386]; sodium:proton antiporter activity [GO:0015385]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071805]; regulation of intracellular pH [GO:0051453]; sodium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:0098719] | 18649358_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18821565_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18937294_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19268276_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20032819_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20032819_results suggest that SLC9A9 may be related to hyperactive-impulsive symptoms in AD/HD and the disruption of SLC9A9 may be responsible for the behavioral phenotype observed in the inversion family 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20732626_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21171650_This review defines NHE6-9 as organellar NHEs that are fairly dynamic, implying that they are subjected to intracellular trafficking and thus they continuously shuttle between organelles and the plasma membrane. 21555518_SLC9A9 is a target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq analysis in HEK 293 cells. 21908519_33 directly measured and 13 derived glycosylation traits in 3533 individuals were identified and three novel gene association (MGAT5, B3GAT1 and SLC9A9) were identified using an additional European cohort. 23508127_find interesting gene expression changes in endosomal NHE6 and NHE9 in postmortem autism brains. 24065030_Loss-of-function mutations in NHE9 may contribute to autistic phenotype by modulating synaptic membrane protein expression and neurotransmitter clearance. 25835977_the expression of SLC9A9 can be a prognostic predictor for ESCC. 25914168_SLC9A9 appears to influence the differentiation of T cells to a proinflammatory fate and may have a broader role in multiple sclerosis disease activity. There is an association between rs9828519(G) and nonresponse to IFNbeta treatment. 25915159_Taken together, our findings demonstrate that NHE9 can be an effective predictor of chemoradiotherapy response in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 27439572_SLC9A9 is a sodium hydrogen exchanger present in the recycling endosome and highly expressed in the brain. 27766536_rs9828519 polymorphism is associated with differential expression of SLC9A9 in occipital cortex, intralobular white matter, and substantia nigra in patients with multiple sclerosis. 28130443_Ectopic expression of NHE9 in human brain microvascular endothelial cells without external cues induced up-regulation of the transferrin receptor (TfR) and down-regulation of ferritin, leading to an increase in iron uptake 28476790_SLC9A9 has an oncogenic function by being related to EGFR signaling, suggesting SLC9A9 may be a novel prognostic indicator and a therapeutic target in colorectal cancer 29268774_downregulation of miR-135a as a potential mechanism underlying the high NHE9 expression observed in subset of glioblastomas 30927234_results provide a detailed understanding of the functions of protein NHE9 and its disrupted interactions, possibly underlying Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Autism Spectrum Disorders. 32400953_Sodium hydrogen exchanger 9 NHE9 (SLC9A9) and its emerging roles in neuropsychiatric comorbidity. 33118634_Structure and elevator mechanism of the mammalian sodium/proton exchanger NHE9. | ENSMUSG00000031129 | Slc9a9 | 129.173895 | 2.263905295 | 1.178814 | 0.15282949 | 59.771800 | 0.0000000000000106518743114691675301343164676921124724921340759520305141450080554932355880737304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000004790945912181052162054624255406927874892039631582463243830716237425804138183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 180.2170695 | 12.8101523 | 79.7277338 | 6.4925227 | |
| ENSG00000182132 | 30820 | KCNIP1 | protein_coding | Q9NZI2 | FUNCTION: Regulatory subunit of Kv4/D (Shal)-type voltage-gated rapidly inactivating A-type potassium channels. Regulates channel density, inactivation kinetics and rate of recovery from inactivation in a calcium-dependent and isoform-specific manner. In vitro, modulates KCND1/Kv4.1 and KCND2/Kv4.2 currents. Increases the presence of KCND2 at the cell surface. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10676964, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11423117, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12829703, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17187064}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Metal-binding;Potassium;Potassium channel;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transport;Voltage-gated channel | This gene encodes a member of the family of cytosolic voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channel-interacting proteins (KCNIPs), which belong to the neuronal calcium sensor (NCS) family of the calcium binding EF-hand proteins. They associate with Kv4 alpha subunits to form native Kv4 channel complexes. The encoded protein may regulate rapidly inactivating (A-type) currents, and hence neuronal membrane excitability, in response to changes in the concentration of intracellular calcium. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. | hsa:30820; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; voltage-gated potassium channel complex [GO:0008076]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; potassium channel activity [GO:0005267]; potassium channel regulator activity [GO:0015459]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; voltage-gated ion channel activity [GO:0005244]; regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1901379] | 15358149_Data show that KChIP1, KChIP2.1, and KChIP2.2 could form homo- as well as hetero-oligomers, and that this oligomerization did not perturb their interaction with Kv4.2 potassium channel. 17057713_X-ray crystallographic and small-angle X-ray scattering data that show that the KChIP1-Kv4.3 N-terminal cytoplasmic domain complex is a cross-shaped octamer bearing two principal interaction sites. 18393943_These results reveal a new role for KChIP3 in the regulation of calcium regulated secretion and also suggest that the functions of each of the KChIPs may be more specialized than previously appreciated. 19550036_EF-hands 3 and 4 of KChIP1 are functionally involved in a specific association with PS on the membrane 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21129448_our findings suggest that KChIP1 interacts with Kv4.3 in interneurons at the stratum lacunosum-moleculare/radiatum junction 24681403_Protein aggregation due to nsSNP resulting in P56S VABP protein is associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 24792378_V234I-VAPB induces ubiquitin aggregation followed by cell death; proposed that V234I-VAPB exhibits the characteristics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in spite of not having the typical aggregation property of different mutations in various neurodegenerative diseases 24886904_KCNIP1 from copy number variations study might function as a type 2 diabetes susceptibility gene whose dysregulation alters insulin production. 26831368_These studies showed that a common copy number variation in KCNIP1 gene is a genetic predictor of atrial fibrillation risk possibly pointing to a functional pathway. 28132811_Study shows that the VAPB-PTPIP51 tethers regulate autophagy and demonstrates that overexpression of VAPB or PTPIP51 to tighten endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria contacts impairs, whereas small interfering RNA-mediated loss of VAPB or PTPIP51 to loosen contacts stimulates, autophagosome formation. 29176790_the current study provides evidence that genetic variants of Kv accessory proteins may contribute to the susceptibility of Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. 29491224_This is the first copy number variation association study of the KCNIP1 gene in Chinese population, and these data indicated that KCNIP1 might function as a type 2 diabetes-susceptibility gene whose dysregulation alters insulin production. | ENSMUSG00000053519 | Kcnip1 | 9.102663 | 5.487063105 | 2.456034 | 0.61688291 | 16.673582 | 0.0000443949629455513158460093492418963023737887851893901824951171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0004995951260517875278793775706276392156723886728286743164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 16.6803990 | 3.2063970 | 2.9136768 | 0.9414779 | |
| ENSG00000182185 | 5890 | RAD51B | protein_coding | O15315 | FUNCTION: Involved in the homologous recombination repair (HRR) pathway of double-stranded DNA breaks arising during DNA replication or induced by DNA-damaging agents. May promote the assembly of presynaptic RAD51 nucleoprotein filaments. Binds single-stranded DNA and double-stranded DNA and has DNA-dependent ATPase activity. Part of the RAD51 paralog protein complex BCDX2 which acts in the BRCA1-BRCA2-dependent HR pathway. Upon DNA damage, BCDX2 acts downstream of BRCA2 recruitment and upstream of RAD51 recruitment. BCDX2 binds predominantly to the intersection of the four duplex arms of the Holliday junction and to junction of replication forks. The BCDX2 complex was originally reported to bind single-stranded DNA, single-stranded gaps in duplex DNA and specifically to nicks in duplex DNA. The BCDX2 subcomplex RAD51B:RAD51C exhibits single-stranded DNA-dependent ATPase activity suggesting an involvement in early stages of the HR pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11751635, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11751636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11842113, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12441335, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23108668, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23149936}. | Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Chromosomal rearrangement;DNA damage;DNA recombination;DNA repair;DNA-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the RAD51 protein family. RAD51 family members are evolutionarily conserved proteins essential for DNA repair by homologous recombination. This protein has been shown to form a stable heterodimer with the family member RAD51C, which further interacts with the other family members, such as RAD51, XRCC2, and XRCC3. Overexpression of this gene was found to cause cell cycle G1 delay and cell apoptosis, which suggested a role of this protein in sensing DNA damage. Rearrangements between this locus and high mobility group AT-hook 2 (HMGA2, GeneID 8091) have been observed in uterine leiomyomata. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. | hsa:5890; | nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; Rad51B-Rad51C-Rad51D-XRCC2 complex [GO:0033063]; replication fork [GO:0005657]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA [GO:0008094]; ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity [GO:0140664]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; double-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003690]; single-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003697]; blastocyst growth [GO:0001832]; DNA recombination [GO:0006310]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; double-strand break repair via homologous recombination [GO:0000724]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0010971]; reciprocal meiotic recombination [GO:0007131]; somite development [GO:0061053] | 11744692_This work describes the in vitro and in vivo identification of the RAD51B/RAD51C heterocomplex 11978964_involved in the frequently occurring t(6;14) (p21;q23-->q24) in pulmonary chondroid hamartomas 12427746_Rad51B and Rad51C function through interactions with the human Rad51 recombinase and play a crucial role in the homologous recombinational repair pathway 12441335_Rad51B protein may have a specific function in Holliday junction processing in the homologous recombinational repair pathway in humans 14704354_a fragment of Rad51B containing amino acid residues 1-75 interacts with the C-terminus and linker of Rad51C, residues 79-376, and this region of Rad51C also interacts with mRad51D and Xrcc3 15701685_motif in the N-terminus of Rad51B serves as an NLS that allows Rad51B to localize to the nucleus independent of Rad51C or BRCA2 18270339_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19329439_EVL protein is a novel recombination factor that may be required for repairing specific DNA lesions, and that may cause tumor malignancy by its inappropriate expression. 19330030_A multistage genome-wide association study in breast cancer identifies two new risk alleles at 1p11.2 and 14q24.1 (RAD51L1). 19330030_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19657362_BCR/ABL fragments were used for identifying the sites of BCR/ABL interaction with RAD51B 19714462_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20095854_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20195514_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237344_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20496165_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20522537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20610542_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20610542_polymorphisms in and haplotypes of the RAD51L1 gene, which is involved in the double-strand break repair pathway, modulate gamma-radiation-induced mutagen sensitivity. 21368091_findings support the notion that DNA repair genes, in particular RAD51L1, play a role in nasopharyngeal carcinoma etiology and development 21533530_our results suggest that RAD51L1 is unlikely to represent a high-penetrance breast cancer susceptibility gene. 21852249_rs11249433 at 1p.11.2, and two highly correlated single-nucleotide polymorphisms rs999737 and rs10483813 (r(2)= 0.98) at 14q24.1 (RAD51L1), for up to 46 036 invasive breast cancer cases and 46 930 controls from 39 studies, were genotyped. 22017238_Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in RAD51L1 gene is associated with glioblastoma. 22454379_Single nucleotide polymorphism in RAD51L1 is associated with breast cancer. 23001122_SNP in RAD51B at 14q24.1 was significantly associated with male breast cancer risk 23108668_Study observed centrosome defects in the absence of XRCC3. While RAD51B and RAD51C act early in homologous recombination, XRCC3 functions jointly with GEN1 later in the pathway at the stage of Holliday junction resolution. 23810717_The HsRAD51B-HsRAD51C complex plays a role in stabilizing the HsRAD51 nucleoprotein filament during the presynaptic phase of homologous recombination. 24022229_This study provides robust evidence for an association of rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility with genes involved in B cell differentiation (BACH2) and DNA repair (RAD51B). 24139550_It confirms that RAD51 paralog mutations confer breast and ovarian cancer predisposition and are rare events. 24498017_Data indicate that complement factor H (CFH) R1210C and common variants in COL8A1 and RAD51B plus six genes contribute predictive information for advanced macular degeneration (AMD) beyond macular and behavioral phenotypes. 24526414_the risk of developing AMD exhibits dose dependency as well as an epistatic combined effect in rs17105278 T>C and rs4902566 C>T carriers and that the elevated risk for rs17105278 T>C carriers may be due to decreased transcription of RAD51B. 25255808_Relative excess risk of breast cancer due to interaction between RAD51L1 single-nucleotide polymorphism and BMI. 25600502_a novel germ line RAD51B nonsense mutation, and reduced expression of RAD51B in melanoma cells indicating inactivation of RAD51B 26261251_Mutations in epithelial ovarian cancer cases were more frequent in RAD51C (14 occurrences, 0.41%) and RAD51D (12 occurrences, 0.35%) than in RAD51B (two occurrences, 0.06%). 26339569_The aim of the present study was to evaluate the relationship between prostate cancer risk and the presence of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the genes involved in Homologous recombination repair, RAD51, RAD51B, XRCC2 and XRCC3. 27149063_common variation is significantly associated with familial breast cancer risk 27334422_our study suggested that miRNA-binding site genetic variants of RAD51B may modify the susceptibility to cervical cancer, which is important to identify individuals with differential risk for this malignancy and to improve the effectiveness of preventive intervention. 27651161_over-expression of RAD51B promoted cell proliferation, aneuploidy, and drug resistance, while RAD51B knockdown led to G1 arrest and sensitized cells to 5-fluorouracil 27683114_hypermethylation of homologous recombination DNA repair genes including RAD51B and XRCC3 is associated with an inflamed phenotype in squamous cell cancers of the head and neck, lung and cervix. 28361912_We successfully identified a common variant, rs911263, as being significantly associated with the disease status . In addition, this SNP was shown to be related to erosion, a clinical assessment of disease severity in RA (P = 2.89 x 10(-5), OR = 0.52). These findings shed light on the role of RAD51B in the onset and severity of Rheumatoid arthritis (RA). 31584931_Here we provide three coherent sets of isogenic mutants, both in transformed and non-transformed human cells. Importantly, using these mutant lines, we report the unanticipated result that RAD51B has a less crucial role in homologous recombination than the other four paralogs, and find that all RAD51 paralogs are critically important for early functions during homologous recombination 32669601_Sequential role of RAD51 paralog complexes in replication fork remodeling and restart. 33622874_TBX15 rs98422, DNM3 rs1011731, RAD51B rs8017304, and rs2588809 Gene Polymorphisms and Associations With Pituitary Adenoma. 34060991_Serum Levels of ARMS2, COL8A1, RAD51B, and VEGF and their Correlations in Age-related Macular Degeneration. 35737913_RAD51B Harbors Germline Mutations Associated With Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000059060 | Rad51b | 40.111818 | 6.512547792 | 2.703222 | 0.88439504 | 8.062857 | 0.0045181888914923654110289419350010575726628303527832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0263946824145713070108865139218323747627437114715576171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 96.2356962 | 62.8380236 | 11.7794101 | 7.7064584 | |
| ENSG00000182389 | 785 | CACNB4 | protein_coding | O00305 | FUNCTION: The beta subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels contributes to the function of the calcium channel by increasing peak calcium current, shifting the voltage dependencies of activation and inactivation, modulating G protein inhibition and controlling the alpha-1 subunit membrane targeting. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11880487}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Calcium channel;Calcium transport;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Ion channel;Ion transport;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain;Transport;Voltage-gated channel | This gene encodes a member of the beta subunit family of voltage-dependent calcium channel complex proteins. Calcium channels mediate the influx of calcium ions into the cell upon membrane polarization and consist of a complex of alpha-1, alpha-2/delta, beta, and gamma subunits in a 1:1:1:1 ratio. Various versions of each of these subunits exist, either expressed from similar genes or the result of alternative splicing. The protein encoded by this locus plays an important role in calcium channel function by modulating G protein inhibition, increasing peak calcium current, controlling the alpha-1 subunit membrane targeting and shifting the voltage dependence of activation and inactivation. Certain mutations in this gene have been associated with idiopathic generalized epilepsy (IGE), juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME), and episodic ataxia, type 5. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. | hsa:785; | cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; synapse [GO:0045202]; voltage-gated calcium channel complex [GO:0005891]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic cytosolic calcium levels [GO:0099626]; adult walking behavior [GO:0007628]; cAMP metabolic process [GO:0046058]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; detection of light stimulus involved in visual perception [GO:0050908]; gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion [GO:0014051]; gamma-aminobutyric acid signaling pathway [GO:0007214]; muscle cell development [GO:0055001]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; neuromuscular junction development [GO:0007528]; neuronal action potential propagation [GO:0019227]; Peyer's patch development [GO:0048541]; positive regulation of protein localization to nucleolus [GO:1904751]; positive regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:1901387]; regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis [GO:2000300]; regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:1901385]; spleen development [GO:0048536]; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0035249]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852]; thymus development [GO:0048538] | 16866717_The novel nucleotide substitution T87C (D29D)in CACNB4 was observed in 2 migrainous vertigo patients and was not present in control DNA samples. 18446307_No pathogenic mutation were identified in CACNB4. 18712068_plays a role in neurotransmitter release. 18755274_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18755274_proband identified with severe myoclonic epilepsy in infancy heterozygous for de novo SCN1A nonsense mutation & CACNB4 missense mutation (R468Q); greater Ca(v)2.1 currents caused by the mutation may increase neurotransmitter release in excitatory neurons 20200978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21220418_The Ca2+ channel beta4c subunit interacts with heterochromatin protein 1 gama via a PXVXL binding motif. 21297076_CACNB4 is associated with acute lung injury in mice 22892567_Cacnb4 directly couples electrical activity to gene expression, a process defective in juvenile epilepsy 23756480_Genome-wide association studies identify CACNB4 mutation releated to juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. 24875574_The nuclear targeting properties of the truncated beta(4b(1-481)) subunit in tsA-201 cells, skeletal myotubes, and in hippocampal neurons, were investigated. 32176688_The homozygous CACNB4 p.(Leu126Pro) variant underlies the severe neurological phenotype in the two siblings. | ENSMUSG00000017412 | Cacnb4 | 196.566394 | 2.458191665 | 1.297597 | 0.13221647 | 96.794389 | 0.0000000000000000000000769137591492074227259159397485150437959718917313160734887899066397620728707806847523897886276245117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000000060442115897703000033490398947751642666060739284854719417794388647280356963165104389190673828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 279.0708162 | 17.8949984 | 113.9506085 | 8.3628188 | |
| ENSG00000182667 | 50863 | NTM | protein_coding | Q9P121 | FUNCTION: Neural cell adhesion molecule. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal | This gene encodes a member of the IgLON (LAMP, OBCAM, Ntm) family of immunoglobulin (Ig) domain-containing glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell adhesion molecules. The encoded protein may promote neurite outgrowth and adhesion via a homophilic mechanism. This gene is closely linked to a related family member, opioid binding protein/cell adhesion molecule-like (OPCML), on chromosome 11. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009]. | hsa:50863; | extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; neuron recognition [GO:0008038] | 12819783_NTM shows close linkage to OPCML on chromosome 11q25. 15379248_Human neurotrimin is expressed on the surface of CHO cells and could strengthen their aggregation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21036197_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21036197_The finding of this study provided evidence that NTM at 11q25 chromosome regions affecting IQ. 22661486_A quantitative analysis of central corneal thickness and a subsequent analysis of primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), SNPs in two cell adhesion molecules, NTM and CNTNAP4, were identified and may increase POAG susceptibility in a subset of cases. 23054244_A translocation breaks intron 1 of a splicing isoform of Neurotrimin at 11q25 in a family with intracranial and thoracic aortic aneurysm. 24616287_The generation and cardiac phenotype of single and double heterozygous gene-targeted OPCML and Neurotrimin knockout mice. 25819087_Both the AFF3 and NTM triglyceride associations were replicated among Multi-ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis study participants (P = 1.00 x 10(-7) and 8.00 x 10(-5), respectively). 26334118_NTM is not a susceptibility gene for autism spectrum disorders. 32033718_Neurotrimin, a neural cell adhesion molecule, is increased in leiomyoma compared to myometrium in patient tissue after estrogen and progesterone treatment. 32710982_Highly Conserved Molecular Features in IgLONs Contrast Their Distinct Structural and Biological Outcomes. | ENSMUSG00000059974 | Ntm | 13.988059 | 3.234141120 | 1.693383 | 0.58495524 | 7.966206 | 0.0047658737037031715863544256706063606543466448783874511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0275475377551239533624460875671502435579895973205566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 23.6130973 | 7.6523537 | 7.0790013 | 2.5710666 | |
| ENSG00000183023 | 6546 | SLC8A1 | protein_coding | P32418 | FUNCTION: Mediates the exchange of one Ca(2+) ion against three to four Na(+) ions across the cell membrane, and thereby contributes to the regulation of cytoplasmic Ca(2+) levels and Ca(2+)-dependent cellular processes (PubMed:1374913, PubMed:11241183, PubMed:1476165). Contributes to Ca(2+) transport during excitation-contraction coupling in muscle (PubMed:1374913, PubMed:11241183, PubMed:1476165). In a first phase, voltage-gated channels mediate the rapid increase of cytoplasmic Ca(2+) levels due to release of Ca(2+) stores from the endoplasmic reticulum (PubMed:1374913, PubMed:11241183, PubMed:1476165). SLC8A1 mediates the export of Ca(2+) from the cell during the next phase, so that cytoplasmic Ca(2+) levels rapidly return to baseline (PubMed:1374913, PubMed:11241183, PubMed:1476165). Required for normal embryonic heart development and the onset of heart contractions (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P70414, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11241183, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1374913, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1476165}. | Alternative splicing;Antiport;Calcium;Calcium transport;Calmodulin-binding;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Sodium;Sodium transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | In cardiac myocytes, Ca(2+) concentrations alternate between high levels during contraction and low levels during relaxation. The increase in Ca(2+) concentration during contraction is primarily due to release of Ca(2+) from intracellular stores. However, some Ca(2+) also enters the cell through the sarcolemma (plasma membrane). During relaxation, Ca(2+) is sequestered within the intracellular stores. To prevent overloading of intracellular stores, the Ca(2+) that entered across the sarcolemma must be extruded from the cell. The Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger is the primary mechanism by which the Ca(2+) is extruded from the cell during relaxation. In the heart, the exchanger may play a key role in digitalis action. The exchanger is the dominant mechanism in returning the cardiac myocyte to its resting state following excitation.[supplied by OMIM, Apr 2004]. | hsa:6546; | axon [GO:0030424]; axon terminus [GO:0043679]; cell periphery [GO:0071944]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; dendritic shaft [GO:0043198]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; intercalated disc [GO:0014704]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynapse [GO:0098794]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; synapse [GO:0045202]; T-tubule [GO:0030315]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; ankyrin binding [GO:0030506]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium:cation antiporter activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:1905060]; calcium:sodium antiporter activity [GO:0005432]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; cytoskeletal protein binding [GO:0008092]; ion antiporter activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential [GO:0099580]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; calcium ion export [GO:1901660]; calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0055074]; calcium ion import [GO:0070509]; calcium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:0098703]; calcium ion transmembrane import into cytosol [GO:0097553]; calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070588]; calcium ion transport into cytosol [GO:0060402]; cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0055013]; cardiac muscle contraction [GO:0060048]; cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction [GO:0086064]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular response to caffeine [GO:0071313]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to reactive oxygen species [GO:0034614]; cellular sodium ion homeostasis [GO:0006883]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; membrane depolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0086012]; metal ion transport [GO:0030001]; muscle contraction [GO:0006936]; negative regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0051481]; negative regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071901]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of fibroblast migration [GO:0010763]; positive regulation of the force of heart contraction [GO:0098735]; regulation of cardiac conduction [GO:1903779]; regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by calcium ion signaling [GO:0010882]; regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion [GO:0010881]; regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling [GO:0010649]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of heart rate [GO:0002027]; regulation of sodium ion transport [GO:0002028]; regulation of the force of heart contraction [GO:0002026]; relaxation of cardiac muscle [GO:0055119]; relaxation of smooth muscle [GO:0044557]; response to ATP [GO:0033198]; response to glucose [GO:0009749]; response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0042542]; response to immobilization stress [GO:0035902]; response to muscle stretch [GO:0035994]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; sodium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:0036376]; sodium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:0098719]; sodium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0035725]; telencephalon development [GO:0021537]; vascular associated smooth muscle contraction [GO:0014829] | 11916852_data are consistent with a stoichiometry for the NCX1.1 protein of 4 Na+ to 1 Ca2+ to 2 charges moved per transport cycle 12031969_Na/Ca exchanger overexpression, by depleting ER Ca(2+) stores, triggers the activation of caspase-12 and increases apoptotic cell death 12502539_Characterization and functional activity of a truncated Na/Ca exchange isoform resulting from a new splicing pattern 14736881_functional and physical interaction of nonselective TRPC cation channels with NCX proteins as a novel principle of TRPC-mediated Ca(2+) signaling. 14981087_collagen-induced increase in [Ca2+](i) in platelets is dependent on concentration of Na+ in the extracellular milieu: the collagen-induced increase in [Ca2+](i) causes reversal of the NCX, resulting in an increase in [Ca2+](i) and platelet aggregation 15033764_Overexpression increases apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum ca-atpase inhibitors and activates caspase-12 15703175_Ca(2+) entry mode operation of the Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger is required for des-Arg(10)-kallidin- and TGF-beta1-stimulated fibrogenesis and participates in the maintenance of the myofibroblast phenotype 15785003_NCX1 is one of the genes related to susceptibility to essential hypertension in the Japanese general population. 15785003_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15824464_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16292983_an ankyrin-B-based macromolecular complex of Na/K ATPase, Na/Ca exchanger 1, and InsP3 receptor that is localized in cardiomyocyte T-tubules in discrete microdomains distinct from classic dihydropyridine receptor/ryanodine receptor 'dyads 16399865_These results highlight the importance of ionic regulation in controlling NCX1 activity under conditions that promote Ca2+ overload. 16679322_plasma membrane Na+/Ca2+ exchangers have inhibitory interactions with the 14-3-3 proteins 16921169_PLM interacts with the intracellular loop of NCX1, most likely at residues 218-358 17541957_Results describe the involvement of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger as well as the role of non-selective-cation channels in cardiac myofibroblast cell function in vitro. 17846126_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17912271_NKCC1 in conjunction with NCX1 plays a role in reperfusion-induced brain injury after ischemia. 18635667_Data show that activity of beta-cell NCX1 splice variants is modulated by acyl-CoAs and is dependent upon the intrinsic properties of the NCX1 splice variant and on the side chain length and degree of saturation of the acyl-CoA moiety. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18996841_Membrane targeting and coupling of NHE1-integrinalphaIIbbeta3-NCX1 by lipid rafts following integrin-ligand interactions trigger Ca2+ oscillations. 19541636_Results indicate the nuclear NCX/GM1 complex acts to gate Ca(2+) transfer from cytosol to ER, an alternate route to the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase pump. 19830548_These results suggest that recovery from intracellular acidosis causes a transient increase in cytosolic Ca(2+) due to reversal of Ca(2+) transport via Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger coactivated with Na(+)/H(+) exchanger, which can cause cell death. 20018762_Results show that the Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger NCLX is enriched in mitochondria, where it is localized to the cristae. 20109173_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20109173_characterization of NCX1 intronic hypervariable non-coding region enriched in human-specific indel variants 20173311_NCX1 protein expression in urinary bladder smooth muscle increases approximately 4-fold in NCX1.3 transgenic mice compared to that in wild-type. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21126331_Taken together, these data demonstrate a potentially important role for NCX1 in control of Ca2+ homeostasis and link store depletion via STIM1 directly with NCX activation. 21321244_Immunohistochemical analysis revealed thatNCKX3 and NCX1 were abundantly localized in the cytoplasm of luminal and glandular epithelial uterine cells throughout the menstrual cycle. NCX1 expression was not affected by estradiol and progesterone. 21382638_Results demonstrate a selective regulation of NCX1, NCX2 and NCX3 isoforms in Alzheimer's disease cortex, specifically in terminals containing amyloid-beta. 21613675_an increase in the NCX1 mRNA due to the apoptosis induction is not regulated by HIF-1alpha 21790537_Human platelets express K(+) -independent Na(+) /Ca(2+) exchangers NCX1.3, NCX3.2 and NCX3.4. 21833492_There were no differences of gene frequency between Alzheimer disease cases and controls for any of three polymorphisms of NCX1 gene. However, among AD patients whose age at onset (AAO) was >65 years, carriers of a 14 bp insertion showed a lower AAO. 21858195_Data suggest that NCX-mediated Ca(2+) fluxes normally exist in human ASM (potentially contributing to rapid Ca(2+) fluxes), and contribute to enhanced [Ca(2+)](i) regulation in airway inflammation. 21873429_Ca(2+) influx through reverse mode NCX is required for the activation and the targeting of PKCalpha to the plasma membrane, an essential step for VEGF-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation and downstream EC functions in angiogenesis 21930298_an essential component in the mechanism governing cardiac steroid-induced slow Ca(2+) oscillations 22270364_a novel function for NHE1 and NCX1 in membrane blebbing and permeability, and establish a link between membrane blebbing and integrin signaling. 22456474_NCX1 is upregulated in chronic atrial fibrillation. A larger I(NCX) for a given SR Ca(2+) release contributes to AF-promoting atrial delayed afterdepolarizations/triggered activity in cAF patients. 22479505_interaction of NCX1 and EAAC1 transporters leads to glutamate-enhanced ATP production in brain mitochondria 22726844_this study validated the association between a SNP, rs13017846, which maps to near SLC8A1 (sodium/calcium exchanger 1 precursor, overall p = 8.0 x 10(-14)), and the QT interval. 22842068_alpha(2)-Na(+) pumps, NCX1, receptor-operated channels, and the sarcoplasmic reticulum regulate Ca(2+) homeostasis and signaling in human arterial smooth muscle cells. 23069678_these results demonstrate that REST, by regulating NCX1 expression, may represent a potential druggable target for the treatment of brain ischemia 23192947_Ncx1 expression is required for increasing sinus rates and in isolated sinoatrial cells. 23224869_NCX1: mechanism of transport. 23224872_Functional and structural properties of the NCKX2 Na(+)-Ca (2+)/K (+) exchanger: a comparison with the NCX1 Na (+)/Ca (2+) exchanger. 23224875_the transcriptional network regulating Ncx1 expression is also mediating many of the other changes in genetic remodeling contributing to the development of cardiac dysfunction 23224883_NCX1 and NCX3 -represent two promising druggable targets for setting on new strategies in stroke therapy. 23224887_the large cytosolic loop of NCX1, NCX2, and NCX3 is involved in acquisition of immunosuppressive drug specificity 23224890_Functional studies, as well as mRNA and protein expression analyses, revealed that NCX1 and NCX3, but not NCX2, were divergently modulated during OPC differentiation into oligodendrocyte. 23224891_human macrophages and monocytes express NCX1 and NCX3 that operate in a bidirectional manner to restore [Ca(2+)](i) to generate Ca(2+) signals and to induce TNF-alpha production. 23224892_NCX1 is a key component of certain distinct signaling pathways that activate VSM contraction in response to stretch (i.e., myogenic response) and to activation of certain G-protein-coupled receptors. 23376057_Biochemical support for a model of NCX1 with 10 transmembrane domains as found in the prokaryotic homologue. 23913256_NCX1 (and EAAT1) are both involved in glutamate-induced ATP synthesis, with NCX1 playing a pivotal role. 24498266_Results indicate that levosimendan inhibited reverse-mode Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger (NCX) activity to protect cardiomyocyte progenitor cells (CPC)-derived cardiomyocytes from anoxia-reoxygenation (A/R)-induced ER stress and cell death. 25035420_Three novel loci were identified in East Asians with cardiac arrhythmias: rs2483280 (PRDM16 locus) and rs335206 (PRDM6 locus) were associated with QRS duration; and rs17026156 (SLC8A1 locus) correlated with PR interval. 25055868_There is a functional role of sodium-calcium exchanger SLC8A1 in human atrial and atrioventricular nodal conduction as suggested by genetically modified mouse models. 25336645_CAPN1 anchors to two NCX1 regions and cleaves at methionine-369, leading to NCX1 inactivation in heart failure. 25481039_Down-regulation of the SLC8A1 gene, most likely mediated by its regulator miR-223, can lead to decreased calcium in penile carcinoma and consequently to suppressed apoptosis and increased tumor cell proliferation 25500693_The expressions of NCX1 and NCKX4 were significantly higher in the patent ductus arteriosus group at both the protein and mRNA levels. 25589784_human osteoblasts and osteoblasts from Ano6(-/-) and WT mice, we demonstrate that NCX1 requires Ano6 to efficiently translocate Ca(2+) out of osteoblasts into the calcifying bone matrix 25633096_NCX1 and the calcium binding protein calretinin cooperate within the striatum to confer tolerance against cerebral ischemia. 25770213_These data confirm the role of NCX1 activity in regulating renal epithelial cell migration. 26045217_ADD2 and NCX1 variants influence the risk and the clinical features of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. 26418268_Palmitoylation of cardiac NCX1 can modify its function, physical interactions, and removal from the sarcolemma by domain-dependent endocytosis. 26418956_NCX1.3 is the predominant NCX variant in the distal convoluted and connecting tubules tubules 26421717_results demonstrate that CaM senses changes in [Ca2+]i and binds to the cytoplasmic loop of NCX1 to regulate exchange activity. 26567603_NCX1 operating in reverse mode plays a prominent role in calcium cytosolic regulation in highly metastatic melanoma cells. 26775040_interaction of NHE1, NCX1 and CaM mediates the effects of IL6 on human hepatocellular carcinoma 27031991_The expression of miR-206 by HUVECs reduced exosome production by regulating ADP-Ribosylation Factor 6 (ARF6) and sodium/calcium exchanger 1 (NCX1). 27108064_CaSR exerts a suppressive function in pancreatic tumorigenesis through a novel NCX1/Ca(2+)/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 27588478_NCX1 expression correlates with the smoking status of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients, and NNK activates the Ca2+ entry mode of NCX1 in ESCC cells, leading to cell proliferation and migration 27879314_SLC8A1 polymorphisms alter calcium flux in cells that mediate coronary artery damage in Kawasaki disease. 28395930_We also observed that acetylcholine attenuated the formation of NCX1-TRPC3-IP3R1 complexes and maintained calcium homeostasis in cells treated with TNF-alpha. 28535874_Diacylglycerol generation downstream of VEGF receptors activatesTRPC3 causing Na(+) influx with subsequent reversal of NCX1, ERK1/2 activation and ultimately contributes to enhanced angiogenesis. 28807015_The results show that estrogen upregulates cardiac L-type Ca(2+) and sodium-calcium exchange in women through genomic mechanisms that account for sex differences in Ca(2+) handling and spatial heterogeneities of repolarization due to base-apex heterogeneities of Cav1.2alpha and NCX1. By analogy with rabbit studies, these effects account for human sex-difference in arrhythmia risk. 29182730_SLC8A1 gene SNPs may contribute to blood pressure change in response to acute sodium loading in a Han Chinese hypertensive population. 29594857_Structure-Dynamic Coupling Through Ca(2+)-Binding Regulatory Domains of Mammalian NCX Isoform/Splice Variants 29955038_The results revealed the potential beneficial effect of glutamate in an in vitro model of hypoxia/reoxygenation injury and focused on the essential role exerted by NCX1. 30466198_possible role of Ca2+ entry mode in the neurotransmitter ATP-induced Ca2+ signalling in the esophageal myenteric neurons 31347915_SERCA2 is more effective in cytosolic calcium removal than the NCX1 in human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. 32562975_BRAF and NRAS mutated melanoma: Different Ca(2+) responses, Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger expression, and sensitivity to inhibitors. 32827867_NCX1 and EAAC1 transporters are involved in the protective action of glutamate in an in vitro Alzheimer's disease-like model. 32899900_Gateways for Glutamate Neuroprotection in Parkinson's Disease (PD): Essential Role of EAAT3 and NCX1 Revealed in an In Vitro Model of PD. 32980495_Topical review: Shedding light on molecular and cellular consequences of NCX1 palmitoylation. 33301895_circSLC8A1 sponges miR-671 to regulate breast cancer tumorigenesis via PTEN/PI3k/Akt pathway. 33931586_The hypoxia sensitive metal transcription factor MTF-1 activates NCX1 brain promoter and participates in remote postconditioning neuroprotection in stroke. 34127021_The downregulation of NCXs is positively correlated with the prognosis of stage II-IV colon cancer. 34724864_Circular RNA circSLC8A1 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells through targeting the miR-106b-5p /FOXJ3 axis. 35882979_NCX1 coupled with TRPC1 to promote gastric cancer via Ca(2+)/AKT/beta-catenin pathway. 35894157_Circ-NCX1 inhibits LPS-induced chondrocyte apoptosis by regulating the miR-133a/SIRT1 axis. | ENSMUSG00000054640 | Slc8a1 | 1221.540368 | 2.046024292 | 1.032823 | 0.06743846 | 232.676249 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001554932615226450598754118177232281767985428909782386403056536313624698643262976517225467411737164359642317896785285559211527765631618777653067 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000293924289483616104416996908005361217835537075399834951543560190963658671877678768373673211604783286426110414864251403339366424359579976766099 | Yes | No | 1645.1309144 | 60.3322649 | 807.4952537 | 31.1655470 | |
| ENSG00000183631 | 100130613 | PRR32 | protein_coding | B1ATL7 | Reference proteome | hsa:100130613; | ENSMUSG00000037086 | Prr32 | 7.721121 | 0.337846190 | -1.565562 | 0.58182358 | 7.551658 | 0.0059954870279915863442998791299487493233755230903625488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0332652487390880588491448577315168222412467002868652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 4.0305930 | 2.6075971 | 12.0257862 | 7.2123737 | |||||
| ENSG00000184371 | 1435 | CSF1 | protein_coding | P09603 | FUNCTION: Cytokine that plays an essential role in the regulation of survival, proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic precursor cells, especially mononuclear phagocytes, such as macrophages and monocytes. Promotes the release of pro-inflammatory chemokines, and thereby plays an important role in innate immunity and in inflammatory processes. Plays an important role in the regulation of osteoclast proliferation and differentiation, the regulation of bone resorption, and is required for normal bone development. Required for normal male and female fertility. Promotes reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, regulates formation of membrane ruffles, cell adhesion and cell migration. Plays a role in lipoprotein clearance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16337366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19934330, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20504948, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20829061}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Proteoglycan;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine that controls the production, differentiation, and function of macrophages. The active form of the protein is found extracellularly as a disulfide-linked homodimer, and is thought to be produced by proteolytic cleavage of membrane-bound precursors. The encoded protein may be involved in development of the placenta. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. | hsa:1435; | CSF1-CSF1R complex [GO:1990682]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor binding [GO:0005157]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; branching involved in mammary gland duct morphogenesis [GO:0060444]; cellular response to parathyroid hormone stimulus [GO:0071374]; developmental process involved in reproduction [GO:0003006]; homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue [GO:0048873]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; macrophage colony-stimulating factor signaling pathway [GO:0038145]; macrophage differentiation [GO:0030225]; macrophage homeostasis [GO:0061519]; mammary duct terminal end bud growth [GO:0060763]; mammary gland fat development [GO:0060611]; microglial cell proliferation [GO:0061518]; monocyte activation [GO:0042117]; monocyte differentiation [GO:0030224]; monocyte homeostasis [GO:0035702]; myeloid leukocyte migration [GO:0097529]; negative regulation of neuron death [GO:1901215]; neutrophil homeostasis [GO:0001780]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; ossification [GO:0001503]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; osteoclast proliferation [GO:0002158]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001954]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0010759]; positive regulation of macrophage colony-stimulating factor signaling pathway [GO:1902228]; positive regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation [GO:0010744]; positive regulation of macrophage differentiation [GO:0045651]; positive regulation of macrophage migration [GO:1905523]; positive regulation of macrophage proliferation [GO:0120041]; positive regulation of microglial cell migration [GO:1904141]; positive regulation of monocyte differentiation [GO:0045657]; positive regulation of mononuclear cell migration [GO:0071677]; positive regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation [GO:0032946]; positive regulation of multicellular organism growth [GO:0040018]; positive regulation of odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042488]; positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045672]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; positive regulation of protein metabolic process [GO:0051247]; positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046579]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation [GO:0010743]; regulation of ossification [GO:0030278]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] | 11792569_Macrophage colony-stimulating factor and receptor activator NF-kappaB ligand fail to rescue osteoclast-poor human malignant infantile osteopetrosis in vitro. 11843897_High M-CSF levels may correlate with cellular or organ damage in patients treated with peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for hematologic diseases. 12032835_Opposite effects of different doses of MCSF on ERK phosphorylation and cell proliferation in macrophages. 12372416_CSF-1 and its receptor are regulated by 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) and its analogue tacalcitol in human monocytes which parallels the inhibition of differentiation into dendritic cells without altering survival 12393446_IFN-gamma shifts monocyte differentiation to macrophages rather than DCs through autocrine M-CSF and IL-6 production. 12456016_in human tumor cells, HGF and M-CSF stimulate osteopontin production (which is subsequently used as a substrate for cell adhesion) 12501178_Time-dependent folding events reveal that recombinant MCSF beta molecules pass through both monomeric and dimeric intermediate states, suggesting that the denatured and dimeric bond-reduced protein folds via multiple pathways. 12548211_macrophage colony-stimulating factor increased platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase secretion by decidual macrophages 12684699_Results suggest that macrophage colony-stimulating factor may autoregulate functional cellular subpopulations of human endometrial stromal cells in an autocrine or a paracrine manner. 12865350_findings directly support the conclusion that membrane-bound colony stimulating factor-1 is functionally active in bone in vivo 12890905_Serum VEGF concentration was increased in arteriosclerosis obliterans (ASO) and thromboangitis obliterans, but increased concentration of M-CSF was seen only in ASO. 12894871_CSF1 has a role in regulating macrophage activation [review] 12928417_Monocytes promote angiogenesis via M-CSF-induced vascular endothelial growth factor production. 12929928_sCSF-1 is a key determinant of bone cell activity in the corticoendosteal envelope 14605992_increased levels of serum macrophage colony stimulating factor markedly precede the development of clinical manifestations of preeclampsia 14634568_Increase in serum M-CSF levels precedes development of preeclampsia. Elevation of serum M-CSF supports M-CSF elevation in placenta. This elevation at 18 weeks of gestation may be related to placental hypoxia, considered cause of preeclampsia. 14654075_findings of co-expression of KIT and/or FMS with their respective ligands implies these receptors might contribute to leukemogenesis in some patients with AML through autocrine, paracrine, or intracrine interactive stimulation. 15001836_The serum M-CSF concentration could be of interest as a tumor marker in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. 15116247_red blood cells from diabetic patients induced an increase in MCSF and VCAM1 expression in HUVEC cells, mediated by AGE-RAGE interaction 15256272_Expreeeion of macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human osteoblast-like cells is suppressed by arginine-vasopressin. 15261158_results suggest that nuclear actin plays a role in regulating CSF-1 gene transcription, and this role does not depend on actin polymerization 15358207_In vitro human osteoclastogenesis is dependent on M-CSF and the stimulatory effects of GM-CSF are mediated by M-CSF. 15494511_Crystal structures of HLA-B*3501 in complex with 14-mer macrophage-colony stimulating factor peptide reveal that the antigenic peptide follows the general rules of major histocompatibility complex binding. 15576295_The MGFS mRNA expression in these cell lines and recent studies have demonstrated that HCs can stimulate tumor progression. 15624698_Interferon-gamma stimulates transcription of the CSF-1 gene through this sequence, which binds STAT1 15640942_A significant serum tumor marker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 15728521_Serum M-CSF levels are markedly increased in Langerhans cell histiocytosis patients who, in addition to bone disease, also show skin or lymph node involvement. 15820145_indicate novel roles of M-CSF in articular cartilage metabolism in collaboration with CTGF/CCN2, particularly during an inflammatory response 15866728_The M-CSF gene was cloned into baculovirus transfer vector pVL1392 under the control of polyhedrin promoter and expressed in the Sf9 cells (Spodoptera frugiperda). 15919699_Uncreased macrophage colony stimulating factor is associated with the process of atherosclerosis in hemodialysis patients 15944252_M-CSF enhances tumor growth in mice by increasing endothelial progenitor cells and activating angiogenesis; the effects of M-CSF are largely based on the induction of systemic VEGF from skeletal muscles. 16204228_catalase has a critical role in CSF-independent survival of human macrophages via regulation of the expression of BCL-2 and BCL-XL 16267391_INI1/hSNF5/BAF47 functions in activation of the colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF1) promoter in HeLa cells. 16318581_MCP-1 and M-CSF, critical for monocyte recruitment, activation, and differentiation, differentially regulate VEGF-A expression and may play an important role in monocyte/macrophage- mediated tumor angiogenesis 16320327_Nurse-like cells are involved in rheumatoid arthritis-induced bone destruction by maintaining osteoclast precursors via production of M-CSF. 16407111_Fusion with COL6A3 overexpresses CSF1, found in some but not all cells in tenosynovial giant-cell tumor and pigmented villonodular synovitis. 16673212_at 35 and 38 weeks, the Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) levels were significantly higher in twin pregnancy than in singleton pregnancy 16844084_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16844084_three polymorphisms located in the colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF1) gene showed a positive association with aggressive periodontitis 16859503_IL-10 may contribute to the inflammatory process by facilitating monocyte differentiation into TNF-alpha-responsive macrophages in the presence of M-CSF in rheumatoid arthritis. 16951369_Different individual CSF-1 isoforms regulate the frequency of activated macrophages in the kidney during experimental unilateral ureteral obstruction. 17108334_CSF1 is involved in regulating macrophage trafficking at the fetal-maternal interface 17192722_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17192722_These data do not support the hypothesis that genetic variability of CSF1 influences the risk for Alzheimer's disease (AD). 17243911_significantly higher levels of macrophage-colony stimulating factor is associated with pancreatic cancer 17355643_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17368603_Significantly higher macrophage-colony stimulating factor level is associated with lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer patients 17420255_a combination of the Src family kinase, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt, phospholipase C, and ERK pathways mediates macrophage proliferation in response to M-CSF 17431224_macrophage colony-stimulating factor(M-CSF) contributes to the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis in patients with IPF through the involvement of mononuclear phagocytes and CCL2 production. 17443671_Increased and prolonged ERK activation led to M-CSF-mediated macrophage differentiation but not to proliferation. 17516513_M-CSF modulates osteoclast-resorbing activity, but is not required for cell survival 17532041_We have shown for the first time that a homeobox gene, HLX1, is a downstream effector gene of CSF-1, that HLX1 regulates placental cell proliferation and that CSF-1 acts, at least in part, through HLX1 to control cell proliferation. 17589498_Monocytopoiesis is controlled by a circuitry involving sequentially miRNA 17-5p-20a-106a, AML1 and M-CSFR, whereby miRNA 17-5p-20a-106a function as a master gene complex interlinked with AML1 in a mutual negative feedback loop. 17916748_M-CSF-driven generation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells and conventional dendritic cells in vitro and in vivo was independent of endogenous Flt-3 ligand 17918257_Csf1 fusion with collagen type VI alpha-3 gene is associated with tenosynovial giant cell tumors. 17922812_Human cardiac cells constitutively express M-CSF and its expression is up-regulated by TNF-alpha. 17967422_CSF-1 and TPA use independent pathways to initiate RIPping, and that the intracellular domain is targeted for degradation through ubiquitination 18219369_Differential constitutive and cytokine-modulated expression of Toll-like receptors in primary neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages is reported. 18322228_CSF-1 stimulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 (ERK5) activation in macrophages. 18435789_Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from periodontitis patients do not need priming by M-CSF to become osteoclast-like cells, suggesting that PBMCs from periodontitis patients are present in the circulation in a different state of activity. 18467591_Discovered IL-34 and its receptor CSF1 by functional screening of the extracellular proteome. 18510570_Expression of M-CSF, CSF-1R and CD3 is a significant prognostic factor in primary prostatic cancers by predicting the development of metastases. 18619508_nuclear c-Abl kinase can activate CSF-1 gene transcription by regulating AP-1 activity in the signaling events induced by L-selectin ligation. 18632616_mM-CSF may be a critical linker between macrophages and malignant cells in the development of hematopoietic malignancies 18668547_CCL23, M-CSF, TNFRSF9, TNF-alpha, and CXCL13 are predictive of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity and may be useful in the definition of disease subphenotypes and in the measurement of response to therapy in clinical studies. 18676750_CSF1, EGFR, and CA IX have roles in increasing survival in early-stage squamous cell carcinoma of the lung 18708368_GAPDH, a multifunctional protein, now adds regulation of mRNA stability to its repertoire. 18718581_Report clinical use of colony-stimulating factor-1 in ovulation induction for poor responders. 18724005_These results suggest that orthodontic tooth movement causes an increase in VEGF and M-CSF levels, which may induce bone remodeling via osteoclastic bone resorption. 18751872_The close correlation between serum M-CSF and serum thyroid hormone levels suggests that high circulating levels of thyroid hormones may directly or indirectly potentiate the production of M-CSF in patients with GD. 18852899_ability of M-CSF to recruit mononuclear phagocytes, increase VEGF levels, and enhance angiogenesis 18996518_Macrophage colony-stimulating factor is involved in follicle development and ovulation and could be an additional predictor for in vitro fertilization outcome. 19004987_CSF-1 represents a further link between inflammation and cardiovascular disease. 19008293_CRP up-regulates M-CSF release from human monocyte-derived macrophages and human aortic endothelial cells and increased macrophage proliferation. 19017797_Calorimetric data indicate that M-CSF cannot dimerize FMS without receptor-receptor interactions mediated by FMS domains D4 and D5 19196448_renal tubular cell derived m-CSF is a stimulus for monocyte activation 19432671_CSF-1 derived from tumor tissues induces macrophages to shift toward the M2 phenotype, which is considered to promote tumor growth 19443701_CSF1 may play an important role in the clinical behavior of leiomyosarcoma 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19561083_CSF-1-induced WASP activation was fully Cdc42-dependent. 19641137_M-CSF inhibits differentiation of murine bone marrow-derived macrophages into prefusion osteoclasts (pOC) in vitro, but induces fusion of pOCs to form multinucleated osteoclasts, making the osteoclast capable of bone resorption. 19711348_Studies demonstrated that increased CSF-1 production by host cells enhances TAM recruitment and NB growth. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19926892_serum and urine CSF-1 levels correlated with lupus activity, and intrarenal CSF-1 expression correlated with the histopathology activity index of lupus nephritis 19950360_possible local and systemic involvement of M-CSF in humans during fracture healing 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20436471_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20436471_These studies provide new insights into the pathogenesis of PDB and identify OPTN, CSF1 and TNFRSF11A as candidate genes for disease susceptibility. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20455868_Macrophage colony-stimulating factor in CSF appears to be a biomarker for diagnosis of mild cognition disorder. 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20504948_The different spatiotemporal expression of IL-34 and CSF-1 allows for complementary activation of the CSF-1R in developing and adult tissues. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20839008_genetic risk for Paget's disease of bone is associated with variants close to CSF1, OPTN, TM7SF4, and TNFRSF11A genes; most significant results are found in the CSF1 gene region 20839921_Increased prevalence of M-CSF in the setting of HIV infection could contribute to neuronal injury and may be predictive of cognitive impairment. 20925194_These results indicate that nuclear NFAT can activate CSF-1 gene transcription by connecting with the CSF-1 promoter in the signaling events induced by L-selectin ligation. 21239715_M-CSF enhances dendritic cell DC-SIGN (CD209) expression on in vitro derived anti-inflammatory macrophages; M-CSF mediates induction of DC-SIGN by fibroblast- and tumor cell-conditioned media. 21481374_CSF-1, in an autocrine fashion, has a direct effect on endometrial epithelial cell proliferation and attachment to peritoneal mesothelial cells, early steps in endometriosis lesion formation on the peritoneum. 21717212_These observations may indicate a pathogenetic role of Macrophage colony-stimulating factor in Hodgkin lymphoma. 21791433_Humanized CSF-1 mice will be a valuable experimental model to study human myeloid cell biology. 21854753_These findings suggest an important role for CSF1 and the resulting tumor-associated macrophage infiltration in the pathological neovascularization of leiomyosarcoma. 21895511_findings demonstrate that NF-kappaB induces M-CSF expression on a promoter level via multiple functional NF-kappaB binding sites 21938481_Treatment of differentiating cells with alendronate or pamidronate decreases the expression of M-CSF, which enhances preosteoclast formation. These results suggest a new mechanism by which BPs inhibit osteoclastogenesis. 21945122_Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor and Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein are elevated in sera of intrinsic asthmatics compared to normal controls. 22028782_CSF-1 dependent Erk activation and proliferation are regulated differentially in progenitors and differentiated cells 22052465_results suggest that budding RCC stimulates the proximal adjacent microenvironment in the kidney to release mediators of CSF-1, CSF-1R, and epidermal growth factor expression in RCCs 22082370_In this review, shedding of macrophage-CSF receptor c-Fms inhibits osteoclastogenesis. 22186992_Studies indicate that Macrophage-colony stimulating factor (CSF-1) signaling through its receptor (CSF-1R) promotes the differentiation of myeloid progenitors. 22365076_Suggest that CSF-1 and its receptor, C-FMS, are involved in the genesis of early endometriotic lesions and that endometriotic lesions contribute to elevated CSF-1 levels in the peritoneal fluid of women with endometriosis. 22678116_Our results reveal a novel mechanism for the therapeutic function of fish oil diet that blocks miR-21, thereby increasing PTEN levels to prevent expression of CSF-1 in breast cancer. 23061794_M-CSF was shown to interact with Epstein-Barr virus-encoded BARF1 via the protruding N-terminal loops involving Val38 and Ala84. 23233531_miR-148b controls malignancy by coordinating a novel pathway involving over 130 genes and, in particular, it directly targets players of the integrin signaling, such as ITGA5, ROCK1, PIK3CA/p110alpha, and NRAS, as well as CSF1 23260168_the feline CSF-1R was cloned and the responsiveness to CSF-1 and IL-34 from a range of species, was examined. 23285029_The percentage of CD14(high)CD16(+) monocytes after trauma correlated strongly with plasma C-reactive protein (CRP) transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta), and macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) levels. 23471483_Nucleolin mediates microRNA-directed CSF-1 mRNA deadenylation but increases translation of CSF-1 mRNA. 23520016_The expression of CSF2 (but not CSF1) was highly up-regulated in glioblastoma patients and we found an inverse correlation between CSF2 expression and patient survival. 23684409_This study is the first to illustrate downstream transcriptional profiles and pathways of IL-34 in comparison with CSF-1 and identify notable differences in CCR2 expression. 23688065_The results indicate usefulness of VEGF and M-CSF in diagnostics of breast cancer patients, especially in combination with CA 15-3. 23870818_high expression correlates with shorter metastasis-free survival in non-small-cell lung cancer patients 23924854_GPNMB expression was regulated by EpCAM and CSF-1 partly through their common downstream product c-myc 24016870_Elevated CSF1 serum level is associated with early breast cancer. 24157873_Regulation of immediate-early gene response by THOC5, a member of mRNA export complex contributes to the M-CSF-induced macrophage differentiation. 24178511_genetic polymorphism is associated with platelet counts 24592910_None of SNPs among rs333967, rs2297706 and rs1058885 in CSF-1 was found statistically significantly associated with CP in Han Chinese with Shanghai origin. haplotype T-C-G showed statistically significant association with decreased risk in males. 24604026_Findings suggest the replacement of the 3'-UTR of CSF1 with other sequences in tenosynovial giant cell tumors. 24748497_The findings of this study regarding the unique functional interplay between M-CSF and IL-32 increase our understanding of the mechanisms that regulate the survival and M1/M2 ratio of macrophages, as well as HIV-1 replication in macrophages. 24769444_In a cohort of 453 human breast tumors, NCOA1 and CSF1 levels correlated positively with disease recurrence, higher tumor grade, and poor prognosis. 24956020_The aim of the present study was to assess the effect of soluble mediators produced by breast cancer cells on human osteoclast maturation in a co-culture model. 25066464_potent profibrotic factor in hepatitis C virus liver fibrosis 25138985_macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) may be involved in the regulation of epiphyseal plate injury and repair in Kashin-Beck disease. 25196912_expression and release, from osteoblasts of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), which is indispensable for osteoclast differentiation, was inhibited by uPAR loss. 25313137_results presented herein suggest a potential cross-talk between cancer cells and the microenvironment controlled by CSF1/Vav1 signaling pathways. 25418473_RGC-32 expression on M2-polarized and tumor-associated macrophages is M-CSF-dependent and enhanced by tumor-derived IL-4. 25420919_FoxO1 is highly expressed in M-CSF-derived (M2-like) macrophage subsets, and this M2-like macrophages showed a preferential FoxO1 enrichment on the IL-10 promoter but not in GM-CSF-derived (M1-like) macrophages 25721620_Colony Stimulating Factors 1, 2, 3 and early pregnancy 25854167_Determination of CSF1 and CSF1R expression may be useful as a prognosticator of the clinical course and/or outcomes of Pigmented villonodular synovitis . 25891874_Our findings also suggest that next generation sequencing may help explore the pathogenesis and aid the diagnosis of Juvenile Paget's disease. 25935153_These findings suggest a high usefulness of M-CSF in diagnosing the serous sub-type of epithelial ovarian cancer and in discriminating between cancer and non-carcinoma lesions 26029847_These findings highlight an essential role for PRKAA1-mediated autophagy during differentiation of human monocytes. 26095744_findings demonstrated that M-CSF binds to IL-34; molecular docking studies predicted the formation of a heteromeric M-CSF/IL-34 cytokine 26235028_Data show crystal structures of CSF1-CSF1R ternary complexes, and propose a mechanism for their cooperative action that relies on the adoption by dimeric CSF-1 of an active conformational state and homotypic receptor interactions. 26245897_study shows up-regulation of MCSF in GBM via a SYK-PI3K-NFkappaB-dependent mechanism and identifies IGFBP1 released by microglial cells as a novel mediator of MCSF-induced angiogenesis 26359491_By identifying the M-CSFM residues critical for M-CSF-c-FMS interactions, we have laid down the basis for a deeper understanding of the M-CSF . c-FMS signaling mechanism 26376111_In patients with CLE, 100 and 150 mg PD-0360324 (monoclonal antibody against MCSF) every 2 weeks for 3 months suppressed a subset of circulating monocytes. 26642091_peripheral nerve injury induced de novo expression of colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF1) in injured sensory neurons. CSF1 was transported to the spinal cord, where it targeted the microglial CSF1 receptor (CSF1R). 26686751_This can be achieved by either blocking the EGF or CSF-1 receptors or supressing the EGF or CSF-1 signal. 27013192_Therefore, our findings indicate that CSF1 signaling is oncogenic during gliomagenesis through a mechanism distinct from modulating glioma-associated microglia/macrophage polarization status 27038418_M-CSF macrophage conversion into foam cells reduces their proinflammatory responses to classical M1-polarizing activation 27107415_miR-1207-5p and CSF1 expression levels and their relationship with lung cancer survival and metastasis status were assayed by means of a lung cancer tissue microarray. 27173404_Upregulation of GM-CSF and M-CSF production by endothelial cells, an effect that appears to be mediated by NF-kappaB and to be independent of IL-1, may be an additional mechanism through which IL-33 contributes to inflammatory activation of the vessel wall. 27445439_M-CSF has been shown to be comparable to CA15-3 and VEGF, specificity, and AUC values only in stages III and IV of BC. 27599777_High CSF1 expression is associated with breast cancer. 28131007_Nucleolin both forms an mRNP complex with the eIF4G and CSF-1 mRNA, and is co-localized with the eIF4G in the cytoplasm further supporting nucleolin's role in translational regulation. 28273887_Results suggest that monocytes from Crohn's disease patients in remission produced high levels of CSF-1 that upregulate CCR5 expression. Consequently, monocytes differentiated in these conditions had a characteristic phenotype and lower production of inflammatory cytokines. 28655719_study, therefore, provided insights into the sequence-structure-function relationships of the M-CSF/c-FMS interaction and of ligand/receptor tyrosine kinase interactions in general. 28656272_It was demonstrated that MCSF and folliclestimulating hormone stimulated the production of estradiol (E2) in luteinized granulosa cells. MCSF may be important in regulating the response of luteinized granulosa cells to gonadotropin and may have a promotive effect in the early phase of follicular development. 28687620_High CSF-1 expression is associated with Breast Cancer. 28779164_study found that age, smoking, periodontitis, manifest caries, and the presence of tumors are associated with the salivary levels of CSF-1. 28875266_Concerning pigmented villonodular synovitis , clinical trials assessing CSF-1R inhibitors have revealed promising initial outcomes. Blocking CSF-1/CSF-1R signaling represents a promising immunotherapy approach and several new potential combination therapies for future clinical testing. 29323162_Data showed that single expression of M-CSF or IL-34 can be observed in lung cancer tissues and correlated with poor survival. Additionally, their high co-expression correlates with disease stages and poor survival. Thus, evaluating the expression of both M-CSF and IL-34 may help to estimate disease progression and malignant degree in lung cancer patients. 29363207_These results highlight heterogeneous effects of M-CSF isoforms on acute myeloid leukemia progression. 29422647_In glioblastoma, colony-stimulating factor-1 and angiocrine IL-6 induce robust arginase-1 expression and macrophage alternative activation, mediated through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma-dependent transcriptional activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha. 29734839_The functional rs2050462 in CSF-1 might have a substantial influence on the renal cell carcinoma susceptibility and evolution in the Chinese population. 29767252_Study find elevated expression of CSF1 in primary gastric cancer tissue (GC) to be significantly associated with the presence of lymph node and peritoneal metastasis, advanced TNM stage, and poor survival. In vitro analysis also revealed a functional role for the CSF1 in GC development, and a prognostic and predictive biomarker for GC. 29801457_at 3 months after cardiopulmonary bypass, monocytes continued to express a new macrophage-like milieu that was associated with the persistent activation of the PU.1/M-CSF pathway. 30012324_Elevated CSF1 levels were identified as a causal risk factor for Coronary Artery Disease with consistent epidemiological results. Furthermore, genetically predicted CSF1 levels were associated with CAD in the UK Biobank 30052166_High M-CSF expression is associated with cervical cancer. 30317027_data unveil a novel epigenetic mechanism whereby a BRG1-centered complex mediates transcriptional activation of CSF1 by Ang II in vascular endothelial cells. 30342176_CSF-1 mRNA decay can be regulated at an epigenetic level, and alteration of the N1methylation status leads to phenotypic changes in cancer cell behavior. 30580386_Expression of M-CSF is related to macrophage activity and tumor progression in sporadic vestibular schwannomas. 30592292_Cytoplasmic MCSF suppressed apoptosis in MCF7 human breast cancer cells by inhibiting the HIF1alpha/BNIP3/Bax signalling pathway, which potentiated the dissociation of Bcl2 from Bcl2BNIP3 compounds and the formation of Bcl2Bax compounds. 30816518_These results suggested that the interaction between CSF1 and its receptor served an important role in promoting macrophage infiltration and progression of EC. 31028249_When monocytes are differentiated into macrophages with CSF-1, CSF-1R is redirected to transcription starting sites, colocalizes with H3K4me3, and interacts with ELK and YY1 transcription factors. 31035945_Data indicate a possible clinical applicability and a high diagnostic power for the combination of macrophage-colony stimulating factor (M-CSF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), CA 125 and SCC-Ag in the diagnosis of both studied types of cervical cancer. 31107544_The frequent deletion of CSF1 exon 9 in the fusion transcripts. 31217507_A Selective FGFR inhibitor AZD4547 suppresses RANKL/M-CSF/OPG-dependent ostoclastogenesis and breast cancer growth in the metastatic bone microenvironment. 31469468_Sequencing confirmed CSF1 breakpoints in 28 cases; in all 28 the breakpoint was found to be downstream of exon 5, replacing or deleting a long 3' UTR containing known miRNA and AU-rich element negative regulatory sequences. 31536655_CSF1-associated decrease in endometrial macrophages may contribute to Asherman's syndrome. 31786501_Who's in charge here? Macrophage colony stimulating factor and granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor: Competing factors in macrophage polarization. 31859421_Schwann cells orchestrate peripheral nerve inflammation through the expression of CSF1, IL-34, and SCF in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 31911555_miR-149 Suppresses Breast Cancer Metastasis by Blocking Paracrine Interactions with Macrophages. 31994318_miR-1254 inhibits progression of glioma in vivo and in vitro by targeting CSF-1. 32149159_Genetic Association and Expression Correlation between Colony-Stimulating Factor 1 Gene Encoding M-CSF and Adult-Onset Still's Disease. 32178869_The alternative spliced 3'-UTR mediated differential secretion of macrophage colony stimulating factor in breast cancer cells. 32264887_MiR-423-5p may regulate ovarian response to ovulation induction via CSF1. 32356483_Diagnostic Values of miR-21, miR-124, and M-CSF in Patients With Early Cervical Cancer. 32487125_Oct4 promotes M2 macrophage polarization through upregulation of macrophage colony-stimulating factor in lung cancer. 33652607_The Presence of Colony-Stimulating Factor-1 and Its Receptor in Different Cells of the Testis; It Involved in the Development of Spermatogenesis In Vitro. 33764399_CSF1/CSF1R-mediated Crosstalk Between Choroidal Vascular Endothelial Cells and Macrophages Promotes Choroidal Neovascularization. 34069563_Tumor-Associated Macrophage Promotes the Survival of Cancer Cells upon Docetaxel Chemotherapy via the CSF1/CSF1R-CXCL12/CXCR4 Axis in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. 34298983_Transfection of Vitamin D3-Induced Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells for the Silencing of Potential Tolerogenic Genes. Identification of CSF1R-CSF1 Signaling as a Glycolytic Regulator. 34627193_CircCDC45 promotes the malignant progression of glioblastoma by modulating the miR-485-5p/CSF-1 axis. 35075211_M-CSF supports medullary erythropoiesis and erythroid iron demand following burn injury through its activity on homeostatic iron recycling. 35260161_CSF-1-induced DC-SIGN(+) macrophages are present in the ovarian endometriosis. 35468468_MiR-145 participates in the development of lupus nephritis by targeting CSF1 to regulate the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. 36071257_Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of 39 tumors, with evidence for a CSF1-producing ''null cell'' population. 36177809_Determining the expression levels of CSF-1 and OCT4, CREM-1, and protamine in testicular biopsies of adult Klinefelter patients: Their possible correlation with spermatogenesis. 36221069_LARRPM restricts lung adenocarcinoma progression and M2 macrophage polarization through epigenetically regulating LINC00240 and CSF1. | ENSMUSG00000014599 | Csf1 | 358.648204 | 0.483041859 | -1.049780 | 0.11495802 | 83.025485 | 0.0000000000000000000810022963146017428567711887265811615701046234748534838158995352586089211399666965007781982421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000055002918487798503207790692392892003879357881588251996674010513288521906360983848571777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 243.2667858 | 30.2921336 | 505.6318311 | 61.6965687 | |
| ENSG00000184445 | 9735 | KNTC1 | protein_coding | P50748 | FUNCTION: Essential component of the mitotic checkpoint, which prevents cells from prematurely exiting mitosis. Required for the assembly of the dynein-dynactin and MAD1-MAD2 complexes onto kinetochores (PubMed:11146660, PubMed:11590237, PubMed:15824131). Its function related to the spindle assembly machinery is proposed to depend on its association in the mitotic RZZ complex. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11146660, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11590237, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15824131, ECO:0000305}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Centromere;Chromosome;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Kinetochore;Mitosis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a protein that is one of many involved in mechanisms to ensure proper chromosome segregation during cell division. Experimental evidence indicated that the encoded protein functioned in a similar manner to that of the Drosophila rough deal protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:9735; | actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; kinetochore microtubule [GO:0005828]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; RZZ complex [GO:1990423]; spindle pole [GO:0000922]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; cell division [GO:0051301]; mitotic sister chromatid segregation [GO:0000070]; mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint signaling [GO:0007094]; protein localization to kinetochore involved in kinetochore assembly [GO:1903394]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of exit from mitosis [GO:0007096] | 18065224_Aurora B kinase activity is required for the accumulation of tension-sensitive mitotic-checkpoint components, such as ZW10 and ROD, in order to maintain mitotic-checkpoint arrest. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 30628654_Kinetochoreassociated protein 1 (KNTC1) is highly expressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cell lines. Knockdown of KNTC1 effectively inhibits cell viability and increases apoptosis. 33639055_Knockdown of KNTC1 Inhibits the Proliferation, Migration and Tumorigenesis of Human Bladder Cancer Cells and Induces Apoptosis. 35389773_Kinetochore-associated protein 1 promotes the invasion and tumorigenicity of cervical cancer cells via matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9. 35933405_shRNAmediated knockdown of KNTC1 inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer through regulating PSMB8. 36273753_Silencing of KNTC1 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cells progression via suppressing PI3K/Akt pathway. | ENSMUSG00000029414 | Kntc1 | 415.615729 | 4.288877147 | 2.100600 | 0.25794924 | 61.669248 | 0.0000000000000040627619076712583746566952549985321372882072533949671111486168229021131992340087890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000001932990257296107737004464001983235729752782366963614890664757695049047470092773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 697.4527689 | 226.4134642 | 159.4045437 | 51.7386663 | |
| ENSG00000184557 | 9021 | SOCS3 | protein_coding | O14543 | FUNCTION: SOCS family proteins form part of a classical negative feedback system that regulates cytokine signal transduction. SOCS3 is involved in negative regulation of cytokines that signal through the JAK/STAT pathway. Inhibits cytokine signal transduction by binding to tyrosine kinase receptors including IL6ST/gp130, LIF, erythropoietin, insulin, IL12, GCSF and leptin receptors. Binding to JAK2 inhibits its kinase activity and regulates IL6 signaling. Suppresses fetal liver erythropoiesis. Regulates onset and maintenance of allergic responses mediated by T-helper type 2 cells (By similarity). Probable substrate recognition component of a SCF-like ECS (Elongin BC-CUL2/5-SOCS-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins (PubMed:15601820). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35718, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15601820}. | Growth regulation;Pharmaceutical;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;Signal transduction inhibitor;Ubl conjugation pathway | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. | This gene encodes a member of the STAT-induced STAT inhibitor (SSI), also known as suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS), family. SSI family members are cytokine-inducible negative regulators of cytokine signaling. The expression of this gene is induced by various cytokines, including IL6, IL10, and interferon (IFN)-gamma. The protein encoded by this gene can bind to JAK2 kinase, and inhibit the activity of JAK2 kinase. Studies of the mouse counterpart of this gene suggested the roles of this gene in the negative regulation of fetal liver hematopoiesis, and placental development. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:9021; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex [GO:0005942]; 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase regulator activity [GO:0046935]; miRNA binding [GO:0035198]; phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784]; protein kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0004860]; branching involved in labyrinthine layer morphogenesis [GO:0060670]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to interleukin-17 [GO:0097398]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046627]; negative regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046426]; negative regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042532]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0046854]; placenta blood vessel development [GO:0060674]; positive regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045597]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0007259] | 11727828_active MKK6 in HepG2 cells enhanced basal activity or IL-6-induced transcriptional activation of a SOCS3 promoter 12027890_evidence for pY429pY431 being a new high affinity binding site for SOCS-3 on the EpoR 12198248_SOCS-3 is a major regulator of growth hormone signaling in insulin-producing cells 12351404_chronic expression confers resistance to IFN-alpha in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells 12403768_These data suggest, that there are two, largely distinct modes of negative regulation of gp130 activity, despite the fact that both SOCS3 and SHP2 are recruited to the same site within gp130. 12459551_translational control plays an important role in stabilization and function of SOCS3 12560330_SOCS-3 may have a role in IL-6-mediated insulin resistance in liver 12565872_Results describe the cloning and characterization of the promoter region of the human SOCS-3 gene. 12626585_Data showing that SOCS3 is not recruited to phosphotyrosine motifs of the IL-10 receptor complex suggest that IL-10 signaling is less sensitive than IL-6 signaling to inhibition by SOCS3. 12654831_induction of SOCS3 by Leishmania donovani provides a potent inhibitory mechanism by which intracellular microorganisms may suppress macrophage activation and interfere with the host immune response 12688541_SOCS-3 plays an important role in the suppression of cytokine signaling by GH in down-regulating the acute phase response after injury. 12783885_acceleration of degradation by tyrosine phosphorylation 12847520_These data indicate that SOCS-3 has an important role in regulating the onset and maintenance of T(H)2-mediated allergic immune disease. 14617776_hypermethylation in CpG islands of the functional SOCS-3 promoter that correlates with its transcription silencing in primary lung cancer tissue samples 15163721_rapidly induced in amnion FL cells in HSV-1 infection and appears to be mainly responsible for suppression of IFN signaling and IFN production during the HSV-1 infection. 15217536_Frequent hypermethylation of the functional SOCS-3 promoter correlates with its transcription silencing in NSCLC cell lines and primary lung cancer tissue samples; methylation silencing of SOCS-3 may be used as a marker for early detection of NSCLC 15240148_Our results demonstrate that SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 proteins inhibit IFN-alpha-induced activation of the Jak-STAT pathway and expression of the antiviral proteins 2',5'-OAS and MxA. 15249995_Homozygosity for the A-allele of the C -920-->A promoter polymorphism of the SOCS3 gene may be associated with increased whole-body insulin sensitivity. 15249995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15300962_Leptin resembles immune molecules called cytokines, which another protein, Socs3, inhibits. Colleagues wondered whether Socs3 also suppresses leptin and promotes resistance to the hormone. 15308667_interleukin-1beta regulates interleukin-6-induced suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 expression 15331532_SOCS-3 expression in human skeletal muscle in vivo is not related to insulin resistance in the presence of elevated IL-6 concentrations suggesting that cytokine action could differ in type 2 diabetic patients and nondiabetic obese subjects. 15361843_SOCS1 and SOCS2 but not SOCS3 suppressed the growth of ovarian and breast cancer cells. 15385932_overexpression of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 is associated with anaplastic large cell lymphoma 15589317_The insertion of amino acid exchanges into the kinase inhibitory regions of SOCS-3 demonstrated a requirement of these domains for a proper inhibitory function. 15607366_The SOCS3 mRNA expression in bone marrow cells from CML patients who responded well to IFN-alpha therapy was significantly lower than that in cells from healthy volunteers and patients who were resistant to IFN-alpha therapy. 15618960_SOCS-3 is not a tumour suppressor but rather a protector of tumour cells. 15629435_SOCS3/CIS3 regulates hepatocyte growth factor-induced keratinocyte migration by inhibiting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 phosphorylation 15939448_The induction of SOCS3 by HSV-1 occurs via STAT3 activation immediately after HSV-1 infection. 16007169_promoter methylation and subsequent transcript downregulation of SOCS-3 transcripts and, to a much lesser extent, SOCS-1 are involved in the multistep carcinogenesis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma 16007195_loss of SOCS-3 by the associated DNA methylation confers cells advantage in growth and migration 16055089_estrogen receptor 1 directly regulates human SOCS-3 promoter activity in human breast cancer cells 16210657_Inhibition of function in dominant-negative SOCS3 transgenic mice clearly reduces the severity of allergic conjunctivitis 16374465_this study suggests a potential novel function of SOCS-3 in regulating keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation in vitro and during skin repair in vivo. 16402267_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16410555_Results suggest a novel interaction between the SOCS1 and SOCS3 proteins and the FGFR3 signaling pathway. 16543409_SOCS-3 inhibits IL-1 signal transduction by inhibiting ubiquitination of TRAF6, thus preventing association and activation of TAK1. 16568091_Able to repress the activity of the Brk non-receptor tyrosine kinase. 16709613_role for IL-11 via pSTAT3 and SOCS3 in initiating and progressing decidualization 16805839_Our data also show that SOCS3 promoted maintenance of neural stem cells 16822822_Data demonstrate that SOCS3 inhibits leptin activation of AMPK and suggest this impairment of leptin signaling in skeletal muscle may contribute to the aberrant regulation of fatty acid metabolism observed in obesity. 16831601_Deletion of the SOCS3 gene in hepatocytes promotes the activation of STAT3, resistance to apoptosis, and an acceleration of proliferation, resulting in enhanced hepatitis-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. 16914720_These data argue for the existence of a novel cAMP/Epac/Rap1/SOCS-3 pathway for limiting IL-6 receptor signaling in Endothelial Cells and illuminate a new mechanism by which cAMP may mediate its potent anti-inflammatory effects. 16920065_Decreased SOCS3 expression in obese adipose tissue may reflect a defective leptin signaling pathway. 16943387_The increase in mRNA for SOCS-3, which correlates with elevated levels of SOCS protein and positive immunostaining in M. avium/HIV-1 co-infected tissues. 17001312_elevated expression of SOCS genes is a specific lesion of breast-cancer cells that may confer resistance to proinflammatory cytokines and trophic factors, by shutting down STAT1/STAT5 signaling that mediate essential functions in the mammary gland 17083795_Upon LPS stimulation, expression of SOCS-3 mRNA is increased in cord blood lymphocytes. 17138568_SOCS3 binds the phosphorylated immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) of sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin (siglec) 7 and targets it for proteasomal-mediated degradation. 17148681_Collectively, our results show that SOCS-3 antagonizes regulation of cellular events by cAMP and is expressed in human prostate cancer. 17241887_SOCS-3 epigenetic silencing is responsible for sustained IL-6/STAT-3 signaling and enhanced Mcl-1 expression in cholangiocarcinoma 17264307_Using RT-PCR, we demonstrated for the first time that neutrophils express mRNA for SOCS-3. It is interesting that IL-4 increased expression of SOCS-3 at the mRNA and protein levels. 17273770_inactivation of the SOCS3 gene by hypermethylation may be involved in the promotion of malignant behavior of melanomas 17297444_SOCS3 overexpression reduced proliferation. 17325857_a defect in expression of SOCS-2 and SOCS-3 genes may be crucial for the IGF-I hypersensitivity and progressive increase in erythroid cell population size characteristic of Polycythemia vera. 17363902_This is the first demonstration of SOCS-mediated ubiquitination and routing of a cytokine receptor and its impact on maintaining an appropriate signaling output. 17374732_SOCS3 may possibly play a role in IL-6 resistance in at least a fraction of tumors. 17438093_Altered SOCS gene expression leads to increased cell signaling through the ERK-MAPK pathway and may play a role in disease pathogenesis by enhancing glioblastoma multiforme radioresistance. 17445271_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17445271_our data do not suggest evidence for a major role of the respective SNPs in SOCS3 in the pathogenesis of extreme obesity in our study groups 17530721_Interleukin-6 (IL-6) was expressed in monocytes and B cells, IL-10 in monocytes, and suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 in monocytes and T cells from patients with active disease. 17589943_Increased expression of mucosal SOCS3, but not of SOCS1, may play a critical role in the development of the colonic inflammation of ulcerative colitis. 17605868_SOCS-3 expression of naive T cells was up-regulated significantly after IL-2 stimulation; expression was down-regulated markedly after OVA(323 - 329) antigen stimulation. 17636039_This study details a novel mechanism of SOCS3 up-regulation by PGE2 in breast cancer cells that appears to be STAT independent and involve Sp1 binding to the promoter. 17668875_SOCS3 expression may influence the response to antiviral therapy and genotype 1b hepatitis C virus might induce its up-regulation. This may account for the different responses to therapy between genotype 1-infected and genotype 2-infected patients. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17881539_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17895321_SOCS3 remained significantly unchanged in polycystic ovarian syndrome women 17935223_The infection of cells with adenovirus CN305 (AdCN305)-SOCS3 and AdCN305-cpp-SOCS3 resulted in dramatic cytotoxicity in liver tumor cells. 18045952_SOCS-3 inhibits androgen-stimulated proliferation by influencing cell cycle regulation in a prostate cancer cell line. 18055217_We conclude that endogenous SOCS3 inhibits AP-1 activity through blocking of JNK phosphorylation. 18097573_Reduced expression of SOCS-3 is closely related to lymph node metastasis. Therefore, SOCS-3 may be a good predictor for lymph node metastasis. 18199397_SOCS-3 may cause tissue damage indirectly in multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. 18240972_Human sarcopenia reveals an increase in SOCS-3 and myostatin and a reduced efficiency of Akt phosphorylation. 18250407_SOCS3 and SOCS1 critically regulate influenza A virus-triggered innate immune responses by inhibiting type I interferon alphabeta receptor (IFNAR)1 antiviral signaling and differentially modulating inflammatory signaling pathways. 18414649_Data found that the level of TLR2 and SOCS-3, genes associated with atopy in the children, were significantly downregulated by presence of S. haematobium infection. 18440067_The methylation status of CpG islands of SOCS3 genes in chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms. 18507841_SOCS3 negatively regulates cell motility and decreased SOCS3 induced by methylation may confer a migration advantage to A549 cells. This suggest a negative role of SOCS3 in PYK2 signaling: previously unidentified regulatory mechanism for PYK2 function. 18538318_the lymphadenitis due to M. tuberculosis was associated with activated lysozymes and SOCS-3 but not SOCS-1 compared to controls, which may play a role in the long-term bacterial replication and altered immune modulation characteristic of the disease. 18549612_There is a statistically significant difference in the expression level of socs3 mRNA in myelo-proliferative disease patients between jak2v617f mutation positive group and negative group. 18571793_Oncostatin M stimulation of astrocytes leads to induction of SOCS-3 expression and activation of ERK1/2 and JNK pathways. 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18656467_monocyte SOCS3 correlated with glomerular filtration rate, urea and diastolic blood pressure 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18687693_SOCS-3 acts as a negative regulator of the cell cycle progression under E2F/DP-1 control by interfering with heterodimer formation between DP-1 and E2F 18752121_Constitutive and altered SOCS-3 expression may have potential roles in a subset of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. 18770864_The methylation of SOCS3 may be involved in the pathogenesis of glioblastoma multiforme and in the resistance of this neoplasm to conventional treatment. 18815196_SOCS3 promoter methylation iss detected in 32% of patients with idiopathic myelofibrosis suggesting a role for SOCS3 methylation in this disorder. 18820827_difference in SOCS1, SOCS2 and SOCS3 transcript levels between normal individuals and SLE patients is not statistically significant 18941624_SOCS3 expression in skeletal muscle is not up-regulated in women, despite very high serum leptin concentrations compared to men 18952062_SOCS3 negatively regulates IL-1beta-induced MUC8 gene expression. 18971287_CCL11 induces SOCS1 and SOCS3 expression in murine macrophages, human monocytes, and dendritic cells and inhibits GM-CSF-mediated STAT5 activation and IL-4-induced STAT6 activation in a range of hematopoietic cells. 18986700_increased ratio of sgp130/sIL-6R production and/or reduced sIL-6R production combined with down-regulation of IL-6R and SOCS-3 expression in trophoblasts may lead to less cytokine inhibitory activity in preeclampsia placentas 18989459_influenza A viruses not only suppress IFNbeta gene induction but also inhibit type I IFN signaling through a mechanism involving induction of the SOCS-3 protein 19027008_These results suggest that the interaction of SOCS3 with MAP1S and the integrity of the microtubule cytoskeleton play an important role in the negative regulation of SOCS3 on IL-6 signaling. 19036437_Enhanced SOCS-3 gene expression could promote IL-10 production by placental trophoblast cells, suggesting that SOCS-3 may play an important role in regulation of cytokine induced anti-inflammatory response in placental trophoblasts. 19052638_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19052638_There is no strong effect of the common genetic variation within the SOCS3 gene on the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus. 19077438_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19083014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19083014_SOCS3 genetic variants play a role in human obesity. 19115200_SOCS3 is a tumor suppressor in breast cancer cells that is regulated by PRL 19129540_Inhibition of cytokine response by IL-25 occurred via a p38 Map kinase-driven Socs-3-dependent mechanism 19164812_Suppressors of cytokine signaling modulate JAK/STAT-mediated cell responses during atherosclerosis. 19225535_SOCS3 inhibits TPO-induced megakaryocytic proliferation in normal and primary myelofibrosis but not the spontaneous growth in primary myelofibrosis 19229050_SOCS3 tyrosine phosphorylation may be a novel bio-marker of myeloproliferative neoplasms resulting from a JAK2 mutation, JAK2 H538QK539L or JAK2 F537-K539delinsL mutations 19231005_Liver expression of SOCS3 is a stronger baseline predictor of antiviral response than viral genotype in determining response to hepatitis c. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19524687_SOCS3, as negative regulators of cytokine signaling, might maintain homeostasis by regulating multiple signaling pathways and reverse cell malignant behavior. 19543316_SOCS-mediated downregulation of mutant Jak2 (V617F, T875N and K539L) counteracts cytokine-independent signaling. 19592492_a role for SOCS1 and -3 in the seemingly paradoxical hyperresponsive state in cells deficient in IL-18Ralpha, supporting the concept that IL-18Ralpha participates in both pro- and anti-inflammatory responses 19595407_These results suggest that RSV infection escapes the innate antiviral response by inducing SOCS1, SOCS3 or CIS expression in epithelial cells. 19617629_adiponectin augmented the expression of A20, suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) 3, B-cell CLL/lymphoma (BCL) 3, TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 1, and TNFAIP3-interacting protein (TNIP) 3. 19634073_Our results show that androgenic -regulation of SOCS-3 leads to inhibition of prolif-eration and secretion in human prostate cancer. 19643162_The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of SOCS-3 on TNFalpha-induced signalling in beta cells. 19737863_overexpression of SOCS3 in T cells reduces IL-17 and accelerates atherosclerosis. 19803812_interactions between the molecular expression of SOCS3, IRS-1 and phospho-AKT mediated by the genotype 1b virus 19913854_Dysregulation of sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c in livers of morbidly obese women is associated with altered suppressor of cytokine signaling-3. 19951849_findings suggest that overexpression of p-STAT3 (Tyr705) occurs in urothelial carcinoma, and that pathways other than SOCS3 may contribute to its activation in this cancer 20005910_SOCS3 expression was increased in liver from patients with HBV-infection and this correlated with the severity of liver inflammation. 20067961_Saturated fat and carbohydrates, components of the high fat meal, known to induce oxidative stress and inflammation, also induce an increase in LPS, TLR-4, and SOCS3 20130595_Forced expression of SOCS3 and SHP-1 inhibits IFN-alpha signaling in psoriatic T cells. 20136974_Probiotic administration increased expression of SOCS-2 and SOCS-3 in Helicobacter pylori infection to limit inflammatory signaling. 20137421_Up regulation of SOCS1 and SOCS5 expression and down-regulation of SOCS3 and CIS may correlate with the development of a Th1 mediated immune response in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease. 20155426_Deficient expression of SOCS3 is associated with an aggressive phenotype and portends a poor clinical outcome in breast carcinoma. 20231901_SOCS-3 and PIAS-3 upregulation impairs IL-12-mediated interferon-gamma response in CD56 T cells in HCV-infected heroin users 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20335309_SOCS-3 is a novel modulator of FGF-2-regulated cellular events in prostate cancer. 20351777_Hepatitis B virus X protein impairs hepatic insulin signaling through degradation of IRS1 and induction of SOCS3 20372794_SOCS1 and SOCS3 expression attenuates Lck-mediated cellular transformation 20375166_SOCS3 suppresses hepatitis C virus replication in an mTOR-dependent manner. 20398276_Data demonstrate that SOCS proteins are expressed in human melanoma cell lines and their modulation can influence the responsiveness of melanoma cells to IFN-alpha and IFN-gamma. 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20433750_Higher mRNA expression levels of SOCS1, 3, 4 and 7 are significantly associated with earlier tumour stage and better clinical outcome in human breast cancer. 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20478455_results suggest that pro-inflammatory cytokines induced SOCS-3 expression. SOCS-3 induction suggests playing important role in negative feedback, suppressing serious destruction of periodontal tissue through a chemokine-dependent mechanism. 20484656_Interferon-gamma-induced SOCS3 expression leads to inhibition of IL-6-induced signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)3 activation and interleukin (IL)-6-dependent expression of anti-, but not pro-inflammatory, target genes. 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20504769_oral administration of HA900 modulates Th-1-type autoimmune disease and inflammation by up-regulating SOCS3 expression and down-regulating pleiotrophin expression via TLR-4 in intestinal epithelial cells 20588308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20631305_Data suggest that SOCS3 may allow HIV-1 to evade the protective innate immune response within the CNS, allowing the recurrence of viral replication and, ultimately, promoting progression toward HAD. 20673263_Authors detected differential expression of SOCS3 between TB patients and LTBIs, but not between TB patients and NIDs, and decreased expression of SOCS3 in T-cells from LTBIs as compared with NIDs. 20689596_Data propose that EBV protein Zta activates SOCS3 protein as an immune escape mechanism that both suppresses optimal IFNalpha secretion by human monocytes and favors a state of type I IFN irresponsiveness in these cells. 20690084_Data conclude that SOCS-3 polymorphism is not a genetic risk factor for RA in Chinese patients. 20690084_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20717995_SOCS3 hypermethylation may be involved in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer and could identify a tumor subset with an aggressive behavior. 20840058_increased expression in kidney and liver of patients who died of anaphylactic shock 20934424_SOCS1 and 3 may control chemotaxis and adhesion 21029588_SOCS3 expression is reduced in placenta of women with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. 21042758_Insights into the development of applications of SOCS3 gene therapy for lung cancer and, possibly, other human cancers. 21173340_Data suggest that increased plasma soluble gp130/soluble IL-6R/IL-6 ratio and reduced membrane transsignaling gp130 expression could contribute to decreased SOCS-3 expression and subsequent reduction in SOCS-3 antiinflammatory activity in preeclampsia. 21190606_High glucose could produce morphological and ultrastructural changes in renal tubular epithelial cells and induce up-regulation of SOCS-1/3 expression. 21263153_SOCS3 overexpression in K562 cells and in primary erythroid cells recapitulated the growth inhibition induced by Sox6, which demonstrates that SOCS3 is a relevant Sox6 effector. 21275162_Huatan Tongluo Granule upregulates SOCS3 and downregulates TNFa patients with acute cerebral infarction. 21308719_SOCS-3 may be one of proteins which influence ability of TRAIL and resveratrol to cause programmed cell death in prostate cancer. 21325601_Serum amyloid A overrides Treg anergy via monocyte-dependent and Treg-intrinsic, SOCS3-associated pathways. 21337543_found higher levels of SOCS-1/3 mRNA levels in CD4(+) T cells of HIV-infected patients than in healthy controls 21354254_suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 regulates cardiac cell signaling crosstalk, between NF-kappaB and p-STAT3, under hypoxic stress 21360047_Suppressor of cytokine signalling protein SOCS3 expression is increased at sites of acute and chronic inflammation 21385272_Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling (SOCS3) balance controls cytotoxicity and IL-10 expression in decidual-like natural killer cell line NK-92. 21451109_In this study, we describe a unique signaling pathway responsible for the SOCS3-mediated downregulation of proinflammatory cytokines 21478033_SOCS3 influences myoblast differentiation. 21481788_data describe the involvement of IL-6 transsignaling/Stat3/Socs3 in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia progression and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma development 21490101_Our study demonstrates that the alpha-IFN resistance of HCV core mutants is attributable to upregulated overexpression of the cellular interferon signal attenuator SOCS3 and that this upregulation is caused by overexpression of interleukin-6. 21545585_gene expression induced by live non-pathogenic Lactobacillus and Streptococcus 21547863_concurrent strength and endurance training reduces fat mass and serum leptin and the ratio leptin/fat mass without significant effects on vastus lateralis OB-Rb protein expression; training does not increase the basal expression of SOCS3 protein in humans 21590492_our findings suggest that SOCS3 inactivation by promoter hypermethylation is mutually exclusive to EGFR activation in gliomas and preferentially promotes glioma cell invasion through STAT3 and FAK activation. 21734367_SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 can prevent tubulointerstitial fibrosis by inhibiting TEMT, which may be connected with the activation of STAT1 and STAT3 21765854_Eosinophils are able to transcribe and translate SOCS3 protein and can contribute to the regulation of the Th1/Th2 balance through SOCS3 production. 21876460_Deregulated expression of pSTAT3 and SOCS3 might possess potential roles in the development and progression of human cutaneous melanoma. 21892197_The polymorphism rs4969168 within or near the SOCS3 gene has a significant effect in the Han nationality, while rs9892622 was associated with obesity in Uygur and Kazakh nationalities in Xinjiang of China. 21898505_Glucocorticoids interfere with IL-6-induced expression of the feedback inhibitor SOCS3, thereby leading to enhanced expression of acute-phase genes in hepatocytes. 21934357_Epigenetic dysregulation of the SOCS3 gene may interfere with the cellular response to the complex cytokine network thus supporting survival and expansion of multiple myeloma cells. 22075701_SOCS3 transgene expression in immature B cells regulates both the maintenance of the germinal center and IgE affinity maturation during a T cell-dependent immune response. 22084247_a new biological activity for CUEDC2 as the regulator of JAK1/STAT3 signaling and the mechanism by which SOCS3 has been linked to suppression of the JAK/STAT pathway 22093833_SOCS3 is an important factor for lipid metabolism and a potential drug-target for treatment of widespread obesity. 22260693_One important aspect of SOCS-3 functionality is its role as the specificity determinant within an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex which targets cellular substrates for polyubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation. [Review] 22266116_TNF-alpha inhibits insulin signaling by increased phosphorylation of IRS-1(Ser307) and insulin receptor(Tyr960), and by increasing SOCS3 levels, all of which block normal insulin signal transduction. 22294695_keratinocytes have a cell type-specific impaired capacity to up-regulate SOCS3 which may crucially determine the course of chronic inflammatory skin diseases. 22311708_ERK-dependent regulation of transcriptional activity that requires codependent activation of multiple transcription factors within the same region of the SOCS-3 gene promoter. 22342841_SOCS3 bound and directly inhibited the catalytic domains of JAK1, JAK2, and TYK2 but not JAK3 via an evolutionarily conserved motif unique to JAKs. Mutation of this motif led to the formation of an active kinase that could not be inhibited by SOCS3. 22425648_SOCS3 expression in the paraventricular nucleus was inversely related to serum leptin. 22487676_SOCS1 and SOCS3 mRNA and protein expression was significantly increased in the nasal mucosa and mononuclear leukocytes of patients with mild and moderate/severe persistent perennial allergic rhinitis. 22488585_SOCS3 epigenetic silencing was occasionally detected in immunodeficiency-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma. 22532676_IFN-gamma-induced phosphorylation of STAT-1 and transcription of CIITA were suppressed in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-inoculated endothelial cells via a mechanism involving SOCS3 (suppressor of cytokine signaling 3). 22535619_High SOCS3 expression is associated with mucosal relapse in ulcerative colitis. 22547065_Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 inhibits breast tumor kinase activation of STAT3. 22560881_results suggest modulation of SOCS3 expression may represent a novel mechanism through which FXR activation could selectively affect cytokine bioactivity in inflammation response 22574771_review of biology and mechanism of action of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 [review] 22575502_these results demonstrate that in results demonstrate that in human endothelial cells resistin up-regulates SOCS3 expression and activates STAT3 transcription factor. 22576756_both SOCS-3 mRNA and SOCS-3 protein are expressed in human arthritic chondrocytes and affect cellular responses involved in cartilage pathology. 22587677_no significant difference in mRNA expression in adipose and placental tissue obtained from pregnant women with and without gestational diabetes mellitus 22591635_SOCS3 protein is an important regulator of cytokine signaling associated with inflammatory bowel disease and IBD-colorectal cancer[review] 22613986_present study demonstrates that Ang II induces angiogenic factors production partly via AT1/ JAK2/STAT3/SOCS3 signaling pathway in MHCC97H cells 22739025_induction of DNMT1 expression in the chronically inflamed colon may release IL-6 signaling towards signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 from inhibition through SOCS3 increasing the propensity to malignant transformation 22739986_the depletion of SOCS3, as well as the chemical inactivation of PI3K activity in psoriatic keratinocytes, definitively unveils the role of PI3K/AKT cascade on the resistance of diseased keratinocytes to apoptosis. 22745793_The results demonstrate that SOCS1 and SOCS3 each play a functionally distinct role in modulating TLR3, JAK/STAT, and CXCR4/CXCR7 signaling in hMSC. 22768656_High SOCS3 is associated with idiopathic short stature. 22787435_Bcr-Abl may critically requires tyrosine phosphorylation of SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 to mediate tumorigenesis when these SOCS proteins are present in cells. 22820139_Over-expression of SOCS-3 mRNA from peripheral blood of NHL patients correlates with advanced disease and poor response to treatment. 22848642_LPS induces upregulation of MCP-1 in DSCs, which may play a critical role in inhibiting the cytotoxicity of NK cells partly by promoting SOCS3 expression 22925925_SOCS3 is involved in repressing the M1 proinflammatory phenotype, thereby deactivating inflammatory responses in macrophages. 22951153_Obese subjects showed a decreased ability to produce IFN-alpha and IFN-beta in response to TLR ligands; this response was associated with increased basal levels of SOCS3 but not SOCS1. 22957141_Reduced expression of miR122 contributes to decreased SOCS3 expression via promoter methylation. 23028842_SOCS3 functions as a tumor suppressor gene in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma with relevance on proliferation and invasion processes. 23030674_SOCS3 expression is increased in human bladder epithelial cells when stimulated with a uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain. 23033269_Higher SOCS3 expression in human T cells favors T helper type 17 cells. Therefore, increased SOCS3 expression in human tuberculosis may reflect polarization toward IL-17-expressing T cells as well as T-cell exhaustion marked by reduced proliferation. 23046072_results suggested that there is no marked association between SOCS3 gene promoter region polymorphisms and the risk of developing metastatic colorectal cancer 23108375_Using two renal cellular models&SOCS-3 siRNA knockdown,we studied SOCS-3 effects on oncostatin M-induced STAT activation, differentiation and proliferation.SOCS-3 knockdown resulted in enhanced pSTAT1/3 phosphorylation & epithelial diff'n. 23111066_Data indicate that knockdown of HDAC8 resulted in the increased expression of SOCS1 and SOCS3, and overexpression of SOCS1 and SOCS3 significantly inhibited cell growth and suppressed JAK2/STAT signaling. 23133602_In HCV-HIV coinfected patients treated with PegIFNalpha and ribavirin, SVR is associated with IL28B rs8099917 polymorphism; HCV treatment-induced neutropenia and thrombocytopenia are associated with SOCS3 rs4969170 polymorphism 23152563_SOCS3 profoundly enhances Fas signal-induced apoptosis by suppression of NF-kappaB-dependent Bfl-1 expression. 23154639_The colon epithelial cell line Caco-2 was stimulated with interferon gamma, interleukin -4 prostaglandin E(2) to allow correlations between SOCS3 expression with STAT1, STAT6 and cyclic amp signaling. 23164156_Intrahepatic SOCS1/3 mRNA levels are associated with cirrhosis but do not predict virological response to therapy in chronic hepatitis C. 23185530_Myocardial infarction is distinguished by the up-regulation of SOCS3 and FAM20A genes within first days in the vast majority of patients. 23206599_In this review SOCS3 (and PTEN) were found to act as negative regulators in such processes as cytoskeleton assembly and axon regeneration. 23226414_The present study investi | ENSMUSG00000053113 | Socs3 | 164.703212 | 0.485101321 | -1.043642 | 0.16722604 | 38.811683 | 0.0000000004667260864933055753065823775447250321146697160656913183629512786865234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000126277843285654910309812891974594328825531874826992861926555633544921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 109.1861620 | 23.8939368 | 226.1588460 | 48.7756875 |
| ENSG00000184949 | 646851 | FAM227A | protein_coding | F5H4B4 | Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | hsa:646851; | ENSMUSG00000042564 | Fam227a | 18.960094 | 2.696229975 | 1.430944 | 0.45825382 | 9.540013 | 0.0020104026794521847286423277267886078334413468837738037109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0136445961572911975828725772430516371969133615493774414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 24.2346212 | 6.8674593 | 9.0960080 | 2.5797474 | |||||
| ENSG00000185507 | 3665 | IRF7 | protein_coding | Q92985 | FUNCTION: Key transcriptional regulator of type I interferon (IFN)-dependent immune responses and plays a critical role in the innate immune response against DNA and RNA viruses (PubMed:28342865). Regulates the transcription of type I IFN genes (IFN-alpha and IFN-beta) and IFN-stimulated genes (ISG) by binding to an interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE) in their promoters (PubMed:17574024, PubMed:32972995). Can efficiently activate both the IFN-beta (IFNB) and the IFN-alpha (IFNA) genes and mediate their induction via both the virus-activated, MyD88-independent pathway and the TLR-activated, MyD88-dependent pathway. Induces transcription of ubiquitin hydrolase USP25 mRNA in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or viral infection in a type I IFN-dependent manner (By similarity). Required during both the early and late phases of the IFN gene induction but is more critical for the late than for the early phase. Exists in an inactive form in the cytoplasm of uninfected cells and following viral infection, double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), or toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling, becomes phosphorylated by IKBKE and TBK1 kinases. This induces a conformational change, leading to its dimerization and nuclear localization where along with other coactivators it can activate transcription of the type I IFN and ISG genes. Can also play a role in regulating adaptive immune responses by inducing PSMB9/LMP2 expression, either directly or through induction of IRF1. Binds to the Q promoter (Qp) of EBV nuclear antigen 1 a (EBNA1) and may play a role in the regulation of EBV latency. Can activate distinct gene expression programs in macrophages and regulate the anti-tumor properties of primary macrophages (By similarity) (PubMed:11073981, PubMed:12374802, PubMed:15361868, PubMed:17404045). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P70434, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11073981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12374802, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15361868, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17404045, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17574024, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28342865, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32972995}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Innate immunity;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes interferon regulatory factor 7, a member of the interferon regulatory transcription factor (IRF) family. It has been shown to play a role in the transcriptional activation of virus-inducible cellular genes, including interferon beta chain genes. Inducible expression of IRF7 is largely restricted to lymphoid tissue. The encoded protein plays an important role in the innate immune response against DNA and RNA viruses. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2021]. | hsa:3665; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; establishment of viral latency [GO:0019043]; immune system process [GO:0002376]; immunoglobulin mediated immune response [GO:0016064]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; MDA-5 signaling pathway [GO:0039530]; negative regulation of macrophage apoptotic process [GO:2000110]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of interferon-alpha production [GO:0032727]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060340]; regulation of adaptive immune response [GO:0002819]; regulation of immune response [GO:0050776]; regulation of monocyte differentiation [GO:0045655]; regulation of MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0034124]; regulation of MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0034127]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of type I interferon production [GO:0032479]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060337] | 11846980_The structure and function of IRF7 are reviewed 11877397_Stimulation of IRF-7 gene expression by tumor necrosis factor alpha: requirement for NFkappa B transcription factor and gene accessibility 11884139_Preferential binding sites for interferon regulatory factors 3 and 7 involved in interferon-A gene transcription 12374802_acetylation of lysine 92 negatively modulates IRF7 DNA binding 12604599_Interferon regulatory factor-7 synergizes with other transcription factors through multiple interactions with p300/CBP coactivators. 12915551_Interferon regulatory factor 7 regulates expression of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1: a regulatory circuit. 14517278_LPS-TLR4 signaling to IRF-3/7 and NF-kappaB involves the toll adapters TRAM and TRIF. 14747533_herpes simplex virus ICP0 blocks interferon regulatory factor IRF7-mediated activation of interferon-stimulated genes; the RING finger domain of ICP0 is essential for this activity 15265881_LPS & HSV upregulate IRF-7 in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. This depends on NF-kappa B activation. Nuclear translocation of IRF-7 occurs rapidly in response to HSV. Activation of IRF-7 contributes to IFN-alpha production in virus-stimulated PDC. 15308637_IRF-5-and IRF-7-induced innate antiviral response results in a broad alteration of the transcriptional profile of cellular genes 15361868_TLR-mediated IFN-alpha induction requires the formation of a complex consisting of MyD88, TRAF6 and IRF7 as well as TRAF6-dependent ubiquitination. 15664995_there are two distinct mechanisms for the activation of the IRF7 promoter, by IFN and by virus infection 15695821_IRF5 and IRF7 are critical mediators of TLR7 signaling 16237059_LPS-induced B7.1 transcription in human monocytic cells may be regulated by JNK-mediated activation of the IRF-7 transcription factor. 16778376_IRF7 and LMP1 interact with each other, and this may relate to the mechanism whereby LMP1 exerts functional effects in B-lymphocytes 17079482_Transduction of active forms of IRF-3 or IRF-7 differentially modulate the apoptotic and antitumor properties of primary macrophages. 17374731_We show that BRCA1, signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)-1, and STAT2 are all required for the induction of IRF-7 following stimulation with IFN-gamma. 17393359_expression patterns of IRF3 & IRF7 in normal lymph nodes, reactive hyperplastic lymph nodes & pediatric lymphomas; the number of IRF7-positive cells was found to be elevated in the reactive hyperplastic lymph nodes and pediatric lymphoma 17404045_In addition to its defined role in type I interferon stimulation, IRF-7 plays a key role in modulating adaptive immune responses by inducing low molecular mass polypeptide-2 (LMP-2) expression, either directly or through induction of IRF-1. 17522209_Results report a novel immune evasion mechanism of KSHV vIRF3 to block cellular IRF7-mediated innate immunity in response to viral infection. 18227218_PI3K selectively controls type I IFN production by regulating IRF-7 nuclear translocation in human pDCs 18397234_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18397234_Our analyses showed a prominent effect of the IRF-7 nonsynonymous SNPs on the risk of developing cirrhosis. 18505922_epigenetic inactivation of the IFN pathway plays a critical role in cellular immortalization, and the reactivation of IFN-regulated genes by transcription factors IRF5 and/or IRF7 is sufficient to induce cellular senescence 18539711_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18635538_SUMO modification and RIG-I activation are an integral part of IRF3 and IRF7 activity that contributes to postactivation attenuation of IFN production 18710948_TRAF6 and its E3 ligase activity are required for LMP1-stimulated IRF7 ubiquitination. 18987133_This screening demonstrates that LF2 specifically interacts with the central inhibitory association domain of IRF7, and this interaction leads to inhibition of the dimerization of IRF7, which suppresses IFN-alpha production and IFN-mediated immunity. 19017798_efficient IRF7 activation required association with LMP1 CTAR2 in proximity to LMP1 CTAR2 mediated kinase activation sites 19152337_Altogether, these data further highlight the respective functions of IRF-3 and IRF-7 to program apoptotic, immune and anti-tumor responses. 19349300_transient binding of both IRF-3 and IRF-7, accompanied by CBP/p300 recruitment to the endogenous IFN-A gene promoters, is associated with transcriptional activation 19404407_IRF-1, IRF-7, type I IFNs, and STAT1 form a signaling feedback loop that is critical in regulating TRAIL expression in HIV-1-infected macrophages. 19426920_mRNA levels of primary Sjogren Syndrome patients were not up-regulated 19515829_Herpes simplex type 1 infection triggered an IRF-3 and IRF-7-dependent antiviral response. 19858727_In contrast, although expression of IRF-7 was higher in Gr II than in the other groups, there was no statistically significant difference (P > 0.05). 19880818_Smokers after infection with influenza is associated with reduced expression of IRF7 in nasal epithelial cells. 20112359_IRF7/PHRF1 variants in combination with systemic lupus erythematosus-associated autoantibodies result in higher serum levels of IFNalpha 20112359_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20154210_IRF7 is activated upon Chlamydia pneumoniae infection and is crucial for type I interferon-beta expression 20209099_interferon regulatory factor 7C has dual roles in Epstein-Barr virus-mediated lymphocyte transformation 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20381110_The authors show that BRLF1 expression decreased induction of IFN-beta, and reduced expression of IRF3 and IRF7. 20392859_A20 negatively regulates LMP1-stimulated IRF7 ubiquitination and activity in EBV latency. 20483755_IRF3 rather than IRF7 regulates poly (I-C)-induced type I IFN responses in human synoviocytes 20588308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20668674_Results suggest that Ro52-mediated ubiquitination promotes the degradation of IRF7 following TLR7 and TLR9 stimulation. 20689596_EBV infection correlated with a blockage in the activation of JAK/STAT pathway members and affected the level of phosphorylated IFN regulatory factor 7 (IRF7). 20810735_HCV infection enhances STAT1 expression but impairs nuclear translocation of IRF-7 and its downstream molecules. These impairments in the IFN-alpha signaling pathway may, in part, be responsible for establishment of chronic HCV infection. 20844090_These findings demonstrate that the lysine residues of IRF-7 play important roles in mediating IFN synthesis and modulating viral lytic replication. 20943654_analysis of IFN-stimulated response elements (ISREs) that bind to both the IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 (ISGF3) as well as to IFN response factor 7 (IRF7) 20962850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20980251_ORF45 may maintain the IRF-7 molecule in the closed form and prevent it from being activated in response to viral infection 20980500_IRF-7-induced HPV8 transcription in primary keterinocytes. 21084487_Neurovirulence of interferon-resistant rabies virus correlates with the capacity of the virus phosphoprotein to prevent activation of IRF3 and IRF7. 21167895_Study did not find signi fi cant relationships between rs4963128 or rs2246614 of IRF7/KIAA1542 and the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus, differing from a previous study of European women 21360504_The major allele of a nonsynonymous polymorphism, rs1131665 (412Q) in IRF7, confers elevated activation of IRF-7 and predisposes to the development of systemic lupus erythematosus in multiple ethnic groups. 21435390_Cigarette smoke suppresses key plasmacytoid dendritic cells functions upon viral infection by a mechanism that involves downregulation of TLR7 expression and decreased activation of IRF-7. 21632682_IRF7 single nucleotide polymorphism rs1061501 TT genotype and T allele are enriched in Taiwanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and seem to be associated with an increased risk of developing SLE. 21926187_IRF7 region is an anticentromere autoantibody propensity locus in systemic sclerosis 21931555_Vaccinia virus protein C6 inhibits the activation of IRF7 by TBK1- and IKKepsilon-dependent pathways. 21940674_The ubiquitin E3 ligase activity of tripartite motif-containing (TRIM)28 protein is specific to IRF7. 22112518_Reconstruction of the wiring diagram of the modules revealed the presence of hyperconnected hub nodes, most notably interferon regulatory factor 7, which was identified as a major hub linking interferon-mediated antiviral responses. 22140520_TRAF6 can regulate HIV-1 production and expression of IRF7 promotes HIV-1 replication. 22194884_IRF5 and IRF7 are key transcription factors in interferon pathway that determine viral sensitivity of lung cancer cells. 22301143_Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus-activated IRF7 upregulates expression of the BST2 gene independently of interferon signaling. 22433914_None of the IRF7 polymorphisms was associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. 22455868_discuss the association of IRF7 and SLE based on recent understandings to render more information about the mechanisms of IRF7 might perform in 22787218_phosphorylation of IRF7 on Ser477 and Ser479 by IKKepsilon or TBK1 is inhibited by KSHV ORF45 22820642_In over 800 breast cancer patients, high expression of Irf7-regulated genes in primary tumors was associated with prolonged bone metastasis-free survival. 23175366_In the present study, the authors report that enterovirus 71 downregulates IRF7 through the 3C protein, which inhibits the function of IRF7. 23490285_Data indicate that knockdown of IRF-7 expression almost completely diminished the enhancing effect of TLR9 signaling on Foxp3 expression, suggesting that IRF-7 is a downstream molecule of TLR9 signaling. 23535064_Tat interaction with the 2 MAPKK and IRF7 promoters in HIV-1-infected cells and the resulting persistent activation of interferon-stimulated genes, which include inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, can contribute to the increased immune activation. 24275658_MAP3K8 mediates the phosphorylation and repression of IRF3 homodimers to promote greater transcriptional activity through utilization of IRF3:IRF7 heterodimers. 24385435_Interferon regulatory factor (IRF)-3 and -7 are the key transcriptional factors for the induction of IL-28A and IL-28B genes, whereas NF-kappaB is an additional requirement for the induction of the IL-29 gene. 24531619_Viral infection induced DAPK1-IRF7 and DAPK1-IRF3 interactions and overexpression of DAPK1 enhanced virus-induced activation of the interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE) and IFN-beta promoters and the expression of the IFNB1 gene. 24722640_Our results demonstrate for the first time that IRF3 and IRF7 are both involved in inducing TLR4-dependent IFN-beta expression in response to HSV-2 in its primary infected genital epithelial cells 25159465_Inhibition of the IRF3 and IRF7 innate immune pathways in patients with atopic dermatitis with a history of eczema herpeticum might be an important mechanism for increased susceptibility to disseminated viral infection. 25225665_phosphorylation-mediated IRF7 transactivation is controlled by a tripod-helix structure. 25300801_Authors found that knockdown of IRF7 leads to growth inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cells, and restoration of IRF7 by exogenous plasmid correlates with growth recovery of the viral transformed cells. 25476905_In TSC2-deficient angiomyolipoma patient cells, IRF7 is a pivotal factor in the Rheb/mTOR pathway. 25520509_Authors conclude that paramyxoviruses trigger the DNA damage response, a pathway required for MSK1 activation of phospho Ser 276 RelA formation to trigger the IRF7-RIG-I amplification loop necessary for mucosal interferon production. 25680411_our results indicate that IRF7 promotes glioma cell invasion and both chemoresistance and radioresistance through AGO2 inhibition 25814066_These findings suggest that IRF7-dependent amplification of type I and III IFNs is required for protection against primary infection by influenza virus in humans. 25835418_The IRF7 GG genotype associate with Cognitive Decline and Dementia. 25911105_The interaction between AIP and IRF7 is enhanced upon virus infection, and AIP potently inhibits IRF7-induced type I IFN (IFN-alpha/beta) production. 26005050_Data indicate that the type-I interferon master regulator gene interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF7) is only hypomethylated in lupus patients with renal involvement. 26597380_Interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF7) is a direct target of miR-762 and overexpression of miR-762 reduced expression of IRF7. 26608321_IRF7 cleavage by the 3C protease of enterovirus D68 abrogated its capacity to activate type I interferon expression and limit virus replication. 26728228_Bcl6, by interacting with the co-factors NcoR2 and HDAC3, plays a pivotal role in controlling IRF7 induction and antiviral signaling priming. 26761402_Human IRF7 was shown to be essential for interferon type I-dependent protective immunity against primary influenza. (Review) 27434537_We show that IRF-7 siRNA knockdown enhanced LPS-induced IL-10 production in human monocyte-derived macrophages, and USP-18 overexpression attenuated LPS-induced production of IL-10 in RAW264.7 cells. Quantitative PCR confirmed upregulation of USP18, USP41, IL10, and IRF7. An independent cohort confirmed LPS induction of USP41 and IL10 genes 27606466_The adaptor molecule RAIDD coordinates IKKepsilon and IRF7 interaction to ensure efficient expression of type I interferon. 27630164_The MYC is shown to be recruited to the IRF7 promoter region through interaction with nuclear receptor corepressor 2/histone deacetylase 3 for its repression. 27697837_the transcription factor NFATC3 binds to IRF7 and functions synergistically to enhance IRF7-mediated IFN expression in Plasmacytoid dendritic cells. 27733217_IRF7 plays a role in reducing bone metastasis of prostate cancer by IFN-beta-mediated NK activity. 28092673_S100A9 knockdown almost completely abrogated the effects of IRF7 deletion on granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (G-MDSC) development and tumor metastasis. IRF7 represents a novel regulator for G-MDSC development in cancer and may have predictive value for tumor progression. 28342865_KSHV-encoded viral IRF4 interacts with the host IRF7 and inhibits interferon-alpha production. 28712115_our results suggest that expression of IRF7 is one of the metastatic effectors of LMP1 signalling in Epstein-Barr virus-associated nasopharyngeal cancer 28952189_Hypomethylation of the IRF7 promoter might play a role in systemic sclerosis pathogenesis, probably through promoting the IRF7 expression in PBMCs of patients with SSc. 28984602_Results showed that INF-lambda serum concentration was increased in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) carrying the IFNL3 T allele compared to healthy controls (HC). Anti-HSV-1 Ab titers were higher in AD and MCI individuals carrying the IRF7 AA genotype compared to HC. IFNL3 rs12979860 and IRF7 rs6598008 polymorphisms may modulate immune responses against HSV-1 via their effect on the IFN-lam... 29222334_cFLIP appears to bind to IKKalpha to prevent IKKalpha from phosphorylating and activating IRF7. 29361124_IRF3 and IRF7 bind to many interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE)-type sites in the virus-response elements (VREs) of IFN promoters. However, strikingly, IRF5 does not bind the VREs. 29431743_Our findings indicate that the synergism of T cells and sorafenib is mediated via reduced ATF4 expression, causing activation of the IRF7-IL-15 axis in leukemia cells and thereby leading to metabolic reprogramming of leukemia-reactive T cells in humans 29712772_SOCS1/3-mediated degradation of IFN regulatory factor 7 directly regulates TLR7 signaling and type I IFN production in pDCs. 30073840_The findings suggest that HIV-1 may alter AKT phosphorylation to inhibit the translocation of IRF-7 into plasmacytoid dendritic cell nucleus, leading to IFN-alpha suppression, and this may be the reason for IFN-alpha abrogation observed in recently infected HIV patients. 30470758_Ablation of inflammsome components reduces SOCS1 induction, and relieves its inhibition on MyD88-IRF7-dependent-IFN-I signaling, leading to high levels of IFN-alpha/beta production and host survival. 30546090_Upregulation of IRF7 in treated cancer cells promoted resistance to chemotherapy. 30598516_Virus nonstructural proteins directly interacted with and sequestered IRF7 to the inclusion bodies, demonstrating a view in which host innate immunity is suppressed by severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus through host-virus interaction. 30745463_our findings demonstrate that asthma exacerbations in children can be divided into IRF7(hi) versus IRF7(lo) phenotypes with associated differences in clinical phenotypes 30927622_TARBP2 participates in the interaction between IRF7 and TRAF6, thereby suppressing TRAF6-mediated K63-linked ubiquitination of IRF7. 30934842_the silence of the eIF4F complex suppressed the protein level of IRF1 and IRF7 that exert potent antiviral effects against rotavirus infection. 31172279_These findings provide further support for the essential role of IRF7 in amplifying antiviral IFN responses to ensure potent and sustained IFN responses during influenza virus infection in humans. 31775040_IRF-7 Is a Critical Regulator of Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Allergic Airway Inflammation. 31856677_Downregulation of miR-155-5p facilitates enterovirus 71 replication through suppression of type I IFN response by targeting FOXO3/IRF7 pathway. 32084337_A Quantitative Genetic Interaction Map of HIV Infection. 32641587_RAGE impairs murine diabetic atherosclerosis regression and implicates IRF7 in macrophage inflammation and cholesterol metabolism. 33205822_Characterization of distinct molecular interactions responsible for IRF3 and IRF7 phosphorylation and subsequent dimerization. 33325089_M2 macrophages contribute to cell proliferation and migration of breast cancer. 33594613_ERVs-TLR3-IRF axis is linked to myelodysplastic syndrome pathogenesis. 34127522_Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Membrane Protein Interacted with IRF7 to Inhibit Type I IFN Production during Viral Infection. 34389779_Role of interferon regulatory factor 7 in corneal endothelial cells after HSV-1 infection. | ENSMUSG00000025498 | Irf7 | 83.761044 | 0.467832818 | -1.095935 | 0.18947420 | 33.696683 | 0.0000000064410422274468095643317035257479491461296561283234041184186935424804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000001516789540025689811833731679077685861045665660640224814414978027343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 53.4100298 | 6.3735148 | 114.6030081 | 12.3608612 | |
| ENSG00000185614 | 389119 | INKA1 | protein_coding | A0A499FIG1 | Mouse_homologues FUNCTION: Inhibitor of the serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK4. Acts by binding PAK4 in a substrate-like manner, inhibiting the protein kinase activity. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q96EL1}. | Proteomics identification;Reference proteome | Enables protein kinase binding activity and protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of catalytic activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within neural tube development. Located in cytoplasm and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | Mouse_homologues mmu:68176; | nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0030291]; neural tube development [GO:0021915] | 26607847_Inka1 is an endogenous inhibitor of PAK4 that binds to the catalytic domain and forms crystals with PAK4 in cells. 30796022_A competitive in vivo gain-of-function screen identifies C3orf54/INKA1 as a gene regulating leukemia stem cells (LSCs) repopulation kinetics. INKA1 overexpression stalls LSC transiently in G0 without abolishing regenerative potential; silencing has the opposite effect. | ENSMUSG00000042106 | Inka1 | 15.126577 | 2.591192576 | 1.373616 | 0.40303154 | 11.906719 | 0.0005593181755927756175494902635136895696632564067840576171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0046239613712717167123833483799444366013631224632263183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 21.8181509 | 3.2033245 | 8.4618794 | 1.6622412 | |
| ENSG00000185745 | 3434 | IFIT1 | protein_coding | P09914 | FUNCTION: Interferon-induced antiviral RNA-binding protein that specifically binds single-stranded RNA bearing a 5'-triphosphate group (PPP-RNA), thereby acting as a sensor of viral single-stranded RNAs and inhibiting expression of viral messenger RNAs. Single-stranded PPP-RNAs, which lack 2'-O-methylation of the 5' cap and bear a 5'-triphosphate group instead, are specific from viruses, providing a molecular signature to distinguish between self and non-self mRNAs by the host during viral infection. Directly binds PPP-RNA in a non-sequence-specific manner. Viruses evolved several ways to evade this restriction system such as encoding their own 2'-O-methylase for their mRNAs or by stealing host cap containing the 2'-O-methylation (cap snatching mechanism). Exhibits antiviral activity against several viruses including human papilloma and hepatitis C viruses. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19008854, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19416887, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21976647, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23334420}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Innate immunity;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;TPR repeat;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes a protein containing tetratricopeptide repeats that was originally identified as induced upon treatment with interferon. The encoded protein may inhibit viral replication and translational initiation. This gene is located in a cluster on chromosome 10 with five other closely related genes. There is a pseudogene for this gene on chromosome 13. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2012]. | hsa:3434; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; host cell [GO:0043657]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; antiviral innate immune response [GO:0140374]; cellular response to exogenous dsRNA [GO:0071360]; cellular response to type I interferon [GO:0071357]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; intracellular transport of viral protein in host cell [GO:0019060]; negative regulation of helicase activity [GO:0051097]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091]; negative regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045071]; positive regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045070]; regulation of defense response to virus [GO:0050688]; response to virus [GO:0009615] | 12708317_The expression of interferon-induced genes IFI-54K and IFI-56K in the infected cells was found to increase 50-100-fold 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16973618_We observed that, although double-stranded RNA or Sendai virus infection induced the two genes with similar kinetics, their induction kinetics in response to interferon-beta were quite different. 19008854_The authors present evidence that P56 (ISG56 protein), the expression of which is strongly induced by IFN, double-stranded RNA and viruses, mediates the anti-HPV effect of IFN. 19416887_ISG56 is a mediator of negative-feedback regulation of virus-triggered induction of type I IFNs and cellular antiviral responses 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21129252_Expression of ifi56 is enhanced significantly when the differentiation of APL cells was induced by all-trans retinoic acid. 21612406_ISG56 interacts with ribosomal protein L15 in gastric cancer cells. 21642987_IFIT1 bound PPP-RNA antagonizes viruses by sequestering specific viral nucleic acids. 21976647_Hepatitis C virus infection suppresses the upregulation of a subset of effector molecules, including ISG56 and IFITM1. 23052390_Data suggested that PIV5 mRNAs are methylated at the 2'-hydroxyl group and that ISG56/IFIT1 inhibits the translation of PIV5 mRNA by some unrecognized mechanism. Also ISG56/IFIT1 is primarily responsible for the IFN-induced inhibition of PIV5. 23334420_crystal structures of human IFIT5, its complex with PPP-RNAs, and an amino-terminal fragment of IFIT1 23363937_ISG56 may play a role in immune and inflammatory reactions induced by toll-like receptor 3 signaling in human mesangial cells. 23529855_protein expression is inhibited by hepatitis C virus 23684765_TLR4 signaling, induced by LPS, increases the expression of melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) and interferon 23785202_Results indicate that miR-203 is an interferon-inducible miRNA that can negatively regulate a number of cellular mRNAs, including an interferon-stimulated gene target, IFIT1/ISG56, by destabilizing its mRNA transcript. 23867918_Data show that interferon-induced proteins with tetratricopeptide repeats 1 and 2 (IFIT1 and IFIT2) contribute to the regulation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication, likely at both transcriptional and posttranscriptional steps. 24098121_The specificity of IFIT1 for 2'O-unmethylated RNA serves as potent antiviral mechanism against viruses lacking 2'O-methyltransferase activity and at the same time allows unperturbed progression of the antiviral program in infected cells. 25905045_Reovirus T3D infection induced STAT-1, ISG-15, IFIT-1, Mx1, and IFIT-3 expression. 26157117_IFIT1 is not a dominant restriction factor against three different families of negative-sense RNA viruses. 26423178_there is a positive feedback loop between phosphorylated STAT1 and ISG56, ISG54 or ISG60. 26980050_Glioblastoma patients with high IFIT1 and low MGMT expression have an improved prognosis. 27240734_Human IFIT1 and mouse IFIT1B have divergent antiviral specificities: only IFIT1 proteins inhibit a virus encoding a cap 2'O-methyltransferase. 27512068_All the rubulaviruses tested were sensitive to the antiviral action of ISG56/IFIT1. 27589693_Taken together, this study revealed that IFIT1 played an important antiviral role in human cytomegalovirus infected fetal astrocytes. 27707917_IFIT1 significantly inhibited human parainfluenza virus type 3, whereas IFIT2, IFIT3, and IFIT5 were less effective or not at all. 27956805_IFIT1 is involved in the regulation of IFNalpha treatment for chronic hepatitis B and its polymorphism rs303218 can predict the end point virological response. 29554348_IFIT1 and IFIT3 interact through a C-terminal motif. IFIT3 stabilizes IFIT1 protein expression, promotes IFIT1 binding to a cap0 Zika virus reporter mRNA and enhances IFIT1 translation inhibition. 29629559_Induction of IFIT1 in response to H9N2 virus infection or viral particle inoculation was more sensitive in HUVECs than in BEAS-2Bs. Data offers new insight into the innate immune response of endothelial cells to H9N2 virus infection. 30282041_Beyond the well-studied role of cytosolic IFIT1 in restricting viral replication, data demonstrate a function for nuclear IFIT1 in differential transcriptional regulation of separate branches of the LPS-induced gene program. 30626937_A statistically positive correlation of p-EGFR(Y1068) expression with IFIT1 and IFIT3 in OSCC tumors. 30702423_HEV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) binds to IFIT1, thereby protecting the viral RNA from IFIT1-mediated translation inhibition. 31444947_Intrahepatic immune changes after hepatitis c virus eradication by direct-acting antiviral therapy. 31502557_The results uncovered a large ensemble of RNA secondary structures of diverse size and shape in the different viruses, which showed little correspondence to the phylogeny of the viruses. Unexpectedly, the 50UTR of several viral genomes in this family did not fold into any structure, suggesting either their extreme sensitivity to IFIT1 or the existence of alternative viral mechanisms of subverting IFIT1 function. 31977029_IFIT1 and IFITM3 were overexpressed in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and indicated poor prognoses for patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 32363951_ISG56 is involved in CXCL10 expression induced by TLR3 signaling in BEAS-2B bronchial epithelial cells. 32962861_Development of bis-ANS-based modified fluorescence titration assay for IFIT/RNA studies. 34763233_Comprehensive analysis of the prognosis and biological significance for IFIT family in skin cutaneous melanoma. 34791638_IFIT1 modulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. | 27.553886 | 0.333662144 | -1.583540 | 0.29725922 | 29.848501 | 0.0000000467157986855039045271551715731578324763972887012641876935958862304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000009680897659449312448804369699018046446781227132305502891540527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 13.9478111 | 4.6953281 | 42.0007554 | 13.2367922 | |||
| ENSG00000185885 | 8519 | IFITM1 | protein_coding | P13164 | FUNCTION: IFN-induced antiviral protein which inhibits the entry of viruses to the host cell cytoplasm, permitting endocytosis, but preventing subsequent viral fusion and release of viral contents into the cytosol. Active against multiple viruses, including influenza A virus, SARS coronaviruses (SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2), Marburg virus (MARV), Ebola virus (EBOV), Dengue virus (DNV), West Nile virus (WNV), human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) (PubMed:26354436, PubMed:33270927). Can inhibit: influenza virus hemagglutinin protein-mediated viral entry, MARV and EBOV GP1,2-mediated viral entry and SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 S protein-mediated viral entry. Also implicated in cell adhesion and control of cell growth and migration (PubMed:33270927). Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 S protein-mediated syncytia formation (PubMed:33051876). Plays a key role in the antiproliferative action of IFN-gamma either by inhibiting the ERK activation or by arresting cell growth in G1 phase in a p53-dependent manner. Acts as a positive regulator of osteoblast differentiation. In hepatocytes, IFITM proteins act in a coordinated manner to restrict HCV infection by targeting the endocytosed HCV virion for lysosomal degradation (PubMed:26354436). IFITM2 and IFITM3 display anti-HCV activity that may complement the anti-HCV activity of IFITM1 by inhibiting the late stages of HCV entry, possibly in a coordinated manner by trapping the virion in the endosomal pathway and targeting it for degradation at the lysosome (PubMed:26354436). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16847454, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20064371, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20838853, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21177806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21253575, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21976647, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22479637, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22634173, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26354436, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33051876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33270927}. | Antiviral defense;Cell membrane;Immunity;Innate immunity;Lipoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Osteogenesis;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA | Interferon-induced transmembrane (IFITM) proteins are a family of interferon induced antiviral proteins. The family contains five members, including IFITM1, IFITM2 and IFITM3 that belong to the CD225 superfamily. The protein encoded by this gene restricts cellular entry by diverse viral pathogens, such as influenza A virus, Ebola virus and Sars-CoV-2. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2021]. | hsa:8519; | lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of viral entry into host cell [GO:0046597]; negative regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045071]; ossification [GO:0001503]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; response to interferon-alpha [GO:0035455]; response to interferon-beta [GO:0035456]; response to type II interferon [GO:0034341]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060337] | 12926988_LEU13 has a novel role different from that in the inhibition of cell proliferation, involved in IFNA-induced refractoriness of RSa cells to X rays 15661263_IFITM1 expression profiling could be used for molecular classification of CML, which may also predict survival 15808405_Overexpression of 9-27 leads to increased migration and invasiveness by suppressing natural killer cells in gastric cancer 18202764_IFITM1 has a role in cellular sensitivity to CDDP in esophageal cancer 18829488_IFITM1 plays an important role for the invasion at the early stage of HNSCC progression 19304549_The positive expression level of IFITM1 is associated with the progression of the carcinogenetic process in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. 19499152_results revealed that the interaction between IFITM1 and CAV-1 could enhance the inhibitory effect of CAV-1 on ERK activation 20064371_Antiviral effect of IFITM family members on H1N1 influenza, West Nile virus, and Dengue virus 20099975_Down regulation of IFITM1 is associated with cervical squamous cell carcinoma. 20220060_Data show that ULBP1, TFR2 and IFITM1 were associated with increased susceptibility to Vgamma9Vdelta2 T-cell cytotoxicity. 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20428811_Activated IFITM1 is associated with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome polyps. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20838853_IFITM1 was expressed in the five human glioma cell lines, and its expressions were positively correlated with their tumorigenicity 21177806_IFITM1, IFITM2, and IFITM3 inhibit HIV-1 replication through interfering with virus entry. 21253575_IFITM proteins differentially restrict the entry of a broad range of enveloped viruses, and modulate cellular tropism independently of viral receptor expression. 21976647_Hepatitis C virus infection suppresses the upregulation of a subset of effector molecules, including ISG56 and IFITM1. 22609115_The results suggest that the expression of IFITM1 controls the invasiveness and migration of gastric cancer. 22634173_IFITM1 knockdown in human alveolar-derived bone marrow stromal cells was associated with inhibition of Runx2 mRNA and protein expression. 22787204_Introduction of anti-miR-130a in hepatocytes increased IFITM1 expression. Hepatocytes stably expressing IFITM1 reduced HCV replication. Together, these results suggested that HCV infection of hepatocytes upregulates miR-130a. 22996292_This study defines IFITM1 as an interferon-stimulated gene effector with action against HCV entry. 23376165_Although their inhibitory activities were modest when compared to that of tetherin, IFITMs, but not tetherin, directly reduced the expression of HIV-1 proteins including Gag, Vif and Nef. 23720721_Authors show that interferon-induced transmembrane protein 1 (IFITM-1), IFITM-2, and IFITM-3 exhibit a broad spectrum of antiviral activity against several members of the Bunyaviridae family. 24072182_IFITM1 is a potential valuable addition to immunohistochemical panels used in the diagnosis of cellular mesenchymal uterine tumors. 24120510_Results suggest that the g.-1920G>A polymorphism in interferon inducible transmembrane protein 1 (IFITM1) may be associated with susceptibility to ulcerative colitis (UC). 24209773_Schizophrenia subjects with higher IFITM mRNA levels in cortical blood vessels have greater disturbances in cortical GABA neurons suggests that these cell-type disturbances might be influenced by a shared upstream insult that involves immune activation. 24603679_IFITM1 is essential for the formation of functional blood vessels and stabilizes EC-EC interactions during endothelial lumen formation by regulating tight junction assembly. 24676393_IFITM1 could be a novel metastasis-promoting gene that enhances the metastatic phenotype in ovarian cancer via epigenetic transcriptional regulation. 25422070_In virus-producing cells, IFITMs coalesce with forming virions and are incorporated into HIV-1 viral particles. 25464829_Incorporation of IFITM1, IFITM2 and IFITM3 into HIV-1 virions impair viral fusion and spread. 25552713_Host IFITM3,IFITM2 and IFITM1 facilitate morphogenesis of the human cytomegalovirus assembly. 25738301_the importance of the C-terminal region of IFITM1 in modulating the antiviral function through controlling protein subcellular localization. 26259513_Suggest that IFITM1 promotes the aggressiveness of colorectal cancer cells via caveolin-1 signaling. 26354436_propose that the IFITM proteins act in a coordinated manner to restrict HCV infection by targeting the endocytosed HCV virion for lysosomal degradation and demonstrate that the actions of the IFITM proteins are indeed virus and cell-type specific 26884876_High expression of IFITM1 is associated with poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. 26897526_These findings indicate that overexpression of IFITM1 enhances the aggressive phenotype of triple-negative SUM149 IBC cells and that this effect is dependent on STAT2/BRG1 interaction. 27124937_Compared with CD10, IFITM1 has superior performance distinguishing endometrial stroma of adenomyosis from mesenchyma surrounding invasive endometrial adenocarcinoma. 27219333_These results indicate that IFITM1 protein can restrict alphavirus infection by inhibiting viral fusion with cellular membranes. 27221933_Overexpression of IFITM1 is associated with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas. 27268505_IFITM1 and IFITM3 inhibit Zika virus infection early in the viral life cycle. 27552157_Strong ifitm1 Expression in CD4 T Cells in HIV Controllers Is Correlated With Immune Activation 27852071_Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) signature was dysregulated by both loss and gain of function of IFITM1, which was partially reverted by Caveolin-1 (CAV1). 28411130_IFITM1 suppression blocks proliferation and invasion of aromatase inhibitor-resistant breast cancer in vivo by JAK/STAT1-mediated induction of p21. 28511927_The transcriptional regulation of IFITM1, 2 and 3 expression. 29043607_High IFITM1 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis and invasion in Gallbladder Adenocarcinomas 29100522_Inactivated viral particle inoculation increased the expression of IFITM1protein at mRNA and protein levels, and mediated the antiviral state in HUVECs. 29263263_Identification of three distinct mutations that converted IFITM1 or IFITM3 from inhibitors to enhancers of MERS-CoV or SARS-CoV spike protein-mediated entry revealed key structural motifs or residues determining the biological activities of IFITM proteins. 29770536_Using a multi-group heat map from GSE9716 analysis of the GEO database, IFITM1 was determined to be a relevant radioresistance gene. Inhibition of IFITM1 in combination with radiotherapy could, indeed, inhibit oral neoplasm cells. 30025446_These results demonstrate that constitutive upregulation of PITX2/IFITM1 cascade is an intrinsic adaptive mechanism during the pathogenesis of letrozole-resistance, and modulation of PITX2/IFITM1 level using different genetic and pharmacological means would thus have a novel therapeutic potential against letrozole resistance in BCa. 30087232_overexpression of IFITM1, 2 and 3 suppressed entry of CXCR4 and CCR5 tropic viruses; entry of transmitted founder HIV-1 in U87 cells is more sensitive to inhibition by IFITM2 and IFITM3 than by IFITM1 30237526_Silencing IFITM1 expression using siRNA specifically lowered gammaherpesvirus infection of cells at a post binding stage of entry. 30266929_These studies identify a novel role for IFITM1, 2, and 3 in inhibiting HIV replication at the level of translation. 30318841_Using non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines and patient-derived samples, study shows that IFITM1 is essentially required for the progression of NSCLC. IFITM1 depletion resulted in a significant reduction in sphere formation, migration, and invasion of NSCLC cells in vitro. High level of IFITM1 expression is associated with a poor overall survival rate in adenocarcinoma but not in squamous cell carcinoma. 30655323_These findings suggest that the presence of MUC1 and IFITM1 in breast tumors confers a poor prognosis for patients. Also, MUC1 and IFITM1 overexpression drives aromatase inhibitor resistance. 30951861_The data have implications for the function of IFITM1/3 in mediating IFNgamma stimulated protein synthesis including ISG15ylation and MHC Class I production in cancer cells. 31075894_The binding between HBc and BAF200 was of vital importance to HBc mediated downregulation of interferon-induced transmembrane protein 1 (IFITM1) expression. 31079850_In lung adenocarcinoma, IFITM1 was an independent prognostic factor for overall survival. Furthermore, high IFITM1 expression was significantly correlated with decreased overall survival rates in each pTNM stage. 31205947_study revealed the role of IFITM1 as a tumor promoter during lung cancer development and the possible molecular mechanism. 31735710_IFITM1 knockdowns in BeWo trophoblasts increased their spontaneous fusion and allowed fusion in the presence of IFN while also making the cells more susceptible to virus infection. 31792954_IFITM1-IFITM3 are expressed by T cells and are directly involved in adaptive immunity; they regulate CD4+ T helper cell differentiation in a T-cell-intrinsic manner. (Review) 31910882_Epigenetic regulation of IFITM1 expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human mesenchymal stromal cells. 32182730_Topology, Antiviral Functional Residues and Mechanism of IFITM1. 32434425_Knockdown of interferon-induced transmembrane protein 1 inhibited proliferation, induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, and suppressed MAPK signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. 32436195_IFITM1 is a Novel, Highly Sensitive Marker for Endometriotic Stromal Cells in Ovarian and Extragenital Endometriosis. 32668617_Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Protein 1 (IFITM1) Promotes Distant Metastasis of Small Cell Lung Cancer. 32865181_Interferon-induced transmembrane protein 1 (IFITM1) is essential for progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma in an Osteopontin/NF-kappaB-dependent manner. 33270927_Opposing activities of IFITM proteins in SARS-CoV-2 infection. 33332692_Expression of IFN-induced transmembrane protein 1 in glomerular endothelial cells. 34022283_Disrupting interferon-alpha and NF-kappaB crosstalk suppresses IFITM1 expression attenuating triple-negative breast cancer progression. 34319159_IFITM Proteins That Restrict the Early Stages of Respiratory Virus Infection Do Not Influence Late-Stage Replication. 34321474_IFITM proteins promote SARS-CoV-2 infection and are targets for virus inhibition in vitro. 34609520_IFITM1 expression determines extracellular vesicle uptake in colorectal cancer. 34933450_Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Proteins Inhibit Infection by the Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus and the Related Rhesus Monkey Rhadinovirus in a Cell-Specific Manner. 35708622_Differential Leukocyte Expression of IFITM1 and IFITM3 in Patients with Severe Pandemic Influenza A(H1N1) and COVID-19. 35761108_Co-expression of DDR2 and IFITM1 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion and inhibits apoptosis. 36008984_Emergent Role of IFITM1/3 towards Splicing Factor (SRSF1) and Antigen-Presenting Molecule (HLA-B) in Cervical Cancer. 36027039_MiR-504-3p Has Tumor-Suppressing Activity and Decreases IFITM1 Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. | ENSMUSG00000025492+ENSMUSG00000060591+ENSMUSG00000025491+ENSMUSG00000065968 | Ifitm3+Ifitm2+Ifitm1+Ifitm7 | 48.522199 | 0.292295750 | -1.774499 | 0.24472953 | 55.030766 | 0.0000000000001186578100915136197781189680810679694931454586370733750300132669508457183837890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000048031713541522536040733319493278711317246765233335281664039939641952514648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 21.7201835 | 4.2380151 | 74.5144420 | 12.7322942 |
| ENSG00000186026 | 342909 | ZNF284 | protein_coding | Q2VY69 | FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. | DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:342909; | nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] | 16817023_This study reports the cloning and characterization of a novel human zinc finger protein cDNA (ZNF284L) from fetal brain cDNA library. The ZNF284L cDNA is 2223 bp in length encoding a 593-aa polypeptide. | 16.432277 | 0.055795716 | -4.163702 | 1.19999637 | 9.344252 | 0.0022368592265443218262965796583330302382819354534149169921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0148925211141846605689131877170439111068844795227050781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 2.1268664 | 2.7058082 | 22.5454944 | 26.4204178 | |||
| ENSG00000186300 | 148254 | ZNF555 | protein_coding | Q8NEP9 | FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. | Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:148254; | nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 26184877_Identification of ZNF555 as a putative transcriptional factor highly expressed in human primary myoblasts that interacts with the beta-satellite repeats enhancer site and impacts the ANT1 promoter activity in facioscapulohumeral dystrophy myoblasts. | ENSMUSG00000055150 | Zfp78 | 81.437679 | 3.321842693 | 1.731984 | 0.55612110 | 9.042382 | 0.0026379172921653141169195944115699603571556508541107177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0170120733438489692146422527230242849327623844146728515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 69.4150353 | 34.6826793 | 18.9666290 | 9.5219144 | |
| ENSG00000186439 | 10345 | TRDN | protein_coding | Q13061 | FUNCTION: Contributes to the regulation of lumenal Ca2+ release via the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release channels RYR1 and RYR2, a key step in triggering skeletal and heart muscle contraction. Required for normal organization of the triad junction, where T-tubules and the sarcoplasmic reticulum terminal cisternae are in close contact (By similarity). Required for normal skeletal muscle strength. Plays a role in excitation-contraction coupling in the heart and in regulating the rate of heart beats. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:E9Q9K5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22422768}. | Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sarcoplasmic reticulum;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes an integral membrane protein found in skeletal and cardiac muscle. The encoded protein plays a role in skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling as part of the calcium release complex and is required for normal skeletal muscle strength. This protein indirectly links triads and microtubules in skeletal muscle. Mutations in this gene are associated with cardiac arrythmia syndrome and some variants in this gene may be associated with sudden cardiac death. [provided by RefSeq, May 2022]. | hsa:10345; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; junctional membrane complex [GO:0030314]; junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0014701]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0016529]; sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0033018]; sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0033017]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cytoplasmic microtubule organization [GO:0031122]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane organization [GO:0090158]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; heart contraction [GO:0060047]; muscle contraction [GO:0006936]; negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity [GO:0060315]; positive regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction [GO:1901846]; positive regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity [GO:0060316]; regulation of cardiac muscle cell membrane potential [GO:0086036]; regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling [GO:0010649]; regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051279]; regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0010880]; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0014808]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617] | 12659871_gene organization and cloning of the major isoform 17526652_Histidine-rich Ca-binding protein may play a key role in the regulation of SR Ca cycling through its direct interactions with SERCA2 and triadin, mediating a fine cross talk between SR Ca uptake and release in the heart. 19890582_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19890582_The researchers found evidence that TRDN may be a susceptibility or marker gene for IgA nephropathy 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20414141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22422768_Data show that triadin (TRDN) is a new gene responsible for an autosomal recessive form of ctecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT). 25922419_TRDN is a novel underlying genetic basis for recessively inherited Long-QT syndrome. 26196381_Common variants in TRDN and CALM1 are associated with increased risk of sudden cardiac death in patients with chronic heart failure. 26200674_We describe a new family with cathecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) linked to the Triadin gene. 26768964_A compound heterozygous mutation in the triadin gene resulted in a particularly arrhythmogenic phenotype with with cardiac arrest in two siblings. 27562070_CLIMP-63 (also known as CKAP4), is the partner of triadin, is responsible for this association of triads and microtubules. 29126880_The lncRNA TRDN-AS regulates the balance between cardiac and skeletal isoforms of triadin. 31437535_A novel homozygous mutation in the TRDN gene causes a severe form of pediatric malignant ventricular arrhythmia. 34415104_Novel cases of pediatric sudden cardiac death secondary to TRDN mutations presenting as long QT syndrome at rest and catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia during exercise: The TRDN arrhythmia syndrome. 34736417_Association of decreased triadin expression level with apoptosis of dopaminergic cells in Parkinson's disease mouse model. 35862102_Cardiomyocyte-Specific Long Noncoding RNA Regulates Alternative Splicing of the Triadin Gene in the Heart. | ENSMUSG00000019787 | Trdn | 53.609226 | 3.546221135 | 1.826283 | 0.24470134 | 57.302883 | 0.0000000000000373607141155142675575799415486155976293732722259832712552451994270086288452148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000015836414213570108752508783024571395263956075094569087013951502740383148193359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 83.3392644 | 8.7628108 | 23.6193633 | 3.1900494 | |
| ENSG00000186810 | 2833 | CXCR3 | protein_coding | P49682 | FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Receptor for the C-X-C chemokine CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11 and mediates the proliferation, survival and angiogenic activity of human mesangial cells (HMC) through a heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathway (PubMed:12782716). Binds to CCL21. Probably promotes cell chemotaxis response. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12782716}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Receptor for the C-X-C chemokine CXCL4 and also mediates the inhibitory activities of CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11 on the proliferation, survival and angiogenic activity of human microvascular endothelial cells (HMVEC) through a cAMP-mediated signaling pathway (PubMed:12782716). Does not promote cell chemotaxis respons. Interaction with CXCL4 or CXCL10 leads to activation of the p38MAPK pathway and contributes to inhibition of angiogenesis. Overexpression in renal cancer cells down-regulates expression of the anti-apoptotic protein HMOX1 and promotes apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12782716}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: Mediates the activity of CXCL11. | Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Apoptosis;Cell membrane;Chemotaxis;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Sulfation;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a G protein-coupled receptor with selectivity for three chemokines, termed CXCL9/Mig (monokine induced by interferon-g), CXCL10/IP10 (interferon-g-inducible 10 kDa protein) and CXCL11/I-TAC (interferon-inducible T cell a-chemoattractant). Binding of chemokines to this protein induces cellular responses that are involved in leukocyte traffic, most notably integrin activation, cytoskeletal changes and chemotactic migration. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. One of the isoforms (CXCR3-B) shows high affinity binding to chemokine, CXCL4/PF4 (PMID:12782716). [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2011]. | hsa:2833; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; C-C chemokine binding [GO:0019957]; C-C chemokine receptor activity [GO:0016493]; C-X-C chemokine binding [GO:0019958]; C-X-C chemokine receptor activity [GO:0016494]; chemokine binding [GO:0019956]; chemokine receptor activity [GO:0004950]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001937]; negative regulation of execution phase of apoptosis [GO:1900118]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of chemotaxis [GO:0050921]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of execution phase of apoptosis [GO:1900119]; positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051281]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of leukocyte migration [GO:0002685] | 11559369_chemokine/CXCR3 activity 11739530_downregulation following T cell-endothelial cell contact 11966764_Graves' disease is associated with an altered CXCR3 expression in thyroid-derived compared to peripheral blood t lymphocytes 11990865_Expression of CXCR3 on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells was significantly reduced after 3 months of interferon beta-1a treatment in multiple sclerosis. 12016104_These findings suggest that the CXCR3/CXCL10 axis may be involved in the T cell recruitment that occurs in peripheral airways of smokers with COPD and that these T cells may have a type-1 profile. 12070001_Most Natural killer t-cells express receptors for extralymphoid tissue or inflammation-related chemokines (CCR2, CCR5, and CXCR3), while few NKT cells express lymphoid tissue-homing chemokine receptors (CCR7 and CXCR5). 12097412_Expression of CXCR3 ligands (MIG, IP-10, and ITAC) in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of transplantation recipients is associated with persistent recruitment of mononuclear cells, a pivotal event in the pathogenesis of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome. 12270371_Gene expression is predictive for the individual response of children with chronic allograft nephropathy to mycophenolate mofetil. 12356205_Significant increase in surface CCR5 in CD4+, CD8+, CD19+ and CD14+ cells as well as an increased percentage of CXCR3 and CXCR4 in CD14+ cells in MS patients. 12444109_migration of murine and human IFN-producing cells to CXCR3 ligands in vitro requires engagement of CXCR4 by CXCL12 12517959_Activation of the CXCR3 receptor in proximal tubular cells might disturb natriuresis during inflammatory and ischemic kidney disease via early growth response gene-1-mediated imbalance of reactive oxygen species. 12688353_CXCR3-Mig-coexpressing lymphoma cells were abundant in high MALT of the stomach and thyroid, but rare in other subtypes 12750173_CXCR3-targeting chemokines control T-cell migration via PTX-sensitive, phospholipase C pathways and phosphatidylinositol kinases other than class I PI3Kgamma. 12782716_alternatively spliced variant of CXCR3 mediates the inhibition of endothelial cell growth 12819030_Data suggest that in oral lichen planus, the presence of CCL5 and CXCL10 in the cytolytic granules of tissue-infiltrating CD8(+)T cells expressing CCR5 and CXCR3 reveals a potential self-recruiting mechanism involving activated effector cytotoxic T cells 12884299_eosinophil responses mediated by chemokines acting at CCR3 may be regulated by two distinct mechanisms: the antagonistic effects of CXCR3 ligands and the sequestration of CCL11 by CXCR3-expressing cells 12919091_Targenic of cxcr3 and/or ICOS may have clinical application in the prevention and treatment of chronic allograft nephropathy. 12953097_Ligands control plasmacytoid dendritic cell responsiveness to the constitutive chemokine (SDF-1)/CXCL12. 12960247_In vitro chemotaxis induced by this chemokine is not necessarily predictive of its in vivo lymphocyte-recruiting activity. 12960302_CXCR3 functions broadly--on recently activated as well as fully differentiated CD4+ T cells and on cells that participate in the germinal center reaction as well as on those that infiltrate peripheral inflammatory sites. 14578618_In restinosis, increased plasma concentrations of IP10 were accompanied by a compensatory decrease in the CXCR3 expression on lymphocytes, but not monocytes, suggesting that a high plasma concentration of IP10 strongly induces monocytes signaling. 14618028_Data demonstrate a significant age-dependent difference in the response of osteoblasts to CXCR3 and CXCR5 activation. 14657006_CXCR3-ligation preferentially augments ongoing Th1 over Th2 responses and suggest that reduced capacity of allergic individuals to respond to CXCR3 ligands promotes the maintenance of human allergic disorders 14742268_interstitial CXCR3 may play an important role during progressive loss of renal function 15126579_Mig and IP-10 may be involved in the recruitment of natural killer cells or other phenomena in the human endometrium. 15150261_Intracellular domains of CXCR3 mediate CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11 function 15155273_autocrine activation of CXCR3 expressed by epithelial cells may contribute to airway inflammation and remodeling in obstructive lung disease by regulating cell migration. 15181567_plays an important role in lymphocyte trafficking to CSF during HIV-1 infection 15254596_CXCR3-deficient mice demonstrated increased mortality with progressive interstitial fibrosis, and a reduced early burst of IFN-g, upon injury. CXCR3 deficiency results a deficiency in lung NK cells. 15265234_The CXCR3 ligands IP-10/CXCL10 & Mig/CXCL9 revealed a proproliferative effect but did not influence apoptosis of mesangial cells, suggesting involvement in processes involved in renal inflammation, regeneration and glomerular homeostasis. 15328188_CXCR3 and CCR4 were heterogeneously expressed in peripheral T-cell lymphomas. 15501397_CXCR3 is the principal inflammatory chemokine receptor involved in Behcet's disease 15528361_A splice variant of CXCR3 despite its severe structural changes still localizes to the cell surface and mediates functional activity of CXCL11. 15578697_LMP1-mediated p38/SAPK2 activation induces expression of the chemokine IP-10 and regulates transcript stability 15687242_Once induced in memory B cells, CXCR3 expression remains part of the individual cellular memory 15713799_studies suggest that IRBP and S-Ag can initiate innate and, in sensitive individuals, adaptive immune response by attracting iDCs and T and B cells expressing CXCR3 and CXCR5 15725351_These data indicate that IFN-gamma mediates the recruitment of lymphocytes into the lung via production of the chemokine CXCL10, resulting in Tc1-cell alveolitis and granuloma formation. 15808644_Marked up-regulation of IP-10 may predict the initial graft injury and the onset of delayed graft function in kidney transplantation. 15843529_CXCR3/IP-10 signaling is associated with the pathogenesis of human myasthenia gravis. 15856455_recruitment of T cells expressing Cxcr3 into the invasive margin of colorectal cancer. 15879427_These results suggest that inhibition of the CXCL10/CXCR3 axis offers a novel target for the treatment of asthma. 15885315_Expression of chemokine receptor CXCR3 mediates the selective accumulation of memory CD4+ T-cells into the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neuroborreliosis. 16033640_These data suggest that the regulation of the CCL2 and CXCL10 expression exhibit significant differences in their mechanisms, and also demonstrate that the alveolar epithelium contributes to the cytokine milieu of the lung. 16034118_CXCR3 plays an important role in controlling inflammation of the central nervous system in transgenic mice during intracerebral infection with noncytolytic lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus 16043121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16043121_Our findings suggest that polymorphisms in CXCR3 might be one of the genetic factors for the risk of asthma development, especially in male atopic subjects. 16127166_Activation of CXCR 3 promotes lymphocyte adhesion and transendothelial migration under flow. 16243485_The frequency of CXCR3-expressing cells in peripheral blood is significantly higher in primary biliary cirrhosis, and CXCR3-positive cells are also found in the portal areas of diseased livers, primarily on CD4-positive T cells. 16339779_Activation of CXCR3 exerts a mitogenic effect in human bronchial epithelial cells. 16368892_CXCL11-dependent CXCR3 internalization and cell migration are regulated by the CXCR3 membrane proximal carboxyl terminus, whereas adhesion is regulated by the 3i loop S245. 16455991_demonstrate an intimate functional relationship among CD4, CCR5, and CXCR3, in which CCR5 can act as an adaptor molecule for CD4 signaling 16456020_epithelial CXCR3 may be involved in postsecretion regulation of chemokine bioavailability 16679918_Patients who had a combined BM relapse had lower IL-8 and CXCR4 expression than those who had an isolated BM relapse om chldhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 16733654_Double immunofluorescense staining demonstrated that cellular sources of MCP-1/CCL2 and IP-10/CXCL10 were hypertrophic astrocytes and that both astrocytes and microglia/macrophages expressed CCR2 and CXCR3. 16787707_IP-10 does not seem to be a risk factor for Alzheimer disease, but a novel rare polymorphism has been identified, which could exert a role in susceptibility. 16847335_Data demonstrate that chemokine activation of CXCR3 involves both high-affinity ligand-binding interactions in the extracellular domains of CXCR3 and a lower-affinity receptor-activating interaction in the second extracellular loop. 16861617_These results together indicate that the expression of CXCR3 is up-regulated on intermediately differentiated memory CD8+ T cells. CXCR3high CD8+ T cells had a greater ability to migrate in response to CXCR3 ligands than CXCR3low ones. 16930533_analysis of human CXCR3 receptor agonists 16934957_These results indicated that CXCL10 inhibited LNCaP cell proliferation and decreased PSA production by up-regulation of CXCR3 receptor. CXCL10 may be potentially useful in the treatment of prostate cancer. 17018607_Activation of Ras plays a critical role in modulating the expression of both CXCL10 and CXCR3-B, which may have important consequences in the development of breast tumors through cancer cell proliferation. 17142783_most circulating human CD4+ T cells store the inflammatory chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CXCR1 within a distinct intracellular compartment 17142784_CXCR3 was expressed in EEC, ESC, and trophoblast cells. Addition of IFN-gamma to EEC increased the chemotactic activity of its culture medium to trophoblast cells and T cells, and the effect was suppressed by Abs of three CXCR3 ligands 17251291_mutant receptor (CXCR3[K300A, S304E]) showed markedly enhanced HIV coreceptor function compared to the wild-type receptor (CXCR3[WT]) 17339184_Low expression of CXCR3 by blood CLL B cells was a clear, independent predictor of death, suggesting that low CXCR3 expression has a role in the invasive capacity and progression of this tumor. 17363734_CD13 rapidly processed CXCL11, but not CXCL8, to generate truncated CXCL11 forms that had reduced binding, signaling, and chemotactic properties for lymphocytes and CXCR3- or CXCR7-transfected cells. 17457216_CXCR3 expression on mononuclear cells and CXCR3 ligands in renal cell carcinoma is increased in response to systemic IL-2 therapy 17560677_In chronic hepatitis C, anti-viral treatment induces an increase in CD8+ cells expressing chemokine receptors. Viral control is associated with an increase in CXCR3(high) expressing CD8+ cells during treatment. 17615381_T cells expressing CCR6, CXCR3, and CXCR6 act coordinately with respective ligands and Th1 inflammatory cytokines in the alveolitic/granuloma phases of the disease. 17666357_an important role of CXCR3 in the development and progression of atopic dermatitis 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17912012_CXCR3 was expressed strongly at the acinar cell membrane in chronic pancreatitis as compared to normal 17947699_IKK2 is also involved in the IFN-gamma-stimulated release of the CXCR3 ligands through a novel mechanism that is independent NF-kappaB 18037659_In clinically inflamed dental pulp, CXCR3 expression was observed mainly on T-cells. 18174362_Human chemokine receptor CXCR3 (CXCR3-B) transduces apoptotic but not chemotactic signals in microvascular endothelial cells following exposure to high concentrations of CXCL4. 18280341_CXCR3 ligand-mediated lymphocyte recruitment is involved in cutaneous lichenoid graft-versus-host disease. 18291705_Aim of this study was to elucidate the effects of CXCR3-B on activation of members of the mitogen-activated protein kinase family, and to explore the relevance of defined signaling pathways to the angiostatic effects of CXCR3-B ligands. 18375741_CXCR3 receptor is expressed by human type II pneumocytes, and the CXCR3-A splice variant mediates chemotactic responses possibly through Ca(2+) activation of both mitogen-activated protein kinase and PI 3-kinase signaling pathways. 18453591_the activities of CXCR3 are tightly controlled following mRNA translation. such tight regulation of CXCR3 may serve as a control to avoid the unnecessary amplification of activated T lymphocyte recruitment. 18485912_Gliadin binds to CXCR3 and leads to MyD88-dependent zonulin release and increased intestinal permeability 18497951_Expression of CXCR3 was significantly associated with lymph node metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma 18616679_We showed that CXCR3 expression was an independent predictive factor for non-responsiveness to H. pylori eradication therapy in patients with gastric MALT lymphoma. 18689270_study revealed that surface expression of the chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CCR5 on CD4+ T cells were increased markedly in patients with active SLE more than SLE patients in remission and the healthy subjects 18729739_IFN-alpha2b possibly controls chemotaxis by regulating the interaction between CXCL10 and CXCR3A 18761554_Lymphocytes from Crohn's disease patients express a spliced variant of the CXCR3 receptor and suggest a role for the colonic epithelial cells in T-lymphocyte migration in intestinal inflammation. 18798334_CXCR3-associated chemokines may play an important role in the development of necroinflammation and fibrosis in the liver.parenchyma in chronic hepatitis C infection. 18832436_Calcineurin inhibitors modulate CXCR3 splice variant expression and mediate renal cancer progression 18962861_rs2280964A allele significantly correlates with decreased CXCR3 gene expression, which would lead to variation in immune cell responses to chemokine-cytokine signals in vitro and ex vivo that includes a decrease in chemotactic activity. 19017998_infiltrated neutrophils from patients with chronic inflammatory lung diseases and rheumatoid arthritis highly express CCR1, CCR2, CCR3, CCR5, CXCR3, and CXCR4 19106589_ratio of CCR4+/CXCR3+ cells was 4.45 in chemotherapy and 0.72 in immunotherapy 19134328_The interactions between CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL12 expressed in decidua and villi and CXCR3, CXCR4 expressed in CD(56)(+) decidua NK cells may influence the CD(56)(+)NK cell recruitment at the maternal-fetal interface. 19232748_Inhibition of CXCR3/IP-10 signaling can be considered as a potential treatment modality for myasthenia gravis. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19344719_Report antifibrotic effects of CXCL9 and its receptor CXCR3 in livers of mice and humans. 19380511_investigated CXCR3-mediated neuronal injury, particularly, its contribution to autophagy suppression and the concomitant effects of antiretroviral therapy 19539215_Recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor significantly decreases the expression of CXCR3 and CCR6 on T cells and preferentially induces T helper cells to a T helper 17 phenotype in peripheral blood harvests 19641142_CXCL10 secreted from beta-cells activates and attracts autoreactive T-cells and macrophages to the islets via CXCR3 in type 1 diabetes. 19703720_Adhesion of haematopoietic stem cells to liver compartments is integrin and CD44 dependent and modulated by CXCR3 and CXCR4. 19734217_A large portion of infiltrating CD4-positive T cells from lupus nephritis patients express CXCR3 on their surface, whereas no significant CXCR3 positivity is seen on resident kidney cells. 19735481_that the chemokine receptors CXCR1, 3 and 4 modulate some aspects of ASM function but their importance in asthma is uncertain. 19758167_Experimental and clinical evidence support the idea that the CXCR3 pathway is involved in the development of autoimmune diseases. 19767105_Stimulation of both CXCR3 and the T cell receptor has the potential to enhance specifically both the proliferation and extravasation of specific T cells during episodes of local inflammation. 19800124_The three-dimensional structure of CXCL9 and CXCR3, and, successively, of the CXCL9/CXCR3 complex were modelled in comparison to CXCL10/CXCR3 and CXCL11/CXCR3 complexes. 20041963_CXCL10 induces cell death in human cultured pancreatic cells leading to apoptosis and DNA fragmentation via CXCR3 signalling 20047517_decreased frequency of the M280 allele is an independent risk factor for carotid atherosclerosis in northern China 20059481_Insulitic lesions were characterized by presence of beta cells, elevated levels of the chemokine CXCL10 and infiltration of lymphocytes expressing the corresponding chemokine receptor CXCR3 in all pancreatic lesions of type 1 diabetes patients 20079227_The intensity of IL-16 and CXCR3 expression were correlated with the index of clinical and pulmonary function in COPD. 20096889_There is over expression of genes related to immune and inflammatory responses, including cytokines such as CXCR3 binding chemokines in interstitial cystitis 20164417_Liver-infiltrating regulatory T lymphocyte(Treg)s use CXCR3 to undergo transendothelial migration across hepatic sinusoidal endothelium into inflamed sites during chronic and autoimmune liver disease. 20185576_CXCR3 signaling has a role in basal cell carcinoma [commentary] 20203286_the absence of CXCR3(-/-) signaling network results in hypertrophic and hypercellular scarring characterized by on-going wound regeneration, cellular proliferation, and scars 20228225_CXCR3 and its ligands may be important autocrine and/or paracrine signaling mediators in the tumorigenesis of basal cell carcinomas 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20377416_The CD27(+) B-cell population was found to highly express CXCR3 in chronic hepatitis C (CHC), thus suggesting that the CD27(+) B-cell population was recruited from peripheral blood to the inflammatory site of the liver of CHC. 20379873_The expression of CXCR3 and its atypical variants at both mRNA and protein levels, was examined. 20429924_Above median expression of CXCR2, CXCR3 and CCR1 in the tumour islets is associated with increased survival in non-small cell carcinoma, and expression of CXCR3 correlates with increased macrophage and mast cell infiltration in the tumour islets. 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20529825_The expression and function of CXCR3 and CXCR7 receptors in cervical carcinoma, rhabdomyosarcoma and glioblastoma cell lines, was evaluated. 20733031_reveal a CXCR3-dependent accumulation and activation of perivascular macrophages as a necessary step in homeostatic arterial remodeling triggered by hemodynamic stress in mice and possibly in humans as well. 20848514_this study provides evidence of the significant overexpression of the CXCR3 axis in active IBD, suggesting it has a role in IBD pathogenesis. 20855888_Down-regulation of CXCR3-B is associated with renal cancer. 20856926_CXCL10 inhibits endothelial cell proliferation independently of CXCR3. 20980681_both CXCR3A and CXCR3B are implicated in the chemotactic and vascular effects of CXCL4L1. 21051441_CXCR3 antagonism exerts a direct anti-glioma effect and this receptor may be a potential therapeutic target for treating human glioma. 21087446_Increased numbers of immature plasma cells may migrate towards inflammatory sites of ulcerative colitis (UC) via the CXCR3 axis, and may participate in UC pathogenesis. 21091908_suggesting that gliadin-induced IL-8 production was CXCR3-dependent gliadin induced IL-8 production only in coeliac disease 21148743_expression of CXC chemokine receptor 3 is reduced with continuous exposure to asbestos in a human T-cell line, MT-2 21255008_Results demonstrated the expression of CXCR3 as well as of two of its known variants, CXCR3-B and CXCR3-alt, in ex vivo activated T lymphocytes. 21303425_Suggest that the renal TWEAK/Fn14 and IP-10/CXCR3 axis may contribute to the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. 21303517_These results show that while the expression of MIG/CXCL9 and IP-10/CXCL10 are elevated in Systemic sclerosis (SSc) serum, the expression of CXCR3 is downregulated on SSc dermal Endothelial cells. 21357438_Suggest decreased CXCR3 expression in CD4+ T cells exposed to asbestos or derived from asbestos-exposed patients may contribute to reduced antitumor immune function. 21426802_CXCR3 was up-regulated in breast cancer and was associated with disease progression. 21538345_Results demonstrate that the peripheral homing receptor CXCR3 is expressed on subset(s) of circulating Tregs and suggest a role for CXCR3 in their recruitment into peripheral sites of inflammation. 21645215_CXCR3 ligands, CXCL9,10,11, are differentially expressed during chronic liver diseases across different disease stages and aetiologies. 21739422_CCR4-, CCR5-, CXCR3-, and selectin ligand-expressing CD4+ T cells preferentially accumulate in the joints of children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 21811993_We describe and characterize a new autocrine/paracrine role of CXCL10/CXCR3 in the regulation of fibroblast-like synoviocyte invasion in rats with arthritis and in rheumatoid arthritis patients. 21962843_Elevated plasma levels of interferon-gamma and Cys-X-Cys chemokine receptor 3-binding chemokines are present in patients with thoracic aortic aneurysms. 22079021_The data supported a role for CCR5, CXCR3, and CXCR6 in the selective recruitment of T cells into renal cell carcinoma tissue and, together with CCR6, in the recruitment of regulatory T cells. 22111598_CD8(+) lymphocytes from HIV/HCV-infected patients expressed more CXCR3 and showed greater upregulatory ability upon activation. 22236567_aberrant expression of CXCR3A and down-regulation of CXCR3B may switch a progression 'stop' to a 'go' signal to promote prostate tumor metastasis via stimulating cell migration and invasion. 22262158_Chemokine gene-expression patterns were consistent with an angiogenic-angiostatic imbalance and a downregulation of CXCR3 receptor-mediated signaling in the PCs from obese subjects. 22369302_CXCR3 expression was associated with epidermotropic T cell tumors but was greatly absent in dermal ones. Scattered or diffuse CD30 expression in transformed mycosis fungoides was not associated with an absence of CXCR3 expression. 22392992_CXCR3 agonist induces receptor cross-phosphorylation within CXCR3-CCR5 heterodimers on the surface of activated T cells 22401929_high level of CXCR3 protein expression was significantly associated with tumor differentiation, tumor size, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, and Dukes' classification in patients with colorectal carcinoma 22675496_The chemokine CXCL12, its truncated form SDF-1(5-67), and the receptors CXCR4 and CXCR3 are expressed in human glaucomatous trabecular tissue and a human trabecular cell line. 22685032_CXCL10 and CXCR3 were upregulated in colonic mucosa in active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The TLR3-ligand poly(I:C) increased release of CXCL10 in colonic epithelial cell lines, suggesting a TLR3-mediated CXCL10 release in IBD patients. 22689289_Both CXCR3 and CXCR4 are involved in metastasis of colorectal cancer to lymph nodes, lungs and liver. 22792160_Intra-hepatic accumulation of the functionally impaired CXCR3(+)CD56Bright NK cell subset might be involved in HCV-induced liver fibrosis. 22796894_CXCR3 promotes recruitment of Th17 cells from the blood into the liver in both human and murine liver injury. Their subsequent positioning near bile ducts is dependent on CCR6 and cholangiocyte-secreted CCL20. 22798340_natural CXCR3(+) T-bet(+) Treg selectively accumulate in ovarian tumors to control type I T-cell responses, resulting in the collateral limitation of efficient antitumor immunity. 22936405_Protein nitration was required for CXCR3 receptor up-regulation by cigarette smoke and for CXCR3-induced cell death. 23121557_Data suggest that co-expression of CCX-CKR (atypical chemokine receptor 4) and CXCR3 in T-lymphocytes results in protein multimerization and prevents CXCR3-mediated chemotaxis; this represents a novel mechanism of regulation of immune cell migration. 23158864_CXCR3 expression was higher in immune thrombocytopenic purpura patients (prior to treatment and in remission) than in healthy controls. 23179902_Bortezomib significantly decreases CXCR3 expression on T cells & their CD4(+)/CD8(+) subsets in a dose-dependent manner. 23298254_Data indicate that women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) responded similar to pregnancy as did healthy women with lower percentages of CCR2+, CCR5+ and CXCR3+ monocytes. 23600831_CXCR3 expression on CD4(+) T cells was fivefold higher in those from CSF than blood, but was not increased in paediatric opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome. 23643635_Upregulation of CXCR3 expression on CD8+ T cells due to the pervasive influence of chronic hepatitis B and C virus infection. 23773308_CXCR3, CXCR4, CXCR7 have similar transmembrane helices, different conformations of N-terminal, C-terminal regions and extracellular loops, and interaction between the three receptors and CXCL11 and CXCL12 are on a hydrophobic and electrostatic basis. 23994383_Post-transplant enhanced CXCL10/CXCR3 signaling in small-for-size liver grafts directly induced endothelial progenitor cell mobilization 24124129_plays a role in insulin resistance and obesity-induced visceral adipose inflammation 24129241_CCR5-Delta32 polymorphism and CXCR3/CCR5 underexpression influence downregulation of the corresponding receptors in TILs. 24135023_Pericytes regulate angiogenic vessel formation, and this is mediated through CXCR3 expressed on endothelial cells. 24318111_Both EMAP II and CXCR3 were essentially required for gp120-induced lung microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis. 24366869_CXCR3-B mediates a growth-inhibitory signal in breast cancer cells through the modulations of nuclear translocation of Bach-1 and Nrf2 and down-regulation of HO-1. 24526602_CXCR3 interacts with CXCL11 on brain microvascular endothelial cells. 24530757_The CXCR3 polymorphism rs34334103 was associated with male gender and pleuritis in patients with SLE. 24586509_the participation of the chemokine CXCL10/CXCR3 axis in celiac disease pathogenesis 24715380_We show here for the first time that CXCL10 and CXCR3 expression are both predictors of favorable outcome in patients treated with tamoxifen. 24890729_interfering with IL-1beta and IL-12 signaling in Th17 cells during inflammation may be a promising therapeutic approach to reduce their differentiation into 'pathogenic' CCR6+ CXCR3+ Th1/17 cells in patients with autoimmune diseases. 24907118_Report crosstalk between TGF-beta1 and CXCR3 signaling in the regulation of urethral fibrosis. 24999582_CXCR3 role in autoimmune thyroiditis [review] 25013801_Higher percentages of CCR4+ CD4 TEM cells in acute RSV infection were accompanied with higher percentages of CXCR3+ CD8 TEM cells, whereas the development of long-lived memory CXCR3+ CD4 and CD8 TCM cells seems to be compromised 25178112_The different groups of clinically stable nonallergic asthmatic patients showed distinct patterns of alterations in subset distribution as well as CCR6, CXCR3, and CCR5 expression on circulating T lymphocytes. 25232565_CXCR3 has been demonstrated to be strongly related to tumour progression in advanced colorectal cancer. 25514189_Expression of CXCR3 in fibroblasts is associated with the expression of IL-13Ralpha2. 25527046_High expression of CXCR3 is associated with glioblastoma patients with an invasive phenotype. 25537642_Targeting of both CXCR3 isoforms may be important to block the stem cell-promoting actions of CXCR3-B, while inhibiting the pro-proliferative and metastasis-promoting functions of CXCR3-A. 25663474_CXCR3-A, the predominant form in hematopoietic cells, mediates tumor 'go' signaling by promoting cell proliferation, survival, chemotaxis, invasion and metastasis; while CXCR3-B, on epithelial cells, mediates 'stop' signaling 25760840_CXCR3 and IP-10 are involved in the pathogenesis of bronchiolitis, and CXCR3 is associated with allergic factors. 25768944_CD4+ T cells demonstrated markedly decreased CXCR3 expression. 25858769_Common variants of CXCR3 and its ligands CXCL10 and CXCL11 are associated with vascular permeability of dengue infection in peninsular Malaysia. 26037167_The expression of the chemokine receptors CXCR3, CXCR4 and CXCR7 and their ligands. 26164305_This study is aimed at the optimization of a new analytical method for metabolic profiling with parallel bioaffinity assessment of CXCR3 ligands of the azaquinazolinone and piperazinyl-piperidine class and their metabolites. 26209629_Results indicate that CXC chemokine receptors 3 (CXCR3) contributes to spontaneous preterm birth (SPTB). 26275313_Speculate that aberrant expression of CXCR3 in marginal zone lymphoma of the skin is associated with migration of lymphoma cells to the epidermis and could lead to an epidermotropic pattern. 26339376_Suggest that aberrant CXCR3 expression may play crucial roles in suppressing prostate carcinoma metastasis by inhibiting cell proliferation and invasion through the PCLbeta signaling pathway. 26394162_CXCR3 was also linked to steatosis through inducing hepatic lipogenic genes 26434630_our study suggested a potential use of CXCR3 overexpression as a prognostic marker for gastric cancer 26506526_congruent with the concept that inflammation plays a key role in the pathogenesis of LV dysfunction, MIG, IP10 and I-TAC add diagnostic accuracy over and beyond NT-pro BNP. 26589908_CXCR3 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells was a strong determinant of a worse clinical outcome. 26732675_CD4(+)CXCR3(+) T cells are highly enriched in the inflamed mucosa of intestinal bowel disease patients. 26801009_The CXCL10/CXCR3 axis mediates T-cell recruitment into the skin in progressive vitiligo. Blocking this chemotactic mechanism may present a new form of therapy. 26823797_CXCR3 expression was upregulated in advanced gastric cancer and was associated with increased CD4+, CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte infiltration and improved overall survival 26831417_Both CXCL10 and CXCR3 appeared to be useful in differentiating T1R reaction in borderline leprosy while CXCR3 alone differentiated BT from BT-T1R 26883105_Alternatively spliced variant of CXCR3 mediates the metastasis of liver cancer. 26965295_monocytes and lymphocytes cooperate to enhance migration towards CXCR3 chemokines and CCL5 in COPD 27273823_Our result showed that CXCR2 expression was correlated with high grade (P = 0.024), advanced stage (P = 0.029) and metastasis (P = 0.018). The log-rank test revealed that high CXCR2 and CXCR3 expressions are related to poorer overall survival (P | ENSMUSG00000050232 | Cxcr3 | 17.105841 | 0.486789213 | -1.038631 | 0.36621197 | 8.199678 | 0.0041897821215832724978112011626762978266924619674682617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0247389921134262627533395573209418216720223426818847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 11.3973136 | 3.4087652 | 23.5238486 | 6.4766279 | |
| ENSG00000186891 | 8784 | TNFRSF18 | protein_coding | Q9Y5U5 | FUNCTION: Receptor for TNFSF18. Seems to be involved in interactions between activated T-lymphocytes and endothelial cells and in the regulation of T-cell receptor-mediated cell death. Mediated NF-kappa-B activation via the TRAF2/NIK pathway. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. The encoded receptor has been shown to have increased expression upon T-cell activation, and it is thought to play a key role in dominant immunological self-tolerance maintained by CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells. Knockout studies in mice also suggest the role of this receptor is in the regulation of CD3-driven T-cell activation and programmed cell death. Three alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene encoding distinct isoforms have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. | hsa:8784; | external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; tumor necrosis factor receptor activity [GO:0005031]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of leukocyte migration [GO:0002687]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 15301860_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15944293_GITR rapidly recruits TNF receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) in a ligand-dependent manner; data indicate that the cytoplasmic domain of GITR contains a single TRAF binding site where acidic residues 202/203 and 211-213 are critical for this interaction. 16955181_Since regulatory T-cells are localized in the vicinity of GITRL-expressing cells in atopic dermatitis skin, the GITR/GITRL interaction may serve to perpetuate the inflammation locally. 17360848_This protein has been shown to stimulate T cell-mediated antitumor immunity in mice, and now in a human tumor cell line. 17538882_These data suggest that, despite abnormal GITR expression during HIV infection, GITR triggering enhances HIV-specific CD4(+) T cell cytokine expression and protects HIV-specific CD4(+) T cells from apoptosis. 18230609_although GITR is an activation marker for NK cells similar to that for T cells, GITR serves as a negative regulator for NK cell activation 18723571_CD4(+)CD25(+) effector memory T-cells expressing CD134 and GITR seem to play a role in disease mechanisms, as suggested by their close association with disease activity and their participation in the inflammatory process in Wegener's granulomatosis. 18924213_mechanism of IgG4 induction by regulatory cells involves GITR-GITR-L interactions, IL-10 and TGF-beta. 18987746_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19155305_Data show that in humans GITRL expression subverts NK cell immunosurveillance of AML. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19547759_mRNA level for CTLA-4, ICOS1, IL-23, IL-27, SMAD3 and GITR were lower in T regulatory cells of children with diabetes compared to the control patients 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21445534_The regulatory SNPs identified in this study will provide useful information for understanding the relevance of sequence polymorphisms in populations of different background and may serve as a basis to study parasite susceptibility in association studies 21557210_Data indicate that CD4(+) CD25(low) GITR(+) cells represent a low percentage of the CD4(+) T-cell population (0.32-1.74%) and are mostly memory cells. 21592113_study concludes, the rs3753348 C/G SNP in the GITR is associated with Hashimoto's disease prognosis and expression on T(reg) and T(eff) cells 21670968_GITR, which transmits a signal that abrogates regulatory T cell functions, was elevated in early rheumatoid arthritis. 21694467_Findings suggest that GITR-expression of TILs is associated with cancer progression. 21705620_Although GITR transgene costimulation can therapeutically enhance T helper (Th) type 2 cell responses, GITR-GITR ligand interactions are not required for development of Th2-mediated resistance or pathology. 22028176_DCs transfected with mRNA encoding a humanized anti-CTLA-4 mAb and mRNA encoding a soluble human GITR fusion protein enhance the induction of anti-tumor CTLs in response to DCs. 22064350_GITRL may contribute to disease pathophysiology and resistance to direct and Rituximab-induced NK reactivity in CLL 22309286_Results suggest that GITR expression might indicate a molecular link between steroid use and complicated acute sigmoid diverticulitis. Increased MMP-9 expression by GITR signalling might explain morphological changes in the colonic wall in diverticulitis. 22516990_GITR is pathologically expressed on Treg cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. 22911397_Liver tumor Tregs up-regulate the expression of glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor compared with Tregs in tumor-free liver tissue and blood. 23432692_Data indicate that the mRNAs of CTLA-4 and GITR genes were expressed at lower levels in CVID patients compared to control group. 23785514_GITR acts as a potential tumor suppressor in MM. 23929911_these results show a higher susceptibility to apoptosis in patients' versus controls' T(reg) cells, suggesting that GITR is a T(reg)-cell marker that would be primarily involved in T(reg)-cell survival rather than in their suppressor function. 23935647_Our findings indicate the possible involvement of GITR-GITRL pathway in the pathogenesis of pSS. 25256257_Data may suggest a key role of regulatory GITR+CD25 low/-CD4+ T cells subset in the modulation of the abnormal immune response in lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. 25293713_Aberrant expression of GITR may contribute to systemic lupus erithematosus pathogenesis. Glucocorticoid may achieve its therapeutic effect partly by inducing GITR expression on Tresps rather than Tregs, which initiates the apoptosis of Tresp cells in SLE patients. 25445616_results suggest that the GITR rs3753348 polymorphism may be involved in the development and susceptibility of CWP. 25961057_GITR is a crucial player in differentiation of thymic regulatory T cells and expansion of regulatory T cells, including both thymic regulatory T cells and peripheral regulatory T cells. 25973846_GITR expression can enhance the sensitivity to Bortezomib by inhibiting Bortezomib-induced NF-kappaB activation. 28101786_HTLV-1 infection can modify the expression of main functional transcription factors, FOXP3 and GITR 28542810_a novel molecular mechanism by which MBD4 inhibits GITR expression in a DNMT1-dependent manner 29427641_GITR cosignal in ILC2s controls allergic lung inflammation. 30484986_The increased expression of FOXP3, CTLA-4 and GITR represent higher activity of Treg cells. 30719701_Agonistic targeting of GITR can enhance functionality of HCC TIL. 30755607_Authors demonstrate that GITR engagement of activated, but not naive, ILC2s improves glucose homeostasis, resulting in both protection against insulin resistance onset and amelioration of established insulin- resistance. 31118027_This work demonstrates abnormal changes in Helios(+) Tregs and soluble GITR in myasthenia gravis, as well as direct regulation of Helios by GITR in the context of Tregulatory cells. 31358539_Characterization and Comparison of GITR Expression in Solid Tumors. 32259529_GITR shapes humoral immunity by controlling the balance between follicular T helper cells and regulatory T follicular cells. 32728688_Glucocorticoid-induced tumour necrosis factor receptor family-related protein (GITR) drives atherosclerosis in mice and is associated with an unstable plaque phenotype and cerebrovascular events in humans. 32889153_Interleukin 3-induced GITR promotes the activation of human basophils. 33122602_Phenotypic Changes of PD-1 and GITR in T Cells Are Associated With Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Seroclearance. 33280089_Experimental Medicine Study to Measure Immune Checkpoint Receptors PD-1 and GITR Turnover Rates In Vivo in Humans. 33654081_Structures of mouse and human GITR-GITRL complexes reveal unique TNF superfamily interactions. 34102305_Glucocorticoid induced TNF receptor family-related protein (GITR) - A novel driver of atherosclerosis. 34589088_GITR Promotes the Polarization of TFH-Like Cells in Helicobacter pylori-Positive Gastritis. 34908008_DNA Methylation and mRNA Expression of OX40 (TNFRSF4) and GITR (TNFRSF18, AITR) in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Correlates With HPV Status, Mutational Load, an Interferon-gamma Signature, Signatures of Immune Infiltrates, and Survival. | ENSMUSG00000041954 | Tnfrsf18 | 43.437807 | 0.376433945 | -1.409531 | 0.34054710 | 16.889085 | 0.0000396288136738843810606344741920281649072421714663505554199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0004514070404481227392901043771189506514929234981536865234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 24.3899093 | 5.9396947 | 64.7814148 | 14.8967487 | |
| ENSG00000187186 | 730098 | protein_coding | H3BQ31 | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA | Reference proteome | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA | Mouse_homologues NA;NA;NA | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA | ENSMUSG00000094695+ENSMUSG00000095234+ENSMUSG00000078747 | Gm21953+Gm21586+Gm20878 | 16.192536 | 0.208569647 | -2.261399 | 0.51390070 | 18.645156 | 0.0000157446773885436273659934464097531758852710481733083724975585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001987694470315417552466058515037161669170018285512924194335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 4.9783128 | 1.9961970 | 23.9222762 | 9.2449217 | |||
| ENSG00000187210 | 2650 | GCNT1 | protein_coding | Q02742 | FUNCTION: Glycosyltransferase that catalyzes the transfer of an N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) moiety in beta1-6 linkage from UDP-GlcNAc onto mucin-type core 1 O-glycan to form the branched mucin-type core 2 O-glycan (PubMed:1329093, PubMed:23027862). The catalysis is metal ion-independent and occurs with inversion of the anomeric configuration of sugar donor (By similarity). Selectively involved in synthesis of mucin-type core 2 O-glycans that serve as scaffolds for the display of selectin ligand sialyl Lewis X epitope by myeloid cells, with an impact on homeostasis and recruitment to inflammatory sites (By similarity). Can also act on glycolipid substrates. Transfers GlcNAc moiety to GalGb4Cer globosides in a reaction step to the synthesis of stage-specific embryonic antigen 1 (SSEA-1) determinant (By similarity). Can use Galbeta1-3GalNAcalpha1- and Galbeta1-3GalNAcbeta1- oligosaccharide derivatives as acceptor substrates (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q09324, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1329093, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23027862}. | Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1329093}.; PATHWAY: Glycolipid biosynthesis. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q09324}. | This gene is a member of the beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase gene family. It is essential to the formation of Gal beta 1-3(GlcNAc beta 1-6)GalNAc structures and the core 2 O-glycan branch. The gene coding this enzyme was originally mapped to 9q21, but was later localized to 9q13. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:2650; | extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi cisterna [GO:0031985]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008375]; beta-1,3-galactosyl-O-glycosyl-glycoprotein beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0003829]; cell adhesion molecule production [GO:0060352]; glycoprotein biosynthetic process [GO:0009101]; kidney morphogenesis [GO:0060993]; leukocyte tethering or rolling [GO:0050901]; O-glycan processing [GO:0016266]; O-glycan processing, core 2 [GO:0016268]; positive regulation of leukocyte tethering or rolling [GO:1903238]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; tissue morphogenesis [GO:0048729] | 12600830_EGF suppressed C2GnT activity in a time- and dose-dependent fashion, and also suppressed core 4 beta1,6 N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (C4GnT) activity 12626388_presence of multiple tissue-specific promoters for the C2GnT I gene 12765965_elevated glucose increases the activity of core 2 GlcNAc-T and adhesion of human leukocytes to retinal capillary endothelial cells, in a dose-dependent manner, through diabetes-activated serine/threonine protein kinase C beta2-dependent phosphorylation 15026421_core 2 beta1-6-N-glucosaminyltransferase and dimerization of P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 have roles in rolling on P-selectin 15483269_C2GnT-1 regulates sLeX expression level during differentiation of pre-B cells 15591039_upregulated by all-trans retinoic acid (RA) and by IL-4 and IL-13 in the H292 airway epithelial cell line 15882971_A/G polymorphism in enzyme is associated with the susceptibility to prostate cancer in a Japanese population 15926890_A differential functional impact of N-glycosylation on C2GnT-1 and FucT-VII and disclose that a strongly reduced FucT-VII activity retains the ability to fucosylate PSGL-1 on the core2-based binding site(s) for the three selectins. 15932919_Core2GnT is an extremely useful prognostic marker for prostate cancer progression. Acquiring Core2GnT in prostate carcinoma cells facilitates adhesion to type IV collagen and laminin causing aggressive tumor formation by prostate cancer cells. 16179912_C2GnT-1 regulates selectin ligand expression; downregulation of the selectin ligand expression level inhibits tissue infiltration of BCP-leukemia cells 16778138_glycosyltransferase haploinsufficiency results in altered cellular glycosylation and resistance to cell death, identifying a new survival mechanism for T-lymphoma cells 17530395_2 beta1,6 N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-I transcription is regulated by Sp1 in lymphocytes and epithelial cells 17947642_regulation of O-glycosylation controls sLe(x) expression, and also suggest that O-glycans may have a function in dendritic cells migration 18815556_Pancreas carcinoma antigen, C2GnT, fused to invariant chain elicits T-cell response and tumor growth inhibition. 19267921_15-fold increase in C2GnT1 mRNA levels in colorectal adenocarcinomas compared to normal colorectal tissues 19524017_Data show that a short glycopeptide Galbeta1-3GalNAcalpha-TAGV was identified as an efficient C2GnT substrate. 20017138_Overexpression of C2GnT-1 enhances the metastatic potential of testicular germ cell tumor. 20841351_Core2 O-glycan structure is essential for expression of SI and DDP-IV during intestinal cell differentiation. 21081110_Data show that the reconstituted membrane system in cells expressing C2GnT-I led to the lipid vesicles exhibiting an enzyme activity 11 times higher than that found in microsomal membranes. 21712812_In C2GnT-expressing bladder tumour cells galectin-3 bound the NKG2D-binding site of MICA, reducing the affinity of MICA for NKG2D on natural killer cells and hence severely impairing natural killer cell activation. 22056345_The X-ray crystal structure (2.3 A resolution) of a mutant form of C2GnT-L (C217S) in complex with UDP was solved. C2GnT-L exists in an 'open' conformation and a 'closed' conformation. 22534569_Down-regulation of C2GnT1 is correlated with breast cancer 23027862_GOLPH3 can regulate cell-cell interaction by controlling Golgi retention of C2GnT1. 23165940_C2GnT-expressing prostate cancer cells evade NK cell immunity and survive longer in the host blood circulation, thereby resulting in the promotion of prostate cancer metastasis. 23617619_Immunohistochemical expression of core 2 beta1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyl transferase 1 (C2GnT1) in endometrioid-type endometrial carcinoma may be a novel potential prognostic factor. 23990450_NMIIA is the master regulator of Golgi fragmentation induced by heat shock or inhibition/depletion of HSP70/90 through interaction with gylosyltransferases. 24854630_GCNT1 is over-expressed in prostate cancer and is associated with higher levels of core 2 O-sLe(x) in PSA, PAP and MUC1 proteins. 25086069_Results show that ST3Gal1 uses GM130-GRASP65 and giantin, whereas C2GnT-L uses only giantin for Golgi targeting and defective giantin dimerization in PC-3 and DU145 prostate cancer cells causes fragmentation of the Golgi and prevents its targeting. 26390303_GCNT1 expression in prostate cancer positively correlates with cancer progression and prostate-specific antigen recurrence. 26768364_GCNT1 expression in prostate biopsy specimen is a significant and independent predictor of recurrence after radical prostatectomy, which can be used in pre-treatment decision making for the patient. | ENSMUSG00000038843 | Gcnt1 | 99.967599 | 5.014990771 | 2.326247 | 0.57542598 | 14.870205 | 0.0001151677433927601951809543967542026621231343597173690795898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0011649914543489165493633796799599622318055480718612670898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 125.8711781 | 57.1300140 | 25.1930082 | 11.5404300 |
| ENSG00000187608 | 9636 | ISG15 | protein_coding | P05161 | FUNCTION: Ubiquitin-like protein which plays a key role in the innate immune response to viral infection either via its conjugation to a target protein (ISGylation) or via its action as a free or unconjugated protein. ISGylation involves a cascade of enzymatic reactions involving E1, E2, and E3 enzymes which catalyze the conjugation of ISG15 to a lysine residue in the target protein (PubMed:33727702). Its target proteins include IFIT1, MX1/MxA, PPM1B, UBE2L6, UBA7, CHMP5, CHMP2A, CHMP4B and CHMP6. Isgylation of the viral sensor IFIH1/MDA5 promotes IFIH1/MDA5 oligomerization and triggers activation of innate immunity against a range of viruses, including coronaviruses, flaviviruses and picornaviruses (PubMed:33727702). Can also isgylate: EIF2AK2/PKR which results in its activation, RIGI which inhibits its function in antiviral signaling response, EIF4E2 which enhances its cap structure-binding activity and translation-inhibition activity, UBE2N and UBE2E1 which negatively regulates their activity, IRF3 which inhibits its ubiquitination and degradation and FLNB which prevents its ability to interact with the upstream activators of the JNK cascade thereby inhibiting IFNA-induced JNK signaling. Exhibits antiviral activity towards both DNA and RNA viruses, including influenza A, HIV-1 and Ebola virus. Restricts HIV-1 and ebola virus via disruption of viral budding. Inhibits the ubiquitination of HIV-1 Gag and host TSG101 and disrupts their interaction, thereby preventing assembly and release of virions from infected cells. Inhibits Ebola virus budding mediated by the VP40 protein by disrupting ubiquitin ligase activity of NEDD4 and its ability to ubiquitinate VP40. ISGylates influenza A virus NS1 protein which causes a loss of function of the protein and the inhibition of virus replication. The secreted form of ISG15 can: induce natural killer cell proliferation, act as a chemotactic factor for neutrophils and act as a IFN-gamma-inducing cytokine playing an essential role in antimycobacterial immunity. The secreted form acts through the integrin ITGAL/ITGB2 receptor to initiate activation of SRC family tyrosine kinases including LYN, HCK and FGR which leads to secretion of IFNG and IL10; the interaction is mediated by ITGAL (PubMed:29100055). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1373138, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16009940, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16112642, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16428300, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16434471, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16872604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18305167, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19270716, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19357168, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2005397, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20133869, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20308324, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20639253, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21543490, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22693631, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22859821, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23229543, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29100055, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33727702, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7526157, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8550581}. | 3D-structure;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Innate immunity;Isopeptide bond;Reference proteome;Repeat;S-nitrosylation;Secreted;Ubl conjugation pathway | The protein encoded by this gene is a ubiquitin-like protein that is conjugated to intracellular target proteins upon activation by interferon-alpha and interferon-beta. Several functions have been ascribed to the encoded protein, including chemotactic activity towards neutrophils, direction of ligated target proteins to intermediate filaments, cell-to-cell signaling, and antiviral activity during viral infections. While conjugates of this protein have been found to be noncovalently attached to intermediate filaments, this protein is sometimes secreted. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2012]. | hsa:9636; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; cytosolic small ribosomal subunit [GO:0022627]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; protein tag [GO:0031386]; structural constituent of ribosome [GO:0003735]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; ISG15-protein conjugation [GO:0032020]; modification-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0019941]; negative regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031397]; negative regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060339]; negative regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045071]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0045648]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032733]; positive regulation of protein oligomerization [GO:0032461]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; protein localization to mitochondrion [GO:0070585]; regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032649]; response to type I interferon [GO:0034340]; response to virus [GO:0009615] | 12055236_The ISG15 gene contains a unique interferon-stimulated response element that enables the binding and recruiting not only of interferon regulatory factors but also of PU.1. 12067988_Interferon stimulated gene 15 constitutively produced by melanoma cells induces e-cadherin expression on human dendritic cells. 14976209_RA treatment of APL and other RA-responsive leukemic cells induced expression of UBE1L and ISG15 as well as intracellular ISG15 conjugates. A physical association was found between UBE1L and ISG15 in vivo. 15670748_Quantitative-PCR and Northern analysis confirmed down-regulation of UCRP and UBE2L6 with BRCA2 knockdown, respectively. 15684817_ISG15 is induced by camptothecin in human tumor cells 15917233_The three-dimensional structure of recombinant ISG15C78S was determined at 2.4-A resolution.The docking model predicts side-chain interactions that presumably define the specificity between the ubiquitin and ISG15 ligation pathways 16009940_ISG15 conjugation targets both IFN-induced and constitutively expressed proteins functioning in diverse cellular pathways. 16122702_identify Lys92 as the only ISG15 modification site in Ubc13, which is the first report about the ISG15 modification site 16139798_These data indicate that ISGylation targets proteins found in several fundamentally important cellular pathways and will contribute to understanding the physiologic role of interferon-induced ISG15 and ISG15 conjugation. 16424026_results suggest that the ISG15 pathway, which is deregulated during tumorigenesis, negatively regulates the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway by interfering with protein polyubiquitination/degradation 16428300_isolated ISG15-modified and unmodified UbcH6 proteins, and analyzed their abilities to form thioester intermediates with ubiquitin 16434471_ISG15 is the critical component in IFN-mediated inhibition of HIV-1 release 16641915_Higher levels of ISG15 protein is associated with muscle-invasive bladder cancer 16884686_Four candidate target proteins were demonstrated to be ISGylated in UBE1L- and UbcH8-dependent manners 17069755_Efp protein could be conjugated with not only ubiquitin but also ISG15. 17097911_review evidence of a role for ISG15 as an endogenous tumor suppressor that, when dysregulated in malignant cells, can be subverted to promote oncogenesis 17222803_Thus we propose that autoISGylation of EFP negatively regulates its ISG15 E3 ligase activity for 14-3-3sigma. 17289916_ISGylation (by ISG15) of 4EHP may play an important role in cap structure-dependent translation control in immune responses. 17653289_ISG15 is a newcomer among ubiquitin-like molecules and utilizes the conjugating but also the deconjugating machinery of its more established relative ubiquitin. 17692280_Our results demonstrate that SARS-CoV PLpro can differentiate between ubiquitin-like modifiers sharing a common C-terminal sequence, and that the debranching activity of the PLpro is linkage type selective. 18287095_a mechanistically novel function of ISG15 in the enhancement of the innate anti-viral response through specific inhibition of Nedd4 Ub-E3 activity 18305167_These data provide evidence of antiviral activity of ISG15 against Ebola virus and suggest a mechanism of action involving disruption of Nedd4 function and subsequent ubiquitination of VP40. 18356159_N-terminal ubiquitin-like domain of ISG15 mainly functions in the ligation step and Influenza B virus NS1 protein inhibits ISGylation by competing with E3 ligases for binding to the N-terminal domain 18566215_These results suggest that ISG15, which interferes with proteasome-mediated repair of TOP1-DNA covalent complexes, is a potential tumor biomarker. 18583345_Ube1L was required for transfer of ISG15 to UbcH8 and for binding of Ube1L to UbcH8 18597038_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18606809_nitrosylation of ISG15 enhances target protein ISGylation 18627608_ISG15 is overexpressed in breast carcinoma cells compared with normal breast tissue, both at the RNA and protein level 18953482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19043203_expression of the ISG15 system suppresses NF-kappaB activation 19073728_Kinetic analysis revealed that mutation of arginine 153 to alanine (R153A) in ISG15 ablated hISG15-hUbE1L binding and transthiolation of UbcH8. 19074853_UBE1L-ISG15 preferentially inhibits cyclin D1 in lung cancer 19357168_Inhibition of influenza A virus gene expression by ISG15 conjugation in human cells is sufficient to result in inhibition of virus replication at early times of infection. 19378789_regulates immune response. (review) 19430494_study describes the modulation of androgen receptor expression by ISGylation components, which affects the proliferation of prostate cancer cells, thereby providing evidence for a novel function of the ISGylation system in malignant transformation 19656964_These results reveal a novel function for ISG15 in the regulation of the IFN-alpha pathway and its antihepatitis C effect. 19846672_ISG15 promotes hepatitis C virus production. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19956859_ISG15 is involved in cell growth and survival of prostate cancer 19959962_Data demonstrated that ISG15 is one of the genes associated with intrinsic gemcitabine sensitivity. 20035788_ISG15 over-expression in human medulloblastoma cells significantly reduced the Japanese encephalitis virus -induced cytopathic effect and inhibited virus replication by reducing the viral titers and genomes. 20093371_NS1B protein exhibits species-specific binding; it binds human and non-human primate ISG15 but not mouse or canine ISG15 20133869_NS1 protein of influenza A virus (NS1A protein), an essential, multifunctional protein, is ISG15 modified in virus-infected cells. 20157543_Upregulation of ISG15 with telomere shortening may contribute to chronic inflammatory states associated with human aging. 20164219_Thus, there appear to be multiple levels of ISG15-induced inhibition acting at different stages of the retrovirus release process. 20219937_The authors demonstrate that influenza B virus NS1 protein potently antagonizes human but not mouse ISGylation, a property dependent on B/NS1 binding the N-terminal domain of human but not mouse ISG15. 20308324_This study characterizes HERC5 as a positive regulator of innate antiviral responses, and show that it sustains IRF3 activation via a novel posttranslational modification, ISG15-ylation. 20542004_Data suggest that, in the context of an interferon-stimulated cell, newly translated viral proteins may be primary targets of ISG15. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20639253_data indicate that the interferon stimulated gene 15, which is induced by HCV-mediated activation of the innate immune system, is a proviral factor that plays an important role in the pathogenesis of HCV. 20946978_In addition to cellular ISGylation targets, recent reports implicate viral proteins as targets of ISG15 modification; these studies provide fresh insights into the antiviral mechanisms of ISG15.[Review] 21245344_Structural basis for the removal of ubiquitin and interferon-stimulated gene 15 by a viral ovarian tumor domain-containing protease 21298066_expression of the ISG15 is elevated in A-T cells derived from various A-T patients, as well as in brain tissues derived from the ATM knockout mice and A-T patients, suggesting that ATM negatively regulates the ISG15 pathway 21399617_Study report that USP21 cleaves Ub polymers, and with reduced activity also targets ISG15, but is inactive against NEDD8. 21544738_Report of nearly complete backbone (1)H(N), (15)N, (13)C', and (13)C(alpha), as well as side chain (13)C(beta), methyl (Ile-delta1, Leu, Val), amide (Asn, Gln), and indole N-H (Trp) NMR resonance assignments for the 157-residue human ISG15 protein. 21757684_analysis of the crystal structure of human ISG15 protein in complex with influenza B virus NS1B 21808041_influenza B virus NS1B-N-terminal region of NS1B binding of ISG15 is responsible for the inhibition of interferon-induced ISG15 conjugation in cells 22093708_The E3 ligase activity of HERC5 was required for blocking HIV-1 Gag particle production and correlated with the post-translational modification of Gag with ISG15. 22100648_Inhibition of R. conorii-induced ISG15 by RNA interference results in significant increase in the extent of rickettsial replication, whereas UBP43 knockdown yields a reciprocal inhibitory effect. 22185919_results suggest that the aberrant activation of the ISG15 pathway confers a motile phenotype to breast cancer cells by disrupting cell architecture and stabilizing proteins involved in cell motility, invasion and metastasis 22706304_ISG15 as a tumor suppressor via its conjugation to a tp63 splice variant 22729740_TNF-alpha elicits the induction of ISG15 and ISG15 conjugates not only via the autocrine stimulation of type I interferon expression, but also through a type I interferon-independent pathway. 22740306_ISG15, is likely to be associated with both dysgenesis and tumorigenesis and may be a potential prognostic marker for oral cancer 22859821_ISG15 plays an essential role as an IFN-gamma-inducing secreted molecule for optimal antimycobacterial immunity. 23212917_ISG15 deregulates autophagy in genotoxin-treated ataxia telangiectasia cells 23229543_Activation of double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase (PKR) by interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) modification down-regulates protein translation 23318454_Findings support the development of ISG15 conjugation inhibitors for treating breast and also other cancers expressing oncogenic Ki-Ras. 23588721_High interferon-stimulated gene ISG-15 expression affects HCV treatment outcome in patients co-infected with HIV and HCV. 23750257_ISG15 does not appear to play a key role in IFN-beta-mediated C2C12 myoblast cell fusion 24024201_Our results suggest that ISG15 overexpression could be developed into a powerful gene-therapeutic tool for treating IFN-alpha-resistant HCC. 24056783_expression of the ISG15 and/or ISGylation system attenuates HIF-1alpha-mediated gene expression and tumorigenic growth. 24237697_These data support the interferon-induced generation of a Tsg101- and ISG15-dependent checkpoint in the secretory pathway that compromises influenza virus release. 24257616_ISG15 is counteracted by vaccinia virus E3 protein and controls the proinflammatory response against viral infection. 24300530_ISG15 is a potential prognostic marker in high-grade serous carcinoma of the ovary 24386835_HIV-1 infection up-regulating expression of ISG15 in cell lines. 24452380_suppression of ISG15 by siRNA sensitized A549-CUG2 cells to vesicular stomatitis virus infection. 24768535_Results showed that ISG15 modification (ISGylation) of PCNA plays a key role in translesion DNA synthesis termination. 24844324_Propose that Isg15-dependent degradation of p53 represents an alternative mechanism of controlling p53 protein levels, and, thus, it is an attractive pathway for drug discovery. 25165091_The ISG15 conjugation system represents a critical innate response mechanism in cardiomyocytes to fight the battle against invading pathogens, limiting inflammatory cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and death. 25238261_Results suggest that high ISG15 expression is an intrinsic feature of hepatocellular carcinoma and a trigger for tumorigenesis and metastasis. 25307056_intracellular ISG15 is IFN-alpha/beta-inducible not to serve as a substrate for ISGylation-dependent antiviral immunity, but to ensure USP18-dependent regulation of IFN-alpha/beta and prevention of IFN-alpha/beta-dependent autoinflammation 25368022_our work demonstrates that ISG15 is a previously unrecognized support factor for CSC in the PDAC microenvironment with a key role in pathogenesis and progression. 25429107_ISG15 conjugation marks proteins for interaction with HDAC6 and p62 upon forced stressful conditions likely as a step toward autophagic clearance 25749047_free ISG15 may have antitumor and immunoregulatory function in vivo in breast cancer 25905045_Reovirus T3D infection induced STAT-1, ISG-15, IFIT-1, Mx1, and IFIT-3 expression. 25906440_that ISGylation of BECN1 at Lys117, as well as Lys263, Lys265, and Lys266 serve an important role in negative regulation of intracellular processes including autophagy 26036210_Microparticles released from Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected human macrophages contain increased levels of the type I interferon inducible protein ISG15. 26226047_Cellular ubiquitin is a substrate of ISG15 and Lys 29 on ubiquitin is the major ISG15 acceptor site. 26259872_These data reveal a previously uncharacterized ISG15-dependent restriction of Listeria infection, reinforcing the view that ISG15 is a key component of the innate immune response. 26361997_The inhibitory effect of ISG15 on HCV RNA replication does not require its conjugation to substrates by HERC5. 26560068_Data show the induction of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)1 and IFN-stimulated gene 15 protein (ISG15) in Rickettsia conorii-infected human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). 26563749_ISG15 is elevated in viremic HIV-1 patients and is associated with high TRAIL and IDO levels. 26617815_ISG15 might serve as a novel prognostic biomarker in drinkers with esophageal squamous cell cancer 26763998_This study shows that interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) lowers Human respiratory syncytial virus growth through protein ISGylation. 26833585_These data indicate that hepatic expression of PSMA6, which is upregulated during viral hepatitis, likely depends on TLR3 activation and, that PSMA6 affects the expression of immunoregulatory ISG15, a proviral factor in the pathogenesis of hepatitis C virus infection. 26844778_ISG15 dysregulation may be involved in the pathogenesis of glomerular inflammation 26872785_The results suggest that integrin-adhesion-induced MRTF-A-SRF activation and ISG15 expression constitute a newly discovered signaling circuit that promotes cell migration and invasion. 26919245_Our study demonstrates a protumor role of ISG15, and suggests that ISG15 is a prognostic predictor and a potential therapeutic target for nasopharyngeal carcinoma 27193971_The species-specific gain-of-function in antiviral immunity observed in ISG15 deficiency is explained by the requirement of ISG15 to sustain USP18 levels in humans. 27534820_Results show that HERC5 mediates covalent ISG15 conjugation to parkin in mammalian cells and that ISG15 is conjugated to the Lys349 and Lys369 residues of parkin which increases its ubiquitin E3 ligase activity. 27545325_DNA damage induces ISG15 conjugation to p53 and this modification markedly enhances the binding of p53 to the promoters of its target genes as well as of its own gene by promoting phosphorylation and acetylation. 27626177_The Interferon-stimulated 15-KDa protein (ISG15) rs1921 variant and ISG15 expression are associated with HBV-related liver diseases. 27659523_ISG15 induces cancer cell apoptosis by disrupting the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. This study highlighted a novel role of ISG15 in tumor suppression. 27882925_ISGylation is a ubiquitin-like modification that controls exosome release. ISGylation induction decreases microvesicular body numbers and impairs exosome secretion. Specifically, ISGylation of the MVB protein TSG101 induces its aggregation and degradation, being sufficient to impair exosome secretion. 27926780_unlike ISG15, ubiquitin and FAT10 are conjugated to a similar degree to newly translated and pre-existing proteins. 28186990_epletion of either ISG15 or UBE2L6/UBCH8 resulted in enhanced endogenous autophagic flux. 28202760_This paper shows that ISG15 directly regulates Human Cytomegalovirus replication and that its accumulation restricts productive virus growth. 28204879_ISG15 expression is relatively high in SLE patients and correlates with disease activity before treatment. ISG15 expression is higher in SLE patients with lymphocytopenia before treatment. 28287327_Mechanism of cell-intrinsic adaptation to Adams-Oliver Syndrome gene DOCK6 disruption highlights ubiquitin-like modifier ISG15 as a regulator of RHO GTPases. 28467275_ISG15 is able to trigger IFN-gamma production and other signaling pathways suggesting it is a potential cytokine that could interact with still unknown receptors. (Review) 28543875_Results suggest that unconjugated ISG15 affects the functions of HCV NS5A through protein-protein interaction. 28630501_These results demonstrate that virus-induced IFN-lambda4 potently blocks IFN-alpha signalling by inducing high protein levels of ISG15 and USP18. Moreover, the data clearly demonstrate that DAA therapy restores IFN-alpha responsiveness in HCV-infected cells. 28724761_This report demonstrates that ISG15 induced by Hepatitis E virus replication in Huh7-S10-3 human liver cells plays an immunomodulatory role by negatively regulating type I Interferon signaling and, thus, Hepatitis E virus sensitivity to type I Interferon. 28881486_The structures of ubiquitin-specific protease 18 (USP18) and a USP18-Interferon-stimulated 15-KDa protein (ISG15) complex indicate the molecular basis of the specificity of the protease and its interaction with the type I interferon receptor [Review]. 28931677_findings revealed that MERS-CoV PLpro chiefly engages human ISG15 through its C-terminal domain; structure of MERS-CoV PLpro was solved to 2.4 A in complex with the C-terminal domain of hISG15; structure of MERS-CoV PLpro in complex with this domain exposed the interface between these two entities 29100055_Extracellular ISG15 signals cytokine secretion through the LFA-1 integrin receptor (CD11a/CD18) in natural killer cells. 29367604_the present study demonstrates that covalent ISG15 conjugation produces a novel CHIP regulatory mode that enhances the tumor-suppressive activity of CHIP. 29463763_Studied foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) Lbpro targeting of ISG15. Show a previously undescribed mechanism by which viruses interfere with the ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like systems. 29518394_ISG15 reduces miR-17-5p levels and thereby promotes Beclin-1-mediated autophagy 29555370_Protein ISG15 mediates the tumorigenesis via c-MET/Fyn/beta-catenin pathway in Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. 29580840_HIV-1 IIIB infection of myeloid ThP-1 cells also reduced the IFN-alpha-mediated induction of the anti-viral gene, ISG15, but not MxA, revealing a functional consequence of this HIV-1-mediated immune evasion strategy. 29626479_IFN-gamma increases free ISG15 levels in the cytoplasm and ISGylation in the nucleus and cytoplasm, but in a manner distinct between MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231cells. 29853735_Hepatitis E virus may promote production of IFN-alpha/beta and expression of ISG15 via ORF3 in the early stages, and increased ISG15 subsequently inhibited the production of IFN-alpha/beta. 30213559_Data suggest that ISG15 is in the pathogenesis of cancer, which could contribute to therapeutic intervention in cancer [Review]. 30411299_The Overexpression of CD80 and ISG15 Are Associated with the Progression and Metastasis of Breast Cancer by a Meta-Analysis Integrating Three Microarray Datasets. 30519829_The authors have found that NS1B-NTR (nonstructural protein NS-1, influenza B virus) can interact with hISG15/hUSP18 complex and form a tertiary complex in vitro. 30529400_Non-muscle myosin IIA is post-translationally modified by interferon-stimulated gene 15 in breast cancer cells 30765861_ISG15 affects cell migration by interacting with Rac1 and regulating Rac1 activity and contributes to lymphatic metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma 30771383_The current study revealed that BAG3 did not interact with ISG15, but positively regulated ISG15 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cancer. 30858391_USP18 and ISG15 coordinately impact on SKP2 and cell cycle progression. 31428903_TNF-alpha, similar to the response by IFN-beta, could directly induce expression of ISG15 and its conjugation machinery, UbE1L and UbcH8, in human lung carcinoma. 31444947_Intrahepatic immune changes after hepatitis c virus eradication by direct-acting antiviral therapy. 31455647_This work clarifies the function and consequences of p53 modification by ISG15 and implicates USP18 in HIV-1 infection and potentially in carcinogenesis. 31501523_Study demonstrated that extracellular free ISG15 played an important role in maintenance of cancer stem cell-like features of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and revealed a novel mechanism by which TRIM29 modulates ISG15 stability via CAPN3-mediated processing, and subsequently extracellular ISG15 maintains the cancer stem cell-like features of PDAC via autocrine mode of action. 31765674_Decoupling deISGylating and deubiquitinating activities of the MERS virus papain-like protease. 32020185_Intestinal Epithelial Cells Express Immunomodulatory ISG15 During Active Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn's Disease. 32127658_Deleting key autophagy elongation proteins induces acquirement of tumor-associated phenotypes via ISG15. 32402279_Systemic Type I IFN Inflammation in Human ISG15 Deficiency Leads to Necrotizing Skin Lesions. 32416603_ISG15 Acts as a Mediator of Innate Immune Response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in C57BL/6J Mouse Corneas. 32423918_Direct Antiviral Activity of IFN-Stimulated Genes Is Responsible for Resistance to Paramyxoviruses in ISG15-Deficient Cells. 32472071_ISG15 and ISGylation is required for pancreatic cancer stem cell mitophagy and metabolic plasticity. 32513696_RIG-I regulates myeloid differentiation by promoting TRIM25-mediated ISGylation. 32553163_Results establish extracellular ISG15 as a cytokine-like protein that bridges early innate and interferon-gamma-dependent immune responses, and indicate that pathogens have evolved to differentially inhibit the intracellular and extracellular functions of ISG15. 32597933_Interferon-stimulated gene 15 accelerates replication fork progression inducing chromosomal breakage. 32641707_ISG15 induces ESRP1 to inhibit lung adenocarcinoma progression. 32686110_Evidence for an involvement of the ubiquitin-like modifier ISG15 in MHC class I antigen presentation. 32738280_Interferon stimulated gene 15 promotes Zika virus replication through regulating Jak/STAT and ISGylation pathways. 32931521_ISG15 overexpression compensates the defect of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus polymerase bearing a protease-inactive ovarian tumor domain. 33024031_ISG15 Connects Autophagy and IFN-gamma-Dependent Control of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Human Cells. 33073304_The prognostic significance of interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) in invasive breast cancer. 33203188_More than Meets the ISG15: Emerging Roles in the DNA Damage Response and Beyond. 33214684_Deletion of the deISGylating enzyme USP18 enhances tumour cell antigenicity and radiosensitivity. 33292152_Molecular Pathways of Interferon-Stimulated Gene 15: Implications in Cancer. 33424843_Tumor Cell-Secreted ISG15 Promotes Tumor Cell Migration and Immune Suppression by Inducing the Macrophage M2-Like Phenotype. 33533212_[Interferon-regulating activity of the celagrip antiviral drug and its influence on formation of reactive oxygen species and expression of innate immunity genes in the follicular lymphoma patients]. 33797839_ISG15 is downregulated by KLF12 and implicated in maintenance of cancer stem cell-like features in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer. 34110168_Conformational Dynamics in the Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease with Human Interferon-Stimulated Gene 15 Protein. 34556814_ISGylation drives basal breast tumour progression by promoting EGFR recycling and Akt signalling. 34599178_Ring finger protein 213 assembles into a sensor for ISGylated proteins with antimicrobial activity. 34661519_HERC5 E3 ligase mediates ISGylation of hepatitis B virus X protein to promote viral replication. 34784198_Unraveling the Molecular Mechanism of Recognition of Human Interferon-Stimulated Gene Product 15 by Coronavirus Papain-Like Proteases: A Multiscale Simulation Study. 34847081_Congenital deficiency reveals critical role of ISG15 in skin homeostasis. 34851141_Roles of ESCRT Proteins ALIX and CHMP4A and Their Interplay with Interferon-Stimulated Gene 15 during Tick-Borne Flavivirus Infection. 35159348_ISG15 and ISGylation in Human Diseases. 35297347_Free ISG15 and Protein ISGylation Emerging in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. 35333911_ISG15 deficiency restricts HIV-1 infection. 35445736_Interferonstimulated gene 15 promotes progression of endometrial carcinoma and weakens antitumor immune response. 35506701_ISG15 enhances glioma cell stemness by promoting Oct4 protein stability. 35538543_Identification of ISG15 and ZFP36 as novel hypoxia- and immune-related gene signatures contributing to a new perspective for the treatment of prostate cancer by bioinformatics and experimental verification. 36053046_ISGylation directly modifies hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha and enhances its polysome association. | ENSMUSG00000035692 | Isg15 | 122.469349 | 0.450356761 | -1.150860 | 0.13782197 | 71.412756 | 0.0000000000000000289792548315128783921084966761052715660116625001879037126784055544703733175992965698242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000017103874117434690242644880135601403621057340015756964568538478488335385918617248535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 78.0052606 | 9.0883531 | 173.9639286 | 18.6881876 | |
| ENSG00000187775 | 8632 | DNAH17 | protein_coding | Q9UFH2 | FUNCTION: Force generating protein component of the outer dynein arms (ODAs) in the sperm flagellum. Produces force towards the minus ends of microtubules. Dynein has ATPase activity; the force-producing power stroke is thought to occur on release of ADP (Probable). Plays a major role in sperm motility, implicated in sperm flagellar assembly and beating (PubMed:31178125). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31178125, ECO:0000305|PubMed:31178125}. | Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cilium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Dynein;Flagellum;Microtubule;Motor protein;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat | Dyneins are microtubule-associated motor protein complexes composed of several heavy, light, and intermediate chains. DNAH17 is a heavy chain associated with axonemal dynein (Milisav and Affara, 1998 [PubMed 9545504]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:8632; | axonemal dynein complex [GO:0005858]; axoneme [GO:0005930]; dynein complex [GO:0030286]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; motile cilium [GO:0031514]; outer dynein arm [GO:0036157]; sperm flagellum [GO:0036126]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; dynein intermediate chain binding [GO:0045505]; dynein light intermediate chain binding [GO:0051959]; microtubule motor activity [GO:0003777]; minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity [GO:0008569]; cilium movement [GO:0003341]; cilium-dependent cell motility [GO:0060285]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018]; outer dynein arm assembly [GO:0036158] | 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 30575322_We found that overexpression of DNAH17 by down-regulation of methylation levels might contribute to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) initiation and progression. In addition, the hypomethylation status of the DNAH17 gene, both in tumor tissue and adjacent non-cancerous tissue, could be a promising biomarker for tumor thrombosis in HCC. 31178125_Mutations in DNAH17 Cause Isolated Male Infertility Due to Asthenozoospermia. 31658987_A DNAH17 missense variant causes flagella destabilization and asthenozoospermia. 31841227_DNAH17 is associated with asthenozoospermia and multiple morphological abnormalities of sperm flagella. 33070343_Novel loss-of-function variants in DNAH17 cause multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella in humans and mice. 33423959_Novel compound heterozygous variants in dynein axonemal heavy chain 17 cause asthenoteratospermia with sperm flagellar defects. | ENSMUSG00000033987 | Dnah17 | 30.131804 | 0.222686903 | -2.166911 | 0.63735988 | 10.653308 | 0.0010987421311235924439170252853159581718500703573226928710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0081925399414481923920927641802336438558995723724365234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 8.3483545 | 3.9520433 | 37.5496322 | 17.4143712 | |
| ENSG00000188290 | 57801 | HES4 | protein_coding | Q9HCC6 | FUNCTION: Transcriptional repressor. Binds DNA on N-box motifs: 5'-CACNAG-3' (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Developmental protein;Differentiation;DNA-binding;Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation | Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in anterior/posterior pattern specification and regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be part of chromatin. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:57801; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 25480889_Epigenetic dysregulation of HES4 could play a critical role in modifying Huntington's disease pathogenesis and severity. 25579220_Overexpression and knockdown studies demonstrated that Hes4 promotes osteogenesis resulting in an increase in Runx2, osteocalcin, osteopontin, and bone sialoprotein expression in BMSC. 27786411_Hes4 overexpression promotes a more aggressive tumor phenotype by preventing osteoblastic differentiation of osteosarcoma cells. Hes4 expression may allow for the stratification of patients into good or poor responders to chemotherapy at diagnosis. 31919081_HES1 and HES4 have non-redundant roles downstream of Notch during early human T-cell development. | 22.874984 | 0.324336675 | -1.624436 | 0.33296044 | 24.997915 | 0.0000005739233503364997425355456366069528684192846412770450115203857421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000099603471768076401807179287573035253444686532020568847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 10.6538249 | 6.9466527 | 32.9972489 | 20.9825711 | |||
| ENSG00000196562 | 55959 | SULF2 | protein_coding | Q8IWU5 | FUNCTION: Exhibits arylsulfatase activity and highly specific endoglucosamine-6-sulfatase activity. It can remove sulfate from the C-6 position of glucosamine within specific subregions of intact heparin. | Alternative splicing;Calcium;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal | Heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) act as coreceptors for numerous heparin-binding growth factors and cytokines and are involved in cell signaling. Heparan sulfate 6-O-endosulfatases, such as SULF2, selectively remove 6-O-sulfate groups from heparan sulfate. This activity modulates the effects of heparan sulfate by altering binding sites for signaling molecules (Dai et al., 2005 [PubMed 16192265]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:55959; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi stack [GO:0005795]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; arylsulfatase activity [GO:0004065]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; glycosaminoglycan binding [GO:0005539]; N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase activity [GO:0008449]; bone development [GO:0060348]; cartilage development [GO:0051216]; chondrocyte development [GO:0002063]; embryonic skeletal system development [GO:0048706]; esophagus smooth muscle contraction [GO:0014846]; glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0035860]; glomerular basement membrane development [GO:0032836]; glomerular filtration [GO:0003094]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan metabolic process [GO:0030201]; innervation [GO:0060384]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; negative regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0040037]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010575]; positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030177] | 12368295_Sulfs are extracellular endosulfatases with strong potential for modulating the interactions of heparan sulfate proteoglycans in the extracellular microenvironment 16192265_HSulf-1 (SULF1) and HSulf-2 (SULF2) are potent inhibitors of myeloma tumor growth in vivo. 16192265_HSulf-1 and HSulf-2 have roles in inhibiting myeloma tumor growth 16331886_Purified recombinant Sulf-2 promoted angiogenesis in the chick chorioallantoic membrane assay. 16417632_Binding of VEGF, FGF-1, & certain chemokines (SDF-1 & SLC) to immobilized heparin was abolished or diminished by pre-treating the heparin with HSulf-2. Recombinant or native HSulf-2 released these soluble proteins from their association with heparin. 18507859_Increased sulf-2 mRNA and protein levels may change the sulfation patterns of heparan sulfate proteoglycans and growth factor activities and thus contribute to abnormal chondrocyte activation and cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis. 18687675_Sulf1 and Sulf2 are two heparan sulfate 6-O-endosulfatases that regulate the activity of multiple growth factors, such as fibroblast growth factor and Wnt, and are essential for mammalian development and survival 19190338_Genetic and pharmacologic perturbation of p53 directly influences SULF2 expression in tumor cell lines. 19520866_analysis of the subdomain organization of sulf-1 and sulf-2 19855436_Our findings support an essential role for Sulf-2 in lung cancer 20707913_Loss of SULF2 is associated with breast cancer. 20725905_Mechanism mediating the oncogenic function of SULF2 in human hepatoma that includes GPC3-mediated activation of Wnt signaling. 21040406_The prosurvival, anti-apoptotic effect of SULF2 in hepatocellular carcinoma is mediated through activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. 21347431_enzymatic activity of HSulf2 21599997_SULF1 and SULF2 are overexpressed in various human cancer types and can be associated to progression and prognosis. 21968018_This study demonstrates that unlike normal adult lung with little or no SULF2 expression, this enzyme is expressed at high levels in most lung tumours showing differential cellular distribution of full length and shorter SULF2 variants in such tumours. 22158045_genes and pathways modulated by epigenetic inactivation of SULF2 and the effects on sensitivity to chemotherapy were characterized in lung cancer in vitro and in vivo; silencing SULF2 primarily increased expression of interferon-inducible genes including ISG15 22293178_Heparan sulfate sulfatase SULF2 regulates PDGFRalpha signaling and growth in human and mouse malignant glioma 22410125_Sulf-2 expression is be critical for human breast cancer progression. 23418199_Sulf2 is overexpressed in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and may play a role in regulating TGF-beta1 signaling in type II alveolar epithelial cells. 23457216_studied the functional consequences of HSulf-2 activity on fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-induced mitogenesis and found that the enzyme could differentially regulate FGF1 and FGF2 activities 23480519_Ectopic expression of SULF1 or SULF2 in HeLa cells, which decreases cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan sulfation, diminished Chlamydia muridarum binding and decreased vacuole formation. 23950901_Knockdown of SULF2 in human corneal epithelial cell line slowed migration, which was restored by overexpression of either mouse SULF2 or human SULF1. 24124496_SULF2 methylation is negatively associated with cisplatin sensitivity in vitro. 24278138_Results indicate that the genetic variation rs2281279 in SULF2 associates with postprandial clearance of remnant TRLs and triglyceride levels in healthy subjects. 24339435_The SULF2 single nucleotide polymorphism was reproducibly associated with lower fasting plasma triglycerides levels in obese type 2 diabetic subjects. 24359226_SULF2 promoter methylation was associated with irinotecan sensitivity in gastric carcinoma. 24726914_SULF1/SULF2 splice variants regulate pancreatic tumor progression. 25036960_pectin induced the expression of HSulf-2 through the interaction with fibronectin, alpha5beta1 integrin, and ERK1/2 25127119_Substrate specificity of human SULF2. 25164011_Our findings define Sulf-2 as a novel positive regulator of neuroblastoma pathogenicity that contributes to MYCN oncogenicity. 25325976_SULF2 expression in human tumor tissue and cell lines, was assessed. 25444749_SULF2 blood levels increased with age in both healthy and cirrhosis patients.SULF2 blood level was higher in cirrhosis patients than healthy individuals. 25477293_Results show that SULF1 or SULF2 overexpression contributes to colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. 25887999_SULF2 have a pro-tumorigenic effect in DU-145 and PC3 cancer cells, suggesting an important role of this enzyme in prostatic cancer metastasis. 26708018_Our data confirmed that Sulf2 promoted breast cancer progression and regulated the expression of tumor-related genes in breast cancer. 26882224_Tumor expression of SULF2 may affect prognosis in NSCLC, while blood SULF2 levels may have a significant role in the diagnosis of this fatal disease. 26895473_results demonstrated that SULF2 can mediate the detrimental effects of ionizing radiation in vivo 26959705_SULF2 is a multifaceted protein involved in triglyceride-rich lipoprotein homeostasis and angiogenesis. [review] 27013228_The SULF1/SULF2 activation thus does not only promote regulated foetal growth and injury-induced liver regeneration but also dysregulated tumour growth. 27223083_Although no change in SULF2 was detected in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSCC) serum, its detection in saliva makes it worthy of further investigation as a potential HNSCC biomarker. 27294358_The short variants of Sulf2 promoted FGF2-induced MDA-MB231 and MCF7 in vitro growth while full-length Sulf1 inhibited growth supporting in vivo mammary tumour cell signalling patterns of growth. 27560551_Most pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas had positive SULF2 staining in tumour cells and intratumoural or tumour-adjacent stroma. Elevated SULF2 in PDAC was associated with advanced tumour stage, vascular invasion, shorter interval to radiological progression and shorter overall survival. 27589337_renal cell carcinoma with lower SULF-2 expression might have a higher potential for cell invasion and proliferation, leading to a poorer prognosis via the activation of VEGF and/or FGF signaling 27748846_Sulf2 facilitated lymphangiogenesis in breast cancer cells by regulating VEGF-D and that the AKT1related signaling pathway was involved. 28193024_The activity of sulfatase 2, a major form of endosulfatase in hepatocellular carcinoma can be studied, in connection with the interactions between heparan sulfate and various growth factors. 28320104_SULF2 promotes the growth and metastasis of CRC probably by activating Akt and Erk1/2 pathways. 29062064_Loss of SULF2 expression is associated with corticospinal tract defect. 29360432_High SULF2 expression is associated with glioma. 29720727_SULF2 plays a key role in sorafenib susceptibility. 30698737_TRF2 positively regulates SULF2 expression increasing VEGF-A release and activity in tumor microenvironment 31499680_miR-527 targeting SULF2 down-regulates SULF2 expression, concurrently, suppresses NSCLC epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion via inhibiting TGF-beta/SMAD signaling pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer 33735525_Sulfatase 2 (SULF2) Monoclonal Antibody 5D5 Suppresses Human Cholangiocarcinoma Xenograft Growth Through Regulation of a SULF2-Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor Beta-Yes-Associated Protein Signaling Axis. 33908819_Extracellular sulfatases as potential blood-based biomarkers for early detection of lung cancer. 35472437_SULF2 enhances GDF15-SMAD axis to facilitate the initiation and progression of pancreatic cancer. 36068294_Extracellular sulfatase-2 is overexpressed in rheumatoid arthritis and mediates the TNF-alpha-induced inflammatory activation of synovial fibroblasts. | ENSMUSG00000006800 | Sulf2 | 88.968078 | 0.447268312 | -1.160788 | 0.29500401 | 15.169733 | 0.0000982659354581178910627986544668033275229390710592269897460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0010129284489227361864410736913555410865228623151779174804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 60.8684970 | 14.0760770 | 136.2479392 | 30.7851781 | |
| ENSG00000196664 | 51284 | TLR7 | protein_coding | Q9NYK1 | FUNCTION: Endosomal receptor that plays a key role in innate and adaptive immunity (PubMed:14976261, PubMed:32433612). Controls host immune response against pathogens through recognition of uridine-containing single strand RNAs (ssRNAs) of viral origin or guanosine analogs (PubMed:31608988, PubMed:27742543, PubMed:12738885, PubMed:32706371). Upon binding to agonists, undergoes dimerization that brings TIR domains from the two molecules into direct contact, leading to the recruitment of TIR-containing downstream adapter MYD88 through homotypic interaction (PubMed:27742543). In turn, the Myddosome signaling complex is formed involving IRAK4, IRAK1, TRAF6, TRAF3 leading to activation of downstream transcription factors NF-kappa-B and IRF7 to induce pro-inflammatory cytokines and interferons, respectively (PubMed:27742543, PubMed:32706371). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12738885, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14976261, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27742543, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31608988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32433612, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32706371}. | 3D-structure;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Leucine-rich repeat;Lysosome;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family which plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. TLRs are highly conserved from Drosophila to humans and share structural and functional similarities. The human TLR family comprises 11 members. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that are expressed on infectious agents, and mediate the production of cytokines necessary for the development of effective immunity. For the recognition of structural components in foreign microorganisms, the various TLRs exhibit different patterns of expression as well; in this way for example, TLR-3, -7, and -8 are essential in the recognition of single-stranded RNA viruses. TLR7 senses single-stranded RNA oligonucleotides containing guanosine- and uridine-rich sequences from RNA viruses, a recognition occuring in the endosomes of plasmacytoid dendritic cells and B cells. This gene is predominantly expressed in lung, placenta, and spleen, and is phylogenetically related and lies in close proximity to another family member, TLR8, on chromosome X. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. | hsa:51284; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; early phagosome [GO:0032009]; endolysosome membrane [GO:0036020]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endosome [GO:0005768]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; pattern recognition receptor activity [GO:0038187]; single-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003727]; siRNA binding [GO:0035197]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; I-kappaB phosphorylation [GO:0007252]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interferon-alpha production [GO:0032727]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0060907]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001932]; toll-like receptor 7 signaling pathway [GO:0034154]; toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002224] | 12032557_Human TLR7 or TLR8 independently confer responsiveness to the antiviral compound R-848. 12045249_Interferon-alpha and interleukin-12 are induced differentially by Toll-like receptor 7 ligands in human blood dendritic cell subsets. 15695821_IRF5 and IRF7 are critical mediators of TLR7 signaling 15778362_Plasmacytoid dendritic cell-derived type I IFN enhanced TLR7 sensitivity of B cells by selectively up-regulating TLR7 expression 16025564_TLR7 acts as a host sensor for human parechovirus 1, and activates signalling that leads to the synthesis of pro-inflammatory molecules by the host. 16116638_The agonist isatoribine resulted in dose-dependent changes in immunologic biomarkers and a statistically significant antiviral effect with relatively few and mild side effects in hepatitis C. 16230478_TLR9 may have a critical role in the promotion of lupus through the induction of IFN-alpha by predendritic cells. 16446426_evidence showing that a ligand of Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) can induce anti-HCV immunity not only by IFN induction, but also through an IFN-independent mechanism 16517754_TLR-7 'licenses' human B cells to respond to cytokines of the adaptive immune system (such as IL-2) and provide a strategy to increase the immunogenicity of lymphoma cells for therapeutic purposes 16623926_Stimulation of in vitro-generated murine Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) knockout DC and human TLR-transfected HEK293 cells with dsRNA fragments gave no evidences for the involvement of pDC-specific TLR7 or TLR9 in the observed IFN-alpha induction. 16887967_A profound sex-dependent pathway of TLR7-induced interferon (IFN)-alpha production is revealed with higher production in females. 16935934_TLR3 agonist poly(I:C) activated epithelial cells, primary endothelial cells, and two types of primary human smooth muscle cells (airway [ASMC] and vascular) directly, while the TLR7/8 agonist R848 required the presence of leukocytes to activate ASMC 16973388_Autoantibody production is largely dependent on Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) and causes kidney pathology in nucleic acid-containing autoantigen knockin mice. 17023556_These data lead us to suggest that ongoing viral activation of TLR7/8 could alter the adaptive immune response by modifying DC differentiation and by down-regulating DC responsiveness to a subsequent bacterial TLR4-mediated signal. 17040905_TLR8 inhibits TLR7 and TLR9, and TLR9 inhibits TLR7 but not vice versa in HEK293 cells transfected with TLRs in a pairwise combination. 17075576_results implicate involvement of toll-like receptors, particularly TLR7, and type 1 specific interferon signaling in the pathogenesis of BA, especially in early stage, which is associated with upregulation of inflammatory cytokines IL-8 17301562_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17371961_Our data reveal for the first time a strong inhibitory effect of TLR7 stimulation on IFN-alpha production induced by CpG-A- and CpG-C-ODNs. 17512627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17512627_The c.1-120G TLR7 allele offers protection from the development of inflammation and fibrosis in male patients with chronic HCV-infection. 17608805_CYLD, a novel deubiquitinase, acts as a negative regulator of TLR7 induction by nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae 17609264_Epstein-Barr virus initially uses TLR7 signaling to enhance B-cell proliferation and subsequently modifies the pathway to regulate IRF-5 activity. 17698957_Both types of compounds induced IFN-gamma-inducible protein 10, but only the 7-deazaguanosine-containing compound that activated both TLR7 and TLR8 induced IFN-alpha in monkeys 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17907191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17907191_relative gene copy number of TLR7 was not significantly increased among our SLE patients as compared with our controls.No trend between the relative gene copy number and the autoantibody profile in SLE patients. 17956986_IFN-alpha produced after HIV-induced TLR7 stimulation was responsible for TRAIL expression and the down-regulation of both CXCR4 and CCR5 by IKpDC 17964520_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18021446_Our results show that PAMP receptors, TLR3, TLR7 and RIG-I mRNA levels are significantly down-regulated in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection when compared with healthy controls. 18088248_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18088248_This study reports the association of TLR7 variants with chronic HCV-infection and with the response to interferon-alpha therapy in patients with chronic HCV-infection. 18215354_There is downregulation of TLR7 expression mRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of hepatitis B virus-infected patients 18250417_Direct involvement of human TLR7 is demonstrated in the induction of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha by single-stranded RNAs in the macrophage-like THP-1 cell line. 18385087_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18385087_TLR variants are unlikely to have a major impact on overall AMD risk, and the common variants studied were not associated with AMD. 18406377_TLR7-9 recognize single-stranded RNA, nucleoside analogs and single-stranded CpG-DNA, respectively, and their activation initiates the immune response against viruses and bacteria [review] 18431484_These results delineate the complex effects of triggering TLR7/8 for an efficient antiviral defense. 18474259_TLR-7 signaling stimulates apoptosis resistance, associated with enhanced iNOS expression (protein and mRNA) and NO release, notably through an NF-kappaB-dependent activation of the NO pathway. 18535206_CD300a and CD300c play an important role in the cross-regulation of TNF-alpha and IFN-alpha secretion from pDCs; CD300a/c RNA and surface expression were downregulated after stimulation of pDCs with TLR7 and TLR9 ligands 18596825_the Toll-like receptor 7 agonist imiquimod inhibits melanogenesis and proliferation of human melanocytes 18682521_replicated association was obtained for SNPs or haplotypes of TLR7 and TLR8, suggesting these genes as novel disease genes for asthma and related disorders. 18686608_Human epidermal keratinocytes constitutively express all TLR 1-10 mRNA, which may enable human keratinocytes to respond to a wide range of pathogenic micro-organisms. 18806803_Divergent TLR7 and TLR9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and nonpathogenic AIDS virus infections. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18949362_Up-regulation of natural killer cell function against head and neck cancer in response to single-stranded immunostimulatory RNA requires TLR7. 18995892_Perturbation of TLR-7 on naive human B cells can lead to the induction of immunoglobulin class switch and IgG production in the absence of B-cell receptor cross-linking and CD40-CD40L interaction. 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19114863_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19120473_inappropriate activation of TLR7 predisposes to systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases; nucleotides with antagonistic effect on TLR7 reported for the treatment 19129482_activation via TLR7 and TLR9 affects several eosinophil functions 19164127_the Jak/STAT signaling pathway was involved in CD40 expression and cytokine production in TLR7-stimulated DCs but negatively regulated CD83 expression and cytokine secretion in DCs activated through TLR8 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19265114_Synergy between TLR4 and TLR7/8 controls the sequential production of regulatory and proinflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-10, interferon (IFN)-gamma, and IL-17A by naive CD4-positive T cells. 19381167_The ligand-induced activation of TLR7 leads to the accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1alpha) protein in THP-1 human myeloid macrophages via redox- and reactive nitrogen species-dependent mechanisms. 19406482_expressed on Fallopian tube and uterus 19452306_The mRNA levels for TLR7 were increased among the children with a history of OME. 19454678_In pDC, recognition of ssRNA and dsRNA oligonucleotides was TLR7-dependent 19473567_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19473567_there were no statistically significant differences between the allele and genotype distribution of TLR5 (toll-like receptor 5) rs5744168 and TLR7 (toll-like receptor 7) rs179008 polymorphisms in Systemic lupus erythematosus patients and controls 19505919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19553637_plasmacytoid dendritic cells , through this unusual TLR7 signaling, have the capacity to promptly respond to viral infection during the early phases of the innate immune response 19564354_Data show that BST2 directly binds to purified ILT7, initiates signaling via the ILT7-FcepsilonRIgamma complex, and regulates TLR7/9 responses in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. 19614650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19740627_Cultured human melanocytes express functional toll-like receptors 2-4, 7 and 9. 19794067_These results reveal a TLR7/9-dependent signaling pathway used by human PBMCs to initiate a type I IFN response to the extracellular bacterium B. burgdorferi. 19821521_Reduced TLR7 expression, due to RNA instability, directly correlates with HCV replication and alters TLR7-induced IRF7-mediated cell activation. These results suggest a role for TLR7 in HCV-mediated evasion of host immune surveillance. 19841637_Activation of endosomal TLRs 7, 8 and 4 leads to downregulation of degradative HIF-1 alpha prolyl hydroxylation. 19887600_TLR3 or TLR7 ligand stimulation of tumor cells enhances the cytotoxic activity of expanded gammadelta T cells of cancer patients in vitro. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19915052_When dendritic cells were triggered with the potent synergistic combination of TLR4 and TLR7/8 in conjunction with a TLR2 ligand, there was a clear shift to more Th2- and Th17-prone responses in the naive and memory T cell subpopulations 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19954299_the abnormal expression of TLR7 in CD8(+) T cells from HIV-1-infected individuals may contribute to the abnormal immune activation in HIV-1 infection 20007807_Plasmacytoid dendritic cells respond to cell-free human T-cell leukemia virus 1 by producing high levels of IFN-alpha and by mobilizing TRAIL on cell surface after TLR7 triggering. 20026744_TLR7 activation in plasmacytoid dendritic cells represents a missing link between innate and adaptive immune mechanisms and contributes to the amplification of T helper cell interleukin (Th)17-driven autoimmune disorders as well as viral host defense. 20042593_Sensing of human metapneumovirus 5' triphosphate RNA is via TLR7 rather than the viral RNA helicase retinoic acid-inducible gene RIG-I. 20100933_Studies show substantial decreases in older compared with young individuals in cytokine production in response to TLR1/2, TLR6, TLR3, TLR5, and TLR8, TLR7 and TLR9 in DCs. 20124101_Data show that TLR activation was associated with significantly increased production of IL-1beta, IL-6, TNF-alpha, and CCL3. 20194452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20227302_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237413_Triggering of TLR7 and TLR8 expressed by human lung cancer cells induces cell survival and chemoresistance. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20309865_Our findings indicate that TLR-3 and TLR-7 are expressed in inflammatory myopathic tissues, particularly in immature myoblast precursors. 20390327_a TLR7-dependent impairment of costimulatory molecule expression caused by HCV persistence may affect DC activity in non-responder patients. 20399690_In individuals affected by primary Sjogren's syndrome, TLR7 mRNA levels are up-regulated in the mononuclear blood cells and TLR7-positive cells exist in the epithelial islands, lymphocytes, and ductal epithelial cells of the parotid glands. 20410486_counterregulation of FcepsilonRI and TLR-7 pathways exists in Plasmacytoid dendritic cells 20412752_TLR8 contributes to lung inflammation, NSCLC progression, cell survival via BCL-2 production & resistance to antineoplastic agents. Review. 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20525845_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20559388_a new role for self nucleic acid recognition by toll-like receptors TLR7 and TLR9 on B cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells 20588308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20592251_Human plasmacytoid predendritic cells were highly sensitive to glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis but they were protected by microbial stimulation through TLR7 and TLR9. 20595247_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20605567_SV5 induced interferon alpha secretion by plasmacytoid dendritic cells requires signaling throught TLR7 and autophagy. pathways. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20733074_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20733074_data established a functional polymorphism in type I IFN pathway gene TLR7 predisposing to systemic lupus erythematosus, especially in Chinese and Japanese male subjects 20819670_The concentrations of TLR1, TLR3, TLR4, TLR7 and TLR9 appeared to be increased in bacterial pleural effusion compared to non-bacterial pleural effusions. 20821041_B cells can be directly activated viaTLR1/TLR2, TLR7, and TLR9 to induce secretion of cytokines, chemokines, and hematopoietic growth factors and suggest a role of B cells in immune response against microbial pathogenesis and immune homeostasis. 20832340_Human CD14dim monocytes patrol and sense nucleic acids and viruses via TLR7 and TLR8 receptors. 20872712_The Toll-like receptor 7 rs179008/Gln11Leu gene variant was associated with the presence of portal lymphoid aggregates in chronic hepatitis C infection. 20977567_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21037581_TLR7 is important for pruritus elicited primarily by nonhistaminergic pruritogens, although a partial role of TLR7 in histamine-dependent itch is not excluded. 21039888_TLR7 regulates DC-dependent B-cell responses through BlyS in the pathogenesis of ITP 21061265_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21092001_Suppressed G-CSF production in the presence of IFN-alpha may contribute to IFN-alpha-induced neutropenia. However, a TLR7/8 agonist elicits G-CSF secretion even in the presence of IFN-alpha. 21167247_There is no suggestive relationship between TLR7 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to Behcet Syndrome. 21354862_TLR 7 and TLR8 expressions are associated with poor outcome and greater inflammatory response in acute ischemic stroke. 21396113_Our findings support a role of TLR7 in predisposition for systemic lupus erythematosus in Asian populations. 21435390_Cigarette smoke suppresses key plasmacytoid dendritic cells functions upon viral infection by a mechanism that involves downregulation of TLR7 expression and decreased activation of IRF-7. 21458848_TLR7 promotes Th1 polarization and may contribute thus in the pathogenesis of immune thrombocytopenia. 21515789_Data show that that TLRs 3, 7, and 9 are expressed by human dorsal root ganglion neurons (DRGNs) and in cultures of primary mouse DRGNs. 21527067_High expression of TLR4, TLR7, and TLR9 may play important roles in the development and progression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical squamous cell carcinoma in Uighur women. 21543762_Toll-like receptor 7 is crucial for development of age-related B cell population. 21677671_Toll-like receptors (TLRs) 6, 7, and 8 are upregulated in keloid scars 21730058_endothelin-1 has a role in linking Toll-like receptor 7-mediated inflammation to fibrosis in congenital heart block 21734241_monoclonal antiphospholipid antibodies as well as IgG fractions from patients with antiphospholipid syndrome increase mRNA expression of the intracellular TLR7 in plasmacytoid dendritic cells and TLR8 in monocytes 21844166_TLR7/9 versus TLR3/MDA5 signaling during virus infections and diabetes. 21947541_we found no evidence of any functional effects of TLR7 or TLR8 polymorphisms on receptor expression, measles-specific cellular responses or measles vaccine antibody responses. 21958189_Study suggests that the regulatory signals associated with CD19 and CD5 in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) are down-regulated by Toll-like receptor-7 (TLR-7) engagement. 21977996_Data suggest that the response pattern of human and rhesus B cells and pDCs to TLR7/8 and TLR9 is similar, although some differences in the cell surface phenotype of the differentiating cells exist. 21990957_Data suggest that TLR3, TLR4, TLR7 and TLR9 expression is important to the biological pathogenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 22022576_Variations in TLR7 and TLR8 genes might impair immune responses during hepatitis C virus infection. 22065095_We suggest that TLR7 rs179008 and TLR9 rs5743836 can be considered systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility factors for women of European descent 22196370_Dual or triple activation of TLR7, TLR8, and/or TLR9 by single-stranded oligoribonucleotides. 22210629_Responsiveness to TLR7/8 stimulation, which have been shown to recognize HIV-1 ssRNA, did not decrease in chronic infection, and may represent a contributing factor to ongoing T-cell immune activation in the setting of chronic viremic HIV-1 infection. 22243920_The study provides evidence that the TLR7 and TLR8 triggering can suppress HIV replication in monocytes and lead to postpone HIV disease progression. 22363482_Segments 1, 2, 3 and 4 may be major determinants of the stimulatory activity exerted on human TLRs 7 and 8. 22423970_Systematic identification of novel cofactors required for TLR7 and TLR9 directed innate immunity signaling responses. 22488361_PACSIN1 represents a pDC-specific adaptor molecule that plays an important role in the TLR7/9-mediated type I IFN responses by pDCs in vitro and in vivo. 22505023_TLR7 gene rs1634323 polymorphism may contribute to SLE susceptibility in females. 22525943_Authors demonstrate the use of ImageStream in DCs to assess TLR7/8 activation-mediated increases in phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of a key transcription factor. 22543675_TLR7 was expressed in macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques. 22610069_extracellular let-7 activates the RNA-sensing Toll-like receptor (TLR) 7 and induces neurodegeneration through neuronal TLR7 22684144_Impaired IFN-alpha production from plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) may contribute to the immunopathogenesis of chronic HBV infection, which may be the result of a reduced amount of pDCs as well as decreased expression of TLR7 and TLR9 on pDCs 22730373_These results suggest that expression of TLR7, but not TLR8, may be a predictor for rheumatoid arthritis disease activity 22786773_These new findings reveal distinct and overlapping signaling mechanisms used by B-cell antigen receptor and IFNAR in the regulation of TLR7 tolerance and activation. 22787112_TLR7, a receptor recognizing self-nucleic acid complexes, is protective in atherosclerosis. 22857391_Single nucleotide polymorphism in the TLR7 gene is associated with allergic rhinitis. 22952664_Toll-like receptor 7 stimulates the expression of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 22952899_The present study was undertaken to characterize responses of B cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients to TLR7 and TLR9 stimulation and to explore the potential role of SIGIRR. 23023703_TLR7 ligation modulates pancreatic cancer by driving stromal inflammation. 23069256_Hepatitis virus induces down-regulation of TLR7 gene expression through IFN-gamma, thereby modulating inflammatory signaling in hepatoma cells. 23150717_Enhanced B-cell TLR7 expression permits specific development of autoantibodies to RNA/protein complexes, which exacerbate the chronic systemic autoimmune disease, systemic lupus erythematosus. 23179584_TLR7 expression was not associated with prognosis in cutaneous malignant melanoma. 23221735_Cervical tumor Langerhans cells lacked TLR9 expression and were functionally anergic to all the 3: TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9 ligands, which may play a crucial role in immune tolerance. 23369718_Studies indicate that the nucleic acid-sensing toll-like receptors (TLRs), which include TLRs 3, 7, 8 and 9 are completely localized within the endosomal compartments of immune cells and recognize RNA and DNA from pathogens. 23376919_IRAK-M mediates TLR7-induced MEKK3-dependent second wave NFjB activation to produce inhibitory molecules 23382558_Type I interferon (IFN)-dependent inhibition of T cell-derived interleukin (IL)-5 is mediated by IFN-alpha acting directly on activated T cells. 23386618_Complement receptor 3 influences toll-like receptor 7/8-dependent inflammation 23425350_Impaired TLR3 and TLR7/8-mediated cytokine responses may contribute to aggressive HCV recurrence postliver transplantation 23468661_Reduced modulation by miR-3148 conferred slower degradation of the risk G-allele containing TLR7 transcripts. These data establish rs3853839 of TLR7 as a shared risk variant of SLE(systemic lupus erythematosus ) 23489702_Liver expression of TLR2, TLR3 and TLR7, which are more involved in the immune-pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis C, was investigated. 23497717_Elevated levels of TLR7 signaling molecules and their positive correlation with disease activity in adult-onset Still's disease patients suggest involvement of the TLR7 signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of this disease 23523654_Results of the current study have shown that some clinical enterovirus strains hold a great potential to elicit cytokines response, which is mediated in part by TLR7 activation. 23526932_homology modeling and molecular docking studies were employed to probe the intermolecular interactions between TLR7 and its agonists 23564191_The presence of anti-ENA and anti-dsDNA autoantibodies in SLE patients was associated with elevated levels of TLR7 and TLR9 respectively. 23636665_our data unveil a novel TLR7-regulated mechanism in in vivo IFN-beta-stimulated whole leukocytes that could be exploited to define new TLR7-based strategies for the treatment of multiple sclerosis 23826189_Study evaluated innate immune profiles following TLR stimulation in HIV-1-infected mothers and newborns, found significantly compromised cytokine responses upon extracellular and intracellular TLR activation. Myeloid dendritic cell (DC) responsiveness appeared to be less impaired than plasmacytoid DCs, and might be enhanced through TLR7/TLR8 activation. 23827939_Neu1 sialidase and matrix metalloproteinase-9 cross-talk regulates nucleic acid-induced endosomal TOLL-like receptor-7 and -9 activation, cellular signaling and pro-inflammatory responses. 23924358_Toll-like receptor 7 is a pattern recognition receptor in the lungs that detects single-stranded RNA genomes. 24046015_Data indicate that TLR-induced IL-1beta overproduction in FANCA- and FANCC-deficient mononuclear phagocyte cell lines and primary cells requires activation of the inflammasome. 24071890_In females, the incidence of the X-linked TLR7 rs179008/Gln11Leu polymorphism was significantly lower in sarcoidosis patients. 24138882_Processing of human toll-like receptor 7 by furin-like proprotein convertases is required for its accumulation and activity in endosomes. 24227841_A-to-I editing of structured viral RNAs facilitated the activation of TLR7 and TLR8. 24269682_Data indicate the ability of C protein to block Toll-like receptor (TLR) 7- and TLR9-dependent IFN-alpha induction. 24347177_TLR7 was expressed by Hela cells. 24375473_Data indicate Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) as a key molecule in TLR9 signaling in plasmacytoid dendritic cells (PDCs) and the TLR7 and TLR9 pathways can be dissociated in PDCs. 24445780_The TLR7 rs179010 T risk allele was also associated with anti-SSA autoantibodies. These findings suggest that TLR7 may play a key role in autoantibody production 24447081_results reveal broad expression patterns of TLR5 and TLR7 in the lung and that the expression is decreased in severe asthma. 24532514_Single nucleotide polymorphism of TLR7 IVS2-151 (rs179009) G/A may be a factor for susceptibility to chronic hepatitis C in the female Han population. 24616506_proapoptotic activity is mediated by a microRNA cargo, miR-21, which signals through the Toll-like 7 receptor on myoblasts to promote cell death 24692849_TLR3, 7, and 9 play a role in the pathogenesis of SLE and have an impact on organ involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus 24719462_Heterogeneous functional effects of concomitant B cell receptor and TLR stimulation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia with mutated versus unmutated Ig genes 24740301_Data show that Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) stimulates B cell proliferation at a higher level. 24747071_the CD4T cell count during the viremic period might be linked to the combination of both TLR7 (Gln11Leu) and TLR9 (1635A/G) genotypes. 24755410_platelet-TLR7 stimulation is independent of thrombosis and has implications to the host immune response and survival. 24771848_Differently, costimulation of TLR2, TLR4, and TLR7/8 enhances IL-1beta secretion but severely inhibits IL-1Ra production. 24773332_In vitro treatment of PBMCs with R484 hijacks the pro inflammatory immune process triggered by TLRs7/8 to mediate anti-inflammatory response. 24813206_TLR7 and TLR8 can signal in two different 'modes' depending on the class of ligand. 24865418_Data indicate that Toll-like receptor 7, Toll-like receptor 9, and interferon-alpha expression levels were significantly increased in lupus patients. 24866018_Different types of neurons traffic TLR7 to distinct membrane locations, affecting the functional response of neurons to let-7b stimulation. 24886842_mRNA and corresponding protein expression of TLR3, TLR7, TLR9, RIG-I and MDA-5 were analyzed in nasal biopsies and various upper airway epithelial cell lines. 24909816_Results suggest that the TLR7 response following Japanese encephalitis virus infection promotes type-1 interferon production and generation of antiviral state which might contribute to protective effect in systemic infection 24919757_Our study confirms the association between the rs3853839 polymorphism of TLR7 and systemic lupus erythematosus in a Danish cohort. 24971541_These data indicate that imiquimod triggers IP3 receptor-dependent Ca(2+) signaling independently of TLR7. 24990399_expression up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue 24994112_TLR7 played an important role in macrophage apoptosis and cytokine secretion through the CHOP-dependent pathway. 25005350_Toll-like receptor 7 may be involved in the development of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis. 25008898_Hepatitis C virus infection decreases the expression of TLR-3 and TLR-7 via upregulation of miR-758. 25034660_The functional polymorphism of TLR7 rs3853839C allele was found to be sex specific and associated with protection against HCV persistence among Chinese females, which may be due to specific IFN-alpha and IL-6 secretion profiles. 25051971_The results argue against a fixed orientation of the tRNA during interaction with TLR7 and, rather, suggest a processive type of inspection. 25108054_TLR7 rs179009 GG genotype and haplotype GCG were associated with an increased risk of the susceptibility to HCV infection among Chinese females, which may be due to the impaired IFN-alpha response. 25126563_TLRs 3, 7, and 8 are prime biomarker candidates for HCV infection mRNA expression analysis which might improve current therapeutic approaches. 25187660_the UNC93B1 tyrosine-based motif regulates trafficking and TLR responses via separate mechanisms. 25204046_Data show that a differential mRNA expression of Toll-like receptors 7 & 8 is associated with different responses to pegylated interferon (PEG-IFN) alpha-2b antiviral therapy in patients with hepatitis C infection. 25211222_TRAM plays a role in TLR7 signaling through a novel signaling axis towards the activation of anti-viral immunity. 25218653_SNPs in TLR7 had a negative effect on spontaneous clearance of hepatitis C virus among males and a protective effect against hepatitis C infection among females. 25229618_Humanized TLR7/8 expression drives proliferative multisystemic histiocytosis in C57BL/6 mice 25309919_The expression of TLR-3, -7, and -9 is increased when the macrophages were treated with the supernatant of cervical cancer cells. 25401424_Silencing of TLR7 markedly decreased the frequency of HIV-1-infected CD4(+) T cells and restored the responsiveness of those HIV-1(+) CD4(+) T cells. 25430040_rs179010 in TLR7 may be associated with the decreased susceptibility to Graves' disease in Chinese Cantonese. 25586463_TLR9 and TLR7 were upregulated both at the mRNA and the protein levels in wounds of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients compared with the non-diabetic patients and may lead to an unresolved inflammatory response and non-healing chronic ulcers. 25650422_This study provides evidence that a high copy number of TLR7 confers risk for BD in a Chinese Han population. 25667414_Data show that chemokine CXCL13 production by monocytes required toll-like receptor 7 activation and secretion of interferon-alpha. 25720442_This study established a correlation between miR-155 and TLR7 during hepatitis B virus infection and also demonstrated in vitro that increased miR-155 level could help to reduce viral load by targeting C/EBP-beta. 25741726_TLR7 receptors are involved in the targeting of axons in the transgenic Drosophila olfactory circuit. 25763771_These studies identify that TLR7 stimulation leads to the expansion of IL-10-producing CD19(+) CD1d(hi) B cells, which can suppress allergic lung inflammation via T regulatory cells. 25785446_an important role of 2'-O-methylation for shaping differential TLR7 or TLR8 activation 25790192_Results show that patients with Sjogren's syndrome present alteration in B cell subpopulation composition compared to controls, but no significant disparities in TLR-7 and -9 expression is detected between the two groups. 25817271_human Toll-like receptor 7 ligand binding domain 25828894_The low expression of TLR-7 in tumour and high expression of TLR-7 in stroma predict a good clinical outcome for oral squamous cell carcinoma patients 25862837_TLR 2, 4, 5, 7 and 9 appear to reflect certain clinicopathological variables and prognostic markers of MCC tumors 25879168_These findings suggest that the TLR7 IVS1 +1817G/T and TLR7 c.4-151A/G polymorphisms may be important in the susceptibility or clinical course of CCHF disease. 25882779_discovery demonstrated that TLR 7 can be activated by coupling an antigen to the terminal carboxyl group at N9 of the inactive ligand adenine analogues 25912131_Present results propose a putative role of TLRs 3,7, and 9 in the growth process of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. 25917086_The data reveal a novel role for the N terminus of hTLR7 as a molecular chaperone that provides processed hTLR7 with the correct targeting instructions to reach the endosomal compartment, ensuring its biological activity. 25923141_A key regulatory cytokine found increased upon TLR7 stimulation. 25941114_High TLR 7 expression is associated with HPV-positive tumors in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 26018863_Plasmacytoid dendritic cells from SLE patients carrying the disease-associated PTPN22 variant LypW showed a reduced capacity for TLR-7 agonist-induced type I IFN production. 26041742_Microenvironmental interleukin-6 suppresses TLR7 signaling in human leukemia cells through miR-17/19A. 26044169_Intranasal GSK2245035 has an acceptable safety profile | ENSMUSG00000044583 | Tlr7 | 210.520252 | 2.078850729 | 1.055786 | 0.16589215 | 40.067914 | 0.0000000002452849568877639893306254705902672355599669629100390011444687843322753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000070452689465011137807695133718384472576445887170848436653614044189453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 290.9667237 | 27.7158446 | 140.8755455 | 13.8823690 | |
| ENSG00000196684 | 84941 | HSH2D | protein_coding | Q96JZ2 | FUNCTION: May be a modulator of the apoptotic response through its ability to affect mitochondrial stability (By similarity). Adapter protein involved in tyrosine kinase and CD28 signaling. Seems to affect CD28-mediated activation of the RE/AP element of the interleukin-2 promoter. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11700021, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12960172, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15284240}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain | T-cell activation requires 2 signals: recognition of antigen by the T-cell receptor (see TCR; MIM 186880) and a costimulatory signal provided primarily by CD28 (MIM 186760) in naive T cells. HSH2 is a target of both of these signaling pathways (Greene et al., 2003 [PubMed 12960172]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:84941; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; negative regulation of B cell apoptotic process [GO:0002903]; negative regulation of mitochondrial depolarization [GO:0051902]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell activation [GO:0042110] | 11700021_involved in tyrosine kinase signaling in hematopoietic cells 12960172_ALX is an adaptor involved in T cell activation and interleukin-2 (IL-2) promoter activation 15284240_the ALX SH2 domain plays a critical role in ALX function downstream of CD28 16169852_ALX exerts its effect on IL-2 up-regulation in the cytoplasm and responds to TCR and CD28 signaling 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20080636_results indicate that RvD1 specifically interacts with both ALX and GPR32 on phagocytes. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20471366_although ALX is inducibly phosphorylated upon TCR/CD28 stimulation, this phosphorylation is not required for ALX to inhibit T cell activation. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 24166736_LXA decreased IgM and IgG production on activated human B cells through ALX/FPR2-dependent signaling. 26248046_pro-inflammatory stimuli lead to FPR2/ALX expression while LXA4 induces an anti-inflammatory response 27860453_Both ALX and ChemR23 were present in human synovium and medial tibial plateau bone obtained following total knee replacement surgery for osteoarthritis. 33000278_HSH2D contributes to methotrexate resistance in human Tcell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. | ENSMUSG00000062007 | Hsh2d | 32.638074 | 0.291648565 | -1.777697 | 0.31752915 | 32.011296 | 0.0000000153278719914548261359369725085818880749854997702641412615776062011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000003447046196406272005618195812537418731835714424960315227508544921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 14.8811019 | 3.6065655 | 51.3351815 | 11.0736334 | |
| ENSG00000196814 | 89853 | MVB12B | protein_coding | Q9H7P6 | FUNCTION: Component of the ESCRT-I complex, a regulator of vesicular trafficking process. Required for the sorting of endocytic ubiquitinated cargos into multivesicular bodies. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Endosome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport | The protein encoded by this gene is a component of the ESCRT-I complex, a heterotetramer, which mediates the sorting of ubiquitinated cargo protein from the plasma membrane to the endosomal vesicle. ESCRT-I complex plays an essential role in HIV budding and endosomal protein sorting. Depletion and overexpression of this and related protein (MVB12A) inhibit HIV-1 infectivity and induce unusual viral assembly defects, indicating a role for MVB12 subunits in regulating ESCRT-mediated virus budding. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. | hsa:89853; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; ESCRT I complex [GO:0000813]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; membrane fission [GO:0090148]; multivesicular body assembly [GO:0036258]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; protein transport to vacuole involved in ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the multivesicular body sorting pathway [GO:0043328]; regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0042058]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the multivesicular body sorting pathway [GO:0043162]; viral budding [GO:0046755]; virus maturation [GO:0019075] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20583170_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20654576_These results suggest that the expression of MVB12B may be normally suppressed through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway that simultaneously regulates the fate of MVB12A and the functions of ESCRT-I. 22232651_The 1.3-A atomic resolution crystal structure of the MVB12B MABP domain reveals a beta-prism fold, a hydrophobic membrane-anchoring loop, and an electropositive phosphoinositide-binding patch. 24518671_Study suggests a novel association between SNPs in FAM125B andintra-ocular pressure in the TwinsUK cohort. | ENSMUSG00000038740 | Mvb12b | 129.969096 | 0.114605105 | -3.125257 | 0.90259238 | 9.788677 | 0.0017558975009391542768805161145451165793929249048233032226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0121712062651818074543452752322991727851331233978271484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 32.2748531 | 15.3280025 | 279.9395721 | 132.7569614 | |
| ENSG00000197506 | 64078 | SLC28A3 | protein_coding | Q9HAS3 | FUNCTION: Sodium-dependent, pyrimidine- and purine-selective (PubMed:11032837, PubMed:15861042, PubMed:16446384, PubMed:17140564, PubMed:21998139). Involved in the homeostasis of endogenous nucleosides (PubMed:11032837, PubMed:15861042). Exhibits the transport characteristics of the nucleoside transport system cib or N3 subtype (N3/cib) (with marked transport of both thymidine and inosine) (PubMed:11032837). Employs a 2:1 sodium/nucleoside ratio (PubMed:11032837). Also able to transport gemcitabine, 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT), ribavirin and 3-deazauridine (PubMed:11032837, PubMed:17140564). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11032837, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15861042, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16446384, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17140564, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21998139}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | Nucleoside transporters, such as SLC28A3, regulate multiple cellular processes, including neurotransmission, vascular tone, adenosine concentration in the vicinity of cell surface receptors, and transport and metabolism of nucleoside drugs. SLC28A3 shows broad specificity for pyrimidine and purine nucleosides (Ritzel et al., 2001 [PubMed 11032837]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:64078; | brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; nucleoside transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005337]; nucleoside:sodium symporter activity [GO:0005415]; purine nucleobase transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005345]; purine-specific nucleoside:sodium symporter activity [GO:0015390]; pyrimidine- and adenine-specific:sodium symporter activity [GO:0015389]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; uridine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015213]; nucleoside transmembrane transport [GO:1901642]; purine nucleobase transmembrane transport [GO:1904823]; purine nucleoside transmembrane transport [GO:0015860]; pyrimidine nucleoside transport [GO:0015864]; pyrimidine-containing compound transmembrane transport [GO:0072531]; uridine transport [GO:0015862]; xenobiotic transmembrane transport [GO:0006855] | 14504928_hCNT3 gene is evolutionarily conserved with hCNT1 and hCNT2. Physiologically, hCNT3 is a glycoprotein, which transports purine and pyrimidine nucleosides in a Na-dependent manner with high affinities. 15738947_genetic analysis and functional characterization of CNT3 variants suggest that this transporter does not tolerate nonsynonymous changes and is important for human fitness 15861042_examination of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the coding regions of the hCNT3 gene 15870078_hCNT3 possesses two Na+-binding sites, only one of which is shared by H+ 16271041_The effects of cysteine substitution mutants spanning transmembrane domains 11-13 on the transport activity of CNT3 expressed in S. cerevisiae are reported. 16446384_Minimal features required for human CNT3 transport are two hydrogen bond acceptors at 3'-OH and 5'-O and the hydrophobic center occupied by the base ring. 17409283_transcripts for CNT3 protein in human kidneys and in cultured proximal tubule cells suggest involvement of CNT3 in renal handling of nucleosides and nucleoside drugs 17412768_CNT3 was inserted into the apical membrane, thus generating, a transepithelial flux of both nucleosides and nucleoside-derived drugs. 17453413_hCNT2 shares common cation specificity and coupling characteristics with hCNT1, which differ markedly from those of hCNT3. 17696452_This study shows that adenosine elimination on human airway epithelia is mediated by ADA1, CNT2, and CNT3, which constitute important regulators of adenosine-mediated inflammation. 17926640_These data suggest that selected genes of the SLC28 and SLC29 families are not only targets of HIV-1 infection, but might also contribute to the development of adipose tissue alterations leading to lipodystrophy. 17993510_A polymorphic variant of the human concentrative nucleoside transporter, CNT3, is found that severely affects its functionality. 18199742_identified a C-terminal intramembranous cysteine residue of hCNT3 (Cys-561) that reversibly binds the hydrophilic thiol-reactive reagent p-chloromercuribenzene sulfonate (PCMBS) 18621735_a pivotal functional role for Cys-561 in Na+- as well as H+-coupled modes of hCNT3 nucleoside transport 18827020_The isolation and charcterization of an alternatively spliced SLC28A3-related mRNA is reported. 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19297449_This evidence suggested that apical CNT3 and basolateral ENT2 are involved in proximal tubular reabsorption of adenosine and some nucleoside drugs and that apical ENT1 is involved in proximal tubular secretion of 2'-deoxyadenosine. 19318496_Pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients with a high expression of hENT1 and hCNT3 immunostaining have a significantly longer survival after adjuvant gemcitabine-based chemoradiation 19380585_identified residues of functional importance and with a revised 15-TM membrane architecture, suggest a novel membrane-associated topology for a region of the protein (TM 11A) that includes the highly conserved CNT family motif (G/A)XKX(3)NEFVA(Y/M/F) 19380587_identified two conserved pore-lining glutamate residues (Glu-343 and Glu-519) with essential roles in CNT3 Na(+)/nucleoside and H(+)/nucleoside cotransport 20028759_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20172853_TGF-beta1 acts through activation of ERK1/2 and the small GTPase RhoA to promote plasma membrane trafficking of the hCNT3 protein. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20495821_H+ drives uridine and adenosine transport by hCNT3 with lower affinity but higher maximal transport rate than Na+. 20643903_Acidic and hydrophobic motifs in the N terminus tail of the hCNT3 control ER export and cell surface expression levels in nonpolarized cells, whereas a putative beta-turn domain contributes to hCNT3 polarized surface expression in epithelial cells. 21346688_A genetic variant in SCL28A3 coding for the concentrative nucleoside transporter 3 protects patients with chronic hepatitis C against hemolytic anemia without affecting sustained virological response in hepatitis C virus genotype 1. 21822668_Data show that ENT1, ENT2, ENT4 and CNT3 protein was detected on ovarian carcinoma cells in all effusions, with expression observed in 1-95% of tumor cells. 23195617_association between ribavirin (RBV) serum levels and SLC28A2 rs11854484 genotype, as well as the replicated association of ITPA and SLC28A3 genetic polymorphisms with RBV-induced anemia and treatment response 23441093_Validation of variants in SLC28A3 and UGT1A6 as genetic markers predictive of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity in children. 24300978_The presence of homozygous major allele for SLC28A3 (CC genotype) were each associated with an almost two-fold increase in the formation clearance of dFdCTP. 24361227_Genetic polymorphisms in SLC28A3, SLC29A1 and RRM1 can influence the clinical outcome of metastatic breast cancer patients treated with paclitaxel-gemcitabine chemotherapy. 25955569_Results show that high CNT3 expression level is associated with overall favorable outcomes and is predictive of clinical outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia patients with t(8;21). 26188009_Genome-wide association analysis on normal hearing function identifies PCDH20 and SLC28A3 as good candidates for modulatory genes in the auditory system. [meta-analysis] 26481311_The co-expression of galectin-4 and CNT3 proteins is not impaired in inflamed colon from patients with Crohn's disease, thereby anticipating the integrity of this system for drug targeting. 27604902_CYR61 negatively regulates the nucleoside transporters hENT1 and hCNT3 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 28385889_results that validate the newly developed structural homology model of CNT membrane architecture for human CNTs, revealed extended conformationally mobile regions within transport-domain TMs, identified pore-lining residues of functional importance, and provided evidence of an emerging novel elevator-type mechanism of transporter function. 28661652_Data suggest that CNT3 forms a homotrimer in solution and membrane-bound inside cells; the quaternary structure creates an aqueous basin that significantly shortens the substrate translocation distance. 28774292_De novo structure prediction of three N-terminal transmembrane helices of the human concentrative nucleoside transporter 3 (hCNT3) homotrimer belonging to the solute carrier 28 family of transporters (SLC28) using Rosetta program and its Broker protocol. 30096006_human CNT3 homology models generated validate previously published PCMBS SCAM data, and confirm an elevator-type mechanism of membrane transport 30778771_Association of SLC28A3 Gene Expression and CYP2B6*6 Allele with the Response to Fludarabine Plus Cyclophosphamide in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patients. 32776918_Cryo-EM structure of the human concentrative nucleoside transporter CNT3. 33910126_Characterization of deoxyribonucleoside transport mediated by concentrative nucleoside transporters. 33974709_Gene-Gene Interactions of Gemcitabine Metabolizing-Enzyme Genes hCNT3 and WEE1 for Preventing Severe Gemcitabine-Induced Hematological Toxicity. 34751688_Allosteric and transport modulation of human concentrative nucleoside transporter 3 at the atomic scale. | ENSMUSG00000021553 | Slc28a3 | 21.449187 | 0.491552274 | -1.024583 | 0.35158466 | 8.511165 | 0.0035297399228928073681987864773645924287848174571990966796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0215716617709885288833859817714255768805742263793945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 12.8515559 | 4.6359699 | 26.2654226 | 9.2282017 | |
| ENSG00000197594 | 5167 | ENPP1 | protein_coding | P22413 | FUNCTION: Nucleotide pyrophosphatase that generates diphosphate (PPi) and functions in bone mineralization and soft tissue calcification by regulating pyrophosphate levels (By similarity). PPi inhibits bone mineralization and soft tissue calcification by binding to nascent hydroxyapatite crystals, thereby preventing further growth of these crystals (PubMed:11004006). Preferentially hydrolyzes ATP, but can also hydrolyze other nucleoside 5' triphosphates such as GTP, CTP and UTP to their corresponding monophosphates with release of pyrophosphate, as well as diadenosine polyphosphates, and also 3',5'-cAMP to AMP (PubMed:27467858, PubMed:8001561, PubMed:25344812, PubMed:28011303). May also be involved in the regulation of the availability of nucleotide sugars in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi, and the regulation of purinergic signaling (PubMed:27467858, PubMed:8001561). Inhibits ectopic joint calcification and maintains articular chondrocytes by repressing hedgehog signaling; it is however unclear whether hedgehog inhibition is direct or indirect (By similarity). Appears to modulate insulin sensitivity and function (PubMed:10615944). Also involved in melanogenesis (PubMed:28964717). Also able to hydrolyze 2',3'-cGAMP (cyclic GMP-AMP), a second messenger that activates TMEM173/STING and triggers type-I interferon production (PubMed:25344812). 2',3'-cGAMP degradation takes place in the lumen or extracellular space, and not in the cytosol where it is produced; the role of 2',3'-cGAMP hydrolysis is therefore unclear (PubMed:25344812). Not able to hydrolyze the 2',3'-cGAMP linkage isomer 3'-3'-cGAMP (PubMed:25344812). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P06802, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10615944, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25344812, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27467858, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28011303, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28964717, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8001561, ECO:0000305|PubMed:11004006}. | 3D-structure;Biomineralization;Calcium;Cell membrane;Diabetes mellitus;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Obesity;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc | This gene is a member of the ecto-nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase (ENPP) family. The encoded protein is a type II transmembrane glycoprotein comprising two identical disulfide-bonded subunits. This protein has broad specificity and cleaves a variety of substrates, including phosphodiester bonds of nucleotides and nucleotide sugars and pyrophosphate bonds of nucleotides and nucleotide sugars. This protein may function to hydrolyze nucleoside 5' triphosphates to their corresponding monophosphates and may also hydrolyze diadenosine polyphosphates. Mutations in this gene have been associated with 'idiopathic' infantile arterial calcification, ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine (OPLL), and insulin resistance. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:5167; | basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004115]; 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate binding [GO:0050656]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP diphosphatase activity [GO:0047693]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; cyclic-GMP-AMP hydrolase activity [GO:0106177]; dinucleotide phosphatase activity [GO:0004551]; exonuclease activity [GO:0004527]; GTP diphosphatase activity [GO:0036219]; insulin receptor binding [GO:0005158]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; nucleoside triphosphate diphosphatase activity [GO:0047429]; phosphatase activity [GO:0016791]; phosphodiesterase I activity [GO:0004528]; polysaccharide binding [GO:0030247]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; scavenger receptor activity [GO:0005044]; UTP diphosphatase activity [GO:0036221]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate metabolic process [GO:0050427]; ATP metabolic process [GO:0046034]; biomineralization [GO:0110148]; bone mineralization [GO:0030282]; cellular phosphate ion homeostasis [GO:0030643]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; generation of precursor metabolites and energy [GO:0006091]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inorganic diphosphate transport [GO:0030505]; melanocyte differentiation [GO:0030318]; negative regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030502]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599]; negative regulation of glucose import [GO:0046325]; negative regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0045719]; negative regulation of hh target transcription factor activity [GO:1990787]; negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046627]; negative regulation of protein autophosphorylation [GO:0031953]; nucleic acid phosphodiester bond hydrolysis [GO:0090305]; nucleoside triphosphate catabolic process [GO:0009143]; phosphate ion homeostasis [GO:0055062]; phosphate-containing compound metabolic process [GO:0006796]; regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030500]; response to ATP [GO:0033198]; response to inorganic substance [GO:0010035]; sequestering of triglyceride [GO:0030730] | 11473061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11771660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11771660_The IVS15-14T --> C substitution in the human NPPS gene is associated not only with susceptibility to, but also with severity of OPLL. 11916943_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12126783_polymorphic in normoalbuminuric type 1 diabetic patients 12147786_in type 1 diabetic patients, the ACE and the PC-1 genes interact in increasing the individual risk of having a faster diabetic nephropathy progression 12147787_Amino acid variant (K121Q) has no impact on progression of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetic patients 12441313_Insulin modulates PC-1 processing and recruitment in cultured human cells.autophosphorylation. Insulin stimulates PC-1 posttranslational processing and translocation to the plasma membrane, which in turn impairs insulin receptor signaling. 12483464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12483464_PC1 has a role in predisposition to early myocardial infarction 12547881_In healthy normoglycemic Finnish subjects, the K121Q polymorphism of the PC-1 gene is associated with insulin resistance but not with impaired insulin secretion or dyslipidemia. 12547881_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12715715_study suggests that both examined polymorphisms: the -308 G/A in the promoter region of TNF-alpha and K121Q amino acid variant of the PC-1 influence the development of insulin resistance as a prediabetic quantitative trait in a Polish population 12740448_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12881724_Mutations in ENPP1 are associated with 'idiopathic' infantile arterial calcification. 14514598_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14671192_PC-1 K121Q polymorphism associates with primary insulin resistance in migrant Asian Indians. High frequency of this polymorphism may be one factor contributing to insulin resistance susceptibility in Asian Indians. 15001634_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15001634_PC-1 Q121 allele is exceptionally prevalent in the Dominican Republic, contributing to both insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. 15045693_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15126519_Interaction between the K121Q polymorphism of the PC-1 gene and birth length affects insulin sensitivity and increases susceptibility to type 2 diabetes and hypertension in adulthood 15374726_The K121Q polymorphism of the plasma cell membrane glycoprotein 1 gene is significantly associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) susceptibility. 15677494_Plays a role in insulin resistance and suggests that animals with overexpression of human PC-1 in liver may be interesting models to investigate insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. 15793263_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15793263_Our study supports the hypothesis that ENPP1 121Q predicts genetic susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in both South Asians and Caucasians. 15802034_Increased lymphocyte PC-1 activity was associated with end-stage renal failure patients on haemodialysis 15834329_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15834329_The IVS20-11delT variant of the NPPS gene and the A861G variant of the leptin receptor gene are associated with more extensive OPLL, but not with the frequency with which it occurs. 16025115_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16186408_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16186408_ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1(ENPP1/PC-1) 121Q variant is associated with a progressive deterioration of the insulin resistance-atherogenic phenotype and earlier onset of type 2 diabetes and myocardial infarction 16207325_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16231022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16272817_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16272817_The K121Q polymorphism of the plasma cell membrane glycoprotein-1 (PC-1) gene is unlikely to be a major genetic factor predisposing to preeclampsia in Finnish women. 16278247_Overexpression of ENPP1 induces insulin resistance and hyperglycemia. 16527214_Analysis of the DNA variations of ENPP1 provides a first molecular basis for the physiopathologic association between severe insulin resistance and obesity, and further type 2 diabetes. 16527214_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16607460_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16607460_the K121Q variant of the ENPP1 gene has very little, if any, impact on type 2 diabetes (T2D) susceptibility in Japanese, but may play a role in the inter-ethnic variability in insulin resistance and T2D 16609882_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16865358_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16865358_the ENPP1 K121Q polymorphism does not seem to influence the risk of insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes in Danish white subjects; however, a meta-analysis of the present and published studies demonstrates evidence of association with type 2 diabetes 16936213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16936213_we found a new SNP, rs997509, in intron 1 that is strongly associated with risk of type 2 diabetes in obese individuals. 16941279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16968801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16968801_role of the K121Q polymorphism or derived ENPP1 haplotypes in increased susceptibility to obesity and early impairment of glucose and insulin metabolism in children. 17026496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17026496_a significant association of PC-1 K121Q with obesity 17043047_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17065358_No evidence that previously associated variants of ENPP1 are associated with type 2 diabetes or obesity in the U.K. population. 17065358_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17065359_No association with three variants and body mass index or type 2 diabetes. 17065359_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17129580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17129580_PC-1 (ENPP1) 121Q allele is associated with the genetic susceptibility for metabolic syndrome in patients with coronary heart disease 17143316_Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase phosphodiesterase 1 as a 'gatekeeper' of insulin receptors. 17192490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17228024_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17287921_There is a lack of correlation between genetic expression of ENPP1 and body mass index. This may suggest that glucose metabolism is more complex than lipid metabolism. 17367703_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17491709_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17493546_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17493546_THE 121Q allele frequency may contribute to increased susceptibility to type 2 diabetes observed in US minority groups. 17563456_Overexpression of ENPP1 in insulin target tissues is an early, intrinsic defect observed in human insulin resistance 17606264_functional interactions between alkaline phosphatase and ENPP1(PC-1) may link insulin resistance to vascular calcification. 17704904_Nominal evidence of association between the K121Q polymorphism and both severe adult obesity at baseline and risk of hyperglycaemia or type 2 diabetes . 17704904_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17719609_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17848394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17986276_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17986276_Our results suggest that the ENPP1121Q allele might contribute to the genetic susceptibility to abdominal obesity among subjects with MS. 18071025_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18071025_The ENPP1 Q121 variant increases risk of type 2 diabetes under a recessive model of inheritance in whites, an effect that appears to be modulated by body mass index. 18176722_K121Q polymorphism is more common among Afro-Brazilian descendants regardless of glycemic status or insulin sensitivity indices. Likewise, insulin sensitivity and DM chronic complications appear not to be related to the polymorphism in this sample. 18176722_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18184924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18184924_Variants in the distal region of the ENPP1 gene may contribute to diabetes or diabetic nephropathy susceptibility in African Americans. 18222177_Results describe the activities of ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase and adenosine deaminase in patients with uterine cervix neoplasia. 18389334_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18389334_Report association between K121Q polymorphism of ENPP1 and peripheral arterial disease. 18426862_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18426862_The Q allele of ENPP1 K121Q is associated with hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in whites. 18464750_ENPP1 is a genetic determinant of obesity-related phenotypes in a Mexican American population with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 18464750_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18498634_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18551113_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18551113_Results did not find association between the frequently studied ENPP1 K121Q variant, nor SNPs in the MCR or POMC genes and obesity or type 2 diabetes. 18583883_ENPP1 121Q genotype (KQ+QQ types) was not associated with type 2 diabetes (odds ratios [OR], 0.854; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.571-1.278) or obesity (OR, 0.933; 95% CI, 0.731-1.190) in South Korea 18583883_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18657335_ENPP1-121Q is involved in the genetic susceptibility of type 2 diabetes in the Tunisian population. 18664022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18664022_The prevalence of the PC-1 121Q allele was significantly higher in type 2 diabetic patients who suffered from CHD, compared to type 2 diabetic patients without CHD. 18690303_Ecto-nucleotide pyrophophastase/phosphodiesterase 1 polymorphism has no association with PCOS. 18690303_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18719658_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18719658_Variants of ENPP1/PC-1 are associated with obesity in the male Turkish population; thus, these variants may contribute to the development of the obesity in these individuals. 18776139_Homozygous carriers of the ENPP1 Q121 variant are characterized by an altered glucose homeostasis 18776139_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18823720_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18940878_ENPP1 rs997509T allele can predispose obese children to MS and IGT and that this variant might drive the association between the ENPP1 121Q allele and insulin resistance. 18940878_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18948963_ENPP1 single nucleotide polymorphism variant may protect against overweight and obesity in Italian chidren. 18948963_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18950909_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18950909_Our data suggest that patients with type 2 diabetes carrying the ENPP1 Q121 variant are at increased risk of decreased GFR. 19017751_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19017751_ENPP1 K121Q is associated with increased diabetes incidence; the DPP lifestyle intervention eliminates this increased risk. 19046915_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19046915_There is an association of K11Q polymorphism in ENPP1 and type 2 diabetes and obesity in a Moroccan population. 19056482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19083193_Data suggest that HSP70, by affecting ENPP1 expression, may be a novel mediator of altered insulin signaling. 19086938_The investigators found evidence of an association between a polymorphism in the ENPP1 gene and the development of generalized arterial calcification of infancy that led to the death of the infant. 19107338_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19107338_The K121Q variant of ENPP1 may be associated with hepatitis C viremia and core antigen levels in HCV carriers 19206175_Generalized arterial calcification of infancy is characterized by calcification of the major arteries and soft tissues and is aassociated with mutations in the ENPP1 gene. 19368707_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19374858_Inhibition of insulin signaling by PC-1 is somewhat specific and is dependent upon the enzymatic activity of the phosphodiesterase/pyrophosphatase. 19399648_K121Q, rs7566605, and rs894160 are not major contributing factors for obesity for ENPP1, INSIG2 and PLIN 19399648_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19403348_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19420105_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19506043_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19506043_epistatic effects of five candidate genes, including ADIPOQ, ENPP1, GHSR, PPAR and TCF7L2, are significantly associated with the risk of DN amongst Taiwanese T2D individuals. 19577557_Suppression of PC-1 expression improves insulin sensitivity in vitro and in an animal model of diabetes 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19643578_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19656007_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19656007_genetic variants of the ENPP1/PC-1 gene are associated with hypertriglyceridemia in male subjects, and may contribute to the development of the insulin resistance/metabolic syndrome in this population 19679831_ENPP1 Q121 variant is associated with increased pulse pressure in vivo and reduced insulin signaling and endothelial dysfunction in vitro 19679831_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19876004_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19888898_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19888898_found evidence for association of bone geometry variation with an SNP in ENPP1, a gene in the mineralization pathway. The alteration of a binding site of the deregulator of extracellular matrix HOXA7 warrants further investigation 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19931660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20015201_NPP1 is down-regulated in calcified advanced plaques. NPP1 levels are higher in severely calcified lesions, most likely reflecting a counter-active mechanism. NPP1 serves as a novel player orchestrating plaque calcification. 20016754_ENPP1 coding region mutations are associated with generalized arterial calcification of infancy. 20091022_ENPP1 K121Q polymorphism determines individual susceptibility to the insulin-sensitising effect of lifestyle intervention 20091022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20092902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20092902_Our study demonstrates that the ENPP1 K121Q and MMP3 -709A>G polymorphisms are associated with type 2 diabetes, and that the ENPP1 Q allele is associated with increased aortic arch calcification in a Korean population. 20137772_The identification of an inactivating mutation in the ecto-nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (ENPP1) gene causing autosomal-recessive hypophosphatemic rickets (ARHR) with phosphaturia, is demonstrated. 20137773_ENPP1 is the fourth gene-in addition to PHEX, FGF23, and DMP1-that, if mutated, causes hypophosphatemic rickets resulting from elevated FGF23 levels. 20176643_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20186155_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20200332_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20231843_Associations were observed between ENPP1 polymorphisms and BMI (P=0.0037) and leptin (P=0.0068). 20231843_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20428609_No association was found between polymorphism K121A of ENPP1 gene and the presence of ischemic heart disease. 20428609_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20446819_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20446819_findings suggest that the upstream, promoter and 3' untranslated regions in the ENPP1 locus harbor genetic variants affecting different aspects of craniofacial morphology 20503258_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20709678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20709678_association of ENPP1 K121Q with type 2 diabetes in Hubei Han Chinese population is more evident in women. 20820885_ENPP1/PC-1 K121Q polymorphism is not associated with type 2 diabetes and related quantitative metabolic traits in North Indian Punjabi population. 20958205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20958205_The specific role of ENPP1 K121Q on ethnic susceptibility to PTDM deserves further investigation in larger cohorts of transplanted patients. 20981035_K121Q of ENPP1 might not have a major role in the susceptibility to T2 diabetes mellitus or obesity in the Chinese Han population. 20981035_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21076580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21153685_The ENPP1 K121Q polymorphism is not associated with type 2 diabetes and related metabolic traits in an Iranian population. 21162834_ENPP1 gene polymorphism rs1409181 was associated with left ventricular hypertrophy in older Chinese people in Guangzhou. 21195542_A correlation is found between the up-regulated expression of NPP1 and the grade of the astrocytic tumor 21198320_We confirmed the association between the rs1044498 SNP in ENPP1 and diabetic nephropathy, especially among obese diabetic patients, in the Taiwanese population. 21282363_The ENPP1 K121Q polymorphism is an independent predictor of major cardiovascular events in high-risk individuals. In type 2 diabetes, this effect is exacerbated by obesity. 21452007_The ENPP1 K121Q polymorphism is not associated with type 2 diabetes in the northern Chinese population. 21565692_The results from the present study have indicated that ENPP1/PC1 Q121 variant may increase the risk of obesity. 21573217_Data clearly indicate that ENPP1, especially when the Q121 variant is operating, affects insulin signaling and glucose metabolism in skeletal muscle- and liver-cells. 21602183_ESRD patients with left ventricular hypertrophy is consistently associated with genetic variability of ENPP1 gene in caucasian patients. 21647535_PC-1 2906C allele was significantly more frequent in patients who suffered from stroke before the age of 40 years. In these patients the risk for ischaemic stroke was increased four-fold. 21738662_Data identified two key mediators of vascular calcification and bone metabolism, ENPP1 and OPG, which offer a molecular explanation for the major phenotypic differences in vascular and bone disease in sporadic and hereditary HGPS. 21810932_In the presence of a high-fat diet, ENPP1 overexpression in adipocytes induces fatty liver, hyperlipidemia, and dysglycemia, thus recapitulating key manifestations of the metabolic syndrome. 22136912_In the Chinese population, the ENPP1 K121Q gene polymorphism was implied to be involved with type 2 diabetes mellitus susceptibility 22209248_ABCC6 mutations accounted for a significant subset of generalized arterial calcification of infancy patients, and ENPP1 mutations could also be associated with pseudoxanthoma elasticum lesions in school-aged children. 22231969_K121Q polymorphism of the ENPP1 gene seems to be associated with insulin resistance and diabetic nephropathy development. 22327785_no association of PC-1 Gln121 gene found with obesity in Amerindians; PC-1 Gln121 gene is associated with higher levels of HDL-cholesterol than PC-1 Lys121 allele; Amerindians have intermediate frequency of PC-1 Gln121 gene compared with African Americans or Han Chinese 22366713_A genetic polymorphism in the intron 9 of the ENPP1 gene was associated with calcific aortic valve disease in a case-control cohort as well as with mRNA expression levels of ENPP1 in aortic valves. 22402064_Individuals carrying the ENPP1 Q121 variant are highly responsive to the effect of weight loss on fasting glucose so the Q121 variant interacts with adiposity in modulating glucose homeostasis. 22484154_Human phosphodiesterase 1 is regulated by a tandem of N-terminal calmodulin/Ca(2+)-binding domains. 22826605_Our results establish PCA-1/ALKBH3 as important gene in pancreatic cancer 22842219_NPP1 is known to play vital roles in calcium/phosphate regulation, and repression of soft tissue mineralisation, as well as maintaining skeletal structure and function. 22846899_The expression of ENTPD1 and ecto-adenosine deaminase in lymphocytes of Chagase disease patients are reported. 22899099_the ENPP-1 Q121 variant plays a role in modulating the risk of premature atherosclerotic events, particularly in obese individuals 23012391_Increased adipose tissue ENPP1 is associated with adipose tissue dysfunction, increased liver triglyceride deposition, and systemic insulin resistance in young normoglycemic men. 23111648_ENPP1 (and PLIN) genes contribute to the risk of type 2 diabetes in a Taiwanese population. 23122642_Mutations in the underlying disease genes ENPP1, ABCC6, NT5E, and SLC20A2, respectively, lead to arterial media calcification. 23422753_mutation in GOLGB1 (Y1212C) and another mutation in ENPP1 (K173Q) were confirmed as having significant associations with a decreased risk for stroke 23433854_Platelets and serum E-NPP1 activity increased in prostate cancer patients. 23451554_The findings suggest that ENPP1 polymorphisms may contribute to different metabolic characteristics, all of which are associated with insulin resistance in mixed ancestry children of South Africa. 23861746_these data suggest a potential role for Enpp1 in the development of breast cancer bone metastasis. 24075184_Biallelic mutations in ENPP1 were shown to underlie a number of recessive conditions characterized by ectopic calcification. 24222241_Specific genotypes of the NPP1 gene IVS20-11delT and A533C SNPs may predict ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament disease outcome after surgical intervention. 24242286_The mutant homozygous genotype of ENPP! K121Q, was more prevalent in diabetic hypertensive MI patients than it was among non-diabetic normotensive MI patients. 24338010_The combined studies expand our understanding of NPP1 and NPP4 substrate specificity and range and provide a rational mechanism by which polymorphisms in NPP1 confer stroke resistance. 24371178_The ENPP1 K121Q gene polymorphism is associated with insulin resistance in an obese North Indian population. 24531536_these results reveal that E-NPP1, by acting upstream of E2F1, is indispensable for the maintenance of glioblastoma stem-like cells in vitro and hence required to keep GSCs in an undifferentiated, proliferative state. 24947519_Both NPP1 and NPP3 ectoenzymes are expressed in N2a cells, their levels dramatically changing when cells differentiate into a neuronal-like phenotype 25025693_Polymorphisms in ALP, ENPP1 and ANKH are important genetic risk factors contributing to Pseudoxanthoma elasticum 25109753_findings show the Q allele of the ENPP1 K121Q gene may contribute to the susceptibility for type 2 diabetes in Caucasians and Asians 25222839_In pregnant women, association of both pre-gestational BMI and age with AA homozygous ENPP1 genotype increased significantly the risk of positive oral glucose tolerance test. 25231727_EphA3 was induced by PC-1 and contributed to the malignant progression of prostate cancer 25344812_ENPP1 2'3'-cGAMP-hydrolyzing activity is repsonsible for tumor progression in humans and mice. 25368487_the ENPP1 K121Q polymorphism is associated with insulin resistance during web-based lifestyle intervention, and the K121 allele has a beneficial effect of weight loss on insulin resistance. 25504209_patterns were confirmed in human teeth, including widespread TNAP, and NPP1 restricted to cementoblasts lining acellular cementum 25594612_ENPP1 rs1805101 polymorphism is associated with Insulin resistance and advanced Diabetic nephropathy. 25615550_this study identified only 1 mutation in ENPP1 in the Chinese pseudoxanthoma elasticum population 25644539_Expression of NPP1 and 5'-nucleotidase by valve interstitial cells promotes the mineralization of the aortic valve through A2aR and a cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway. 25741938_Loss of function mutation in ENPP1 is associated with early onset hearing loss in autosomal recessive hypophosphatemic rickets. 25794151_The present meta-analysis detected a significant association between the ENPP1K121Q polymorphism and increased susceptibility of diabetic kidney disease in European and Asian populations. 26065921_ENPP1 was also identified as a substrate of the 26S proteasome, the activity of which is downregulated in CSCs 26405014_we found that patients with severe asthma exacerbation had reduced activity of leukocyte ectonucleotidases and reduced expression of E-NPP1 in PMNs. 26617416_Results suggest that heterozygous mutations in the SMB domains of ENPP1 are necessary, but not always sufficient in themselves to cause Cole disease. 26868433_In this exploratory analysis, IRS1, ENNP1 and TRIB3, known to be associated with type 2 diabetes and harboring genes playing a prominent role in mediating insulin signaling, may modulate a number of cardiometabolic phenotypes in patients of Italian ancestry with newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes. 26958016_Our findings demonstrate that ENPP1, TCF7L2, and FTO may predispose to T2DM in the mixed-ancestry population. 27029882_A rare type of idiopathic infantile arterial calcification resulting from a mutation in the gene encoding for the ENPP1 enzyme. 27029896_ENPP1 defines a subset of human B cells that differs significantly from mouse peritoneal B-1a and proposed human B-1 cells. 27219689_The K121Q polymorphism of ENPP1 shows no direct correlation with metabolic syndrome in Han Chinese. 27238374_The ENPP1 rs1044498 SNP is associated with T2D. 27467858_Results identified four mutants (p.Tyr471Cys, p.Ser504Arg, p.Tyr659Cys, p.His777Arg) in ENPP1 gene with residual NPP activity, inorganic pyrophosphate generation and plasma membrane localization. 27519661_We have identified TT genotype of SNP rs858339 (ENPP1 gene) as a protective factor against TMD in a population of patients with dentofacial deformities. 27835608_PC-1 works in conjunction with E3 ligase CHIP to regulate androgen receptor stability and activity. 28011303_study provides rational and meaningful explanations of the substrate promiscuity of NPP1 by combining biochemical and molecular docking data; biochemical data provide detailed information including all relevant kinetic parameters of NPP1 obtained for a broad range of natural nucleotides and an artificial substrate 28080219_Evidence of a causative link between ENPP1 and alterations in insulin signaling, glucose uptake, and lipid metabolism in subcutaneous abdominal Adipose tissue of gestational diabetes, which may mediate insulin resistance and hyperglycemia in Gestational diabetes. 28381371_This study identifies the genetic variant rs9373000 as a potentially causal variant for mandibular condyle geometry variation for patients presenting with dento-facial deformities. 28415752_these results show that ENPP1 polymorphism influences lower anterior face height, the distance from the upper lip to the nasal floor, and lip shape 28942038_Single nucleotide polymorphism in ENPP1 gene is associated with developing of bone disorders in type 2 diabetes. 28951309_Single nucleotide polymorphism in ENPP1 gene is associated with Gender differences in type 2 diabetes. 28964717_Study concludes that germline ENPP1 cysteine-specific mutations, primarily affecting the melanocyte lineage, cause a clinical spectrum of dyschromatosis, in which the p.Cys120Arg allele represents a recessive and more severe form of Cole disease. 29103441_We investigated whether ENPP1 gene which contribute to sagittal and vertical malocclusions also contribute to facial asymmetries and temporomandibular disorders before and after orthodontic and orthognathic surgery treatment 29194839_this study shows that ENPP1 is biomarker candidate for endometriosis 29244957_This study for the first time analyzed the effect of decreased PPi on dental development in individuals with generalized arterial calcification of infancy (GACI) due to loss-of-function mutations in the ENPP1 gene.These findings reveal a novel dental phenotype in GACI and identify ENPP1 genetic mutations associated with hypercementosis. 29783211_ENPP1 rs997509 polymorphism is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus development in Ukrainian population. 29958952_ENPP1 gene variants may have a potential impact on the occurrence of T2 diabetes mellitus in Northern Iranians. 29979387_This meta-analysis revealed that the K121Q (rs1044498 C > A) in the ENPP1 gene is a risk factor for Coronary Heart Disease. 30099416_ENPP1 K121Q polymorphism is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Ukrainian population. In carriers of the minor Q-allele the risk of T2DM is 1.4x higher than in homozygotes in the main K-allele. The risk increases in patients with BMI >/= 25 kg/m2 30188771_These studies demonstrate the cooperative metabolism between diadenosine triphosphate and ENPP1 function to provide a significant source of adenosine, subserving its role in inflammatory resolution. 30356045_Findings provide insights into how ENPP1 hydrolyzes both ATP and cGAMP to participate in the two distinct biological processes. 30799235_The ENPP1 is well known for its role in regulating skeletal and soft tissue mineralization. It primarily exerts its function through the generation of pyrophosphate, a key inhibitor of hydroxyapatite formation. 30985656_Pilot study examined 3 candidate genes, ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase (ENPP1), ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 6 (ABCC6), and 5'-Nucleotidase Ecto (NT5E) involved in pyrophosphate (PPi) and inorganic phosphate (Pi) metabolism, which may predispose to coronary arterial or valvular calcification; report 4 new genetic variants potentially related to coronary calcification. 31250990_The first-ever report about the genotype of PC-1 gene in a Pakistani Punjabi population indicates that the PC-1 rs1044498 (K121Q) polymorphism was not found associated with insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. 31318911_The aim of this study was t | ENSMUSG00000037370 | Enpp1 | 127.844816 | 0.495356852 | -1.013460 | 0.21338884 | 22.306706 | 0.0000023239368430249737333985124432267355132353259250521659851074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000359593236285766951025599791336162525112740695476531982421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 63.1737403 | 15.0706333 | 128.1044252 | 30.0414837 | |
| ENSG00000197646 | 80380 | PDCD1LG2 | protein_coding | Q9BQ51 | FUNCTION: Involved in the costimulatory signal, essential for T-cell proliferation and IFNG production in a PDCD1-independent manner. Interaction with PDCD1 inhibits T-cell proliferation by blocking cell cycle progression and cytokine production (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | 3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Involved in negative regulation of activated T cell proliferation; negative regulation of interferon-gamma production; and negative regulation of interleukin-10 production. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be active in external side of plasma membrane. Biomarker of pulmonary tuberculosis. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:80380; | endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; immune response [GO:0006955]; negative regulation of activated T cell proliferation [GO:0046007]; negative regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032693]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; negative regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032689]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295] | 12538684_Blockade of PD-L2 during T cell responses initiated by allogenic dendritic cells increases T cell proliferation and cytokine production, showing that PD-L2 functions to inhibit T cell activation. 12893276_Binding properties of B7-DC to programmed death-1. 14515261_regulatory role of PD-1 and the differential roles of B7-H1 and B7-DC in hapten-induced immune responses. 14724428_Administration of anti-PD-L2 mAb did not significantly affect the prolongation of graft survival. 15253154_Two novel splice variants of PD-L2 were cloned and identified. 15837746_Data suggest that PD-L2 status may be a new predictor of prognosis for patients with esophageal cancer. 16278812_Via its interaction with programmed death-1 (PD-1) on human T cells, PD-L2 acts only as a negative regulator of T cell activity, inhibiting proliferation, IL-2 production, and IFN-gamma production. 16598819_PD-L2 negatively regulates human T cell activation and thus might be a candidate molecule for immunotherapeutic approaches aimed to attenuate pathological immune responses. 17136123_data do not support an association between systemic lupus erythematosus and SNP's within the genes of the PDCD1 ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 17203303_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17311651_Modulation of PD-L2 system may play a role in the development of autoimmune liver diseases. 17343323_PD-L2 47103 T may be associated with susceptibility to SLE in Taiwan 17597384_Polymorphisms of PD-L2 are not associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in Taiwan. 18203952_deficient cellular immunity observed in Hodgkin lymphoma patients can be explained by 'T-cell exhaustion,' which is led by the activation of PD-1-PD-L signaling pathway 18322304_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18378285_HRV-16 infection or exposure to dsRNA induces epithelial B7-H1 and B7-DC 18479731_Programmed death 1 is a marker of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma and B-cell small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 18566376_PD-1 has a key regulatory role during the immune response of the host to the pathogen 18992148_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19729380_Isolated decidual stromal cells constitutively express B7DC and B7H1; B7DC and B7H1 expression can be up-regulated (by IFN-gamma or TNF-alpha); B7DC and B7H1 appear to function in cell-to-cell communication. 19739236_All forms of chronic necroinflammatory liver disease examined correlate with increased B7-H1 and B7-DC expression on Kupffer cells, liver sinusoidal epithelial cells, and leukocytes. 20066438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20390427_Findings demonstrate that the pretreatment of tumor cells with IFN-gamma enhances B7-DC expression through ERK and JNK pathways. 20445553_the PD-1 pathway is active in immature Langerhans cells and inhibits iLC activities, but expression of receptor and ligands reverses upon maturation and PD-L1 and PD-L2 on mLC function to inhibit T-cell responses 20587542_PD-L1 and PD-L2 bound PD-1 with comparable affinities, but striking differences were observed at the level of the association and dissociation characteristics 20661763_Results suggest that over-expression of PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 within liver may participate in local immune dysfunction, which could be one of the mechanisms involved in the chronicity of HBV infection and chronic inflammation seen in CHB patients. 20682852_PD-L1 and PD-L2 knockdown dendritic cells showed superior potential to expand minor histocompatibility antigen-specific CD8(+) effector and memory T cells from leukemia patients early after donor lymphocyte infusion and later during relapse. 20709947_Transgenic PD-L2 affects transition to memory when expressed on antigen (Ag)-presenting cells at the beginning of interaction with T cells; notably, interaction with PD-1 on T cells is required during the initial encounter with Ag. 20722638_REVIEW: role of PD-L1 and PD-L2 and ligands in allergic disease and asthma. 21457347_increased expression of PD-L2, as a costimulatory molecule, may have an important modulatory function on the local immune responses of OLP in vivo. 21752471_These observations indicate that PD-L2 is expressed following activation and is involved in the regulation of T cell function 21791547_Our results suggest that PD-1 G-536A, PD-L1 A8923C and PD-L2 C47103T polymorphisms are associated with the presence of ankylosing spondylitis. 21876620_Data suggest that PD-L1 may contribute to negative regulation of the immune response in chronic hepatitis B, and that PD-1 and PD-L1 and 2 may play a role in immune evasion of tumors. 22067141_Data suggest that brain endothelial cells contribute to control T cell transmigration into the CNS and immune responses via PD-L2 but not PD-L1 expression. 22322668_Data show that PD-1, PD-L1, PD-L2, CCL17, and CCL22 mRNA was identified in papillomas. 22895698_expression of PD-1 and its ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, in liver biopsies from HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure (HBV-ACLF) and chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients were analyzed; results showed all 3 molecules were observed in the HBV-ACLF samples and levels were significantly higher than in CHB 23388330_PD-L1 and PD-L2 expressed on hPMSCs could inhibit the hPMSCs-mediated up-regulation on the expression of IL-17 secreted by peripheral blood T cells 23533995_Macrophages from infected animals show increased expression of PDL2 and CD80 that was dependent from the sex of the host. 24270737_High Expression of PD-L2 is associated with myelodysplastic syndromes. 24406080_PD-1/PD-Ls pathways on PMCs inhibited proliferation and adhesion activity of CD4+ T cells, suggesting that Mycobacterium tuberculosis might exploit PD-1/PD-Ls pathways to evade host cell immune response in human. 24497532_Recurrent genomic rearrangement events in CD274 and PDCD1LG2 underlie an immune privilege phenotype in a subset of B-cell lymphomas. 24532425_Data indicate that the bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) signaling pathway regulates PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression in monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MoDCs) during the maturation process. 25025450_conclude that PD-L2 protein is robustly expressed by the majority of primary mediastinal (thymic) large B-cell lymphomas 25349132_Results show that human-derived chordoma cell lines demonstrate inducible expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2, and that primary chordoma tissue shows variable expression of PD-1 and PD-L1 in infiltrating immune cells 25662388_PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression in pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma is associated with an increased number of CD8(+) tumor infiltrating lymphocytess and increased MET expression. 25675203_Suggest role for PD-L2 in recurrence of hepatitis C infection post orthotopic liver transplantation. 26081225_the inflammatory environment in Barrett's esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma may contribute to the expression of PD-L2. 26133691_We suggest that decreased expression of programmed death-ligand 1, 2 on psoriatic epidermis can contribute to its chronic unregulated inflammatory characteristics. 26317899_Genomic amplification of 9p24.1 targeting JAK2, PD-L1, and PD-L2 is enriched in high-risk triple negative breast cancer. 26329973_Data indicate that pulmonary pleomorphic carcinoma (PC) very frequently express CD274 antigen (PD-L1) and CD273 antigen (PD-L2). 26424759_PD-L2 expression was neither associated with VEGF-TKI responsiveness nor patients' outcome 26432559_PDL2 could promote the ability of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stromal cells to augment the secretion of IL-10. 26464193_High PD-L2 expression is associated with Renal Cell Carcinoma. 26541326_Report PD-L2 expression in breast neoplasms. 26599163_knocking down in dendritic cells results in activation of inflammatory T cells 26752545_PD-L1 and PD-L2 are useful new markers for identifying select histiocyte and dendritic cell disorders and reveal novel patient populations as rational candidates for immunotherapy 26913631_We observed cogain or coamplification of CD274 and PDCD1LG2 in 32 of 48 cervical and 10 of 23 vulvar squamous cell carcinomas 26980034_PDL2 was overexpressed in Epstein Barr virus-associated gastric adenocarcinoma. 27050074_PD-L2 copy number gains were not related to PD-L2 augmentation in non-small cell lung cancer. 27069084_PD-L1/PD-L2 copy number alterations are a defining feature of classical Hodgkin lymphoma. 27268263_stable ectopic expression of wild-type PDCD1LG2 and the PDCD1LG2-IGHV7-81 fusion showed, in coculture, significantly reduced T-cell activation. 27447090_the binding affinities of the PD-1-PD-L1/PD-L2 co-inhibitory receptor system, was characterized. 27456947_Overexpression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma 27533014_this study shows that higher PD-L2 expression on blood dendritic cells, from Plasmodium falciparum-infected individuals, correlates with lower parasitemia 27564404_an IL-27/Stat3 axis induces expression of programmed cell death 1 ligands (PD-L1/2) on infiltrating macrophages in lymphoma 27609582_The expression levels of PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 in CD3(+) T cells and CD19(+) B cells and serum IFN-gamma level in progressive hepatocellular carcinoma patients were significantly higher than controls. 27837027_in some tumor types, PD-L2 expression is more closely linked to Th1/IFNG expression and PD-1 and CD8 signaling than PD-L1 27921410_Downregulation of the immunosuppressive molecules, PD-1 and PD-L1, may imply that over-activation of immune cells in multiple sclerosis occurs through signaling dysfunction of these molecules and PD-L2 plays no important role in this context 28052400_higher expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 on CD1a(+) cells than that on CD83(+) cells in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma tumour tissues may contribute to negative regulation in anti-tumour immune responses 28369778_PDCD1LG2 (PD-L2) RNA in situ hybridization is a sensitive, specific, and practical marker of primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. 28488345_Low PD-L2 expression is associated with pediatric solid tumors. 28494868_PD-L2 is regulated by both interferon beta and gamma signaling. 28546465_The biopsy tumor key protein measurements demonstrate substantial between-tumor variation in expression ratios of these proteins and suggest that programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 PD-L2 is present in some tumors at levels sufficient to contribute to programmed cell death-1 PD-1-dependent T-cell regulation and possibly to affect responses to PD-1- and programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 PD-L1-blocking drugs. 28561677_PD-L2 expression has been reported in 52% of esophageal adenocarcinomas but little is known about the expression of other immune checkpoints 28619999_Clinical response to pembrolizumab in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC)may be related partly to blockade of PD-1/PD-L2 interactions. Therapy targeting both PD-1 ligands may provide clinical benefit in these patients. 28754154_the positive rate of PD-L2 did not show any differences between primary tumors and metastatic lymph nodes. In multivariate analysis, PD-L1 expression, PD-L2 expression, a low density of CD8(+) T cells in primary tumors, and PD-1 expression on CD8(+) T cells in primary tumors were associated with poor prognosis. 29038297_Tumor PDCD1LG2 expression is inversely associated with Crohn-like lymphoid reaction to colorectal cancer, suggesting a possible role of PDCD1LG2-expressing tumor cells in inhibiting the development of tertiary lymphoid tissues during colorectal carcinogenesis. 29061851_Data suggest that hormonal 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D is a direct transcriptional inducer of genes encoding PDL1 and PDL2 in myeloid cells/macrophages; this up-regulation of gene expression appears to be species- and cells-specific. 29112015_PD-L1 and PD-L2 are differentially expressed by macrophages or tumor cells in primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type. 29122656_Our results confirm and extend prior studies of PD-L1 and provide new data of PD-L2 expression in lymphomas 29676849_HOXC10 directly binds to the PD-L2 and TDO2 promoter regions thus stimulating proliferation, invasion and induction of immunosuppressive gene expression in glioma. 29890018_The high-affinity PD-1 mutant could compete with the binding of antibodies specific to PD-L1 or PD-L2 on cancer cells. 30036273_These results suggest the potential involvements of the EV beta2 integrin, as well as EV PD-L2 and soluble PD-L1, in the septic pathogenesis that occurs with the systemic immune activation leading to multiple organ dysfunctions. 30104397_soluble PD-1 ligands are elevated in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia (WM) patients and, in addition to surface-bound ligands in WM BM, could regulate T-cell function. Given the capability of secreted forms to be bioactive at distant sites, soluble PD-1 ligands have the potential to promote disease progression in WM. 30236595_CD 274 antigen/CD273 antigen/Janus kinase 2 gene amplification was associated with durable response to immunotherapy for cutaneous melanoma and mucosal melanoma 30275216_High PD-L2 expression may be a target of immunotherapy in patients with PD-L1-negative Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. 30348714_PD-L2-positive lung adenocarcinomas are less radiologically malignant and invasive than their PD-L1-positive counterparts 30555574_FISH technique and qPCR data coupled with immunofluorescence revealed that genetic alterations of 9p24.1 robustly contributed to PD-L1 and PD-L2 upregulation. In addition, increased expression of PD-L1 instead of PD-L2 also predicted poor survival by multivariate analyses. Meanwhile, high infiltration of PD-1(+) immune cells also indicated dismal survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. 30594267_The data indicate that a genetically determined individual difference in a non-synonymous missense SNP of PD-L2 might influence the susceptibility to chronic lymphatic filariasis in a South Indian population. 30633894_A subset of ocular invasive conjunctival squamous carcinomas express high levels of PD-L1 and CD8 and therefore may respond therapeutically to immune checkpoint inhibition. 30659749_Peripheral blood PD-L1 expression might be a prognostic marker for OSCC patients and a possible parameter to monitor immune dysfunction in malign diseases. In the peripheral blood, PD-L1 might be more relevant for immune tolerance than PD-L2. 30683910_High frequency of PD-L2 involving genetic aberrations was associated with EBV-positive lymphomas. 30761875_Studied expression levels of PDCD1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) and programmed death ligand 2 (PD-L2) in patients with hematologic malignancies. 30815803_Low PD-L2 expression is associated with Lung Adenocarcinoma. 30864556_we noticed that chronic inflammation of colonic mucosa may lead to up-regulation of PD-L1 and -L2 expression in patients with UC, which may result in regulation of immune responses against this chronic inflammation and then prevent progressive and acute inflammation of the disease. 30886151_The study reveals a pro-metastatic functional mechanism for PD-L2 in osteosarcoma. 30992011_PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 were differentially expressed between primary and metastatic tumors. Histopathological examination of these immune check points in metastatic lesions of mRCC should be noticed, and its accurate diagnosis may be one of the effective ways to realize the individualized treatment. 31076547_Immune Suppression by PD-L2 against Spontaneous and Treatment-Related Antitumor Immunity. 31379843_TLR9 Mediated Tumor-Stroma Interactions in Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)-Positive Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Up-Regulate PD-L1 and PD-L2. 31394407_Strong PD-1/PD-L1/PD-L2 expression in Kaposi's sarcoma tissues from a cohort of HIV-co-infected patients indicates the effect of Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus on immune escape. 31464648_High PD-L2 expression is associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 31727844_Formation of a prominent pocket in the PD-1 protein upon binding PD-L2 was revealed by X-ray crystal structures of the PD-1/PD-L2 complex. 31825827_A Tumor-Specific Super-Enhancer Drives Immune Evasion by Guiding Synchronous Expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2. 31856276_EBV miR-BHRF1-2-5p bound to PD-L1 and PD-L2 3'UTRs to reduce PD-L1/L2 surface protein expression. Results indicate a novel mechanism by which EBV miR-BHRF1-2-5p plays a context-dependent counterregulatory role to fine-tune the expression of the LMP1-driven amplification of these inhibitory checkpoint ligands. 31882544_The structural features that distinguish PD-L2 from PD-L1 emerged in placental mammals. 32012401_Our findings indicate that cisplatin-upregulated PD-L2 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) via STAT1/3 activation and the expression of PD-L2 are likely to be associated with malignancy in OSCC. The PD-L2 expression in cisplatin-resistant OSCC cells may be a critical factor in prognosis of advanced OSCC patients. 32089543_PD-L1/L2 protein levels rapidly increase on monocytes via trogocytosis from tumor cells in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. 32210369_Prognostic and clinical impact of PD-L2 and PD-L1 expression in a cohort of 437 oesophageal cancers. 32248797_PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression in the tumor microenvironment including peritumoral tissue in primary central nervous system lymphoma. 32264742_Serum levels of soluble programmed cell death protein 1 and soluble programmed cell death protein ligand 2 are increased in systemic lupus erythematosus and associated with the disease activity. 32268011_Increased expression of immune checkpoint programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) on T cell subsets of bone marrow aspirates in patients with B-Lymphoblastic leukemia, especially in relapse and at diagnosis. 32401663_PD-L1 and PD-L2 Mutations in Pediatric Hodgkin Lymphoma: Do They Have Any Prognostic Significance? 32405745_Expression of PD-L1, PD-L2, and IDO1 on tumor cells and density of CD8-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma according to histological subtype. 32586358_Prognostic and predictive value of PD-L2 DNA methylation and mRNA expression in melanoma. 32596285_Profiles of PD-1, PD-L1, PD-L2 in Gastric Cancer and Their Relation with Mutation, Immune Infiltration, and Survival. 32661872_Increasing the expression of programmed death ligand 2 (PD-L2) but not 4-1BB ligand in colorectal cancer cells. 32684057_PD-1, CTLA4, PD-L1 and PD-L2 DNA methylation in papillary thyroid carcinoma. 32730911_High Expression of Programmed Death Ligand 1 and Programmed Death Ligand 2 in Ophthalmic Sebaceous Carcinoma: The Case for a Clinical Trial of Checkpoint Inhibitors. 32820659_The influence of programmed cell death ligand 2 (PD-L2) expression on survival outcome and tumor microenvironment in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. 32854650_DLBCL with amplification of JAK2/PD-L2 exhibits PMBCL-like CNA pattern and worse clinical outcome resembling those with MYD88 L265P mutation. 32915645_Lower PDL1, PDL2, and AXL Expression on Lung Myeloid Cells Suggests Inflammatory Bias in Smoking and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 33182023_Prognostic and clinicopathological utility of PD-L2 expression in patients with digestive system cancers: A meta-analysis. 33231797_AKT/mTOR Signal Cascade and Expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 in Gastric Cancer. 33337915_Comprehensive assessment of PD-L1 and PD-L2 dysregulation in gastrointestinal cancers. 33339860_Prognostic relevance of programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 (PDCD1LG2/PD-L2) in patients with advanced stage colon carcinoma treated with chemotherapy. 33404124_ANO9 regulates PD-L2 expression and binding ability to PD-1 in gastric cancer. 33424844_PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression in Cervical Cancer: Regulation and Biomarker Potential. 33469839_PD-1 and PD-L2 expression predict relapse risk and poor survival in patients with stage III colorectal cancer. 33671892_High PD-L1/IDO-2 and PD-L2/IDO-1 Co-Expression Levels Are Associated with Worse Overall Survival in Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. 33721375_Soluble programmed cell death protein 1 (sPD-1) and the soluble programmed cell death ligands 1 and 2 (sPD-L1 and sPD-L2) in lymphoid malignancies. 33930105_The role of PD-1/PD-Ls in the pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease. 33955303_Characterization of the Clinical Significance of PD-1/PD-Ls Expression and Methylation in Patients With Low-Grade Glioma. 34125179_Immune evasion in primary testicular and central nervous system lymphomas: HLA loss rather than 9p24.1/PD-L1/PD-L2 alterations. 34131208_Adipogenesis in triple-negative breast cancer is associated with unfavorable tumor immune microenvironment and with worse survival. 34167064_Phospho-beta-catenin expression in primary and metastatic melanomas and in tumor-free visceral tissues, and associations with expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2. 34347720_Molecular and Immune Correlates of PDCD1 (PD-1), PD-L1 (CD274), and PD-L2 (PDCD1LG2) DNA Methylation in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. 34382413_DNA Methylation Patterns in the HLA-DPB1 and PDCD1LG2 Gene Regions in Patients with Autoimmune Thyroiditis from Different Water Iodine Areas. 34563045_Regulation of Immunity in Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma: Role of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2. 34697216_PD-L2 glycosylation promotes immune evasion and predicts anti-EGFR efficacy. 34768993_Clinical and Prognostic Value of Antigen-Presenting Cells with PD-L1/PD-L2 Expression in Ovarian Cancer Patients. 34899719_Inhibition of PI3Kdelta Differentially Regulates Poly I:C- and Human Metapneumovirus-Induced PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. 35037417_PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and their correlation with immune infiltrates and DNA damage response molecules. 35169863_Differential expression of PDL1 and PDL2 is associated with the tumor microenvironment of TILs and M2 TAMs and tumor differentiation in nonsmall cell lung cancer. 35489160_Clinical relevance of PD-L2 expression in surgically resected lung adenocarcinoma. 35613340_Exome sequencing identifies PD-L2 as a potential predisposition gene for lymphoma. 36138073_FAK promotes stromal PD-L2 expression associated with poor survival in pancreatic cancer. 36172747_Investigation of pd-l1 (cd274), pd-l2 (pdcd1lg2), and ctla-4 expressions in malignant pleural mesothelioma by immunohistochemistry and real-time polymerase chain reaction methods. | ENSMUSG00000016498 | Pdcd1lg2 | 63.981550 | 0.077726451 | -3.685451 | 1.26091044 | 6.713420 | 0.0095690046746982823644422921915975166484713554382324218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0477698920020269701680604157445486634969711303710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 9.9877321 | 7.3936621 | 118.4913133 | 87.1166208 | |
| ENSG00000197893 | 4892 | NRAP | protein_coding | Q86VF7 | FUNCTION: May be involved in anchoring the terminal actin filaments in the myofibril to the membrane and in transmitting tension from the myofibrils to the extracellular matrix. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80XB4}. | Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;LIM domain;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc | Predicted to enable actin filament binding activity and muscle alpha-actinin binding activity. Predicted to be involved in cardiac muscle thin filament assembly. Predicted to be located in fascia adherens; muscle tendon junction; and myofibril. Predicted to be active in Z disc. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:4892; | fascia adherens [GO:0005916]; muscle tendon junction [GO:0005927]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; muscle alpha-actinin binding [GO:0051371]; vinculin binding [GO:0017166]; cardiac muscle thin filament assembly [GO:0071691] | 12789664_Highly conserved and exclusively expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscle. Candidate cause for cardiac and skeletal myopathies 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20808825_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 28611399_Loss-of-function mutation in NRAP gene is associated with dilated cardiomyopathy. 33534821_Biallelic loss-of-function in NRAP is a cause of recessive dilated cardiomyopathy. | ENSMUSG00000049134 | Nrap | 40.901912 | 2.061626179 | 1.043783 | 0.25908653 | 16.304345 | 0.0000539401140772089238216262241376597330599906854331493377685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0005936383286483072011657791122729577182326465845108032226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 50.6340791 | 11.1193358 | 24.7507048 | 5.7181617 | |
| ENSG00000197989 | 85028 | SNHG12 | lncRNA | This gene produces a long RNA that is overexpressed in tumor cells. This RNA may promote tumorigenesis by acting as a sponge for microRNAs. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2017]. | 25695231_These results suggested a potential function of ASLNC04080 in endometrial carcinoma genesis and progression 26486328_The lncRNA SNHG12 promotes cell proliferation and migration by upregulating AMOT gene expression in osteosarcoma cells in vivo and in vitro. 28073380_Results showed that SNHG12 was strongly overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues and significantly associated with clinicopathological variables and prognosis. There were direct interactions between miR-199a/b-5p and the binding site of SNHG12. SNHG12 functioned as an endogenous sponge for miR-199a/b-5p to regulate the expression of the NF-kappaB pathway. 28872894_High SNHG12 expression is associated with Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. 29229388_we found that SNHG12 was significantly upregulated in both osteosarcoma tissues and cell lines and osteosarcoma patients with high levels of SNHG12 tended to have a poor prognosis 29533945_The knockdown of SNHG12 expression suppressed cell proliferation and invasion by modulating miR-424-5p expression. 29565487_lncRNA SNHG12 may play an important role in tumorigenesis and may serve as a molecular target for the malignant gastric carcinoma and lncRNA SNHG12 acts as a sponge for microRNA-199a/b-5p to act on its downstream genes. 29630517_The SNHG12 expression is relatively high in PTC tissues and cells. In-vivo/in-vitro experiments prove that SNHG12 can promote the proliferation and metastasis of PTC cells through influencing the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 30015836_RNA immunoprecipitation and RNA pull-down assays in glioma cell lines demonstrated that SNHG12 was associated with and was stabilized by Hu antigen R. Glioma patients with high levels of SNHG12 exhibited a reduced 5-year overall survival rate. 30098431_Data showed that SNHG12 expression was enhanced and high-expressed in the glioma tissue and cell lines, especially in the advanced clinical grade, and that SNHG12 harbored the complementary binding sites with miR-101-3p at 3'-UTR, acting as a miRNA 'sponge'. Also, its Knockdown impaired the proliferation and migration of glioma cells in vitro. 30243082_Down-regulation of DUXAP8 and SNHG12 could inhibit bladder cancer cells proliferation in vitro. 30246459_SNHG12 promotes the progression of cervical cancer via modulating miR-125b/STAT3 axis 30452404_knockdown of SNHG12 suppressed nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cells proliferation, migration and invasion. Mechanistic investigations showed that knockdown of SNHG12 suppressed the activation of EMT and Notch-1 signal pathway. 30825244_c-Myc mediated upregulation of long noncoding RNA SNHG12 regulates proliferation and drug sensitivity in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. 30945357_Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 promotes cell proliferation and activates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in prostate cancer through sponging microRNA-195. 30964158_LncRNA SNHG12 accelerates the progression of ovarian cancer via absorbing miRNA-129 to upregulate SOX4. 31348766_RT-qPCR and Western blot showed that WWP1 was positively regulated by SNHG12 and negatively regulated by miR-129-5p at the mRNA level and protein level. Overexpression of WWP1 significantly increased proliferation and invasion of laryngeal cancer cells. 31355416_Long noncoding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 12 promotes papillary thyroid carcinoma cell growth and invasion by targeting miR-16-5p. 31743769_lncSNHG12 silencing inhibited OS metastasis and growth by targeting the miR-195-5p/IGF1R axis. 31773972_We identified that lncRNA SNHG12 and LINC00152 might act as independent indicators were associated with the occurrence and progression for PTC 31943193_Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 modulated by human papillomavirus 16 E6/E7 promotes cervical cancer progression via ERK/Slug pathway. 32039732_DNA-methylation-mediated activating of lncRNA SNHG12 promotes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. 32086782_Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 suppresses esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through competing endogenous RNA networks. 32239639_Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 induces proliferation, migration, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and stemness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via post-transcriptional regulation of BMI1 and CTNNB1. 32339345_Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 promotes vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration via regulating miR-199a-5p/HIF-1alpha. 32386479_Upregulation of SNHG12 accelerates cell proliferation, migration, invasion and restrain cell apoptosis in breast cancer by enhancing regulating SALL4 expression via sponging miR-15a-5p. 32432698_LncRNA SNHG12 contributes proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer cells by absorbing miRNA-320b. 32506729_SNHG12/miR-326/E2F1 feedback loop facilitates the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 32529873_Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of trophoblast cells by regulating the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell cycle. 32641718_Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 promotes tumour progression and sunitinib resistance by upregulating CDCA3 in renal cell carcinoma. 32901847_lncRNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 12 promotes renal cell carcinoma progression by modulating the miR200c5p/collagen type XI alpha1 chain pathway. 32945395_Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 regulates cell proliferation, invasion and migration in endometrial cancer by targeting miR4429. 33000228_SNHG12 inhibits oxygenglucose deprivationinduced neuronal apoptosis via the miR181a5p/NEGR1 axis. 33294456_Prognostic Value of Long Noncoding RNA SNHG12 in Various Carcinomas: A Meta-Analysis. 33426070_Long Noncoding RNA SNHG12 Promotes Prostate Tumor Occurrence and Progression via AKT Regulation. 33464650_LncRNA SNHG12 alleviates hypertensive vascular endothelial injury through miR-25-3p/SIRT6 pathway. 33589923_LncRNA SNHG12 downregulates RAGE to attenuate hypoxia-reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cells. 33774129_LncRNA SNHG12 promotes proliferation and epithelial mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma through targeting HEG1 via miR-516a-5p. 33787057_SNHG12 promotes carcinogenesis of human renal cell cancer via functioning as a competing endogenous RNA and sponging miR-30a-3p. 33994849_YY1-modulated long non-coding RNA SNHG12 promotes gastric cancer metastasis by activating the miR-218-5p/YWHAZ axis. 34002487_LncRNA SNHG12 regulates the miR-101-3p/CUL4B axis to mediate the proliferation, migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer. 34018346_Silencing of lncRNA SNHG12 inhibits proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via targeting miR-766-5p/EIF5A axis. 34278490_ZIC2 upregulates lncRNA SNHG12 expression to promote endometrial cancer cell proliferation and migration by activating the Notch signaling pathway. 34313533_LncRNA SNHG12 regulates ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury by the miR-218-5p/IGF2 axis in atherosclerosis. 34783303_Long noncoding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 12/microRNA-138-5p/nuclear factor I/B regulates neuronal apoptosis, inflammatory response, and oxidative stress in Parkinson's disease. 34847450_SNHG12 regulates biological behaviors of ox-LDL-induced HA-VSMCs through upregulation of SPRY2 and NUB1. 35014944_LncRNA SNHG12 in extracellular vesicles derived from carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promotes cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells. 35023690_LncRNA SNHG12 Promotes Osteoarthritis Progression Through Targeted Down-Regulation of miR-16-5p. 35658874_Molecular mechanism of lncRNA SNHG12 in immune escape of non-small cell lung cancer through the HuR/PD-L1/USP8 axis. 36183925_Identification of stemness index-related long noncoding RNA SNHG12 in human bladder cancer based on WGCNA. | 218.264577 | 0.133582612 | -2.904196 | 0.89325295 | 9.028296 | 0.0026583219737762952238069313892765421769581735134124755859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0170885145998082819962515799261382198892533779144287109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 51.9464526 | 39.4382163 | 391.3055773 | 296.8886814 | ||||||||
| ENSG00000198270 | 89894 | TMEM116 | protein_coding | Q8NCL8 | Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:89894; | plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189] | 34789718_TMEM116 is required for lung cancer cell motility and metastasis through PDK1 signaling pathway. | ENSMUSG00000029452 | Tmem116 | 114.630761 | 8.331473994 | 3.058572 | 0.51280819 | 30.798438 | 0.0000000286268150803125433726229219022832439556225381238618865609169006347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000006208246346409486115651985352337227652697038138285279273986816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 213.3249085 | 85.7760433 | 25.7927377 | 10.3907287 | ||
| ENSG00000198467 | 7169 | TPM2 | protein_coding | P07951 | FUNCTION: Binds to actin filaments in muscle and non-muscle cells. Plays a central role, in association with the troponin complex, in the calcium dependent regulation of vertebrate striated muscle contraction. Smooth muscle contraction is regulated by interaction with caldesmon. In non-muscle cells is implicated in stabilizing cytoskeleton actin filaments. The non-muscle isoform may have a role in agonist-mediated receptor internalization. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P58774, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P58775}. | Acetylation;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Muscle protein;Nemaline myopathy;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene encodes beta-tropomyosin, a member of the actin filament binding protein family, and mainly expressed in slow, type 1 muscle fibers. Mutations in this gene can alter the expression of other sarcomeric tropomyosin proteins, and cause cap disease, nemaline myopathy and distal arthrogryposis syndromes. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. | hsa:7169; | actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; actin filament [GO:0005884]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; muscle thin filament tropomyosin [GO:0005862]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; structural constituent of muscle [GO:0008307]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; muscle contraction [GO:0006936]; regulation of ATP-dependent activity [GO:0043462] | 15208309_beta-tropomyosin exon 6B splicing requires hnRNP A1 and ASF/SF2 and SC35 17339586_We describe two patients, a woman and her daughter, with muscle weakness and distal arthrogryposis (DA) type 2B, caused by a heterozygous missense mutation, R133W. 17430991_R133W beta-Tm mutation induces alterations in myosin-actin kinetics causing a reduced number of myosin molecules in the strong actin-binding state, resulting in overall muscle weakness in the absence of muscle wasting. 17846275_results indicate that mutations in TPM2 may cause nemaline myopathy as well as cap disease with a dominant mode of inheritance; these disorders may thus be phenotypic variants of the same genetic defect 18246790_Tropomyosin 2 plays a role in growth and metastasis of hepatic tumors. 18422639_beta-TM gene mutations can alter the expression of other sarcomeric TM isoforms 19047562_Mutations in TPM2 seem to be a frequent cause of cap disease. 19142688_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19142688_Skeletal muscle contractile gene (TNNT3, MYH3, TPM2) mutations not found in vertical talus or clubfoot. 19155175_This first report of the clinical expression of the complete absence of TPM2 in human indicated that TPM2 expression at the early period of prenatal life plays a major role for normal fetal movements. 19214762_The destabilizing effect of the disease-causing arginine91glycine mutation spreads along the coiled-coil, reflecting the high extent of cooperativity within this part of the beta-tropomyosin molecule. [review] 19345583_Our patient has an identical TPM2 mutation to the first genetically diagnosed cap disease patient, a denovo heterozygous three base pair deletion that removes glutamic acid 139 from the centre of beta-tropomyosin. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20336778_While demonstrating suppressed levels of Tm1 in the prostate cancer cell lines LNCaP, PC3, and DU-145 compared to normal prostate epithelial cell primary isolates, a novel splice variant of the TPM2 gene was identified. 20381070_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the anterior cingulate cortex from patients with schizophrenia 20457903_in cells expressing R133W beta-tropomyosin mutation, during activation, switching of positive to neutral charge at position 133 partially hinders calcium- and myosin-induced tropomyosin movement over the thin filament blocking actin conformation change 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22084935_actin binding was weak in three of five mutants suggesting that abnormal binding between actin and aberrant Tm is the pathogenetic mechanism causing muscle weakness in patients with nemaline and cap myopathy. 22519952_Molecular genetic investigations revealed pathogenic mutations in MYH3, TPM2, and TNNI2 in one sporadic and 19 familial cases of distal arthrogryposis. 22749895_distal arthrogryposis syndromes associated with TPM2 mutations include the less severe forms[review] 22798622_The TPM2-null mutations decreased cooperative thin filament activation in combination with reductions in the myosin cross-bridge number and force production 22832343_Novel de novo missense mutations in TPM2 were found to be associated with marked fibre size disproportion in two patients with congenital fibre type disproportion. 22980765_This study demonistrated that most patients with TPM2 mutations show a predominant involvement of masticatory and distal leg muscles with the other regions relatively spared. 23015096_expanding the spectrum of TPM2 myopathies to very mild patients who could still be pathologically recognized by the presence of cap structures 23205574_Elevated TPM1 and TPM2 expression is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lens epithelial cells. 23378224_p.K7del is a common hetreozygous recurrent TPM2 mutation associated with nemaline myopathy. 23413262_A novel beta-tropomyosin mutation is described that is associated with two clinical-histopathological phenotypes not previously associated with it. 23621580_We showed that TPM2, CLU, and COL4A6 mRNA levels are downregulated in prostate cancer. 23678273_The p.R133W mutation in TPM2 is associated with Sheldon-Hall syndrome. 23689010_The E117K mutation in tropomyosin beta chain that causes nemaline myopathy shifts the tropomyosin strands to the closed position and suppresses their conformational rearrangements on the thin filament. 23792823_In addition to CLIC1 and TPM1, which were the proteins initially discovered in a xenograft mouse model, CLIC4, TPM2, TPM3, and TPM4 were present in ovarian cancer patient sera at significantly elevated levels compared with controls. 24039757_Histopathological phenotype association of muscle fibers expressing Beta-tropomyosin mutational variants that occur in human myopathies. 24507666_in a cohort of 94 patients with congenital myopathy, 2 related female patients and 2 sporadic male patients were found to carry mutations in TPM2 and TPM3 genes respectively; clinical presentation and muscle morphological findings differed in the patients 24657080_effect of the skeletal myopathy-causing E117K mutation in human beta-tropomyosin on actomyosin structure during the ATPase cycle 24692096_Patients with TPM2 mutations tended to present with milder symptoms than those with TPM3 mutations, DA being present only in the TPM2 group. 25224486_Changes for CRMP2, TCP1epsilon, TPM2 and 14-3-3gamma were confirmed in experimental tumors and in a series of 28 human SI-NETs. 25660542_Myo1c significantly increases the frequency of kinesin-1-driven microtubule-based runs that begin at actin/microtubule intersections. The actin-binding protein tropomyosin 2 abolishes Myo1c-specific effects on both run initiation and run termination. 26619148_tropomyosin 2.1 acts as a suppressor of growth on soft matrices by supporting proper rigidity sensing 26708479_Despite its reduced affinity for actin in co-sedimentation assay, the Q147P mutant incorporates into the muscle fiber ..Q147P tropomyosin (TPM2)binds to actin in ghost muscle fiber. 27020427_Promoter variants in HOXA9, TPM1, and TPM2, alter promoter expression suggesting that they have a functional role in clubfoot. 27108600_The increased expression of TPM1lambda and the decreased expression of TPM1delta RNA and TPM2beta may lead to decreased stress fiber formation and malignant transformation in human breast epithelial cells. 27333992_TPM2 appears to be commonly silenced by aberrant DNA methylation in colon cancer. TPM2 loss is associated with RhoA activation and tumor proliferation. 27976512_Stress fibre formation and up-regulation of alpha-smooth muscle actin (alphaSMA) induced by TGFbeta2 could be reversed by Tpm1/2 knock-down by siRNA. 29414807_Hypoxia may regulate cell invasiveness partly by TPM2 down-regulation mediated changes of MMP2 expression, which is also a new pathway by which hypoxia regulates cancer progression. TPM2 is a potential novel tumour suppressor gene in breast cancer. 30285720_Novel mutations in TPM2 and PIEZO2 are responsible for distal arthrogryposis (DA) 2B and mild DA in two Chinese families. 30535593_Tropomyosin Tpm 2.1 loss induces glioblastoma spreading in soft brain-like environments. Study demonstrate that Tpm 2.1 depletion by siRNA induces cell spreading and elongation in soft 3D hydrogels, irrespective of matrix composition. 30545627_Structural and functional properties of alpha-beta-Tpm heterodimers with myopathic mutations Q147P and K49del in the beta-chain differ significantly from the properties of beta-beta-Tpm homodimers with the same substitutions in both beta-chains. Mutations Q147P and K49del strongly increased the stability of calorimetric domain previously assigned to the N-terminal part of Tpm molecule. 31487691_TPM2 as a potential predictive biomarker for atherosclerosis. 32092148_A recurrent pathogenic variant in TPM2 reveals further phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity in multiple pterygium syndrome-related disorders. 32957762_[Expression of tropomyosin 2 in aortic dissection tissue]. 33066566_Looking for Targets to Restore the Contractile Function in Congenital Myopathy Caused by Gln(147)Pro Tropomyosin. 33919826_Mutations Q93H and E97K in TPM2 Disrupt Ca-Dependent Regulation of Actin Filaments. | ENSMUSG00000028464 | Tpm2 | 729.244117 | 0.433615253 | -1.205513 | 0.06549646 | 342.046281 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002286813846797866745854709736192577598777969943478406870961886144827349793676217600288776943568440242275779594353926362 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000666415668521011742410403536544209249085109533501589476658675467115977353476557767772859055346078708372089178169980083 | Yes | No | 456.1591262 | 17.7034068 | 1056.7407057 | 36.0964055 | |
| ENSG00000198691 | 24 | ABCA4 | protein_coding | P78363 | FUNCTION: Flippase that catalyzes in an ATP-dependent manner the transport of retinal-phosphatidylethanolamine conjugates like the 11-cis and all-trans isomers of N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine from the lumen to the cytoplasmic leaflet of photoreceptor outer segment disk membranes, where N-cis-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine (N-cis-R-PE) is then isomerized to its all-trans isomer (N-trans-R-PE) and reduced by RDH8 to produce all-trans-retinol (all-trans-rol) and therefore prevents the accumulation of excess of 11-cis-retinal and its schiff-base conjugate and the formation of toxic bisretinoid (PubMed:24097981, PubMed:22735453, PubMed:23144455, PubMed:20404325, PubMed:10075733, PubMed:29847635, PubMed:33375396). May display both ATPase and GTPase activity that is strongly influenced by the lipid environment and the presence of retinoid compounds (PubMed:22735453). Binds the unprotonated form of N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine with high affinity in the absence of ATP, and ATP binding and hydrolysis induce a protein conformational change that causes the dissociation of N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:F1MWM0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10075733, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20404325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22735453, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23144455, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24097981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29847635, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33375396}. | 3D-structure;Age-related macular degeneration;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cone-rod dystrophy;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Retinitis pigmentosa;Sensory transduction;Stargardt disease;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Vision | The membrane-associated protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intracellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the ABC1 subfamily. Members of the ABC1 subfamily comprise the only major ABC subfamily found exclusively in multicellular eukaryotes. This protein is a retina-specific ABC transporter with N-retinylidene-PE as a substrate. It is expressed exclusively in retina photoreceptor cells, and the gene product mediates transport of an essental molecule, all-trans-retinal aldehyde (atRAL), across the photoreceptor cell membrane. Mutations in this gene are found in patients diagnosed with Stargardt disease, a form of juvenile-onset macular degeneration. Mutations in this gene are also associated with retinitis pigmentosa-19, cone-rod dystrophy type 3, early-onset severe retinal dystrophy, fundus flavimaculatus, and macular degeneration age-related 2. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2019]. | hsa:24; | cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; photoreceptor disc membrane [GO:0097381]; photoreceptor outer segment [GO:0001750]; rod photoreceptor disc membrane [GO:0120202]; 11-cis retinal binding [GO:0005502]; ABC-type transporter activity [GO:0140359]; all-trans retinal binding [GO:0005503]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity [GO:0140326]; ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042626]; flippase activity [GO:0140327]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; lipid transporter activity [GO:0005319]; N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity [GO:0140347]; phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity [GO:0090555]; phospholipid transporter activity [GO:0005548]; retinoid binding [GO:0005501]; retinol transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0034632]; lipid transport [GO:0006869]; phospholipid transfer to membrane [GO:0006649]; phospholipid translocation [GO:0045332]; photoreceptor cell maintenance [GO:0045494]; phototransduction, visible light [GO:0007603]; retinal metabolic process [GO:0042574]; retinoid metabolic process [GO:0001523]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085]; visual perception [GO:0007601] | 11328725_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11346402_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11444963_The nucleotide binding domain 1 (NBD1) of the retina-specific ATP-binding cassette transporter is a general ribonucleotidase capable of binding ATP, CTP, GTP and UTP. 11726554_Of the 21 missense ABCR mutations reported in patients with AMD, 16 (76%) show abnormalities in protein expression, ATP-binding or ATPase activity. 11919200_Biochemical defects in retina-specific human ATP binding cassette transporter nucleotide binding domain 1 mutants associated with macular degeneration 11973624_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11973624_The ABCA4 2588G>C Stargardt mutation 12202497_Three novel ABCA4 gene mutations were identified in Japanese patients with STGD and arRP. 12442277_Genotype-phenotype correlations highlighted the function of ABCA4 in retinitis pigmentosa (RP),cone-rod dystrophy (CRD) and Stargardt/Fundus Flavimaculatus disease (STGD/FFM). 12515255_The ABCA4 gene in autosomal recessive cone-rod dystrophies 12592048_ABCA4 splicing mutations may be associated with a small proportion of AMD (Age-related macular degeneration) cases. 12592048_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12754711_genomic deletion in patients with Stargardt disease: genomic alterations contribute to only a small fraction of retinopathy-associated alleles 12796258_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12796258_Patients with autosomal recessive cone-rod dystrophy are likely to harbor a mutation in the ABCA4 gene as the cause of their disease. 12824224_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12824224_This study confirmed the very high degree of ABCA4 sequence polymorphism in the general population 12888572_nucleotide binding and ATPase activities of the N and C halves of ABCR individually and co-expressed 15017103_A homozygous nonsense mutation 2971G>T (G991X) was detected in a patient diagnosed with cone-rod dystrophy. 15223829_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15375613_a pilot study by analyzing 8 exudative ARMD patients for allelic variations in the GPX gene and three statistically significant mutations in the ABCR gene (R943Q, G1961E and D2177N) 15494742_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15947798_ABCA4 splicing mutations may be associated with a small proportion of AMD (Age-related macular degeneration) cases. 16303926_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16533065_These data indicate that changes in the oligomeric state of the nucleotide binding domains of ABCR are coupled to ATP hydrolysis and might represent a possible signal for the TMDs of ABCR to export the bound substrate. 16546111_Homozygous null mutations in ABCA4 produced a severe widespread retinal degeneration that showed marked central retinal involvement. 16604398_ABCA4 splicing mutations may be associated with a small proportion of AMD (Age-related macular degeneration) cases. 16681420_a new 6730-16del44 deletion is the first de novo mutation associated with cone-rod dystrophy and may contribute to a better understanding of the role of ABCA4 mutations in macular dystrophies [case report] 16917483_Major disease-associated allele, R1129L, which accounted for 24% of the mutated alleles detected, and a high frequency (12%) of complex alleles. 17325136_In the population studied, ABCA4 plays an important role in the pathogenesis of autosomal recessive cone-rod dystrophy . However, mutations in this gene are less frequently identified in other retinal dystrophies. 17325136_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17724221_Genotype-phenotype correlation of ABCA4, show that homozygosity for the novel c.4254-15del23 splicing mutation is associated with a severe progressive form of Stargardt-like disease. 17932850_Finding a high proportion of novel mutations merits the use of scanning methodologies to analyze the whole coding region of the ABCA4 gene. 17982420_ABCA4 mutation spectrum within relatively stable populations might be skewed due to founder effects. Patients either homozygous or compound heterozygous for N965S mutation show that this mutation has early and profound effect on retinal function. 17982420_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17997789_We report the unusual association of a retinal astrocytic hamartoma and Stargardt's disease in a patient with ABCR mutation. 18024811_Variations in the ABCA4 gene are common in bull's-eye maculopathy. 18214793_Stargardt's disease is caused by mutations in the ABCR (ABCA4) gene on chromosome 1. 18285826_Disease-associated ABCA4 alleles were identified in 20 of 64 patients with autosomal recessive cone (arCD) and cone rod dystrophy (arCRD). 18285826_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18334942_Two distinct retinal dystrophies with mutations affecting two different genes ABCA4 and CRB1 genes cosegregated in this family. 18506364_Data show that photoreceptor cell-specific ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABCA4) gene was found to be mutated in patients with Stargardt disease (STGD) and autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa (RP). 18523590_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18523590_associations between clinical outcomes of congenital toxoplasmosis and polymorphisms at ABCA4 and COL2A1 provide novel insight into the molecular pathways that can be affected by congenital infection with this parasite 18649358_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18854780_Stargardt disease (STGD) can present with peripapillary atrophy. This relatively uncommon phenotype may arise from specific combinations of STGD ABCA4 mutations rather than single mutations. 18977788_Calculated prevalence of arSTGD based on the ABCA4 carrier frequency could be higher than previous estimation and this discrepancy between observed and estimated prevalence could be due to the existence of non-pathological or low penetrance alleles. 18977788_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19015224_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19028736_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19028736_a huge number of ABCA4 disease-associated alleles were identified, representing an increment of 4% of novel variants described in this gene, as 500 sequence changes have been described so far. 19056738_Role of the C terminus of the photoreceptor ABCA4 transporter in protein folding, function, and retinal degenerative diseases. 19074458_ABCA4 mutations lead to a wide spectrum of severity in retinal diseases. 19217903_the G1961E allele contributes to localized macular changes rather than generalized retinal dysfunction, and is a cause of bull's eye maculopathy in either the homozygosity or heterozygosity state 19265867_In STGD patients, 71 mutations were identified in 68 patients, 43 mutations had been reported in the literature, whereas 28 mutations had not been previously described and were not detected in 150 unaffected control individuals of Italian origin. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19352439_study identified 2 novel ABCA4 mutations, c.655A>T & c.5312+3A>T; in the compound heterozygous state, the mutations cause a phenotype of retinal dystrophy that initially manifests as Stargardt disease and slowly progresses to a severe cone-rod dystrophy 19365039_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19365039_Validated ABCR400 results provide an unequivocal molecular diagnosis, allowing family members to be offered diagnostic, predictive, carrier, and prenatal testing. 19365591_This study represents the first report of ABCA4 mutations in Portuguese Stargardt patients. 19430638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19578016_In these patients with Stargardt disease and a Gly1961Glu mutation, most showed a clinical phenotype characterized by fundus changes localized to the foveal and parafoveal regions, normal ERG amplitudes. 19625466_This study shows that hepatitis delta virus p24 and p27 proteins inhibit HBV replication by trans-repressing its enhancers and by trans-activating the IFN-alpha-inducible MxA gene. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19959634_ABCA4 should be analyzed by an optimal screening technique, to perform further characterization of pathologic alleles. 20029649_ABCA4 microarray screening is usually requested in daily clinical practice to strengthen the diagnosis when the disease is atypical. 20128570_The presence of two severe mutations in the two alleles of ABCA4 gene was associated with a larger atrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium in the macular area. 20163366_Genetic analysis with direct DNA sequencing of amplified products revealed four reported polymorphisms and one novel mutation, Met280Thr, in exon 7 of the ABCA4 gene 20335603_Families showing a variable macular dystrophy phenotype caused by mutations in PRPH2 should be tested for additional mutations in ABCA4 and ROM1, as they may alter the progression of the PRPH2 phenotype. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20404325_three macular degeneration-associated mutations lead to significant changes in the secondary structure of the ECD2 domain of ABCA4, as well as in its interaction with all-trans-retinal 20436469_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20436469_Replication studies from several populations showed confirming evidence, with families of European ancestry giving stronger evidence for markers in 8q24, whereas Asian families showed stronger evidence for association with MAFB and ABCA4. 20591486_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20647261_Multiple regression analysis was used to estimate the pathogenicity of specific alleles of ABCA4 in patients with retinal phenotypes ranging from Stargardt disease to retinitis pigmentosa. 20661590_Mutations found in diseased dogs are a basis for association studies of mutations in this protein in retinal diseases in humans 20696155_Loss of peripapillary sparing is likely associated with the more deleterious mutations of the ABCA4 gene. 20711710_The pathogenesis of diseases caused by mutations in ABCA4 is complex, comprising a loss-of-function component as well as photoreceptor stress caused by protein mislocalization and misfolding. Review. 20801516_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 21330655_polymorphisms were identified that may act as risk factors (p.Asn1868Ile) and others that may act as protection factors (p.His423Arg and IVS10+5 delG). 21510770_ABCA4 mutations in diseases [Review] 21567910_An association of ABCA4 and MAFB with non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate. 21721517_Using human ABCA4 mutants heterologously expressed in mammalian cells, we showed that the Stargardt disease-associated alanine mutation in the phosphorylation site at position 901 led to protein misfolding and degradation 21786275_This case report reveals that ABCA4 gene mutation may be complicated by multiple and bilateral choroidal neovascularization. 21834038_none of any ABCA4 genotypes or alleles was associated with risk of nonsyndromic orofacial clefts or their subgroups. 21911583_The authors detected a total of 57 previously unknown, possibly pathogenic, variants: 29 missense, 4 nonsense, 9 small deletions and 15 splice-site-altering variants. 22060670_Mutations were detected in the ABCA4 gene by chip screening; SD-OCT revealed marked atrophy of the retina in the central macula, with focal defects in the RPE with disruptions in Bruch membrane and herniation of the retina 22220722_Progression of retinal degeneration in Abca4-deficient Rdh8-deficient mice is affected by differential vulnerability of rods and cones to light. 22229821_Scandinavian patients with ABCA4-related retinopathy appear to have a distinct mutation spectrum, which can be identified in patients of diverse clinical phenotypes. 22247458_Macular function in ABCA4-RD patients transitioned from lower sensitivity at the parafovea to higher sensitivity in the perifovea. RP patients had the inverse pattern. 22312191_The G1961E mutation in ABCA4, which has been considered 'mild,' yields a more severe phenotype in a family with Stargardt disease than the A1038V mutation, which has been considered 'severe.' 22395892_Mutations in ABCA4 that reduce or abolish this flippase activity result in the formation of toxic bisretinoids that can either injure the photoreceptors directly or accumulate in the underlying RPE 22427542_findings provide support for a complex role of ABCA4 in the etiology of a minor proportion of patients with age-related macular degeneration 22449572_Late-onset STGD1 is at the mild end of the spectrum of retinal dystrophies caused by ABCA4 mutations. The visual acuity is frequently preserved in late-onset STGD1 patients owing to foveal sparing. 22589445_A reduction in ABCA4 activity in the photoreceptors results in the increased production and accumulation of A2E and related bisretinoids within RPE cells. 22661473_Homozygous G1961E mutation in ABCA4 results in a range of retinal pathology. The phenotype usually is at the milder end of the disease spectrum, with severe phenotypes linked to the presence of additional ABCA4 variants. 22706241_FtMt mutation may determine a condition similar to haploinsufficiency resulting in a reduced protection from iron-dependent oxidative stress in mitochondria 22753311_ABCA4 gene has a functional role in the development of orofacial clefting in hispanic population. 22948568_Three novel heterozygous missense mutations in the ABCA4 gene were identified: c:2633C>A (p:Ser878X), c:5646G>A (p:Met1882Ile). 23096905_Four novel missense mutations in the ABCA4 gene are associated with autosomal recessive Stargardt disease. 23143460_A range of phenotypes can be associated with mutations in ABCA4 ; therefore, genetic testing is important in establishing a firm diagnosis. 23144455_The nucleotide binding domain 1 of ABCA4 is specific for 11-cis-retinal binding. 23167473_Study results support a potential role for ABCA4 in the etiology of cleft lip/palate in Caucasian individuals from Brazil, confirming previous findings in other population groups. 23419329_Our results expand the mutational spectrum of Stargardt disease by adding 12 novel ABCA4 pathogenic variants and support the occurrence of a founder effect for the p.A1773V mutation in the Mexican population. 23443024_Four patients with Leber congenital amaurosis were homozygous for a novel mutation in the CRB1 gene, while of two cases with Stargardt disease, one was homozygous for c.5461-10T>C in the ABCA4 gene and another was carrier of the same mutation. 23512105_All four of the genes originally identified as showing genome-wide significance (IRF6, ABCA4 and MAF, plus the 8q24 region) were confirmed in this independent sample of trios (who were primarily of European and Southeast Asian ancestry). 23755510_ABCR gene mutation is present in Stargardt disease. 23755871_Patients with classical arRP phenotypes, especially from the onset of the disease, should be screened first for mutations in known arRP genes and not ABCA4. 23769331_The common alleles identified, p.Gly1961Glu and p. Leu2027Phe, both have a mild structural and functional effect on the adult retina; the latter is associated with relatively retained photoreceptor architecture and function at the fovea. 23882696_Autosomal recessive STGD is caused by mutations in the ABCA4 gene, which encodes a transporter protein located in the outer segment disc membranes of the photoreceptors. 23918662_mutations near rare alternate splice junctions in ABCA4 might cause disease by increasing the probability of mis-splicing at these sites 23940504_Data found pathogenic DNA variants in the genes RP1, USH2A, CNGB3, NMNAT1, CHM, and ABCA4, responsible for retinitis pigmentosa, Usher syndrome, achromatopsia, Leber congenital amaurosis, choroideremia, or recessive Stargardt/cone-rod dystrophy cases. 23949494_Analysis of the entire coding region of the ABCA4 gene revealed a (missense) mutation as well as a frameshift mutation in Stagartds disease. A splice sequence change was additionally found. 23953153_The presence of 2 distinct phenotypes of Stargardt disease (foveal sparing and foveal atrophy) suggests that there may be more than 1 disease mechanism in ABCA4 retinopathy. 23982839_Application of the NGS platform for ABCA4 screening enabled detection of the second disease-associated allele in approximately half of the patients in a British cohort where one mutation had been detected with the arrayed primer extension (APEX) array. 24011517_Three ABCA4 sequence variations were identified exclusively in 10 unrelated African American patients 24097981_structure-function relationships of ABCA1 and ABCA4 are broadly similar despite the fact that they transport different phospholipids in different directions. 24265018_ABCA4 variants were identified in 57 patients. There was a significant association between AF subtype and genotype. 24342785_To our knowledge, we reported for the first time the homozygous state of the c.2041C>T mutation. Among homozygous patients, the age at onset of Stargardt disease was early, the loss of visual acuity was important and the prognosis was severe. 24397708_Diagnosis of concurrent Stargardt disease and CSNB was made on the ophthalmic history; genetic testing revealed two previously reported mutations in the ABCA4 gene and two novel deletions in the GRM6 gene. 24428930_ABCA4 screening detected three variants; two variants p.L541V and p.A1038V commonly co-inherited in a complex allele and a third novel variant p.R881C. Patient 1 had all three variants and her sibling harboured the complex allele (p.L541V/p.A1038V). 24453473_This study confirms that ABCA4 mutations lead to a spectrum of retinal degenerations. 24457364_Select sequence variations in ABCA4 may confer a specific phenotype. The present data will help in assessing patients for emerging therapies. 24585425_In this family two sibs homozygous for the ABCA4 c.1937+1G>A splice-site variant have a less severe phenotype of Stargardt disease. 24632595_one novel ABCA4 mutation in Chinese patients with Stargardt disease 24664696_Mutations in CRB1 and ABCA4 were found in a Swedish family with Leber congenital amaurosis and Stargardt disease. 24713488_Most of the ABCA4 mutations were classified as 'severe' explaining the early onset, panretinal degeneration, and fast progression of the disease. 24763286_Seven disease-causing mutations in ABCA4 and two in PROM1 identified by capture next generation sequencing. 25082829_New mutations have been described in the ABCA4 genomic locus in Stargardt disease. 25139735_observed thickening of the ELM in STGD1 patients may be an early protective response of Muller cells to the stress elicited by ABCA4-deficiency. 25265374_The histopathology of the retina in this patient with Stargardt disease displayed a highly degenerated fovea. In all retinal locations studied, cones were more severely affected than rods. 25283059_The qAF method can differentiate between ABCA4-associated and non-ABCA4-associated BEM and may guide clinical diagnosis and genetic testing. 25301883_The optical gap phenotype in STGD1 can be structurally divided into three progressive stages spanning several years. This particular phenotype also appears to be highly associated with the p.G1961E mutation of ABCA4. 25312043_The relatively high proportion of deleterious ABCA4 variants supports the hypothesis that earlier onset disease is often owing to more severe variants in ABCA4 than those found in adult-onset disease. 25324290_The anatomy, metabolism, and biochemistry of the retina, as well as genetic variations in genes other than ABCA4, can influence the etiology of foveal sparing. 25346251_Study reveals high frequency of the deep intronic variant c.4539+2001G>A (V4)in ABCA4 gene that has founder effect and moderate-to-severe impact in the phenotype of Autosomal-recessive Stargardt disease Belgian patients. 25363634_Results show the presence of heterozygous deep-intronic and exonic variants and deletions in ABCA4 in patients with retinal dystrophies. 25444351_Thus, early-onset Stargardt lies at the severe end of the spectrum of ABCA4-associated retinal phenotypes. 25499508_Our study provides further evidence regarding the roles of genetic markers in ABCA4 in NSCL/P development in this northern Chinese Han population. G allele of rs560426 may be a risk factor for developing NSCL/P. 25640233_Two known disease-causing mutations in ABCA4 were identified in proband 1; c.4234C>T, p.(Gln1412*) in exon 28; and c.5882G>A, p.(Gly1961Glu) in exon 42. 25712131_The ABCA4 L541P;A1038V mutation causes severe retinal degenerations whereas the V mutation alone causes mild disease. 25884411_Our findings demonstrate that minor alleles of common genetic variants in ABCA4 significantly reduce susceptibility to develop toxic maculopathy under chloroquine treatment. 25921964_Significant evidence was found for a relationship between the G1961E and D2177N variants in ABCA4 with increased susceptibility to AMD, specifically for Americans 25922843_Identification of Novel Mutations in ABCA4 Gene: Clinical and Genetic Analysis of Indian Patients with Stargardt Disease. 26024099_high qAF levels of ABCA4-positive patients are a hallmark of ABCA4-related disease 26092729_Stargardt eye disease ABCA4 R1108C and R1129C are both temperature-sensitive processing mutants that engage the cellular quality control mechanism and show a strong interaction with the chaperone Hsp 27. 26261413_ABCA4 carriers demonstrated reduced macular function measured by mERG along with none to subtle and even extensive morphological retinal changes. The c.768 G>T, c.5461-10T>C, and c.319 C>T mutations were associated with the most deviant ERGs. 26261643_633C>A (CC+CA) genotype, 5646G>A and 6389T>A polymorphisms of ABCA4 gene and smoking are susceptible factors for age-related macular degeneration 26311262_A transient SD-OCT phenotype ascribed to patients with hydroxychloroquine retinopathy is associated with an early subtype of STGD1. 26527198_This family epitomizes the clinical and genetic complexity of ABCA4-associated diseases. It contained variants from all classes of mutations 26551331_With few exceptions, individuals heterozygous for ABCA4 mutations and between the ages of 9 and 60 years do not present with elevated qAF. 26593885_A combination of p.[(L541P; A1038V)] and/or a truncating ABCA4 mutation always resulted in an early disease onset. Identification of ABCA4 retinopathies provides a specific molecular diagnosis and justifies a prompt introduction of simple precautions that may slow disease progression. 26720470_This study indicates that carriers of monoallelic ABCA4 mutations are phenotypically normal. 26780318_The mutation spectrum of the ABCA4 gene in Chinese patients is quite different from that for Caucasian patients. The establishment of the mutation profile will facilitate ABCA4 screening and risk evaluation for Chinese patients with STGD1. 26806561_seven out of 27 families, displaying mutations in the ABCA4, RP1, RP2 and USH2A genes, could be genetically or clinically reclassified. These results demonstrate the potential of our panel-based NGS strategy in RP diagnosis 26976702_The ABCA4 variant c.5461-10T-->C is located on a founder haplotype lacking other disease-causing rare sequence variants. In vitro studies revealed that it leads to mRNA exon skipping and ABCA4 protein truncation. 27527345_Results identified nonsynonymous variants in MYH9 and ABCA4 to be the most frequent risk loci in nonsyndromic orofacial clefts in the Taiwanese population. 27583828_Nullizygosity for ABCA4 is associated with early onset cone-rod dysfunction with rapid progression shown by enlargement of central atrophy on FAF, decline of ERG amplitudes with age, and a high risk of reaching legal blindness by the fourth decade. 27739528_Two novel pathogenic ABCA4 mutations were identified in Chinese families with Stargardt disease. 27775217_This study describes the functional effect and the molecular mechanism of the pathogenic ABCA4 variant c.5461-10T>C. The variant is functionally important as it leads to splicing defects and a reduced level of ABCA4 protein. 27820952_study to determine the effect of 15 individual ABCA4 mutations on retinal disease severity; in the hemizygous state, 2/15 ABCA4 alleles retain preserved peripheral retinal function; 7/15 are associated with either preserved or only mildly abnormal retinal function, worse in older patients; 6/15 behave like null mutations 27939946_Ten novel ABCA4 variations are detected of which 8 belongs to non-Slavonian population. Most of the detected known variations are found in European and American Stargardt disease populations 28005406_Of the 225 genetic tests performed, 150 were for recessive IRD, and 75 were for dominant IRD. A positive molecular diagnosis was made in 70 (59%) of probands with recessive IRD and 19 (26%) probands with dominant IRD. Thirty-two novel variants were identified; among these, 17 sequence changes in four genes were predicted to be possibly or probably damaging including: ABCA4 (14), BEST1 (2), PRPH2 (1), and TIMP3 28044389_Studies indicate that variants in ABCA4 are associated with a wide variety of inherited retinal diseases. 28118664_Genetic risk score estimates suggest that defined common ABCA4 variants influence disease risk in carriers of a single pathogenic ABCA4 allele. 28290600_1268A>G missense variant of the ABCA4 gene has often been reported as causative of disease, and in other cases protective of disease, in our family case, the variant appears to reduce or delay the risk of onset of Stargardt disease. 28327576_Thirty six SNP including 9 previously not described, were identified in juvenile-onset blindness patients of south Asian decent. 28726568_We report an unusual phenotype in a child with a clinical diagnosis of recessive Stargardt disease (STGD1) and two pathogenic variants in the ABCA4 gene. 28885670_Our analyses allowed us to classify novel variants in ABCA4 as being clearly loss-of-function mutations, and thus pathogenic variants. 28947085_The ROC phenotype is a unique classification of ABCA4 disease, which is caused by deleterious null biallelic ABCA4 mutations and is characterized by the rapid deterioration of retinal pigment epithelium and photoreceptor layers in the macula and significant choroidal thinning within the first 2 decades of life. 28980559_High prevalence of p.L541P, p.A1038V, and p.G1961E mutations of the ABCA4 gene has been established in patients with Stargardt disease by performing massive parallel sequencing of all coding regions of the ABCA4 gene. 29114839_Segregation analysis is important in order to confirm the molecular diagnosis of patients with Stargardt disease, given the frequency of complex alleles in the ABCA4 gene. The various pathogenic variation combinations observed in this study were associated with different phenotypes. 29162642_ABCA4 midigenes reveal the full splice spectrum of all reported noncanonical splice site variants in Stargardt disease. 29178665_In Stargardt patients with ABCA4 pathogenic mutations, the photopic negative response of the full-field photopic ERG is a very sensitive disease read-out. 29207047_These findings expand the mutation spectrums of ABCA4 and LRP5, and will be valuable for genetic counseling and development of therapeutic interventions for patients with Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. 29310964_In childhood-onset ABCA4-associated retinopathy, the earliest stages of macular atrophy involve the parafovea and spare the foveola. 29386879_Full-field electroretinography is a predictor of the natural course of ABCA4-associated retinal degeneration. 29422768_The results indicate that the p.Ala1773Val mutation in ABCA4 is associated with a severe retinal phenotype and thus, could be classified as null. 29461686_Two intronic variants c.4773+3A>G and c.5461-10T>C, both predicted to affect splicing, are indeed disease-causing mutations due to skipping of exons 33, 34, 39 and 40 of ABCA4 gene. The experimental proof that ABCA4 mutations in STGD patients affect protein function is crucial for their inclusion to future clinical trials. 29526278_neighboring deep-intronic ABCA4 variants (c.4539+2001G>A and c.4539+2028C>T) result in a retina-specific 345-nt pseudoexon insertion. 29847635_the expression and residual activity of ABCA4 mutants play a major role in determining the disease severity of STGD1 patients. 29847651_These studies corroborate RPE melanin as the major source of NIR-AF but also indicate that bisretinoid lipofuscin, when present at sufficient concentrations, contributes to the NIR-AF signal. Ocular melanin attenuates the SW-AF signal. 29902293_A clinically small best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) loss was observed during 2 years, and the change rate varied depending on baseline BCVA. Eyes without lesion in the fovea had better BCVA at baseline and showed minimal change of BCVA throughout 2 years. Eyes with no or modest acuity impairment but with a foveal lesion at baseline had the fastest loss rate. 29925512_There is a large spectrum of ABCA4 sequence variants, including 50 novel variants, in a well-characterised cohort thereby further adding to the unique allelic heterogeneity in STGD1. Approximately half of the cohort harbours missense variants only, indicating a relatively mild phenotype of the ProgStar cohort. 29971439_A significant fraction of genetically unexplained STGD1 cases carries p.Asn1868Ile as a second variant. Our findings suggest exceptional differences in disease expression or even nonpenetrance of this ABCA4 variant, pointing toward an important role for genetic or environmental modifiers in STGD1. 29975949_Novel ABCA4 gene mutations were found in Korean patients with STGD1. This study will facilitate better understanding of the relationships between ABCA4 gene mutations and clinical symptoms in Korean patients. 30060493_The study broadens the spectrum of ABCA4 mutations with 60 likely pathogenic or pathogenic variants, all associated with Stargardt disease. 30093795_Next-generation sequencing was effective for the molecular diagnosis of genetic diseases and specifically allowed a conclusive diagnosis in 80% (40/50) of the patients. As the ABCA4 gene does not show a preferential region for pathogenic variants, the diagnosis of Stargardt disease depends on broader analysis of the gene. The most common pathogenic variants in the ABCA4 gene described in the literature were also found. 30156925_Mutation in ABCA4 gene is associated with Stargardt disease as well as Stickler's Syndrome . 30166513_This article reviews the literature on incidence of IRD caused by mutations in the ABCA4 gene and characteristics of the clinical progression of retinal diseases associated with various types of mutations, and presents analysis of clinical and genetic correlations in terms of the effect the mutation has on the structure or function of the protein [review] 30190494_Searching the second hit in patients with inherited retinal dystrophies and monoallelic variants in ABCA4, USH2A and CEP290 by whole-gene targeted sequencing. 30204727_CLINICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF STARGARDT DISEASE PATIENTS WITH THE p.N1868I ABCA4 MUTATION. 30347566_patients with hereditary retinal disease that carried ABCA4 gene mutations were featured with characteristics of early onset age, rapid progress and severe visual impairment 30563929_Identification of novel pathogenic ABCA4 variants in a Han Chinese family with Stargardt disease has been reported. 30643219_Sequencing of ABCA4 was performed in 8 STGD1 cases with one variant and p.Asn1868Ile in trans, 25 cases with one variant, and 3 cases with no ABCA4 variant...Our data demonstrate the importance of assessing noncoding variants in geneti | ENSMUSG00000028125 | Abca4 | 37.504962 | 0.312689603 | -1.677197 | 0.54293974 | 8.837201 | 0.0029515152555542253920428663604980101808905601501464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0186391852797708826305900231545820133760571479797363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 14.5267286 | 9.8365366 | 46.8934105 | 31.4903515 | |
| ENSG00000198719 | 28514 | DLL1 | protein_coding | O00548 | FUNCTION: Transmembrane ligand protein of NOTCH1, NOTCH2 and NOTCH3 receptors that binds the extracellular domain (ECD) of Notch receptor in a cis and trans fashion manner (PubMed:11006133). Following transinteraction, ligand cells produce mechanical force that depends of a clathrin-mediated endocytosis, requiring ligand ubiquitination, EPN1 interaction, and actin polymerisation; these events promote Notch receptor extracellular domain (NECD) transendocytosis and triggers Notch signaling through induction of cleavage, hyperphosphorylation, and nuclear accumulation of the intracellular domain of Notch receptors (NICD) (By similarity). Is required for embryonic development and maintenance of adult stem cells in many different tissues and immune systeme; the DLL1-induced Notch signaling is mediated through an intercellular communication that regulates cell lineage, cell specification, cell patterning and morphogenesis through effects on differentiation and proliferation (PubMed:11581320). Plays a role in brain development at different level, namely by regulating neuronal differentiation of neural precursor cells via cell-cell interaction, most likely through the lateral inhibitory system in an endogenous level dependent-manner. During neocortex development, Dll1-Notch signaling transmission is mediated by dynamic interactions between intermediate neurogenic progenitors and radial glia; the cell-cell interactions are mediated via dynamic and transient elongation processes, likely to reactivate/maintain Notch activity in neighboring progenitors, and coordinate progenitor cell division and differentiation across radial and zonal boundaries. During cerebellar development, regulates Bergmann glial monolayer formation and its morphological maturation through a Notch signaling pathway. At the retina and spinal cord level, regulates neurogenesis by preventing the premature differentiation of neural progenitors and also by maintaining progenitors in spinal cord through Notch signaling pathway. Also controls neurogenesis of the neural tube in a progenitor domain-specific fashion along the dorsoventral axis. Maintains quiescence of neural stem cells and plays a role as a fate determinant that segregates asymmetrically to one daughter cell during neural stem cells mitosis, resulting in neuronal differentiation in Dll1-inheriting cell. Plays a role in immune systeme development, namely the development of all T-cells and marginal zone (MZ) B-cells (By similarity). Blocks the differentiation of progenitor cells into the B-cell lineage while promoting the emergence of a population of cells with the characteristics of a T-cell/NK-cell precursor (PubMed:11581320). Also plays a role during muscle development. During early development, inhibits myoblasts differentiation from the medial dermomyotomal lip and later regulates progenitor cell differentiation. Directly modulates cell adhesion and basal lamina formation in satellite cells through Notch signaling. Maintains myogenic progenitors pool by suppressing differentiation through down-regulation of MYOD1 and is required for satellite cell homing and PAX7 expression. During craniofacial and trunk myogenesis suppresses differentiation of cranial mesoderm-derived and somite-derived muscle via MYOD1 regulation but in cranial mesoderm-derived progenitors, is neither required for satellite cell homing nor for PAX7 expression. Also plays a role during pancreatic cell development. During type B pancreatic cell development, may be involved in the initiation of proximodistal patterning in the early pancreatic epithelium. Stimulates multipotent pancreatic progenitor cells proliferation and pancreatic growth by maintaining HES1 expression and PTF1A protein levels. During fetal stages of development, is required to maintain arterial identity and the responsiveness of arterial endothelial cells for VEGFA through regulation of KDR activation and NRP1 expression. Controls sprouting angiogenesis and subsequent vertical branch formation througth regulation on tip cell differentiation. Negatively regulates goblet cell differentiation in intestine and controls secretory fat commitment through lateral inhibition in small intestine. Plays a role during inner ear development; negatively regulates auditory hair cell differentiation. Plays a role during nephron development through Notch signaling pathway. Regulates growth, blood pressure and energy homeostasis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97677, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61483, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11006133, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11581320}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Autism spectrum disorder;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Epilepsy;Glycoprotein;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Notch signaling pathway;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation | DLL1 is a human homolog of the Notch Delta ligand and is a member of the delta/serrate/jagged family. It plays a role in mediating cell fate decisions during hematopoiesis. It may play a role in cell-to-cell communication. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:28514; | adherens junction [GO:0005912]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; Notch binding [GO:0005112]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; Tat protein binding [GO:0030957]; astrocyte development [GO:0014002]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell fate determination [GO:0001709]; cerebellar molecular layer formation [GO:0021688]; cerebellar Purkinje cell layer structural organization [GO:0021693]; clathrin-dependent endocytosis [GO:0072583]; compartment pattern specification [GO:0007386]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; endothelial tip cell fate specification [GO:0097102]; energy homeostasis [GO:0097009]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; inhibition of neuroepithelial cell differentiation [GO:0002085]; inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0042491]; lateral inhibition [GO:0046331]; left/right axis specification [GO:0070986]; loop of Henle development [GO:0072070]; marginal zone B cell differentiation [GO:0002315]; myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0030099]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell differentiation [GO:2000726]; negative regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045596]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of epidermal cell differentiation [GO:0045605]; negative regulation of epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030857]; negative regulation of glial cell apoptotic process [GO:0034351]; negative regulation of hemocyte differentiation [GO:0045611]; negative regulation of inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0045608]; negative regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032693]; negative regulation of myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0045638]; negative regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045662]; negative regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045665]; negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045746]; nephron development [GO:0072006]; neuroepithelial cell differentiation [GO:0060563]; neuron fate specification [GO:0048665]; neuronal stem cell population maintenance [GO:0097150]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; Notch signaling pathway involved in arterial endothelial cell fate commitment [GO:0060853]; organ growth [GO:0035265]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of endocytosis [GO:0045807]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue growth [GO:0048633]; positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903672]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; proximal tubule development [GO:0072014]; proximal/distal pattern formation [GO:0009954]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of cell division [GO:0051302]; regulation of growth [GO:0040008]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; regulation of skeletal muscle tissue growth [GO:0048631]; regulation of somitogenesis [GO:0014807]; regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:1900746]; retina development in camera-type eye [GO:0060041]; retina morphogenesis in camera-type eye [GO:0060042]; skeletal muscle tissue growth [GO:0048630]; skin epidermis development [GO:0098773]; somite specification [GO:0001757]; somitogenesis [GO:0001756]; spinal cord development [GO:0021510]; type B pancreatic cell development [GO:0003323] | 12393852_Delta-1 can enhance myeloid and lymphoid marrow-repopulating ability and promote the generation of thymus-repopulating T cell precursors. 12684674_suppresses the self-renewal capacity and long-term growth of two myeloblastic leukemia cell lines 12794186_Dll1 is a substrate for regulated intramembrane proteolysis, and its intracellular region possibly fulfills a specific function in the nucleus 12826675_Delta and Jagged undergo ADAM-mediated ectodomain processing followed by PS-mediated intramembrane proteolysis to release signaling fragments 14769803_induces a NIH 3T3 cell tranformed phenotype mediated by FGF signaling. 15254769_Delta-1 and Jagged-1 have roles in growth suppression in two myeloid leukemia cell lines 15492857_Notch ligand, Delta-1, reduced the TNF-alpha-induced growth suppression and apoptosis in U937 cells. 15781650_Down-regulation of Notch-1, Delta-like-1, or Jagged-1 by RNA interference induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation in multiple glioma cell lines. 15851488_Density of the Notch ligand Delta1 determines generation of B and T cell precursors from hematopoietic stem cells. 15905513_When a dominant-negative form of kuzmanian in transgenic mice impairs Notch signaling in receiving T-cells, increasing Delta-1 on sending cells overcomes this defect. 15908431_Dll1 is presented on the surface of AJs formed at the apical termini of processes through interaction with MAGI1 to activate Notch on neighboring cells in the developing central nervous system 15976178_culture with increased amounts of Delta1(ext-IgG) induced apoptosis of CD34+ precursors resulting in decreased cell numbers, without affecting generation of CD7+ cells 16225865_The expression of the intracellular domain of Delta1 results in a non-proliferating senescent-like cell phenotype which is dependent on the expression of the cell cycle inhibitor, p21. 16307184_Data describe the immunohistochemical staining pattern of four Notch receptors (Notch1-4) and their ligands (Delta1 and Jagged1) in synovial tissues obtained from rheumatoid arthritis patients. 16317090_DL1-induced activation of the Notch1 pathway controls the lineage commitment of early thymic precursors by altering the levels between Spi-B and GATA-3. 17234965_Dll1 was expressed in arterial endothelial cells, not venous Ecs or capillaries. Notch signaling by induction of Dll1 is necessary & sufficient to regulate ephrin-B2 expression & EphB2- & EphB4-dependent branching morphogenesis in arterial EC. 17301032_with supervised resistance exercise training, expression of Notch1 and Hes6 genes were increased and Delta-like 1 and Numb expression were decreased. 17584735_Tbx18 interacts with Gata4 and Nkx2-5 and competes Tbx5-mediated activation of the cardiac Natriuretic peptide precursor type a-promoter. Tbx18 down-regulates Tbx6-activated Delta-like 1 expression in the somitic mesoderm in vivo 17939407_Notch ligand Delta-1 enhances the sIL-6R-mediated effects of IL-6 on the generation of erythroid cells. 18320325_Report the antitumor effects of COX2 inhibitors may be associated with effects on the Delta1/Notch1 pathway in colon tumor cells. 18676613_The intracellular region of Notch ligands Dll1 and Dll3 regulates their trafficking and signaling activity 19150223_Delta1 and Jagged1 are expressed in human umbilical cord epithelial cells at the mRNA and protein level. 19590514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19603167_DLL1 was found downregulated in immune thrombocytopenic purpura. 19680556_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19724883_Findings suggest a positive feedback loop between Notch1 and DLL1 in the U251MG glioma cell line. 20170633_these results suggest a link between Dll1 expression and human goblet cell differentiation that might be mediated by a function that is distinct from its role as a Notch receptor ligand. 20418862_revealed a striking difference between the responses of Notch to trans- and cis-Delta: whereas the response to trans-Delta is graded, the response to cis-Delta is sharp and occurs at a fixed threshold, independent of trans-Delta 20554499_Delta1 protein is involved in the cytodifferentiation of squamous odontogenic tumors of the mandible. 20812035_Relapse-free survival and overall survival showed a significantly shorter survival in acute myeloid leukemia patients with higher Notch1 expression, higher Jagged1 expression, or higher Delta1 expression. 21196490_findings implicate DLL1 in early patterning of the forebrain and identify NOTCH as a new signaling pathway involved in Holoprosencephaly. 21238798_In this study, Delta 1 ligand was detected in the lining epithelium of human periapical cysts with limited inflammation, showing Notch pathway activation in those cells. 21372153_we have investigated their influence on early human hematopoiesis and show that Jagged2 affects hematopoietic lineage decisions very similarly as Delta-like-1 and -4, but very different from Jagged1 21392732_growth rate of Delta1-deficient dental pulp stem cells was significantly suppressed as compared with wild type cells 21602525_The stromal cell-mediated antiapoptotic effect on B- ALL cells is mediated by Notch-3 and -4 or Jagged-1/-2 and DLL-1 in a synergistic manner. 21602795_Notch1 and its ligand Delta-like 1(DLL1) are miR-449 bona fide targets 21643850_regulates Notch1 signaling through disruption of the Notch1-IC-RBP-Jk transcription activator complex 21726900_The receptors Notch2, -3, -4 and their ligands Jagged1, -2 and Delta1, -4 were detected at both the mRNA and protein level in early and late placenta 21742847_DLL1, which encodes Delta-like 1, the ligand for Notch3, is strongly implicated as the chromosome 6q27 Visceral leishmaniasis susceptibility gene. 21911304_as compared to MSC, OP9 cells were more efficient at inducing self-renewal and/or de novo generation of primitive (CD34(+) CD38(-) Lin(-)) cells, and suggest that such effects were due, at least in part, to the presence of Jagged-1 and DL1. 21931765_MiR-34a targeting of Notch ligand delta-like 1 impairs CD15+/CD133+ tumor-propagating cells and supports neural differentiation in medulloblastoma 21949024_An anti-delta1 Notch protein-blocking monoclonal antibody is able to prolong allograft survival in a fully histocompatibility-mismatched model of cardiac transplantation. 22080880_Notch1, Jagged1, and Delta1 expressions might be useful markers for clinical prognosis of ovarian carcinomas. 22094583_Dll1 and Notch interaction accelerates multiple myeloma disease development by promoting CD138+ MM-cell proliferation. 22561395_Twenty-one SNPs were genotyped in 941 visceral leishmaniasis cases and 992 controls. Gene expression profiling was done and DLL1 was the only gene to show differential expression that was higher (P | ENSMUSG00000014773 | Dll1 | 96.635488 | 0.438673665 | -1.188780 | 0.32120684 | 13.349263 | 0.0002585242690456103823413991360524732954218052327632904052734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0023604683259856383374664101637563362601213157176971435546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 60.0212259 | 15.4907497 | 138.1507615 | 34.8832395 | |
| ENSG00000198720 | 124930 | ANKRD13B | protein_coding | Q86YJ7 | FUNCTION: Ubiquitin-binding protein that specifically recognizes and binds 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitin. Does not bind 'Lys-48'-linked ubiquitin. Positively regulates the internalization of ligand-activated EGFR by binding to the Ub moiety of ubiquitinated EGFR at the cell membrane. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22298428}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Cell membrane;Endosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat | Enables ubiquitin-dependent protein binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of receptor internalization. Located in endosome; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:124930; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ubiquitin-dependent protein binding [GO:0140036]; negative regulation of receptor internalization [GO:0002091] | 22298428_overexpression of wild-type as well as truncated-mutant Ankrd 13A, 13B and 13D proteins strongly inhibited rapid endocytosis of ubiquitinated EGFR from the surface in EGF-treated cells | ENSMUSG00000037907 | Ankrd13b | 14.277503 | 0.460425470 | -1.118960 | 0.40983936 | 7.574537 | 0.0059198583861650765428064069340052810730412602424621582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0329124774319124527299784688239014940336346626281738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 8.7983425 | 2.2718414 | 19.1897549 | 4.3508086 | |
| ENSG00000198796 | 115701 | ALPK2 | protein_coding | Q86TB3 | FUNCTION: Protein kinase that recognizes phosphorylation sites in which the surrounding peptides have an alpha-helical conformation (PubMed:10021370). Regulates cardiac development and cardiomyocyte differentiation by negatively regulating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling (PubMed:29888752). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29888752, ECO:0000303|PubMed:10021370}. | Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase | Predicted to enable ATP binding activity; protein serine kinase activity; and protein serine/threonine kinase activity. Involved in several processes, including epicardium morphogenesis; heart development; and negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway involved in heart development. Acts upstream of or within regulation of gene expression. Colocalizes with basolateral plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:115701; | basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0055013]; epicardium morphogenesis [GO:1905223]; establishment of cell polarity [GO:0030010]; heart morphogenesis [GO:0003007]; negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway involved in heart development [GO:0003308]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468] | 19690890_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22641666_ALPK2 is crucial for luminal apoptosis and expression of DNA repair-related genes, possibly in the transition of normal colonic crypt to adenoma. 28668886_Results showed that p.Q1853E variant of ALPK2, which had been accumulating in the Japanese population, induced a metastatic phenotype of colorectal tumors by disrupting ALPK2 function. 32330508_Knockdown of ALPK2 blocks development and progression of renal cell carcinoma. 33705408_A genomic variant of ALPK2 is associated with increased liver fibrosis risk in HIV/HCV coinfected women. 34210956_ALPK2 acts as tumor promotor in development of bladder cancer through targeting DEPDC1A. 34705617_Hsa_circ_0065217 promotes growth and metastasis of renal cancer through regulating the miR-214-3p-ALPK2 axis. 35813220_Alpha Protein Kinase 2 Promotes Esophageal Cancer via Integrin Alpha 11. | ENSMUSG00000032845 | Alpk2 | 91.352928 | 0.011343133 | -6.462037 | 1.39697036 | 12.336851 | 0.0004441035689288194200120829524536247845389880239963531494140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0037855702146108016065140233763486321549862623214721679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 1.6993689 | 2.7320372 | 154.3194125 | 241.9148004 | |
| ENSG00000198825 | 22876 | INPP5F | protein_coding | Q9Y2H2 | FUNCTION: Inositol 4-phosphatase which mainly acts on phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate. May be functionally linked to OCRL, which converts phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate to phosphatidylinositol, for a sequential dephosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate at the 5 and 4 position of inositol, thus playing an important role in the endocytic recycling (PubMed:25869669). Regulator of TF:TFRC and integrins recycling pathway, is also involved in cell migration mechanisms (PubMed:25869669). Modulates AKT/GSK3B pathway by decreasing AKT and GSK3B phosphorylation (PubMed:17322895). Negatively regulates STAT3 signaling pathway through inhibition of STAT3 phosphorylation and translocation to the nucleus (PubMed:25476455). Functionally important modulator of cardiac myocyte size and of the cardiac response to stress (By similarity). May play a role as negative regulator of axon regeneration after central nervous system injuries (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CDA1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17322895, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25476455, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25869669}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coated pit;Endosome;Hydrolase;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | The protein encoded by this gene is an inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) 5-phosphatase and contains a Sac domain. The activity of this protein is specific for phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. | hsa:22876; | axon [GO:0030424]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle [GO:0045334]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; inositol monophosphate 1-phosphatase activity [GO:0008934]; inositol monophosphate 3-phosphatase activity [GO:0052832]; inositol monophosphate 4-phosphatase activity [GO:0052833]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate 4-phosphatase activity [GO:0034596]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate 5-phosphatase activity [GO:0034595]; phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate phosphatase activity [GO:0043812]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; adult locomotory behavior [GO:0008344]; cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress [GO:0014898]; clathrin-dependent endocytosis [GO:0072583]; negative regulation of axon regeneration [GO:0048681]; negative regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033137]; negative regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042532]; phosphatidylinositol biosynthetic process [GO:0006661]; phosphatidylinositol catabolic process [GO:0031161]; phosphatidylinositol dephosphorylation [GO:0046856]; phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling [GO:0048015]; positive regulation of receptor recycling [GO:0001921]; regulation of cell motility [GO:2000145]; regulation of endocytic recycling [GO:2001135]; regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051896] | 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19875726_Inpp5f is a polyphosphoinositide phosphatase that regulates cardiac hypertrophic responsiveness. 25476455_These findings suggest that INPP5F is a potential tumor suppressor in gliomas via inhibition of STAT3 pathway, and that deregulation of INPP5F may lead to contribution to gliomagenesis. 25869669_Sac2 colocalizes with early endosomal markers and is recruited to transferrin-containing vesicles during endocytic recycling. 26430724_we identified inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase F (INPP5F) as a prognostic factor for progression-free survival in Chronic lymphocytic leukemia 32693431_Imprinting aberrations of SNRPN, ZAC1 and INPP5F genes involved in the pathogenesis of congenital heart disease with extracardiac malformations. 35848021_Parkinson's Disease rs117896735 Variant Regulates INPP5F Expression in Brain Tissues and Increases Risk of Alzheimer's Disease. | ENSMUSG00000042105 | Inpp5f | 111.284543 | 0.113285143 | -3.141969 | 0.96279331 | 8.816801 | 0.0029846949668492308606337903853500392870046198368072509765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0187724429839420149657147618427188717760145664215087890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 19.3384581 | 19.8054622 | 173.7012768 | 178.0427925 | |
| ENSG00000198829 | 56670 | SUCNR1 | protein_coding | Q9BXA5 | FUNCTION: Receptor for succinate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15141213}. | Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a G-protein-coupled receptor for succinate, an intermediate molecule of the citric acid cycle. It is involved in the promotion of hematopoietic progenitor cell development, and it has a potential role in renovascular hypertension which has known correlations to renal failure, diabetes and atherosclerosis. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. | hsa:56670; | extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; macrophage activation involved in immune response [GO:0002281]; positive regulation of chemotaxis [GO:0050921]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; regulation of angiotensin metabolic process [GO:0060177]; renin secretion into blood stream [GO:0002001]; response to calcium ion [GO:0051592] | 15141213_GPR91 is a receptor for succinate and mediates succinate-induced hypertension. 15141213_This paper describes function in another species. 19204147_Succinate stimulates cell proliferation through GPR91 and requires activation of the Erk MAPK pathway. 22497252_A review of how neuron-derived factors, GPR91 and Semaphorin 3A, guide retinal vascularization and are major contributors to the pathogenesis of retinopathy of prematurity . 23770096_results show that GPR91 when expressed in HEK293s cells couples exclusively through the Galphai pathway and acts through Galphai not only to inhibit cAMP production but also to increase intracellular Ca(2+) 23833031_These findings suggest that deficiency in SUCNR1 is a possible contributing factor to the pathogenesis of dry age-related macular degeneration. 25539979_These results show for the first time that succinate plays an important role in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through GPR91 activation and extend our understanding of how ischemia can induce hypertrophic cardiomyopathy 26051274_results show that succinate plays an important role in HSC activation through GPR91 induction, and suggest that succinate and GPR91 may represent new therapeutic targets for modulating hepatic fibrosis 26759054_Through GPR91, succinate is involved in functions such as regulation of blood pressure, inhibition of lipolysis in white adipose tissue, development of retinal vascularization and cardiac hypertrophy. [review] 26808164_We give an exhaustive overview of the known and hypothetical signaling partners of SUCNR1 in different in vitro and in vivo systems and also discuss the link between SUCNR1 intracellular pathways and its pathophysiological roles. 26824665_The findings indicate that succinate-GPR91 signaling may be involved in right ventricular hypertrophy via PI3K/Akt signaling in vivo and in vitro. 27481132_Succinate is abundant in synovial fluids from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, and these fluids elicit IL-1beta release from macrophages in a GPR91-dependent manner. 27527650_This study reports the expression of GPR91 on mouse and human mast cells and reveals a hyperactive behavior of mouse Sucnr1-/- mast cells in a mechanistic in vivo model of skin inflammation. 28061458_Data show that succinate upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression by activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and extracellular regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 via its receptor G-protein coupled receptor 91 (GPR91). 28382382_activation of SUCNR1 in macrophages is important for both infiltration and inflammation of adipose tissue in obesity 28974722_succinate promotes DRP1-mediated mitochondrial fission via GPR91, consequently stimulating the hMSC migration through mtROS-induced F-actin formation. 29278707_This study shows that metformin can attenuate activation of HSCs by activating the AMPK pathway and inhibiting the succinate-GPR91 pathway. Metformin has therapeutic potential for treating steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis. 31304868_Study demonstrates that the T allele of rs13079080 in SUCNR1 disrupts a binding site for miRNA-4470, potentially increasing SUCNR1 expression and consequently increasing the capacity of sensing and dealing with oxidative stress. Also, genotyping rs13079080 in an AMD case-control cohort revealed a protective effect of the TT genotype on age-related macular degeneration (AMD) compared to the CC genotype. 31735641_These effects are mediated by SUCNR1-triggered PI3K-hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) axis. 32377163_Inhibition of GPR91 Reduces Inflammatory Mediators Involved in Active Labor in Myometrium. 32946811_pH-Gated Succinate Secretion Regulates Muscle Remodeling in Response to Exercise. 32992522_GPR91 Receptor Mediates Protection against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity without Altering Its Anticancer Efficacy. An In Vitro Study on H9C2 Cardiomyoblasts and Breast Cancer-Derived MCF-7 Cells. 33127268_Associations of SUCNR1, GRK4, CAMK1D gene polymorphisms and the susceptibility of type 2 diabetes mellitus and essential hypertension in a northern Chinese Han population. 33776908_Succinate Mediates Tumorigenic Effects via Succinate Receptor 1: Potential for New Targeted Treatment Strategies in Succinate Dehydrogenase Deficient Paragangliomas. 34133934_Extracellular succinate hyperpolarizes M2 macrophages through SUCNR1/GPR91-mediated Gq signaling. 34769478_SUCNR1 Is Expressed in Human Placenta and Mediates Angiogenesis: Significance in Gestational Diabetes. 34813893_Succinate receptor 1 inhibits mitochondrial respiration in cancer cells addicted to glutamine. | ENSMUSG00000027762 | Sucnr1 | 62.141910 | 2.038458562 | 1.027479 | 0.22224247 | 21.466381 | 0.0000036008667216798934349064088833447527804310084320604801177978515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000534932164784401246570427757021093384537380188703536987304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 82.9703640 | 7.8005765 | 40.9210941 | 4.4152837 | |
| ENSG00000203799 | 221262 | CCDC162P | transcribed_unitary_pseudogene | This gene is the ortholog of the mouse coiled-coil domain containing 162 gene. This locus is transcribed, but is represented as a unitary pseudogene because there are multiple changes in the coding sequence, including multiple changes that result in premature stop codons, relative to the mouse coding sequence. Transcripts from this locus are expected to encode truncated proteins, and may be candidates for nonsense-mediated decay (NMD). [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2018]. | 47.027721 | 3.615152500 | 1.854057 | 0.31877743 | 33.538014 | 0.0000000069884704427287305535883636632091958640344842024205718189477920532226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000001634694390516546603642352667590254000629101938102394342422485351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 78.6372318 | 10.2248754 | 22.0336172 | 3.4561921 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000204044 | 109729184 | SLC12A5-AS1 | lncRNA | 40.954358 | 0.405065255 | -1.303774 | 0.24159785 | 30.005073 | 0.0000000430917369095345835331498497797891866767372448521200567483901977539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000009023461315727092282840517481479203354410856263712048530578613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 23.4411080 | 10.5121972 | 58.0908524 | 25.5634356 | ||||||||||
| ENSG00000204287 | 3122 | HLA-DRA | protein_coding | P01903 | FUNCTION: An alpha chain of antigen-presenting major histocompatibility complex class II (MHCII) molecule. In complex with the beta chain HLA-DRB, displays antigenic peptides on professional antigen presenting cells (APCs) for recognition by alpha-beta T cell receptor (TCR) on HLA-DR-restricted CD4-positive T cells. This guides antigen-specific T-helper effector functions, both antibody-mediated immune response and macrophage activation, to ultimately eliminate the infectious agents and transformed cells (PubMed:29884618, PubMed:17334368, PubMed:8145819, PubMed:15322540, PubMed:22327072, PubMed:27591323, PubMed:31495665, PubMed:15265931, PubMed:9075930, PubMed:24190431). Typically presents extracellular peptide antigens of 10 to 30 amino acids that arise from proteolysis of endocytosed antigens in lysosomes (PubMed:8145819). In the tumor microenvironment, presents antigenic peptides that are primarily generated in tumor-resident APCs likely via phagocytosis of apoptotic tumor cells or macropinocytosis of secreted tumor proteins (PubMed:31495665). Presents peptides derived from intracellular proteins that are trapped in autolysosomes after macroautophagy, a mechanism especially relevant for T cell selection in the thymus and central immune tolerance (PubMed:17182262, PubMed:23783831). The selection of the immunodominant epitopes follows two processing modes: 'bind first, cut/trim later' for pathogen-derived antigenic peptides and 'cut first, bind later' for autoantigens/self-peptides (PubMed:25413013). The anchor residue at position 1 of the peptide N-terminus, usually a large hydrophobic residue, is essential for high affinity interaction with MHCII molecules (PubMed:8145819). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15265931, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15322540, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17182262, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17334368, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22327072, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23783831, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24190431, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25413013, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27591323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29884618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31495665, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8145819, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9075930}. | 3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Isopeptide bond;Lysosome;Membrane;MHC II;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation | HLA-DRA is one of the HLA class II alpha chain paralogues. This class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha and a beta chain, both anchored in the membrane. This molecule is expressed on the surface of various antigen presenting cells such as B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, and monocytes/macrophages, and plays a central role in the immune system and response by presenting peptides derived from extracellular proteins, in particular, pathogen-derived peptides to T cells. The alpha chain is approximately 33-35 kDa and its gene contains 5 exons. Exon 1 encodes the leader peptide, exons 2 and 3 encode the two extracellular domains, and exon 4 encodes the transmembrane domain and the cytoplasmic tail. DRA does not have polymorphisms in the peptide binding part and acts as the sole alpha chain for DRB1, DRB3, DRB4 and DRB5. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. | hsa:3122; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane [GO:0012507]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; MHC class II protein complex [GO:0042613]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; transport vesicle membrane [GO:0030658]; MHC class II protein complex binding [GO:0023026]; MHC class II receptor activity [GO:0032395]; peptide antigen binding [GO:0042605]; polysaccharide binding [GO:0030247]; T cell receptor binding [GO:0042608]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II [GO:0002491]; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II [GO:0019886]; antigen processing and presentation of peptide or polysaccharide antigen via MHC class II [GO:0002504]; cognition [GO:0050890]; immune response [GO:0006955]; myeloid dendritic cell antigen processing and presentation [GO:0002469]; peptide antigen assembly with MHC class II protein complex [GO:0002503]; positive regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation [GO:2000516]; positive regulation of CD4-positive, CD25-positive, alpha-beta regulatory T cell differentiation [GO:0032831]; positive regulation of memory T cell differentiation [GO:0043382]; positive regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050870]; positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001916]; regulation of T-helper cell differentiation [GO:0045622] | 11181188_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11239948_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11260509_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11294926_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11298540_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11320565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11361223_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11464148_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11742191_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11854199_P. gingivalis membrane vesicles apparently inhibited IFN-gamma-induced MHC class II (HLA-DRalpha) by disrupting the IFN-gamma signaling transduction pathway. 12006557_IFN-gamma-induced HLA-DRA expression was inhibited by nitric oxide (NO) and antioxidants such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate, and N-acetylcysteine 12073071_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12074713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12117677_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12370403_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12373032_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14736971_The donor TNFRSF6 polymorphism dierctly or indirectly influences acute kidney rejection episodes. 14976194_different regions of the cytoplasmic tails are involved in the association and the recruitment of HLA-DR(A & B1) into different compartments. HLA-DP and -DR interact differently with the cytoskeleton. 15105429_Data show that Oct-1 occupies the endogenous HLA-DRA promoter when the HLA-DRA promoter is inactive in retinoblastoma protein-defective cells. 15301866_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15361126_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15467430_Overexpression of HLA-DRA is associated with ovarian and other cancers 15536412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15688398_Downregulation of HLA-DRA is associated with early intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma 15836703_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17660530_Alleles of IL2RA and IL7RA and those in the HLA locus are identified as heritable risk factors for multiple sclerosis. 17662350_frequency of HLA antigens was significantly increased suggesting that brain cavernoma susceptibility may be associated with HLA antigens 18270567_HLA-DR alpha 2 domain (sHLA-DRalpha2) induces negative signals by engaging TIRC7 on lymphocytes, inhibiting proliferation and inducing apoptosis in CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells via activation of the intrinsic pathway 18371160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18846964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18931722_DNMT1 and HLA-DRalpha are prognostic factors for hepatocelluar carcinoma. 18932050_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18939942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18987644_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19046302_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19047245_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19116923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19117940_although lysine 219 is absolutely required for modification of DRalpha, other features of the DRalpha tail act to limit the extent of ubiquitination. 19120278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19143821_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19188433_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19648278_T cell receptor view of HLA-DRA in pocket 9 shows that the arrangement of residues in this pocket promotes anchoring of either large aliphatic or aromatic amino acids at this position. 19660582_Findings show that Sug1 is crucial for regulating histone H3K4me3 and H3R17me2 at the cytokine inducible MHC-II and CIITA promoters. 19834503_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19834503_Studies indicate that five SNPs showed genome-wide significant association with MS: HLA-DRA, IL7R, IL2RA, CD58 and CLEC16A. 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19861958_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20118277_Data show that pollen grains triggered the production of IL-8, TNF-alpha, IL-6 and strongly upregulated the membrane expression of CD80, CD86, CD83, HLA-DR and caused only a slight increase in the expression of CD40. 20202859_Continuous veno-venous hemofiltration is effective in removal of many plasma cytokines and in improvement of monocyte HLA-DR expression in septic patients. 20232575_predictive value of expression in diagnosis of acute promyelocytic leukemia 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20362271_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20378664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20497195_Upregulation of HLA-DRA is associated with acute pancreas allograft rejection. 20546939_The skeletal muscles of myasthenia gravis up regulation of MHC class @@. 20584675_HLA-DR4, PAD4 and STAT4 are overexpressed in rheumatoid arthritis and may be involved in the pathogenesis of RA. 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20711177_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21072187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21282653_HLA-DR(+) endothelial cells regulate the local inflammatory allogeneic response, promoting either an IL-6/STAT-3-dependent Th17 response or a contact-CD54-dependent regulatory response according to the cytokine environment. 21482477_This study indicated that the association between rs3129882 and parkinson disease remains unclear and requires further study. 21791235_The rs3129882 noncoding variant in intron 1 of HLA-DRA is associated with late-onset sporadic Parkinson disease in a Chinese Han population. 21804607_small interfering RNA-mediated knock-down of AIM2 resulted in reduced expression of HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB and CIITA in IFN-gamma-treated cells 21898163_Molecular Dynamics simulations of the MuBetaRho 83-99 (Phe91) and MuBetaRho 83-99 (Tyr91) peptide analogues in complex with HLA-DR2 (DRA, DRB1*1501) and T-cell receptors were performed. 22096524_SNP1 is a Parkinson's disease-associated variant in HLA-DRA and is associated with HLA-DRA, DRB5 and DQA2 gene expression. 22243834_In this study observe no association between this single nucleotide polymorphism of HLA-DRA and Parkinson's disease in a Taiwanese population. 22391069_genetic polymorphism is associated with the presence of nasal polyposis in asthmatic patients 22889831_Data indicate that 25 +/- 1.3% of CD74 and 17 +/- 0.3% of HLA-DR are colocalized. 22890421_2 SNPs in the HLA-DRA gene were studied in Caucasian patients from 2 large studies of alcohol dependence. rs2239803 & rs4935356 were associated with AD in both cohorts. 23083294_The SNP rs3129882 in intron 1 of HLA-DRA has been shown to be most robustly associated with the Parkinson's disease. 23579001_The HLA-DRA variation rs3129882 is not associated with Parkinson's disease in Sweden.( 23878500_The expression of human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-DR in epithelial cells and cluster of differentiation (CD8)-positive lymphocytes as possible markers of chronic ocular graft versus host disease, was investigated. 24039160_The effects of rs11248051 and rs1564282 variants of GAK, and the rs3129882 variant of HLA-DRA, were investigated in Parkinson's disease patients. 24214983_Data indicate five members of of DPbeta chains containing Lys-69 and GGPM 84-87, which assemble with DRalpha. 24384427_HLA-DOA, HLA-DRA, and HLA-DQA1 associated with spontaneous autoimmunity 24493819_suggest that binding of MAM to HLA-DR leads to a conformational change in MAM structure allowing its interaction with TLR2 and TLR4 and a better recognition by T cells. 24636145_Increased CD14+ monocytes with loss of HLA-DR expression were seen in patients with higher stage disease, more aggressive pathology, and in relapse or refractoriness to treatment. 24849299_This meta-analysis showed that the HLA-DRA rs3129882 A/G polymorphism was not a risk factor for Parkinson's disease in Chinese. 25224099_HLA-DRA variants predict penicillin allergy in genome-wide fine-mapping genotyping 25319953_The results suggest that rs3129882 polymorphism in HLA-DR may be a risk factor for Parkinson's disease in Iranian. 25695487_CD14+HLA-DR(-/low) cells were significantly increased in gastric cancer tissue and were shown to have a critical role in CD4+T-cell immunosuppression. 25720714_No significant association was found for HLA-DRA/PARK18 rs3129882 polymorphism and Parkinson's disease risk (meta-analysis). 25792471_The frequency of CD14(+)HLA-DR-/low MDSCs could be considered as a poor prognostic predictor in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) and the elimination of MDSCs during medical interventions may improve the prognosis of SCLC patients. 27144640_In this prospective study we evaluated dynamic changes in monocyte HLA-DR expression during sepsis in relation to changes in HLA-DRA gene expression and Class II transactivator (CIITA), measured by quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR). 27356905_Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus RTA not only downregulated HLA-DRalpha at the protein level through direct binding and degradation through the proteasome pathway but also indirectly downregulated the protein level of HLA-DRalpha by enhancing the expression of MARCH8, a member of the membrane-associated RING-CH (MARCH) proteins. 28131168_Case-control study in Han Chinese from the southwest of the country suggests that risk of ALS is increased by the AA genotype at rs9268856 in the HLA-DRA/HLA-DRB5 gene, but not by the SNPs rs9268877 in HLA-DRA/HLA-DRB5, rs1980493 in BTNL2 or rs302668 in RAB38/CTSC 28229240_This study demonstrated that only the non-suicidal depressed subgroup revealed significantly lower microglial reaction, i.e., a decreased density of HLA-DR positive microglia versus both depressed suicide victims and controls. 28771573_Low HLA-DRA expression is associated with sepsis. 29905830_Identified an intergenic variant between HLADRA and HLA-DRB that is associated with Ulcerative Colitis prognosis, but not with susceptibility, and confirmed its clinical impact on 30-year outcomes. 30962219_We report that risk for type 1 diabetes in HLA-DR3 homozygotes is increased significantly by a previously unreported haplotype of three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the first intron of HLA-DRA1. 31082373_Cd64 is up-regulated in neutrophils, but HLA-DR antigens are down-regulated in monocytes in septic shock patients. 31237711_The 3A6-TCR/superagonist/HLA-DR2a complex shows similar interface and reduced flexibility compared to the complex with self-peptide. 31386235_The dynamic changes in HLA-DRA expression in peripheral blood can accurately reflect the immune status of sepsis patients, and the reduction in HLA-DRA may be an important reason for the abnormal T cell differentiation. 31617688_Insights into the polymorphism in HLA-DRA and its evolutionary relationship with HLA haplotypes. 32180339_Coronary artery bypass grafting is associated with immunoparalysis of monocytes and dendritic cells. 32253955_The rs3129882/rs4248166 in HLA-DRA and rs34372695 in SYT11 are not associated with sporadic Parkinson's disease in Central Chinese population. 32306077_Loss of HLA-DR expression is associated with colorectal cancer development. 33022050_Shared Signature of Recent Positive Selection on the TSBP1-BTNL2-HLA-DRA Genes in Five Native Populations from North Borneo. 34311991_Tri-SNP polymorphism in the intron of HLA-DRA1 affects type 1 diabetes susceptibility in the Finnish population. 34402606_Identification of three novel HLA-DRA alleles by next-generation sequencing. 34858413_Combination of HLA-DR on Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Specific Cells and Tuberculosis Antigen/Phytohemagglutinin Ratio for Discriminating Active Tuberculosis From Latent Tuberculosis Infection. 35543859_Expression of NOTCH1, NOTCH4, HLA-DMA and HLA-DRA is synergistically associated with T cell exclusion, immune checkpoint blockade efficacy and recurrence risk in ER-negative breast cancer. 35794593_HLA class II molecule HLA-DRA identifies immuno-hot tumors and predicts the therapeutic response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in NSCLC. 35895219_Genetic polymorphism of HLA-DRA and alcohol consumption affect hepatitis development in the Korean population. | ENSMUSG00000036322 | H2-Ea | 27.867165 | 0.411626271 | -1.280593 | 0.30073718 | 18.610335 | 0.0000160348877359371213299852471090289895983005408197641372680664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0002017050446495399730270636773354908655164763331413269042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 16.8996538 | 4.5243853 | 41.1830823 | 10.1809222 | |
| ENSG00000204305_ENSG00000204304 | 97.675920 | 0.291562079 | -1.778125 | 0.38984998 | 19.876396 | 0.0000082614090722918851053069647094595495673274854198098182678222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001119599378690238060830158817182677921664435416460037231445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 48.8136532 | 13.5036938 | 160.5228765 | 42.9457172 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000204564 | 221545 | C6orf136 | protein_coding | Q5SQH8 | Alternative splicing;Reference proteome | Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:221545; | 22461910_C6orf136 was found to be differentially methylated and differentially expressed in human squamous cell carcinomas | ENSMUSG00000050705 | 2310061I04Rik | 28.532141 | 0.470727511 | -1.087036 | 0.34109139 | 10.107393 | 0.0014767570207999570087303853327398428518790751695632934570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0105070585996692757169146403839476988650858402252197265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 17.7910536 | 4.6207478 | 37.9837837 | 9.5064020 | |||
| ENSG00000204577_ENSG00000131042 | 33.162145 | 0.477536205 | -1.066318 | 0.29698078 | 13.011581 | 0.0003095704506050576130041229738765196088934317231178283691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0027687157692222160235151484641846764134243130683898925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 22.3722419 | 5.4186472 | 47.0416266 | 10.6815564 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000204642 | 3134 | HLA-F | protein_coding | P30511 | FUNCTION: Non-classical major histocompatibility class Ib molecule postulated to play a role in immune surveillance, immune tolerance and inflammation. Functions in two forms, as a heterotrimeric complex with B2M/beta-2 microglobulin and a peptide (peptide-bound HLA-F-B2M) and as an open conformer (OC) devoid of peptide and B2M (peptide-free OC). In complex with B2M, presents non-canonical self-peptides carrying post-translational modifications, particularly phosphorylated self-peptides. Peptide-bound HLA-F-B2M acts as a ligand for LILRB1 inhibitory receptor, a major player in maternal-fetal tolerance. Peptide-free OC acts as a ligand for KIR3DS1 and KIR3DL2 receptors (PubMed:28636952). Upon interaction with activating KIR3DS1 receptor on NK cells, triggers NK cell degranulation and anti-viral cytokine production (PubMed:27455421). Through interaction with KIR3DL2 receptor, inhibits NK and T cell effector functions (PubMed:24018270). May interact with other MHC class I OCs to cross-present exogenous viral, tumor or minor histompatibility antigens to cytotoxic CD8+ T cells, triggering effector and memory responses (PubMed:23851683). May play a role in inflammatory responses in the peripheral nervous system. Through interaction with KIR3DL2, may protect motor neurons from astrocyte-induced toxicity (PubMed:26928464). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23851683, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24018270, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26928464, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27455421, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28636952}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Lysosome;Membrane;MHC I;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA | This gene belongs to the HLA class I heavy chain paralogues. It encodes a non-classical heavy chain that forms a heterodimer with a beta-2 microglobulin light chain, with the heavy chain anchored in the membrane. Unlike most other HLA heavy chains, this molecule is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, with a small amount present at the cell surface in some cell types. It contains a divergent peptide-binding groove, and is thought to bind a restricted subset of peptides for immune presentation. This gene exhibits few polymorphisms. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. These variants lack a coding exon found in transcripts from other HLA paralogues due to an altered splice acceptor site, resulting in a shorter cytoplasmic domain. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:3134; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane [GO:0012507]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; MHC class I protein complex [GO:0042612]; MHC class Ib protein complex [GO:0032398]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; 14-3-3 protein binding [GO:0071889]; beta-2-microglobulin binding [GO:0030881]; peptide antigen binding [GO:0042605]; TAP1 binding [GO:0046978]; TAP2 binding [GO:0046979]; antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class Ib [GO:0002476]; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class Ib [GO:0002477]; antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class I [GO:0002474]; negative regulation of natural killer cell cytokine production [GO:0002728]; negative regulation of natural killer cell degranulation [GO:0043322]; negative regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0045953]; negative regulation of neuron death [GO:1901215]; negative regulation of T cell cytokine production [GO:0002725]; positive regulation of natural killer cell cytokine production [GO:0002729]; positive regulation of natural killer cell degranulation [GO:0043323]; positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001916] | 12874228_This is the first example of placental HLA-F expression--primarily in trophoblasts that have invaded the maternal decidua--in the same cells that simultaneously express the other two nonclassical class I antigens HLA-E and HLA-G. 14607927_HLA-F surface expression on B cell and monocyte cell lines correlates with the presence of a limited amount of endoglycosidase H (Endo H)-resistant HLA-F; however, clearly not all surface-expressed HLA-F is fully glycosylated. 16570139_The results of this analysis confirmed several previously reported coding sequence variants, identified several new allelic variants, and also defined extensive variation in intron and flanking sequences. 16709803_HLA-F is entirely dependent on its cytoplasmic tail for export from the endoplasmic reticulum. 17157219_strong positive directional selection is acting for maintaining the observed low polymorphism on HLA-E, -F and -G loci 17971048_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18658158_the role of NKG2D and 2B4 is not focussed on trophoblast recognition in normal pregnancy, but is more likely involved in cross-talk among maternal cells of the placental bed 18941505_Across HIV Gag protein, the rise of polymorphisms from independent origin during the last twenty years of epidemic was related to an association with an HLA allele accumulated in one of either B or F subtypes 19622345_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19664746_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20483783_These data suggest that HLA-F is expressed independently of peptide and that a physical interaction specific to MHC-I HC plays a role in the function of MHC-I HC expression in activated lymphocytes. 20593013_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20865824_surface marker on activated lymphocytes 22490650_Mifepristone can inhibit the effects of progesterone by down-regulating the expressions of HLA-G, HLA-E and HLA-F mRNA in trophoblasts during the first trimester. 22544725_Upregulated HLA-F expression (p = 0.026) and downregulated HLA I expression (p = 0.013) could be an independent unfavorable prognostic factor. 23542057_expression in gastric cancer lesion was unrelated to patient prognosis 23851683_A previously unrecognized model of Ag cross-presentation mediated by HLA-F & MHC-I open conformers on activated lymphocytes & monocytes may significantly contribute to the regulation of immune system functions & the immune defense. 24018270_HLA-F and MHC class I open conformers are ligands for NK cell Ig-like receptors. 25413105_This is the first study regarding HLA-F polymorphisms in a Euro-Brazilian population contributing to the Southern Brazilian genetic characterization. 25420801_Review of the impact of human leukocyte antigen molecules E, F, and G on the outcome of transplantation. 25461528_The effect of Japanese encephalitis virus and TNF-alpha exposure on NFkappaB-mediated induction of HLA-F is reported. 25862890_We identified that the HLA-E and HLA-F in gastric cancer independently affected clinical factors, including postoperative outcome 26332651_provides substantial evidence that the rs7903146 variant is significantly associated with the risk of diabetic retinopathy in Caucasian populations 26928464_Overexpression of a single MHCI molecule, HLA-F, protects human MNs from ALS astrocyte-mediated toxicity, whereas knockdown of its receptor, the killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor KIR3DL2, on human astrocytes results in enhanced motor neurons death 27447835_Two eSNPs were associated with fecundability at a FDR of 5%; both were in the HLA region and were eQTLs for the TAP2 gene (P = 1.3x10-4) and the HLA-F gene (P = 4.0x10-4), respectively. 27455421_this study established HLA-F as a ligand of KIR3DS1 and have demonstrated cell-context-dependent expression of HLA-F that might explain the widespread influence of KIR3DS1 in human disease, including delayed progression of disease caused by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 27522114_Data suggest that the immunoproteasome is involved in pathologic MHC class I (HLA-A, B, C, F and G) expression and maintenance of myokine production in Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs). 28185362_In this study, we describe and confirm the distinct expression of HLA-F, HLA-G, HLA-E, and HLA-C in placental tissue 28636952_the results of this study provide a blueprint of the molecular details of HLA-F, which will inform future exploration of its roles in human health and allow for the development of additional, targeted therapeutics 30031767_interactions between KIR3DS1 and HLA-F contribute to NK cell-mediated control of HCV. 30245028_The rs2523393 A allele creates a GATA2 binding site in a progesterone-responsive distal enhancer that loops to the HLA-F promoter. 30510890_high HLA-F expression is associated with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma (NPC) local recurrence and distant metastasis and may be regarded as a poor prognostic factor for NPC patients. 30755240_This study showed that the HLA-F expression was positively correlated with malignant phenotype and negatively correlated with overall survival. 31717259_HLA-F variants bound to selected peptides, were structurally compared. 31863778_HLA-F-AS1 also enhanced the expressions of PFN1, which was validated as a target gene of miR-330-3p. CONCLUSION: HLA-F-AS1 promoted colorectal cancer progression via regulating miR-330-3p/PFN1 axis 32020202_Variation in the HLA-F gene locus with functional impact is associated with pregnancy success and time-to-pregnancy after fertility treatment. 34257557_Development of a Novel Prognostic Signature Based on Antigen Processing and Presentation in Patients with Breast Cancer. 35181585_HLA-E and HLA-F Are Overexpressed in Glioblastoma and HLA-E Increased After Exposure to Ionizing Radiation. 35276697_LncRNA HLA-F-AS1 attenuates the ovarian cancer development by targeting miR-21-3p/PEG3 axis. 35925520_Evolution and molecular interactions of major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-G, -E and -F genes. | ENSMUSG00000037130+ENSMUSG00000048231+ENSMUSG00000037334+ENSMUSG00000073411+ENSMUSG00000079507+ENSMUSG00000054128+ENSMUSG00000091705+ENSMUSG00000035929+ENSMUSG00000073402+ENSMUSG00000060550+ENSMUSG00000037537+ENSMUSG00000067235+ENSMUSG00000024448+ENSMUSG00000079492+ENSMUSG00000067201+ENSMUSG00000067212+ENSMUSG00000024459+ENSMUSG00000016206+ENSMUSG00000058124+ENSMUSG00000023083+ENSMUSG00000073409+ENSMUSG00000056116+ENSMUSG00000037246+ENSMUSG00000092243+ENSMUSG00000079491+ENSMUSG00000016283+ENSMUSG00000064308+ENSMUSG00000061232 | H2-M10.6+H2-M10.4+H2-M1+H2-D1+H2-Q1+H2-T3+H2-Q2+H2-Q4+Gm8909+H2-Q7+H2-M11+H2-Q10+H2-M10.1+Gm11127+H2-M9+H2-T23+H2-M5+H2-M3+H2-M10.3+H2-M10.2+H2-Q6+H2-T22+H2-M10.5+Gm7030+H2-T10+H2-M2+2410137M14Rik+H2-K1 | 14.794930 | 0.341374711 | -1.550572 | 0.51924008 | 8.648947 | 0.0032725045045608538996084746486303629353642463684082031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0202906883908675617078642972046509385108947753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 7.6239961 | 2.8490875 | 22.1820224 | 7.9648006 |
| ENSG00000204650 | 147081 | LINC02210 | transcribed_unitary_pseudogene | 13.230564 | 4.047217100 | 2.016930 | 0.58775990 | 11.325799 | 0.0007643761094536228022783275193319241225253790616989135742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0060067938309198180488190921266777877463027834892272949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 14.5253680 | 7.4184424 | 3.6410316 | 1.9259610 | ||||||||||
| ENSG00000204745 | 102724642 | unprocessed_pseudogene | 237.536831 | 0.031430548 | -4.991689 | 1.32750734 | 9.046864 | 0.0026314583405015021418116294427136381273157894611358642578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0169782468943427168606152832808220409788191318511962890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 16.3720348 | 17.4662229 | 530.2922571 | 566.4891402 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000204791 | SMPD5 | transcribed_unitary_pseudogene | 8.821169 | 0.321535379 | -1.636951 | 0.53750687 | 9.682258 | 0.0018605581745701094565498268096348510880488902330398559570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0127638488209351110697076236988323216792196035385131835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 4.4572944 | 1.3291103 | 13.8358317 | 3.0928029 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000205086 | 400950 | LINC02898 | lncRNA | 30.065454 | 2.682939809 | 1.423815 | 0.46194925 | 9.184496 | 0.0024407374356109064021669308175432888674549758434295654296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0159723023940405647880247386183327762410044670104980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 41.8705820 | 11.1258623 | 15.5598829 | 4.2485691 | ||||||||||
| ENSG00000205560 | 1375 | CPT1B | protein_coding | Q92523 | Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Fatty acid metabolism;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; fatty acid beta-oxidation. | The protein encoded by this gene, a member of the carnitine/choline acetyltransferase family, is the rate-controlling enzyme of the long-chain fatty acid beta-oxidation pathway in muscle mitochondria. This enzyme is required for the net transport of long-chain fatty acyl-CoAs from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene, and read-through transcripts are expressed from the upstream locus that include exons from this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2009]. | hsa:1375; | mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; carnitine O-palmitoyltransferase activity [GO:0004095]; carnitine metabolic process [GO:0009437]; carnitine shuttle [GO:0006853]; fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0006635]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; long-chain fatty acid transport [GO:0015909]; response to blue light [GO:0009637] | 12015320_Genetic analysis, comparison, and tissue distribution of CPT1b 12565845_Leucine-764 near the extreme C-terminal end of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I is important for enzyme activity. 15356291_Transcriptional activation of the CPT1B promotor by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors-alpha and myocyte-specific enhancer-binding-factor 2C. 15579906_muscle carnitine palmitoyltransferase I has a single cysteine residue (Cys-305) important for catalysis 15647998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17089095_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17987377_Three replacements of nucleotides resulting in missense mutations of I66V, S427C, and E531K were observed in the M-CPTI gene of patients showing abnormal fatty acid metabolism 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18820697_A single nucleotide polymorphism located between CPT1B and CHKB, was associated with narcolepsy in Japanese (rs5770917[C], odds ratio (OR) = 1.79, combined P = 4.4 x 10(-7)) and other ancestry groups (OR = 1.40, P = 0.02). 18820697_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19404393_Japanese CNS hypersomnias (essential hypersomnia: EHS) other than narcolepsy with cataplexy was significantly associated with SNP rs5770917 (located between CPT1B and CHKB) and HLA-DRB1*1501-DQB1*0602 haplotype 19404393_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19553926_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19553926_There is a novel association between common nonsynonymous coding variants in CPT1B and ectopic skeletal muscle fat among middle-aged and older African ancestry men. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19937377_C305 was replaceable with aspartic acid but that substitution with other amino acids caused both loss of function and reduced expression. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22177342_The study extends on the observation of a strong multiethnic association of polymorphisms in the TCRA and P2RY11 with narcolepsy, but does not confirm the association of CPT1B/CHKB (rs5770917) in the Chinese population. 22538307_Genetic mutations causative for McArdle disease, carnitine palmitoyl transferase deficiency 2, myoadenylate deaminase deficiency, and malignant hyperthermia have all been associated with Exertional rhabdomyolysis. 22809552_present results confirm the association of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1B coding polymorphisms with the metabolic syndrome 23566841_CPT1B heterozygous variants of G320D and S427C among control subjects showed significantly higher levels of total and free carnitine in the blood compared to acute myocardial infarction patients. 24571861_study identified a novel haplotype consisting of the indel variation, which had not been detected in previous studies in Japanese and Korean populations, and observed four single-nucleotide polymorphisms in CHKB/CPT1B 24905907_E531K substitution in CPT1B decreases the mitochondrial beta-oxidation pathway, which increases the non-protein respiratory quotient value during recovery from exercise. 26041663_CPT1 is active on the outer surface of mitochondria and serves as a regulatory site for fatty acid oxidation due to its sensitivity for malonyl-CoA. CPT1b is the muscle isoform. 26058865_Differential DNA methylation may underlie the depressed expression of CPT1B in response to lipid, contributing to the metabolic inflexibility associated with severe obesity. 26080315_In subjects with PTSD, significant over-expression of CPT1B was also observed in the two common dysregulated pathways: fatty acid metabolism and PPAR. 29657112_CPT1b overexpression could be helping to maintain metabolic health with increasing age. Thus, it is suggested that targeting CPT1b expression might be an interesting strategy to counteract frailty at an early stage. In addition, future studies should examine the role of sirtuin in CPT1b expression regulation. 30846479_Low expression of CPT1B in high-grade urinary bladder cancer was associated with low fatty acid oxidation and low acyl carnitine levels. 32648618_Targeting CPT1B as a potential therapeutic strategy in castration-resistant and enzalutamide-resistant prostate cancer. 33675111_Resting skeletal muscle PNPLA2 (ATGL) and CPT1B are associated with peak fat oxidation rates in men and women but do not explain observed sex differences. 34176754_The impact of CPT1B rs470117, LEPR rs1137101 and BDNF rs6265 polymorphisms on the risk of developing obesity in an Italian population. 35810398_Low carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 activity is a risk factor for narcolepsy type 1 and other hypersomnia. | ENSMUSG00000078937 | Cpt1b | 40.377828 | 0.448094236 | -1.158126 | 0.39694484 | 8.500172 | 0.0035511297469529756916373219866045474191196262836456298828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0216818869054466283052828856625637854449450969696044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 24.7334872 | 5.3402036 | 55.5222374 | 11.0687625 | |
| ENSG00000205795 | 192668 | CYS1 | protein_coding | Q717R9 | Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cilium;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Reference proteome | Predicted to enable chromatin binding activity and transcription corepressor activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within animal organ development and regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Predicted to be located in cytoskeleton; membrane raft; and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:192668; | ciliary membrane [GO:0060170]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829] | 12733055_genomic region comprises three coding exons, which span 22 kb and the transcript harbors an open reading frame of 477 nucleotides encoding a protein with 158 amino acid residues, which is called cystin 34521872_Cystin genetic variants cause autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease associated with altered Myc expression. | ENSMUSG00000062563 | Cys1 | 19.073698 | 0.451051010 | -1.148637 | 0.38437744 | 9.071754 | 0.0025958797967362170870664339616951110656373202800750732421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0168029461345424353801991657064718310721218585968017578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 12.1714413 | 5.4839389 | 26.9826281 | 11.7135225 | ||
| ENSG00000206127 | 728047 | GOLGA8O | protein_coding | A6NCC3 | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;FUNCTION: Peripheral membrane component of the cis-Golgi stack that acts as a membrane skeleton that maintains the structure of the Golgi apparatus, and as a vesicle thether that facilitates vesicle fusion to the Golgi membrane (PubMed:28028212). Required for normal protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus and the cell membrane (PubMed:28028212). Together with p115/USO1 and STX5, involved in vesicle tethering and fusion at the cis-Golgi membrane to maintain the stacked and inter-connected structure of the Golgi apparatus. Plays a central role in mitotic Golgi disassembly: phosphorylation at Ser-37 by CDK1 at the onset of mitosis inhibits the interaction with p115/USO1, preventing tethering of COPI vesicles and thereby inhibiting transport through the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. Also plays a key role in spindle pole assembly and centrosome organization (By similarity). Promotes the mitotic spindle pole assembly by activating the spindle assembly factor TPX2 to nucleate microtubules around the Golgi and capture them to couple mitotic membranes to the spindle: upon phosphorylation at the onset of mitosis, GOLGA2 interacts with importin-alpha via the nuclear localization signal region, leading to recruit importin-alpha to the Golgi membranes and liberate the spindle assembly factor TPX2 from importin-alpha. TPX2 then activates AURKA kinase and stimulates local microtubule nucleation. Upon filament assembly, nascent microtubules are further captured by GOLGA2, thus linking Golgi membranes to the spindle (By similarity). Regulates the meiotic spindle pole assembly, probably via the same mechanism (PubMed:21552007). Also regulates the centrosome organization (By similarity). Also required for the Golgi ribbon formation and glycosylation of membrane and secretory proteins (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q08379, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21552007, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28028212}. | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA | Predicted to be involved in Golgi organization. Predicted to be located in Golgi apparatus. Predicted to be active in Golgi cis cisterna; Golgi cisterna membrane; and cis-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:728047; | cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; Golgi cis cisterna [GO:0000137]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030] | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;21552007_GM130 regulates microtubule organization and might cooperate with the MAPK pathway to play roles in spindle organization, migration and asymmetric division during mouse oocyte maturation 26083584_In oocyte meiosis, GM130 localization and expression patterns are regulated by FMNL1. 28028212_Deletion of GM130 in neurons causes fragmentation. 28055014_the GM130-deficient mouse provides a valuable model for investigating the etiology of human globozoospermia. 29128360_Therefore, we confirmed the associations among Golgi function, fibrosis, and autophagy. Moreover, GOLGA2 knockout mice may be a potentially valuable animal model for studying autophagy-induced fibrosis. 30630895_knockdown of GM130 (also known as GOLGA2) or p115 (also known as USO1), two regulators of the early secretory pathway, impairs GC and ERES reorganisation. This in turn results in inhibition of myotube fusion and M-cadherin (also known as CDH15) transport to the sarcolemma. 32873390_Loss of GM130 does not impair oocyte meiosis and embryo development in mice. | ENSMUSG00000075425+ENSMUSG00000002546 | Gm13547+Golga2 | 39.171428 | 0.146783237 | -2.768241 | 0.86894613 | 9.372854 | 0.0022022234155863085365567588524982056696899235248565673828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0147390914532159258976129478924121940508484840393066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 11.1187890 | 13.5791579 | 104.0832788 | 115.7307682 |
| ENSG00000206384 | 131873 | COL6A6 | protein_coding | A6NMZ7 | FUNCTION: Collagen VI acts as a cell-binding protein. {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Collagen;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal | This gene encodes a large protein that contains multiple von Willebrand factor domains and forms a component of the basal lamina of epithelial cells. This protein may regulate epithelial cell-fibronectin interactions. Variation in this gene may be implicated in skin diseases. [provided by RefSeq, May 2017]. | hsa:131873; | collagen trimer [GO:0005581]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198] | 18400749_The discovery of three additional collagen VI chains doubles the collagen VI family and adds a layer of complexity to collagen VI assembly and function in the extracellular matrix. 20882040_localization of alpha5, and to a lesser extent alpha6, is restricted to the papillary dermis, where the protein mainly colocalizes with collagen fibrils; both chains were found around blood vessels 21406227_collagen VI alpha 6 is an important basal lamina component involved in the regulation of epithelial cell behavior most notably as a regulator of epithelial cell-fibronectin interactions 22226732_The collagen VI alpha6 chain, but not the alpha5 chain, is up-regulated in dystrophic muscles. 24907562_Reduced collagen VI alpha6 chain expression in the skeletal muscle is associated with collagen VI-related myopathies. 26321861_A whole-exome sequencing approach led to identification of a deletion in RHO through detection of a new linked variant in COL6A6 in autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. 28125976_Study identified SNPs in COL6A6 associated with atopic dermatitis suggesting that COL6A6 variants may constitute candidate risk factors for early-onset atopic dermatitis. 30577800_Whole-genome sequencing reveals possible role of deleterious mutation of COL6A6 in ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the thoracic spine in the Chinese population. 35333290_New COL6A6 Variant Causes Autosomal Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa in a Four-Generation Family. | ENSMUSG00000043719 | Col6a6 | 148.424412 | 0.013833869 | -6.175652 | 1.60679229 | 7.018099 | 0.0080689870672701405340809799326962092891335487365722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0420843334568687596486391555572481593117117881774902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 3.7932694 | 5.5346857 | 293.7007086 | 420.6465097 | |
| ENSG00000213366_ENSG00000168765 | 5.945680 | 0.058684794 | -4.090869 | 1.05767079 | 15.597655 | 0.0000783516946160097262422117303515278763370588421821594238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0008359904685650221744727672579244881490012630820274353027343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 0.7566746 | 0.7652808 | 14.8255592 | 11.2332965 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000213809 | 22914 | KLRK1 | protein_coding | P26718 | FUNCTION: Functions as an activating and costimulatory receptor involved in immunosurveillance upon binding to various cellular stress-inducible ligands displayed at the surface of autologous tumor cells and virus-infected cells. Provides both stimulatory and costimulatory innate immune responses on activated killer (NK) cells, leading to cytotoxic activity. Acts as a costimulatory receptor for T-cell receptor (TCR) in CD8(+) T-cell-mediated adaptive immune responses by amplifying T-cell activation. Stimulates perforin-mediated elimination of ligand-expressing tumor cells. Signaling involves calcium influx, culminating in the expression of TNF-alpha. Participates in NK cell-mediated bone marrow graft rejection. May play a regulatory role in differentiation and survival of NK cells. Binds to ligands belonging to various subfamilies of MHC class I-related glycoproteins including MICA, MICB, RAET1E, RAET1G, RAET1L/ULBP6, ULBP1, ULBP2, ULBP3 (ULBP2>ULBP1>ULBP3) and ULBP4. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10426994, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11224526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11777960, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15240696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19658097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21898152, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23298206, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28559451}. | 3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Lectin;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Natural killer (NK) cells are lymphocytes that can mediate lysis of certain tumor cells and virus-infected cells without previous activation. They can also regulate specific humoral and cell-mediated immunity. NK cells preferentially express several calcium-dependent (C-type) lectins, which have been implicated in the regulation of NK cell function. The NKG2 gene family is located within the NK complex, a region that contains several C-type lectin genes preferentially expressed in NK cells. This gene encodes a member of the NKG2 family. The encoded transmembrane protein is characterized by a type II membrane orientation (has an extracellular C terminus) and the presence of a C-type lectin domain. It binds to a diverse family of ligands that include MHC class I chain-related A and B proteins and UL-16 binding proteins, where ligand-receptor interactions can result in the activation of NK and T cells. The surface expression of these ligands is important for the recognition of stressed cells by the immune system, and thus this protein and its ligands are therapeutic targets for the treatment of immune diseases and cancers. Read-through transcription exists between this gene and the upstream KLRC4 (killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily C, member 4) family member in the same cluster. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. | hsa:100528032;hsa:22914; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; MHC class I protein binding [GO:0042288]; MHC class Ib receptor activity [GO:0032394]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; natural killer cell activation [GO:0030101]; natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0042267]; negative regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0034260]; negative regulation of natural killer cell chemotaxis [GO:2000502]; nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0006809]; positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0045954]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002223]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295] | 11777960_NKG2D is the receptor for UL16-binding proteins expressed on primary natural killer cells. 12384702_binding of MICA and MICB induces endocytosis and downregulation of NKG2D, and in turn severe impairment of the responsiveness of tumour-antigen-specific effector T cells 12594848_Selective intracellular retention of virally induced NKG2D ligands by the human cytomegalovirus UL16 glycoprotein. 12646700_Expression of this receptor, inhibited by TGF-beta1, affects NK-mediated killing of dendritic cells 12679019_Results suggest that ligands appear to utilize different strategies to interact with structurally conserved elements of the consensus NKG2D binding site. 12732206_ULBP4 is a novel ligand for NKG2D (ULBP4) 12902493_In the thymus NKG2D may be a signal allowing newly matured CD8+ T cells to emigrate to the periphery; in thymomas there is a decreased percentage of NKG2D-positive thymocytes, which express a less mature phenotype than in normal thymus. 14523385_NKG2D signalling enhances innate and adaptive immune responses (review) 15051759_Cell surface organization of stress-inducible proteins ULBP and MICA that stimulate human NK cells and T cells via NKG2D. 15065764_NKG2D structure, ligands, function, and tissue distribution (review) 15070686_NKG2D triggering accounts for the majority of major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-unrestricted cytotoxicity of activated and expanded CD8+ T cells, likely through DAP10-mediated signaling. 15187109_incubation of NK cells and LAK cells with TGF-beta1 resulted in dramatic reduction of surface NKG2D expression associated with impaired NK cytotoxicity 15328155_natural cytotoxicity receptor (NCR) and NK receptor member D of the lectin-like receptor family (NKG2D) were the key NK activating receptors for bone marrow-derived myeloma cell recognition 15652646_analysis of functional sites in NKG2D-MICA interaction in mouse and human 15657183_NKG2D, NKp30, NKp44, and NKp46 acitvation affected by ligand-negative phenotype in bone marrow-derived progenitor cells, acquisition of cell-surface ligands during myeloid differentiation, defective expression of ligands on malignant transformation 15699119_NKG2D engagement by ligand or monoclonal antibody is not sufficient to costimulate naive or effector CD8+ T cell responses in conventional T cell populations. 15699512_Polymorphic MICA in HLA Class I interacts with non-polymorphic NKG2d receptor on NK cells. 15814668_NKG2D serves as a costimulatory receptor for TCR induced Ca2+ mobilization and proliferation in naive CD8+ T cells 15885603_tumor exosome-phenotype showed positive expression of several NKG2D ligands, important in driving the reduction in the proportion of NKG2D-positive effector cells 16081780_Remarkable similarities in NKG2D function in natural killer (NK) and Vgamma9 Vdelta2 T cells may open new perspectives for Vgamma9 Vdelta2 T cell-based immunotherapy 16136475_expression increased by Il-15 in NK cells 16210654_Freshly isolated natural killer (NK) cells lyse porcine endothelial cells exclusively in an NKG2D-dependent fashion; lysis of porcine endothelial cells mediated by activated human NK cells depends on both NKp44 and NKG2D 16239914_acute myeloid leukemia cells expressed the NKG2D receptor and its signal-transducing adaptator DAP 10, which were functional as confirmed by redirected lysis experiments 16272287_NKG2D/MHC-I-related stress-inducible molecule A and/or NKG2D/UL-16 binding protein 3 engagement is responsible for the delivery of a lethal hit 16293707_The role of TLR3 in the immunobiology of muscle is reported; its implications for the understanding of the pathogenesis of inflammatory myopathies or therapeutic interventions are included. 16517727_soluble MHC class I chain-related molecules in pregnancy serum were able to interact with NKG2D and down-regulate the receptor on PBMC from healthy donors, with the consequent inhibition of the NKG2D-dependent cytotoxic response 16568261_Engagement of MIC by NKG2D promotes spontaneous HAM/TSP T cell proliferation and, apparently, CTL activities against HTLV-1-infected T cells. 16630603_down-regulation of NKG2D by soluble ULBP provides a potential mechanism by which gastric cancer cells escape NKG2D-mediated attack by the immune cells 16690951_defect in cytotoxic effector function is associated with a reduced surface expression of activating NK receptors (NKp30, NKp46, and NKG2D) on CD56(dim) NK cells compared with uninfected newborns. 16732291_Observations with normal peripheral blood NKG2D(+)CD8(+) T cells demonstrated unrecognized NKG2D-mediated immune functions, whereby FasL release promotes tumor cell death and NKG2D costimulation prolongs T cell survival. 16849432_NKG2D and MICB in the cytotoxic NK cell immune synapse have roles in NK cell cytotoxic function 16887974_NKG2D mediates xenogeneic human anti-pig endothelial cell NK cell cytotoxicity by binding to the surface of porcine endothelial cells and to porcine UL16-binding protein 1 (pULBP1). 16901903_ULBP1 is a human ligand of the NKG2D receptor 16914326_Recent insights into the regulation of NKG2D function, the control over NKG2D ligand expression and the role of NKG2D in tumor immunity. 17043026_To be fully sensitive to triggering, optimal natural killer (NK) cell reactivity requires a threshold of NKG2D expression above that of receptor levels in resting NK cells. 17109473_Functions as a prototypic costimulatory receptor in a subset of human cytomegalovirus-specific CD4+ T lymphocytes. 17173658_Significant elevated levels of NKG2D mRNA could be further detected in urine sediment prior to acute rejection, suggesting this receptor as a new candidate marker for the diagnosis of acute and chronic allograft rejection. 17202358_reveal distinct modes of activation of the genes for the MHC class I-related chain ligands of NKG2D and provide a molecular framework for analyses of gene regulation under different cellular insult conditions 17217747_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17255258_NKG2D expression may have a role in immune evasion by tumors in gastric cancer 17267578_NKG2D-NKG2D ligand interactions can potentially contribute to cytotoxic responses mediated by activated immune effector cells in the inflamed central nervous system, as observed in multiple sclerosis. 17405908_Natural killer cell lysis of T lymphocytes via NKG2D may be an additional mechanism to limit T-cell responses.0 17470428_free soluble ULBP protein, RAET1E2, that may impair NKG2D-mediated NK cell cytotoxicity to tumors 17570210_Role of MICA-NKG2D in activation of unique subset of CD4(+) T cells with inflammatory and cytotoxic properties in Crohn's disease. 17584663_Data show that expression of NKG2D ligands MICA and MICB on CNE2 and CNE2/DDP cells is correlated with NK cell-mediated lysis. 17609265_HTLV-1-infected CD4+ T cells did not express ligands for NK cell activating receptors, NCR and NKG2D, although they did express ligands for NK cell coactivating receptors, NTB-A and 2B4. 17625602_upregulation of MICA and MICB by treatment with TsA leads to enhancement of the susceptibility of leukemic cells to the cytotoxicity of NKG2D-expressing cells 17635809_Results indicate for the first time that the NKG2D pathway is involved in the lysis of different melanomas, pancreatic adenocarcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck, and lung carcinoma. 17661204_Expression levels of NKG2D ligands in tissues as well as cells, and suggested that the gastrointestinal tumors might be good candidates for natural killer cell-based cancer immunotherapy. 17875681_NK cell-mediated killing of myeloma cell lines was dependent on either DNAM-1 or NKG2D but not both molecules. 17923698_Engagement of NKG2D by itself is sufficient to stimulate the formation of the natural killer cells immunological synapse (NKIS), with recruitment of NKG2D to the center synapse. 17991774_blockade of an NKG2D-ligand interaction completely prevents the HBV- and CD1d-dependent, nonclassical NKT cell-mediated acute hepatitis and liver injury 18006849_NKG2D, with cytokines, has a role in inhibiting systemic T-cell lymphoma growth 18023027_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18023027_single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with an increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma: rs11053781 and rs2617167 18024793_Co-expression of NKG2D and 4-1BB may represent an important biomarker for defining competency of tumor infiltrating CD8(+) T cells 18070447_NKG2D expression in peripheral lymphocytes correlates with the differentiation and stage of osteosarcoma. 18094399_NKG2D is a biomarker of the status of cytotoxic t-lymphocyte activation in the tumor microenvironment and its expression is relevant to tumor growth 18094430_NKG2D+ T cells have a role in the immunologic response against tumor 18097042_Ap-1 is an important transcription factor for regulating DAP10 gene expression in human NK and T cells, it plays a key role in the transactivation of DAP10 promoter following TCR stimulation. 18174257_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18174257_the HNK1 genotype, associated with high NK cell activity, might be an independent protective factor for colorectal cancer among the Japanese population 18202175_Alterations in the NKG2D pathway are associated with progression from monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance to full-blown multiple myeloma. 18230726_The down-regulation of ligands for both the NKG2D and NKp80 activation pathways provides KSHV with a powerful mechanism for evasion of NK cell antiviral functions. 18275895_in NK cells cultured with IL-15, we observed an up-regulation of the activating receptors NKG2D, NKp30, and NKp46, associated with an increase in anti-tumor lytic activity. 18280748_results show that IL-15 can improve the function of NK cells via up-regulating NKG2D expression, and also augmenting the expression of cytotoxic effector molecules and the phosphorylation of STAT1 and ERK1/2, which may also contribute the NK lysis 18287244_while infection with wild-type Ad enhances synthesis of the NKG2D ligands, MICA and MICB, their expression on the cell surface is actively suppressed. 18313361_Cluster-like formations of 'Wegener's autoantigen' PR3 were surrounded by NKG2D+ and NKG2D-ligand MIC+ cells in WG-granulomata, but not in disease controls. 18316620_different types of stress can trigger up-regulated expression of different sets of NKG2D ligands 18354183_identifies a novel strategy developed by melanoma cells to evade NK cell-mediated immune surveillance based on the intracellular sequestration of immature forms of MICA in the endoplasmic reticulum 18360276_NKG2D ligand induction may participate in the amplification loop that leads to tissue damage during acute graft-versus-host disease. 18361934_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18394936_NKG2D is not necessary for natural killer (NK) cell development but is critical for immunosurveillance of epithelial and lymphoid malignancies in two transgenic models of de novo tumorigenesis. 18398827_NKG2D polymorphisms, previously associated with cholangiocarcinoma, do not seem to confer risk of sporadic colorectal cancer (CRC). 18398831_Interactions between NKG2D genotype and lifestyle exposure were statistically significant: opposite impact of NKG2D genotype by lifestyle (drinking and smoking)exposure to the risk of aerodigestive tract cancer among a Japanese population. 18398831_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18417514_in coculture lysis of bronchial epithelial cells depended on NK group 2 member D signalling; respiratory epithelium has an antigen presenting function and directly alloactivates cytotoxic CD8+ T-cells 18490724_data show that NKG2D is a likely physiological target for exosome-mediated immune evasion in cancer 18490733_findings show macrophage migration inhibitory factor may contribute to the immune escape of ovarian carcinoma by transcriptionally down-regulating NKG2D in vitro and in vivo which impairs NK cell cytotoxicity toward tumor cells 18508446_Release of NKG2DL has been observed in a broad variety of human tumor entities and is thought to interfere with NKG2D-mediated tumor immunity in several ways[REVIEW] 18564160_NKG2D expression on CD8+ T cells was significantly inversely correlated with the frequency of CD4_CD25+ Treg cells in esophageal cancer patients. 18599182_ChNKG2D T cells respond to human myeloma cells and can be generated using clinically applicable cell culture techniques. 18619507_results demonstrate that IL-12 improves the cytotoxicity of NK cells in an NKG2D-dependent manner and augments the expression of cytotoxic effector molecules 18657862_EWS tumor cells are recognized and lysed by resting and with higher efficacy by activated NK cells through NKG2D and DNAM-1 dependent pathways. 18658158_the role of NKG2D and 2B4 is not focussed on trophoblast recognition in normal pregnancy, but is more likely involved in cross-talk among maternal cells of the placental bed 18700876_No significance was observed between the inhibitory (NKG2A) or activating (NKG2C and NKG2D) receptor genotypes and the presence of RF, ANA, or bony erosions in Rheumatoid arthritis. 18700876_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18754036_NKG2D expressed on Sezary syndrome patients natural killer cells is functional and capable to induce degranulation 18832705_NKG2D-mediated activation of lung NK cells following respiratory infection with an opportunistic pathogen and further establish the importance of NKG2D in the host response against P. aeruginosa respiratory infection. 18941207_Brain-infiltrating natural killer (NK) cells might restrict innate and adaptive immune responses via elimination of resting microglia; this cell killing is dependent on cell contact, NKG2D, and NKp46. 19032228_KIR/HLA genotype and expression of NKG2C and NKG2D might play a significant role in regulating natural killer cell function and anti-cytomegalovirus immunity after kidney transplantation. 19038287_NK stimulation with anti-NKGD2 antibodies results in re-organization of mitochondria towards the site of interaction with tumour cells (immune synapse) 19086992_the NKG2D-of MHC Class I chain-related protein interaction is an important molecular mechanism that is involved in the innate immune response to microbial signals in the human uterine endometr 19087227_Intrahepatic CD8+ T cells display increased NKG2D expression in chronic viral hepatitis in comparison with circulating CD8+ T cells. 19118515_These findings provide a novel insight into the mechanisms evolved by hepatitis C virus to escape from the natural killer cell response. 19124832_Activated CD4(+) T cells expressing NKG2DLs can efficiently prevent NKG2D-mediated CD8(+) T-cell functions; this suggest that the NKG2D/NKG2DL interaction can regulate immune responses. 19140827_KLRK1 is involved in cancer immunosurveillance and possibly in prenatal selection. 19140827_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19155520_Both low NKG2D expression and up-regulation of its ligand MICA are related to reactive oxygen species production and may be involved in the immune deficiency of end-stage renal disease patients. 19200602_CD14(+) monocytes promote NKG2D(+)CD4(+) T cells activation through the NKG2D-MIC engagement in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erytematosus. 19237603_Cytosolic phospholipase A(2) (cPLA(2)) is identified as a central molecule in NKG2D-mediated cytolysis in cytotoxic T lymphocytes. 19289577_Immunosuppressive NKG2D(+)CD4(+) T cells appear functionally uncompromised in juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. 19303396_In this work, the glycan ligands of NKG2D and CD94 for the first time were resolved. 19319200_human Dendritic cell-derived exosomes harbor NKG2D ligands on their surface leading to a direct engagement of NKG2D and NK cell activation 19329438_the rapid degradation of NKG2D/DAP10 observed coincident with recruitment of the receptor to the cytotoxic immune synapse may explain the loss of NKG2D receptor expression after chronic exposure to NKG2D ligands 19363685_Increased expression of MICA associated with downregulation of the receptor NKG2D contributes to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 19424970_RAET1G, like ULBP2, appears broadly expressed, but exhibits a lower apparent avidity for NKG2D due to a mutation in the center of the MHC-like fold. 19436053_data suggest that ULBP4 functions as a ligand for both TCRgammadelta and NKG2D and may play a key role in immune surveillance of tumor development and clearance of viral infection 19454690_an interaction between the regulatory subunit of PI3K, p85, and the adaptor protein CrkL is required for efficient NKG2D-mediated cellular cytotoxicity 19489688_NKG2D, CD158a and CD158b expression in MM patients may represent several clinically useful 'biomarkers' of suppressed NK function. 19498463_On co-culture with some melanomas, activated CD4(+) T cells promoted NKG2D- and NKp46-dependent IFN-gamma secretion by NK cells, probably owing to the capture of NKG2D and NKp46 ligands from the tumour-cell surface (trogocytosis). 19508374_Data show upon HSV-1 infection of cell lines, surface levels of NKG2D ligands MICA antigen and UL16 binding protein 2 were downmodulated due to late viral ICP0 gene product(s). 19542445_NKG2D ligand-bearing placental exosomes play a role in immune escape of the fetus, supporting the view of placenta as a unique immunosuppressive organ. 19555665_NKG2D and CD94 bind to heparin and sulfate-containing polysaccharides. 19569244_Cosuppression of HLA Class I and NKG2D ligands and genes encoding peptide transporters or proteasomal genes mediates between RAS activation, DNMT activity and disruption of the antigen presenting system controlling immune recognition in CRC cells. 19587005_binding of NKG2D to UL-16 binding protein (ULB)1 contributes to IL-23-dependent IL-17 production by CD4(+) cells in human M. tuberculosis infection. 19658097_ULBP6 bound to recombinant NKG2D 19711124_There is a significant positive correlation of NKG2D expression with NK cytotoxicity. 19735685_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19735685_systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with the single-nucleotide polymorphism rs2255336 of NKG2D. 19794085_In patients with standard risk hematologic malignancies, the donor NKG2D-HNK1 haplotype is associated with significantly improved overall survival. 19861434_NKG2D ligands are expressed by the majority of colorectal tumors 20008788_Vpr is a key determinant responsible for HIV-1-induced up-regulation of NKG2D ligands 20012119_increased CD8+ T-cell subsets as well as the abnormal expression of NKG2A and NKG2D on CD3+ T and CD3-CD56 + NK cells may play a role in the etiology of systemic lupus erythematosus 20024547_reduced expression in multiple myeloma patients 20045334_The immune-escape of pituitary adenoma is related to the down-regulation of NKG2D and the up-regulation of its ligand MICA. 20074451_Report decreased phosphorylation of ERK1/2 following decreased expression of NKG2D in human K562 cells exposed to asbestos. 20080967_analysis of differential mechanisms of shedding of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored NKG2D ligands 20150362_NKG2D downregulation was primarily caused by tumor-derived tumor growth factor-beta in glioblastoma patients 20354827_the present study has suggested that a deficiency in MICA-NKG2D immune surveillance may contribute to pancreatic cancer progression. 20393128_Inhibition of NKG2D expression in NK cells by cytokines secreted in response to human cytomegalovirus infection. 20415540_heat shock protein 70 and NKG2D ligands are expresseed in acute myeloid leukemia cell lines 20460636_MICA-NKG2D played a role in disease pathogenesis in the majority of patients in our cohort of cases of large granular lymphocyte leukemia 20488792_stimulation allows expression of NKG2D ligands through multiple pathways 20511557_The protein kinase C transduction pathway is identified as a main regulator of the NKG2D-mediated costimulation of antitumor Vgamma9Vdelta2 cytolytic T cell responses. 20519648_An orthopoxvirus histocompatibility class I-like protein binds with high affinity in an NKG2D-independent manner to marginal zone and B1 B cells and monocytes/macrophages, implicating NKG2D in antiorthopoxvirus immunity. 20530257_In a transgenic mouse model of chronic NKG2D ligand expression, constant exposure to NKG2D ligand RNA export 1 homolog (Rae-1 epsilon) does not functionally impair NK cells or CD8-positive T cells in the context of viral infection. 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20648603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20648603_The single nucleotide polymorphism rs2617160 in NKG2D associated with susceptibility to chronic hepatitis B in a Han Chinese population. 20800424_cytokines induce significant up-regulation of NKG2D expression while only IFN-alpha induced significant up-regulation of CD161 20844584_The functional status of CD8+ T cells is determined by CD28 but not NKG2D expression. 20863413_Among gated CD3-expressing cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, the percentage of CD8+ NKG2D+ cells is enhanced in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and smokers with normal lung function, compared to never-smokers. 20926796_these results indicate that pathological NKG2D ligand expression leads to simultaneous impairment of multiple CD3zeta-dependent receptor functions 20959069_Lung cancer has low expression of NKG2D in CD8+NKT cells 21061445_IL-2-activated haploidentical NK cells restore NKG2D-mediated NK-cell cytotoxicity in neuroblastoma patients by scavenging of plasma MICA. 21074271_The polyspecific NKG2D binding site is more tolerant of structural alteration in general than either an antibody-antigen or protein-peptide binding site, and this tolerance may adapt NKG2D to a broad range of protein surfaces with micromolar affinity. 21085608_Downmodulation of NKG2D is associated with defective NK cell responses through NS5A-mediated imbalance of inflammatory cytokines during Hepatitis C virus infection. 21115900_Induction of NKG2D ligands by VPA increased the susceptibility of cancer cells that are recognised by NKG2D to cytolysis by gammadelta T-cells. 21179506_Results demonstrate that receptor-ligand dimensions, NKG2D/MICA and KIR2DL1/HLA-C, are important in NK cell recognition. 21277902_down-regulation of NKG2D by EBV-induced IDO metabolite provides a potential mechanism by which EBV escapes NKG2D-mediated attack by immune cells. 21307295_Transgenic natural killer (NK) cells shape CD8-positive T cell fate by killing recently activated CD8-positive T cells in a perforin- and NKG2D-dependent manner. 21321202_results suggest that tumor co-option of NKG2D immunoreceptor expression may complement the presence of its ligands for stimulation of tumor growth 21469127_contributes to the anti-infectious activity of Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells against Brucella suis 21477352_tumor epithelial cells express the NKG2D receptor that was thought to be exclusive to natural killer cells and cytotoxic lymphocytes 21518478_The positive expression rate of NKG2D and NKG2A on NK cells and CD3(+) T cells in ALL patients was no significantly different from that in AML patients. 21518928_NKG2D receptor regulates human effector T-cell cytokine production. 21554925_Data indicate that the increased frequency of CD8(+) effector-memory T cells with activating NKR KIR2DS4, NKG2C and NKG2D, and cytotoxicity toward hematopoietic cell lines suggests involvement in bone marrow failure and clonal expansion in PNH. 21590763_the CD4- subset of human NKT cells can mediate direct lysis of target cells via NKG2D engagement independent of CD1d, and NKG2D also functions as a co-stimulatory receptor in these cells 21598106_The NKG2D 72Thr gene variant may protect against the incidence of systemic lupus erythematosus. 21600899_NKG2D is a functional marker of CD4+ T cells that produce IL-17 in patients with Crohn's disease, via costimulation of the T-cell receptor and NKG2D. 21626292_Decreased NKG2D expression on NK cells may be one of the key mechanisms responsible for NK cell dysfunction in gastric cancer 21689246_It is now postulated that the characteristic T cell 'swarm of bees' infiltrate seen in alopecia areata is the result of T cells being attracted to the hair follicle by NKG2D-activating ligands 21706044_HMBOX1 negatively regulates the expression of NKG2D and the activation of the NKG2D/DAP10 signaling pathway in NK cells. 21712812_In C2GnT-expressing bladder tumour cells galectin-3 bound the NKG2D-binding site of MICA, reducing the affinity of MICA for NKG2D on natural killer cells and hence severely impairing natural killer cell activation. 21789015_TGF-BETA1 down-modulates surface NKG2D expression by controlling the transcriptional and translational levels of DAP10. 21816829_Other gamma(c) cytokines act similarly to IL-2 in up-regulating DAP10 expression and NKG2D-DAP10 surface expression. 22102694_Study shows that tumor-suppressive miR-34a and miR-34c act as ULBP2 repressors. Findings also implicate p53 in ULBP2 regulation, emphasizing the role of the specific NKG2DL in tumor immune surveillance 22104546_The NKG2D/ligand interaction is a critical molecular link in the vicious cycle of chronic inflammation and metabolic dysfunction that promotes atherosclerosis. 22105417_decreased expression is associated with altered NK-cell function in pediatric transplant patients with PTLD 22143889_CEACAM1 dampens antitumor immunity by down-regulating NKG2D ligand expression on tumor cells. 22167753_Data show that the lymph node (LN) stroma displayed in situ high levels of transcription and expression of the disulfide-isomerase ERp5 and of the disintegrin-metalloproteinase ADAM10, able to shed the ligands for NKG2D (NKG2D-L) from the cell membrane. 22170554_Several SNPs belonging to NFKB1A and NKG2D showed a trend of association with susceptibility to HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis in Peruvian patients. 22200673_Data revealed that the decrease in NKG2D expression levels may have been associated with suppression of NK cell activity in CRC patients. 22242197_The expression of CD85j, NKG2D, NKp30, NKp44, KIR2DL1/S1 and KIR2DL2/L3/S2 receptors at the cell surface evolves between 8 and 12 weeks of gestation. 22252158_Decreased number and reduced NKG2D expression of Vdelta1 gammadelta T cells are involved in the impaired function of Vdelta1 gammadelta T cells in the tissue of gastric cancer. 22304689_results suggest that histamine down-regulates NKG2D ligands through the activation of an histamine H1 receptor (H1R)- and H2R-mediated ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and consequently reduces susceptibility to NK cells 22316211_these results suggest that differential expression of NKG2D-ligands in cervical cancer cell lines might be associated with the down-modulation of NKG2D, as well as with changes in the cytotoxic activity of NKL cells after cell-cell contact with the tumor cells. 22360401_NKG2D levels remain stable on the natural killer cells that persist at one week post-liver transplant in pediatric patients. 22384114_Cytotoxicity of CD56(bright) NK cells towards autologous activated CD4+ T cells is mediated through NKG2D, LFA-1 and TRAIL and dampened via CD94/NKG2A 22438812_TGF-beta1 may reduce the expression of NKG2D/DAP10 and 2B4/SAPin patients with hepatitis B. 22449797_NK cell induction of hepatic stellate cell apoptosis in HCV infection was contact dependent and could partly be blocked by antibodies specific for TRAIL, NKG2D and FasL. 22480139_studies may suggest that the women with cervical cancer bearing the NKG2D 72Thr gene variant might be protected against progression to advanced stages of this cancer 22507622_NKG2D haplotypes are associated with the expression levels of NKG2D protein on NK and CD8 T cells, resulting in inter-individual variations in human cytotoxic response. 22555808_We conclude that NKG2D-NKG2D ligand interaction may be one of the mechanisms by which CIK cells kill MM cells. 22585739_study describes that both N-WASp and WASp participate in the inhibition of NK-cell chemotaxis in response to NKG2D WASp engagement, and that this effect is not dependent on the regulation of F-actin dynamics 22613008_high killing activity of natural killer cells against K562 was abolished through the addition of a NKG2D blocking antibody 22640649_Report expression of NKG2D and CD107 in CD8(+) effector memory lymphocytes in Churg-Strauss syndrome. 22715368_IL-15+IL-12 has an immunomodulatory effect on NK cell subsets from HIV-infected individuals viz down-regulation of iNKRs, elevation of activatory receptors NKp46 and NKG2D, and induction of coreceptor NKp80. 22730533_NKG2DL expression on leukemia cells is relevant for natural kiiller (NK) cell immunosurveillance as well as involvement of soluble NKG2DL in NKG2D downregulation, which results in impaired NK reactivity against leukemia targets. 22798674_Upregulation of NKG2D ligands by H-RasV12 increased sensitivity of cells to NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity 22806577_Simultaneous knockdown of multiple ligands (MICA/B, ULBP2, and ULBP3) significantly attenuated NK cell cytolysis against human NKG2D ligand-positive hepatocyte L-02 cells. 22870231_The ability to express NKG2D at the cell surface was primarily determined by the activation or differentiation status of the CD4(+) T-cells and not by the antigen presenting cells 22942430_Decreased expression of NKG2D in transgenic mice in response to IL-4 is associated with inhibition of NKG2D-dependent CD8 T cell activation. 23020627_TGF-beta1 secreted by multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells is responsible for impaired cytotoxic t-cells and natural killer function by down-modulating surface NKG2D expression. 23115291_Here, the authors show that cowpox virus-encoded OMCP binds the NKG2D homodimer as a monomer and competitively blocks host ligand engagement. 23235109_These findings suggest that differential NKG2D expression in the different cell subsets is regulated by epigenetic mechanisms. 23298206_NKG2D is expressed by all natural killer (NK) cells but is not limited to NK cells, as it is also expressed by many T cells, including all CD8-positive T cells in humans. 23298273_Results suggest that aberrantly decreased levels of NKG2D expression on NK cells and CD8(+) T cells might be one of the factors led to disturbed immunological function in Kawasaki disease (KD). 23302231_cytotoxic potential of NK cells against a wide spectrum of tumor subtypes could be markedly enhanced by expression of NKG2D-DAP10-CD3zeta receptors 23360454_data describe immune escape mechanism of monoclonal gammopathy/multiple myeloma occuring via downregulation of 3 major activating NK receptors (NCR3/NKp30, NKG2D and CD244/2B4/p38) in bone marrow, that was undetectable in peripheral blood. 23413900_Studies indicate that a crosstalk between CTLA-4 and NKG2D can modulate the function of effector CD8+ T cells. 23417963_NKG2D is functionally expressed on CD4CD28(-) and CD8 T-cells in giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. NKG2D-ligands are present in temporal arteries and may co-stimulate NKG2D expressing T-cells. 23445485_resveratrol consistently upregulated the NKG2D receptor expression and enhanced NKG2D-mediated functions in resting NK cells obtained from healthy individuals 23772752_Data suggest that a common polymorphism in MICA (MICA*008)--a ligand for NKG2D--results in protein that exists in soluble and membrane-bound forms and is attached to membranes by glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) which controls transit to exosomes. 23846901_these data illustrate in vivo that NKG2D is regulated by [Mg2+]i and apparently plays a key role in Epstein-Barr virus control. 23913973_The tumor-associated expression of NKG2D ligands helps destroy malignant cells but in advanced cancer, NKG2D & its ligands are targeted for immune invasion & suppression, autocrine stimulation, & progression. Review. 23945543_Oligoclonal expansions of mucosal T cells in Crohn's disease predominate in NKG2D-expressing CD4 T cells. 23947399_significant increase within the CD4+NKG2D+ T cell population in CIN 1 patients might be the result of a chronic exposure to viral and/or pro-inflammatory factors, and concomitantly might also influence the clearance of CIN 1-type lesion | ENSMUSG00000030149 | Klrk1 | 34.874537 | 8.043353343 | 3.007797 | 0.82712624 | 12.248492 | 0.0004656343158534353467159494499583161086775362491607666015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0039331478322209264056330546566186967538669705390930175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 15.2317359 | 11.4312685 | 1.8772054 | 1.4576276 | |
| ENSG00000213928 | 10379 | IRF9 | protein_coding | Q00978 | FUNCTION: Transcription factor that plays an essential role in anti-viral immunity. It mediates signaling by type I IFNs (IFN-alpha and IFN-beta). Following type I IFN binding to cell surface receptors, Jak kinases (TYK2 and JAK1) are activated, leading to tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT2. IRF9/ISGF3G associates with the phosphorylated STAT1:STAT2 dimer to form a complex termed ISGF3 transcription factor, that enters the nucleus. ISGF3 binds to the IFN stimulated response element (ISRE) to activate the transcription of interferon stimulated genes, which drive the cell in an antiviral state. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30143481}. | Activator;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes a member of the interferon regulatory factor (IRF) family, a group of transcription factors with diverse roles, including virus-mediated activation of interferon, and modulation of cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune system activity. Members of the IRF family are characterized by a conserved N-terminal DNA-binding domain containing tryptophan (W) repeats. Mutations in this gene result in Immunodeficiency 65. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2020]. | hsa:10379; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; ISGF3 complex [GO:0070721]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; immune system process [GO:0002376]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] | 12509459_the IFN-activated ISGF3 transcription factor regulates transcription through contact with DRIP150 15194680_IRF9 functions to recruit RNA polymerase II to the promoter of interferon-stimulated genes and requires histone deacetylases 15668228_the conserved DNA-binding domain of STAT2 has a role specific to the activity of ISGF3-independent STAT2-containing complexes 15714000_defects in ISGF3 can cause resistance to IFN-alpha(2a) treatment 16318580_GBF1 is recruited to the endogenous IRF-9 promoter, and interacts with C/EBP-beta, IL-1, and IL-6 16595158_Pretreatment of Huh-7 cells with 0.5-1 mM H2O2 resulted in the suppression of the IFN-alpha-induced antiviral protein MxA and of IRF-9 mRNA expression. 16689942_Data reveal the existence of a collection of GAS-regulated target genes whose expression is interferon-inducible and independent of ISGF3 but highly dependent on the STAT2 DNA binding domain. 16849320_Results identify Viperin as a tightly regulated ISGF3 target gene, which is counter-regulated by PRDI-BF1. 17559358_Suggest that the JAK-STAT pathway may play a major role in mediating the effects of IFN-alpha against hepatitis b virus, and that ISGF3 might be a key factor. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18370868_These data define the role of the ISGF3 members in IFN-beta inhibitory signaling. 18456457_The data suggest that liberation of the IFNaR2-ICD by regulated proteolysis could trigger a novel mechanism for moving the transcription factor Stat2 to the nucleus. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19604093_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19752753_a key factor for eliciting the antiproliferative activity of IFN-alpha in tumors 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20389019_NOD1 can activate the ISGF3 signaling pathway that is usually associated with protection against viral infection to provide robust type I IFN-mediated protection from H. pylori and possibly other mucosal infections 20403236_STAT2 may interact with IRF-9 in a STAT1-independent manner. The complex STAT2/IRF-9 is the key factor mediating the expression of RIG-G gene regulated by IFN-alpha. 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20943654_analysis of IFN-stimulated response elements (ISREs) that bind to both the IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 (ISGF3) as well as to IFN response factor 7 (IRF7) 20964804_Results suggest that the amount of cellular IRF9 is a crucial determinant for amplification of early dynamics of IFNalpha-mediated signal transduction. 20980339_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21268015_Signals ensued by IFN-alpha and IL-4 induce cytoplasmic sequestration of IL-4-activated STAT6 and IFN-alpha-activated STAT2:p48 in B cells through the formation of pY-STAT6:pY-STAT2:p48 complex. 21697347_Western blot and electrophoretic mobility-shift assays identified the interferon-stimulated gene factor-3 (ISGF-3) components STAT1 and IRF-9 as the proximal targets of human herpesvirus 8 vIRF-2 activity. 21957129_HDAC1 and HDAC2 differentially modulate STAT activity in response to IFNalpha2: while they are required for the induction of ISGF3-responsive genes, they impair the transcription of STAT3-dependent genes. 22902549_The hepatitis C virus (HCV) non-structural 5A (NS5A) protein, which is known to modulate the IFN response, competes with IRF9 for CypA binding and can prevent the formation of IRF9-CypA complexes. 23913484_IL6 is an inducer of IRF9 expression in prostate cancer and a sensitizer for the antiproliferative effects of IFNalpha2. 25150882_IRF9 mediated myocardial reperfusion injury 25156627_STAT2 and IRF9 overexpression is sufficient to drive interferon-related DNA damage signature expression upon cell crowding. 25278262_DC-SIGN-induced ISGF3 by fucose-based PAMPs has an essential role in driving IL-27 and subsequent TFH polarization, which might be harnessed for vaccination design 25319116_IRF9 is a vascular injury-response molecule that promotes VSMC proliferation. IRF9 expression is upregulated during neointima formation. 26216956_U-ISGF3 induced by IFN-lambdas and -beta drives prolonged expression of a set of IFN-stimulated genes during HCV infection 26397446_Interferonstimulated gene factor 3 complex, which consists of STAT1, STAT2 and IRF9, is required for the induction of SAMHD1 expression by IFN-alpha in SMMC-7721 cells. 26987614_Recent studies have revealed a unique role for IRF9 as a conductor of the cellular responses to IFN-Is. Intriguingly, novel roles for IRF9 outside of the antiviral response are also being identified. 28318807_these findings identify miR-302d as a key regulator of type I IFN driven gene expression via its ability to target IRF9 and regulate ISG expression, underscoring the importance of non-coding RNA in regulating the IFN pathway in SLE. 28441586_PKV VP3 associated with STAT2 and IRF9, and interfered with the formation of the STAT2-IRF9 and STAT2-STAT2 complex. 28442624_Decreased IRF9 expression was accompanied by increased replication of hepatitis C virus and hepatitis E virus. 29317535_Surface features in the interacting domains of IRF9 and STAT2 have diverged to enable specific interaction between these family members and to enable the antiviral response. 29581268_Priming cells with IFNbeta synergistically enhances IL6 induction in response to treatments that activate NF-kappaB, in a process that depends upon the recruitment of STAT2, IRF9. 30143481_findings show that human IRF9- and ISGF3-dependent type I and III IFN responsive pathways are essential for controlling IAV. 30147694_this review outlines the structural basis of IRF9 that guides its regulation and interaction in antiviral immunity and other diseases 30355451_Thus after VHL inactivation, HIF induces ISGF3, which is reversed by the loss of secondary tumor suppressors, suggesting that this is a key negative feedback loop in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 30446226_the type I IFN receptor signal elicits an increase in PD-L1 expression in lung cancer cells through IRF9-dependent and independent pathways. 30679726_Transcription factor STAT3 is activated upstream of IRF9 and binds to the IRF9 promoter in multicellular spheroids (MCS) of HCT116 colorectal carcinoma cells. STAT3 mediates expression of IRF9 and interferon stimulated genes. 32581091_The Measles Virus V Protein Binding Site to STAT2 Overlaps That of IRF9. 32772027_IRF9 Affects the TNF-Induced Phenotype of Rheumatoid-Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes via Regulation of the SIRT-1/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. 33936086_SARS-CoV-2 Spike Targets USP33-IRF9 Axis via Exosomal miR-148a to Activate Human Microglia. 34272232_Pseudorabies Virus DNA Polymerase Processivity Factor UL42 Inhibits Type I IFN Response by Preventing ISGF3-ISRE Interaction. 35148998_Increased IRF9-STAT2 Signaling Leads to Adaptive Resistance toward Targeted Therapy in Melanoma by Restraining GSDME-Dependent Pyroptosis. 35182547_Aberrant inflammatory responses to type I interferon in STAT2 or IRF9 deficiency. 36059459_SCD2-mediated cooperative activation of IRF3-IRF9 regulatory circuit controls type I interferon transcriptome in CD4(+) T cells. 36132546_IRF9 and XAF1 as Diagnostic Markers of Primary Sjogren Syndrome. 36357830_Positive selection-driven fixation of a hominin-specific amino acid mutation related to dephosphorylation in IRF9. | ENSMUSG00000002325 | Irf9 | 162.720605 | 0.467796678 | -1.096046 | 0.24483458 | 19.663780 | 0.0000092335005737289786270334882023469447176466928794980049133300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001244298709299816545464228978445930806628894060850143432617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 118.7153225 | 23.0727828 | 255.1765870 | 48.5788322 | |
| ENSG00000214193 | 79729 | SH3D21 | protein_coding | A4FU49 | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome;SH3 domain | Located in nucleoplasm and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:79729; | nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; cell migration [GO:0016477] | ENSMUSG00000073758 | Sh3d21 | 22.036224 | 0.454562852 | -1.137448 | 0.35678629 | 10.083248 | 0.0014962339817914456930464384143419920292217284440994262695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0106294164232091127575419164941195049323141574859619140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 13.2348903 | 2.8881922 | 29.5540256 | 5.9093097 | |||
| ENSG00000215041 | 84461 | NEURL4 | protein_coding | Q96JN8 | FUNCTION: Promotes CCP110 ubiquitination and proteasome-dependent degradation. By counteracting accumulation of CP110, maintains normal centriolar homeostasis and preventing formation of ectopic microtubular organizing centers. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22261722, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22441691}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway | The protein encoded by this gene is predicted and it includes two isoforms resulting from two alternatively spliced transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:84461; | centriole [GO:0005814]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630] | 22261722_the NEURL4-HERC2 complex participates in the ubiquitin-dependent regulation of centrosome architecture 22441691_Neurl4 counteracts accumulation of CP110, thereby maintaining normal centriolar homeostasis and preventing formation of ectopic microtubular organizing centres 28385950_The data support a model in which the daughter centriole promotes ciliogenesis through Neurl-4-dependent regulation of CP110 levels at the mother centriole. 35157000_Neuralized-like protein 4 (NEURL4) mediates ADP-ribosylation of mitochondrial proteins. | ENSMUSG00000047284 | Neurl4 | 150.319904 | 0.429983821 | -1.217646 | 0.27963655 | 18.470566 | 0.0000172548682038370410519057679410437344813544768840074539184570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0002158864905503331960145985135568480473011732101440429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 88.9337427 | 18.1361016 | 207.6510376 | 41.9651434 | |
| ENSG00000215769_ENSG00000266820_ENSG00000291117 | 100.781797 | 0.304972733 | -1.713248 | 0.32066258 | 27.528346 | 0.0000001548088885528136549721615021490972452511414303444325923919677734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000029302662152594822713813464687415688558758120052516460418701171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 40.6721017 | 12.8320042 | 126.0982056 | 38.7856776 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000215817 | 643136 | ZC3H11B | protein_coding | A0A1B0GTU1 | FUNCTION: May play a role in mRNA transport. {ECO:0000305}. | Coiled coil;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA | Predicted to enable mRNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | Mouse_homologues mmu:70579;;mmu:70579; | metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus [GO:0016973] | 26485405_Genetic variants in ZC3H11B, RSPO1, and GJD2 are associated with susceptibility to the development of high myopia in a Han Chinese population. 31300455_Association of the ZC3H11B, ZFHX1B and SNTB1 genes with myopia of different severities. | ENSMUSG00000116275+ENSMUSG00000102976 | Zc3h11a+Zc3h11a | 25.266317 | 0.468723802 | -1.093190 | 0.31492845 | 12.229830 | 0.0004703149140326332694993227701019122832803986966609954833984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0039679873722536672039917782228712894720956683158874511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 15.8653310 | 4.4522562 | 33.7722867 | 8.9026872 |
| ENSG00000224186 | 100996485 | PITX1-AS1 | lncRNA | 34431063_Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes block malignant behaviors of hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells through a lncRNA C5orf66-AS1/microRNA-127-3p/DUSP1/ERK axis. | 22.295787 | 0.404670834 | -1.305179 | 0.36962308 | 12.763665 | 0.0003534176967355446598306745187301203259266912937164306640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0031189947898654884865521363934703913400880992412567138671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 12.3986636 | 2.9709816 | 30.5819330 | 6.4085640 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000224578 | 642659 | HNRNPA1L3 | protein_coding | A0A2R8Y4L2 | Mouse_homologues FUNCTION: Involved in the packaging of pre-mRNA into hnRNP particles, transport of poly(A) mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and modulation of splice site selection. Plays a role in the splicing of pyruvate kinase PKM by binding repressively to sequences flanking PKM exon 9, inhibiting exon 9 inclusion and resulting in exon 10 inclusion and production of the PKM M2 isoform. Binds to the IRES and thereby inhibits the translation of the apoptosis protease activating factor APAF1. May bind to specific miRNA hairpins. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P09651}. | Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding | Predicted to enable RNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in RNA splicing and mRNA processing. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | Mouse_homologues mmu:15382; | nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; RNA binding [GO:0003723] | Mouse_homologues 11774503_data provide evidence that hnRNP A1 is directly or indirectly involved in mouse hepatitis virus RNA transcription and replication 11774505_study provides direct in vivo evidence demonstrating a functional role for hnRNP A1 in mouse hepatitis virus RNA synthesis 12560094_results are consistent with a model in which the binding of hnRNP A1 to the 71 nt putative hairpin-loop region in the CYP2A5 mRNA 3' UTR upregulates mRNA levels possibly by protecting the mRNA from degradation 15390079_Both hnRNP A1 and alternative splicing factor/splicing factor 2 contents rose in adenomas and during injury-induced hyperplasia compared to control lungs 18562319_hnRNP A1 has a role in mediating rapamycin-induced alterations of cyclin D1 and c-myc IRES activity in an Akt-dependent manner and provide the first direct link between Akt and the regulation of IRES activity 20133837_splicing repressors hnRNP A1 and A2, as well as the polypyrimidine-tract-binding protein PTB, contribute to control of pyruvate kinase isoform M1 and M2 expression 20338999_eIF2alpha phosphorylation during hypertonic stress promotes apoptosis by sequestration of specific mRNAs in SGs in a process mediated by the cytoplasmic accumulation of hnRNP A1 21454539_the phosphorylation status of hnRNP A1 serine 199 regulates the AKT-dependent sensitivity of cells to rapamycin and functionally links IRES-transacting factor annealing activity to cellular responses to mTOR complex 1 inhibition. 22345078_MMP-3-triggered Rac1 splicing regulation is modulated by hnRNP A1 23704325_Heteronuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 interacts with an element that overlaps the 5' splice site of Mag exon 12. 23946460_This study provides evidence that PCBP2 and hnRNP A1 bind to the 5' and 3' ends of the murine norovirus 1 viral RNA and contribute to RNA circularization, playing a role in the virus life cycle. 24152440_Relevant to biological processes anticipated for hnRNP A1 and HuR. 25901972_hnRNP A1 improves intestinal injury in anti-CD3 antibody-induced enteritis mice through the upregulation of TFF2, which regulates apoptosis and enhances epithelial restoration 27151978_A1 and A2/B1, which are required for transcript degradation 28024152_this study identified hnRNPA1, an RNA-binding protein and auxiliary splicing factor, as a substrate of TRAF6; TRAF6 ubiquitination of hnRNPA1 regulated alternative splicing of Arhgap1, which resulted in activation of the GTP-binding Rho family protein Cdc42 and accounted for hematopoietic defects in TRAF6-expressing hematopoietic stem/ progenitor cells 28077597_Study demonstrated that hnRNPA1 plays a critical and irreplaceable role in embryonic muscle development by regulating the expression and alternative splicing of muscle-related genes. 28088441_Resveratrol causes a shift from the mesenchymal-specific forms of these factors to the respective epithelial forms and increases the expression of the RNA-binding proteins KHSRP and hnRNPA1. 28115626_PRMT5 regulates internal ribosome entry site-dependent translation via methylation of hnRNP A1. 28220845_Knockdown of hnRNP A1 led to a decrease in endogenous Nfil3 protein level, which could be due to a reduction in IRES-mediated translation. 28912364_hnRNPA1 is a critical regulator of vascular smooth muscle cell function and behavior in the context of neointima hyperplasia via miR-124/IQGAP1 regulatory axis. 29077485_Report direct role for hnRNPA1 in MYLK alternative splicing in lung endothelial cells. 29367466_Loss of Hnrnpa1 expression leads to dysregulation of cardiac transcription networks and multiple signaling pathways, including BMP, FGF, and Notch in the second heart field. Finally, two rare heterozygous mutations of HNRNPA1 were detected in human congenital heart defects. These findings suggest a role of Hnrnpa1 in embryonic heart development in mice and humans. 31169879_Loss of hnRNP A1 in murine skeletal muscle exacerbates high-fat diet-induced onset of insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis. 32086392_these studies suggest that CUG(exp) RNA triggers abnormal expression of multiple nuclear RNA binding proteins, including CELF1 and HNRNPA1, that antagonize MBNL activity to promote fetal splicing patterns 32960212_Post-translational modifications of hnRNP A1 differentially modulate retroviral IRES-mediated translation initiation. 33115498_LncRNAH19 improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle by regulating heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1. 33692334_HNRNPA1-mediated exosomal sorting of miR-483-5p out of renal tubular epithelial cells promotes the progression of diabetic nephropathy-induced renal interstitial fibrosis. 33951764_Irisin ameliorates endoplasmic reticulum stress and liver fibrosis through inhibiting PERK-mediated destabilization of HNRNPA1 in hepatic stellate cells. 34944075_hnRNP Q and hnRNP A1 Regulate the Translation of Cofilin in Response to Transient Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation in Hippocampal Neurons. | ENSMUSG00000046434 | Hnrnpa1 | 34.724695 | 0.436312669 | -1.196566 | 0.31150343 | 14.887102 | 0.0001141407638940844640257007980288506132637849077582359313964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0011605960543693491504591008833813248202204704284667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 21.9747276 | 10.3961543 | 50.4059247 | 23.3731572 | |
| ENSG00000224596 | 283050 | ZMIZ1-AS1 | lncRNA | 89.327320 | 0.389745474 | -1.359396 | 0.17165050 | 64.209050 | 0.0000000000000011189357617499940131630444344452280241127071873374898558495260658673942089080810546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000555023880686486348757729938542325348366408832578855481187929399311542510986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 46.8990867 | 8.1506623 | 120.7259588 | 19.8470897 | ||||||||||
| ENSG00000225434 | 100507540 | LINC01504 | lncRNA | 46.603521 | 0.220155483 | -2.183405 | 0.73343900 | 7.851090 | 0.0050790088976189178698872339623449079226702451705932617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0289980312081197649787256409581459593027830123901367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 16.7998014 | 8.0836244 | 77.2260143 | 37.2602757 | ||||||||||
| ENSG00000228477 | processed_pseudogene | 42.885960 | 0.472163804 | -1.082641 | 0.27139386 | 16.042271 | 0.0000619439652123317995241827405017431829037377610802650451660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0006732495612976667704110966816699601622531190514564514160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 27.2672766 | 4.9384849 | 58.0045497 | 9.6111370 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000229314 | 5004 | ORM1 | protein_coding | P02763 | FUNCTION: Functions as transport protein in the blood stream. Binds various ligands in the interior of its beta-barrel domain. Also binds synthetic drugs and influences their distribution and availability in the body. Appears to function in modulating the activity of the immune system during the acute-phase reaction. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17008009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17321687}. | 3D-structure;Acute phase;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transport | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA | This gene encodes a key acute phase plasma protein. Because of its increase due to acute inflammation, this protein is classified as an acute-phase reactant. The specific function of this protein has not yet been determined; however, it may be involved in aspects of immunosuppression. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:5004; | blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; platelet alpha granule lumen [GO:0031093]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; acute-phase response [GO:0006953]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 production [GO:0032732]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; regulation of immune system process [GO:0002682] | 11814462_Different ORM1 phenotypes may affect the disposition of quinidine 11911961_demonstrate that orosomucoid and/or its glycoforms affects thyroid cell function in vitro and that it does so by influencing the second messenger cAMP probably by interacting directly with the TSH receptor 11925509_The effect of alpha2,6-linked sialic acid on anti-IgM antibody-induced apoptosis in Ramos cells. 12480518_folds as a highly symmetrical all-beta protein dominated by a single eight-stranded antiparallel beta-sheet 12576428_exerts significant effects on the pharmacokinetics, plasma concentrations, and intracellular distribution of imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia patients 15013397_tertiary structure analysis 15111541_Urinary levels are increaed in normoalbuminuric type 2 diabetic patients. 16261636_the N-linked glycosylation pattern of AGP was explored 16290938_The binding of coumarin enantiomers to ORM1 is studied. 17048007_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17321687_The drug binding site of AGP was gained from circular dichroism and electronic absorption spectra. 17675532_Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 1 may be an endogenous ligand for Siglec-5 as a signaling molecule that participates directly in the regulation of neutrophil responses. 17944232_Different ORM1 genotypes affect the protein binding percentage and the concentration of serum free nortriptyline. 17944232_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17987628_A different distribution of the area percentage of AGP forms is observed when comparing samples from diseased and healthy individuals, the most acidic AGP forms being present in a higher proportion in the samples from cancer patients. 18273814_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18273814_Polymorphisms of the human ORM1 gene in Mexico have been evaluated. 18510947_Bile pigment biliverdin and is the endogenous ligand of AAG. 18680736_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18823996_The crystal structure of the recombinant unglycosylated human AGP at 1.8 A resolution, which was solved using the new method of UV-radiation-damage-induced phasing, is reported. 18981009_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19018521_The ORM1 variant is predominantly responsible for the acute-phase property of alpha-1 acid glycoprotein. 19141860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19198000_A site-directed mutagenesis study of drug-binding selectivity in genetic variants of AGP1 is reported. 19395425_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19395425_ORM1*S/*S genotype predicted failure to complete a 6-week trial of antidepressants, whereas elevated plasma concentration of orosomucoid predicted failure to respond to antidepressant therapy at 6 weeks. 19459043_The present study investigated enhanced fucosylation of AGP in the sera of chronic hepatitis B (HBV-CH) and hepatitis B cirrhosis (HBV-LC) patients. 19616527_Results describe modifications in alpha-1-acid glycoprotein fucosylation in relation to different stages of human pregnancy. 19794411_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19958090_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20371432_Almost all of the acute-phase proteins were closely related to rheumatoid arthritis activity (based on DAS28) and their places in the downgrade scale were as follows: CRP, Tf, AGP, Hp and AAT. 20442402_ORM integrates inflammatory and metabolic signals to modulate immune responses to protect adipose tissue from excessive inflammation and thereby from metabolic dysfunction. 20617306_Characterized are more than 150 human Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein isoforms, differing both in the amino acid sequence and in the glycosylation. 20959405_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21300760_Data suggest that GDC-0449 pharmacokinetics are mediated by AAG binding. 21349832_analysis of differences in drug-binding selectivity between two forms of human alpha1-acid glycoprotein genetic variants, the A and F1*S forms 21621584_Importance of pH and disulfide bridges on the structural and binding properties of human alpha-acid glycoprotein. 21638284_Identify ORM genetic variations/haplotype structure associated with serum alpha-1-acid glycoprotein level and the pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel in Japanese cancer patients. 21726491_The distribution of the AGP phenotypes did not differ significantly among the disease groups studied 22048274_Leukocytospermia was associated with the alterations of terminal monosaccharide expression in human seminal fibronectin and alpha{1}-acid glycoprotein 22147846_Urinary MCP1 and AGP are biomarkers of lupus nephritis in patients with juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus, providing insight into its pathophysiology 22216449_In this study, the potential of CZE-UV and CZE-ESI-MS analysis of intact AGP isoforms to study the correlation of this protein with bladder cancer is shown. 22574522_Characterization of 6-mercaptopurine binding site on human alpha1-acid glycoprotein (orosomucoid) using molecular docking. 22587817_The binding properties of the polymyxin class of antibiotics for human alpha-1-acid glycoprotein (AGP) have been characterized. 22633841_AGP has a direct effect in brain microvasculature and may play an important role in altering blood brain barrier integrity in inflammatory-related diseases. 22708402_change of the maintenance of three acute phase proteins: ceruloplasmin, alpha1-antitripsin and orosomucoid in an oral fluid and blood plasma at paradontitis and myocardial infarction 22807450_alpha(1)-Acid glycoprotein up-regulates CD163 via TLR4/CD14 protein pathway: possible protection against hemolysis-induced oxidative stress. 22908695_Analyses of Nicaraguan population surveillance data suggest that preschool children with elevated AGP1 levels have higher prevalence of anemia than children with normal AGP1 levels. 23192962_Drug-binding energetics of human alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. 23526947_A cross-sectional study was conducted to evaluate the relationship between periodontitis and the common systemic inflammatory markers in 32 morbidly obese patients. The severity of periodontitis was associated with the plasma level of orosomucoid. 23936770_analysing the glycosylation of AGP in patients receiving methadone may aid in determining whether the therapy is likely to be effective. 23940561_The ORM1 A113G polymorphism was associated with the PKs variability after taking telmsiartan, as well as ABCC2 C3972T. The heterozygotes of ORM1 113AG showed a larger AUC and a notable BP change(%) from the baseline compared with the wild-type. 23973664_The ORM1 may be considered as a signaling molecule involved in the maintenance of tissue homeostasis and remodeling. 24357727_Identified is the ORM1 gene, coding for orosomucoid, as a novel locus associated with lag time variability, reflecting the initiation process of thrombin generation. 24359035_Data suggest that human serum albumin (HSA) might serve as a carrier in delivering chitooligomers to target tissues than alpha-1-glycoprotein (AGP) which has pharmacological importance 24389491_These findings suggest that the ORM distal promoter region differentially regulates expression of ORM genes at basal level and in acute phase responses. 25408356_Data indicate that the band intensity of sialic acid content in alpha-1 Acid glycoprotein (AGP) of alcoholic liver cirrhosis was found to be lower than that in pooled control group. 25689617_ORM1 stimulates quiescent monocytes to polarize to M2b monocytes. 26193215_The results of this study suggest that the expression of VEGF-A and ORM-1 may be associated with two mechanisms (angiogenesis and tumor structural viscosity) that may influence tumor growth in odontogenic myxoma. 26563422_Glycosylated Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 1 is ostensibly expressed in lung cancer patients and is a potential lung cancer serum biomarker. 26563517_Altogether, these results indicate that alpha1-3 fucosylated glycoforms of AGP are increased in PDAC and could be potentially regarded as a PDAC biomarker. 27021626_Results indicate that advanced extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma (ENKL) patients with unfavourable treatment outcomes displayed higher levels of S100A9 and ORM1. 27754964_Data suggest that serum haptoglobin, fetuin-A, platelet factor-4, hs-CRP (high sensitive-C-reactive protein), SAP (serum amyloid P), AGP (alpha1-acid glycoprotein) levels of adolescents with metabolic syndrome are significantly higher than those of controls subjects. 28554261_Studies suggest plasma alpha-1-acid glycoprotein (AAG) as a potential predictive biomarker of docetaxel non-haematological AEs namely oral mucositis and rash. 28927749_Data provide evidence that Orm1 is induced in response to hepatic injury and executes liver regeneration by activating cell cycle progression in hepatocytes. 31399619_Evaluation of AGP Fucosylation as a Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma of Three Different Etiologies. 31482685_Dramatically changed immune-related molecules as early diagnostic biomarkers of non-small cell lung cancer. 31601857_Fucosylated alpha1-acid glycoprotein as a biomarker to predict prognosis following tumor immunotherapy of patients with lung cancer. 31736338_Taken together, AFP and ORM1 in the urine may be used as a diagnostic or screening biomarker of Hepatocellular carcinoma 31930291_Orosomucoid 1 is involved in the development of chronic allograft rejection after kidney transplantation. 33070381_Different glycoforms of alpha-1-acid glycoprotein contribute to its functional alterations in platelets and neutrophils. 33459949_miR-362-3p Targets Orosomucoid 1 to Promote Cell Proliferation, Restrain Cell Apoptosis and Thereby Mitigate Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Cardiomyocytes Injury. 33580265_Proteomic Profile of Urinary Extracellular Vesicles Identifies AGP1 as a Potential Biomarker of Primary Aldosteronism. 33640788_Acute phase alpha1-acid glycoprotein as a siderophore-capturing component of the human plasma: A molecular modeling study. 33813392_Serum Proteomic Profiling Reveals Differentially Expressed IGHG3 and A1AG1 as Potential Predictors of Chemotherapeutic Response in Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. 34210751_alpha1-Acid Glycoprotein Enhances the Immunosuppressive and Protumor Functions of Tumor-Associated Macrophages. 34265865_The connection of alpha-1 acid glycoprotein inflammatory marker with anthropometric, hormonal, and metabolic characteristic of women with polycystic ovary syndrome. 34654351_Orosomucoid 1 promotes epirubicin resistance in breast cancer by upregulating the expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9. 34758357_The structural basis for high affinity binding of alpha1-acid glycoprotein to the potent antitumor compound UCN-01. 34963738_Orosomucoid in liver diseases. 35188865_Characterization of alpha-1-acid glycoprotein as a potential biomarker for breast cancer. 35272364_Integrated GWAS and Gene Expression Suggest ORM1 as a Potential Regulator of Plasma Levels of Cell-Free DNA and Thrombosis Risk. 35765957_ORM 1 as a biomarker of increased vascular invasion and decreased sorafenib sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000061540+ENSMUSG00000028359+ENSMUSG00000039196 | Orm2+Orm3+Orm1 | 30.359015 | 0.475039324 | -1.073881 | 0.41102863 | 6.727964 | 0.0094912891029206129800410707275659660808742046356201171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0474799951055077107398005864524748176336288452148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 19.5384735 | 7.4246150 | 41.4489860 | 15.2633879 |
| ENSG00000229953 | lncRNA | 29.862799 | 2.584025473 | 1.369620 | 0.30860980 | 19.990863 | 0.0000077813085133757186223927779233910939638008130714297294616699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001063977942180836246902769781641495683288667351007461547851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 43.9907223 | 6.9497304 | 17.0898095 | 3.1287401 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000230107 | lncRNA | 70.156065 | 3.326059712 | 1.733814 | 0.58467040 | 7.917052 | 0.0048971003985435806668546909747874451568350195884704589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0281582309846791778440433517971541732549667358398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 97.4873190 | 57.2956261 | 32.0936671 | 18.9010561 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000230724 | LINC01001 | lncRNA | 12.092952 | 0.056622323 | -4.142485 | 0.96149367 | 16.989667 | 0.0000375838095043162971425031171346375913344672881066799163818359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0004319821917390109246824569932954318574047647416591644287109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 1.4565055 | 0.8933374 | 18.6202682 | 8.8049073 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000231877_ENSG00000234464 | 37.165894 | 2.489836390 | 1.316051 | 0.32155302 | 16.755492 | 0.0000425190065672448598934653196668165264782146550714969635009765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0004796418256956621771133764120520481810672208666801452636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 54.1754445 | 5.9838782 | 21.8170236 | 2.9973386 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000232648 | ING2-DT | lncRNA | 11.741473 | 3.063707497 | 1.615279 | 0.58371711 | 7.128868 | 0.0075852602545365020378365095155004382831975817680358886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0400387246945119179564187561481958255171775817871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 15.8088504 | 5.8500285 | 5.0213766 | 1.9421019 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000233024 | 100288332 | NPIPA9 | protein_coding | A0A0B4J1W7 | Reference proteome | Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] | 212.850660 | 0.372320558 | -1.425383 | 0.33987426 | 16.937610 | 0.0000386286078493938014682095027918506957576028071343898773193359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0004410914013039350786357650768820803932612761855125427246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 94.9210017 | 28.7593996 | 255.8700927 | 77.2179286 | ||||||
| ENSG00000233143 | DIRC3-AS1 | lncRNA | 34.430724 | 0.321716395 | -1.636139 | 0.49180586 | 10.455525 | 0.0012228312736099720969829007799489772878587245941162109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0089695667830394804759253091219761699903756380081176757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 14.3513153 | 6.2734417 | 46.1134634 | 19.8608757 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000233429 | 100506311 | HOTAIRM1 | lncRNA | This non-coding locus is located in the HOX gene cluster. Transcription of this locus is induced by retinoic acid, and transcripts likely function in regulation of myelopoiesis through transcriptional activation of several genes in the HOXA cluster, in addition to several beta-2 integrins. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]. | 19144990_HOTAIRM1 plays a role in the myelopoiesis through modulation of gene expression in the HOXA cluster. 24824789_These results indicate that HOTAIRM1 provides a regulatory link in myeloid maturation by modulating integrin-controlled cell cycle progression at the gene expression level. 26436590_The lincRNA HOTAIRM1, located in the HOXA genomic region, is expressed in acute myeloid leukemia, impacts prognosis in patients in the intermediate-risk cytogenetic category, and is associated with a distinctive microRNA signature. 27146823_PU.1 directly activates the expression of HOTAIRM1 through binding to the regulatory region of HOTAIRM1 during granulocytic differentiation. 27307307_Down-regulation of HOTAIRM1 can serve as a biomarker for colorectal cancer. 27740626_Up-regulated expression of HOTAIRM1 could enhance ATRA-induced PML-RARA degradation by affecting autophagic flux and could control myeloid cell differentiation in APL cells. 28180285_HOTAIRM1 contributes to three-dimensional chromatin organization changes required for the temporal collinear activation of HOXA genes. Distinct HOTAIRM1 variants preferentially associate with either UTX/MLL or PRC2 complexes to modulate the levels of activating and silencing marks at the bivalent domain. 29662483_this study illustrates that HOTAIRM1/HOXA1 downregulates the immunosuppressive function of myeloid-derived suppressor celsl and may be a potential therapeutic target in lung cancer. 30070317_HOTAIRM1 is down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue, which promotes the apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by suppressing the Wnt pathway. 30302796_LncRNA HORAIRM1 suppressed the PI3K/AKT pathway in gastric cancer (GC) and inhibited the progression of GC by serving as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-17-5p, mediating the expression of PTEN. 30376874_Results showed that HOTAIRM1 was up-regulated in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) with grade malignancy correlation. Further data revealed that HOTAIRM1 was an oncogenic factor that regulated HOXA1 gene expression, promoting tumorigenesis by serving as a scaffold to sequester the chromosome modification enzyme G9a, EZH2 and DNA methyltransferases away from the promoter of HOXA1 gene. 30551410_HOTAIRM1-1 is downregulated in OA cartilages. 30613920_High HOTAIRM1 expression is associated with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. 31261026_HOTAIRM1 might act as a tumor-suppressor in 5-fluorouracil resistant colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo through downregulating miR-17-5p/BTG3 pathway and inhibiting multi-drug resistance. 31468286_These results show that the lncRNAs PCA3 and HAM-1 are upregulated during thyroid tumor development and progression and may function as oncogenes during tumor progression 31477638_Long non-coding RNA, HOTAIRM1, promotes glioma malignancy by forming a ceRNA network. 31512358_LncRNA HOTAIRM1 promotes osteogenesis by controlling JNK/AP-1 signalling-mediated RUNX2 expression. 31691127_Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIRM1 Maintains Tumorigenicity of Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells Through Regulation of HOX Gene Expression. 31862408_HOTAIRM1 lncRNA is downregulated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and inhibits the hypoxia pathway. 31876683_Over-expression of long noncoding RNA HOTAIRM1 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in human glioblastoma by up-regulating SP1 via sponging miR-137. 31904363_HOTAIRM1 knockdown suppressed the glucose consumption and lactate production, as well as the expression of PFKP in acute myeloid leukemia cells. 31935390_study showed that HOTAIRM1 suppressed ovarian cancer progression through derepression of ARHGAP24 by sponging miR-106a-5p 32147422_Genome-wide screening of functional long noncoding RNAs in the epicardial adipose tissues of atrial fibrillation. 32180085_HOTAIRM1, an enhancer lncRNA, promotes glioma proliferation by regulating long-range chromatin interactions within HOXA cluster genes. 32324272_lncRNA HOTAIRM1 promotes osteogenesis of hDFSCs by epigenetically regulating HOXA2 via DNMT1 in vitro. 32661334_HOTAIRM1 regulates neuronal differentiation by modulating NEUROGENIN 2 and the downstream neurogenic cascade. 32951513_Genomic amplification of long noncoding RNA HOTAIRM1 drives anaplastic thyroid cancer progression via repressing miR-144 biogenesis. 32964965_Inactivation of lncRNA HOTAIRM1 caused by histone methyltransferase RIZ1 accelerated the proliferation and invasion of liver cancer. 33048872_Long noncoding RNA HOTAIRM1 promotes myeloid-derived suppressor cell expansion and suppressive functions through up-regulating HOXA1 expression during latent HIV infection. 33323548_Upregulation of HOTAIRM1 increases migration and invasion by glioblastoma cells. 33328510_LncRNA HOTAIRM1 promotes MDSC expansion and suppressive functions through the HOXA1-miR124 axis during HCV infection. 33368390_The function of long noncoding RNA HOTAIRM1 in the progression of prostate cancer cells. 33404645_HOTAIRM1 promotes osteogenic differentiation and alleviates osteoclast differentiation by inactivating the NF-kappaB pathway. 33537917_LncRNA HOTAIRM1 knockdown inhibits cell glycolysis metabolism and tumor progression by miR-498/ABCE1 axis in non-small cell lung cancer. 33650656_lncRNA HOTAIRM1 regulates cell proliferation and the metastasis of thyroid cancer by targeting Wnt10b. 33939846_Investigating function of long noncoding RNA of HOTAIRM1 in progression of SKOV3 ovarian cancer cells. 34262023_The long noncoding RNA HOTAIRM1 controlled by AML1 enhances glucocorticoid resistance by activating RHOA/ROCK1 pathway through suppressing ARHGAP18. 34298885_Developmental Inhibition of Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNA, HOTAIRM1, Impairs Dopamine Neuron Differentiation and Maturation. 34584066_The long non-coding RNA HOTAIRM1 promotes tumor aggressiveness and radiotherapy resistance in glioblastoma. 34615546_Mutant NPM1-regulated lncRNA HOTAIRM1 promotes leukemia cell autophagy and proliferation by targeting EGR1 and ULK3. 34929342_IRF4 transcriptionally activate HOTAIRM1, which in turn regulates IRF4 expression, thereby affecting Th9 cell differentiation and involved in allergic rhinitis. 35185915_Inhibiting KDM6A Demethylase Represses Long Non-Coding RNA Hotairm1 Transcription in MDSC During Sepsis. | 35.470634 | 5.191433080 | 2.376133 | 0.77184497 | 8.476358 | 0.0035979162579769267613083449930400092853233218193054199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0219292603993818113750080556201282888650894165039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 54.4660632 | 32.0762937 | 10.4844814 | 6.1641928 | ||||||||
| ENSG00000233695 | GAS6-AS1 | lncRNA | 66.915531 | 0.475425910 | -1.072708 | 0.28057691 | 14.434833 | 0.0001450936150985317077497654958406769765133503824472427368164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0014272640562575679683970930611280891753267496824264526367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 38.7867360 | 5.8647496 | 81.9580048 | 11.7943818 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000234409 | 388849 | CCDC188 | protein_coding | H7C350 | Coiled coil;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | membrane [GO:0016020] | ENSMUSG00000090777 | Ccdc188 | 10.430640 | 0.367531941 | -1.444058 | 0.46990736 | 9.675015 | 0.0018679074683024946869347449052156662219204008579254150390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0127983258660185842542356127182756608817726373672485351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 5.3421806 | 1.3647252 | 14.4817603 | 3.1140345 | ||||
| ENSG00000234464 | lncRNA | 75.119757 | 6.399678240 | 2.677999 | 0.53555534 | 22.716872 | 0.0000018771242730396498821411220211952119996112742228433489799499511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000296691687359080449729650114099044344584399368613958358764648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 76.3174900 | 40.0329324 | 11.5160270 | 6.1950771 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000235027 | lncRNA | 13.777507 | 0.371332969 | -1.429215 | 0.49178074 | 8.441561 | 0.0036674129749597241673120251448381168302148580551147460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0222945557121845376602475852223506080918014049530029296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 8.2166150 | 2.7221309 | 21.2447229 | 6.1988624 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000235703 | 100272228 | EOLA2-DT | lncRNA | 10.962362 | 0.354639861 | -1.495573 | 0.51512990 | 8.546441 | 0.0034619851316858660933428737394024210516363382339477539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0212700892322084215979582921818291652016341686248779296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 4.2198734 | 2.1550667 | 11.8118700 | 5.7030269 | ||||||||||
| ENSG00000237541 | 3117 | HLA-DQA2 | protein_coding | P01906 | FUNCTION: Binds peptides derived from antigens that access the endocytic route of antigen presenting cells (APC) and presents them on the cell surface for recognition by the CD4 T-cells. The peptide binding cleft accommodates peptides of 10-30 residues. The peptides presented by MHC class II molecules are generated mostly by degradation of proteins that access the endocytic route, where they are processed by lysosomal proteases and other hydrolases. Exogenous antigens that have been endocytosed by the APC are thus readily available for presentation via MHC II molecules, and for this reason this antigen presentation pathway is usually referred to as exogenous. As membrane proteins on their way to degradation in lysosomes as part of their normal turn-over are also contained in the endosomal/lysosomal compartments, exogenous antigens must compete with those derived from endogenous components. Autophagy is also a source of endogenous peptides, autophagosomes constitutively fuse with MHC class II loading compartments. In addition to APCs, other cells of the gastrointestinal tract, such as epithelial cells, express MHC class II molecules and CD74 and act as APCs, which is an unusual trait of the GI tract. To produce a MHC class II molecule that presents an antigen, three MHC class II molecules (heterodimers of an alpha and a beta chain) associate with a CD74 trimer in the ER to form a heterononamer. Soon after the entry of this complex into the endosomal/lysosomal system where antigen processing occurs, CD74 undergoes a sequential degradation by various proteases, including CTSS and CTSL, leaving a small fragment termed CLIP (class-II-associated invariant chain peptide). The removal of CLIP is facilitated by HLA-DM via direct binding to the alpha-beta-CLIP complex so that CLIP is released. HLA-DM stabilizes MHC class II molecules until primary high affinity antigenic peptides are bound. The MHC II molecule bound to a peptide is then transported to the cell membrane surface. In B-cells, the interaction between HLA-DM and MHC class II molecules is regulated by HLA-DO. Primary dendritic cells (DCs) also to express HLA-DO. Lysosomal microenvironment has been implicated in the regulation of antigen loading into MHC II molecules, increased acidification produces increased proteolysis and efficient peptide loading. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22407913}. | Adaptive immunity;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Immunity;Lysosome;Membrane;MHC II;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene belongs to the HLA class II alpha chain family. The encoded protein forms a heterodimer with a class II beta chain. It is located in intracellular vesicles and plays a central role in the peptide loading of MHC class II molecules by helping to release the CLIP molecule from the peptide binding site. Class II molecules are expressed in antigen presenting cells (B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages) and are used to present antigenic peptides on the cell surface to be recognized by CD4 T-cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. | hsa:3118; | clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane [GO:0012507]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; MHC class II protein complex [GO:0042613]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; transport vesicle membrane [GO:0030658]; MHC class II protein complex binding [GO:0023026]; MHC class II receptor activity [GO:0032395]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II [GO:0019886]; immune response [GO:0006955]; peptide antigen assembly with MHC class II protein complex [GO:0002503]; positive regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050870] | 18065200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19116923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20159242_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20159242_a significant single nucleotide polymorphism , rs3998159, between HLA-DQB1 and HLA-DQA2 was identified in patients with asthma 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20711174_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22096524_Parkinson's disease-associated SNP4 is correlated (r2=0.95) with variants that are associated with HLA-DQA2 expression. 22125590_Results indicate that two SNPs rs9468925 in HLA-C/HLA-B and rs2858881 in HLA-DQA2 were repeatedly selected in all models, suggesting that multiple loci outside PSOR1 locus were associated with psoriasis. 22407913_HLA-DQA2 and HLA-DQB2 genes are expressed in human Langerhans cells and encode a new HLA class II molecule. 23257407_HLA-DQB1/HLA-DQA2 rs9275328 may play a part in influencing the systemic lupus erythematosis susceptibility in Malays and Chinese in Malaysia. 31605414_Association of GWAS-supported noncoding area loci rs404860, rs3117098, and rs7775228 with asthma in Chinese Zhuang population. | 176.597075 | 0.411127302 | -1.282343 | 0.13949187 | 85.150863 | 0.0000000000000000000276447019510848164440733759539152144272043786608402803506995271121127188962418586015701293945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000019629141669633218168887083823828234779771615774429226880526400123017083387821912765502929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 99.6121804 | 47.0554681 | 243.4235437 | 114.5321200 | |||
| ENSG00000237973 | 107075141 | MTCO1P12 | unprocessed_pseudogene | 8.077534 | 0.271908708 | -1.878806 | 0.59815200 | 10.664905 | 0.0010918746493642594690143265978576891939155757427215576171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0081584631042511089604740703862262307666242122650146484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 3.7093248 | 1.4202933 | 13.4018379 | 3.9170561 | ||||||||||
| ENSG00000238035 | lncRNA | 26.830084 | 0.327254413 | -1.611515 | 0.38344107 | 17.881754 | 0.0000235064041389916319817979944994945640246442053467035293579101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0002869176100316011657036241455642766595701687037944793701171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 16.8255738 | 10.0432241 | 51.2070225 | 29.4963862 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000238045 | MVP-DT | lncRNA | 27.953951 | 0.393085326 | -1.347086 | 0.50668077 | 6.765107 | 0.0092957362351704653224970797964488156139850616455078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0466889617441883161830240567269356688484549522399902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 13.9279966 | 4.6300191 | 34.9445231 | 11.1785924 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000239440 | 105377180 | LINC02008 | lncRNA | 53.668633 | 6.483206130 | 2.696707 | 0.51547076 | 24.527326 | 0.0000007326341473774946042705103095571406157660021563060581684112548828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000124219229739592680220950163261228738065256038680672645568847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 70.9058998 | 35.6831707 | 10.5235388 | 5.2699358 | ||||||||||
| ENSG00000239445 | ST3GAL6-AS1 | lncRNA | 24.389604 | 0.444710751 | -1.169061 | 0.36202398 | 10.384942 | 0.0012704718968834173738191584135392986354418098926544189453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0092669431132150550944892586358037078753113746643066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 16.5245819 | 4.3867892 | 37.2079253 | 9.4022971 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000240053 | 58496 | LY6G5B | protein_coding | Q8NDX9 | Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | LY6G5B belongs to a cluster of leukocyte antigen-6 (LY6) genes located in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class III region on chromosome 6. Members of the LY6 superfamily typically contain 70 to 80 amino acids, including 8 to 10 cysteines. Most LY6 proteins are attached to the cell surface by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor that is directly involved in signal transduction (Mallya et al., 2002 [PubMed 12079290]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:58496; | external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802] | 17975119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19023099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19143814_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) | ENSMUSG00000043807 | Ly6g5b | 82.254443 | 0.435974457 | -1.197684 | 0.26338362 | 20.413036 | 0.0000062403259353961276100679692047101809748710365965962409973144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000871154482877455429469526482222363483742810785770416259765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 49.6507009 | 8.0589917 | 114.5724325 | 17.5801733 | ||
| ENSG00000240583 | 358 | AQP1 | protein_coding | P29972 | FUNCTION: Forms a water-specific channel that provides the plasma membranes of red cells and kidney proximal tubules with high permeability to water, thereby permitting water to move in the direction of an osmotic gradient. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1373524}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Blood group antigen;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | This gene encodes a small integral membrane protein with six bilayer spanning domains that functions as a water channel protein. This protein permits passive transport of water along an osmotic gradient. This gene is a possible candidate for disorders involving imbalance in ocular fluid movement. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. | hsa:358; | apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; axon [GO:0030424]; basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; brush border [GO:0005903]; brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; ammonium transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008519]; carbon dioxide transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0035379]; ephrin receptor binding [GO:0046875]; glycerol transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015168]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; intracellular cGMP-activated cation channel activity [GO:0005223]; nitric oxide transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0030184]; potassium channel activity [GO:0005267]; potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015079]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; water channel activity [GO:0015250]; water transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005372]; ammonium transmembrane transport [GO:0072488]; camera-type eye morphogenesis [GO:0048593]; carbon dioxide transmembrane transport [GO:0035378]; carbon dioxide transport [GO:0015670]; cell volume homeostasis [GO:0006884]; cellular homeostasis [GO:0019725]; cellular hyperosmotic response [GO:0071474]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; cellular response to copper ion [GO:0071280]; cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus [GO:0071549]; cellular response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0070301]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to inorganic substance [GO:0071241]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular response to mercury ion [GO:0071288]; cellular response to nitric oxide [GO:0071732]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; cellular response to salt stress [GO:0071472]; cellular response to UV [GO:0034644]; cellular water homeostasis [GO:0009992]; cerebrospinal fluid secretion [GO:0033326]; cGMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019934]; corticotropin secretion [GO:0051458]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; establishment or maintenance of actin cytoskeleton polarity [GO:0030950]; fibroblast migration [GO:0010761]; glomerular filtration [GO:0003094]; glycerol transmembrane transport [GO:0015793]; hyperosmotic response [GO:0006972]; lateral ventricle development [GO:0021670]; lipid digestion [GO:0044241]; metanephric descending thin limb development [GO:0072220]; metanephric glomerulus vasculature development [GO:0072239]; metanephric proximal convoluted tubule segment 2 development [GO:0072232]; metanephric proximal straight tubule development [GO:0072230]; multicellular organismal water homeostasis [GO:0050891]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043154]; nitric oxide transport [GO:0030185]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; pancreatic juice secretion [GO:0030157]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of fibroblast migration [GO:0010763]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of saliva secretion [GO:0046878]; potassium ion transport [GO:0006813]; renal water absorption [GO:0070295]; renal water homeostasis [GO:0003091]; renal water transport [GO:0003097]; secretory granule organization [GO:0033363]; sensory perception of pain [GO:0019233]; transepithelial water transport [GO:0035377]; water transport [GO:0006833]; wound healing [GO:0042060] | 11884383_transmembrane biogenesis is cotranslational in intact mammalian cells 11909995_A novel role for aquaporin-1 as a gated ion channel reshapes our current views of this ancient family of transmembrane channel proteins. 11922632_These data suggest that the transcription of the AQP1 by hypertonicity in renal cells is upregulated by the interaction with putative DNA binding proteins to a novel HRE located at -54 to -46 in the AQP1 gene. 12002613_This study showed the distinct localization of AQP1 in the mesangial cells of human glomeruli, suggesting its role in water movement through these cells. 12027013_visualization of the water-selective pathway at 3.7A resolution in a three-dimenional density map (REVIEW) 12237771_In astrocytomas, aquaporin 1 expressed in microvessel endothelia and neoplastic astrocytes. In metastatic carcinomas, aquaporin 1 present in microvessel endothelia and reactive astrocytes. Aquaporin 1 may participate in formation of brain tumour oedema. 12399631_Data suggest that variations found in plasma osmolarity during hemodialysis may induce aquaporin 1 expression on the membrane of intact red blood cells. 12498798_Data present a detailed comparison between the cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography model structures of the human and bovine water channel aquaporin-1 (AQP1). 12781664_Transmembrane helices at the periphery of the hAQP1 tetramer exhibited smaller extraction forces than helices at the interface between hAQP1 monomers. 14514735_substantial and striking upregulation of AQP-1 in the glomeruli of most diseased kidneys. 14592814_presence of AQP-1 in endothelia and water-transporting epithelia and new locations: mammary epithelium, articular chondrocytes, synoviocytes, and synovial microvessels where it may be involved in milk, chondrocyte volume, synovial fluid, and homeostasis. 14701836_lack of significant cyclic guanine nucleotide ion channel activity rules out a secondary role of aquaporin 1 water channels in cellular signal transduction 14753493_Increased expression. Over-expression occurred on astrocytic processes. Induction of AQP1 and AQP4 on reactive astrocytes in subarachnoid hemorrhage. May be involved in brain edema formation or resolution. 14753494_Intense upregulation of AQP1 expression was found in all glioblastomas. Expression of aquaporins in glioblastomas suggests pathologic role. Selective AQP inhibition might be new therapeutic option for tumor-associated cerebral edema. 15024704_AQP1 has a role in the movement of extracellular matrix and metabolic water across the membranes of chondrocytes and synoviocytes 15135660_AQP1 co-localizes with t-tubular and caveolar proteins 15502805_Aquaporin-1 is a reliable marker for clear cell renal cell carcinomas of lower grades but not for higher grades. 15563082_The expression of AQP-1 mRNA was positively correlated with Bcl-2 mRNA expression in nasal polyps. AQP-1 contributes to the survival of eosinophils in nasal polyps. 15667881_AQP-1 may be a possible critical reabsorption factor, acting to reduce abnormal fluid retention in endotubular cells and the extracellular matrix and, to a lesser extent, in Leydig cells. 15783300_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15809704_increased AQP1 expression in some human adenocarcinomas may be a consequence of angiogenesis and important for the formation or clearance of tumor edema 15847654_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16300893_AQP1 expression heavely in cystic hemangioblastomas. 16481371_Aquaporin (AQP) 1 is predominantly situated in the apical plasma membrane domain of the human choroid plexus, although distinct basolateral and endothelial immunoreactivity is also observed. 16515633_high AQP1 expression may play an important role in ovarian carcinogenesis, disease progression, and ascites formation. 16534779_AQPs are differentially expressed in the peripheral versus central nervous system and that channel-mediated water transport mechanisms may be involved in peripheral neuronal activity by regulating water homeostasis in nerve plexuses and bundles. 16574458_Review. In Colton (null) RBC ghosts, lack of AQP1 resulted in about 30% reduction of the alkalinization rates. 16698771_aquaporin-1-mediated CO(2) permeation is to be expected only in membranes with a low intrinsic CO(2) permeability 16814974_These results in human fetal brain lend morphological support to the previous findings that aquaporin-1 and aquaporin-4 play different roles in the regulation of the water homeostasis of the brain. 16871401_Significant increased expression levels of AQP1 and AQP4 were seen in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, but not in advanced Alzheimer's disease and diffuse Lewy body disease. 17012249_AQP1 is responsible for 60% of the high P(CO2) of red cells and that another, so far unidentified, CO2 pathway is present in this membrane that may account for at least 30% of total P(CO2). 17077939_In hemangioblastomas, expression of AQP1 was predominantly localized on membranes of stromal cells. The expression level of AQP1 in cystic group of hemangioblastomas is much higher than that of solid group. 17219999_Inhibiting AQP-1 with acetazolamide may significantly induce apoptosis of Hep-2 cells. 17273788_The deregulation of aquaporin-1 in menorrhagia may be involved in abnormal endometrial vascular growth and permeability. 17408468_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17409744_AQP1 is expressed at the endomysial capillary endothelial cell and further AQP1 may be expressed at the human skeletal myofiber plasma membrane. 17511167_AQP1 mRNA and protein expression level in laryngeal tumor tissues is remarkably stronger than that in normal tissues. 17545093_Data show that AQP-1, 3, 8, 9 mRNA expression was detected in both amnion and chorion and can be associated with intramembranous transport and volume regulation of amniotic fluid. 17549682_Only the presence of AQP1, but not AQP4, enhanced cell growth and migration, typical properties of gliomas, while AQP4 enhanced cell adhesion suggesting differential biological roles for AQP1 and AQP4 in glioma cell biology. 17632520_In AQP1, Asn49 and Lys51 interact with Asp185 at the C terminus of TM5 to form a polar, quaternary structural motif that influences multiple stages of folding. 17854859_AQP-1 is up-regulated in biliary dysplasia...and down-regulation of AQP-1 is associated with mucin production and aggressive progression of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 17890385_These results establish the nature and determinants of AQP1 diffusion in cell plasma membranes and demonstrate long-range nonanomalous diffusion of AQP1. 17894331_a detailed mechanism for ion exclusion in aquaporin-1 (AQP1) at an atomistic level is investigated by calculating the free energy for transport of ions in AQP1 17898873_Increased AQP1 expression may relieve intracellular acidosis and edema in highly glycolytic glioma cells. 18052958_Aquaporin 1 may be involved in the pathophysiology of migraine. 18067501_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18080132_These data illustrate the potential of the peritoneal membrane as an experimental model in the investigation of the role of AQP1--REVIEW 18202181_For small solutes permeating through AQP1, a remarkable anticorrelation between permeability and solute hydrophobicity is observed, rendering AQP1 a selective filter for small polar solutes. 18247144_The aim of this study was to use immunohistochemsitry to investigate the expression of aquaporins 1, 2 and 3 within the human intervertebral disc. 18275976_AQP1 is involved in hypoxia-inducible angiogenesis in retinal vascular endothelial cells through a mechanism that is independent of the VEGF signaling pathway. 18280225_AQP1 is not expressed in human airway epithelial cells from the A549 adeoncarcinoma cell line. 18282122_The genomic, structural and functional aspects of AQP1 are briefly described. Its role in human tumors and, in particular, those of the kidney is discussed. Review. 18313673_AQP1 may be involved in the tumorigenesis and progression of endometrioid adenocarcinoma by promoting angiogenesis, and AQP1 level may be both a tumor indicator and a new therapeutic target. 18392839_Our study shows that AQP4 downregulation can occur in muscular dystrophies with either normal or disrupted expression of dystrophin-associated proteins, and that this might be associated with upregulation of AQP1. 18509662_These observations suggest the possible association of astrocytic AQP1 with Abeta deposition in Alzheimer disease brains. 18510579_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18538351_Modulation of AQP1 expression by maternal hormones may regulate invasion and fetal-placental-amnion water homeostasis during gestation. 18544259_We show high expression of AQP1 water channels in intractable epilepsy and suggest two mechanisms to explain this finding. Increased AQP1 expression of astrocytes may be a cause or a consequence of IE. 18563339_AQP1 and HIF1 interact each other and regulate the oncogenesis of breast cancer 18575775_The objective of this study was to evaluate the AQP1 expression in endometrial blood vessels during normal cycle and after mifepristone treatment. 18841368_AQP1 expression in invasive breast carcinomas is associated with a basal-like phenotype and poor prognosis. 19080511_The expression level of AQP1 of patients with preeclampsia increases in placenta and peritoneum and decreases in embryolemma. 19253825_Hypoxia regulates the expression of AQP1 in vascular endothelial cells. 19306058_AQP1 expression is a new characteristic feature of a particularly aggressive subgroup of basal-like breast carcinomas. 19424603_AQP1-specific siRNA knockdown impaired water permeability of ARPE-19 cells. 19472194_These results provide evidence that NPA motifs are important for water permeation but not essential for the expression, intracellular processing and the basic structure of human aquaporin 1. 19522191_The expression of AQP1 in tumor cells and micro-angiogenesis of primary laryngeal carcinoma are higher than normal. 19545896_Alteration of aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 3 expression in fetal membranes and placenta may be important in the pathophysiology of isolated oligohydramnios. 19619954_AQP-1 was overexpressed in hepatitis B virus associated cirrhotic liver tissues. AQP-1, similar to CK19, might be a more specific and more sensitive marker than CK7 for the identification of HPCs. 19670620_The expression of AQP1 and VEGF in laryngeal carcinoma was significantly higher than that in vocal cord polyps and normal controls. 19726340_The expression of AQP1 mRNA was significantly lower in oligohydramnios placenta than in normal pregnancy placenta at term. 19772916_TXA(2) receptor mediates water influx through aquaporins in astrocytoma cells via TXA(2) receptor-mediated activation of G alpha(12/13), Rho A, Rho kinase and Na(+)/H(+)-exchanger. 19787701_AQP1 activity of cell membrane affects HT20 colon cancer cell migration. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20063900_An increase in the level of water transport in response to changing osmotic conditions in the cellular environment may be due to a protein kinase C-dependent increase in AQP1 membrane localization. 20101282_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20101282_There was no association between common sequence variants in the AQP1 or SLC4A10 genes and primary open-angle glaucoma in the Caucasian population. 20137115_Inhibiting AQP1 expression with siRNA can inhibit the proliferation and induce apoptosis of K562 cells. 20149606_Potential role for synovial AQP1 and other aquaporins in joint swelling and vasogenic edema. 20360993_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20409716_Aquaporin 1 is localized in the dura mater following chronic subdural hematoma; the outer membrane might be the source of increased fluid accumulation responsible for chronic hematoma enlargement. 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20431033_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20461409_Expression of AQP1, AQP4, or AQP6 mRNA did not differ in vestibular endorgans from patients with Meniere's disease. 20578142_AQP-1 enhances osmotic water permeability and FGF-induced dynamic membrane blebbing in liver endothelial cell and thereby drives invasion and pathological angiogenesis during cirrhosis. 20628061_Data identify miR-320a as a potential modulator of aquaporin 1 and 4 and explore the possibility of using miR-320a to alter the expression of aquaporin 1 and 4 in normal and ischemic conditions. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20739606_Compared with human AQP1, zebrafish Aqp1a has about twice the selectivity for CO(2) over NH(3). 20795314_The physiology and molecular basis of the Colton blood group antigen AQP1 is discussed. Review. 20806077_The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of down-regulation of Aquaporin 1 (AQP1) and Aquaporin 5 (AQP5) on cell proliferation and migration in human corneal endothelial (HCEC) and human corneal epithelial (CEPI17) cell lines, respectively. 20828513_The expression level of aquaporin-1 in nasopharyngeal cancer tissue could be involved in tumour migration. 20965731_Expression of AQP1 in pediatric brain tumors. Increased in ependymomas in posterior fossa and in pilocytic astrocytomas. Not expressed in medulloblastoma, primitive neuroectodermal tumor, germinoma. 20969805_This review outlines newly emerging evidence indicating that AQP-1 plays an important role in pain signal transduction and migraine. 21063116_After sequencing analysis of the coding regions and exon-intron boundaries one single variation, no significant mutation in AQP 1 was found. 21063116_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21107133_No difference is found between aquaporin 1 expression in Alzheimer's disease brain and its expression in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. 21237499_Expression patterns of aquaporin 1, 3, and 5 in lung cancer cells are mostly associated with cellular differentiation. 21244858_AQP1 and AQP5 might play an important role in the development of lung edema and lung injury 21252246_The late rise of AQP1 suggests a role in corpus luteum formation. 21271497_The researchers found an association between carriers of the AQP1 single nucleotide polymorphism and greater fluid loss in long-distance running. 21360438_An important role of AQP1 in tumor angiogenesis is sustained by the abundant expression of this protein in the endothelia of tumor capillaries. 21373963_Water flux through human aquaporin 1 was studied under osmotic challenges and the inhibition by intracellular furosemide. 21395179_AQP1 and VEGF had a higher expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissues than in non-tumor tissues. 21538271_AQP-1 expression is increased in colorectal carcinoma while the expression of AQP-3 is not. There is no correlation between the expression of AQP-1 and AQP-3 in CRC. 21551254_AQP1 is a promising oncogene candidate for ACC and is transcriptionally regulated by promoter hypomethylation. 21612401_hypoxia-induced expression of AQP1 requires transcriptional activation, and the HIF-1 binding site of the 5'-promoter is necessary for transcriptional activation 21760919_Negative stain transmission electron microscopy and single particle analysis of KCC4 and the aquaporin-1 AQP1 water channel, revealed the expected quaternary structures within homogeneous preparations, and thus correct protein folding and assembly. 21784068_REVIEW: summarizes literature data concerning the involvement of AQP-1 and -4 in human brain tumor growth and edema formation 21793635_our results suggest, for the first time, that the rs1049305 (C/G, UTR3) AQP1 polymorphism could be involved in the genetic susceptibility to develop water retention in patients with liver cirrhosis. 21839760_This study demonistrated that AQP1 in inner ear plays an important role in the development of motion sickmness, and might be a potential target for the prevention or management of motion sickness. 21896312_The mean concentration of AQP1 in CSF was significantly elevated in patients with BM (BM: 3.8+/-3.4ng/ml, controls 22006723_Phosphorylation of tyrosine Tyr253 in the carboxyl terminal domain, acts as a master switch regulating responsiveness of AQP1 ion channels to cGMP, and the tetrameric central pore is the ion permeation pathway. 22093331_Aberrant expressions of AQP1 in periportal sinusoidal regions in human cirrhotic liver indicate the proliferation of arterial capillaries directly connected to the sinusoids, contributing to microvascular resistance in cirrhosis. 22269467_AQP1 is normally expressed in the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disc with a role in the maintenance of TMJ homeostasis 22310126_regulates microvessel permeability and barrier function and contributes to blood vessel formation 22334691_novel pathway in mammalian cells whereby a hypotonic stimulus directly induces intracellular calcium elevations through transient receptor potential channels, which trigger AQP1 translocation 22348807_A new AQP1 null allele identified in a Gypsy woman who developed an anti-CO3 during her first pregnancy. 22372348_We found AQP1 and AQP4 in lung cancer cell extravasation and spread, which may provide a functional explanation for the expression of AQP1 and AQP4 in lung cancer tissues and lung cancer cell lines. 22472942_expression of aquaporin 1 and 5 was higher in uterine leiomyomata than in unaffected uteri 22901156_AQP1 expression significantly increased in advanced stage of cervical cancer, deeper infiltration, metastatic lymph nodes and larger tumor volume. 22901921_Exosomal AQP1 is downregulated after the release of ureteropelvic junction obstruction. This may be due to locally increased TGF-beta-1 in the postobstructed kidney. 22964306_Data indicate reconstitution of AQP-1 into cholesterol-containing vesicles leads to drastic increases in P(CO2). 23029502_Selective expression of AQP1 in the trigeminal neurons innervating the oral mucosa indicates an involvement of AQP1 in oral sensory transduction. 23219802_Stomatin interacts with GLUT1/SLC2A1, band 3/SLC4A1, and aquaporin-1 in human erythrocyte membrane domains 23220481_This study demonstrated that laminar shear stress stimulates the endothelial expression of AQP1 that plays a role in wound healing. 23268390_K562 cells show a significant increase of AQP1 expression after retinoic acid-induced erythroid differentiation. 23276695_AQP1(+) cells immediately beneath the epithelial basement membrane may be stromal niche-like cells that directly interact with N-cad(+) limbal basal epithelial progenitor cells. 23313295_High AQP1 expression is associated with malignant pleural mesothelioma. 23317544_These findings suggest that NKCC1 and AQP1 participate in meningioma biology and invasion 23332061_hAQP1 is a constitutively open channel that closes mediated by membrane-tension increments. 23361277_AQP1-immunoexpression had a good correlation with high-grade tumors. 23393355_AQP1 expression correlates with the grade of malignancy in astrocytoma and is associated with angiogenesis, as well as with invasion of grade IV tumour in areas of tumour infiltration 23450058_Estrogen induces AQP1 expression by activating ERE in the promoter of the Aqp1 gene, resulting in tubulogenesis of vascular endothelial cells. 23549977_AQP-1 appears to be involved in the arterial capillary proliferation in the cirrhotic liver. [Review] 23928039_AQP1 and 4 gene expression levels did not differ between mesial temporal sclerosis patients and control groups 23949237_Aquaporin-1 is associated with arterial capillary proliferation and hepatic sinusoidal transformation contributing to portal hypertension in primary biliary cirrhosis. 23974882_The data suggest that the increased expression of AQP1 and AQP3 in pterygial tissues may be involved in the pathogenesis of pterygia 24014128_Cox-regression analyses revealed the AQP1 -783G/C genotype status as an independent prognostic-factor when jointly considering other predictors of survivalin glioblastoma multiforme. 24028651_Aquaporin-1 is induced in leukocytes of patients with sepsis and exhibits higher expression in septic shock. 24086369_Anti-AQP1 autoantibodies are present in a subgroup of patients with chronic demyelination in the central nervous sytem and similarities with anti-AQP4-seronegative neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. 24169407_Over expression of aquaporin 1 causes increased intracranial pressure, and downregulation reduces pressure and alleviates the symptomatology and complications of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. 24252214_Report is the first to establish astrocytic water channel loss in a subset of human central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) cases and suggests AQP1 and AQP4 may be involved in the pathogenesis of CPM 24333057_the prevalence of this AQP1 c.601delG allele in the ethnic minority of Romani 24493792_AQP1 promoter hypomethylation is common in ACC, and AQP1 tends to be overexpressed in these tumors. Increased AQP1 methylation is associated with improved prognosis. 24688444_the expression of AQP1, at both the mRNA and protein levels, in membranes from PVR and ERM. 24777974_Results show that in AQP1, helix 3 inverts its orientation in the membrane after the initial insertion, whereas this does not occur in the homologous AQP4. 24803718_Freshly obtained urine samples from renal cell carcinoma patients are positive for AQP1 whereas archived samples and fresh healthy control samples are negative. 24918928_Aquaporin 1 and 3 were upregulated in cervical cancer compared to mild cervicitis and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2-3 (P | ENSMUSG00000004655 | Aqp1 | 26.278531 | 0.482685053 | -1.050846 | 0.34868238 | 9.030369 | 0.0026553092385488918057701024366679121158085763454437255859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0170848507952262654296937682829593541100621223449707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 16.5095730 | 12.6620734 | 34.3649900 | 26.1763155 | |
| ENSG00000240990 | 221883 | HOXA11-AS | lncRNA | This gene produces a long non-coding RNA in antisense to transcription of the homeobox A11 gene. This transcript may associate with chromatin factors such as Polycomb repressive complex and act as a sponge for microRNAs, thereby participating in the regulation of expression of target genes. High levels of this transcript may be associated with tumor progression. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2017]. | 26430965_These findings demonstrate for the first time a role for HOXA11-AS in epithelial ovarian cancer with effects that could be modified by germline variants 27651312_a model in which the EZH2/HOXA11-AS/LSD1 complex and HOXA11-AS/miR-1297/EZH2 cross-talk serve as critical effectors in gastric cancer tumorigenesis. 27737536_These findings highlight the clinical significance of HOXA11as to predicting the prognosis of SOC patients and suggest its potential in promoting tumor aggressiveness via regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), MMP-9, and EMT-related mechanisms. 27792998_HOXA11-AS overexpression correlated with poor survival in patients with cervical cancer. 28441948_Findings show that HOXA11-AS not only could promote gastric cancer (GC) cells migration and invasion in vitro, but also promotes GC cells metastasis in vivo, at least in part, by regulating beta-catenin and KLF2. 28717185_HOXA11-AS plays a significant role in non-small cell lung cancer proliferation, invasion, migration, apoptosis and cell cycle. 28791375_our data suggested that the transcript level of HOXA11AS was highly upregulated in breast cancer both in vivo and in vitro. Knockdown of HOXA11AS in MDAMB231 and MDAMB436 cells inhibited colony formation and cell proliferative rate, and caused cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase. 28942241_increased expression of HOXA11-AS is a risk factor for poor clinical outcomes in numerous tumors 28946213_HOXA11-AS acted as an oncogenic long non-coding RNA that promoted cell growth and metastasis of glioma through regulating miR-214-3p/EZH2 axis. 29017417_study findings suggest that homeobox (HOX)A11-AS1 (HOXA11-AS1) lncRNA may play a role in the development of peritoneal endometriosis, but HOXA11-AS1 may not influence endometrial receptivity in endometriosis-associated infertility. 29164588_HOXA11-AS suppressed cell proliferation and promoted cell apoptosis via targeting mir-124-3p and knockdown inhibited cell apoptosis. 29953617_HOXA11-AS could promote renal cancer cells growth and invasion by modulating miR-146b-5p-MMP16 axis. 30064227_Glioma patients with high LncRNA HOXA11-AS expression had shorter overall survival time than those with low expression. Silencing HOXA11-AS significantly increased miR-124-3p expression. 30099826_lncRNA HOXA11-AS acted as a ceRNA to promote cisplatin resistance of human LUAD cells via the miR-454-3p/Stat3 axis. 30657566_lncRNA HOXA11-AS was overexpressed in glioma and overexpression was correlated with advanced stages of glioma and poor prognosis. Downregulating HOXA11-AS expression significantly suppressed proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma cells and increased their apoptosis. HOXA11-AS exerted its oncogenic effects by binding to miR-130a-5p, thereby neutralizing the suppressive effect of miR-130a-5p on HMGB2. 31013434_Propofol promotes apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells via alleviating the suppression of lncRNA HOXA11-AS on miRNA let-7i. 31099097_HOXA11-AS regulates JAK-STAT pathway by miR-15a-3p/STAT3 axis to promote the growth and metastasis in liver cancer. 31144606_Data found that HOXA11-AS was upregulated in cisplatin resistant lung adenocarcinoma tumors and cell lines. Functional analysis showed that the knockdown of HOXA11-AS expression in A549 cells inhibits cell proliferation, induces G1 phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. 31235999_Up-regulation of HOXA11-AS was found in gastric cancer (GC) tissues, cell lines, and serum samples. Decreased serum HOXA11-AS levels were negatively related with tumor size, TNM stage, and lymph node metastasis and were associated with a better overall survival rate. HOXA11-AS promoted GC cell proliferation and invasion. SRSF1 may be the target regulated by HOXA11-AS in GC cells. 31275988_The findings highlight the importance of HOXA11-AS/miR-214-3p/PIM1 axis in the drug resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 31680444_LncRNA HOXA11-AS regulates calcium oxalate crystal-induced renal inflammation via miR-124-3p/MCP-1. 31731187_LncRNA HOXA11-AS promotes OSCC progression by sponging miR-98-5p to upregulate YBX2 expression. 31878829_Long non-coding RNA HOXA11-AS accelerates the progression of keloid formation via miR-124-3p/TGFbetaR1 axis. 31971633_CTCF was validated to activate HOXA11-AS transcription in PCa cells. 32009419_LncRNA HOXA11-AS promotes migration and invasion through modulating miR-148a/WNT1/beta-catenin pathway in gastric cancer. 32236611_Recent advances in unraveling the molecular mechanisms and functions of HOXA11AS in human cancers and other diseases (Review). 33115978_Long Noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS Modulates the Resistance of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells to Cisplatin via miR-454-3p/c-Met. 33261854_LncRNA HOXA11-AS Aggravates Keloid Progression by the Regulation of HOXA11-AS-miR-205-5p-FOXM1 Pathway. 33514011_Long Noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS and Transcription Factor HOXB13 Modulate the Expression of Bone Metastasis-Related Genes in Prostate Cancer. 33839699_Inhibition of long non-coding RNA HOXA11-AS against neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease model via targeting miR-124-3p mediated FSTL1/NF-kappaB axis. 34050851_Long noncoding HOXA11-AS knockdown suppresses the progression of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating miR-3619-5p/SALL4 axis. 34337714_LncRNA HOXA11-AS promotes cell growth by sponging miR-24-3p to regulate JPT1 in prostate cancer. 34655977_LncRNA HOXA11-AS aggravates the keloid formation by targeting miR-148b-3p/IGFBP5 axis. 34974809_Long non-coding RNA HOXA11 antisense RNA upregulates spermatogenesis-associated serine-rich 2-like to enhance cisplatin resistance in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing microRNA-518a. 35114391_Increased expression of HOXA11-AS attenuates endometrial decidualization in recurrent implantation failure patients. 35320748_Uterine HOXA11 antisense long non-coding RNA prevents decidualization: A new pathway-regulating pregnancy. 35700456_The minor allele of rs17427875 in long non-coding RNA-HOXA11-AS influences the prognosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) via modulating miR-15a and STAT3 expression. 35706412_Long non-coding RNA HOXA11-AS knockout inhibits proliferation and overcomes drug resistance in ovarian cancer. 36142607_An Axis between the Long Non-Coding RNA HOXA11-AS and NQOs Enhances Metastatic Ability in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. | 24.727362 | 3.651269073 | 1.868398 | 0.60334792 | 8.939360 | 0.0027909041679381810241444838993629673495888710021972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0178342473737411050249690447344619315117597579956054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 26.9172772 | 16.4568286 | 7.0131991 | 4.3171233 | ||||||||
| ENSG00000241489 | protein_coding | B3KWA1 | Reference proteome | sulfuric ester hydrolase activity [GO:0008484] | 159.301160 | 0.382481569 | -1.386538 | 0.40325785 | 11.142687 | 0.0008436358613994087481818828777591079415287822484970092773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0065305912724155671875148065907978889299556612968444824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 87.3360292 | 24.9811899 | 233.5485175 | 66.4751559 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000242948 | EPS15P1 | transcribed_processed_pseudogene | 207.896483 | 0.480538472 | -1.057276 | 0.12979813 | 66.560523 | 0.0000000000000003393138054026060006388151544782094476528503984753826205889026823570020496845245361328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000178433139472618520727230758058699731826899324838020532979498966597020626068115234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 140.4768623 | 42.8611827 | 293.7613990 | 89.0168459 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000243302 | processed_pseudogene | 11.769639 | 0.046565687 | -4.424589 | 1.00164194 | 19.361110 | 0.0000108187970963518415230038977048465653751918580383062362670898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001426327368367290683928705341543263784842565655708312988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 0.8414087 | 1.0105181 | 15.7801529 | 16.5790682 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000244242 | 402778 | IFITM10 | protein_coding | A6NMD0 | Cell membrane;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:402778; | plasma membrane [GO:0005886] | ENSMUSG00000045777 | Ifitm10 | 56.974557 | 0.300008837 | -1.736923 | 0.25943811 | 45.067634 | 0.0000000000190345500174062007888990240794493307222023936731147841783240437507629394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000006191983387057627529268955121014711417970488582795951515436172485351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 29.1118856 | 12.9470559 | 96.7601474 | 42.2573689 | |||
| ENSG00000244479 | OR2A1-AS1 | lncRNA | 94.215469 | 9.122244730 | 3.189389 | 0.97166049 | 9.131106 | 0.0025129970669613833737787711442024374264292418956756591796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0163877869336390841192852008134650532156229019165039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 173.1917859 | 130.1768608 | 17.9676314 | 13.5297988 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000244482 | 79168 | LILRA6 | protein_coding | Q6PI73 | FUNCTION: May act as receptor for class I MHC antigens. {ECO:0000250}. | Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA | Predicted to enable inhibitory MHC class I receptor activity. Predicted to be involved in cytokine-mediated signaling pathway. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | Mouse_homologues NA;;mmu:100038909;;NA;;mmu:232801;;mmu:18733; | plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; inhibitory MHC class I receptor activity [GO:0032396]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221] | 19617579_Allogeneic disparities in immunoglobulin-like transcript 5 induce potent antibody responses in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24096970_LILRA6 copy number variation may influence the level of the activating receptor on the cell surface, potentially affecting signaling upon LILRB3/A6 ligation 27333811_LILRA6 copy number variation correlates with susceptibility to atopic dermatitis. 33526815_Characterization of LILRB3 and LILRA6 allelic variants in the Japanese population. | ENSMUSG00000081665+ENSMUSG00000030427+ENSMUSG00000074417+ENSMUSG00000089942+ENSMUSG00000074419+ENSMUSG00000070873+ENSMUSG00000058818 | Pira1+Lilra6+Pira12+Pira2+Pira13+Lilra5+Pirb | 22.820869 | 0.309217168 | -1.693308 | 0.35343117 | 23.695087 | 0.0000011287033810808549837069892501917323102134105283766984939575195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000184012854248939407503585230507781034248182550072669982910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 10.7475512 | 3.2526549 | 34.8718834 | 9.5469159 |
| ENSG00000247095 | 100506211 | MIR210HG | lncRNA | 31399552_The long noncoding RNA MIR210HG promotes tumor metastasis by acting as a ceRNA of miR-1226-3p to regulate mucin-1c expression in invasive breast cancer. 32087604_MIR210HG promotes cell proliferation and invasion by regulating miR-503-5p/TRAF4 axis in cervical cancer. 33516697_Long noncoding RNA expression profiling identifies MIR210HG as a novel molecule in severe preeclampsia. 34110962_MIR210HG regulates glycolysis, cell proliferation, and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells through miR-125b-5p/HK2/PKM2 axis. 34154318_[Expression of lncRNA MIR210HG in preeclampsia placental tissue and its functional analysis]. 34897892_Hypoxia-inducible lncRNA MIR210HG interacting with OCT1 is involved in glioblastoma multiforme malignancy. 34918962_Knockdown of long non-coding MIR210HG inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in hepatoblastoma via the microRNA-608-FOXO6 axis. 35146790_MIR210HG is aberrantly expressed in the seminal plasma of varicocele patients and associated with varicocele-related dyszoospermia. 36197580_ceRNA network of lncRNA MIR210HG/miR-377-3p/LMX1A in malignant proliferation of glioma cells. | 17.703025 | 0.128432142 | -2.960922 | 0.45868392 | 44.740077 | 0.0000000000225004347277568520037527829371181288357905980745954366284422576427459716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000007235312206249721125305218114845060006778965089324628934264183044433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 4.4022240 | 1.7335176 | 33.8218450 | 11.2261176 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000249319 | protein_coding | H7C0S8 | DNA-directed RNA polymerase;Nucleus;Proteomics identification;Reference proteome;Transcription;Urea cycle | PATHWAY: Amino-acid biosynthesis; L-arginine biosynthesis. {ECO:0000256|ARBA:ARBA00004730}.; PATHWAY: Nitrogen metabolism; urea cycle; L-arginine and fumarate from (N(omega)-L-arginino)succinate: step 1/1. {ECO:0000256|ARBA:ARBA00005214}. | cytosol [GO:0005829]; DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex [GO:0000428]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; argininosuccinate lyase activity [GO:0004056]; nucleotide binding [GO:0000166]; arginine biosynthetic process via ornithine [GO:0042450]; DNA-templated transcription initiation [GO:0006352]; urea cycle [GO:0000050] | 88.722619 | 0.002872054 | -8.443701 | 1.83436936 | 6.807284 | 0.0090786742863840849682155464961397228762507438659667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0458787918778687103804614366708847228437662124633789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 3.7523558 | 7.5324836 | 334.0553782 | 606.0530118 | ||||||||
| ENSG00000249395 | 101805492 | CASC9 | lncRNA | 27431358_The results indicated that CASC9 is significantly upregulated in ESCC tissues and may represent a new marker of poor prognosis and a potential therapeutic target for esophageal cancer intervention. 28146436_Data suggest that expression of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)CASC9 correlated with aggressive pathological characteristics of gastric cancer (GC), it may serve as a potential oncogene to regulate proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance of GC cells. 28398871_Oncogenic role of CASC9 in promoting the progression of NPC through regulating HIF1alpha, which imply that modulation of CASC9 expression may be a promising target in cancer therapy. 28854977_lncRNA CASC9 functions as an oncogene by negatively regulating PDCD4 expression through recruiting EZH2 and subsequently altering H3K27me3 level. Our study implicates lncRNA CASC9 as a valuable biomarker for ESCC diagnosis and prognosis. 29311567_high levels of CASC9.5 expression promote the proliferation, metastasis and metabolism of lung adenocarcinoma cells and might serve as a prognostic indicator. 29424900_Inhibition of CASC9 could suppress proliferation, migration, and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma . Aberrant CASC9 expression could modulate the expression levels of markers of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition . 29511340_Both CASC9 and LAMC2 depletion reduced the phosphorylation of FAK, PI3K, and Akt, which are downstream effectors of the integrin pathway. Moreover, the reduction in phosphorylation caused by CASC9 depletion was rescued by LAMC2 overexpression. 29790588_CASC9 is an oncogenic lncRNA. It is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and associated with patient survival. Depletion of CASC9 decreases viability and proliferation. Depletion of CASC9 increases apoptosis of HCC cells. CASC9 interacts with HNRNPL. The CASC9:HNRNPL complex regulates the expression of AKT-signaling associated genes. The DNA damage signaling/response (DDR) is induced upon CASC9 and HNRNPL silencing. 29790588_CASC9:HNRNPL complex Is a clinically relevant viability-associated lncRNA/protein complex which affects AKT signaling and DNA damage sensing in hepatocellular carcinoma. 30106089_The study demonstrated the oncogenic role of CASC9 in drugresistant breast cancer by binding to EZH2 and regulating the MDR1 gene. Modulation of CASC9 expression may be a promising target in the therapy of breast cancer and drugresistant breast cancer. 30270508_our results concluded that CASC9 promotes STAT3 expression via sponging miR-519d, in return, STAT3 activate CASC9 transcription, forming a positive feedback loop of CASC9/miR-519d/STAT3. The novel finding provides a potential therapeutic target for glioma. 30537154_A novel undefined regulatory signaling pathway, namely the CASC9/miR-758-3p/LIN7A axis, involved in ovarian cancer progression. 30543527_Identification of oncogenic long noncoding RNAs CASC9 and LINC00152 in oral carcinoma through genome-wide comprehensive analysis. 30674868_Findings demonstrate that lncRNA CASC9 promotes OSCC progression through enhancing cell proliferation and suppressing autophagy-mediated cell apoptosis via the AKT/mTOR pathway. 30896821_Study revealed the overexpression and clinicopathological significance of CASC9 in lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC). Further data suggest that CASC9 serves as an oncogene in LUSC. 31178137_CASC9 enhances cervical cancer progression by promoting metastasis through the meditation of miR-215/TWIST2 signaling associated with TGF-beta expression 31186036_CASC9 is a promising prognostic predictor for patients with CRC and the CASC9-CPSF3-TGFbeta2 axis is a potential therapeutic target for CRC treatment. 31412811_Cancer susceptibility 9 long noncoding RNA (CASC9) is significantly overexpressed in head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) tumor tissues. Specificity of HNSCC detection by CASC9 is further improved by combination with tumor biomarker HOTAIR. Overexpression of CASC9 is found across other entities including bladder, liver, lung and stomach cancers and especially in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the lung. 31642035_LncRNA CASC9 Suppressed the Apoptosis of Gastric Cancer Cells through Regulating BMI1. 31669650_CASC9 was positively correlated with GLUT-1 expression. 31908394_Control samples showed significantly lower CASC9 expression than hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissue samples; the low CASC9 expression HCC group had a higher survival rate than the high CASC9 expression group, and the HCC group showed significantly increased expression of serum CASC9. CASC9 is expected to be a potential diagnostic and prognostic indicator of HCC. 31943867_Long noncoding RNA CASC9 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of papillary thyroid cancer via sponging miR-488-3p. 32221619_Down-regulation of lncRNA CASC9 aggravates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by regulating miR-195-5p/PDK4 axis. 32570259_CASC9 Facilitates Cell Proliferation in Bladder Cancer by Regulating CBX2 Expression. 32677984_Long non-coding RNA CASC9 promotes tumor growth and metastasis via modulating FZD6/Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in bladder cancer. 32772636_Long non-coding RNA CASC9 promotes the progression of retinoblastoma via interacting with miR-145-5p. 32905814_Long non-coding RNA ESCCAL-1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by down regulating the negative regulator of APOBEC3G. 32940174_Oncogenic LncRNA CASC9 in Cancer Progression. 33056982_Long non-coding RNA CASC9 promotes gefitinib resistance in NSCLC by epigenetic repression of DUSP1. 33200222_lncRNA CASC9 sponges miR7583p to promote proliferation and EMT in bladder cancer by upregulating TGFbeta2. 33345395_CASC9 plays a role in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma in vitro by upregulation of ACLY. 33346094_LncRNA CASC9 promotes proliferation, migration and inhibits apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by down-regulating miR-424-5p. 33478874_Long non-coding RNA CASC9 promotes the progression and development of gastric cancer via regulating miR-370/EGFR axis. 34595994_LncRNACASC9 promotes proliferation, metastasis, and cell cycle inovarian carcinoma cells through cyclinG1/TP53/MMP7 signaling. 34612783_Long non-coding RNA CASC9 promotes tumor progression in oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating microRNA-545-3p/laminin subunit gamma 2. 34619168_FOXO3-induced oncogenic lncRNA CASC9 enhances gefitinib resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer through feedback loop. 34711117_Long non-coding RNA (LncRNA) CASC9/microRNA(miR)-590-3p/sine oculis homeobox 1 (SIX1)/NF-kappaB axis promotes proliferation and migration in breast cancer. 35427373_Silencing LncRNA CASC9 inhibits proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by MiR-542-3p/ILK. 35587261_Abnormal expression of lncRNA CASC9 in pneumonia children with respiratory failure and its feasible value for the clinical diagnosis of patients. 35860965_LncRNA CASC9 activated by STAT3 promotes the invasion of breast cancer and the formation of lymphatic vessels by enhancing H3K27ac-activated SOX4. 36266695_LncRNA CASC9 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in osteosarcoma through targeting miR-874-3p/SOX12 axis. | 37.510244 | 2.135761903 | 1.094751 | 0.29712113 | 13.551569 | 0.0002320972794851129607403283916511327333864755928516387939453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0021514756430999074435228557433674723142758011817932128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 51.5785896 | 8.4366401 | 24.3429662 | 4.3257345 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000250091 | DNAH10OS | lncRNA | 12.053149 | 2.339975343 | 1.226493 | 0.44389646 | 7.789080 | 0.0052562942870580265514179885144585568923503160476684570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0298397096133797348760374745779699878767132759094238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 17.0240352 | 3.4968016 | 7.3092341 | 1.8018252 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000250506 | 1018 | CDK3 | protein_coding | Q00526 | FUNCTION: Serine/threonine-protein kinase that plays a critical role in the control of the eukaryotic cell cycle; involved in G0-G1 and G1-S cell cycle transitions. Interacts with CCNC/cyclin-C during interphase. Phosphorylates histone H1, ATF1, RB1 and CABLES1. ATF1 phosphorylation triggers ATF1 transactivation and transcriptional activities, and promotes cell proliferation and transformation. CDK3/cyclin-C mediated RB1 phosphorylation is required for G0-G1 transition. Promotes G1-S transition probably by contributing to the activation of E2F1, E2F2 and E2F3 in a RB1-independent manner. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15084261, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18794154, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8846921}. | ATP-binding;Cell cycle;Cell division;Kinase;Mitosis;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase | This gene encodes a member of the cyclin-dependent protein kinase family. The protein promotes entry into S phase, in part by activating members of the E2F family of transcription factors. The protein also associates with cyclin C and phosphorylates the retinoblastoma 1 protein to promote exit from G0. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:1018; | cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex [GO:0000307]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004693]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; cell division [GO:0051301]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; G0 to G1 transition [GO:0045023]; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000082]; negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045746]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468] | 15084261_A non-cdk8-associated cellular pool of cyclin C combines with cdk3 to stimulate pRb phosphorylation at S807/811 during the G0/G1 transition, and this phosphorylation is required for cells to exit G0 efficiently. 18794154_Expression level of cdk3 is higher in human cancer cell lines and glioblastoma tissue compared with normal brain tissue. cdk3 phosphorylates activating transcription factor 1 (ATF1)and enhances the transactivation and transcriptional activities of ATF1. 21067790_The Walleye dermal sarcoma virus cyclin functions as a structural ortholog of cyclin C in spite of its limited amino acid sequence identity with C cyclins or with any known cyclins and activates Cdk8 and Cdk3. 24691537_CDK3 is associated with the progression of NPC, and may be a potential biomarker for prediction of the prognosis of patients with NPC. 25531331_Mir-873 inhibits ESR1 activity and cell growth via targeting CDK3. 26498144_Data indicate that microRNA miR-214 has tumor-suppressive activity in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) through inhibition of E2F2 transcription factor (E2F2), cyclin-dependent kinases CDK3 and CDK6. 26755651_High Cdk3-promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activating AP-1 is involved in colorectal cancer metastasis. 27893713_These results provided evidence supporting the oncogenic potential of NFAT3 and suggested that CDK3-mediated phosphorylation of NFAT3 has an important role in skin tumorigenesis. 28108217_The analysis of tumor and matched normal lung tissues indicates that miR-150 downregulation in lung tumors correlates with higher CDK3 levels. In addition, miR-150 transfection experiments with cancer-derived cell lines reveal that miR-150-mediated CDK3 suppression directly induces growth inhibition. 28501005_ectopic expression of HuR promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and survival by directly binding to and stabilizing CDK3 mRNA. 28939591_These results suggest that miR-125a-3p can function as a novel tumor suppressor in ER(+) breast cancer by targeting CDK3, which may be a potential therapeutic approach for TamR breast cancer therapy 29344850_HuR facilitated lung cancer stemness dependent on CDK3 expression. miR-873 or miR-125a-3p level was negatively correlated with HuR and CDK3 expression levels in lung cancer tissues. HuR facilitates lung cancer stemness via regulating miR-873/CDK3 and miR-125a-3p/CDK3 axis. 33504681_circRNA_141539 can serve as an oncogenic factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by sponging miR-4469 and activating CDK3 gene. | ENSMUSG00000092300 | Cdk3 | 39.398687 | 0.478815801 | -1.062457 | 0.39226102 | 7.290353 | 0.0069325846120457520690982811117919482057914137840270996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0371828963011104213221003078615467529743909835815429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 26.1130996 | 6.6052221 | 53.9753870 | 12.9968762 | |
| ENSG00000251301 | LINC02384 | lncRNA | 17.771984 | 0.024764122 | -5.335605 | 1.01415783 | 26.729075 | 0.0000002340727847540162011259539873164747803002683212980628013610839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000043025100041250705217997681029107326367011410184204578399658203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 0.9485016 | 1.3149471 | 39.5676478 | 49.1216168 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000251364 | 100506258 | SYT9-AS1 | lncRNA | 11.265154 | 0.278883147 | -1.842267 | 0.67129944 | 7.116915 | 0.0076359979832379670100506174890142574440687894821166992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0402913390379225494486448155839752871543169021606445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 5.2028371 | 2.2361022 | 18.5145010 | 7.1009982 | ||||||||||
| ENSG00000254102 | 401463 | BHLHE22-AS1 | lncRNA | 20.987421 | 2.528210534 | 1.338117 | 0.38144864 | 12.390206 | 0.0004315916679699329417015107868138557023485191166400909423828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0036924185024852728374822330437154960236512124538421630859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 30.6716265 | 4.5507318 | 12.2819493 | 2.2150181 | ||||||||||
| ENSG00000254870 | 100532737 | ATP6V1G2-DDX39B | protein_coding | F2Z307 | FUNCTION: Subunit of the V1 complex of vacuolar(H+)-ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme composed of a peripheral complex (V1) that hydrolyzes ATP and a membrane integral complex (V0) that translocates protons. V-ATPase is responsible for acidifying and maintaining the pH of intracellular compartments and in some cell types, is targeted to the plasma membrane, where it is responsible for acidifying the extracellular environment. {ECO:0000256|RuleBase:RU364019}. | Hydrogen ion transport;Ion transport;Reference proteome;Transport | This locus represents naturally occurring read-through transcription between the neighboring ATP6V1G2 (ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 13kDa, V1 subunit G2) and DDX39B (DEAD box polypeptide 39B) genes located in the major histocompatibility complex class III region of chromosome 6. The read-through transcript and is a candidate for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD), and is thus unlikely to produce a protein product. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. | vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex [GO:0016471]; proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism [GO:0046961] | 118.766856 | 2.389192118 | 1.256523 | 0.25188649 | 24.471340 | 0.0000007542347262810473209449597595255276871739624766632914543151855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000127572374258999870507260213092770584353274898603558540344238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 166.1456603 | 87.1524827 | 67.4820445 | 35.5585463 | |||||
| ENSG00000255031 | lncRNA | 14.242484 | 0.410258211 | -1.285396 | 0.45073457 | 8.271861 | 0.0040264223431544076542420995679094630759209394454956054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0239768393938032571555130090246166219003498554229736328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 8.6210774 | 2.1449657 | 21.0891476 | 4.2916939 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000257242 | 256021 | LINC01619 | lncRNA | 29334763_study demonstrates that LINC01619 functions as a competing endogenous RNA and regulates miR-27a/FOXO1-mediated ER stress and podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy | 9.820696 | 0.235252005 | -2.087721 | 0.58270975 | 12.874492 | 0.0003330910949473545978709310144694200062076561152935028076171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0029601513571306204905542180938482488272711634635925292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 3.1993125 | 1.3151098 | 13.2887287 | 4.8986319 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000257258 | lncRNA | 64.899449 | 3.594472293 | 1.845780 | 0.26677282 | 46.828847 | 0.0000000000077464725571140667598620791133194672488382348518598519149236381053924560546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000002604751397329604822795621225174677107472298587254044832661747932434082031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 106.1029095 | 12.8551670 | 29.5883876 | 3.9172482 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000258017 | lncRNA | 75.032593 | 23.058537571 | 4.527229 | 0.70072069 | 36.173619 | 0.0000000018049756278566915688361849782746053338922109787745284847915172576904296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000456564178706318270502031975675849562179564600228331983089447021484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 45.0040253 | 20.2047617 | 1.9604538 | 0.9847528 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000258623 | lncRNA | 16.481711 | 0.361736591 | -1.466989 | 0.39203828 | 14.419273 | 0.0001462973514840242982449486364160406992596108466386795043945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0014380937122688206269288668792682983621489256620407104492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 8.8883811 | 2.8322751 | 24.6119337 | 7.0603946 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000259066 | protein_coding | G3V3Q6 | Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000256|ARBA:ARBA00004906}. | membrane [GO:0016020]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270] | 12.884570 | 0.082154186 | -3.605522 | 1.22917733 | 7.356685 | 0.0066813863049076322245256598364449018845334649085998535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0361264907742744334484541468555107712745666503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 1.3658810 | 1.9672003 | 18.3484214 | 24.3356661 | ||||||||
| ENSG00000259081 | lncRNA | 5.959707 | 0.134190191 | -2.897649 | 0.81996061 | 14.923094 | 0.0001119836949233350237254899783856387784908292815089225769042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0011408797702750258628440205299625631596427410840988159179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 1.6272365 | 0.7918964 | 9.5875554 | 3.0519439 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000259878_ENSG00000291297 | 8.658254 | 0.011522387 | -6.439417 | 1.14223999 | 43.769243 | 0.0000000000369465908358523104128139471350654671547020235777836205670610070228576660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000011510220770866417409947374893394896055998088968408410437405109405517578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 0.2032372 | 0.2458724 | 18.0359019 | 14.7822112 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000260428 | 642658 | SCX | protein_coding | Q7RTU7 | FUNCTION: Plays an early essential role in mesoderm formation, as well as a later role in formation of somite-derived chondrogenic lineages. {ECO:0000250}. | Activator;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation | Enables DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and bHLH transcription factor binding activity. Contributes to E-box binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nucleus. Part of transcription regulator complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:642658; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; bHLH transcription factor binding [GO:0043425]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; E-box binding [GO:0070888]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus [GO:0071560]; chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0002062]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; deltoid tuberosity development [GO:0035993]; developmental process [GO:0032502]; DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006351]; embryonic skeletal system development [GO:0048706]; endochondral ossification [GO:0001958]; face morphogenesis [GO:0060325]; heart valve formation [GO:0003188]; heart valve morphogenesis [GO:0003179]; mesoderm formation [GO:0001707]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; positive regulation of cartilage development [GO:0061036]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of gastrulation [GO:2000543]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of cartilage development [GO:0061035]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; sclerotome development [GO:0061056]; Sertoli cell differentiation [GO:0060008]; skeletal muscle cell differentiation [GO:0035914]; tendon cell differentiation [GO:0035990]; tendon development [GO:0035989]; tendon formation [GO:0035992]; tissue homeostasis [GO:0001894] | 17129431_Scleraxis was expressed in periodontal ligament cells, bone marrow cells, and gingival fibroblasts, and may play an important role in differentiation of periodontal ligament cells. 19087640_High glucose inhibited osteogenetic differentiation of periodontal ligament cells and up-regulated Scleraxis expression. 19828133_Scx and E47 might modulate the primary chondrogenesis by associating with the Sox9-related transcriptional complex, and by binding to the conserved E-box on Col2a1 promoter. 21988170_collagen type I and several T/L-related proteoglycans were upregulated in hMSC-Scx cells 22796342_Scleraxis thus appears to play a key role in the transcriptional regulation of type I collagen synthesis. 24157418_These studies identify an important role for Scx in regulating proteoglycans in embryonic and mature valve cells. 26851078_Abnormal upregulation of HIF-2alpha served as a key switch to direct TSPCs differentiation into osteochondral-lineage rather than teno-lineage. Notably, Scleraxis (Scx), an essential tendon specific transcription factor, was suppressed on constitutive activation of HIF-2alpha and mediated the effect of HIF-2alpha on TSPCs fate decision. 29750994_The transcription factor scleraxis is an important inducer of extracellular matrix gene expression in the heart that also control MMP2 expression. The scleraxis can exert control over both extracellular matrix synthesis and breakdown, and thus may contribute to matrix remodeling in wound healing and disease. 29906225_Scleraxis regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition via direct transactivation of the Twist1 and Snai1 genes. 32027517_Scleraxis as a prognostic marker of myocardial fibrosis in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (SPARC) study. 32183051_Tenogenic Contribution to Skeletal Muscle Regeneration: The Secretome of Scleraxis Overexpressing Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhances Myogenic Differentiation In Vitro. 32708589_The Transcription Factor SCX is a Potential Serum Biomarker of Fibrotic Diseases. 32795590_The transcription factor scleraxis differentially regulates gene expression in tenocytes isolated at different developmental stages. 35563778_Regulation of Cardiac Fibroblast GLS1 Expression by Scleraxis. | ENSMUSG00000034161 | Scx | 13.309272 | 0.463944860 | -1.107975 | 0.43131848 | 6.717480 | 0.0095472454824634712944320114047513925470411777496337890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0476782826878611315501999001753574702888727188110351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 8.7291704 | 2.1082007 | 18.5870694 | 3.7365805 | |
| ENSG00000261150 | 83481 | EPPK1 | protein_coding | P58107 | FUNCTION: Cytoskeletal linker protein that connects to intermediate filaments and controls their reorganization in response to stress (PubMed:15671067, PubMed:27206504, PubMed:23398049). In response to mechanical stress like wound healing, is associated with the machinery for cellular motility by slowing down keratinocyte migration and proliferation and accelerating keratin bundling in proliferating keratinocytes thus contributing to tissue architecture (PubMed:27206504, PubMed:23398049). However in wound healing in corneal epithelium also positively regulates cell differentiation and proliferation and negatively regulates migration thereby controlling corneal epithelium morphogenesis and integrity. In response to cellular stress, plays a role in keratin filament reorganization, probably by protecting keratin filaments against disruption. During liver and pancreas injuries, plays a protective role by chaperoning disease-induced intermediate filament reorganization (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8R0W0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15671067, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23398049, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27206504}. | Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Tight junction | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the plakin family of proteins, which play a role in the organization of cytoskeletal architecture. This family member is composed of several highly homologous plakin repeats. It may function to maintain the integrity of keratin intermediate filament networks in epithelial cells. Studies of the orthologous mouse protein suggest that it accelerates keratinocyte migration during wound healing. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2013]. | hsa:83481; | apicolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016327]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; cell periphery [GO:0071944]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; hemidesmosome [GO:0030056]; intermediate filament cytoskeleton [GO:0045111]; keratin filament [GO:0045095]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinucleolar compartment [GO:0097356]; intermediate filament binding [GO:0019215]; keratin filament binding [GO:1990254]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; intermediate filament bundle assembly [GO:0045110]; intermediate filament cytoskeleton organization [GO:0045104]; intermediate filament organization [GO:0045109]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of keratinocyte migration [GO:0051548]; negative regulation of keratinocyte proliferation [GO:0010839]; negative regulation of wound healing [GO:0061045]; regulation of epithelium regeneration [GO:1905041]; wound healing [GO:0042060] | 15671067_Epiplakin may be a cytolinker involved in maintaining the integrity of intermediate filaments networks in simple epithelial cells. 33827480_KLF5-mediated Eppk1 expression promotes cell proliferation in cervical cancer via the p38 signaling pathway. | ENSMUSG00000118671 | Eppk1 | 7.162351 | 0.171601005 | -2.542870 | 0.73906877 | 13.992234 | 0.0001835673111159768253024260342698426029528491199016571044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0017575219355854098789854189632819725375156849622726440429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 2.2712603 | 0.9747850 | 10.9375715 | 3.3435187 | |
| ENSG00000261732 | protein_coding | J3QT63 | Reference proteome | nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; pattern specification process [GO:0007389] | 15.843965 | 0.123764574 | -3.014330 | 0.57545252 | 26.681509 | 0.0000002399063971832618665351870464175210173607410979457199573516845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000043924223609940663044944562931615195111589855514466762542724609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 2.4147091 | 0.8622937 | 19.6292467 | 6.2887453 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000262468 | LINC01569 | lncRNA | 14.823939 | 2.694586174 | 1.430064 | 0.51724517 | 7.456484 | 0.0063208348867344887889174742667819373309612274169921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0346864803435237498141496814696438377723097801208496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 21.6924327 | 5.9297815 | 7.9727190 | 2.3112870 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000267512 | lncRNA | 16.896755 | 0.104226114 | -3.262211 | 0.75737931 | 18.544185 | 0.0000166010903027370820806384033030411728759645484387874603271484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0002084524696182103156629622509043997524713631719350814819335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 3.2966619 | 3.7734400 | 42.2790892 | 42.9060003 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000269378 | ITGB1P1 | processed_pseudogene | 34.853222 | 0.031227584 | -5.001035 | 1.50283491 | 8.371368 | 0.0038117859968996416555886419530452258186414837837219238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0229824407433759404784101576524335541762411594390869140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 0.9998212 | 1.8128435 | 40.5136561 | 68.7496068 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000269720 | 110806280 | CCDC194 | protein_coding | A0A1B0GVG4 | Coiled coil;Reference proteome;Signal | ENSMUSG00000108900 | Ccdc194 | 14.459873 | 0.400224040 | -1.321120 | 0.46746974 | 8.037405 | 0.0045821123021360108187871595930573676014319062232971191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0267172100384654095939218620969768380746245384216308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 11.0810177 | 3.2510445 | 27.7076660 | 7.2311765 | ||||||
| ENSG00000270580 | 105369154 | PKD1P6-NPIPP1 | lncRNA | This locus represents naturally-occurring readthrough transcription between two unprocessed pseudogenes, PKD1P6 (polycystic kidney disease 1 (autosomal dominant) pseudogene 6) and NPIPP1 (nuclear pore complex interacting protein pseudogene 1). The individual pseudogene loci are not curated as transcribed regions. Readthrough transcripts likely do not encode functional proteins. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. | 37.183001 | 0.010590722 | -6.561055 | 1.58805985 | 12.704098 | 0.0003648550354178826862078244275267024931963533163070678710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0032017517160761246874933760864223586395382881164550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 1.0431284 | 1.6259026 | 110.4113204 | 149.1857634 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000271216 | LINC01050 | lncRNA | 190.469867 | 0.358273545 | -1.480867 | 0.19725622 | 55.255945 | 0.0000000000001058137760791902573274845901967310367048757252517177107620227616280317306518554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000043405369495475470053265761954135784064442993290811045881127938628196716308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 99.1655111 | 20.8896935 | 277.7961533 | 57.2797681 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000271270 | 100507032 | TMCC1-DT | lncRNA | 63.925703 | 2.005593389 | 1.004029 | 0.26876156 | 13.723196 | 0.0002118220882656743028239765269660210833535529673099517822265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0019899042113232052672588956454546860186383128166198730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | Yes | 82.7778897 | 13.5092766 | 41.5934471 | 6.6418594 | ||||||||||
| ENSG00000271857 | lncRNA | 9.642445 | 0.247161095 | -2.016476 | 0.58686567 | 12.340541 | 0.0004432266215826002387669080295751200537779368460178375244140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0037803987699374466159574215140537489787675440311431884765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 3.9406364 | 1.2248702 | 15.6739476 | 3.2521282 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000272030_ENSG00000189171 | 7.277624 | 0.098437408 | -3.344650 | 1.21037459 | 7.109241 | 0.0076687574197941959369684283842616423498839139938354492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0404336897052699623111848836742865387350320816040039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 1.1849732 | 1.5410455 | 8.7902301 | 10.5106578 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000272068 | BCAN-AS1 | lncRNA | 25.026947 | 2.526365003 | 1.337063 | 0.32020319 | 17.789259 | 0.0000246772441101035243144097564016448131951619870960712432861328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0002996400092119167629135800812179013519198633730411529541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 36.4783217 | 4.5272218 | 14.5162058 | 2.3047736 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000272405 | lncRNA | 193.971914 | 2.256586893 | 1.174142 | 0.11671760 | 102.458159 | 0.0000000000000000000000044057536500927967659816541034414201622045999815728911732841757437767471472511715546716004610061645507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000000000000000003646608405769115105830565028708150189300780484752895318071902637513392875234785606153309345245361328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 269.9525017 | 14.2537874 | 120.1652438 | 7.4527280 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000274272 | lncRNA | 111.116437 | 0.467243058 | -1.097755 | 0.21051925 | 27.033319 | 0.0000001999785218260279625735310968931424113748107629362493753433227539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000037397052985327260304947768337902047619536460842937231063842773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 73.1441444 | 9.8158823 | 156.1890090 | 19.6713479 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000274386 | 100129924 | TMEM269 | protein_coding | A0A1B0GVZ9 | Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | membrane [GO:0016020] | 13.533715 | 0.324350298 | -1.624375 | 0.56736292 | 8.007561 | 0.0046582436727780123994491212613411335041746497154235839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0270708402554295166075881695633142953738570213317871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 6.8789771 | 2.4052458 | 21.0127456 | 6.7997330 | ||||||
| ENSG00000275131 | PDE4DIPP2 | transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene | 24.455014 | 0.143819726 | -2.797667 | 0.70965734 | 13.749026 | 0.0002089291583102352329193857061184758094896096736192703247070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0019653672269290991918289090989446776802651584148406982421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 5.2590060 | 3.4174051 | 37.6503713 | 23.6643181 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000275888 | lncRNA | 9.523270 | 0.230913195 | -2.114577 | 0.63544419 | 11.698086 | 0.0006256443573256556794220939465844821825157850980758666992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0051118652279621909495510578835819615051150321960449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 3.6956451 | 1.3451673 | 14.7881036 | 4.1142753 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000275993 | 72.029684 | 0.497925666 | -1.005998 | 0.17677854 | 32.981281 | 0.0000000093050463318976075672870075495245190122517442432581447064876556396484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000002147838087303362034489101267328847733040220191469416022300720214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 47.6890690 | 6.5534157 | 95.9864686 | 12.1325320 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000276231 | 146850 | PIK3R6 | protein_coding | Q5UE93 | FUNCTION: Regulatory subunit of the PI3K gamma complex. Acts as an adapter to drive activation of PIK3CG by beta-gamma G protein dimers. The PIK3CG:PIK3R6 heterodimer is much less sensitive to beta-gamma G protein dimers than PIK3CG:PIK3R5 and its membrane recruitment and beta-gamma G protein dimer-dependent activation requires HRAS bound to PIK3CG. Recruits of the PI3K gamma complex to a PDE3B:RAPGEF3 signaling complex involved in angiogenesis; signaling seems to involve RRAS. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21393242}. | Angiogenesis;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Reference proteome | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma is a lipid kinase that produces the lipid second messenger phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. The kinase is composed of a catalytic subunit and one of several regulatory subunits, and is chiefly activated by G protein-coupled receptors. This gene encodes a regulatory subunit, and is distantly related to the phosphoinositide-3-kinase, regulatory subunit 5 gene which is located adjacent to this gene on chromosome 7. The orthologous protein in the mouse binds to both the catalytic subunit and to G(beta/gamma), and mediates activation of the kinase subunit downstream of G protein-coupled receptors. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2014]. | hsa:146850; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex [GO:0005942]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex, class IA [GO:0005943]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex, class IB [GO:0005944]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase regulator activity [GO:0046935]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase activity [GO:0046934]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; immune response [GO:0006955]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of T cell differentiation [GO:0045582]; regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0042269] | 16476736_p87PIKAP is a novel regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma that is highly expressed in heart and interacts with PDE3B [p87PIKAP] 18323525_ablation of PI3Kgamma reduced SDF1alpha-induced integrin activation in human EPCs and in murine Lin(-) BM-derived progenitor cells 18596232_RACK1 regulates directional cell migration by acting on G betagamma at the interface with its effectors PLC beta and PI3K gamma 21996737_knockdown of p84 in MDA-MB-231 cells enhanced Akt phosphorylation and lung colonization 22728827_GPCR activation of Ras and PI3Kc in neutrophils depends on PLCb2/b3 and the RasGEF RasGRP4. 24014027_expression and activities of PI3Kgamma are modified differently by p87 and p101 in vitro and in living cells, arguing for specific regulatory roles of the non-catalytic subunits in the differentiation of PI3Kgamma signaling pathways. 25753393_Our findings suggest that p84 binding to p110gamma may represent a novel negative feedback signal that terminates PI3Kgamma activity. 33155192_RBBP6 aggravates the progression of ovarian cancer by targeting PIK3R6. | ENSMUSG00000046207 | Pik3r6 | 53.091422 | 0.149111702 | -2.745535 | 0.84126540 | 9.067928 | 0.0026013164059769900912644224888481403468176722526550292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0168303486988002487523274908198800403624773025512695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 20.4076164 | 13.6743215 | 137.9577305 | 91.5479395 | |
| ENSG00000278996 | lncRNA | 14.340268 | 0.046144591 | -4.437695 | 0.97925872 | 19.034379 | 0.0000128384402547998213326915784016080124274594709277153015136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001656963017249821104159152040935509830887895077466964721679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 0.8402913 | 1.3159314 | 19.8254592 | 28.2571475 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000280061 | TEC | 12.687700 | 0.465607059 | -1.102815 | 0.43184894 | 6.652995 | 0.0098989281095834737861371976919144799467176198959350585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0491014916300899426082615661925956374034285545349121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 8.2519804 | 1.9080973 | 17.8545478 | 3.3078857 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000280195 | lncRNA | 16.243480 | 0.432927482 | -1.207803 | 0.39385541 | 9.580244 | 0.0019668221376769592576017053886516805505380034446716308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0134269927095291875807081538596321479417383670806884765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 9.8167265 | 2.3151519 | 22.6677024 | 4.5057902 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000283208 | 1203 | protein_coding | A0A1B0GW94 | Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane | lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; hydrolase activity, acting on glycosyl bonds [GO:0016798]; lysosome organization [GO:0007040] | 10.813120 | 0.351561295 | -1.508152 | 0.53937995 | 7.776454 | 0.0052931598183934393600513779176708339946344494819641113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0300124521847131876806091810294674360193312168121337890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 5.3125809 | 2.0680704 | 14.0742503 | 5.0611616 | ||||||||
| ENSG00000283787 | 102724536 | PRR33 | protein_coding | A0A1W2PPC1 | Proteomics identification;Reference proteome | Predicted to act upstream of or within response to wounding. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | ENSMUSG00000043795 | Prr33 | 12.154570 | 0.381894600 | -1.388754 | 0.50674302 | 7.657512 | 0.0056536418072258287637055218510795384645462036132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0316966499396692941159514589344325941056013107299804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 6.5980927 | 2.6789749 | 17.3256874 | 6.4349719 | |||||
| ENSG00000284095 | TEC | 14.166774 | 0.043271451 | -4.530441 | 0.98835847 | 19.329534 | 0.0000109991808276723964429150148802705189154949039220809936523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0001447380446072262199889990608170364794204942882061004638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 1.5792865 | 1.3642499 | 36.0604850 | 24.8239859 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000284690 | 100130520 | CD300H | protein_coding | A0A0K2S4Q6 | FUNCTION: May play an important role in innate immunity by mediating a signal for the production of a neutrophil chemoattractant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26221034}. | Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene belongs to the CD300 gene family, which in turn, belongs to the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. This gene is located within a CD300 cluster on chromosome 17. The encoded protein may be involved in innate immunity as well as autoimmune response. A G>A mutation, represented by the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs905709, at the splice donor site of the 5' terminal exon may be associated with lack of expression of this gene in homozygous (AA) individuals. The human reference assembly (GRCh38.p2) represents the 'A' allele at this SNP. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. | hsa:100130520; | extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593] | 26221034_Results suggest that CD300H may play an important role in innate immunity. | 28.847976 | 0.358260596 | -1.480919 | 0.34812870 | 18.117316 | 0.0000207703929871694272185720514523055157951603177934885025024414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0002562048122614866974000591426374739967286586761474609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 15.4052994 | 12.5322573 | 43.2094158 | 34.8322065 | |||
| ENSG00000287097 | lncRNA | 51.785621 | 0.362048175 | -1.465746 | 0.22001672 | 46.053987 | 0.0000000000115038819399694067166079117644036282699926410089119599433615803718566894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000000003795195768308774499815696619963410751719123936709365807473659515380859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 27.6276730 | 14.9688418 | 76.6507416 | 41.0006724 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000287255 | 101929667 | lncRNA | 53.548146 | 10.188960971 | 3.348935 | 0.62939049 | 24.381732 | 0.0000007901441434106503612001966806166475265627013868652284145355224609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000133002843297571328543557958590248802011046791449189186096191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 69.3785112 | 25.3075211 | 6.7451890 | 2.6054349 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000287562 | lncRNA | 18.239881 | 0.487006101 | -1.037988 | 0.39006177 | 7.156490 | 0.0074693238002266426969755208631340792635455727577209472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0395638591314395257625413648838730296120047569274902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 12.2619596 | 2.8045660 | 25.2729979 | 5.0463062 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000287721 | lncRNA | 13.383889 | 0.361790744 | -1.466773 | 0.50429395 | 8.530932 | 0.0034916078553528856129317681222801184048876166343688964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0213948422683083866457920407810888718813657760620117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 7.4418117 | 2.0324719 | 20.5546215 | 4.5432338 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000287823 | lncRNA | 25.597212 | 0.437024996 | -1.194212 | 0.31155437 | 15.010415 | 0.0001069194487500333323650586470066059519012924283742904663085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0010948676787082476085516402619646214589010924100875854492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 15.7720046 | 4.0490826 | 36.4161926 | 8.5740876 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000288931 | lncRNA | 132.415497 | 2.265874755 | 1.180068 | 0.31284280 | 13.913573 | 0.0001914112694633769056265504282521305867703631520271301269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0018218452883682300074558169100669147155713289976119995117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 184.2039332 | 46.0685393 | 82.1296881 | 20.8082816 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000289444 | lncRNA | 117.991617 | 0.023159934 | -5.432225 | 1.44925909 | 8.774734 | 0.0030543168037498271728813481473707724944688379764556884765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0191329079493294147706894392513277125544846057891845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 5.3998828 | 6.7995057 | 238.8856928 | 301.6980201 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000289623 | 101929614 | lncRNA | 14.650035 | 0.426010414 | -1.231039 | 0.44662008 | 7.644561 | 0.0056943757384159869941453457897750922711566090583801269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0318994504721517163625676971605571452528238296508789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 8.4296140 | 2.9320189 | 19.6712018 | 6.3985277 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000289740 | 109136579 | TALAM1 | lncRNA | 29.280912 | 0.170086253 | -2.555662 | 0.65262014 | 14.885350 | 0.0001142467673171790104244549546308462595334276556968688964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0011605960543693491504591008833813248202204704284667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 5.8684026 | 7.4233100 | 37.8956781 | 46.3793749 | ||||||||||
| ENSG00000289757 | lncRNA | 14.737926 | 0.391468416 | -1.353032 | 0.42430660 | 10.436942 | 0.0012351959218754875353962763284698667121119797229766845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0090460317042902194106801516682025976479053497314453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 8.6037519 | 2.2975093 | 22.2657828 | 4.9654932 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000291006 | 730101 | lncRNA | 28943432_Overexpression of LOC730101 prompted the proliferation of non-small-cell lung cancer both in vitro and in vivo while Silencing observed opposite phenomenon. 29253564_Taken together, our findings enlarged the knowledge about the roles of LOC730101 in osteosarcoma progression. 30024599_LOC730101 was significantly upregulated in human osteosarcoma tissues compared with corresponding adjacent normal tissues; elevated LOC730101 expression was correlated with advanced clinical stage and distant metastasis | 33.962800 | 2.826695492 | 1.499116 | 0.30904898 | 23.838901 | 0.0000010474408367428322539277379607525197968698194017633795738220214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0000172169241179303610740549540514265913770941551774740219116210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 49.4025156 | 6.6297892 | 17.5633213 | 2.8699967 | ||||||||||
| ENSG00000291010 | 100887750 | MRPS31P5 | lncRNA | 32992457_Transcriptome and Gene Fusion Analysis of Synchronous Lesions Reveals lncMRPS31P5 as a Novel Transcript Involved in Colorectal Cancer. | 35.558209 | 0.328837085 | -1.604555 | 0.37958133 | 17.240254 | 0.0000329382765734148545548089226375765292686992324888706207275390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0003862033635447836886836481262719189544441178441047668457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 16.0105979 | 4.4566203 | 49.5485269 | 13.4987997 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000291088 | 440434 | NPEPPSP1 | lncRNA | Predicted to enable metalloaminopeptidase activity; peptide binding activity; and zinc ion binding activity. Predicted to be involved in peptide catabolic process and proteolysis. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | 16.762989 | 0.398508818 | -1.327316 | 0.39747139 | 11.474595 | 0.0007055400903408006471964619699122067686403170228004455566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0056583403166542787371406930674311297480016946792602539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 8.4994646 | 2.2597689 | 22.1120557 | 5.0541729 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000291092 | 5387 | PMS2P3 | lncRNA | Predicted to be involved in mismatch repair. Predicted to be part of mismatch repair complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) | 22.847893 | 0.350773460 | -1.511389 | 0.52230871 | 8.108876 | 0.0044049039611115661449480818134816217934712767601013183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0258455522684683698664276363388125901110470294952392578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 10.5321135 | 3.2447831 | 29.9511665 | 8.4900560 | ||||||||
| ENSG00000291092_ENSG00000272391 | 45.012916 | 3.585512382 | 1.842179 | 0.68844942 | 6.639131 | 0.0099762610550153986432864172684276127256453037261962890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.0494324972148619951051173870837374124675989151000976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | Yes | No | 70.0035139 | 54.2591224 | 20.6515206 | 16.1594491 |
- Note:
- The spreadsheet above contains the genes with significantly changes in expression (P-value < 0.05 and |log2FC| > 1). Please Click HERE to check all mapped genes in a Microsoft .excel file.
- The comparisons made can be identified from the website name. “pgKDN_inf vs pgwt_inf” means that “pgwt_inf” is considered the ground state and “pgKDN_inf” the changed state. This also means that a positive log2FC value indicates that the gene expression is increased in “pgKDN_inf” compared to “pgwt_inf”.
- Click HERE to check all parameters of DESeq2 model for all detected genes of the current samples set in a Microsoft .excel file. For more detials of the DESeq2 model, please Click HERE.
Gene Biotype
| Biotype | Amount of Genes |
|---|---|
| lncRNA | 62 |
| processed_pseudogene | 3 |
| protein_coding | 338 |
| TEC | 2 |
| transcribed_processed_pseudogene | 1 |
| transcribed_unitary_pseudogene | 3 |
| transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene | 2 |
| unprocessed_pseudogene | 3 |
AS in non-DEGs
Spreadsheet
| Ensembl gene ID | Entrez ID | Gene Name | Biotype | UniProtKBID | UniProtFunction | UniProtKeywords | UniProtPathway | RefSeqSummary | KEGG | GO | GeneRif | H.sapiens homolog ID | H.sapiens homolog symbol | baseMean | FoldChange | log2FC | lfcSE | stat | pvalue | padj | Is.Sig. | Has.Sig.AS | Intercept_pgKDN-inf | SE_Intercept_pgKDN-inf | Intercept_pgwt-inf | SE_Intercept_pgwt-inf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSG00000007237 | 8522 | GAS7 | protein_coding | O60861 | FUNCTION: May play a role in promoting maturation and morphological differentiation of cerebellar neurons. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;SH3 domain | Growth arrest-specific 7 is expressed primarily in terminally differentiated brain cells and predominantly in mature cerebellar Purkinje neurons. GAS7 plays a putative role in neuronal development. Several transcript variants encoding proteins which vary in the N-terminus have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:8522; | actin filament [GO:0005884]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; actin filament polymerization [GO:0030041]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812] | 15948147_This work reports the identification of two human Gas7 cDNA: hGas7-a with 2,427 nucleotides, which encodes 330 amino acids, and hGas7-b with 2,610 nucleotides, which encodes 412 amino acids according to predicted open-reading-frames. 19801671_hGas7b has a role in microtubular maintenance and is possibly implicated in Alzheimer disease 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19861958_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20890993_Knockdown of Gas7 by shRNA preferentially suppressed the Gas7b protein isoform in human preneuronal cells and to reduce apoptosis induced either by serum starvation or by the antineoplastic agents in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. 21452305_regulates the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts by enhancing Runx2-dependent gene expression 22496485_The results suggest that regulation to maintain an appropriate concentration of hGas7b is required for healthy neurotransmission. 22570627_Intraocular pressure (IOP)was significantly associated with rs11656696, located in GAS7 at 17p13.1 and with rs7555523, located in TMCO1 at 1q24.1.These data suggest that we have identified two clinically relevant genes involved in IOP regulation. 22662195_These findings indicate that Gas7 is involved in motor neuron function associated with muscle strength maintenance. 24151073_We conclude that lower neuronal Gas7b levels may impact Alzheimer disease progression. 26506240_Low GAS7C increases cancer cell motility by promoting N-WASP/FAK/F-actin cytoskeleton dynamics. It also enhances beta-catenin stability via hnRNP U/beta-TrCP complex formation. 27189492_These results demonstrate GAS7 as a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia. 29022762_Polymorphism rs11656696 is not associated with primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) nor any of its endophenotypic traits such as intraocular pressure and cup/disk ratio and is thus not a risk factor for POAG in this Saudi cohort 29261660_Among 8 SNPs in 3 loci that showed at least nominal association (P | ENSMUSG00000033066 | Gas7 | 743.560125 | 1.1903686 | 0.251408422 | 0.06121659 | 16.85909581714 | 0.0000402599213787015744936068073478452333802124485373497009277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00045673623701968985759760966125497816392453387379646301269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 835.450336 | 38.050146 | 705.156360 | 32.350592 | |
| ENSG00000008294 | 9043 | SPAG9 | protein_coding | O60271 | FUNCTION: The JNK-interacting protein (JIP) group of scaffold proteins selectively mediates JNK signaling by aggregating specific components of the MAPK cascade to form a functional JNK signaling module (PubMed:14743216). Regulates lysosomal positioning by acting as an adapter protein which links PIP4P1-positive lysosomes to the dynein-dynactin complex (PubMed:29146937). Assists PIKFYVE selective functionality in microtubule-based endosome-to-TGN trafficking (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q58A65, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14743216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29146937}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Lysosome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a member of the cancer testis antigen gene family. The encoded protein functions as a scaffold protein that structurally organizes mitogen-activated protein kinases and mediates c-Jun-terminal kinase signaling. This protein also binds to kinesin-1 and may be involved in microtubule-based membrane transport. This protein may play a role in tumor growth and development. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. | hsa:9043; | acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; JUN kinase binding [GO:0008432]; kinesin binding [GO:0019894]; MAP-kinase scaffold activity [GO:0005078]; signaling receptor complex adaptor activity [GO:0030159]; lysosome localization [GO:0032418]; negative regulation of dendrite extension [GO:1903860]; negative regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045665]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045666]; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi [GO:0042147]; striated muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051146]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] | 14662895_Testicular antigen PHET is an auutoantigen recognized by sera from systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients with extensive fibrotic changes; the autoantibody response to PHET is induced by ectopic overexpression of PHET in dermal fibroblasts of SSc patients. 15693750_first report of sperm-associated JNK-binding protein (SPAG9) that may have a role in spermatozoa-egg interaction 16077255_SPAG9 is a new member of c-Jun NH2 -terminal kinase (JNK) interacting protein exclusively expressed in testis 16356479_The present investigation will eventually extend the application of SPAG9 siRNA in in vivo targeting experiments that aim to define the SPAG9 functional genomics in tumor and reproductive biology. 16959808_Recombinant human protein is adsorbed on alum is highly immunogenic in macaca model and therefore represents a suitable sperm-based vaccine immunogen for fertility trials in macaque. 18922895_SPAG9 may have a role in tumor development and metastasis and thus could serve as a novel target for early detection and treatment of renal cell carcinoma. 19056739_Kinesin adapter JLP links PIKfyve to microtubule-based endosome-to-trans-Golgi network traffic of furin. 19644450_structural analysis of ARF6 in a complex with JIP4 19820019_Findings support a potential role for SPAG9 as diagnostic biomarker as well as a possible therapeutic target in thyroid cancer treatment. 19947555_SPAG9 protein is found in the equatorial plate and flagella of human spermatozoa. 20138665_SPAG9 mRNA& protein are expressed in CML patients (88%) and in K562 & KCL-22 cells. 90% CML chronic-phase patients showed humoral response against SPAG9. 21177868_N-cadherin expression had an inhibitory effect on JLP-mediated p38 MAPK signal activation by decreasing the interaction between JLP and p38 MAPK 21356354_These findings collectively suggest that SPAG9 may have a role in tumor development and early spread. 22146769_SPAG9 is positively expressed in endometrial cancer, and with a high humoral immune response in patients. It may serve as a new type of endometrial cancer markers for early detection, diagnosis and treatment. 23696027_SPAG9 serves as an important oncoprotein in human astrocytoma by regulating cell proliferation and invasion. 23711689_SPAG9 depletion could inhibit the activity of p-JNK. 24330581_down regulation of SPAG9 reduces growth and invasive potential of triple-negative breast cancer cells, suggesting that SPAG9 may be a potential target for therapeutic use. 24349057_data in clinical specimens indicated that SPAG9 is potential biomarker and therapeutic target for bladder TCC. 24460345_High SPAG9 expression is associated with endometrial cancer. 24740566_SPAG9 is overexpressed in human prostate cancers and contributes to prostate cancer cell growth, possibly through cyclin protein regulation. 24788963_SPAG9 upregulates PODXL expression in human astrocytoma cells at the PODXL gene promoter/transcriptional level through a JNKdependent mechanism. 24801907_SPAG9 is overexpressed in human HCC and serves as a prognostic marker. SPAG9 contributes to cancer cell growth through regulation of cyclin proteins. 25033008_SPAG9 was upregulated in nonmelanoma skin cancer when compared with normal skin. 25244576_knockdown of Sec8 enhances the binding of JIP4 to MAPK kinase 4, thereby decreasing the phosphorylation of MAPK kinase 4, JNK, and p38. 25310386_SPAG9 expression is significantly increased in prostate cancer and it may be involved in the process of prostate cancer cell motility, migration and angiogenesis. 26291670_PLK1 binding to JIP4 was found in G2 phase and mitosis, and PLK1 binding was self-primed by PLK1 phosphorylation of JIP4. 26293216_SPAG9 overexpression in gastric cancer correlates with poor prognosis and contributes to gastric cancer cell proliferation 26468278_FOXK1 protein levels and activity are regulated by associating with JLP and PLK1 26631164_SPAG9-elevated expression contributes to malignant behavior and poor prognosis of breast cancer and may support a potential indicator in treatment selection. 26790956_Study suggest that suppression of miR-141 may cause an aberrant overexpression of SPAG9 promoting growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 26797273_Based on in vitro assays, we found miR-200a-3p significantly inhibit cancer cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis. 26934841_SPAG9 mRNA and protein overexpression in lung cancer tissue, and the presence of SPAG9 IgG antibody in peripheral blood of lung cancer patients indicates that it has potential as a biomarker for lung cancer diagnosis. 27352556_expression of SPAG9 in ECC cells with TGF-beta1 treatment and spheroids formation was increased 27655714_Aberrant expression of JNK-associated leucine-zipper protein, JLP, promotes accelerated growth of ovarian cancer 29146937_these data suggest that the TFEB/TMEM55B/JIP4 pathway coordinates lysosome movement in response to a variety of stress conditions. 29480665_AKAP4 and SPAG9 genes may find use as diagnostic biomarkers for CRC. 31485599_High SPAG9 expression is associated with drug resistance in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. 31690808_Structural characterization of the RH1-LZI tandem of JIP3/4 highlights RH1 domains as a cytoskeletal motor-binding motif. 32503577_miR-874 inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation by targeting SPAG9. 32776977_Sperm associated antigen 9 promotes oncogenic KSHV-encoded interferon regulatory factor-induced cellular transformation and angiogenesis by activating the JNK/VEGFA pathway. 33788575_Overlapping roles of JIP3 and JIP4 in promoting axonal transport of lysosomes in human iPSC-derived neurons. 34319782_Phosphorylation of JIP4 at S730 Presents Antiviral Properties against Influenza A Virus Infection. 34380828_Significance of cancer testis-associated antigens (SPAG9 and FBXO39) in colon cancer. | ENSMUSG00000020859 | Spag9 | 1341.585561 | 1.0956027 | 0.131724706 | 0.06466162 | 4.14703267849 | 0.0417075518856920290922118965681875124573707580566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.14447876071744925052797725584241561591625213623046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1510.166273 | 62.144231 | 1384.837420 | 57.102765 | |
| ENSG00000008517 | 9235 | IL32 | protein_coding | P24001 | FUNCTION: Cytokine that may play a role in innate and adaptive immune responses. It induces various cytokines such as TNFA/TNF-alpha and IL8. It activates typical cytokine signal pathways of NF-kappa-B and p38 MAPK. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15664165}. | Alternative splicing;Cytokine;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | This gene encodes a member of the cytokine family. The protein contains a tyrosine sulfation site, 3 potential N-myristoylation sites, multiple putative phosphorylation sites, and an RGD cell-attachment sequence. Expression of this protein is increased after the activation of T-cells by mitogens or the activation of NK cells by IL-2. This protein induces the production of TNFalpha from macrophage cells. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:9235; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; defense response [GO:0006952]; immune response [GO:0006955]; negative regulation of viral life cycle [GO:1903901]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:1905636]; positive regulation of type III interferon production [GO:0034346] | 16410314_results strongly indicate that IL-32 is involved in activation-induced cell death in T cells, probably via its intracellular actions 16488976_Proteinase 3 is a specific IL-32alpha binding protein, independent of its enzymatic activity 16492735_IL-32, strongly associated with TNFalpha, IL-1beta, and IL-18, appears to play a role in human rheumatoid arthritis and may be a novel target in autoimmune diseases. 16903774_IL-32 is a cell-associated proinflammatory cytokine, which is specifically stimulated by mycobacteria through a caspase-1- and IL-18-dependent production of interferon gamma. 17619821_review of important role of IL32 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis 18287021_Dysregulation of IL-32 in myelodysplastic syndrome and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia modulates apoptosis and impairs NK function. 18289868_Data suggest that the constitutive expression of IL-32 mRNA as well as the predominant production of a smaller sized IL-32 isoform in Jurkat cells may implicate a role for IL-32 in human T cell leukemia. 18296636_induction of TNF, IL-1beta, and IL-6 by IL-32 is mediated by p38-MAPK; IL-32-induced monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation is mediated through nonapoptotic, caspase-3-dependent mechanisms 18414668_the interleukin-32 pro-inflammatory pathway is activated in response to influenza A virus infectio 18768856_Constitutive expression of IL-32 in an immature monocyte-derived dendritic cell subset may be related to the potency of expressed Venezuelan equine encephalitis (VEE) particle vector system as well as potentially to the pathogenesis of VEE. 19017495_The N-terminal IL-32 isoform gamma separate domain evidenced the highest levels of biological activity among the IL-32 separate domains. 19228941_This study introduces IL-32 as a critical regulator of endothelial function, expanding the properties of this cytokine relevant to coagulation, endothelial inflammation, and atherosclerosis. 19248119_IL-32 may be a newly identified prognostic biomarker in rheumatoid arthritis. Production of IL-32 in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts is regulated by Syk/PKCdelta/JNK-mediated signaling events. 19291698_Influenza A virus infection activates IL-32 and iNOS expression by a heretofore unrecognized complex mechanism, in which the two pro-inflammatory factors regulate each other, involving positive and negative feedback regulatory loops. 19364659_Data show that the IL-32 gene is expressed in human endothelial cells and Akt strongly induces its expression. 19386602_High IL-32 is associated with Pancreatic Cancer. 19628777_IL-32 was differentially expressed by lung cancer histotypes;with strong expression in most adenocarcinomas (AC) and their precursors, as well large-cell carcinomas and small-cell lung cancers; lacking in squamous cell carcinoma 19740314_IL-32beta upregulates the production of an anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10, and then IL-10 suppresses proinflammatory cytokines. 19880327_These data suggest that IL-32, which induces IL-1beta, IL-6, and chemokines, is not only involved in host defense against pathogens, but also might play a role in chronic inflammatory diseases. 20112365_IL-32gamma is a potent mediator of active osteoclast generation in the presence of sRANKL 20190143_IL-32 plays a host defense role against M. tuberculosis in differentiated THP-1 human macrophages. 20221440_IL-32 has an important role in vascular inflammation and sepsis development 20227751_The present study demonstrates keratinocytes (KCs) as a source of IL-32, which modulates KC apoptosis and contributes to the pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20400971_These results show that genetic modification of DU145 cells with NK4 cDNA yields a significant effect on their proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis. 20470879_The results showed that Orientia tsutsugamushi infection activated the NOD1 pathway followed by IL-32 secretion, thus resulting in the production and expression of IL-1beta, IL-6, IL-8, and ICAM-1 endothelial cells. 20480520_Butyrate stimulated IL-32alpha expression in epithelial cell lines. An epigenetic mechanism, such as histone hyperacetylation, might be involved in the action of butyrate on IL-32alpha expression. 20541181_human IL-32alpha and IL-32beta regulates on xenograft rejection in cellular xenotransplantation 20615213_IL-32 synthesis by fibroblast-like synoviocytes is tightly regulated by innate immunity in rheumatoid arthritis 20888796_The results from the present study suggest that IL-32 may play a role in the regulation of neuroinflammatory responses in several neurological disease conditions such as ischemia and Alzheimer's disease. 20889550_We have demonstrated the anti-influenza virus function of IL-32 20926308_Demonstration of membrane association for both intracellular and released IL-32 suggests this unique cytokine may have a complex biosynthetic pathway and mechanism of action. 21078994_the role of IL-32 in intestinal inflammation 21152864_IL-32alpha mRNA expression depends on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and the NF-kappaB system 21208204_the high-risk variant of human papillomavirus induces IL-32 expression 21321117_Data show that IL-32alpha stimulates Fas and ULBP2 expression via activation of p38 MAPK, which increases NK susceptibility of chronic myeloid leukemia cells. 21346229_A central role is discovered for IL-32 in the immune response to vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (an RNA virus) and DNA virus human herpesvirus type 2. 21383200_naturally occurring IL-32gamma can be spliced into IL-32beta, which is a less potent proinflammatory mediator. Splicing of IL-32gamma into IL-32beta is a safety switch in controlling the effects of IL-32gamma and thereby reduces chronic inflammation. 21423208_significant pathophysiological roles of IL-32gamma 21452292_Our findings indicate that overexpression of IL-32 together with a clear Th1 response immunologically characterizes the inflammatory response in giant cell arteritis. In particular, IL-32 seems to be an important mediator of artery inflammation in GCA. 21468596_Stable transfection of the new IL-32 isoform significantly decreased TNF-alpha-induced IL-8 mRNA expression in HT-29 cells. 21469100_promotes hematopoietic progenitor expansion 21481941_in conclusion, IL-32 is induced by HBx in Huh7 cells; results suggest that IL-32 might play an important role in inflammatory response after HBV infection 21487807_This study suggests the possibility that IL-32 might contribute to myasthenia gravis pathogenesis or immunoregulation 21525393_Data suggest that IL-32 moderates chronic immune activation to avert associated immunopathology but at the same time dampens the antiviral immune response and thus paradoxically supports HIV-1 replication and viral persistence. 21551364_IL-32gamma could effectively induce the maturation and activation of immature dendritic cells (DC), leading to enhanced Th1 and Th17 responses as the result of increased IL-12 and IL-6 production in DCs. 21602493_hypothesize that p300 and DAPK-1 represent nodes where the inflammatory networks of IL-32 and IL-17 overlap, and that these proteins would affect both TNF-R1-dependent and -independent pathways 21649914_A common IL-32 genotype, rs12934561, is associated with the risk of Acute Lung Injury (ALI) as well as the need for prolonged mechanical ventilatory support. 21725974_Transcriptional profiling of ATRA-treated SCC-9 cells showed downregulation of IL-32, which has been implicated in metastasis in a variety of tumors. 21899560_Overproduction of IL-32 may be involved in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis 22037460_these data suggest that IL-8 and IL-32 play a role in regulating the cancer stem cell -like properties that promote tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer cells in both autocrine and paracrine manners. 22043900_It was shown that IL-32 enhanced the cytotoxic effect of natural killer cells on protate cancer cells through activation of DR3 and caspase-3. 22198481_suggest that IL-32alpha is involved in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and may be a useful biomarker for diagnosis and therapeutic target of hepatocellular carcinoma 22203669_IL-32 binds to the extracellular domain of integrins and to intracellular proteins like paxillin and FAK 22277801_The present results suggest that IL-32gamma expression and its genetic variation in individual could be an important aspect of viral infections. 22486709_these data demonstrated a potential role for IL-32 in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis 22563781_IL-10, IL-17, IL-32 and TGF-beta- producing regulatory B cells. 22613074_These results show that IL-32alpha contributed to the development of inflammatory arthritis and endotoxin lethality. 22687868_These results suggest that IL-32 could be implicated in chronic hepatitis B-related liver inflammation/fibrosis. 22927445_the intracellular interaction of IL-32alpha with PKCepsilon and STAT3 promotes STAT3 binding to the IL-6 promoter by enforcing STAT3 phosphorylation, which results in increased production of IL-6. 23148681_Data indicate that CD4+ T cells and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) interact with each other by direct contact and cytokine secretion, and amplifies the expression of IL-17 and IL-32. 23180362_plasma IL-32alpha levels are associated with inflammatory responses in NMO patients. 23359495_Overexpression of IL32 is associated with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 23402302_IL-32 expression was induced by active human cytomegalovirus infection and could be functionally down-regulated by ectopically expressed human cytomegalovirus-miR-UL112-1. 23479179_Tumor invasion in gastric cancer is more severe in the IL-32 positive expression group than in cancer cells lacking IL-32. 23486016_An association of a germ-line polymorphism in the promoter of the IL32 gene with increased thyroid cancer susceptibility is observed. 23517397_The levels of IL-32 and TNF-alpha in the peripheral blood of patients with active RA are significantly higher than in that of patients with stable RA and healthy people. 23534905_These findings demonstrate that IL-32 is induced by microbial ligands through TLR-mediated innate signaling pathways, suggesting an important role of corneal epithelium in inflammatory disease. 23567618_Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interferon (IFN)-gamma and IL-1beta significantly increased both IL-33 protein and IL-33 mRNA expression in HACF and HACM as well as in human coronary artery smooth muscle cells (HCASMC). 23607494_involved the pathogenesis of cholangitis in biliary atresia 23703385_IL-32beta inhibits tumor growth by increasing cytotoxic lymphocyte numbers, and by inactivating the NF-kappaB and STAT3 pathways through changing of cytokine levels in tumor tissues. 23727326_IL-32 acts as a proinflammatory factor and may be implicated in the inflammatory cascade contributing to atherosclerosis. 23729669_IL-32 levels during viral infection mediate antiviral effects by stimulating the expression of IFN-lambda1. 23814099_IL-32beta-mediated C/EBPalpha Ser-21 phosphorylation by PKCdelta suppressed C/EBPalpha binding to IL-10 promoter, which promoted IL-10 production in U937 cells. 24114327_Data indicate that the IL-32beta-VEGF-STAT3 pathway affects the migration of MDA-MB-231 cells. 24129891_IL-32-PAR2 axis is an innate immunity sensor providing alternative signaling for LPS-TRIF axis. 24140068_These studies demonstrate that IL-32 plays a role in the tumor-associated inflammatory microenvironment and that overexpression of IL-32 contributes to invasion and metastasis in primary lung adenocarcinoma. 24226419_Our results suggest that IL-32 has a role in the formation and maintenance of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma lesions. 24295830_bacterial infection-mediated activation of NOD1,2, together with IL-32gamma, can synergize the activation of eosinophils interacting with bronchial epithelial cells. 24337385_VEGF-independent to the portfolio of IL-32. 24396867_IL-32delta interacts with IL-32beta and down-regulates IL-10 expression. 24472437_IL-32 may have diverse intracellular effects through the interactions with its different isoforms. 24553842_These studies disclosed that antiviral IFN-induced MxA and APOBEC3G/3F mRNA levels were increased after IL-32gamma treatment of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. 24579465_Serum IL-32 expression level was increased in patients with HBV-related liver failure and was associated with the severity of inflammation. 24602839_Our results clearly suggest that IL-32 is an important mediator for gastric cancer metastasis and independent prognostic predictor of gastric cancer. 24703937_IL-32alpha-mediated STAT3 S727 phosphorylation induced C/EBPalpha association, which inhibited PU.1 expression, and then resulted in the down-regulation of CD18 expression. 24743568_These results suggest that IL-32gamma enhances an innate immune response against local infection but inhibits the spread of immune responses, leading to systemic immune disorder. 24748497_The findings of this study regarding the unique functional interplay between M-CSF and IL-32 increase our understanding of the mechanisms that regulate the survival and M1/M2 ratio of macrophages, as well as HIV-1 replication in macrophages. 24761997_Study indicated the overexpression of IL-32 in induced sputum of smokers and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients, which was correlated with smoking exposure index and the degree of airway obstruction. It demonstrated that IL-32 might play critical role in smokers with COPD. 24854197_IL-32alpha can prevent cerebral ischemia damage via STAT3 activation and inhibition of NF-kappaB activation. 24879659_Although more studies are required, the pathogenic roles of IL-32 in some lupus nephritis patients could be supposed 24884781_major role in the inflammatory process caused by Leishmania (Viannia) spp. 24938282_IL32 may play a unique role in mycosis fungoides progression as an autocrine cytokine 24996056_IL-32theta; reduces PKCdelta-mediated phosphorylation of PU.1, resulting in attenuation of IL-1beta production 25022955_overexpression of IL-32gamma contributes to initial islet beta-cells injury and inflammation in pancreas and aggravates streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes. 25100201_Analysis of several GEO datasets showed differential expression of IL32 in patient samples previously designated as basal and/or triple negative breast cancer compared to normal and luminal breast samples. 25143364_These results identify IL-32 as one functional marker and potential correlate of protection against active tuberculosis. 25159479_These results suggest that IL-32beta could activate NF-kappaB and STAT3, and thus affect neuroinflammation as well as amyloidogenesis, leading to worsening memory impairment. 25176527_soluble IL-6R expression upregulated the levels of its own ligand, IL-6 and those of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-32. 25178676_Data suggest that interleukin-32alpha (IL-32alpha) associates with leukemia zinc finger (PLZF) and protein kinase c epsilon (PKCvarepsilon), and then inhibits PLZF sumoylation, resulting in suppression of the transcriptional activity of PLZF. 25245533_IL-32alpha inhibits BCL6 SUMOylation by activating PKCepsilon, resulting in the modulation of BCL6 target genes and cellular functions of BCL6. 25275312_IL-32 gamma delays, in a dose-dependent manner, the spontaneous apoptosis of human blood neutrophils by activating mainly p38 MAPK through rapid p38 phosphorylation. 25280942_IL-32theta;, through its interaction with PKCdelta, downregulates CCL5 expression by mediating the phosphorylation of STAT3 on Ser727 to render it transcriptionally inactive. 25583360_IL-32gamma prevents ethanol-induced hepatic injury via the inhibition of oxidative damage and inflammatory responses. 25645248_Transgenic mice that express human interleukin-32 are protected from high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis. 25663496_This study demonstrates that IL-32 gene polymorphisms are significantly associated with increased endometrial cancer susceptibility in Chinese Han women 25726525_we demonstrate that the newly discovered isoform, IL-32theta;, suppresses monocyte differentiation by regulating the expression of the PU.1 transcription factor. 25754842_Data show that toll-like receptor 3/TRIF protein signalling regulates cytokines IL-32 and IFN-beta secretion by activation of receptor-interacting protein-1 (RIP-1) and tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) in cornea epithelial cells. 25810549_The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1-induced IL-32 traps protein kinase Cdelta in the cytoplasm and prevents it from binding to the Zta promoter, which is the key event for virus activation. 25820174_IL-32gamma enhances host immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. 25846944_IL-32 stimulation promotes the invasion and motility of osteosarcoma cells, possibly via the activation of AKT and the upregulation of MMP-13 expression. 25887904_The anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis effects of IL-32gamma are mediated through classical caspase-3-dependent apoptosis as well as caspase-3-independent apoptosis. 25889282_High IL-32 expression may stimulate the organic metastasis and the lymph node metastasis of colorectal cancer. 25909160_In IL-32alpha-Tg mice, azoxymethane-induced colon cancer incidence was decreased, but expression of TNFR1 and TNFR1-mediated apoptosis was increased. IL-32alpha increased ROS production, prolonging JNK activation. In colon cancer patients, IL-32alpha was increased. 26057774_data further confirms that reduced IL32 methylation is associated with JIA, and that SNPs play an interactive role 26144292_highlight some of the potential mechanisms by which the immunomodulatory effect of IL-32 occurs against mycobacterial infections but also areas where mechanistic clarifications are needed 26151454_IL-32 is involved in the pathogenesis of airway inflammation. 26219901_serum levels of IL-32 and TNF-alpha may be diagnostic markers, and serum IL-29 levels may be associated with good prognosis in patients with gastric cancer 26241657_Our results suggest that NKP30-B7-H6 interaction can aggravate hepatocyte damage, probably through up-regulation of IL-32 expression in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure 26358252_These findings suggested that IL-18RAP rs917997, IL-32 rs2015620, IL-22 rs1179251, and interactions between these polymorphisms and H. pylori infection were associated with risks of gastric lesions 26516703_High IL32 expression is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 26551670_High IL32 expression is associated with Sezary syndrome. 26634249_Additional IL-32gamma stimulation in precursor cells enhanced osteoblast differentiation potentially 26678222_This study demonstrates that IL-32gamma and IL-32beta can induce caspase-8-dependent cell death whereas this was not observed for IL-32alpha 26824417_Low IL-32 expression is associated with colon cancer. 26978598_Data identify interleukin-32 (IL-32) as a potential therapeutic target. 27069296_Results show low plasma IL-32 levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and the rs28372698 SNP was associated with the susceptibility to SLE suggesting a possible role as a candidate marker to monitor SLE disease stability and screening in future. 27173130_This study showed that the induction level of IL-32 was increased in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps compared to normal nasal mucosa and that LPS-induced IL-32 expression in nasal polyp-derived fibroblasts was regulated via the TLR4/JNK/AKT/CREB signaling pathway. 27302771_this study shows that IL-32 might be involved in the pathogenesis of hepatic fibrosis by inducing TIMP-1 expression 27589563_High IL32 expression is associated with lung metastasis in melanoma. 27775437_the importance of IL-32 polymorphism and mRNA expression in susceptibility and influence of survival status in lung cancer 28079119_Results indicate that interleukin-32 gamma (IL-32gamma) plays a protective role for bone loss, providing clinical evidence of a negative correlation between IL-32gamma and DKK1 (Dickkopf-1) as bone metabolic markers. 28134327_Our study shows a functional effect of a promoter single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in IL32 on lipid profiles in RA patients and individuals, suggesting a possible protective role of this SNP against CVD. 28241012_Thus, endogenous IL-32 is a crucial cytokine involved in the host defense against Leishmania parasites. 28378461_In Behcet's disease, IL-32 levels showed weak positive correlations with disease activity and were associated with certain disease manifestations, including articular symptoms. 28470472_high expression of both IL17A and IL32 leads to enhancement of T cell responses in breast tumors 28701509_findings show that IL-32alpha acts on NK cells to inhibit IL-15-mediated STAT5 phosphorylation and to suppress their IL-15-induced effector molecule expression and cytolytic capacity. IL-32alpha also acted on DCs by downregulating IL-15-induced IL-18 production, an important cytokine in NK cell activity. 28709468_In transgenic mice, the presence of IL-32gamma contributes to the lesion healing caused by Leishmania braziliensis but not by Leishmania amazonensis. 28716229_The increase in serum levels of IL-32 in accordance with additive effect of the presence of C allele in Multiple sclerosis patients might introduce IL-32 as a key player in MS pathogenesis or immunedysregulation 28740544_Collectively, these results demonstrated that IL-32alpha upregulates the atheroprotective genes Timp3 and Reck by downregulating microRNA-205 through regulation of the Rprd2-Dgcr8/Ddx5-Dicer1 biogenesis pathway. 28747035_Strong expression of IL-32 was detected in cardiomyocytes from heart failure patients. 29037857_In Kaposi sarcoma (KS) splicing ratio of the IL-32 isoforms showed IL-32gamma as the highest expressed isoform, followed by IL-32beta, in HIV-related KS cases compared with controls. Our data suggest a possible survival mechanism by the splicing of IL-32gamma to IL-32beta and also IL-6, IL-8, and CXCR1 signaling pathways to reverse the proapoptotic effect of the IL-32gamma isoform, leading to tumor cell survival and th... 29277790_Three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (rs28372698, rs12934561, rs4786370) of the IL32 gene have been proposed as modifiers for different diseases. The present study found no significant differences in the genotypic frequencies between the patients and healthy controls and no relation to survival for any of the SNPs. 29286122_High IL32 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 29467412_IL-32gamma may increase TIMP-3 expression via hypomethylation through inactivation of NF-kappaB activity, and thereby reduce lung tumor growth. 29507875_rs4349147-G promotes transcription of non-IL-32alpha isoforms, generating a proinflammatory environment more conducive to HIV infection. 29524862_Regulation of IL-32 in human primary liver cells, HepG2 and THP-1cells strongly influences the mRNA expression of ABCA1, ABCG1, LXRalpha and apoA1 and affects intracellular lipid concentrations. 29551246_Interleukin 32 (IL-32) is important to limit the parasite dissemination from the site of infection [Review]. 29562285_The peritoneal fluid concentration of IL-32 was significantly higher in patients with advanced stage endometriosis compared with the controls. 29747940_Studies indicate that some interleukin 32 (IL-32) isoforms have been linked to disease outcome and were shown to positively influence tumor development and progression in various different malignancies [Review]. 29748157_IL-32 may be an important pro-inflammatory molecule involved in calcific aortic valve disease. 29806155_Study using a human skin explant model demonstrated for the first time, that IL-32 is a molecular link between keratinocytes and Langerhans cells (LCs) in healthy skin, provoking LC migration from the epidermis to the dermis prior to their migration to the draining lymph nodes. 30006119_The levels of IL-32, IL-1, and IFN-gamma protein and transcripts in serum and PBMCs from hepatitis B patients were higher than those in healthy volunteers. 30115930_IL-32gamma functions as intracellular effector in hepatocytes for suppressing hepatitis b virus replication. 30232372_Study shows that IL-32 mRNA and protein production was higher in rheumatoid arthritis patients compared to healthy individuals. Moreover, a slightly higher IL-32 expression was observed in patients bearing the CC-genotype for the IL-32 promoter SNP (rs4786370). These patients also tended to produce more pro-inflammatory cytokines in-vitro. 30257681_IL-32 is involved in fibrosis progression in the lungs 30391782_Tumor associated fibroblast-secreted IL32 promotes breast cancer cell invasion and metastasis via integrin beta3-p38 MAPK signalling. 30486830_Findings indicated that IL-32gamma suppressed skin carcinogenesis through the inhibition of both stemness and the inflammatory tumor microenvironment by the downregulation of TIMP-1 and ITGAV via inactivation of NF-kappaB signaling. 30660652_IL-32gamma secreted by multiple myeloma cells promotes the immunosuppressive function of macrophages. 30760247_IL32 blood levels are higher in latent tuberculosis patients than in patients with active tuberculosis. 30824537_hypomethylation status of transcriptional regulatory elements in IL-32 was maintained for a long time (several weeks), causing elevated IL-32 expression even in the absence of TNFalpha 30848577_IL-17A and IL-32 SNPs might be associated with predisposition to polycystic ovary syndrome in Iranian women. 30910260_Increased expression of IL-32 correlates with IFN-gamma, Th1 and Tc1 in virologically suppressed HIV-1-infected patients. 30941928_IL-32gamma could be associated with the activity and development of lupus nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus. 30953519_Expression of IL32 in human melanoma can be induced by TNFalpha or IFNgamma and correlates with a treatment-resistant dedifferentiated genetic signature. 31099938_Serum IL-32 levels are elevated in patients with endometriosis, and with combination of serum CA-125 levels, it may serve as a potential biomarker for endometriosis. 31201646_TAM-derived TNFalpha induces IL-32beta in thyroid cancer cells. Although IL-32beta does not affect thyroid cancer cell migration, alternative splicing of IL-32 towards the IL-32beta isoform may be beneficial for thyroid cancer cell survival through induction of the pro-survival cytokine IL-8. 31326419_Both the coronary artery and circulating IL-32 levels were increased in coronary artery disease (CAD) patients and IL-32 may be a marker of noninvasive diagnosis of CAD 31378983_IL-32 and its splice variants are associated with protection against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and skewing of Th1/Th17 cytokines. 31398626_Transgenic mice expressing human IL-32 develop adipokine profiles resembling those of obesity-induced metabolic changes. 31479874_Serum levels of IL-32 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and its relationship with TNF-alpha and IL-6. 31484076_beta-Glucan-Induced Trained Immunity Protects against Leishmania braziliensis Infection: a Crucial Role for IL-32. 31595570_Effects of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells with NK4 gene expression on glioblastoma multiforme cell lines. 31714430_Our data report on the differential expression of IL- 32 isoforms and highlight the potential role of IL-32, particularly the gamma isoform, in fueling persistent inflammation and transcription of viral reservoir in HIV-1 infection. 32023240_This study showed that the IL32 rs4786370 genetic variant was associated with protection against American tegumentary leishmaniasis, whereas the IL32 rs4349147 was associated with susceptibility to the development of localized cutaneous and mucosal leishmaniasis. 32096477_IL-32 serum levels expression correlated positively with ANCA-associated vasculitis severity. 32434199_Altered IL-32 Signaling in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. 32487240_Interleukin-32 in systemic sclerosis, a potential new biomarker for pulmonary arterial hypertension. 32694699_Correlation between serum IL-32 concentration and clinical parameters of stable COPD: a retrospective clinical analysis. 32860786_Admission IL-32 concentration predicts severity and mortality of severe community-acquired pneumonia independently of etiology. 33087256_Natural Killer Cell Transcript 4 promotes the development of Sjgren's syndrome via activation of Rap1 on B cells. 33097029_IL-32 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition by triggering endoplasmic reticulum stress in A549 cells. 33112553_Impact of Bone Marrow Natural Killer Cells (NK); Soluble TNF-alpha and IL-32 Levels in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Patients. 33204366_Associations between Interleukin-32 Gene Polymorphisms rs12934561 and rs28372698 and Susceptibilities to Bladder Cancer and the Prognosis in Chinese Han Population. 33254483_Interleukin 32: A novel player in perioperative neurocognitive disorders. 33495843_IL-32 exacerbates adenoid hypertrophy via activating NLRP3-mediated cell pyroptosis, which promotes inflammation. 33681363_IL-32 Promotes the Radiosensitivity of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell through STAT3 Pathway. 33707686_Placenta-derived IL-32beta activates neutrophils to promote preeclampsia development. 33936102_Upregulated IL-32 Expression And Reduced Gut Short Chain Fatty Acid Caproic Acid in People Living With HIV With Subclinical Atherosclerosis. 34086163_Serum levels of IL-32 in patients with coronary artery disease and its relationship with the serum levels of IL-6 and TNF-alpha. 34138488_Association of IL-32 rs28372698 polymorphism with active chronic HBV infection. 34138771_Brief Report: Subclinical Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis Is Associated With Increased Expression of Peripheral Blood IL-32 Isoforms Among Women Living With HIV. 34271417_Impact of interleukin-32 germ-line rs28372698 and intronic rs12934561 polymorphisms on cancer development: A systematic review and meta-analysis. 34280028_Interleukin-32 in Pathogenesis of Atopic Diseases: Proinflammatory or Anti-Inflammatory Role? 34346819_Association between interleukin-32 gene polymorphism and susceptibility to preeclampsia. 34743576_Identification of molecular subtyping system and four-gene prognostic signature with immune-related genes for uveal melanoma. 34784560_Protective immune response mediated by neutrophils in experimental visceral leishmaniasis is enhanced by IL-32gamma. 34799941_Effects of IL-32 polymorphisms and IL-32 levels on the susceptibility and severity of coronary artery disease. 35097133_Interleukin-32gamma in the Control of Acute Experimental Chagas Disease. 35122427_Interleukin-21 and Interleukin-32 gene expression levels and their relationship with clinicopathological parameters in colorectal cancer. 35123164_Elevated levels of IL-32 in cerebrospinal fluid of neuro-Behcet disease: Correlation with NLRP3 inflammasome. 35131367_Interleukin 32 gene promoter polymorphism: A genetic risk factor for multiple sclerosis in Kashmiri population. 35281008_A Paradoxical Effect of Interleukin-32 Isoforms on Cancer. 35371618_Myeloma-derived IL-32gamma induced PD-L1 expression in macrophages facilitates immune escape via the PFKFB3-JAK1 axis. 35428295_Extracellular vesicle IL-32 promotes the M2 macrophage polarization and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via FAK/STAT3 pathway. 35545774_IL-32 promotes the occurrence of atopic dermatitis by activating the JAK1/microRNA-155 axis. 35880892_Interleukin 32 as a Potential Marker for Diagnosis of Tuberculous Pleural Effusion. | 36.239496 | 1.1627789 | 0.217576740 | 0.29150792 | 0.55648286552 | 0.4556808308076748526005417261330876499414443969726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.67811820385719678849767433348461054265499114990234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 38.397950 | 6.863566 | 33.144888 | 6.000770 | |||
| ENSG00000010244 | 7756 | ZNF207 | protein_coding | O43670 | FUNCTION: Kinetochore- and microtubule-binding protein that plays a key role in spindle assembly (PubMed:24462186, PubMed:24462187, PubMed:26388440). ZNF207/BuGZ is mainly composed of disordered low-complexity regions and undergoes phase transition or coacervation to form temperature-dependent liquid droplets. Coacervation promotes microtubule bundling and concentrates tubulin, promoting microtubule polymerization and assembly of spindle and spindle matrix by concentrating its building blocks (PubMed:26388440). Also acts as a regulator of mitotic chromosome alignment by mediating the stability and kinetochore loading of BUB3 (PubMed:24462186, PubMed:24462187). Mechanisms by which BUB3 is protected are unclear: according to a first report, ZNF207/BuGZ may act by blocking ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of BUB3 (PubMed:24462186). According to another report, the stabilization is independent of the proteasome (PubMed:24462187). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24462186, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24462187, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26388440}. | Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Centromere;Chromosome;Chromosome partition;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;DNA-binding;Kinetochore;Metal-binding;Microtubule;Mitosis;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Enables microtubule binding activity. Involved in several processes, including mitotic nuclear division; mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint signaling; and protein stabilization. Located in kinetochore; nuclear lumen; and spindle matrix. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:7756; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; kinetochore [GO:0000776]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; spindle [GO:0005819]; spindle matrix [GO:1990047]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; attachment of spindle microtubules to kinetochore [GO:0008608]; cell division [GO:0051301]; microtubule bundle formation [GO:0001578]; microtubule polymerization [GO:0046785]; mitotic sister chromatid segregation [GO:0000070]; mitotic spindle assembly [GO:0090307]; mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint signaling [GO:0007094]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of chromosome segregation [GO:0051983] | 26388440_BuGZ forms temperature-dependent liquid droplets alone or on microtubules in physiological buffers. Coacervation in vitro or in spindle and spindle matrix depends on hydrophobic residues in BuGZ. BuGZ coacervation and its binding to microtubules and tubulin are required to promote assembly of spindle and spindle matrix in Xenopus egg extract and in mammalian cells. 29074706_the two zinc fingers of BuGZ directly bind to AurA and BuGZ coacervation appears to promote AurA activation during spindle assembly. 30349051_a distinct isoform of ZNF207 functions in hESCs at the nexus that balances pluripotency and differentiation to ectoderm. 31113916_ZNF207 expression is elevated in hepatocellular carcinoma 32820050_BuGZ facilitates loading of spindle assembly checkpoint proteins to kinetochores in early mitosis. 35246476_System analysis based on the cancer-immunity cycle identifies ZNF207 as a novel immunotherapy target for hepatocellular carcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000017421 | Zfp207 | 1426.401217 | 1.1042265 | 0.143036160 | 0.07550228 | 3.58482505557 | 0.0583095559906313676279410174174699932336807250976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.18267280385150092003598842893552500754594802856445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1569.874033 | 83.870172 | 1427.980426 | 76.324460 | |
| ENSG00000010610 | 920 | CD4 | protein_coding | P01730 | FUNCTION: Integral membrane glycoprotein that plays an essential role in the immune response and serves multiple functions in responses against both external and internal offenses. In T-cells, functions primarily as a coreceptor for MHC class II molecule:peptide complex. The antigens presented by class II peptides are derived from extracellular proteins while class I peptides are derived from cytosolic proteins. Interacts simultaneously with the T-cell receptor (TCR) and the MHC class II presented by antigen presenting cells (APCs). In turn, recruits the Src kinase LCK to the vicinity of the TCR-CD3 complex. LCK then initiates different intracellular signaling pathways by phosphorylating various substrates ultimately leading to lymphokine production, motility, adhesion and activation of T-helper cells. In other cells such as macrophages or NK cells, plays a role in differentiation/activation, cytokine expression and cell migration in a TCR/LCK-independent pathway. Participates in the development of T-helper cells in the thymus and triggers the differentiation of monocytes into functional mature macrophages. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16951326, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24942581, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2823150, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7604010}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Primary receptor for human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) (PubMed:2214026, PubMed:16331979, PubMed:9641677, PubMed:12089508). Down-regulated by HIV-1 Vpu (PubMed:17346169). Acts as a receptor for Human Herpes virus 7/HHV-7 (PubMed:7909607). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12089508, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16331979, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17346169, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2214026, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7909607, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9641677}. | 3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes the CD4 membrane glycoprotein of T lymphocytes. The CD4 antigen acts as a coreceptor with the T-cell receptor on the T lymphocyte to recognize antigens displayed by an antigen presenting cell in the context of class II MHC molecules. The CD4 antigen is also a primary receptor for entry of the human immunodeficiency virus through interactions with the HIV Env gp120 subunit. This gene is expressed not only in T lymphocytes, but also in B cells, macrophages, granulocytes, as well as in various regions of the brain. The protein functions to initiate or augment the early phase of T-cell activation, and may function as an important mediator of indirect neuronal damage in infectious and immune-mediated diseases of the central nervous system. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified in this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2020]. | hsa:920; | clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; T cell receptor complex [GO:0042101]; coreceptor activity [GO:0015026]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; interleukin-16 binding [GO:0042011]; interleukin-16 receptor activity [GO:0042012]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; MHC class II protein binding [GO:0042289]; MHC class II protein complex binding [GO:0023026]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein tyrosine kinase binding [GO:1990782]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus [GO:0097011]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; enzyme-linked receptor protein signaling pathway [GO:0007167]; helper T cell enhancement of adaptive immune response [GO:0035397]; immune response [GO:0006955]; interleukin-15-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0035723]; macrophage differentiation [GO:0030225]; maintenance of protein location in cell [GO:0032507]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0050850]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of monocyte differentiation [GO:0045657]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050870]; positive regulation of viral entry into host cell [GO:0046598]; regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051924]; regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050863]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell activation [GO:0042110]; T cell differentiation [GO:0030217]; T cell selection [GO:0045058]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] | 11140838_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11878912_the role of CD4, CXCR4, and CCR5 in HIV envelope-mediated apoptosis was examined in peripheral blood mononuclear cells 11893391_Degradation of the HIV receptor CD4 by the proteasome, mediated by the HIV-1 protein Vpu, is crucial for the release of fully infectious virions. 11906183_Role of CD4 hinge region in GP120 utilization by immunoglobulin domain 1 11920312_cytokine regulation of CD4 expression on monocytes, monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs), and microglia was investigated 11922627_Results show that the presence of an alpha-helix N-cap in the CD4 cytoplasmic domain increases CD4 affinity to Nef. 11959143_NF-kappaB activation upon interaction of HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins with cell surface CD4 involves IkappaB kinases. 11994538_All of the human testicular macrophages expressed the markers CD45 and MAC387 and most also expressed CD4. 12008044_Ligation of human CD4 interferes with antigen-induced activation of primary T cells derived from CD4 transgenic mice 12055221_CD4 represents a critical turning point that governs the apoptotic and survival programs in T cells, without modifying the physical association with the TCR-CD3 complex. 12213222_CD4 is active as a signaling molecule on the human monocytic cell line Thp-1 12218108_The CD4 coreceptor mediates tolerance-inducing signals when triggered by an appropriate ligand in vivo. 12368305_coreceptor binding domain, the V3 region of the surface envelope (SU) glycoprotein, was replaced by the V3 loop of a CD4- and CXCR4-tropic HIV-1 strain; the resulting virus, termed SIVagm3-X4mc, exclusively used CD4 and CXCR4 for cell entry 12444132_CD4 dimerization is necessary for helper T cell function. 12462973_study of structural and functional homology between human apolipoprotein A-I and envelope proteins of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in CD4 receptor binding 12517957_Palmitoylation of Cys394 and Cys397 in the CVRC motif of CD4 and CD4's association with Lck are essential for keeping CD4 highly concentrated in lipid rafts. 12531788_evidence that neutrophils from both HIV-1-infected and uninfected donors express endogenous CD4 with conformation similar to that of CD4 expressed on T lymphocytes, and that binds HIV gp120, significantly influencing the biodistribution of HIV 12531905_physical association of CD4 and CCR5 results in receptor cross talk with allosteric CD4-dependent regulation of the binding and signaling properties of CCR5 12586555_HIV-1 entry involves a chemokine-receptor-dependent but CD4-independent entry in neural cells. 12639247_Modulation of NFI-B2 by HIV-1 may represent yet another mechanism by which HIV infection reduces cell surface expression of CD4 12695117_Involvement of the CD4 extracellular domain for the inhibitory effect of oxidative stress on activation-induced CD4 down-regulation in T cells. 12702212_RT-PCR, and related methodologies are not useful substitutes for assessment of CD4 and CD8 cell numbers in HIV-infected persons 12767984_overexpression of CD4 can inhibit T-cell killing by limiting CCR5-using HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein processing and membrane fusion 12816953_CD4 is downregulated by HIV-1 nef 12864967_The degree of human CD4 dependence of the agonist effects of gp120IIIB at the rat CXCR4 receptor is cell-type specific. 13679604_CD4 di-leucine motif is dispensable for nef binding. In contast, this motif is essential for CD4 down modulation. 14500983_examined the folding and solution structures of ternary CD4-Lck-Zn2+ and CD8alpha-Lck-Zn2+ complexes;coreceptor tails and the Lck N-terminus are unstructured in isolation but assemble in the presence of zinc to form compactly folded heterodimeric domains 14557639_downregulated by HIV-1 Nef protein in coorelation with AIDS clinical progression 14570906_Raft localization of CD4 is not required for hiv-1 entry, however, post-binding fusion/entry steps may require lipid raft assembly. 14697933_The number of CD4+CD28- cells in patients after renal transplantation, especially in graft recipients with chronic graft rejection, suggests a role of these cells in chronic graft destruction. 14705953_When undergoing endocytosis, a small fraction of CD4 on the surface membranes of lymphoblastoid cells is targeted to clathrin-coated pits where it becomes associated with CD71 molecules that are also targeted for endocytosis into the same pit. 14747534_downregulated by Hiv-1 Nef protein in association with lipid rafts 15063762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15194762_down-regulated by SIVcpz and HIV-1 group N or O nef alleles 15308751_CCR5 HIV coreceptor is significantly more mobile than CD4 and it requires membrane cholesterol for mobility 15317218_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15326605_We have shown that 3D domain swapping is a likely candidate for the conformational change which influences permissiveness of cells to HIV infection; the hinge loop, or linker, is loop E - F. 15371410_HIV uptake by CD4 T cells requires cellular contacts mediated by the binding of gp120 to CD4 and intact actin cytoskeleton 15489307_entropy calculation of HIV-1 Env gp120, its receptor CD4, and their complex 15611114_CD4 recycling from the plasma membrane and the nascent CD4 in transit to the plasma membrane are susceptible to intracellular retention in HIV-1 Nef-expressing cells 15616015_Deficiency in function of the CD4(+)CD25(+) T-cell population may influence the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes. 15665762_The T cells exclusively originating from preexisting CD4CD25 regulatory T cells and proves anergic and highly suppressive on isolation. 15714205_The presence of CD4+CD25+ (regulatory T cells in head and neck cancer patients might be, in part, responsible for downregulation of antitumour immune responses. 15731180_CD4(+)CD25(+) fetal T cells are present in the human fetus from week 14 onwards, which shows that generation of regulatory-suppressor T cells is consubstantial to the generation of a functional and self-tolerant immune system 15748900_Cell surface rearrangements in response to CD4 engagement may serve as a means to enhance cell-to-cell signaling at the immunological synapse and modulate chemokine responsiveness, as well as facilitate HIV entry. 15767435_The first is a lag phase that is caused in part by the concentration-dependent reversible association of virus with CD4 and CCR5 to form an equilibrium assemblage of complexes. 15821887_association of CD4+ T lymphocyte nadir with the extent of immune reconstitution in HIV-infected individuals suggests that HIV-1 may cause irreparable immune system damage 15823605_down regulated by four SIVcpz Vpu proteins 15890908_adaptation to microglia correlates with the generation of a gp120 that forms a more stable interaction with CD4 15956605_Nef-induced CD4 down-regulation is not implicated in the Nef/CD4 complex formation in the cellular context. 15972448_Phenotypic studies demonstrated decreased frequency of CD4+CD25+ T cells in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease 16284180_determination of the structure of V3 in the context of an HIV-1 gp120 core complexed to the CD4 receptor and to the X5 antibody at 3.5 angstrom resolution 16309726_HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins from the brain of an infected patient had a lower CD4 dependence, since they efficiently mediated fusion in the presence of low levels of CD4 on the target cell membrane 16314494_Runx1 blocks the elongation by RNAPII, which may contribute to CD4 silencing during T-cell development. 16631599_We hypothesized that LA might induce dissociation of p56(Lck) from CD4, thus leading to its downmodulation. 16721558_molecular modeling of the global complex of CCR5, gp120 including the V3 loop and CD4 16758122_CD4 and CD25 in T cells, which are increased in breast cancer, are decreased after vaccination with a HER2/neu peptide (E75) and GM-CSF vaccine 16762062_Monomeric forms of CD4 are preferentially used by HIV-1 to gain entry into target cells, thus implying that the dimer/monomer ratio at the cell surface of HIV-1 target cells may modulate the efficiency of HIV-1 entry. 16821115_The results reported in this study demonstrate the activation of both gammadelta- and alphabeta-T cell responses in healthy elderly after influenza vaccination. 16873261_Contribution of Vpu, Env, and Nef to CD4 down-modulation was compared. 16951326_Present and functional on natural killer (NK) cells, CD4 plays a role in innate immune responses as a chemotactic receptor and by increasing cytokine production. 16955142_CD4+ CD45RO+ Foxp3+ CD25hi T lymphocytes are highly proliferative, with a doubling time of 8 days, compared with memory CD4+ CD45RO+ Foxp3- CD25- (24 days). 16979207_This study of tissue-derived HIV-1 Nefs demonstrates that CD4 and MHC-I downregulation are highly conserved Nef functions, while Pak2 association is variable in late stage AIDS patients. 16987062_CD4, complement receptors, and CXCR4 chemokine receptors are required for complement mediated antibody dependent enhanced entry of HIV into MT2 cells. 17020785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17020785_The result, including a total of 2640 MS patients and 2194 controls shows no significant association with CD4 and LAG3 and MS. We conclude that these genes are of minor importance in regard of genetic predisposition to the MS. 17065205_human herpesvirus 7 suppresses the replication of CCR5-tropic (R5) HIV-1 in coinfected blocks of lymphoid tissue by downregulation of CD4 17175221_These data support studies using in vitro generated and expanded human CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells with indirect allospecificity as therapeutic reagents to promote donor-specific transplantation tolerance. 17235436_The CD4 mRNA expression level strongly correlated with the CD4(+) infiltration score in the cancer epithelium (r(s) = 0.858, P | ENSMUSG00000023274 | Cd4 | 1112.262185 | 1.2334553 | 0.302705456 | 0.05857428 | 26.69709292744 | 0.0000002379792890474053693575972245541350069686359347542747855186462402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000436284966604863274773802583883508532380801625549793243408203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1231.024990 | 43.332174 | 1002.619036 | 35.799029 | |
| ENSG00000012232 | 2137 | EXTL3 | protein_coding | O43909 | FUNCTION: Glycosyltransferase which regulates the biosynthesis of heparan sulfate (HS). Important for both skeletal development and hematopoiesis, through the formation of HS proteoglycans (HSPGs) (PubMed:28132690, PubMed:28148688). Required for the function of REG3A in regulating keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation (PubMed:22727489). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22727489, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28132690, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28148688}. | 3D-structure;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Intellectual disability;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | PATHWAY: Glycan metabolism; heparan sulfate biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28132690, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28148688}. | This gene encodes a single-pass membrane protein which functions as a glycosyltransferase. The encoded protein catalyzes the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine to glycosaminoglycan chains. This reaction is important in heparin and heparan sulfate synthesis. Alternative splicing results in the multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2012]. | hsa:2137; | endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; glucuronyl-galactosyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0001888]; glycosyltransferase activity [GO:0016757]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0015012]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; protein glycosylation [GO:0006486] | 10753861_These results suggest that EXTL3/EXTR1 is a cell surface Reg receptor that binds to Reg protein. 18543267_We conclude that EXTL3 promoter methylation and its related loss of EXTL3 expression are involved in the loss of HS expression in mucinous CRCs. 19158046_HIP enhanced EXTL3 translocation from the membrane to the nucleus, in support of a model whereby EXTL3 mediates HIP signaling for islet neogenesis. 19653241_A missense mutation involving the exon 3 of the EXTL3 gene in the case of obstructing colon cancer is described in a 31-year-old patient affected by hereditary multiple exostoses. 19690583_Lysosomal glycosaminoglycan levels in mucopolysaccharidosis are reduced by EXTL3 gene silencing. 22158612_Regenerating islet-derived 1alpha (Reg-1alpha) protein is new neuronal secreted factor that stimulates neurite outgrowth via exostosin Tumor-like 3 (EXTL3) receptor. 25829497_Recombinant EXTL2 showed weak ability to transfer N-acetylgalactosamine to heparan sulfate precursor molecules but also, that EXTL2 exhibited much stronger in vitro N-acetylglucosamine-transferase activity related to elongation of heparan sulfate chains. 28132690_We show that biallelic mutations in EXTL3 disturb glycosaminoglycan synthesis and thus lead to a recognizable syndrome characterized by variable expression of skeletal, neurological, and immunological abnormalities. 28148688_EXTL3 mutations as a novel cause of severe immune deficiency with skeletal dysplasia and developmental delay and underline a crucial role of HS in thymopoiesis and skeletal and brain development. 28331220_EXTL3 missense mutation is associated with spondylo-epi-metaphyseal dysplasia. 28446799_EXTL3 mutations are associated with spondylo-epi-metaphyseal dysplasia with immunodeficiency. 29346724_Human lumenal N-glycosylated EXTL3 (EXTL3DeltaN) was cloned, expressed in human embryonic kidney cells, and purified. Various biophysical and biochemical approaches were then employed to elucidate the N-glycosylation sites and the function of their attached N-glycans. 31467315_EXTL3-interacting endometriosis-specific serum factors induce colony formation of endometrial stromal cells. 34089299_Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia EXTL3-deficient type: Long-term follow-up and review of the literature. 34099862_REG3A/REG3B promotes acinar to ductal metaplasia through binding to EXTL3 and activating the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK signaling pathway. | ENSMUSG00000021978 | Extl3 | 357.606987 | 1.0130047 | 0.018640815 | 0.12277869 | 0.02302629555 | 0.8793887116396074121738024587102700024843215942382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.94702358136999209570205948693910613656044006347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 368.496897 | 38.998301 | 365.917197 | 38.579176 |
| ENSG00000013364_ENSG00000280893 | 187.244633 | 0.6892821 | -0.536833611 | 0.16146421 | 11.03497617897 | 0.0008940882489384484365160798979843548295320942997932434082031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00687170682755550415315992651699161797296255826950073242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 149.745460 | 15.332818 | 218.248151 | 21.898631 | |||||||||||||
| ENSG00000023228 | 4719 | NDUFS1 | protein_coding | P28331 | FUNCTION: Core subunit of the mitochondrial membrane respiratory chain NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I) which catalyzes electron transfer from NADH through the respiratory chain, using ubiquinone as an electron acceptor (PubMed:30879903, PubMed:31557978). Essential for catalysing the entry and efficient transfer of electrons within complex I (PubMed:31557978). Plays a key role in the assembly and stability of complex I and participates in the association of complex I with ubiquinol-cytochrome reductase complex (Complex III) to form supercomplexes (PubMed:30879903, PubMed:31557978). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30879903, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31557978}. | 2Fe-2S;3D-structure;4Fe-4S;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Electron transport;Iron;Iron-sulfur;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;NAD;Oxidoreductase;Primary mitochondrial disease;Reference proteome;Respiratory chain;Transit peptide;Translocase;Transport;Ubiquinone | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the complex I 75 kDa subunit family. Mammalian complex I is composed of 45 different subunits. It locates at the mitochondrial inner membrane. This protein has NADH dehydrogenase activity and oxidoreductase activity. It transfers electrons from NADH to the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme is believed to be ubiquinone. This protein is the largest subunit of complex I and it is a component of the iron-sulfur (IP) fragment of the enzyme. It may form part of the active site crevice where NADH is oxidized. Mutations in this gene are associated with complex I deficiency. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]. | hsa:4719; | mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I [GO:0005747]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; 2 iron, 2 sulfur cluster binding [GO:0051537]; 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding [GO:0051539]; electron transfer activity [GO:0009055]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity [GO:0008137]; aerobic respiration [GO:0009060]; apoptotic mitochondrial changes [GO:0008637]; ATP metabolic process [GO:0046034]; cellular respiration [GO:0045333]; mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone [GO:0006120]; mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I assembly [GO:0032981]; proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis [GO:0042776]; reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:0072593]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0051881] | 15824269_A patient with Leigh syndrome had a mutation in the NDUFS1 protein of Complex I of the Respiratory Chain. Identifying nuclear mutations will help us understand how molecular defects can lead to complex I deficiency. 16478720_mutations in the NDUFS1 and NDUFS4 genes of complex I cause dysfunction in cellular oxidative metabolism 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19064571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19405953_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the Wernicke's Area from patients with schizophrenia. 19836344_Mutations in electron Transport Complex I is associated with Leber hereditary optic neuropathy failing to compensate for impaired oxidative phosphorylation. 20382551_report 3 patients with low residual complex I activity who displayed novel mutations in the NDUFS1 gene. One mutation introduces a premature stop codon, 3 mutations cause a substitution of amino acids and another mutation a deletion of one amino acid. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21183487_data suggest that gamma oscillations are especially energy demanding and require both high complex I expression and strong functional performance of mitochondria. 21203893_homozygous c.1783A>G (p.Thr595Ala) mutation in NDUFS1 in two inbred siblings with isolated complex I deficiency associated to a progressive cavitating leukoencephalopathy 21540367_The peripheral leukocyte oxidative phosphorylation enzyme activity assay was found to be a reliable method for the diagnosis of mitochondrial diseases. 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 24952175_Some mutations in NDUFS1 cause a milder phenotype with a more benign course despite the initial decompensation phase. Homozygosity for the c.755A > G missense mutation may correlate with the milder clinical picture in the patient. 25354934_NDUFS1 may confer susceptibility to schizophrenia in male subjects, acting as a causative factor for the severity of negative symptoms in schizophrenia. 25615419_The presented clinical courses of NDUFV1 and NDUFS1 mutation-based complex I deficiencies are characterized by leukoencephalopathy or early death and expand the already heterogeneous phenotypic spectrum. 26053550_Results found nominal significant associations of 2 SNPs in the NDUFS1 gene and 4 SNPs in the NDUFS2 gene with early onset schizophrenia (EOS), but none of these associations survived the Bonferroni correction. 26235939_Loss of FOXRED1, coupled with protein, choline and/or folate-deficient diets results in the depletion of glutathione, the dysregulation of nitric oxide metabolism and the peroxynitrite-mediated inactivation of complex I. 26987334_High NDUFS1 expression is associated with cognitive impairment in lung cancer. 27516145_Results show that NDUFS1 protein and mRNA levels are down-regulated in lung neoplasm and correlate with poor overall survival. 30879903_MDM2 directly binds and sequesters NDUFS1, preventing its mitochondrial localization and ultimately causing complex I and supercomplex destabilization and inefficiency of oxidative phosphorylation. 31557978_The biallelic mutations in NDUFS1 led to a decreased stability of the entire N-module of electron transport complex I and disrupted the electron transfer between two iron-sulfur clusters. | ENSMUSG00000025968 | Ndufs1 | 508.970935 | 1.0786359 | 0.109207960 | 0.08012562 | 1.85658490292 | 0.1730194693989411947043777217913884669542312622070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.37771455270964116035514734903699718415737152099609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 575.906720 | 32.128247 | 536.558293 | 29.936361 | |
| ENSG00000023330 | 211 | ALAS1 | protein_coding | P13196 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP)-dependent condensation of succinyl-CoA and glycine to form aminolevulinic acid (ALA), with CoA and CO2 as by-products. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16234850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17975826}. | Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Heme biosynthesis;Hydroxylation;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Pyridoxal phosphate;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transit peptide;Ubl conjugation | PATHWAY: Porphyrin-containing compound metabolism; protoporphyrin-IX biosynthesis; 5-aminolevulinate from glycine: step 1/1. | This gene encodes the mitochondrial enzyme which is catalyzes the rate-limiting step in heme (iron-protoporphyrin) biosynthesis. The enzyme encoded by this gene is the housekeeping enzyme; a separate gene encodes a form of the enzyme that is specific for erythroid tissue. The level of the mature encoded protein is regulated by heme: high levels of heme down-regulate the mature enzyme in mitochondria while low heme levels up-regulate. A pseudogene of this gene is located on chromosome 12. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]. | hsa:211; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; 5-aminolevulinate synthase activity [GO:0003870]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; pyridoxal phosphate binding [GO:0030170]; erythrocyte development [GO:0048821]; heme biosynthetic process [GO:0006783]; hemoglobin biosynthetic process [GO:0042541]; protoporphyrinogen IX biosynthetic process [GO:0006782]; response to bile acid [GO:1903412] | 11929042_REVIEW:active site and mechanistic analysis, protein folding, structure and function. 11929048_REVIEW: mechanisms involving ALAS deficiency, point mutations, post translational processing, and complex formation with succinyl CoA synthetase subunit B in the pathogenesis of hereditary sideroblastic anemia. 12433930_ALAS expression is regulated by AP-1 complex through sequestration of cAMP-response element protein (CRE)-binding protein (CBP) coactivator in human cells 15123725_ALAS gene expression is regulated by Hepatic nuclear factor 3 and nuclear factor 1 15477213_First described frameshift ALAS2 mutation, CD506-507 (-C). 15547665_in the liver of Acute liver failure patients, there may be an increase in free heme concentration which down-regulating ALAS1 gene expression 15710391_Alternative splicing of human ALAS1 generates two mRNAs with different 5'-UTRs: a major one, where exon 1B is omitted, and a minor form containing exon 1B. 15797241_5-aminolevulinate synthase gene repression by the potent tumor promoter, TPA, involves multiple signal transduction pathways 17628775_Expression of candidate genes HPRT1 and ALAS1 in malignant and non-malignant prostate tissue samples after microdissection. 18719978_Differential regulation of human ALAS1 mRNA and protein levels by heme and cobalt protoporphyrin. 19477221_In this study, we show significant reductions of the rate-limiting enzymes involved in heme biosynthesis, ALAS1 in the postmortem cortex of Alzheimer's disease subjects, providing additional evidence of abnormal heme homeostasis in Alzheimer's disease. 19656447_The -853T variant functions as an enhancer in the presence of estrogen and speculates that the -1253A variant reduces transcription activity. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21659532_Lon peptidase 1 (LONP1)-dependent breakdown of mitochondrial 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase protein by heme in human liver cells. 23024262_These results indicate that ALAS1 is a novel NR5A-target gene and participates in steroid hormone production. 26062020_ALAS1 mRNA and activity were elevated approximately ~3- and 5-fold, and HMB synthase activity was approximately half-normal (~42%) 27496948_the heme-binding site in the N-terminal region of the mature ALAS1 protein is also necessary for the heme-dependent oxidation of ALAS1. 28874591_The mutation in CLPX inactivates its ATPase activity, resulting in coassembly of mutant and WT protomers to form an enzyme with reduced activity. The presence of low-activity CLPX increases the posttranslational stability of ALAS, causing increased ALAS protein and ALA levels, leading to abnormal accumulation of PPIX. 32270771_Inhibition of ALAS1 activity exerts anti-tumour effects on colorectal cancer in vitro. 33199206_5-Aminolevulinate dehydratase porphyria: Update on hepatic 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase induction and long-term response to hemin. 34704252_Heme-dependent recognition of 5-aminolevulinate synthase by the human mitochondrial molecular chaperone ClpX. | ENSMUSG00000032786 | Alas1 | 1736.288601 | 1.1230221 | 0.167386329 | 0.04510065 | 13.76938044116 | 0.0002066774721458869217786263883240849281719420105218887329101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00194942985864913413511512185749552372726611793041229248046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1773.627782 | 85.499214 | 1585.689673 | 76.501417 |
| ENSG00000023697 | 51071 | DERA | protein_coding | Q9Y315 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes a reversible aldol reaction between acetaldehyde and D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to generate 2-deoxy-D-ribose 5-phosphate. Participates in stress granule (SG) assembly. May allow ATP production from extracellular deoxyinosine in conditions of energy deprivation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25229427}. | Cytoplasm;Lyase;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Schiff base | PATHWAY: Carbohydrate degradation; 2-deoxy-D-ribose 1-phosphate degradation; D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and acetaldehyde from 2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate: step 2/2. | Enables deoxyribose-phosphate aldolase activity. Involved in deoxyribonucleoside catabolic process. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:51071; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; deoxyribose-phosphate aldolase activity [GO:0004139]; carbohydrate catabolic process [GO:0016052]; deoxyribonucleoside catabolic process [GO:0046121]; deoxyribonucleotide catabolic process [GO:0009264]; deoxyribose phosphate catabolic process [GO:0046386]; pentose-phosphate shunt [GO:0006098] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 32659474_Genetic variants in TKT and DERA in the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate pathway predict melanoma survival. 33067875_A case of pericytic neoplasm in the shoulder with a novel DERA-GLI1 gene fusion. | ENSMUSG00000030225 | Dera | 57.965243 | 1.1738263 | 0.231218892 | 0.20412689 | 1.28129615308 | 0.2576581766141392559887890456593595445156097412109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.48579627638207034667772177272127009928226470947265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 66.833063 | 8.431339 | 56.945205 | 7.181063 |
| ENSG00000025770 | 29781 | NCAPH2 | protein_coding | Q6IBW4 | FUNCTION: Regulatory subunit of the condensin-2 complex, a complex that seems to provide chromosomes with an additional level of organization and rigidity and in establishing mitotic chromosome architecture (PubMed:14532007). May promote the resolution of double-strand DNA catenanes (intertwines) between sister chromatids. Condensin-mediated compaction likely increases tension in catenated sister chromatids, providing directionality for type II topoisomerase-mediated strand exchanges toward chromatid decatenation. Required for decatenation of chromatin bridges at anaphase. Early in neurogenesis, may play an essential role to ensure accurate mitotic chromosome condensation in neuron stem cells, ultimately affecting neuron pool and cortex size (By similarity). Seems to have lineage-specific role in T-cell development (PubMed:14532007). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BSP2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14532007}. | Alternative splicing;Chromosome;DNA condensation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene encodes one of the non-SMC subunits of the condensin II complex. This complex plays an essential role in mitotic chromosome assembly. Alternate splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. | hsa:29781; | cell junction [GO:0030054]; condensed nuclear chromosome [GO:0000794]; condensin complex [GO:0000796]; intercellular bridge [GO:0045171]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; female meiosis chromosome separation [GO:0051309]; meiotic chromosome condensation [GO:0010032]; mitotic chromosome condensation [GO:0007076]; mitotic sister chromatid separation [GO:0051306]; positive regulation of chromosome condensation [GO:1905821]; positive regulation of chromosome segregation [GO:0051984]; positive regulation of chromosome separation [GO:1905820]; T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033077] | 14532007_The CAP-H2 subunit of the condensin II complex implicated in chromosome assembly and segregation 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 26017022_CAPH2 protein accumulates as cells approach senescence, and knockdown of CAPH2 inhibits senescence. 26742120_DNA methylation in the NCAPH2/LMF2 promoter region is significantly decreased in Alzheimer disease. 27356276_Results suggest that DNA methylation in the NCAPH2/LMF2 promoter region is associated with hippocampal atrophy through apoptosis 28717250_Data found that the abundance of CAP-H2 is increased in mitosis by a Plk1 kinase activity-dependent manner and that inhibition of Plk1 induces a degradation of CAP-H2 through Cdc20-mediated ubiquitin-proteasome machinery. These results suggest that the expression levels of CAP-H2 are regulated by Plk1 and Cdc20 for proper chromosomal organization during mitosis. 29028794_Condensin II(CAP-D3 and CAP-H2) and GAIT subunits associate with L1 RNA in a co-dependent manner, independent of IFN-gamma. These findings suggest that cooperation between the Condensin II and GAIT complexes may facilitate a novel mechanism of L1 repression, thus contributing to the maintenance of genome stability in somatic cells 31026066_NCAPH2 promotes telomere stability, possibly through a direct interaction with the TRF1 shelterin component 33078399_Cancer-associated mutations in the condensin II subunit CAPH2 cause genomic instability through telomere dysfunction and anaphase chromosome bridges. 34768935_OCT1 Is a Poor Prognostic Factor for Breast Cancer Patients and Promotes Cell Proliferation via Inducing NCAPH. | ENSMUSG00000008690 | Ncaph2 | 230.179142 | 0.8532669 | -0.228930928 | 0.12025542 | 3.62206138876 | 0.0570181833491013034809213877451838925480842590332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.18007910333872861885495808564883191138505935668945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 212.604373 | 25.662843 | 249.390312 | 29.739529 | |
| ENSG00000027697 | 3459 | IFNGR1 | protein_coding | P15260 | FUNCTION: Receptor subunit for interferon gamma/INFG that plays crucial roles in antimicrobial, antiviral, and antitumor responses by activating effector immune cells and enhancing antigen presentation (PubMed:20015550). Associates with transmembrane accessory factor IFNGR2 to form a functional receptor (PubMed:7615558, PubMed:2971451, PubMed:7617032, PubMed:10986460, PubMed:7673114). Upon ligand binding, the intracellular domain of IFNGR1 opens out to allow association of downstream signaling components JAK1 and JAK2. In turn, activated JAK1 phosphorylates IFNGR1 to form a docking site for STAT1. Subsequent phosphorylation of STAT1 leads to dimerization, translocation to the nucleus, and stimulation of target gene transcription (PubMed:28883123). STAT3 can also be activated in a similar manner although activation seems weaker. IFNGR1 intracellular domain phosphorylation also provides a docking site for SOCS1 that regulates the JAK-STAT pathway by competing with STAT1 binding to IFNGR1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P15261, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10986460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20015550, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28883123, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2971451, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7615558, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7617032, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7673114}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation | This gene (IFNGR1) encodes the ligand-binding chain (alpha) of the gamma interferon receptor. Human interferon-gamma receptor is a heterodimer of IFNGR1 and IFNGR2. A genetic variation in IFNGR1 is associated with susceptibility to Helicobacter pylori infection. In addition, defects in IFNGR1 are a cause of mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease, also known as familial disseminated atypical mycobacterial infection. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:3459; | plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; type II interferon receptor activity [GO:0004906]; astrocyte activation [GO:0048143]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; microglial cell activation [GO:0001774]; negative regulation of amyloid-beta clearance [GO:1900222]; positive regulation of amyloid-beta formation [GO:1902004]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060333] | 11240951_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11857344_IL-12R beta 1- and IFN-gamma R1 signals co-ordinately regulate IFN-gamma production, but only IL-12 negatively controls IL-4 production. IL-12 and IFN-gamma signals are each sufficient for IFN-gamma production but both are needed for optimal production. 11865431_partial IFNGR1 mutations in Japanese patients with BCG osteomyelitis 12020266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12023780_IFNGR1 gene promoter polymorphisms may be assocaited with susceptibility to cerebral malaria 12023780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12027427_Mutations in interferon-gamma receptor 1. 12034035_This study identified a further role of IFN-gamma on IL-4 responses, including reduced IL-4R surface expression by human monocytes. 12165521_Lipid microdomains are required sites for the selective endocytosis and nuclear translocation of IFN-gamma receptor-1. 12244188_Partial deficiency of IFN-gamma receptor 1 results in abrogation of IFN-gamma-induced killing of Salmonella typhimurium and Toxoplasma gondii due to IFN-gamma unresponsiveness of patients' cells of the monocyte/macrophage lineage. 12438563_FRET was used to demonstrate that the IFNGR chains were preassembled on the cell membrane. 12454749_suppressed by 2- to 3-fold in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells, which is expected to increase CLL cell survival 12516030_Genome analysis identified polymorphism in the human interferon gamma receptor affecting Helicobacter pylori infection. 12543882_MHC Class II proteins, interferon-alpha, interferon-gamma receptor and the capacity to present antigen may be crucial in HIV-associated nephropathy pathogenesis. 12743658_Mutations have no association with the susceptibility to lepromatous leprosy in the Korean population. 12743658_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12753505_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12753505_Unidentified allelic variations in the IFNGR1 gene might elevate or decrease the risk in the Croatian population, as a part of the multigenic predisposition to tuberculosis. 12851715_In this study, although IFN-gamma production in the allergic patients with L467P was equivalent to that in the non-allergic subjects, their serum IgE levels were high and they had allergic diseases 12851715_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14734726_IFN-gamma receptor deficiency alters the epitope hierarchy of the pool of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-specific memory CD8 T cells without significantly affecting the immunodominance of the primary CD8 T cell response in an acute infection. 14763782_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15004750_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15047947_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15182327_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15207788_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15527154_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15756299_disease susceptibility in Schistosoma mansoni infection to hepatic fibrosis is linked to a SNP in the interferon gamma receptor locus (P=0.000001). 15952126_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15952126_The IFN-GammaR2 Arg64/Arg64 genotype does not determine susceptibility to SLE in Chinese people, and the combination of IFN-Gamma R2 Arg64/Arg64 genotype and IFN-Gamma R1 Val14/Val14 genotype does not, either. 16115485_IFNG T874A, IFNGR1 C-56T and IFNGR2 A839G genotypes were not associated with the incidence of angiographic and clinical restenosis (P>0.23). 16115485_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16233916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16233916_The relationship between polymorphisms at IFNGR1 and susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis is reported in Iranian patients. 16476014_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16491350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16563189_IFNGR1 does not contribute to susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in Caucasians, although a single nucleotide polymorphisms exist in this disease. 16563189_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16690980_Novel tuberculosis association was found with the 56CC genotype of the IFNGR1 promotor. 16690980_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16785527_Interferon (IFN)-gamma and its receptor subunit IFNGR1 bind to the IFN-gamma-activated sequence (GAS) response element in the promoter region of IFN-gamma-activated genes. This binding results in enhanced activation of IFN-gamma-induced genes. 16867043_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16944293_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16944293_no statistically significant association with susceptibility to persistent HBV infection was observed with the IFN-gamma, IFNGR-1 and 2, and IRF-1 gene polymorphisms under the codominant, dominant, and recessive models 17023216_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17030574_Infection of HEK 293 cells with C. psittaci increased IFN-gammaR expression only in cells expressing either TLR2 or TLR4 and the adaptor protein MD-2. 17136124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17136124_The results suggest a complex pattern of haplotypic variation at the IFNGR1 promoter locus associated with post-kala-azar dermal leishmanaisis susceptibility. 17152005_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17166914_The K3 and K5 proteins of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) both specifically target IFN-gammaR1 and induce its ubiquitination, endocytosis, and degradation. 17251453_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17251453_The -56T allele in the IFNGR1 promoter results in higher IFNGR1 transcriptional activity and represents a genetic risk factor for atopic cataracts. 17339358_expression downregulated by Mycobacterium tuberculosis in human cells as immune evasion mechanism. 17348823_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17392024_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17431682_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17431682_analyzed candidate genes related to TNFalpha regulation and found that interleukin (IL)-10, interferon-gamma receptor 1 (IFNGR1), and TNFalpha receptor 1 (TNFR1) genes were linked and associated to both tuberculosis and TNFalpha 17477815_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17513528_A deletion in this receptor produces a truncated form of IFNgammaR1, which has a dominant-negative effect on IFNgamma signal transduction through altered receptor stability. 17546485_Variation in transcriptional activity of genes encoding INF-gamma receptor subunits may affect function of microvasculature and thereby participate in the pathology of cardiac syndrome X 17572155_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17618444_IFNGR polymorphisms (Val14Met and Gln64Arg) are protective in systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese patients 17618444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17697357_expressed IFNgamma and IFNgamma-Ralpha together with the nuclear localization of IFNgamma-Rbeta, could be a tumoral cell response 17986123_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17986123_The IFN-gamma receptor 1 gene polymorphism does not appear to be responsible for host susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis in the Korean population. 18287876_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18414508_Frequent mutations in microsatellite-instable (MSI-H) tumours and cell lines of a conserved A14 repeat within the 3'-untranslated region of the interferon-gamma receptor 1 gene (IFNGR1). 18548239_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18548239_The polymorphisms in the IFNG and IFNGR1 genes were studied with the aim of clarifying the relationships among these polymorphisms, penicillin allergy and anti-penicillin antibodies. 18555234_Regulation of the IFN-gamma R and its signaling response in human endometrial stromal cells during decidualization. 18593809_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18593809_results indicate that the IFNGR1 -56C/T polymorphism is a relevant host susceptibility factor for Gastric Carcinoma development. 18620489_with progression of HIV-1 infection, interferon-gamma production declines whereas expression of interferon-gamma receptors (R1 and R2) increases 18633131_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18702743_allele (CA)(25)of the interferon gamma receptor 1 gene appeared to be susceptible to TB, while the allele (CA)(26) was protective towards TB 18809513_The urine evaluation of the balance between IFN-gammaR1 and IL4R receptors might be informative for the immune states of HUS patients. 18931463_Finds lack of association between functional polymorphisms in intron 1 of IFN-gamma gene at position +874 and silicosis and pulmonary tuberculosis in Chinese iron miners 18953482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19141860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19172849_the transcriptional of IFNgRb/IFNgRa in the heart bioptates appeared to be an early and sensitive marker of inflammatory status of patients with myocarditis 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19269302_Results show a significant down regulation in expression of the alpha-chain of the IFN-gamma receptor on surfaces of alveolar macrophages acquired from smokers when compared with non-smokers. 19279332_Tat impaired the IFNgamma-receptor signaling pathway at the level of STAT1 activation, possibly via Tat-dependent induction of SOCS-2 activity. 19488747_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19488747_Results show that that a functional -56C/T SNP in IFNGR1 promoter is associated with the clinical outcome of HBV infection in this Chinese population. 19575238_Strong association with this gene and pulmonary tuberculosis susceptibility in African Americans. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19681704_The interleukin-12/interferon-gamma axis appears to be critical for control of coccidioidomycosis and mycobacteriosis in interferon-gamma receptor 1 deficiency with a IFNGR1 mutation 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19712753_A case-control association analysis failed to detect significant association between the IFNGR1 polymorphisms and cerebral malaria in the Thai population 19723394_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19734231_A putative SOCS-1 binding site, tyrosine 441 on IFN-gamma receptor subunit 1, contributes to the regulation of interferon-gamma signaling through recruitment of SOCS-1 in wild-type but not mutant cells. 19739012_The urinary soluble IFN-gamma receptor levels did not correlate with the clinical severity of vesicoureteral reflux 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20015550_Functional analysis of naturally occurring amino acid substitutions in human IFN-gammaR1. 20055726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20070287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20070287_study showed a positive association between -56C/C genotype of IFNGR1 (OR = 1.7; 95% CI = 1.1-2.7) and pre-eclampsia. 20196868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20399512_Clinical trial of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20412699_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20412699_results do not show an implication of IFNGR1gene polymorphisms in the susceptibility to and clinical expression of giant cell arteritis 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20500698_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20588308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20799037_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20959405_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20980339_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21190998_IL-29 up-regulated, whereas IFNalpha down-regulated, the surface expression of the IFNgamma receptor 1 chain on macrophages, thereby resulting in differential responsiveness of TLR-challenged macrophages to IFNgamma. 21221749_The Japanese patients with a genetic mutation in the IFN-gamma-R1 gene were more susceptible to developing recurrent disseminated mycobacterial infections. 21460021_The autosomal recessive disorder, because of a single mutation in interferon-gamma receptor-1(IFNGR1) at position -56, was found to be associated with susceptibility to leprosy in children of the same family. 21722521_CD74 gene over-expression in TEC can increase IFN-gammaR mRNA expression 21731057_IFNGR1 is a modifier gene of cystic fibrosis disease. 21859832_Single nucleotide polymorphism in IFNGR1 gene is associated with rectal cancer. 22564607_Monocyte-derived CD40 expression is regulated by interferon-gamma/interferon-gamma receptor-1 pathway when acting as a bridge during their interaction with T cells and allogeneic endothelial cells. 22595141_A novel endocytosis motif shares characteristics of tyrosine-based and dileucine-based internalization sequences and is highly conserved in IFN-gamma receptors across species. 22644879_Interaction of IFNgammaR1 with TRAF6 regulates NF-kappaB activation and IFNlambdaR1 stability. 22711893_Absence of early innate IFN-gamma production in transgenic mice with combined defects in both IL-12 and type I IFN receptor negates the impact of programmed death ligand-1 blockade. 23040881_An association study of functional polymorphic genes .... IFNGR-1, ...... with disease progression, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, and viral load in chronic hepatitis B and C. 23935197_These data suggest that type I IFN stimulation induces a rapid recruitment of a repressive Egr3/Nab1 complex that silences transcription from the ifngr1 promoter. 24199198_Increasing affinity of interferon-gamma receptor 1 to interferon-gamma by computer-aided design. 24220318_A novel heterozygous frameshift mutation (805delT) encoding the IFN-gamma receptor 1 (IFNGR1) was identified, presenting in a case of Mycobacterium intracellulare infection. 24254535_Intact IFN-gammaR1 expression and function distinguishes Langerhans cell histiocytosis from mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease. 24453034_work aimed to evaluate single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of IFNGR1, GSTT1, and GSTP1 genes samples in gastric cancer 24680779_Genetic polymorphisms in IFNGR1 gene are involved in the risk of tuberculosis in the Chinese population. 25108563_FcgammaRIIa cross-talk with TLRs, IL-1R, and IFNgammaR selectively modulates cytokine production in human myeloid cells. 25242146_The study identifies a mechanism of cellular signaling regulated by extracellular vesicles -associated IFN-gamma/Ifngr1 complexes, which grafted stem cells may use to communicate with the host immune system. 25382336_The study did not provide enough powerful evidence to identify a significant association between IFNGR1 -56C/T polymorphism and tuberculosis susceptibility (meta-analysis). 25466928_Uniformly low expression of IFN and IFNGR1 in post Kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis skin biopsies could explain parasite persistence and is consistent with prior demonstration of genetic association with IFNGR1 polymorphisms. 25708927_In an African-American population, a significant difference in IFNGR1 expression between patients with RA and controls. However, IFNGR1 expression levels were not statistically significantly associated with erosion status or other radiographic outcomes. 25815589_Statistical analyses revealed that four genetic variants in IFNGR1 were marginally associated with the risk of Tuberculosis (P = 0.02-0.04), while other single nucleotide polymorphisms in IFNGR1 and IFNGR2 did not exhibit any associations 26251056_Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacteria due to a partial dominant mutation of the interferon gamma receptor 1 gene. 26343451_Targeted deep sequencing identifies rare loss-of-function variants in IFNGR1 for risk of atopic dermatitis complicated by eczema herpeticum 26931784_The deletion of IFNGR1 causes complete IFN-gammaR1 deficiency. Despite the deletion ending very close to the IL22RA2 gene, it does not appear to affect IL22RA2 transcription. 27020872_A significant association of IFN-gammaR1 and P2X7 genes polymorphisms with risk of developing TB in Iranian population. 27069113_B cell type 1 IFN receptor signals accelerate, but are not required for, lupus development. 27356097_All patients tested were positive for mycobacteria; one was heterozygous for the IFNGR1 exon 5 single-nucleotide-missense substitution 27941164_the cause of active TB in the patients seems to be due to the lack of effective IFNgamma function or the lack of effective signaling connection between IFNgamma and its receptor in presence of -56 C/T polymorphism in promoter region of IFNgammaR1 gene 28652404_Data suggest IFNG plays various roles in dynamics of inflammation in subjects with underlying autoimmunity modeled as 'canonical' and 'non-canonical' pathways; in canonical pathway, IFNG dimerizes and binds to IFNGR1 in IFNGR1/IFNGR2 hetero-multimer; STAT transcription factors are involved in non-canonical pathway. (IFNG = interferon gamma; IFNGR = IFNG receptor; STAT = signal transducers and activators of transcription) 28719321_results showed a significant correlation between IFNGR1- T-56CSNP and Nontuberculous mycobacteria infection among studied populations 28744922_All known mutations, as well as 287 other variations, have been deposited in the online IFNGR1 variation database . In this article, we review the function of IFN-gammaR1 and molecular genetics of human IFNGR1. 29209098_Positive reaction in interferon-gamma release tests is not associated with IFNGR1 SNPs. 29249666_Impaired IFNgamma-Signaling and Mycobacterial Clearance in IFNgammaR1-Deficient Human iPSC-Derived Macrophages. 29343571_cellular kinase, casein kinase 1alpha (CK1alpha), is crucial for IAV HA-induced degradation of both IFNGR1 and IFNAR1. 29441481_discovered that a rare variant c.G40A in interferon gamma receptor 1 potentially contributes to the myasthenia gravis pathogenesis 29516882_The two genetic variants were found to have potential risk in association with active disease development among Sudanese patients. 31310896_Genetic variants in IFNG and IFNGR1 and tuberculosis susceptibility. 31585982_Data data demonstrate that there are multiple mechanisms by which IFNGR1 availability is regulated in myeloid cells, which is counter to the accepted dogma that IFNGR is constitutively expressed. 31687049_IFNG and IFNGR1 polymorphisms are associated with latent tuberculosis infection 31760574_Mutual alteration of NOD2-associated Blau syndrome and IFNgammaR1 deficiency. 32271156_Regulation of Interferon-gamma receptor (IFN-gammaR) expression in macrophages during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. 32284542_A negative correlation between ELF5, FBXW7 and IFNGR1 expression in the tumours of patients with TNBC. 32770644_Risk factors for recurrence of Helicobacter pylori infection after successful eradication in Chinese children: A prospective, nested case-control study. 33017569_Promoting effect of long non-coding RNA SNHG1 on osteogenic differentiation of fibroblastic cells from the posterior longitudinal ligament by the microRNA-320b/IFNGR1 network. 33393726_Genetic Association of a Gain-of-Function IFNGR1 Polymorphism and the Intergenic Region LNCAROD/DKK1 With Behcet's Disease. 33501617_Complete IFN-gammaR1 Deficiency in a Boy Due to UPD(6)mat with IFNGR1 Novel Splicing Variant. 33667716_Paraspeckle Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immune Escape by Sequestering IFNGR1 mRNA. 34148879_PD_BiBIM: Biclustering-based biomarker identification in ESCC microarray data. 34181338_Predictive Value of Interferon gamma Receptor Gene Polymorphisms for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Susceptibility. 34646402_Genetic Polymorphisms of IFNG, IFNGR1, and Androgen Receptor and Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome in a Chinese Han Population. 35074548_Early diagnosis of partial interferon-gamma receptor 1 deficiency prevents the development of Bacille de Calmette et Guerin osteomyelitis. 35918221_Genetic Variations in IFNGR1, BDNF and IL-10 May Predict the Susceptibility to Depression and Anxiety in Chinese Women With Breast Cancer. 36148347_Association between IFNGR1 gene polymorphisms and tuberculosis susceptibility: A meta-analysis. 36260452_Correlation of single-nucleotide polymorphism at interferon-gamma R1 (at Position - 56) in positive purified protein derivative health workers with COVID-19 infection. | ENSMUSG00000020009 | Ifngr1 | 4570.781720 | 1.7708659 | 0.824454999 | 0.02482381 | 1106.38738644572 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000135091 | 0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001259769 | No | Yes | 5794.472054 | 70.454929 | 3287.584274 | 43.546348 | |
| ENSG00000028310 | 65980 | BRD9 | protein_coding | Q9H8M2 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in chromatin remodeling and regulation of transcription (PubMed:22464331, PubMed:26365797). Acts as a chromatin reader that recognizes and binds acylated histones: binds histones that are acetylated and/or butyrylated (PubMed:26365797). Component of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling subcomplex GBAF that carries out key enzymatic activities, changing chromatin structure by altering DNA-histone contacts within a nucleosome in an ATP-dependent manner (PubMed:29374058). Orchestrates also the RAD51-RAD54 complex formation and thereby plays a role in homologous recombination (HR) (PubMed:32457312). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22464331, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26365797, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29374058, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32457312}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Bromodomain;Chromatin regulator;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation | Enables lysine-acetylated histone binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nucleoplasm. Part of SWI/SNF complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:65980; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; GBAF complex [GO:0140288]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; SWI/SNF complex [GO:0016514]; lysine-acetylated histone binding [GO:0070577]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; negative regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045596]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance [GO:1902459]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26365797_The bromodomains of BRD9, CECR2, and the second bromodomain of TAF1 recognize the longer butyryl mark on histones. In addition, the TAF1 second bromodomain is capable of binding crotonyl marks. 30431433_BRD9 supports oncogenic mechanisms underlying the SS18-SSX fusion in synovial sarcoma. 30660651_miR-140-3p inhibited squamous cell lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion in vitro and in vivo by targeting BRD9 expression. 31000582_Synergistic inhibition of BDs encoded in BAZ2A/B, BRD9, and BET proteins induces apoptosis of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) by a combinatorial suppression of ribosomal DNA transcription and ETS-regulated genes. 31000698_BRD9 is overexpressed in acute myeloid leukemia cells including ex vivo primary blasts compared with CD34(+) cells. By targeting BRD9 expression in AML, we observed an alteration in proliferation and survival, ultimately resulting in the induction of apoptosis. 31015438_Study results demonstrate that mutation of SMARCB1 in malignant rhabdoid tumors (RTs) results in a specific dependence upon a BRD9-SWI/SNF complex that lacks SMARCB1. While BRD9 bromodomain is dispensable, the DUF3512 domain of BRD9 is essential for SWI/SNF integrity survival of SMARCB1-mutant RTs. 31504061_oncogenic roles in human cancers 32276436_High-Throughput Sequencing Identifies 3 Novel Susceptibility Genes for Hereditary Melanoma. 32457312_The bromodomain containing protein BRD-9 orchestrates RAD51-RAD54 complex formation and regulates homologous recombination-mediated repair. 33355184_BRD9 Is a Critical Regulator of Androgen Receptor Signaling and Prostate Cancer Progression. 34370992_Bromodomain-containing protein 9 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via activating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 34415102_Bromodomain-containing protein 9 is a prognostic biomarker associated with immune infiltrates and promotes tumor malignancy through activating notch signaling pathway in negative HIF-2alpha clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 34667163_BRD9 inhibition promotes PUMA-dependent apoptosis and augments the effect of imatinib in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 34944438_Exploring the Value of BRD9 as a Biomarker, Therapeutic Target and Co-Target in Prostate Cancer. 34983841_BRD9 regulates interferon-stimulated genes during macrophage activation via cooperation with BET protein BRD4. 35853853_BRD9 degraders as chemosensitizers in acute leukemia and multiple myeloma. 35883603_The Functional Role and Regulatory Mechanism of Bromodomain-Containing Protein 9 in Human Uterine Leiomyosarcoma. 36100643_Ultra-Rare BRD9 Loss-of-Function Variants Limit the Antiviral Action of Interferon. | ENSMUSG00000057649 | Brd9 | 357.169438 | 0.8290207 | -0.270520043 | 0.15990015 | 2.85693253121 | 0.0909808452380009291537987792253261432051658630371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.24824397086663196887457161210477352142333984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 326.698977 | 31.887481 | 395.960967 | 38.427361 | |
| ENSG00000033800 | 8554 | PIAS1 | protein_coding | O75925 | FUNCTION: Functions as an E3-type small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) ligase, stabilizing the interaction between UBE2I and the substrate, and as a SUMO-tethering factor. Plays a crucial role as a transcriptional coregulation in various cellular pathways, including the STAT pathway, the p53 pathway and the steroid hormone signaling pathway. In vitro, binds A/T-rich DNA. The effects of this transcriptional coregulation, transactivation or silencing, may vary depending upon the biological context. Sumoylates PML (at'Lys-65' and 'Lys-160') and PML-RAR and promotes their ubiquitin-mediated degradation. PIAS1-mediated sumoylation of PML promotes its interaction with CSNK2A1/CK2 which in turn promotes PML phosphorylation and degradation (By similarity). Enhances the sumoylation of MTA1 and may participate in its paralog-selective sumoylation. Plays a dynamic role in adipogenesis by promoting the SUMOylation and degradation of CEBPB (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O88907, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14500712, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21965678}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Restricts Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) lytic replication by acting as an inhibitor for transcription factors involved in lytic gene expression (PubMed:29262325). The virus can use apoptotic caspases to antagonize PIAS1-mediated restriction and express its lytic genes (PubMed:29262325). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29262325}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein sumoylation. | This gene encodes a member of the protein inhibitor of activated STAT (PIAS) family. PIAS proteins function as SUMO E3 ligases and play important roles in many cellular processes by mediating the sumoylation of target proteins. This protein plays a central role as a transcriptional coregulator of numerous cellular pathways includign the STAT1 and nuclear factor kappaB pathways. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. | hsa:8554; | nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PML body [GO:0016605]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; SUMO ligase activity [GO:0061665]; SUMO transferase activity [GO:0019789]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; positive regulation of protein sumoylation [GO:0033235]; protein sumoylation [GO:0016925]; receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0007259]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 11451946_novel function of PIAS1 in the induction of JNK-dependent apoptosis, independent of the previously known inhibitory activity of PIAS1 in STAT-mediated gene activation. 11788578_protein inhibitor of activated Stat1 (PIAS1) interacts with the tetramerization and C-terminal regulatory domains of p53 in yeast two-hybrid analyses 11877418_Protein inhibitors of activated STAT resemble scaffold attachment factors and function as interacting nuclear receptor coregulators. 12177000_PIAS1 and PIASxalpha modulate the AR-dependent transactivation, which, at least in part, can be attributed to their SUMO-E3 activity toward AR. 12393906_PIAS1 has a role in sumoylation of MDM2 in the cell nucleus 12855578_found to strongly stimulate sumoylation of STAT1 at Lys703; results suggest a negative regulatory function for sumoylation. 14500761_PIAS1 interacts with the N-terminal domain of human mineralocorticoid receptor and represses its ligand-dependent transcription. 15133049_three-dimensional structure and its binding duality are discussed in conjunction with the biological functions of PIAS1 as a SUMO ligase 15337742_GATA4 is a SUMO-1-targeted transcription factor and together with PIAS1 is a potent regulator of cardiac gene activity 15572666_PIAS1 is a checkpoint regulator which affects exit from G1 and G2 by sumoylation of p73. 15572677_PIAS1 interacts with DNA cross-link repair SNM1A in nuclear focus formation. 15611122_data support a physiological role of Ubc9 and PIAS1 as transcriptional coactivators in COUP-TFI-mediated CYP11B2 transcription 15901746_Results suggest that recombinant human interleukin-12 upregulates STAT-1 expression and that increased expression may be dose dependent. 16135793_PIAS1 modulates transcriptional activation of smooth muscle cells marker genes through cooperative interactions with both serum response factor and class I basic helix-loop-helix proteins proteins. 16144832_Pias1 binds to and sumoylates metabotropic glutamate receptor 8 16563226_In this study, we demonstrate that MEF2A undergoes sumoylation primarily at a single lysine residue (K395) both in vitro and in vivo. We also show that the nuclear E3 ligase, PIAS1, promotes sumoylation of MEF2A. 16600910_PIAS1 is required for the appropriate localization and retention of Msx1 at the nuclear periphery in myoblast cells. 17371985_TGF-beta rapidly suppresses IFN-gamma-driven STAT1 signaling by reducing DNA binding via promotion of STAT1--PIAS1 interactions and not inhibition of STAT1 activation. 17509614_These results suggest that KyoT2 is a substrate of SUMO modification catalyzed by PIAS1, and that SUMOylation may modulate the transcriptional repression effect of KyoT2 on the Notch/RBP-J signaling pathway [Kyot2]. 17606919_PIASy cooperates with PIAS1 to down-regulate the specificity and magnitude of NF-kappa B/STAT1-mediated gene activation. 17934332_the transcriptional repressor activity of ZNF133 is regulated by both the KRAB domain and the zinc finger motifs, and that the repressive effect by zinc finger motifs is mediated by PIAS1 18190974_The data show that HCV NS3/4a is able to block the Jak-Stat signaling pathway at the stage of Stat-1 serine 727 phosphorylation. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19288270_PIAS1 staining of the colon cancer tissue microarrays indicated a strong correlation of normal colon cells, and adenomas, with high expression of both PIAS1 and IRF-1 19604093_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20209145_FOXL2 interacts with PIAS1 and UBC9, and sumoylated in both human and mouse 20351170_Data show that regulation of SATB1 sumoylation and caspase cleavage is controlled by SATB1 phosphorylation; specifically, PIAS1 interaction with SATB1 is inhibited by phosphorylation. 20711444_Pias1-dependent SUMOylation influences Gli protein activity 21338522_PIAS1 is a common partner for two cancer-related nuclear factors, c-Myb and FLASH. 21467194_Ubc9 and PIAS1 potentiated SF-1-mediated transactivation of human CYP17, CYP11A1, and CYP11B1 but not CYP11B2 promoters. 21676946_PIAS1 determines the level of JNK activity in human endometrial stromal cells , couples ROS signaling to the SUMO pathway, and promotes oxidative cell death. 21717107_PIAS1 negatively regulates ubiquitination of Msx1 homeoprotein independent of its SUMO ligase activity. 21925039_There are differences in the PIAS3 expression from different stages of gastric precancerous conditions/lesions to GC, which may reveal a close relationship between expression reduction or loss of PIAS3 and gastric tumorigenesis. 22283414_PIAS1 promotes SUMOylation of AIB1 and represses its transcriptional activity. 22449952_The data reveal an important new role for PIAS1 in the regulation of cell proliferation in prostate cancer. 22539995_PIAS1 is a SUMO ligase for GATA4 that differentially regulates GATA4 transcriptional activity independent of SUMO ligase activity and GATA4 sumoylation. 22972521_data suggest that PIAS1 may function as a tumor suppressor to regulate gastric cancer cell metastasis by targeting the MAPK signaling pathway 22976298_Data suggest that the pro-apoptotic protein Daxx specifically interacts with one or more substrates SUMOylated by PIAS1 and this interaction leads to apoptosis following UV irradiation. 23202365_MAPK-activated protein kinase-2 limits endothelial inflammation via the PIAS1 S522 phosphorylation-mediated increase in PIAS1 transrepression and SUMO ligase activity. 23472246_Levels of STAT1 andor the protein expression of its negative regulators, PIAS1 and SOCS3, may be a good predictor of hepatitis C virus response to therapy 24036127_Further study indicated that PIAS1 interacted with IRF3 and inhibited the DNA binding activity of IRF3. 24052079_Smad2 and PIAS1 proteins were significantly upregulated resulting in dramatically increased interactions between Smad2/4 and PIAS1 in the presence of zinc. 24174529_Phosphorylation of serine residues adjacent to the PIAS1 SUMO-interacting motif favors formation of the non covalent PIAS1.SUMO.UBC9 ternary complex 24586797_Elevated PIAS1 expression was observed in breast tumor samples. 24872413_PIAS1 is the E3 ligase responsible for SUMOylation of HMGN2. 24911587_Our data suggest that necdin suppresses PIAS1 both by inhibiting SUMO E3 ligase activity and by promoting ubiquitin-dependent degradation. 25474038_the presented data indicate that PIAS1 is crucial for parental and docetaxel resistant prostate cancer cell survival 25895136_c-Myc is targeted to the proteasome for degradation in a SUMOylation-dependent manner, regulated by PIAS1, SENP7 and RNF4 26219822_Results show that apocrine breast cancer and prostate cancer cells share a core AR cistrome and target gene signature linked to cancer cell growth, and PIAS1 plays a similar coregulatory role for AR in both cancer cell types. 26257066_PIAS1 is a determinant of poor survival and acts as a positive feedback regulator of AR signaling through enhanced AR stabilization in prostate cancer 26403403_the expression of SENP8, SAE1, PIAS1, PIAS2 and ZMIZ1 is deregulated in the majority of PTC tissues, likely contributing to the PTC phenotype. 26450775_Data demonstrate that PIAS1 interacts with TRF2 and mediates its sumoylation serving as a molecular switch that controls the level of TRF2 at telomeres. 27032383_PIAS1 enhances p300 recruitment to c-Myb-bound sites through interaction with both proteins. In addition, the E3 activity of PIAS1 enhances further its coactivation 27099310_identified the SUMO ligase PIAS1 as a constituent PML-NB antiviral protein. This finding distinguishes a SUMO ligase that may mediate signaling events important in promyelocytic leukemia nuclear body mediated intrinsic immunity. 27146268_PIAS1 overexpression exacerbated mutant Huntingtin-associated phenotypes and aberrant protein accumulation 27239040_these results indicate that PIAS1 is a positive regulator of MYC. 27276529_HBs protein-induced hPIAS1 transcription requires TAL1, E47, MYOG, NFI, and MAPK signal pathways 27811911_Rad18, independently of its ubiquitin ligase activity, promotes DNA polymerase eta SUMOylation by facilitating its interaction with its SUMO ligase PIAS1 and is required for DNA polymerase eta function at difficult to replicate loci. 28493978_PIAS1 is a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer 29262325_PIAS1 as a key regulator of Epstein-Barr Virus lytic replication. PIAS1 acts as an inhibitor for transcription factors involved in lytic gene expression. 29848755_A novel function of p14ARF to inhibit PIAS1 by enhancing SUMOylation. 30419807_These findings demonstrate the crucial role of PIAS1-mediated PPARgamma SUMOylation in protecting against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. 30861611_PIAS genes as disease markers in bipolar disorder. 31084243_PIAS1expression of PIAS1 gene was increased in patients with MS compared to healthy subjects; also, there was a significant correlation between the expression of PIAS1 and PIAS2 genes with disease severity of multiple sclerosis 31752909_The SUMO3 modification of PIAS1 is also required for androgen receptor ubiquitination and degradation by recruiting ubiquitin E3 ligase MDM2. 31870601_The current investigation highlights the role of PIAS1 downregulation in the evolution of graft rejection and potentiates this gene as a predictive marker for transplant fate. 32047143_The small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) protein is an ubiquitin-like (UBL) protein that is highly dynamic and can reversibly target lysine residues on a wide range of proteins involved in several essential cellular events, including protein translocation and degradation.Quantitative SUMO proteomics identifies PIAS1 substrates involved in cell migration and motility. 32493705_Novel Variants of ELP2 and PIAS1 in the Interferon Gamma Signaling Pathway Are Associated with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Survival. 32770107_PIAS1 and TIF1gamma collaborate to promote SnoN SUMOylation and suppression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 33468657_PIAS1 modulates striatal transcription, DNA damage repair, and SUMOylation with relevance to Huntington's disease. 33759814_Functional genomics study of protein inhibitor of activated STAT1 in mouse hippocampal neuronal cells revealed by RNA sequencing. 33763841_Expression of PIAS Genes in Migraine Patients. 34537242_Linking nuclear matrix-localized PIAS1 to chromatin SUMOylation via direct binding of histones H3 and H2A.Z. 34951052_A PIAS1 Protective Variant S510G Delays polyQ Disease Onset by Modifying Protein Homeostasis. 35007836_Roles of the SUMO-related enzymes, PIAS1, PIAS4, and RNF4, in DNA double-strand break repair by homologous recombination. 36050397_Crosstalk between SUMOylation and ubiquitylation controls DNA end resection by maintaining MRE11 homeostasis on chromatin. | ENSMUSG00000032405 | Pias1 | 390.645748 | 0.8473572 | -0.238957779 | 0.14209015 | 2.82174694075 | 0.0929951402130694687597767256193037610501050949096679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.25219387772400458924693111839587800204753875732421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 384.269944 | 46.405129 | 455.608252 | 55.026895 |
| ENSG00000035664 | 23604 | DAPK2 | protein_coding | Q9UIK4 | FUNCTION: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine/threonine kinase involved in multiple cellular signaling pathways that trigger cell survival, apoptosis, and autophagy. Regulates both type I apoptotic and type II autophagic cell death signals, depending on the cellular setting. The former is caspase-dependent, while the latter is caspase-independent and is characterized by the accumulation of autophagic vesicles. Acts as a mediator of anoikis and a suppressor of beta-catenin-dependent anchorage-independent growth of malignant epithelial cells. May play a role in granulocytic maturation (PubMed:17347302). Regulates granulocytic motility by controlling cell spreading and polarization (PubMed:24163421). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17347302, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24163421, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26047703}.; FUNCTION: Isoform 2 is not regulated by calmodulin. It can phosphorylate MYL9. It can induce membrane blebbing and autophagic cell death. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;ATP-binding;Calmodulin-binding;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase | This gene encodes a protein that belongs to the serine/threonine protein kinase family. This protein contains a N-terminal protein kinase domain followed by a conserved calmodulin-binding domain with significant similarity to that of death-associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1), a positive regulator of programmed cell death. Overexpression of this gene was shown to induce cell apoptosis. It uses multiple polyadenylation sites. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:23604; | autophagosome lumen [GO:0034423]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; anoikis [GO:0043276]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of eosinophil chemotaxis [GO:2000424]; positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090023]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of autophagy [GO:0010506]; regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001242] | 11839660_High frequency of promoter hypermethylation of the death-associated protein-kinase gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its detection in the peripheral blood of patients 11839665_distinct methylation pattern in bladder cancer with frequent methylation of RARbeta, DAPK, E-cadherin, and p16. 12087472_gene expression in colorectal and gastric cancer silenced by DNA methylation and histone deacetylation 17347302_Results implicate a novel role for DAPK2 in the regulation of normal myelopoiesis. 18521079_DAPK2 as a novel Sp1-dependent target gene for E2F1 and KLF6 in cell death response. 18957423_beta-catenin-induced down-regulation of DAPk-2 represents a novel signaling mechanism by which beta-catenin promotes the survival of malignant epithelial cells 19221469_Results showed that the inactivation of RASSF1A, RARbeta2 and DAP-Kinase by hypermethylation is a key step in NPC tumorigenesis and progression. 21408167_DRP-1 and ZIPk most likely evolved from their ancient ancestor gene DAPk by two gene duplication events that occurred close to the emergence of vertebrates 22160140_Sodium butyrate induced DAPK1/2 expression in human gastric cancer cells and this expression prompted apoptosis by decreasing FAK levels. 23700042_DAPK2 is upregulated in uterosacral ligaments in pelvic organ prolapse 24038216_The tumor suppressor gene DAPK2 is induced by the myeloid transcription factors PU.1 and C/EBPalpha during granulocytic differentiation but repressed by PML-RARalpha in APL. 24163421_The defect in chemotaxis in DAPK2-inactive granulocytes is likely a result of reduced polarization of the cells, mediated by a lack of MLC phosphorylation, resulting in radial F-actin and pseudopod formation. 25361081_DAPK2 is a novel kinase of mTORC1 and is a potential new member of this multiprotein complex, modulating mTORC1 activity and autophagy levels under stress and steady-state conditions. 25741596_DAPK2 regulates oxidative stress in cancer cells by preserving mitochondrial function 25982274_miR-520h suppresses Death-associated protein kinase 2 (DAPK2) expression, as restoring DAPK2 abolished miR-520h-promoted drug resistance, and knockdown of DAPK2 mitigated cell death caused by the depletion of miR-520h. 26038578_This study links adipocyte expression of an autophagy-regulating kinase, lysosome-mediated clearance and fat cell lipid accumulation; it demonstrates obesity-related attenuated autophagy in adipocytes, and identifies DAPK2 dependence in this regulation. 26047703_DAPK2-induced apoptosis is negatively regulated by Akt and 14-3-3 proteins. 26483415_that Death-associated protein kinase 2 effector functions are influenced by the protein's subcellular localization 27049921_This study suggests that miR-520g contributes to tumor progression and drug resistance by post-transcriptionally downregulating DAPK2 in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer 27653365_Thyroid hormone promotes selective autophagy via induction of DAPK2-SQSTM1 cascade, which in turn protects hepatocytes from diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatotoxicity or carcinogenesis. 29717115_study reveals a unique calmodulin-independent mechanism for DAPK2 activation, critical to its function as a novel downstream effector of AMPK in autophagy 30243997_remission effect of DAPK2 on placental cell oxidative damage and apoptosis in HDCP via mTOR activation 31116076_The intracellular signaling pathways that lead to Ser289 phosphorylation are mutually-exclusive and different for each kinase. In addition, Ser289 phosphorylation in fact enhances DAPK1 catalytic activity, similar to the effect on DAPK2. Thus, Ser289 phosphorylation activates both DAPK1 and DAPK2, but in response to different intracellular signaling pathways. 32244500_miR-1285-3p Controls Colorectal Cancer Proliferation and Escape from Apoptosis through DAPK2. 34298122_Cigarette smoking induces aberrant N(6)-methyladenosine of DAPK2 to promote non-small cell lung cancer progression by activating NF-kappaB pathway. 34413451_14-3-3 proteins inactivate DAPK2 by promoting its dimerization and protecting key regulatory phosphosites. | ENSMUSG00000032380 | Dapk2 | 92.065693 | 0.5262466 | -0.926189062 | 0.23976336 | 14.72468492532 | 0.0001244067683566588166689526051555958474637009203433990478515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00124745654177271922055658670558386802440509200096130371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 67.755068 | 11.075323 | 128.180060 | 20.758674 | |
| ENSG00000035862 | 7077 | TIMP2 | protein_coding | P16035 | FUNCTION: Complexes with metalloproteinases (such as collagenases) and irreversibly inactivates them by binding to their catalytic zinc cofactor. Known to act on MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-7, MMP-8, MMP-9, MMP-10, MMP-13, MMP-14, MMP-15, MMP-16 and MMP-19. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11710594, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2554304, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2793861}. | 3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Metal-binding;Metalloenzyme inhibitor;Metalloprotease inhibitor;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Zinc | This gene is a member of the TIMP gene family. The proteins encoded by this gene family are natural inhibitors of the matrix metalloproteinases, a group of peptidases involved in degradation of the extracellular matrix. In addition to an inhibitory role against metalloproteinases, the encoded protein has a unique role among TIMP family members in its ability to directly suppress the proliferation of endothelial cells. As a result, the encoded protein may be critical to the maintenance of tissue homeostasis by suppressing the proliferation of quiescent tissues in response to angiogenic factors, and by inhibiting protease activity in tissues undergoing remodelling of the extracellular matrix. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:7077; | collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; metalloendopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0008191]; molecular function inhibitor activity [GO:0140678]; peptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0030414]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; negative regulation of endopeptidase activity [GO:0010951]; negative regulation of membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0051045]; negative regulation of metallopeptidase activity [GO:1905049]; response to cytokine [GO:0034097]; response to hormone [GO:0009725]; response to organic substance [GO:0010033] | 11606052_The growth of the primary melanoma cell lines was stimulated by TIMP-1 and inhibited by TIMP-2. In contrast, the growth of the visceral metastatic melanoma cell line was stimulated by TIMP-2. 11757622_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11912288_TIMP-2 may be involved in the pathogenesis of gestational trophoblastic disease 12147251_role in activating ras proteins 12372458_endometrium from women with endometriosis expressed higher levels of MMP-2 and MT1-MMP and lower levels of TIMP-2 than did endometrium from normal women 12374789_investigation of structural and functional differences between TIMP-4 and TIMP-2 by mutagenesis into C-terminal tails 12406369_This protein is present in normal and azoospermic human semen. 12439941_correlation between expression of MMP-2, TIMP-2 protein and the ratio of MMP-2/TIMP-2 and clinical-pathological parameters of patients with gallbladder carcinoma 12446683_TIMP2 expression is regulated by the ERK/MAPK pathway 12470034_Changes in plasma MMP-2 and TIMP-2 concentrations during cardiopulmonary bypass may play an important role in LV remodeling after cardiac surgery. 12475252_Progress curve analysis of MMP inhibition by TIMP-2 shows that it has lower reactivity with MMPs at less acidic conditions than TIMP-4. 12479097_The over-expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2 may play a key role in invasion and lymph-node metastasis of in squamous carcinoma of the cervix. 12602913_TIMP-2 expression in breast cancer is related to survival. 12614934_TIMP-2 was significantly increased in CSF of Alzheimer's disease and Huntington's disease patients. 12887919_TIMP-2 mediated inhibition of angiogenesis is an MMP-independent mechanism. 12900406_TIMP-2 possesses two distinct types of anti-angiogenic activities which can be uncoupled from each other 12970394_TIMP-2 expression is markedly increased in clear cell carcinoma of the ovary, suggesting a role of TIMP-2 in its unique characteristics among ovarian cancers 12970724_palpable tumours demonstrated significantly more MMP-2 and significantly less MMP-9 expression than nonpalpable tumours 14517716_A bivariate analysis revealed a modest but significant genetic correlation between TIMP-1 and TIMP-2. 14598888_A gradual, time-dependent decline in TIMP-2 mRNA expression was observed in the presence of the synthetic androgen analogue R1881. 14604886_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14605322_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14605322_Our analysis of the entire coding region of TIMP-1, -2, and -3, which are the main inhibitors of metalloproteinase activity in the extracellular matrix, failed to show an association between genetic polymorphisms and an intracranial aneurysm 14654538_TIMP-2 stromal cell expression only was associated with adverse prognosis of urothelial bladder cancer patients. 14661256_effect of titanium, zirconia and alumina ceramics on activity and secretion in human osteoblasts 14710472_Tissue from lateral and medial rectus muscles had different levels of expression of TIMP-1 and 2, MMP-2, and BMP-4, which may underlie different characteristics of these extraocular muscles and may influence wound healing after strabismus surgery. 14712492_TIMP-2 is hypermethylated in human cervical cancer 14744773_MMP-26 was colocalized with MMP-9, TIMP-2, and TIMP-4 in breast cancer cells. 14962256_TIMP-2 is shown to correlate with systemic symptoms in Hodgkin lymphoma 14973177_MMP and TIMP may be involved in the feto-neonatal development and may contribute to the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia and/or intraventricular hemorrhage in critically ill preterm neonates 14983226_MMP-2, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 are downregulated in human orthotopic liver transplantation 15052627_hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy is not caused by point mutations of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 15056834_TIMP-2 correlated negatively with fractional shortening & positively with LV dimension. Changes in the release & activity of TIMP-2 may be associated with the mechanisms responsible for cardiac remodeling in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 15147743_TIMP2 promotes growth of A549 lung cells, accompanied by increase in NF-kappaB activity and downregulation of IkappaBalpha and beta proteins and later increases in Bcl-3, IkappaB, and cyclin D1 proteins. 15193960_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15247230_ERK 1/2- and p38 MAPK-modulated TIMP-2 expression regulates MT1-MMP activity and control TGF-beta1-induced pericellular collagenolysis 15248826_marked difference in MMPs and their inhibitors in the in vitro fertilized women and normally ovulating women 15277439_Plasma levels are increased in type 2 diabetic patients 15308656_analysis of the molecular basis of the inactivity of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 against tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme 15351863_data suggest that the MMP-2/TIMP2 system and an activated extrinsic coagulation pathway could cooperate in conditions of elevated SOX and could influence arterial remodeling resulting in the presence of CVD in haemodialysis patients 15489233_clearance of pro-matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2.tissue inhibitor of MMPs (TIMP-2) complex involves binding to the cell membrane and subsequent low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP)-dependent internalization and degradation 15557756_The expression of MMP-9, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 was lower in the benign and low malignancy ovarian tumors compared with the malignant ones. 15567754_MMP-2 plays an essential role in tumor invasion and metastasis, while TIMP-2 is shown to strongly inhibit cancer invasion and metastasis. 15616792_This study found an up-regulation of TIMP-1, TIMP-2 and MMP-2 RNA in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy muscle. 15628723_Expression in colorectal carcinomas relating to size and invasiveness of the tumor. 15672858_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15691234_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15691353_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15754326_Down-regulation of TIMP-2 is associated with nonsmall cell lung carcinoma 15797648_altered MMP/TIMP ratios in maternal blood during gestational hypertension 15841325_evidence that cell density influences the invasive potential of tumor cells via regulation of MMPs and TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 by AP-1, NF kappa B and CRE transcription factors 15870703_promoter hypermethylation of TIMP-2 is a novel epigenetic event in the pathogenesis of lymphoid malignancies 15944607_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16036783_A decreased activity of TIMP-2 plays a role in inguinal hernia development. 16042227_a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measure of disease activity in multiple sclerosis patients during treatment with rIFNbeta-1a. 16103240_Cardiac expression of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 is significantly increased in chronic pressure-overloaded human hearts compared with controls and is related to the degree of interstitial fibrosis 16142392_TIMP-2 may play an important role in the invasion and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 16142692_Pro-MMP-2 and TIMP-2 levels negatively correlated in herniated discs samples 16237750_With tumor progression and development of heterogeneity, the abnormal expressions of MMP-9, TIMP-2, and E-cadherin or DNA aneuploid rate or high SPF gradually increases, suggesting that they play a crucial role in gastric carcinoma progression 16275157_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16326706_Shp-1 mediates the antiproliferative activity of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 16424893_Results of this study provide evidence that TIMP-2 immunoreactive protein is prognostic in estimation of the aggressive clinical course of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 16425263_The colocalization of EMMPRIN, MT1-MMP and TIMP-2 in human cervical carcinomas seems to be involved in a specific distribution pattern of tumor cell bound MMP-2, which is related with local proteolytic activity. 16429190_TIMP-2 regulates the activity of MMPs in the extracellular matrix. The high frequency of GG genotype in the TIMP-2 gene promoter showed this site was unsuitable for studies of DNA polymorphism-disease associations in the studied population. 16491114_TIMP-2-mediated inhibition of Src kinase activity leads to the signaling switch from Rac1 to Rap1, thereby leading to enhanced RECK expression. 16623785_TIMP-2 reactivity in capillaries and fibroblasts was decreased in congenital diaphragmatic hernia lungs. 16631927_TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 are major serum factors that stimulate the induction of TIMP-1 mRNA in quiescent human gingival fibroblasts (Gin-1 cells) at mid-G1 (6-9 h after serum stimulation) of the cell cycle, but not that of TIMP-2. 16716258_TIMP-2 mediated alteration in cell morphology requires Rap1, TIMP-2 may recruit Rap1 to sites of actin cytoskeleton remodeling necessary for cell spreading, and enhanced cell adhesion by TIMP-2 expression may hinder cell migration 16723886_Presence of a G/C heterozygous genotype at position -418 in TIMP2 promoter could be a genetic predisposing factor for familial moyamoya disease. 16728425_an imbalance between the MMP-2 and TIMP-2, caused primarily by an increase in TIMP-2 activity, contributes to the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. 16772717_Increase in serum levels eight days after IVIG treatment in neuromuscular disease. 16776850_When all three proteases are studied in combination, a tendency was found for tumors with high MMP-2, high MMP-14 and low TIMP-2 expression to predict a poor prognosis but the results did not reach significance 16940985_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17008230_TIMP-1 may serve as a useful laboratory marker to predict the clinical outcome of patients presenting with severe sepsis. 17030988_TIMP-2 has a role in the pericyte-induced stabilization of newly formed vascular networks that are predisposed to undergo regression and reveal specific molecular targets of the inhibitors regulating these events. 17067460_Expression of TIMP-2 consequently increased with the increase of MMP2 and MT1-MMP in oral lichen planus. 17071711_TIMP-2 is abundant in the ovarian perifollicular stroma. Its median level increased in the early ovulatory phase. 17106248_Expression of TIMP-2 enhances the antitumor efficacy of a replicating adenovirus in vivo, by reducing both tumor growth and angiogenesis. 17130843_TIMP2 and TIMP3 play functional role in LPA-induced invasion as negative regulators. 17203468_Results describe the opposite effects of high glucose on matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 in human endothelial cells. 17222415_TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 have a differential relationship with haemostatic proteins and roles in hemostasis and thrombogenesis 17226791_The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of P. gingivalis on the expression and production of MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2 by oral fibroblasts and epithelial cells. 17236757_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17325663_downregulation of the TIMP-2 gene is associated with promoter methylation and that this may play an important role in prostate cancer progression during the invasive and metastatic stages of the disease 17342343_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17342343_TIMP-2 polymorphism is strongly associated with an increased risk of OSCC in Europeans carrying the low C allele expression. 17350093_Positive correlation was found between hepatosplenomegaly and the MMP-2/TIMP-2 ratios (p=0.005 and 0.009) and between CNS involvement and the MMP-2/TIMP-2 ratio 17374529_The results indicate that TIMP-2 and MMP-2:TIMP-2 complex associate with favorable clinical course and could be used as a novel prognostic indicators in bladder cancer. 17448043_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17448043_the -418G to C gene polymorphism is associated with generalized aggressive periodontitis in Chinese subjects 17493172_The expression of TIMP2 is significantly decreased in floppy valves compared to normal valves. 17493602_Results of this study suggest that Systemic sclerosis patients with anticentromere antibodies positivity, after a primary fibrogenetic noxa, react with a more abundant release of MMP/TIMP, whereas patients with anti-Scl70 antibody show a normal response. 17495113_MMP/TIMP balance seems to play an essential role in transferring mechanical signals into mesenchymal stem cells function. 17564313_Expression of TIMP2 was evaluated in hepatocellular carcinoma and surrounding non-tumor tissue. 17572184_incidental clear cell renal cell carcinomas strongly expressing MMP-9 and TIMP-2 have a higher nulclear grade(worse prognosis). 17589947_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17613170_Results determine the level of MMP-2, its natural inhibitor TIMP-2, their ratio and HER-2/neu as diagnostic and prognostic factors in breast cancer. 17706812_MMP-9, but not TIMP-1 nor MMP-2 expression is increased in plaques causing acute coronary syndrome. 17786346_Increased Timp-2 is assopciated with squamous cell laryngeal carcinoma 17868665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17868665_elderly Chinese with TIMP2 C-allele have higher magnitude of QT dispersion and QTc dispersion prolongation 17886098_MMP-2, MT1-MMP and TIMP-2 mRNA expression levels were correlated with clinical stages and histological subtypes of thymic epithelial tumours. The activation of pro-MMP-2 might be mediated by MT1-MMP and TIMP-2 up-regulation. 17893005_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17901377_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17954022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17954022_TIMP-2 G-418C polymorphism increases risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population, especially in younger subjects and smokers. 17979129_gravitational unloading led to induction of TIMP2, an inhibitor of angiogenesis, in microvascular endothelial cells 17991754_Findings illustrate a novel role for MT1-MMP-TIMP-2 interaction, which controls cell functions by a mechanism independent of extracellular matrix degradation. 18025061_No significant difference was seen in gene expression level of MMPs, TIMPs and ratio of MMPs/TIMPs in ascending aorta and AV between patients with BAV and TAV. 18042068_MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 play an important role in the pathogenesis of non-melanoma skin cancer. The immunoexpression of these proteins may be useful indicators of cutaneous cancer invasion and progression. 18177649_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18177649_Report association of polymorphisms of the MMP-2 and TIMP-2 genes with the risk of endometriosis in North Chinese women. 18217401_MMP-2, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 levels are significantly higher and MMP-9 lower in children with chronic hepatitis B 18260263_There was correlation between TIMP-2 expression and tumor size and grading observed. We didn't find any correlation between TIMP-2 and nodal metastases, recurrence and survival. 18265895_Crucial participants in tumour invasion and metastases are matrix metalloproteinases, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase inhibitors and cellular adhesion molecules. They play roles in tumour invasion and metastasis in non-small-cell lung carcinomas. 18288718_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18288718_There was no association with TIMP-2 polymorphisms and risk of adenomyosis in North Chinese women. 18291374_TIMP-1, -2, and -3 are significantly reduced by chorionic gonadotropin in endometrial stromal cells. 18301898_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18301898_no significant association between TIMP-2 polymorphisms and Osteoarthritis was observed 18329693_This study suggests that MMP14 is involved mostly in prostate cancer implantation and that MMP2 and TIMP2 expression by reactive stromal cells might be used as predictors of diease-free survival in T3N0-2M0 Pca. 18424416_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18424416_The TIMP-2 G-418C SNP may be associated with the risk of different histological subtypes of epithelial ovarian cancer. 18469019_Identification of two previously unreported SNPs in FGFR1 and FABP3 associated with BMD and a third SNP in TIMP2 related to risk for non-vertebral osteoporotic fractures. 18469019_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18472160_TIMP-2 overproduction is associated with bone marrow stromal cells in multiple myeloma 18474097_Upregulation of TIMP-2 production is one mechanism by which prodrug JS-K mediates its anti-invasive effects 18477480_Comparison of TIMP2 levels in preeclampsia and gestational hypertension with those found in normotensive pregnancies. 18487063_hematopoiesis was not adversely affected by TIMP-1 or TIMP-2 18498066_Aggressive forms of gastric cancer are associated with low TIMP-2 expression. 18543216_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18543216_TIMP-2 -418G/C polymorphisms were not associated with the risk of developing endometriosis or adenomyosis 18634035_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18674955_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18702016_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18702016_This case-control study investigates the possible impact of genetic variants of the TIMP-2 gene in the aetiology of AAA and to reproduce a recently described significant difference in allele frequency of the SNP 303G>A in a German population. 19020757_Serous and mucinous ovarian tumors express different profiles of TIMP-2. 19088110_uterine decidua possesses protease activity in situ and in vitro and uterine natural killer cells are a major source of MMP-2 and TIMP-2 19141395_The results revealed that mononuclear cells were highly immunoreactive for TIMP-1, TIMP-2 and MMP-9 during viral meningitis and that the expression of TIMPs in polymorphonuclear cells was even higher during bacterial meningitis. 19187648_TIMP-2 expression in human malignant glioma cells was up regulated by mutant IkappaBalpha. 19241124_selective COX-2 inhibition suppresses the invasion activity of OSCC cells via down-regulation of an MMP-2-activating mechanism involving TIMP-2 and production of the MMP-2 protein by an interaction between cancer cells and stromal fibroblasts 19267203_TFPI-2 downregulation can contribute to tumour invasion of lung cancer cells 19317417_Study showed that MMP-9 and TIMP-2 were highly produced in brain microvessels while MMP-10 was notably increased in neurons of the ischemic brain but not in healthy areas. 19331801_Combined hyperlipidemic patients have increased levels of prothrombotic and microinflammatory parameters and higher levels of MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2 than control subjects. 19358835_Obese children and adolescents had higher circulating MMP-8 concentrations, lower plasma TIMP-1 concentrations, and higher MMP-8/TIMP-1 ratios than non obese controls. 19383344_TIMP-1 was up-regulated in human colorectal cancer samples compared with normal tissue, while TIMP-2 was down-regulated. 19391484_Our study revealed increased immunoexpression of MMP-2, MMP-9 and TIMP-2 in acute cellular rejection of renal allografts. 19431211_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19431211_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the TIMP-2 gene is associated with breast cancer. 19438747_increased expression of TIMP-2 in keloids compared with mature scars 19464975_TIMP2 higher expression in scar tissues than controls 19546837_Data show there was a significant correlation between the level of TGF-[beta]1 and the levels of MMP-2 and TIMP-2 immunostainings in pancreatic ductal epithelium. 19551542_The migration of bone marrow (BM) mesenchymal stromal cells was the result of the variable level of MMP/TIMP in response to inflammatory stimuli. 19551841_both the interactions of TIMP-2 with MT1-MMP, and the conventional inhibition of MT1-MMP's catalytic activity by TIMP-2, play a role in the invasion-promoting function of MT1-MMP 19596921_expression of TIMP-2 mRNA in the stage IA and stage IBIIIB tumors did not register any statistically significant difference 19640333_Determination of TIMP-2 in pleural fluid may contribute to differentiate TP from MP. The results suggest that overproduction of MMP-9 and TIMP-2 is associated with accumulation of the pleural effusion in malignancy. 19698156_Higher amniotic fluid MMP-2 and TIMP-2 levels are found in women who eventually develop preeclampsia. 19709349_Of MMP-2/TIMP-2/MMP-14 complex, high expression of MMP-2, TIMP-2 & MMP-14 mRNA may contribute to local invasiveness of ameloblastoma; local invasive capacity of ameloblastoma more likely related to high transcription levels of TIMP-2 and MMP-14. 19723139_TIMPs were immunoreactive mainly in epithelium rather than in stroma of pleomorphic adenomas of salivary glands. 19727008_Mitral TIMP2 expression is higher in patients with mitral chordae tendinae rupture and there is a synergistic effect of mitral TIMP2 staining with hypertension on its occurrence 19758569_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19821096_in the degenerative phase of hemangioma, TIMP-2 can inhibit the proliferation of endothelial cells 19844095_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19844095_TIMP-2 gene polymorphism is associated with intracerebral hemorrhage. 19875168_evaluates the mRNA expression profile of genes TIMP1, TIMP2, MMP2 and MMP9 in diagnostic bone marrow samples from 134 consecutive ALL children by real-time quantitative PCR 19883732_Endogenously expressed TIMP-2 has a neuroprotective role, and they imply that the inhibition of TIMP-2 expression by MPP(+) or 6-OHDA may contribute, in part, to neuronal cell death. 19889076_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19933216_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20041335_The primary tumors from patients with LR showed significantly higher percentage of TIMP-2 expression in stromal cells compared to primary tumors from patients with distant metastasis or primary tumors from patients without tumoral progression. 20084057_TIMP-2 suppresses endothelial mitogenesis and angiogenesis by at least two mechanisms, one mediated by protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibition of VEGFR-2 activation, another involving direct activation of an IBMX-sensitive phosphodiesterase activity. 20138860_The TIMP-2 -418G>C polymorphism is significantly associated with an increased susceptibility to atrial fibrillation in Chinese Han patients with hypertensive heart disease. 20149706_This study assessed the impact of exercise on inflammatory markers and MMPs, and TIMPs. No significant changes were found in body mass index, waist/hip ratio, insulin-resistance indices, MMP-2 and TIMP-1 throughout the study in either group. 20195229_Study confirms an altered TIMP2 expression in subjects with chronic C hepatitis and such alterations can contribute to development of liver fibrosis. 20215736_changes in the extracellular matrix metabolism during the ageing process influence the level of circulating MMP-3 and MMP-10, as well as their tissue inhibitors TIMP-1 and TIMP-2, in a healthy population 20216978_TIMP-2 protein level also increased significantly in the hypoxia/reoxygenation groups, compared with the normoxic group. 20233321_Observations show an increased expression of TIMP-2 in periodontitis-affected gingival tissues. Moreover, the balance between MT1-MMP and its inhibitor TIMP-2 was altered in periodontitis-affected tissues. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20484597_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20514432_Data show that gene expression rates of MMP-2 and TIMP-1 were higher in ONFH biopsies whereas TIMP-2 and MMP-9 gene expression was not significantly altered. 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20598922_A higher TIMP expression favours deposition of connective tissue and thus thicker vein wall, reducing matrix turnover by suppression of protease activity in varicose veins. 20616161_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20627004_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20627004_The SNP-418G/C in the promoter region of TIMP-2 gene may be associated with abnormal growth pattern and curve progression of thoracic adolescent idiopathic thoracic scoliosis. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20672350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20685029_An increase in MMP-2 mRNA and a decrease in TIMP-2 mRNA expression in uterosacral ligament are related to uterine prolapse in women without urinary incontinence. 20694560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20707923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20718757_Findings provide evidence that one of the mechanisms of the increase in angiogenesis in diffuse-type gastric carcinoma is the downregulation of the anti-angiogenic protein TIMP2. 20730428_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20889295_Short-term use of statins is not associated in reducing levels of TIMP 2 in areas of low and peak wall stress in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms. 20940305_insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor is a binding partner of Loop 6/TIMP 20941509_Downregulation of TIMP-2 by 17beta-estradiol in male patients would not be articular cartilage protective. 20948207_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21086628_Expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 and their tissue inhibitors 1 and 2 in papillary thyroid cancer: an association with the clinical, morphological and ultrastructural characteristics of a tumor 21148412_Hypoxia reduces TIMP-2 secretion from human primary monocytes and from monocyte-like cell lines by inhibiting TIMP-2 transcription through mechanisms that involve the transcription factor SP-1. 21195432_Polymorphisms in the promoter region of MMP-9 and TIMP-2 are associated with varicose veins in the Chinese population. 21228746_The TIMP-2 gene is a disease-modifier gene of thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. 21254651_TIMP2 may play a critical role in assisting nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to degrade basement membrane to invade surrounding tissues and to form metastatic colonies in lymph nodes. 21261731_Specific single-nucleotide polymorphism in TIMP2 and MMP2/9 appeared to be associated with tumorigenesis and biological behavior in colorectal cancer. 21421877_MMP2, TIPM2, and TIMP3 genes were not associated with high myopia in this Chinese sample and hence are unlikely to play a major role in the genetic susceptibility to high myopia. 21427648_The levels of TIMP-2 were significantly elevated in patients with inguinal hernia and significantly reduced in patients with aortic aneurysm. 21432777_differences in histological features between nasal polyposis and chronic rhinosinusitis might be related to the expression of MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-8 and their tissue inhibitor-2 21437624_Data indicate that the balance between MMPs and TIMPs in women with PCOS is altered, probably due to androgen excess found in these women. 21454617_analysis of interactions of the catalytic domain (cd) of MMP-1 with the inhibitory domains of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 (N-TIMPs) and MMP-3cd with N-TIMP-2 21462296_Polymorphisms in TIMP2 and WNT9B are novel loci predisposing to cleft palate. 21463121_Findings show significant correlations between MMP-2, -9, and syndecan-1 and hemostatic parameters in hematologic malignancies, in contrast, the MMP inhibitors, TIMP1- and -2, were not correlated with any of the hemostatic parameters. 21478099_Results indicate the better usefulness of TIMP-2 than MMP-2 in the diagnosis of colorectal cancer, especially in combined use with classic tumor marker of CRC, e.g. carcinoembryonic antigen. 21526499_results suggest the greater importance of serum MMP-2 and TIMP-2 than of the classical tumor markers CEA and CA 19-9 in the diagnosis of gastric cancer 21620625_Serum levels of MMP-2/TIMP-2 were significantly higher in patients with matured arteriovenous fistulas vs levels in those that failed. 21715326_phage display was used to identify variants of human TIMP-2 that are selective inhibitors of human MMP-1 21786179_The aim of our study was to compare the immunohistochemical expression of TIMP1 and TIMP2 between an uncontrollably invasive phenomenon (cancer) and an 'in situ' process (trophoblast invasion) 21839835_The C-terminal domain of TIMP-2 inhibits cell surface activation of proMMP-2. 21871510_TIMP-2 integrin-binding peptides retain anti-mitogenic activity in vascular endothelial growth factor A stimulated human microvascular endothelial cells. 22020421_tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 promoter gene polymorphisms are associated with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. 22051851_During labor, TIMP2, TIMP1 and MMP-7 were significantly increased in cervicovaginal fluid. 22110735_NDRG2 contributed to an increase in the ratio of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2) to tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase 2 22122951_TIMP-2 levels are significantly higher in osteoarthritic knees with clinical effusion than in knees without effusion. 22169692_TIMP2 polymorphism is significantly related with occurrence and development of gastric cancer. 22200256_an increase in the immunodistribution of MMP-2 and -9 and TIMP-1 and -2 in lichen sclerous compared to normal vulvar skin was observed. 22200690_Failed to demonstrate any prognostic relevance of TIMP2 levels in advanced epithelial ovarian neoplasms. 22262409_In hepatocellular carcinoma miR-519d is up-regulated by p53 and DNA hypomethylation and targets CDKN1A/p21, PTEN, AKT3 and TIMP2. 22270451_Data show that positive immunoreaction for inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (TIMP-2) correlated with favorable cancer-specific and overall survival. 22272343_Results suggest that EZH2-mediated transcriptional repression of TIMP3 directly leads to activation of MMP-9. 22302011_found increased plasma MMP-2 and TIMP-2 levels in end-stage kidney disease patients compared to controls , and hemodialysis decreased MMP-2 (but not TIMP-2) levels. 22374248_TIMP2 (-418) GC was found to be involved in progression of PCa but not in initiation 22427646_Data show that TIMP-1 inhibits the MMP-10 with a K(i) of 1.1 x 10(-9) M, and TIMP-2 inhibits the MMP-10 with a K(i) of 5.8 x 10(-9) M. 22438955_effect of HPV16 oncoproteins on the expression and activity of MMP-2, MMP-9, MT1-MMP, and their inhibitors TIMP-2 and RECK in cultures of keratinocytes 22511598_This study supports the concept of TIMP-2 expression in the stromal compartment of ovarian cancer(OC) as a promising marker of prognosis and response to cisplatin- and paclitaxel-based chemotherapy in OC patients. 22512703_The level of MMP-2 activation was significantly elevated in tissues with Dupuytren's contracture. RT-PCR demonstrated significantly higher expression of MMP-2, TIMP-2, TGF-beta1, and DCN mRNA in the pathological tissues 22532131_The the roles of TIMP-2 in Esophageal cancer (EC) development, tumor progression and formation of metastases have been most extensively characterized and best recognized. 22546345_Knockdown of GRP78 decreases ECM degradation, and downregulates the expression and activity of TIMP-2 22551568_cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61 may promote trophoblast cell migration and invasion through upregulation of NUR77 protein leading to the increase of matrix metalloproteinase 2(MMP2) release and the downregulation of tissue inhibitor of MMP2 | ENSMUSG00000017466 | Timp2 | 849.171930 | 1.1133553 | 0.154914023 | 0.05228719 | 8.77732371250 | 0.0030499836306058614003589024576967858592979609966278076171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.01911432393589372266684556223026447696611285209655761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 895.892052 | 24.185200 | 808.493047 | 21.879652 | |
| ENSG00000039319 | 9765 | ZFYVE16 | protein_coding | Q7Z3T8 | FUNCTION: May be involved in regulating membrane trafficking in the endosomal pathway. Overexpression induces endosome aggregation. Required to target TOM1 to endosomes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11546807, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14613930}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes an endosomal protein that belongs to the FYVE zinc finger family of proteins. The encoded protein is thought to regulate membrane trafficking in the endosome. This protein functions as a scaffold protein in the transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway and is involved in positive and negative feedback regulation of the bone morphogenetic protein signaling pathway. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]. | hsa:9765; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; 1-phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0005545]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding [GO:0005547]; endosomal transport [GO:0016197]; protein targeting to lysosome [GO:0006622]; regulation of endocytosis [GO:0030100]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; vesicle organization [GO:0016050] | 14613930_marked recruitment of TOM1 to endosomes was observed in cells overexpressing endofin or its carboxyl-terminal fragment 16775010_The key mode of action of Trx-SARA was to reduce the level of Smad2 and Smad3 in complex with Smad4 after TGF-beta1 stimulation. 17272273_Facilitates TGF-beta signaling as a scaffold protein to promote the R-Smad-Smad4 complex formation by bringing Smad4 to the proximity of the receptor complex. 17570516_our study is the first to identify and validate Endofin, DCBLD2, and KIAA0582 as part of a complex EGF phosphotyrosine signaling network 19887107_Disruption of proper localization to the endosomes and the Y515 phosphorylation of Endofin enhanced MAPK activation suggesting that Endofin negatively modulates EGFR signaling following receptor endocytosis. 26944198_Two SNPs located near the ZFYVE16 gene on chromosome 5 may have played a role in the early, multicompartment sacrocolpopexy failure. | 578.716986 | 0.9426289 | -0.085238150 | 0.39451491 | 0.04658484720 | 0.8291161846681824876270638924324885010719299316406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.92220715578391665445678881951607763767242431640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 573.089715 | 115.501374 | 611.077997 | 122.973678 | |||
| ENSG00000040608 | 65078 | RTN4R | protein_coding | Q9BZR6 | FUNCTION: Receptor for RTN4, OMG and MAG (PubMed:12037567, PubMed:12068310, PubMed:12426574, PubMed:12089450, PubMed:16712417, PubMed:18411262, PubMed:12839991, PubMed:19052207). Functions as receptor for the sialylated gangliosides GT1b and GM1 (PubMed:18411262). Besides, functions as receptor for chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (By similarity). Can also bind heparin (By similarity). Intracellular signaling cascades are triggered via the coreceptor NGFR (PubMed:12426574). Signaling mediates activation of Rho and downstream reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton (PubMed:16712417, PubMed:22325200). Mediates axonal growth inhibition (PubMed:12839991, PubMed:19052207, PubMed:28892071). Plays a role in regulating axon regeneration and neuronal plasticity in the adult central nervous system. Plays a role in postnatal brain development. Required for normal axon migration across the brain midline and normal formation of the corpus callosum. Protects motoneurons against apoptosis; protection against apoptosis is probably mediated via interaction with MAG. Acts in conjunction with RTN4 and LINGO1 in regulating neuronal precursor cell motility during cortical development. Like other family members, plays a role in restricting the number dendritic spines and the number of synapses that are formed during brain development (PubMed:22325200). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99PI8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12037567, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12426574, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12839991, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14966521, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16712417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18411262, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19052207, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28892071}. | 3D-structure;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Leucine-rich repeat;Lipid-binding;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Schizophrenia;Signal | This gene encodes the receptor for reticulon 4, oligodendrocyte myelin glycoprotein and myelin-associated glycoprotein. This receptor mediates axonal growth inhibition and may play a role in regulating axonal regeneration and plasticity in the adult central nervous system. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:65078; | axonal growth cone [GO:0044295]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; dendritic shaft [GO:0043198]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; chondroitin sulfate binding [GO:0035374]; ganglioside GM1 binding [GO:1905573]; ganglioside GT1b binding [GO:1905576]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; neuregulin receptor activity [GO:0038131]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; corpus callosum development [GO:0022038]; negative regulation of axon extension [GO:0030517]; negative regulation of axon regeneration [GO:0048681]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; neuronal signal transduction [GO:0023041]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035025] | 12068310_Oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein is a Nogo receptor ligand that inhibits neurite outgrowth 12378589_Nogo-66-R mRNA expression in humans and mice was observed in neurons of the developing nervous system; expression was downregulated in the adult spinal cord of both species, and specific expression patterns were seen in the adult brain. 12422217_P75 interacts with the Nogo receptor as a co-receptor for Nogo, MAG (myelin-associated glycoprotein) and OMgp 15331667_Nogo-66 receptor (NgR) proteolysis occurs within the human nervous system indicating a potential cellular mechanism for the regulation of NgR function at the level of the receptor 15532024_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15532024_the role of the RTN4R as a candidate gene for schizophrenia 15749087_Expression of the genes encoding Nogo and its receptor, NgR, between weeks eight and 23 of human embryonic development. 16342940_analysis revealed a novel disulfide structure in the C-terminal region (CT) of the NgR1, wherein the two Cys residues, Cys-335 and Cys-336, in the CT stalk are disulfide-linked to Cys-266 and Cys-309 in the LRRCT region 16897606_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16897606_results suggest that there is no significant association between the genetic polymorphisms in the RTN4R gene and schizophrenia in the Han Chinese population 17182778_The molecular requirements for cerebral amyloid-beta peptide interaction with NgR are defined and correlated with the affinity of these polypeptides to improve spatial memory impairments in Alzheimer disease model mice. 17188332_results showed that NgR immunoreactivity was present in more than 50% of the pyramidal layer cells of the CA1 to CA4 subfields of the hippocampus; results suggest that NgR may be related to the formation of tangles in Alzheimer's disease 17959786_Review highlights the function of Nogo-66 receptor-1 (NgR-1) during myelin inhibition. 18043741_RTN4R may modulate the genetic risk or clinical expression of schizophrenia in a subset of patients and identify additional studies that will be necessary to clarify the role of RTN4R in psychiatric phenotypes 19052207_For a restricted subset of individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia, the expression of dysfunctional NGR variants may contribute to increased disease risk. 19052207_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19328785_We conclude that NgR1 alters the motility of immune cells exposed to myelin and may thus impact their behaviour within the CNS, particularly under conditions when immune cell activation is heightened. 19386899_This review summarizes recent research that generates interest in the Nogo-66 receptor (NgR1) as a focus of study in central nervous system injury and for its function in increasing susceptibility to developing schizophrenia. 19439611_Nogo-66 receptor (NgR)is identified as a high affinity receptor for BLyS; BLyS can function independently of myelin-associated inhibitors & likely serves as a redundant NgR ligand that negatively influences axonal outgrowth in the central nervous system 20398908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20524398_Hypermethylation of NOGOR gene is associated with adenocarcinoma. 20697954_Kiaa0319-like protein interacts with Nogo Receptor 1, supporting the idea that Kiaa0319-like protein participates in axon guidance. 20844138_In acute slices of adult mice, transgenic NGR suppresses long-term potentiation when locally applied to hippocampal CA1 synapses. 21377214_The results of this study suggested that Lack of association of the RTN4R genetic variations with risk of schizophrenia and SPEM abnormality in a Korean population. 21454605_A multi-domain fragment of Nogo-A protein is a potent inhibitor of cortical axon regeneration via Nogo receptor 1. 21681431_Expression of Nogo-66 receptor in human astrocytoma is correlated with tumor malignancy. 21906273_These results indicate that a lack of NgR1/2 expression promotes the adhesion of DCs to myelin. 22133682_Nogo receptor 3, a paralog of NgR1,functions as a NgR1 co-receptor for Nogo-66. 22728374_After optic nerve crush injury, transgenic NgR1-deficient neurons regenerate retinal ganglion axons as extensively as do zymosan-injected, macrophage-activated wild-type mice. 22903127_Strong overexpression of Nogo receptor 1 in forebrain neurons impairs aspects of cognitive function but does not alter plaque load in plaque-forming transgenic animals. 23982337_knockdown of NgR enhanced invasion and adhesion but increased cell apoptosis in C6 cells, suggesting that Nogo-66/NgR might have complex effects on glioma cells. 24321711_This study demonistrated that alterations in DTI metrics suggest white matter microstructural anomalies of the cerebral cortex in 22q11.2DS. Structural differences in ALIC appear to be associated with the Nogo-66 receptor gene. 24922571_NgR1 is a neural entry mediator for mammalian reovirus.NgR1 is required for efficient infection of primary cortical neurons by reovirus. 24956133_Authors highlight the structural and biochemical aspects of the interaction of Nogo receptors (R1 and R2) with myelin inhibitors such as MAG, Nogo A and OMgp.[Review] 25666623_Data indicate that leucine-rich repeat neuronal protein 1 (LINGO-1) is intracellular and competes with Nogo-66 receptor (NgR) for binding to p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR). 26083872_Messenger RNA expression from RTN4R in human cortical brain tissue correlated significantly with the genotypes of rs701427. Observations suggest that a functional RTN4R gene variant is associated with sporadic ALS. 26768609_(188)Re-NGR-VEGI has the potential as a theranostic agent. 27288754_Panax notoginseng saponins provide neuroprotective effects in a rat model of cerebral ischemia and SH-SY5Y cells exposed to oxygen/glucose deprivation injury by inhibiting the overexpression of NgR1, RhoA, and ROCK2. 27956620_NgR1 ligand has a role in in oligodendrocyte progenitor cells fate in the context of a specific and common type of stroke 28139055_Allelic variation of the rs701428 SNP of RTN4R was significantly associated with volumetric differences in gray matter of the lingual gyrus and cuneus of the occipital lobe. Moreover, occipital gray matter volumes were robustly associated with ultra high risk symptoms of psychosis in the presence of the G allele of rs701428. 28755979_Results indicate an association between RTN4R genetic variation and phenotypes linked to prefrontal function. In an hierarchical approach, a SNP (rs696884) selected based on its association with RTN4R postmortem mRNA expression in the prefrontal cortex was shown to modulate prefrontal activity during working memory processing. 29615517_Nociceptin receptor ORL1 increases the cell surface expression of reticulon 4 receptor (NgR1) in HEK293T cells. 30312597_miR-10 can promote microglia cell proliferation and inhibit the inflammatory cytokine secretion via targeting the NgR gene to down-regulate its expression. 31649250_the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme cells with TGFb1 suppressed NgR maturation. We showed that NgR and vimentin interact, which could be a possible mechanism for the suppression of NgR maturation. 31728810_SATB2 and NRG1 overexpression induced many of the signaling pathways. 33479772_Modulation of Nogo receptor 1 expression orchestrates myelin-associated infiltration of glioblastoma. 34758294_RTN4/NoGo-receptor binding to BAI adhesion-GPCRs regulates neuronal development. | ENSMUSG00000043811 | Rtn4r | 10.308100 | 0.9542789 | -0.067517159 | 0.53057582 | 0.01591568880 | 0.8996073341910909570984244965075049549341201782226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.95502214211151914557973441333160735666751861572265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 10.382047 | 3.256054 | 10.728922 | 3.346810 | |
| ENSG00000048052 | 9734 | HDAC9 | protein_coding | Q9UKV0 | FUNCTION: Responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Histone deacetylation gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Represses MEF2-dependent transcription. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11535832}.; FUNCTION: Isoform 3 lacks active site residues and therefore is catalytically inactive. Represses MEF2-dependent transcription by recruiting HDAC1 and/or HDAC3. Seems to inhibit skeletal myogenesis and to be involved in heart development. Protects neurons from apoptosis, both by inhibiting JUN phosphorylation by MAPK10 and by repressing JUN transcription via HDAC1 recruitment to JUN promoter. | Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Chromosomal rearrangement;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc | Histones play a critical role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression, and developmental events. Histone acetylation/deacetylation alters chromosome structure and affects transcription factor access to DNA. The protein encoded by this gene has sequence homology to members of the histone deacetylase family. This gene is orthologous to the Xenopus and mouse MITR genes. The MITR protein lacks the histone deacetylase catalytic domain. It represses MEF2 activity through recruitment of multicomponent corepressor complexes that include CtBP and HDACs. This encoded protein may play a role in hematopoiesis. Multiple alternatively spliced transcripts have been described for this gene but the full-length nature of some of them has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:9734; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; histone deacetylase complex [GO:0000118]; histone methyltransferase complex [GO:0035097]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; histone deacetylase activity [GO:0004407]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; histone H4K16 deacetylase activity [GO:0034739]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; protein lysine deacetylase activity [GO:0033558]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; B cell activation [GO:0042113]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; heart development [GO:0007507]; histone deacetylation [GO:0016575]; histone H3 deacetylation [GO:0070932]; histone H4 deacetylation [GO:0070933]; histone H4-K16 deacetylation [GO:1990678]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001818]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of lipoprotein lipase activity [GO:0051005]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; peptidyl-lysine deacetylation [GO:0034983]; positive regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090050]; regulation of skeletal muscle fiber development [GO:0048742]; regulation of striated muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051153] | 12054582_Chromosomal organization on chromsome 7 15194749_ICP0 of Herpes simplex virus Type 1 interacts with and controls the repressor activity of class II HDAC7 15567413_The crystal structure of a histone deacetylase 9 (HDAC9)/myocyte enhancer factor-2 (MEF2)/DNA complex reveals that HDAC9 binds to a hydrophobic groove of the MEF2 dimer. 16399788_Moraxella catarrhalis-induced cytokine expression is regulated by acetylation of histone residues and controlled by histone deacetylase activity. 16980305_The role of ACTN4 in MEF2A transcription via HDAC7 antagonism is reported. 17360565_FOXP3 interactions with histone acetyltransferase and class II histone deacetylases are required for repression 17980413_Endogenous HDAC activity plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of pre-established T(H)1-like and T(H)2-like responses, inhibiting excessive T(H)2 immunity. 18438919_amino enhancer of split has apoptotic activity in neurons and suggest that neuroprotection by histone deacetylase-related protein is mediated by the inhibition of this activity through direct interaction. 18549475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19522008_Analysis of chromatin modification patterns shows that HDAC are recruited to the c-myc promoter leading to appearance of repressive chromatin marks. 19624894_HDAC suppresses the activation of PPARgamma in the gastric carcinoma cell line SGC-7901. 19723072_Results demonstrate that histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) in different combinations with RA, act as cell growth inhibitors. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20031566_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20298200_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20844743_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20947501_Histone deacetylase 9 (HDAC9) regulates the functions of the ATDC (TRIM29) protein 21078662_enforced HDAC9 expression increased gamma-globin mRNA levels by 2.5-fold with a simultaneous 7-fold increase in HbF. 21247901_Histone deacetylases 9 and 10 are required for homologous recombination. 21247904_MITR plays a master switch role to balance osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of MSCs through regulation of PPARgamma-2 transcriptional activity. 21708950_HDAC9 acts as an epigenetic switch in effector T cell-mediated systemic autoimmunity. 21806350_Data indicate a pronounced deregulation of HDAC genes HDAC9 and HDAC11 in patients with Philadelphia-negative chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms: essential thrombocythemia (ET), polycythemia vera (PV) and primary myelofibrosis (PMF). 21987446_Treated the seminoma-like cell line TCam-2 with the HDAC-inhibitor Depsipeptide. 22032556_The results show that hdac9 is the third androgenic alopecia susceptibility gene 22297573_The results imply that HDAC9 is involved in the transcriptional regulation of human odontoblasts in vivo. 22306652_We identified a new association for large vessel stroke within HDAC9 on chromosome 7p21.1. 22487525_LBH589 and TSA may translationally regulate some HDAC encoding genes in pancreatic tumors. 22884548_Regression models consistently identified rs2522129, rs2675231, and rs2389963 as having among the highest predictive values for explaining differences related to brain volume measures 22945647_We propose that CtBP2 is an ovarian cancer oncogene that regulates gene expression program by modulating HDAC activity. 23288173_HDAC9 promotes angiogenesis and transcriptionally represses the endothelial cell miR-17-92 cluster. 23297420_Dephosphorylation at a conserved SP motif governs cAMP sensitivity and nuclear localization of class IIa histone deacetylases HDAC4, 5 and 9 23393555_SNP, rs12155400, in the histone deacetylase 9 gene (HDAC9) on chromosome 7, was associated with retinopathy in analysis of participants without hypertension 23449258_Our results are consistent with the 7p21.1 association acting via promoting atherosclerosis, and consistent with alterations in HDAC9 expression mediating this increased risk. 23674352_In vivo sorafenib + HDAC inhibitor toxicity against tumors was increased. 23771909_study reports gene expression in skeletal muscle tissue of women with metabolic syndrome is enriched in inflammatory response-related genes; IL6R, HDAC9 and CD97 expression correlated negatively with insulin sensitivity; suggests a role for these 3 inflammatory genes in development of skeletal muscle insulin resistance in women 23784969_These data suggest that HDAC9 variants may be selected for during cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis 23828597_HDAC9 gene is significantly associated with large-vessel stroke risk in Chinese population. 24427341_These results suggest that HDAC9 may be a suppressor and its downregulation might promote the progression process, especially in lung adenocarcinomas. 24562770_The hydroxamic acid pan-HDAC inhibitor TSA synergistically inhibit the viability. 24650256_The results elucidate the genetic etiology of lung adenocarcinoma by demonstrating that SNP rs10248565 in the HDAC9 gene may be a potential biomarker of cancer susceptibility. 25388417_Gene expression studies in peripheral blood mononuclear cells revealed increased mRNA levels of HDAC9. Analysis of human atherosclerotic plaques revealed no association between rs2107595 and specific plaque characteristics. 25613642_Data show that miR-376a and HDAC9 expression are inversely correlated in hepatocellular carcinoma and suggest that HDAC9-mediated epigenetic modification may contribute to the down-regulation of the miR-376 cluster in hepatocellular carcinoma. 25760078_HDAC9 promotes tumor formation of glioblastoma via TAZ-mediated EGFR pathway activation. 26084607_the results of this study suggest that targeting HDACs by ST-3595 might represent as a novel and promising anti-pancreatic cancer strategy. 26093197_results indicate that HDAC9 variant rs2107595 may be not associated with IS risk in southern Han Chinese 26347468_Polymorphisms of HDAC9 is associated with Ischemic Stroke. 26420860_Data suggest, in chronic hepatitis C virus infection, HDAC9 (histone deacetylase 9) induction in liver regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis and systemic insulin resistance via deacetylation of FoxO1 (Forkhead box O 1) and HDAC3 (histone deacetylase 3). 26621503_These results highlighting the significant correlation between TWIST and HDAC9 gene expression suggest that both genes may contribute to plaque stability in a coordinated way 26930713_Data show that the gene encoding the transcription factor SOX9 was identified by a global transcriptomic approach as an HDAC9 target gene. 26992905_overexpression of HDAC9 contributes to OSCC carcinogenesis via targeting a transcription factor, MEF2D, and NR4A1/Nur77, a pro-apoptotic MEF2 target 27033599_HDAC9 was commonly expressed in retinoblastoma tissues and HDAC9 was overexpressed in prognostically poor retinoblastoma patients. 27100479_HDAC9 is an important epigenetic factor regulating ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell apoptosis and inflammatory factor expression. 27250566_decline in HDAC9c expression over time was accompanied by increased EZH2 expression. 27312341_post-translational modification of Nkx3.2 employing HDAC9-PIASy-RNF4 axis plays a crucial role in controlling chondrocyte viability and hypertrophic maturation during skeletal development in vertebrates. 27333946_PC3/Tis21 associates with HDAC1, HDAC4, and HDAC9 in vivo, in fibroblast cells. 27466490_The aurora kinase A inhibited by MLN 8054 are both implicated in cell cycle progression and, thus, in cellular proliferation.Epigenetic regulators were targeted by SAHA inhibiting HDACs and by DZNep inhibiting the histone methyltransferase EZH2, which silences genes by trimethylating histone H3K27.Combinations of small molecular inhibitors act synergistically in rhabdoid tumor 27494404_The minor allele A of SNP rs2107595 increased coronary artery disease risk and the severity of coronary atherosclerosis in a Chinese Han population. 27495233_Downregulation of HDAC9 promotes gliomas. 27633396_HDAC9 may be involved in the process of diabetic nephropathy. 27642596_Studied HDAC9 gene's association with an increased susceptibility to acute coronary syndrome (ACS) in Chinese Han population. The results revealed a significant association of rs2240419 with ACS risk in which the A allele (P = 0.047) and the A allele carriers (AA + AG) (P = 0.037) were more likely to be in ACS group as compared to those in the control group. 27799148_HDAC9 might contribute to lymphomagenesis by altering pathways involved in growth and survival, as well as modulating BCL6 activity and p53 tumor suppressor function. 27833022_Based on this study, it is suggested that HDAC9 regulates the formation of APBs and could be a candidate for the target of ALT-cancer therapy. 28145521_the T allele of rs2107595 in HDAC9 increases the risk of stroke but that the G allele of rs2389995 decreases the risk of stroke in the Chinese population (Meta-Analysis) 28267394_HDAC9 is a target of miR-377 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 28343758_M4 macrophages are a possible source for HDAC9 and MMP12 expression in advanced human carotid plaques. 28419090_in leiomyosarcomas (LMS), this two-faced trait of MEF2 is relevant for tumor aggressiveness. Class IIa HDACs are overexpressed in 22% of LMS, where high levels of MEF2, HDAC4 and HDAC9 inversely correlate with overall survival. The knock out of HDAC9 suppresses the transformed phenotype of LMS cells, by restoring the transcriptional proficiency of some MEF2-target loci 28733598_the key role of the HDAC9-FoxO1 signalling axis in regulating gluconeogenic genes, transcriptional factors, gluconeogenesis metabolism, and HCV-induced gluconeogenesis in hepatocytes. 29520069_HDAC9, in cooperation with BRG1 and MALAT1, mediates a critical epigenetic pathway responsible for vascular smooth muscle cells dysfunction. 29651704_The HDAC9 risk allele at rs2107595 was associated with differences in blood cell gene expression in patients with Large Vessel Atherosclerotic Stroke. 29691366_HDAC9 and miR-17 formed an inhibitory loop, regulating osteogenesis of human periodontal ligament stem cells in inflammatory conditions. 29936177_This study highlights HDAC9 as a mediator of cell invasion and angiogenesis in Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells through VEGF and MAPK3 by modulating miR-206 expression and suggests that selective inhibition of HDAC9 may be an efficient route for TNBC therapy. 30074176_HDAC9 may be a new indicator for assessing chronic heart failure. 30565168_HDAC9 polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility, severity, and short-term outcome of large artery atherosclerotic stroke. 30656483_The relationship between the prognosis of children with acute arterial stroke and polymorphisms of CDKN2B, HDAC9, NINJ2, NAA25 genes. 30715128_HDAC9 promotes trophoblast cell migration and invasion by repressing TIMP3 through promoter histone hypoacetylation. Thus, the findings of our study suggest that dysregulated HDAC9 and TIMP3 are relevant to PE. 30919159_the risk allele Rs10230207 for patients with intracranial aneurysm is not associated with changes in FERD3L gene expression, but is associated with increased HDAC9 and decrease in TWIST1 mRNA expression 31078148_HDAC9 may be a potential prognostic indicator of hepatocellular carcinoma. 31090223_These results indicated that HDAC9 downregulation mediated the anti-non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) actions of melatonin, and targeting HDAC9 may be the novel therapeutic strategy for NSCLC. 31099456_HDAC9 inhibits estrogen receptor-alpha expression and activity in MCF7 breast cancer cells. 31137112_HDAC [histone deacetylases] may be involved in the pathogenesis of COP [cryptogenic organizing pneumonia] and IPF [idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis]. 31451695_Knockdown of HDAC9 inhibits cell growth, reduces colony formation, and induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. These results suggest that HDAC9 has an oncogenic role in Gastric cancer. 31500558_our findings imply allele-specific transcriptional regulation of HDAC9 via E2F3 and Rb1 as a major mechanism mediating vascular risk at rs2107595. 31659325_Increased expression of HDAC9 in human aortic smooth muscle cells promoted calcification and reduced contractility in atherosclerosis. 31754707_We demonstrate that these regions, recognized by MEF2D/HDAC4/HDAC9 repressive complexes, show the features of active enhancers. In these regions HDAC4 and HDAC9 can differentially influence H3K27 acetylation. 31974610_High HDAC9 is associated with poor prognosis and promotes malignant progression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 32284067_Association between rs2107595 HDAC9 gene polymorphism and advanced carotid atherosclerosis in the Slovenian cohort. 32347025_Histone Deacetylase 9: Its Role in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes and Other Chronic Diseases. 32402768_Decreased expression and hypomethylation of HDAC9 lead to poor prognosis and inhibit immune cell infiltration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 32524326_HDAC inhibitors promote pancreatic stellate cell apoptosis and relieve pancreatic fibrosis by upregulating miR-15/16 in chronic pancreatitis. 32677473_LINC00162 participates in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy via modulating the miR-383/HDAC9 signalling pathway. 32945466_Long noncoding RNA CBR3 antisense RNA 1 promotes the aggressive phenotypes of nonsmallcell lung cancer by sponging microRNA5093p and competitively upregulating HDAC9 expression. 32961570_Interactive Effects of a Combination of the HDAC3 and HDAC9 Genes with Diabetes Mellitus on the Risk of Ischemic Stroke. 33042272_Truncated HDAC9 identified by integrated genome-wide screen as the key modulator for paclitaxel resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. 33079409_A novel long noncoding RNA, LOC440173, promotes the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating the miR-30d-5p/HDAC9 axis and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 33480300_Histone deacetylase 9 inhibition upregulates microRNA-92a to repress the progression of intracranial aneurysm via silencing Bcl-2-like protein 11. 33693951_Knockdown of long noncoding RNA HCP5 suppresses the malignant behavior of retinoblastoma by sponging miR36195p to target HDAC9. 33963859_HDAC9 exacerbates myocardial infarction via inactivating Nrf2 pathways. 34006836_IL-4 inhibits regulatory T cells differentiation by HDAC9-mediated epigenetic regulation. 34175397_HDAC9 rs11984041 polymorphism is associated with diabetic retinopathy in Slovenian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 34318404_Histone deacetylase (HDAC) 9: versatile biological functions and emerging roles in human cancer. 34823425_Hsa_circ_0000527 Downregulation Suppresses the Development of Retinoblastoma by Modulating the miR-27a-3p/HDAC9 Pathway. 34872444_Hsa_circ_0001879 promotes the progression of atherosclerosis by regulating the proliferation and migration of oxidation of low density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced vascular endothelial cells via the miR-6873-5p-HDAC9 axis. 34935488_HDAC9 in the Injury of Vascular Endothelial Cell Mediated by P38 MAPK Pathway. 35239708_An HDAC9-associated immune-related signature predicts bladder cancer prognosis. 35592642_Knockdown of HDAC9 Inhibits Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Partially by Suppressing the MAPK Signaling Pathway. 35710300_HDAC9 structural variants disrupting TWIST1 transcriptional regulation lead to craniofacial and limb malformations. 35894849_Downregulation of HDAC9 by the ketone metabolite beta-hydroxybutyrate suppresses vascular calcification. 35941971_Histone Deacetylase9 Represents the Epigenetic Promotion of M1 Macrophage Polarization and Inflammatory Response via TLR4 Regulation. 36078104_Sex-Dependent Role of Adipose Tissue HDAC9 in Diet-Induced Obesity and Metabolic Dysfunction. | ENSMUSG00000004698 | Hdac9 | 1248.449190 | 1.9721970 | 0.979803660 | 0.27609026 | 12.33468246720 | 0.0004446197286717196357243297999417563914903439581394195556640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00378766185423874213525352594444939313689246773719787597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1492.509730 | 290.638751 | 751.548991 | 146.570215 | |
| ENSG00000048707 | 55187 | VPS13D | protein_coding | Q5THJ4 | FUNCTION: Mediates the transfer of lipids between membranes at organelle contact sites (By similarity). Functions in promoting mitochondrial clearance by mitochondrial autophagy (mitophagy), also possibly by positively regulating mitochondrial fission (PubMed:29307555, PubMed:29604224). Mitophagy plays an important role in regulating cell health and mitochondrial size and homeostasis. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q07878, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29307555, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29604224}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Lipid transport;Neurodegeneration;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transport | This gene encodes a protein belonging to the vacuolar-protein-sorting-13 gene family. In yeast, vacuolar-protein-sorting-13 proteins are involved in trafficking of membrane proteins between the trans-Golgi network and the prevacuolar compartment. While several transcript variants may exist for this gene, the full-length natures of only two have been described to date. These two represent the major variants of this gene and encode distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:55187; | extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; lipid transport [GO:0006869]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; positive regulation of mitophagy [GO:1901526]; protein retention in Golgi apparatus [GO:0045053]; protein targeting to vacuole [GO:0006623] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20610895_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25896417_genetic polymorphism is associated with il-6 production and mortality in patients with septic shock 29518281_findings underline the importance of the VPS13 complex in neurological diseases and a possible role in mitochondrial function 29604224_heterozygous mutations in VPS13D cause movement disorders along the ataxia-spasticity spectrum 31876103_VPS13D-related disorders presenting as a pure and complicated form of hereditary spastic paraplegia. 31943017_A VPS13D spastic ataxia mutation disrupts the conserved adaptor-binding site in yeast Vps13. 32020600_Genetic heterogeneity in Leigh syndrome: Highlighting treatable and novel genetic causes. 33623047_An ESCRT-dependent step in fatty acid transfer from lipid droplets to mitochondria through VPS13D-TSG101 interactions. 33758164_The lncRNA Snhg1-Vps13D vesicle trafficking system promotes memory CD8 T cell establishment via regulating the dual effects of IL-7 signaling. 33891012_VPS13D promotes peroxisome biogenesis. 33891013_VPS13D bridges the ER to mitochondria and peroxisomes via Miro. 34019822_Vmp1, Vps13D, and Marf/Mfn2 function in a conserved pathway to regulate mitochondria and ER contact in development and disease. 34133214_VPS13D interacts with VCP/p97 and negatively regulates endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria interactions. 36156252_VPS13D-based disease: Expansion of the clinical phenotype in two brothers and mutation diversity in the Turkish population. | ENSMUSG00000020220 | Vps13d | 488.578139 | 1.2214607 | 0.288607502 | 0.43923895 | 0.42376532686 | 0.5150641739688750497805358463665470480918884277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.72482069069181331855133976205252110958099365234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 488.036464 | 199.252392 | 391.474073 | 159.914897 | |
| ENSG00000055955 | 3700 | ITIH4 | protein_coding | Q14624 | FUNCTION: Type II acute-phase protein (APP) involved in inflammatory responses to trauma. May also play a role in liver development or regeneration. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19263524}. | Acute phase;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine protease inhibitor;Signal | The protein encoded by this gene is secreted into the blood, where it is cleaved by plasma kallikrein into two smaller forms. Expression of this gene has been detected only in liver, and it seems to be upregulated during surgical trauma. This gene is part of a cluster of similar genes on chromosome 3. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. | hsa:3700; | blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; platelet dense granule lumen [GO:0031089]; endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004866]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; acute-phase response [GO:0006953]; hyaluronan metabolic process [GO:0030212]; response to cytokine [GO:0034097] | 14661079_Genetic variation at ITIH4 locus is one of the likely candidate determinants for plasma cholesterol metabolisms 14661079_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16271702_ITIH4 and MTJ1 co-immunoprecipitate from total liver protein extracts and SANT domain of HTJ1 protects the ITIH4(588-930) recombinant fragment 18455532_The inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4 (ITIH4) protein was significantly present more in interstial cystitis than controls 19263524_ITIH4 is an anti-inflammatory protein, and suggests that further investigation into its potential use in the diagnosis and prognosis of acute ischemic stroke is warranted. 19367581_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21331437_Findings suggest that ITI-H4 expression may be used as a biomarker, which could facilitate the development of novel diagnostic and therapeutic tools. 23417432_A truncated fragment of inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4 was the sole protein found to be significantly enhanced in the prostate cancer patients compared to the controls. 23436019_Expression of the 85 kDa ITIH4 was substantial in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis compared with controls or patients with muscular dystrophy, Alzheimer diseases, or Parkinson diseases 24461634_A novel association between suicide attempt and the ITIH3/4-region in a combined group of patients with bipolar disorder, schizophrenia and related psychosis spectrum disorders. 24836184_Worse survival among HCC patients with low ITIH4. 24861553_Four novel body mass index-associated loci near the KCNQ1(rs2237892), ALDH2/MYL2 (rs671, rs12229654), ITIH4 (rs2535633) and NT5C2 (rs11191580) genes are identified in East Asian-ancestry populations. 24884609_Isoform-specific ITIH4 glycosylation and utilization of O-glycosylation sites on ITIH4 differs between cell lines and serum. 25977605_Serum ITIH4 may be a PM10-specific biomarker in COPD and may be related to inflammation. 26206863_confirmed the association of schizophrenia with ITIH3/4 in a Han Chinese population 26408095_ITIH4 peptide isoform as a preterm birth biomarker and its associated SNP implications 26991396_this report has further supported for associations of genetic variants in the ITIH4 and CALN1 genes with schizophrenia and provided the first evidence that the variants regulate ITIH4 AND CALN1 expression in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex 28828637_Low ITIH4 expression is associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 29992445_ITIH4 SNPs rs3821831 and rs2239547 were studied in pregnant depressed Japanese women. Compared with the TT genotype of ITIH4 SNP rs2239547, the CC genotype was significantly related to a reduced risk of depressive symptoms during pregnancy. SNP rs3821831 was not related to these symptoms.The GCCT haplotype of rs2535629, rs736408, rs3821831, and rs2239547 was significantly positively associated with depressive symptoms. 30348621_The ITI-H4 (N(688)) might be a crucial inflammatory factor which contributes to the pathogenesis of recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL). Moreover, it is expected that this study would give some insights into potential functional mechanisms underlying RPL. 31955064_sgp120 or ITIH4 is cleaved when the contact system is activated and this cleavage could be used as a biomarker in patients with hereditary angioedema with normal C1 inhibitor 33238047_Citrullinated inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4 in arthritic joints and its potential effect in the neutrophil migration. 33348064_ITIH4, as an inflammation biomarker, mainly increases in bacterial bloodstream infection. 34247200_Associations between KCNQ1 and ITIH4 gene polymorphisms and infant weight gain in early life. 34687700_ITIH4 is a novel serum biomarker for early gastric cancer diagnosis. | ENSMUSG00000021922 | Itih4 | 14.041448 | 0.2719292 | -1.878697256 | 0.71699319 | 6.55125068366 | 0.0104810459225017516687872287661775771994143724441528320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.05131567041090462355512613612518180161714553833007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 6.426881 | 2.791187 | 23.883811 | 10.529194 | |
| ENSG00000060138 | 8531 | YBX3 | protein_coding | P16989 | FUNCTION: Binds to the GM-CSF promoter. Seems to act as a repressor. Binds also to full-length mRNA and to short RNA sequences containing the consensus site 5'-UCCAUCA-3'. May have a role in translation repression (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation | Enables RNA binding activity. Involved in cellular hyperosmotic response; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor; and negative regulation of programmed cell death. Located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:8531; | bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; synapse [GO:0045202]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; polysome binding [GO:1905538]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; 3'-UTR-mediated mRNA stabilization [GO:0070935]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular hyperosmotic response [GO:0071474]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; ectopic germ cell programmed cell death [GO:0035234]; fertilization [GO:0009566]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to osmotic stress [GO:1902219]; negative regulation of necroptotic process [GO:0060546]; negative regulation of reproductive process [GO:2000242]; negative regulation of skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0048642]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of cytoplasmic translation [GO:2000767]; positive regulation of organ growth [GO:0046622]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] | 12239625_human dbpA has a role in accelerating hepatocarcinogenesis 14728692_identification of complexes, binding to the vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA 5'- and 3'-UTR, that contain cold shock domain and polypyrimidine tract binding RNA binding proteins 16508013_ZONAB regulates the transcription of genes that are important for G1/S-phase progression and links tight junctions to the transcriptional control of key cell cycle regulators and epithelial cell differentiation. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19328795_The symplekin/ZONAB complex inhibits intestinal cell differentiation by the repression of AML1/Runx1. 19749785_The expression of human DBPA was upregulated in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines. siRNA treatment successfully silenced DBPA expression. 20133480_ZONAB is an important component of the mechanisms that sense epithelial density and participates in the complex transcriptional networks that regulate the switch between proliferation and differentiation 21473684_In human skeletal muscle cells, CSDA was upregulated during hypoxia when cells were damaged and apoptosis was induced. 22159460_DbpA promoter was methylated in 37.7% of HCC samples. 22711822_We demonstrate that ZONAB promotes cell survival in response to proinflammatory, hyperosmotic, and cytotoxic stress and that stress-induced ZONAB activation involves the Rho regulator GEF-H1. 24817634_In the prenatal brain, the cold shock domain protein A were found to be abundantly expressed in radial glial cells, neuroblasts and neurons. 24885929_Stratification according to Fuhrman grade disclosed higher YBX3 expression levels. 27430286_Data suggest that DNA binding protein A (dbpA) may be used as a therapeutic target in colorectal cancer (CRC). 27569444_dbpA knockdown in SW620 cells altered the expression of carcinogenesis-associated genes in Colorectal cancer. 29227750_Authors examined, for the first time in a Turkish population, the association between protamine gene alleles (PRM1 c.-190C>A, PRM1 c.197G>T, and PRM2 c.248C>T), and YBX2 (c.187T>C and c.1095 + 16A>G) and male infertility. 30784285_ZONAB is up-regulated in bladder cancer cell lines, which promotes invasion, demonstrating the important role it plays in tumorogenesis and cancer progression 31189097_YBX3 binds within the 3' UTR of SLC7A5 to stabilize the transcript. 31944153_YB-3 substitutes YB-1 in global mRNA binding. 32553055_Y-Box-Binding Protein 3 (YBX3) Restricts Influenza A Virus by Interacting with Viral Ribonucleoprotein Complex and Imparing its Function. 32652867_Knockdown of DNA-binding protein A enhances the chemotherapy sensitivity of colorectal cancer via suppressing the Wnt/beta-catenin/Chk1 pathway. 36059530_Identification and verification of YBX3 and its regulatory gene HEIH as an oncogenic system: A multidimensional analysis in colon cancer. | ENSMUSG00000030189 | Ybx3 | 517.774174 | 1.0663470 | 0.092676988 | 0.09782778 | 0.89636199567 | 0.3437590704175743638870699214749038219451904296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.57593746281004076781329104051110334694385528564453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 495.085319 | 42.820590 | 467.077214 | 40.319516 | |
| ENSG00000062194 | 65056 | GPBP1 | protein_coding | Q86WP2 | FUNCTION: Functions as a GC-rich promoter-specific transactivating transcription factor. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6NXH3}. | Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation | This gene was originally isolated by subtractive hybridization of cDNAs expressed in atherosclerotic plaques with a thrombus, and was found to be expressed only in vascular smooth muscle cells. However, a shorter splice variant was found to be more ubiquitously expressed. This protein is suggested to play a role in the development of atherosclerosis. Studies in mice suggest that it may also function as a GC-rich promoter-specific trans-activating transcription factor. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. | hsa:65056; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] | 11256614_This publication discusses both human and mouse GC-rich promoter binding protein. 12842993_Vasculin is a novel vascular protein differentially expressed in human atherogenesis 17672918_occurrence of an unusual TG 3' splice site in intron 9 | ENSMUSG00000032745 | Gpbp1 | 509.980066 | 0.9382748 | -0.091917642 | 0.12867040 | 0.50967133334 | 0.4752811679793518262471252455725334584712982177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.69361105692605529160488231354975141584873199462890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 468.900203 | 43.902980 | 501.364234 | 46.890503 | |
| ENSG00000064115 | 51768 | TM7SF3 | protein_coding | Q9NS93 | FUNCTION: Involved in the inhibition of cytokine-induced death of pancreatic beta cells. Involved in the promotion of insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells (PubMed:21853325). Is a downstream transcriptional target of p53/TP53, and acts as a pro-survival homeostatic factor that attenuates the development of cellular stress. Maintains protein homeostasis and promotes cell survival through attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and the subsequent induction of unfolded protein response (UPR) (PubMed:27740623). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21853325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27740623}. | Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Stress response;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Involved in cellular response to unfolded protein; negative regulation of programmed cell death; and positive regulation of insulin secretion. Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:51768; | extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cellular response to unfolded protein [GO:0034620]; negative regulation of programmed cell death [GO:0043069]; positive regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0032024] | 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21853325_Data indicate that TM7SF3 plays a role in inhibition of cytokine-induced cell death/apoptosis in pancreatic beta cells and in inhibition of insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. 27740623_Lack of TM7SF3 activates nitric oxide production and the PKR-like ER kinase arm of the unfolded protein response that involves inhibition of eIF2alpha activity, enhanced expression of ATF4 and ATF3, and induction of CHOP that culminates in apoptosis. | ENSMUSG00000040234 | Tm7sf3 | 491.623448 | 0.9857548 | -0.020699234 | 0.12344438 | 0.02808651981 | 0.8669055765649357203628255774674471467733383178710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.94133252034334169433549277528072707355022430419921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 492.887978 | 39.763243 | 502.342396 | 40.680486 | |
| ENSG00000064652 | 28966 | SNX24 | protein_coding | Q9Y343 | FUNCTION: May be involved in several stages of intracellular trafficking. {ECO:0000250}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport | Predicted to enable phosphatidylinositol phosphate binding activity. Predicted to be involved in protein transport. Predicted to be located in cytoplasmic vesicle membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:28966; | cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate binding [GO:1901981]; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding [GO:0032266]; phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding [GO:0070273]; phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate binding [GO:0010314]; protein transport [GO:0015031] | 35021601_Sorting nexin 24 is required for alpha-granule biogenesis and cargo delivery in megakaryocytes. | ENSMUSG00000024535 | Snx24 | 30.999259 | 1.3939495 | 0.479178288 | 0.44153023 | 1.15410129984 | 0.2826922468207891392388830809068167582154273986816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.51488270163140603674634121489361859858036041259765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 36.756845 | 9.932955 | 26.568754 | 7.182238 | |
| ENSG00000066651 | 60487 | TRMT11 | protein_coding | Q7Z4G4 | FUNCTION: Catalytic subunit of an S-adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent tRNA methyltransferase complex that mediates the methylation of the guanosine nucleotide at position 10 (m2G10) in tRNAs. {ECO:0000250}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Methyltransferase;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase;tRNA processing;tRNA-binding | Predicted to enable tRNA (guanine-N2-)-methyltransferase activity. Predicted to be involved in tRNA methylation. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:60487; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; methyltransferase activity [GO:0008168]; tRNA (guanine-N2-)-methyltransferase activity [GO:0004809]; tRNA binding [GO:0000049] | 22386179_SNPs associated with androgen deprivation failure in advanced prostate cancer | ENSMUSG00000019792 | Trmt11 | 102.863203 | 0.9769434 | -0.033653129 | 0.24115080 | 0.01935492789 | 0.8893537522826195917957647907314822077751159667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.95120611922723485864850090365507639944553375244140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 100.352134 | 17.523100 | 102.819409 | 18.061832 | |
| ENSG00000068366 | 2182 | ACSL4 | protein_coding | O60488 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the conversion of long-chain fatty acids to their active form acyl-CoA for both synthesis of cellular lipids, and degradation via beta-oxidation (PubMed:24269233, PubMed:22633490, PubMed:21242590). Preferentially activates arachidonate and eicosapentaenoate as substrates (PubMed:21242590). Preferentially activates 8,9-EET > 14,15-EET > 5,6-EET > 11,12-EET. Modulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by regulating the levels of unesterified EETs (By similarity). Modulates prostaglandin E2 secretion (PubMed:21242590). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35547, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21242590, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22633490, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24269233}. | Alport syndrome;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Deafness;Disease variant;Elliptocytosis;Endoplasmic reticulum;Fatty acid metabolism;Hereditary hemolytic anemia;Intellectual disability;Ligase;Lipid metabolism;Magnesium;Membrane;Microsome;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Peroxisome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is an isozyme of the long-chain fatty-acid-coenzyme A ligase family. Although differing in substrate specificity, subcellular localization, and tissue distribution, all isozymes of this family convert free long-chain fatty acids into fatty acyl-CoA esters, and thereby play a key role in lipid biosynthesis and fatty acid degradation. This isozyme preferentially utilizes arachidonate as substrate. The absence of this enzyme may contribute to the cognitive disability or Alport syndrome. Alternative splicing of this gene generates multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. | hsa:2182; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0044233]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; peroxisomal membrane [GO:0005778]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; arachidonate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0047676]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity [GO:0004467]; palmitoyl-CoA ligase activity [GO:0090433]; very long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity [GO:0031957]; embryonic process involved in female pregnancy [GO:0060136]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; lipid biosynthetic process [GO:0008610]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; long-chain fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0001676]; long-chain fatty-acyl-CoA biosynthetic process [GO:0035338]; long-chain fatty-acyl-CoA metabolic process [GO:0035336]; negative regulation of prostaglandin secretion [GO:0032307]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0032024] | 11731423_Fatty acid CoA ligase 4 is up-regulated in colon adenocarcinoma. 11889465_FACL4, encoding fatty acid-CoA ligase 4, is mutated in nonspecific X-linked mental retardation 12525535_FACL4 is highly expressed in hippocampal and cerebellar neurons and may have a role in X linked mental retardation. 12824887_Overexpression of Fatty acid-CoA ligase 4 is associated with human hepatocellular carcinoma 15108178_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15849811_FACL4 is involved in the hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis and both cAMP and p38 MAPK pathways are associated with the regulation of FACL4 16276108_Disruption of DMD and the absence of ACSL4 in a patient are responsible for neuromuscular disease and cognitive impairment. 17934335_FACL4 affects HCC cell growth and suggest that modulation of FACL4 expression/activity is an approach for treatment of HCC. 18059177_FACL4 might play a role in the growth of hepatic cancer cells. 18614287_No association between polymorphisms in the FACL4 (fatty acid-CoA ligase 4) gene and nonspecific mental retardation in Qin-Ba mountain region of China. 18614287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19346733_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19346733_The common SNP (C to T substitution) in the first intron of the FACL4 gene is associated with altered Fatty Acid composition of plasma phosphatidylcholines in patients with metabolic syndrome . 19617635_ACSL4 can substitute the functions of dAcsl(l(2)44DEa in organismal viability, lipid storage and the neural wiring in visual center. 20351714_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20452052_This study found no significant relationship between FACL4 and cognitive function. 21085606_Data suggest that the development of combinatory therapies that profit from the ACSL4, lipooxygenase and COX-2 synergistic action may allow for lower medication doses and avoidance of side effects. 21242590_CSL4 modulates PGE release from human erial smooth muscle cells. 21384559_A total of six novel and 11 known single nucleotide polymorphisms were identified. Further studies are warranted to analyze the candidate genes at Xq11.1-q21.33. 21903867_the involvement of SHP2 activity in the regulation of the expression of the fatty acid-metabolizing enzyme ACSL4 22808264_The functional interaction between Acyl-CoA synthetase 4, 5-lipooxygenase and cyclooxygenase-2 controls tumor growth. 24155918_ACSL4 can serve as both a biomarker for, and mediator of, an aggressive breast cancer phenotype. 24201376_conclude that in our model system exogenous fatty acids are channeled preferentially towards phosphatidylinositol by ACSL4 overexpression 24576478_MiR-205 down-regulates ACSL4 through targeting its 3'UTR in hepatoma cells. 24879802_studies have identified a novel substrate-induced posttranslational regulatory mechanism by which AA downregulates ACSL4 protein expression in hepatic cells. 25500141_Upregulation of ACSL4 is responsible for the increase in triacylglycerol species containing long polyunsaturated fatty acids during activation of hepatic stellate cells. 25645621_Report PPARdelta-mediated regulatory mechanism for ACSL4 expression in liver tissue and cultured hepatic cells. 26282205_In vitro analysis showed that a recombinant COX-2 enzyme more effectively metabolized 5(S)-HETE to 5-11-diHETE compared to COX-1 enzyme. 26536660_we demonstrate that ACSL4 can be considered a novel activator of the mTOR pathway 26636648_Suggest role for ACSL4 expression in development of castration-resistant prostate cancer. 26949059_ACSL4 plays a tumor-suppressive role in gastric cancer. 27565726_ACSL4 is not only a sensitive monitor of ferroptosis, but also an important contributor of ferroptosis. 27928700_Data show that ELOVL7, SOCS3, ACSL4 and CLU were upregulated while PRKAR1A and ABCG1 were downregulated in the phlegm-dampness group. 28193492_ACLS4 and ACLS3 have roles in insulin secretion 28334272_Silencing of ACSL4 eliminated the 17beta-estradiol-induced increase in AA and EPA uptake. 28498416_These results suggest that ACSL1, ACSL4 and ACSL5 expression is regulated by ER signaling pathways and ACSL5 is a potential novel biomarker for predicting prognosis of breast cancer patients. 28887439_Study demonstrated that ACSL4 was overexpressed in HCC. 29450800_ACSL3 distribution closely overlapped with proteins involved in trafficking from the trans-Golgi network and endosomes. In contrast, the ACSL4 localisation pattern more closely followed that of calnexin which is an endoplasmic reticulum resident chaperone. 30264402_The regulatory network among peroxisomal ABCD2:ACSL4:VLCFA serves as a novel regulator of cartilage homeostasis, and these data may provide novel insights into the role of peroxisomal fatty acid metabolism in pathogenesis of human osteoarthritis (OA). 30414939_ACSL4 role in the drug resistance in breast cancer cell lines. 31160087_the A20-ACSL4 axis plays important roles in erastin-induced endothelial ferroptosis. 31311992_Regulatory mechanisms leading to differential Acyl-CoA synthetase 4 expression in breast cancer cells. 31672604_LncRNA NEAT1 promotes docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer by regulating ACSL4 via sponging miR-34a-5p and miR-204-5p. 31789401_Study shows that the expression of ACSL4 is downregulated in human glioma tissues and cells and demonstrates that ACSL4 protects glioma cells and exerts antiproliferative effects by activating a ferroptosis pathway. These results also highlight the pivotal role of ferroptosis regulation by ACSL4 in its protective effects on glioma. 32286604_Immunohistochemical staining reveals differential expression of ACSL3 and ACSL4 in hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic gastrointestinal metastases. 33038905_Tumor suppressor miR-424-5p abrogates ferroptosis in ovarian cancer through targeting ACSL4. 33068124_New inhibitor targeting Acyl-CoA synthetase 4 reduces breast and prostate tumor growth, therapeutic resistance and steroidogenesis. 33340617_ACSL4 reprograms fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma via c-Myc/SREBP1 pathway. 33539003_Cytochrome P450 reductase (POR) as a ferroptosis fuel. 34288826_Long non-coding RNA H19 protects against intracerebral hemorrhage injuries via regulating microRNA-106b-5p/acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4 axis. 34358518_Acyl-CoA synthetase-4 mediates radioresistance of breast cancer cells by regulating FOXM1. 34482070_Predictive and prognostic impact of ferroptosis-related genes ACSL4 and GPX4 on breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. 35197442_Thrombin induces ACSL4-dependent ferroptosis during cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. 35567995_ACSL4 promotes colorectal cancer and is a potential therapeutic target of emodin. 35603967_CRISPR/Cas9 Screens Reveal that Hexokinase 2 Enhances Cancer Stemness and Tumorigenicity by Activating the ACSL4-Fatty Acid beta-Oxidation Pathway. 35868067_ACSL4 is overexpressed in psoriasis and enhances inflammatory responses by activating ferroptosis. | ENSMUSG00000031278 | Acsl4 | 3188.248809 | 0.8274999 | -0.273168968 | 0.23799548 | 1.30939102056 | 0.2525049439963229502836838946677744388580322265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.47957082914060633616060158601612783968448638916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 2950.470561 | 414.724696 | 3588.188659 | 504.445635 | |
| ENSG00000069849 | 483 | ATP1B3 | protein_coding | P54709 | FUNCTION: This is the non-catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of Na(+) and K(+) ions across the plasma membrane. The exact function of the beta-3 subunit is not known. | Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Potassium;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Sodium;Sodium transport;Sodium/potassium transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of Na+/K+ and H+/K+ ATPases beta chain proteins, and to the subfamily of Na+/K+ -ATPases. Na+/K+ -ATPase is an integral membrane protein responsible for establishing and maintaining the electrochemical gradients of Na and K ions across the plasma membrane. These gradients are essential for osmoregulation, for sodium-coupled transport of a variety of organic and inorganic molecules, and for electrical excitability of nerve and muscle. This enzyme is composed of two subunits, a large catalytic subunit (alpha) and a smaller glycoprotein subunit (beta). The beta subunit regulates, through assembly of alpha/beta heterodimers, the number of sodium pumps transported to the plasma membrane. The glycoprotein subunit of Na+/K+ -ATPase is encoded by multiple genes. This gene encodes a beta 3 subunit. This gene encodes a beta 3 subunit. A pseudogene exists for this gene, and it is located on chromosome 2. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:483; | apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sodium:potassium-exchanging ATPase complex [GO:0005890]; sperm flagellum [GO:0036126]; ATPase activator activity [GO:0001671]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; cellular potassium ion homeostasis [GO:0030007]; cellular sodium ion homeostasis [GO:0006883]; membrane repolarization [GO:0086009]; positive regulation of ATP-dependent activity [GO:0032781]; positive regulation of potassium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:1903288]; positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:1901018]; positive regulation of sodium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:1903278]; potassium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:1990573]; potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071805]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; sodium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:0036376]; sodium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0035725] | 12456588_role in T and B lymphocyte activation 17176442_These results evidenced that the beta3 subunit of Na, K ATPase is expressed on RBC membrane but the epitope recognized by mAb P-3E10 is hidden in normal RBCs. we showed the association of beta3 subunit and alpha subunit of Na, K ATPase. 17446412_Elevated Na+ -K+ -ATPase activity postexercise may contribute to reduced fatigue after training. 24236063_B7H3 and ATP1B3 are overexpressed in tumor endothelial cells, favoring an angiogenic phenotype. 26694617_Data suggest that ATP1B3 is binding partner of BST-2 and regulates stability of BST-2; ATP1B3 is co-factor that accelerates BST-2 degradation and reduces BST-2-mediated restriction of HIV-1 replication/tropism and NFkappaB activation. 27240146_Our study demonstrated that ATP1B3 inhibit EV71 replication by enhancing the production of type-I interferons, which could act as a potential therapeutic target in EV71 infection. 29940031_ligation of the Na, K ATPase beta3 subunit on monocytes by mAb P-3E10 arbitrated T cell hypofunction. This mAb might be a promising novel immunotherapeutic antibody for the treatment of hyperresponsive T cell associated diseases. 30792309_These results demonstrate that CASPR1 binds with ATP1B3 and thereby contributes to the regulation of Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase maturation and trafficking to the plasma membrane in brain microvascular endothelial cells. 33534085_ATP1B3 Restricts Hepatitis B Virus Replication Via Reducing the Expression of the Envelope Proteins. 33868261_Integrative Transcriptomic, Proteomic and Functional Analysis Reveals ATP1B3 as a Diagnostic and Potential Therapeutic Target in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 35790431_[Screening and identification of key genes ATP1B3 and ENAH in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma: based on data mining and clinical validation]. | ENSMUSG00000032412 | Atp1b3 | 1134.611750 | 0.9659388 | -0.049996295 | 0.05917830 | 0.71373250762 | 0.3982074876508425731458373775240033864974975585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.62591359763884413247581051109591498970985412597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1133.316998 | 47.120304 | 1178.724614 | 48.751681 | |
| ENSG00000070423 | 55658 | RNF126 | protein_coding | Q9BV68 | FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that mediates ubiquitination oF target proteins (PubMed:23277564, PubMed:24275455, PubMed:24981174). Depending on the associated E2 ligase, mediates 'Lys-48'- and 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of substrates (By similarity). Part of a BAG6-dependent quality control process ensuring that proteins of the secretory pathway that are mislocalized to the cytosol are degraded by the proteasome. Probably acts by providing the ubiquitin ligase activity associated with the BAG6 complex and be responsible for ubiquitination of the hydrophobic mislocalized proteins and their targeting to the proteasome (PubMed:24981174, PubMed:29042515). May also play a role in the endosomal recycling of IGF2R, the cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor (PubMed:24275455). May play a role in the endosomal sorting and degradation of several membrane receptors including EGFR, FLT3, MET and CXCR4, by mediating their ubiquitination (PubMed:23418353). By ubiquitinating CDKN1A/p21 and targeting it for degradation, may also promote cell proliferation (PubMed:23026136). May monoubiquitinate AICDA (PubMed:23277564). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91YL2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23277564, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23418353, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24275455, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24981174, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29042515, ECO:0000305|PubMed:23026136}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23026136, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24981174}. | The protein encoded by this gene contains a RING finger domain, a motif present in a variety of functionally distinct proteins and known to be involved in protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:55658; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; epidermal growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005154]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; cytoplasm protein quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system [GO:0071629]; negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0042059]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein K48-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070936]; protein K63-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070534]; protein monoubiquitination [GO:0006513]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi [GO:0042147]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the multivesicular body sorting pathway [GO:0043162] | 23026136_These findings suggest that RNF126 promotes cancer cell proliferation by targeting p21 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation 23277564_identify a unique cofactor, RING finger protein 126 (RNF126), verify its interaction by traditional techniques, and show that it has functional consequences as RNF126 is able to ubiquitylate activation-induced cytidine deaminase 23418353_RNF126 and Rabring7 play a role in the ubiquitin-dependent sorting and downregulation of membrane receptors. 24275455_The ubiquitin ligase RNF126 has a role in the retrograde sorting of the CI-MPR. 24981174_RNF126 is recruited to the N-terminal Ubl domain of Bag6 and preferentially ubiquitinates juxtahydrophobic lysine residues on Bag6-associated clients. 26234677_this results suggest a novel role of RNF126 in promoting Homologous recombination-mediated repair through positive regulation on BRCA1 expression by direct interaction with E2F1. 27193484_Studies present the solution structure of the RNF126_NZF (N-terminal zinc finger domain) as well as the structure of RNF126_NZF/BAG6_UBL complex and characterize the interaction of RNF126 with the UBL domains from both BAG6 and UBL4A from the BAG6 sortase complex. 27227488_These data suggested that RNF126 might be related to the progression of tongue cancer through regulating AKT signaling pathway. 27895153_RNF126 is a novel regulator of NHEJ that promotes completion of DNA repair by ubiquitylating Ku80 and releasing Ku70/80 from damaged DNA. 28228265_RNF126 depletion results in frataxin accumulation in cells derived from FRDA patients. 29326282_CHEK1 inhibition targets breast cancer cells expressing higher levels of RNF126 by enhancing replication stress. 30529286_RNF126 negatively regulates RNF168 function in DNA damage response and its appropriate cellular expression levels are essential for homologous recombination-mediated DNA double-strand break repair. 31371451_We conclude that the RNF126/BAG6 complex contributes to G0S2 degradation and that interventions to prevent G0S2 degradation may offer a therapeutic strategy for managing ischemic diseases. 32132033_RNF126 expression was significantly associated with tumor depth and presence of venous invasion. 32147403_Roles of RNF126 and BCA2 E3 ubiquitin ligases in DNA damage repair signaling and targeted cancer therapy. 32254065_High Expression of RING Finger Protein 126 Predicts Unfavorable Prognosis of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. 32645369_RNF126-Mediated Reubiquitination Is Required for Proteasomal Degradation of p97-Extracted Membrane Proteins. 33664240_E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF126 affects bladder cancer progression through regulation of PTEN stability. 34388456_CHFR-mediated degradation of RNF126 confers sensitivity to PARP inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer cells. 34533052_Overexpression of RNF126 is associated with poor prognosis and contributes to the progression of lung adenocarcinoma. 36068398_RNF126 contributes to stem cell-like properties and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma through ubiquitination and degradation of LKB1. | ENSMUSG00000035890 | Rnf126 | 293.047878 | 0.7720195 | -0.373290736 | 0.09161622 | 16.63031072724 | 0.0000454193370345236892477759627073652382023283280432224273681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00050826054915113392466269326419592289312276989221572875976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 256.854440 | 15.653268 | 334.470388 | 19.608646 |
| ENSG00000071537 | 6400 | SEL1L | protein_coding | Q9UBV2 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in the endoplasmic reticulum quality control (ERQC) system also called ER-associated degradation (ERAD) involved in ubiquitin-dependent degradation of misfolded endoplasmic reticulum proteins (PubMed:16186509, PubMed:29997207). Enhances SYVN1 stability. Plays a role in LPL maturation and secretion. Required for normal differentiation of the pancreas epithelium, and for normal exocrine function and survival of pancreatic cells. May play a role in Notch signaling. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z2G6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16186509, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29997207}. | Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Notch signaling pathway;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is part of a protein complex required for the retrotranslocation or dislocation of misfolded proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum lumen to the cytosol, where they are degraded by the proteasome in a ubiquitin-dependent manner. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. | hsa:6400; | Derlin-1 retrotranslocation complex [GO:0036513]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Hrd1p ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000836]; Hrd1p ubiquitin ligase ERAD-L complex [GO:0000839]; ERAD pathway [GO:0036503]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; protein secretion [GO:0009306]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol [GO:0030970]; triglyceride metabolic process [GO:0006641]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433] | 11349831_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11544613_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11809711_SEL1L expression decreases breast tumor cell aggressiveness in vivo and in vitro. 12030374_Allele frequency of two intragenic microsatellite loci of SEL1L gene in Northern Italian population. 12030374_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12553058_Notch signal transduction is not regulated by SEL1L in leukaemia and lymphoma cells in culture. 14729273_Region within SEL1L between amino acid residues 659-794 contains a functionally relevant domain since a deletion mutant impairs SEL1L's ability to suppress tumor cell growth. 16331677_SEL1L has a very complex structure consisting of 21 exons featuring several alternative transcripts encoding for putative protein isoforms. Its complexity ensures protein flexibility and specificity. 16331889_SEL1L alters the expression of mediators involved in the remodeling of the extracellular matrix by creating a microenvironment that is unfavorable to invasive growth. 16412574_A possible role of the novel polymorphism as independent susceptibility factor of Alzheimer's dementia is shown 17822620_Overexpression of SEL1L protein is likely an early event during the pathogenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 17967421_endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced HRD1 and SEL1 expressions are mediated by IRE1-XBP1- and ATF6-dependent pathways, respectively 18264092_OS-9 and GRP94 deliver mutant alpha1-antitrypsin to the Hrd1-SEL1L ubiquitin ligase complex for ERAD 18314878_These findings reveal a role for SEL1L and HRD1 in IgM quality control. 18502753_XTP3-B forms an endoplasmic reticulum quality control scaffold with the HRD1-SEL1L ubiquitin ligase complex and BiP 18711132_identified AUP1, UBXD8, UBC6e, and OS9 as functionally important components of this degradation complex formed by proteins that interact with SEL1L 18811591_knockdown of SEL1L [sel-1 suppressor of lin-12-like (Caenorhabditis elegans)], a member of an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex involved in ER protein extraction, rescued significant amounts of Cln6(G123D) and Cln6(M241T) polypeptides. 19204006_SEL1L-B and -C participate to novel molecular pathways that, in parallel with ERAD, contribute to the disposure of misfolded/unfolded or orphan proteins through degradation or secretion 20416077_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21359144_Two new SEL1L variants are engaged in endosomal trafficking and secretion via vesicles, which could contribute to relieve ER stress in tumorigenic cells. 21454652_regulation of the stability and assembly of the HRD1-SEL1L complex is critical to optimize the degradation kinetics of ERAD substrates 21656579_the rs12435998 SNP in SEL1L gene plays a role in modifying age at diagnosis of PDA in Caucasian nonsmokers. 22350780_SEL1L expression is a potential colorectal cancer (CRC) tissue biomarker since its expression is significantly higher in adenoma cells with respect to normal mucosa; the levels of expression decrease in undifferentiated CRC cancers 23363602_ERdj5, by binding to Sel1L, triggers BiP-Cholera toxin interaction proximal to the Hrd1 complex; postulate this scenario enables the Hrd1-associated retrotranslocation machinery to capture the toxin efficiently once the toxin is released from BiP 23661430_Low expression of SEL1L is associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 24043630_ATF6 represents a novel type of ERAD-Lm substrate requiring SEL1L for degradation despite its transmembrane nature. 24311781_SEL1L down-modulation synergy enhances valporic acid cytotoxic effects by influencing glioma stem cells proliferation and self-renewal properties. 24324549_Data revealed close interaction of these two proteins in regulating the cross-talk between extracellular matrix and insulin signalling to create a favourable micro-environment for ss-cell development and function. 25948789_this is the first study reporting a significant association of the SEL1L SNP rs12435998 constitutive genetic variant with an improved overall survival in glioblastoma multiforme patients 26471130_The SEL1L critically regulates HRD1-mediated disposal of misfolded cargo through its short membrane spanning stretch. 27373828_Together, these results suggest that ER stress might comprise an important factor in GCD2 pathophysiology and that the effects of 4-PBA treatment might have important implications for the development of GCD2 therapeutics. 29371607_In summary, ER retention of pathogenic VLDLR mutants involves binding to calnexin, elevated endoplasmic reticulum stress, and delayed degradation which is dependent on SEL1L. 29532409_we found key statistical differences for the proteins SEL1, Notch3 and SOCS3 in the progression of uterine cervical cancer 29997207_Silencing of SEL1L during infection also stabilized an interaction of gO with the ER lectin OS-9, which likewise suggests that gO is an ER-associated degradation (ERAD) substrate. Taken together, our results identify an intriguing interaction of UL148 with the ERAD machinery and demonstrate that gO behaves as a constitutive ERAD substrate during infection. 31111685_SEL1L plays a major role in human malignant gliomas. 32182217_Sel1L-Hrd1 ER-associated degradation maintains beta cell identity via TGF-beta signaling. 32575107_Narrowing down the Common Cytogenetic Deletion 14q to a 5.6-Mb Critical Region in 1p/19q Codeletion Oligodendroglioma-Relapsed Patients Points to Two Potential Relapse-Related Genes: SEL1L and STON2. 33576152_SEL1L degradation intermediates stimulate cytosolic aggregation of polyglutamine-expanded protein. | ENSMUSG00000020964 | Sel1l | 1041.967139 | 0.8050504 | -0.312848924 | 0.11837489 | 6.96695366560 | 0.0083028728769274206394923609764191496651619672775268554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.04287212469636794698324422370205866172909736633300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 979.004072 | 72.909188 | 1221.606331 | 90.984620 | |
| ENSG00000073792 | 10644 | IGF2BP2 | protein_coding | Q9Y6M1 | FUNCTION: RNA-binding factor that recruits target transcripts to cytoplasmic protein-RNA complexes (mRNPs). This transcript 'caging' into mRNPs allows mRNA transport and transient storage. It also modulates the rate and location at which target transcripts encounter the translational apparatus and shields them from endonuclease attacks or microRNA-mediated degradation (By similarity). Preferentially binds to N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-containing mRNAs and increases their stability (PubMed:29476152). Binds to the 5'-UTR of the insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) mRNAs (PubMed:9891060). Binding is isoform-specific. Binds to beta-actin/ACTB and MYC transcripts. Increases MYC mRNA stability by binding to the coding region instability determinant (CRD) and binding is enhanced by m6A-modification of the CRD (PubMed:29476152). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23640942, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29476152, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9891060}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative initiation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;mRNA transport;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;Translation regulation;Transport | This gene encodes a protein that binds the 5' UTR of insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) mRNA and regulates its translation. It plays an important role in metabolism and variation in this gene is associated with susceptibility to diabetes. Alternative splicing and promoter usage results in multiple transcript variants. Related pseudogenes are found on several chromosomes. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. | hsa:10644; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic stress granule [GO:0010494]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; P-body [GO:0000932]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; mRNA 5'-UTR binding [GO:0048027]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; N6-methyladenosine-containing RNA binding [GO:1990247]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; translation regulator activity [GO:0045182]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; CRD-mediated mRNA stabilization [GO:0070934]; mRNA transport [GO:0051028]; negative regulation of translation [GO:0017148]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001817]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of RNA metabolic process [GO:0051252] | 15225648_HMGA2 differentially regulates expression of IMP family members during mouse embryogenesis. 15618018_Study suggests that there is a significant association between expression of IMP-2 and the growth of tumor cells, in which IMP-2 is associated with apoptosis induced by tretinoin. 17296566_VICKZ exhibits differential expression in lymphoma subtypes and thus may be a marker of potential value in the diagnosis and study of hematopoietic neoplasia. 17426251_we provide evidence that there is a strong and statistically significant correlation between HMGA2 and IMP2 gene expression in human liposarcomas. 17463246_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17463248_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17463249_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17804762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17827400_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17928989_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18162508_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18162508_The association of 6 loci with type 2 diabetes risk in Japanese patients is reported. 18259684_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18426861_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18430866_Novel evidence for a rare variant in the 3' downstream region of IGF2BP2 in type 2 diabetes in French Caucasians. 18430866_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18443202_Little evidence of association was observed between SNPs in IGF2BP2 and type 2 diabetes in African Americans. 18469204_Data confirmed the associations of single nucleotide polymorphisms in IGF2BP2 with risk for type 2 diabetes in Asians. 18469204_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18477659_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18516622_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18544707_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18591388_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18597214_Gene variants of CDKAL1, PPARG, IGF2BP2, HHEX, TCF7L2, and FTO predispose to type 2 diabetes in the German KORA 500 K study population. 18597214_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18598350_IGF2BP2 SNPs revealed a significant association with type 2 diabetes 18598350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18618095_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18618095_Variants of CDKAL1 and IGF2BP2 attenuate the first phase of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion but show no effect on the second phase of insulin secretion in hyperglycmia and type 2 diabetes. 18633108_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18633108_The results indicate that in Chinese Hans, common variants in IGF2BP2 loci independently or additively contribute to type 2 diabetes risk, likely mediated through beta-cell dysfunction. 18694974_Study show that polymorphisms in IGF2BP2 were associated with type 2 diabetes risk in the studied population. 18719881_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18853134_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18984664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18991055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19002430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19008344_Data show that SNPs in IGF2BP2 did not confer a significant risk for type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians. 19008344_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19018773_IGF2BP2 stimulation increases radiosensitivity of a pancreatic cancer cell line through endoplasmic reticulum stress under hypoxic comditions. 19020323_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19020324_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19033397_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19033397_Type 2 diabetes susceptibility of IGF2BP2 was confirmed in Japanese. 19082521_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19139842_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19148120_IGF2BP2 single-nucleotide polymorphisms are associated with body fat and this effect on body fat influences insulin resistance which may contribute to type 2 diabetes mellitus risk. 19148120_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19225753_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19228808_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19247372_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19258404_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19258437_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19258437_The IGF2BP2 variant shows a nominal interaction with exposure to famine in wartime in utero and predisposition to type 2 diabetes. 19279076_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19401414_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19502414_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19592620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19602701_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19720844_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19741166_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19741467_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19794065_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19808892_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19862325_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19892838_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19933996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20043145_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20075150_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20142250_prostate cancer was inversely associated with the IGF2BP2 rs4402960 T allele 20161779_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20203524_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20215779_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20384434_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424228_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20490451_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20509872_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20523342_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20523342_findings show that IGF2BP2 rs1470579 and rs4402960 polymorphisms may be associated with the development of type 2 diabetes and these polymorphisms may affect the therapeutic efficacy of repaglinide in Chinese T2DM patientsmellitus 20550665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20580033_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20616309_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20627640_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20627640_non-replications of IGF2BP2 associations with type 2 diabetes 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20712903_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20802253_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20816152_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20879858_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20889853_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20929593_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20956565_Data reveal how the posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression by IMP-2 contributes to the control of adhesion structures and stable microtubules and demonstrate an important function for IMP-2 in cellular motility. 21145819_The induction of a steatotic phenotype implies that p62 plays a role in hepatic pathophysiology 21422097_IGF2 is emerging as an important gene for ovarian cancer. 21576258_Double phosphorylation promotes IMP2 binding to the IGF2 leader 3 mRNA 5' untranslated region, and the translational initiation of this mRNA 21771882_involved in the selective autophagic clearance of non-ubiquitylated aggregation-prone substrates 21839790_meta-analysis suggested that IGF2BP2 rs4402960 polymorphism conferred elevated risk of T2DM, especially in European, East Asian and South Asian populations 22015911_rs4402960 and rs1470579 lymorphisms of the IFG2BP2po is a risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. 22032244_IGF2BP2 genetic variation is associated with type 2 diabetes. 22096510_Six SNP(rs7754840 in CDKAL1, rs391300 in SRR, rs2383208 in CDKN2A/2B, rs4402960 in IGF2BP2, rs10830963 in MTNR1B, rs4607517 in GCK)risk alleles of type 2 diabetes were associated with GDM in pregnant Chinese women. 22245690_Data validate that IGF2BP2 susceptibility variants rs4402960 and rs1470579 associate with T2DM in Lebanese Arabs. 22427968_Two isoforms of the mRNA binding protein IGF2BP2 are generated by alternative translational initiation. 22770937_genetic association studies: Data suggest that an SNP in IGF2BP2 (rs4402960) is associated with type 2 diabetes; IGF2BP2 may have genetic interactions with insulin-like growth factor II with a protective effect in male patients with type 1 diabetes. 22899010_oncofetal insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IMP2, IGF2BP2) regulates oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) in primary glioblastoma (GBM) sphere cultures (gliomaspheres) 22923468_Association to type 2 diabetes was found for rs13266634 (SLC30A8), rs7923837 (HHEX), rs10811661 (CDKN2A/2B), rs4402960 (IGF2BP2), rs12779790 (CDC123/CAMK1D), and rs2237892 (KCNQ1). 23029108_IGF2BP2 alternative variants were associated with GADA negative diabetes. The IGF2BP2 haplotypes and diplotypes increased the risk of diabetes in Malaysian subject. 23144361_In African Americans, seven of the 29 SNPs examined were found to be associated with T2D risk at P = 0.05, including rs6769511 (IGF2BP2). 23257922_p62 exerts IGF2-independent antiapoptotic action, which is facilitated via phosphorylation of ERK1/2. 23364967_Polymorphisms in PPARgamma(2) and IGF2BP2 were shown to be highly correlated with GDM occurrence, whereas no correlation was found for KCNQ1 polymorphisms. 23403707_IGF2BP2 genetic variants contribute to insulin resistance in Russian NIDDM patients. 23418049_Our results revealed two novel genes (IGF2BP2 and TNFRSF13B), whose function could account for the biologic pathways influencing MetS phenotypes. 23421499_there is a strong immune response of anti-p62 in sera from patients with colon cancer compared with normal human sera (NHS). 23536553_findings implicate the HMGA2-IGFBP2-NRAS signaling pathway as a critical oncogenic driver in embryonic rhabdomyosarcoma 23656854_IGF2BP2 may play a role in susceptibility to schizophrenia in Han Chinese, supporting the hypothesis that the co-occurrence of type 2 diabetes mellitus and schizophrenia may be explained by shared genetic risk variants. 23670970_TCF7L2 was replicated in this study (P = 0.004; combined analysis P = 3.8 x 10(-6)), and type 2 diabetes SNPs at or near CDKAL1, CDKN2A/B, and IGF2BP2 were associated with CFRD 24229666_IGF2BP2 was strongly associated with the risk of T2DM in Chinese Han population. 24636221_rs4402960 of IGF2BP2 gene is a strong candidate for Type 2 diabetes susceptibility and overweight/obesity risk. 24814803_VICKZ1 and VICKZ2 are overexpressed in ovarian carcinoma effusions suggesting a biological role at this anatomical site, and appear to have a role in proteolysis and invasion. VICKZ2 may be a prognostic marker in ovarian serous carcinoma effusions. 24898818_The case-control study and meta-analysis revealed a significant association between the IGF2BP2 rs4402960 variant and type 2 diabetes in Moroccan and Arab populations.[meta-analysis] 25062844_The present study provided data suggesting that the wild C allele of IGF2BP2 (rs4402960) had a protective effect against T2DM in obese subjects of Chinese Han population. 25247335_The IGF2BP2 gene rs1470579 and rs4402960 polymorphisms were associated with type 2 diabetes patients and therapeutic efficacy of pioglitazone in this Chinese population 25661373_The IGF2BP2 gene rs4402960 polymorphism increases the breast cancer risk of Chinese females with Han nationality, and is a breast cancer predisposing gene. 25719943_Imp2 regulates the activity of IGF2, which further activates PI3K/Akt signaling. 25721883_Data suggest that autoantibody against IGF2 mRNA-Binding Protein 2 (IMP2/p62) may be a useful serum biomarker for early-stage breast cancer screening and diagnosis. 26107517_HPV16 Down-Regulates the Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 2 to Promote Epithelial Invasion 26115082_Our results suggest IGF2BP2 and KCNQ1 polymorphisms might be independent predictors of chemotherapeutic response 26160756_Data show that insulin-like growth factor-2-mRNA-binding proteins IGF2BP1, IGF2BP2, and IGF2BP3 are direct targets of microRNA-1275 (miR-1275). 26416451_p62/IMP2 stimulates cell migration and reduces cell adhesion, contributing to breast cancer progression. 26889980_IMP2 expression is higher in ovarian and endometrial high-grade serous carcinomas (HGSC) than in ovarian or endometrial endometrioid carcinoma. Knockdown in ovarian HGSC cell line decreased cell proliferation. 27153315_IGF2BP2 as a post-transcriptional regulatory mRNA-binding factor that contributes to Colorectal carcinogenesis. 27184842_insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IMP2) binds to let-7 miRNA recognition elements (MREs) and prevents let-7 target gene silencing. 27294943_Our data suggests that IGF2BP2 polymorphisms are associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Asian populations. 27391348_IGF2BP2/IMP2 expression is linked to short survival and metastasis in esophageal adenocarcinoma 27625022_Study conclude that integration of genomic and transcriptomic data implicate circulating IGF2BP2 mRNA levels associated with glucose and insulin homeostasis 27733218_miR-1193 suppressed proliferation and invasion of human breast cancer cells via translational suppression of IGF2BP2. 28753127_IGF2BP2 protein is a tumor promoter that drives cancer proliferation through its client mRNAs IGF2 and HMGA1. 29217458_Data show that insulin-like growth factor-II mRNA-binding protein 2 and 3 (IMP2/3)-miR-200a-progesterone receptor axis represents a double-negative feedback loop and serves as a new potential therapeutic target for the treatment of Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). 29339719_miR-181a-5p suppresses the invasion and migration of cytotrophoblasts, and its inhibitory effects were at least partially mediated by the suppression of IGF2BP2 expression 29410390_rs4402960 (IGF2BP2) and rs2736098 (TERT) are identified as independent risk factors for type 2 diabetes. The simultaneous presence of both risk alleles confers a three-fold increased risk of developing the disease. 29476152_The direct binding of IGF2BPs to RNA N(6)-methyladenosine through their KH domains enhances mRNA stability and translation. 29510198_The miR-485-5p/IGF2BP2 axis orchestrates the growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. 30220054_IGF2BP2 and HMGA2 are significantly upregulated in metaplastic carcinoma compared to other breast cancer subtypes. 30242153_RNA interference-mediated knockdown of the Drosophila ortholog of IGF2BP2 in insulin-producing cells, a model for mammalian beta cells, conferred increased insulin output. 30247605_HMGA2 and IGF2 mRNA binding protein 2 (IMP2) were highly expressed in the granulosa cells (GCs) of women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and the HMGA2/IMP2 pathway promoted GC proliferation. Cyclin D2 and SERPINE1 mRNA binding protein 1 were regulated by IMP2 and were highly expressed in women with PCOS. 30335898_This study suggests that IGF2BP2 rs1470579 A > C and IGFBP3 rs6953668 G > A polymorphisms may decrease genetic susceptibility to Esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma in eastern Chinese Han population. 30371117_neither rs4402960 nor rs11705701 associated with gestational diabetes; rs4402960 and/or rs11705701 may affect length of gestation and Apgar score of newborn 30513526_The results showed that IGF2BP2 was overexpressed in Acute Myelocytic Leukemia patients. 31064983_Study generated a high-resolution, genome-wide map of chromatin architecture in pancreatic islets and used this map to annotate candidate target genes of islet enhancers. At the IGF2BP2 locus, type 2 diabetes risk alleles reduce islet chromatin accessibility and expression of target gene IGF2BP2 and that conditional knockout of IGF2BP2 homolog Imp2 in mouse islets impairs glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. 31089713_Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) enhances aerobic glycolysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells through stabilizing glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT1) mRNA. 31230592_Study showed that the expression of IGF2BP2 was significantly increased in colorectal carcinoma (CRC) tumor tissues. Also, IGF2BP2 enhanced SOX2 mRNA stability via an m6A-dependent manner. 31692433_RHPN1-AS1 Drives the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Regulating miR-596/IGF2BP2 Axis. 31791342_the in vivo experiments further identified the antitumor effects of inhibiting LINRIS in CRC, and the analysis of LINRIS/IGF2BP2 expression in the tissues from patients indicated their unique role in the development of CRC. 31804607_IGF2BP2 regulates DANCR by serving as an N6-methyladenosine reader. 31852504_We comprehensively reveal the oncogenic role of IGF2BP2 in pancreatic cancer carcinogenesis and confirm that genomic amplification and the silencing of miR-141 contribute to its activation. Our findings highlight that IGF2BP2 may be a promising molecular target for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. 31938912_rs11927381 Polymorphism and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Contribution of Smoking to the Realization of Susceptibility to the Disease. 32329795_Influence of IGF2BP2, HMG20A, and HNF1B genetic polymorphisms on the susceptibility to Type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese Han population. 32662505_Lack of association between IGF2BP2 rs4402960 polymorphism and gestational diabetes mellitus: a case-control study, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. 32668274_Initiation of stress granule assembly by rapid clustering of IGF2BP proteins upon osmotic shock. 32713259_IGF2BP2 stabilized FBXL19-AS1 regulates the blood-tumour barrier permeability by negatively regulating ZNF765 by STAU1-mediated mRNA decay. 32767321_Functional characterization of the long noncoding RNA MIR22HG as a tumour suppressor in cervical cancer by targeting IGF2BP2. 32784624_IGF2BP2 Polymorphisms Are Associated with Clinical Characteristics and Development of Oral Cancer. 33390804_Evidence of association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms in lipid metabolism-related genes and type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Chinese population. 33452460_Overexpression of Hmga2 activates Igf2bp2 and remodels transcriptional program of Tet2-deficient stem cells in myeloid transformation. 33526059_LINC00460/DHX9/IGF2BP2 complex promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis by mediating HMGA1 mRNA stability depending on m6A modification. 33561557_Identification of proteins related with pemetrexed resistance by iTRAQ and PRM-based comparative proteomic analysis and exploration of IGF2BP2 and FOLR1 functions in non-small cell lung cancer cells. 33705986_RNA m6A reader IMP2/IGF2BP2 promotes pancreatic beta-cell proliferation and insulin secretion by enhancing PDX1 expression. 33754909_Identification of Prognostic RBPs in Osteosarcoma. 33758932_microRNA-320b suppresses HNF4G and IGF2BP2 expression to inhibit angiogenesis and tumor growth of lung cancer. 33824282_ZEB1-induced LINC01559 expedites cell proliferation, migration and EMT process in gastric cancer through recruiting IGF2BP2 to stabilize ZEB1 expression. 34185427_m(6) A modification of lncRNA PCAT6 promotes bone metastasis in prostate cancer through IGF2BP2-mediated IGF1R mRNA stabilization. 34309973_IGF2BP2 promotes the progression of colorectal cancer through a YAP-dependent mechanism. 34340128_IGF2BP2 knockdown suppresses thyroid cancer progression by reducing the expression of long non-coding RNA HAGLR. 34345216_SUMOylation of IGF2BP2 promotes vasculogenic mimicry of glioma via regulating OIP5-AS1/miR-495-3p axis. 34380038_Actinin BioID reveals sarcomere crosstalk with oxidative metabolism through interactions with IGF2BP2. 34518440_lncRNA HCG11 suppresses human osteosarcoma growth through upregulating p27 Kip1. 34608837_Targeting PD-L1 (Programmed death-ligand 1) and inhibiting the expression of IGF2BP2 (Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2) affect the proliferation and apoptosis of hypopharyngeal carcinoma cells. 34624573_LncRNA HCG11 mediated by METTL14 inhibits the growth of lung adenocarcinoma via IGF2BP2/LATS1. 34696797_CircCD44 plays oncogenic roles in triple-negative breast cancer by modulating the miR-502-5p/KRAS and IGF2BP2/Myc axes. 34705667_Identification of the function and mechanism of m6A reader IGF2BP2 in Alzheimer's disease. 34709120_N6-methyladenosine reader YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 3 or insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 knockdown protects human bronchial epithelial cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inactivating p38 MAPK, AKT, ERK1/2, and NF-kappaB pathways. 34743750_N6-methyladenosine reader IMP2 stabilizes the ZFAS1/OLA1 axis and activates the Warburg effect: implication in colorectal cancer. 34750570_Loss of Hilnc prevents diet-induced hepatic steatosis through binding of IGF2BP2. 34753397_Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 regulates proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis of keratinocytes by modulating heparanase stability. 35011587_WT1-AS/IGF2BP2 Axis Is a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Lung Adenocarcinoma According to ceRNA Network Comprehensive Analysis Combined with Experiments. 35014946_Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2-stabilized long non-coding RNA Taurine up-regulated gene 1 (TUG1) promotes cisplatin-resistance of colorectal cancer via modulating autophagy. 35089636_Insulin-like growth factor II-producing colonic carcinoma presenting with non-islet cell tumor hypoglycemia: An autopsy report revealing neuroendocrine differentiation in the metastatic foci and literature review. 35092501_The analysis of N6-methyladenosine regulators impacting the immune infiltration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 35129592_IGF2BP2 maybe a novel prognostic biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 35163144_Deep Resequencing of 9 Candidate Genes Identifies a Role for ARAP1 and IGF2BP2 in Modulating Insulin Secretion Adjusted for Insulin Resistance in Obese Southern Europeans. 35173309_LINC01021 maintains tumorigenicity by enhancing N6-methyladenosine reader IMP2 dependent stabilization of MSX1 and JARID2: implication in colorectal cancer. 35318440_m(6)A demethylase ALKBH5 promotes tumor cell proliferation by destabilizing IGF2BPs target genes and worsens the prognosis of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. 35446451_The ''m6A writer'' METTL3 and the ''m6A reader'' IGF2BP2 regulate cutaneous T-cell lymphomas progression via CDKN2A. 35502827_N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) reader IGF2BP2 promotes gastric cancer progression via targeting SIRT1. 35526050_LncRNA-PACERR induces pro-tumour macrophages via interacting with miR-671-3p and m6A-reader IGF2BP2 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 35561648_Circ_0000775 promotes the migration, invasion and EMT of hepatic carcinoma cells by recruiting IGF2BP2 to stabilize CDC27. 35706003_The role of insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding proteins in female reproductive pathophysiology. 35707044_lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 Facilitates Tumorigenesis and Ferroptosis Resistance through SLC7A11 by IGF2BP2 Pathway in Melanoma. 35763110_N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) reader IGF2BP2 stabilizes HK2 stability to accelerate the Warburg effect of oral squamous cell carcinoma progression. 35894142_Decreased RNAbinding protein IGF2BP2 downregulates NT5DC2, which suppresses cell proliferation, and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in diffuse large Bcell lymphoma cells by regulating the p53 signaling pathway. 35907138_Circular RNA circPBX3 promotes cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer cells via interacting with IGF2BP2 to stabilize ATP7A mRNA expression. 35919812_Cytoplasmic IGF2BP2 Protein Expression in Human Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Prognostic and Clinical Implications. 36281789_IGF2BP2 serves as a core m6A regulator in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 36416324_Construction and clinical evaluation of N6-methyladenosine risk signature of YTHDC2, IGF2BP2, and HNRNPC in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000033581 | Igf2bp2 | 303.468008 | 0.8599889 | -0.217610049 | 0.11257446 | 3.73111597466 | 0.0534076995702613480099252285526745254173874855041503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.17170004633160554363691119306167820468544960021972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 260.146522 | 17.411559 | 303.816452 | 20.338895 | |
| ENSG00000074706 | 26034 | IPCEF1 | protein_coding | Q8WWN9 | FUNCTION: Enhances the promotion of guanine-nucleotide exchange by PSCD2 on ARF6 in a concentration-dependent manner. {ECO:0000250}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | Predicted to enable peroxidase activity. Predicted to be involved in response to oxidative stress. Predicted to be located in cytosol and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:26034; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; oxygen carrier activity [GO:0005344]; peroxidase activity [GO:0004601]; oxygen transport [GO:0015671]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979] | 12920129_IPCEF1 increases the in vitro and in vivo stimulation of ARFGTP formation by cytohesin 2 17067457_PTEN may down-regulate the expression of PIP3, and then down-regulate the expression of cyclin D1, which leads to the suppression of cell growth. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20016009_protein-protein interaction mediated by ARNO coiled-coil domain required for ARNO induced motility; coiled-coil domain promotes assembly of multiprotein complex containing ARNO and Dock180; assembly of complex requires coiled-coil domain, GRASP and IPCEF 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22085542_CNK3 and IPCEF1 produce a single protein that is required for HGF dependent Arf6 activation and migration. 34165176_Circular RNA profiling reveals a potential role of hsa_circ_IPCEF1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000064065 | Ipcef1 | 2385.232619 | 1.0177974 | 0.025450444 | 0.34916059 | 0.00529153079 | 0.9420107026280908346649312079534865915775299072265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.97389842633863532572746635196381248533725738525390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 2379.212721 | 543.259650 | 2360.804082 | 539.321157 | |
| ENSG00000075711 | 1739 | DLG1 | protein_coding | Q12959 | FUNCTION: Essential multidomain scaffolding protein required for normal development (By similarity). Recruits channels, receptors and signaling molecules to discrete plasma membrane domains in polarized cells. May play a role in adherens junction assembly, signal transduction, cell proliferation, synaptogenesis and lymphocyte activation. Regulates the excitability of cardiac myocytes by modulating the functional expression of Kv4 channels. Functional regulator of Kv1.5 channel. During long-term depression in hippocampal neurons, it recruits ADAM10 to the plasma membrane (PubMed:23676497). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10656683, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12445884, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14699157, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15263016, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19213956, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20605917, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23676497}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain;Synapse;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes a multi-domain scaffolding protein that is required for normal development. This protein may have a role in septate junction formation, signal transduction, cell proliferation, synaptogenesis and lymphocyte activation. A multitude of transcript variants deriving from alternative splicing and the use of multiple alternate promoter have been observed, including some splice variants that may be specific to brain and other tissues. An upstream uORF may regulate translation at some splice variants of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2018]. | hsa:1739; | adherens junction [GO:0005912]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basement membrane [GO:0005604]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; cell projection membrane [GO:0031253]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; intercalated disc [GO:0014704]; lateral loop [GO:0043219]; lateral plasma membrane [GO:0016328]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; MPP7-DLG1-LIN7 complex [GO:0097025]; myelin sheath abaxonal region [GO:0035748]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; node of Ranvier [GO:0033268]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density membrane [GO:0098839]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; synaptic membrane [GO:0097060]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; cytoskeletal protein binding [GO:0008092]; guanylate kinase activity [GO:0004385]; L27 domain binding [GO:0097016]; mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase binding [GO:0031434]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0004721]; potassium channel regulator activity [GO:0015459]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; structural constituent of postsynaptic density [GO:0098919]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; actin filament polymerization [GO:0030041]; activation of protein kinase activity [GO:0032147]; amyloid precursor protein metabolic process [GO:0042982]; astral microtubule organization [GO:0030953]; bicellular tight junction assembly [GO:0070830]; branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0001658]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; cortical actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030866]; cortical microtubule organization [GO:0043622]; embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048704]; endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001935]; establishment of centrosome localization [GO:0051660]; establishment or maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0007163]; establishment or maintenance of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity [GO:0045197]; hard palate development [GO:0060022]; immunological synapse formation [GO:0001771]; lens development in camera-type eye [GO:0002088]; membrane raft organization [GO:0031579]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; negative regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1903753]; negative regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051898]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane [GO:0099645]; peristalsis [GO:0030432]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of potassium ion transport [GO:0043268]; positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903078]; protein kinase B signaling [GO:0043491]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein-containing complex localization [GO:0031503]; receptor clustering [GO:0043113]; receptor localization to synapse [GO:0097120]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of membrane potential [GO:0042391]; regulation of myelination [GO:0031641]; regulation of potassium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:1903764]; regulation of potassium ion import [GO:1903286]; regulation of protein localization to synapse [GO:1902473]; regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1902305]; regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0098911]; regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization [GO:1903760]; reproductive structure development [GO:0048608]; smooth muscle tissue development [GO:0048745]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098] | 10779557_PDZ2 domain binds TOPK/PBK, a novel mitotic kinase. 11723125_We identify the functions of the two alternatively spliced regions. The N-terminal alternatively spliced region is capable of binding several SH3 domains and also moderates the level of protein oligomerization. 12081647_results suggest that the SH3, HOOK and GK domains of hDLG are important for its cytoplasmic localization 12419826_changes in expression in high-grade premalignant cervical neoplasias; data suggest that loss of hDlg at sites of intercellular contact may be an important step in the development of epithelial cancers 12668732_SAP97 is an intracellular binding partner of TACE and may have a role in the regulation of TACE shedding activity 12807908_alternatively spliced I3 insertion plays a critical role in recruiting hDlg to the lateral membrane in epithelial cells via its interaction with protein 4.1R 12902344_Upon hyperphosphorylation, hDlg interacts with the beta-TrCP ubiquitin ligase receptor through a DSGLPS motif, and consequently, overexpression of beta-TrCP enhances ubiquitination of Dlg protein and decreases its stability. 12970345_multiple isoforms of SAP97 were identifed in human heart atrium specimens; isoforms were found to co-immunoprecipiate with hKv1.5; isoforms were found to have distinct effect on hKv1.5 current and spatial channel organization 14699157_hDlg may be a determinant in E-cadherin-mediated adhesion and signaling in mammalian epithelial cells 15221964_Dlg downregulation and/or alterations in its localization may contribute to transformation and may explain some of the characteristics of cervix neoplasms. 15286176_hDlg stabilizes HTLV-1 envelope glycoproteins at the virological synapse formed between infected and target cells, hence assisting the cell-to-cell transmission of the virus 15485825_Delta1 recruits Dlg1 at cell-cell contacts and regulates cell migration. 16228013_AKAP79/150 coordinates different enzyme combinations to modulate the activity of two distinct neuronal ion channels: AMPA-type glutamate receptors and M-type potassium channels 16466689_specific inhibition of kinase C by Calphostin C eliminated the increase in wild-type potassium channel protein Kv1.5 currents associated with SAP97 overexpression suggesting a role for this kinase in the response 16619250_Down-regulation of DLG1 is associated with colon cancer progression 17069616_Crystal structure of the second PDZ domain of SAP97 in complex. 17172448_Dlgh1 also regulates smooth muscle orientation, and human DLG1 mutations may contribute to hereditary forms of hydronephrosis 17332497_MPP7 targets to the lateral surface of epithelial cells via its L27N domain, through an interaction with Dlg1. 17574238_The different hDlg isoforms play distinct roles at various stages of epithelial differentiation. 17696365_Binding of the SH3-I3-GUK module of hDlg to GAKIN activates the microtubule-stimulated ATPase activity of GAKIN by approximately 10-fold. We propose: the cargo-mediated regulation of motor activity is a general paradigm for the activation of kinesins. 17713926_Isothermal titration calorimetry with a series of peptides showed that HPV-18 E6 bound hDlg PDZ2 about 5-fold stronger than HPV-16 E6; the binding was disabled by phosphorylation at Thr156. 17980554_MARCH2 is co-localized with DLG1 at sites of cell-cell contact. 18245566_SAP97 regulates the K(+) current in cardiac myocytes by retaining and immobilizing Kv1.5 subunits in the plasma membrane. 18461433_Dlg1, through the interaction with GLUT1 and Env, plays a positive role in the syncytium formation induced by HTLV-1. 18665322_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18665322_The present findings suggest that the SAP97 gene may be a susceptibility factor in male schizophrenics and that the modification of the glutamate receptors-SAP97 signaling pathway could be involved in the disease pathophysiology. 18725271_Data suggest a role for Snail transcription factors in the control of DLG1 expression and provide a basis for understanding the transcriptional regulation of DLG1 18760273_Results suggest that human discs large and GAKIN play functional roles in the maintenance of midbody architecture during cytokinesis. 18930083_DLG1 participates in the control of TGFalpha bioavailability through its dynamic interaction with the growth factor precursor and TACE. 19017653_Muscarinic-induced recruitment of plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase involves PSD-95/Dlg/Zo-1-mediated interactions. 19066288_These findings establish phosphorylation events by CDKs 1 and 2 as key regulators of Discs Large 1 localisation and function. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19213956_SAP97 is a major partner for surface expression and CaMKII-dependent regulation of cardiac Kv4.2 and kv4.3 channels. 19307009_nuclear forms of Dlg phosphorylated on its CDK phospho-acceptor sites has enhanced susceptibility to E6-induced degradation 19586902_Net1 requires interaction with PDZ domain proteins, such as Dlg1, to protect it from proteasome-mediated degradation and to maximally stimulate RhoA and that this interaction is regulated by cell-cell contact. 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20356847_analysis of the crystal structure of a small protein domain, SAP97 PDZ2 I342W C378A, and its folding pathway 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20398908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20551903_These results uncover a crucial function for ezrin, Dlg1 and microtubules in the organization of the immune synapse and TCR signal down-regulation. 20605917_In response to hyperosmotic stress, p38 also regulates formation of complexes between hDlg and PSF. 20643107_these results reveal a previously unreported pathway for hDlg phosphorylation in mitosis and show that ERK5 pathway mediates hDlg cell cycle dependent phosphorylation. 20691406_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20702775_The Dlg1-MPP7-Mals3 heterotrimer consists of 2 pairs of heterodimeric L27 domains. These 2 dimers are asymmetric due to the large difference between the N- and C-terminal tandem L27 domain of MPP7. 20980075_These findings not only indicate SAP97 as a point of convergence between amyloid cascade and synaptic failure in AD, but also allow a different interpretation of AD which can be now perceived as synaptic trafficking defect pathology. 21041448_The Dlg1 interacts with dynein via the scaffolding protein GKAP and together, Dlg1, GKAP, and dynein control microtubule dynamics and organization near the cell cortex and promote centrosome positioning. 21113079_the higher off rate constants of HPV16 E6, as compared with those of the HPV18 E6 mimic E6L151V, account for its lower affinity toward the SAP97 PDZ domains, in particular for PDZ2 and PDZ3 21164104_SAP97 and dystrophin macromolecular complexes determine two pools of cardiac sodium channels Nav1.5 in cardiomyocytes. 21489588_HPV16 E6 association with PDZ domain-containing proteins, MAGI1, Dlg1 or Scrib, stabilized the levels of E6. 21595829_Studies represent first analyses of 5'-UTR of DLG1 transcripts; data suggest that differential expression of alternatively spliced 5'-UTRs with different translational properties result in changes in DLG1 expression. 21615688_hDlg acts as a MEK2-specific scaffold protein for the ERK signaling pathway. 21849460_These findings indicate that binding of NS1 to Scribble and Dlg1 functions to disrupt the cellular tight junction and that this effect likely contributes to the severe disease associated with highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza A viruses. 21850710_Low-to-moderate penetrance protein coding mutations or non-coding mutations at DLG1 and/or PAK2, or a nearby gene, may reproduce the behavioral characteristics of the 3q29 microdeletion. 21858148_Results provide new insights into the binding mode of a defined C-terminal segment of APC by the PDZ domains of DLG1. 22027822_Data establish the requirement of scaffolding to DLG1 for PKCalpha to promote cellular migration. 22185284_E-cadherin is necessary for localization of DLG1 but not phosphorylated MEK2 to the midbody ring during cytokinesis. 22225629_These findings further support the possible involvement of the SAP97 gene variation in the susceptibility to schizophrenia in males and in the genetic basis for sex differences in the disorder 22272285_Data suggest that the effect of Dlg1 on HIV-1 infectivity is at the stage of virus entry. 22307621_Dlgh1 operates independently of the negative feedback pathway mediated by the related adapter protein Carma1 and thus presents an array of unique targets to selectively manipulate Treg function 22377151_Mutations in the coding sequence of LAMC1 and DLGH1 may not be associated with Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser Syndrome. 22378744_Knockdown of Dlg1, which binds Kv1.3 channels to tyrosine kinase Lck, abolishes modulation of Kv1.3 channels. 22383878_Dlg1 has a distinct oncogenic function in the context of HPV induced malignancy, one of the outcomes of which is increased RhoG activity and increased invasive capacity. 22434720_Data suggest that hDlg may serve as a platform to bring in proximity APC and PTEN tumor suppressor activities. 22657348_Dlg is a physiologically relevant regulator of Cx43 in transformed epithelial cells. 22792261_During anoikis, hScrib and hDlg1 have distinct and opposing functions in human keratinocytes. 23532850_Discs large 1 (Dlg1) scaffolding protein participates with clathrin and adaptator protein complex 1 (AP-1) in forming Weibel-Palade bodies of endothelial cells. 23576434_studies show that SAP97 interactions with CRFR1 attenuate CRFR1 endocytosis and that SAP97 is involved in coupling G protein-coupled receptors to the activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. 23624197_The C-terminal tail of DLG1 is bound to the peptide-binding site of an adjacent symmetry-related DLG1 guanylate kinase molecule. 23864692_our findings suggest a molecular mechanism by which CASK binding regulates SAP97 conformation and its subsequent sorting and synaptic targeting of AMPARs and NMDARs during trafficking to synapses. 24324269_the nature of the residue at position -3 in the PDZ regulated whether the beta1-AR was internalized alone or in complex with SAP97. 24503895_MPP3 and Dlg, membrane-associated guanylate kinase homologs (MAGuK) proteins, connect CADM1 with p85 of PI3K by forming a multi-protein complex at the periphery of cells. 24788832_E4-ORF1 interacts with Dlg1 and PI3K to assemble a ternary complex where E4-ORF1 hijacks the Dlg1 oncogenic function to relocate cytoplasmic PI3K to the membrane for constitutive activation. 24937328_Novel genetic variants in the coding regions of DLG1 gene associated with susceptibility to Crohn's disease. 24989932_SAP97 plays a conserved role in regulating 5-HT2AR endocytosis and ERK1/2 signaling, but plays a novel role in regulating 5-HT2AR G protein coupling. 25253337_These findings indicate that most, if not all, human adenovirus E4-ORF1 proteins share a conserved molecular mechanism of PI3K activation via Dlg1 binding and confer a common capacity to promote oncogenic transformation. 25268382_Trans-homophilic interaction of CADM1 activates PI3K by forming a complex with MAGuK-family proteins MPP3 and Dlg. 25275262_DLG1, XIST, DDX3Y and RPS4Y1 genes can classify samples into different group clearly, and they are regarded as high confidence distinct gene biomarkers of Parkinson disease. 25429624_the synapse-associated protein-97 (SAP97), an excitatory synapse scaffolding element, governs ADAM10 trafficking from dendritic Golgi outposts to synaptic membranes, mediated by a previously uncharacterized protein kinase C. 25499266_While other domains of SAP97 were involved in forward trafficking of GluN1-3 out of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the SH3 domain was necessary and sufficient to block the ER retention. 25720117_The study provides new evidence for understanding the transcriptional regulation of DLG1 and the changes in DLG1 expression during different biological processes. 26440542_Reduced cortical expression of a newly identified splicing variant of the DLG1 gene in patients with early-onset schizophrenia was identified. 26653181_Human papillomavirus oncoproteins E6 and E7 induce the loss of DLG1 from the cell borders and an increase in the level of DLG1 protein, reflecting the pattern observed in cervical lesions. 27026592_Findings suggest that synapse-associated protein of 97-kDa molecular weight and disrupted in schizophrenia 1 contribute to maintaining Wnt/beta-catenin signaling activity within a homeostatic range by regulating glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta phosphorylation. 27240320_that Pten, through the Dlg1-binding ability of its PDZ-binding domain , accumulates phosphorylated Eg5 at duplicated centrosomes to establish symmetrical bipolar spindles that properly segregate chromosomes 27760079_Low expression of DLG1 is associated with Crohn's disease. 28040505_Results suggest that discs large tumour suppressor (DLG1) expression may have an important role in the progression of early dysplastic cervical lesions, giving prognostic information. 28195572_BAIAP2 is a candidate gene for mediating dendritic spine density abnormalities in schizophrenia. Data suggest that altered DNA methylation in schizophrenia may be a mechanism for schizophrenia-related dendritic spine density reductions. 28244171_These data support diverging presynaptic and postsynaptic roles of SAP97 N-terminal isoforms in synapse maturation and plasticity 28652577_Comparison with expanded cord blood-derived CD4(+)CD25(hi) tTreg and expanded Teffs from the same donors indicate that iTreg are intermediate between expanded CD4(+)CD25(hi) tTregs and Teffs, whereas modulation of suppressive activities by PKC-theta; and Dlgh1 signaling pathways are shared. 28926086_we identified a novel cleft-susceptibility locus at chromosome 3q29 with a DLG1 as a novel candidate gene for this common craniofacial anomaly. 28990294_Single nucleotide polymorphism in DLG1 gene is associated with schizophrenia. 29168728_By fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), we detected the direct binding of Tax to DLG1 within the cell. The interaction specifically affects the cellular distribution of not only DLG1, but also Tax. The aggregates distribute into the Golgi apparatus in spatial association with the microtubule-organizing center (MTOC). 29263038_the increased expression of DLG1 may be predictive of an unfavorable prognosis in colorectal cancer. 30517074_focus on some of the latest findings regarding DLG1 alterations in different diseases as well as its potential use as a biomarker for pathological progression. We further address the current knowledge on the molecular mechanisms regulating DLG1 expression and the posttranslational modifications that may affect DLG1 cell localization and functions 32224225_SAP97 polymorphisms associated with early onset Parkinson's disease. 32264889_HPV E6 and E7 oncoproteins cooperatively alter the expression of Disc Large 1 polarity protein in epithelial cells. 32293058_Scrib and Dlg1 polarity proteins regulate Ag presentation in human dendritic cells. 32411799_The Scribble Complex PDZ Proteins in Immune Cell Polarities. 32612162_The p.P888L SAP97 polymorphism increases the transient outward current (Ito,f) and abbreviates the action potential duration and the QT interval. 32692143_The genetic variations in SAP97 gene and the risk of schizophrenia in the Chinese Han population: a further study. 33486056_An internal class III PDZ binding motif in HPV16 E6* protein is required for Dlg degradation activity. 33945310_Whole-Exome Sequencing Identified DLG1 as a Candidate Gene for Familial Exudative Vitreoretinopathy. 34400226_Application of quantitative immunofluorescence assays to analyze the expression of cell contact proteins during Zika virus infections. 34911533_The circular RNA circDLG1 promotes gastric cancer progression and anti-PD-1 resistance through the regulation of CXCL12 by sponging miR-141-3p. 35039052_The SF3B1(R625H) mutation promotes prolactinoma tumor progression through aberrant splicing of DLG1. 35163460_Analysis of mRNA and Protein Levels of CAP2, DLG1 and ADAM10 Genes in Post-Mortem Brain of Schizophrenia, Parkinson's and Alzheimer's Disease Patients. 35380688_PDZ Proteins SCRIB and DLG1 Regulate Myeloma Cell Surface CD86 Expression, Growth, and Survival. | ENSMUSG00000022770 | Dlg1 | 257.880507 | 1.1494060 | 0.200888485 | 0.30191622 | 0.43855974854 | 0.5078184237634486564161306887399405241012573242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.71961686597244933771833075297763571143150329589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 288.986384 | 55.097961 | 251.916142 | 48.088963 | |
| ENSG00000076944 | 6813 | STXBP2 | protein_coding | Q15833 | FUNCTION: Involved in intracellular vesicle trafficking and vesicle fusion with membranes. Contributes to the granule exocytosis machinery through interaction with soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) proteins that regulate membrane fusion. Regulates cytotoxic granule exocytosis in natural killer (NK) cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19804848, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19884660}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Exocytosis;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport | This gene encodes a member of the STXBP/unc-18/SEC1 family. The encoded protein is involved in intracellular trafficking, control of SNARE (soluble NSF attachment protein receptor) complex assembly, and the release of cytotoxic granules by natural killer cells. Mutations in this gene are associated with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]. | hsa:6813; | azurophil granule [GO:0042582]; cytolytic granule [GO:0044194]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; specific granule [GO:0042581]; tertiary granule [GO:0070820]; syntaxin binding [GO:0019905]; syntaxin-1 binding [GO:0017075]; syntaxin-3 binding [GO:0030348]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001909]; neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0007269]; neutrophil degranulation [GO:0043312]; regulation of mast cell degranulation [GO:0043304]; vesicle docking involved in exocytosis [GO:0006904]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] | 12198139_binds to syntaxins 1A, 2, and 3 and regulates vesicle transport to the apical plasma membrane 18588921_Munc18-2 acts as a regulator of primary granule exocytosis, while Munc18-3 may preferentially regulate the fusion of secondary granules 19804848_Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 5 (FHL-5) is caused by mutations in Munc18-2 and impaired binding to syntaxin 11 19884660_STXBP2 is required at a late step of the secretory pathway for the release of cytotoxic granules by binding syntaxin 11, another component of the intracellular membrane fusion machinery. 20558610_mutation analysis, clinical presentation, and functional analysis of NK cells in patients with mutations in STXBP2 encoding Munc18-2, recently associated with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 5 20695848_Munc18b is functionally coupled to the assembly of exocytic SNARE complexes and increases exocytosis by interacting with the N-peptide and closed-conformation C-terminus of Stx3, thereby neutralizing the secretion-inhibitory effect of this SNARE. 20798128_Biallelic STXBP2 mutations were identified in families with familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 20823128_Data show that all but one patient with atypical familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis carried at least one splice-site mutation in UNC13D or STXBP2. 21152410_Data show that 3 novel mutations of STXBP2 gene were confirmed. 21881043_Missense and splice-site sequence variants in PRF1, MUNC13-4, and STXBP2 were found in 25 (14%) of the adult patients. The A91V-PRF1 genotype was found in 12 of these patients (48%). 22336081_Novel mutation in STXBP2 prevents IL-2-induced natural killer cell cytotoxicity in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 22451424_We report the largest cohort of patients with FHL5 so far, describe an extended disease spectrum, and demonstrate for the first time a clear genotype-phenotype correlation. 23382066_Mutations in STXBP2 do not only affect cytotoxic T lymphocytes but also cause changes in the intestinal and renal epithelium resulting in severe, osmotic diarrhea and renal proximal tubular dysfunction 23487749_Double knockdown of Munc18-1 and Munc18-2 in mast cells eliminates both IgE-dependent and ionomycin-induced degranulation and causes a significant reduction in syntaxin-11 without altering expressions of the other syntaxin isoforms examined. 23687090_We report that FHL-5 neutrophils have a profound defect in granule mobilization, resulting in inadequate bacterial killing, in particular, of gram-negative Escherichia coli, but not of Staphylococcus aureus. 24194549_Munc18-2 binds the N-terminal peptide of Stx11 with a ~20-fold higher affinity than Stx3, suggesting a potential role in selective binding. 25564401_Munc18-2(R65Q) and Munc18-2(R65W) retain the ability to interact with and stabilize STX11. However, presence of Munc18-2(R65Q/W) in patient-derived lymphocytes and forced expression in control CTLs and NK cells diminishes degranulation and cytotoxicity. 25947952_mutations result in severe chronic active Epstein-Barr virus disease 26320718_red blood cells express Munc18-2 and that erythroid cells from patients with FHL-5 exhibit intrinsic defects caused by STXBP2/Munc18-2 mutations. 26451869_two novel mutations of STXBP2: c.184A>G and c.577A>C. c.184A>G (p.Asn62Asp) was located within a highly conserved region of the STXBP2 protein and predicted to be deleterious. 27513731_STXBP2 Gene Polymorphism is associated with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistocytosis. 27781387_Mutation in STXBP2 gene is associated with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 28163042_Data show that Munc18b overexpression increased fusion of not only newcomer secretory granule (SG), but also predocked SGs in type-2 diabetes (T2D) human and Goto-Kakizaki Rat Islets. 28380445_Among these nine polymorphisms, rs188212047 [G/T (L212F)] of STXBP2 was significantly (dominant model; P = 4.84 x 10-8; odds ratio, 2.94) associated with myocardial infarction. STXBP2 may thus be a novel susceptibility locus for myocardial infarction in Japanese. 29044293_Neonatal platelets exhibit low levels of the Stx11-Munc18b complex (essential component of the SNARE machinery) and of beta1-tubulin. These developmental deficiencies are associated with defects in platelet adhesion, spreading and secretion. 29599780_In the current study, we have made the unexpected observation that congenital deficiency of the STXBP2 protein may also affect the expression of STXBP1. Further analysis identified an unsuspected functional role for STXBP1 in secretory granule-mediated NK and T-cell cytotoxicity. 30364784_Loss of Munc18-2/Stxbp2 recapitulated the pathologic features observed in patients with MUNC18-2 deficiency. 31651726_Different Clinical Presentation of 3 Children With Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis With 2 Novel Mutations. 33162974_STXBP2-R190C Variant in a Patient With Neonatal Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) and G6PD Deficiency Reveals a Critical Role of STXBP2 Domain 2 on Granule Exocytosis. 34339548_Spectrum mutations of PRF1, UNC13D, STX11, and STXBP2 genes in Vietnamese patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. | ENSMUSG00000004626 | Stxbp2 | 662.770839 | 0.8659867 | -0.207583256 | 0.10557620 | 3.85995706305 | 0.0494515938702653964909039530084555735811591148376464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.16293924105416335290641427491209469735622406005859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 569.120242 | 40.509139 | 660.985981 | 46.862887 | |
| ENSG00000077238 | 3566 | IL4R | protein_coding | P24394 | FUNCTION: Receptor for both interleukin 4 and interleukin 13. Couples to the JAK1/2/3-STAT6 pathway. The IL4 response is involved in promoting Th2 differentiation. The IL4/IL13 responses are involved in regulating IgE production and, chemokine and mucus production at sites of allergic inflammation. In certain cell types, can signal through activation of insulin receptor substrates, IRS1/IRS2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8124718}.; FUNCTION: Soluble IL4R (sIL4R) inhibits IL4-mediated cell proliferation and IL5 up-regulation by T-cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8124718}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes the alpha chain of the interleukin-4 receptor, a type I transmembrane protein that can bind interleukin 4 and interleukin 13 to regulate IgE production. The encoded protein also can bind interleukin 4 to promote differentiation of Th2 cells. A soluble form of the encoded protein can be produced by proteolysis of the membrane-bound protein, and this soluble form can inhibit IL4-mediated cell proliferation and IL5 upregulation by T-cells. Allelic variations in this gene have been associated with atopy, a condition that can manifest itself as allergic rhinitis, sinusitus, asthma, or eczema. Polymorphisms in this gene are also associated with resistance to human immunodeficiency virus type-1 infection. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. | hsa:3566; | centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; interleukin-4 receptor activity [GO:0004913]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; defense response to protozoan [GO:0042832]; immune response [GO:0006955]; immunoglobulin mediated immune response [GO:0016064]; negative regulation of T-helper 1 cell differentiation [GO:0045626]; ovulation [GO:0030728]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of immunoglobulin production [GO:0002639]; positive regulation of macrophage activation [GO:0043032]; positive regulation of mast cell degranulation [GO:0043306]; positive regulation of myoblast fusion [GO:1901741]; positive regulation of T-helper 2 cell differentiation [GO:0045630]; production of molecular mediator involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002532]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627]; response to odorant [GO:1990834]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T-helper 1 cell differentiation [GO:0045063]; T-helper 2 cell differentiation [GO:0045064] | 11035134_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11164908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11233912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11354638_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11491529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11528525_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11544427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11678851_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11709756_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11709756_gene-gene interaction in asthma: IL4RA and IL13 in a Dutch population with asthma 11714803_Tyrosine-phosphorylated IL4R peptides coprecipitate SH2-containing tyrosine phosphatase-1, SH2-containing tyrosine phosphatase-2, and SH2-containing inositol 5'-phosphatase, demonstrating a regulatory role for the ITIM motif in IL-4-induced proliferation. 11786020_high-affinity interaction of human IL-4 and the receptor alpha chain is constituted by two independent binding clusters 11801567_internalization of interleukin 4 receptor alpha increases cytotoxic effect of interleukin 4-receptor-targeted cytotoxin in cancer cells. 11811777_Characterization of IL-4 receptor components expressed on monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages: variation associated with differential signaling by IL-4 11922633_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11922633_These results suggest TXA2 receptor polymorphism strongly interacts with IL-4R alpha polymorphism as a major determinant of high serum immunoglobulin E levels in atopic dermatitis. 11991671_Endogenous interferon-alpha production by differentiating human monocytes regulates expression and function of the IL-2/IL-4 receptor gamma chain 12020266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12047364_a single gene effect of IL4Ralpha variants or any other gene on chromosome 16 could not be shown in a selected population of children with asthma 12047365_no evidence for linkage of the IL4R gene locus with sarcoidosis 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12100043_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12115161_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12133990_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12171893_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12401728_association of haplotype with type 1 diabetes 12420205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12422339_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12442007_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12454749_up-regulated 5-fold in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells, probably leading to increased responsiveness to IL4 and resistance to apoptosis 12459556_role of Tyr-713 in the interleukin-4 receptor alpha in regulating dephosphorylation of Stat6 12508140_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12558814_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12594065_Allele frequency of IL4RA polymorphism was associated with rapid decline of lung function in smokers. 12594065_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12743452_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12748907_IL4R is associated with diabetes mellitus, type 1 in Filipinos. 12748907_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12753568_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12871855_Th2 cytokines enhance TARC expression in human airway smooth muscle cells in IL-4Ralpha genotype-dependent fashion. 12897746_No genotypic effects on total serum IgE levels. 12897746_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12900808_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12940513_IL-4R alpha chain 576R/R genotypes confer genetic susceptibility to allergic asthma in Chinese. 12940513_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12973929_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14523823_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14523823_The prevalence of the mutant variant of the IL-4ra gene was lower in neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) compared with those without NEC, suggesting that this mutation might protect against the development of NEC in VLBW infants. 14615367_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14745651_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14745651_functional variants within the IL4R gene predispose to hip osteoarthritis in Caucasian females 14984008_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14984008_investigated the frequency and genotypes of S503P and Q576R SNPs and their association with traits of allergic asthma in a Hawaii population 15005726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15007345_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15007345_polymorphisms of IL1A (G/T at +4845) and IL4RA (T/C at +22446) show an epistatic effect on the risk of atopy 15007352_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15007352_variants in the IL4, IL13, and IL4RA genes play an important role in controlling specific IgE response in atopy 15021309_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15057902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15122773_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15161635_Certain interstitial pneumonia patients can be modulated in a manner that is dependent on the IL-4 and IL-13 receptor subunit expression by these cells. 15170937_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15194285_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15298559_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15356556_V50R551 IL-4R alpha variant has enhanced function alone, but with Q110 IL-13 variant the 2 have a synergistic effect on IL-13-dependent gene induction. 15361128_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15367225_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15479272_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15497451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15497451_Polymorphisms of IL-4R previously associated with other immune mediated diseases, do not confer susceptibility to Graves' disease in white Caucasians in the United Kingdom. 15521376_differences in the potency of IL-13- and IL-4-mediated induction of eotaxin-3 might be explained by expression of types 1 and 2 IL-4 receptors in bronchial epithelium 15564773_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15566952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15660293_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15712015_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15733644_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15737301_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15842262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15969687_The IL-4RalphaQ576R polymorphism may involve in the development of penicillins allergy, and through modulating specific serum IgE levels. 15981567_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16024651_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16046318_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16100774_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16184405_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16189667_IL$R alpha V50 homozygosity associates with slow progression and that exon 12 U-haplotypes might be associated with both susceptibility to infection via parenteral route and resistance to infection via sexual exposure. 16189667_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16226465_The soluble receptor balance (sIL-2R/sIL-4R) in patients with severe hemolytic uremic syndrome may shift, depending on the disease state of the patients 16264039_In conclusion, these results suggest that viral airway infection may enhance interleukin-4-induced eotaxin-3 production through upregulation of the interleukin-4 receptor in airway epithelial cells. 16280132_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16313303_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16313681_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16387595_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16403098_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16503977_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16538488_No association between type 1 diabetes and any SNP or haplotype was found by the transmission disequilibrium test. 16538488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16551465_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16551465_This is the first demonstration of sex-specific association of the two foremost genes of the IL-4 signalling cascade with chronic inflammatory arthropathies. 16600026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16613701_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16625214_Multifactor dimensionality reduction (MDR) test was applied to detect epistasis, and identified single-IL4R(Q576R)- and three-IL4R(Q576R), IL5RA(-80), CD14(-260)- locus association models that predict multiple sclerosis risk with 75-76% accuracy. 16625214_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16640778_A structure/function analysis of the IL-4 ligand-receptor interaction, using various mutations of both the ligand and the receptor, is reported. 16646030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16681592_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16699452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16750991_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16757160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16842617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16867043_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16914241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16917945_Results show sequence variations as a possible way of altering alternative splicing selection of IL4R in vivo. 16938461_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16950281_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16961803_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17001290_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17006724_Homozygotes with the low activity allele of the A398G polymorphism in the IL4R gene had a modest increase in risk of atrophic gastritis (OR = 1.52, 95% CI: 1.05-2.21), compared with homozygotes of the high activity allele. 17006724_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17045041_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17045041_The Ile50Val polymorphism of IL-4R alpha gene is not associated with bronchial asthma in Han nationality patients. 17083349_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17083349_Variants in the IL4RA gene alone may not exert any major influence on susceptibility to asthma-related diseases in childhood, but in combination with other genes, such as IL9R, IL4RA may be an important gene for disease susceptibility 17091279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17115186_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17121586_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17143971_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17143971_Our findings of higher frequency of IL4 and IL4RA genotypes and alleles with rheumatoid arthritis. 17152005_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17170387_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17170387_SNPs in IL4Ralpha, which are more common in African Americans, are associated with severe asthma exacerbations, lower lung function, and increased mast cell-related tissue inflammation 17179726_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17201240_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17209513_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17257312_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17258448_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17284225_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17291854_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17303794_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17315188_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17362266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17420820_IL4+33 and IL4R*Q551 polymorphisms may have a promoting role of TH2 mediators in African MS descendants. IL4 and IL4R genes are susceptibility factors for Brazilian MS but may be able to modify ethnicity-dependent disease risk and penetrance. 17420820_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17444864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17523428_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17536219_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17548690_IL4 and IL4R polymorphisms and haplotypes were neither significantly associated with IgE levels in controls nor associated with glioma status 17548690_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17586032_A meta-analysis of results from case-control studies strongly supports the conclusion that the R551 IL4R variant imparts a modest yet significant risk for atopic asthma 17586032_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17600229_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17627763_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17688234_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17688234_The IL-4R 75V variant was associated with increased risk of cervical tumors, cases homozygote for 75V had an odds ratio of 1.91 (1.27-2.86) with a tendency that the association was stronger in noncarriers of the DQB1*0602 allele. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17714919_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17823973_IL4R gene polymorphisms may have roles in asthma in Chinese populations 17823973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17889143_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17900677_analysis of polymorphisms of Ile50Val (rs.1805010), Ser478Pro (rs.1805015), and Gln551Arg (rs.1801275) in the IL4R gene between Japanese patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Japanese healthy volunteers 17901851_IL-4R overexpression on newborns' monocytes and lymphocytes could be an early risk marker of allergy development. 17988330_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17988330_The IL-4R Ile50/Ile50 and IL-10R2 G520/G520 and G520/A520 genotypes were shown to determine the susceptibility to SLE(systemic lupus erythematosus)in a Chinese population 18006935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18031948_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18031948_we studied the association of variants in IL-4 (C-589T, G3017T) and IL-4R alpha (Gln576Arg) with allergies and with risk of pancreatic cancer 18095154_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18179773_IL-4 and IL-4RA gene polymorphisms concur in selecting the H. pylori infecting strain, probably influencing the IL-4 signalling pathway 18179773_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18263811_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18263811_combined polymorphisms in the IL-13/IL-4R signaling pathway were associated with SJS/TEN with ocular surface complications. 18389618_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18425216_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18433792_Analyses of genotype distributions and allele frequencies of study subjects revealed that rs 180275 polymorphism in IL4R was associated with an increase in BMI in Korean population. 18433792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18448485_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18538381_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18547691_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18576348_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18576348_our data indicate that the AA genotype of the IL4R 150V SNP is associated with joint erosions in psoriatic arthritis 18610831_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18610832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18625055_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18625055_There is a lack of association or interactions between the IL-4, IL-4Ralpha and IL-13 genes, and rheumatoid arthritis. 18628242_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18632425_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18633131_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18674658_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18691306_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18715339_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18773331_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18774776_This study demonstrated upregulation of type 1 IL-4R by IFN-gamma, which resulted in enhanced IL-4-induced production of CCL26 from keratinocytes. 18781131_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18809513_The urine evaluation of the balance between IFN-gammaR1 and IL4R receptors might be informative for the immune states of HUS patients. 18813073_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18849614_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18849614_Single nucleotide polymorphisms of IL4RA are not associated with olive pollen allergy or asthma, but the interaction between IL4RA I50V/Q551R was strongly associated with the asthma phenotype. 18927306_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18927306_Polymorphisms in the interleukin-4 receptor gene are associated with better survival in patients with glioblastoma 18931892_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18936436_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18957266_data indicate inactivation of receptor-associated protein tyrosine phosphatase activity by cytokine-generated reactive oxygen species is a physiologic mechanism for amplification of IL-4 receptor activation revealing a role for ROS in cytokine crosstalk 18974840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19011907_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19028820_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19109239_IL-4 activates signaling pathways through type I IL-4Rs qualitatively differently from IL-13, which cooperate to induce optimal gene expression. 19117745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19131662_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19263529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19264973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19279357_IL4RA (1902/G:G) polymorphism was found to be positively (susceptible) associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Macedonians. 19332120_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19382262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19382262_The present study for the first time suggests an association of IL-4Ralpha I50 allele with increased likelihood of HIV-1 infection in North Indian population. 19408823_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19414811_IL4Ralpha is up-regulated in both myeloid populations but its presence correlates with an immunosuppressive phenotype only when mononuclear cells, but not granulocytes, of tumor-bearing patients are considered. 19420105_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19421745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19421745_The IL4Ralpha Q576 allele is related to penicillin allergy, and the IL-4Ralpha I75 allele is associated with the symptom of urticaria. The Q576/I75 haplotype may be related with an allergy to penicillin. 19447482_These results suggest that day care attendance is associated with serum IgE levels, and this effect is modified by CD14-550C/T and IL4R Ile50Val polymorphisms. 19470040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19479237_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19505916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19508433_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19515749_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19515749_These data support the role for host germline gene variations of immunologically important factors like the IL4R I75V gene variation to predict the survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19531027_Data show that IL-4 receptors are functionally competent in pancreatic beta-cells and that they signal via PI3K and JAK/STAT pathways. 19544559_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19548368_IL4Ralpha could be a candidate gene for assessing the risk of renal cell carcinoma. 19548368_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19555572_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19559392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19590686_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19594368_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19657898_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19674346_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19683555_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19729601_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19739012_The urinary soluble IL-4 receptor levels did not correlate with the clinical severity of vesicoureteral reflux 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773451_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19783684_association of Syk to IL-4R(alpha) is of biological significance and IL-4R(alpha) is a new candidate to be added to the few cytokine receptor components which associate with Syk. 19819209_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19860911_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19862939_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19863607_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19863607_The results suggest that the genetic polymorphisms of IL-4R and TGF-beta1 are associated with the risk of colorectal cancer in a Korean population. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19956098_38 single-nucleotide polymorphisms in IL4R were genotyped using the Sequenom iPLEX Gold MassARRAY technology in 2042 multiplex families from nine cohorts. 20002627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20002627_Variations within the IL4R gene are associated with allergic diseases in children, preferably with eczema and disease phenotypes of ARC and asthma. 20040389_Data show that flavones inhibited the phosphorylation of STAT6, janus kinase 3, and IL-4Ralpha, whereas IL-4 signaling mediated through type II IL-4R was unaffected by flavones. 20072140_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20085599_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20085599_Significant associations of single nucleotide polymorphisms with wheeze in the past year were detected in only four genes (IL4R, TLR4, MS4A2, TLR9). Variants in IL4R and TLR4 were also related to allergen-specific IgE. 20128416_association between promoter polymorphisms and asthma in Iranian patients 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20163933_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20176658_Proliferation appears to be directly mediated via IL4Ralpha on the epithelial tumor cells 20213229_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20219689_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20298583_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20299965_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20378664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20394509_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20416077_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20417488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20444266_IL4R SNPs, rs1801275 and rs1805010, are associated with rheumatoid nodules in autoantibody-positive African-American rheumatoid arthritis patients with at least one HLA-DRB1 allele encoding the shared epitope. 20444266_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20459687_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20484924_IL4R polymorphisms were associated with asthma in the asthma 20484924_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20517665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20536507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20603037_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20603050_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20654748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20703737_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20716621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20729386_Data show differences in IL-4/IL-13 receptor subunit expression and responsiveness to IL-4 based on the extent of airway epithelial cell differentiation and suggest that these differences may have functional consequences in airway inflammation. 20811626_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21054877_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21061265_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21070662_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21071541_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21211370_IL-4RA Q576R polymorphisms impart a modest yet significant risk for asthma. 21251883_We found that levels of sIL-4R were strikingly reduced in all forms of TB, particularly meningeal. 21489615_Single nucleotide polymorphisms of CD14, IL-13 and IL-4 receptor are associated with hexamethylene diisocyanate asthma. 21497535_IL-4Ralpha polymorphisms were associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and may be helpful in early detection of erosive rheumatoid arthritis. 21536546_IL-4R drives dedifferentiation, mitogenesis, and metastasis in rhabdomyosarcoma. 21729106_IL4RA polymorphism may make a modest but significant contribution to a person's genetic susceptibility to chagasic cardiomyopathy. 21733492_The Q551R IL-4RA polymorphism is a putative risk indicator for severe chronic periodontitis, but was not significant associated to AP. 21734400_Studies indicate that RAD50 and PTPRE of crude associations with asthma at a Bonferroni-corrected level of significance, while IL4R, CCL5 and TBXA2R of nominal significance. 21913997_did not identify any SNPs in the IL-4, IL-4R and IL-13Ralpha2 genes that were associated with atopic dermatitis 21918367_Interactions of the IL-4RA loci may play a role both conferring susceptibility and modulating severity of Atopic dermatitis (AD). 22045834_Data showed that polymorphisms in IL4, IL13, and their receptors do not play a role in SSc and do not influence the exp | ENSMUSG00000030748 | Il4ra | 555.309981 | 0.9395691 | -0.089928888 | 0.07496764 | 1.43890130427 | 0.2303172160503863530323087616125121712684631347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.45269635835624272290900194093410391360521316528320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 528.579747 | 23.052978 | 565.247588 | 24.264163 | |
| ENSG00000078043 | 9063 | PIAS2 | protein_coding | O75928 | FUNCTION: Functions as an E3-type small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) ligase, stabilizing the interaction between UBE2I and the substrate, and as a SUMO-tethering factor. Plays a crucial role as a transcriptional coregulator in various cellular pathways, including the STAT pathway, the p53 pathway and the steroid hormone signaling pathway. The effects of this transcriptional coregulation, transactivation or silencing may vary depending upon the biological context and the PIAS2 isoform studied. However, it seems to be mostly involved in gene silencing. Binds to sumoylated ELK1 and enhances its transcriptional activity by preventing recruitment of HDAC2 by ELK1, thus reversing SUMO-mediated repression of ELK1 transactivation activity. Isoform PIAS2-beta, but not isoform PIAS2-alpha, promotes MDM2 sumoylation. Isoform PIAS2-alpha promotes PARK7 sumoylation. Isoform PIAS2-beta promotes NCOA2 sumoylation more efficiently than isoform PIAS2-alpha. Isoform PIAS2-alpha sumoylates PML at'Lys-65' and 'Lys-160'. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15920481, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15976810, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22406621}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein sumoylation. | This gene encodes a member of the protein inhibitor of activated STAT family, which function as SUMO E3 ligases and play important roles in many cellular processes by mediating the sumoylation of target proteins. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. Isoforms of the encoded protein enhance the sumoylation of specific target proteins including the p53 tumor suppressor protein, c-Jun, and the androgen receptor. A pseudogene of this gene is located on the short arm of chromosome 4. The symbol MIZ1 has also been associated with ZBTB17 which is a different gene located on chromosome 1. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. | hsa:9063; | nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PML body [GO:0016605]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; SUMO ligase activity [GO:0061665]; SUMO transferase activity [GO:0019789]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; negative regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060766]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; protein sumoylation [GO:0016925]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 12716907_PIASx may function as a co-repressor of Stat4 15580267_Required for upregulation of a large group of genes in response to DNA damage, a function that is regulated by c-Myc, but not by 14-3-3eta and represses the expression of many genes 16148010_the repressive properties of PIASxalpha/ARIP3 require its physical interaction with FLI-1, identifying PIASxalpha as a novel corepressor of FLI-1 16460827_findings show that Epstein-Barr virus Rta interacts and colocalizes with PIASxalpha and PIASxbeta in the nucleus; these interactions seem to enhance Rta sumoylation 16713578_PIASxalpha acts as a key signal integrator that permits different responses from the same transcription factor, depending on the signaling pathway that is activated. 21156324_These findings suggest that SUMO-1 modification of MDA5 possibly via PIAS2beta may play a role in the MDA5-mediated interferon response to viral infections. 24344134_PIASxalpha is a novel SUMO E3 ligase for PTEN, and it positively regulates PTEN protein level in tumor suppression. 25434787_UXT is a binding protein of PIAS2, and interaction between PIAS2 and UXT may be important for the transcriptional activation of AR. 26403403_the expression of SENP8, SAE1, PIAS1, PIAS2 and ZMIZ1 is deregulated in the majority of PTC tissues, likely contributing to the PTC phenotype. 28973998_results indicated that PIAS2-mediated SUMOylation constrained HCV replication 30783905_the results presented demonstrate that in heat-stressed HeLa cells, p38 MAPK pathway-dependent SUMOylation of Elk-1 and phosphorylation of PIAS2 correlate with the downregulation of transactivation by Elk-1. 30861611_PIAS genes as disease markers in bipolar disorder. 31084243_PIAS1expression of PIAS1 gene was increased in patients with MS compared to healthy subjects; also, there was a significant correlation between the expression of PIAS1 and PIAS2 genes with disease severity of multiple sclerosis 31582715_We are the first to reveal that mutations of rs644731 in the PIAS2 gene were significantly correlated with the progression of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy in kidney transplant recipients. 32249212_SUMOylation of the transcription factor ZFHX3 at Lys-2806 requires SAE1, UBC9, and PIAS2 and enhances its stability and function in cell proliferation. 33763841_Expression of PIAS Genes in Migraine Patients. 34234281_PIAS2-mediated blockade of IFN-beta signaling: a basis for sporadic Parkinson disease dementia. 36251411_Integrative transcriptome analysis reveals TEKT2 and PIAS2 involvement in diabetic nephropathy. | ENSMUSG00000025423 | Pias2 | 147.706503 | 1.1733540 | 0.230638365 | 0.27631846 | 0.69290435853 | 0.4051782541162455286709587198856752365827560424804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.63325513056737903205828388308873400092124938964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 172.739505 | 27.978999 | 148.318976 | 24.067352 |
| ENSG00000082014 | 6604 | SMARCD3 | protein_coding | Q6STE5 | FUNCTION: Involved in transcriptional activation and repression of select genes by chromatin remodeling (alteration of DNA-nucleosome topology). Component of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes that carry out key enzymatic activities, changing chromatin structure by altering DNA-histone contacts within a nucleosome in an ATP-dependent manner. Stimulates nuclear receptor mediated transcription. Belongs to the neural progenitors-specific chromatin remodeling complex (npBAF complex) and the neuron-specific chromatin remodeling complex (nBAF complex). During neural development a switch from a stem/progenitor to a postmitotic chromatin remodeling mechanism occurs as neurons exit the cell cycle and become committed to their adult state. The transition from proliferating neural stem/progenitor cells to postmitotic neurons requires a switch in subunit composition of the npBAF and nBAF complexes. As neural progenitors exit mitosis and differentiate into neurons, npBAF complexes which contain ACTL6A/BAF53A and PHF10/BAF45A, are exchanged for homologous alternative ACTL6B/BAF53B and DPF1/BAF45B or DPF3/BAF45C subunits in neuron-specific complexes (nBAF). The npBAF complex is essential for the self-renewal/proliferative capacity of the multipotent neural stem cells. The nBAF complex along with CREST plays a role regulating the activity of genes essential for dendrite growth (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6P9Z1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29374058, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8804307, ECO:0000303|PubMed:22952240, ECO:0000303|PubMed:26601204}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the SWI/SNF family of proteins, whose members display helicase and ATPase activities and which are thought to regulate transcription of certain genes by altering the chromatin structure around those genes. The encoded protein is part of the large ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complex SNF/SWI and has sequence similarity to the yeast Swp73 protein. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene, but the biological validity of some variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:6604; | brahma complex [GO:0035060]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nBAF complex [GO:0071565]; npBAF complex [GO:0071564]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; SWI/SNF complex [GO:0016514]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; nuclear receptor binding [GO:0016922]; nuclear receptor coactivator activity [GO:0030374]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; transcription coregulator binding [GO:0001221]; cardiac right ventricle formation [GO:0003219]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; muscle cell differentiation [GO:0042692]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neural retina development [GO:0003407]; nucleosome disassembly [GO:0006337]; positive regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045597]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of double-strand break repair [GO:2000781]; positive regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045663]; positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation [GO:0002052]; positive regulation of T cell differentiation [GO:0045582]; regulation of G0 to G1 transition [GO:0070316]; regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000045]; regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition [GO:0030071]; regulation of nucleotide-excision repair [GO:2000819]; regulation of protein binding [GO:0043393]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; secondary heart field specification [GO:0003139] | 14701856_BAF60c represents a new coregulator that constitutes an important anchoring point by which the SWI/SNF complex is recruited to nuclear receptors and other transcription factors 16687403_Tat-mediated activation of the HIV promoter requires the SWI/SNF complex in synergy with the coactivator p300. 18816825_Baf60c is re-expressed in the Muller glial cells that re-enter the cell cycle after neurotoxic damage 21694703_GTNB directs cardiogenesis from human embryonic stem cells and induces correct cardiac development. 22068056_BAF60c phosphorylation on a conserved threonine is the signal that promotes incorporation of MyoD-BAF60c into a Brg1-based SWI/SNF complex, which remodels the chromatin & activates transcription of MyoD-target genes. 22833560_Data show a combination of only five genes (-BCL6, T (BRACHYURY), c-MYC, MITF and BAF60C (SMARCD3) rapidly and efficiently convert postnatal chorion and decidual cells into chondrocytes. 23219531_BAF60c promotes lipogenesis in vivo and increases triglyceride levels, demonstrating its role in metabolic adaption to activate the lipogenic program in response to feeding and insulin. 23563706_Deptor is induced by the Baf60c-Six4 transcriptional complex and mediates activation of Akt and glycolytic metabolism by Baf60c in a cell-autonomous manner 23716599_Inhibition of Wnt5a by either RNAi knockdown or blocking antibody reversed Smarcd3 -induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Thus, Smarcd3 epigenetically regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition by activating WNT signaling pathways. 26071180_Data show that the combination of GATA binding protein 4 (Gata4), T-box transcription factor 5 (Tbx5) and BRG1-associated factor 60C protein (Baf60c) is sufficient for inducing adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSCs) to form cardiomyocytes. 33125346_SMARCD3 is a potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target in CAFs. 36066968_BAF60c prevents abdominal aortic aneurysm formation through epigenetic control of vascular smooth muscle cell homeostasis. | ENSMUSG00000028949 | Smarcd3 | 33.298048 | 0.5552981 | -0.848665606 | 0.38492350 | 4.76691210843 | 0.0290118164582825535657839566283655585721135139465332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.11096999962221940072559789314254885539412498474121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 22.244156 | 6.847280 | 40.103200 | 12.165888 | |
| ENSG00000082269 | 57579 | FAM135A | protein_coding | Q9P2D6 | Alternative splicing;Reference proteome | Predicted to be involved in cellular lipid metabolic process. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:57579; | cellular lipid metabolic process [GO:0044255] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20549515_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20970119_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) | ENSMUSG00000026153 | Fam135a | 147.742143 | 0.8138022 | -0.297249844 | 0.19737441 | 2.25913404170 | 0.1328283177217604027475772454636171460151672363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.31962885055771278475233998506155330687761306762695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 119.956318 | 25.217365 | 148.231322 | 31.169680 | ||
| ENSG00000088325 | 22974 | TPX2 | protein_coding | Q9ULW0 | FUNCTION: Spindle assembly factor required for normal assembly of mitotic spindles. Required for normal assembly of microtubules during apoptosis. Required for chromatin and/or kinetochore dependent microtubule nucleation. Mediates AURKA localization to spindle microtubules (PubMed:18663142, PubMed:19208764). Activates AURKA by promoting its autophosphorylation at 'Thr-288' and protects this residue against dephosphorylation (PubMed:18663142, PubMed:19208764). TPX2 is inactivated upon binding to importin-alpha (PubMed:26165940). At the onset of mitosis, GOLGA2 interacts with importin-alpha, liberating TPX2 from importin-alpha, allowing TPX2 to activates AURKA kinase and stimulates local microtubule nucleation (PubMed:26165940). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18663142, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19208764, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26165940}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Isopeptide bond;Microtubule;Mitosis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation | Enables importin-alpha family protein binding activity and protein kinase binding activity. Involved in activation of protein kinase activity; microtubule cytoskeleton organization; and negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization. Located in intercellular bridge; mitotic spindle; and nucleoplasm. Colocalizes with spindle pole. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:22974; | axon hillock [GO:0043203]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intercellular bridge [GO:0045171]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; mitotic spindle [GO:0072686]; nuclear microtubule [GO:0005880]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; spindle [GO:0005819]; spindle pole [GO:0000922]; importin-alpha family protein binding [GO:0061676]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; protein kinase activator activity [GO:0030295]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; activation of protein kinase activity [GO:0032147]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell division [GO:0051301]; microtubule nucleation [GO:0007020]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; mitotic spindle assembly [GO:0090307]; negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization [GO:0007026]; regulation of mitotic spindle organization [GO:0060236] | 12177045_TPX2 is required for targeting Aurora-A kinase to the spindle apparatus and Aurora-A might regulate the function of TPX2 during spindle assembly 12389033_spindle formation requires the function of TPX2 to generate a stable bipolar spindle with overlapping antiparallel microtubule arrays 12477396_observations reveal a structural role for hTPX2 in spindles and provide evidence for a balance between microtubule-based motor forces and structural spindle components 12612055_molecular cloning; overexpression provokes accumulation of cells in G(2)-M phase and subsequent polyploidization, suggesting that excess repp86 may interfere with correct nuclear division 16287863_APC/C(Cdh1) controls the stability of TPX2, thereby ensuring accurate regulation of the spindle assembly in the cell cycle 16489064_Aberrant expression of TPX2 may play important role(s) in both malignant transformation of respiratory epithelium and progression of squamous cell lung cancer and could serve as a prognostic predictor for the disease. 17705509_TPX2 binding decreases the size and accessibility of a hydrophobic pocket, adjacent to the ATP site, to inhibitors. 17716627_Data show that Siah2 is an important mediator of repp86 protein degradation. 18663142_Chromosome nucleation is involved in spindle pole separation and setting spindle length. A second Aurora A-independent function of TPX2 is required to bipolarize spindles. 19148505_human TPX2 mRNA is closely linked to increased or abnormal cell proliferation in malignant salivary gland tumors. 19208764_Data provide a molecular explanation for the assembly of the apoptotic microtubule network, and suggest important similarities with the process of RanGTP- and TPX2-mediated mitotic spindle formation. 19424574_Overexpression of TPX2 is associated with oral squamous cell carcinomas. 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19801554_Data show that Aurora A(S155R) mutant reduced cellular activity and mislocalization are due to loss of interaction with TPX2. 20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20599806_TPX2 expression is associated with the progression of malignant astrocytoma. 20708655_association of Aurora-A and TPX2 gives rise to a novel functional unit with oncogenic properties.[review] 21099343_Decreased AurA-TPX2 complex formation in response to irradiation results from reduced cellular levels of TPX2, as a result of protein degradation and decreased translation of TPX2 mRNA. 21147853_TPX2 protects Aurora-A from degradation both in interphase and in mitosis. 21187329_Results demonstrate a role for PP6 as the T-loop phosphatase regulating Aurora A activity bound to its activator TPX2 during mitotic spindle formation. 21347367_two switches determining Aurora A activation 22207630_TPX2 promote 20q amplicon-driven progression of colorectal adenoma to carcinoma. 22307108_TPX2 shows potential to be used as a new marker for cervical cancer diagnosis and therapy. 22560880_The data support the role of TPX2 as a novel co-activator of Aurora kinase B. 22761906_AIM1, ERGIC1, and TPX2 were shown to be highly expressed especially in prostate cancer tissues, and high mRNA expression of ERGIC1 and TMED3 associated with AR and ERG oncogene expression 23045526_the regulation of gamma-H2AX signals by TPX2 is not associated with apoptosis or the mitotic functions of TPX2. 23328114_Data indicate that the sensitivity of cell-lines with amplification of AURKA depends upon the activity of the kinase, which correlates with the expression of the regulatory gene products TPX2 and HMMR/RHAMM. 23333597_GLIPR1 interacts with Hsc70, and GLIPR1 overexpression or Hsc70 knockdown leads to transcriptional suppression of AURKA and TPX2. 23357462_Data indicate that expression-based risk indices of three genes UBE2C, TPX2, and MELK were more strongly associated with poor 5-year survival in adenocarcinoma patients. 23444224_Data show that five genes CKAP5, KPNB1, RAN, TPX2 and KIF11 were shown to be essential for tumor cell survival in both head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC)and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but most particularly in HNSCC. 23725757_The expression of TPX2 protein and mRNA were correlated with invasive depth and lymphatic metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 23873098_Data indicate that TPX2 (target protein for Xklp2) may play a role in the development and progression of bladder carcinoma, and suggest that inhibition of TPX2 level may be a novel strategy for therapy of the patients with bladder carcinoma. 23963785_TPX2 expression is associated with cell proliferation and poor prognosis among patients with resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 24341487_TPX2 plays an important role in promoting tumorigenesis and metastasis of human colon cancer, and may represent a novel prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for the disease 24488334_TPX2 overexpression is associated with medullary thyroid carcinoma. 24556998_This review provides an historic overview of the discovery of TPX2 and summarizes its cytoskeletal and signaling roles with relevance to cancer therapies. [review] 24625450_RAN nucleo-cytoplasmic transport and mitotic spindle assembly partners XPO7 and TPX2 have roles in serous epithelial ovarian cancer 24718984_The results demonstrated that TPX2 is important in the regulation of tumor growth in cervical cancer and therefore may be a potential therapeutic target as a novel treatment strategy. 24867643_the molecular mechanisms of two distinct activation strategies (autophosphorylation and TPX2-mediated activation) in human Aurora A kinase, was elucidated. 24875404_Identify RHAMM as a critical regulator of TPX2 location/ Aurora kinase A signaling and suggest that RHAMM ensures bipolar spindle assembly and mitotic progression through the integration of biochemical and structural pathways. 25239289_TPX2 siRNA transfection significantly reduced tumor growth. 25302620_In vitro studies found that TPX2 knockdown significantly inhibited cell proliferation and viability in both Hep3B and HepG2 cells. 25365214_our study is the first indication of a constitutive control of TPX2 on H4K16ac levels, with potential implications for DNA damage response. 25632068_Propose TPX2 and AURKA as novel co-regulators on the MYC pathway in colorectal neoplasms. 25830658_a causative link between altered function of AURKA-HMMR-TPX2-TUBG1 and breast carcinogenesis in BRCA1/2 mutation carriers 25914189_These results indicated that TPX2 has an impact on tumor angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer. 26018074_Dimeric, but not monomeric, Eg5 was differentially inhibited by full-length and truncated TPX2, demonstrating that dimerization or residues in the neck region are important for the interaction of TPX2 with Eg5. 26240182_Aurora A-dependent TPX2 phosphorylation controls mitotic spindle length through regulating microtubule flux. 26257190_the levels and distribution of TPX2 are likely to be determinants of when and where kinesin-5 acts in neurons. 26279431_TPX2 was a target gene of miR-491. 26414402_Data show that cytoskeleton associated protein 5 (chTOG) only weakly promotes importin-regulated microtubule nucleation, but acts synergistically with TPX2 protein. 26624896_expression of both TPX2 and PD-L1 are associated with persistence/recurrence of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia after cervical conization 27053618_MiR-491 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion and migration by downregulating the expression of TPX2. 27314162_detection of TPX2 overexpression could serve as a prognostic marker and therapeutic target for gastric cancer 27775325_This study concludes that the helical region of TPX2 folds upon binding Aurora-A, and that stabilization of this helix does not compromise Aurora-A activation. 28069036_High TPX2 expression is associated with gastric cancer. 28108243_We show TPX2, a regulator of Aurora-A, is associated with high grade and stage of ccRCC, and is an independent predictor of recurrence. 28636807_TPX2 was correlated with cell radioresistance 28799673_Data found that TPX2 was highly expressed in human bladder cancer tissues. Its overexpression promoted bladder cancer growth and correlated with tumor grade and stage, lymph node metastasis, and poor prognosis. These results support that TPX2 acts as a tumor promoter in human bladder tumor development. 28869599_Study suggests AURKA and TPX2 as potential stratification markers for taxane-based radiochemotherapy. lung adenocarcinoma cohort, high expression levels of AURKA and TPX2 were associated with specifically improved overall survival upon taxane-based radiochemotherapy. 29120325_Together, these results suggest a molecular mechanism of how the Ran-GTP gradient can regulate TPX2-dependent microtubule formation. 29276125_Eg5 localization and centrosome separation in prophase depend on the nuclear microtubule-associated protein TPX2, a pool of which localizes to the centrosomes before nuclear envelope breakdown. This localization involves the kinase Nek9, which phosphorylates TPX2 nuclear localization signal preventing its interaction with importin and nuclear import. 29548937_VPS28, an ESCRT-I protein, interacts with Gbetagamma and Eg5-TPX2. VPS28 organizes Aster Microtubules via Gbetagamma. VPS28 recruits Eg5 and TPX2 to regulate mitotic spindle bipolarity. 29865033_TPX2 promotes the proliferation and migration of human OC cells by regulating PLK1 expression. 29925526_These findings unveil a novel function of ADD1 in maintaining spindle pole integrity through its interaction with TPX2. 30123975_The results show that at metaphase both Eg5-EGFP and TPX2-EGFP are enriched toward spindle poles, but only TPX2-EGFP is enriched relative to microtubules. Eg5-EGFP and TPX2-EGFP show distinct localization patterns in anaphase, with Eg5-EGFP relocalizing to the midzone earlier than TPX2-EGFP. 30177840_findings reveal that BRCA2-deficient cancer cells show enhanced sensitivity to inactivation of TPX2 or its partner Aurora-A, which points at an actionable dependency of genomically unstable cancers. 30257313_Inhibiting TPX2 by miR-330-3p suppresses the proliferation of melanoma cell lines; miR-330-3p/TPX2 pathway expressed differently between melanoma patients and healthy people 30257343_TPX2 expression in cholangiocarcinoma tissues was significantly higher than that paracancerous tissue. 30412141_A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis found that overexpression of TPX2 is related to poor survival rate in most solid tumors, which indicates that the expression level of TPX2 is a significant prognostic parameter and potential therapeutic target in various solid tumors. 30454896_TPX2 silencing negatively regulates the PI3K/AKT and activates p53 signaling pathway by which breast cancer cells proliferation were inhibited whereas cellulars apoptosis were accelerated. 30588191_Study indicated that AURKA, CDC20 and TPX2 are over-expressed in smoking related lung adenocarcinoma tissues and their higher mRNA expression levels have a worse prognosis. 30602538_Mitotic regulators TPX2 and Aurora A protect DNA forks during replication stress by counteracting 53BP1 function. 30633364_We showed that miR-8075 that was downregulated in cervical cancer tissues repressed cervical cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Furthermore, we validated that upregulation of TPX2 by hsa_circRNA_101996-mediated inhibition of miR-8075 contributed to cervical cancer proliferation, migration, and invasion 31272499_Results suggest activation of CDK5 is associated with HCC tumorigenesis. CDK5-mediated phosphorylation and stabilization of TPX2 promotes hepatocellular proliferation and tumorigenicity. 31494045_TPX2 as a Novel Prognostic Indicator and Promising Therapeutic Target in Triple-negative Breast Cancer. 31638175_TPX2 may suppress the growth of Hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and thus, TPX2 may be a potential target for the treatment of liver cance 31676293_This review highlights the physiological and pathophysiological properties of AURKA, the structure of the AURKA/TPX2 complex and the main structural features that can be explored for the design of selective AURKA inhibitors. 31799669_MiR-491 suppresses migration and invasion via directly targeting TPX2 in breast cancer. 32041138_Excess TPX2 Interferes with Microtubule Disassembly and Nuclei Reformation at Mitotic Exit. 32193808_Aurora A kinase and its activator TPX2 are potential therapeutic targets in KRAS-induced pancreatic cancer. 32239565_Long non-coding RNA LINC00337 induces autophagy and chemoresistance to cisplatin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via upregulation of TPX2 by recruiting E2F4. 32356447_miR-485-3p suppresses colorectal cancer via targeting TPX2. 32503626_Epigenome-wide association study in healthy individuals identifies significant associations with DNA methylation and PBMC extract VEGF-A concentration. 32535036_Knockdown of circ_0003340 induces cell apoptosis, inhibits invasion and proliferation through miR-564/TPX2 in esophageal cancer cells. 32705231_Identification of early stage recurrence endometrial cancer biomarkers using bioinformatics tools. 32748897_TPX2 Promotes Metastasis and Serves as a Marker of Poor Prognosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 33029085_Comprehensive analysis of TPX2-related ceRNA network as prognostic biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma. 33093951_Structural bioinformatics predicts that the Retinitis Pigmentosa-28 protein of unknown function FAM161A is a homologue of the microtubule nucleation factor Tpx2. 33275894_The Aurora-A/TPX2 Axis Directs Spindle Orientation in Adherent Human Cells by Regulating NuMA and Microtubule Stability. 33556637_TPX2 mediates prostate cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition through CDK1 regulated phosphorylation of ERK/GSK3beta/SNAIL pathway. 33622270_High nuclear TPX2 expression correlates with TP53 mutation and poor clinical behavior in a large breast cancer cohort, but is not an independent predictor of chromosomal instability. 33907841_RHPN1AS1 promotes ovarian carcinogenesis by sponging miR4855p and releasing TPX2 mRNA. 34287649_Aurora A kinase activation: Different means to different ends. 34302807_Interaction of spindle assembly factor TPX2 with importins-alpha/beta inhibits protein phase separation. 34597712_Secretory autophagy-induced bladder tumour-derived extracellular vesicle secretion promotes angiogenesis by activating the TPX2-mediated phosphorylation of the AURKA-PI3K-AKT axis. 34982022_Circular RNA circ-LARP1B contributes to cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma progression by targeting microRNA-515-5p/TPX2 microtubule nucleation factor axis. 35273149_Downregulation of TPX2 impairs the antitumor activity of CD8+ T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. 35356748_TPX2 Serves as a Cancer Susceptibility Gene and Is Closely Associated with the Poor Prognosis of Endometrial Cancer. 35771632_CHD1 Promotes Sensitivity to Aurora Kinase Inhibitors by Suppressing Interaction of AURKA with Its Coactivator TPX2. 36198346_SPI1 mediates transcriptional activation of TPX2 and RNF2 to regulate the radiosensitivity of lung squamous cell carcinoma. 36304254_Comprehensive Analysis of the Oncogenic Role of Targeting Protein for Xklp2 (TPX2) in Human Malignancies. | ENSMUSG00000027469 | Tpx2 | 526.030758 | 0.9204595 | -0.119573876 | 0.06690117 | 3.19555937078 | 0.0738385057894650198573316401962074451148509979248046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.21571700480013297762660329226491739973425865173339843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 505.679606 | 21.661096 | 552.044793 | 23.095122 | |
| ENSG00000088808 | 23368 | PPP1R13B | protein_coding | Q96KQ4 | FUNCTION: Regulator that plays a central role in regulation of apoptosis via its interaction with p53/TP53 (PubMed:11684014, PubMed:12524540). Regulates TP53 by enhancing the DNA binding and transactivation function of TP53 on the promoters of proapoptotic genes in vivo. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11684014, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12524540}. | 3D-structure;ANK repeat;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain | This gene encodes a member of the ASPP (apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53) family of p53 interacting proteins. The protein contains four ankyrin repeats and an SH3 domain involved in protein-protein interactions. ASPP proteins are required for the induction of apoptosis by p53-family proteins. They promote DNA binding and transactivation of p53-family proteins on the promoters of proapoptotic genes. Expression of this gene is regulated by the E2F transcription factor. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:23368; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator [GO:0072332]; negative regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045786] | 15731768_target of E2F transcription factor 15757645_ASPP1 CpG island aberrant methylation could be one molecular and genetic alteration in wild-type p53 tumours. 15782125_Mdm2 and mdmx prevent ASPP1 and ASPP2 from stimulating the apoptotic function of p53 by binding and inhibiting the transcriptional activity of p53. 16139958_role of ASPP1, ASPP2, and iASPP as apoptotic specific regulators of p53 [review] 16314841_results demonstrate that decreased expression of ASPP1 in patients with ALL is due to an abnormal methylation of its promoter and is associated with a poor prognosis 20034025_ASPP1 and ASPP2 genes are frequently down-regulated by DNA methylation in HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma, which may play important roles in the development of HCC 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20601096_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21041410_Data show that Lats2 and ASPP1 shunt p53 to proapoptotic promoters and promote the death of polyploid cells. 21041411_Data show that ASPP1 enhances nuclear accumulation of YAP/TAZ and YAP/TAZ-dependent transcriptional regulation. 21102414_Suggest that downregulation of ASPP1 by hypermethylation may be involved in the pathogenesis and progress of gestational trophoblastic disease, probably through its effect on apoptosis. 21479363_overexpression of ASPP1 rendered MCF-7 and MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells more sensitive to resveratrol-mediated apoptosis via the E2F pathway 22068052_The ability of ASPP1 to activate YAP results in the decreased expression of LATS2, which lowers the ability of p53 to induce p21, cell-cycle arrest and senescence. 22169642_ASPP1 promoter methylation may be associated with the malignant progression of non-small cell lung cancer, and ASPP1 expression promotes cellular apoptosis. 22552744_the mRNA expression of ASPP1 and ASPP2 was frequently dowregulated in tumor tissues, and this decreased significantly in samples expressing wild-type p53 23088536_When the Px(T)PxR motif is deleted or mutated via insertion of a phosphorylation site mimic (T311D), PP-1c fails to bind to all three ASPP proteins, ASPP1, ASPP2 and iASPP. 23392125_ASPP1 and ASPP2 cooperate with oncogenic RAS to enhance the transcription and apoptotic function of p53. 25660448_ASPP1/2 interacted with centrosome linker protein C-Nap1. Co-depletion of ASPP1 and ASPP2 inhibited re-association of C-Nap1 with centrosome at the end of mitosis. 26595804_ASPP1/2-PP1 complexes are required for chromosome segregation and kinetochore-microtubule attachments. 27177208_Increased expression of p53 and ASPP1 and downregulation of iASPP. 28103919_Results showed that the protein expression levels of ASPP1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) tissues and in paired noncancerous tissues were similar but was significantly associated with histological differentiation and invasive depth which suggest that it might be involved in the progression of ESCC. 28594407_results provide new insights into EGR-1/ASPP1 regulatory loop in sensitizing Quercetin-induced apoptosis. EGR-1/ASPP1, therefore, may be potentially used as therapeutic targets to improve cancer's response to pro-apoptosis treatments. 32269211_ASPP1 deficiency promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer. 32987288_Apoptosis stimulating protein of p53 (ASPP) 1 and ASPP2 m-RNA expression in oral cancer. | ENSMUSG00000021285 | Ppp1r13b | 90.428990 | 1.1633664 | 0.218305560 | 0.27170202 | 0.64279387221 | 0.4227009027021794707046353778423508629202842712402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.64948571358654683116640171647304669022560119628906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 84.713822 | 12.542726 | 73.478084 | 10.882217 | |
| ENSG00000089053 | 51433 | ANAPC5 | protein_coding | Q9UJX4 | FUNCTION: Component of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C), a cell cycle-regulated E3 ubiquitin ligase that controls progression through mitosis and the G1 phase of the cell cycle. The APC/C complex acts by mediating ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of target proteins: it mainly mediates the formation of 'Lys-11'-linked polyubiquitin chains and, to a lower extent, the formation of 'Lys-48'- and 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18485873}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Mitosis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat;Ubl conjugation pathway | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. | This gene encodes a tetratricopeptide repeat-containing component of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C), a large E3 ubiquitin ligase that controls cell cycle progression by targeting a number of cell cycle regulators such as B-type cyclins for 26S proteasome-mediated degradation through ubiquitination. The encoded protein is required for the proper ubiquitination function of APC/C and for the interaction of APC/C with transcription coactivators. It also interacts with polyA binding protein and represses internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. These differences cause translation initiation at a downstream AUG and result in a shorter protein (isoform b), compared to isoform a. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2008]. | hsa:51433; | anaphase-promoting complex [GO:0005680]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; spindle [GO:0005819]; protein phosphatase binding [GO:0019903]; anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process [GO:0031145]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell division [GO:0051301]; positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition [GO:0045842]; protein K11-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070979]; regulation of meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051445]; regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0007346] | 15082755_Results show that Apc5 binds the poly(A) binding protein (PABP), which directly binds the internal ribosome entry site (IRES) element of platelet-derived growth factor 2 mRNA. 16319895_APC5 and APC7 suppress E1A-mediated transformation in a CBP/p300-dependent manner, indicating that these components of the APC/C may be targeted during cellular transformation 19826416_Studies indicate that APC/C(Cdh1) is required to maintain genomic stability. 20686030_Inactivation and disassembly of the anaphase-promoting complex during human cytomegalovirus infection is associated with degradation of the APC5 and APC4 subunits and does not require UL97-mediated phosphorylation of Cdh1. 28731177_coexpression of APC5 and Axin genes significantly downregulated Wnt signaling in human SW480 CRC cells and inhibited cell growth. | ENSMUSG00000029472 | Anapc5 | 760.606064 | 0.8987249 | -0.154048601 | 0.17167547 | 0.80363605052 | 0.3700084688370888219566268162452615797519683837890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.60217317767227440672428429024876095354557037353515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 695.912700 | 91.287000 | 778.082732 | 102.131466 |
| ENSG00000089248 | 10961 | ERP29 | protein_coding | P30040 | FUNCTION: Does not seem to be a disulfide isomerase. Plays an important role in the processing of secretory proteins within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), possibly by participating in the folding of proteins in the ER. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal | This gene encodes a protein which localizes to the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). It is a member of the protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) protein family but lacks an active thioredoxin motif, suggesting that this protein does not function as a disulfide isomerase. The canonical protein dimerizes and is thought to play a role in the processing of secretory proteins within the ER. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. | hsa:10961; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; smooth endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005790]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050709]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein secretion [GO:0009306]; protein unfolding [GO:0043335]; regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1902235] | 12362325_Expression and tissue distribution of ERp29 [review] 16677078_ERp29 is an unusual redox-inactive member of the thioredoxin family [review] 17012915_ERP29 is expressed in a subset of basal-cell carcinoma of the skin, with the infiltrating carcinomas exhibiting the highest incidence of immunopositivity. 17073718_Results found that ERp29 comprises significant alpha-helical structure. 17296603_mutants of the D-domain of ERp29 prevent transport of a substrate protein (Pipe) in a manner consistent with the presence of a discrete, conserved peptide binding site in the D-domain 17881435_ERp29-activated polyomavirus perforates the physiologically relevant ER membrane, an event that likely initiates viral penetration. 18395818_lactating mammary glands were expressing ERp29 while the resting glands did not 19084538_there are two putative peptide binding sites of ERp29 and different processing activity of the human and Drosophila proteins in vivo does not stem from differences in peptide binding properties. 19265690_The level of ER protein 29 (ERp29) was shown to be decreased in the CK19-expressing BT549 breast cancer cell line. 19321666_This supports a new role for ERp29 as a chaperone that helps stabilize monomeric Cx43 to enable oligomerization to occur in the Golgi apparatus. 19770839_ERp29 is a novel regulator leading to cell growth arrest and cell transition from a proliferative to a quiescent state. 20920593_High expression of ERp29 inversely correlates to tumor progression. 21419175_Results identify ERp29 as a novel regulator of PERK and provide evidence for the role of ER resident factors in the regulation of chemotherapeutic efficacy. 21479953_Overexpression of ERp29 increases the radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 21525008_ERp29 is a 4PBA-regulated ER chaperone that regulates WT-CFTR biogenesis and can promote DeltaF508-CFTR trafficking in CF epithelial cells 21903368_Eurycomanone affects the transcription of Erp28, annexin 1 and prohibitin resulting in reduced expression of these proteins. 22064321_interplay between p38 phosphorylation and p58(IPK) upregulation has key roles in modulating ERp29-induced cell-growth arrest and survival 22160175_Suggest that ERp29 associates with radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and may be potential biomarker for predicting response to radiotherapy. 22543584_ERp29 is a novel molecule that regulates MET and epithelial cell integrity in breast cancer cells. 23558074_S1P1 overexpression or ERp29 absence is related to the carcinogenesis and progression, and may be potential biomarkers for early detection of gallbladder adenocarcinoma. 24391750_Apoptosis related proteins ERp29, PRDX6 and MPO were differentially expressed in placentas of pregnant women with intrahepatic cholestasis and in healthy pregnant women. 24780196_overexpression of ERp29 may play a key role in apoptosis in HTR-8/SVneo cells via activation of p38, which may participate in the pathogenesis of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy 24916695_CLIC4, ERp29, and Smac/DIABLO integrated into a novel panel based on cancer stem-like cells in association with metastasis stratify the prognostic risks of colorectal cancer. 24944201_ERp29 directs ENaC toward the Golgi, where it undergoes cleavage during its biogenesis and trafficking to the apical membrane. 26420420_our studies prove a novel function of ERp29MGMT in cancer cell survival against radiation. Targeting ERp29MGMT axis may be useful for providing better treatment efficacy in combination with radiotherapy in breast cancer. 26431474_Endoplasmic reticulum protein 29 attenuates CSE-induced ER stress and enhances cell viability and barrier integrity of RPE cells, and therefore may act as a protective mechanism for RPE survival and activity. 26887611_High ERP29 expression is associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. 28456374_Results of further analyses by using a CNX mutant imply that ERp29 and ERp57 recognize the same domain of CNX, whereas the mode of interaction with CNX might be somewhat different between them. 28534505_The anti-aggregation peptide ReACp53 significantly decreased ERP29 expression and suppressed the chemoresistant effect. These findings highlight a role of ERP29 in the acquired chemoresistance of cancer cells expressing the aggregating p53 mutant Arg282Trp. 28874138_Downregulation of ERp29 was commonly found in GC tissues and highly correlated with more aggressive phenotypes and poorer prognosis. 29721972_ERp29 plays a critical role in protein folding, trafficking, and secretion, cell survival and apoptosis, and ER homeostasis. Though ubiquitously expressed, ERp29 is upregulated in response to ER stress and is found at higher levels in certain cell types such as secretory epithelial cells and neurons. It may be involved in neuroprotection in retinal and neurodegenerative diseases. Review. 30569094_ERp29 protected colorectal cancer (CRC) cells from endoplasmic reticulum stressmediated reduction of malignancy to promote metastasis and may be a potential target of medical intervention for CRC therapy. 30877198_ERp29-MSec interaction appeared to require the presence of other bridging protein(s), perhaps triggered by post-translational modification of ERp29 31251997_Study established a novel regulatory network of LncRNA MEG3/miR483-3p/ERp29 in HCC which may be helpful in better understanding the effect of high glucose on poor prognosis of HCC. 31586554_role of ERp29 in ICP 31981282_ERp29 affects the migratory and invasive ability of human extravillous trophoblast HTR-8/SVneo cells via modulating the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 32433667_ERp29 as a regulator of Insulin biosynthesis. 33046743_Role of a genetic variation in the microRNA-4421 binding site of ERP29 regarding risk of oropharynx cancer and prognosis. 33360823_Dimerization of ER-resident molecular chaperones mediated by ERp29. 33377711_[Silencing ERp29 promotes the invasiveness of human PCa cells in vitro: Molecular mechanisms]. 34667160_ERp29 forms a feedback regulation loop with microRNA-135a-5p and promotes progression of colorectal cancer. | ENSMUSG00000029616 | Erp29 | 447.381746 | 0.8356389 | -0.259048470 | 0.14602565 | 3.12932424510 | 0.0768956082729023576716187449164863210171461105346679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.22170388958953404778817741771490545943379402160644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 413.142715 | 43.757465 | 497.606670 | 52.661056 | |
| ENSG00000090376 | 11213 | IRAK3 | protein_coding | Q9Y616 | FUNCTION: Putative inactive protein kinase which regulates signaling downstream of immune receptors including IL1R and Toll-like receptors (PubMed:10383454, PubMed:29686383). Inhibits dissociation of IRAK1 and IRAK4 from the Toll-like receptor signaling complex by either inhibiting the phosphorylation of IRAK1 and IRAK4 or stabilizing the receptor complex (By similarity). Upon IL33-induced lung inflammation, positively regulates expression of IL6, CSF3, CXCL2 and CCL5 mRNAs in dendritic cells (PubMed:29686383). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K4B2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10383454, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29686383}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Asthma;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a member of the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase protein family. Members of this family are essential components of the Toll/IL-R immune signal transduction pathways. This protein is primarily expressed in monocytes and macrophages and functions as a negative regulator of Toll-like receptor signaling. Mutations in this gene are associated with a susceptibility to asthma. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. | hsa:11213; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070498]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002755]; negative regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0001960]; negative regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045824]; negative regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032695]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0010936]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; negative regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0042177]; negative regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly [GO:0043242]; negative regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0034122]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; positive regulation of macrophage tolerance induction [GO:0010933]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly [GO:0043244]; response to exogenous dsRNA [GO:0043330]; response to interleukin-1 [GO:0070555]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to peptidoglycan [GO:0032494]; response to virus [GO:0009615] | 12054681_Identification and characterization of murine IRAK-M 14592437_Thus, our data indicate that IRAK-M could play a pivotal role in the process of endotoxin tolerance in human monocytes and provide evidence that PI3K is involved in regulating its expression. 15728517_IRAK-M is rapidly upregulated in human monocytes pre-exposed to tumor cells and could be involved in deactivation of tumor-infiltrating monocytes mediated by tumor cells. 16432636_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16437636_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17379480_These findings indicate that IRAK-M selectively attenuates p38 activation and inhibits innate immunity through stabilizing MKP-1. 17503328_IRAK-M is involved in the pathogenesis of early-onset persistent asthma. 17503328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17558906_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17558906_no evidence to suggest association between inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn's disease (CD), ulcerative colitis (UC) or subsets of CD & UC and IRAK-M; an interaction was found between IRAK-M and CARD15 in UC patients 17982103_LPS tolerance in human endotoxemia models is associated with IRAK-M up-regulation. 18156187_Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide upregulates IRAK-M in macrophages. 18354163_observed striking up-regulation of IRAK-M in monocytes, but without concomitant proinflammatory cytokine production 18987746_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19013233_Analysis of single single nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotypes did not reveal a significant association between polymorphisms in the IRAK-M gene and atopic dermatitis in this cohort. 19013233_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19114913_Immunosuppression in sepsis caused by B. pseudomallei is associated with an upregulation of IRAK-M and an indicator of poor outcome. 19264973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19372141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19414798_IRAK-M is a major mediator of globular adiponectin-induced endotoxin tolerance in primary macrophages 19423540_Nine SNPs distributed across eight genetic regions (ALOX5, IRAK3, ITGB2, NCF2, NFKB1, SELP, SOD1, and STAT1) were associated with risk of glioma with P value of | ENSMUSG00000020227 | Irak3 | 274.923427 | 0.5945103 | -0.750226219 | 0.24986338 | 8.82106242785 | 0.0029777324205921724964429841975288582034409046173095703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.01874550904556404606893238451448269188404083251953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 197.150741 | 30.426663 | 333.846726 | 51.270617 | |
| ENSG00000090905 | 27327 | TNRC6A | protein_coding | Q8NDV7 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in RNA-mediated gene silencing by both micro-RNAs (miRNAs) and short interfering RNAs (siRNAs). Required for miRNA-dependent repression of translation and for siRNA-dependent endonucleolytic cleavage of complementary mRNAs by argonaute family proteins. As a scaffolding protein, associates with argonaute proteins bound to partially complementary mRNAs, and can simultaneously recruit CCR4-NOT and PAN deadenylase complexes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16284622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16284623, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17596515, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17671087, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19056672, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19304925}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Epilepsy;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;RNA-mediated gene silencing;Translation regulation | This gene encodes a member of the trinucleotide repeat containing 6 protein family. The protein functions in post-transcriptional gene silencing through the RNA interference (RNAi) and microRNA pathways. The protein associates with messenger RNAs and Argonaute proteins in cytoplasmic bodies known as GW-bodies or P-bodies. Inhibiting expression of this gene delocalizes other GW-body proteins and impairs RNAi and microRNA-induced gene silencing. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:27327; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; P-body [GO:0000932]; RISC complex [GO:0016442]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; cellular response to starvation [GO:0009267]; endoderm development [GO:0007492]; miRNA-mediated gene silencing [GO:0035195]; miRNA-mediated gene silencing by inhibition of translation [GO:0035278]; positive regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening [GO:0060213] | 11950943_GW ribonucleoprotein complex is involved in the posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression 15494374_gene knockdown of GW182 led to the disappearance of GW bodies demonstrating that GW182 is a critical component of GW bodies 16284622_data support a model in which GW182 and/or the microenvironment of the cytoplasmic GWBs contribute to the RNA-induced silencing complex and to RNA silencing 16284623_results support a functional link between GW182 and the ability of a microRNA to repress expression of a target mRNA 18345015_findings show that miRNA function is effected by AGO1-GW182 complexes and the role of GW182 in silencing goes beyond promoting deadenylation 18946079_Data show that siRNA transfection induces up-regulated expression of both GW182, a key P-body component, and Ago2, indicating that P-body localization and interaction with GW182 and Ago2 are important in siRNA-mediated RNAi. 19056672_A novel 210-kDa isoform of human GW182, provisionally named trinucleotide GW1 (TNGW1)was reported.TNGW1 was expressed independently of GW182 and was present in human testis and various human cancer cells. 19324964_Tethering the C-terminal half of Ago2 to the 3'-UTR of reporter mRNA recapitulated translational repression comparable to that of tethered Ago2, and this repression was greatly impaired upon GW182 knockdown. 19383768_Our findings indicate that TNRC6A, is recruited to miRNA targets through an interaction between their N-terminal domain and an Argonaute protein 20181956_Structural basis of binding of P-body-associated proteins GW182 and ataxin-2 by the Mlle domain of poly(A)-binding protein.( 20198652_data indicate that frameshift mutations in AGO2 and TNRC6A and their losses of expression are common in GCs and CRCs with MSI-H, and suggest that these alterations may contribute to the cancer development by deregulating miRNA regulation. 20402672_over-expression of Ago2 and TNRC6A may be related to miRNA functions and might play a role in tumorigenesis of prostate carcinomas and esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. 21131274_Alanine substitution showed that GW/WG motifs in Delta12 (Delta12a, amino acids 896-1045) were important for the silencing activity of GW182. 21984184_Data demonstrate that in human and Drosophila melanogaster cells, the critical repressive features of both the N-terminal and C-terminal effector domains of GW182 proteins are Gly/Ser/Thr-Trp (G/S/TW) or Trp-Gly/Ser/Thr (WG/S/T) motifs. 21984185_Data suggest that GW182 serves as both a platform that recruits deadenylases and as a deadenylase coactivator that facilitates the removal of the poly(A) tail by CCR4-NOT. 22891262_Mammalian GW proteins have distinctive functions in the miRNA pathway, with GW220/TNGW1 being essential for aggregation and formation of GW/P bodies that sequester and stabilize translationally repressed target mRNA. 22898980_HSP90 and GW182 are important factors in the pathomechanism of alcohol-induced augmentation of HCV replication. 23090477_we have identified a new function of GW182 in protecting mature miRNA from being degraded by interacting with Argonaute (AGO) proteins 23150874_Analysis of the results suggested that TNRC6A plays an important role in navigating Argonaute protein into the nucleus to lead miRNA-mediated gene silencing. 23224966_GW182 plays a critical role in miRNA-mediated gene silencing. (Review) 23224969_GW182 proteins function as scaffold proteins for the assembly of the multiprotein complex that silences miRNA targets. (Review) 23224974_28.6% of patients containing autoantibodies to the trinucleotide repeat region of the TNRC6A were shown to have a single nucleotide polymorphism at c.344C>A in the CAG/CCA/G-rich region of TNRC6A. 23224975_Sinse Argonaute and GW182 are the core proteins of the RNA-silencing complex (RISC), it seems appropriate to suggest that the RISC is the main target of human autoantibodies. (Review) 24778252_TRIM65 relieves miRNA-driven suppression of mRNA expression through ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of TNRC6. 26446993_The results indicate that TNRC6A subcellular localization is substantially controlled by the interaction with Argonaute proteins. 27009120_miRNAs, AGOs, GW182, the CCR4-NOT complex, and DDX6/Me31B repress and degrade polyadenylated mRNA targets that are translated via scanning-independent mechanisms in both human and Drosophila melanogaster cells 28488892_The results suggest that overexpressed Dcp1a and GW182 can form different cytoplasmic aggregates and play distinct biological roles in the miRNA pathway. 28781232_In miRNA-mediated gene silencing, the physical interaction between human Argonaute (hAgo) and GW182 (hGW182) is essential for facilitating the downstream silencing of the targeted mRNA. hGW182 can recruit up to three copies of hAgo via its three GW motifs. This may explain the observed cooperativity in miRNA-mediated gene silencing. 28813667_Functional analysis implicates TNRC6A, NAT10, MED14, and WDR5 in RNA-mediated transcriptional activation. 28837617_that the interactions observed between TNRC6A and importin-alpha are conserved between mouse and human complexes. Our results highlight the ability of monopartite cNLS sequences to maximise contacts at the importin-alpha major binding site, as well as regions outside the main binding cavities 29080206_The structure of GW182 protein silencing domain, including RNA recognition motif. 29726904_Study results demonstrate that TNRC6A regulates the biogenesis of the circRNA circ0006916, which regulates lung cancer cells proliferation by binding to miR-522-3p and inhibiting PHLPP1 activity. 29791863_Besides the role of GW182 as part of repressor complexes inside the cell, they function in wide variety of cellular processes including pathogenesis, circadian rhythm and cell cycle. (Review) 31400113_we report the important roles of GW182 and DDX6, but not Dicer, Ago2 and DCP1A, in PB formation, and that Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) lytic infection reduces PB formation through several specific interactions with viral RNA-binding protein ORF57 31670606_Expression of TNRC6 (GW182) Proteins Is Not Necessary for Gene Silencing by Fully Complementary RNA Duplexes. 33040085_DNA analysis of benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy reveals associations between the pathogenic TTTCA repeat insertion in SAMD12 and the nonpathogenic TTTTA repeat expansion in TNRC6A. 33668648_Identification of Phosphorylated Amino Acids in Human TNRC6A C-Terminal Region and Their Effects on the Interaction with the CCR4-NOT Complex. 33962210_Acute necrotizing encephalopathy-linked mutations in Nup358 impair interaction of Nup358 with TNRC6/GW182 and miRNA function. 34108231_Impact of scaffolding protein TNRC6 paralogs on gene expression and splicing. 35822830_N-terminal Ago-binding domain of GW182 contains a tryptophan-rich region that confer binding to the CCR4-NOT complex. | ENSMUSG00000052707 | Tnrc6a | 259.549839 | 0.8629819 | -0.212597771 | 0.11953047 | 3.15873055083 | 0.0755218887012451267626289563850150443613529205322265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.21906057971839767994914893733948701992630958557128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 230.577344 | 16.960999 | 268.354627 | 19.562817 | |
| ENSG00000092036 | 54930 | HAUS4 | protein_coding | Q9H6D7 | FUNCTION: Contributes to mitotic spindle assembly, maintenance of centrosome integrity and completion of cytokinesis as part of the HAUS augmin-like complex. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19369198, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19427217}. | Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Microtubule;Mitosis;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a subunit of the centrosome complex termed the human augmin complex. The encoded protein localizes to the spindle microtubules and may play a role in mitotic spindle assembly and maintenance of centrosome integrity during cell division. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome 1. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. | hsa:54930; | centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; HAUS complex [GO:0070652]; mitotic spindle microtubule [GO:1990498]; microtubule minus-end binding [GO:0051011]; cell division [GO:0051301]; centrosome cycle [GO:0007098]; spindle assembly [GO:0051225] | ENSMUSG00000022177 | Haus4 | 155.766344 | 0.7879361 | -0.343849450 | 0.24287292 | 1.98776378858 | 0.1585748914336245762868315978266764432191848754882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.35747712834384215430105768973589874804019927978515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 137.353258 | 20.409566 | 175.205269 | 25.853271 | ||
| ENSG00000092108 | 23256 | SCFD1 | protein_coding | Q8WVM8 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in SNARE-pin assembly and Golgi-to-ER retrograde transport via its interaction with COG4. Involved in vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;ER-Golgi transport;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport | Predicted to enable syntaxin binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of autophagosome assembly; regulation of protein transport; and response to toxic substance. Located in cis-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:23256; | cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; Golgi-associated vesicle [GO:0005798]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; syntaxin binding [GO:0019905]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006888]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; negative regulation of autophagosome assembly [GO:1902902]; post-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006892]; regulation of ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0060628]; regulation of protein transport [GO:0051223]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0006890]; toxin transport [GO:1901998]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] | 19536132_Study shows that the SM protein, Sly1, interacts directly with the conserved oligomeric Golgi (COG) tethering complex; Sly1-COG interaction is mediated by the Cog4 subunit, which also interacts with Syntaxin 5 through a different binding site. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 27455348_Mutation in SCFD1 gene is associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 29260601_The found of this study confirmed the lack of association of SCFD1 rs10139154 with the risk for ALS in a large Chinese population. 31267315_SCFD1 rs10139154 is associated with a decreased risk of developing Alzheimer disease. 34785650_mTOR-mediated phosphorylation of VAMP8 and SCFD1 regulates autophagosome maturation. 35234271_Lack of an association between SCFD1 rs10139154 polymorphism and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. | ENSMUSG00000020952 | Scfd1 | 294.540799 | 1.2742150 | 0.349608753 | 0.23138109 | 2.26857652853 | 0.1320211139368374919644821829933789558708667755126953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.31850833765927610841117711970582604408264160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 388.821750 | 56.906639 | 306.508505 | 44.827342 | |
| ENSG00000092148 | 25831 | HECTD1 | protein_coding | Q9ULT8 | FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase which accepts ubiquitin from an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in the form of a thioester and then directly transfers the ubiquitin to targeted substrates (PubMed:33711283). Mediates 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of HSP90AA1 which leads to its intracellular localization and reduced secretion (By similarity). Negatively regulating HSP90AA1 secretion in cranial mesenchyme cells may impair their emigration and may be essential for the correct development of the cranial neural folds and neural tube closure (By similarity). Catalyzes ubiquitination and degradation of ZNF622, an assembly factor for the ribosomal 60S subunit, in hematopoietic cells, thereby promoting hematopoietic stem cell renewal (PubMed:33711283). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q69ZR2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33711283}. | 3D-structure;ANK repeat;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Ubl conjugation pathway | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33711283}. | Predicted to enable ubiquitin protein ligase activity. Predicted to be involved in anatomical structure development; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; and protein K63-linked ubiquitination. Predicted to act upstream of or within several processes, including animal organ development; negative regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane; and protein autoubiquitination. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:25831; | nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; anatomical structure development [GO:0048856]; aorta development [GO:0035904]; heart valve development [GO:0003170]; natural killer cell differentiation [GO:0001779]; negative regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903077]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein autoubiquitination [GO:0051865]; protein K63-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070534]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein polyubiquitination [GO:0000209]; spongiotrophoblast differentiation [GO:0060708]; trophoblast giant cell differentiation [GO:0060707]; ventricular septum development [GO:0003281] | 23277359_HectD1 promotes the APC-Axin interaction to negatively regulate Wnt signaling. 24667607_our high-resolution structures show a new fold composed of five small helices where H3 and H4 are tilted in a novel arrangement; we call this fold the Basic Tilted Helix Bundle (BTHB) domain. 28073378_Hectd1 regulates the protein level of IQGAP1 through ubiquitination. 29306077_HECTD1 may be involved in the regulation of ABCA1-mediated cholesterol export from unloaded macrophages to apoA-I. 29540674_SiO2 concomitantly increased circHECTD1 expression, which, in turn, inhibited HECTD1 protein expression. 31799632_we have now identified HECTD1 as an important factor in promoting Base excision repair (BER) in chromatin. 32319576_HECTD1 regulates the expression of SNAIL: Implications for epithelialmesenchymal transition. 32675746_CircHECTD1 up-regulates mucin 1 expression to accelerate hepatocellular carcinoma development by targeting microRNA-485-5p via a competing endogenous RNA mechanism. 33561315_Circular RNA circHECTD1 facilitates glioma progression by regulating the miR-296-3p/SLC10A7 axis. 33853758_The deubiquitinase TRABID stabilizes the K29/K48-specific E3 ubiquitin ligase HECTD1. 35915203_The E3 ubiquitin ligase HECTD1 contributes to cell proliferation through an effect on mitosis. | ENSMUSG00000035247 | Hectd1 | 605.588895 | 1.0303625 | 0.043151971 | 0.12669442 | 0.11576483618 | 0.7336740506354512136866219407238531857728958129882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.86611803698950906582609832184971310198307037353515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 603.950119 | 45.793451 | 588.399923 | 44.676930 |
| ENSG00000099622 | 1153 | CIRBP | protein_coding | Q14011 | FUNCTION: Cold-inducible mRNA binding protein that plays a protective role in the genotoxic stress response by stabilizing transcripts of genes involved in cell survival. Acts as a translational activator. Seems to play an essential role in cold-induced suppression of cell proliferation. Binds specifically to the 3'-untranslated regions (3'-UTRs) of stress-responsive transcripts RPA2 and TXN. Acts as a translational repressor (By similarity). Promotes assembly of stress granules (SGs), when overexpressed. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11574538, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16513844}. | 3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;RNA-binding;Stress response | Enables mRNA 3'-UTR binding activity and small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding activity. Involved in mRNA stabilization; positive regulation of translation; and response to UV. Located in cytoplasm and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:1153; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic stress granule [GO:0010494]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; spliceosomal complex [GO:0005681]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding [GO:0070181]; translation repressor activity [GO:0030371]; mRNA stabilization [GO:0048255]; positive regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0048026]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727]; response to cold [GO:0009409]; response to UV [GO:0009411]; stress granule assembly [GO:0034063] | 12819390_results suggest that cold inducible RNA binding protein may participate in the cell cycle regulation of normal endometrium and the loss of its expression may be involved in endometrial carcinogenesis 15075239_RBM3 and CIRP are adaptatively expressed in response to hypoxia by a mechanism that involves neither HIF-1 nor mitochondria 19158277_CIRP enhanced extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) phosphorylation, and treatment with an MEK inhibitor decreased the proliferation caused by CIRP. 19277990_pharmacological modulation of RBM3 and CIRBP may represent novel therapeutic approaches for prostate cancer. 23437386_CIRBP contributes to ultraviolet light- and lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of IL1beta by regulating NFkappaB activity. 23437386_CIRBP regulates the expression of interleukin-1beta in an NF-kappaB-dependent fashion. 24097189_report increased levels of cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) in the blood of individuals admitted to the surgical intensive care unit with hemorrhagic shock 25027624_High levels of CIRP protein expression was associated with a short survival rate in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. 25187386_Cirp promotes the development of intestinal inflammation and colorectal tumors through regulating apoptosis and production of TNFalpha and IL23 in inflammatory cells. 25934796_The expression of CIRP in pituitary adenoma is closely related with tumor proliferation and invasion, and its significantly elevated expression level indicates post-op recurrence. 26188505_CIRP inhibits DNA damage-induced apoptosis by regulating p53 protein.CIRP suppresses p53 upregulation during apoptosis.CIRP regulates the expression of genes involved in apoptosis. 26361390_Study shows that CIRP elevated plasma concentration is significantly associated with poor prognosis among patients with sepsis. Therefore, CIRP is a potential predictor of sepsis prognosis. 26673712_CIRP protein regulates telomerase activity in a temperature-dependent manner by regulating the level of TERT mRNAs. 26824322_Clinically, CIRP overexpression is significantly correlated with Cushing's disease recurrence. CIRP appears to play a critical tumorigenesis function in Cushing's disease and its expression might be a useful biomarker for tumor recurrence. 26824423_hnRNP A18 can promote tumor growth in in vivo models by coordinating the translation of pro-survival transcripts to support the demands of proliferating cells and increase survival under cellular stress. 26936526_In human abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) tissue, Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) exhibited a 5.6-fold and 93% increase in mRNA and protein expression, respectively. In a rat AAA model, CIRP was upregulated significantly in a time-dependent manner in the serum and AAA tissue. 27184164_CIRP was expressed in the bronchi of human COPD patients and was involved in inflammatory factors and MUC5AC expression after cold stimulation through the ERK and NF-kappaB pathways 27315340_The serum and synovial concentrations of CIRP in the rheumatoid arthritis patients were increased, suggesting that CIRP mediates inflammation and is a potential marker for synovial inflammation. 27395339_We found out that the link between CIRP and Snail is mediated by ERK and p38 pathways. EMT is a critical component of carcinoma metastasis and invasion. As demonstrated in this study, the biological role of CIRP in EMT may explain why CIRP overexpression has been associated with a bad prognosis in cancer patients. 27423012_this study shows that CIRP expression in bronchial airway epithelial cells of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is higher than that in healthy person 27477308_cold temperature can induce an airway inflammatory response and excess mucus production via a CIRP-mediated increase in mRNA stability and protein translation 27837912_We generated a transgenic mouse model overexpressing human CIRP in the mammary epithelium to ask if it plays a role in mammary gland development. Effects of CIRP overexpression on mammary gland morphology, cell proliferation, and apoptosis were studied from puberty through pregnancy, lactation and weaning 27840101_Increased synovial fluid CIRP concentrations were closely associated with the severity of knee osteoarthritis 27864909_CIRP Expression Is Induced in Skin Cancer Cells and in Keratinocytes Exposed to Lower-Dose But Not Higher-Dose UVB Radiation. 28368279_Crystal structure of the hnRNP A18 RNA recognition motif has been reported. 28373441_Low CIRP expression is associated with colon Cancer. 28536481_Cold induction of serine and arginine rich splicing factor 5 (SRSF5) is independent of cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) and RNA-binding motif protein 3 (RBM3). 29432179_This study reports that cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRBP) is a newly identified key regulator in DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair. 29981150_CIRP mediates the activation of STAT3-Bag-1 signaling cascade via activating the Janus kinase family proteins and NF-kappaB signaling pathways upon UV irradiation. 30315244_CIRBP could be a novel oncogene in human bladder cancer inducing transcription of HIF-1alpha. 31054221_Compared with pre-operation levels, CIRP levels significantly increased 6 h after cardiovascular surgery with CPB. Multiple linear regression analysis showed that the length of CPB time contributed to CIRP production (P=0.013). 31405566_downregulation of CIRP may render cardiac cells prone to apoptosis in heart failure. 32027618_Extracellular CIRP as an endogenous TREM-1 ligand to fuel inflammation in sepsis. 32689999_Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein might determine the severity and the presences of major/minor criteria for severe community-acquired pneumonia and best predicted mortality. 33172965_Cold-inducible RNA binding protein promotes breast cancer cell malignancy by regulating Cystatin C levels. 33429432_CIRP Sensitizes Cancer Cell Responses to Ionizing Radiation. 33638934_Human antigen R (HuR) and Cold inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) influence intestinal mucosal barrier function in ulcerative colitis by competitive regulation on Claudin1. 33902703_Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) potentiates uric acid-induced IL-1beta production. 33991007_ATP regulates RNA-driven cold inducible RNA binding protein phase separation. 34233365_CIRP Secretion during Cardiopulmonary Bypass Is Associated with Increased Risk of Postoperative Acute Kidney Injury. 34351954_Clinical relevance for circulating cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) in patients with adult-onset Still's disease. 34465343_CIRP promotes the progression of non-small cell lung cancer through activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling via CTNNB1. 34953031_The role of Cold-Inducible RNA-binding protein in respiratory diseases. 35226160_MiR-383-5p promotes apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cells by targeting CIRP through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. 35531472_Prognostic Value of Plasma Cold-Inducible RNA-Binding Protein in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome. 35541895_CIRBP-OGFR axis safeguards against cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiotoxicity induced by chemotherapy. 35800223_Downregulation of CIRP Prone Cells to Oxidative Injury via Regulating Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. 35926374_ETS-1 facilitates Th1 cell-mediated mucosal inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases through upregulating CIRBP. 36061308_CIRBP Regulates Pancreatic Cancer Cell Ferroptosis and Growth by Directly Binding to p53. 36211820_Resetting Proteostasis of CIRBP with ISRIB Suppresses Neural Stem Cell Apoptosis under Hypoxic Exposure. | ENSMUSG00000045193 | Cirbp | 855.247657 | 0.8538384 | -0.227965097 | 0.06228476 | 13.39841958280 | 0.0002518363982617444034317610856987812439911067485809326171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00230844530726427316774662656939653970766812562942504882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 830.874181 | 41.483483 | 977.661950 | 48.045860 | |
| ENSG00000100300 | 706 | TSPO | protein_coding | P30536 | FUNCTION: Can bind protoporphyrin IX and may play a role in the transport of porphyrins and heme (By similarity). Promotes the transport of cholesterol across mitochondrial membranes and may play a role in lipid metabolism (PubMed:24814875), but its precise physiological role is controversial. It is apparently not required for steroid hormone biosynthesis. Was initially identified as peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor; can also bind isoquinoline carboxamides (PubMed:1847678). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1847678, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24814875}. | Alternative splicing;Lipid transport;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | Present mainly in the mitochondrial compartment of peripheral tissues, the protein encoded by this gene interacts with some benzodiazepines and has different affinities than its endogenous counterpart. The protein is a key factor in the flow of cholesterol into mitochondria to permit the initiation of steroid hormone synthesis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been reported; one of the variants lacks an internal exon and is considered non-coding, and the other variants encode the same protein. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. | hsa:706; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; androgen binding [GO:0005497]; benzodiazepine receptor activity [GO:0008503]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; cholesterol transfer activity [GO:0120020]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; adrenal gland development [GO:0030325]; aging [GO:0007568]; anion transport [GO:0006820]; behavioral response to pain [GO:0048266]; C21-steroid hormone biosynthetic process [GO:0006700]; cellular hypotonic response [GO:0071476]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to zinc ion [GO:0071294]; chloride transport [GO:0006821]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; contact inhibition [GO:0060242]; glial cell migration [GO:0008347]; heme biosynthetic process [GO:0006783]; maintenance of protein location in mitochondrion [GO:0072656]; negative regulation of ATP metabolic process [GO:1903579]; negative regulation of autophagy of mitochondrion [GO:1903147]; negative regulation of corticosterone secretion [GO:2000853]; negative regulation of glial cell proliferation [GO:0060253]; negative regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045019]; negative regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031397]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; peripheral nervous system axon regeneration [GO:0014012]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051928]; positive regulation of glial cell proliferation [GO:0060252]; positive regulation of mitochondrial depolarization [GO:0051901]; positive regulation of necrotic cell death [GO:0010940]; positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000379]; protein targeting to mitochondrion [GO:0006626]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of cholesterol transport [GO:0032374]; regulation of steroid biosynthetic process [GO:0050810]; response to acetylcholine [GO:1905144]; response to manganese ion [GO:0010042]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570]; response to testosterone [GO:0033574]; response to vitamin B1 [GO:0010266]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; steroid metabolic process [GO:0008202] | 11304832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12374690_Overexpression of the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor is associated with colorectal cancer 12547158_This gene is amplified in MDA-MB-231 aggressive breast cancer cells 14584048_demonstrated that PBR is expressed in mesenchymal stem cells and that their ligands affect their proliferation and differentiation 14626449_These results indicate that elevated peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor (PBR) expression is not common in aggressive tumors, but may be limited to certain cancers where elevated PBR expression is associated with tumor progression. 15041726_High expression of PBR in this patient subgroup may be used to identify a new high risk population in breast cancer for which a more specific therapy would be beneficial. 15296476_involvement of PBRs in human pancreatic beta-cell function and survival. 15473257_our results supported the hypothesis that PBR controls T-cell maturation and suggested mechanisms through which PBR may regulate thymocyte-positive selection. 15648546_Our results represent first evidence of PBRs in parathyroid glands and suggest for them a role in influencing PTH release. A clear trend of PBR up-regulation in parathyroid adenoma was also found. 15769477_the subcellular localisation of PBR defines its function and that this receptor could be a possible target for new strategies against cancer 16511838_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16511838_Study provides new and important evidence that variation in the PBR gene influences susceptibility to panic disorder. 16868661_the intensity and extent of staining for PBR had a strong direct correlation with the grade of malignancy of the tumor, along with proliferative and apoptotic indices. The highest expression of PBR was in glioblastomas grade IV. 16919618_Our results showed an up-regulation of peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor (PBR) in platelets of FM patients, and this seems to be related to the severity of fibromyalgic symptoms. 17561806_TSPO is located in mitochondrial membranes of HT-29 and reveal that its activation induces a rise in cytosolic Ca(2+), leading to the stimulation of Cl(-) secretion. 18054208_TSPO expression evaluation is a useful biological marker of Adult Separation Anxiety Disorder 18158327_These findings reveal a previously unidentified pathway of the membrane integration of MOM proteins with multiple TMSs of the PBR. 18256758_Sharp inhibition of apoptosis and changes in the levels of cell proliferation in tumor cells were paralleled by decreased expression of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor in patients with squamous cell carcinoma & skin melanoma. 18670869_VDAC activation by the 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO), implications for apoptosis. 18791274_TSPO may serve to open the mitochondrial permeability transition pore in response to anti-cancer drugs such as erucylphosphohomocholine 18806692_TSPO knockdown by genetic manipulation transforms the human HT29 cancer line to a more malignant type in-vitro. 19077109_results show variety of CNS cells capable of expressing TSPO; pattern of expression differs between normal & diseased CNS & among different diseases & cell types; microglia & macrophages remain chief cell type upregulating TSPO expression in brain disease 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19525461_(11)C-AC-5216 is a promising PET ligand for quantifying PBR in the human brain. 19525468_(18)F-PBR06 is a longer-lived and promising alternative to (11)C-labeled radioligands to measure TSPOs as a biomarker of inflammation in the brain. 19598235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19617321_Studies in patient populations will help determine whether (11)C-DPA-713 provides better sensitivity for evaluating increased TSPO expression. 19668118_Two allelic variants of TSPO gene, were tested for association with the presence of adult separation anxiety disorder. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19789311_Blocking TSPO function in tumor cells induces cell death and denotes a survival role for TSPO in prostate cancer . 19846611_Results demonstrate that the Ala147Thr spontaneous amino acid substitution within TSPO is able to affect pregnenolone production, and should encourage further studies to investigate its potential role in polygenic dyslipidemias. 20056222_TSPO is expressed in macrophages in human carotid atherosclerosis 20085808_High TSPO protein levels are associated with oral cancer. 20222126_Overexpression of translocator protein is associated with inflammatory bowel disease. 20424634_reduction in [(11)C]PBR28 binding may not be interpreted simply as a reduction in TSPO density 20491643_Following exposure of saliva to cigarette smoke a three-fold decrease in the affinity of salivary TSPO to its specific ligand, [(3)H]PK 11195 (p 0.05). Interactions were confirmed for TSPOxbipolar disorder(F5,525=3.9, p=0.002) and for TSPOxalcohol use disorders (F5,525=2.8, p=0.017). 29641545_Effects of genetic variants in the TSPO gene on protein structure and stability 29777199_Study found no alcohol use disorder (AUD) group differences on [11C]PBR28 binding in our clinical study and no group differences in [11C]PBR28 uptake in the brain of alcohol-dependent versus -nondependent rats. However, when separately analyzing by TSPO genotype, found lower [11C]PBR28 binding in the brain of AUD patients than in healthy controls for medium-affinity binders only. 29860333_this study assessed the feasibility of utilizing PET imaging with the TSPO tracer, [18F]PBR06, to detect activated microglia in two HD mouse models and to monitor response to treatment with LM11A-31, a p75NTR ligand known to reduce neuroinflammation in HD mice. 29906515_Authors investigated the link between mitochondrial TSPO and structural brain characteristics in key brain regions such as dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of a large group of participants including individuals at clinical high risk (CHR) for psychosis, first-episode psychosis (mostly antipsychotic-naive) patients, and healthy volunteers. 30030837_This study demonstrated that TSPO was expressed in microglia and neurons in drug-resistant mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. 30044440_An increase in the expression levels of Tspo mRNA is not necessarily a good diagnostic biomarker in most cancers with changes not being large enough to be significantly different when detected by in situ hybridisation. 30575805_Data reported suggest that TSPO-VDAC complex upregulation in bipolar disorder patients, the simultaneous downregulation of mitophagic proteins and NLRP3 inflammasome activation could lead to an accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria, resulting in inflammation and apoptosis. 30893912_These data provide biochemical insights into TSPO-associated function in retinal pigment epithelial cells. 31144767_There may be a role for TSPO PET for evaluation of patients with suspected neocortical seizure foci, particularly when other imaging modalities are unrevealing 31260948_In rheumatoid arthritis patients, lower cerebral TSPO binding was associated with higher disease activity. 31276244_Characterization of the 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO) expression in post-mortem normal and Alzheimer's disease brains. 31295884_TSPO expression is upregulated by CS, suggesting that TSPO plays a role in cell death processes induced by CS exposure. Alterations in TSPO-related cell death processes suggest that TSPO may be involved in the tissue damage caused by CS. 31363804_Effects of age, BMI and sex on the glial cell marker TSPO - a multicentre [(11)C]PBR28 HRRT PET study. 31510070_The translocator protein (TSPO) silencing increased and reduced the release of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, respectively. 31515530_TSPO ligands prevent the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and attenuate neointima formation through AMPK activation. 31563962_TSPO deficiency induces mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to hypoxia, angiogenesis, and a growth-promoting metabolic shift toward glycolysis in glioblastoma. 31578541_These observations establish a quantitative framework for interpretation of TSPO in multiple sclerosis and highlight the need for neuropathological characterization of TSPO expression for the interpretation of TSPO PET in other neurodegenerative disorders 31713961_TSPO polymorphism in individuals with alcohol use disorder: Association with cholesterol levels and withdrawal severity. 31963507_Glioblastoma Exhibits Inter-Individual Heterogeneity of TSPO and LAT1 Expression in Neoplastic and Parenchymal Cells. 32076115_[(11)C]PBR28 MR-PET imaging reveals lower regional brain expression of translocator protein (TSPO) in young adult males with autism spectrum disorder. 32172519_Translocator protein 18 kDa: a potential therapeutic biomarker for post traumatic stress disorder. 32482385_Translocator protein (18 kDa) (TSPO) ligands activate Nrf2 signaling and attenuate inflammatory responses and oxidative stress in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. 32529881_Usefulness of postoperative serum translocator protein as a predictive marker for delirium after breast cancer surgery in elderly women. 32662626_Tracing the History of the Human Translocator Protein to Recent Neurodegenerative and Psychiatric Imaging. 32682565_Meta-analysis of the Glial Marker TSPO in Psychosis Revisited: Reconciling Inconclusive Findings of Patient-Control Differences. 32802194_[(18)F]CB251 PET/MR imaging probe targeting translocator protein (TSPO) independent of its Polymorphism in a Neuroinflammation Model. 32804124_Astrocytic TSPO Upregulation Appears Before Microglial TSPO in Alzheimer's Disease. 32842621_Microglia Implicated in Tauopathy in the Striatum of Neurodegenerative Disease Patients from Genotype to Phenotype. 32933996_TSPO-targeted PET and Optical Probes for the Detection and Localization of Premalignant and Malignant Pancreatic Lesions. 32988856_Novel TSPO-targeted Doxorubicin Prodrug for Colorectal Carcinoma Cells. 33006604_Brain TSPO-PET predicts later disease progression independent of relapses in multiple sclerosis. 33067627_Expression of mitochondrial TSPO and FAM173B is associated with inflammation and symptoms in patients with painful knee osteoarthritis. 33216461_Increased transcription of TSPO, HDAC2, and HDAC6 in the amygdala of males with alcohol use disorder. 33260618_Downregulation of Mitochondrial TSPO Inhibits Mitophagy and Reduces Enucleation during Human Terminal Erythropoiesis. 33301812_Cigarette smoke induces apoptosis via 18 kDa translocator protein in human bronchial epithelial cells. 33357157_Prognostic significance of serum translocator protein in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hematomapreliminary findings. 33433698_Cellular sources of TSPO expression in healthy and diseased brain. 33652554_The Interplay of Cholesterol and Ligand Binding in hTSPO from Classical Molecular Dynamics Simulations. 33664474_The translocator protein (TSPO) is prodromal to mitophagy loss in neurotoxicity. 33769215_Variation rs6971 in the Translocator Protein Gene (TSPO) is Associated with Aggressiveness and Impulsivity but Not with Anxiety in a Population-Representative Sample of Young Adults. 33803741_De novo Neurosteroidogenesis in Human Microglia: Involvement of the 18 kDa Translocator Protein. 34142769_The translocator protein gene is associated with endogenous pain modulation and the balance between glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid in fibromyalgia and healthy subjects: a multimodal neuroimaging study. 34145928_Activated microglia do not increase 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO) expression in the multiple sclerosis brain. 34320915_Neuroinflammation and psychiatric disorders: Relevance of C1q, translocator protein (18 kDa) (TSPO), and neurosteroids. 34405276_Preclinical evaluation of (S)-[(18)F]GE387, a novel 18-kDa translocator protein (TSPO) PET radioligand with low binding sensitivity to human polymorphism rs6971. 35285861_Serum Iba-1, GLUT5, and TSPO in Patients With Diabetic Retinopathy: New Biomarkers for Early Retinal Neurovascular Alterations? A Pilot Study. 35430971_Translocator Protein 18-kDa: A Promising Target to Treat Neuroinflammation- related Degenerative Diseases. 35475466_Translocator protein (18 kDa) regulates the microglial phenotype in Parkinson's disease through P47. 35522669_Differential mitochondrial protein interaction profile between human translocator protein and its A147T polymorphism variant. 36071748_Translocator Protein 18 kDa (TSPO) as a Novel Therapeutic Target for Chronic Pain. | ENSMUSG00000041736 | Tspo | 338.571024 | 0.9196544 | -0.120836296 | 0.08582786 | 1.98273052070 | 0.1591030474056046029041056044661672785878181457519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.35815425919098875517931901413248851895332336425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 325.160648 | 18.194384 | 355.263090 | 19.319492 | |
| ENSG00000100320 | 23543 | RBFOX2 | protein_coding | O43251 | FUNCTION: RNA-binding protein that regulates alternative splicing events by binding to 5'-UGCAUGU-3' elements. Prevents binding of U2AF2 to the 3'-splice site. Regulates alternative splicing of tissue-specific exons and of differentially spliced exons during erythropoiesis (By similarity). RNA-binding protein that seems to act as a coregulatory factor of ER-alpha. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11875103}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Methylation;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding | This gene is one of several human genes similar to the C. elegans gene Fox-1. This gene encodes an RNA binding protein that is thought to be a key regulator of alternative exon splicing in the nervous system and other cell types. The protein binds to a conserved UGCAUG element found downstream of many alternatively spliced exons and promotes inclusion of the alternative exon in mature transcripts. The protein also interacts with the estrogen receptor 1 transcription factor and regulates estrogen receptor 1 transcriptional activity. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:23543; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030520]; mRNA processing [GO:0006397]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; regulation of alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000381]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; RNA metabolic process [GO:0016070]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380] | 16260614_Fox-1 and Fox-2 isoforms specifically activate splicing of neuronally regulated exons, which requires UGCAUG enhancer elements 16537540_Fox-1 and Fox-2 splicing factors have roles in alternative splicing of protein 4.1R 18573872_Fox-1/Fox-2 proteins block prespliceosome complex formation at two distinct steps through binding to two functionally important UGCAUG elements. 18573884_These results establish hnRNP H and hnRNP F as being repressors of exon inclusion and suggest that Fox proteins enhance their ability to antagonize ASF/SF2. 18794351_predict thousands of Fox-1/2 targets with conserved binding sites, at a false discovery rate of approximately 24%, including many validated experimentally, suggesting a surprisingly extensive splicing regulatory networks 19136955_These findings suggest that FOX2 functions as a critical regulator of a splicing network, and that FOX2 is important for the survival of human embryonic stem cells. 20131247_Fox-2 plays an integral role in the regulation of LH2 splicing and knockdown of Fox-2 may suggest a novel approach to strategies directed against scleroderma. 21747913_the negative regulation of Rbfox2 by Rbfox3 through a novel mechanism 21876675_functional significance of EMT-associated alternative splicing depletion of RBFOX2 in mesenchymal cells 22083953_This study characterizes the mechanism by which RBFOX2 regulates protein 4.1R exon 16 splicing through the downstream intronic element UGCAUG. 22666429_FOX-2 is involved in splicing of ataxin-2 transcripts and that this splicing event is altered by overexpression of ataxin-1 23143756_RBFOX2 polymorphism is associated with breast cancer. 23149937_RBFOX2 drives mesenchymal tissue-specific splicing in both normal and cancer tissues. 24048253_MBNL1 and RBFOX2 cooperate to establish a splicing programme involved in pluripotent stem cell differentiation. 25065397_RBFOX2 SNPs showed evidence for effects across multiple reading and language traits. 25087874_Results show that the conserved Rbfox2 RNA binding protein regulates 30% of the splicing transitions observed during myogenesis and is required for the specific step of myoblast fusion. 25524026_RBFOX proteins can facilitate the splicing of micro-exons. We also found that PTBP1 likely regulates the inclusion of micro-exons, possibly by repressing the inclusion of micro-exons that are enhanced by RBFOX proteins and other splicing factors.[RBFOX] 25921069_CPSF2 and SYMPK, are RBFOX2 cofactors for both inclusion and exclusion of internal exons. 27001519_Some of the widespread cellular functions of Rbfox2 protein are attributable to regulation of miRNA biogenesis, and might include the mis-regulation of miR-20b and miR-107 in cancer and neurodegeneration. 27146458_Data show that while RBFOX1 and RBFOX2 do not mediate neuron-specific processing of UBE3A-ATS, these proteins play important roles in developing neurons and are not completely functionally redundant. 27211866_RBFox2 interactis with chromatin in a nascent RNA-dependent manner. RBFox2 inactivation eradicates PRC2 targeting on the majority of bivalent gene promoters and leads to transcriptional de-repression. 27239029_RBFOX2 dysregulation by dominant-negative RBFOX2 is an early pathogenic event in diabetic hearts. 27485310_Rbfox2 nonsense mutation is associated with hypoplastic left heart syndrome. 27911856_Results showed that the expression patterns of these genes were indicative of the onset of EMT in in-vitro models, but not in tissue samples. However, the ratio between ESRP1 or ESRP2 and RBFOX2 significantly decreased during EMT and positively correlated with the EMT-specific phenotype in cell models. Low ESRP1/RBFOX2 ratio value was associated with a higher risk of metastasis in early breast cancer patients. 28894257_The authors report that a subset of cell cycle-related genes including retinoblastoma 1 is the target of Rbfox2 in cytoplasmic stress granules, and Rbfox2 regulates the retinoblastoma 1 mRNA and protein expression levels during and following stress exposure. 28993448_Rbfox2 modulates the functions of vascular CaV1.2 calcium channel by dynamically regulating the expressions of alternative exons 9* and 33, which in turn affects the vascular myogenic tone. 30294913_Results provide evidence that RBFOX2 expression in epithelial ovarian cancer is regulated by MALAT1 which its alternative splicing. 31128090_Data show that exon 10, responsible for nuclear localization, of RBFOX2. was absent in calcific tendons. 32109384_Aberrant Expression of a Non-muscle RBFOX2 Isoform Triggers Cardiac Conduction Defects in Myotonic Dystrophy. 32762877_Trophoblast lineage specific expression of the alternative splicing factor RBFOX2 suggests a role in placental development. 32807990_Concentration-dependent splicing is enabled by Rbfox motifs of intermediate affinity. 34009296_ERG transcription factors have a splicing regulatory function involving RBFOX2 that is altered in the EWS-FLI1 oncogenic fusion. 34180133_RBFOX2/GOLIM4 Splicing Axis Activates Vesicular Transport Pathway to Promote Nasopharyngeal Carcinogenesis. 34244793_RBFOX2 alters splicing outcome in distinct binding modes with multiple protein partners. 34346508_Alternative microexon splicing by RBFOX2 and PTBP1 is associated with metastasis in colorectal cancer. 34548489_SON drives oncogenic RNA splicing in glioblastoma by regulating PTBP1/PTBP2 switching and RBFOX2 activity. 35269658_The Splicing of the Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter Genuine Activator MICU1 Is Driven by RBFOX2 Splicing Factor during Myogenic Differentiation. 35404107_Alternative Splicing of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Nuclear Translocator (ARNT) Is Regulated by RBFOX2 in Lymphoid Malignancies. 36466711_The Role of Alternative Splicing Factors hnRNP G and Fox-2 in the Progression and Prognosis of Esophageal Cancer. | ENSMUSG00000033565 | Rbfox2 | 161.068445 | 0.8367091 | -0.257201956 | 0.34696057 | 0.53146546102 | 0.4659914000927299349008592344034695997834205627441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.68606333064910074437392495383392088115215301513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 125.157775 | 36.382949 | 145.216615 | 42.295932 | |
| ENSG00000100359 | 27352 | SGSM3 | protein_coding | Q96HU1 | FUNCTION: May play a cooperative role in NF2-mediated growth suppression of cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15541357}. | Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Growth arrest;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain | Enables GTPase activator activity and small GTPase binding activity. Involved in several processes, including Rap protein signal transduction; positive regulation of GTPase activity; and regulation of Rab protein signal transduction. Located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:27352; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; gap junction [GO:0005921]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; plasma membrane to endosome transport [GO:0048227]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0045732]; Rap protein signal transduction [GO:0032486]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of Rab protein signal transduction [GO:0032483] | 15541357_MAP decreased the AP-1-dependent promoter activity additively with merlin in NIH3T3 cells.Results suggest that MAP may play a cooperative role in the merlin-mediated growth suppression of cells. 17509819_Identification of novel protein SGSM3 which modulates small G protein (RAP and RAB)-mediated signaling pathway. 23586710_The CIP85 was observed to interact with clathrin, which suggested a role for CIP85 in the clathrin-mediated internalization of Cx43. 23918301_rs56228771 may contribute to hepatocarcinogenesis, possibly by affecting SGSM3 expression through a miRNA-mediated regulation. 27432265_SGSM3 gene polymorphism is associated with the risk of breast cancer in Chinese population. 29693742_findings support an association between 4-bp ins/del polymorphism in the 3'UTR of SGSM3 and the risk of bladder cancer in an Iranian population. | ENSMUSG00000042303 | Sgsm3 | 178.861634 | 0.9985530 | -0.002089158 | 0.29371156 | 0.00005000579 | 0.9943578243690079920824587134120520204305648803710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.99656640017723618907297122859745286405086517333984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 168.056217 | 31.895886 | 169.790369 | 32.152228 | |
| ENSG00000100575 | 26520 | TIMM9 | protein_coding | Q9Y5J7 | FUNCTION: Mitochondrial intermembrane chaperone that participates in the import and insertion of multi-pass transmembrane proteins into the mitochondrial inner membrane. May also be required for the transfer of beta-barrel precursors from the TOM complex to the sorting and assembly machinery (SAM complex) of the outer membrane. Acts as a chaperone-like protein that protects the hydrophobic precursors from aggregation and guide them through the mitochondrial intermembrane space. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14726512}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Chaperone;Disulfide bond;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Translocation;Transport;Zinc | TIMM9 belongs to a family of evolutionarily conserved proteins that are organized in heterooligomeric complexes in the mitochondrial intermembrane space. These proteins mediate the import and insertion of hydrophobic membrane proteins into the mitochondrial inner membrane.[supplied by OMIM, Apr 2004]. | hsa:26520; | mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; mitochondrial intermembrane space protein transporter complex [GO:0042719]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; TIM22 mitochondrial import inner membrane insertion complex [GO:0042721]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; membrane insertase activity [GO:0032977]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; protein insertion into mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0045039]; protein targeting to mitochondrion [GO:0006626]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605] | 14726512_in contrast to yeast, only a small fraction of Tim9-Tim10a-Tim10b complex is in a stable association with Tim22 16387659_The crystal structure of TIM9.10 described here reveals a previously undescribed alpha-propeller topology in which helical 'blades' radiate from a narrow central pore lined with polar residues. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27720672_in gastric cancer patients, a borderline association was found between overexpression of TIMM9 and vascular invasion; patients with high expression levels of TIMM9 achieved a significantly lower disease-free survival rate compared with those with low expression levels | ENSMUSG00000021079 | Timm9 | 86.289591 | 0.7791532 | -0.360021144 | 0.23569096 | 2.32287417258 | 0.1274842765754172491110551845849840901792049407958984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.31166391152984573853501615303684957325458526611328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 72.799350 | 13.219373 | 93.896622 | 17.023251 | |
| ENSG00000100731 | 22990 | PCNX1 | protein_coding | Q96RV3 | Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes an evolutionarily conserved transmembrane protein similar to the pecanex protein in Drosophila. The fly protein is a component of the Notch signaling pathway, which functions in several developmental processes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. | hsa:22990; | membrane [GO:0016020] | 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 28789966_High PCNX expression is associated with lung cancer. | ENSMUSG00000021140 | Pcnx | 376.549496 | 1.0180818 | 0.025853439 | 0.21551914 | 0.01436043126 | 0.9046138423780962778408820668119005858898162841796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.95723870392501786419359177671140059828758239746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 359.595004 | 122.911965 | 343.866543 | 117.496111 | ||
| ENSG00000100815 | 9321 | TRIP11 | protein_coding | Q15643 | FUNCTION: Is a membrane tether required for vesicle tethering to Golgi. Has an essential role in the maintenance of Golgi structure and function (PubMed:25473115, PubMed:30728324). It is required for efficient anterograde and retrograde trafficking in the early secretory pathway, functioning at both the ER-to-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC) and Golgi complex (PubMed:25717001). Binds the ligand binding domain of the thyroid receptor (THRB) in the presence of triiodothyronine and enhances THRB-modulated transcription. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10189370, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25473115, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25717001, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30728324, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9256431}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Dwarfism;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene was identified based on the interaction of its protein product with thyroid hormone receptor beta. This protein is associated with the Golgi apparatus. The N-terminal region of the protein binds Golgi membranes and the C-terminal region binds the minus ends of microtubules; thus, the protein is thought to play a role in assembly and maintenance of the Golgi ribbon structure around the centrosome. Mutations in this gene cause achondrogenesis type IA.[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. | hsa:9321; | cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment [GO:0005793]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; inner acrosomal membrane [GO:0002079]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; outer acrosomal membrane [GO:0002081]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; cartilage development [GO:0051216]; chondrocyte differentiation involved in endochondral bone morphogenesis [GO:0003413]; endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006888]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; Golgi ribbon formation [GO:0090161]; inner ear receptor cell stereocilium organization [GO:0060122]; protein glycosylation [GO:0006486]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; ventricular septum development [GO:0003281]; vesicle tethering to Golgi [GO:0099041] | 12383348_The overexpression of this protein blocks anterograde and retrograde transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. 15485806_demonstrate that the thyroid hormone receptor/retinoblastoma-interacting protein 230 (TRIP230) interacts directly with aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator(ARNT) and is essential for both hypoxic and TCDD-mediated transcriptional responses 18451304_the attachment of golgin GMAP-210 to lipid membranes 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19715559_Localisation of GMAP-210 (TRIP11) to Golgi is the result of the combined action of two domains (N- and C-terminal) that recognize different sub-regions of the Golgi apparatus. 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20089971_identification of a mutation affecting GMAP-210 in mice, and then in humans, as the cause of a lethal skeletal dysplasia 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24919196_Rb is present in HIF1alpha-ARNT/HIF1beta transcriptional complexes associated with TRIP230 as determined by co-immuno-precipitation, GST-pull-down and ChIP assays 25473115_GMAP-210 has a role for membrane tethering in maintaining Golgi structure and a role for Rab2 binding in linking tethering with downstream docking and fusion events at the Golgi apparatus. 25717001_role for GMAP-210 in several trafficking steps at the ER-Golgi interface 27458799_The authors conclude that the Golgi uses GMAP-210 as a filter to select transport vesicles according to their size and bulk lipid composition. 29022645_Decreased expressions of TRIP11, THRA, and THRB correlated with poor survival of renal cell cancer patients. Expressions of TRIP11 and HIF-1beta correlated with tumor grades. 30518689_A common pathogenic mechanism in GMAP-210- and LBR-related diseases attributable to defective secretory trafficking at the Golgi apparatus. 31903676_Pathogenic variants in the TRIP11 gene cause a skeletal dysplasia spectrum from odontochondrodysplasia to achondrogenesis 1A. 33746040_Description of four patients with TRIP11 variants expand the clinical spectrum of odontochondroplasia (ODCD) and demonstrate the existence of common variants. 34057271_Biallelic deep intronic variant c.5457+81T>A in TRIP11 causes loss of function and results in achondrogenesis 1A. | ENSMUSG00000021188 | Trip11 | 347.616189 | 0.5336172 | -0.906122829 | 0.44172549 | 4.00295383167 | 0.0454205973400153215080443658280273666605353355407714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.15350164667604115908972062243265099823474884033203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 260.408220 | 111.723630 | 494.659272 | 212.367560 | |
| ENSG00000100908 | 51016 | EMC9 | protein_coding | Q9Y3B6 | FUNCTION: Part of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein complex (EMC) that enables the energy-independent insertion into endoplasmic reticulum membranes of newly synthesized membrane proteins (PubMed:30415835, PubMed:29809151, PubMed:29242231, PubMed:32459176). Preferentially accommodates proteins with transmembrane domains that are weakly hydrophobic or contain destabilizing features such as charged and aromatic residues (PubMed:30415835, PubMed:29809151, PubMed:29242231). Involved in the cotranslational insertion of multi-pass membrane proteins in which stop-transfer membrane-anchor sequences become ER membrane spanning helices (PubMed:30415835, PubMed:29809151). It is also required for the post-translational insertion of tail-anchored/TA proteins in endoplasmic reticulum membranes (PubMed:29809151, PubMed:29242231). By mediating the proper cotranslational insertion of N-terminal transmembrane domains in an N-exo topology, with translocated N-terminus in the lumen of the ER, controls the topology of multi-pass membrane proteins like the G protein-coupled receptors (PubMed:30415835). By regulating the insertion of various proteins in membranes, it is indirectly involved in many cellular processes (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29242231, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29809151, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30415835, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32459176, ECO:0000305}. | 3D-structure;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Reference proteome | Contributes to membrane insertase activity. Involved in protein insertion into ER membrane by stop-transfer membrane-anchor sequence and tail-anchored membrane protein insertion into ER membrane. Located in cytoplasm. Part of EMC complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:51016; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; EMC complex [GO:0072546]; protein insertion into ER membrane by stop-transfer membrane-anchor sequence [GO:0045050]; tail-anchored membrane protein insertion into ER membrane [GO:0071816] | 34102206_Circular RNA circ-FAM158A promotes retinoblastoma progression by regulating miR-138-5p/SLC7A5 axis. | ENSMUSG00000022217 | Emc9 | 23.836862 | 0.8675007 | -0.205063135 | 0.34960751 | 0.34238437201 | 0.5584561400222702864937218691920861601829528808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.75389590021584185208780581888277083635330200195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 20.170196 | 4.168687 | 23.035737 | 4.516818 | |
| ENSG00000101347 | 25939 | SAMHD1 | protein_coding | Q9Y3Z3 | FUNCTION: Protein that acts both as a host restriction factor involved in defense response to virus and as a regulator of DNA end resection at stalled replication forks (PubMed:19525956, PubMed:21613998, PubMed:21720370, PubMed:23602554, PubMed:23601106, PubMed:22056990, PubMed:24336198, PubMed:26294762, PubMed:26431200, PubMed:28229507, PubMed:28834754, PubMed:29670289). Has deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTPase) activity, which is required to restrict infection by viruses, such as HIV-1: dNTPase activity reduces cellular dNTP levels to levels too low for retroviral reverse transcription to occur, blocking early-stage virus replication in dendritic and other myeloid cells (PubMed:19525956, PubMed:21613998, PubMed:21720370, PubMed:23602554, PubMed:23601106, PubMed:23364794, PubMed:25038827, PubMed:26101257, PubMed:22056990, PubMed:24336198, PubMed:28229507, PubMed:26294762, PubMed:26431200). Likewise, suppresses LINE-1 retrotransposon activity (PubMed:24035396, PubMed:29610582, PubMed:24217394). Not able to restrict infection by HIV-2 virus; because restriction activity is counteracted by HIV-2 viral protein Vpx (PubMed:21613998, PubMed:21720370). In addition to virus restriction, dNTPase activity acts as a regulator of DNA precursor pools by regulating dNTP pools (PubMed:23858451). Phosphorylation at Thr-592 acts as a switch to control dNTPase-dependent and -independent functions: it inhibits dNTPase activity and ability to restrict infection by viruses, while it promotes DNA end resection at stalled replication forks (PubMed:23602554, PubMed:23601106, PubMed:29610582, PubMed:29670289). Functions during S phase at stalled DNA replication forks to promote the resection of gapped or reversed forks: acts by stimulating the exonuclease activity of MRE11, activating the ATR-CHK1 pathway and allowing the forks to restart replication (PubMed:29670289). Its ability to promote degradation of nascent DNA at stalled replication forks is required to prevent induction of type I interferons, thereby preventing chronic inflammation (PubMed:27477283, PubMed:29670289). Ability to promote DNA end resection at stalled replication forks is independent of dNTPase activity (PubMed:29670289). Enhances immunoglobulin hypermutation in B-lymphocytes by promoting transversion mutation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q60710, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19525956, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21613998, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21720370, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22056990, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23364794, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23601106, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23602554, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23858451, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24035396, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24217394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24336198, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25038827, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26101257, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26294762, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26431200, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27477283, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28229507, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28834754, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29610582, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29670289}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome;Allosteric enzyme;Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;Chromosome;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;DNA damage;DNA repair;DNA replication;GTP-binding;Host-virus interaction;Hydrolase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation;Zinc | This gene may play a role in regulation of the innate immune response. The encoded protein is upregulated in response to viral infection and may be involved in mediation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha proinflammatory responses. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. | hsa:25939; | nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; site of double-strand break [GO:0035861]; tetraspanin-enriched microdomain [GO:0097197]; deoxynucleoside triphosphate hydrolase activity [GO:0106375]; dGTP binding [GO:0032567]; dGTPase activity [GO:0008832]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; ribonuclease activity [GO:0004540]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; single-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003697]; triphosphoric monoester hydrolase activity [GO:0016793]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; dATP catabolic process [GO:0046061]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; deoxyribonucleotide catabolic process [GO:0009264]; dGTP catabolic process [GO:0006203]; DNA strand resection involved in replication fork processing [GO:0110025]; double-strand break repair via homologous recombination [GO:0000724]; immune response [GO:0006955]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060339]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289]; regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045088]; somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes [GO:0016446] | 18546154_SAMHD1 mediates TNF-alpha stimulation of lung fibroblasts. 19525956_Study describes mutations in SAMHD1 as the cause of Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome (AGS) at the AGS5 locus and present data to show that SAMHD1 may act as a negative regulator of the cell-intrinsic antiviral response. 20156774_I510T mutation of p63 was detected in both RHS and AEC syndrome patients and mutation of S541 residue can lead to either RHS (S541Y) or AEC syndrome (S541F). 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20358604_Arthropathy with progressive contractures should now be considered part of the spectrum of Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome because of SAMHD1 mutations. 20842748_report on four adult siblings with c.490C>T (p.Arg164X) mutation in SAMHD1, a gene most recently described in Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome, on both alleles in all affected siblings 21102625_A homozygous deletion of the SAMHD1 gene caused atypical Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome, presenting in utero with white matter destruction and associated with multiple mtDNA deletions. 21204240_Autosomal dominant inheritance of a heterozygous mutation in SAMHD1 causing familial chilblain lupus. 21402907_The inflammatory vasculopathies of the brain found in the patients with SAMHD1 mutation indicate its important roles in immunoregulation and cerebral vascular hemeostasis. 21613998_Vpx induces proteasomal degradation of SAMHD1 21633013_conclude that intracerebral large artery disease is a common phenomenon in patients with SAMHD1 mutations 21720370_Vpx relieves the inhibition of lentivirus infection in macrophages by loading SAMHD1 onto the CRL4(DCAF1) E3 ubiquitin ligase, leading to highly efficient proteasome-dependent degradation of the protein 21740548_SAMHD1 functions as a myeloid-cell-specific HIV-1 restriction factor by inhibiting viral DNA synthesis.[Review] 22056990_human SAMHD1 is a potent dGTP-stimulated triphosphohydrolase that converts deoxynucleoside triphosphates to the constituent deoxynucleoside and inorganic triphosphate 22069334_Vpx targets SAMHD1 for degradation in a viral strategy to control cellular deoxynucleotide levels for efficient replication 22174685_we propose that SAMHD1 protects primary CD14+ monocytes from HIV-1 infection 22327569_Vpx prevented the SAMHD1-mediated decrease in dNTP concentration and induced the degradation of human and rhesus macaque SAMHD1 but had no effect on mouse SAMHD1 22461318_Data suggest that SAMHD1 has a role in the nucleus that, if disrupted by mutation, leads to cytosolic accumulation of SAMHD1 and autoimmune disease. 22530776_Polymorphisms of SAMHD1 are unlikely to contribute to the infection and natural control of HIV-1 in European and African-American individuals. 22589553_Vpx degradation of SAMHD1 is sufficiently rapid to enable appropriate progression of reverse transcription in monocyte-derived macrophages 22691373_Cytoplasmic variants of SAMHD1 potently block lentiviral infection and are resistant to Vpx-mediated degradation. 22926205_In this Progress article, we describe how SAMHD1 regulates the pool of intracellular nucleotides to control HIV replication and the innate immune response. 22972397_SAMHD1 imposes an effective restriction to HIV-1 infection in the large pool of noncycling CD4(+) T cells in vivo. 22973040_SAMHD1 is targeted by HIV-2 Vpx for ubiquitination and degradation in the nucleus. 22978176_anti-HIV activity of SAMHD1 22999946_Studies indicate that restriction factors APOBEC3G, TRIM5, Tetherin and SAMHD1 exhibit direct antiviral activity. 23076149_there are several Vpx residues required for SAMHD1 degradation 23092122_Here, authors identified SAMHD1 as the restriction factor preventing efficient HIV-1 viral DNA synthesis in non-cycling resting CD4+ T-cells. 23092512_Here, authors identified two naturally occurring splice variants lacking exons 8-9 and 14, respectively. 23158101_results showed that SAMHD1 blocks infection of HIV-2, feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV), bovine immunodeficiency virus (BIV), Equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV), N-tropic murine leukemia virus (N-MLV), and B-tropic murine leukemia virus (B-MLV) 23231760_SAMHD1-mediated reduction of the intracellular dNTP pool in DCs is a common mechanism of HIV-1 restriction in myeloid cells. Endogenous expression of SAMHD1 in primary DCs or CD4+ T-lymphocytes is not upregulated by type I IFNs. 23269793_SAMHD1, by controlling the sensitivity of monocyte-derived dendritic cells to HIV-1 infection during intercellular contacts, impacts their ability to sense the virus and to trigger an innate immune response. 23364794_The nuclease activity of SAMHD1 could represent an additional mechanism contributing to HIV-1 restriction and suppression of the autoimmune response through direct cleavage of viral and endogenous nucleic acids. 23371319_Mutations associated with Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome exhibit both impaired nucleic acid-binding and complex formation implicating interaction with nucleic acids as an integral aspect of SAMHD1 function. 23426363_Promoter methylation regulates SAMHD1 gene expression in human CD4+ T cells 23426366_SAMHD1 tetramers are the biologically active form of this dNTPase and provide new insights into the functional organization of SAMHD1. 23497255_The results suggest that SAMHD1 has broad anti-retroviral activity against which most viruses have not found an escape. 23497283_Effective immune control of viral replication in HIV-2-infected individuals is not associated with increased Vpx-mediated degradation of SAMHD1. 23526823_SAMHD1 overexpression induced by IL-12/IL-18 was not dependent on IFN-gamma. 23601106_SAMHD1 phosphorylated on residue T592 is unable to block retroviral infection. 23602554_The phosphorylation of SAMHD1 at Thr592 by cyclin A2/CDK1 is a key regulatory mechanism of its antiviral activity. 23677995_direct down-modulation of Vpx catalytic activity, mediated by the same binding event that leads to SAMHD1 recruitment to the E3 ubiquitin ligase for proteasome-dependent degradation 23744077_Data indicate that SAMHD1 controls HIV-1 sensitivity to nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs). 23825958_SAMHD1 is a potential innate anti-viral player that suppresses the replication of a wide range of DNA viruses, as well as retroviruses, which infect non-dividing myeloid cells. 23858451_Synthesis by the reductase peaks during S-phase, and catabolism by SAMHD1 is maximal during G1 phase when large dNTP pools would prevent cells from preparing for a new round of DNA replication 23874202_Data suggest that, in an evolutionary model of virus-host interactions, binding between Vpx/Vpr and SAMHD1 (and subsequent degradation of SAMHD1) exhibits dynamic requirements that have toggled back and forth. 23874389_Multiple regions in SAMHD1 are critical for Vpx-mediated nuclear degradation. 23880768_SAMHD1 has the ability to hydrolyze base-modified nucleotides, indicating that the active site of SAMHD1 is not restrictive to such modifications 23884314_SAMHD1 mRNA levels aresignificantly downregulated in leukocytes from Sezary syndrome patients. 23966382_These results indicate that SAMHD1 phosphorylation may be a negative regulator of SAMHD1 restriction activity. 23986575_These findings support deoxynucleoside triphosphate pool depletion as the primary mechanism of SAMHD1 restriction of HIV-1 and argue against a nucleolytic mechanism, which would not be reversible. 24035396_SAMHD1 inhibits ORF2p-mediated LINE-1 reverse transcription in isolated LINE-1 ribonucleoproteins by reducing ORF2p level. Thus, SAMHD1 may be a cellular regulator of LINE-1 activity that is conserved in mammals. 24067963_SAMHD1 inhibits replication of herpes simplex virus 1 in nondividing macrophages. 24139400_This study provides a mechanistic explanation for abortive HTLV-1 infection of monocytes and reports a link between SAMHD1 restriction, HTLV-1 reverse transcription intermediate sensing by STING, and initiation of IRF3-Bax driven apoptosis. 24141705_Binding of dGTP to four allosteric sites promotes tetramerization and induces a conformational change in the substrate-binding pocket to yield the catalytically active enzyme. 24173216_The ability of SIV Vpx to restrict SAMHD1 among different primate species is a manifestation of the SAMHD1 evolutionary pattern among those species 24217394_structural and functional analysis of tetrameric SAMHD1 deoxynucleoside triphosphate triphosphohydrolase 24219908_These results suggested that SAMHD1 oligomerization is not required for the ability of the protein to block HIV-1 infection. 24317272_analysis of the different activities of SAMHD1 splice variants in regulating drug sensitivity implied that the exon4 insertion might act as an indicator of the occurrence of liver cancer. 24335234_SAMHD1 may have a function in DNA repair and the presence of SAMHD1 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia promotes leukemia development. 24336198_the crystal structure of a ternary complex of Vpx with the human E3 ligase substrate adaptor DCAF1 and the carboxy-terminal region of human SAMHD1 24352659_Here, we report that SAMHD1 regulation of the dNTP concentrations influences HIV-1 template switching efficiency, particularly in macrophages. 24445253_SAMHD1 is required for genome integrity by maintaining balanced dNTP pools. dNTP imbalances due to SAMHD1 deficiency cause DNA damage, leading to intrinsic activation of IFN signalling. 24554663_CD4(+) memory T cells with stem cell-like properties are targets for HIV infection, become productively or latently infected at low levels, and SAMHD1 expression promotes abortive infection of this important memory cell subset. 24574390_These results demonstrate that cross talk with lymphocytes downregulates SAMHD1 expression in dendritic cells, triggering HIV-1 replication and an antiviral immune response. 24599229_These results indicated that SAMHD1 moderately restricts even a macrophage-tropic HIV-1 strain in monocyte-derived macrophages. 24623419_Authors identified and validated two additional host proteins interacting with human SAMHD1, namely, cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) and S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (SKP2). 24712655_This work extends published observations on SAMHD1 nuclear localization to a natural cell type for HIV-1 infection and identifies KPNA2/KPNB1 as cellular proteins important for SAMHD1 nuclear import. 24753578_SAMHD1 can remain active long after dNTP pools have been reduced to a level that would lead to inactivation. This property would be important in resting CD4(+) T cells, where dNTP pools are reduced to nanomolar levels to restrict infection by HIV-1. 24828500_Allosteric regulation by dATP and dTTP works similarly in human and mouse SAMHD1. 25010268_All studied SAMHD1 variants block HIV-1 and HIV-2 infection. 25015816_these findings identify a direct relationship between control of the cell cycle by CDK6 and SAMHD1 activity, which is important for replication of lentiviruses, as well as other viruses whose replication may be regulated by intracellular dNTP availability. 25019997_findings suggested that IFN-alpha-inducible SAMHD1 inhibited HBV replication in liver cells 25038827_the RNase activity of SAMHD1 is responsible for preventing HIV-1 infection by directly degrading the HIV-1 RNA. 25063780_SAMHD1 plays a role in controlling virus replication in HIV+ individuals. 25201733_miR-181 regulates the level of post-transcriptional SAMHD1 expression negatively by directly binding to the 3'UTR in SAMHD1. 25267621_These data demonstrate how SAMHD1 is activated by binding of GTP or dGTP at allosteric site 1 and a dNTP of any type at allosteric site 2. 25288794_Data indicate that sterile alpha motif and histidine-aspartate domain-containing protein 1 (SAMHD1) forms a tetramer with GTP and dNTPs and exhibits enzymatic activity. 25392215_Authors report for the first time that macrophages are one of the main HIV-1 target cells in the endometrium and that infection of macrophages from both the endometrium and the decidua is restricted by SAMHD1 25423367_eEF1A1 may mediate SAMHD1 turnover by targeting it to the proteosome for degradation through association with Cullin4A and Rbx1. 25449277_SAMHD1 promoter is highly methylated in lung adenocarcinoma, which may inhibit its gene expression; over-expression of SAMHD1 reduces dNTP level and inhibits the proliferation of lung tumor cells 25532805_Therefore, cyclin L2-mediated control of SAMHD1 levels in macrophages supports HIV-1 replication. 25646359_study establishes the first cross-sectional protein expression profile of SAMHD1 in human tissues and provides insight into its cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and unresponsiveness to multiple proinflammatory cytokines 25715102_CD4 T-cell subsets known to be more susceptible to HIV-1 infection, for example, T-helper 17 and follicular helper T cells, display lower levels of SAMHD1. 25760601_the level of dNTP pools is elegantly regulated by the self-sensing ability of SAMHD1 through a novel activation mechanism. 25825449_HIV-1 replication does not trigger immune activation in DCs, but that HIV-1 escapes immune surveillance by actively suppressing DC maturation independent of SAMHD1. 25890101_increased SAMHD1 in human astrocytes is in part responsible for the HIV restriction, silencing of which relieves this restriction 25926647_These results demonstrate that the antiviral activity of SAMHD1 impacts HIV-1 antigen presentation by dendritic cells, highlighting the link that exists between restriction factors and adaptive immune responses. 25936766_Data indicate that proline residue P109 within the C-terminal poly-proline motif (PPM) of Vpx protein plays a unique role in the regulation of SAM domain and HD domain 1 protein SAMHD1 degradation. 25996507_Data suggest that critical role of vpx (Simian immunodeficiency virus vpx protein) in vivo/in vitro is to promote degradation of SAMHD1 in memory CD4+ T-lymphocytes, thereby generating high levels of plasma viremia and induction of immunodeficiency. 26032178_The results presented herein suggest that the RNase activity of SAMHD1 is sufficient to control the replication of retroviruses, but not that of non-retro RNA viruses. 26294762_The phosphomimetic mutation results in a significant decrease in the population of active SAMHD1 tetramers, and hence the dNTPase activity is substantially decreased. 26342080_results prove the importance of SAMHD1 in the regulation of all dNTP pools and suggest that dGK inside mitochondria has the function of recycling the deoxyguanosine derived from endogenous dGTP degraded by SAMHD1 in the nucleus 26397446_Interferonstimulated gene factor 3 complex, which consists of STAT1, STAT2 and IRF9, is required for the induction of SAMHD1 expression by IFN-alpha in SMMC-7721 cells. 26416562_This review summarizes the latest advances in understanding the importance of dNTP metabolism in cancer development and the novel function of SAMHD1 in regulating this process. 26431200_SAMHD1 phosphorylation also ablates restriction and tetramer formation but without affecting triphosphohydrolase steady-state kinetics 26504826_Studied whether one or more SAMHD1 gene mutations are associated with cerebrovascular disease in the general population using a Chinese stroke cohort. 26606981_SAMHD1 may facilitate some aspects of THP-1 cell differentiation. 26655245_These results argue against a requirement for additional myeloid-specific host factors for SAMHD1 function but further support the notion that SAMHD1 possesses an additional dNTP-independent function contributing to lentiviral restriction. 26733158_The SAMHD1 restricts HIV-1 infection in non-cycling cells by limiting the pool of deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, thereby interfering with HIV-1 reverse transcription. 26779819_Therefore, our findings revealed that factors in addition to Vpx-SAMHD1 binding influence the efficiency of Vpx-mediated SAMHD1 degradation. 26923586_cytokines play a major role in the reservoir establishment not only by driving homeostatic proliferation but also by increasing susceptibility of CD4+ lymphocytes to HIV-1 infection through SAMHD1 inactivation. 27071091_These observations suggest that heterozygous cancer-associated SAMHD1 mutations increase mutation rates in cancer cells. 27179347_These results indicate that SAMHD1 inhibits HBV replication at the reverse transcription step, most likely through the depletion of cellular dNTPs. 27183329_Our results suggest that SAMHD1, through its dNTPase activity, affects cell proliferation, cell cycle distribution and apoptosis, and emphasize a key role of SAMHD1 in the interplay between cell cycle regulation and HIV-1 infection. 27219130_MiR-181a is an important mediator for interferons-induced SAMHD1 expression in astrocytes and microglia, but not for inhibition of HIV-1 infection induced by IFN-alpha. 27229711_These results suggest that SAMHD1 is a relevant restriction factor for HBV and restricts reverse transcription through its dNTPase activity 27387229_Our findings will facilitate more advanced studies into the role of the SAMHD1 RNase function in the cellular pathogenesis implicated in nucleic acid-triggered inflammatory responses and the anti-retroviral function of SAMHD1. 27411355_Upregulation of endogenous SAMHD1 expression is attributed to the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of IRF3. 27511536_Studies of the phosphomimetic and tetramerization-defective mutants of SAMHD1 reveal poor correlation between tetramerization propensity and dNTPase activity observed in vitro and the ability of the proteins to deplete cellular dNTPs and to restrict retroviral restriction. These results suggest that enzymatic activity of SAMHD1 may be subject to additional cellular regulatory mechanisms that have not yet been elucidated. 27566548_Comparison of the wild-type SAMHD1 and the T592D mutant reveals that the phosphomimetic mutation affects the rates of tetramer dissociation, but has no effect on the equilibrium of allosteric activation by deoxynucleotides. 27643693_This study reviewed that Neurologic Phenotypes Associated with Mutations in SAMHD1 in patients with Aicardi-Goutieres Syndrome. 27775344_data suggest an antagonistic regulatory mechanism in which the mutually exclusive oligomeric state requirements for ssNA binding and dNTP hydrolase activity modulate these two functions of SAMHD1 within the cell 27815502_the mechanisms by which SAMHD1 is phosphorylated and suggest the contribution of cyclin binding to SAMHD1 expression and stability in dividing cells. 27889686_miR-181 is an important regulator of SAMHD1 protein expression in neoplastic CD4+ T-cells, likely through a mechanism of translational inhibition 27922067_Immune activation during HIV-1 infection influences SAMHD1 expression and degradation. 27929746_SAMHD1 acts as an inhibitor in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cell growth. 28046007_stereoselective 2' substitutions that reveal nucleotide substrate specificity for SAMHD1, and a novel inhibitory mechanism for the dNTPase activity of SAMHD1, are reported. 28122869_Cell cycle-associated changes of proteins are induced by activation of the Raf/MEK/ERK kinase cascade, culminating in upregulation of CDK1 with subsequent SAMHD1 T592 phosphorylation and deactivation of its antiviral activity. 28220857_SAMHD1 activity can significantly enhance or decrease the anti-HIV-1 efficacy of nucleotide analogue reverse transcription inhibitors presumably as a result of modulating dNTP pools that compete for recruitment by viral polymerases. 28228523_These results indicate that Vpx, in addition to SAMHD1, overcomes a previously unappreciated restriction for lentiviruses at the level of reverse transcription (RT)that acts independently of dNTP concentrations and is specific to resting CD4 T cells. 28229507_our work genetically separated the ability of SAMHD1 to negatively regulate the type I IFN response from its ability to restrict HIV-1. 28321930_Allosteric regulation of SAMHD1 has been uncovered through molecular dynamics simulations. 28359840_SAMHD1 is active in HIV-1 permissive cells, does not modify susceptibility to HIV-1 infection but strongly affects sensitivity to nucleoside inhibitors. 28389709_The activation of interferon-induced genes is controlled by the JAK-STAT system; therefore, JAK inhibitors were successfully used in several cases to treat type 1 interferonopathies. Experience with this treatment modality is continuously growing. 28398823_Study identify three critical cysteine residues of SAMHD1 (Cys341, Cys350, and Cys522) that create a ''redox switch'' through the formation of intrachain disulfide bonds to reversibly inhibit SAMHD1 tetramerization and dNTPase activity. SAMHD1 is oxidized in cells in response to proliferative signals and colocalizes with sites of protein oxidation outside of the nucleus. 28436707_SAMHD1 may constitute a promising target to improve a wide range of therapies for both hematological and non-haematological malignancies. 28502830_Studies indicate the ambiguous properties of sterile alpha motif and histidine/aspartic acid domain-containing protein 1 (SAMHD1) as both an inhibitor of uncontrolled proliferation and a resistance factor limiting the efficacy of anticancer treatments. 28834754_Findings define a dNTPase-independent function for SAMHD1 in HR-mediated DSB repair by facilitating CtIP accrual to promote DNA end resection, providing insight into how SAMHD1 promotes genome integrity. 28871089_results demonstrate that the interaction of CD81 with SAMHD1 controls the metabolic rate of HIV-1 replication by tuning the availability of building blocks for reverse transcription, namely dNTPs 28931685_expression of p21 potentially can contribute to inhibition of HIV-1 replication in monocyte-derived dendritic cells through multiple mechanisms. p21 decreased size of the intracellular dNTP pool; p21 prevented SAMHD1 phosphorylation and promoted SAMHD1 dNTPase-independent antiviral activity 29084722_Low SAMHD1 expression is associated with HIV-1 infection. 29274141_Study demonstrates a consistent resistance profile to PARPi and a unique cross-resistance profile to non-PARPi drugs in different PARPi-resistant U251 glioblastoma cells and reveals 53BP1 loss and SAMHD1 overexpression as the primary mechanisms responsible for their resistance to PARPi and Ara-C, respectively. 29321329_results indicate that the RXL motif is critical for tetramer formation, dNTPase activity, and HIV-1 restriction. These findings help us understand SAMHD1 interactions with other host proteins and the mechanisms regulating SAMHD1 structure and functions in cells. 29352181_study considerably extends the picture of pathways involved in molecular pathogenesis of T-PLL and identifies the tumor suppressor gene SAMHD1 with ~20% of T-PLL affected by destructive lesions likely as major player in T-PLL pathogenesis. 29515139_The results show that the susceptibility of Monocyte-derived macrophages to HIV-1 infection can be affected by stimuli that alter the phosphorylation state of SAMHD1, one of which is the DNA damage response. 29610295_Compared with control cells, infection of SAMHD1-silenced human monocytic cells or primary macrophages with Sendai virus or HIV-1, or treatment with inflammatory stimuli, induces significantly higher levels of NF-kappaB activation and IFN-I induction. SAMHD1 down-regulates innate immune responses to viral infections and inflammatory stimuli. 29614270_SAMHD1 is not localized in dot-like structures under DNA double-strand break induction in HeLa cells. 29670289_SAMHD1 is thus an important player in the replication stress response, which prevents chronic inflammation by limiting the release of single-stranded DNA from stalled replication forks 29698322_The ability of SAMHD1 to act as a restriction factor for SIV/HIV in the brain is likely bypassed in proliferating brain macrophages through the phosphorylation-mediated inactivation, not Vpx-mediated degradation of SAMHD1. 29764952_SAMHD1 activation is the predominant mechanism of HIV-1 restriction induced by type I, type II, and type III IFN signaling in macrophages. 29782647_cyclin E2 participates in regulating viral replication through the CDK2/SAMHD1 phosphorylation pathway in an HBV infection system. 29793958_findings indicate a novel role for SAMHD1 in regulating HIV-1 latency, which enhances our understanding of the mechanisms regulating proviral gene expression in CD4(+) T cells. 29884836_Data show that SAM Domain and HD Domain-Containing Protein 1 (SAMHD1) is specifically targeted by protein phosphatase 2 regulatory subunit Balpha protein (PP2A-B55alpha) holoenzymes during mitotic exit. 29911928_SAMHD1 regulates acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation via modulation of the PI3K-Akt-p27 signaling axis, and that SAMHD1 may affect tumorigenicity by downregulating inflammation. 29963825_Multiple domains of SAMHD1(e.g., N-terminus, nuclear localization signal, linker, HD domain, and C-terminus)are essential for Vpx-induced degradation.[review] 30039733_SAMHD1 is active during the entire cell cycle and performs an important regulatory role during S-phase by contributing with ribonucleotide reductase to maintain dNTP pool balance for proper DNA replication. 30044979_Results reveal that enzymatic activation of SAMHD1 via nucleotide-dependent tetramerization is not sufficient for the establishment of the antiviral state and that retroviral restriction depends on the ability of the protein to undergo redox transformations. 30099227_the state of type I IFN induction and response to, in SAMHD1 knockout (KO) human monocytic cells, was examined. 30104243_the interaction of ODNPs25 in HD or phosphorylation of Thr592 by TCR stimulation interferes with nuclease activity of SAMHD1, thereby stabilizing 3' untranslated region of Foxp3 and Helios mRNAs in long-term culture. 30181218_findings suggest that accessory protein-mediated proteosomal degradation of SAMHD1 did not exist among the ancestral non-primate lentiviruses and was uniquely gained by some primate lentiviruses after their transmission to primate species. 30299483_The authors conclude that SAMHD1 is an essential modulator of infectivity in a sex-dependent manner in macrophages, constituting a novel component of sex differences in innate immune control of HIV-1. 30316304_This finding identifies the Endogenous reverse transcription step as an additional step of HIV-1 replication cycle that SAMHD1 restricts in nondividing myeloid target cells. 30341277_we have shown that low-level SAMHD1 expression in AML blasts at diagnosis identifies a sizeable patient subset with favorable EFS and OS upon treatment with HDAC-containing consolidation regimens. 30474474_Exogenous SAMHD1 expression suppresses in vitro cell transformation independently of its dNTPase activity, and that endogenous SAMHD1 affects AML tumorigenicity and disease progression in vivo. 30739781_SAMHD1 is a nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein. SAMHD1 in the cytoplasm is more effective in LINE-1 suppression. 30767852_Highlight SAMHD1 as a potential barrier to PERV transmission from pig transplants to human recipients during xenotransplantation. 30918010_These results highlight a dual role for SAMHD1, both as a host-dependency factor and as a restriction factor, depending on the stage in the hepatitis B virus life cycle. 30959264_SAMHD1 restriction of HIV-1 was found to be defective in non-dividing cells that did not express MxB. 30959732_these results suggest that IFITs are involved in the restriction of replication of CHIKV and ZIKV and provide, as yet unreported, evidence for a proviral role of SAMHD1 in arbovirus infection of human skin cells. 31003777_lentiviral accessory protein Vpx exploits DCAF1 to counteract Vpx-mediated SAMHD1 degradation 31015445_Study identified that PIM1 and PIM3 phosphorylate HIV-2 Vpx at Ser13 and stabilize the interaction of Vpx with SAMHD1 thereby promoting ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of SAMHD1 and revealed a regulatory mechanism of virus-host interaction that governs viral escape from an intrinsic cellular immune defense via the post-translational modification of viral protein. 31291579_SAMHD1 Modulates Early Steps during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection by Limiting NF-kappaB Activation. 31291580_Conserved Herpesvirus Protein Kinases Target SAMHD1 to Facilitate Virus Replication. 31375673_Study shows that decitabine triphosphate is both an activator and a substrate of SAMHD1. SAMHD1 ablation increases the antileukemic activity of decitabine in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell lines, primary leukemic blasts, and xenograft models. AML cells acquire resistance to decitabine partly by SAMHD1 up-regulation. 31391281_specific interaction between SAMHD1 and HPV16 that regulates host cell proliferation and viral replication 31462561_SAMHD1 function during modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) infection of human DCs was studied with recombinant MVA-vpx expressing Vpx. Infection of human DCs with MVA-vpx decreased SAMHD1 protein amounts, enabling MVA DNA replication and expression of late viral genes. 31492497_The SAMHD1 mutant K288T was defective for dNTPase activity but showed potent activity against LINE-1 retrotransposition. 31548682_HCMV interferes with SAMHD1 steady-state expression and actively induces SAMHD1 phosphorylation using the viral kinase pUL97 and by hijacking cellular kinases. These actions convert SAMHD1 to its inactive phosphorylated form. This mechanism of SAMHD1 inactivation by phosphorylation might also be used by other viruses to overcome intrinsic immunity. 31797533_TRIM21-mediated proteasomal degradation of SAMHD1 regulates its antiviral activity. 31914403_The dNTPase activity of SAMHD1 is important for its suppression of innate immune responses in differentiated monocytic cells. 31914608_indicated a mutator phenotype suggesting that SAMHD1 is a caretaker gene whose deficiency is per se mutagenic, promoting genome instability in non-transformed cells 32062129_Generation of three induced pluripotent cell lines (iPSCs) from an Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome (AGS) patient harboring a deletion in the genomic locus of the sterile alpha motif and HD domain containing protein 1 (SAMHD1). 32075911_The C-terminal domain of feline and bovine SAMHD1 proteins has a crucial role in lentiviral restriction. 32209460_TLR4-Mediated Pathway Triggers Interferon-Independent G0 Arrest and Antiviral SAMHD1 Activity in Macrophages. 32402273_SAMHD1 Limits the Efficacy of Forodesine in Leukemia by Protecting Cells against the Cytotoxicity of dGTP. 32468062_SAMHD1 expression is associated with low immune activation but not correlated with HIV1 DNA levels in CD4+ T cells of patients with HIV1. 32511795_SAMHD1-mediated dNTP degradation is required for efficient DNA repair during antibody class switch recombination. 32576829_Crystal structures of SAMHD1 inhibitor complexes reveal the mechanism of water-mediated dNTP hydrolysis. 32581304_SAMHD1 is a key regulator of the lineage-specific response of acute lymphoblastic leukaemias to nelarabine. 32656092_The SAMHD1 rs6029941 (A/G) Polymorphism Seems to Influence the HTLV-1 Proviral Load and IFN-Alpha Levels. 32850489_Degradation of SAMHD1 Restriction Factor Through Cullin-Ring E3 Ligase Complexes During Human Cytomegalovirus Infection. 32986788_SAMHD1 phosphorylation and cytoplasmic relocalization after human cytomegalovirus infection limits its antiviral activity. 33135886_Dimeric Hold States of Anti-HIV Protein SAMHD1 are Redox Tunable. 33528031_Expression of the novel tumour suppressor sterile alpha motif and HD domain-containing protein 1 is an independent adverse prognostic factor in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. 33563288_Vpx enhances innate immune responses independently of SAMHD1 during HIV-1 infection. 33591315_SAMHD1 restrains aberrant nucleotide insertions at repair junctions generated by DNA end joining. 33857133_Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome-associated gene SAMHD1 preserves genome integrity by preventing R-loop formation at transcription-replication conflict regions. 33883225_SAMHD1 Inhibits Multiple Enteroviruses by Interfering with the Interaction between VP1 and VP2 Proteins. 33979727_SAMHD1 mutations in mantle cell lymphoma are recurrent and confer in vitro resistance to nucleoside analogues. 33988981_Probing the Catalytic Mechanism and Inhibition of SAMHD1 Using the Differential Properties of Rp- and Sp-dNTPalphaS Diastereomers. 34180901_Analysis of SAMHD1 Restriction by Flow Cytometry in Human Myeloid U937 Cells. 34321470_SUMOylation of SAMHD1 at Lysine 595 is required for HIV-1 restriction in non-cycling cells. 34480199_SAMHD1 in cancer: curse or cure | ENSMUSG00000027639 | Samhd1 | 670.521322 | 0.8348870 | -0.260347183 | 0.06123930 | 18.08430400337 | 0.0000211336410090568583381928635667179605661658570170402526855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00026022655848123886013559258323368794663110747933387756347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 604.306906 | 27.865639 | 727.149570 | 32.916492 | |
| ENSG00000101972 | 10735 | STAG2 | protein_coding | Q8N3U4 | FUNCTION: Component of cohesin complex, a complex required for the cohesion of sister chromatids after DNA replication. The cohesin complex apparently forms a large proteinaceous ring within which sister chromatids can be trapped. At anaphase, the complex is cleaved and dissociates from chromatin, allowing sister chromatids to segregate. The cohesin complex may also play a role in spindle pole assembly during mitosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12034751}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Centromere;Chromosome;Chromosome partition;Disease variant;Holoprosencephaly;Meiosis;Mitosis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of the cohesin complex, which regulates the separation of sister chromatids during cell division. Targeted inactivation of this gene results in chromatid cohesion defects and aneuploidy, suggesting that genetic disruption of cohesin is a cause of aneuploidy in human cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]. | hsa:10735; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; chromosome [GO:0005694]; chromosome, centromeric region [GO:0000775]; cohesin complex [GO:0008278]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitotic spindle pole [GO:0097431]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; cell division [GO:0051301]; establishment of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion [GO:0034087]; meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051321]; mitotic spindle assembly [GO:0090307]; sister chromatid cohesion [GO:0007062] | 14660624_evidence suggests STAG2 functions as a transcriptional co-activator by a mechanism involving protein-protein interactions with transcription factors 15737063_Phosphorylation of SA2 is essential for cohesin dissociation during prophase and prometaphase, but is not required for cohesin cleavage by separase. 15737064_Cohesion between sister chromatids is essential for their bi-orientation on mitotic spindles is mediated by a multisubunit complex called cohesin. 19822671_cohesin(SA1) and cohesin(SA2) are differentially required for telomere and centromere cohesion, respectively. 21444719_results demonstrate specific sites on C terminus of CTCF are essential for cohesin binding and insulator function; only direct interaction between CTCF and cohesin involves contact with SA2, which is external to the cohesin ring 21852505_study has shown that diverse human cancers harbor mutations in the X-linked chromatid cohesion gene STAG2 and that these mutations cause aneuploidy 22132872_Somatic mutation of STAG2, an aneuploidy-related gene, is rare in acute leukemias. 22668012_Low STAG2 expression and not mutation is associated with neoplasms. 22715410_Nuclear import and export signals of human cohesins SA1/STAG1 and SA2/STAG2 expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. 23874961_Rad21 binds to SA proteins through two SA-binding motifs on Rad21. 24088605_Inactivating point mutations in the STAG2 gene are not common in neuroblastoma tumors 24121789_STAG2 is one of the most commonly mutated genes in bladder cancer. 24121791_STAG2 is a new urothelial bladder cancer tumor suppressor acting through mechanisms that are different from its role in preventing aneuploidy. 24270882_Loss of STAG2 function is associated with non-invasive bladder cancer. 24324008_cohesin-SA1 and cohesin-SA2 participate in the DNA damage response 24335498_Mutations in STAG2 is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 24356817_These data suggest that PARP is a potential target for tumors harboring inactivating mutations in STAG2, and strongly recommend that STAG2 status be determined and correlated with therapeutic response to PARP inhibitors 24733578_our study identifies the duplication of XIAP and STAG2 as the minimal duplicated region leading to the ID, facial morphological anomalies, and speech delay, specific to the patients with Xq25 duplication. 24822266_Aneuploidy in human salivary gland carcinomas is not driven by loss of expression of STAG2. 25006131_Cross-sectional deep-sequencing analysis for clonal hierarchy demonstrated STAG2, SMC3, and RAD21 mutations to be ancestral in 18%, 18%, and 47% of cases, respectively, and each expanded to clonal dominance concordant with disease transformation 25010205_In an independent EFT tissue microarray cohort, we show that STAG2 loss as detected by immunohistochemistry may be associated with more advanced disease (p = 0.15) and a modest decrease in overall survival (p = 0.10). 25074805_STAG2 promotes the correction of kMT attachment errors to ensure faithful chromosome segregation during mitosis. 25186949_Loss of STAG2 expression occurs in 15% of tumors and is associated with metastatic disease, suggesting a potential genetic vulnerability in Ewing sarcoma 25223734_Genomic landscape of Ewing sarcoma defines an aggressive subtype with co-association of STAG2 and TP53 mutations 25450604_Microduplication of chromosome Xq25 encompassing STAG2 gene in a boy with intellectual disability 25677961_We suggest that increased STAG2 gene copy number and dysregulation of its downstream target genes may be responsible for the specific clinical findings of this syndrome. 25867412_Data show a significantly higher stromal antigen 2 (STAG2) mRNA and protein levels in normal bladder cells than bladder cancer cells. 25979289_Characterization of C-terminal nuclear localization signal of the human SA2 stromalin 26838030_results indicated that the complete loss of STAG2 expression was predictive for better recurrence-free survival and cancer-specific survival, suggesting its potential value as a prognostic biomarker in bladder cancer 27207471_TAG2 is the most commonly mutated subunit, and in a recent analysis was identified as one of only 12 genes that are significantly mutated in four or more cancer types. 27341316_There is LOH at STAG1 and STAG2 loci in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), but OSCC and NM showed similar transcriptional levels of STAG1, STAG2, and PDS5B. 27500726_Loss of STAG2 or STAG3, which encode subunits of the cohesin complex, in melanoma cells results in resistance to BRAF inhibitors (BRAFi). Loss-of-function mutations in STAG2, as well as decreased expression of STAG2 or STAG3 proteins were found in several tumor samples from patients with acquired resistance to BRAFi and in BRAFi-resistant melanoma cell lines. 28296084_the clinical features of these three cases are remarkably similar to those observed in other well-established cohesinopathies. Herein, we suggest that STAG2 is a dosage-sensitive gene and that heterozygous loss-of-function variants lead to a cohesinopathy. 28430577_Data indicate that cohesin subunit SA-1 (STAG1) is a promising therapeutic target in cancers with inactivating alterations of cohesin subunit SA-2 (STAG2). 28627627_these data suggest that STAG2 acts as a tumor suppressor gene in bladder cancer and may be a potential therapeutic target in bladder cancer 28691904_Here the authors demonstrate that the most frequently mutated subunit of the cohesin complex, STAG2, displays a strong synthetic lethal interaction with its paralog STAG1. Mechanistically, STAG1 loss abrogates sister chromatid cohesion in STAG2 mutated but not in wild-type cells leading to mitotic catastrophe, defective cell division and apoptosis. 28819029_Extending the lifespan of normal human cells due to inactivation of STAG2 could promote tumorigenesis by extending the period during which tumor-driving mutations occur. 28967037_STAG2 loss of Expression is Associated with Cancer Progression in Upper Urinary Tract Carcinoma. 29501732_STAG2 is the most frequently mutated cohesin subunit and was recently identified as a gene that is commonly altered in bladder cancer. The significance of these mutations remains controversial. Some studies associate loss of STAG2 expression with low stage and low grade bladder tumors, as well as with improved clinical outcomes. [review] 29649003_We uncovered the cohesion subunit SA1 as a putative synthetic-essential target in cancers carrying inactivating mutations of its paralog, SA2. In SA2-deficient Ewing sarcoma and bladder cancer, further depletion of SA1 profoundly and specifically suppressed cancer cell proliferation, survival, and tumorigenic potential. 29662124_STAG2 deficiency induces interferon responses via cGAS-STING pathway and restricts virus infection. 29954776_we report a STAG2 biomarker validation study using two independent cohorts of clinically annotated papillary papillary papillary non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer(NMIBC) tumors from the United States and Europe...STAG2 IHC is a simple, binary, new assay for risk stratification in papillary papillary non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. 30004110_MDS associated with myeloproliferative features had more EZH2, ASXL1 and STAG2 mutations 30602061_Finding that patients with higher mutational burden are more likely to have STAG2 or TP53 alterations, both of which are negative prognostic factors in Ewing sarcoma (ES), supports the hypothesis that more aggressive subtypes of localized ES are marked by genomic instability. 30975996_Study identifies a critical role for STAG2 in replication fork procession and elucidate a potential therapeutic strategy for cohesin-mutant cancers. 31334757_Holoprosencephaly was associated with variants in the two X-linked cohesion complex genes, STAG2 and SMC1A. 31421907_Study provides a comprehensive review of the function of STAG1/2 in human physiology and disease and an integrative analysis of available omics data on STAG alterations in a wide array of cancers, comprising 53 691 patients and 1067 cell lines. 31495782_Cohesin Members Stag1 and Stag2 Display Distinct Roles in Chromatin Accessibility and Topological Control of HSC Self-Renewal and Differentiation. 31897485_BET inhibition prevents aberrant RUNX1 and ERG transcription in STAG2 mutant leukaemia cells. 32294612_Specialized functions of cohesins STAG1 and STAG2 in 3D genome architecture. 32467316_STAG1 vulnerabilities for exploiting cohesin synthetic lethality in STAG2-deficient cancers. 32883299_Chronic loss of STAG2 leads to altered chromatin structure contributing to de-regulated transcription in AML. 33930311_STAG2 mutations alter CTCF-anchored loop extrusion, reduce cis-regulatory interactions and EWSR1-FLI1 activity in Ewing sarcoma. 34129824_STAG2 loss rewires oncogenic and developmental programs to promote metastasis in Ewing sarcoma. 34244384_Mapping the cellular origin and early evolution of leukemia in Down syndrome. 34462321_Paralogous synthetic lethality underlies genetic dependencies of the cancer-mutated gene STAG2. 34529785_ASXL1 and STAG2 are common mutations in GATA2 deficiency patients with bone marrow disease and myelodysplastic syndrome. 34648034_STAG2 loss-of-function affects short-range genomic contacts and modulates the basal-luminal transcriptional program of bladder cancer cells. 35203280_Modeling Down Syndrome Myeloid Leukemia by Sequential Introduction of GATA1 and STAG2 Mutations in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells with Trisomy 21. | ENSMUSG00000025862 | Stag2 | 860.178752 | 1.2407265 | 0.311185168 | 0.06240859 | 24.85129463099 | 0.0000006192744126773895883014838491253950536474803811870515346527099609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00001065487144468797668498717678975395983798080123960971832275390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 906.555090 | 34.558121 | 734.402380 | 28.322818 | |
| ENSG00000102125 | 6901 | TAFAZZIN | protein_coding | Q16635 | FUNCTION: Acyltransferase required to remodel newly synthesized phospholipid cardiolipin (1',3'-bis-[1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho]-glycerol or CL), a key component of the mitochondrial inner membrane, with tissue specific acyl chains necessary for adequate mitochondrial function (PubMed:12930833, PubMed:19700766, PubMed:19164547, PubMed:26908608, PubMed:33096711). Its role in cellular physiology is to improve mitochondrial performance (PubMed:32234310). CL is critical for the coassembly of lipids and proteins in mitochondrial membranes, for instance, remodeling of the acyl groups of CL in the mitochondrial inner membrane affects the assembly and stability of respiratory chain complex IV and its supercomplex forms (By similarity). Catalyzes the transacylacion between phospholipids and lysophospholipids, with the highest rate being between phosphatidylcholine (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine or PC) and CL. Catalyzes both 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (lysophosphatidylcholine or LPC) reacylation and PC-CL transacylation, that means, it exchanges acyl groups between CL and PC by a combination of forward and reverse transacylations. Also catalyzes transacylations between other phospholipids such as phosphatidylethanolamine (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine or PE) and CL, between PC and PE, and between PC and phosphatidate (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate or PA), although at lower rate. Not regiospecific, it transfers acyl groups into any of the sn-1 and sn-2 positions of the monolysocardiolipin (MLCL), which is an important prerequisite for uniformity and symmetry in CL acyl distribution. Cannot transacylate dilysocardiolipin (DLCL), thus, the role of MLCL is limited to that of an acyl acceptor. CoA-independent, it can reshuffle molecular species within a single phospholipid class. Redistributes fatty acids between MLCL, CL, and other lipids, which prolongs the half-life of CL. Its action is completely reversible, which allows for cyclic changes, such as fission and fusion or bending and flattening of the membrane. Hence, by contributing to the flexibility of the lipid composition, it plays an important role in the dynamics of mitochondria membranes. Essential for the final stage of spermatogenesis, spermatid individualization (By similarity). Required for the initiation of mitophagy (PubMed:33096711). Required to ensure progression of spermatocytes through meiosis (By similarity). Exon 7 of human tafazzin is essential for catalysis (PubMed:19700766). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q06510, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91WF0, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9V6G5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12930833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19164547, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19700766, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26908608, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33096711, ECO:0000303|PubMed:19700766, ECO:0000303|PubMed:32234310}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Catalyzes the transacylation between lysophosphatidate (such as 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate) and phosphatidylglycerol (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1'-sn-glycerol)) (PubMed:19700766). Contributes to cardiolipin (1',3'-bis-[1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho]-glycerol or CL) remodeling (PubMed:12930833, PubMed:19700766). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12930833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19700766}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: Catalyzes the transacylation between lysophospholipids and phospholipids, and plays a fundamental role in cardiolipin (1',3'-bis-[1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho]-glycerol or CL) metabolism and remodeling. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12930833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19416660, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19700766}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 5]: Catalytically inactive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12930833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19700766}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 7]: Catalytically inactive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19700766}. | Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Cardiomyopathy;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Reference proteome;Transferase | PATHWAY: Phospholipid metabolism. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:12930833, ECO:0000305|PubMed:19700766}. | This gene encodes a protein that is expressed at high levels in cardiac and skeletal muscle. Mutations in this gene have been associated with a number of clinical disorders including Barth syndrome, dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), hypertrophic DCM, endocardial fibroelastosis, and left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC). Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. A long form and a short form of each of these isoforms is produced; the short form lacks a hydrophobic leader sequence and may exist as a cytoplasmic protein rather than being membrane-bound. Other alternatively spliced transcripts have been described but the full-length nature of all these transcripts is not known. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:6901; | mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase activity [GO:0003841]; 1-acylglycerophosphocholine O-acyltransferase activity [GO:0047184]; O-acyltransferase activity [GO:0008374]; cardiac muscle contraction [GO:0060048]; cardiac muscle tissue development [GO:0048738]; cardiolipin acyl-chain remodeling [GO:0035965]; cardiolipin biosynthetic process [GO:0032049]; cardiolipin metabolic process [GO:0032048]; cristae formation [GO:0042407]; heart development [GO:0007507]; heart morphogenesis [GO:0003007]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; inner mitochondrial membrane organization [GO:0007007]; mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled electron transport [GO:0042775]; mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I assembly [GO:0032981]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; mitophagy [GO:0000423]; muscle contraction [GO:0006936]; positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process [GO:2001171]; positive regulation of cardiolipin metabolic process [GO:1900210]; skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0007519]; spermatocyte division [GO:0048137] | 11896212_Mutations in the Xq28 gene G4.5 lead to dilated cardiomyopathy associated with ultrastructural changes in mitochodria of heart, liver and skeletal muscle. 12930833_one splice variant of TAZ most likely represents the only physiologically important mRNA, at least with regard to cardiolipin metabolism 15304507_human TAZ has a role in mitochondrial dysfunction in Barth syndrome 15499385_Motif, critical for the glycerolphosphate acyltransferase family, was observed in human tafazzin. The presence of a mutation in this region in Barth syndrome patients indicates that this motif is essential for tafazzin function. 18799610_Data show that the tafazzin 1 interactome defined here provides novel insight into the variable respiratory defects and morphological abnormalities observed in mitochondria of BTHS patients. 19261493_A 5.5-month old boy with Barth's syndrome phenotype had a novel missense T43P mutation in exon 2 of the TAZ gene. His mother was heterozygous for this mutation. 19700766_the characteristic fatty acid profile of cardiolipin is not determined by the substrate specificity of tafazzin 20474083_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 23031367_A novel, hemizygous nonsense mutation in TAZ exon 7 (c.583G>T, p.Gly195X) was detected in an infant with Barth syndrome with dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure and in his great-uncle with left ventricular noncompaction. 23200781_Tafazzin activity is critical for the differentiation of cardiomyocytes. (Review) 23345479_The identification of TAZ mutation has major impact on their medical care as the surveillance needs to be expanded to cover for the Barth syndrome, a severe metabolic phenotype also caused by TAZ mutation, in addition to DCM. 23359024_data suggest that genes other than G4.5 are responsible for the familial form of noncompaction of the ventricular myocardium 23409742_study reports five new TAZ gene mutations in six unrelated Barth Syndrome patients, including two new gross gene rearrangements 23432031_The underlying molecular defects in Barth syndrome are truncation, deletion or substitution mutations in the TAZ gene, resulting in loss-of-function of tafazzin. Review. 23523468_Basal levels of superoxide anion production were slightly higher in patients' cells than in control cells as previously evidenced via an increased protein carbonylation in the taz1Delta mutant in the yeast. 24093814_Three novel hemizygous mutations in the TAZ gene were found (c.584G>T; c.109+6T>C; c.86G>A). We conclude that Barth syndrome should be included in differential diagnosis of cardiomyopathy in childhood. 24342716_Results show that in both healthy controls and in Barth syndrome patients, a greater variety of alternatively spliced forms than previously described was found. It includes a sizeable proportion of minor splice variants besides the four dominant isoforms. 24858921_Strong expression of TAZ protein seems to be related to rectal cancer development and RT response, it can be a predictive biomarker of distant recurrence in patients with preoperative RT. 25247053_mitochondria-targeted antioxidant prevents cardiac dysfunction induced by tafazzin gene knockdown in cardiac myocytes 25776009_novel mutation in exon 1 of the TAZ gene and female mosaicism in three generations of a Polish family with Barth syndrome 25782672_two novel and non-identical TAZ gene rearrangements were found in the offspring of a single female carrier of Barth syndrome. 25919711_Tafazzin deficiency in mouse embryonic fibroblasts also led to impaired oxidative phosphorylation and severe oxidative stress 26164234_ability of CL-ND to elicit a physiological response was examined in an HL60 cell culture model of Barth Syndrome neutropenia. siRNA knockdown of the phospholipid transacylase, tafazzin (TAZ), induced apoptosis in these cells 26845103_TAZ mutation-confirmed diagnosis of Barth syndrome (BTHS) was available for 39/42 of the participants. Of 39 patients, 13 have a missense mutation, 6 have a nonsense mutation, 8 have a splicing mutation, 6 have a small out-of-frame insertion or deletion, 2 have a small in-frame insertion, and 4 have a large deletion encompassing several exons 26853223_Molecular analysis of at risk female family members identified the patient's sister and mother as heterozygous carriers. Apparently harmless synonymous variants in the TAZ gene can damage gene expression. Such findings widen our knowledge of molecular heterogeneity in Barth syndrome. 26908608_TAZ mutation is associated with Barth syndrome. 28183324_This is the first report of systematic mutation screening of TAZ in a large cohort of pediatric patients with primary cardiomyopathy using the NGS approach. TAZ mutations were found in 4/114 (3.5%) male patients with primary cardiomyopathy. Our findings indicate that the inclusion of TAZ gene testing in cardiomyopathy genetic testing panels may contribute to the early diagnosis of BTHS. 28489874_TAZ is overexpressed in cervical cancer and may promote tumorigenicity of cervical cancer cells and inhibit apoptosis. 29129703_intrinsic mitochondrial localization sequences in the human TAZ protein, were identified. 29508483_Report left ventricular non-compaction associated with Barth Syndrome due to triple mutations in TAZ, DTNA, and SDHA genes in multiple members of one family. 29514840_we show that TAZ is abundant in human aRMS tumor samples, and that TAZ suppression decreases proliferation, promotes differentiation, and inhibits cancer cell stemness. TAZ-deficient aRMS cells are also enriched in G2-M, suggesting that TAZ may be important for G2-M cell-cycle progression. 30122738_Impact of Tafazzin Variants on Dilated Cardiomyopathy Phenotype in Left Ventricular Non-Compaction Patients in Early Infancy. 30226969_We report a novel TAZ gene mutation in male and female siblings with left ventricular noncompaction and hypotonia. Additionally, the brother presented an intermittent neutropenia and increased urinary levels of 3-methylglutaconic and 3-methylglutaric acid. The molecular genetic testing showed that both siblings carry the mutation: c.253insC, p.(Arg85Profs*54) in exon 3 of the TAZ gene. Normal karyotype female. 30251684_Study characterized structural and metabolic adaptations in Barth syndrome patients primary skin fibroblasts and provided novel insights into the molecular details of supercomplex destabilization, aberrant cristae morphology and metabolic changes resulting from TAZ mutations. 30332638_Tafazzin deficiency is associated with defective remodeling of the mitochondrial phospholipid cardiolipin causing cardiomyopathy in Barth syndrome. 31056533_This study demonstrated that overexpression of TAZ caused by downregulation of miR-125b promoted resistance of glioma cells to TRAIL. MiR-125b/TAZ axis may represent a potential strategy to reverse the TRAIL in glioma. 31209945_Truncated TEAD-binding protein of TAZ inhibits glioma survival through the induction of apoptosis and repression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 31559736_This is the first case of the association of Barth syndrome with cystic fibrosis. Pedigree analysis revealed similar sudden infant deaths in close relatives. Further analysis revealed that the patient had exon 1 mutation c51.G> C (p.Trp17X); TAZ gene mutation was also detected in our patient as previously described in his cousin. 31598953_Barth syndrome due to the c.481G>A mutation of the TAZ gene probably underlies the recurrent hydrops fetalis and fetal dilated cardiomyopathy in this family. 31729175_Delayed appearance of 3-methylglutaconic aciduria in neonates with early onset metabolic cardiomyopathies: A potential pitfall for the diagnosis. 32234310_The Function of Tafazzin, a Mitochondrial Phospholipid-Lysophospholipid Acyltransferase. 33096711_Tafazzin Mutation Affecting Cardiolipin Leads to Increased Mitochondrial Superoxide Anions and Mitophagy Inhibition in Barth Syndrome. 34314685_Diverse mitochondrial abnormalities in a new cellular model of TAFFAZZIN deficiency are remediated by cardiolipin-interacting small molecules. 34549308_miR125a5p reverses epithelialmesenchymal transition and restores drug sensitivity by negatively regulating TAFAZZIN signaling in breast cancer. 35676289_N-oleoylethanolamide treatment of lymphoblasts deficient in Tafazzin improves cell growth and mitochondrial morphology and dynamics. | ENSMUSG00000009995 | Tafazzin | 143.579937 | 1.0193832 | 0.027696476 | 0.19835447 | 0.01941430689 | 0.8891852502511514710903384184348396956920623779296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.95116751503841534542971203336492180824279785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 146.293057 | 20.078802 | 143.469731 | 19.527099 |
| ENSG00000102796 | 79758 | DHRS12 | protein_coding | A0PJE2 | FUNCTION: Putative oxidoreductase. {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;NAD;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a member of the short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR) family, which has over 46,000 members. Members in this family are enzymes that metabolize many different compounds, such as steroid hormones, prostaglandins, retinoids, lipids and xenobiotics. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants and protein isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2012]. | hsa:79758; | oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491] | 32250163_DHRS12 inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma via Wnt3a/beta-catenin pathway. | 17.916079 | 1.0096169 | 0.013808010 | 0.38263985 | 0.00129156266 | 0.9713315426674342667467954015592113137245178222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.98644550757191173939730788333690725266933441162109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 17.561354 | 5.055125 | 17.157169 | 4.743400 | |||
| ENSG00000102858 | 23295 | MGRN1 | protein_coding | O60291 | FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase. Mediates monoubiquitination at multiple sites of TSG101 in the presence of UBE2D1, but not of UBE2G1, nor UBE2H. Plays a role in the regulation of endosome-to-lysosome trafficking. Impairs MC1R- and MC4R-signaling by competing with GNAS-binding to MCRs and inhibiting agonist-induced cAMP production. Does not inhibit ADRB2-signaling. Does not promote MC1R ubiquitination. Acts also as a negative regulator of hedgehog signaling (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9D074, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17229889, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19703557, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19737927}. | Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Myristate;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. | Mahogunin (MGRN1) is a C3HC4 RING-containing protein with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity in vitro.[supplied by OMIM, Apr 2004]. | hsa:23295; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; endosome to lysosome transport [GO:0008333]; negative regulation of cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0043951]; negative regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045744]; negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045879]; protein monoubiquitination [GO:0006513]; protein polyubiquitination [GO:0000209]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] | 17229889_a role for Mahogunin in a proteasome-independent ubiquitylation pathway: TSG101 is a specific Mahogunin substrate 19320733_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19524515_Study shows that both (Ctm)PrP and cyPrP can interact with and disrupt the function of Mahogunin (Mgrn), a cytosolic ubiquitin ligase whose loss causes spongiform neurodegeneration. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21862608_It therefore seems probable that the role of MGRN1 in the adrenal relates to the trafficking and/or degradation of the melanocortin 2 receptor. 23756845_data suggest that MGRN1 selectively targets misfolded proteins for degradation and may exhibit viable therapeutic potential for the treatment of spongiform neurodegeneration 24556679_Mahogunin-mediated alpha-tubulin ubiquitination via noncanonical K6 linkage regulates microtubule stability and mitotic spindle orientation. 26743086_Catalytic inactivation of MGRN1 results in elevated levels of GP78 and a consequential increase in the initiation of mitophagy. 27577081_Hypomethylation of CpG sites in RPTOR, MGRN1 and RAPSN in blood is associated with breast cancer. 27713096_Regulation of Mfn1 by MGRN1 and the proteasome modulates mitochondrial fusion. 28475871_With aging, the neuroprotective e3 ligase MGRN1 relocates from the cytosol to the nucleus of neurons, where it associates with chromatin and potentiates the cellular response to proteotoxic stress. This nuclear shift is due to a proteasome impairment dependent increase of a monoubiquitinated form of MGRN1. 28902452_epletion of MGRN1 activity may hamper physiologically important processes like mitochondrial movement in neuronal processes and intracellular transport of ligands through the endosomal pathway thereby contributing to the pathogenesis of neurodegeneration in certain types of prion diseases 28947386_In a heterologous expression system, MC1R-dependent Arrestins B ubiquitination was enhanced by overexpression of MGRN1 and was impaired by siRNA-mediated MGRN1 knockdown thus pointing to MGRN1 as the responsible E3-ligase. 34921635_Mahogunin Ring Finger 1 regulates pigmentation by controlling the pH of melanosomes in melanocytes and melanoma cells. | ENSMUSG00000022517 | Mgrn1 | 434.764689 | 0.7705185 | -0.376098443 | 0.18726932 | 4.01167402446 | 0.0451862646454458324885017361793870804831385612487792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.15304801114021984731472514340566704049706459045410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 385.127469 | 46.349385 | 503.034156 | 60.316147 |
| ENSG00000102879 | 11151 | CORO1A | protein_coding | P31146 | FUNCTION: May be a crucial component of the cytoskeleton of highly motile cells, functioning both in the invagination of large pieces of plasma membrane, as well as in forming protrusions of the plasma membrane involved in cell locomotion. In mycobacteria-infected cells, its retention on the phagosomal membrane prevents fusion between phagosomes and lysosomes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10338208}. | Acetylation;Actin-binding;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation;WD repeat | This gene encodes a member of the WD repeat protein family. WD repeats are minimally conserved regions of approximately 40 amino acids typically bracketed by gly-his and trp-asp (GH-WD), which may facilitate formation of heterotrimeric or multiprotein complexes. Members of this family are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including cell cycle progression, signal transduction, apoptosis, and gene regulation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. A related pseudogene has been defined on chromosome 16. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010]. | hsa:11151; | actin filament [GO:0005884]; axon [GO:0030424]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cortical actin cytoskeleton [GO:0030864]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; membrane [GO:0016020]; phagocytic cup [GO:0001891]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; actin monomer binding [GO:0003785]; cytoskeletal protein binding [GO:0008092]; myosin heavy chain binding [GO:0032036]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding [GO:0043548]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; calcium ion transport [GO:0006816]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0031589]; cellular response to interleukin-4 [GO:0071353]; early endosome to recycling endosome transport [GO:0061502]; epithelial cell migration [GO:0010631]; homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue [GO:0048873]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; leukocyte chemotaxis [GO:0030595]; natural killer cell degranulation [GO:0043320]; negative regulation of actin nucleation [GO:0051126]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of vesicle fusion [GO:0031339]; nerve growth factor signaling pathway [GO:0038180]; neuron apoptotic process [GO:0051402]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; phagolysosome assembly [GO:0001845]; positive chemotaxis [GO:0050918]; positive regulation of T cell migration [GO:2000406]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030833]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051279]; T cell homeostasis [GO:0043029]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098]; thymocyte migration [GO:0072679]; uropod organization [GO:0032796]; vesicle fusion [GO:0006906] | 15601263_These results demonstrate that p57/coronin-1 forms homodimers, that the association is mediated by the leucine zipper structure in the C-terminal region, and that it plays a role in the cross-linking of F-actin in the cell. 15800061_The leukocyte plasma membrane associates with the actin cytoskeleton through coronin-1. 16040207_downregulation of TACO gene transcription restricts entry/survival of mycobacteria within macrophages 16467882_Our results strongly suggested that there was a new actin-binding region at the C-terminus of p57. 17442961_Coronin-1 accumulates at the leading edge of migrating neutrophils and at the nascent phagosome. 18693254_phosphorylation of p57/coronin-1 down-regulates its association with actin and modulates the reorganization of actin-containing cytoskeleton 18836449_Findings establish a function for coronin 1A in T cell egress, identify a surface of coronin involved in Arp2/3 regulation. 19454722_Circulating neutrophils from CF patients had more coronin-1 expression, associated with a lower apoptosis rate 21339362_Instead of regulating the F-actin cytoskeleton, coronin 1 functions in balancing pro- and antiapoptotic signals by regulating divalent calcium ion fluxes and calcineurin activation downstream of the T cell receptor. 21873980_Coronin 1A promotes a cytoskeletal-based feedback loop that facilitates Rac1 translocation and activation 23100250_Constitutive turnover of phosphorylation at Thr-412 of p57/coronin-1 regulates its interaction with actin. 23252456_PU.1 and CEBPA are direct transcriptional regulators of CORO1A in acute promyelocytic leukemia and acute myeloid leukemia. 23522482_Our findings define a new clinical entity of a primary immunodeficiency with increased susceptibility to EBV-induced lymphoproliferation in patients associated with hypomorphic Coronin-1A mutation. 23745754_These results demonstrate that coronin-1a is a novel antibody target for clinically isolated syndrome and multiple sclerosis. 24239742_Nox4-mediated redox regulation of PTP1B serves as a modulator, in part through coronin-1C, of the growth and migration of glioblastoma cells. 24760828_show a critical role for F-actin deconstruction in cytotoxic function and immunological secretion and identify Coro1A as its mediator 24980436_Results indicate that Coronin1 proteins are at the center of a regulatory hub that coordinates Rac1 activation, effector exchange, and the F-actin organization state during cell signaling. 25073507_mutatiions result in abnormal T-cells, severe combined immunodeficiency of an epidermodysplasia verruciformis-human papilloma virus mucocutaneous syndrome with B and NK defects and shortened telomeres 25217836_Coronin 1 trimerization is essential to promote mycobacterial survival within macrophages 25269405_Absence of coronin 1A is associated with severe combined immunodeficiency in humans, hypomorphic mutations lead to a profound defect in naive T cells, expansion of oligoclonal memory T cells, and susceptibility to Epstein Barr B lymphoproliferation. 25889880_Together, these findings both in Jurkat T cells as well as in primary T cells indicate a regulatory role of Coro1A on PKCtheta; recruitment and function downstream of the TCR leading to NF-kappaB transactivation. 25936522_These findings suggest that coronin 1A modulates endothelial cell apoptosis by regulating p38beta expression and activation. 26476480_Our studies demonstrate the importance of intact CORO1A C-terminal domains in thymic egress and T-cell survival, as well as in defense against viral pathogens. 27779207_Levels of p21 and p27 were decreased in TACO or pAKT overexpressing HCC due to SKP2 upregulation. 27835684_It has been shown that WDR26 promotes Rac1 membrane translocation following a Coro1A-like and Coro1A-dependent mechanism. 28215292_Data suggest that CORO1A plays key role in neuronal signaling; roles of CORO1A in multiple signaling pathways suggest that CORO1A may influence cross talk between key pathways. [REVIEW] 30453345_Coro1A has a role in platelet biology with impact on spreading, aggregation and thrombosis 35526384_Carbamazepine-modified HLA-A*24:02-bound peptidome: Implication of CORO1A in skin rash. 35915349_Serum exosomal coronin 1A and dynamin 2 as neural tube defect biomarkers. | ENSMUSG00000030707 | Coro1a | 5871.223896 | 0.9012298 | -0.150033057 | 0.02494088 | 36.18677143139 | 0.0000000017928342865911940557599411950905933521571711253272951580584049224853515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000004551391288718261817890925469143326154153328388929367065429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 5562.431415 | 124.809325 | 6201.632834 | 138.320027 | |
| ENSG00000103197 | 7249 | TSC2 | protein_coding | P49815 | FUNCTION: In complex with TSC1, this tumor suppressor inhibits the nutrient-mediated or growth factor-stimulated phosphorylation of S6K1 and EIF4EBP1 by negatively regulating mTORC1 signaling (PubMed:12271141, PubMed:28215400, PubMed:35772404). Acts as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) for the small GTPase RHEB, a direct activator of the protein kinase activity of mTORC1 (PubMed:15340059). May also play a role in microtubule-mediated protein transport (By similarity). Also stimulates the intrinsic GTPase activity of the Ras-related proteins RAP1A and RAB5 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P49816, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12271141, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15340059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28215400, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35772404}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Epilepsy;GTPase activation;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tumor suppressor;Ubl conjugation | This gene is a tumor suppressor gene that encodes the growth inhibitory protein tuberin. Tuberin interacts with hamartin to form the TSC protein complex which functions in the control of cell growth. This TSC protein complex negatively regulates mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling which is a major regulator of anabolic cell growth. Mutations in this gene have been associated with tuberous sclerosis and lymphangioleiomyomatosis. [provided by RefSeq, May 2022]. | hsa:7249; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; TSC1-TSC2 complex [GO:0033596]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; Hsp90 protein binding [GO:0051879]; phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; anoikis [GO:0043276]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; heart development [GO:0007507]; insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048009]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046627]; negative regulation of mitophagy [GO:1901525]; negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014067]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; negative regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051898]; negative regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032007]; negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030178]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; positive chemotaxis [GO:0050918]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016239]; protein import into nucleus [GO:0006606]; protein kinase B signaling [GO:0043491]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of endocytosis [GO:0030100]; regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046626]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] | 11112665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11403047_missense mutation in the GTPase activating protein homology region in families with tuberous sclerosis complex 11686512_negative regulators of cell division; control of transition from G0/G1 to S phase 11781698_Detected two sequence changes involving the TSC2 stop codon. 11811958_calmodulin signaling in the propagation of this TSC2 activity 11836366_Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis in a patient with an acrofacial dysostosis-like phenotype, tuberous sclerosis, and polycystic kidney disease shows a microdeletion of approximately 280 kb including the TSC2 gene on chromosome 16p13.3. 12015165_Novel TSC1 and TSC2 mutations in Japanese patients with tuberous sclerosis complex. 12062115_TSC1 and TSC2 mutations in tuberous sclerosis - used DHPLC analysis to facilitate the detection of a mosaic mutation, in the presence of a coexisting constitutional polymorphism. 12127687_effect on EHEN-induced renal and hepatocarcinogenesis in the suppressor gene transgenic rats 12172553_TSC2 is phosphorylated and inhibited by Akt and suppresses mTOR signalling. 12176984_tuberin binds with 14-3-3 zeta to regulate phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 12271141_hamartin and tuberin function together to inhibit mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-mediated signaling to eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1) and ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) 12364343_associates with 14-3-3 in vivo 12468542_TSC2 expression is regulated by 14-3-3 beta in human cells 12547695_A link exists between this protein and kidney diseases 12581886_Estrogen action induces tyrosine phosphatase activity that regulates stability of tuberin, which may play a crucial role in cellular specific functions such as endocytosis. 12582162_MK2 phosphorylates TSC2, which creates a 14-3-3 binding site and thus regulates the cellular function of the TSC2 tumor suppressor protein 12711473_Mutation in TSC2 and activation of mammalian target of rapamycin signalling pathway in renal angiomyolipoma. 12766909_We conclude that the hamartin/tuberin complex exerted a direct effect on the morphology and adhesive properties of 293 cells through regulation of the level and/or activity of cellular E-cadherin/beta-catenin 12773159_mutated in suberous sclerosis (REVIEW). 12773162_Mutated in tuberous sclerosis. 12773163_mutated in sporadic tumors (REVIEW) 12820960_TSC2 is a GAP for rheb and insulin-mediated rheb activation is PI3K dependent. 12842888_TSC2 binds to rheb and has a role in S6 kinase activation 12869586_Rheb GTPase is a direct target of TSC2 GAP activity and regulates mTOR signaling. 12894220_Human TSC2 triggers mammalian cell size reduction and a dominant-negative TSC2 mutant induces increased size. 14551205_data support a model in which phosphorylation of hamartin regulates the function of the hamartin-tuberin complex during the G2/M phase of the cell cycle 14559897_the TSC1.TSC2 complex is regulated by pam and its ortholog highwire 14680818_Western blot analyses confirmed the deregulation of 14-3-3 proteins upon ectopic overexpression of TSC1 and TSC2. 14756965_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14756965_TSC2 gene, which is responsible for tuberous sclerosis was identified, and all the exons of TSC2 were analyzed by using polymerase chain reaction-single strand conformation polymorphism (PCR-SSCP) from peripheral blood of 28 patients . 14871804_A novel mechanism of post-translational inactivation of the TSC2 protein, tuberin, by physiologically inappropriate phosphorylation is demonstated. 14985384_people with TSC2 mutations were significantly more likely than those with TSC1 mutations to have autistic disorder, a low IQ, and a history of infantile spasms; low IQ was independently associated with both TSC2 mutations and a history of infantile spasm 15059224_Down regulation or loss of tuberin and/or hamartin expression may be permissive to fibrocyte proliferation or promote collagen production leading to fibroepithelial polyp formation. 15066998_Tuberin (TSC2) interact with smad2/smad3 during TGF-beta1 growth regulation. 15072102_tsc2 gene expression is reduced in the majority of subependymal giant cell astrocytomas 15150271_inhibition of B-Raf kinase via Rheb is an mTOR-independent function of tuberin 15175323_Binding with HPV16 E6 causes the proteasome-mediated degradation of Tuberin 15231735_Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and other benign tumor syndromes could be caused by dysregulation of the TSC2 pathway 15340059_To investigate the function of TSC2 and Rheb in mTOR signaling, we analyzed the TSC2-stimulated Rheb GTPase activity. 15355997_Tuberin has a role in binding p27 and negatively regulating its interaction with Skp2 15477556_Cortical tuber giant cells in a case of epileptogenic tuberous sclerosis showed predominantly nuclear hamartin, cytosolic tuberin, and hyperphosphorylation of S6. 15579767_data suggest that PGE2 signaling may promote endometrial tumorigenesis by inactivation of tuberin after its phosphorylation via the Akt signaling pathway 15595939_A total of 12 mutations were detected in 24 Indian TSC families in TSC genes. 15624760_Five of 6 subependymal giant cell astrocytomas(SEGAs) also showed evidence of biallelic mutation of TSC1 or TSC2, suggesting that SEGAs develop due to complete loss of a functional tuberin-hamartin complex. 15647351_monitored 14 previously uncharacterized and six known phosphorylation events after phorbol ester stimulation in the ERK/p90 ribosomal S6 kinase-signaling targets, TSC1 and TSC2, and a protein kinase C-dependent pathway to TSC2 phosphorylation 15798777_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15851026_Erk may modulate mTOR signaling and contribute to disease progression through phosphorylation and inactivation of TSC2. 15874888_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15963462_identified three sites of TSC2 phosphorylation and a novel site of TSC1 phosphorylation, and investigated the roles of these sites in regulating the activity of the TSC1-TSC2 complex 16053916_investigation of the ability of different opioid receptors to regulate the phosphorylation and degradation of tuberin 16192644_Growth of smooth muscle cells derived from TSC2-renal angiomyolipoma demonstrates that epidermal growth factor is required. 16211238_study provides new insights into cellular roles of TSC proteins and promotes discussion on whether separable functions of these proteins might be associated with clinical differences of TSC1- and TSC2-associated disease 16213898_Reduced expression of tuberin might be involved in the progression of pancreatic cancer. 16237225_patient should be considered as having Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma that developed from two somatic hit mutations in TSC2 16258273_Tuberous sclerosis tumor suppressors TSC1 and TSC2 form a protein complex that integrates and transmits cellular growth factor and stress signals to negatively regulate checkpoint kinase TOR activity, as described in this review. 16341938_Data show that tuberin protein levels are decreased in the frontal cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease. 16388022_TSC2 may play a critical role in modulating cell migration and invasiveness, which contributes to the pathobiology of LAM. 16537497_Overexpression of TSC2 rescues the migration phenotype of myr-Akt1-expressing tumor cells, and high levels of TSC2 in breast cancer patients correlate with increased metastasis and reduced survival. 16554133_Denaturing high performance liquid chromatography and DNA sequencing analysis of TSC1 and TSC2 revealed 13 types of mutations (30%). Nine novel mutations of TSC2 were identified. 16624901_The genome of Schizosaccharomyces pombe contains tsc1(+) and tsc2(+), homologs of human Tsc1 and Tsc2, respectively. Deletion of either tsc1(+) or tsc2(+) affects gene induction upon nitrogen starvation. 16835931_mutation in the TSC2 gene has a role in acrochordons and pancreatic islet-cell tumors in tuberous sclerosis [case report] 16897363_According to Knudson's two-hit model of tumorigenesis, second-hit mutation and resulting loss of heterozygosity of a tumor suppressor gene (tsc1 and tsc2) is necessary for tumor formation 16905638_Fractionation of synchronized airway smooth cells showed that tuberin enters the nucleus in late G(1), and passage through the cell cycle is necessary for nuclear entry. 16940165_documents the incidence, natural history, and outcome of cardiac tumors in patients with TSC in the largest series yet reported and provides a comparison of these features with TSC1 versus TSC2 mutation 17018601_The TSC/Rheb/mTOR pathway plays a critical role in the regulation of E(2)-induced proliferation. 17114181_mTOR-dependent pathways have roles in IFN signaling and 4E-BP1 and TSC1-TSC2 are key components in the generation of IFN-dependent biological responses 17114346_These findings suggest a link between tuberin nuclear localization and a variety of intracellular signaling events that have direct implications with respect to the role of tuberin in the pathology of tuberous sclerosis and lymphangioleiomyomatosis. 17234746_These functional data indicate that the Crumbs complex is a potential regulator of the mTORC1 pathway, cell metabolism and survival through a direct interaction with TSC1/2. 17273797_During conditions of cell stress, GADD34 forms a stable complex with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) 1/2, causes TSC2 dephosphorylation, and inhibits signaling by mammalian target of the rapamycin (mTOR). 17287951_We conclude that large deletions in TSC1 and TSC2 account for about 0.5 and 6% of mutations seen in TSC patients, respectively, and MLPA is a highly sensitive and accurate detection method, including for mosaicism. 17304050_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17373211_implications for the development of cystic kidney disease [REVIEW] 17458623_study presents the cytoplasmic/nuclear distribution of tuberin in cell lines 17470459_p27 localization during the mammalian cell cycle is under the control of the tumor suppressor tuberin 17592551_Angiomyolipoma-derived smooth muscle TSC2-/- cells express survivin when exposed to IGF-1. Survivn expression is also triggered whenever culture conditions perturb normal TSC2-/- cell function. 17632432_Pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis can appear sporadically or be associated with tuberous sclerosis with abnormalities of the TSC2 suppressor gene. 17671177_Erk-mediated TSC2 phosphorylation occurred at a high incidence and positively correlated with mitogen activated protein kinase and mammalian target of rapamycin activation in Tuberous Sclerosis and cancers 17888633_novel tandem-duplication mutation od TSC2 in Chinese tuberous sclerosis patient 17922028_This is the first description of a functional interaction between the tumor suppressor tuberin and the oncogene Ras in regulating apoptosis. 17975002_CD44v6-positive sorted lymphangioleiomyomatosis cells showed loss of heterozygosity at the TSC2 locus; binding of CD44v6 antibody resulted in loss of cell viability. 17989114_Tuberin regulates a specific DNA repair enzyme, OGG1. This regulation may be important in the pathogenesis of kidney tumors in patients with tuberous sclerosis complex. 18032745_Patients with a TSC1 mutation are more likely to have a less severe neurologic and cognitive phenotype than those with a TSC2 mutation. 18060739_Analysis of 15 tuberous sclerosis patient samples in which deletions in TSC2 extended into PKD1 showed no evidence of clustering of breakpoints near the polypyrimidine tract 18085521_Our observations of frequent deletion of TSC2 and the mTOR signalling pathway provide evidence that the oncogenetic lineage of PEComa, as a distinct TSC2-linked neoplasm, is similar to that of angiomyolipoma. 18094073_IFNbeta augments TSC2-dependent inhibition of TSC2-null ELT3 and human lymphangioleiomyomatosis-derived cell proliferation. 18302728_Functional characterisation of TSC2 variants can help identify pathogenic changes in individuals with tuberous sclerosis complex, and assist in the diagnosis and genetic counselling of the index cases and/or other family members 18320306_Results suggest that tuberin dysfunction may represent a mechanism for neuronal damage in Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease with dementia (PD/DLB), and a mouse model of PD. 18342602_Data show that loss of TSC1 or TSC2 in cell lines and mouse or human tumors causes endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and activates the unfolded protein response (UPR). 18368626_loss of tuberin in balloon cells of both cortical dysplasia type IIB in tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC)-related and sporadic patients suggests that Focal cortical dysplasia type IIB may represent the focal form of TSC. 18381890_Results indicate that FBW5-DDB1-CUL4-ROC1 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase regulating TSC2 protein stability and TSC complex turnover. 18411301_the TSC1-TSC2 complex inhibits mTORC1 and activates mTORC2, which through different mechanisms promotes Akt activation 18451215_Inactivation of TSC2 via loss of expression or phosphorylation occurred frequently in endometrial carcinoma to activate mTOR signaling 18538015_Involvement of TSC genes and other members of the mTOR signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. LOH and promoter methylation are two important mechanisms for downregulation of TSC genes. 18794342_in addition to the kinase LKB1, the Tsc1-Tsc2 complex, acting through TORC1, also modulates SAD to regulate axon formation 18794346_results reveal key roles of TSC1/TSC2 in neuronal polarity, suggest a common pathway regulating polarization/growth in neurons and cell size in other tissues, and have implications for the understanding of the pathogenesis of TSC 18807177_This study suggests a pivotal role of PI3 K, MAPK and mTOR pathways, via tuberin, in post-transcriptional control of CXCR4 18848473_These data identify the TSC2-mTOR pathway as a key regulator of innate immune homeostasis with broad clinical implications for infectious and autoimmune diseases, vaccination, cancer, and transplantation. 18926585_Dysregulation of the TSC-mTOR pathway may cause not only tumor development but also metabolic disorders such as diabetes and its comp 18958173_Anti-EGFR antibody efficiently and specifically inhibits human TSC2-/- smooth muscle cell proliferation. 18974095_a novel interaction between DAPK and TSC2 proteins that has revealed a positive link between growth factor stimulation of DAPK and mTORC1 signaling that may ultimately affect autophagy, cell survival, or apoptosis. 19005330_TSC2 which codes for tuberin plays a central role in regulating cell survival and proliferation signaling pathways 19058789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19175396_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19250671_Hypermethylation and downregulation of TSC2 gene is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 19259131_Data suggest that the three mutations were most likely de novo, as parents of affected patients did not present any features of TSC. 19265534_The data suggest that tuberin and OGG1 are important proteins in the pathogenesis of angiomyolipoma in tuberous sclerosis complex patients. 19332694_Cyst-like cortical tubers in the brain are strongly associated with TSC2 gene mutation in tuberous sclerosis complex. 19332694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19357198_A hypomorphic allele of Tsc2 highlights the role of TSC1/TSC2 in signaling to AKT and models mild human TSC2 alleles 19357198_AKT activity is downregulated when Tsc1/Tsc2 function is reduced. 19395678_found increased MMP-2 expression in cells lacking TSC1/TSC2 compared with their respective controls 19419980_Conducted a retrospective review of the chest computed tomography (CT) of 45 female and 20 male patients with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) and found cysts consistent with Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) in 22 (49%) women and two (10%) men. 19422538_mineralized focal cortical dysplasias with balloon cells revealed an increased frequency of TSC2 allelic variants but not TSC1 19443708_that methylation of the TSC2 promoter might cause a complete loss of tuberin in TSC2 cells. 20042714_Tuberin-null cells become nonadherent and invasive and these nonadherent cells express cleaved forms of beta-catenin. 20145209_ARD1 functions as an inhibitor of the mTOR pathway and that dysregulation of the ARD1-TSC2-mTOR axis may contribute to cancer development 20146692_In the brain, TSC2 has been implicated in cell body size, dendritic arborization, axonal outgrowth and targeting, neuronal migration, cortical lamination, and spine formation [REVIEW]. 20160076_results identify a cytoplasmic pathway for ROS-induced ATM activation of TSC2 to regulate mTORC1 signaling and autophagy, identifying an integration node for the cellular damage response 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20219685_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237422_These findings link TACC3 to novel structural and cell division functions of TSC2. 20304964_p22(phox)-based Nox oxidases maintain HIF-2alpha protein expression through inactivation of tuberin and downstream activation of ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1/4E-BP1 pathway 20354165_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20363874_AMPK functions to inhibit IGF-I-stimulated PI3K pathway activation through stimulation of IRS-1 serine 794 phosphorylation. 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20530489_TSC2 has a role in controlling cell polarity and migration by regulating CDC42 and RAC1 activation 20605525_The rare occurrence of complete loss of TSC1/TSC2 function in human tumors suggests that retaining growth suppressor activity might be beneficial during tumour evolution, perhaps by promoting survival when cells grow in a nutrient-limited environment. 20622004_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20639436_Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM), occurring sporadically (S-LAM) or in patients with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), results from abnormal proliferation of LAM cells exhibiting mutations or loss of heterozygosity (LOH) of the TSC genes, TSC1 or TSC2. 20658316_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20658316_analysis of polymorphic variants in TSC1 and TSC2 and their association with breast cancer phenotypes 20671064_One of the targets of HtrA1 activity during fetal development is the TSC2-TSC1 pathway. 20818424_Rheb controls proliferation of TSC2-deficient cells by a mechanism that involves regulation of AMPK and p27, and that Rheb is a potential target for TSC/LAM therapy. 20882401_These findings establish a mouse model for TSC-related anxiety phenotypes and suggest that anxiety disorders in TSC have a biological foundation. 21036916_Lymphangioleiomyomatosis is characterized by cystic lung destruction, resulting from proliferation of smooth-muscle-like cells, which have mutations in the tumor suppressor gene TSC2. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21134130_TSC2 binds to the death domain of DAPK. This interaction is required for TSC2 to reduce DAPK protein levels and half-life. DAPK is regulated by the lysosome pathway. Lysosome inhibition blocks TSC2-mediated degradation of DAPK. 21145542_Increased expression of tuberin in human uterine leiomyoma. 21243421_Rattus norvegicus and Mus musculus TSC1 and TSC2 showed very high similarity to the human sequences, this was not the case for Danio rerio, Drosophila melanogaster, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, Schizosaccharomyces pombe or Disctyostelium discoideum. 21252315_study identified six TSC2 mutations, one indel, one nonsense, and four missense in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors 21309039_Functional assessment of variants in the TSC2 genes identified in individuals with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex 21329690_REVIEW: TSC signaling in the CNS 21332470_TSC2 R1200W variant, and four other TSC2 missense variants associated with a mild TSC phenotype, confirmed that the changes disrupted the TSC1-TSC2 function. The TSC1-TSC2 interaction was not affected by the amino acid substitution. 21345208_results support the possibility that allele-specific variation in TSC mRNA expression contributes to the variable severity of symptoms in tuberous sclerosis complex patients 21407201_Human TSC2-null fibroblast-like cells induce hair follicle neogenesis and hamartoma morphogenesis. 21412983_TSC1, TSC2 and Rheb function independently of TORC1 in tuberous sclerosis complex.[Review] 21419848_Tuberous sclerosis complex protein TSC2 plays a critical role in Purkinje cell survival by regulating endoplasmic reticulum and oxidative stress. 21449900_In a cohort of tuberous sclerosis patients, there was a trend towards greater severity for patients with TSC2 mutations compared with their TSC1 counterparts, particularly for autistic spectrum disorder 21533174_presence of TSC2 mutations, in addition to TSC1 mutations, underlines the involvement of mTOR signaling in urothelial carcinoma 21555252_This study suggested that allelic imbalances of TSC2 in nonlesional focal epileptic tissue. 21784859_Redox regulates mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) activity by modulating the TSC1/TSC2-Rheb GTPase pathway. 21795849_ULK1 negatively regulates the kinase activity of mTORC1 and cell proliferation in a manner independent of Atg5 and TSC2 21846442_Eighty percent of cardiac rhabdomyomas are associated with tuberous sclerosis. In this case, molecular testing for tuberous sclerosis identified two variants in the TSC2 gene. 21900748_Tuberin regulates the cellular localization of cyclin B1. 21910228_Two females cases with typical manifestations of Tuberous sclerosis complex, horseshoe kidney, and an identical variant c.5138G>A in exon 39 (p.Arg1713His) of TSC2 gene. 21949787_Mutations in TSC2 is associated with angiomyolipoma. 22090422_study found tuberin and PRAS40 to be potent anti-apoptotic gatekeepers in early mammalian stem-cell differentiation; data allow new insights into the regulation of early stem-cell maintenance and differentiation and identify a new role of the tumor suppressor tuberin and the oncogenic protein PRAS40 22189265_TSC2 protein-truncating mutations and small in-frame mutations are associated with distinctly different intelligence profiles, providing further evidence that different types and locations of TSC germline mutations 22251200_Patients with mutations in TSC2 tended to have a higher frequency of hepatic angiomyolipomas than those with mutations in TSC1 or those with no mutations detected. 22287548_The results defined the TSC2-mTOR pathway as a key determinant in the differentiation of monocytes into M2 phenotype tumor-associated macrophages that promote angiogenesis. 22456611_Perivascular epithelioid cell tumors with TFE3 gene fusions demonstrated intact, robust tuberin protein labeling and no TSC2 loss of heterozygosity. 22490766_This study presented that the mutation rate of the TSC1 and TSC2 genes in Korean patients with tuberous sclerosis complex was 100%. 22608477_TSC2 mutations are more frequent in patients with retinal findings than in those without retinal findings. 22707510_Patient with TSC2 1801A>G mutation was found to have five facial features of TSC, including a rash of facial angiofibromas, a shagreen patch, a forehead plaque, gingival fibromas, and dental pitting. 22795129_The TSC1-TSC2-TBC1D7 (TSC-TBC) complex is the functional complex that senses specific cellular growth conditions and possesses Rheb-GAP activity. 22867869_Missense mutations located in the central region of TSC2 (exons 23-33) are associated with significantly reduced incidence of infantile spasms. 22903760_Data suggest that different, nonterminating TSC2 mutations can have distinct effects on TSC1-TSC2 function, and therefore, on Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) pathology. 23217510_Genetic investigation of the coding exons of TSC1 and TSC2 revealed a 4 bp deletion at nucleotides 3693-3696 in exon 30 of the TSC2 gene. 23254740_Two novel TSC2 mutations in Chinese patients with tuberous sclerosis complex. 23348097_Our results suggest that XLID CUL4B mutants are defective in promoting TSC2 degradation and positively regulating mTOR signaling in neocortical neurons. 23389244_No differences emerged in mutation distributions and types in precedent studies, excepting low frequency of the TSC2 nonsense mutation 23689538_Our results suggest that tuberin and p27 are aberrantly expressed in malignant breast tissue 23818547_Pim2 directly phosphorylates TSC2 on Ser-1798 and relieves the suppression of TSC2 on mTOR-C1, leading to multiple myeloma cells proliferation. 23846400_An increased frequency of C>G/G>C and C>T/G>A mutations in the coding strand was found in TSC2. 23867796_OPG stimulated proliferation of cells cultured from explanted LAM lungs, and selectively induced migration of lymphangioleiomyomatosis cells identified by the loss of heterozygosity for TSC2. 23878245_Data indicate a nitrosative-stress signaling pathway that engages ATM, LKB1, AMPK and TSC2 tumor suppressors to repress mTORC1 and regulate autophagy. 23878397_Data indicate that sunitinib inhibited TORC1 in endothelial cells in a Tsc1/Tsc2-dependent manner 23947572_Data show growth-inhibitory and proapoptotic effects of simvastatin on TSC2-null lymphangioleiomyomatosis cells compared with atorvastatin. 24075384_Prenatal diagnosis of an intrathoracic lesion with a family history of parental epilepsy should raise a suspicion of fetal cardiac rhabdomyoma and tuberous sclerosis. 24077282_Alpha B-crystallin has an essential role in TSC1/2 complex deficiency-mediated tumorigenesis. 24271014_TSC2 somatic second-hit mutations are associated with angiofibroma development in tuberous sclerosis. 24318044_This work indicates a novel role for this TSC2 gene, which encodes an activator of cell proliferation in response to androgen stimulation. 24398473_Covalent modification of TSC2 by iNOS-derived NO is associated with impaired TSC2/TSC1 dimerization, mTOR pathway activation, and proliferation of human melanoma. 24444419_oxidative stress induces Tnfaip8 l1/Oxi-beta, which results in increased autophagy by its exclusive binding with FBXW5 to stabilize TSC2 24529380_These data suggest that regulation of TSC2 subcellular localization may be a general mechanism to control its activity and place TSC2 in the amino-acid-sensing pathway to TORC1. 24599401_Findings indicate that neuronal Tsc1/2 complex activity is required for the coordinated regulation of autophagy by AMPK. 24606538_The features of alpha-smooth muscle cells of a patient affected by lymphangioleiomyomatosis associated with Tuberous sclerosis complex, named LAM/TSC cells, bearing a TSC2 mutation and an epigenetic defect causing the absence of tuberin, were investigated. 24683199_Two novel gross deletions of TSC2 gene in Malay patients with tuberous sclerosis complex and TSC2/PKD1 contiguous gene deletion syndrome, respectively. 24698169_In children with tuberous sclerosis complex, nonsense mutations in the TSC2 gene had a correlation with autistic behavior. 24748662_TSC2 also functions as a transcription factor. 24794161_study describes 2 cases of genetically proven TCS2, sharing the same genotype; detected a novel, small and in frame deletion/insertion TSC2 mutation on exon 30 (c.3664_3665delinsTT-p.Asp1222Phe) 24917535_TSC2 mutations are associated with a more severe, earlier presenting tuberous sclerosis complex phenotype. 25114899_Studied conditions that increase the sensitivity of cancer cells to MK-2206. and found reduction by salinomycin of Akt and downregulation of pAkt, pGSk3beta, pTSC2, and p4EBP1 by cotreatment with MK-2206. 25185584_This study demonstrates that TSC2-deficient tumor cells are hypersensitive to oxidative stress-dependent cell death, and provide critical proof of concept that TSC2-deficient cells can be therapeutically targeted 25281918_This is the first mutation and multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) analyses of TSC2 in Korean Angiomyolipomas that focus on tuberous sclerosis complex. 25355409_A short segment of chromosome 16 encodes the tumor suppressor gene tuberin as well as the protein polycystin 1, which are responsible for tuberous sclerosis complex type 2 and autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease type 1, respectively. 25432535_Multiple mutations in TSC2 during kidney development lead to severe phenotype of multifocal renal cell carcinoma. 25476905_In TSC2-deficient angiomyolipoma patient cells, IRF7 is a pivotal factor in the Rheb/mTOR pathway. 25498131_Compared to patients with TSC1 mutations, individuals with TSC2 mutations had a significantly higher frequency of epilepsy and tended to have a higher frequency of infantile spasms. 25563326_a novel frame shift Tuberous Sclerosis Complex-2 Mutation in three patients with Tuberous sclerosis complex but with different severity of symptoms 25565629_PLK1 protein levels are increased in hamartin and tuberin deficient cells and Lymphangioleiomyomatosis patient-derived specimens, and that this increase is rapamycin-sensitive. 25654764_TSC2/mTORC1 signaling contributes to the maintenance of intestinal epithelium homeostasis by regulating Notch activity. 25724664_Data shows frequent loss of TSC2 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HCC) and that TSC2-null cell lines were more sensitive to mTOR inhibition by everolimus suggesting that TSC2 loss is a predictive biomarker for the response to everolimus in HCC patients. 25780943_these results demonstrate that TSC2-deficient cells have enhanced choline phospholipid metabolism and reveal a novel function of the TSC proteins in choline lysoglycerophospholipid metabolism 25782670_Results confirm strong association between TSC2 mutation and angiomyolipoma burden, and they indicate that everolimus response occurs regardless of mutation type or location or when no mutation in TSC1 or TSC2 has been identified. 25927202_previously unidentified TSC1 and TSC2 mutations in tuberous sclerosis complex 25972538_pUL38 can activate mTORC1 in both TSC2-dependent and -independent manners. 26252095_A novel frame-shifting mutation c.4258-4261delTCAG in the TSC2 gene is associated with tuberous sclerosis in a Chinese family. 26318033_AKT3 has a role in prostate cancer proliferation through regulation of Akt, B-Raf, and TSC1/TSC2 26393489_Tuberous sclerosis is a syndrome caused by dominant mutations in Tuberin (TSC2),causing Autism spectrum disorder - like behaviors, seizures, intellectual disability and characteristic brain and skin lesions. 26408672_IQ/DQ correlates inversely with predicted levels and/or deleterious biochemical effects of mutant TSC1 or TSC2 protein in tuberous sclerosis complex. 26412398_PAK2 is a direct effector of TSC1-TSC2-RHEB signaling and a new target for rational drug therapy in TSC. 26540169_TSC-related tumors can increase the mutation detection rate, indicate that it is not likely that a third TSC gene exists, and enable provision of genetic counseling to the substantial population of TSC individuals who are currently NMI 26563443_results confirm the consistent finding of TSC2 mutations in LAM samples, and highlight the benefit of laser capture microdissection and in-depth allele analyses for detection, such as NGS 26703369_Our evidence suggests that variants in TSC2 exons 25 or 31 are very unlikely to cause classical TSC, although a role for these exons in tissue/stage specific development cannot be excluded. 26728384_Data show that 10 pathogenic mutations were quickly identified, 7 were located in tuberous sclerosis 1 protein (TSC1) and 3 were observed in tuberous sclerosis 2 protein (TSC2). 26742086_By interfering with TSC-Rheb complex, arginine relieves allosteric inhibition of Rheb by TSC. Arginine cooperates with growth factor signaling which further promotes dissociation of TSC2 from lysosomes and activation of mTORC1. 26831717_Mutations in MTOR, TSC1, or TSC2 were more common in patients who experienced clinical benefit from rapalogs than in those who progressed. 26868506_Lysosomal recruitment of TSC2 is a universal response to stimuli that inactivate | ENSMUSG00000002496 | Tsc2 | 515.090909 | 0.8203626 | -0.285666290 | 0.26442198 | 1.16306316095 | 0.2808311725264284741676590329007012769579887390136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.51256086133868494769671997346449643373489379882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 417.434009 | 89.552830 | 508.904539 | 109.071310 | |
| ENSG00000103222 | 4363 | ABCC1 | protein_coding | P33527 | FUNCTION: Mediates export of organic anions and drugs from the cytoplasm (PubMed:7961706, PubMed:16230346, PubMed:9281595, PubMed:10064732, PubMed:11114332). Mediates ATP-dependent transport of glutathione and glutathione conjugates, leukotriene C4, estradiol-17-beta-o-glucuronide, methotrexate, antiviral drugs and other xenobiotics (PubMed:7961706, PubMed:16230346, PubMed:9281595, PubMed:10064732, PubMed:11114332). Confers resistance to anticancer drugs by decreasing accumulation of drug in cells, and by mediating ATP- and GSH-dependent drug export (PubMed:9281595). Hydrolyzes ATP with low efficiency (PubMed:16230346). Catalyzes the export of sphingosine 1-phosphate from mast cells independently of their degranulation (PubMed:17050692). Participates in inflammatory response by allowing export of leukotriene C4 from leukotriene C4-synthezing cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35379, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10064732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11114332, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16230346, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17050692, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7961706, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9281595}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Deafness;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lipid transport;Membrane;Non-syndromic deafness;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra-and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This full transporter is a member of the MRP subfamily which is involved in multi-drug resistance. This protein functions as a multispecific organic anion transporter, with oxidized glutatione, cysteinyl leukotrienes, and activated aflatoxin B1 as substrates. This protein also transports glucuronides and sulfate conjugates of steroid hormones and bile salts. Alternatively spliced variants of this gene have been described but their full-length nature is unknown. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. | hsa:4363; | apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; lateral plasma membrane [GO:0016328]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ABC-type glutathione S-conjugate transporter activity [GO:0015431]; ABC-type transporter activity [GO:0140359]; ABC-type vitamin B12 transporter activity [GO:0015420]; ABC-type xenobiotic transporter activity [GO:0008559]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATPase-coupled inorganic anion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0043225]; ATPase-coupled lipid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0034040]; ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042626]; carboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0046943]; efflux transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015562]; glutathione transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0034634]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787]; xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042910]; carboxylic acid transmembrane transport [GO:1905039]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cellular response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904646]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; cobalamin transport [GO:0015889]; export across plasma membrane [GO:0140115]; glutathione transmembrane transport [GO:0034775]; heme catabolic process [GO:0042167]; leukotriene metabolic process [GO:0006691]; leukotriene transport [GO:0071716]; phospholipid translocation [GO:0045332]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; sphingolipid translocation [GO:0099039]; transepithelial transport [GO:0070633]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805]; xenobiotic transport [GO:0042908]; xenobiotic transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:1990962] | 11439001_sequence deletion in Pseudoxanthoma elasticum 11600213_Immunolabeling and dye efflux assays indicate that MRP activity and functional expression levels are elevated in monocyte-derived dendritic cells when compared to those present in parental monocytes. 11689020_polyclonal antibodies recognizing both human and rodent MRP1 11755464_MDR transpiorter proteins have a limited role in the treatment failure of patients treated with ifarubicin-based regimens 11771758_overexpression of MRP1 in DS brain may have some relevance to the disorder either by deranging substrate homeostasis or limiting drug access. 11809686_In vivo analysis of human multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1) activity using transient expression of fluorescently tagged MRP1. 11820781_Expression of MRP1 can be induced by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in a reactive oxygen species-dependent but cyclooxygenase-2-independent manner. 11925441_determination of substrate specificity 11937269_MRP1 mRNA was detected in non-HTLV-1 Tax producing ATL cell lines, but MRP1 is not activated by transfected HTLV-1 Tax expression. 11986944_no difference of expression between diagnosis and relapse of AML; not associated with clinical resistant disease in AML 11995968_Antisense hairpin loop oligonucleotides as inhibitors of expression of multidrug resistance-associated protein 1: their stability in fetal calf serum and human plasma 11996108_Multidrug resistance-associated protein--reduction of expression in human leukaemia cells by antisense phosphorothioate olignucleotides 12018890_rate of uptake of arsenic trioxide and of antimony tartrate in GLC4 and GLC4/ADR cells overexpressing MRP1 12034727_ATP hydrolysis causes a conformational change in MRP1 that reduces the affinity of the protein for this inhibitor 12042670_Mutations in mrp1 results in decreased organic anion transport and increased doxorubicin resistance in Hela cells 12084474_directly interacts with several tyrosine kinase inhibitors 12119019_cytoplasmic retraction of the amino terminus 12135486_S-decyl-glutathione nonspecifically stimulates the ATPase activity of the nucleotide-binding domains of the human multidrug resistance-associated protein, MRP1 (ABCC1). 12146977_evidence for the role of glycosylation in accessibility of the extracellular domains of human MRP1 12163030_Results show efficient GTP hydrolysis by the N-terminal nucleotide binding domain (NBD1) of MRP1 12186871_importance of Lys(332) and His(335) in determining substrate specificity and of Asp(336) in overall transport activity 12235150_the amino terminus of human MRP1 is important and that the Cys(7) residue plays a critical role in maintaining the proper structure and function of human MRP1 12388549_Trp residues are critical for the transport activity and substrate specificity of MRP1 12486126_MRP1 has a functional role in the maintenance of cellular folate homeostasis 12576456_RNA expression of this protein in breast cancer correlates with response to chemotherapy. 12628490_down- and up-regulation of MRP1 (and MRP3) expression can influence cellular folate homeostasis, in particular when cellular retention by polyglutamylation of folates is attenuated. 12646196_MRP1 and MRP5 increase with trophoblast maturation, suggesting a particular role for these proteins in the organ functional developmen 12653207_MRP1 does not have a role in increased resistance to oxidative stress 12783859_ATP binding at nucleotide binding domain 1 at low concentration plays a more important regulatory role than the binding at high concentration and that ATP hydrolysis at nucleotide binding domain 2 plays a dominant role in LTC4 transport. 12856092_A novel silent mutation G816A in exon 8 was found 12856092_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12890151_MRP1 and MRP2 were expressed in peripheral blood cells, with more than sevenfold higher MRP1 expression in all cell populations investigated. The MRP1 mRNA expression was highest in CD4+ cells >, followed by CD8+ > CD19+ > CD56+ cells. 12954082_Trp653 is involved in the binding of ATP to the nucleotide-binding domain 1 of multidrug-resistance-associated protein 1. 12954620_importance of polar and charged amino acid residues in transmembrane helix 14 of multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1/ABCC1) 12960109_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14561746_structural data for MRP1 that might be used to elucidate its mechanism of transport 14578045_phospholipid translocation in the erythrocyte membrane depends on ATP and glutathione 14580377_Basal membrane localization of MRP1 in the placental trophoblast. 14722114_MRP1 transport function requres helices TM6, TM8, TM10, TM11, and TM14 and CL7 may play a differential role in coupling the activity of the nucleotide binding domains to the translocation of different substrates across the membrane 14737110_MRP1 may be a target for MYCN-mediated gene regulation 14984901_Refractory epilepsy phenotype in tuberous sclerosis can be associated with the expression of multidrug resistance MRP-1 transporter in epileptogenic cortical tubers. 15155846_both signature sequences of MRP1 are involved in ATP hydrolysis and must be intact for the ATP hydrolysis and the transport by MRP1. 15161912_MRP1 transports inorganic arsenic as a tri-GSH conjugate, and GSTP1-1 may have a synergistic role in this process 15208328_Glu(1204) serves a dual role in membrane expression of MRP1 and a step in its catalytic cycle subsequent to initial substrate binding 15245331_MRP1 mediates ATP-dependent cellular export of unconjugated bilirubin and supports its role in protecting cells from bilirubin toxicity 15252017_suggest that the conserved glycine residues in both LSGGQ segments are part of the conformational network, which is responsible for the accelerated hydrolytic activity upon interaction of the protein with its transported substrates 15269137_MRP1 gene undergoes alternative splicing at a higher frequency in ovarian tumors than in matched normal tissues, and some of these splice variants confer resistance to doxorubicin. 15355964_properties of multidrug resistance protein 1 are altered by mutation of the aromatic amino acid interacting with adenine moiety of ATP to a polar residue 15472893_MRP1 overexpression is associated with DNA aneuploid carcinomatous cells in non-small cell lung canc 15623154_analysis of nucleotide binding domains and conformation of MRP1 15628876_Hgh-resolution map of leukotriene c4 binding domains in MRP1 and first direct evidence for LTC(4) binding. 15810950_For accurate assessment of changes in MRP1 expression between tumour and normal tissues both protein and mRNA detection are necessary. 15856298_Altered MRP1 levels is associated with intrinsic treatment resistance of non-small cell lung cancer 16014004_The interaction between the 2 nucleotide binding domains of MRP1 and the effects of their binding properties on its ATPase activity are reported. 16041239_ABCB1, ABCC1, ABCC2, and ABCG2 haplotypes influence response to nelfinavir 16041239_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16041243_analysis of MRP1/ABCC1 variants, none of which are likely by themselves to have major deleterious effects in healthy individuals 16156793_Plant flavonoids were able to reverse drug resistance in human cells transfected with ABCC4; direct inhibition of MRP1-mediated [3H]dinitrophenyl S-glutathione in inside-out vesicles prepared from human erythrocytes was observed. 16230346_cluster of basic amino acids at the TM15/CL7 interface are important for both MRP1 expression and activity and each of the three residues plays a distinct role in the substrate specificity and catalytic activity of the transporter 16278376_ABCB1, ABCC1, and ABCG1 are expressed differently in gastric and nongastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors and do not impair the initial response of the tumor to imatinib 16293801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16330681_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16410721_it is concluded that CIAPIN1 confers multidrug resistance in gastric cancer cells, likely by upregulating MDR-1 and MRP-1 16464259_A novel polymorphism in the 5'UTR of the MRP1 gene. 16464259_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16481346_expression of MRP1 on resting and activated human T cells, and T cell activation dependence upon MRP1 function 16547352_MRP1 expression and its localization in detergent-resistant membranes were not affected by ganglioside depletion. 16551273_mutations of the Walker A lysine residue, K684L and K1333L, alter tertiary structure; the mutations alter ATP binding and hydrolysis 16565074_GSH has a role in estrone sulfate binding and translocation by the multidrug resistance protein 1 16621983_MRP1 seems to fulfill an important physiological role in dendritic cells development and dendritic cells functions 16697012_the first high-resolution crystal structure of human MRP1 nucleotide binding domain 1. 16784241_Taken together, these results suggest that glutathione conjugation and MRP1-mediated conjugate transport can attenuate nitrolinoleic acid (LNO(2)) bioactivity and thereby play important roles in the regulation of cellular signaling by LNO(2). 16821592_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16883578_results indicate that two K+ currents (MaxiK and Kv) and the organic anion transporter MRP1 are reciprocally expressed in H69 and H69AR cells 16914551_the ABCC1 amino terminus has a U-shaped folding with a gating function 16946557_The mRNA induction of MDR1, MRP1, MRP2 and MRP3 by rifampicin (Rif), dexamethasone (Dex) and omeprazole (Ome) was investigated in primary cultures of cryopreserved human and rat hepatocytes. 16960658_Data show that tetrahydrocurcumin inhibits the efflux function of ABCB1, ABCC1, and ABCG2 and it is able to extend the multidrug resistance reversing activity of curcuminoids in vivo. 17033200_In locally advanced breast cancer, ABC1 gene expression during chemotherapy dos not contribute to clinical unresponsiveness. 17050692_Transport of sphingosine-1-phosphate by ABCC1 influenced migration of mast cells toward antigen but not degranulation 17203221_MDR1 expression, MRP1 expression, and MRP7 expression are refractory factors in head and neck cancer chemotherapy; induction of MRP7 expression is involved in drug resistance to natural products, especially to docetaxel in salivary gland adenocarcinoma 17215852_PI3K/Akt activation may lead to the development of chemoresistance in AML blasts through a mechanism involving a p53-dependent suppression of MRP1 expression. 17264072_the amino-terminal membrane-spanning domain of human ABCC1/MRP1 has a role in regulation of function by dimerization 17295059_The molecular mechanism of ATP-dependent solute transport by MRP1 is addressed. 17336270_Triton X-100 extraction of detergent-resistant membranes provide evidence that MRP1 is not located in raft-like structures and that its activity is downregulated by cholesterol 17350479_Data suggest that the increase in MRP1 gene dosage observed in drug resistant leukemic cell lines is not responsible for the upregulation of MRP1 expression in leukemic patients. 17445775_MRP1 was significantly hypersensitive against KP772. 17494643_MRP1-Pro(1150), MRP2-Pro(1158), and MRP3-Pro(1147) in the cytoplasmic loop 7 differ in their influence on substrate specificity but share a common role in the nucleotide interactions at nucleotide binding domain 2 of these transporters. 17596751_Retinoblastoma intrinsically expresses both P-gp and MRP-1 and their expressions are not related to tumor differentiation. The expressions of P-gp and MRP-1 do not seem to be induced by chemotherapy and are not related to the degree of tumor invasion. 17606722_neither MRP1 nor MRP2 appears to have a role in response to cisplatin-based chemotherapy in resected non-small cell lung cancer 17710652_Results identified MRP1 as the major transporter of BCPCF in the human erythrocyte membrane and showed for the first time that the active transport of fluorescent substrate into inside-out vesicles can be monitored by flow cytometry. 17852453_The expression analyses of MRP1 and MDR1 drug efflux proteins in doxorubicin-sensitive and -resistant HL60 cells revealed that there was an upregulation of MRP1 gene in HL60/DOX cells as compared to parental sensitive cells. 17875533_statistically significant correlations between MRP1 and LRP expression and between MRP1 or LRP expression and MDR1 expression 17890284_This study showed that manipulation of drug efflux transporters may be a useful strategy for increasing the intracellular concentration and thereby enhancing the clinical efficacy of lopinavir. 17925548_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17980150_comparative modeling has been used to generate models of human MRP1 18038766_induction of ABCC2 and ABCG2 by tBHQ is mediated by the Nrf2/Keap1 system, whereas the induction of ABCC1 may involve a Keap1-dependent but Nrf2-independent mechanism. 18056276_Infection with Sb-resistant (Sb r) L. donovani induces the upregulation of MRP1 and P-gp in host cells, resulting in a nonaccumulation of intracellular Sb following treatment with sodium antimony gluconate (SAG) favoring parasite replication. 18200595_Determination of P-glycoprotein, MDR-related protein 1, breast cancer resistance protein, and lung-resistance protein expression in leukemic stem cells of acute myeloid leukemia. 18204073_Expression of MRP1 in breat cancer cells greatly reduces sulforaphane accumulation. 18256692_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18280247_These results suggest that guggulsterone, a natural dietary hypolipidemic agent have dual inhibitory effects on P-gp and MRP1 and the potencies to cause food-drug interactions. 18316614_MRP-overexpressing teniposide-resistant T-cell lymphoma xenografts are inhibited by a tubulin-binding agent 18336795_The functional role of Proline1150 in ABCC1 is investigated. 18381794_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18400250_MRP1 expression can be used as a molecular risk factor and guide for chemotherapeutic regimens in patients with advanced stages of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 18439156_Expression and localization MRP1 were significantly higher in hepatoid than in control adenocarcinoma 18621020_Results demonstrate that basal and apoptotic glutathione release are markedly enhanced in cells overexpressing multidrug resistance-associated protein 1. 18680196_Results compare the relative amounts of ABCb1 (Pgp) and ABCc1 (Mrp1)at the blood-brain and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers, located respectively at the brain capillary endothelium and the choroid plexus epithelium. 18690847_Celecoxib upregulates MRP1 in colon cancer and results in lack of synergy with standard chemotherapy. 18702307_in prostate cancer cells at least two mechanisms of drug resistance are interconnected. PTEN and mTOR signaling were shown: to be involved into regulation of MRP1 and BCRP 18711657_findings suggest that high MRP1 expression was associated with poor clinical outcome and was correlated with the M5 subtype and poor cytogenetic subgroups among AML patients but not among ALL patients. 18713069_MRP1-deficient cells accumulated significantly more UCB and suffered greater cytotoxicity than controls. 18775981_Results suggest that Tyr(440) of MRP1 makes a major contribution to recognition of GSH and the GSH moiety of conjugates such as LTC4. 18799096_the expression of MRP(multiple drug resistance-associated protein)1, MRP2, and MRP3 molecules in systemic lupus erythematosus mononuclear cells was not different from normal 18838379_MRP1 protects intestinal epithelial cells against inflammation-induced apoptotic cell death and provides a functional role for MRP1 in the inflamed intestinal epithelium of IBD patients. 18851956_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18924151_doxorubicin but not daunorubicin challenged-MRP1 overexpressing HL-60 cells have elevated cytosolic pH 19019175_Although expression of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase is a significant prognostic factor in diagnosis and prediction of chemotherapy effects in glioblastoma, neither Mrp-1 nor P-glycoprotein expression is a prognostically significant factor. 19063607_the rate of release of ADP bynucleotide binding domain 1 in the D793E background may be the rate-limiting step in the transport cycle of MRP1. 19065772_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19065772_high expression of MRP1 was associated with the MDR phenotype in both acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. 19067123_Pharmacogenomics approach reveals MRP1 (ABCC1)-mediated resistance to geldanamycins. 19107762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19107762_The current study demonstrated that common polymorphisms in the 3' untranslated region of ABCB1 and ABCC1 may contribute to the etiology of lung cancer. 19129072_ABCC1 gene did not have a significant influence on either disease-free or overall survival in patients with locally advanced breast cancer 19165709_ABCC1 immunostaining was prominent early in the choroid plexus and ventricular ependyma, and noted later in large pyramidal neurons in infants born at 22 (0/7)-42 (0/7) weeks of gestation. 19214143_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19214144_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19214144_The allelic frequency of the Arg723Gln mutation is relatively higher than other SNPs in mainland Chinese population and therefore this mutation significantly reduces MRP1/ABCC1 activity in multidrug resistance. 19235593_MRP1 overexpression can mediate Multidrug resistance in patients. 19285030_results suggest a direct interaction mediated by GST between the two NBDs of MRP1 leading to conformational changes which would enhance its ATPase activity 19291917_We were able to show a significant correlation between the expression of the multidrug resistant protein (P-gp and MRP1) and their functional activity in adult AML and paediatric ALL samples. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19349540_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19393132_61 % of renal cell carcinoma samples revealed positive results for MRP1. 19438741_In summary, in patients with primary ovarian cancer, overexpression of MRP1 is an adverse marker for patient outcome and cancer aggressiveness. 19513507_The overexpression of ABCC1 and gankyrin contribute to arsenic trioxide resistance in liver and gastric cancer cells. 19552816_Although these findings do not prove a causal role, the high frequency of tumours expressing these efflux pumps suggests that they may be important contributors to the chemoresistance of this tumour type. 19622290_High expression of MDR1, MRP1, ABCG2 proteins in gastric cancer is related with the resistance to epirubicin. 19636555_Data revealed that high FPGS gene expression, low GGH gene expression and low ABCC1 gene expression in CRC tissues were predictive factors for a high reduced folate level after LV administration. 19672972_expression levels below the median of the ABCG2 and ABCC1 genes were associated with a greater chance of death due to treatment toxicity for the high-risk group 19687781_ABCC1 polymorphisms contribute to level and decline of lung function. 19687781_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19723058_Results suggest that 15d-PGJ(2) induces MRP1 upregulation via Nrf2-ARE signaling. 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19875192_mRNA expression predicts chemotherapy response and survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer who received neoadjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy 19883630_findings demonstrating the involvement of miR-326 in multidrug resistance mediated by MRP-1 provide new evidence about the roles of microRNAs determining MDR development of tumor cells 19885582_cyclooxygenase-2 and ABC-transporters MRP1, MRP2 and BCRP may have roles in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas 19897579_Identification of multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1/ABCC1) as a molecular gate for cellular export of cobalamin. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19924384_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19940267_Results identify key membrane transporters OATP2B1, MRP1, MRP4, and MRP5 as modulators of skeletal muscle statin exposure and toxicity. 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19956635_Uncategorized study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19969351_Lucena cells showed an over-expression of the ABCB1 gene and a high expression of the Oct-4, ABCG2 and ABCC1 genes as compared to K562 cells. 19969624_Patients expressing both lung resistance protein and multidrug resistance-related protein genes had poorer outcomes and had worse 2-year survivalts. 20004175_This experimental study suggests an interfacial location for both transmembrane (TM) TM16 and TM17 of multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 in membrane mimics. 20093746_Data suggest that direct interactions between tumour and normal cells influence the expression of HSP27, HSP72 and MRP, and alter IL-6 and NO production. 20109555_Using electron cryomicroscopy of 2D crystals, data at 1/6per A(-1) resolution was generated for the full-length ABCC1 protein in the absence of ATP 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20200426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20233511_Higher positive expression of multiple drug resistance-associated protein is associated with multidrug resistance in gastric cancer. 20234362_contributors to the inherent aggressive and resistant nature of malignant melanoma. 20388502_Etoposide intervention glioblastoma stem-like cells showed a stronger resistance to apoptosis and deat hand MRP1 appeared to be related with transporting chemotherapeutics out of glioblastoma stem-like cells. 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20487524_Link MRP1 SNPs with lung function and inflammatory markers in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients, suggesting a role of MRP1 SNPs in the severity of COPD in addition to their association with MRP1 protein level in bronchial biopsies. 20487524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20520284_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20520284_Polymorphisms in multidrug resistance-associated protein-1 (MRP1) are associated with response to citalopram treatment in patients with major depressive disorder. 20530282_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20532504_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20604746_Data suggest that extensive sphingolipid depletion does not affect the function of the lipid-raft-associated protein MRP1. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20689807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20922799_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21090806_It appears that the hydrophobicity of transmembrane segment 5 and the length of extracellular loop 3 but not their amino acid sequences contribute to ABCC1 dimerization. 21143841_HIF-1alpha and MRP1 may play a role in the multidrug resistance of chordoma to chemotherapy. 21177244_data demonstrate the multiple roles for cytoplasmic loop CL5 in the membrane expression and function of MRP1 21182225_Data show that the MRP1 -1666GG genotype predicted a worse outcome and was an independent predictor of poor survival in patients with HCC from Southeast China. 21315686_MRP1 has higher affinity for Mn.ATP than for Mg.ATP and the Mn.ATP-dependent leukotriene-C4 transport activities of Q713N/Q1375N and Q713M/Q1375M are significantly higher than that of wtMRP1 21317832_ABCC1 G2012T single nucleotide polymorphism altered stability of the ABCC1 gene transcript and associated with patient outcome in primary neuroblastoma and altered stability of the ABCC1 gene transcript. 21435954_cystic fibrosis patients with the rare CC genotype were chronically colonized by Pseudomonas around 6 years earlier (mean +/- SD: 11.2 year +/- 7.8, 95% CI for the mean: 5.7-16.8) than those with the GG or the CG alleles 21520403_P-glycoprotein expression was more frequently observed in early chronic (P = 0.00) and in advanced (P = 0.02) chronic myeloid leukemia phases when it was compared to MRP1 expression 21609321_This study showed that nearly complete oxidation of free cholesterol in the plasma membrane of MRP1-expressing baby hamster kidney cells did not affect MRP1 localization in lipid rafts or its efflux function. 21701864_orientation of transmembrane fragments 4 and 10 from hMRP1/ABCC1 in membrane mimics 21736601_The Arg723Gln (2168G > A) polymorphism of ABCC1 appears to be a potential susceptibility marker for lung cancer in the Chinese population. 21793937_results suggest that the high expression of MRP1 in patients with tongue carcinoma indicates that intrinsic drug resistance may exist in tongue carcinoma, and is associated with tumor differentiation and cisplatin resistance in tongue carcinoma. 21799180_Inhibition of ABCC1 statistically significantly inhibited neuroblastoma development in hMYCN transgenic mice. Suppression of ABCC1 in vitro inhibited wound closure & clonogenicity. 21929509_The ABCC1 rs3743527TT genotype and rs3743527TT-rs246221TC/TT genotype combination were associated with lower LVFS (left ventricular fractional shortening) after chemotherapy. 21956451_ABCB1/MDR1, ABCC1/MRP1 and ABCG2/BCRP expression correlated with pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis and drug resistance in a mechanism that is independent of promoter methylation 22026728_Up-regulation of MRP1 transgenic expression only in neurons causes resistance to anti-epileptic drugs in seizure flies. 22037714_MDR1, MRP1 and BCL-2 have potential clinical relevance in adult patients with acute leukemia in the context of induction chemotherapy. 22084240_DNIC storage function of GST P1-1 and ability of MRP1 to efflux DNICs are vital in protection against NO cytotoxicity 22086004_A review of recent advances in understanding the role and mechanism of MRP1/ABCC1 polymorphisms in drug resistance, disease susceptibility and severity, and prognosis prediction. 22117969_LRP and MRP play a role in multidrug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and are related to prognosis in patients with NSCLC 22143792_Notch1 regulates the expression of the multidrug resistance gene ABCC1/MRP1 in cultured cancer cells 22182917_Polymorphisms in ABCC1 are associated with multiple myeloma. 22188235_An interactive proteomics study was done to examine proteins that bind heterocomplexes with ABCC1 using coimmunoprecipitation and MS/MS analyses. We found that ATP synthase alpha binds to ABCC1 in plasma membranes with a ratio of 2:1. 22232552_the critical and complex role of CL5 for stable expression of MRP1 at the plasma membrane 22272278_Findings show that the gene expression of ATP-dependent efflux transporters MRP1, -3, -4, -5, and p-gp fluctuated during stem cell-derived retinal pigment epithelial cells (hESC-RPE) maturation. 22293538_These data suggest that decreased MRP1-dependent GS-HNE efflux contributes to increased doxorubicin toxicity in HEKG671V and potentially in individuals carrying the G671V variant. 22353810_For the first time, we have identified MRP-1 with efflux activity in human mitochondria. 22445357_We have demonstrated that vincristine resistance mediated by CD40 activation was induced by an increased expression of MRP1 by AKT signaling in human multiple myeloma cell lines. 22511347_Substitution of two of these residues with alternative amino acids has allowed us to produce an almost cysless form of DeltaMRP1 that traffics to the plasma membrane 22664042_ABCB1 and ABCC1 expression correlates with different prognostic factors in pediatric patients with acute leukemia. 22695718_CK2alpha and MRP1 interact physically, and recombinant CK2 phosphorylates MRP1-derived peptide in vitro in a Thr249-dependent manner. 22787275_collagen/beta1 integrin/ERK signaling up-regulates the expression and function of ABCC1 22798502_ABCB1 expression is limited to endothelial cells, whereas ABCC1 expression could mark a minority of tumor cells approaching a stem-like status. 22871336_Expression of ABCC1 by HRS cells in CHL patients predicts a higher risk of treatment failure and is marginally associated with poorer failure-free survival using standard frontline chemotherapy regimens. 22899102_ABCC1 mediates the basolateral and ABCC2 the apical excretion of BPDE glutathione conjugates in human Caco-2 cells. 22925562_Immunohistochemical detection of the expression of MRP1 and wild-type p53 at the time of diagnosis might assist in choosing specific chemotherapeutics to improve prognosis and therapy. 22982023_This is the first study showing significant associations of a higher MRP1 protein expression with less accelerated FEV1 decline in COPD patients using long-term therapy with inhaled corticosteroids 23052202_expression of MRP1 may lead to HL-60 cells resistance to trivalent arsenic compounds. 23178537_MRP1 activity as an efflux pump is increased after long term (7 days) myriocin treatment. 23396606_Genetic variability in ABCC1 is associated with severe hematological toxicity induced by combined chemotherapy protocol. 23580527_study found a cytomegalovirus UL138-mediated loss of cell surface MRP1 and reduction of substrate export by MRP1; cytomegalovirus latency-associated loss of MRP1 and accumulation of vincristine, an MRP1 substrate, depleted virus from naturally latent progenitors all of which are in vivo sites of latency 23667609_Nrf2-idant response elements pathway is required for the regulatory expression of Mrp1. 23686318_The change of ABCC1 protein expression was associated with an alternation in mRNA expression. 23765166_results demonstrated that VEGF enhanced the expression of MRP1, and the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and SP1 may be involved in this modulation 23799853_cell membrane expression of MRP-1 or loss of exon 9 is predictive of outcome in Ewing's sarcoma family of tumours but not the number of splicing events or expression of Pgp 23896815_ABCB1, ABCC1, and ABCC2 single nucleotide polymorphisms are associated with Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS) score after traumatic brain injury. 23917219_The study reports the acquisition and dissemination of functional MRP1 via microparticle mediated intercellular transfer. 23996099_A significant association was detected between genetic polymorphisms of ABCB1 and ABCC1 with virological failure of first-line antiretroviral regimens containing protease inhibitors, when controlled by clinical factors, such as sex, age and race. 24013781_Nuclear MRP1 contributes to multidrug-resistance mainly through regulating MDR1 expression in mucoepidermoid carcinoma. 24024181_These results suggest that in epithelial ovarian cancer, ABCC1/MRP1 may be a marker for aggressiveness because its expression was associated with tumor grade and support that ABCC4/MRP4 may play an unfavourable role in disease outcome. 24030729_High expression of MRP-1 significantly influences overall survival in acute myeloid leukemia. 24080162_Six in silico analyses co | ENSMUSG00000023088 | Abcc1 | 464.855088 | 0.7665156 | -0.383612980 | 0.07563033 | 25.77754563801 | 0.0000003831198307554563218483168612893408067066047806292772293090820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000683556147016240208113277768142701518172543728724122047424316406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 382.334357 | 18.138250 | 501.181816 | 22.539428 | |
| ENSG00000103549 | 9810 | RNF40 | protein_coding | O75150 | FUNCTION: Component of the RNF20/40 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex that mediates monoubiquitination of 'Lys-120' of histone H2B (H2BK120ub1). H2BK120ub1 gives a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional activation and is also prerequisite for histone H3 'Lys-4' and 'Lys-79' methylation (H3K4me and H3K79me, respectively). It thereby plays a central role in histone code and gene regulation. The RNF20/40 complex forms a H2B ubiquitin ligase complex in cooperation with the E2 enzyme UBE2A or UBE2B; reports about the cooperation with UBE2E1/UBCH are contradictory. Required for transcriptional activation of Hox genes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16307923, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19410543}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Coiled coil;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. | The protein encoded by this gene contains a RING finger, a motif known to be involved in protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions. This protein was reported to interact with the tumor suppressor protein RB1. Studies of the rat counterpart suggested that this protein may function as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase, and facilitate the ubiquitination and degradation of syntaxin 1, which is an essential component of the neurotransmitter release machinery. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2011]. | hsa:9810; | axon terminus [GO:0043679]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; HULC complex [GO:0033503]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000151]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; syntaxin-1 binding [GO:0017075]; ubiquitin conjugating enzyme binding [GO:0031624]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; histone H2B conserved C-terminal lysine ubiquitination [GO:0071894]; histone H2B ubiquitination [GO:0033523]; histone monoubiquitination [GO:0010390]; positive regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process [GO:1901800]; positive regulation of protein polyubiquitination [GO:1902916]; response to peptide hormone [GO:0043434]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] | 12121982_Functional Analysis of the rat counterpart 16307923_Formation of trimeric complex UbcH6 and RNF20/40 with PAF stimulates histone 2B monoubiquitination activity in vitro 20738173_the observed defects in the radiation response of Bre1a/b-deficient cells 21827756_Studies indicate that H2B monoubiquitylation is driven primarily by an E3 ubiquitin ligase composed of the two RING finger proteins RNF20 and RNF40. 22031019_RNF40 cooperates with SUPT16H to induce dynamic changes in chromatin structure during DNA double-strand break repair. 22155569_our results suggest that RNF20 and RNF40, either via ubiquitylation of H2B or other targets, are coupled to the proliferation of prostate cancer cells. 22354749_We show that Bre1 (human BRE1A/B (RNF20/40) and mouse Bre1a/b (Rnf20/40)) acts as an important suppressor of chromosomal instability 27557628_the RNF20/40 complex, a major ubiquitin ligase catalysing histone H2B monoubiquitination, interacts with the motor protein Eg5 during mitosis and participates in spindle assembly. 27569044_The authors also show that the RING domains of RNF20 and RNF40 can form a stable heterodimer that is active. 27798111_Manipulation of key H2Bub1 E3 ubiquitin ligases, RNF20, RNF40 and BRCA1, in ovarian cancer cell line models modulated H2Bub1 levels, indicative of the role of these RING finger ligases in monoubiquitination of H2Bub1 in vitro 30321325_Our findings suggest that RNF40 plays a central role in the maintenance of tumorigenic features and inflammatory signaling by promoting nuclear NF-kappaB activity. 30649429_Cooperative physical interactions among eEF1BdeltaL, RNF20/40, and HSF1 synergistically promote expression of heat shock-responsive genes. In addition, eEF1BdeltaL is a novel ubiquitylation target of RNF20/40 and elucidating its function. This provides a molecular mechanism for the cooperative function of distinct transcription factors in heat shock-responsive gene transcription. 31152661_The RNF20/40 complex regulates p53-dependent gene transcription and mRNA splicing. 31266541_Findings reveal that RNF40 is essential for maintaining tumorigenic features of colorectal cancer cells in vitro by controlling the expression of genes encoding central apoptotic regulators. 32341358_The H2B ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF40 is required for somatic cell reprogramming. 33070155_The histone H2B ubiquitin ligase RNF40 is required for HER2-driven mammary tumorigenesis. 33199825_Epigenetic modification and a role for the E3 ligase RNF40 in cancer development and metastasis. | ENSMUSG00000030816 | Rnf40 | 691.133416 | 0.8436495 | -0.245284348 | 0.10228577 | 5.74042844622 | 0.0165787479699098828922476656089202151633799076080322265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.07242458669678308869066540864878334105014801025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 621.233799 | 44.012915 | 740.047297 | 52.286603 |
| ENSG00000103966 | 30844 | EHD4 | protein_coding | Q9H223 | FUNCTION: ATP- and membrane-binding protein that probably controls membrane reorganization/tubulation upon ATP hydrolysis. Plays a role in early endosomal transport. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17233914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18331452}. | Acetylation;ATP-binding;Calcium;Cell membrane;Endosome;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | Enables cadherin binding activity. Involved in endocytic recycling and protein homooligomerization. Located in endoplasmic reticulum and recycling endosome membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:30844; | early endosome [GO:0005769]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; endosomal transport [GO:0016197]; pinocytosis [GO:0006907]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; regulation of endocytosis [GO:0030100] | 18331452_EHD4 is involved in the control of trafficking at the early endosome and regulates exit of cargo toward both the recycling compartment and the late endocytic pathway. 20489164_A new class of cardiac trafficking proteins(EHD1, EHD2, EHD3, EHD4) regulates cardiac membrane protein targeting. 21187387_Retrograde signaling through Pincher-generated Trk-multivesicular bodies is distinctively refractory to signal termination by lysosomal processing 23325686_Ezrin and EHD4 appear to be involved in the ability of Nef to increase hiv-1 virus infectivity. 24019528_evidence that the functions of both EHD1 and EHD4 are primarily in TRE membrane vesiculation, whereas EHD3 is a membrane-tubulating protein. 32800345_Identification of phostensin in association with Eps 15 homology domain-containing protein 1 (EHD1) and EHD4. 32966336_Eps15 Homology Domain Protein 4 (EHD4) is required for Eps15 Homology Domain Protein 1 (EHD1)-mediated endosomal recruitment and fission. 33972531_A junctional PACSIN2/EHD4/MICAL-L1 complex coordinates VE-cadherin trafficking for endothelial migration and angiogenesis. | ENSMUSG00000027293 | Ehd4 | 1036.725907 | 1.1847960 | 0.244638706 | 0.05730055 | 18.22564861908 | 0.0000196218574052643755876307318786189171078149229288101196289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00024332494803620396007365345170114778738934546709060668945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1120.749760 | 41.135322 | 950.453393 | 35.235959 | |
| ENSG00000104043 | 79895 | ATP8B4 | protein_coding | Q8TF62 | FUNCTION: Component of a P4-ATPase flippase complex which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled to the transport of aminophospholipids from the outer to the inner leaflet of various membranes and ensures the maintenance of asymmetric distribution of phospholipids. Phospholipid translocation seems also to be implicated in vesicle formation and in uptake of lipid signaling molecules (Probable). {ECO:0000305}. | ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Golgi apparatus;Lipid transport;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | This gene encodes a member of the cation transport ATPase (P-type) family and type IV subfamily. The encoded protein is involved in phospholipid transport in the cell membrane. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]. | hsa:79895; | Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; phospholipid-translocating ATPase complex [GO:1990531]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity [GO:0140326]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; phospholipid translocation [GO:0045332] | 17998437_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26473621_ATP8B4 gene was associated with a significant increase in the risk of systemic sclerosis. ATP8B4 is overexpressed in systemic sclerosis patients. 28141915_Study did not find statistically significant differences in the frequency of the ATP8B4 rs55687265*C allele between the SSc patients and controls. 30664179_Study found that circATP8B4 in extracellular vesicles isolated from radioresistant U251 glioma cells acts as a U251 miR766 sponge, which may be involved in glioma radioresistance. | ENSMUSG00000060131 | Atp8b4 | 878.254800 | 0.8948978 | -0.160205126 | 0.06430326 | 6.20581733535 | 0.0127331140908713003057073365198448300361633300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.05950912125062070290315574538908549584448337554931640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 801.471489 | 68.175083 | 898.601616 | 76.231304 | |
| ENSG00000104164 | 26258 | BLOC1S6 | protein_coding | Q9UL45 | FUNCTION: Component of the BLOC-1 complex, a complex that is required for normal biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles (LRO), such as platelet dense granules and melanosomes. In concert with the AP-3 complex, the BLOC-1 complex is required to target membrane protein cargos into vesicles assembled at cell bodies for delivery into neurites and nerve terminals. The BLOC-1 complex, in association with SNARE proteins, is also proposed to be involved in neurite extension. May play a role in intracellular vesicle trafficking, particularly in the vesicle-docking and fusion process. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17182842, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21998198}. | Albinism;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | The protein encoded by this gene may play a role in intracellular vesicle trafficking. It interacts with Syntaxin 13 which mediates intracellular membrane fusion. Mutations in this gene cause symptoms associated with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome-9. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. A pseudogene related to this gene is located on the X chromosome. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015]. | hsa:26258; | axon cytoplasm [GO:1904115]; BLOC-1 complex [GO:0031083]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043227]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; syntaxin binding [GO:0019905]; anterograde axonal transport [GO:0008089]; anterograde synaptic vesicle transport [GO:0048490]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; endosome to melanosome transport [GO:0035646]; intracellular transport [GO:0046907]; melanocyte differentiation [GO:0030318]; melanosome organization [GO:0032438]; melanosome transport [GO:0032402]; membrane fusion [GO:0061025]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; positive regulation of natural killer cell activation [GO:0032816]; positive regulation of pigment cell differentiation [GO:0050942]; secretion of lysosomal enzymes [GO:0033299]; synaptic vesicle docking [GO:0016081] | 12191018_role in biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles 12576321_no defects in the known components of pallidin-muted complex (BLOC-1)have been identified in 142 patients with HPS, suggesting that BLOC-1 function may be critical in humans. 23750231_Mecp2 regulates the expression of components belonging to the dysbindin interactome 26288249_Results from a study on gene expression variability markers in early-stage human embryos shows that BLOC1S6 (PLDN) is a putative expression variability marker for the 3-day, 8-cell embryo stage. 28075530_PLDN is a direct target of RUNX1 and its dysregulation is a mechanism for platelet dense granule deficiency associated with RUNX1 haplodeficiency | ENSMUSG00000005804 | Bloc1s6 | 605.635127 | 1.0565599 | 0.079374503 | 0.06694548 | 1.40547970325 | 0.2358082400280088475330586561540258117020130157470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.45970858040407536204696725690155290067195892333984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 602.723985 | 26.292483 | 572.903365 | 25.040918 | |
| ENSG00000104894 | 951 | CD37 | protein_coding | P11049 | Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily, also known as the tetraspanin family. Most of these members are cell-surface proteins that are characterized by the presence of four hydrophobic domains. The proteins mediate signal transduction events that play a role in the regulation of cell development, activation, growth and motility. This encoded protein is a cell surface glycoprotein that is known to complex with integrins and other transmembrane 4 superfamily proteins. It may play a role in T-cell-B-cell interactions. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:951; | extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886] | 14978098_CD37 cross-linking on human T cells transduces signals that lead to complete inhibition of CD3-induced T cell proliferation. 17182550_CD37 is important for dectin-1 stabilization in APC membranes and controls dectin-1-mediated IL-6 production. 17440052_provide strong justification for CD37 as a therapeutic target and introduce small modular immunopharmaceuticals as a novel class of targeted therapies for B-cell malignancies 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20709950_In the absence of both CD37 and Tssc6, immune function is further altered when compared with CD37- or Tssc6-deficient transgenic mice, demonstrating a complementary role for these two molecules in cellular immunity. 22624718_Identify two tyrosine residues in tetraspanin CD37 directly mediating transduction of survival and apoptotic signals. 23883821_Data indicate that enhanced antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) is observed against chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and is sustained at concentrations of SMIP-016(GV) as low at 5E(-6) microg/mL on cells expressing minimal CD37 antigen. 24445867_The CD37-targeted antibody-drug conjugate IMGN529 is highly active against human CLL and in a novel CD37 transgenic murine leukemia model. 25934707_Data indicate that cell differentiation antigen 37 (CD37) is well expressed and a potential drug target in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). 27760757_CD37 is a critical determinant of rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 30089630_CD37 is highly expressed in human lymphoma. 30185523_tetraspanin CD37 controls CLEC-2 membrane organization and provides new molecular insights into the mechanisms underlying CLEC-2-dependent dendritic cell migration. 30854931_Low CD37 expression is associated with brain metastasis in lung cancer. 31089249_The anti-CD37 antibody BI 836826 in relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 31366619_From a cohort of 137 primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) samples. CD37 mutations were exclusively identified in immune-privileged site-associated DLBCL (IP-DLBCL) cases but absent in non-IP-DLBCL cases. Modeling and functional analysis of CD37 missense mutations revealed loss of function by impaired CD37 protein expression at the plasma membrane of human lymphoma B cells. 32400873_CD37 high expression as a potential biomarker and association with poor outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. 35171311_CD37 expression in follicular lymphoma. | ENSMUSG00000030798 | Cd37 | 666.308254 | 1.0653823 | 0.091371257 | 0.07255422 | 1.58560129415 | 0.2079557135999612338395081678754650056362152099609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.42546212108179876087987736354989465326070785522460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 682.640021 | 26.039259 | 643.546197 | 24.256376 | ||
| ENSG00000104915 | 8677 | STX10 | protein_coding | O60499 | FUNCTION: SNARE involved in vesicular transport from the late endosomes to the trans-Golgi network. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18195106}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | This gene belongs to the syntaxin family and encodes a soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE). The encoded protein is involved in docking and fusion events at the Golgi apparatus. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2012]. | hsa:8677; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; SNARE complex [GO:0031201]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; SNAP receptor activity [GO:0005484]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; syntaxin binding [GO:0019905]; Golgi vesicle transport [GO:0048193]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; regulation of protein localization [GO:0032880]; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi [GO:0042147]; vesicle docking [GO:0048278]; vesicle fusion [GO:0006906] | 16154903_May have a hitherto unrecognized function in the trans-Golgi network-endosome boundary. 26442221_Loss of syntaxin 10 leads to defects in normal chlamydial maturation including: variable inclusion size with fewer chlamydial organisms per inclusion, fewer infectious progeny, and delayed or halted reticulate body-elementary body differentiation. | 286.565954 | 1.3780645 | 0.462643399 | 0.14040184 | 10.81266238560 | 0.0010080822815405712268577165247052107588388025760650634765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00762631419912899490010094183389810496009886264801025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 333.461334 | 30.161977 | 243.107956 | 21.939963 | |||
| ENSG00000104946 | 79735 | TBC1D17 | protein_coding | Q9HA65 | FUNCTION: Probable RAB GTPase-activating protein that inhibits RAB8A/B function. Reduces Rab8 recruitment to tubules emanating from the endocytic recycling compartment (ERC) and inhibits Rab8-mediated endocytic trafficking, such as that of transferrin receptor (TfR) (PubMed:22854040). Involved in regulation of autophagy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22854040, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24752605}. | Alternative splicing;Autophagy;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endosome;GTPase activation;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport | Predicted to enable GTPase activator activity. Involved in retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi. Located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:79735; | autophagosome [GO:0005776]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi [GO:0042147] | 22854040_Optineurin acts as an adaptor to bring together Rab8 and its GTPase-activating protein TBC1D17. 24569479_Demonstrate that TBC1D15 and TBC1D17 mediate proper autophagic encapsulation of mitochondria by regulating Rab7 activity at the interface between mitochondria and isolation membranes. 34045668_AMPK-mediated phosphorylation enhances the auto-inhibition of TBC1D17 to promote Rab5-dependent glucose uptake. | ENSMUSG00000038520 | Tbc1d17 | 577.880613 | 0.7746923 | -0.368304679 | 0.09051866 | 16.54872391262 | 0.0000474158830514973886880759901263360234224819578230381011962890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00052764786962955089084925663911462834221310913562774658203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 491.106181 | 28.079048 | 636.899460 | 35.022551 | |
| ENSG00000105176 | 8725 | URI1 | protein_coding | O94763 | FUNCTION: Involved in gene transcription regulation. Acts as a transcriptional repressor in concert with the corepressor UXT to regulate androgen receptor (AR) transcription. May act as a tumor suppressor to repress AR-mediated gene transcription and to inhibit anchorage-independent growth in prostate cancer cells. Required for cell survival in ovarian cancer cells. Together with UXT, associates with chromatin to the NKX3-1 promoter region. Antagonizes transcriptional modulation via hepatitis B virus X protein.; FUNCTION: Plays a central role in maintaining S6K1 signaling and BAD phosphorylation under normal growth conditions thereby protecting cells from potential deleterious effects of sustained S6K1 signaling. The URI1-PPP1CC complex acts as a central component of a negative feedback mechanism that counteracts excessive S6K1 survival signaling to BAD in response to growth factors. Mediates inhibition of PPP1CC phosphatase activity in mitochondria. Coordinates the regulation of nutrient-sensitive gene expression availability in a mTOR-dependent manner. Seems to be a scaffolding protein able to assemble a prefoldin-like complex that contains PFDs and proteins with roles in transcription and ubiquitination. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Oncogene;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase inhibitor;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation | This gene encodes member of the prefoldin family of molecular chaperones. The encoded protein functions as a scaffolding protein and plays roles in ubiquitination and transcription, in part though interactions with the RNA polymerase II subunit RPB5. This gene may play a role in multiple malignancies including ovarian cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene, and a pseudogene of this gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 22. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. | hsa:8725; | chaperone complex [GO:0101031]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RPAP3/R2TP/prefoldin-like complex [GO:1990062]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; phosphatase inhibitor activity [GO:0019212]; phosphoprotein binding [GO:0051219]; protein phosphatase inhibitor activity [GO:0004864]; RNA polymerase II complex binding [GO:0000993]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; cellular response to steroid hormone stimulus [GO:0071383]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001243]; negative regulation of phosphatase activity [GO:0010923]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to virus [GO:0009615] | 14615539_a component of a signaling pathway that coordinates nutrient availability with gene expression 17936702_Data show that URI and PP1gamma are components of an S6K1-regulated mitochondrial pathway dedicated to oppose sustained S6K1 survival signaling and to ensure that the threshold for apoptosis is set based on nutrient and growth factor availability. 19450687_Is part of an RNA polymerase II-associated complex with possible chaperone activity. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21397856_Data show that URI is an 'addicting' oncogene selectively required for the survival of ovarian cancer cells with increased URI copy number. 21730289_Data show that while Art-27 can bind AR directly, URI is bound to chromatin prior to hormone-dependent recruitment of AR, suggesting a role for URI in modulating AR recruitment to target genes. 24228101_Higher level of URI/RMP expression in high-grade endometrioid adenocarcinomas compared to tissues of adjacent endometrium or gland suggests a diagnostic and possibly, a prognostic value of URI/RMP in endometrioid adenocarcinoma. 24625985_URI may have an important role in the development of multiple myeloma and chemotherapeutic resistance through activation of the IL-6/STAT3 pathway. 25453901_Results show that URI expression is essential for hepatocarcinogenesis and associated with poor survival. 25527175_High URI1 expression is associated with epithelial ovarian cancer. 25605019_RMP status in tumors may be a useful marker in estimating prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and in assisting in the selection of patients who are likely to benefit from adjuvant TACE to prevent relapse. 27105489_These findings suggest that URI1 has properties of a 'non-oncogene' that supports the oncogenic phenotype of those cancer cells that have evolved a dependency on this molecular chaperone system for survival 27505673_This work uncovers that URI-regulated OGT confers c-MYC-dependent survival functions in response to glucose fluctuations. 27582547_Amplification of 19q12 CCNE1/URI was found in 10.4% (28/270) and was significantly associated with type II endometrial cancer (EC) high grade, advanced FIGO stage, and aberrant tumor supressor p53 expression. 27780869_that KAP1 phosphorylation is decreased following recruitment of PP2A by URI. 28423737_Collectively, these findings indicate that RMP promotes Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through NF-kappaB/CSN2/Snail pathway. These results suggest that RMP and p65 may serve as potential candidates of the targets in the treatment of metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. 31739577_HBx and c-MYC are involved in URI1 expression in HCC-B. URI1 expression may play important roles in the development and progression of HCC-B because HBx and c-MYC are well-known oncogenic factors in the virus and host 34421352_URI1 suppresses irradiation-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) by activating autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. | ENSMUSG00000030421 | Uri1 | 309.065261 | 1.2167258 | 0.283004055 | 0.09980062 | 8.03479538544 | 0.0045887193418617808551851489085038338089361786842346191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.02673344696125055930391312131177983246743679046630859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 337.231341 | 23.397285 | 278.272589 | 19.432240 | |
| ENSG00000105221 | 208 | AKT2 | protein_coding | P31751 | FUNCTION: AKT2 is one of 3 closely related serine/threonine-protein kinases (AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3) called the AKT kinase, and which regulate many processes including metabolism, proliferation, cell survival, growth and angiogenesis. This is mediated through serine and/or threonine phosphorylation of a range of downstream substrates. Over 100 substrate candidates have been reported so far, but for most of them, no isoform specificity has been reported. AKT is responsible of the regulation of glucose uptake by mediating insulin-induced translocation of the SLC2A4/GLUT4 glucose transporter to the cell surface. Phosphorylation of PTPN1 at 'Ser-50' negatively modulates its phosphatase activity preventing dephosphorylation of the insulin receptor and the attenuation of insulin signaling. Phosphorylation of TBC1D4 triggers the binding of this effector to inhibitory 14-3-3 proteins, which is required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. AKT regulates also the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen by phosphorylating GSK3A at 'Ser-21' and GSK3B at 'Ser-9', resulting in inhibition of its kinase activity. Phosphorylation of GSK3 isoforms by AKT is also thought to be one mechanism by which cell proliferation is driven. AKT regulates also cell survival via the phosphorylation of MAP3K5 (apoptosis signal-related kinase). Phosphorylation of 'Ser-83' decreases MAP3K5 kinase activity stimulated by oxidative stress and thereby prevents apoptosis. AKT mediates insulin-stimulated protein synthesis by phosphorylating TSC2 at 'Ser-939' and 'Thr-1462', thereby activating mTORC1 signaling and leading to both phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and in activation of RPS6KB1. AKT is involved in the phosphorylation of members of the FOXO factors (Forkhead family of transcription factors), leading to binding of 14-3-3 proteins and cytoplasmic localization. In particular, FOXO1 is phosphorylated at 'Thr-24', 'Ser-256' and 'Ser-319'. FOXO3 and FOXO4 are phosphorylated on equivalent sites. AKT has an important role in the regulation of NF-kappa-B-dependent gene transcription and positively regulates the activity of CREB1 (cyclic AMP (cAMP)-response element binding protein). The phosphorylation of CREB1 induces the binding of accessory proteins that are necessary for the transcription of pro-survival genes such as BCL2 and MCL1. AKT phosphorylates 'Ser-454' on ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), thereby potentially regulating ACLY activity and fatty acid synthesis. Activates the 3B isoform of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE3B) via phosphorylation of 'Ser-273', resulting in reduced cyclic AMP levels and inhibition of lipolysis. Phosphorylates PIKFYVE on 'Ser-318', which results in increased PI(3)P-5 activity. The Rho GTPase-activating protein DLC1 is another substrate and its phosphorylation is implicated in the regulation cell proliferation and cell growth. AKT plays a role as key modulator of the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway controlling the tempo of the process of newborn neurons integration during adult neurogenesis, including correct neuron positioning, dendritic development and synapse formation. Signals downstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI(3)K) to mediate the effects of various growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I). AKT mediates the antiapoptotic effects of IGF-I. Essential for the SPATA13-mediated regulation of cell migration and adhesion assembly and disassembly. May be involved in the regulation of the placental development.; FUNCTION: One of the few specific substrates of AKT2 identified recently is PITX2. Phosphorylation of PITX2 impairs its association with the CCND1 mRNA-stabilizing complex thus shortening the half-life of CCND1. AKT2 seems also to be the principal isoform responsible of the regulation of glucose uptake. Phosphorylates C2CD5 on 'Ser-197' during insulin-stimulated adipocytes. AKT2 is also specifically involved in skeletal muscle differentiation, one of its substrates in this process being ANKRD2. Down-regulation by RNA interference reduces the expression of the phosphorylated form of BAD, resulting in the induction of caspase-dependent apoptosis. Phosphorylates CLK2 on 'Thr-343'. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;ATP-binding;Carbohydrate metabolism;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Diabetes mellitus;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glucose metabolism;Glycogen biosynthesis;Glycogen metabolism;Glycoprotein;Kinase;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Sugar transport;Transferase;Translation regulation;Transport;Ubl conjugation | This gene is a putative oncogene encoding a protein belonging to a subfamily of serine/threonine kinases containing SH2-like (Src homology 2-like) domains, which is involved in signaling pathways. The gene serves as an oncogene in the tumorigenesis of cancer cells For example, its overexpression contributes to the malignant phenotype of a subset of human ductal pancreatic cancers. The encoded protein is a general protein kinase capable of phophorylating several known proteins, and has also been implicated in insulin signaling. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2019]. | hsa:208; | cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; molecular function activator activity [GO:0140677]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; carbohydrate transport [GO:0008643]; cellular response to high light intensity [GO:0071486]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; glucose metabolic process [GO:0006006]; glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0005978]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; intracellular protein transmembrane transport [GO:0065002]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; mammary gland epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0060644]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of long-chain fatty acid import across plasma membrane [GO:0010748]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; peripheral nervous system myelin maintenance [GO:0032287]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell motility [GO:2000147]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0032000]; positive regulation of glucose import [GO:0046326]; positive regulation of glucose metabolic process [GO:0010907]; positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0045725]; positive regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0010918]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane [GO:0090314]; positive regulation of vesicle fusion [GO:0031340]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein modification process [GO:0036211]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of translation [GO:0006417]; retinal rod cell apoptotic process [GO:0097473]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 12114503_In renal tubular epithelial cell, Akt phosphorylation is up-regulated in an effort to minimize cell death. 12480711_Activation of AKT consequent to binding of albumin by CLL cells blocks chlorambucil- and radiation-induced apoptosis. 12482965_a new mechanism for androgen-mediated prostate cancer cell survival and establish FKHR as nuclear target for both AKT-dependent and -independent survival signals in prostate cancer cells. 12517337_Results describe the structure of an inactive and unliganded Akt2 kinase domain, and several features that distinguish it from other kinases. 12517798_data indicate that AKT2 mediates PI3-K-dependent effects on adhesion, motility, invasion, and metastasis in vivo 12545160_These results indicate that PI3k/Akt pathway is involved in the signaling cascade of glioma cells required to induce cell migration. 12663464_results show that a defect in the ability of insulin to activate Akt-2 and -3 may explain the impaired insulin-stimulated glucose transport in insulin resistance 12733712_both p70S6K and Akt are activated in the majority of human papillary cancer cells. 12808085_Akt regulates basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor-coactivator complex formation and activity during neuronal differentiation 14504284_Akt2 phosphorylates MLK3, which results in the disassembly of the JNK complex bound to POSH and down-regulation of the JNK signaling pathway 14612499_Akt2 may be an important regulator of both Xiap and p53 contents in ovarian cancer after CDDP challenge. 14637151_Our data suggest that Akt is an endogenous inhibitor during TRAIL-mediated synovial cell apoptotic pathway. 14654898_Findings suggest that Akt2 is a novel independent predictor for the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma . 14699494_Lipid rafts(LR) may play important role in determining function of PI 3-K/Akt2 signaling, including stimulation of intestinal Na absorption. LR-associated Akt2 may be involved in enterocyte differentiation. 14735903_data suggest that upstream perturbations of the PI3K/AKT pathway contribute to frequent activation of AKT2 in pancreatic cancer, which may contribute to the pathogenesis of this highly aggressive form of human malignancy 15010337_Thus a physiological concentration of insulin stimulated Akt-1 & Akt-2 phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle in the absence of hyperglycemia, but Akt-2 expression is impaired in muscle of obese patients with atypical diabetes with severe hyperglycemia. 15102693_activated Akt and Akt2 have roles in progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma 15111130_These results suggest that cross-talk between the PKB and caspase-8 pathways may regulate the balance between cell survival and cell death in ECV304. 15166380_a mutation in AKT2 in a family showing autosomal dominant inheritance of severe insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus is described; the mutant kinase in cultured cells disrupted insulin signaling and inhibited the function of coexpressed, wild-type AKT 15531580_Akt2 is a critical kinase that regulates ezrin phosphorylation and activation 15557754_AKT2 plays an important role in glioma cell motility and invasion 15890450_Kinetic analysis of GST-AKT2 demonstrates that phosphorylation of Thr309 in the activation loop of the kinase is largely responsible for observed reduction in Km & for a subsequent 150-fold increase in the catalytic efficiency (k(cat)/Km) of the enzyme. 15987444_in breast cancer patients, Akt activation is associated with tumour proliferation and poor prognosis, particularly in the subset of patients with ErbB2-overexpressing tumours 16365168_In this study, we provide evidence for isoform-specific positive and negative roles for Akt1 and -2 in regulating growth factor-stimulated phenotypes in breast epithelial cells 16402276_results suggest that AKT pathway may play an important role in the development and progression of gliomas 16982699_These data show that specific interaction of the Akt2 isoform with p21 is key to its negative effect on normal cell cycle progression. 17012749_Akt1 and Akt2 have opposing roles in Rac/Pak signaling and cell migration 17276404_Akt1 induces CREB phosphorylation at Ser-133 and CREB target gene expression. 17327441_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17327441_Sequencing of the entire coding region and splice junctions of AKT2 and the relationship of genetic variations in the gene with multiple metabolic diseases is reported. 17332325_Twist as a positive transcriptional regulator of AKT2 expression; Twist-AKT2 signaling is involved in promoting invasive ability and survival of breast cancer cells. 17372934_Changes in tissue pressure during inflammation may regulate macrophage phagocytosis by activation of PI-3K, which activates Akt2, mTOR, and p70S6K. 17482291_the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway is involved in regulation of SphK1, with AKT2 playing a key role in PDGF-induced SphK1 expression 17576055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17576055_Two variants in 5' regulatory region of Akt2 gene are associated and may modulate susceptibility to insulin resistance and related metabolic abnormalities. 17804734_AKT2 up-regulation is characteristic of skin squamous cell carcinoma and coincident AKT2 activation through serine phosphorylation correlates with malignancy. 17825284_Pressure did not stimulate translocation of AKT2 to the plasma membrane. 17895832_PKB[alpha] and/or PKB[gamma] and not PKB[beta] alone are involved in gemcitabine resistance mechanisms. 17908691_Akt2 is required for rapamycin-induced vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation, whereas Akt1 appears to oppose contractile protein expression. 17914025_Akt1 and Akt2 mediate GPIb-IX signaling via the cGMP-dependent signaling pathway. 18048359_a key regulatory role of the Akt/mTOR pathway in the generation of the effects of As(2)O(3) 18281467_Functional convergence of Twist and AKT2 underscores the importance of this signaling pathway in tumor development and progression. 18316591_Dlx5 can act as an oncogene by cooperating with Akt2 to promote lymphomagenesis 18353613_Results suggest that Akt2 directly mediates EGF-induced chemotactic signaling pathways through PKCzeta and its expression is critical during the extravasation of circulating cancer cells. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18768676_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18768676_Polymorphisms in two components of the insulin signaling pathway, AKT2 and GSK3B, are associated with polycystic ovary syndrome. 18842333_Akt2 down-regulation sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to paclitaxel-induced apoptosis, and inhibits survivin expression 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19074768_an important role of PKC-delta and PI3K/Akt1,2 pathways in activating mTOR as an endogenous modulator to ensure a tight regulation of NF-kappaB signaling of ICAM-1 expression in endothelial cells. 19075230_the consequence of PTEN loss and Akt2 overexpression function synergistically to promote metastasis 19079138_mtDNA depletion prevents detachment-induced apoptosis (anoikis) and promotes migratory capabilities onto basement membrane proteins through upregulation of p85 and p110 phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) subunits, which results in Akt2 activation 19110052_Akt2 up-regulates beta1 integrins & promotes adhesion & invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro & also metastasis in vivo. It opposes Akt1. Review. 19164214_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19164214_genetic variations in akt2 were associated with survival in esophageal cancer 19197940_Akt2 plays an essential role in both CSF-1- and chemokine-induced chemotaxis of macrophages. 19261608_Bcr-Abl represses the expression of PHLPP1 and PHLPP2 and continuously activates Akt1, -2, and -3 via phosphorylation on Ser-473, resulting in the proliferation of CML cells 19435822_Findings indicate that AP-1 has an important function in pancreatic cancer cells and provide evidence for a previously unknown Akt-mediated mechanism of c-Jun activation. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19771908_The positive rate of AKT2 protein expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma was significantly higher than that in peri-cancer tissue and normal laryngeal epithelium, and was correlated with tumor site, lymph node metastasis and clinical stage. 19797172_mTOR/Akt2 is required for optimal PPARgamma activation. Patients who receive SESs during concomitant RSG treatment may be at risk for delayed stent healing. 19825827_induction of EMT is controlled by microRNAs whose abundance depends on the balance between Akt1 and Akt2 rather than on the overall activity of Akt 19843246_Taken together, these results showed that, in addition to the MAPK pathway previously reported being a downstream target of stimulated Grm1, AKT2 is another downstream target in Grm1 mediated melanocyte transformation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19933843_These findings provide further evidence of the importance of mediators of the growth factor signaling in ER regulation, introducing the Akt2/FoxO3a axis as a pursuable target in therapy for ER-positive breast cancer. 20018949_Akt2 was located in the mitochondria of human cell lines. 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20056908_Plasmin triggers chemotaxis of monocyte-derived dendritic cells through an Akt2-dependent pathway and promotes a T-helper type-1 response. 20059950_By using yeast two-hybrid systems with full-length human Akt2 as bait, we found a stable interaction between the tetratricopeptide (TPR) repeat domain 3 (TTC3) and Akt; finding could underlie important clinical manifestations of Down syndrome. 20102399_In breast cancer AKT3 amplifications and AKT1 and AKT2 deletions were seen by FISH 20109457_Results represent the first indication that Akt isoforms regulate intermediate filament protein expression and support the hypothesis that IFs are involved in PI3K/Akt pathway. 20116920_Akt2 may play a critical role in the development of gliomas and present a potential therapeutic target for malignant gliomas 20133737_Data show that AKT1 and AKT2 appeared to regulate growth through FOXO proteins, but not through either GSK3beta or mTOR, and in contrast, inactivation of PDPK1 affected GSK3beta and mTOR activation. 20167810_Our data suggest that Akt2 and Akt3 play an important role in the viability of human malignant glioma cells. 20186503_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20186503_We evaluated the presence of mutations in PIK3CA, AKT1, AKT2, AKT3, PTEN, and PDPK1 genes in 83 papillary thyroid carcinomas 20354455_AKT2 mutation coexisted with EGFR and PIK3CA mutations was associated with lung cancer. 20354455_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20398329_Studies indicate that three different isoforms Akt1, Akt2, and Akt3 have distinct expression patterns and functions. 20409325_MYCN contributes to tumorigenesis, in part, by repressing miR-184, leading to increased levels of AKT2, a direct target of miR-184 20447721_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20514445_AKT2 expression is associated with more advanced and especially aggressive gliomas and critical for cell survival and invasion. 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20687898_SGK3 is not required for insulin-induced PFK-2 activation and that this effect is likely mediated by PKBalpha. 20688159_The expression levels and activities of exogenous Akt1 and Akt2 are almost identical, Akt2 exerted a greater inhibitory effect on both proliferation and cell migration. 20691427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20848774_The positive expression of p-AKT2 in lung adenocarcinoma was higher than that in lung squamous carcinomas. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21050850_Akt signaling regulates the stability of palladin 21092549_Expressions of Akt1, Akt2 and PI3K were decreased in ovarian epithelial cancer cells transduced with PTEN. 21179235_Advanced glycation end products of BSA can induce endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition of cultured human and monkey endothelial cells and AKT2 may play a role in this process. 21182834_Data suggest that Akt2/B23 functions as an oncogenic unit to drive tumorigenesis of A549 lung cancer cells. 21297943_Akt2 augments cell proliferation by facilitating cell cycle progression through the upregulation of the cell cycle engine, and protects a cell from pathological autophagy by modulating mitochondrial homeostasis. 21432781_analysis of the roles of Akt1 and Akt2 in cancer [review] 21507933_loss of Akt1 or Akt2 decreased proliferation of Pten wild-type astrocytes, whereas combined loss of multiple isoforms was needed to inhibit proliferation of Pten-null astrocytes 21518566_The Akt2 gene is not a major cause of diabetes in a non-obese Chinese Han population characterized by insulin resistance. 21590431_Transcriptional activation of the Akt2 pathway indicates that it is involved in lumbar disc degeneration. 21618512_Data suggest a regulation pathway of B-cell-lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) by cisplatin, via the activation of PKC and Akt2, which has impact on resistance to cisplatin-induced apoptosis in endometrial cancer cells. 21636708_High AKT2 is associated with glioma progression. 21680733_Angiopoietin-2, an angiogenic regulator, promotes initial growth and survival of breast cancer metastases to the lung through the integrin-linked kinase (ILK)-AKT1,2-B cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) pathway. 21722267_AKT1 and AKT2 both contribute to cell survival, albeit via different mechanisms; the effects on cell growth and migration are predominantly regulated by AKT1 21932427_This study revealed a novel mechanism of Akt2 regulation by ErbB2 in prostate cancer cells. 21979934_3 unrelated children with unexplained, recurrent and severe fasting hypoglycemia and asymmetrical growth were found to carry the same de novo mutation, p.Glu17Lys, in AKT2, in 2 cases as heterozygotes and in 1 case in mosaic form 21979951_Akt2 kinase suppresses glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH)-mediated apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells via phosphorylating GAPDH at threonine 237 and decreasing its nuclear translocation 22031698_analysis of resistance of Akt kinase and PP2A to dephosphorylation through ATP-dependent conformational plasticity 22107784_The prognostic impact of Akt (Akt1) phosphorylated at threonine308 and serine473, Akt2, Akt3, PI3K and PTEN, alone and in coexpression with ER and PgR in non-gastrointestinal stromal tumor soft tissue sarcomas. 22158034_Unexpected roles of Akt2 in transcriptional control and phosphorylation of Thr45 in histone H3 as a new epigenetic mark related to Snail1 and Akt2 action. 22261254_Akt2 is a negative regulator of NFAT activation through its ability to inhibit calcium mobilization from the endoplasmic reticulum. 22480544_study concludes that Akt2 is indispensable for the regulation of preadipocyte and adipocyte number, whereas Akt1 and Akt2 are equally important for the regulation of insulin-stimulated metabolic pathways in adipocytes 22556379_Although there is an association of PI3 kinase signaling and chemoresistance in advanced ovarian cancer, there is no clear evidence that this is driven specifically by AKT2 mutations. 22748472_amplification of AKT1 and/or AKT2 and high-level polysomy were found in 16% of total lung carcinoma cases, and this defined subset was characterized by the overexpression/activation of Akt, reciprocal to EGFR aberrations. 22778840_In transfected HEK2 cells, basal activity of Akt2 regulates DAT cell surface expression. 22809628_these data define an inhibitory role for both AKT1 and AKT2 in prostate cancer migration and invasion and highlight the cell type-specific actions of AKT kinases in the regulation of cell motility. 23018889_An Akt2/PKBbeta-targeted siRNA inhibited the 8-Cl-cAMP- and AICAR-mediated phosphorylation of AMPK and p38 MAPK. 23092922_CD40L-provoked signaling results in the production of several cytokines. Among these, IL-6 expression is mediated through Akt and NF-kappaB pathways. 23250987_In cultured human aortic vascular smooth muscle cells, AKT2 inhibited the expression of MMP-9 and stimulated the expression of TIMP-1 by preventing the binding of transcription factor forkhead box protein O1 to the MMP-9 and TIMP-1 promoters. 23305873_Data indicate that the prognostic value of Akt2 increases with higher oestrogen receptor (ER) expression, motivating further mechanistic studies on the role of Akt2 in ER+ breast cancer. 23321478_Data suggest that although COOH-terminal dephosphorylation is likely necessary for glycogen synthase (GS) activation, Akt2-dependent NH2-terminal dephosphorylation is the site for 'fine-tuning' insulin-mediated GS activation in skeletal muscle. 23444369_Insulin signaling via Akt2 switches plakophilin 1 function from stabilizing cell adhesion to promoting cell proliferation. 23464484_In a manner that depended on the level of phosphorylated AKT1/2 protein. 23468863_Akt2 regulates metastatic potential in neuroblastoma. 23567263_AKT1 and AKT2 have non-redundant roles in the regulation of prostate cancer cell proliferation and migration. 23777806_Depletion of both Akt2 and ASAH1 is much more potent than depleting each alone at inhibiting neoplastic cell viability/proliferation and invasion. 23823123_the direct interaction of AKT2 and EF2 was found to be dynamically regulated in embryonic rat cardiomyocytes 23900341_Findings suggest an important role of Gli1 as a tumor suppressor in neuroblastoma, and offer a mechanism by which AKT2 regulates the subcellular localization, and in turn, inhibits the tumor-suppressive function of Gli1 in neuroblastoma. 23929892_detected and measured all three AKT isoforms 1, 2 and 3 to enable the study of the multiple and variable roles that these isoforms play in AKT breast tumorigenesis 24030155_overexpression of 4EBP1, p70S6K, Akt1 or Akt2 could promote the Coxsackievirus B3-induced apoptosis. 24039187_AKT2 is closely linked to Type II diabetes and the implications of various types of mutations are discussed 24056770_results disclose a new function of Akt2 and identify a potential therapeutic target for preserving glomerular function in CKD 24123662_Akt2 downregulation favors limbal keratinocyte stem cell maintenance as a result of a gain of FOXO functions. 24244431_Knockdown of RPS7 resulted in increased expression of P85alpha, P110alpha, and AKT2. 24247267_Experimental validation indicate that AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3 proteins may all be novel unfavorable prognostic factors for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. 24321521_in a defined subset of bone and soft tissue tumors, including benign tumors, Akt was frequently overexpressed and activated, and AKT1/2 copy number was increased 24337067_Results show that miR-302b inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and growth in vitro and in vivo by targeting AKT2. 24565443_AA induces Akt2 activation and invasion in MDA-MB-231 cells. Akt2 activation requires the activity of Src, EGFR, and PIK3, whereas migration and invasion require Akt, PI3K, EGFR and metalloproteinases activity. 24642468_AKT2 inhibition reduced heterotypic aggregation of neutrophils and platelets isolated from sickle cell disease patients, suggesting that AKT2 is important for neutrophil recruitment and neutrophil-platelet interactions. 24656454_AKT2 may play an important role in the development of meningioma. High AKT2 labeling index indicates higher grade of meningioma, and therefore AKT2 may be a useful molecular marker for predicting the prognosis of meningioma. 24699302_We examined the response of 80 samples of primary cells from acute myeloid leukemia patients to selective inhibitors of the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K)/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) axis. 24769357_CK2-dependent phosphorylation is therefore a crucial event which, discriminating between Akt1 and Akt2, can account for different substrate specificities. 24819169_SchA-FAK-p85 complex subsequently selectively recruited and activated Akt2, not Akt1 24838891_The specific role of AKT2 in tumor maintenance provides a rationale for the development of isoform-specific inhibitors for patients with PTEN-deficient cancers. 24946858_Findings suggest that adding chloroquine to EGF receptor (EGFR) and AKT2 inhibition has the potential to improve tumor responses in EGFR M+ non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). 24970808_Findings indicate that miR-137 is a valuable biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) prognosis and the forkhead box D3 (FoxD3)/miR-137/AKT2 regulatory network plays an important role in HCC progression. 25025572_Role of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor in Akt2-mediated plasma membrane translocation of GLUT4 in insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle. 25059120_Knockdown of Akt2 using siRNAs or the PI3K inhibitor Ly294002 inhibited TGF-beta1-induced phosphorylation of GSK3beta and expression of Snail1 25134663_the biological effect of Akt2 in colorectal cancer cells 25162660_AKT isoform-specific knock down combined with quantitative phosphoproteomics provided a powerful strategy to unravel AKT isoform-specific signaling 25173755_Mutations in genes such as AKT2, CCNA1, MAP3K4, and TGFBR1, were associated significantly with Epstein-Barr-positive gastric tumors, compared with EBV-negative tumors. 25233414_Data suggest that three isoforms of the serine/threonine protein kinase Akt (Akt1, Akt2, Akt3) regulate cell survival, cell growth, cell proliferation, and cell metabolism in breast cancer cells. [REVIEW] 25246356_The individual contribution of each Akt isoform in p120 RasGAP fragment N-mediated cell protection against Fas ligand induced cell death, was investigated. 25253241_Akt1 and Akt2 are involved in albumin endocytosis, and phosphorylation of Dab2 by Akt induces albumin endocytosis in proximal tubule epithelial cells. 25263462_miR-29b plays an important role in TGF-beta1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ARPE-19 cells by targeting Akt2. 25285168_MiR-194 deregulation contributes to colorectal carcinogenesis via reducing the expression AKT2. 25288334_let-7b/g inhibited AKT2 expression by directly binding to its 3'UTR, reduced p-AKT (S473) activation and suppressed expression of the downstream effector pS6. 25304263_Our study uncovers a novel molecular mechanism by which AEG-1 augments glioma progression and offers a rationale to block AEG-1-Akt2 signaling function as a novel GBM treatment. 25428377_findings suggested that AKT2 may be one of the targets of miR29s in gastric cancer 25733895_The results indicate that BCAM-AKT2 expression is a new mechanism of AKT2 kinase activation in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. 25771729_PIK3CA and AKT2 mutations occurred at low frequency in gastric cancer. 25856297_miR-615-5p inhibits pancreatic cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting AKT2 25894377_we assayed expression of myosin II.. this assay is a powerful predictor of the use of ZEB2/Akt2 as a marker for tumor progression in serous ovarian cancers. 25936945_QSAR based docking studies identify marine algal callophycin A as inhibitor of protein kinase B beta. 25951903_Up-regulation of AKT2 was associated with chemoresistance in renal cell carcinoma. 26102366_miR-137 which is frequently down-regulated in gastric cancer is potentially involved in gastric cancer tumorigenesis and metastasis by regulating AKT2 related signal pathways 26158514_miR-612 directly suppressed AKT2, which in turn inhibited the downstream epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related signaling pathway. 26229955_the correlation between RLN2 and p-AKT or RLN2 and p-ERK1/2 expression was investigated. 26234648_Akt2 role in the human lung cancer cell proliferation, growth, motility, invasion and endothelial cell tube formation 26254095_miR-302b inhibits SMMC-7721 cell invasion and metastasis by targeting AKT2 26265781_Combined PI3K/Akt and Hsp90 targeting synergistically suppresses essential functions of alloreactive T cells and increases Tregs. 26318486_AKT1 but not AKT2 protects islet cells from apoptosis and drives proliferation. 26475619_High constitutive Akt2 activity in U937 promonocytes: effective reduction of Akt2 phosphorylation by the histamine H2-receptor and the beta2-adrenergic receptor 26512921_High AKT2 expression is associated with ovarian cancer. 26711268_Active, phosphorylated Akt2 translocates to the nucleus in Notch-expressing cells, resulting in GSK-3beta inactivation in this compartment. 26803515_High AKT2 expression is associated with gallbladder cancer. 26828791_No association has been found between AKT2 polymorphisms and oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma risk. 26855332_Akt1 and Akt2 activated both SREBP-1 and SREBP-2, whereas Akt3 upregulated SREBP-1 to enhance hepatitis C virus translation. 26953242_Studies provide evidence that AKT2 counteracts oxidative-stress-induced apoptosis and is required for alpha-beta thymocyte survival and differentiation. Also, it plays a critical role in antagonizing cardiomyocyte apoptosis. [review] 26971877_controls endothelial Jagged1 expression and, thereby, Notch signalling regulating VSMC maintenance. 27067543_TGF-beta signaling through Akt2 induces phosphorylation of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein E1 (hnRNP E1) at serine-43 (p-hnRNP E1), driving epithelial to mesenchymal transition and metastasis. 27105349_Data indicate that proto-oncogene protein c-akt (Akt) phosphorylates distinct sites than SRPK1 protein within the arginine-serine (RS) domain of Lamin B Receptor (LBR). 27189341_AKT2 can regulate miR-200a in a histology- or stage-specific manner and this regulation is independent of subsequent involvement of miR-200a in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 27545875_IRF5 and IRF5 disease-risk variants increase glycolysis and human m1 macrophage polarization by regulating proximal signaling and Akt2 activation. 27663592_Analysis of genomic data from TCGA demonstrated coamplification of CCNE1 and AKT2 Overexpression of Cyclin E1 and AKT isoforms, in addition to mutant TP53, imparted malignant characteristics in untransformed fallopian tube secretory cells, the dominant site of origin of high-grade serous ovarian cancer 27871477_The expression levels of AKT2 and CDC25C showed lower expression in neural tube defects. And the percentage of methylated region of AKT2 promoter were increased in neural tube defects. 27878243_This was further verified in gene expression analyses, showing downregulation of genes involved in glucose metabolism. Additionally, both AKT1 KO and AKT2 KO demonstrated an impaired fatty acid metabolism. However, genes were upregulated in the Wnt and cell proliferation pathways, which could oppose this effect. AKT inhibition should therefore be combined with other effectors to attain the best effect. 27906180_This study demonstrates novel regulatory circuits involving miR-148a-3p/ERBB3/AKT2/c-myc and DNMT1 that controls bladder cancer progression, which may be useful in the development of more effective therapies against bladder cancer. 28026019_Both in our animal model and in human Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), the AKT2-NF-kappaB-LCN-2 signalling axis is involved in activating the inflammatory response. 28036396_Quinoline-type inhibitors bind in the Akt2 PH domain. 28068324_Data identify MTSS1 as a new Akt2-regulated gene, and point to suppression of MTSS1 as a key step in the metastasis-promoting effects of Akt2 in CRC cells. 28129626_MiR-650 could inhibit the proliferation, migration and invasion of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts through targeted regulation of AKT2 expression. 28271235_High expressions of AKT1 and AKT2 through possible relation with androgen may cause granulosa cells dysfunction in the +HA PCOS patients. 28287129_Data show while overexpression of AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 (AKT1) promoted local tumor growth, downregulation of AKT1 or overexpression of AKT serine/threonine kinase 2 (AKT2) promoted peritumoral invasion and lung metastasis. 28341696_identified a novel association between the coding variant (p.Pro50Thr) in AKT2 and fasting plasma insulin (FI), a gene in which rare fully penetrant mutations are causal for monogenic glycemic disorders. Carriers of the FI-increasing allele had increased 2-h insulin values, decreased insulin sensitivity, and increased risk of type 2 diabetes. 28404925_miR-143-3p acts as a novel tumor suppressive miRNA by regulating gastric tumor growth, migration and invasion through directly targeting AKT2 gene 28440469_Our findings suggest that Akt2 might be associated with the resistance to anti-EGFR therapies, especially the use of erlotinib against PC, and that this resistance can be overcome by combined treatment with a PI3K inhibitor. Akt2 expression could become a predictive biomarker for erlotinib resistance in PC. 28455433_Results indicate that AKT2 modulates pulmonary fibrosis through inducing TGF-beta1 and IL-13 production by macrophages, and inhibition of AKT2 may be a potential strategy for treating Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 28456993_Studied action of linoleic acid (LA) on cell migration and neoplasm invasiveness of breast cancer cells. Findings show Akt2 activation requires EGFR and PI3K activity, whereas migration and invasion are dependent on FFAR4, EGFR and PI3K/Akt activity. 28534950_miR296 is downregulated in tissue from patients with pancreatic cancer and pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. These findings suggested that it may function as a tumor suppressor via inhibiting the growth, migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. AKT2 was validated as a direct target of miR296 in pancreatic cancer cells. 28541532_The p.Glu17Lys mutation of AKT2 confers low-level constitutive activity upon the kinase and produces hypoglycemia with suppressed fatty acid release from adipose tissue, but not fatty liver, hypertriglyceridemia, or elevated hepatic de novo lipogenesis. 28557977_This review summarises and discusses the consequences of genetic deletions of Akt isoforms in adult mice and their implications for cancer therapy. Whereas combined Akt1 and Akt2 rapidly induced mortality, hepatic Akt inhibition induced liver injury that promotes hepatocellular carcinoma. 28586057_miR2965p/AKT2 axis serves important roles in Hepatocellular carcinoma carcinogenesis and progression. 28650848_Recent studies reveal that AKT2-NOX2 signaling has critical roles in Ca mobilization, ROS generation, degranulation, and control of the ligand-binding function of cell surface molecules, thereby promoting heterotypic cell-cell interactions in thromboinflammation. 28689659_Akt2, Erk2, and IKK1/2 phosphorylate Bcl3, converting Bcl3 into a transcriptional coregulator by facilitating its recruitment to DNA. 28837154_Findings demonstrate that DSBs trigger pro-survival autophagy in an ATM- and p53-dependent manner, which is curtailed by AKT2 signaling. 28931550_Report frequency of genetic variation in Akt2 and discuss link to type 2 diabetes. 29025710_AKT1 and AKT2 isoforms have opposing roles in smooth muscle cell proliferation, migration, differentiation, and rapamycin response in vitro and in vascular injury in vivo. 29075783_Authors present the first evidence that miR-608 behaves as a tumour suppressor in A549 and SK-LU-1 cells through the regulation of AKT2. 29141982_genetic association studies in population of men in Finland: Data suggest that a partial loss-of-function variant in AKT2 (p.Pro50Thr) is associated with type 2 diabetes in the population studied; this AKT2 variant is associated with reduced insulin-mediated glucose uptake in multiple insulin-sensitive tissues. 29153407_AKT2 drives de novo lipogenesis in adipocytes by stimulating ChREBPbeta transcriptional activity and | ENSMUSG00000004056 | Akt2 | 543.586687 | 1.0329023 | 0.046703748 | 0.11039418 | 0.17882460609 | 0.6723853073021284210142312076641246676445007324218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.83189660439382684398168521511252038180828094482421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 553.915884 | 49.498899 | 538.419195 | 47.998378 | |
| ENSG00000105401 | 11140 | CDC37 | protein_coding | Q16543 | FUNCTION: Co-chaperone that binds to numerous kinases and promotes their interaction with the Hsp90 complex, resulting in stabilization and promotion of their activity (PubMed:8666233). Inhibits HSP90AA1 ATPase activity (PubMed:23569206). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23569206, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8666233}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation | The protein encoded by this gene is highly similar to Cdc 37, a cell division cycle control protein of Sacchromyces cerevisiae. This protein is a molecular chaperone with specific function in cell signal transduction. It has been shown to form complex with Hsp90 and a variety of protein kinases including CDK4, CDK6, SRC, RAF-1, MOK, as well as eIF2 alpha kinases. It is thought to play a critical role in directing Hsp90 to its target kinases. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:11140; | chaperone complex [GO:0101031]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; HSP90-CDC37 chaperone complex [GO:1990565]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; heat shock protein binding [GO:0031072]; Hsp90 protein binding [GO:0051879]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein kinase regulator activity [GO:0019887]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; positive regulation of mitophagy in response to mitochondrial depolarization [GO:0098779]; post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression [GO:0010608]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; protein targeting [GO:0006605]; regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0000079]; regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060338]; regulation of type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060334] | 11864612_Tnf-induced recruitment and activation of the IKK complex require Cdc37 and Hsp90. 11916974_role in regulating Hsp90 ATPase activity 12176997_CDC37 binds to Akt and HSP90 in the signal transduction pathway in human tumor cells 12489981_Results show that Cdc37 and heat shock protein 90 bind specifically to the kinase domain of LKB1. 12930845_phosphorylation of Cdc37 on Ser13 is critical for its ability to coordinate Hsp90 nucleotide-mediated conformational switching and kinase binding 14668798_Heteromeric comlpexes containing the molecular chaperones Hsp90 and Cdc37/p50 interacts with the kinase domain of LKB1. 14701845_the interaction of Cdc37 with its client protein kinases requires amino acid residues within a motif that is present in many protein kinases 15001580_Hsp90/p50cdc37 is required for mixed-lineage kinase (MLK) 3 signaling 15647277_the Hsp90.Cdc37 molecular chaperone module has a central role in interleukin-1 receptor-associated-kinase-dependent signaling by toll-like receptors 15850399_Cdc37 is found to heterodimerize with heat-shock protein 90 (Hsp90)-associating relative of Cdc37 (Harc) in vitro. 16132836_Nuclear magnetic resonance study of binding to to HSP90. 16156789_results suggest that a region of Cdc37 other than the client-binding site may be responsible for discriminating client protein kinases from others 16280321_JAK1/2 are client proteins of Hsp90 alpha and beta; Hsp90 and CDC37 play a critical role in types I and II interferon pathways 16611982_N-terminal glycine-rich loop of protein kinases is essential for physically associating with Cdc37. 16949366_The data shows the expression and purification of an Hsp90-Cdc37-Cdk4 complex, defining its stoichiometry, and determining its 3D structure by single-particle electron microscopy. 17223712_these observations support the hypothesis that there is a specific coordination between the activation of the cytosolic Ah receptor and the c-Src- and cdc37-containing HSP90 complex. 17728246_The present data denote Hsp90-Cdc37 as a transiently acting essential regulatory component of IKK signaling. 18003639_identify Pink1 as a novel Cdc37/Hsp90 client kinase 18089825_Cdc37 is essential for maintaining prostate tumor cell growth and may represent a novel target in the search for multitargeted therapies. 18922470_These data reveal a cyclic regulatory mechanism for Cdc37, in which its constitutive phosphorylation is reversed by targeted dephosphorylation in Hsp90 complexes. 18931700_CDC37 in concert with HSP90 plays an essential role in maintaining oncogenic protein kinase clients including ERBB2, CRAF, CDK4, CDK6, & phosphorylated AKT. 19073599_The human Cdc37.Hsp90 complex studied by heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy. 19091746_C-terminal tail and determinants in the alphaE-helix of the catalytic domain allows the chaperones Hsp90 and Cdc37 to bind newly synthesized PKC beta II, a required event in the processing of PKC by phosphorylation 19858214_celastrol may represent a new class of Hsp90 inhibitor by modifying Hsp90 C terminus to allosterically regulate its chaperone activity and disrupt Hsp90-Cdc37 complex. 20056645_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20299663_Hsp90-Cdc37 complex acta as an endogenous regulator of noncanonical p38alpha activity. 21367866_the Hsp90 kinase co-chaperone Cdc37 regulates tau stability and phosphorylation dynamics 21871133_The primary mechanisms by which apigenin kill multiple myeloma cells is by targeting the trinity of CK2-Cdc37-Hsp90. 22199355_Cdc37-mediated direct interaction between Hsp90/Cdc37 and an IRE1alpha cytosolic motif is important to maintain basal IRE1alpha activity and contributes to normal protein homeostasis and unfolded protein response under physiological stimulation. 22674575_Data show that part of the normal clearance cascade for TDP-43 involves the Cdc37/Hsp90 complex. 22727666_A series of tyrosine phosphorylation events, involving both p50(Cdc37) and Hsp90, are minimally sufficient to provide directionality to the chaperone cycle. 22912728_an essential role for surface Cdc37 in concert with HSP90 on the cell surface during cancer cell invasion processes 23281476_analysis of a novel interaction between the co-chaperone Cdc37 and Rho GTPase exchange factor Vav3 promotes androgen receptor activity and prostate cancer growth 23428871_ERK5 interacts with the Hsp90-Cdc37 chaperone in resting cells, and inhibition of Hsp90 or Cdc37 results in ERK5 ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation. 23569206_Cdc37 (cell division cycle 37) restricts Hsp90 (heat shock protein 90) motility by interaction with N-terminal and middle domain binding sites. 23584476_CDC37 is a crucial HSP90-cofactor for KIT oncogenic expression in gastrointestinal stromal tumors 24292678_CDC37 has an important role in chaperoning protein kinases; it stabilizes kinase clients by a mechanism that is not dependent on a substantial direct interaction between CDC37 and HSP90, but requires HSP90 activity 24379398_SGK3 stability and kinase activation are regulated by the Hsp90-Cdc37 chaperone complex. 24869908_Correlation between PDZK1, Cdc37, Akt and breast cancer malignancy: the role of PDZK1 in cell growth through Akt stabilization by increasing and interacting with Cdc37 24927996_As a novel Hsp90 inhibitor, FW-04-806 binds to the N-terminal of Hsp90 and inhibits Hsp90/Cdc37 interaction, resulting in the disassociation of Hsp90/Cdc37/client complexes and the degradation of Hsp90 client proteins. 25098386_Suppressing expression of the cochaperone CDC37 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells inhibits cell cycle progression and cell growth. 25619116_The N-terminal tail serves as an intramolecular chaperone ensuring that CDC37 assumes one of two interconvertible states in a manner impacting the interaction of the client binding N-domain and the MC-domains, involved in dimerization and HSP90 binding. 25852146_RIP3 activation following the induction of necroptosis requires the activity of an HSP90 and CDC37 cochaperone complex. 26511315_Apart from these distinct Cdc37/Hsp90 interfaces, binding of the B-Raf protein kinase to the cochaperone is conserved between mammals and nematodes. 27105117_Cdc37 performs a quality control of protein kinases, including b-raf, where induced conformational instability acts as a 'flag' for Hsp90 dependence and stable cochaperone association. 27620500_The authors find that the interaction between sB-Raf and the Hsp90 chaperone system is based on contacts with the M domain of Hsp90, which contributes in forming the ternary complex with Cdc37 as long as the kinase is not stabilized by nucleotide. 28073914_Ulk1 promoted the degradation of Hsp90-Cdc37 client kinases, resulting in increased cellular sensitivity to Hsp90 inhibitors. Thus, our study provides evidence for an anti-proliferative role of Ulk1 in response to Hsp90 inhibition in cancer cells 28284560_Niclosamide ethanolamine disrupted the interaction between cell division cycle 37 and heat shock protein 90 in hepatocellular carcinoma, reducing tumor growth. 28784328_The results suggest a re-evaluation of the role of Cdc37 in the kinase lifecycle, and suggest that such interactions potentially allow kinases to more rapidly respond to key signals while simultaneously protecting unstable kinases from degradation and suppressing unwanted basal activity. 29267381_findings suggested that this mechanism may be exploited by the Hsp90-Cdc37 chaperone to recruit and protect intrinsically dynamic kinase clients from degradation 29288563_Study showed that Cdc37 gene was up-regulated in human colorectal adenocarcinoma (CRC). Furthermore, knockdown of Cdc37 effectively reduced cell proliferation activity, enhanced apoptosis, and inhibited G1-S transition in CRC cells, and vice versa. For the mechanism, Cdc37 increased CDK4 stability to promote the phosphorylation of RB1, which finally promoted the progression of CRC. 29343704_During the kinase chaperone cycle, Cdc37 phosphorylated at Y298 acts as a platform for docking of non-receptor tyrosine kinases through their regulatory domains to drive the coupled Hsp90 phosphorylation at Y197 and specifically regulate kinase chaperoning. 29432007_results of this integrative computational study are compared with a wide range of structural, biochemical, and cell-based experiments, offering a robust network-centric model of allosteric regulation and client kinase recognition by the Hsp90-Cdc37 chaperone machine 29478821_Results found that several disease-linked mutations convert FGFR3 to a stronger client of Hsp90/Cdc37. Enhanced interaction with Cdc37 is underpinned by a weakened N-lobe network. Cdc37 binding to unrelated kinases induces their common, extensive remodeling. Kinase remodeling and the kinase/Cdc37 architecture allow recognition by Hsp90. 31226489_The results suggested that more complicated mechanisms might be necessary to explain the phosphorylation-activated interaction of Cdc37 with various kinases. 31555737_results demonstrated DDO-5936 as an identified specific small-molecule inhibitor of the Hsp90-Cdc37 PPI that could be used to comprehensively investigate alternative approaches targeting Hsp90 chaperone cycles for cancer therapy. 31662027_Medium-Throughput Detection of Hsp90/Cdc37 Protein-Protein Interaction Inhibitors Using a Split Renilla Luciferase-Based Assay. 32656999_Hsp90 interacts with Cdc37, is phosphorylated by PKA/PKC, and regulates Src phosphorylation in human sperm capacitation. 33374422_The Activity and Stability of p56Lck and TCR Signaling Do Not Depend on the Co-Chaperone Cdc37. 33786814_The CDC37-HSP90 chaperone complex co-translationally degrades the nascent kinase-dead mutant of HIPK2. 34147560_Protein quality control of DYRK family protein kinases by the Hsp90-Cdc37 molecular chaperone. 34627434_[Cdc37 Expression in Multiple Myeloma and Its Role in Cell Proliferation]. 35165364_Differential maturation and chaperone dependence of the paralogous protein kinases DYRK1A and DYRK1B. 35400341_The Therapeutic Potential of Targeting Hsp90-Cdc37 Interactions in Several Diseases. | ENSMUSG00000019471 | Cdc37 | 1678.972377 | 0.8835298 | -0.178649337 | 0.04873019 | 13.43529955834 | 0.0002469335507284754803805637557445606944384053349494934082031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00226945237029560790628646138600288395537063479423522949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1580.616935 | 44.609529 | 1796.804407 | 50.036591 | |
| ENSG00000105643 | 27106 | ARRDC2 | protein_coding | Q8TBH0 | Alternative splicing;Reference proteome | Predicted to be involved in protein transport. Located in cytoplasmic vesicle and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:27106; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein transport [GO:0015031] | ENSMUSG00000002910 | Arrdc2 | 224.608961 | 0.8013412 | -0.319511404 | 0.13958114 | 5.23808883230 | 0.0220975366533178764483213996072663576342165470123291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.09064526179079486489786887659647618420422077178955078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 189.669214 | 14.927585 | 237.673337 | 18.204472 | |||
| ENSG00000105750 | 7639 | ZNF85 | protein_coding | Q03923 | FUNCTION: May be a transcriptional repressor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9839802}. | Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA | Enables DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:7639; | nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA | ENSMUSG00000055341+ENSMUSG00000048280+ENSMUSG00000057842 | Zfp457+Zfp738+Zfp595 | 63.105864 | 1.8092529 | 0.855394097 | 0.40126789 | 4.43789034621 | 0.0351496561813786217998156757857941556721925735473632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.12827377789332744528749685741786379367113113403320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 78.527094 | 19.373981 | 43.784845 | 10.894328 |
| ENSG00000105808 | 10156 | RASA4 | protein_coding | O43374 | FUNCTION: Ca(2+)-dependent Ras GTPase-activating protein, that switches off the Ras-MAPK pathway following a stimulus that elevates intracellular calcium. Functions as an adaptor for Cdc42 and Rac1 during FcR-mediated phagocytosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11448776}. | Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;GTPase activation;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a member of the GAP1 family of GTPase-activating proteins that suppresses the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in response to Ca(2+). Stimuli that increase intracellular Ca(2+) levels result in the translocation of this protein to the plasma membrane, where it activates Ras GTPase activity. Consequently, Ras is converted from the active GTP-bound state to the inactive GDP-bound state and no longer activates downstream pathways that regulate gene expression, cell growth, and differentiation. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:10156; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0034260]; negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046580] | 11448776_CAPRI (Ca2+-promoted Ras inactivator) a Ca2+-dependent Ras GTPase-activating protein (Ras GAP). Switches off the Ras-MAPK pathway following G protein-coupled receptor stimulated intracellular Ca2+ elevation that recruits CAPRI to the plasma membrane. 16009725_CAPRI seems to low-pass filter the Ca2+ signal, converting different intensities of stimulation into different durations of Ras activity. 21460216_Ca2+-dependent monomer and dimer formation switches CAPRI Protein between Ras GTPase-activating protein (GAP) and RapGAP activities 25147919_RASA4 isoform 2 promoter methylation correlated with clinical parameters predicting poor prognosis (older age, elevated fetal hemoglobin), with higher risk of relapse after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, and with PTPN11 mutation. 34094999_Treponema denticola-Induced RASA4 Upregulation Mediates Cytoskeletal Dysfunction and MMP-2 Activity in Periodontal Fibroblasts. 34675073_Ras inhibitor CAPRI enables neutrophil-like cells to chemotax through a higher-concentration range of gradients. 34752201_RASA4 inhibits the HIFalpha signaling pathway to suppress proliferation of cervical cancer cells. | ENSMUSG00000004952 | Rasa4 | 514.071348 | 0.5874844 | -0.767377661 | 0.13876961 | 30.30600467166 | 0.0000000368981858571484529428068663628459411540916335070505738258361816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000078083483172434576963520831693887913615981233306229114532470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 429.870943 | 91.936306 | 732.558960 | 156.326265 | |
| ENSG00000106003 | 3955 | LFNG | protein_coding | Q8NES3 | FUNCTION: Glycosyltransferase that initiates the elongation of O-linked fucose residues attached to EGF-like repeats in the extracellular domain of Notch molecules. Modulates NOTCH1 activity by modifying O-fucose residues at specific EGF-like domains resulting in inhibition of NOTCH1 activation by JAG1 and enhancement of NOTCH1 activation by DLL1 via an increase in its binding to DLL1 (By similarity). Decreases the binding of JAG1 to NOTCH2 but not that of DLL1 (PubMed:11346656). Essential mediator of somite segmentation and patterning (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O09010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11346656}. | Alternative splicing;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene is a member of the glycosyltransferase 31 gene family. Members of this gene family, which also includes the MFNG (GeneID: 4242) and RFNG (GeneID: 5986) genes, encode evolutionarily conserved glycosyltransferases that act in the Notch signaling pathway to define boundaries during embryonic development. While their genomic structure is distinct from other glycosyltransferases, these proteins have a fucose-specific beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity that leads to elongation of O-linked fucose residues on Notch, which alters Notch signaling. The protein encoded by this gene is predicted to be a single-pass type II Golgi membrane protein but it may also be secreted and proteolytically processed like the related proteins in mouse and Drosophila (PMID: 9187150). Mutations in this gene have been associated with autosomal recessive spondylocostal dysostosis 3. [provided by RefSeq, May 2018]. | hsa:3955; | extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular vesicle [GO:1903561]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008375]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; O-fucosylpeptide 3-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0033829]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; compartment pattern specification [GO:0007386]; marginal zone B cell differentiation [GO:0002315]; negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway involved in somitogenesis [GO:1902367]; ovarian follicle development [GO:0001541]; positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051446]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; positive regulation of protein binding [GO:0032092]; regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0008593]; regulation of somitogenesis [GO:0014807]; somitogenesis [GO:0001756]; T cell differentiation [GO:0030217] | 16385447_Mutation of the LFNG gene causes spondylocostal dysostosis with a severe vertebral phenotype, reinforcing the hypothesis that proper regulation of the Notch signaling pathway is an absolute requirement for the correct patterning of the axial skeleton. 22624713_Reduced LFNG expression facilitates JAG/NOTCH luminal progenitor signaling and cooperates with MET/CAVEOLIN basal-type signaling to promote basal-like breast cancer. 24709423_LFNG expression correlates with expansion of cancer stem cell populations and NKX3.1 expression in human prostate cancer. 26279302_a potent tumor-suppressive function for Lfng 27156840_TGFBR2 signaling can affect Notch1 glycosylation via regulation of glycosyltransferase LFNG expression and provide a first mechanistic example for altered glycosylation in microsatellite instability colorectal tumor cells. 28938159_Genetic interaction between lunatic fringe and TP53 was identified in breast cancer tumorigenesis. 29193607_LFNG expression plays a functional role in regulating melanoma metastasis. 30531807_LFNG mutation is associated with spondylocostal dysostosis. 33562410_Bioinformatics and Functional Analyses Implicate Potential Roles for EOGT and L-fringe in Pancreatic Cancers. 33894418_Lunatic fringe promotes the aggregation of CADASIL NOTCH3 mutant proteins. | ENSMUSG00000029570 | Lfng | 208.696315 | 0.8006780 | -0.320705927 | 0.12562196 | 6.52008424604 | 0.0106662950395105069617551762917173618916422128677368164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.05191375609348398284526027168794826138764619827270507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 187.272753 | 19.938718 | 235.004692 | 24.635701 | |
| ENSG00000106771 | 23731 | TMEM245 | protein_coding | Q9H330 | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:23731; | membrane [GO:0016020] | 23382809_we detected five SNPs in the first two genes/loci - BCL9 and C9orf5 - strongly associated with negative symptoms of schizophrenia | ENSMUSG00000055296 | Tmem245 | 649.656037 | 1.1294539 | 0.175625326 | 0.09101737 | 3.72007128734 | 0.0537620756010412023662148328639887040480971336364746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.17249058829458707720050369971431791782379150390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 707.754037 | 42.672493 | 629.140717 | 37.793839 | ||
| ENSG00000107331 | 20 | ABCA2 | protein_coding | Q9BZC7 | FUNCTION: Probable lipid transporter that modulates cholesterol sequestration in the late endosome/lysosome by regulating the intracellular sphingolipid metabolism, in turn participates in cholesterol homeostasis (PubMed:15238223, PubMed:21810484, PubMed:24201375) (Probable). May alter the transbilayer distribution of ceramide in the intraluminal membrane lipid bilayer, favoring its retention in the outer leaflet that results in increased acid ceramidase activity in the late endosome/lysosome, facilitating ceramide deacylation to sphingosine leading to the sequestration of free cholesterol in lysosomes (PubMed:24201375). In addition regulates amyloid-beta production either by activating a signaling pathway that regulates amyloid precursor protein transcription through the modulation of sphingolipid metabolism or through its role in gamma-secretase processing of APP (PubMed:22086926, PubMed:26510981). May play a role in myelin formation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P41234, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15238223, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21810484, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22086926, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24201375, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26510981, ECO:0000305|PubMed:15999530}. | Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Disease variant;Endosome;Epilepsy;Glycoprotein;Intellectual disability;Lysosome;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | The membrane-associated protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intracellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the ABC1 subfamily. Members of the ABC1 subfamily comprise the only major ABC subfamily found exclusively in multicellular eukaryotes. This protein is highly expressed in brain tissue and may play a role in macrophage lipid metabolism and neural development. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:20; | ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex [GO:0043190]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; endosome [GO:0005768]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ABC-type transporter activity [GO:0140359]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042626]; ceramide floppase activity [GO:0099038]; endopeptidase regulator activity [GO:0061135]; lipid transporter activity [GO:0005319]; nucleotide binding [GO:0000166]; cellular sphingolipid homeostasis [GO:0090156]; central nervous system myelin formation [GO:0032289]; ceramide translocation [GO:0099040]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; ganglioside metabolic process [GO:0001573]; glycosphingolipid metabolic process [GO:0006687]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; lipid transport [GO:0006869]; locomotory behavior [GO:0007626]; negative regulation of cholesterol efflux [GO:0090370]; negative regulation of intracellular cholesterol transport [GO:0032384]; negative regulation of low-density lipoprotein receptor activity [GO:1905598]; negative regulation of phospholipid biosynthetic process [GO:0071072]; negative regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis involved in cholesterol transport [GO:1905601]; negative regulation of sphingolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0090155]; negative regulation of steroid metabolic process [GO:0045939]; positive regulation of amyloid precursor protein biosynthetic process [GO:0042986]; positive regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process [GO:1902993]; positive regulation of amyloid-beta formation [GO:1902004]; positive regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle receptor catabolic process [GO:0032805]; regulation of intracellular cholesterol transport [GO:0032383]; regulation of post-translational protein modification [GO:1901873]; regulation of protein glycosylation [GO:0060049]; regulation of protein localization to cell periphery [GO:1904375]; regulation of protein localization to cell surface [GO:2000008]; regulation of steroid metabolic process [GO:0019218]; response to cholesterol [GO:0070723]; response to steroid hormone [GO:0048545]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; sphingomyelin metabolic process [GO:0006684]; sphingosine biosynthetic process [GO:0046512]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] | 12363033_roles for this largest known ABC protein in neural transmembrane lipid export 12560508_Reciprocal regulation of expression of the ABCA2 promoter by the early growth response-1 and Sp-family transcription factors. 15093135_It is likely that expression of ABCA2 by two independent promoters constitutes locus of regulation controlling expression of the protein to meet requirements in different tissues. 15155565_Increased expression of ABCA2 may be causally linked with altered expression of genes associated with the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. 15649702_Among the 45 ABCA2 single nucleotide polymorphisms(SNPs) we tested, one synonymous SNP (rs908832) was found significantly associated with AD in both samples. 15850583_the expression patterns of ABCA2 in combination with other markers showed phenotypic heterogeneity in schwannomas 16752360_Data suggest that ABCA2 may exert population-dependent effects on the genetic risk for sporadic Alzheimer's disease and support a role of ABC lipid transporters in the pathogenesis of this disease. 16752360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18336955_No association of ABCA2 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism on chromosome 9 with Alzheimer's disease. 18336955_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20167577_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20704561_A possible biochemical mechanism links ABCA2 expression, amyloid precursor protein processing, and Alzheimer's disease. 21041019_we demonstrate that ABCA2-deficiency inhibits prostate tumor metastasis in vivo and decreases chemotactic potential of cells 21072184_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21707071_SLC2A1/GLUT1, SLC1A3/EAAT1, and SLC1A2/EAAT2 were the main SLC proteins whereas ABCG2/BCRP, ABCB1/MDR1, ABCA2 and ABCA8 were the main ABC quantified in isolated brain microvessels 22086926_Down-regulation of the ATP-binding cassette transporter 2 (Abca2) reduces amyloid-beta production by altering Nicastrin maturation and intracellular localization. 24145140_Our findings indicate a considerable and direct relationship between mRNA expression levels of ABCA2, ABCA3, MDR1, and MRP1 genes and positive minimal residual disease (MRD) measured after one year of treatment. 29224028_The analyses results suggested ABCA2 mRNA expression was upregulated significantly in AD compared with controls in all datasets. 29630744_High expression of ABCA2 is associated with drug resistance in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 32752121_Results from a Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) in Mastocytosis Reveal New Gene Polymorphisms Associated with WHO Subgroups. | ENSMUSG00000026944 | Abca2 | 444.861142 | 0.7922701 | -0.335935706 | 0.15776962 | 4.51978672400 | 0.0335050078298374243157553564742556773126125335693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.12356131018290690548599997100609471090137958526611328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 380.957963 | 38.381855 | 482.861221 | 48.456908 | |
| ENSG00000107581 | 8661 | EIF3A | protein_coding | Q14152 | FUNCTION: RNA-binding component of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 (eIF-3) complex, which is required for several steps in the initiation of protein synthesis (PubMed:17581632, PubMed:25849773). The eIF-3 complex associates with the 40S ribosome and facilitates the recruitment of eIF-1, eIF-1A, eIF-2:GTP:methionyl-tRNAi and eIF-5 to form the 43S pre-initiation complex (43S PIC). The eIF-3 complex stimulates mRNA recruitment to the 43S PIC and scanning of the mRNA for AUG recognition. The eIF-3 complex is also required for disassembly and recycling of post-termination ribosomal complexes and subsequently prevents premature joining of the 40S and 60S ribosomal subunits prior to initiation (PubMed:17581632, PubMed:11169732). The eIF-3 complex specifically targets and initiates translation of a subset of mRNAs involved in cell proliferation, including cell cycling, differentiation and apoptosis, and uses different modes of RNA stem-loop binding to exert either translational activation or repression (PubMed:25849773, PubMed:27462815). {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03000, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11169732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17581632, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25849773, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27462815}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Essential for the initiation of translation on type-1 viral ribosomal entry sites (IRESs), like for HCV, PV, EV71 or BEV translation (PubMed:23766293, PubMed:24357634). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23766293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24357634}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) In case of FCV infection, plays a role in the ribosomal termination-reinitiation event leading to the translation of VP2 (PubMed:18056426). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18056426}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Host-virus interaction;Initiation factor;Phosphoprotein;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding | Enables RNA binding activity. Contributes to translation initiation factor activity. Involved in IRES-dependent viral translational initiation; formation of cytoplasmic translation initiation complex; and viral translational termination-reinitiation. Located in cytosol; nucleolus; and nucleoplasm. Part of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:8661; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; eukaryotic 43S preinitiation complex [GO:0016282]; eukaryotic 48S preinitiation complex [GO:0033290]; eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex [GO:0005852]; eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex, eIF3e [GO:0071540]; eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 complex, eIF3m [GO:0071541]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; multi-eIF complex [GO:0043614]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; receptor tyrosine kinase binding [GO:0030971]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; translation initiation factor activity [GO:0003743]; formation of cytoplasmic translation initiation complex [GO:0001732]; IRES-dependent viral translational initiation [GO:0075522]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; translation reinitiation [GO:0002188]; translational initiation [GO:0006413]; viral translational termination-reinitiation [GO:0075525] | 15946946_The complex formation of eIF3 and its association with the ribosomes might contribute to increased translation rates during T lymphocyte activation. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16497727_Consequently, eIF3c appears to be involved in NF2 pathogenesis and deserves to be investigated as a prognostic marker for NF2 and target for treatment of NF2 patient tumors 16829125_REVIEW of roles of subunits of eIF3 in regulating translation of specific mRNAs encoding proteins important for cell growth control, and how altered expression may cause cancer and/or affect prognosis 17381544_May play some roles in development and differentiation; decreased eIF3a expression may be a pre-requisite of intestinal epithelial cell differentiation. 17581632_Extensive deletion analyses suggest that three evolutionarily conserved subunits (eIF3a, eIF3b, and eIF3c) and three non-conserved subunits (eIF3e, eIF3f, and eIF3h) comprise the functional core of mammalian eIF3. 18568671_was no difference in the expression of EGFR, p185(erbB-2) or Bcl-2, or in nuclear accumulation of p53 in these IDC from pre- vs. post-menopausal women. 18599441_interaction map allows comparison of free eIF3 with that bound to the hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site (HCV-IRES) RNA 18725400_eIF3-Paip1 stabilizes the interaction between PABP and eIF4G, which brings about the circularization of the mRNA. 19327350_eIF3a expression oscillated with cell cycle and peaked in S phase. Reducing eIF3a expression also reduced cell proliferation rate by elongating cell cycle but did not change the cell cycle distribution. 20056645_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20399188_analysis of the COP9 signalosome and its common architecture with the 26S proteasome lid and eIF3 20647036_some studies have identified eIF3a to be involved in cancer development, while other results indicate that it could provide protection against evolution into higher malignancy.[review] 20818067_Docetaxel could slightly increase the expression of eIF3a mRNA, and eIF3a does not regulate the expression of alpha-tubulin in A549 cells. 21610145_eIF3a plays an important role in regulating the expression of DNA repair proteins. 21625209_conclude that eIF3a has an important role in the CDDP response and in NER activity of NPCs by suppressing the synthesis of NER proteins 22022972_POLR2J interacts with three different subunits of eIF3, eIF3a, eIF3i, and eIF3m. 22634302_Iron promotes the translation initiation of hepatitis C virus by stimulating the expression of eIF3A and La proteins. 23127338_Lung cancer patients carrying rs3740556 A allele tended to have a favorable prognosis after treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. 23393223_eIF3a regulates RPA2 synthesis by regulating its internal ribosome entry site activity 23437357_NDRG1 is regulated by eukaryotic initiation factor 3a (eIF3a) during cellular stress caused by iron depletion. 23530232_MLN51, alone or as part of the EJC, interacts directly with the pivotal eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF3 23623729_results highlight the conserved architecture of eIF3 and how it scaffolds key factors that control translation initiation in higher eukaryotes, including humans 23766293_Mutations in the RNA-binding motif of subunit eIF3a weaken eIF3 binding to the HCV IRES and the 40S ribosomal subunit, thereby suppressing eIF2-dependent recognition of the start codon. 23921387_eukaryotic initiation factor 3a spectrin domain is the docking site for formation of the a:b:i:g subcomplex 24250809_Taken together, these results show that Neurospora crassa eIF3 provides a tractable system for probing the structure and function of human-like eIF3 in the context of living cells. 24320561_The correct folding of subunits of translation initiation factor eIF3 is mediated by interaction with chaperonin containing TCP-1 (CCT). 24386425_Of the total, the deregulation of several genes (CDK1, CDK2, CDK4, MCM2, MCM3, MCM4, EIF3a and RPN2) were potentially associated with disease development and progression. 24396066_The Paip1-eIF3 interaction is impaired by the mTORC1 inhibitors. 24789280_findings suggested altered eIF3a expression closely correlated with p27 status, and the association was of prognostic value for resected NSCLC 24912683_eIF3a and eIF3c control abundance and assembly of the entire eIF3 and thus represent its crucial scaffolding elements critically required for formation of preinitiation complexes. 25070653_Data conclude that eIF3a expression may have a profound effect on the urinary bladder cancer phenotype and, in addition, may serve as a prognostic marker for low grade UBCs. 25509353_At 37 degrees C, P185(HER2) internalized through coated pits and vesicles and concentrated in the endosomes and multivesicular bodies in the cells of both cell lines, as well as in lysosomes in cells BT-474 25732572_eIF3a SNPs are significantly correlated with platinum-based chemotherapy toxicities in Chinese non-small cell lung carcinoma patients. 25898924_Collybistin forms a complex with mTOR and eIF3 and by sequestering these proteins downregulates mTORC1 signaling and protein synthesis potentially contributing to intellectual disability and autism. 26172298_eIF3 has a role in controlling cell size independently of S6K1-activity 26213845_eIF3a improves ovarian cancer patients' response to cisplatin-based chemotherapy by down regulating XPC and p27(Kip1). 27262813_eIF3a may function as a novel regulator to modulate hepatic stellate cell activation, potentially through inhibiting the TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling pathway. 27333287_An association between eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3a (eIF3a) gene rs77382849 polymorphism and susceptibility to gastric cancer was observed in Chinese patients. 27733651_DHX29 and eIF3 cooperate in scanning on structured mRNAs. Our findings support previous genetic data on the role of eIF3 during scanning 27924037_The human eIF3b and octameric eIF3a subunits serve as the nucleation core around which other subunits assemble in an ordered way into two interconnected modules: the yeast-like core and the octamer. 28007963_interaction involves the first FF motif of p190A and the winged helix/PCI domain of eIF3A, is enhanced by serum stimulation and reduced by phosphatase treatment 28074905_miRNA-488 participates in eIF3a mediated cisplatin resistance in non-small-cell lung cance cells. 28359406_The eIF3a Arg803Lys C>T polymorphism is connected with a higher susceptibility to cervical carcinoma and may affect chemoradiotherapy efficacy in and prognosis of cervical carcinoma. 28981723_Studies suggest that eukaryotic initiation factor eIF3, which coordinates the progress of most of the initiation steps, does not come off the initiation complex upon subunit joining, but instead it remains bound to 80S ribosomes. 29286129_Knockdown of elF3a inhibits TGFB1-induced extracellular matrix protein expression in keloid fibroblasts. 30006345_siRNA-mediated silencing of eIF3a reduced the polysome-to-monosome ratio in F508del-expressing cells, which, in turn, decreased the translation of CFTR variants, leading to increased CFTR stability, trafficking, and function at the cell surface. 31197975_Results found EIF3A highly expressed lung cancer and has a significant effect on the survival rate of the patients. 31414986_Here, the authors show that human eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 (eIF3) acts as a distinct repressor of FTL mRNA translation, and eIF3-mediated FTL repression is disrupted by a subset of single nucleotide polymorphisms in FTL that cause hyperferritinemia. 33000235_MicroRNA8755p inhibits tumor growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit a. 33389493_LncRNA H19 promotes keloid formation through targeting the miR-769-5p/EIF3A pathway. 33595813_Knockdown of eIF3a attenuated cell growth in K1 human thyroid cancer cells. 34022189_The effect of eIF3a on anthracycline-based chemotherapy resistance by regulating DSB DNA repair. 34648968_eIF3a R803K mutation mediates chemotherapy resistance by inducing cellular senescence in small cell lung cancer. 35279705_eIF3a regulation of mTOR signaling and translational control via HuR in cellular response to DNA damage. 35595099_Translation initiation factor eIF3a regulates glucose metabolism and cell proliferation via promoting small GTPase Rheb synthesis and AMPK activation. 35708211_YTHDF3 Facilitates eIF2AK2 and eIF3A Recruitment on mRNAs to Regulate Translational Processes in Oxaliplatin-Resistant Colorectal Cancer. | ENSMUSG00000024991 | Eif3a | 1841.873624 | 0.9934480 | -0.009483607 | 0.03637252 | 0.06798513004 | 0.7942933389238179264779660115891601890325546264648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.90249169237806547982927440898492932319641113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1840.915857 | 43.406032 | 1861.903228 | 43.787625 | |
| ENSG00000107833 | 10360 | NPM3 | protein_coding | O75607 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in the regulation of diverse cellular processes such as ribosome biogenesis, chromatin remodeling or protein chaperoning (PubMed:22362753, PubMed:20073534). Modulates the histone chaperone function and the RNA-binding activity of nucleolar phosphoprotein B23/NPM (PubMed:22362753). Efficiently mediates chromatin remodeling when included in a pentamer containing NPM3 and NPM (PubMed:15596447). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15596447, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20073534, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22362753}. | Acetylation;Chaperone;Direct protein sequencing;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | The protein encoded by this gene is related to the nuclear chaperone phosphoproteins, nucleoplasmin and nucleophosmin. This protein is strongly expressed in diverse cell types where it localizes primarily to the nucleus. Based on its similarity to nucleoplasmin and nucleophosmin, this protein likely functions as a molecular chaperone in the cell nucleus. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. | hsa:10360; | actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364]; rRNA transcription [GO:0009303] | 19710011_Acetylation of transition protein 2 (TP2) by KAT3B (p300) alters its DNA condensation property and interaction with putative histone chaperone NPM3. 20073534_NPM3 lacks intrinsic histone chaperone activity, inhibits histone assembly activity of NPM1 in vitro, and dramatically enhances transcription in a cellular system. 22362753_Characterization of the sperm chromatin decondensation and nucleosome assembly activities of homo- and hetero-oligomers of NPM1,NPM2 and NPM3. 22968912_Studies indicate that histone chalerones nucleoplasmin (NPM2/NPM3) preferentially associated with histones H2A-H2B in the egg and the nuclear autoantigenic sperm protein (NASP) families. | ENSMUSG00000056209 | Npm3 | 36.824394 | 1.5742291 | 0.654645518 | 0.27054827 | 5.82730250450 | 0.0157793009949088319787691148121666628867387771606445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.06978212529775046357727319445984903723001480102539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 47.188963 | 9.394104 | 29.951064 | 6.061208 | |
| ENSG00000108179 | 10105 | PPIF | protein_coding | P30405 | FUNCTION: PPIase that catalyzes the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides and may therefore assist protein folding (PubMed:20676357). Involved in regulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) (PubMed:26387735). It is proposed that its association with the mPTP is masking a binding site for inhibiting inorganic phosphate (Pi) and promotes the open probability of the mPTP leading to apoptosis or necrosis; the requirement of the PPIase activity for this function is debated (PubMed:26387735). In cooperation with mitochondrial p53/TP53 is involved in activating oxidative stress-induced necrosis (PubMed:22726440). Involved in modulation of mitochondrial membrane F(1)F(0) ATP synthase activity and regulation of mitochondrial matrix adenine nucleotide levels (By similarity). Has anti-apoptotic activity independently of mPTP and in cooperation with BCL2 inhibits cytochrome c-dependent apoptosis (PubMed:19228691). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99KR7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19228691, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20676357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22726440, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26387735}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Isomerase;Mitochondrion;Necrosis;Reference proteome;Rotamase;S-nitrosylation;Transit peptide | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase) family. PPIases catalyze the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides and accelerate the folding of proteins. This protein is part of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Activation of this pore is thought to be involved in the induction of apoptotic and necrotic cell death. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:10105; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrial permeability transition pore complex [GO:0005757]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; cyclosporin A binding [GO:0016018]; peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity [GO:0003755]; apoptotic mitochondrial changes [GO:0008637]; cellular response to arsenic-containing substance [GO:0071243]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; cellular response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0070301]; mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in programmed cell death [GO:1902686]; necroptotic process [GO:0070266]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of ATP-dependent activity [GO:0032780]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001243]; negative regulation of oxidative phosphorylation [GO:0090324]; negative regulation of oxidative phosphorylation uncoupler activity [GO:2000276]; negative regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090201]; positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090200]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein peptidyl-prolyl isomerization [GO:0000413]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability [GO:0046902]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability involved in programmed necrotic cell death [GO:1902445]; regulation of necrotic cell death [GO:0010939]; regulation of proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism [GO:0010849]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931] | 12077116_Cyclophilin D protects cell from cell death. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18076075_Crystal structure of human cyclophilin D in complex with its inhibitor, cyclosporin A at 0.96-A resolution, using a K133I mutant of human CypD 18614807_There was increased [Ca(2+)](c), [Ca(2+)](m), mCICR, MPTP opening, and expression of cyclophilin D and decreased DeltaPsim in POAG TM cells compared with control cells. 19735641_Cyclophilin D may play a role as a redox sensor in mitochondria of mammalian cells transmitting information on the redox environment to target proteins. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20978188_Data show that show that the molecular chaperone heat shock protein 60 (Hsp60) directly associates with cyclophilin D (CypD). 21121808_adult viable human brain and liver mitochondria possess an active CypD-sensitive mitochondrial permeability transition 22013052_Human coronavirus-induced neuronal programmed cell death required cyclophilin d but not caspase 3 caspase 9 activities. 22892127_These results suggest Cyp-D's critical role in UVB/oxidative stress-induced skin cell death. 23303179_CypD directs mitochondria-to-nuclei inflammatory gene expression in normal and tumor cells 23845906_cisplatin-induced non-apoptotic death requires mitochondria Cyp-D-p53 signaling in pancreatic cancer cells 24343341_The p53/Cyp-D mitochondrial complexation was prevented by CsA or Cyp-D silencing. 24946211_In summary, the results of the present study provide mechanistic evidence that both apoptosis and programmed necrosis attribute to berberine's cytotoxicity in prostate cancer cells. 25445707_molecular determinants necessary for Cyclophilin D activity regulation and binding to proposed pore constituents thereby regulating the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. 25837584_Cyp-D silencing down-regulated mitochondrial transcripts initiated from the heavy strand promoter 2 [i.e., NADH dehydrogenase 1 (ND1) by 11-fold; cytochrome oxidase 1 (COX1) by 4-fold; and ATP synthase subunit 6 (ATP6) by 6.5-fold. 26387735_Results show that CypD interacts with SPG7 and VDAC to form the mitochondrial permeability transition pore complex (PTP)and its CsA-binding region is necessary for PTP formation. 27515399_The influx of unfolded p53 into the mitochondrial matrix in response to oxidative stress indirectly activates the normally inhibited CypD by displacing it from Trap1 complexes. This activates CypD's isomerase activity. Liberated CypD then isomerizes multiple proteins including p53 (causing p53 aggregation) and the structural components of the mPTP pore, inducing pore opening. 27864141_cyclophilin D may modify mitochondrial features by inducing the translocation of molecules to the mitochondria through the mechanism associated with cellular energy metabolism 27916505_CyPD regulates mitochondrial metabolism, and likely cell survival, by promoting more efficient electrons flow through the respiratory chain via increased supercomplex formation 27993675_The present study is to investigate the role of CypD in regulating the mitochondrial dynamics relevant to oxidative stress induced neuron dysfunctions. 28351946_Binding of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) to cyclophilin D (CypD) was important for reducing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production after oxidative stress. 28378042_This review discusses previous studies to provide comprehensive information on the physiological role of cyclophilin D as well as PTP opening in the cell that can be taken into consideration for the development of new PTP inhibitors. [review] 30558250_the important yet enigmatic nature of CyPD (PPIF) somehow makes it a master regulator, yet a troublemaker, for mitochondrial function. 31884421_Targeting cyclophilin-D by miR-1281 protects human macrophages from Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced programmed necrosis and apoptosis. 32041924_microRNA-1203 targets and silences cyclophilin D to protect human endometrial cells from oxygen and glucose deprivation-re-oxygenation. 32275395_RNase T1 Refolding Assay for Determining Mitochondrial Cyclophilin D Activity: A Novel In Vitro Method Applicable in Drug Research and Discovery. 33495413_Overexpression of TICRR and PPIF confer poor prognosis in endometrial cancer identified by gene co-expression network analysis. 34681682_Formation of High-Conductive C Subunit Channels upon Interaction with Cyclophilin D. | ENSMUSG00000021868 | Ppif | 2699.711395 | 0.7557508 | -0.404017580 | 0.03144503 | 165.31676102076 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000780035961142955334230512973076724698631395899117446152469790534645779367175387800302022330103154500874351739980738784652203321456909179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000000000000000000000000000000001113381941272210153874252563232962188855775587198019012216781966595028263948243927430444081541280332281473874900257214903831481933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 2329.307450 | 77.796240 | 3096.716163 | 102.018262 | |
| ENSG00000108352 | 51195 | RAPGEFL1 | protein_coding | Q9UHV5 | FUNCTION: Probable guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Reference proteome | Predicted to enable guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity. Predicted to be involved in G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway and nervous system development. Predicted to be located in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:51195; | membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265] | ENSMUSG00000038020 | Rapgefl1 | 21.939731 | 0.7811377 | -0.356351201 | 0.51534182 | 0.46612124793 | 0.4947770087141764583371639218967175111174583435058593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.70882228573268135640716991474619135260581970214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 19.013804 | 6.032823 | 24.259432 | 7.467243 | ||
| ENSG00000108465 | 80279 | CDK5RAP3 | protein_coding | Q96JB5 | FUNCTION: Substrate adapter for ufmylation, the covalent attachment of the ubiquitin-like modifier UFM1 to substrate proteins, in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress (PubMed:23152784, PubMed:30635284). Negatively regulates NF-kappa-B-mediated gene transcription through the control of RELA phosphorylation (PubMed:17785205, PubMed:20228063). Probable tumor suppressor initially identified as a CDK5R1 interactor controlling cell proliferation (PubMed:12054757, PubMed:12737517). Also regulates mitotic G2/M transition checkpoint and mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint (PubMed:15790566, PubMed:19223857). Through its interaction with CDKN2A/ARF and MDM2 may induce MDM2-dependent p53/TP53 ubiquitination, stabilization and activation in the nucleus, thereby promoting G1 cell cycle arrest and inhibition of cell proliferation (PubMed:16173922). May also play a role in the rupture of the nuclear envelope during apoptosis (PubMed:23478299). May regulate MAPK14 activity by regulating its dephosphorylation by PPM1D/WIP1 (PubMed:21283629). Required for liver development (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99LM2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12054757, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12737517, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15790566, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16173922, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17785205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19223857, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20228063, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21283629, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23152784, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23478299, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30635284}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) May be negatively regulated by hepatitis B virus large envelope protein mutant pre-s2 to promote mitotic entry. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21971960}. | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes a protein that has been reported to function in signaling pathways governing transcriptional regulation and cell cycle progression. It may play a role in tumorigenesis and metastasis. A pseudogene of this gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 20. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. | hsa:80279; | centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; cyclin binding [GO:0030332]; MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding [GO:0097371]; mitogen-activated protein kinase binding [GO:0051019]; NF-kappaB binding [GO:0051059]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding [GO:0044389]; apoptotic nuclear changes [GO:0030262]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; definitive erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0060318]; endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response [GO:0030968]; liver development [GO:0001889]; mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0007095]; mitotic G2/M transition checkpoint [GO:0044818]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; negative regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0042177]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity by regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0044387]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; negative regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071901]; positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus [GO:1900182]; positive regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031398]; positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:1901798]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein ufmylation [GO:0071569]; regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0000079]; regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0007346]; regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045664]; regulation of phosphatase activity [GO:0010921]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976] | 12054757_IC53 is a novel gene, mainly expressed in vascular endothelial cells and mediates cell proliferation 15790566_results strongly indicate that in response to genotoxic stress, Cdk5 activator-binding protein C53(C53) serves as an important regulatory component of DNA damage checkpoint through modulating cyclin dependent kinase 1-cyclin B1 function 16173922_It is suggested that LZAP can regulate ARF biochemical and biological activity; additionally, LZAP has p53-dependent cell-cycle effects that are independent of ARF. 17549666_it is concluded that CDK5RAP3, CCNB2, and RAGE genes may be used as a very reliable biomarkers of lung adenocarcinoma 17785205_LZAP has a role in NF-kappaB regulation and tumor suppression. 19223857_CDK5 regulatory subunit associated protein 3 promotes checkpoint kinase 1 activation and mitotic entry in both unperturbed cell-cycle progression and DNA damage response. 19541669_Endothelium-specific overexpression of human IC53 downregulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity and elevates systolic blood pressure in mice. 20228063_found that C53/LZAP and DDRGK1 became more susceptible to the proteasome-mediated degradation in RCAD knockdown cells, whereas their ubiquitination was significantly attenuated by RCAD overexpression 21283629_the ability of LZAP to alter p38 phosphorylation depended, at least partially, on the p38 phosphatase, Wip1 21385901_Findings reveal that CDK5RAP3 is widely overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and that overexpression of CDK5RAP3 promotes HCC metastasis through PAK4 activation. 21394385_Data indicate that IC53 is a positive mediator for colon cancer progression, and IC53-rs2737 may serve as protection from the onset of colorectal cancer. 21465471_Nuclear gamma-tubulin interacts with tumor suppressor protein C53 that is involved in regulation of DNA damage 21971960_our results strongly suggest that the binding of hepatitis viral pre-S2 LHBs with C53 is a novel negative regulator of the checkpoint response 22028922_LZAP may play an important role in hepatocellular carcinoma progression 22860085_our findings provide the new evidence that overexpression of CDK5RAP3 promotes HCC metastasis via downregulation of p14(ARF). 23478299_C53/LZAP protein bound indirectly to the microtubule (MT), and expression of the C53/LZAP cleavage product caused abnormal MT bundling and NE rupture. 27793695_CDK5RAP3 negatively regulates the beta-catenin signaling pathway by repressing GSK-3beta phosphorylation in gastric neoplasms. 29540196_Our results demonstrated that CDK5RAP3 negatively regulates the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway by repressing AKT phosphorylation, which leads to better survival of patients with gastric cancer. 30228783_Prognostic analysis showed that the co-expression of CDK5RAP3 and DDRGK1 was an independent prognostic factor correlating with the overall survival of gastric cancer patients. 30864700_Study demonstrated that CDK5RAP3/C53 isoform d (IC53d) was upregulated in gastric cancer tissues and was associated with tumor Tstage. Furthermore, overexpression of IC53d promoted the proliferation, colony formation and G1/S phase transition of gastric cancer cells, leading to enhancement of tumorigenesis in vitro and in vivo. 30954448_The current findings advance innovation in drug discovery and highlight C53 as a novel pGC-B activator with sustained in vivo activity and anti-fibrotic actions in vitro. 31061682_CDK5RAP3 is associated with autophagy and down-regulated in renal cancer. 32606358_CDK5RAP3 as tumour suppressor negatively regulates self-renewal and invasion and is regulated by ERK1/2 signalling in human gastric cancer. 35219640_CDK5RAP3 acts as a putative tumor inhibitor in papillary thyroid carcinoma via modulation of Akt/GSK-3beta/Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. | ENSMUSG00000018669 | Cdk5rap3 | 596.437472 | 0.9015273 | -0.149556910 | 0.08634690 | 2.99904565187 | 0.0833135795066318879387168294670118484646081924438476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.23381052361867277200602188713673967868089675903320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 586.880648 | 35.108691 | 654.181502 | 38.398297 | |
| ENSG00000108510 | 9969 | MED13 | protein_coding | Q9UHV7 | FUNCTION: Component of the Mediator complex, a coactivator involved in the regulated transcription of nearly all RNA polymerase II-dependent genes. Mediator functions as a bridge to convey information from gene-specific regulatory proteins to the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. Mediator is recruited to promoters by direct interactions with regulatory proteins and serves as a scaffold for the assembly of a functional preinitiation complex with RNA polymerase II and the general transcription factors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16595664}. | Activator;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation | This gene encodes a component of the mediator complex (also known as TRAP, SMCC, DRIP, or ARC), a transcriptional coactivator complex thought to be required for the expression of almost all genes. The mediator complex is recruited by transcriptional activators or nuclear receptors to induce gene expression, possibly by interacting with RNA polymerase II and promoting the formation of a transcriptional pre-initiation complex. The product of this gene is proposed to form a sub-complex with MED12, cyclin C, and CDK8 that can negatively regulate transactivation by mediator. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:9969; | mediator complex [GO:0016592]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; nuclear receptor coactivator activity [GO:0030374]; nuclear thyroid hormone receptor binding [GO:0046966]; nuclear vitamin D receptor binding [GO:0042809]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0060261]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; triglyceride homeostasis [GO:0070328] | 19240132_Med12 and Med13 are critical for human CDK8 subcomplex -dependent repression, whereas CDK8 kinase activity is not 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25422356_Cardiac overexpression of MED13 in transgenic mice confers a lean phenotype that is associated with increased lipid uptake, beta-oxidation and mitochondrial content in white adipose tissue and liver 26182352_Data suggest that MED13, MED12, CDK8 and cyclin C (CycC) comprise a four-subunit 'kinase' module of the Mediator complex that functions as a major ingress of oncogenic and developmental signaling/gene expression in humans. [REVIEW] 27129500_Each of HSPA4 and MED13 mutations were detected in GC. 29740699_De novo mutations in MED13, a component of the Mediator complex, are associated with a novel neurodevelopmental disorder. 33258286_Could the MED13 mutations manifest as a Kabuki-like syndrome? 33390853_Potential roles of mediator Complex Subunit 13 in Cardiac Diseases. | ENSMUSG00000034297 | Med13 | 728.977603 | 0.7546356 | -0.406148025 | 0.18341744 | 4.88459598807 | 0.0270973755594626983245198914573848014697432518005371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.10578791217576451189064101754411240108311176300048828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 663.311545 | 78.714762 | 882.953343 | 104.848001 | |
| ENSG00000108591 | 1819 | DRG2 | protein_coding | P55039 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the conversion of GTP to GDP through hydrolysis of the gamma-phosphate bond in GTP. When hydroxylated at C-3 of 'Lys-21' by JMJD7, may bind to RNA and play a role in translation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29915238}. | Cytoplasm;GTP-binding;Hydrolase;Hydroxylation;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes a GTP-binding protein known to function in the regulation of cell growth and differentiation. Read-through transcripts containing this gene and a downstream gene have been identified, but they are not thought to encode a fusion protein. This gene is located within the Smith-Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. | hsa:1819; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; cytoplasmic translation [GO:0002181]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 15113831_overexpression of DRG2 in Jurkat cells affects genes regulating cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis, and that these molecular changes may be important in the growth or differentiation of cells 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21296692_Basal expression level of DRG2 is regulated by the Sp1 transcription factor. 26572100_miR19153p functions as a silencer of apoptosis, which regulates lung cancer apoptosis via targeting DRG2/PBX2. 26582392_Results demonstrate that DRG2 is an endosomal protein and a key regulator of Rab5 deactivation and Tfn recycling. 27669826_Authors observed that knockdown of DRG2 in HeLa cells affected growth in a wound-healing assay, and tumorigenicity in nude mice xenografts. 28363867_Taken together, our data demonstrate that DRG2 acts as a regulator of mitochondrial fission by controlling the expression of Drp1. 30281872_Results show that the SNP (rs2257609 C>T) located in the intron region of SLC5A10 variant does not affect the expression of SLC5A10 mRNA, but alters the mRNA expression and promoter activity of DRG2. It is significantly associated with worse overall and disease-free survival of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. 30453731_Using immunoprecipitation, authors show that DRG2 interacts with tau, which regulates microtubule polymerization. Collectively, these data demonstrate that DRG2 may aid in affecting microtubule dynamics in HeLa cells. 31199931_Knockdown of DRG2 in HeLa cells treated with epidermal growth factor (EGF) affects microtubule dynamics, perinuclear Golgi stacking, and cell migration. 31693298_DRG2 supports the growth of primary tumors and metastases of melanoma by enhancing VEGF-A expression. 34190439_Developmentally regulated GTP-binding protein 2 levels in prostate cancer cell lines impact docetaxel-induced apoptosis. 34520979_Developmentally regulated GTP-binding protein-2 regulates adipocyte differentiation. 34664086_Developmentally regulated GTPases: structure, function and roles in disease. | ENSMUSG00000020537 | Drg2 | 86.573647 | 1.0738107 | 0.102739673 | 0.20276370 | 0.25605857057 | 0.6128409932405600724081295993528328835964202880859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.78943544069265902951570978984818793833255767822265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 88.613792 | 12.666560 | 82.381505 | 11.689359 | |
| ENSG00000108599 | 11216 | AKAP10 | protein_coding | O43572 | FUNCTION: Differentially targeted protein that binds to type I and II regulatory subunits of protein kinase A and anchors them to the mitochondria or the plasma membrane. Although the physiological relevance between PKA and AKAPS with mitochondria is not fully understood, one idea is that BAD, a proapoptotic member, is phosphorylated and inactivated by mitochondria-anchored PKA. It cannot be excluded too that it may facilitate PKA as well as G protein signal transduction, by acting as an adapter for assembling multiprotein complexes. With its RGS domain, it could lead to the interaction to G-alpha proteins, providing a link between the signaling machinery and the downstream kinase (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | 3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transit peptide | This gene encodes a member of the A-kinase anchor protein family. A-kinase anchor proteins bind to the regulatory subunits of protein kinase A (PKA) and confine the holoenzyme to discrete locations within the cell. The encoded protein is localized to mitochondria and interacts with both the type I and type II regulatory subunits of PKA. Polymorphisms in this gene may be associated with increased risk of arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]. | hsa:11216; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; protein kinase A binding [GO:0051018]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 12206784_deuterium exchange-mass spectrometry (DXMS) and limited proteolysis to probe the folded regions of D-AKAP2, providing for the first time insight into the intra-domain dynamics of a scaffold protein 12646697_A variant of the kinase-binding domain of this enzyme involves a disease susceptibility polymorphism. 15488188_Results describe the structural features of dual-specificity A kinase-anchoring protein 2 (D-AKAP2) and its interaction with protein kinase A (PKA). 16956908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17143557_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17485678_These studies suggest a role for AKAP10 in heart rhythm control. 17786291_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19056482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19209010_AKAP10 2073A>G variation is associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer in the Chinese population. 19209010_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19462906_There was a significant association between AKAP10 gene 2073A/G polymorphism and colorectal cancer. 19496216_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19496216_the AKAP10 Val allele predicted greater resting heart rate and heart rate variability 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19797056_D-AKAP2 promotes accumulation of recycling proteins in the Rab4/Rab11-positive endocytic recycling compartment 19857670_AKAP10 single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with increased risk of arrhythmia during kidney transplantation. 19857670_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20159461_Results describe the structures of the protein kinase A RIalpha subunit D/D domain alone and in complex with D-AKAP2. 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21701445_Results suggest G1936 polymorphism in A-kinase-anchoring protein is preventative factor against preterm birth, in contrast with previously asserted negative effects in adults. 22817328_There is possible association between a 1936G AKAP10 variant and blood pressure in Polish newborns. 23092224_No significant differences were found in AKAP10 genotype or allele distribution between the age groups (newborn vs. nonagenerian) for either gender. 23095189_Questioned whether 1936A>G is associated with metabolic changes in newborns that are predictive of the metabolic phenotype in adults. Demonstrate an association between 1936G variant and total cholesterol level in cord blood of Polish newborns. 23468363_Studied the clinicopathologic significance of A-kinase anchoring proteins 10 (AKAP 10) expression and the relationship with its polymorphism in colorectal cancer. 25213315_Its signaling pathway is associated with the progression and prognosis of colorectal neoplasms. 25348485_Described is a structure of D-AKAP2 in complex with two interacting partners and the exact mechanism by which a segment that on its own is disordered presents an alpha-helix to PKA and a beta-strand to PDZK1. 26110499_Significant association between the AKAP10 polymorphisms and reduced risk of Preterm birth in the Malays was observed. 28553927_Here, using zebrafish, murine, and human models, the authors show that erythropoietin (EPO) signaling, together with the GATA1 transcriptional target, AKAP10, regulates heme biosynthesis during erythropoiesis at the outer mitochondrial membrane. | ENSMUSG00000047804 | Akap10 | 142.046238 | 1.8832211 | 0.913202405 | 0.33144007 | 7.43124111130 | 0.0064101116646664612133688088135841098846867680549621582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.03508006336672709474244769012329925317317247390747070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 206.579547 | 43.612055 | 109.415289 | 23.122787 | |
| ENSG00000108654 | 1655 | DDX5 | protein_coding | P17844 | FUNCTION: Involved in the alternative regulation of pre-mRNA splicing; its RNA helicase activity is necessary for increasing tau exon 10 inclusion and occurs in a RBM4-dependent manner. Binds to the tau pre-mRNA in the stem-loop region downstream of exon 10. The rate of ATP hydrolysis is highly stimulated by single-stranded RNA. Involved in transcriptional regulation; the function is independent of the RNA helicase activity. Transcriptional coactivator for androgen receptor AR but probably not ESR1. Synergizes with DDX17 and SRA1 RNA to activate MYOD1 transcriptional activity and involved in skeletal muscle differentiation. Transcriptional coactivator for p53/TP53 and involved in p53/TP53 transcriptional response to DNA damage and p53/TP53-dependent apoptosis. Transcriptional coactivator for RUNX2 and involved in regulation of osteoblast differentiation. Acts as transcriptional repressor in a promoter-specific manner; the function probably involves association with histone deacetylases, such as HDAC1. As component of a large PER complex is involved in the inhibition of 3' transcriptional termination of circadian target genes such as PER1 and NR1D1 and the control of the circadian rhythms. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12527917, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15298701, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15660129, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17011493, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17960593, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18829551, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19718048, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21343338}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Biological rhythms;Cytoplasm;Helicase;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;Spliceosome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes a member of the DEAD box family of RNA helicases that are involved in a variety of cellular processes as a result of its role as an adaptor molecule, promoting interactions with a large number of other factors. This protein is involved in pathways that include the alteration of RNA structures, plays a role as a coregulator of transcription, a regulator of splicing, and in the processing of small noncoding RNAs. Members of this family contain nine conserved motifs, including the conserved Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD) motif, important to ATP binding and hydrolysis as well as RNA binding and unwinding activities. Dysregulation of this gene may play a role in cancer development. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2017]. | hsa:1655; | catalytic step 2 spliceosome [GO:0071013]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; MH2 domain binding [GO:0035500]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; nuclear androgen receptor binding [GO:0050681]; pre-mRNA binding [GO:0036002]; primary miRNA binding [GO:0070878]; promoter-specific chromatin binding [GO:1990841]; R-SMAD binding [GO:0070412]; ribonucleoprotein complex binding [GO:0043021]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA helicase activity [GO:0003724]; SMAD binding [GO:0046332]; alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000380]; androgen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030521]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0001837]; intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030520]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator [GO:0072332]; miRNA transcription [GO:0061614]; mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000398]; mRNA transcription [GO:0009299]; myoblast differentiation [GO:0045445]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process [GO:0000956]; positive regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:0043517]; primary miRNA processing [GO:0031053]; regulation of alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000381]; regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060765]; regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045667]; regulation of skeletal muscle cell differentiation [GO:2001014]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; rhythmic process [GO:0048511] | 12101238_Essential for pre-mrna splicing in vitro; may function in destabilizing the U1-5'ss interaction. Depletion of p68 RNA helicase arrested spliceosome assembly at the prespliceosome stage 12527917_synergism with transcriptional coactivators CBP and p300 12665590_role in c-H-ras alternative splicing regulation 15298701_p68 is an important transcriptional regulator, functioning as a co-activator and/or co-repressor depending on the context of the promoter & the transcriptional complex. AA 1-478 of p68 can repress transcription as well as the full-length protein. 15304501_there is a tightly controlled expression and nucleolar localization of p68 in keratinocytes in vitro and during skin repair in vivo that functionally contributes to keratinocyte proliferation and gene expression 15660129_mechanism by which p68 may act as a tumour cosuppressor in governing p53 transcriptional activity 15927448_data suggest that function(s) of p68 RNA helicase may be subjected to the regulation of multiple cell signal pathways 15950181_In addition, it could be demonstrated that increasing the Tlk1 activity in HT1080 cells by forced Tlk1 overexpression leads to an increased phosphorylation of endogenous p68. 16697732_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16697732_Patient with chronic hepatitis C carrying DDX5 haplotypes are at an increased risk of developing advanced liver fibrosis. 17018282_Data show that P68 RNA helicase mediates platelet-derived growth factor-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition by displacing Axin from beta-catenin. 17369852_SUMO modification of the DEAD box protein p68 modulates its transcriptional activity and promotes its interaction with HDAC1 17384675_A mutant that carries mutations at the phosphorylation sites (Y593/595F) dramatically sensitizes TRAIL-resistant cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis, suggesting a potential therapeutic strategy to overcome TRAIL resistance. 17540040_The percentage correlation between Q-RT-PCR and microarray were 70% and 48% by using DDX5 and GAPDH as internal controls, respectively. 17699760_p68/p72 may contribute to colon cancer formation by directly up-regulating proto-oncogenes and indirectly by down-regulating the growth suppressor p21(WAF1/CIP1). 17724023_P68 RNA helicase is an essential component of the let-7 microRNA pathway 18005418_The DEAD-box proteins p68(Ddx5) and p72(Ddx17) were used as models for this coexpression frequency analysis as there are defined functions for these proteins in splicing and transcription. 18239468_DEAD-box RNA helicase p68 is not required for nuclear translocation of beta-catenin in colon cancer cells. 18794152_A ubiquitously expressed, androgen-insensitive gene, DDX5, fused in frame with ETV4, leading to the expression of a DDX5-ETV4 fusion protein was identified in prostate cancer. 18829551_p68 is a novel AR transcriptional coactivator that is significantly overexpressed in PCa with a possible role in progression to hormone-refractory disease. 19171422_Upregulated in at least 50% of multiple myeloma cases tested. 19224332_the Ddx5 (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp box polypeptide 5) protein showed specific interaction with SARS-CoV helicase. 19718048_Distinct but important roles for both p68 and p72 in regulating ERalpha activity in breast cancer. 20022962_DDX5 is a repressor of fibrogenic genes in HSCs through interaction with transcriptional complexes. 20124720_crystallization and preliminary diffraction analysis of N-terminal region of DDX5 is reported.X-ray diffraction data were processed to a resolution of 2.7 A. 20663877_Pleiotropic effects of p300-mediated acetylation on p68 and p72 RNA helicase. 20818423_a striking inverse association of p68 and delta133p53 expression in primary breast cancers was identified. 20966046_DEAD-box RNA helicase p68 (DDX5) and its associated noncoding RNA, steroid receptor RNA activator (SRA), form a complex with CTCF that is essential for insulator function 21343338_Using an RNA affinity pulldown-coupled mass spectrometry approach the study identified DDX5/RNA helicase p68 as an activator of TAU exon 10 splicing. 22086602_High DDX5 is associated with basal breast cancer cells. 22266867_Data indicate that transcriptional coregulator ddx5/ddx17 RNA helicases can simultaneously regulate the transcriptional activity and alternative splicing of NFAT5 transcription factor. 22476084_The DEAD box RNA helicase p68, also referred to as DDX5, directly interacts with VDR. 22640416_there is a direct interaction between DDX5 and NS5B and DDX5 has two independent NS5B-binding sites 22750847_Results show a novel role for DDX5 in cancer cell proliferation and suggest DDX5 as a therapeutic target in breast cancer treatment. 22810421_High p68 RNA helicase expression is associated with glioma. 23022728_RNA helicases Ddx17 and Ddx5 contribute to tumor-cell invasiveness by regulating alternative splicing of several DNA- and chromatin-binding factors, including the macroH2A1 histone. 23108395_DDX5 might be critical for NOTCH1-mediated T-ALL pathogenesis and thus is a potential new target for modulating the Notch signaling in leukemia 23322042_p68, in the presence of Ca-calmodulin, can function as a microtubule motor. 23349811_Data show that p68/DdX5 immunoprecipitated with RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) and suggest p68 is important in facilitating beta-catenin and androgen receptor (AR) transcriptional activity in prostate cancer cells. 23608157_Results suggest that distinct DDX DEAD-box RNA helicases DDX3 and DDX5 cooperate to modulate the HIV-1 Rev function. 23741449_DDX5 facilitates HIV-1 replication as a cellular co-factor of Rev. 24035833_In conclusion, authors identified DDX5 as a positive regulator for Japanese encephalitis virus replication via its binding to viral 3' UTR. 24626184_The data provide a model in which p68 and p53 interplay regulates PLK1 expression, and which describes the behavior of these molecules, and the outcome of their interaction, in human breast cancer. 24644279_Data indicate that armadillo repeat protein ARVCF interacts with the splicing factors the splicing factor SRSF1 (SF2/ASF), the RNA helicase p68 (DDX5), and the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein hnRNP H2. 24910429_AML is dependent on DDX5 and that inhibiting DDX5 expression slows AML cell proliferation. 24910439_Downregulation of DDX5 and DDX17 protein expression during myogenesis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transdifferentiation contributes to the switching of splicing programs during these processes. 25745998_Results show that a new mechanism of oncogenesis is attributed to p68 by upregulation of AKT and consequent nuclear exclusion and degradation of tumor suppressor FOXO3a. 25963660_Data indicate that cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) correlates inversely to microRNA 183 (miR-183) and directly to DEAD-box helicase p68 (DDX5). 26035968_DDX5 protein is essential for normal cell proliferation; (2) the transition from G1 to S/G2 phase is accompanied by an increase of DDX5 protein concentration in the cells. 26080402_study shows that correction of p68 may reduce toxicity of the mutant RNAs in DM1 and in DM2 26209609_Systematic Determination of Human Cyclin Dependent Kinase (CDK)-9 Interactome Identifies Novel Functions in RNA Splicing Mediated by the DEAD Box DDX5 and DDX17 RNA Helicases 26212035_DDX5 played an important role in the proliferation and tumorigenesis of non-small-cell lung cancer cells by activating the beta-catenin signaling pathway. 26314252_Cervical cancer cell DDX5 gene is transcriptionally upregulated by calcitriol through a VDRE located in its proximal promoter. 26587974_p53 gain-of-function mutations accelerate endometrial carcinoma progression and metastasis by interfering with Drosha and p68 binding and pri-miR-26a-1 processing, resulting in reduced miR-26a expression and EZH2 overexpression. 26739063_LMTK3 escapes tumour suppressor miRNAs via sequestration of DDX5. 28216662_Results showed that DDX5 was significantly up-regulated in gastric cancer tissues and revealed a novel role of DDX5 in gastric cancer cell proliferation via the mTOR pathway. 28244855_The role of DDX5 in regulating esophageal cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis.DDX5 is highly expressed in esophageal cancer. 28411202_Results show refined biochemical and biological comparison of yeast Dbp2 and human DDX5 enzymes. Human DDX5 possesses a 10-fold higher unwinding activity than Dbp2, partially due to the presence of a mammalian/avian specific C-terminal extension. Also, ectopic expression of DDX5 rescues the cold sensitivity, cryptic initiation defects, and impaired glucose import in dbp2Delta cells, suggesting functional conservation. 28557706_Downregulation of p68 RNA Helicase (DDX5) Activates a Survival Pathway Involving mTOR and MDM2 Signals.( 29227193_RIP-seq analysis in HEK293T cells identifies a complete repertoire of DDX5/p68 interacting transcripts including LOC284454 lncRNA. 29540201_our study demonstrated that MIAT was upregulated and may function as a ceRNA to increase DDX5 expression by sponging miR-141, which consequently contributed to GC growth and metastasis. 29642538_DDX5 is shown to be involved in RNA metabolism and viral infection, especially for RNA virus which seems to hijack host DDX5 to facilitate its own replication. However, DDX5 exhibits a role in antiviral responses during HBV and MYXV infection. Its opposite roles between DNA and RNA infection likely reflect the different modes of the biosynthesis of RNA and DNA viruses. [review] 30042133_A significant overlap between hnRNPA1 and DDX5 splicing targets and they share many closely linked binding sites. 30119889_DDX5 played a crucial role in hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and tumorigenesis 30185232_Findings indicated that NEAT1 activated Wnt signaling to promote colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. 30387548_Data show that dual specificity phosphatase 5 (DUSP5) is a downstream target of p68 RNA helicase (p68). 30419318_This review affirms that DDX5 plays an indisputable role in human malignancies 30484950_DDX5 O-GlcNAcylation is associated with colorectal cancer progression. 30506978_The DDX5/Dbp2 subfamily of DEAD-box helicases act as chaperones for complexes formed by RNA molecules and proteins (RNP) in vivo. 30720177_miR-431 expression was significantly lower in lung cancer (LCa) tissue samples or cell lines compared to adjacent normal tissues or lung bronchial epithelial cell line, respectively. Overexpression of miR-431 significantly inhibited proliferation, invasion and migration of A549 cells. Downregulation of miR-431 accelerated cell growth and metastasis of H1650 cells. DDX5 was proved to be a direct target for miR-431 in LCa. 31015574_reveal a role for DDX5 as a regulatory protein of Fra-1 signaling and suggest DDX5 as a potential therapeutic target for triple-negative breast cancer 31267554_Study defines a new function for DDX5 in R-loop resolution and reveals a regulatory role for the methylation of its RGG/RG motif in modulating its function. The C-terminal RGG/RG motif of DDX5 was methylated by PRMT5 and required for R-loop resolution, as amino acid substitution of its arginines in the RGG/RG motif with lysines (RK) failed to reverse the accumulation of R-loops in siDDX5 cells. 31379208_Long noncoding RNA DLEU1 aggravates osteosarcoma carcinogenesis via regulating the miR-671-5p/DDX5 axis 31387890_In nucleus, CCAT1 acts as a scaffold for DDX5 (P68) and AR transcriptional complex to facilitate the expression of AR-regulated genes, thus stimulating CRPC progression. 31445188_DDX56 cooperates with FMDV 3A to enhance FMDV replication by inhibiting the phosphorylation of IRF3. 31626956_Knockdown of DEAD-box RNA helicase DDX5 selectively attenuates serine 311 phosphorylation of NF-kappaB p65 subunit and expression level of anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2. 31870221_these results indicate that DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box protein 5 is a potential target for inhibiting basal cell carcinoma cells growth, migration, and invasion by downregulating JAK2/STAT3 pathway. 31994189_Knockdown of terminal differentiation induced ncRNA (TINCR) suppresses proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting the miR-218-5p/DEAD-box helicase 5 (DDX5) axis. 32008867_Upregulation of DEAD box helicase 5 and 17 are correlated with the progression and poor prognosis in gliomas. 32228614_DDX5 potentiates HIV-1 transcription as a co-factor of Tat. 32724471_RNA helicase p68 inhibits the transcription and post-transcription of Pkd1 in ADPKD. 32747416_Genome-wide R-loop analysis defines unique roles for DDX5, XRN2, and PRMT5 in DNA/RNA hybrid resolution. 32920730_Circ-XPR1 promotes osteosarcoma proliferation through regulating the miR-214-5p/DDX5 axis. 32939012_LncRNA SLC26A4-AS1 suppresses the MRN complex-mediated DNA repair signaling and thyroid cancer metastasis by destabilizing DDX5. 33042264_Restoration of RNA helicase DDX5 suppresses hepatitis B virus (HBV) biosynthesis and Wnt signaling in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. 33068674_The expression analyses of RMRP, DDX5, and RORC in RRMS patients treated with different drugs versus naive patients and healthy controls. 33097588_Low expression of DDX5 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 33108271_The S-phase-induced lncRNA SUNO1 promotes cell proliferation by controlling YAP1/Hippo signaling pathway. 33169694_Decreased expression of DEAD-Box helicase 5 inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinomas by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy. 33550957_Silencing of Long Non-Coding RNA FGD5-AS1 Inhibits the Progression of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Regulating the miR-493-5p/DDX5 Axis. 33634895_BRCA2 promotes DNA-RNA hybrid resolution by DDX5 helicase at DNA breaks to facilitate their repairdouble dagger. 33754075_LncRNA PRADX-mediated recruitment of PRC2/DDX5 complex suppresses UBXN1 expression and activates NF-kappaB activity, promoting tumorigenesis. 33819916_MSC-AS1 induced cell growth and inflammatory mediators secretion through sponging miR-142-5p/DDX5 in gastric carcinoma. 33909701_The RNA helicase DDX5 promotes viral infection via regulating N6-methyladenosine levels on the DHX58 and NFkappaB transcripts to dampen antiviral innate immunity. 34021034_RNA helicase DDX5 enables STAT1 mRNA translation and interferon signalling in hepatitis B virus replicating hepatocytes. 34308648_Molecular Insights into the Recruiting Between UCP2 and DDX5/UBAP2L in the Metabolic Plasticity of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. 34697388_Thrap3 promotes R-loop resolution via interaction with methylated DDX5. 34890713_Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and p68 conjointly regulate CHIP in colorectal carcinoma. 35007564_The RNA helicases DDX5 and DDX17 facilitate neural differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells NTERA2. 35184719_P68 RNA Helicase (DDX5) Required for the Formation of Various Specific and Mature miRNA Active RISC Complexes. 35549637_Knockdown of KRAB domain-associated protein 1 suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of thyroid cancer cells by regulating P68/DEAD box protein 5. 36044855_The RNA helicase DDX5 cooperates with EHMT2 to sustain alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma growth. 36246972_Cleavage of AUF1 by Coxsackievirus B Affects DDX5 Regulatory on Viral Replication through iTRAQ Proteomics Analysis. | ENSMUSG00000020719 | Ddx5 | 5533.082335 | 0.7599388 | -0.396044923 | 0.36903402 | 1.14481391970 | 0.2846374152616495400991425412939861416816711425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.51761676607903717162173506949329748749732971191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 5257.985313 | 1584.484631 | 6948.328086 | 2094.501130 | |
| ENSG00000108883 | 9343 | EFTUD2 | protein_coding | Q15029 | FUNCTION: Required for pre-mRNA splicing as component of the spliceosome, including pre-catalytic, catalytic and post-catalytic spliceosomal complexes (PubMed:28502770, PubMed:28781166, PubMed:28076346, PubMed:29361316, PubMed:30315277, PubMed:29360106, PubMed:29301961, PubMed:30705154). Component of the U5 snRNP and the U4/U6-U5 tri-snRNP complex, a building block of the spliceosome (PubMed:16723661). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16723661, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28076346, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28502770, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28781166, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29301961, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29360106, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29361316, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30315277, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30705154}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;GTP-binding;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Spliceosome;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes a GTPase which is a component of the spliceosome complex which processes precursor mRNAs to produce mature mRNAs. Mutations in this gene are associated with mandibulofacial dysostosis with microcephaly. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. | hsa:9343; | Cajal body [GO:0015030]; catalytic step 2 spliceosome [GO:0071013]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; U2-type catalytic step 2 spliceosome [GO:0071007]; U2-type precatalytic spliceosome [GO:0071005]; U4/U6 x U5 tri-snRNP complex [GO:0046540]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; U5 snRNA binding [GO:0030623]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466]; mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000398]; response to cocaine [GO:0042220] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22305528_Validation studies of eight additional individuals with MFDM demonstrated causative EFTUD2 mutations in all affected individuals tested. 23188108_EFTUD2 haploinsufficiency leads to syndromic oesophageal atresia. 23239648_Novel mutations in EFTUD2 were discovered in 3 patients. These mutations expand the clinical features in patients with EFTUD2 mutations and demonstrate an overlap with oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum. 23879989_the phenotype in patients with EFTUD2 mutations is much broader than previously anticipated; in addition to AFD type Guion-Almeida and syndromic esophageal atresia, oto-facial syndrome also belongs to the EFTUD2 mutation spectrum 24266672_A de nove deletion mutation at 17q21.31, encompassing the EFTUD2 gene, is associated with congenital mandibulofacial dysostosis with microcephaly. 24470203_Study describes loss-of-function mutations in EFTUD2 gene in patients with different clinical manifestations of Mandibulofacial dysostosis, Guion-Almeida type syndrome. 25387991_Three different mutations in EFTUD2 gene were found in patients with mandibulofacial dysostosis type Guion-Almeida syndrome 25450007_Results show that SNW1 directly associates with EFTUD2 and SNRNP200 and that disruption of SNW1 association with these proteins promotes the apoptosis of breast cancer cells. 25735261_Novel heterozygous mutations in EFTUD2, detected by exome sequencing, in mandibulofacial dysostosis with Microcephaly syndrome. 25790162_We report a clinical and extensive molecular study, including TCOF1, POLR1D, POLR1C, and EFTUD2 genes, in a series of 146 patients with TCS. 25878102_These data demonstrate that EFTUD2 restricts Hepatitis C Virus infection mainly through an RIG-I/MDA5-mediated, JAK-STAT-independent pathway, thereby revealing the participation of EFTUD2 as a novel innate immune regulator. 26507355_An update on mandibulofacial dysostosis with microcephaly and EFTUD2 mutations has been presented. (Review) 29381487_we report two individuals of Asian ancestry with Mandibulofacial dysostosis type Guion-Almeida (MFDGA), each harboring a novel, pathogenic splice site variant in EFTUD2 30343593_report 2 cases of mandibulofacial dysostosis with microcephaly (MFDM) with different and novel de novo mutations in the elongation factor Tu GTP binding domain containing 2 gene 32333448_EFTUD2 missense variants disrupt protein function and splicing in mandibulofacial dysostosis Guion-Almeida type. 32447180_Spliceosome protein EFTUD2 is upregulated in the trophoblast of spontaneous miscarriage and hydatidiform mole. 32541334_A novel EFTUD2 mutation identified an adult male with mandibulofacial dysostosis Guion-Almeida type. 33024090_EFTUD2 maintains the survival of tumor cells and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the activation of STAT3. 33247512_Mandibulofacial dysostosis with microcephaly: An expansion of the phenotype via parental survey. 34436958_Association of Elongation Factor Tu GTP-binding Domain-containing 2 Gene (EFTUD2) Polymorphism with the Risk of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. 35843132_The Pregnancy Zone Protein (PZP) is significantly downregulated in the placenta of preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome patients. | ENSMUSG00000020929 | Eftud2 | 977.887001 | 0.9157595 | -0.126959350 | 0.08872774 | 2.04622142946 | 0.1525844750899959523238180736370850354433059692382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.34861694127228132211726574496424291282892227172851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 923.370896 | 59.881751 | 1013.152564 | 65.585610 | |
| ENSG00000109332 | 7323 | UBE2D3 | protein_coding | P61077 | FUNCTION: Accepts ubiquitin from the E1 complex and catalyzes its covalent attachment to other proteins. In vitro catalyzes 'Lys-11'-, as well as 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitination. Cooperates with the E2 CDC34 and the SCF(FBXW11) E3 ligase complex for the polyubiquitination of NFKBIA leading to its subsequent proteasomal degradation. Acts as an initiator E2, priming the phosphorylated NFKBIA target at positions 'Lys-21' and/or 'Lys-22' with a monoubiquitin. Ubiquitin chain elongation is then performed by CDC34, building ubiquitin chains from the UBE2D3-primed NFKBIA-linked ubiquitin. Acts also as an initiator E2, in conjunction with RNF8, for the priming of PCNA. Monoubiquitination of PCNA, and its subsequent polyubiquitination, are essential events in the operation of the DNA damage tolerance (DDT) pathway that is activated after DNA damage caused by UV or chemical agents during S-phase. Associates with the BRCA1/BARD1 E3 ligase complex to perform ubiquitination at DNA damage sites following ionizing radiation leading to DNA repair. Targets DAPK3 for ubiquitination which influences promyelocytic leukemia protein nuclear body (PML-NB) formation in the nucleus. In conjunction with the MDM2 and TOPORS E3 ligases, functions ubiquitination of p53/TP53. Supports NRDP1-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of ERBB3 and of BRUCE which triggers apoptosis. In conjunction with the CBL E3 ligase, targets EGFR for polyubiquitination at the plasma membrane as well as during its internalization and transport on endosomes. In conjunction with the STUB1 E3 quality control E3 ligase, ubiquitinates unfolded proteins to catalyze their immediate destruction. Together with RNF135, catalyzes the viral RNA-dependent 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of RIGI to activate the downstream signaling pathway that leads to interferon beta production (PubMed:28469175). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10329681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11743028, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12646252, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15247280, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15280377, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15496420, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16628214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18284575, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18508924, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18515077, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18948756, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20061386, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20347421, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21532592, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28469175}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;DNA damage;DNA repair;Endosome;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Ubl conjugation pathway | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00388}. | The modification of proteins with ubiquitin is an important cellular mechanism for targeting abnormal or short-lived proteins for degradation. Ubiquitination involves at least three classes of enzymes: ubiquitin-activating enzymes, or E1s, ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, or E2s, and ubiquitin-protein ligases, or E3s. This gene encodes a member of the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family. This enzyme functions in the ubiquitination of the tumor-suppressor protein p53, which is induced by an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2017]. | hsa:7323; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity [GO:0061631]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030514]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of protein targeting to mitochondrion [GO:1903955]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein autoubiquitination [GO:0051865]; protein K11-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070979]; protein K48-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070936]; protein modification process [GO:0036211]; protein monoubiquitination [GO:0006513]; protein polyubiquitination [GO:0000209]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] | 12215439_Transducin beta-gamma is a substrate of UbcH5c (UBE2D3), UbcH7 (UBE2L3) and the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway only following the dissociation of transducin alpha from beta-gamma. Transducin beta-gamma is protected from ubiquitylation by phosducin. 15280377_UbcH5B/C are E2s for Mdm2, which contribute to the maintenance of low levels of p53 and Mdm2 in unstressed cells; inhibition of p53 ubiquitination and degradation by targeting UbcH5B/C is not sufficient to up-regulate p53 transcriptional activity. 17420285_Knocking down UBE2D3 by RNA interference leads to blockage oof retinoic acid induced chclin D1 degradation and cell cycle arrest. 18515077_These results suggest that UbcH5 regulates ZIPK accumulation in PML-NBs by interacting with ZIPK and stimulating its ubiquitination. 20051513_role of WW3 and WW4 domains of Nedd4-2 in dopamine transporter ubiquitination was demonstrated; siRNA analysis demonstrated that this polyubiquitination is mediated by Nedd4-2 cooperation with UBE2D and UBE2L3 E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes 20332099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20347421_Combined Actions of UbcH5c and Cdc34 Promote Rapid and Efficient Polyubiquitination of IkBa 20696396_determined structures of E4B U box free and bound to UbcH5c and Ubc4 E2s; findings show E4B U box is a monomer stabilized by a network of hydrogen bonds; findings suggest allosteric regulation of UbcH5c and Ubc4 by E4B U box 20860768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21226485_UbcH5c approximately Ub conjugate populates an array of extended conformations, and the population of Ubc13 approximately Ub conjugates favors a closed conformation in which the hydrophobic surface of Ub faces helix 2 of Ubc13 21772249_The crystal structure of a complex of the Bmi1/Ring1b RING-RING heterodimer & UbcH5c shows that UbcH5c interacts with Ring1b only. 23550736_although a reduction in interdomain dynamics of UbcH5c~Ub is observed upon binding to E4B, Ub retains an extensive degree of flexibility 23741361_UBE2D3 participates in the process of radiosensitivity in human breast cancer cells by regulating TERT and cyclin D1. 24296361_This study demonistrated by Gene expression profile that UBE3D3 upregulaion in fibroblasts of Huntington's disease patients. 24403071_These data reveal novel insights into the Otub1 inhibition of E2 wherein monoubiquitination promotes the interaction of Otub1 with UbcH5 and the function to suppress it. 24446487_UbcH5c~Ubiqitin binding stabilizes an active conformation of the Shigella flexneri OspG kinase, greatly enhancing its activity. 26502057_Data show that ubiquitin E2 enzymes UBE2D1/2/3 and E3 ligase RNF138 accumulate at DNA-damage sites and act at early resection stages by promoting CtIP protein ubiquitylation and accrual. 27105523_Findings indicate that UBE2D3 enhances radiosensitivity of EC109 cells by degradating hTERT through the ubiquitin proteolysis pathway. 28469175_Together with Riplet, Ube2D3 promotes covalent conjugation of polyubiquitin chains to RIG-I, while Ube2N preferentially facilitates production of unanchored chains. In the presence of these chains, RIG-I induces MAVS aggregation directly on the mitochondria. Data thus reveal two essential mechanisms underlying the activation of RIG-I and MAVS for triggering innate immune signaling in response to viral infection in cells. 32145025_Evolution of an Amniote-Specific Mechanism for Modulating Ubiquitin Signaling via Phosphoregulation of the E2 Enzyme UBE2D3. 32401531_UbcH5 Interacts with Substrates to Participate in Lysine Selection with the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase CHIP. 34416429_UBCH5 Family Members Differentially Impact Stabilization of Mutant p53 via RNF128 Iso1 During Barrett's Progression to Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. | 1853.163929 | 1.0268007 | 0.038156230 | 0.05477605 | 0.48505092516 | 0.4861433189066480808904202604026068001985549926757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.70271359287783508040803326366585679352283477783203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1986.275009 | 65.975558 | 1943.464546 | 64.637226 | ||
| ENSG00000109381 | 1998 | ELF2 | protein_coding | Q15723 | FUNCTION: Isoform 1 transcriptionally activates the LYN and BLK promoters and acts synergistically with RUNX1 to transactivate the BLK promoter.; FUNCTION: Isoform 2 may function in repression of RUNX1-mediated transactivation. | Activator;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation | Enables DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated; and regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in cytosol and nuclear body. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:1998; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 11967990_angiopoietin-1 regulates expression of NERF2 and its own receptor in hypoxic cells. 12447867_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14970218_NERF/ELF-2 physically interacts with AML1 and mediates opposing effects on AML1-mediated transcription of the B cell-specific blk gene 17368566_These findings indicate that ELF2/NERF promotes VCP transcription and that ELF2/NERF-VCP pathway might be important for cell survival and proliferation under cytokine stress. 18544453_ELF2 transactivates VCP promoter through binding to two motifs, with a predominant contribution of the upstream one. 18754678_Affinity of the CAL PDZ domain for the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) C-terminus is much weaker than that of the NHERF1/NHERF2 domains, enabling wild-type CFTR to avoid premature entrapment in the lysosomal pathway. 26968954_Our findings collectively support a potential role of triiodothyronine and its receptor in tumor growth inhibition through regulation of ELF2 28728844_PCAT7 contributed to the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through regulating miR-134-5p/ELF2 signaling pathway. 29632131_Mutations in eIF2B genes cause vanishing white matter disease due to translation defects. 35239093_Circ_0028007 Aggravates the Malignancy of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Regulating miR-656-3p/ELF2 Axis. | ENSMUSG00000037174 | Elf2 | 140.469011 | 1.0641794 | 0.089741334 | 0.14206624 | 0.39885966989 | 0.5276787591137431787657874338037800043821334838867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.73470802353108100035683492023963481187820434570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 146.132118 | 10.118368 | 138.089538 | 9.706254 | |
| ENSG00000109685 | 7468 | NSD2 | protein_coding | O96028 | FUNCTION: Histone methyltransferase which specifically dimethylates nucleosomal histone H3 at 'Lys-36' (H3K36me2) (PubMed:27571355, PubMed:22099308, PubMed:19808676, PubMed:29728617, PubMed:33941880). Also monomethylates nucleosomal histone H3 at 'Lys-36' (H3K36me) in vitro (PubMed:22099308). Does not trimethylate nucleosomal histone H3 at 'Lys-36' (H3K36me3) (PubMed:22099308). However, specifically trimethylates histone H3 at 'Lys-36' (H3K36me3) at euchromatic regions in embryonic stem (ES) cells (By similarity). By methylating histone H3 at 'Lys-36', involved in the regulation of gene transcription during various biological processes (PubMed:16115125, PubMed:22099308, PubMed:29728617). In ES cells, associates with developmental transcription factors such as SALL1 and represses inappropriate gene transcription mediated by histone deacetylation (By similarity). During heart development, associates with transcription factor NKX2-5 to repress transcription of NKX2-5 target genes (By similarity). Plays an essential role in adipogenesis, by regulating expression of genes involved in pre-adipocyte differentiation (PubMed:29728617). During T-cell receptor (TCR) and CD28-mediated T-cell activation, promotes the transcription of transcription factor BCL6 which is required for follicular helper T (Tfh) cell differentiation (By similarity). During B-cell development, required for the generation of the B1 lineage (By similarity). During B2 cell activation, may contribute to the control of isotype class switch recombination (CRS), splenic germinal center formation, and the humoral immune response (By similarity). Plays a role in class switch recombination of the immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) locus during B-cell activation (By similarity). By regulating the methylation of histone H3 at 'Lys-36' and histone H4 at 'Lys-20' at the IgH locus, involved in TP53BP1 recruitment to the IgH switch region and promotes the transcription of IgA (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BVE8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16115125, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19808676, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22099308, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27571355, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29728617, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33941880}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Histone methyltransferase which specifically dimethylates nucleosomal histone H3 at 'Lys-36' (H3K36me2). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22099308}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 4]: Histone methyltransferase which specifically dimethylates nucleosomal histone H3 at 'Lys-36' (H3K36me2) (PubMed:22099308). Methylation of histone H3 at 'Lys-27' is controversial (PubMed:18172012, PubMed:22099308). Mono-, di- or tri-methylates histone H3 at 'Lys-27' (H3K27me, H3K27me2 and H3K27me3) (PubMed:18172012). Does not methylate histone H3 at 'Lys-27' (PubMed:22099308). May act as a transcription regulator that binds DNA and suppresses IL5 transcription through HDAC recruitment (PubMed:11152655, PubMed:18172012). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11152655, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18172012, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22099308}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Chromosomal rearrangement;Chromosome;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Intellectual disability;Metal-binding;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repeat;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a protein that contains four domains present in other developmental proteins: a PWWP domain, an HMG box, a SET domain, and a PHD-type zinc finger. It is expressed ubiquitously in early development. Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (WHS) is a malformation syndrome associated with a hemizygous deletion of the distal short arm of chromosome 4. This gene maps to the 165 kb WHS critical region and has also been involved in the chromosomal translocation t(4;14)(p16.3;q32.3) in multiple myelomas. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Some transcript variants are nonsense-mediated mRNA (NMD) decay candidates, hence not represented as reference sequences. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:7468; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; histone H3K36 methyltransferase activity [GO:0046975]; histone H4K20 methyltransferase activity [GO:0042799]; histone lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0018024]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; atrial septum primum morphogenesis [GO:0003289]; atrial septum secundum morphogenesis [GO:0003290]; bone development [GO:0060348]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; double-strand break repair [GO:0006302]; histone H3-K36 methylation [GO:0010452]; histone H4-K20 methylation [GO:0034770]; membranous septum morphogenesis [GO:0003149]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of isotype switching to IgA isotypes [GO:0048298]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining [GO:2001032]; regulation of establishment of protein localization [GO:0070201] | 12433679_data indicate that t(4;14)(p16;q32) and loss of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 occurred at a very early stage of multiple myeloma and suggest that activation of multiple myeloma SET domain protein may be transforming event of this translocation 12715353_connection between the syndrome phenotype and cytogenetic abnormalities, through gradual shortening of the length of the critical region WHSCR (finally up to 165 kb), and sequencing it, at least 2 genes (WHSC1 and WHSC2) were identified. 15677557_different transcripts detected, multiple myeloma SET domain containing protein (MMSET I), MMSET II, Exon 4a/MMSET III, and response element II binding protein (RE-IIBP), are produced by alternative splicing 16682010_Overexpression of WHISTLE repressed transcription of the SV40 promoter. Our results suggest that WHISTLE is a novel SET domain containing a protein with specific H3K4 and H3K27 HMTase activity. 17239852_Our results suggest that HMTase WHISTLE induces apoptosis in an HMTase activity-dependent manner and represses transcription of target genes through HDAC1 recruitment. 17942756_that MMSET plays a significant role in t(4;14) MM and suggest that therapies targeting this gene could impact this particular subset of poor-prognosis patients. 18036184_MM Patients showing the t(4;14) chromosomal translocation at FGFR3 and MMSET genes had a significant elevation of serum crosslaps, reported to be the marker most reliably correlated with the extent of bone resorption 18156491_MMSET influences gene expression and potentially acts as a pathogenic agent in multiple myeloma 18172012_RE-IIBP is upregulated in leukemia. SET domain Cys483 & Arg477 are needed for histone methyltransferase activity. Overexpression causes histone H3-K27 methylation, HDAC recruitment, & histone H3 hypoacetylation on the IL-5 promoter repressing expression. 18182627_WHSC1 expression increases with ascending tumor proliferation activity. 19059936_dysregulation of MMSET affects the expression of several genes involved in the regulation of cell cycle progression, cell adhesion and survival 19121287_These data suggest that MMSET potentially acts as a pathogenic agent in many cancers. 19481544_NSD2 protein is recruited to the enhancer region of the PSA gene by AR in an agonist-enhanced manner. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20974671_overexpression of multiple myeloma SET domain protein is associated with the translocation t(4;14)in multiple myeloma. 21293379_a pathway involving gammaH2AX-MDC1-MMSET regulates the induction of H4K20 methylation on histones around DSBs, which, in turn, facilitates 53BP1 recruitment 21385930_The histone methyltransferase and putative oncoprotein MMSET is overexpressed in a large variety of human tumors. 21527557_MMSET is implicated in neuroblastomagenesis possibly by supporting proliferation of progenitor cells and negatively regulating their differentiation. 21788515_WHSC1 regulates the methylation status of the histone H4 K20 residue and is required for the recruitment of 53BP1 to sites of DNA damage. 22028615_Data show significant up-regulation of WHSC1 expression in bladder and lung cancer cells at both transcriptional and the protein levels. 22099308_NSD2 links dimethylation of histone H3 at lysine 36 to oncogenic programming. 22645312_NSD2 is a key chromatin regulator of NF-kappaB and mediator of the cytokine autocrine loop for constitutive NF-kappaB activation and emphasize the important roles played by NSD2 in cancer cell proliferation and survival and tumor growth. 22751105_ACA11, an orphan box H/ACA class small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) encoded within an intron of WHSC1, was highly expressed in t(4;14)-positive multiple myeloma and other cancers 22797064_Depletion of TWIST1 in MMSET-overexpressing cells blocked cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition, indicating that TWIST1 is a critical target of MMSET, responsible for the acquisition of an invasive phenotype. 22972034_Overexpression of the histone methyltransferase MMSET is associated with myeloma. 23159737_The EZH2-MMSET-histone methylase axis coordinately functions as a master regulator of transcriptional repression, activation, and oncogenesis. 23225158_Overexpression of MMSET was significantly associated with Edmondson stage. 23241889_MMSET, a gene often deleted in Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome, regulates class switch recombination provides one possible mechanism for Ab deficiency observed in these patients. 23566000_High MMSET expression correlated with the advanced extent of serous ovarian carcinoma and poor outcome. 23823660_it will be of interest to determine whether inhibition of MMSET activity can be beneficial not only for t(4;14)thorn MM patients but also for patients who express a mutant allele of this protein. 23900284_In this study it was found MMSET knockdown could reduce SLAMF7 levels in t(4;14) MM cells. Furthermore, we found MMSET proteins were enriched in the SLAMF7 promoter region and regulated the transcription level of SLAMF7. 23963300_Haploinsufficiency of WHSC1 and/or LETM1 contributes to Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome, but that loss of distinct and/or additional genes in 4p16.3 is necessary for the expression of the core Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome phenotype. 24019522_all of the H3K36-specific methyltransferases, including ASH1L, HYPB, NSD1, and NSD2 were inhibited by ubH2A, whereas the other histone methyltransferases, including PRC2, G9a, and Pr-Set7 were not affected by ubH2A. 24809779_Gastric cancer patients with high MMSET and BRCA1 attain a longer median survival compared with those with high BRCA1 and low MMSET. 24923560_The role of the shorter isoform (REIIBP) in myeloma cells was characterized and identified a clear and novel interaction of REIIBP with members of the SMN complex. 25280969_Results show that WHSC1 is overexpressed in Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN) and that it promotes cell-cycle progression through activation of NEK7, indicating its potential role as an oncogenic force in SCCHN. 25494638_The results describe the binding of NSD1, 2 and 3 catalytic domains (CD) on histone tails through recognition of histone-lysine and methylation properties. 25942451_Studies indicate that the NSD methyltransferases NSD1, NSD2/WHSC1/MMSET and NSD3/WHSC1L1 were overexpressed, amplified or somatically mutated in multiple types of cancer, suggesting their critical role in cancer. 26206755_It was observed that RE-IIBP induces MEIS1-mediated apoptosis, which was dependent on H2BK120 ubiquitination by RNF20. 26272979_Results showed that high levels of MMSET in the myeloma-like cells drove the formation of hypermethyled proteoforms containing H3K36me2 co-existent with the repressive marks H3K9me2/3 and H3K27me2/3. 26771714_In MMSET-depleted cells there are defects in DNA replication and a decreased association with chromatin. 26787850_NSD2 preferentially catalyzes the dimethylation of H3K36 along with a reduced preference for H3K36 monomethylation 26847058_MMSET-like gene signature captures a subset of high-risk myeloma patients underrepresented by conventional risk stratification platforms and defines a distinct biologic subtype. 26912663_results identify a pivotal role for NSD2 binding to its catalytic product in regulating its cellular functions, and suggest a model for how this interaction may facilitate epigenetic spreading and propagation of H3K36me2. 27109101_In a murine xenograft model using t(4;14)+ KMS11 MM cells harboring an inducible MMSET shRNA, depletion of MMSET enhanced the efficacy of chemotherapy, inhibiting tumor growth and extending survival. 27164560_NSD2 overexpression is significantly associated with high risk of relapse and poor survival in tamoxifen-treated ER-positive breast cancer patients via coordinated activation of pentose phosphate pathway enzymes. 27404348_data suggest multiple myeloma SET domain containing protein(MMSET) may play a role in the inhibitory effect of metformin on prostate cancer and could serve as a potential novel therapeutic target for prostate cancer 27604143_The histone methyltransferase NSD2/WHSC1/MMSET is overexpressed in a number of solid tumors but its contribution to the biology of these tumors is not well understood. Here, we describe that NSD2 contributes to the proliferation of a subset of lung cancer cell lines by supporting oncogenic RAS transcriptional responses. 28260054_Results show that WHSC1 is hypomethylated in cervical cancer cells and tissues. Both methylation and mRNA expression of WHSC1 were significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis and the overall survival of patients. 28512191_These findings indicate that the miR-2392-MAML3/WHSC1-Slug/Twist1 regulatory axis plays a critical role in GC metastasis. 29176703_Mutations in NSD1 or NSD2 are independent favorable prognostic biomarkers for laryngeal cancer. 29233865_The MMSET is required for efficient NER and that it catalyzes the dimethylation of histone H4 at lysine 20 (H4K20me2). 29727714_miR-154 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human skin SCC cells by down-regulating WHSC1 and blocking the P53 signaling pathway 29742153_Herein we report on the first fully validated WHSC1 inhibitor, PTD2, a norleucine-containing peptide derived from the histone H4 sequence. This peptide exhibits micromolar affinity towards WHSC1 in biochemical and biophysical assays. Furthermore, a crystal structure was solved with the peptide in complex with SAM and the SET domain of WHSC1L1 29884796_WHSC1 mutation is associated with growth delay, intellectual disability, and to the facial dysmorphism. 29892088_Our study expands the list of microdeletion syndromes that are solved at the single-gene level, and establishes WHSC1 as a disease gene in humans. 30013191_MMSET is a regulator of p53 stability via methylation of AURKA in proliferating cells. 30066931_NSD2 promoted the proliferation of pancreatic beta cell lines. Moreover, ectopic expression of NSD2 significantly promoted insulin secretion. In addition, NSD2 served as a transfection factor and it was identified that NSD2 transcriptionally regulated PDX1 expression through its H3K36me2 methyltransferase activity. 30171259_Transcriptional profiling demonstrates that mutant NSD2 aberrantly activates factors commonly associated with neural and stromal lineages in addition to signaling and adhesion genes. Identification of these pathways provides new avenues for therapeutic interventions in NSD2 dysregulated malignancies. 30345613_loss-of-function variation in WHSC1 may lead to a mild form of Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome, and also may suggest that the developmental delays, facial dysmorphisms, and short stature seen in WHS may be due to disruption of WHSC1 gene. 30470837_GLO1 may be of functional importance target downstream of MMSET I. 30518758_NSD2 is a driver of metastatic prostate cancer progression. 30683853_NSD2 is upregulated in osteosarcoma patients, especially in cisplatin-resistant osteosarcoma patients, and that lower NSD2 expression predicts better prognoses in osteosarcoma patients. NSD2 knockdown can enhance osteosarcoma apoptosis and sensitize osteosarcoma to cisplatin by directly decreasing H3K36me2 levels at BCL2 and SOX2 gene loci. 31092221_Study provides evidence that WHSC1 overexpression in ovarian clear cell carcinoma (OCCC) induces cell growth and its expression is, at least in part, regulated by EZH2. 31177108_Study found that WHSC1 expression was up-regulated in human salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma (SACC) tissues. WHSC1 knockdown significantly inhibited cell proliferation, and increased apoptosis in SACC cells. 31217297_Study reports that DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) promote NSD2-mediated dimethylation of PTEN at K349, which is read by the tudor domain of 53BP1 to recruit PTEN into DNA-damage sites to govern the timely repair of DSBs in part through dephosphorylating gammaH2AX. 31218784_CCND1, NSD2, and MAF gene rearrangements were estimated accurately by IHC, suggesting that conventional FISH assays can be replaced by IHC. 31248990_This work provides clear evidence of cross-talk between PARylation and histone methylation and offers new directions to characterize NSD2 function in DNA damage response, transcriptional regulation, and other pathways. 31332986_role of NSD2 and EZH2 in the pathogenesis of endometrial carcinoma 31382906_De novo truncating variant in NSD2gene leading to atypical Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome phenotype. 31526565_Findings indicate that NSD2 protein (NSD2) exhibited a pattern of gradual up-regulation from normal cervix (NC) to cervical carcinoma in situ (CIS) and then to invasive cervical cancer (ICC). 31649247_In multiple myeloma, a 4;14 translocation induces overexpression of the histone methyltransferase, NSD2, resulting in expansion of H3K36me2 and shrinkage of antagonistic H3K27me3 domains. Using isogenic cell lines producing high and low levels of NSD2, here we find oncogene activation is linked to alterations in H3K27ac and CTCF within H3K36me2 enriched chromatin. 31692936_NSD2 mRNA was amplified in several types of renal cancer, especially in metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Expression level of NSD2 was elevated in ccRCC tissues, but not correlated with tumor grading. The migratory and invasive properties were significantly repressed in NSD2-silenced RCC cells, concurrent with an increase of E-cadherin expression and a decrease of N-cadherin and Vimentin expression. 32014459_Twist-1 is upregulated by NSD2 and contributes to tumour dissemination and an epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like gene expression signature in t(4;14)-positive multiple myeloma. 32091270_The prognostic impact of tumour NSD2 expression in advanced prostate cancer. 32169559_The interaction of histone modification related H3F3B and NSD2 genes increases the susceptibility to schizophrenia in a Chinese population. 32234906_The frequencies of high enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) and multiple myeloma SET domain (MMSET) expression were significantly higher in both MBC and TNDC than in normal tissue.EZH2 and MMSET may be useful therapeutic targets in Metaplastic breast carcinoma. 32314642_WHSC1 promotes wnt/beta-catenin signaling in a FoxM1-dependent manner facilitating proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. 32332049_The NSD2 p.E1099K Mutation Is Enriched at Relapse and Confers Drug Resistance in a Cell Context-Dependent Manner in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. 32826945_Proteosomal degradation of NSD2 by BRCA1 promotes leukemia cell differentiation. 33276791_The first familial NSD2 cases with a novel variant in a Chinese father and daughter with atypical WHS facial features and a 7.5-year follow-up of growth hormone therapy. 33361816_Molecular basis of nucleosomal H3K36 methylation by NSD methyltransferases. 33410156_CircWHSC1 serves as an oncogene to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression. 33420361_Hypoxia-induced CREB cooperates MMSET to modify chromatin and promote DKK1 expression in multiple myeloma. 33589522_WHSC1/NSD2 regulates immune infiltration in prostate cancer. 33589584_Targeting NSD2-mediated SRC-3 liquid-liquid phase separation sensitizes bortezomib treatment in multiple myeloma. 33621919_Mutation and expression alterations of histone methylation-related NSD2, KDM2B and SETMAR genes in colon cancers. 33742125_NSD2 promotes tumor angiogenesis through methylating and activating STAT3 protein. 34083510_Targeting H3K36 methyltransferases NSDs: a promising strategy for tumor targeted therapy. 34166916_Multiple myeloma driving factor WHSC1 is a transcription target of oncogene HMGA2 that facilitates colon cancer proliferation and metastasis. 34271259_Histone and DNA binding ability studies of the NSD subfamily of PWWP domains. 34546854_Exosomal-mediated transfer of APCDD1L-AS1 induces 5-fluorouracil resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma via miR-1224-5p/nuclear receptor binding SET domain protein 2 (NSD2) axis. 34551195_Circular RNA WHSC1 exerts oncogenic properties by regulating miR-7/TAB2 in lung cancer. 34555356_NSD2 dimethylation at H3K36 promotes lung adenocarcinoma pathogenesis. 34671018_Identification of histone methyltransferase NSD2 as an important oncogenic gene in colorectal cancer. 34782608_Structural basis of the regulation of the normal and oncogenic methylation of nucleosomal histone H3 Lys36 by NSD2. 34782742_A chemical probe targeting the PWWP domain alters NSD2 nucleolar localization. 35230972_Histone methyltransferase WHSC1 loss dampens MHC-I antigen presentation pathway to impair IFN-gamma-stimulated antitumor immunity. 35354439_METTL3 enhances NSD2 mRNA stability to reduce renal impairment and interstitial fibrosis in mice with diabetic nephropathy. 35364436_NSD2 activates the E2F transcription factor 1/Y-box binding protein 2 axis to promote the malignant development of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 35389552_Posttranslational modification of Aurora A-NSD2 loop contributes to drug resistance in t(4;14) multiple myeloma. 35532818_The role of NSD1, NSD2, and NSD3 histone methyltransferases in solid tumors. | ENSMUSG00000057406 | Nsd2 | 692.730725 | 0.8864105 | -0.173953135 | 0.07473846 | 5.41248901828 | 0.0199931892246725598227818920804566005244851112365722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.08373195535171251702166728136944584548473358154296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 584.802020 | 112.036805 | 663.292053 | 127.060055 | |
| ENSG00000110455 | 84680 | ACCS | protein_coding | Q96QU6 | FUNCTION: Does not catalyze the synthesis of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate but is capable of catalyzing the deamination of L-vinylglycine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11470512}. | Alternative splicing;Pyridoxal phosphate;Reference proteome | Enables identical protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in biosynthetic process. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:84680; | identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; pyridoxal phosphate binding [GO:0030170]; transaminase activity [GO:0008483]; amino acid metabolic process [GO:0006520]; biosynthetic process [GO:0009058] | 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) | ENSMUSG00000040272 | Accs | 188.072921 | 0.8270550 | -0.273944804 | 0.18889651 | 2.09344659400 | 0.1479320011963089487316835857200203463435173034667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.34137714897620835552416451719182077795267105102539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 168.469446 | 17.304432 | 204.085946 | 20.871336 | |
| ENSG00000110801 | 5715 | PSMD9 | protein_coding | O00233 | FUNCTION: Acts as a chaperone during the assembly of the 26S proteasome, specifically of the base subcomplex of the PA700/19S regulatory complex (RC). During the base subcomplex assembly is part of an intermediate PSMD9:PSMC6:PSMC3 module, also known as modulator trimer complex; PSMD9 is released during the further base assembly process. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19490896}. | Alternative splicing;Chaperone;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | The 26S proteasome is a multicatalytic proteinase complex with a highly ordered structure composed of 2 complexes, a 20S core and a 19S regulator. The 20S core is composed of 4 rings of 28 non-identical subunits; 2 rings are composed of 7 alpha subunits and 2 rings are composed of 7 beta subunits. The 19S regulator is composed of a base, which contains 6 ATPase subunits and 2 non-ATPase subunits, and a lid, which contains up to 10 non-ATPase subunits. Proteasomes are distributed throughout eukaryotic cells at a high concentration and cleave peptides in an ATP/ubiquitin-dependent process in a non-lysosomal pathway. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides. This gene encodes a non-ATPase subunit of the 19S regulator. Three transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]. | hsa:5715; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; proteasome regulatory particle [GO:0005838]; bHLH transcription factor binding [GO:0043425]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; negative regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0046676]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0032024]; proteasome regulatory particle assembly [GO:0070682]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] | 12778072_Presence is associated with high nuclear grade, large tumor size, and poor prognosis for glioma patients. 17360176_The researchers found evidence of increased positive identification of p27 following neoadjuvant therapy in colorectal cancer patients, p27 was a good predictor of FR in the pre-radiation biopsy, and p27(+) markers in specimens lived longer at 3 years. 17516568_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17516568_PSMD9 gene variants contribute rarely to late-onset type 2 diabetes in Italians. 18504423_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18694622_Polymorphisms of p21 and p27 jointly contribute to an earlier age at diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. 18701138_We report a direct correlation between cyclin D3 and p27 expression in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 19041685_Bortezomib arrests the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells HepG2 and JHH6 by differentially affecting p27 level. 19118035_In RCC, p27 is phosphorylated at T157 of the NLS, with increasing tumor grade associated with cytoplasmic p27. 19657726_The expression of p53 and p27 was not related to HPV genotype in cervical carcinomas 19877155_PSMD9 gene in the NIDDM2 locus is linked to type 2 diabetes in Italians. 20069546_Show that the MODY3 mutation and the PSMD9 IVS3 + nt460A/IVS3 + nt437T/G197 SNPs are risk factors for type 2 diabetes in Italian families. 20878082_Cul1 regulates melanoma cell growth and cell cycle progression through degradation of p27 21439668_Data show that the PSMD9 IVS3 + nt460, IVS3 + nt437, E197G T2D risk SNPs are in linkage with diabetic nephropathy. 21448710_This study is the first to demonstrate the expression of Bridge-1 in human breast carcinomas. Bridge-1 expression is increased by activin A stimulation and itself seems to influence activin A signaling by affecting the expression of Smad2, 3 and 4. 21477582_Analysis of Gem-resistant sub lines also showed that loss of UBE2M and increased p27(Kip1) expression were associated with the acquisition of drug resistance. 21496327_PSMD9 IVS3+nt460A/G, +nt437C/T and exon E197G A/G SNPs are linked to coronary artery disease, stroke/TIA and macrovascular pathology of type 2 diabetes in Italians. 21554682_PSMD9 SNPs IVS3 + nt460 A >G, IVS3 + nt437 C > T and E197G A > G are linked to the hypercholesterolemia phenotype in Italian type 2 diabetes families. 21728808_In summary, the PSMD9 IVS3+nt460, IVS3+nt437, E197G SNPs are linked to diabetic retinopathy and non-diabetic retinopathy in Italians. 21813292_genetic association studies in a population in Italy: SNPs in PSMD9 are strongly linked to diabetic neuropathy in subjects with type 2 diabetes; these associations show significance for an additive model-based inheritance. 21837501_overexpression of Jab1, cytoplasmic p27, and pSer10p27 proteins is correlated with poor outcome in patients with glioma 21862167_Brief Report: PSMD9 SNPs show linkage to carpal tunnel syndrome in Italian type 2 diabetics. 21871126_PSMD9 gene SNPs are linked to elevated blood pressure/hypertension in Italian families with type 2 diabetes. 22015693_the PSMD9 IVS3 + nt460, IVS3 + nt437, E197G SNPs are linked via the recessive model to microvascular pathology of type 2 diabetes (T2D) in Italians 22934761_PSMD9 IVS3+nt460 A>G and +nt437 C>T and exon 5 E197G A>G single nucleotide polymorphisms studied and/or any variants in linkage disequilibrium with them are linked to depression in our type 2 diabetes Italian families. 23282078_The PSMD9 single nucleotide polymorphism(SNP)s IVS3+nt460, IVS3+nt437, and 197G are in linkage with overweight condition and waist circumference in Italians. 23464457_Expression of Hath1, Muc2, cyclin D1 and p27 in the xenograft tumors was also detected. 23618860_Surprisingly, we found that GRP/GRP-R differentially induced expressions of p21 and p27. Silencing GRP/GRP-R decreased p21, but it increased p27 expressions in neuroblastoma cells. 23689538_Our results suggest that tuberin and p27 are aberrantly expressed in malignant breast tissue 24648162_Describe PSMD9 gene SNPs in linkage to generalized anxiety disorder in type 2 diabetic families. 24673853_PSMD9 expression predicts radiotherapy response in breast cancer. 24852133_Staining intensities of cell cycle inhibitors p27 and p57 significantly increased in all parts of preeclamptic placentas compared to control 25545366_The present study provided the first evidences that miR-1470 mediated lapatinib induced p27 upregulation by targeting c-jun. 26166263_The PSMD9 intronic SNPs rs74421874 (IVS3+nt460 G>A) and rs3825172 (IVS3+nt437 C>T) remain significantly associated with insomnia only when taking into account anxiety -and not depression- as covariate. 26191286_recurrence rate of p27 and/or PTEN-negative patients was higher than that of the positive ones,that should be followed up closely after treatment 26447892_p53 immunopositivity was more frequent in SCC (65%) than in VC (23%) (P=0.001). VC had lower p53 as compared with well-differentiated SCC and SCC without lymph node metastasis. No significant difference was seen in pRb, p16, and p27 expression 26624926_Studies have found significant associations of the treatment response with the 26S proteasome non-ATPase subunit 9 (PSMD9), proteasome alpha type 7 subunit (PSMA7) and PSMD13 genes. 26917264_Loss of p27 associated with risk for endometrial carcinoma arising in the setting of obesity. 28325896_These data suggest that Schistosoma japonicum Sjp40 might inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation by promoting cellular senescence via SKP2/P27 signaling pathway. 28650473_human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2) levels, were correlated well with TSP50/p-Samd2/3 and TSP50/p27 expression status. Thus, our studies revealed a novel regulatory mechanism underlying TSP50-induced cell proliferation and provided a new favorable intervention target for the treatment of breast cancer 28919423_Furthermore, inhibition of COPS5 resulted in an elevation of Akt expression and sensitized SOC cells to Akt inhibitor MK2206. Suppression of COPS5 and Akt offers a potential strategy for the treatment of SOC. 31180541_Molecular experiments showed that miR2213p was able to bind with the 3'untranslated region (UTR) of p27 and decreased the expression of p27 in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. 31287951_Novel Determinant of PSMD9 PDZ Binding 32356429_Proteasome modulator 9 (PSMD9) gene rs14259 polymorphism in Alzheimer's disease. 33589597_UBE2S interacting with TRIM28 in the nucleus accelerates cell cycle by ubiquitination of p27 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma development. 34077860_PSMD9 ribosomal protein network maintains nucleolar architecture and WT p53 levels. 35439960_KIF14 affects cell cycle arrest and cell viability in cervical cancer by regulating the p27(Kip1) pathway. | ENSMUSG00000029440 | Psmd9 | 151.524325 | 1.0477131 | 0.067243729 | 0.18122275 | 0.13727047244 | 0.7110097529206057531681040018156636506319046020507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.85318730581225299403058670577593147754669189453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 167.104596 | 18.846922 | 160.574499 | 17.968013 | |
| ENSG00000111911 | 135114 | HINT3 | protein_coding | Q9NQE9 | FUNCTION: Exhibits adenosine 5'-monophosphoramidase activity, hydrolyzing purine nucleotide phosphoramidates with a single phosphate group such as adenosine 5'monophosphoramidate (AMP-NH2) to yield AMP and NH2 (PubMed:17870088). Hydrolyzes lysyl-AMP (AMP-N-epsilon-(N-alpha-acetyl lysine methyl ester)) generated by lysine tRNA ligase (PubMed:17870088). Hydrolyzes 3-indolepropionic acyl-adenylate and fluorogenic purine nucleoside tryptamine phosphoramidates in vitro (PubMed:17870088). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17870088}. | Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome | Histidine triad proteins, such as HINT3, are nucleotide hydrolases and transferases that act on the alpha-phosphate of ribonucleotides (Brenner, 2002 [PubMed 12119013]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:135114; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; adenosine 5'-monophosphoramidase activity [GO:0043530]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; nucleotide binding [GO:0000166] | 17870088_Results show that significant differences in phosphoramidase activity, oligomeric state, and cellular localization suggest that Hint3s should be placed in a distinct branch of the histidine triad superfamily. | ENSMUSG00000019791 | Hint3 | 209.919621 | 1.1835976 | 0.243178675 | 0.11476782 | 4.48994115216 | 0.0340948512924594132611488817019562702625989913940429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.12514268692703287011447343957115663215517997741699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 226.646190 | 15.471392 | 192.431060 | 13.278722 | |
| ENSG00000112200 | 26036 | ZNF451 | protein_coding | Q9Y4E5 | FUNCTION: E3 SUMO-protein ligase; has a preference for SUMO2 and SUMO3 and facilitates UBE2I/UBC9-mediated sumoylation of target proteins (PubMed:26524493, PubMed:26524494). Plays a role in protein SUMO2 modification in response to stress caused by DNA damage and by proteasome inhibitors (in vitro). Required for MCM4 sumoylation (By similarity). Has no activity with SUMO1 (PubMed:26524493). Preferentially transfers an additional SUMO2 chain onto the SUMO2 consensus site 'Lys-11' (PubMed:26524493). Negatively regulates transcriptional activation mediated by the SMAD4 complex in response to TGF-beta signaling. Inhibits EP300-mediated acetylation of histone H3 at 'Lys-9' (PubMed:24324267). Plays a role in regulating the transcription of AR targets (PubMed:18656483). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8C0P7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18656483, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24324267, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26524493, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26524494}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein sumoylation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26524493, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26524494}. | Enables SUMO ligase activity and transcription corepressor activity. Involved in negative regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; and protein sumoylation. Located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:26036; | nucleus [GO:0005634]; PML body [GO:0016605]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; SUMO ligase activity [GO:0061665]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; transcription regulator inhibitor activity [GO:0140416]; negative regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0060633]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein sumoylation [GO:0016925]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468] | 18656483_Data describe ZNF451, a nuclear protein that can be associated with promyelocytic leukemia bodies, and exerts its effects via SUMO modification machinery and trafficking of transcription regulators between promyelocytic leukemia bodies and nucleoplasm. 24324267_ZNF451 acts as a transcriptional corepressor for Smad3/4 and negatively regulates TGF-beta signaling. 26524494_The authors show that ZNF451 is SUMO2 specific and that SUMO modification of ZNF451 may contribute to activity by providing a second molecule of SUMO that interacts with E2. 28912134_These findings uncover a ZNF451-TDP2-catalyzed and SUMO2-modulated pathway for direct resolution of TOP2 cleavage complex. 29532883_The findings of this study indicate that BC032020 suppresses the survival of PDAC cells by inhibiting ZNF451 expression. 33548202_Stress-induced nuclear condensation of NELF drives transcriptional downregulation. | ENSMUSG00000042197 | Zfp451 | 443.217177 | 0.9388467 | -0.091038529 | 0.12598509 | 0.52079173147 | 0.4705041471780802009305944011430256068706512451171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.68980316641096173224667609247262589633464813232421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 371.233543 | 64.966299 | 391.921431 | 68.614609 |
| ENSG00000112651 | 51069 | MRPL2 | protein_coding | Q5T653 | 3D-structure;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;Ribonucleoprotein;Ribosomal protein;Transit peptide | Mammalian mitochondrial ribosomal proteins are encoded by nuclear genes and help in protein synthesis within the mitochondrion. Mitochondrial ribosomes (mitoribosomes) consist of a small 28S subunit and a large 39S subunit. They have an estimated 75% protein to rRNA composition compared to prokaryotic ribosomes, where this ratio is reversed. Another difference between mammalian mitoribosomes and prokaryotic ribosomes is that the latter contain a 5S rRNA. Among different species, the proteins comprising the mitoribosome differ greatly in sequence, and sometimes in biochemical properties, which prevents easy recognition by sequence homology. This gene encodes a 39S subunit protein that belongs to the EcoL2 ribosomal protein family. A pseudogene corresponding to this gene is found on chromosome 12q. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. | hsa:51069; | mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial large ribosomal subunit [GO:0005762]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; structural constituent of ribosome [GO:0003735]; mitochondrial translation [GO:0032543] | 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) | ENSMUSG00000002767 | Mrpl2 | 155.169774 | 0.7856988 | -0.347951814 | 0.14607681 | 5.67295749164 | 0.0172283864512263393264923649894626578316092491149902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.07472578904798574117585019394027767702937126159667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 136.629211 | 14.174727 | 174.414471 | 17.842893 | ||
| ENSG00000113360 | 29102 | DROSHA | protein_coding | Q9NRR4 | FUNCTION: Ribonuclease III double-stranded (ds) RNA-specific endoribonuclease that is involved in the initial step of microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis. Component of the microprocessor complex that is required to process primary miRNA transcripts (pri-miRNAs) to release precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA) in the nucleus. Within the microprocessor complex, DROSHA cleaves the 3' and 5' strands of a stem-loop in pri-miRNAs (processing center 11 bp from the dsRNA-ssRNA junction) to release hairpin-shaped pre-miRNAs that are subsequently cut by the cytoplasmic DICER to generate mature miRNAs. Involved also in pre-rRNA processing. Cleaves double-strand RNA and does not cleave single-strand RNA. Involved in the formation of GW bodies. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10948199, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14508493, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15531877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15565168, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15574589, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15589161, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16751099, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16906129, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17159994, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26027739, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26748718}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Endonuclease;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Manganese;Metal-binding;Nuclease;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ribosome biogenesis;RNA-binding;RNA-mediated gene silencing | This gene encodes a ribonuclease (RNase) III double-stranded RNA-specific ribonuclease and subunit of the microprocessor protein complex, which catalyzes the initial processing step of microRNA (miRNA) synthesis. The encoded protein cleaves the stem loop structure from the primary microRNA (pri-miRNA) in the nucleus, yielding the precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA), which is then exported to the cytoplasm for further processing. In a human cell line lacking a functional copy of this gene, canonical miRNA synthesis is reduced. Somatic mutations in this gene have been observed in human patients with kidney cancer. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. | hsa:29102; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; microprocessor complex [GO:0070877]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; DEAD/H-box RNA helicase binding [GO:0017151]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; lipopolysaccharide binding [GO:0001530]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; primary miRNA binding [GO:0070878]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; R-SMAD binding [GO:0070412]; ribonuclease III activity [GO:0004525]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; SMAD binding [GO:0046332]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; miRNA metabolic process [GO:0010586]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; pre-miRNA processing [GO:0031054]; primary miRNA processing [GO:0031053]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; regulation of miRNA metabolic process [GO:2000628]; regulation of regulatory T cell differentiation [GO:0045589]; RNA processing [GO:0006396]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364] | 14508493_identification of another RNase III, human Drosha, as the core nuclease that executes the initiation step of miRNA processing in the nucleus 15531877_human Drosha is a component of two multi-protein complexes; both components of the smaller complex, termed Microprocessor, are necessary and sufficient in mediating the genesis of miRNAs from the primary miRNA transcript 15565168_Data show that human Drosha selectively cleaves RNA hairpins bearing a large (>/=10 nucleotides) terminal loop. 15574589_nuclear RNase III Drosha cleaves primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs) to release hairpin-shaped pre-miRNAs that are subsequently cut by the cytoplasmic RNase III Dicer to generate mature miRNAs 15932881_processing of primary microRNA hairpins by Drosha requires flanking nonstructured RNA sequences 15987463_Dicer gene expression in human breast cells is regulated by alternative promoter selection to alter the length and composition of the 5'-leader sequence of its mRNA 17121874_We found that RNASEN expression levels were enhanced in a fraction of esophageal cancers. 17255951_Drosha may cleave intronic miRNAs between the splicing commitment step and the excision step, thereby ensuring both miRNA biogenesis and protein synthesis from a single primary transcript. 17581865_identify specific miRNAs up-regulated in leukemias triggered by All1 fusions. All1 fusion protein-mediated recruitment of Drosha to target genes encoding miRNAs is demonstrated 17626073_miR-BHRF1-2 in 3' cleavage of BHRF1 mRNA in the cytoplasm and Drosha in cleavage of latency III EBNA and EBV replication-associated BHRF1 transcripts in the nucleus. 18559093_Integrative genomics analysis of chromosome 5p gain in cervical cancer reveals target over-expressed genes, including Drosha. 19047128_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19092150_Our findings indicate that levels of Dicer and Drosha mRNA in ovarian-cancer cells have associations with outcomes in patients with ovarian cancer. 19135890_The Drosha-DGCR8 complex cleaves the hairpin in the DGCR8 mRNA and thus destabilizes the mRNA; DGCR8 stabilizes Drosha protein via protein interaction; this crossregulation between Drosha and DGCR8 may contribute to the control of miRNA biogenesis. 19138993_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19721432_The mRNA for microprocessor component DROSHA was found to be significantly upregulated in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in tissues from schizophrenic patients. 19759829_a Microprocessor, containing the RNA binding protein Dgcr8 and RNase III enzyme Drosha, is responsible for processing primary microRNAs to precursor microRNAs 20083228_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20210522_Report dysregulation of microRNA processing enzymes Drosha and Dicer in epithelial skin tumors when compared to healthy control samples. 20211803_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20585341_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20705240_Smad proteins bind a conserved RNA sequence to promote microRNA maturation by Drosha. 20721975_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20732906_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20805302_Findings of growth promotion by Drosher silencing implies its potential use as therapeutic targets for neuroblastoma. 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21559780_This study revealed for the first time that expression alterations of Dicer and Drosha are present in endometrial cancer tissue and could be potentially responsible for altered microRNAs profiles observed in this malignancy. 21683814_the selectivity of Drosha action contributes greatly to the specificity and efficiency of miRNA biogenesis 21690333_Drosha, an endoribonuclease best known for its role in the biogenesis of microRNAs, can also function to directly regulate viral gene expression of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus 21697496_The authors report that Drosha cleavage of latency III BHRF1 RNA and cis-acting splicing effects inhibit splicing and inhibit BHRF1 RNA and protein expression. 21769619_Our results suggest that Drosha, Dicer, and Ago2 are possibly implicated in colorectal carcinoma pathobiology 21794839_Drosha regulates human mesenchymal stem cells cell cycle progression through a miRNA independent mechanism, potentially by regulating rRNA processing. 21898071_Low drosha expression is associated with breast cancer. 21953080_Drosha and Dicer expression was dysregulation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma compared with healthy control samples. 22162762_PTEN-mediated miR-21 regulation is achieved by inhibiting the interaction between the Drosha complex and RNH1, revealing previously unidentified role of PTEN in the oncogenic miR-21 biogenesis 22371183_mesenchymal stromal cells from MDS patients show low gene and protein expression of DICER1 and DROSHA which are involved in the microRNA biogenesis, as well as their target gene SBDS. 22381205_The results showed that genetic variants of DROSHA may modify the risk of abnormal semen parameters, which could result in male infertility. 22393237_DGCR8 and Drosha are targeted post-transcriptionally to chromosome 19 microRNA cluster pri-miRNAs as a preformed complex but dissociate separately. 22394132_results provide novel evidence that Drosha, is probably involved in the pathobiology of human smooth muscle neoplasms 22479364_Data show that down-regulation of either Dicer or Drosha had no effect on the sensitivity of cells to irradiation. 22496623_Rare Drosha splice variants are deficient in microRNA processing but do not affect general microRNA expression in cancer cells 22554933_Gene silencing of hepatitis B virus X protein by RNA interference significantly restored the expression of Drosha. 22647351_Drosha, Dicer, Argonaute 1, and Argonaute 2 are differentially expressed at different metastatic sites in ovarian carcinoma compared with primary carcinomas. 22766726_Dicer, Drosha, and Exportin 5 genes were up-regulated in bladder urothelial carcinoma compared to normal urothelium. Silencing these genes induced cell proliferation inhibition and apoptosis in bladder urothelial carcinoma cells. 22796965_DGCR8-mediated cleavage of snoRNAs was independent of Drosha, suggesting the involvement of DGCR8 in cellular complexes with other endonucleases. Binding of DGCR8 to cassette exons is a new mechanism for regulation of alternatively spliced isoforms. 22935707_A subset of Lin28 mRNA targets are destabilized in a Drosha-dependent manner. 23225145_Drosha protein potentially plays an important role in breast cancer progression. 23266047_Data indicate that tumour sample showed a significantly higher Drosha expression versus normal mucosa, while Dicer levels did not differ. 23272639_miRNA regulatory effect is a heritable trait in humans; a polymorphism of the DROSHA gene contributes to the observed inter-individual differences. 23305493_Primary microRNA structure reveals deviations from canonical double-stranded RNA structure in the stem adjacent to the Drosha cut site. The necessity of these deformable sites for efficient processing is demonstrated through Drosha processing assays. 23349018_Levels of DICER1, DROSHA and five different miRNAs were measured in NSCLC specimens. 23370771_Our results demonstrate a reduced nuclear expression of DROSHA in melanoma 23663110_It is a miRNA processing enzyme and altered in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. 23863141_RNase III enzyme Drosha and the double-stranded RNA-binding protein DGCR8 binds and regulates a large variety of cellular RNAs 23969986_Our results suggest that Drosha affects the biological activity of cervical cancer cells by regulating the expression of numerous tumour-associated proteins. 23974981_results indicate a block of miRNA maturation at the DROSHA processing step 23995758_Ectopic AKAP95 stimulates expression of a chromosomal reporter gene in synergy with MLL1 or MLL2, whereas AKAP95 depletion impairs retinoic acid-mediated gene induction in embryonic stem cells 24009686_Acetylation of Drosha on those N-terminal lysine sites prevents Drosha ubiquitination, thereby preventing its degradation. 24297910_If the distances are not optimal, Drosha tends to cleave at multiple sites, which can, in turn, generate multiple 5' isomiRs. 24312312_DROSHA rs10719T>C polymorphism may be associated with bladder cancer risk in a Chinese population, and hsa-miR-27b can influence the expression of DROSHA protein by binding with 3'UTR 24360955_Drosha regulates nascent gene transcription trhough interaction with CBP80 and RNA PolII. 24574065_Low Drosha expression is associated with invasive breast carcinoma. 24589731_The Microprocessor complex of Drosha and DGCR8 proteins, which is responsible for the processing of the primary transcripts during the generation of microRNAs, destabilizes the mRNA of Aurora kinase B. 24677349_Change in Drosha expression can be a biologically relevant mechanism by which eukaryotic cells control miRNA profiles 24725360_The altered expression of Dicer and Drosha may serve as markers for disrupted miRNA biogenesis in Triple negative breast cancer 24769857_Association between recurrent pregnancy loss development and the polymorphism of the miRNA machinery gene RAN and combined genotype of DROSHA/DICER. 24786770_conclude that Drosha can function like a splicing enhancer and promote exon inclusion. Our results reveal a new mechanism of alternative splicing regulation involving a cleavage-independent role for Drosha in splicing 24854622_The pri-miRNA stem, defined by internal and flanking structural elements, guides the binding position of Drosha-DGCR8, which consequently determines the cleavage site. 24909261_data underscore the pivotal role of the miRNA biogenesis pathway in WT tumorigenesis, particularly the major miRNA-processing gene DROSHA 24909689_The involvement of E2F1-dependent DROSHA activation in pri-miRNA processing under DNA damage stress will provide further insight into the regulation of miRNA biosynthesis. 25058539_To inhibit the expression of Drosha. 25190313_DROSHA RNase IIIB mutations globally inhibit miRNA biogenesis through a dominant-negative mechanism in Wilms tumors. 25295740_Drosha is upregulated in gestational diabetes. 25439752_We aimed to evaluate the expression of the major components of microRNA biogenesis machinery including Drosha, Dicer and DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 8 (DGCR8) in multiple sclerosis patients 25656609_EIF2C2, Dicer, and Drosha are more highly expressed in bladder carcinoma, promote the development of bladder cancer, and suggested a poor prognosis 25670082_in tumors with DGCR8 E518K and DROSHA exon 29 (miRNAPG-HS) mutations ... greater prevalence of tumors with blastemal predominant histology in patients with miRNAPG-HS and/or SIX1/2 Q177R mutations 25670083_Recurrent mutations included a hotspot mutation (Q177R) in the homeo-domain of SIX1 and SIX2 in tumors with high proliferative potential (18.1% of blastemal cases); mutations in the DROSHA/DGCR8 microprocessor genes 25699712_p38 MAPK directly phosphorylates Drosha at its N terminus promoting its nuclear export and degradation. 25756586_Drosha protein was identified as a new component of dipeptide-repeat aggregates in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and tauopathy. 25867481_The sequence and structural features of Drosha and Dicer cleavage sites. 26027739_Together with a 23-amino acid peptide from DGCR8, DROSHA constitutes a minimal functional core. DROSHA serves as a 'ruler' by measuring 11 bp from the basal ssRNA-dsRNA junction. DGCR8 interacts with the stem and apical elements through its dsRNA-binding domains and RNA-binding heme domain, respectively, allowing efficient and accurate processing. 26147304_Variations in DROSHA rs10719 of Korean patients are significantly associated with their risk of colorectal cancer. 26156018_DICER1 and DROSHA copy number variation may be an important mechanism of upregulation/downregulation of miRNAs in lung cancer 26227789_Results indicate the role of Drosha, Dicer and Ago2 proteins in the development of non-small cell lung carcinomas (NSCLC) and suggest that Dicer may be implicated in the progression of these tumors to advanced stages. 26522361_Drosha expression was reduced gradually with the degrading histological differentiation of gastric adenocarcinoma, and the knock-down of Drosha expression could promote gastric adenocarcinoma cell invasion. 26683315_DGCR8 and Drosha assemble into a heterotrimeric complex on RNA, comprising two DGCR8 molecules and one Drosha molecule. 26694172_Gradual loss of cytoplasmic Drosha was accompanied by tumor progression in both gastric cancer tissues and cell lines, and was inversely associated with tumor volume (P = 0.002), tumor grade (P DROSHA gene might be associated with a risk of laryngeal cancer occurrence in the Polish population. 28214904_miR-27b mimics, DROSHA siRNA, and miR-27b inhibitors to verify the negative regulatory relationship between MiR-27b and DROSHA. The presence of rs10719 disrupted the interaction between miR-27b and DROSHA, which might be the underlying mechanism of the observation that rs10719 is significantly associated with risk of primary hypertension. 28252644_Overexpression of LAMC2 and knockdown of CD82 markedly promoted GC cell invasion and activated EGFR/ERK1/2-MMP7 signaling via upregulation of the expression of phosphorylated (p)-EGFR, p-ERK1/2 and MMP7. 28388279_Increased Drosha expression was found in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients without chromosomal deletions. 28400409_Results show that Mammalian DROSHA genes have evolved a conserved hairpin structure spanning a specific exon-intron junction serving as a substrate for the microprocessor in human but not in murine cells. This hairpin element decides whether the overlapping exon is alternatively or constitutively spliced. Also, DROSHA promotes skipping of the overlapping exon in human cells independently of its cleavage function. 28431232_Report DROSHAnumerous processing sites on primary microRNAs and noncanonical substrates which may serve as cis-elements for DROSHA-mediated gene regulation. 28448850_HPV E6/E7 increased expression of DROSHA and DICER mRNA and protein in cervical carcinoma cells. 28665784_It has been reported that the gene encoding human DROSHA also encodes a potential miRNA and that this miRNA may act upon, at least, one of DROSHA transcripts. 28716689_BRG1 and SMARCAL1, members of the ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling family, are shown to co-regulate the transcription of DROSHA, DGCR8, and DICER in response to double-strand DNA breaks 28833944_Taken together, our results provided the potential evidence that rs10719 and rs493760 might contribute to the risk of CL/P and suggested potential genetic basis and mechanisms of CL/P. 28846091_Mechanistic dissection reveals that NEAT1 broadly interacts with the NONO-PSF heterodimer as well as many other RNA-binding proteins and that multiple RNA segments in NEAT1, including a 'pseudo pri-miRNA' near its 3' end, help attract the Drosha-DGCR8 Microprocessor. 29109067_point mutations in the RNaseIIIb domain of Drosha implicated in Wilms tumors differentially affected cleavage of the 5' and 3' strands of pri-miRNAs in vitro. 29157048_The Drosha rs10719TC and CC genotypes were associated with PE risk. The CC-GG combined genotype and C-G haplotype of Drosha rs10719 and rs6877842 polymorphisms may increase PE susceptibility. 29170488_Primary microRNA transcripts (pri-miRs) are cleaved by Microprocessor, a complex containing the RNase Drosha and its partner protein, DGCR8. Although DGCR8 is known to bind heme, the molecular role of heme in pri-miR processing is unknown. Here we show that heme is critical for Microprocessor to process pri-miRs with high fidelity. 29236960_Our study provides mechanistic insights into the function of miR-128-3p as a key regulator of the malignant phenotype of lung cancer cells...and in particular it highlights a role for Drosha in non-small-cell lung cancer cells migration 29339534_DROSHA mutations contribute to the development of vascular abnormalities in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. 29416038_Depletion of drosha ribonuclease III (Drosha) significantly reduces DNA repair by both homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). 29475968_Methylation of three CpGs (DROSHA: cg23230564, TNRC6B: cg06751583, and TNRC6B: cg21034183) was prospectively associated with time to cancer development (positively for cg06751583, inversely for cg23230564 and cg21034183), whereas methylation of one CpG site (DROSHA: cg16131300) was positively associated with cancer prevalence. 29654164_The DROSHA rs10719, rs6877842 SNPs, and DGCR8 rs417309 SNP play pivotal roles in carcinogenesis. (Review, Meta-analysis) 29892896_Different genotypes frequency of DROSHA (rs10719, rs642321 and rs2291102) were determined by sequencing method in 385 infertile men and 120 fertile controls. No significant differences were seen between cases and controls for DROSHA expression. 30030436_analysis of the recurrent homozygous deletion of DROSHA and microduplication of PDE4DIP in pineoblastoma 30168106_Study observed that mRNA expression levels of Drosha, Dicer, and DGCR8 were significantly upregulated in gastric cancer tumoral tissues compared with marginal tissues. Upregulation of these genes was not correlated with clinical manifestations of the patients. Upregulation of Drosha, Dicer, and DGCR8 plays a role in the development of cancer, probably through dysregulated the expression level of miRNAs. 30367465_Study in mouse lines with either a targeted deletion of Drosha or an inducible expression of human DROSHA carrying a Wilms tumor (WT)-specific E1147K mutation that acts in a dominant negative manner underscores the importance of a viable self-renewing progenitor pool for kidney development, but there was no evidence of WT formation through impaired DROSHA function. 30631133_The effect of the placental DROSHA rs10719 and rs6877842 polymorphisms on PE susceptibility and mRNA expression. 30701851_a significant decrease in the number of DROSHA and DICER transcripts in peripheral blood leukocytes of patients with the development of lung sarcoidosis has been found, which can contribute to the pathogenesis of this disease. 30855334_Recent evidence suggests that Drosha-mediated microRNA biogenesis contributes significantly to the control of vascular development and homeostasis by TGFbeta. Loss or reduction of Drosha function may predispose carriers to hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia and possibly other vascular diseases. 31250375_Association between Genetic Polymorphisms in microRNA Machinery Genes and Risk of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. 31434287_The results suggest that DROSHA promotes AIM2 (the Absent In Melanoma 2) inflammasome activation-dependent lung inflammation during idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 31659796_The effects of DICER1 and DROSHA polymorphisms on susceptibility to recurrent spontaneous abortion. 31956890_the internal loop located in the lower stem of numerous pri-miRNAs selectively inhibits the cleavage of Microprocessor on their 3p-strand, thereby, facilitating the single cleavage on their 5p-strand. 32124011_Pineoblastoma is uniquely tolerant of mutually exclusive loss of DICER1, DROSHA or DGCR8. 32142918_Drosha-independent miR-6778-5p strengthens gastric cancer stem cell stemness via regulation of cytosolic one-carbon folate metabolism. 32220645_Structural Basis for pri-miRNA Recognition by Drosha. 32220646_Cryo-EM Structures of Human Drosha and DGCR8 in Complex with Primary MicroRNA. 32302542_Genomic Clustering Facilitates Nuclear Processing of Suboptimal Pri-miRNA Loci. 32317642_Microprocessor is a trimeric protein complex, which is composed of an RNase III enzyme, DROSHA, and DGCR8; its processing of primary microRNA is governed by mismatched and wobble pairs 32412691_Dicer and Drosha expression in patients with nephrotic syndrome. 32770606_Analysis of microRNA processing machinery gene (DROSHA, DICER1, RAN, and XPO5) variants association with end-stage renal disease. 32819190_Novel, abundant Drosha isoforms are deficient in miRNA processing in cancer cells. 32859993_Oncogenic AURKA-enhanced N(6)-methyladenosine modification increases DROSHA mRNA stability to transactivate STC1 in breast cancer stem-like cells. 32894467_Differences in the Drosha and Dicer Cleavage Profiles in Colorectal Cancer and Normal Colon Tissue Samples. 33037012_Molecular determinants that govern scaRNA processing by Drosha/DGCR8. 33052778_Tissue-specific and transcription-dependent mechanisms regulate primary microRNA processing efficiency of the human chromosome 19 MicroRNA cluster. 33389538_Evaluation of the clinical significance of RNase III enzyme DROSHA in pediatrics acute lymphocytic leukemia. 33535080_DROSHA rs10719 and DICER1 rs3742330 polymorphisms in endometriosis and different diseases: Case-control and review studies. 33801773_High Glucose Treatment Limits Drosha Protein Expression and Alters AngiomiR Maturation in Microvascular Primary Endothelial Cells via an Mdm2-dependent Mechanism. 34287278_Evaluating the Effect of 3'-UTR Variants in DICER1 and DROSHA on Their Tissue-Specific Expression by miRNA Target Prediction. 34320405_A quantitative map of human primary microRNA processing sites. 34528746_p38 MAPK-mediated loss of nuclear RNase III enzyme Drosha underlies amyloid beta-induced neuronal stress in Alzheimer's disease. 34572006_Towards Understanding the Pathogenicity of DROSHA Mutations in Oncohematology. 34576018_Impact of DICER1 and DROSHA on the Angiogenic Capacity of Human Endothelial Cells. 34855193_The impact of Dicer, Drosha, and Exportin-5 levels in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) diagnosis and phenotyping. 34914716_Sequencing of Argonaute-bound microRNA/mRNA hybrids reveals regulation of the unfolded protein response by microRNA-320a. 35405010_The microRNA processor DROSHA is a candidate gene for a severe progressive neurological disorder. 36210981_The Drosha-Independent MicroRNA6778-5p/GSK3beta Axis Mediates the Proliferation of Gastric Cancer Cells. | ENSMUSG00000022191 | Drosha | 346.792189 | 0.5526033 | -0.855683974 | 0.16100167 | 27.90878606262 | 0.0000001271709967627033592316534472976830016932581202127039432525634765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000245699986563079367265474868553543075222478364594280719757080078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 220.437544 | 25.315405 | 400.962597 | 45.908801 | |
| ENSG00000113407 | 6897 | TARS1 | protein_coding | P26639 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the attachment of threonine to tRNA(Thr) in a two-step reaction: threonine is first activated by ATP to form Thr-AMP and then transferred to the acceptor end of tRNA(Thr) (PubMed:25824639, PubMed:31374204). Also edits incorrectly charged tRNA(Thr) via its editing domain, at the post-transfer stage (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9D0R2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25824639, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31374204}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Ligase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;tRNA-binding;Ubl conjugation | Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases catalyze the aminoacylation of tRNA by their cognate amino acid. Because of their central role in linking amino acids with nucleotide triplets contained in tRNAs, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are thought to be among the first proteins that appeared in evolution. Threonyl-tRNA synthetase belongs to the class-II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:6897; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; threonine-tRNA ligase activity [GO:0004829]; tRNA binding [GO:0000049]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; threonyl-tRNA aminoacylation [GO:0006435] | 23375620_Our series mainly underscores that interstitial lung disease is frequent in anti-PL7(tars antibody)patients, leading to high morbidity. 23425968_A previously undiscovered function for TARS as an angiogenic, pro-migratory extracellular signaling molecule. 25163878_Results show that TARS expression is increased in epithelial ovarian cancer. 29328069_Threonyl-tRNA synthetase regulates MUC1 biosynthesis and is associated with pancreatic cancer cell migration. 30902983_This work highlights the functional significance of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases in the emergence and control of higher order organisms. 31374204_Bi-allelic TARS Mutations Are Associated with Brittle Hair Phenotype. 34159625_Contribution of upregulated aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis to metabolic dysregulation in gastric cancer. | ENSMUSG00000022241 | Tars | 613.499872 | 1.0619272 | 0.086684870 | 0.10254346 | 0.71395557566 | 0.3981337759398508313601894315070239827036857604980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.62591359763884413247581051109591498970985412597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 598.012221 | 47.895612 | 566.025333 | 45.264373 | |
| ENSG00000113716 | 22993 | HMGXB3 | protein_coding | Q12766 | DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome | This gene is one of the non-canonical high mobility group (HMG) genes. The encoded protein contains an HMG-box domain found in DNA binding proteins such as transcription factors and chromosomal proteins. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. | Mouse_homologues | nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677] | 34155128_Regulation of closely juxtaposed proto-oncogene c-fms and HMGXB3 gene expression by mRNA 3' end polymorphism in breast cancer cells. 34274607_Circular RNA EGLN3 silencing represses renal cell carcinoma progression through the miR-1224-3p/HMGXB3 axis. | ENSMUSG00000024622 | Hmgxb3 | 1026.290812 | 0.7887692 | -0.342324913 | 0.07028107 | 23.68457160971 | 0.0000011348871518401332368928885116488025630587799241766333580017089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00001845907148830207473739345447327764304645825177431106567382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 891.475349 | 41.663961 | 1136.279290 | 52.519156 | ||
| ENSG00000114315 | 3280 | HES1 | protein_coding | Q14469 | FUNCTION: Transcriptional repressor of genes that require a bHLH protein for their transcription. May act as a negative regulator of myogenesis by inhibiting the functions of MYOD1 and ASH1. Binds DNA on N-box motifs: 5'-CACNAG-3' with high affinity and on E-box motifs: 5'-CANNTG-3' with low affinity (By similarity). May play a role in a functional FA core complex response to DNA cross-link damage, being required for the stability and nuclear localization of FA core complex proteins, as well as for FANCD2 monoubiquitination in response to DNA damage. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18550849}. | 3D-structure;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation | This protein belongs to the basic helix-loop-helix family of transcription factors. It is a transcriptional repressor of genes that require a bHLH protein for their transcription. The protein has a particular type of basic domain that contains a helix interrupting protein that binds to the N-box rather than the canonical E-box. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:3280; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; E-box binding [GO:0070888]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; HLH domain binding [GO:0043398]; JUN kinase binding [GO:0008432]; N-box binding [GO:0071820]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription corepressor binding [GO:0001222]; adenohypophysis development [GO:0021984]; amacrine cell differentiation [GO:0035881]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; artery morphogenesis [GO:0048844]; ascending aorta morphogenesis [GO:0035910]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; Cajal-Retzius cell differentiation [GO:0021870]; cardiac neural crest cell development involved in outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0061309]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell fate determination [GO:0001709]; cell maturation [GO:0048469]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation [GO:0048667]; cellular response to fatty acid [GO:0071398]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus [GO:1990090]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cochlea development [GO:0090102]; comma-shaped body morphogenesis [GO:0072049]; common bile duct development [GO:0061009]; embryonic heart tube morphogenesis [GO:0003143]; establishment of epithelial cell polarity [GO:0090162]; forebrain radial glial cell differentiation [GO:0021861]; glomerulus vasculature development [GO:0072012]; hindbrain morphogenesis [GO:0021575]; inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0042491]; inner ear receptor cell stereocilium organization [GO:0060122]; labyrinthine layer blood vessel development [GO:0060716]; lateral inhibition [GO:0046331]; liver development [GO:0001889]; lung development [GO:0030324]; metanephric nephron tubule morphogenesis [GO:0072282]; midbrain development [GO:0030901]; midbrain-hindbrain boundary morphogenesis [GO:0021555]; negative regulation of amacrine cell differentiation [GO:1902870]; negative regulation of calcium ion import [GO:0090281]; negative regulation of cell fate determination [GO:1905934]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of forebrain neuron differentiation [GO:2000978]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of glial cell proliferation [GO:0060253]; negative regulation of inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0045608]; negative regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045665]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; negative regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048715]; negative regulation of pancreatic A cell differentiation [GO:2000227]; negative regulation of pro-B cell differentiation [GO:2000974]; negative regulation of stem cell differentiation [GO:2000737]; negative regulation of stomach neuroendocrine cell differentiation [GO:0061106]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neuronal stem cell population maintenance [GO:0097150]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; oculomotor nerve development [GO:0021557]; outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003151]; pancreatic A cell differentiation [GO:0003310]; pharyngeal arch artery morphogenesis [GO:0061626]; positive regulation of astrocyte differentiation [GO:0048711]; positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030513]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043388]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle, embryonic [GO:0045977]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050678]; regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045598]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0043254]; regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046425]; regulation of secondary heart field cardioblast proliferation [GO:0003266]; regulation of timing of neuron differentiation [GO:0060164]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; renal interstitial fibroblast development [GO:0072141]; response to alkaloid [GO:0043279]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; response to thyroid hormone [GO:0097066]; S-shaped body morphogenesis [GO:0072050]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224]; somatic stem cell population maintenance [GO:0035019]; stomach neuroendocrine cell differentiation [GO:0061102]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098]; telencephalon development [GO:0021537]; thymus development [GO:0048538]; trochlear nerve development [GO:0021558]; ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0060675]; vascular associated smooth muscle cell development [GO:0097084]; ventricular septum development [GO:0003281]; ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0060412] | 12065598_acid alpha-glucosidase gene is a novel target of the Notch-1/Hes-1 signaling pathway 12406868_HES-1 preserves the long-term reconstituting hematopoietic activity of 34-KSL stem cells ex vivo. 12535671_These results indicate that the molecular association between HES1-, HEY2- and SIRT1-related proteins is conserved among metazoans, from Drosophila to human, and suggest that the Sir2-bHLH interaction also plays important roles in human cells. 12972610_Hes1 transcription repression activity is inhibited by Hes6. 14722248_the estrogen receptor and AhR signaling pathways regulate HES-1, but with opposing effects, suggests the existence of a new pathway by which AhR represses E2-signaling. 15467735_HES-1 inhibits both estrogen- and heregulin-beta1-stimulated growth of breast cancer cells 15536134_IkappaBalpha is recruited to the promoter regions of the Notch-target gene, hes1 15563463_Notch1 inhibits the development of erythroid/megakaryocytic cells by suppressing GATA-1 activity through HES1 16214363_For marking and purifying neural stem cells to ascertain whether differences exist, we generated transgenic mice using promoters from Hes genes (pHes1 or pHes5) to drive expression of destabilized enhanced green fluorescent protein. 16253247_HES-1 is an upstream negative regulator of REST expression. 16322473_HES-1 alone is not able to substitute for Notch-1 signaling to induce T-cell differentiation of human CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells. 16365048_Notch protein binding to Hes5-GFP is extinguished fast and recovered slowly, whereas Hes1-GFP is inhibited late and recovered quickly 16894395_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17072841_Expression of HES1 increased significantly during chondrogenesis in chondrocytes while expression in mesenchymal stem cells was maintained at a low level. 17301032_Increased expression of Notch3, Jagged1, Hes1, and Hes6 gene transcripts were observed during differentiation of cultured human skeletal muscle cells. 17388915_expression significantly higher in squamous cervical carcinoma than in CIN as well as higher in CIN than normal cervical epithelia 17822320_Overexpression of hes1 is associated with breast cancer 18274550_Notch-mediated Hes1 expression contributes to the maintenance of the proliferative crypt compartment of the small intestine by transcriptionally repressing two CDK inhibitors. 18491256_lack of nuclear expression of HES1 may contribute to the abundance of ASCL1 and to tumorigenesis in the endocrine pancreas. 18524252_regulates brain development process.[review] 18550849_HES1 interaction with Fanconi anemia (FA) core complex members is dependent on a functional FA pathway. Cells depleted of HES1 exhibit an FA-like phenotype. 18599525_Inhibition of HES-1 expression using shRNA resulted in significantly reduced pancreatic beta-cell replication and dedifferentiation 18719287_it is concluded that HES1 safeguards against irreversible cell cycle exit both during normal cellular quiescence and pathologically in the setting of tumorigenesis 18821565_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19039095_These findings are consistent with a novel type of repressive estrogen response element in the distal 3' region of the HES-1 gene. 19058789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19116245_The Notch signaling mediator, Hes1, potently suppressed V2 promoter activity through interaction with two Hes sites within the V2 exon. 19118200_ChIP-on-chip data reveal 3 oncogenic transcription factors, NOTCH1, MYC, and HES1, bind to several thousand target gene promoters 19321451_FA core complex interferes with HES1 binding to the co-repressor transducin-like-Enhancer of Split, suggesting that the core complex affects transcription both directly and indirectly. 19322650_we showed that SOX9 binding to the HES-1 enhancer was induced by retinoic acid 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19603167_Hes1 protein expression was also found elevated in immune thrombocytopenic purpura and Hes1 of ITP was found expressed higher in cellular nucleus than that of controls. 19724860_Notch1 signaling pathway was activated in laryngeal carcinoma accompanied with up-regulation of Notch1 and Hes1 expression 19808903_This study first reports HES1-dependent SRC/STAT3 pathway that provides a functional link between Notch signaling and hypoxia pathway. 19861684_Hes1 is a key molecule in blast crisis transition in CML. 19880519_Hyperactivation of BRAF-MEK signaling activates MAP2 expression in melanoma cells by two independent mechanisms, promoter demethylation or down-regulation of neuronal transcription repressor HES1. 19891787_Expression of Hes-6 resulted in induction of E2F-1, a crucial target gene for the transcriptional repressor Hes-1. 19935883_Data show that inhibition of Hes1 activity can promote insulin expression and glucose responsiveness in gall bladder epithelial cells. 20022559_HES1 repressed gene expression in part by recruiting histone deacetylases in tumor cells.[Review] 20091184_The expression of HES1 is increased in advanced ovarian serous adenocarcinomas, and HES1 high-expression probably is a potential poor prognostic factor for the patients. 20515776_data suggest IkappaBalpha regulates Hes1-mediated activity in osteoclast differentiation and resorption, which supports a cross-talk between NF-kappaB and Notch in osteoclast activity 20668890_Combining Hes1 knockout studies and ptf1a-Cre-mediated lineage tracing showed that the inactivation of Hes1 induced the misexpression of ptf1a in discrete regions of the primitive stomach and duodenum, as well as the common bile duct. 20816878_Data show that HES-1 Orange domain is well folded in all conditions, forms stable dimers, and greatly increases protein resistance to thermal denaturation. 20832754_Hes1, a canonical Notch target and transcriptional repressor, is responsible for sustaining IKK activation in T-ALL. Hes1 exerts its effects by repressing the deubiquitinase CYLD, a negative IKK complex regulator. 21103979_Results suggest that common variants in HES1 are not strongly associated with diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes among white individuals. Findings cannot exclude these genes from involvement in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. 21106062_The studies support coordinated regulation of delta-catenin expression by both the activating transcription factor E2F1 and repressive transcription factor Hes1 in prostate cancer progression. 21125297_HES1 gene expression was unchanged toward the terminal ileum. HES1-positive cells were found in the crypt base in all regions of the small intestine. 21169257_Notch may directly suppress Hedgehog via Hes1 mediated inhibition of Gli1 transcription, and targeting both pathways simultaneously may be more effective at eliminating glioblastoma multiform cells. 21224467_The novel interaction of HES1 and PARP1 in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia modulates the function of the HES1 transcriptional complex and signals through PARP1 to induce apoptosis 21238798_In this study, HES 1 transcription factor was detected in the lining epithelium of human periapical cysts with limited inflammation, showing Notch pathway activation in those cells. 21495212_Hes1 overactivation is associated with cell differentiation, thereby resulting in uterine carcinogenesis. 21866461_Epigallocatechin-3-gallate down-regulated HES1 gene expression in HT29 and HCT-8 cells very slightly. 21984123_These indicate that HES1 is uncoupled from Notch in ESFT, that EWS-FLI1-mediated inhibition of Notch contributes to ESFT aggressive cell growth, and support a role for Notch in ESFT tumour suppression 22036964_Data suggest that HEs-1/Hey-1 transcriptional modulation of insulin degrading enzyme may impact amyloid beta metabolism by providing a functional link between Notch signaling and the amyloidogenic pathway. 22333607_The expression of Hes1 is correlated with pathological types and differentiation types of colorectal cancer, but is not correlated with the long-term survival rate. 22411914_High Hes1 expression is associated with medulloblastoma. 22705236_Down-regulation of Notch1 and Notch3 in two hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines resulted in Hes1 down-regulation, CDKN1C/P57 up-regulation, and reduced cell growth. 22846929_High HES1 are associated with Glucocorticoid resistance of T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. 22871495_High Hes-1 expression is associated with glioma. 23037857_Expression of Notch receptor and its target gene Hes-1 in bone marrow CD34+ cells from patients with psoriasis. 23235341_Notch1/Hes1-signaling pathway is activated during early pancreatic embryogenesis and reaches the highest at birth. 23379739_Data show that the periodontal ligament-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hPDLSCs) on a Jagged-1-modified surface had increased expression of Notch signaling target genes, Hes-1 and Hey-1, suggesting the involvement of Notch signaling in hPDLSCs. 23423517_The Notch1-Hes1 signalling axis suppresses neuroendocrine differentiation and maintains tubular/acinar features in adenocarcinoma and non-neoplastic epithelium in the biliary tree. 23860410_Notch signaling can directly downregulate MUC5AC promoter activity through Hes1-dependent mechanisms. 23900217_HES1 was overexpressed in colorectal cancer tumors relative to normal colonic mucosa. 24342613_Hes1-mediated enhancement of IL-22-STAT3 signaling significantly increased the induction of genes encoding antimicrobial peptides, such as REG1A, REG3A and REG3G, in human intestinal epithelial cells. 24346283_HES1 was identified as a direct target of microRNA-9 in medulloblastoma, and restoration of microRNA-9 was shown to trigger cell cycle arrest, to inhibit clonal growth and to promote medulloblastoma cell differentiation 24486648_Hes1 upregulation contributes to the development of FIP1L1-PDGRA-positive leukemia in blast crisis. 24492635_The results from this study indicate that Hes1 plays a quantitative role in the development and progression of colon cancer and the maintenance of the stemness of cancer stem cells, which remains to be fully characterized. 24684754_In prostate tumors, the overexpression of PTOV1 was associated with decreased expression of HEY1 and HES1, and this correlation was significant in metastatic lesions. 24825862_Data indicate that chronic myelogenous leukemia blast crisis showed that MMP-9 was highly expressed in three, with two exhibiting high levels of HES1 expression. 24885297_The tumor suppressor function of LSAMP is most likely exerted by reducing the proliferation rate of the tumor cells, possibly by indirectly upregulating one or more of the genes HES1, CTAG2 or KLF10. 24894488_the present results revealed, for the first time, that Hes-1 could be SUMO-modified by PIAS1 and GADD45alpha is a novel target of Hes-1 25037575_Hes-1 protein expression was gradually increased from normal to dysplasia to oral carcinoma, revealing Hes-1 role in the progression of oral cancer. 25107895_This study revealed that Notch signaling-related molecules (including Notch1, Hes1, and others) are expressed in L929 and MRC-5 cells and that Notch signaling regulates the expression of col1alpha1 and col1alpha2 in both cell lines. 25139105_This study is the first report that elucidated the HES1 underexpression in ESCC and revealed its correlation with the invasiveness of ESCC. 25216517_CPEB1 specifically suppressed the translation of HES1 and SIRT1 by interacting with a cytoplasmic polyadenylation element. 25234168_Hes1 suppresses acute myeloid leukemia development through FLT3 repression. 25605780_Hes1 oscillation sustains a dynamic proliferation state that is well adapted for versatile fate decisions in both single- and two-cell neural progenitor systems. 25636905_HES1 has a role in metastasis and predicts poor survival in patients with colorectal cancer 25672829_Pancreatic stellate cells promoted Hes 1 expression in both PANC-1 and BxPC-3 cell lines and induced chemoresistance to gemcitabine. High Hes 1 expression was seen in pancreatic cancer patients with shorter overall and progression-free survival times. 25733872_Hes1 cooperated with CaMK2delta to modulate OA pathogenesis through induction of catabolic factors, including Adamts5, Mmp13, Il6, and Il1rl1 25781910_we summarize the recent data supporting the idea that Hes1 may have an important function in the maintenance of cancer stem cells self-renewal, cancer metastasis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process induction 25784680_Hairy and Enhancer of Split 1 (HES1), a transcriptional repressor controlled by NOTCH1, is a critical mediator of NOTCH1-induced leukemogenesis strictly required for tumor cell survival. 25817041_OR1A1 activation suppresses hepatic triglyceride metabolism by modulating HES-1, PPARG, and mtGPAT expression. 25849484_High Hes1 expression is associated with chronic myeloid leukemia. 25906782_HES1 DMROI methylation predicted differences in early infant behaviour, known to be associated with academic success. In vitro, methylation of HES1 inhibited ETS transcription factor binding, suggesting a functional role of this site. 25920606_Interference with Notch1 increased the expression level of Hes-1. 25987042_Decreased HES1 expression is associated with higher lung metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma 26092281_overexpression of HES1 in primary AML cells inhibited growth of AML in a xenograft mice model. In conclusion, we demonstrated the tumor suppressor role of HES1 in AML. 26448192_Suggest that loss of Hes1 could be used as a sensitive and specific marker to differentiate sessile serrated adenomas/polyps from hyperplastic polyps. 26452025_Results suggest that Hes1 plays an important role in the invasion and metastasis of NPC through inhibiting PTEN expression to trigger EMT-like phenotypes. 26452029_Results provide functional and mechanistic links between Hes1 and Bmi-1/PTEN/Akt/GSK3beta signaling in the development and progression of colon cancer. 26563369_PNA-antimiR-182 reduced the levels of NICD, Hes1, HIF-1alpha, and p-Akt in both cell groups, while it augmented the intracellular content of FOXO1 and Numb suppressor proteins. In other words, PNA-antimiR-182-mediated upregulation of Numb was associated with downregulation of HIF-1alpha and Hes1. Consequently, downregulation of miR-182 might find therapeutical value for overcoming trastuzumab resistance 26650241_High expression of Hes1 is associated with Colorectal Cancer. 26678889_Low HES1 expression is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 26988248_we demonstrate for the first time an essential role of HPV oncoprotein E6 that selectively overexpresses in CaCxSLCs and participates in maintenance of stem cell phenotype and stemness through upregulation of Hes1 while preponderance of E7 leads to differentiation. 27353377_We demonstrated that ZNF70 interacts with ZFP64 and activates HES1 transcription by binding to the HES1 promoter. In addition, HES1 gene expression is increased in ILDR2-knockdown HepG2 cells, in which ZNF70 is translocated from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, suggesting that ZNF70 migration to the nucleus after dissociating from the ILDR2-ZNF70 complex activates HES1 transcription. These results support a novel link betwee 27476040_Loss of nuclear expression of Hes1 occurs in 83% of colorectal adenocarcinomas and is associated with female sex, right-sided location, BRAFV600E mutation, microsatellite instability, larger tumor size, and significantly worse survival. 27567696_In SNSCC, the subgroup of patients with high expression (5th quintile) of HES1 mRNA was associated with better survival (P = .04); however these patients with high expression of HES1 mRNA had also a more favorable tumor stage and grade and more unfavorable resections representing potential confounders. 27612417_A three-molecule score based on the expression of Notch pathway molecules: Jagged1, intracellular Notch1 (ICN1) and Hes1 (JIH score) to assess prognostic value in non-metastasis clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). 27639167_Hes1 plays a key role in acinar cell integrity and plasticity on cellular insults. 27677287_High expression of Hes1 is associated with radiation resistance in pancreatic cancer. 28013292_Low Hes1 expression is associated with left ventricle hypertrabeculation/non-compaction and Menetrier-like gastropathy. 28079885_The phenotype was rescued by ectopic expression of miRNA182-5p in Delta182 cells. A bioinformatic analysis and Hes1 modulation data suggested that Hes1 could be a putative target of miRNA182-5p. A reciprocal relationship between miRNA182-5p and Hes1 was seen in the context of TK inhibition 28122586_miR-182 reveals its oncogenic capacity in medullary thyroid carcinoma by directly contributing to the invasive behavior through loss of the tumor suppressive HES1/Notch1 signaling circuit. 28245235_Cells could therefore regulate the proportion of Wnt- and Notch-mediated control of the Hes1 promoter to coordinate the timing of cell fate selection as they migrate through the intestinal epithelium and are subject to reduced Wnt stimuli. Furthermore, mutant cells characterised by hyperstimulation of the Wnt pathway may, through coupling with Notch, invert cell fate in neighbouring healthy cells, enabling an aberrant cel 28420872_Hes-1 knockdown promotes osteopontin expression in HUVECs and enhances OPN-induced angiogenesis. 28423527_These results suggest that HES1 promotes extracellular matrix protein expression and inhibits proliferative and migratory functions in the trabecular meshwork cells under oxidative stress, thereby providing a novel pathogenic mechanism underlying and a potential therapeutic target to primary open-angle glaucoma 28451898_In the present study, the authors reported the first observation of Hes1 oscillatory expression in human neural progenitor /stem cells, with an approximately 1.5 hour periodicity and a Hes1 protein half-life of about 17 (17.6 +/- 0.2) minutes. Human cytomegalovirus infection disrupts the Hes1 rhythm and down-regulates its expression. 28464285_GPR146 has an antiviral role in fighting against viral infection, although the GPR146-mediated protection is eliminated by IRF3/HES1-signalling. 28536281_Hes1 disruption leads to tumor regression without perturbing normal stem cell homeostasis, preclinically validating Hes1 as a cancer therapeutic target. 28750047_IE1 is involved in Hes1 degradation by assembling a ubiquitination complex and promoting Hes1 ubiquitination as a potential E3 ubiquitin ligase, followed by proteasomal degradation of Hes1. 28974640_Notch signaling and Id2/3 regulate neurogenesis in a complementary manner and ID factors can induce neural stem cell maintenance and quiescence in the absence of Notch. 29436668_Our results suggest that KN promotes goblet cell differentiation by regulating Wnt, Notch, and AhR signals and expression of Hes1 and Hath1. 29458175_The Sox17-Notch1-Hes1 pathway is critical for maintaining the undifferentiated state of IAHCs. 29463306_HES1 is mono-ubiquitinated in a Fanconi anemia core complex-dependent manner. 29491143_Depletion of HES1 increased cell death in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress in mouse and human cells, in a manner that depended on the pro-apoptotic gene growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD34. 29523683_High HES1 expression is associated with pancreatic neoplasms. 29665790_The results of this study demonstrate that HES1 is a specific downstream gene of NOTCH1 and that it contributes to SACC proliferation, apoptosis and metastasis. 29981167_High HES1 expression is associated with invasiveness and tumorigenicity of non-small cell lung cancer. 30107165_MiR-182 alleviates the development of cyanotic congenital heart disease by suppressing HES1 30548309_Data indicate that hairy/enhancer of split-1 (Hes1) protein, overexpressed under the influence of Juglone, is apparently involved in Juglone-induced apoptosis among K562 cells. 30615540_Among all HPV-16-positive precancers the major HES1 protein expression positivity signal was present from cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grades 2 and 3 that develops into invasive squamous cell carcinoma. 30653033_Annexin A10 and HES-1 Immunohistochemistry in Right-sided Traditional Serrated Adenomas Suggests an Origin From Sessile Serrated Adenoma. 30895661_We defined the KK-LC-1/presenilin-1/Notch1/Hes1 as a novel signalling pathway that was involved in the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 31109645_The significant role of NK1R in mediating ESCC cell proliferation depended on the activation of SP and might be related to the downstream regulation of Hes1. 31232134_HES1 demonstrates uniform robust (+++) nuclear staining pattern in the tumor cells of all the neuroendocrine neoplasms (32/32), regardless of the origin of the system and the grade of the tumor. 31919081_HES1 and HES4 have non-redundant roles downstream of Notch during early human T-cell development. 32173531_Inhibition of NOTCH signaling pathway chemosensitizes HCC CD133(+) cells to vincristine and 5-fluorouracil through upregulation of BBC3. 32329442_Inhibition of HES-1 might play a protective role in endothelial cells under cholesterol stimulation via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. 32879444_MYEOV increases HES1 expression and promotes pancreatic cancer progression by enhancing SOX9 transactivity. 32949667_High expression of miR-374a-5p inhibits the proliferation and promotes differentiation of Rencell VM cells by targeting Hes1. 32972441_microRNA-216b enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in osteosarcoma MG63 and SaOS-2 cells by binding to JMJD2C and regulating the HIF1alpha/HES1 signaling axis. 33067264_Hes1 Is Essential in Proliferating Ductal Cell-Mediated Development of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. 33390847_HES1 promotes breast cancer stem cells by elevating Slug in triple-negative breast cancer. 33531431_Hes1 overexpression leads to expansion of embryonic neural stem cell pool and stem cell reservoir in the postnatal brain. 33544929_IL-6 and IL-8, secreted by myofibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment, activate HES1 to expand the cancer stem cell population in early colorectal tumor. 34278469_Sirt3 promotes the autophagy of HK2 human proximal tubular epithelial cells via the inhibition of Notch1/Hes1 signaling. 34354706_ILC2 Cells Promote Th2 Cell Differentiation in AECOPD Through Activated Notch-GATA3 Signaling Pathway. 34582650_LGR5, HES1 and ATOH1 in Young Rectal Cancer Patients in Egyptian. 34725165_Differential phase register of Hes1 oscillations with mitoses underlies cell-cycle heterogeneity in ER(+) breast cancer cells. 34738458_MicroRNA-361-5p Aggravates Acute Pancreatitis by Promoting Interleukin-17A Secretion via Impairment of Nuclear Factor IA-Dependent Hes1 Downregulation. 34804002_Oxidative Stress Leads to beta-Cell Dysfunction Through Loss of beta-Cell Identity. 35640677_Induction of Transcriptional Inhibitor HES1 and the Related Repression of Tumor-Suppressor TXNIP Are Important Components of Cell-Transformation Program Imposed by Oncogenic Kinase NPM-ALK. 35975741_Ischemic preconditioning/ischemic postconditioning alleviates anoxia/reoxygenation injury via the Notch1/Hes1/VDAC1 axis. 36037042_Identification and targeting of a HES1-YAP1-CDKN1C functional interaction in fusion-negative rhabdomyosarcoma. 36206597_Loss of Hes1 in embryonic stem cells caused developmental disorders in retinal pigment epithelium morphogenesis and specification. 36321463_HES1 promoter activation dynamics reveal the plasticity, stemness and heterogeneity in neuroblastoma cancer stem cells. | ENSMUSG00000022528 | Hes1 | 92.724692 | 1.1067208 | 0.146291271 | 0.15132109 | 0.93495388203 | 0.3335789617716152788418071395426522940397262573242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.56625304058549474905959186799009330570697784423828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 96.962408 | 11.314953 | 88.013174 | 10.339215 | |
| ENSG00000114520 | 8723 | SNX4 | protein_coding | O95219 | FUNCTION: Involved in the regulation of endocytosis and in several stages of intracellular trafficking (PubMed:12668730, PubMed:17994011, PubMed:32513819, PubMed:33468622). Plays a role in recycling endocytosed transferrin receptor and prevent its degradation (PubMed:17994011). Involved in autophagosome assembly by regulating trafficking and recycling of phospholipid scramblase ATG9A (PubMed:32513819, PubMed:33468622). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12668730, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17994011, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32513819, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33468622}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Endosome;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport | This gene encodes a member of the sorting nexin family. Members of this family contain a phox (PX) domain, which is a phosphoinositide binding domain, and are involved in intracellular trafficking. This protein associated with the long isoform of the leptin receptor and with receptor tyrosine kinases for platelet-derived growth factor, insulin, and epidermal growth factor in cell cultures, but its function is unknown. This protein may form oligomeric complexes with family members. Two transcript variants, one protein coding and the other non-protein coding, have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2012]. | hsa:8723; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic dynein complex [GO:0005868]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic endosome [GO:0098830]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; SNARE complex [GO:0031201]; epidermal growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005154]; insulin receptor binding [GO:0005158]; leptin receptor binding [GO:1990460]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding [GO:0032266]; transferrin receptor binding [GO:1990459]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; positive regulation of autophagosome assembly [GO:2000786]; positive regulation of histamine secretion by mast cell [GO:1903595]; protein transport [GO:0015031] | 12668730_Sorting nexin 4 and amphiphysin 2 have roles in endocytosis and intracellular trafficking 17319803_study indicates that hVps34 and its product PI(3)P are involved in endosome to Golgi transport of ricin, and that SNX2 and SNX4 are likely to be effectors in this pathway 17994011_by driving membrane tubulation, SNX4 coordinates iterative, geometric-based sorting of the TfnR with the long-range transport of carriers from early endosomes to the ERC 19529763_clathrin serving as a regulator of SNX4-dependent transport; upon clathrin release, dynein may bind SNX4 and mediate retrograde movement 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21973056_SNX4, but not SNX1 and SNX8, is associated with the Rab11-recycling endosomes and that a high frequency of SNX4-mediated tubule formation is observed as endosomes undergo Rab4-to-Rab11 transition. 24690921_alpha-taxilin interacts with SNX4 and plays a role in the recycling pathway of TfnR. 28109317_Results indicate that SNX4-mediated regulation of the steady-state levels and trafficking of BACE1, as well as the subsequent increase in BACE1-mediated cleavage, may be relevant to Alzheimer's disease progression. 33468622_The phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate-binding protein SNX4 controls ATG9A recycling and autophagy. | ENSMUSG00000022808 | Snx4 | 291.254925 | 1.2623929 | 0.336161009 | 0.15786501 | 4.52048836328 | 0.0334912701705622553594032808632618980482220649719238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.12354321918402554059124298646565875969827175140380859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 338.268256 | 32.200797 | 268.994148 | 25.763021 | |
| ENSG00000114988 | 81562 | LMAN2L | protein_coding | Q9H0V9 | FUNCTION: May be involved in the regulation of export from the endoplasmic reticulum of a subset of glycoproteins. May function as a regulator of ERGIC-53. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12878160}. | Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Intellectual disability;Lectin;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a protein belonging to the L-type lectin group of type 1 membrane proteins, which function in the mammalian early secretory pathway. These proteins contain luminal carbohydrate recognition domains, which display homology to leguminous lectins. Unlike other proteins of the group, which cycle in the early secretory pathway and are predominantly associated with post endoplasmic reticulum membranes, the protein encoded by this gene is a non-cycling resident protein of the ER, where it functions as a cargo receptor for glycoproteins. It is proposed to regulate exchange of folded proteins for transport to the Golgi and exchange of misfolded glycoproteins for transport to the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. | hsa:81562; | COPII-coated ER to Golgi transport vesicle [GO:0030134]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment [GO:0005793]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mannose binding [GO:0005537]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; endoplasmic reticulum organization [GO:0007029]; endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006888]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein transport [GO:0015031] | 12878160_VIPL terminates in the sequence KRFY, characteristic for proteins recycling between the ER and ERGIC/cis-Golgi; and knock-down of VIPL mRNA slowed secretion of two glycoproteins (35 and 250 kDa), suggesting that VIPL may function as an ER export receptor. 18025080_selective interaction of VIPL and VIP36 with the deglucosylated trimannose in the D1 branch of high-mannose-type oligosaccharides but with different pH dependence. 22182935_The results of this study suggested that significant novel association signals near the genes LMAN2L and provide supportive evidence for the previously reported association signals near ANK3 and within the 3p21.1 locus. 24914473_Study showed a significant association between LMAN2L and risk of both bipolar disorder and schizophrenia 26566883_Homozygous missense mutation p.R53Q in the LMAN2L gene causes autosomal recessive intellectual disability and seizures. 31020005_segregate a NM_001142292.1:c.1073delT mutation that eliminates LMAN2L's endoplasmic reticulum retention signal and mislocalizes the protein from that compartment to the plasma membrane | ENSMUSG00000001143 | Lman2l | 169.672034 | 0.8514518 | -0.232003239 | 0.14036396 | 2.73051675696 | 0.0984474263055660353538556250896363053470849990844726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.26200201658338234667056099169712979346513748168945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 157.898472 | 13.935392 | 186.259663 | 16.201938 | |
| ENSG00000115310 | 57142 | RTN4 | protein_coding | Q9NQC3 | FUNCTION: Required to induce the formation and stabilization of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) tubules (PubMed:27619977, PubMed:25612671, PubMed:24262037). They regulate membrane morphogenesis in the ER by promoting tubular ER production (PubMed:27619977, PubMed:25612671, PubMed:24262037, PubMed:27786289). They influence nuclear envelope expansion, nuclear pore complex formation and proper localization of inner nuclear membrane proteins (PubMed:26906412). However each isoform have specific functions mainly depending on their tissue expression specificities (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24262037, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25612671, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26906412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27619977, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27786289, ECO:0000305}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform A]: Developmental neurite growth regulatory factor with a role as a negative regulator of axon-axon adhesion and growth, and as a facilitator of neurite branching. Regulates neurite fasciculation, branching and extension in the developing nervous system. Involved in down-regulation of growth, stabilization of wiring and restriction of plasticity in the adult CNS (PubMed:10667797, PubMed:11201742). Regulates the radial migration of cortical neurons via an RTN4R-LINGO1 containing receptor complex (By similarity). Acts as a negative regulator of central nervous system angiogenesis. Inhibits spreading, migration and sprouting of primary brain microvascular endothelial cells (MVECs). Also induces the retraction of MVECs lamellipodia and filopodia in a ROCK pathway-dependent manner (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99P72, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10667797, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11201742}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform B]: Mainly function in endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells, is also involved in immune system regulation (Probable). Modulator of vascular remodeling, promotes the migration of endothelial cells but inhibits the migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. Regulates endothelial sphingolipid biosynthesis with direct effects on vascular function and blood pressure. Inhibits serine palmitoyltransferase, SPTLC1, the rate-limiting enzyme of the novo sphingolipid biosynthetic pathway, thereby controlling production of endothelial sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). Required to promote macrophage homing and functions such as cytokine/chemokine gene expression involved in angiogenesis, arteriogenesis and tissue repair. Mediates ICAM1 induced transendothelial migration of leukocytes such as monocytes and neutrophils and acute inflammation. Necessary for immune responses triggered by nucleic acid sensing TLRs, such as TLR9, is required for proper TLR9 location to endolysosomes. Also involved in immune response to LPS. Plays a role in liver regeneration through the modulation of hepatocytes proliferation (By similarity). Reduces the anti-apoptotic activity of Bcl-xl and Bcl-2. This is likely consecutive to their change in subcellular location, from the mitochondria to the endoplasmic reticulum, after binding and sequestration (PubMed:11126360). With isoform C, inhibits BACE1 activity and amyloid precursor protein processing (PubMed:16965550). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99P72, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11126360, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16965550, ECO:0000305}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform C]: Regulates cardiomyocyte apoptosis upon hypoxic conditions (By similarity). With isoform B, inhibits BACE1 activity and amyloid precursor protein processing (PubMed:16965550). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99P72, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16965550}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene belongs to the family of reticulon encoding genes. Reticulons are associated with the endoplasmic reticulum, and are involved in neuroendocrine secretion or in membrane trafficking in neuroendocrine cells. The product of this gene is a potent neurite outgrowth inhibitor which may also help block the regeneration of the central nervous system in higher vertebrates. Alternatively spliced transcript variants derived both from differential splicing and differential promoter usage and encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:57142; | anchoring junction [GO:0070161]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum tubular network [GO:0071782]; endoplasmic reticulum tubular network membrane [GO:0098826]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; axonal fasciculation [GO:0007413]; blastocyst formation [GO:0001825]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cardiac epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0060317]; cell adhesion involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0120078]; cell migration involved in vasculogenesis [GO:0035441]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular sphingolipid homeostasis [GO:0090156]; central nervous system vasculogenesis [GO:0022009]; cerebral cortex radial glia-guided migration [GO:0021801]; endoplasmic reticulum organization [GO:0007029]; endoplasmic reticulum tubular network formation [GO:0071787]; endoplasmic reticulum tubular network membrane organization [GO:1990809]; endoplasmic reticulum tubular network organization [GO:0071786]; leukocyte migration involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002523]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation [GO:1902430]; negative regulation of axon extension [GO:0030517]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of vasculogenesis [GO:2001213]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; nuclear pore complex assembly [GO:0051292]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of artery morphogenesis [GO:1905653]; positive regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010634]; positive regulation of ERBB3 signaling pathway [GO:1905580]; positive regulation of hepatocyte proliferation [GO:2000347]; positive regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0060907]; positive regulation of macrophage migration [GO:1905523]; positive regulation of mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0033601]; positive regulation of neutrophil migration [GO:1902624]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum [GO:1905552]; positive regulation of Rac protein signal transduction [GO:0035022]; positive regulation of toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway [GO:0034165]; protein localization to lysosome [GO:0061462]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of branching morphogenesis of a nerve [GO:2000172]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334] | 12270696_The alteration in Nogo gene expression in muscle biopsy represents a potential diagnostic tool for the early stages of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 12425946_Elevated expression of Nogo mRNA in schizophrenia was confirmed by RT-PCR. Nogo mRNA was found to contain a CAA insert polymorphism in the 3'-untranslated region. 12488097_results describe the regulation of nogo expression through its promoter region 12510146_ASY may be multi-functional, regulating apoptosis, tumor development, and neuronal regeneration [review] 12618765_ER stress of highly overexpressed Nogo-B may lead to aversive cellular reactions under particular conditions. Our data do not support a function of Nogo-B as a physiological pro-apoptotic protein in certain types of cancer. 12811824_ASYIP(ASY-interacting) protein co-localized with ASY in endoplasmic reticulum. Characterization of ASYIP gene may help clarify mechanism of ASY-induced apoptosis or Nogo-involved inhibition of neuronal regeneration in central nervous system. 14741411_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14741411_this study found a similar frequency of the CAA insertion for patients and controls in both populations, but a large difference in CAA insertion frequency between the European American and the African American. 15034570_Nogo-B is a regulator of vascular homeostasis and remodeling broadens the functional scope of this family of proteins 15147731_The steady-state level of reticulon 4-B mRNA was shown to be up-regulated by pressure, but not by mechanical stretch; close association with endoplasmic reticulum 15234466_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15245492_In temporal lobe epilepsy Nogo-A mRNA and immunoreactivity were markedly up-regulated in most neurons and their processes throughout the hippocampal formation. 15661375_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15749087_Expression of the genes encoding Nogo and its receptor, NgR, between weeks eight and 23 of human embryonic development 15820318_Nogo CAA 3'UTR insertion polymorphism is not associated with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder 15820318_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15953657_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15953657_There was a statistically significant difference at the allelic level for both the CAA (chi2 = 4.378, df = 1, P value = 0.036) and TATC (chi2 = 5.807, df = 1, P = 0.016) polymorphisms in the female subgroup. 16095439_results identify Nogo-B as a new physiological substrate of MAPKAP-K2 16629624_Nogo-A is possibly the best characterized of a variety of neurite growth inhibitors present in CNS myelin--REVIEW 16646068_ASY/Nogo gene may act as a suppressor against adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma progression, independent of Tax expression 16772867_Reticulon proteins such as Nogo-A participate in the neuronal responses stemming from hippocampal formation during senescence, and particularly in Alzheimer disease . 16835300_identify a previously uncharacterized Nogo-B receptor specific for the amino terminus of Nogo-B 16835300_identify a previously uncharacterized Nogo-B receptor specific for the amino terminus of Nogo-B. 16905119_Expressed in HEK293 cells, Nogo-C confers apoptosis by inducing caspase-3 and p53 activation through the c-jun N-terminal kinase-c-Jun-dependent pathway. 16979658_Results describe the mapping of interaction domains mediating binding between BACE1 and RTN3/Nogo proteins. 17022955_Nogo C to be overexpressed by 26% in the schizophrenia tissues And Nogo B was reduced by 17% in the frontal cortices who had severe depression. 17022955_There is a direct correlation between the expression of Nogo A and C and the presence of alleles with a CAA insert in 3' UTR. New sample group shows Nogo C upregulation in schizophrenia and Nogo B downregulation in depression. 17029193_Data show that the C-terminal of Nogo protein interacts with CX26. 17242333_Soluble Nogo-A may be specific for the cerebrofinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis and may predict failure of axonal regeneration in the central nervous system. 17437522_systematic substitution analysis of all 6 Cys residues of Nogo-A indicated that this domain forms 2 structural disulfide bonds among Cys residues 424, 464, 559 & 597, whereas the Cys residues at positions 699 & 912 seem to be dispensable for folding. 17455292_The detection of Nogo-A in muscle biopsy samples from LMNS patients correctly identified patients who further progressed to ALS with 91% accuracy, 94% sensitivity, and 88% specificity. 17592524_Nogo-A expression was negatively correlated with the malignancy grade of oligodendroglial tumors. 17626519_The presence of Nogo-A in diseased human muscle biopsies is not limited to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 17645629_Reduction of Nogo-B protein expression in thoracic aortic aneurysms is closely correlated to the formation of aneurysm and that Nogo-B may play a protective role in the pathological process of aneurysms. 17764014_Accordingly, two novel mechanisms, A beta PP overexpression and ER stress, are involved in Nogo-B and Nogo-A expression in human muscle. 17971502_Data is the first report to demonstrate the relationship between Nogo expression and heart failure, including cell-type specificity, in human HF and phenotypic rescue. 18080785_found A172G (Thr58Ala), A340G (Arg114Gly), A571G (Ile191Val) mutations of Nogo-C in hepatocellular carcinoma patients from Qidong in China 18234903_Inhibition of integrin signaling by Amino-Nogo (nucleotide fragment 540-2592) contributes to the failure of central nervous system axon regeneration. 18495952_A 25 kD band is detectable on Western blots stained with Nogo-A antibody in almost all CSF specimens, but is not likely to be a useful biomarker for multiple sclerosis. 18583979_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18685489_Nogo-a expression in glial CNS tumors may be a marker to differentiate between oligodendrogliomas and other gliomas. 18948092_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18948092_RTN4 allele (TATC)(2) and (TATC)(2)/(TATC)(2) genotype are associated with DCM. 19035836_analysis of the interaction between ubiquitin ligase WWP1 and Nogo-A 19054571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19336839_Phosphorylation of Nogo receptors by casein kinase II (CK2) inhibits binding of the myelin-associated proteins. 19405102_An RTN4-C mutant lacking the C-terminal domain bound to BACE1 comparably to wild-type RTN4-C & reduced Abeta40 & Abeta42 secretion by cells expressing Swedish mutant APP. 19508346_verified the molecular interaction of Nogo-A with 2', 3'-cyclic nucleotide 3'-phosphodiesterase (CNP), which could act as a conformational stabilizer for the intrinsically unstructured large segment of Amino-Nogo 19587271_A Nogo deletion mutant mouse line created via Cre-loxP-mediated recombination is confirmed to be a complete Nogo null allele, lacking expression of all known Nogo isoforms. 19654939_findings suggest that fibroatheroma progression is inversely associated with Nogo-B expression 19889996_In a transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Nogo-A contributes to the proper function of the resident endoplasmic reticulum chaperone protein disulfide isomerase, and is protective against ALS-like neurodegeneration. 20018888_identified Akt1 as a new signaling component of the amino-Nogo pathway. Akt1 phosphorylation is decreased by amino-Nogo. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20487307_Nogo-A is highly expressed in oligodendroglial tumors; however, it does not serve as a definite marker specific for oligodendroglial tumors 20599731_Fibulin-5, a secreted extracellular matrix protein, was identified as a binding partner of Nogo-B. 20717916_Reticulons, the only molecular so far to participate in all three apoptosis signaling pathways, may be a novel player in the progress of atherosclerosis. 20938157_These results suggest a role for neuronal Nogo-A in maintaining a spine phenotype in neocortical pyramidal cells 20971739_Nogo-B may regulate macrophage recruitment after unilateral ureteral obstruction, although it does not greatly affect the degree of tissue injury or fibrosis in this model. 20975041_Epithelial reticulon 4B (Nogo-B) is an endogenous regulator of Th2-driven lung inflammation. 21111015_The data identify, for the first time, an effect of Nogo B in the brain and specifically show that its expression is increased in conditions where synaptic plasticity is compromised. 21166502_No significant differences in 3'UTR TATC and CAA insertion/deletion polymorphism genotype and allele frequencies were observed between the ventricular septal defect patients and controls. 21183689_Using leukocytes and endothelial cells, we show mechanistically that the silencing of Nogo-B with siRNA impairs the transmigration of neutrophils and reduces ICAM-1-stimulated phosphorylation of VE-cadherin. 21251247_Endogenous Nogo-B, which may exert its effects through ARPC 2/3 and MYL-9, is necessary for the migration and contraction of airway smooth muscle cells. 21454605_A multi-domain fragment of Nogo-A protein is a potent inhibitor of cortical axon regeneration via Nogo receptor 1. 21503119_The presence of Nogo-A in diseased human muscle biopsies is not limited to ALS, therefore it cannot be the standard for ALS diagnosis. 21697531_Data showd that Nogo-B, a regulator of ER structure, was induced by hypoxia in pulonary artery smooht muscle cells but not the systemic vasculature through activation of the ER stress-sensitive transcription factor ATF6. 21835431_Nogo-A is a useful marker for the diagnosis of oligodendroglioma and for identifying 1p19q codeletion 22133682_Nogo receptor 3, a paralog of NgR1,functions as a NgR1 co-receptor for Nogo-66. 22313113_CAA and TATC insertion/deletion polymorphisms of RNT4 gene may not be a useful marker to predict the susceptibility of ASD in Chinese Han population 22320844_genetic variation in RTN4 3'-UTR contributes to the susceptibility to CSCC 23042479_Overexpression of Nogo-B promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cervical cancer via Fibulin-5. 23146900_The results demonstrate a significant change in the expression of Nogo-A during the development of the human brain 23313137_The absence of Nogo-B enhances apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells in experimental cirrhosis. 23479081_Studied premenopausal women with uterine leiomyoma. No significant association was observed between the TATC in/del polymorphism and UL risk, but increased UL risk was associated with CAA in/del polymorphism in the recessive and codominant model. 23982337_knockdown of NgR enhanced invasion and adhesion but increased cell apoptosis in C6 cells, suggesting that Nogo-66/NgR might have complex effects on glioma cells. 24129566_the association of RhoGDIalpha with TROY contributed to TROY-dependent RhoA activation and neurite outgrowth inhibition after Nogo-66 stimulation. 24278366_The Nogo-B-PirB axis controls macrophage-mediated vascular remodeling. 24372562_The expression of Nogo-B, in arterial intima, is impeded in the early stages of atherosclerosis. Macrophage infiltration is not accompanied by Nogo-B expression in atherosclerotic arteries. 24401759_Neither migration speed, nor cell proliferation, or layer area sizes were influenced by Nogo-A deletion, hence suggesting another role for early postnatal Nogo-A expression in the premigratory zone of the external granule layer. 24626842_the present study found that Nogo-A depletion was capable of inhibiting HCC SMMC-7721 cell proliferation by promoting G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. 24966913_Identify Nogo-C as a tumor suppressor gene in hepatocellular carcinoma and B-raf as a novel interacting protein. 25040983_The RTN4 del allele could significantly increase NSCLC risk. 25075030_Nogo-A/B expression decreased with increasing squamous cell carcinoma malignancy grade (p=0.026). 25331889_a novel mechanism that functionally couples cAMP signaling with the proteolytic turnover of NOGO-A, positively impacting on neurite outgrowth in mammalian brain. 25847052_RTN4-C knockdown blocks cell cycle progression and cell growth in colorectal cancer cell lines. 25907690_Epithelial RTN-4B/NOGO-B was downregulated in human and experimental inflammatory bowel disease 26472601_Data show that the mean peak serum neuroglobin and Nogo-A concentrations were both significantly higher in patients with an unfavorable outcome at 6 months after traumatic brain injury (TBI). 26656426_Nogo-B expression is down-regulated in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, the implication of which, however, remains to be investigated. 26826187_LILRA3 significantly reversed Nogo-66-mediated inhibition of neurite outgrowth and promoted synapse formation in primary cortical neurons through regulation of the ERK/MEK pathway. 27353365_observations suggest that Rtn4A counteracts the Nrdp1-mediated degradation of ErbB3 by sequestering the ubiquitin ligase into ER tubules. 27354599_NOGO-A/B may be a negative prognostic factor of malignant melanoma. 27786289_NOGO-B/RTN4B and NOGO-A/RTN4A are simultaneously expressed in cultured epithelial, fibroblast and neuronal cells. Morphological analysis of cells with manipulated levels of NOGO-B/RTN4B revealed that it is required for maintenance of normal endoplasmic reticulum shape. 28144881_CAA and TATC Insertion/Deletion Genetic Polymorphisms of RTN4 3'-UTR are associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma 28408340_This review aims at presenting our current knowledge on the role of Nogo-A in the visual system and to discuss how its therapeutic targeting may promote visual improvement in ophthalmic diseases. 28628795_Nogo-B is expressed aberrantly in HCCs and plays an oncogenic role. These findings support that Nogo-B may be a novel anti-HCC therapeutic target. 28687970_Study provide evidence for the first time that the TATC insertion/deletion polymorphism in RTN4 3'-UTR may contributes to clear cell renal cell carcinoma risk in Chinese Han population. 29412690_Platelets drive a p38-MK2-RTN4-Bcl-xl pathway associated with the regulation of the endoplasmic reticulum and platelet phosphatidylserine exposure, modulating procoagulant phenotype. 29684585_Nogo-B was shown to play an important negative role in apoptotic signaling through its interaction with c-FLIP in colorectal cancer cells. 30019429_This study found that the expression level of Nogo-B is positively correlated with tumor vessel density in hepatocellular carcinoma. 30078441_Study reports that RTN4 expression inversely predicts survival from lung, breast, cervical, kidney, and ovarian cancers. RTN4 regulates cancer cell proliferation through dysregulations within AKT pathway activation that are accompanied by aberrant phospholipid homeostasis and cytoskeleton destabilization. 30480803_RTN4 might somehow participate in prostate tumor progression. 31062076_RhoA-mediated perturbation of IRE1alpha-regulated mRNA decay leads to SPARC translation. Once translation is initiated, glioblastoma cells rapidly secrete SPARC to block Nogo-A from inhibiting migration via RhoA. A conserved disordered region of Nogo-A-Delta20 is central for its interaction with S1PR2 and SPARC. 31092426_A statistically significant positive correlation of CHI3L1 and Nogo-A expression (r=0.474, p>0.0001) and a positive correlation of Nogo-A and VEGFC expression (r=0.280, p=0.013) were found. CHI3L1 and Nogo-A are important in angiogenesis in invasive ductal breast carcinoma 31249451_Plasma PlGF levels were higher while Nogo-A levels were lower in patients with liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Biomarkers showed moderate predictive value in determining clinically significant portal hypertension and severe portal hypertension. 31358770_Data suggest targeting the reticulon-4 (Nogo-B) pathway may represent a therapeutic strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) arising from the metabolic syndrome. 31469817_High-speed (40 ms/frame) live cell STED imaging shows that RTN4a and CLIMP-63 regulate dynamic nanoscale lumenal compartmentalization along peripheral ER tubules. RTN4a enhances and CLIMP-63 disrupts the local accumulation of lumenal ERmoxGFP at spatially defined sites along ER tubules. 31622291_A missense mutation was found on exon 2 of Reticulon 4 gene was found to be not involved in Charcot- Marie-Tooth disease. 31654717_Identification of Nogo-B as a new molecular target of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. 31748413_A proteolytic C-terminal fragment of Nogo-A (reticulon-4A) is released in exosomes and potently inhibits axon regeneration. 31764777_The plasma level of RTN4 was significantly higher in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma in comparison with the controls. Furthermore, we observed that patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma carrying the rs2920891 A/C+C/C genotype had a higher RTN4 level than those carrying the A/A genotype.Our findings indicated that the rs2920891 polymorphism may be associated with increased susceptibility to nasopharyngeal carcinom 33517425_Neurite Outgrowth Inhibitor (NogoA) Is Upregulated in White Matter Lesions of Complex Cortical Malformations. 33721786_Association between the promoter haplotype of RTN4 gene and schizophrenia in a Korean population. 33924890_The Implication of Reticulons (RTNs) in Neurodegenerative Diseases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches. 34758294_RTN4/NoGo-receptor binding to BAI adhesion-GPCRs regulates neuronal development. 34824275_NogoA-expressing astrocytes limit peripheral macrophage infiltration after ischemic brain injury in primates. 34943877_Co-Expression of Nogo-A in Dopaminergic Neurons of the Human Substantia Nigra Pars Compacta Is Reduced in Parkinson's Disease. 34983537_CircRTN4 promotes pancreatic cancer progression through a novel CircRNA-miRNA-lncRNA pathway and stabilizing epithelial-mesenchymal transition protein. 34998825_Inhibition of high-fat diet-induced obesity via reduction of ER-resident protein Nogo occurs through multiple mechanisms. 35075114_Nogo-B promotes invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via RhoA-SRF-MRTFA pathway. 35771867_An Rtn4/Nogo-A-interacting micropeptide modulates synaptic plasticity with age. | ENSMUSG00000020458 | Rtn4 | 4133.210477 | 1.1245045 | 0.169289441 | 0.03122996 | 29.37302593551 | 0.0000000597028931471032169736668838468107711747734356322325766086578369140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000122272923768913587058563326864790710146735364105552434921264648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 4299.887655 | 80.696115 | 3841.828719 | 72.179534 | |
| ENSG00000115641 | 2274 | FHL2 | protein_coding | Q14192 | FUNCTION: May function as a molecular transmitter linking various signaling pathways to transcriptional regulation. Negatively regulates the transcriptional repressor E4F1 and may function in cell growth. Inhibits the transcriptional activity of FOXO1 and its apoptotic function by enhancing the interaction of FOXO1 with SIRT1 and FOXO1 deacetylation. Negatively regulates the calcineurin/NFAT signaling pathway in cardiomyocytes (PubMed:28717008). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15692560, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16652157, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18853468, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28717008}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Isopeptide bond;LIM domain;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a member of the four-and-a-half-LIM-only protein family. Family members contain two highly conserved, tandemly arranged, zinc finger domains with four highly conserved cysteines binding a zinc atom in each zinc finger. This protein is thought to have a role in the assembly of extracellular membranes. Also, this gene is down-regulated during transformation of normal myoblasts to rhabdomyosarcoma cells and the encoded protein may function as a link between presenilin-2 and an intracellular signaling pathway. Multiple alternatively spliced variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. | hsa:2274; | focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; bHLH transcription factor binding [GO:0043425]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; transcription factor binding [GO:0008134]; atrial cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0055014]; heart trabecula formation [GO:0060347]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade [GO:0070885]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; response to hormone [GO:0009725]; ventricular cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0055015] | 11821401_Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 (IGFBP-5) interacts with a four and a half LIM protein 2 (FHL2). 12067710_TUCAN/CARDINAL and DRAL participate in a common pathway for modulation of NF-kappaB activation. 12145280_evidence of a functional interaction between the promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger protein (PLZF) and DRAL/FHL2 12466281_FHL2 might enforce beta-catenin transactivation activity in cancer cells 14550570_-FHL2 interaction may be involved in transcriptional regulation and play a significant role in cancer cell growth 14680945_both the recombinant and the natural proteins are post-translationally modified and indicate that such modifications may lead to an abnormal electrophoretic behavior of natural human FHL2 15117962_FHL2 and FHL3, respectively, are colocalized with alpha(7)beta(1) integrin receptor at the periphery of Z-discs, suggesting a role in mechanical stabilization of muscle cells 15161045_pp125FAK and FHL2 form a protein complex in human ovarian carcinoma. 15572674_The interaction and functional cooperation between FHL2, CITED4, and CTNNB were studied. 15692560_FHL2 inhibits FOXO1 activity in prostate cancer cells by promoting the deacetylation of FOXO1 by SIRT1 16311053_In conclusion, our findings are consistent with the hypothesis that FHL-2 and ADAM-9 are important modulators of IGFBP-5 actions and are, in part, regulated in a coordinated manner in bone. 16343438_Overall, our findings indicate that FHL2 can also regulate p53 via a direct association with HIPK2. 16355270_FHL2 plays an important role in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. 16378916_specific expression in tumor tissue points to an important functional role of FHL2 in human breast cancer 16652157_findings show that full-length E4F1 protein but not its E1A-activated & truncated form interacts in vitro & in vivo with FHL2; this E4F1-FHL2 association occurs in the nuclear compartment & inhibits the capacity of E4F1 to block cell proliferation 17093190_the interaction of FHL2 with HPV-16 E7 leads to a promoter-specific impairment of FHL2 function and this may contribute to cell transformation. 17145880_Data suggest that nuclear FHL2 may serve as a novel biomarker predictive for prostate cancer with aggressive biology and point to a role of FHL2 in constitutive activation of AR-mediated growth signals. 17192406_PELP1 functions as a molecular adaptor, coupling FHL2 with nuclear receptors, and PELP1-FHL2 interactions may have a role in prostate cancer progression. 17383428_Suppression of FHL2 induces cell differentiation and inhibits tumorigenesis in gastrointestinal cancers. 17416352_Functional analysis demonstrated that the FHL2 mutation affected the binding to titin/connectin. 17682292_Data indicate that overexpression of the transcriptional cofactor FHL2 contributes to breast cancer development by mediating transcriptional activation of MAPK target genes known to be involved in cancer progression, such as p21. 17975004_These results suggest a novel indirect mechanism of androgen action on FHL2 expression and provide evidence that SRF is an important determinant of AR action in prostate cancer cells. 18224250_Data suggest that IL-1beta is involved in the regulation of various cytoskeletal components in human chondrocytes including the multifunctional protein FHL2, which might be relevant for the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. 18356303_Role of FHL2 in bundling of focal adhesion structures, in integrin-mediated ERK activation, and subsequently in proper allocation of matrix proteins on the cell surface. 18615633_Overexpression of FHL2 increases the tumorigenicity of glioblastoma cells in nude mice and decreases the mRNA levels of p53. 18653765_FHL2-beta-catenin interaction potentiates beta-catenin nuclear translocation and TCF/LEF transcription, resulting in increased Runx2 and alkaline phosphatase expression, which was inhibited by the Wnt inhibitor DKK1. 18680509_The physiological implication of HERG-FHL2 interaction showed a significant increase in the HERG current amplitude and a faster deactivation of the tail current in human embryonic kidney 293 cells co-expressing HERG and FHL2. 19139564_Human four-and-a-half LIM family members suppress tumor cell growth through a TGF-beta-like signaling pathway. 19325137_FHL-2 suppresses VEGF-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt activation via interaction with sphingosine kinase-1. 19417068_Ectopic FHL2 expression in neuroblastoma cells markedly reduces the transcriptional and cell-cycle promoting functions of Id2. 19465923_Data suggest that in the absence of its ligand Shh the dependence receptor Patched serves as the anchor for a caspase-activating complex that includes DRAL, and caspase-9. 19815066_Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) modulation of androgen receptor activity is differentially altered by the level of FHL2 and AhR present in the cell. 20442768_In human colorectal carcinoma but not in low-grade dysplasia, we detected up-regulation and enhanced nuclear localization of FHL2, indicating the activation of FHL2 during the development of malignancy 20460358_FHL2 is a potent epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) inducer and might be an important mediator for invasion and/or metastasis of colon cancer. 20592280_In the absence of transgenic FHL2, CCL19-induced bone marrow-derived dendritic cell migratory speed, persistence, and directionality were markedly increased in vitro and in vivo. 20607723_Sp1 up-regulates FHL2 expression in gastrointestinal cancers through transcription regulation. 20734429_cooperative regulation of estrogen signaling by FHL2 and Smad4 in breast cancer cells, and might provide a new regulation mechanism underlying breast cancer development and progression 21308406_Our data suggest a role of FHL2 in odontoblast differentiation and dentin formation both in normal and in carious teeth 21377781_our results indicate FHL2 could exert anti-apoptotic effect independent of tumor growth suppression 21826055_Overexpression of FHL2 in peritumoural myofibroblasts correlated to lymphatic metastasis in sporadic colon cancer but not in hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer. 22049082_association of FHL2 with Nur77 plays a pivotal role in vascular disease. 22219185_FHL2 directly interacts with HIF-1alpha to repress transcriptional activity. 22417706_On influenza A virus infection FHL2 translocates into the nucleus, potentiating the IRF-3-dependent transcription of the IFNbeta gene. 22796152_The four and a half LIM-only protein 2 regulates liver homeostasis and contributes to carcinogenesis. 22851699_FHL2 modulates calcineurin-dependent activation of NFAT target genes. 22882857_Overexpression of Id3 markedly promoted the proliferation and invasive capacity of MCF-7 cells; however, these effects were significantly suppressed by the overexpression of FHL2. 23212909_FHL2 increases the stability of the TGF-beta pathway positive regulator Arkadia by inhibiting its ubiquitination and cooperates with Arkadia to activate TGF-beta signaling. 23383046_FHL2 acts as an oncogene in osteosarcoma cells and contributes to tumorigenesis through Wnt signaling 23413425_Deletion of FHL2 protein by FHL2 small interfering RNA impaired VEGF production under hypoxia conditions, and also suppressed endothelial progenitor cell angiogenic functions. 23585479_PCBP2 is an RNA-binding protein that modulates glioma growth by regulating FHL3 23756870_higher FHL2 expression in malignant epithelial cells correlates with progressive disease in patients with colorectal cancer, suggesting that FHL2 is a prognostic indicator for the development of metachronous metastases and for overall survival 23801747_The calpain-cleaved filamin fragment and FHL2 are present in the nucleus only in CRPC. 24008552_High FHL2 expression is associated with colon cancer. 24219103_Data suggest Fhl1 (four-and-a-half LIM domains protein 1) and FHL2 (four-and-a-half LIM domains protein 2) bind to and regulate activity of Prkd1 (protein kinase D 1) in cardiac/ventricular myocytes; knockdown of FHL2 down-regulates Prkd1 activation. 25179730_FHL2 downregulation has a role in the pathogenesis of myeloid malignancies. 25332231_FHL2 is a transcriptional coactivator of LXRs and may be an important determinant of cholesterol metabolism in SMCs 25358972_FHL2 is down-regulated in HCM; both FHL2 wild type and variants partially protected phenylephrine- or endothelin-1-induced hypertrophy in cardiac myocytes 25477051_tumoural TGF-beta1 secretion seems to induce nuclear translocation of co-factor FHL2 mediating progressive keratin expression in pilomatricoma. 25540819_HPV16 E6 oncoprotein interacted and impaired the subcellular distribution of FHL2. 25554651_Tumoral expression of nuclear cofactor FHL2 is associated with lymphatic metastasis in sporadic but not in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer-associated colorectal cancer. 25596251_Enhanced FHL2 and TGF-beta1 expression is correlated with poor survival in human malignant melanoma 25662359_FHL2 overexpression could enhance the differentiation and mineralization of human dental pulp cells 25855776_we conclude that FHL2 has both structural and functional protein-protein interactions with b-catenin in the podocyte nucleus and that FHL2 protein inhibition can mitigate Wnt/b-catenin-induced podocytopathy. 25917075_results provide evidence for the importance of the focal adhesion protein FHL2 in pancreatic cancer cell survival, proliferation and radiosensitivity 26211626_Describe the molecular network governing FHL2 expression, and FHL2-linked cancers and the underlying molecular machinery. Review. 26222912_These results identify FHL2 as a novel gene associated with asthma severity in human. 26320172_KLF8-induced FHL2 activation is a novel and critical signaling mechanism underlying human colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. 26548523_Studies indicate that the LIM-only protein FHL2 interactome is functionally involved in the cardiovascular system. 26759258_FHL2 might interact with Runx2 to mediate mesenchymal cell differentiation at the early stages of tooth development and human dental pulp cell differentiation. 26759260_FHL2 overexpression could contribute to the growth, proliferation, invasiveness, and metastasis of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma. 26973248_we determined the molecular mechanism responsible for IER3 degradation, involving a ternary complex of IER3, MDM2 and FHL2, which may contribute to cervical tumor growth. Furthermore, we demonstrated that FHL2 serves as a scaffold for E3 ligase and its substrate during the ubiquitination reaction, a function that has not been previously reported for this protein 27129278_findings show that mAbp1 and FHL2 are novel binding partners that differentially regulate Rho GTPase signaling and MTLn3 breast cancer cell invasion 27415427_FHL2 facilitates ovarian granulosa cell tumor progression via controlling AKT1 transcription. 27742790_FHL2 phosphorylation by FAK is a critical, mechanically dependent step in signaling from soft matrices to the nucleus to inhibit cell proliferation by increasing p21 expression. 28349819_FHL2 interacts with ADAM-17 in normal, dysplastic and malignant colon epithelial cells. Colocalisation of these proteins is more frequent in malignant than in normal and dysplastic cells, suggesting a role for ADAM-17/FHL2 complex in the development of colorectal cancer. 28402264_FHL2 and iASPP interacted with each other and co-localized in both nucleus and cytoplasm. Either FHL2 or iASPP silenced could reduce cell proliferation, induce cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase, and increase cell apoptosis. 29321665_FHL2 interacts with EGFR and EGFRvIII to increase their levels and this promotes glioma growth, representing a novel mechanism that may be therapeutically targetable. 29800735_FHL2 is an important prognostic factor in cervical cancer (CC) and that it plays a crucial oncoprotein role by promoting cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis in CC. 29910468_Acute myeloid leukemia patients with high expressions of FHL2 and iASPP had shorter event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) than patients with low expressions. 30154409_PARP12 is a tumor suppressor that plays an important role in HCC metastasis through the regulation of FHL2 stability and TGF-beta1 expression. 30745335_Fhl2-deficiency in the brain interrupts the maintenance and the balanced differentiation of adult neural stem cells (NSCs), resulting in preferentially glial differentiation and early exhaustion of the NSC pool required for adult neurogenesis 31040292_FHL2 mediates podocyte Rac1 activation and foot process effacement in hypertensive nephropathy. 31467128_LIM-only protein FHL2 attenuates vascular tissue factor activity, inhibits thrombus formation in mice and FHL2 genetic variation associates with human venous thrombosis. 31896750_FHL2-GLI2 fusion gene is a defining feature of the ovarian sclerosing stromal tumors. 31927599_Deletion of FHL2 in fibroblasts attenuates fibroblasts activation and kidney fibrosis via restraining TGF-beta1-induced Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 31963815_Four-And-A-Half LIM-Domain Protein 2 (FHL2) Deficiency Aggravates Cholestatic Liver Injury. 32346031_The CDK inhibitor p57(Kip2) enhances the activity of the transcriptional coactivator FHL2. 33092075_Four and a Half LIM Domains 2 (FHL2) Contribute to the Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Carcinogenesis. 33932144_c-Abl kinase regulates cell proliferation and ionizing radiation-induced G2/M arrest via phosphorylation of FHL2. 34119536_Four-and-a-half LIM domain protein 2 (FHL2) deficiency protects mice from diet-induced obesity and high FHL2 expression marks human obesity. 34342639_FHL2 anchors mitochondria to actin and adapts mitochondrial dynamics to glucose supply. 34685595_How (Epi)Genetic Regulation of the LIM-Domain Protein FHL2 Impacts Multifactorial Disease. 35366027_High level of FHL2 exacerbates the outcome of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients and the malignant phenotype in NSCLC cells. 36227138_High FHL2 mRNA expression and its prognostic value in lung cancer. | ENSMUSG00000008136 | Fhl2 | 29.420916 | 0.5199479 | -0.943561006 | 0.27983897 | 11.47362182468 | 0.0007059097566631506543918805895998502819566056132316589355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00565834031665427873714069306743112974800169467926025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 21.051647 | 3.911957 | 40.737416 | 6.986622 | |
| ENSG00000115677 | 3069 | HDLBP | protein_coding | Q00341 | FUNCTION: Appears to play a role in cell sterol metabolism. It may function to protect cells from over-accumulation of cholesterol. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cholesterol metabolism;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;HDL;Lipid metabolism;Lipid transport;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;Steroid metabolism;Sterol metabolism;Transport | The protein encoded by this gene binds high density lipoprotein (HDL) and may function to regulate excess cholesterol levels in cells. The encoded protein also binds RNA and can induce heterochromatin formation. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. | hsa:3069; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; high-density lipoprotein particle [GO:0034364]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; polysome [GO:0005844]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; lipid transport [GO:0006869] | 14500828_RNA interference studies indicate vigilin is essential for cell viability but is not a global regulator of translation. 15109574_evidence that vigilin is bound to the ribosomal complex. 18648073_C-terminal domain of human vigilin binds to the histone methyltransferase SUV39H1 in vivo;a new model for vigilin-mediated, RNA-induced gene silencing is presented. 19878569_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19950580_Expression profiles of human VIGILIN, H19, and IGF2 mRNA increased with cell-cycle prograssion. 20442750_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20974809_identified a competition for binding the 69-nt sequence, through which vigilin and HuR exert opposing effects on c-fms expression, suggesting a role for vigilin in suppression of breast cancer progression 21500547_Vigilin may have a relationship with hepatocellular carcinoma progression and proliferation. 24561205_CTCF may regulate vigilin behavior and thus indirectly influence the binding of HP1alpha to the satellite 2 locus 24676454_progressively upregulated vigilin may serve as a molecular risk marker for hepatocellular carcinoma development, and targeting vigilin may help to inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth, survival and migration. 28356383_this study shows that vigilin (HDLBP) binds and negatively regulates MICB expression through its 5'UTR, and that vigilin downregulation in target cells leads to NK cell activation against said target cells 28975734_vigilin has been shown to bind over 700 mRNAs and has been associated with cancer progression and cardiovascular disease. 29157910_Our data reveal that vigilin is essential for maintenance of imprinting of IGF2 gene via functional interaction between KH1-7 domains of vigilin and zinc-finger domains of CTCF. 33888601_TSC2 Interacts with HDLBP/Vigilin and Regulates Stress Granule Formation. 35585045_HDLBP binds ER-targeted mRNAs by multivalent interactions to promote protein synthesis of transmembrane and secreted proteins. 36122630_The lipid transporter HDLBP promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through BRAF-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition. | ENSMUSG00000034088 | Hdlbp | 2513.453530 | 0.8646491 | -0.209813342 | 0.06275869 | 11.16549372045 | 0.0008333278952490551444790001234252940776059404015541076660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00646114246732148837792930606838126550428569316864013671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 2099.079501 | 99.364411 | 2439.198186 | 115.364930 | |
| ENSG00000115827 | 80067 | DCAF17 | protein_coding | Q5H9S7 | FUNCTION: May function as a substrate receptor for CUL4-DDB1 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16949367}. | Alternative splicing;Deafness;Diabetes mellitus;Hypotrichosis;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation pathway | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. | This gene encodes a nuclear transmembrane protein that associates with cullin 4A/damaged DNA binding protein 1 ubiquitin ligase complex. Mutations in this gene are associated with Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. | hsa:80067; | Cul4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0080008]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] | 19026396_Mutations in C2orf37, encoding a nucleolar protein, cause hypogonadism, alopecia, diabetes mellitus, mental retardation, and extrapyramidal syndrome. 20507343_C2orf37 mutational spectrum in Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome patients 21044051_A novel C2orf37 mutation causes the first Italian cases of Woodhouse Sakati syndrome 21963443_Pakistani family with clinical manifestations of Woodhouse-Sakati Syndrome; DNA sequence analysis revealed a novel splice site mutation (c.321 + 1 G > A) in the gene C2orf37, mapped on chromosomes 2q22.3-2q35 21964978_Mutations in C2orf37 are responsible for Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome. 23418071_The results of this study demonistrated that the syndrome of deafness-dystonia is cause by mutation of DCAF17. 24015686_Direct sequencing of the C2orf37 gene revealed that the c.436delC (p.Ala147Hisfs*9) mutation was present in a homozygous state in all affected siblings and in a heterozygous state in the parents and a healthy sister. 26440089_two novel frameshift mutations in C2orf37 present in the compound heterozygous state in an Indian family with Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome, is reported. 26612766_This signifies the vital yet unexplored role of DCAF17 both in development and maintenance of adult tissues homeostasis. 29178422_Exome sequencing in 5 women with syndromic hypergonadotropic hypogonadism from 2 unrelated families revealed novel pathogenic variants in the DCAF17 gene. DCAF17 exon 2 (c.127-1G > C) novel homozygous variants were discovered in 4 Turkish siblings, while 1 American was compound heterozygous for 1-stop gain variant in exon 5 (c.C535T; p.Gln179*) and previously described stop gain variant in exon 9 (c.G906A; p.Trp302*). 29574468_The phenotypic variability of Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome due to c.436delC founder DCAF17 mutation may have a wider range than previously recognized. 31323129_Analysis of the exome data revealed a start loss sequence variant (c.1A>G, p.M1?) in DCAF17 in a Pakastani family with Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome. This variant is predicted to abolish translation of the DCAF17 polypeptide. To our knowledge, this is the first start loss variant identified in the DCAF17. 34732557_Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome (WSS): A case report of 3 Saudi sisters with urogenital anomalies. 34877714_Novel splicing-site mutation in DCAF17 gene causing Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome in a large consanguineous family. | ENSMUSG00000041966 | Dcaf17 | 96.346022 | 1.3889367 | 0.473980851 | 0.31659256 | 2.21653035910 | 0.1365396071791170340414822703678510151803493499755859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.32476041918406545194741852355946321040391921997070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 119.692883 | 27.386456 | 86.464396 | 19.734206 |
| ENSG00000115970 | 63892 | THADA | protein_coding | Q6YHU6 | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene is the target of 2p21 choromosomal aberrations in benign thyroid adenomas. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in this gene may be associated with type 2 diabetes and polycystic ovary syndrome. The encoded protein is likely involved in the death receptor pathway and apoptosis. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. | hsa:63892; | cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0098554]; enzyme regulator activity [GO:0030234]; adaptive thermogenesis [GO:1990845]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088]; negative regulation of ATPase-coupled calcium transmembrane transporter activity [GO:1901895]; negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion concentration [GO:0032471]; tRNA methylation [GO:0030488]; tRNA nucleoside ribose methylation [GO:0002128] | 12955091_identification of the target gene of 2p21 aberrations in thyroid adenomas tentatively referred to as thyroid adenoma-associated gene (THADA); gene spans roughly 365 kbp; based on preliminary results, it encodes a death receptor-interacting protein [THADA] 17123335_intronic sequence of PPAR(gamma) is fused to exon 28 of THADA in thyroid tumors of follicular origin including carcinomas as well as adenomas 18372903_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18567820_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18591388_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18714373_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19020323_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19020324_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19139842_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19247373_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19324937_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19502414_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19602701_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19670153_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19720844_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19741467_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19767753_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19794065_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19833888_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19862325_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19933996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20075150_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20203524_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20490451_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20564319_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20571754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20712903_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20816152_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20878950_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20879858_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20889853_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22180642_At least two of the PCOS susceptibility loci identified in the Chinese PCOS GWAS (DENND1A and THADA) are also associated with PCOS in European derived populations. 23028138_DNA methylation of genes in retinol metabolism and calcium signaling pathways (P | ENSMUSG00000024251 | Thada | 185.043858 | 0.7456708 | -0.423389336 | 0.33768380 | 1.54518778517 | 0.2138472625303445839861637978174258023500442504882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.43195603007573429854559776686073746532201766967773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 153.080415 | 34.270646 | 206.868475 | 46.318306 | ||
| ENSG00000116001 | 7072 | TIA1 | protein_coding | P31483 | FUNCTION: RNA-binding protein involved in the regulation of alternative pre-RNA splicing and mRNA translation by binding to uridine-rich (U-rich) RNA sequences (PubMed:8576255, PubMed:11106748, PubMed:12486009, PubMed:17488725). Binds to U-rich sequences immediately downstream from a 5' splice sites in a uridine-rich small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (U snRNP)-dependent fashion, thereby modulating alternative pre-RNA splicing (PubMed:11106748, PubMed:8576255). Preferably binds to the U-rich IAS1 sequence in a U1 snRNP-dependent manner; this binding is optimal if a 5' splice site is adjacent to IAS1 (By similarity). Activates the use of heterologous 5' splice sites; the activation depends on the intron sequence downstream from the 5' splice site, with a preference for a downstream U-rich sequence (PubMed:11106748). By interacting with SNRPC/U1-C, promotes recruitment and binding of spliceosomal U1 snRNP to 5' splice sites followed by U-rich sequences, thereby facilitating atypical 5' splice site recognition by U1 snRNP (PubMed:11106748, PubMed:12486009, PubMed:17488725). Activates splicing of alternative exons with weak 5' splice sites followed by a U-rich stretch on its own pre-mRNA and on TIAR mRNA (By similarity). Acts as a modulator of alternative splicing for the apoptotic FAS receptor, thereby promoting apoptosis (PubMed:11106748, PubMed:1934064, PubMed:17488725). Binds to the 5' splice site region of FAS intron 5 to promote accumulation of transcripts that include exon 6 at the expense of transcripts in which exon 6 is skipped, thereby leading to the transcription of a membrane-bound apoptotic FAS receptor, which promotes apoptosis (PubMed:11106748, PubMed:1934064, PubMed:17488725). Binds to a conserved AU-rich cis element in COL2A1 intron 2 and modulates alternative splicing of COL2A1 exon 2 (PubMed:17580305). Also binds to the equivalent AT-rich element in COL2A1 genomic DNA, and may thereby be involved in the regulation of transcription (PubMed:17580305). Binds specifically to a polypyrimidine-rich controlling element (PCE) located between the weak 5' splice site and the intronic splicing silencer of CFTR mRNA to promote exon 9 inclusion, thereby antagonizing PTB1 and its role in exon skipping of CFTR exon 9 (PubMed:14966131). Involved in the repression of mRNA translation by binding to AU-rich elements (AREs) located in mRNA 3' untranslated regions (3' UTRs), including target ARE-bearing mRNAs encoding TNF and PTGS2 (By similarity). Also participates in the cellular response to environmental stress, by acting downstream of the stress-induced phosphorylation of EIF2S1/EIF2A to promote the recruitment of untranslated mRNAs to cytoplasmic stress granules (SGs), leading to stress-induced translational arrest (PubMed:10613902). Formation and recruitment to SGs is regulated by Zn(2+) (By similarity). Possesses nucleolytic activity against cytotoxic lymphocyte target cells (PubMed:1934064). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P52912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10613902, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11106748, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12486009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14966131, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17488725, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17580305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1934064, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8576255}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform Short]: Displays enhanced splicing regulatory activity compared with TIA isoform Long. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17488725}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Neurodegeneration;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding | The product encoded by this gene is a member of a RNA-binding protein family and possesses nucleolytic activity against cytotoxic lymphocyte (CTL) target cells. It has been suggested that this protein may be involved in the induction of apoptosis as it preferentially recognizes poly(A) homopolymers and induces DNA fragmentation in CTL targets. The major granule-associated species is a 15-kDa protein that is thought to be derived from the carboxyl terminus of the 40-kDa product by proteolytic processing. Alternative splicing resulting in different isoforms has been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2017]. | hsa:7072; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic stress granule [GO:0010494]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear stress granule [GO:0097165]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; mRNA 3'-UTR AU-rich region binding [GO:0035925]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; poly(A) binding [GO:0008143]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; mRNA processing [GO:0006397]; negative regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001818]; negative regulation of translation [GO:0017148]; protein localization to cytoplasmic stress granule [GO:1903608]; regulation of alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000381]; regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0048024]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380]; stress granule assembly [GO:0034063] | 11106748_apoptosis-promoting factor TIA-1 is a regulator of alternative pre-mRNA splicing 12486009_binding of TIA-1 in the vicinity of a 5' ss helps to stabilize U1 snRNP recruitment, at least in part, via a direct interaction with U1-C 12885872_Data suggest that TIA-1 functions as a translational silencer of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression and support the hypothesis that dysregulated RNA-binding of TIA-1 promotes COX-2 expression in neoplasia. 12949814_Increased TIA-1 gene expression is associated with sensitize endothelial cells to proapoptotic stimuli present in the tumor microenvironment and enhance NK cell cytotoxic activity against cancer cells in advanced soft tissue sarcoma 14966131_data indicate that, in CFTR exon 9, TIA-1 binding to the polypyrimidine-rich controlling element recruits U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein to the weak 5'-ss and induces exon inclusion 15280467_activated during HSV-1 infection and accumulated in cytoplasm of cells 6 hr after infection 16227602_TIA-1 represses the translation of target transcripts. 16820934_Results describe the gene expression of tristetraprolin, T-cell intracellular antigen and Hu antigen R in synovial tissues from rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients. 17135269_FAST K synergizes with TIA-1/TIAR proteins to regulate Fas alternative splicing 17488725_TIAR regulates the relative expression of TIA-1 isoforms. 17493234_Cytotoxic molecule (CM) expression, specifically TIA1 and granzyme B, is predictive of prognosis in Hodgkin's-like anaplastic large cell lymphoma. 17580305_dual role for TIA-1 in shuttling between DNA and RNA ligands to co-regulate COL2A1 expression at the level of transcription and pre-mRNA alternative splicing. 17599736_Positive correlations between TIA1 protein gene expression in patients with rheumatoid and healthy persons. 17711853_TIA-1-induced polysome disassembly is required for enhanced mRNA decay 18456862_Simultaneous knockdown of TIA1 and TIAL1 resulted in increased skipping of alternatively spliced exons associated with U-rich motifs, but did not affect alternatively spliced exons that are not associated with U-rich motifs. 18642007_Basophilic inclusions from patients with adult-onset atypical motor neuron disease were distinctly labeled with the antibodies against poly(A)-binding protein 1, T cell intracellular antigen 1, and ribosomal protein S6. 18753794_These data demonstrated that TIA-1 inhibits HBsAg expression by interacting with the posttranscriptional regulatory element (PRE) of hepatitis B virus. 18775331_Reults describe codependent functions of RSK2 and the apoptosis-promoting factor TIA-1 in stress granule assembly and cell survival. 19110540_TIA1 and TIAL1 regulate the alternate splicing of lysyl hydroxylase 2 19386911_The carboxyl-terminal domain of TIA-1 is responsible for its recruitment into inclusions containing mutant huntingtin protein. 19615357_Sam68 is recruited into stress granules through complexing with TIA-1 in response to oxidative stress 19641607_Host immune responses to EOC vary widely according to histological subtype and the extent of residual disease. TIA-1, FoxP3 and CD20 emerge as new positive prognostic factors in high-grade serous EOC from optimally debulked patients 20599318_Down-regulation of the IGFBP-3 transcripts correlated with the up-regulation of the TIA-1 transcripts in primary HCC biopsies. 20675271_Data show that apoptotic (TIAR and TIA-1) marker expression in thyroid tissues from adolescents with immune thyroid diseases is higher than in non-immune thyroid diseases. 20980400_Severe hypoxia caused co-aggregation of TIAR/TIA-1 and these proteins suppressed HIF-1alpha expression. 21048981_Data show that TIA1 and TIAL1 bind at the same positions on human RNAs, and are consistent with a model where TIA proteins shorten the time available for definition of an alternative exon by enhancing recognition of the preceding 5' splice site. 21179245_TIA-1 cytotoxic granule-associated RNA binding protein has a role in preventing progression of mismatch repair-proficient colorectal cancer 21189287_TIA1 and TIAR proteins are intron-associated positive regulators of SMN2 exon 7 splicing. 21257637_TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) regulates stress granule dynamics via differential regulation of G3BP and TIA-1. 21284605_A role for TIA proteins as growth/tumour-suppressor genes. 21846467_Results characterise the C-terminal RRM2 and RRM3 domains of T-cell intracellular antigen-1 protein. 22154808_Three RNA recognition motifs participate in RNA recognition and structural organization by the pro-apoptotic factor TIA-1. 23348830_the TIA1 mutation causes perturbed RNA splicing and cellular stress resulting in WDM. 23401021_Welander distal myopathy is caused by mutated TIA1 through a dominant pathomechanism probably involving altered stress granule dynamics. 23830997_Work described here examined the punctate pattern of SRp20 localization in the cytoplasm of poliovirus-infected cells, demonstrating the partial co-localization of SRp20 with the stress granule marker protein TIA-1. 23902765_RNA binding mediated by either isolated RRM3 or the RRM23 construct is controlled by slight environmental pH changes due to the protonation/deprotonation of TIA-1 RRM3 histidine residues. 24433873_TIA1 gene expression do not predict prognosis in patients diagnosed with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. 24566137_TIA1 inhibition of the exon 8 exclusion led to a decrease in SIRT1-Exon8 mRNA levels. 24682828_Structural insights into the role of binding avidity and the contributions of the TIA-1 RNA recognition motifs for recognition of pyrimidine-rich RNAs. 24766723_TIA proteins can function as long-term regulators of the ACTB mRNA metabolism in mouse and human cells. 24927121_TIA1-knockdown HeLa cells show an increase in ribosomes and translational machinery components. 25224594_Alternative splicing of TIA-1 in human colon cancer regulates VEGF isoform expression, angiogenesis, tumour growth and bevacizumab resistance. 25405991_TIA proteins play a role in the regulation and/or modulation of cellular homeostasis related to focal/cell adhesion, extracellular matrix and membrane and cytoskeleton dynamics. 25673011_SERPINE1 mRNA dissociates from the translational repressor proteins Ago2 and TIA-1 upon platelet activation 26363455_results suggest that TIA-1 and TIAR are two new host factors that interact with 5-UTR of EV71 genome and positively regulate viral replication 26681690_AT1R mRNA is regulated by TIA-1 in a ER stress-dependent manner. 26738979_This study showed that reactive oxygen species such as H2O2 oxidize the cytoplasmic stress granules (SG)-nucleating protein TIA1, thereby inhibiting SG assembly. 26958940_findings uncover a novel oncogenic function of TIA1 in esophageal tumorigenesis 27612012_Downregulation of TIA-1-enhanced mitochondrial elongation, whereas ectopic expression of TIA-1 resulted in mitochondria fragmentation. In addition, TIA-1 increased mitochondrial activity, including the rate of ATP synthesis and oxygen consumption. 28174264_YAP (Yes-associated protein) expression negatively regulates TIA1 (Rox8 ortholog) expression and cell invasion in human cancer cells. 28184449_Here we designed UC-rich and CU-rich 10-nt sequences for engagement of both RRM2 and RRM3 and demonstrated that the TIA-1 RRM23 construct preferentially binds the UC-rich RNA ligand. Together our data support a specific mode of TIA-1 RRM23 interaction with target oligonucleotides consistent with the role of TIA-1 in binding RNA to regulate gene expression 28193846_The results provide a mechanism for exon 16 3' splice site activation in which a coordinated effort among TIA1, Pcbp1, and RBM39 stabilizes or increases U2 snRNP recruitment, enhances spliceosome A complex formation, and facilitates exon definition through RBM39-mediated splicing regulation. 28257633_miR-19a could promote cell proliferation and migration in CRC cells and accelerated tumor growth in xenograft mice by targeting TIA1. 28298474_Data suggest that TPD52 (tumor protein D52) and a TPD52 fragment (residues 78-280) along with TIA-1 (T-cell intracellular antigen-1) and TIAR (TIA-1-related protein) contribute to mRNA stability as cis-acting and trans-acting factors; 3prime-untranslated regions of TPD52, TPD53, and TPD54 regulate expression of their respective genes in a post-transcriptional manner by altering mRNA stability. 28817800_studied a novel Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis/Frontotemporal Dementia (ALS/FTD) family and identified the P362L mutation in the low-complexity domain (LCD) of TIA1; genetic association analyses showed an increased burden of TIA1 LCD mutations in ALS patients compared to controls; TIA1 mutations significantly increased the propensity of TIA1 protein to undergo phase transition 29216908_The purpose of this report is to provide a detailed description of the clinical and neuropathological features associated with the recently identified TIA1 mutations that cause ALS +/- FTD. 29298433_These findings suggest that Zn(2+) is a physiological ligand of TIA-1, acting as a stress-inducible second messenger to promote multimerization of TIA-1 and subsequent localization into stress granules. 29370934_TIA1 is a novel causative gene of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 29457785_identification of a TIA1 variant that drives myodegeneration in multisystem proteinopathy with SQSTM1 mutations 29496454_expressions of TIA-1 and MFF were augmented in the cancerous liver tissues compared to the corresponding non-tumor tissues at mRNA and protein level, while the levels of miR-200a-3p and miR-27a/b were relatively lower in the cancerous liver tissues 29555582_TIA-1 knockdown by siRNA mimicked the effect of SAHA on COX-2 expression. These findings suggest SAHA can prevent TGF-beta1-induced COX-2 repression in lung fibroblasts post-transcriptionally through a novel TIA-1-dependent mechanism and provide new insights into the mechanisms underlying its potential antifibrotic activity 29699721_TIA1 LCD mutations are not common in Chinese ALS/ALS-FTD 29773329_TIA1 mutation is an uncommon genetic cause for ALS in the Chinese population. 29886022_TIA1 variants are not associated with frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in European patient cohort. 30144499_The repression of TIA-1 by miR-487a promoted cell proliferation and suppressed cell apoptosis in vitro, and the knockdown of miR-487a had the opposite effects. 31541970_Single-nucleotide polymorphism in the human TIA1 gene interacts with stressful life events to predict the development of pathological anxiety symptoms in a Swedish population. 31941779_Typical Stress Granule Proteins Interact with the 3' Untranslated Region of Enterovirus D68 To Inhibit Viral Replication. 33621982_Tandem RNA binding sites induce self-association of the stress granule marker protein TIA-1. 34310938_Disease-associated mutations affect TIA1 phase separation and aggregation in a proline-dependent manner. 34410578_Identification of TIA1 mRNA targets during human neuronal development. 34750982_Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) linked mutation in Ubiquilin 2 affects stress granule assembly via TIA-1. 35163320_The Multifunctional Faces of T-Cell Intracellular Antigen 1 in Health and Disease. 35799293_Intracellular accumulation of tau inhibits autophagosome formation by activating TIA1-amino acid-mTORC1 signaling. 35872367_The role of peritumoral CD8 + /TIA1 + lymphocytes in hepatocellular carcinoma aggressiveness and recurrence after surgical resection. 36112647_ALS mutations in the TIA-1 prion-like domain trigger highly condensed pathogenic structures. | ENSMUSG00000071337 | Tia1 | 685.056657 | 0.8983017 | -0.154728011 | 0.10017898 | 2.38215356102 | 0.1227282549645578035857340637448942288756370544433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.30470763763653435640677002993470523506402969360351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 745.121869 | 56.241818 | 833.890819 | 63.395105 | |
| ENSG00000116685 | 90231 | KIAA2013 | protein_coding | Q8IYS2 | Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Located in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:90231; | membrane [GO:0016020] | ENSMUSG00000044496 | 2510039O18Rik | 716.539847 | 0.9003141 | -0.151499631 | 0.06159096 | 6.05233294421 | 0.0138879357064456004922092802189581561833620071411132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.06352663330992840140520883096542092971503734588623046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 665.494191 | 30.373546 | 742.682716 | 33.461197 | |||
| ENSG00000117399 | 991 | CDC20 | protein_coding | Q12834 | FUNCTION: Required for full ubiquitin ligase activity of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) and may confer substrate specificity upon the complex. Is regulated by MAD2L1: in metaphase the MAD2L1-CDC20-APC/C ternary complex is inactive and in anaphase the CDC20-APC/C binary complex is active in degrading substrates. The CDC20-APC/C complex positively regulates the formation of synaptic vesicle clustering at active zone to the presynaptic membrane in postmitotic neurons. CDC20-APC/C-induced degradation of NEUROD2 induces presynaptic differentiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9637688, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9734353, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9811605}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Differentiation;Isopeptide bond;Mitosis;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;WD repeat | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. | CDC20 appears to act as a regulatory protein interacting with several other proteins at multiple points in the cell cycle. It is required for two microtubule-dependent processes, nuclear movement prior to anaphase and chromosome separation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:991; | anaphase-promoting complex [GO:0005680]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitotic checkpoint complex [GO:0033597]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; spindle [GO:0005819]; spindle pole [GO:0000922]; anaphase-promoting complex binding [GO:0010997]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; ubiquitin ligase activator activity [GO:1990757]; anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process [GO:0031145]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell division [GO:0051301]; mitotic sister chromatid cohesion [GO:0007064]; mitotic spindle assembly [GO:0090307]; mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint signaling [GO:0007094]; negative regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0051444]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process [GO:1905786]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of synapse maturation [GO:0090129]; positive regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0031915]; positive regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:1904668]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of dendrite development [GO:0050773]; regulation of meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051445]; regulation of meiotic nuclear division [GO:0040020]; regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0007346] | 11891222_localization in tail-to-tail array and expression in proliferating cells 12198152_Destruction-box specificities of APC/C(fzy) and APC/C(fzr)& successive activation of APC/C by fzy & fzr establish the temporal substrate degradation pattern, explaining why some endogenous RXXL substrates are degraded by fzy & others by fzr complexes. 14743218_These findings implicate RASSF1A in the regulation of both APC-Cdc20 activity and mitotic progression. 15388328_These results indicate that Bub3 and Cdc20 play additional roles in the integration of cell cycle arrest as transcriptional repressors. 15623561_activation of APC(Cdc20) by Tax provides an explanation for the mitotic abnormalities in HTLV-I-infected cells and is likely to play an important role in the development of adult T cell leukemia 15701830_Up-regulation of cdc20 is associated with gastric cancer 16497171_Functional analysis suggests that an optimum Mad2 binding efficiency of Cdc20 is required during checkpoint arrest and release. 16572426_High level of Cdc20 appears to be more tightly associated with a poor prognosis. 16777988_Overexpression of Cdc20 leads to impairment of the spindle assembly checkpoint and aneuploidization in oral cancer 16795040_These results suggest that targeting molecules involved in spindle mitotic checkpoint, such as p55CDC/Cdc20, might account for the high cytotoxicity of HDAC inhibitors versus malignant cells. 17598981_There is no interaction between RASSF1A and Cdc20. 17873905_Overexpression of CDC20 is associated with cancer 17908926_SCF(Skp2) and APC(Cdc20) mark MLL for degradation at S phase and late M phase, respectively. 18471975_Data show that Cdc20 and Cks1 direct the spindle checkpoint-independent destruction of cyclin A2. 18591651_Both MCF2 and MCC inhibit APC/C by antagonizing Cdc20, possibly by interaction with the Cdc20-binding site of APC/C. 18953566_Over-expression of mRNA levels of IGFBP-2 and CDC20 is highly related to glioblastomas. 18997788_Ubiquitylation of human Cdc20 is not required to release it from the checkpoint complex, but to degrade it to maintain mitotic arrest. 19098431_The degradation of Cdc20 represents a critical control mechanism to ensure inactivation of APC/C(Cdc20) in response to the spindle assembly checkpoint. 19117984_BubR1 competes with Cdc20 for binding to securin. Interaction of BubR1 and securin is increased by the depletion of Cdc20. Regulation of BubR1 may generate an anaphase-inhibitory signal through the Cdc20-independent interaction of BubR1 with securin. 19154722_Results support a model in which immobilized Mad1/Mad2 at kinetochores provides a template for initial assembly of Mad2 bound to Cdc20 that is then converted to a final mitotic checkpoint inhibitor with Cdc20 bound to BubR1. 19197151_Results show that even an almost complete knockdown of Cdc20 below the detection limit in western blots does neither cause a mitotic block nor significant stabilization of the APC/C(Cdc20) substrates cyclin B and securin. 19426592_regulated but the expression of CDK9, CDC20 and CLK3 was down- regulated in azoospermic testes. 19738611_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19826003_hMDC1 functionally regulates the normal metaphase-to-anaphase transition by modulating the Cdc20-dependent activation of the APC/C 20053638_Results indicate that Cdc20 also contributes to post-anaphase activation of the APC/C. 20054826_In summary, accelerated ubiquitination and proteolysis of Cdc20 is essential for prometaphase arrest that is mediated via the p38 signaling during SAC activation. 20526282_Data suggest that phosphorylation of Mcl-1 by CDK1-cyclin B1 and its APC/C(Cdc20)-mediated destruction initiates apoptosis if a cell fails to resolve mitosis. 20624902_Mps1 directs the assembly of Cdc20 inhibitory complexes during interphase and mitosis to control M phase timing and spindle checkpoint signaling. 20729194_the sequential actions of the APC-c(Cdc20) and APC-c(Cdh1) ubiquitin ligases regulate the clearance of Mps1 levels and are critical for Mps1 functions during the cell cycle in human cells. 20733051_Data show that the N terminus of cyclin A binds directly to Cdc20 and with sufficient affinity that it can outcompete the spindle assembly checkpoint proteins. 20739533_elevated levels of Ubch10 and Cdc20 degrade cyclin B in hpv-16 iinfected cells, required for exit from mitosis, permitting initiation of the next round of DNA synthesis and cell cycle progression. 20948288_These data suggest that APC/C(Cdc20) specifically targets E2F1 for degradation in early mitosis and reveal a novel mechanism for limiting free E2F1 levels in cells, failure of which may compromise cell survival and/or homeostasis. 21454660_Spindle assembly checkpoint protein Cdc20 transcriptionally activates expression of ubiquitin carrier protein UbcH10. 21926987_Anaphase promoting complex subunit 15(APC15) mediates the constant turnover of CDC20 and mitotic checkpoint protein complexes, allowing the spindle checkpoint assembly to respond to the attachment state of kinetochores. 21937719_both p31(comet) and ubiquitination of Cdc20 are critical mechanisms of checkpoint inactivation. They act redundantly to promote Mad2 dissociation from Cdc20. 22086178_These findings expand our knowledge of both Sp100 and Cdc20 as well as their role in ubiquitination. 22100920_p31(comet) negatively regulates the spindle assembly checkpoint by extracting Mad2 from the MCC. 22322943_CDC20-mediated degradation of conductin regulates Wnt/beta-catenin signalling for maximal activity during G1/S. 22426463_APC/C(Cdc20) or APC/C(Cdh1) complexes regulate RAP80 stability during mitosis to the G(1) phase, and these events are critical for a novel function of RAP80 in mitotic progression. 22475564_Aberrant CDC20 expression may play an important role in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis and progression and may thus be useful as a marker of disease progression and prognosis and as a therapeutic target. 22566641_The binding of p31(comet) to Mad2 in the mitotic checkpoint complex may trigger a conformational change in Cdc20 that facilitates its phosphorylation by Cdk, and that the latter process may promote its dissociation from BubR1. 22692537_Data identify Cdc20, USP44, and Wee1 as relevant Fcp1 targets. 23091007_The crystal structures of human Cdc20 alone or bound to a BubR1 KEN box, is reported. 23288039_Nek2A binds with high affinity to apo-APC/C and is degraded by the pool of Cdc20 that avoids inhibition by the spindle assembly checkpoint. 23405241_High CDC20 expression is associated with cervical cancer. 23643811_phosphorylation on CRY-box by Polo-like kinase-1 is required for Cdh1-dependent degradation of Cdc20 during somatic cell cycle 23758705_CDC20 is increased in patients with colorectal cancer with poor prognosis 23775192_Geminin is a target of the spindle checkpoint and APC/C(Cdc20). 23791783_Mad2 Binding Induces a Functional Switch in Cdc20,Enabling BubR1 Binding. 23979597_PHF8 is regulated by APC(cdc20) and plays an important role in the G2/M transition. 23995871_increased expression of CDC20 and MAD2 is related to poor prognosis of urothelial carcinoma of the human bladder 24464857_IR motif integrity is particularly important for stable binding to the APC/C. 24551295_CDC20 upregulation was associated with aggressive progression and poor prognosis in gastric cancer. 24747134_Mad2, the kinetochore localization of Cdc20, is disrupted in Chk1 depleted cells. 24853182_high Cdc20 and securin immunoexpression identified a patient subgroup with extremely short, on average 2.4 years, breast cancer survival and triple-negative breast cancer subtype. 24871945_These results reveal an important role for APC(Cdc20) in governing apoptosis, strengthening the rationale for developing specific Cdc20 inhibitors as effective anticancer agents. 25069850_Results show that increased expression of CDC20 was demonstrated to be associated with the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. 25083970_MAD2 and CDC20 overexpression was increased in high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions and squamous cell carcinomas, suggesting their involvement in the initiation of cervical cancers. 25139956_The master cell cycle regulator Cdc20 regulates ciliary length and disassembly of the primary cilium. 25368385_excess E2F1 due to Rb inactivation recruits the complex of Cdc20 and the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome to deregulate the expression of UBCH10 25383541_the mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC) can inhibit a second CDC20 that has already bound and activated the APC/C; the MCC inhibits active APC/C and this is essential for the spindle assembly checkpoint 25482201_a Cdc20 binding site in BubR1 facilitates both spindle assembly checkpoint signalling and silencing 25505175_the BubR1M-Cdc20 interaction indirectly contributes to mitotic checkpoint complex homeostasis 25637637_CDC20, MAD2 and Aurora-B protein expression are associated with chromosomal abnormalities and poor prognosis in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. 25669885_The ABBA motif in cyclin A is required for its proper degradation in prometaphase through competing with BUBR1 for the same site on CDC20 25673878_spindle checkpoint release further increases APC/C(Cdc20) catalytic activity 25698537_BUB1B expression was highly correlated to CDC20 and CCNB1 expression in multiple myeloma cells, leading to increased cell proliferation. 25938542_These results suggest CDC20 is a critical regulator of TIC proliferation and survival, linking two key TIC nodes-FOXM1 and p21CIP1/WAF1-elucidating a potential point for therapeutic intervention. 26074073_CDC20 is essential for the in vivo tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells. CDC20 is prognostic of overall survival in Proneural subtype glioblastoma patients. 26148513_The presence of this segment correlates with SAC activity and efficient binding of CDC20 but not of MAD1 to kinetochores. 26245990_CDC20 may have a role in carcinoma of the breast, colon, endometrium, and prostate 26626260_Results show that CYP1B1 may promote renal cell carcinoma development by inducing CDC20 expression and inhibiting apoptosis through the down-regulation of DAPK1. 26889981_Overexpression of Cdc20 may serve as an independent predictor for biochemical recurrence in patients of clinically localized prostate cancer undergoing laparoscopic radical prostatectomy without neoadjuvant therapy. 26912231_Bub1-Plk1-mediated phosphorylation of Cdc20 constitutes an anaphase-promoting complex or cyclosome-inhibitory mechanism that is parallel, but not redundant, to mitotic checkpoint complex formation. 26960431_Study describes a positive feedback loop centred on cyclin A2-Cdk2 inhibition of interphase APC/C-Cdc20 to allow further cyclin A2 accumulation and mitotic entry. 26993778_c-Myc is a driver when combined with kRas/Akt3 oncogenic signals in gliomagenesis, whereas Cdc20 overexpression is a passenger 27097363_These results provide novel insight into the mechanisms underlying the aberrant capability of NUP98 oncoproteins to interact with APC/C(Cdc20) and to interfere with its function. 27633058_High CDC20 expression is associated with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer growth and reduces chemosensitivity . 27780719_Prostate cancer-derived SPOP mutants failed to interact with Cdc20 to promote its degradation. As a result, SPOP-deficient prostate cancer cells with elevated Cdc20 expression became resistant to a pharmacological Cdc20 inhibitor. 27939943_The ABBA-KEN-ABBA amino acid motif cassette holds the Mitotic Checkpoint Complex (MCC) onto the Anaphase-Promoting Complex-Cyclosome (APC/C) by binding the two Cdc20 molecules in the MCC-APC/C complex. 28112196_we demonstrate that the CDC20-MAD2 complex could also be formed independently of the SAC. Moreover, in prolonged arrest caused by nocodazole treatment, the overall levels of the CDC20-MAD2 complex are gradually, but significantly, reduced and this is associated with lower levels of cyclin B1, which brings a new insight into the mechanism of mitotic 'slippage' of the arrested cells. 28202332_It discuses the roles of Cdc20 in SAC signalling and mitotic exit, describe how the integration of traditional approaches with emerging technologies has revealed new details of Cdc20 functions, comment about the potential of Cdc20 as a therapeutic target for the treatment of human malignancies. 28349831_In lung adenocarcinoma patients, overexpression of cell division cycle 20 was significantly associated with bigger primary tumor size, higher MKI67 level, higher DNA ploidy level, and poor prognosis. 28366743_Data provide support for the recent structure-based models and functionally dissect three elements of Cdc20 inhibition: sequestration of Cdc20 in the core mitotic checkpoint complex, sufficient at low Cdc20 concentrations; inhibition of a second Cdc20 through the Mad3 C terminus, independent of Mad2 binding to this Cdc20 molecule; and occupancy of the APC/C with full MCC, where Mad3 and Apc15 are involved. 28404789_A mitotic phosphorylation site on Cdc20, known to be a substrate of PP2A(B56), modulates APC/C(Cdc20) assembly. 28617439_Cdc20 functions as an important negative regulator of SMAR1 in higher grades of cancer 28980876_Cdc20 exerts its oncogenic role partly due to regulation of Bim and p21 in osteosarcoma cells. 29108461_Knockdown of CDC20 enhanced the drug sensitivity of TR cells to Temozolomide. 29489909_Long non-coding RNA SPRY4-IT1 promotes cell proliferation and invasion by regulation of Cdc20 in pancreatic cancer cells 29605876_our data collectively demonstrated that Cdc20 overexpression facilitates the docetaxel resistant of the castration-resistant prostate cancer cell lines in a Bim-dependent manner 29608985_Results showed that CENPA, CDK1 and CDC20 were highly expressed in lung adenocarcinoma (LAC) tissue with co-expression patterns. Also, the integrated microarray analysis demonstrated that CENPA, CDK1 and CDC20 might serve as novel cluster of prognostic biomarkers for LAC. 29642183_CDC20 gene, related to cell proliferation in protein complex A, might play momentous roles in the initiation and development of consecutive Trauma-Induced Sepsis. 29901174_Cdc20 may be a promising molecular target for chemotherapy. 30393234_The expression levels of CDC20 and PTGDS were able to predict overall survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. 30448220_MAD2 and CDC20 are the most expressed in high grade dysplasia, suggesting their roles in the early stage of gastric carcinogenesis, whereas their overexpressions in gastric cancer are associated with intestinal histology and favorable clinicopathological parameters, which may be useful for immunohistochemical classification of chromosomal instability-type gastric cancer. 30588191_Study indicated that AURKA, CDC20 and TPX2 are over-expressed in smoking related lung adenocarcinoma tissues and their higher mRNA expression levels have a worse prognosis. 30765611_The up-regulation of BUB1B, CCNA2, CDC20, CDK1, and WEE1 in tumor tissues are associated with worse overall survival and disease-free survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and is correlated with advanced tumor stage and tumor development. 30816486_Study demonstrated that CDC20 is overexpressed in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) tissues and cell lines, and its expression is associated with tumor progression. Knockdown of CDC20 suppressed cell growth and migration, and promoted apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in cSCC. 30877245_findings suggest that application of the CDC20-M signature may permit more selective use of adjuvant therapies for glioma patients and that dysregulated CDC20-M members may provide a therapeutic vulnerability in glioma. 30904606_knockdown of CDC20 can be used for therapeutic benefit and represents an effective adjuvant anti-cancer treatment to eliminate CSCs during prostate cancer progression. 31036696_This results in elevated levels of APC/CCDH1 substrates, including CDC20. We also demonstrate that small-molecule inhibition of APC/CCDH1/CDC20 can increase mitotic abnormalities and reduce cancer stem-like cells (CSC) viability. 31081056_Study indicates that CDC20 knockdown inhibited migration, a key component of the tumor metastatic process, in chemoresistant pancreatic cancer cells and metastatic breast cancer cells. By contrast, the overexpression of CDC20 by plasmid transfection promoted the metastasizing capacities of these cells. Results suggest that CDC20 is a critical regulator of cancer metastasis. 31278532_CDC20 gene is overexpressed in osteosarcoma and associated with poor prognosis outcomes in osteosarcoma patients. 31945194_Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome-Cdc-20 promotes Zwint-1 degradation. 32066746_Analysis of TET2 and EZH2 gene functions in chromosome instability in acute myeloid leukemia. 32082966_GTSE1, together with CDC20, PCNA, and MCM6, may synergistically promote adverse prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by activating cell cycle. 32165320_APC/C ubiquitin ligase: Functions and mechanisms in tumorigenesis. 32285914_Cell division cycle proteinising prognostic biomarker of breast cancer. 32458533_CDC20 inhibitor Apcin inhibits embryo implantation in vivo and in vitro. 32677673_Identification of cell division cycle 20 as a candidate biomarker and potential therapeutic target in bladder cancer using bioinformatics analysis. 32755477_PP1 promotes cyclin B destruction and the metaphase-anaphase transition by dephosphorylating CDC20. 32932732_Downregulation of CDC20 Increases Radiosensitivity through Mcl-1/p-Chk1-Mediated DNA Damage and Apoptosis in Tumor Cells. 33039559_APC(CDC20)-mediated degradation of PHD3 stabilizes HIF-1a and promotes tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33118830_Downregulation of CDC20 suppressed cell proliferation, induced apoptosis, triggered cell cycle arrest in osteosarcoma cells, and enhanced chemosensitivity to cisplatin. 33290869_Cdc20 induces the radioresistance of bladder cancer cells by targeting FoxO1 degradation. 33310066_Tank Binding Kinase 1 modulates spindle assembly checkpoint components to regulate mitosis in breast and lung cancer cells. 33384373_CDC20 assists its catalytic incorporation in the mitotic checkpoint complex. 33411691_Notch-1 promotes the malignant progression of osteosarcoma through the activation of cell division cycle 20. 33683667_Novel Mutations in CDC20 Are Associated with Female Infertility Due to Oocyte Maturation Abnormality and Early Embryonic Arrest. 33788826_Connection Between CDC20 Expression and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prognosis. 33813687_Inhibition of Cdc20 suppresses the metastasis in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). 33819340_Coupling of Cdc20 inhibition and activation by BubR1. 33881746_CDC20 and PTTG1 are Important Biomarkers and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Metastatic Prostate Cancer. 33907851_CDC20 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating epithelialmesenchymal transition. 34218387_The homozygous p.Tyr228Cys variant in CDC20 causes oocyte maturation arrest: an additional evidence supporting the causality between CDC20 mutation and female infertility. 34358419_MYBL2 in synergy with CDC20 promotes the proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of gastric cancer cells. 34512169_CDC20 regulates the cell proliferation and radiosensitivity of P53 mutant HCC cells through the Bcl-2/Bax pathway. 34728400_NF2 Gene Participates in Regulation of the Cell Cycle of Meningiomas by Restoring Spindle Assembly Checkpoint Function and Inhibiting the Binding of Cdc20 Protein to Anaphase Promoting Complex/Cyclosome. 35093867_The A20/TNFAIP3-CDC20-CASP1 Axis Promotes Inflammation-mediated Metastatic Disease in Triple-negative Breast Cancer. 35402624_A Novel Gene Signature Based on CDC20 and FCN3 for Prediction of Prognosis and Immune Features in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 35616161_REC8 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by targeting CDC20. 35622386_The bioinformatics and experimental analysis of the novel roles of virus infection-associated gene CDC20 for prognosis and immune infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma. 35737702_CDC20 regulates sensitivity to chemotherapy and radiation in glioblastoma stem cells. 35800227_The Prognostic Assessment of CDC20 in Patients with Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma and Its Relationship with Body Immunity. 35913887_Germline Missense Variants in CDC20 Result in Aberrant Mitotic Progression and Familial Cancer. 35988650_Impaired Cdc20 signaling promotes senescence in normal cells and apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. 36001690_Role of phosphorylation of Cdc20 in the regulation of the action of APC/C in mitosis. 36056439_Knockdown of CDC20 promotes adipogenesis of bone marrow-derived stem cells by modulating beta-catenin. 36193067_CDC20 May Serve as a Potential Biomarker-Based Risk Score System in Predicting the Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000006398 | Cdc20 | 981.211417 | 0.7049234 | -0.504461512 | 0.05221114 | 93.47294339329 | 0.0000000000000000000004117914267551541715115427087505444633380087953962888142590511621199400593695827410556375980377197265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000000000000000003096848643790911989863624005995376483172005244658584409943313797697328482172451913356781005859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 790.585957 | 26.060637 | 1126.763413 | 35.723604 |
| ENSG00000117984 | 1509 | CTSD | protein_coding | P07339 | FUNCTION: Acid protease active in intracellular protein breakdown. Plays a role in APP processing following cleavage and activation by ADAM30 which leads to APP degradation (PubMed:27333034). Involved in the pathogenesis of several diseases such as breast cancer and possibly Alzheimer disease. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27333034}. | 3D-structure;Alzheimer disease;Aspartyl protease;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lysosome;Neurodegeneration;Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Zymogen | This gene encodes a member of the A1 family of peptidases. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate multiple protein products. These products include the cathepsin D light and heavy chains, which heterodimerize to form the mature enzyme. This enzyme exhibits pepsin-like activity and plays a role in protein turnover and in the proteolytic activation of hormones and growth factors. Mutations in this gene play a causal role in neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis-10 and may be involved in the pathogenesis of several other diseases, including breast cancer and possibly Alzheimer's disease. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. | hsa:1509; | collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endosome lumen [GO:0031904]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; aspartic-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004190]; aspartic-type peptidase activity [GO:0070001]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004197]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II [GO:0019886]; autophagosome assembly [GO:0000045]; insulin catabolic process [GO:1901143]; insulin receptor recycling [GO:0038020]; lipoprotein catabolic process [GO:0042159]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043280]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of establishment of protein localization [GO:0070201] | 11198280_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11304834_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11436125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11780226_Evaluation of Cath-D can act as a predictor of distant metastasis of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma (SACC) and direct the clinical treatment. 11840502_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11840502_polymorphism unrelated to Alzheimer disease in a Spanish population. 11906282_Molecular dynamics and free energy analyses of cathepsin D-inhibitor interactions. 12011767_expression of cathepsin D in cholesteatoma 12083803_procathepsin D interacts with prosaposin in human breast and ovarian cancer cells. (procathepsin D) 12140763_Down-regulation of cathepsin-D expression by antisense gene transfer inhibits tumor growth and experimental lung metastasis of human breast cancer cells. 12147324_Cathepsin D polymorphism in Italian sporadic and familial Alzheimer's disease. patients and controls. our data do not support a role for the catD gene as a genetic risk factor in the development of AD. 12147324_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12151789_Cerebrospinal fluid levels of beta-amyloid(42) in patients with Alzheimer's disease are related to the exon 2 polymorphism of the cathepsin D gene. 12185597_cathepsin-D stimulates tumor growth by acting as a mitogenic factor on cancer and endothelial cells independently of its catalytic activity. Our results give the first evidence on the role of cathepsin-D at tumor progression steps, affecting angiogenesis 12556904_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12556904_QTL associated with general intelligence is located within exon 2 of the cathepsin D (CTSD) gene. 12651610_Expressed in breast cancer and specifically cleaves the chemokines macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha, macrophage inflammatory protein-1 beta, and SLC protein that are also expressed in breast cancer. 12782337_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12782632_Cat D triggers Bax activation, Bax induces the selective release of mitochondrial AIF, and the latter is responsible for the early apoptotic phenotype in T-cells 12811635_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12826741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12970159_COX-2 exerts a negative feedback on the expression of cathepsin D to reduce the generation of the antiangiogenic factor angiostatin, hence promoting a proangiogenic environment. 14767531_cathepsin D has a role in promoting cancer cell proliferation and invasion 15003956_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, genetic testing, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 15081423_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15158911_intracellular accumulation of poorly degradable, oxidized lipid-protein cross-links, may alter the turnover of cathepsin D, causing its mistargeting into the extracellular space 15168727_Review. Cathepsin D seems to facilitate early phases of tumor progression such as cell proliferation and local dissemination. 15192082_Cleaves prolactin whose fragments are potentially physiological antiangiogenic inhibitors of tumor growth. 15211064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15211070_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15258139_defective acidification results in the aberrant secretion of proCD in certain cancer cells and interferes mainly with the normal disassembly of the receptor-enzyme complexes and efficient receptor reutilization in the Golgi 15318816_The inhibition of cathepsin D activity by pepstatin A decreased the number of apoptotic cells in catL-deficient A549 cells after anti-Fas treatment. 15668295_cathepsin D is crucial for fibroblast invasive outgrowth and could act as a key paracrine communicator between cancer and stromal cells, independently of its catalytic activity. 15739123_Plasma cathepsin D isoforms and their active metabolites increase after myocardial infarction and contribute to plasma renin activity. 15843343_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15896324_Our results showed that lowering cathepsin D activity in antisense cell conditioned media abolished their inhibitory effect on osteoblast cell calcification. 16046058_review of cath-D action in cancer progression and metastasis, as well as its dual function in apoptosis [review] 16081416_The minimal lysosomal enzyme recognition domain has been identified in CPSD. 16127101_CTSD*T allele frequency showed a statistically significant increasing trend from Northern to Southern regions of Europe in AD patients and controls 16127101_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16263712_CatD induces apoptosis via degradation of Trx protein, which is an essential anti-apoptotic and reactive oxygen species scavenging protein in endothelial cells 16331270_results imply that cytosolic cath-D stimulates apoptotic pathways by interacting with a member of the apoptotic machinery rather than by cleaving specific substrate(s) 16354654_Functional analysis indicated that proteolytic processing of DCD-1L by Cathepsin D in human sweat modulates the innate immune defense of human skin. 16417614_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16543533_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16543533_Possession of the CTSD T allele has a modulating effect on the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease by increasing the amount of Abeta deposited as senile plaques in the brain. 16608402_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16652347_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16709808_A model is proposed in which cathepsin D inactivates CCL20 and possibly prevents the establishment of an effective antitumoral immune response in melanomas. 16784755_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16784755_Our data suggest that the CTSD-T allele of the CTSD-C/T polymorphism is associated with an increased relative risk for late-onset AD and, more interestingly, the combination of CTSD-T with the A2M-G allele seems to increase this risk. 16850161_Glucosamine sulfate-induced K562 cell apoptosis involves the translocation of cathepsin D from the lysosome to the cytosol. 17032648_Cathepsin D regulates intracellular transport of phospholipid and cholesterol and ABCA1-mediated lipid efflux. 17112520_The influence of aluminum (Al) on the Abeta peptide degradation by cathepsin D, was demonstrated. 17176069_Functional mapping of the N-terminal sequence of procathepsin D is reported; peptides derived from this sequence were used to localize and characterize the structural determinants involved in activity regulation of the enzyme's catalytic core. 17188016_mutagenized the region of aminoacids (comprising the beta-hairpin loop) involved in the latter proteolytic maturation step and generated a mutant CD that cannot be converted into the mature double-chain form 17284061_cathepsin D was a typical secretory protein that exhibited the increased abundance inM-BE, a SV40T-transformed human bronchial epithelial cell line with the phenotypic features of early tumorigenesis at high passage 17289576_Myocardial STAT3 protein levels are reduced and serum levels of activated cathepsin D and 16 kDa prolactin are elevated in postpartum cardiomyopathy patients. 17340625_Results confirm that the proapoptotic effect of cathepsin D in the cytosol is independent of its catalytic activity and suggest that the interaction of cathepsin D with the downstream effector does not involve the active site of the enzyme. 17395004_Lysosome is the primary target and the axis cathepsin D-Bax as the effective pathway of hydrogen peroxide lethal activity in neuroblastoma cells. 17532541_Secretion of procathepsin D is not only linked to cancer cells but also plays a role in normal physiological conditions like wound healing and tissue remodeling. 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17875703_Overexpression of S100P leads to increased expression of another early pancreatic cancer marker, S100A6, as well as the aspartic protease cathepsin D, both of which are involved in cellular invasion. 18177262_The kinetic constants (kcat, Km, kcat/Km) for cleaving peptides with beta-sites of the WT or the mutated Swedish families (SW) APP by human BACE 1 and cathepsin D were determined and found to be similar. 18202773_the entire 27-44 amino acid region of activation peptide is necessary for the stimulatory actions of procathepsin D on breast cancer cells 18248894_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18248894_This data do not support a role of two gene polymorphisms of the CTSD rs17571 as a possible susceptibility factors for sporadic AD. 18307033_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18367545_Missorting of cathepsin D in GARP-depleted cells results from accumulation of recycling MPRs in a population of light, small vesicles downstream of endosomes. 18387691_treatment with human interferon-gamma and/or human tumor necrosis factor-alpha had little effect on intracellular levels of Cath D, whereas cytokine stimulation increased the extracellular presence of ProCath D in endothelial cell cultures 18396902_Results describe cathepsin D and aldo-keto reductase 1C2 and 1B10 dysregulation in Barrett's esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. 18426579_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18426579_alterations in the amyloid processing activity of cathepsin D may affect the neuropathogenesis of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease 18431031_GGA2 is recruited to the trans-Golgi network independently of the other Golgi-localized, gamma-ear-containing, ARF-binding proteins and is required for the efficient sorting of lysosomal enzymes 18494001_breast cancer cells, which are devoid of Maspin, are refractory to IFN-gamma with respect to changes in vacuolar pH and CatD 18559512_up-regulation of cathepsin D enhances angiogenesis, growth, and metastasis 18566016_role of cathepsin D in antiapoptotic signaling in neuroblastoma cells and suggest a novel mechanism for the development of chemotherapy resistance in neuroblastoma. 18566385_Activities of cathepsins B and D in the lysate of necrotic rho0 cells were inhibited by the addition of apoptotic parental Jurkat cell lysate 18702517_cathepsin D is the main lysosomal enzyme involved in alpha-synuclein degradation 18830724_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19061927_cathepsin D serum level in diabetic patients 19109932_Data show that cathepsin D is decreased in the CSF of temporal lobe epilepsy patients. 19115690_In women with cervical cancer, serum cathepsin D activity was higher both before and after brachytherapy sessions as compared to controls; after the end of therapy, the activity reverted back to the values characteristic for healthy women 19203374_CathD promotes 'synucleinase' activity and enhancing its function may lower aSyn concentrations in vivo. 19221643_Comparative study of expression of cathepsin D in breast tumors and tumor-like breast lesions. 19383337_ERalpha is crucial for long-distance regulation of CTSD expression involving a looping mechanism. 19487283_Cathepsin D and eEF1 are promising markers for the detection of cellular senescence induced by a variety of treatments. 19494521_differentialy expressed in dendritic cells upon stimulation of with with the major house dust mite allergen Der p 1 19571726_the cathepsin D position 224 polymorphism alone is not a significant risk or disease-modifying factor in sporadic or genetic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease 19802014_Data show that Hsc70 appears active in breast cancer cells and hypersecreted by direct cath D inhibition. 19828951_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19828951_Our study does not show a significant difference in genotype and allele frequencies of CTSD C224T between sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease patients and normal controls 19854241_increased cathepsin D in the cerebellum of autistic subjects suggests that, through its regulation of apoptosis, the altered activities of cathepsin D in the autistic brain may play an important role in the pathogenesis of autism 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19919557_Because heparin also stimulated the activity of pseudoCD, proenzyme activation was probably accelerated by interaction of heparin with the catalytic domain of pseudocathepsin D. It is possible that heparin may also activate the proenzyme directly. 19926167_Cathepsin D increases the risk of Alzheimer disease, although the effect size is moderate in this large meta-analysis. 19926167_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19950226_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20071328_OPN is highly susceptible to cleavage near its integrin-binding motifs, and the protein is a novel substrate for plasmin and cathepsin D 20083556_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20083556_Screening of the rs17571 shows a significantly higher proportion of T-allele carriers among male Alzheimer patients (28.5%) when compared with male controls (13.8%, p = .013, p(corr) = .039). 20125193_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20385381_Cathepsin D expression in ovarian endometriosis. 20399529_increased mRNA and protein expression in autistic lymphoblasts 20430722_Results suggest a role for syndecan-1 and cathepsins D and K in growth and invasiveness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 20597865_A significant difference is not found in genotype and allele frequencies of cathepsin D exon 2 polymorphisms between vascular dementia patients and normal controls in a Korean population. 20597865_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20666480_Candidate biomarkers were in situ verified in tissue arrays, and relative concentrations were validated in 84 CRC patients and controls. Alpha1 antitrypsin (A1AT) and cathepsin D (CTSD)were further examined due to the possible importance in human cancers. 20666745_data indicate that the CTSD gene is altered in gastric and colorectal carcinomas by somatic mutation and loss of expression 20826454_secreted by breast cancer cells, promotes fibroblast outgrowth in a LRP1-dependent manner 20855565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20926008_Immunohistochemistry studies showed EGBs to exhibit pronounced reactivity to antibodies against lysosome-associated membrane proteins (LAMP)-1 and LAMP-2, and the lysosomal enzyme cathepsin D. 21148553_lucanthone is a novel autophagic inhibitor that induces apoptosis via cathepsin D accumulation and enhances vorinostat-mediated cell death in breast cancer models. 21298030_Lysosomal membrane permeabilization (LMP) and cytosolic translocation of activated cathepsin D occur prior to activation of a mitochondrial pathway of macrophage apoptosis. 21311773_Key role of cath-D in the control of adipogenesis, suggests that cath-D may be a novel target in obesity. 21470957_protection of AGT and resistance to nitrosamine-induced genotoxicity critically depends on GSNOR in hepatocytes 21533003_Data show that EGF and cathepsin D were measured as breast cnacer markers. 21632707_Induction of cathepsin D plays a previously unrecognized role in lipid processing for CD1d antigen-restricted lipid presentation by dendritic cells. 21709160_Cathepsin D is the protease responsible for heme-binding protein (HEBP)1 precursor processing in conditioned cell medium, and the bioactive product is identified as acetylated formyl peptide F2L 21789704_Cath-D and E-Cad essays may useful in identifying neck lymph node involvement. 21948970_AGR2 is a novel surface antigen that promotes the dissemination of pancreatic cancer cells through regulation of cathepsins B and D. 22081071_cath-D modulates the growth of fibroblasts by inhibiting LRP1-regulated intramembrane proteolysis in the breast tumor microenvironment 22244896_Data show that incubation of C5 with cathepsin D resulted in generation of C5a, which was inhibited by the aspartate protease inhibitor pepstatin A. 22302483_Data indicate that cathepsin D+/caspase 3- and cathepsin D+/p53+ showed clinicopathological significance. 22388353_a model of Aven activation by which its N-terminal inhibitory domain is removed by CathD-mediated proteolysis, thereby unleashing its cytoprotective function. 22399610_Cathepsin-D was significantly up-regulated in all the study groups compared to controls. No difference was found between primary tumors and their corresponding recurrences or metastases 22439866_c-Myb regulates matrix metalloproteinases 1/9, and cathepsin D: implications for matrix-dependent breast cancer cell invasion and metastasis. 22476353_This showed that cath-D was an indicator of malignancy in serous ovarian carcinoma 22528489_cathepsin D is able to initiate the caspase cascade by direct activation of caspase-8. 22542809_inhibition of autophagy could be a novel strategy for the adjuvant chemotherapy of CatD-expressing cancers 22627201_Cathepsin D plays an important role in both nasal polyp pathogenesis and recurrence. 22816225_There is real possibility to use Cath D as an independent prognostic factor in human glioma progression. 22824147_Cathepsin D expression is indicated to be a possible prognostic marker for lung adeno-carcinoma and to correlate with a more poorly differentiated form. 22898924_Data indicate degradation of cystatin C by cathepsin D secreted by breast cancer cells at acidic pH. 22949512_Reduced cathepsins B and D cause impaired autophagic degradation that can be almost completely restored by overexpression of these two proteases in Sap C-deficient fibroblasts. 22964611_Three cathepsin D-specific cleavage sites in Bid, Phe24, Trp48, and Phe183, were identified. 22996917_The study presented here demonstrates increased CathD expression is seen in human cancer associated fibroblasts. 23042275_The effect of heavy metal cations on the activity of cathepsin D, was studied. 23065739_Data indicate that a serum biomarker panel consisting of CA19-9, cathepsin D, and MMP-7 may provide the most effective screening test currently feasible for Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 23107604_The beta-hairpin loop of human pro-cathepsin D, absent in the zebrafish protein, acts as recognition peptide for the enzymes involved in post translational processing. 23219593_4-tert-octylphenol can adversely affect human health by promoting cancer proliferation and metastasis through the amplification of cathepsins B and D via the estrogen receptor-mediated signaling pathway 23250759_These results suggest that increased release/activation of cathepsin D can trigger neurodegeneration and possibly development of Niemann-Pick type C disease pathology. 23415546_A Cathepsin D variant co-segregating with PSEN1 mutation was linked to cerebellar dysfunction and dementia. 23439581_These data point to an evident correlation between cathepsins S and D expression and clinical stage of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis 23466190_Increased concentrations of cathepsins B, D and G in the proliferative eutopic endometrium may play a role in the implantation of endometrial tissue outside the uterine cavity. 23483898_Quantification of immunohistochemistry showed that there is no difference in the global expression of CTSD, CTSH and CTSK between asthmatics and non-asthmatics. 23499937_Cathepsin D activity was decreased in ATP13A2-knockdown cells that displayed lysosome-like bodies characterized by fingerprint-like structures 23840360_Substrate specificities and proteolytic cleavage characterisitics of human cathepsin D. 23868063_Cathepsin D release from lysosomes and subsequent Bid cleavage is mediated by exposure of cells to an HSP70 inhibitor. 23871913_These data provide a better understanding of Cathepsin D behavior in tumor microenvironment conditions and this knowledge can be used to develop more specific tools for diagnosis and drug delivery. 23954850_Cathepsin D levels are reduced in patients with preeclampsia in Korean population.Cathepsin D level is an important factor that may contribute to the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. 24044567_Determination of cathepsin D status in breast cancer might identify patients at different risk for relapse 24138030_These observations point to a critical regulatory role for that endogenous CD activity in dopaminergic cells in alpha-synuclein homeostasis which cannot be compensated for by increased Cathepsin B. 24198402_Human herpesvirus 8 IL6 contributes to primary effusion lymphoma cell viability via suppression of cathepsin D interaction with VKORC1v2. 24259486_Knockdown of cathepsin D (CD) expression mediated by siRNA significantly inhibited the in vitro invasion of two hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines, SNU449 and SNU473, which normally secrete high-levels of CD. 24281128_T-carrying genotype is associated with a 2.5-fold increased risk for developing Alzheimer disease compared to C/C genotype. There was also a synergistic interaction with APOE epsilon4 leading to a 6.25-fold increased risk of the disease. 24423188_In this meta-analysis no association is found betweeen cathepsin D C224T polymorphism and the risk of Alzheimer's disease. 24467213_CTSD, FKBP10, and SLC2A1 are novel genes that participate in the acquisition and maintenance of the adriamycin-resistant phenotype in leukemia cells. 24511668_Upregulation of cathepsin D may be critically involved in the malignant transformation and progression of melanocytic tumors. 24656773_No differences in Cathepsin D were observed in the study when comparing male breast cancer tissues to those of female patients. 24898658_These results suggest that decreased expression of cathepsin D in the peripheral monocytes is a potential signature of Alzheimer disease,and that this decreased expression is involved in Abeta degradation and Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. 25095637_Cathepsin D and B activities in the serum of patients with urothelial bladder cancer are directly proportional to disease severity and significantly higher compared with control group. 25611836_There was a significant difference between groups with and without endothelial dysfunction in terms of cathepsin D levels, and negative and significant correlations were found between brachial artery FMD% and cathepsin D levels. Cathepsin D, which is known to be associated with atherosclerosis, may play a role in the proce 25712867_NOS-3 overexpression resulted in an increased sensitivity to anti-Fas induced cell death, independently of AR expression and CatD activity. 25911051_Serum CatD activity as a marker of healthy endogenous phagocytosis and remodeling was impaired in patients with new-onset cardiac dysfunction. 26018151_Human Herpesvirus 8-encoded viral interleukin-6 promotes endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of procathepsin D. 26086961_the clues provided by the yeast model unveiled a novel CatD function in the degradation of damaged mitochondria when autophagy is impaired, which protects colorectal cancer cells from acetate-induced apoptosis. 26183398_Data show that co-silencing of tricho-rhino-phalangeal-syndrome (TRPS1) and cathepsin D (Cath-D) in breast cancer cells (BCC) affects the transcription of cell cycle and proliferation. 26203049_A proteomics workflow identified CTSD as an over-expressed protein in osteosarcomas and pulmonary metastases and may thus serve as a new biomarker for individualized treatment regimes for patients with osteosarcomas, even at metastastic stage. 26344002_Fenhexamid and cyprodinil can promote ovarian cancer metastasis by increasing the protein expression of cathepsin D via an estrogen receptor dependent pathway. 26351775_Variations in CTSD and MnSOD showed no association with the development of Alzheimer's Disease, whereas the presence of the Ala224Val polymorphism in CTSD had a positive association with the development of AD 26448324_Transcellular transmission of alpha-synuclein aggregates is increased in CTSD mutated cells. 26507101_Fibroblasts from Niemann-Pick type C (NPC) disease patients with low levels of NPC1 protein have high amounts of procathepsin D but reduced quantities of the mature protein, thus showing a diminished cathepsin D activity. 26519755_study provides evidence that hTERT overexpression is responsible for the upregulation of the cysteine protease cathepsin D by regulating EGR-1 to activate invasiveness in cancer progression 26657266_Results show that lowering endogenous cathepsin D abundance induced senescence in HeLa cells, leading to reduced cell proliferation, impaired tumorigenesis in a mouse model, and increased permeability of lysosomal membrane and reactive oxygen species accumulation. These results suggest that CTSD is involved in cancer cells in maintaining lysosomal integrity, redox balance, and Nrf2 activity, thus promoting tumorigenesis. 26718887_Data indicate that cathepsin D (CD) protein is elevated in the retinas of diabetic mice and serum of human patients with diabetic macular edema (DME). 26867770_Cathepsin D facilitates the TRAIL-induced apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells in enzymatic activity-dependent manner. Caspase-8 and Bid proteins are the CD targets. The modulatory role of CD in cell response to TRAIL was also confirmed in another breast cancer cell line SKBR3. 26943237_Gene expression level of CTSD is significantly higher in AD patients when compared to normal controls. 26995190_Serum CTSB and CTSD concentrations were found to have a diagnostic value in NPC. However, the CTSB and CTSD serum levels had no prognostic role for the outcome in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. 27271556_Study shows that CtsD expression was upregulated in damaged tubular cells in nephrotoxic and ischemia reperfusion induced acute kidney injury (AKI) models. Also, the results provide compelling evidence for CtsD as an important mediator for apoptotic cell death during AKI. 27291402_The S-nitrosation of a non-catalytic cysteine residue in the lysosomal aspartyl protease cathepsin D (CTSD) inhibited proteolytic activation. 27922112_Plasma cathepsin D correlates with histological classifications of fatty liver disease in adults. 28073925_Secreted PGRN is incorporated into cells via sortilin or cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor, and facilitated the acidification of lysosomes and degradation of CTSDmat. Moreover, the change of PGRN levels led to a cell-type-specific increase of insoluble TDP-43. In the brain tissue of FTLD-TDP patients with PGRN deficiency, CTSD and phosphorylated TDP-43 accumulated in neurons 28218663_CTSD, in need of its catalytic activity, may promote proliferation in advanced glycation end products-treated human umbilical vein endothelial cells independent of the autophagy-lysosome pathway. 28336215_Data suggest that, compared to control individuals, serum cathepsin-D levels are up-regulated in patients with T2DM-Y (young onset type 2 diabetes) with and without diabetic retinopathy. This study was conducted in India. 28390177_The lysosomal enzyme cathepsin D (CTSD) mediates the proteolytic cleavage of PSAP precursor into saposins A-D. Myc-CLN3 colocalized with CTSD and activity of CTSD decreased as myc-CLN3 expression increased, and clearly decreased under hyperosmotic conditions 28493053_Study demonstrate that PGRN interacts with the lysosomal protease CTSD and maintains its proper activity in vivo. Therefore, by regulating CTSD activity, PGRN may modulate protein homeostasis. This could potentially explain the TDP-43 aggregation observed in frontotemporal lobar degeneration with GRN mutations. 28543404_apoptosis is accompanied by degradation of the cysteine cathepsin inhibitor stefin B (StfB). CatD did not exhibit a crucial role in this step. However, this degradation was partially prevented through pre-incubation with the antioxidant N-acetyl cysteine 28791438_VPS52 activated the apoptotic pathway through cathepsin D in gastric cancer cells. 28917980_Study results suggest that the CTSD rs17571 variant may not be associated with risk of Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Han Chinese. 29024694_Epithelial ovarian (EOC) cancer secreted Cathepsin D acts as an extracellular ligand and may play an important pro-angiogenic, and thus pro-metastatic, role by activating the omental microvasculature during EOC metastasis to the omentum. 29036611_This work identifies PGRN as an activator of lysosomal cathepsin D activity, and suggests that decreased cathepsin D activity due to loss of PGRN contributes to both FTD and NCL pathology in a dose-dependent manner. 29375176_Newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes demonstrated significantly higher circulating cathepsin D concentrations than controls. 29501392_CatD plays a major role in intracellular advanced glycation end products (AGEs) degradation. Decreased CatD expression and activity impairs intracellular AGEs degradation in photoaged fibroblasts. 29993134_Exploring the putative role of kallikrein-6, calpain-1 and cathepsin-D in the proteolytic degradation of alpha-synuclein in multiple system atrophy. 30037983_We identified a missense variant in CLN5 c.A959G (p.Asn320Ser) that segregated with Alzheimer's disease (AD). The AD-associated CLN5 variant is shown here to reduce the normal processing of cathepsin D and to decrease levels of full-length amyloid precursor protein (APP), suggestive of a defect in retromer-dependent trafficking. 30051532_CTSD (catD) expression is increased in neocortical regions of Alzheimers' patients and its expression correlates with neurofibrillary tangle (NFT)-containing neurons. 30227221_Data indicate a critical cathepsin D (CtsD)-hepsin signaling in migration and metastasis, which may contribute to understanding of the function and molecular mechanism in breast cancer progression. 30278264_Higher contents of cathepsin A, D, and E in the wall of the aortic aneurysms and a positive correlation between the concentration of cathepsin A and D and the width of the aneurysmal widening, suggests the participation of these enzymes in the pathogenesis of the aneurysm. 30644102_Three genes were upregulated in both the emergency department patients and concussion clinic patients: CDC2, CSNK1A1, and CTSD ( p | ENSMUSG00000007891 | Ctsd | 12843.989216 | 0.6328338 | -0.660101373 | 0.01994924 | 1092.14546808137 | 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000168278239 | 0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001384632948 | No | Yes | 10063.333190 | 136.830880 | 15976.786802 | 211.025864 | |
| ENSG00000118292 | 79630 | C1orf54 | protein_coding | Q8WWF1 | Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal | Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:79630; | extracellular region [GO:0005576] | ENSMUSG00000038543 | BC028528 | 210.785106 | 1.2452631 | 0.316450534 | 0.11651580 | 7.36805411015 | 0.0066392739590504833493977976388578099431470036506652832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.03595438023197761179261533470707945525646209716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 244.165506 | 19.342693 | 197.245719 | 15.675233 | |||
| ENSG00000118960 | 64342 | HS1BP3 | protein_coding | Q53T59 | FUNCTION: May be a modulator of IL-2 signaling. {ECO:0000250}. | Acetylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | The protein encoded by this gene shares similarity with mouse Hs1bp3, an Hcls1/Hs1-interacting protein that may be involved in lymphocyte activation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:64342; | endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981] | 15699368_The 828C-->G mutation causes a substitution of a glycine for an alanine residue in the HS1-BP3 protein. It was found in 2 unrelated patients with familial essential tremor. 16116142_HS1PB3 protein is mutated in essential tremor combined with Parkinson disease. 19524641_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19524641_Results do not support a role for these DRD3 and HS1BP3 variants in PD. 21699750_Results suggest that HS1BP3 regulates apoptosis via HS1 and stimulates AP-1-mediated transcription. 28004827_HS1BP3 is localized to ATG16L1- and ATG9-positive autophagosome precursors and we show that HS1BP3 binds phosphatidic acid (PA) through its PX domain. Furthermore, we find the total PA content of cells to be significantly upregulated in the absence of HS1BP3. | ENSMUSG00000020605 | Hs1bp3 | 131.306304 | 0.9838218 | -0.023531107 | 0.15257704 | 0.02378324686 | 0.8774377085751549065761878409830387681722640991210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.94596512782705632904622916612424887716770172119140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 129.594270 | 12.148475 | 132.300307 | 12.325586 | |
| ENSG00000119185 | 9270 | ITGB1BP1 | protein_coding | O14713 | FUNCTION: Key regulator of the integrin-mediated cell-matrix interaction signaling by binding to the ITGB1 cytoplasmic tail and preventing the activation of integrin alpha-5/beta-1 (heterodimer of ITGA5 and ITGB1) by talin or FERMT1. Plays a role in cell proliferation, differentiation, spreading, adhesion and migration in the context of mineralization and bone development and angiogenesis. Stimulates cellular proliferation in a fibronectin-dependent manner. Involved in the regulation of beta-1 integrin-containing focal adhesion (FA) site dynamics by controlling its assembly rate during cell adhesion; inhibits beta-1 integrin clustering within FA by directly competing with talin TLN1, and hence stimulates osteoblast spreading and migration in a fibronectin- and/or collagen-dependent manner. Acts as a guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor (GDI) by regulating Rho family GTPases during integrin-mediated cell matrix adhesion; reduces the level of active GTP-bound form of both CDC42 and RAC1 GTPases upon cell adhesion to fibronectin. Stimulates the release of active CDC42 from the membranes to maintain it in an inactive cytoplasmic pool. Participates in the translocation of the Rho-associated protein kinase ROCK1 to membrane ruffles at cell leading edges of the cell membrane, leading to an increase of myoblast cell migration on laminin. Plays a role in bone mineralization at a late stage of osteoblast differentiation; modulates the dynamic formation of focal adhesions into fibrillar adhesions, which are adhesive structures responsible for fibronectin deposition and fibrillogenesis. Plays a role in blood vessel development; acts as a negative regulator of angiogenesis by attenuating endothelial cell proliferation and migration, lumen formation and sprouting angiogenesis by promoting AKT phosphorylation and inhibiting ERK1/2 phosphorylation through activation of the Notch signaling pathway. Promotes transcriptional activity of the MYC promoter. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11741838, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11807099, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11919189, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12473654, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15703214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17916086, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20616313, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21768292, ECO:0000269|Ref.19}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Biomineralization;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Differentiation;Membrane;Mitogen;Notch signaling pathway;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation | The cytoplasmic domains of integrins are essential for cell adhesion. The protein encoded by this gene binds to the beta1 integrin cytoplasmic domain. The interaction between this protein and beta1 integrin is highly specific. Two isoforms of this protein are derived from alternatively spliced transcripts. The shorter form of this protein does not interact with the beta1 integrin cytoplasmic domain. The longer form is a phosphoprotein and the extent of its phosphorylation is regulated by the cell-matrix interaction, suggesting an important role of this protein during integrin-dependent cell adhesion. Several transcript variants, some protein-coding and some non-protein coding, have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. | hsa:9270; | cell periphery [GO:0071944]; centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; GDP-dissociation inhibitor activity [GO:0005092]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; activation of protein kinase B activity [GO:0032148]; biomineral tissue development [GO:0031214]; blood vessel diameter maintenance [GO:0097746]; blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002043]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus [GO:0044344]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; integrin activation [GO:0033622]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; myoblast migration [GO:0051451]; negative regulation of cell adhesion involved in substrate-bound cell migration [GO:0006933]; negative regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090051]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of fibroblast migration [GO:0010764]; negative regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051895]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; negative regulation of protein targeting to membrane [GO:0090315]; negative regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900025]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051894]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane [GO:0090314]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; receptor clustering [GO:0043113]; regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033628]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087]; regulation of integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:2001044]; tube formation [GO:0035148] | 11741908_Site-directed mutagenesis showed that Leu(135), Ile(138), and Ile(139) of Icap1 alpha, and Leu(82) and Tyr(144), are required for the Icap1 alpha-beta(1) integrin interaction 11854171_Integrin-binding protein also interacts with Krit 1 protein, cause of CCM1. (ICAP-1, integrin cytoplasmic domain-associated protein 1) 15166238_beta(1) integrin viability signal in collagen matrices is transduced by focal adhesion kinase 15703214_ICAP-1 shuttles between the nucleus and cytoplasm in a beta1 integrin-dependent manner 17133355_TNF-alpha induced expression of c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 via MAP kinases, but not via NF-kappaB, and that MAP kinases participated in the inhibition of apoptosis by induction of c-IAPs in TNF-alpha-stimulated endothelial cells 18812969_integrin cytoplasmic domain-associated protein-1 alpha (icap1alpha) act concordantly to play a critical role in beta1-integrin-mediated cell proliferation. 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20616313_Identify ICAP1 as a novel regulator to prevent excessive sprouting angiogenesis. 22736399_Annexin A1 is associated with gastric cancer survival and promotes gastric cancer cell invasiveness through the formyl peptide receptor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase/integrin beta-1-binding protein 1 pathway. 23317506_The structural basis for KRIT1 antagonized ICAP1-modulated integrin-beta1 activation. 23695561_The cocrystal structure of ICAP1 in complex with krev interaction trapped protein (KRIT)1 is characterized here. 28003363_nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of ICAP1 influences both integrin activation and KRIT1 localization, presumably impacting nuclear functions of KRIT1. 28049720_ICAP-1 monoubiquitylation helps in switching from ROCK2-mediated to MRCKalpha-mediated cell contractility. 32005669_Serine phosphorylation of the small phosphoprotein ICAP1 inhibits its nuclear accumulation. | ENSMUSG00000062352 | Itgb1bp1 | 445.211113 | 1.0887212 | 0.122634503 | 0.07717892 | 2.52393275484 | 0.1121306224461476597209497185758664272725582122802734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.28690015488873488180843196460045874118804931640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 485.744897 | 24.265455 | 448.255364 | 22.451683 | |
| ENSG00000119471 | 84263 | HSDL2 | protein_coding | Q6YN16 | FUNCTION: Has apparently no steroid dehydrogenase activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19703561}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Hydroxylation;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Peroxisome;Reference proteome | Predicted to enable oxidoreductase activity. Located in mitochondrion and peroxisome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:84263; | membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491] | 20583170_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27658777_High expression of HSDL2 is associated with glioma. 29894468_Study shows that HSDL2 upregulation is associated with ovarian cancer progression. HSDL2 knockdown inhibited cell proliferation, colony formation, motility, and tumorigenesis. 31101684_Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase like 2 (HSDL2) expression was increased in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) tissues and cells, which could promote tumor progression in vitro and in vivo. 31217732_Study reported that HSDL2 was upregulated in two human bladder cancer cell lines 5637 and T24 compared to normal human urothelial cells. Lentiviral-mediated HSDL2 knockdown inhibited the proliferation and colony formation while promoted the apoptosis of human bladder cancer T24 cells in vitro and in nude mice T24 derived xenografts in vivo. Results suggest that HSDL2 plays an oncogenic role in bladder cancer. 32211805_Knockdown of HSDL2 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma progression via down-regulating AKT2 expression. 33738911_Lipid metabolism regulator human hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-like 2 (HSDL2) modulates cervical cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. | ENSMUSG00000028383 | Hsdl2 | 115.535195 | 1.0428903 | 0.060587469 | 0.13717194 | 0.19509124979 | 0.6587125690235681174655724134936463087797164916992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.82349749883038347864072648008004762232303619384765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 118.100507 | 9.764981 | 113.768728 | 9.403326 | |
| ENSG00000119979 | 404636 | DENND10 | protein_coding | Q8TCE6 | FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) regulating homeostasis of late endocytic pathway, including endosomal positioning, maturation and secretion, possibly through activating Rab proteins such as RAB27A and RAB27B. Seems to promote the exchange of GDP to GTP, converting inactive GDP-bound RAB27A and RAB27B into their active GTP-bound form. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30771381}. | Alternative splicing;Endosome;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Reference proteome | Enables guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity and small GTPase binding activity. Involved in endosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway; protein transport; and regulation of early endosome to late endosome transport. Located in late endosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:404636; | late endosome [GO:0005770]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; endosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway [GO:0032509]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; regulation of early endosome to late endosome transport [GO:2000641] | 30771381_FAM45A defines a novel regulatory step in the homeostasis of late endocytic pathway, including endosomal positioning, maturation and secretion, possibly through activating Rab proteins such as Rab27a/b. | ENSMUSG00000024993 | Dennd10 | 63.089862 | 1.1978180 | 0.260408677 | 0.25693746 | 1.01817084130 | 0.3129532839784273101635392322350526228547096252441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.54563013041134755809480338939465582370758056640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 68.386025 | 9.990119 | 57.000820 | 8.461385 | |
| ENSG00000120137 | 79646 | PANK3 | protein_coding | Q9H999 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the phosphorylation of pantothenate to generate 4'-phosphopantothenate in the first and rate-determining step of coenzyme A (CoA) synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17631502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20797618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27555321, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30927326}. | 3D-structure;ATP-binding;Coenzyme A biosynthesis;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transferase | PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; coenzyme A biosynthesis; CoA from (R)-pantothenate: step 1/5. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17631502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20797618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27555321, ECO:0000305|PubMed:30927326}. | This gene encodes a protein belonging to the pantothenate kinase family. Pantothenate kinase is a key regulatory enzyme in the biosynthesis of coenzyme A (CoA) in bacteria and mammalian cells. It catalyzes the first committed step in the universal biosynthetic pathway leading to CoA and is itself subject to regulation through feedback inhibition by CoA. This family member is expressed most abundantly in the liver. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:79646; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; acetyl-CoA binding [GO:1905502]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; pantothenate kinase activity [GO:0004594]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; vitamin binding [GO:0019842]; coenzyme A biosynthetic process [GO:0015937]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310] | 17631502_analysis of the homodimeric structures of the catalytic cores of PanK1alpha and PanK3 in complex with acetyl-CoA and the the structural effects of the PanK2 mutations that have been implicated in neurodegeneration 27555321_Biochemical analyses showed that the transition between the inactive and active conformations, as assessed by the binding of either ATP.Mg(2+) or acyl-CoA to PANK3, is highly cooperative indicating that both protomers move in concert. | ENSMUSG00000018846 | Pank3 | 892.977450 | 0.8755809 | -0.191687535 | 0.15813625 | 1.45829191066 | 0.2272020912573224638020263910220819525420665740966796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.44837794194517871515515139435592573136091232299804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 894.366853 | 91.756097 | 1026.503378 | 105.544992 |
| ENSG00000120318 | 64411 | ARAP3 | protein_coding | Q8WWN8 | FUNCTION: Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent GTPase-activating protein that modulates actin cytoskeleton remodeling by regulating ARF and RHO family members. Is activated by phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P3) binding. Can be activated by phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P2) binding, albeit with lower efficiency. Acts on ARF6, RAC1, RHOA and CDC42. Plays a role in the internalization of anthrax toxin. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11804589, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15569923}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;GTPase activation;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a phosphoinositide binding protein containing ARF-GAP, RHO-GAP, RAS-associating, and pleckstrin homology domains. The ARF-GAP and RHO-GAP domains cooperate in mediating rearrangements in the cell cytoskeleton and cell shape. It is a specific PtdIns(3,4,5)P3/PtdIns(3,4)P2-stimulated Arf6-GAP protein. An alternatively spliced transcript has been found for this gene, but its biological validity has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. | hsa:64411; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding [GO:0005547]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding [GO:0043325]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; negative regulation of Rac protein signal transduction [GO:0035021]; negative regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035024]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] | 12832619_The catalytic domain of ARF-GAP alone is sufficient to initiate uncoating of liposome-derived COPI-coated vesicles. ARF-GAP activity is not required for COPI coat assembly & does not seem to be an essential coat component of COPI vesicles. 15546919_ARAP3 has a role in integrin-mediated tyrosine kinase signalling pathways controlling Rho GTPases and cell spreading 15569923_ARAP3 deficiency produced by antisense expression of an ARAP3 EST impaired entry of anthrax PA and its bound toxigenic moieties into both human and mouse cells, resulting in reduced toxin sensitivity 17314030_In a yeast two-hybrid screen for new interaction partners of Arap3, the PI 5'-phosphatase SHIP2 was identified as an interaction partner of Arap3. 19786092_None of the individual PH domains can bind to PtdIns(3,4,5)P3; rather, a fragment comprising two PH domains and an N-terminal linker is minimally required for binding. 21076469_ARAP3 is a unique Src substrate that suppresses peritoneal dissemination of scirrhous gastric carcinoma cells. 22750419_The structural basis for the interaction between Arap3 and Vav2, hydrophobic pockets and binding specificity. 23180820_Phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase (PI3K) is input into the regulation of beta2 integrin activity, and processes dependent on its responses, by signaling through its effector ARAP3. 23239578_structural and binding affinity between odin and arap3 27311713_Structural Basis for the Specific Recognition of RhoA by the Dual GTPase-activating Protein ARAP3. | ENSMUSG00000024451 | Arap3 | 246.420305 | 1.2211365 | 0.288224524 | 0.14617412 | 3.87928790362 | 0.0488852873484043395913012375331163639202713966369628906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.16173306514415325407796331091958563774824142456054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 264.159619 | 19.924278 | 216.811166 | 16.660345 | |
| ENSG00000121933 | 57413 | TMIGD3 | protein_coding | P0DMS9 | FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Plays a suppressive role in osteosarcoma malignancy by inhibiting NF-kappa-B activity (PubMed:27886186). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27886186}. | Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a transmembrane and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, one of which shares its 5' terminal exon with that of the overlapping adenosine A3 receptor gene (GeneID:140), thus resulting in a fusion product. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2014]. | hsa:57413; | membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; activation of adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0007190]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; regulation of heart contraction [GO:0008016]; response to wounding [GO:0009611]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 27886186_Protein expression of TMIGD3 and A3AR is lower in human osteosarcoma tissues than normal tissues. Mechanistically, TMIGD3 isoform 1 and A3AR commonly inhibit the PKA-Akt-NF-kappaB axis. | ENSMUSG00000074344 | Tmigd3 | 81.811154 | 1.2890979 | 0.366361801 | 0.21290658 | 2.95214697645 | 0.0857635514812417759644702641708136070519685745239257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.23821694958689634824544612001773202791810035705566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 91.479727 | 10.256919 | 71.157459 | 8.101282 | |
| ENSG00000122515 | 83637 | ZMIZ2 | protein_coding | Q8NF64 | FUNCTION: Increases ligand-dependent transcriptional activity of AR and other nuclear hormone receptors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16051670}. | Alternative splicing;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | ZMIZ2 and ZMIZ1 (MIM 607159) are members of a PIAS (see MIM 603566)-like family of proteins that interact with nuclear hormone receptors. ZMIZ2 interacts with androgen receptor (AR; MIM 313700) and enhances AR-mediated transcription (Huang et al., 2005 [PubMed 16051670]).[supplied by OMIM, May 2010]. | hsa:83637; | mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nuclear replication fork [GO:0043596]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; nuclear receptor coactivator activity [GO:0030374]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 16051670_hZimp7 modulates androgen receptor and/or other nuclear receptor-mediated transcription, possibly through alteration of chromatin structure by SWI/SNF-like BAF complexes. 20159969_there is an interaction between Zimp7 and PIAS proteins with higher preference for PIAS3, in androgen receptor-mediated transcription 31527801_LINC00265 promotes colorectal tumorigenesis via ZMIZ2 and USP7-mediated stabilization of beta-catenin. | ENSMUSG00000041164 | Zmiz2 | 950.264296 | 0.9714137 | -0.041842244 | 0.15048465 | 0.07715144749 | 0.7811954518456772911250141078198794275522232055664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.89458550801615510650321994035039097070693969726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 916.541379 | 114.833028 | 949.277208 | 118.563372 | |
| ENSG00000124193 | 6431 | SRSF6 | protein_coding | Q13247 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in constitutive splicing and modulates the selection of alternative splice sites. Plays a role in the alternative splicing of MAPT/Tau exon 10. Binds to alternative exons of TNC pre-mRNA and promotes the expression of alternatively spliced TNC. Plays a role in wound healing and in the regulation of keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation via its role in alternative splicing. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12549914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15009664, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22767602, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24440982}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Isopeptide bond;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;RNA-binding;Ubl conjugation | The protein encoded by this gene is involved in mRNA splicing and may play a role in the determination of alternative splicing. The encoded nuclear protein belongs to the splicing factor SR family and has been shown to bind with and modulate another member of the family, SFRS12. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. In addition, two pseudogenes, one on chromosome 17 and the other on the X chromosome, have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010]. | hsa:6431; | nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; pre-mRNA binding [GO:0036002]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000380]; mRNA splice site selection [GO:0006376]; mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000398]; negative regulation of cell death [GO:0060548]; negative regulation of keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0045617]; negative regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0048025]; negative regulation of type B pancreatic cell apoptotic process [GO:2000675]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in lung morphogenesis [GO:0060501]; regulation of alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000381]; regulation of keratinocyte proliferation [GO:0010837]; regulation of wound healing [GO:0061041]; response to insulin [GO:0032868] | 12531473_interacts with calcitonin/CGRP exon 4 exonic splice enhancer(ESE); binding of SRp55 to an ESE required for calcitonin mRNA splicing suggests that the different levels of SRp55 in different cell types may regulate calcitonin/CGRP alternative splicing 12549914_SRp55 binding to a suboptimal RNA binding site in the calcitonin/CGRP pre-mRNA exonic splice enhancer, or increasing the amount of SRp55 in cells, is required for calcitonin mRNA production. 12779084_Higher relative expression of SR55 protein in breast tumors was associated with altered pattern of CD44 variants incorporating exon v7 18315555_ASF/SF2 and SRp55 appear to interact with the variable TF exon 5 through exonic splicing enhancers at bases 39 and 87-117. Weakening of the above ESE modulates splicing of TF exon 5. 18571879_These findings show that modulation of splicing activity in p53-deficient cells during the early response to sub-lethal DNA damage results in a change in the splicing of target genes, thus modifying the cellular response to genotoxic agents. 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20427542_Here, the authors report that specific SR proteins, particularly SRp40 and SRp55, promote human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Gag translation from unspliced (intron-containing) viral RNA. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20685659_Serine- and arginine-rich proteins 55 and 75 (SRp55 and SRp75) induce production of HIV-1 vpr mRNA by inhibiting the 5'-splice site of exon 3. 21345357_SRp55 aids in the generation of partially spliced and unspliced HIV-1 mRNAs. 22516966_Report upregulation of Bim and the splicing factor SRp55 in melanoma cells from patients treated with selective BRAF inhibitors. 22767602_Phosphorylation of SRp55 by Dyrk1A suppressed its ability to promote Tau exon 10 inclusion. 23132731_The splicing factor SRSF6 is an oncoprotein that regulates the proliferation and survival of lung and colon cancer cells. 23648111_Zinc inhibits the activity of SRSF6 and promotes elimination of exon 4, leading to preferential generation of BimS. 24440982_SRSF6 is a regulator of wound healing and tissue homeostasis in skin. 25889056_The authors propose that splicing at 3'ss A3 is dependent on binding of the enhancing SR proteins SRSF2 and SRSF6 to the HIV-1 tat ESE and ESE2 sequence. 27443606_LINC01133 inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transformation and metastasis in colorectal neoplasms by directly binding to SRSF6 as a target mimic. 27529534_The recent studies suggest that correcting the SRSF6-driven missplicing and/or microtubule-associated imbalance might be of therapeutic value in Huntington's disease. 29114070_SRSF6 functions the important roles in mediating CRC progression through regulating AS, and indacaterol is repositioned as an antitumour drug through targeting SRSF6. 29246973_Data suggest that regulation of pancreatic beta-cell function and survival/apoptosis involves alternative splicing modulated by key splicing regulator SRP55; SRP55-regulated alternative splicing includes modulation of function of pro-apoptotic proteins (BIM, BAX), JNK signaling, and endoplasmic reticulum stress. (BIM = BCL-2 interacting protein BIM; BAX = apoptosis regulator BAX) 30260058_Results identified SRSF6 protein as one of the factors involved in modulating the splicing of the DDC mutated (c.714+4A>T) transcript. 31201803_Data indicate the extent of inter-individual variation in myocardial dual specificity tyrosine phosphorylation regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A)-serine and arginine rich splicing factor 6 (SRSF6)-troponin T2, cardiac type protein (TNNT2) expression in the context of Down syndrome. 32444465_Posttranslational Regulation of the Exon Skipping Machinery Controls Aberrant Splicing in Leukemia. 32820193_Silencing Srsf6 does not modulate incomplete splicing of the huntingtin gene in Huntington's disease models. 32901876_SRSF6 regulates alternative splicing of genes involved in DNA damage response and DNA repair in HeLa cells. 33050987_Relative strength of 5' splice-site strength defines functions of SRSF2 and SRSF6 in alternative splicing of Bcl-x pre-mRNA. 33376132_The RNA-binding profile of the splicing factor SRSF6 in immortalized human pancreatic beta-cells. 33397371_LncRNA CRNDE attenuates chemoresistance in gastric cancer via SRSF6-regulated alternative splicing of PICALM. 33905374_Splicing factor SRSF6 mediates pleural fibrosis. 34614409_DRAK2 aggravates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression through SRSF6-associated RNA alternative splicing. 34665708_A candidate gene study reveals association between a variant of the SRp55 splicing factor gene and systemic sclerosis. | ENSMUSG00000016921 | Srsf6 | 1557.266508 | 0.9297473 | -0.105089418 | 0.05404478 | 3.77963753921 | 0.0518798978591474557742202478038961999118328094482421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.16888434052914932936850789246818749234080314636230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1639.488482 | 61.788438 | 1771.631342 | 66.017429 | |
| ENSG00000124275 | 4552 | MTRR | protein_coding | Q9UBK8 | FUNCTION: Key enzyme in methionine and folate homeostasis responsible for the reactivation of methionine synthase (MTR/MS) activity by catalyzing the reductive methylation of MTR-bound cob(II)alamin (PubMed:17892308). Cobalamin (vitamin B12) forms a complex with MTR to serve as an intermediary in methyl transfer reactions that cycles between MTR-bound methylcob(III)alamin and MTR bound-cob(I)alamin forms, and occasional oxidative escape of the cob(I)alamin intermediate during the catalytic cycle leads to the inactive cob(II)alamin species (Probable). The processing of cobalamin in the cytosol occurs in a multiprotein complex composed of at least MMACHC, MMADHC, MTRR and MTR which may contribute to shuttle safely and efficiently cobalamin towards MTR in order to produce methionine (PubMed:27771510). Also necessary for the utilization of methyl groups from the folate cycle, thereby affecting transgenerational epigenetic inheritance (By similarity). Also acts as a molecular chaperone for methionine synthase by stabilizing apoMTR and incorporating methylcob(III)alamin into apoMTR to form the holoenzyme (PubMed:16769880). Also serves as an aquacob(III)alamin reductase by reducing aquacob(III)alamin to cob(II)alamin; this reduction leads to stimulation of the conversion of apoMTR and aquacob(III)alamin to MTR holoenzyme (PubMed:16769880). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8C1A3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16769880, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17892308, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27771510, ECO:0000305|PubMed:19243433}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Amino-acid biosynthesis;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;FAD;Flavoprotein;FMN;Methionine biosynthesis;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine | This gene encodes a member of the ferredoxin-NADP(+) reductase (FNR) family of electron transferases. This protein functions in the synthesis of methionine by regenerating methionine synthase to a functional state. Because methionine synthesis requires methyl-group transfer by a folate donor, activity of the encoded enzyme is important for folate metabolism and cellular methylation. Mutations in this gene can cause homocystinuria-megaloblastic anemia, cbl E type. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. | hsa:4552; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; intermediate filament cytoskeleton [GO:0045111]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; [methionine synthase] reductase activity [GO:0030586]; FAD binding [GO:0071949]; flavin adenine dinucleotide binding [GO:0050660]; FMN binding [GO:0010181]; NADPH binding [GO:0070402]; NADPH-hemoprotein reductase activity [GO:0003958]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on metal ions, NAD or NADP as acceptor [GO:0016723]; DNA methylation [GO:0006306]; folic acid metabolic process [GO:0046655]; homocysteine catabolic process [GO:0043418]; homocysteine metabolic process [GO:0050667]; methionine biosynthetic process [GO:0009086]; negative regulation of cystathionine beta-synthase activity [GO:1904042]; S-adenosylmethionine cycle [GO:0033353] | 10791559_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 11472746_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11592436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11806787_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11807890_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12020105_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12375236_Variants influence the risk of spina bifida via the maternal rather than the embryonic genotype. 12416982_The kinetic and spectroscopic properties of the M22/S175 and I22/S175 and the I22/L175 and I22/S175 pairs of polymorphic variants of MSR have been compared. 12482550_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12590188_polymorphisms should be regarded as independent risk factors for spina bifida 12642343_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12649067_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12649067_results indicate that MTRR and MTR genes may interact to increase the infants' Neural tube defects risks 12716294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12801615_No differences in mean homocysteine, prevalence of hyperhomocysteinemia and significant coronary artery disease between genotypes AA, AG, GG. 12801615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12807760_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12810988_Results of screening mutations 2756A-->G and 66A-->G in MTR and MTRR genes respectively show that are might have an effect on NTDs incidence (neural tube defects). 12855226_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12876480_Methionine synthase polymorphism is a risk factor for Alzheimer disease. 12923861_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12923861_polymorphisms in methionine synthase reductase is associated with increased risk for Down syndrome 12939653_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14632302_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14652285_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14716779_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14967039_Common MSR polymorphisms, I22/L175 and M22/S175, which result in less effective methionine synthase activation, do not have effects on flavin potentials or electron transfer kinetics that would impinge on catalytic efficiency of the variants. 14977639_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15059614_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15135249_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15159311_MTRR polymorhism in the genes for folate and methionine metabolism might play a role in the occurance in patient with ALL and NHL. 15159311_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15216546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15347655_Results describe two common polymorphic variants of ATP:cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase that are found in normal individuals, and their interactions with methionine synthase reductase. 15354395_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15514263_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15514263_findings indicate that when the homozygous variant for the MTHFR 677CT polymorphism coexists with the MTRR 66 AG genotype, plasma homocysteine is significantly elevated relative to the other genotype groups 15514969_Polymorphisms in the folate metabolic pathway were associated with a lower likelihood of Cervical intrepithelial neoplsia. 15612980_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15612980_SNPs in this enzyme affects homocysteine-regulating genes and may be important determinants of vitamin metabolism in heart transplantation. 15714522_3 new MTRR mutations (c.7A>T, c.1573C>T, and c.1953-6_1953-2del5) were detected. The identification of mutations in MTRR, & restoration of methionine synthesis following MTRR minigene expression confirms that MTRR gene defects cause cblE homocystinuria. 15797993_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15866085_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15889417_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15894670_Finds MTRR variant AA genotype associated with a significantly decreased squamous cell head and neck cancer risk. 15894670_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15979034_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16006998_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16013960_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16115349_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16268464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16316363_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16351505_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16470748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16485733_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16575899_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16580699_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16580699_the MTRR AA genotype acts to increase the micronuclei frequency resulting from cigarette smoking 16769880_we propose that MSR serves as a special chaperone for human methionine synthase and as an aquacobalamin reductase, rather than acting solely in the reductive activation of MS 16820193_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16861746_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16861746_we showed the first genetic evidence that MTHFR C677T, MS A2756G and MTRR A66G genotypes were independently associated with male infertility. Each SNP of the three enzymes may have a different impact on the folate cycle during spermatogenesis 16894458_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16947783_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16985020_Clinical trial of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17009228_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17024475_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17024475_The MTRR polymorphism is a maternal risk factor for spina bifida. 17035141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17074544_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17079868_66G/524C haplotype of the MTRR gene affect bone turn over rate. 17079868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17087642_Data indicate that maternal MTRR 66A>G polymorphism is not a risk factor for congenital heart defects (CHD), but maternal MTRR 66GG genotype with compromised vitamin B(12) status may possibly result in increased CHD risk. 17087642_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17101561_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17113603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17119116_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17136115_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17152488_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17220339_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17311259_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17311260_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17376725_Distributions for the homozygous mutant form of MTRR were similar between cases and controls, polymorphisim did not increase the risk of placental abruption. 17376725_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17417062_Since MTR genes are located in 1q43 loci, our findings support the significance of chromosome 1q in etiopathogenesis of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. 17436311_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17454638_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17461517_MTRR 2756A > G polymorphisms interact with elevated total homocysteine levels, leading to an increased risk of ischemic stroke. 17477549_Structure and function of activation and conformational heterogeneity of recombinant proteins. 17522601_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17522601_The interaction between low levels of serum cobalamin and MTHFR (C677T or A1298C) or MTRR A66G gene polymorphisms was associated with increased tHcy. 17533396_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17546637_MTRR polymorphism may play an important role in the risk of multiple myeloma. 17546637_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17553479_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17553479_These results not only highlight the involvement of the MSR and CBS genes in the etiology of cardiovascular disease, but also emphasize the strength of haplotype analyses in association studies. 17554763_methionine synthase reductase modulates the phenotype of a disease-causing mutation 17581676_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17581676_Results suggest that the alterations of folate metabolism related to MTHFR, MTR and MTRR polymorphisms are not involved in clefting in South Brazil. 17596206_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17611986_In our population of methotrexate (MTX)-treated rheumatoid arthritis patients the 2756GG genotype of the methionine synthase reductase gene was more common than expected and was associated with MTX-induced accelerated rheumatoid nodulosis. 17636160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17655928_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17655928_similar frequencies of the MTHFR, the MTRR and the TYMS genotypes were seen in patients and controls 17822659_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17853476_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17853476_The risk of having a child with congenital malformation or FACS was three to four times higher for mothers who were MTHFR 677TT homozygotes compared with MTHFR 677CC homozygotes 17892308_Mechanism of coenzyme binding to human MSR revealed through the crystal structure of the FNR-like module and isothermal titration calorimetry. 17904392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17925002_MTRR polymorphism is related with disease activity in Crohn's disease 17925002_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17934692_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17967524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17967524_no association between prostate cancer and the MTRR A66C polymorphism 17993766_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17993766_These findings suggest that in obese subjects, homocysteine cycle efficiency is impaired by MTHFR, MTR, and MTRR inability to supply methyl-group donors, providing evidence that MTHFR, MTR, and MTRR gene polymorphisms are genetic risk factors for obesity. 18004208_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18023275_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18034637_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18034637_The MTRR 66GG genotype was found to be associated with 2.74-fold risk (95% CI: 1.73, 4.34) for deep vein thrombosis among South Indians. This risk is increased further to 3.46-fold (95% CI: 1.38, 8.63) in the presence of the MTHFR 677CT/1298AC genotype. 18061941_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18174236_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18174236_the MTHFR and MTRR polymorphisms are associated with individual susceptibility to breast cancer among postmenopausal women 18199722_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18204969_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18221906_MSR protein is restricted to the cytosol but, based on the Leal study, suggest that a similar protein may interact with MMAB to reduce the mitochondrial cobalamin substrate in the generation of adenosylcobalamin 18222012_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18226574_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18249021_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18257130_MTHFR and MTRR gene mutation alleles are related to Down syndrome, and CT, TT and GG gene mutation types increase the risk of Down syndrome 18257130_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18378576_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18386810_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18427977_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18435414_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18483342_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18483342_The MTRR A66G and GG genotypes were significantly associated with risk of meningioma but not glioma. 18485163_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18510611_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18515090_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18515090_Study suggested a common missense SNP of the MTRR gene as a novel pancreatic cancer susceptibility factor with a functional significance in folate-related metabolism and the genome-wide methylation status. 18590621_Observational study and meta-analysis of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18607581_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18610829_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18610829_polymorphic variants of genes GSTT1, GSTM1, NAT2 and MTRR can modulate the risk of childhood acute leukemia, residents of European part of Russia. 18614746_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18614746_We found a significant interaction between MTHFR 677C-->T and MTRR 66A-->G on serum homocysteine concentrations among non-Hispanic whites. 18635682_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18682255_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18700049_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18771981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18774170_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18774994_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18774994_The MTRR 66GG and MTHFR 1298 CC genotypes may confer protection against early nephropathy 18785313_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18792976_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18792976_study evaluated the importance of the polymorphisms in the MTHFR, MTRR, and CBS genes for hyperhomocysteinemia, considering B12 and folate levels; results confirm that genetic interactions can influence on the homocysteine status 18830263_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18836720_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18842997_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18843018_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18843018_Risk of pancreatic cancer was increased with alcohol consumption in subjects with the MTRR 66 G allele. 18936436_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18983896_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18988749_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18992148_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19019492_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19020309_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19035314_The MTHFR 1298A>C and the MTRR 66A>G genotypes were associated with an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in this Korean population. 19048631_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19064571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19064578_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19112534_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19161160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19254790_In a population with a high prevalence of the mutated T allele, maternal MTRR A66G, but not MTHFR, polymorphisms are associated with Down syndrome. 19254790_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19263808_relationship between occurrence of hyperlipidemia, plasma homocysteine and polymorphisms of methylenetetra hydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene and methionine synthase (MS) gene 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19336437_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19339913_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19339913_The MTRR 66A>G gene variant is not associated with peak elevated postoperative plasma total homocysteine after nitrous oxide anesthesia. 19348062_MTRR A66G polymorphism was not associated with the total homocysteine plasma concentration because the same genotype frequency distribution was detected in both patients and healthy individuals. 19348062_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19353223_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19394322_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19427504_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19461557_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19493349_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19533788_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19657388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19706844_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19729796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19737740_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19760026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19760026_there was no significant association between most SNPs in methionine synthase reductase , and the risk of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer in Korean women. 19774638_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19776626_Polymorphisms in methionine synthase, methionine synthase reductase and serine hydroxymethyltransferase, folate and alcohol intake, and colon cancer risk. 19776634_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19777601_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19812220_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19837268_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19843671_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19852428_Molecular analysis of 12 genetic polymorphisms involved in the folate metabolism revealed that the mother is heterozygous for the MTHFR C677T and TC2 A67G polymorphisms, and homozygous for the mutant MTRR A66G polymorphism. 19858780_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19936946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20031554_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20047525_A66G polymorphism not significantly associated with increased risk for neural tube defects 20047525_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20056620_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20082058_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20085490_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20099281_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20120036_A deep intronic mutation is the direct cause of MTRR pseudoexon inclusion and the pseudoexon is normally not recognized due to a suboptimal 5' splice site. 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20180013_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20209990_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20209990_Patients with hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy) had statistically significant increase of allele MTHFR 677T and MTRR 66GG as compared both with the control group and with the group of patients without HHcy. 20373852_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20378615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20386493_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20411324_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20411324_Meta-analysis strongly suggests that MTRR A66G polymorphism is not associated with breast cancer risk, especially in Caucasians and Asians. 20437058_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20447924_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20458436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20466634_Data show that MTHFR 677C>T and MTRR 66A>G polymorphisms are two independent risk factors for DS pregnancies in young women, but RFC-1 80G>A and MTR 2756A>G polymorphism are not independent risk factor. 20466634_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20511665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20544798_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20549016_Germ line polymorphisms in the folate- and methyl-associated genes MTHFR, MTR and MTRR, were analyzed in colorectal cancer patient cohort to find a possible link between these genetic variants and p16 hypermethylation. 20549016_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20615890_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20647221_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20718043_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20726305_study results do not demonstrate an association between A66G MTRR polymorphism and colorectal cancer or breast cancer in Romanian patients 20737570_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20852008_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20883119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20888556_No association was found between MTHFR/MTRR genetic variants and sperm counts. 20888556_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20948192_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20955826_The MTHFR 677C>T SNP and the MTRR 66A >G SNP were identified as determinants of impaired bone mineral density (total body) in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. 20960050_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20962453_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21041608_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21045269_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21055808_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21070756_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21070756_the synergistic effects of polymorphisms in the folate metabolic pathway genes in Parkinson's disease susceptibility 21092627_These results suggest that MTRR G66A polymorphism may play a role in coronary artery disease susceptibility. 21204909_5-Fluorouracil-based chemotherapy for colorectal cancer and MTHFR/MTRR genotypes 21211571_No difference in the distribution between cases and controls was observed for the haplotypes based on the four polymorphisms in the MTRR gene. 21349258_The genotype and allele frequencies of the MTR Asp919Gly, MTHFR Ala222Val, MTHFD1 Arg653Gln and MTRR Ile22Met gene variants did not display statistical differences between patients with cervical cancer and controls. 21438757_Linkage disequilibrium (LD) analysis found possible protective role of MTRR 66 AA in sporadic colon cancer. The significant LD between two loci (MTHFR A1298C and MTRR A66G) located on different chromosomes indicates a selective force for their linkage. 21472912_ELDOR spectroscopy was used to identify multiple conformational intermediates in methionine synthase reductase and analyse their relative stabilities. 21547363_MTRR A66G polymorphism is a potential biomarker for cancer risk. 21603981_These data suggest that all polymorphisms coding for MTHFR, MTR, MTRR and TS have consistent roles in the increased risk of sporadic colorectal adenocarcinoma among the southeastern population of Brazil. 21774403_The heterozygous genotype MTRR 66AG was associated with the 5.56-fold increased CL/P risk (OR = 5.56) and for mothers with 2.6-fold increased risk of delivering a CL/P offspring (OR = 2.6). 21775772_MTRR polymorphisms did not appear to be an important genetic factor predisposing to idiopathic infertility in Brazilian men. 21780915_MTR A2756G polymorphism, but not MTRR A66G and MTHFR A1298C, is associated with risk of coronary heart disease for Europeans. 21947961_The variant allele and genotypic frequencies in MTRR A66G gene was significantly higher in patients with UC compared to healthy controls. 21987236_MTRR A66G and cSHMT C1420T polymorphisms influence CpG island methylator phenotype of BNIP3, thus epigenetically regulating BNIP3 in breast cancer 22005284_Constituents of the folate cycle could be involved in the etiology of idiopathic intellectual disability. 22057956_MTRR A66G and C524T polymorphisms are associated with increased risk of CHDs. 22097960_Data indicate the while W697 in MSR attenuates hydride transfer, it ensures coenzyme selectivity and accelerates FAD to FMN electron transfer (i.e., controls kinetics of interflavin electron transfer). 22179537_We have demonstrated that the MTRR c.56+781 A>C variant is an important genetic marker for increased congenital heart disease risk because this variant results in functionally reduced MTRR expression at the transcriptional level. 22236648_the single-nucleotide polymorphism A66G MTRR is not involved in the development of breast cancer. 22339686_Known common single-nucleotide polymorphisms in MTRR and BHMT genes may not be significant risk factors for cororonary artery disease. 22373582_Studies suggest that polymorphisms in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) and methionine synthase reductase (MTRR) modulate the risk for breast cancer, particularly the A1298C polymorphism of the MTHFR gene. 22475273_The 66GG and AG genotypes were associated with decreased odds ratios for heart defects. This overall association was driven by decreased risk for ventricular septal defect for 66GG and AG and decreased odds ratio for aortic valve stenosis for 66AG. 22479380_Data indicate that genetic variants in folate pathway genes showed associations including infant MTRR 66G>A genotype and maternal MTHFR 677C>T genotype with IGF2 methylation. 22665368_studies suggest that SNPs in CBS and MTRR have sex-specific associations with aberrant methylation in the lung epithelium of smokers that could be mediated by the affected one-carbon metabolism and transsulfuration in the cells 22706675_MTHFR and MTRR genetic polymorphisms were not associated with childhood ALL. However, AL was positively associated with homozygosity for any of the MTHFR polymorphisms and carriership of both MTRR variant alleles. 22719222_Meta-analysis suggested that MTHFR 677T allele might provide protection against CRC in worldwide populations, while MTRR 66G allele might increase the risk of CRC in Caucasians. 22796266_Results indicate the importance of four gastric cancer susceptibility polymorphisms of IL-10, NOC3L, PSCA and MTRR in the Chinese Han population. 22813657_MTHFR and MTRR polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to schizophrenia and support th | ENSMUSG00000034617 | Mtrr | 230.561930 | 1.1498728 | 0.201474276 | 0.22127581 | 0.82507034161 | 0.3637018755579277673462001985171809792518615722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.59567410342522764121753198196529410779476165771484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 240.284688 | 45.088706 | 208.999110 | 39.231066 | |
| ENSG00000124333 | 6845 | VAMP7 | protein_coding | P51809 | FUNCTION: Involved in the targeting and/or fusion of transport vesicles to their target membrane during transport of proteins from the early endosome to the lysosome. Required for heterotypic fusion of late endosomes with lysosomes and homotypic lysosomal fusion. Required for calcium regulated lysosomal exocytosis. Involved in the export of chylomicrons from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cis Golgi. Required for exocytosis of mediators during eosinophil and neutrophil degranulation, and target cell killing by natural killer cells. Required for focal exocytosis of late endocytic vesicles during phagosome formation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10888671, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16677249, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18042464}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Exocytosis;Golgi apparatus;Lysosome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Synapse;Synaptosome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | This gene encodes a transmembrane protein that is a member of the soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) family. The encoded protein localizes to late endosomes and lysosomes and is involved in the fusion of transport vesicles to their target membranes. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. | hsa:6845; | azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; platelet alpha granule [GO:0031091]; pseudopodium [GO:0031143]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; SNARE complex [GO:0031201]; synapse [GO:0045202]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; transport vesicle membrane [GO:0030658]; SNAP receptor activity [GO:0005484]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; calcium-ion regulated exocytosis [GO:0017156]; endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006888]; endosome to lysosome transport [GO:0008333]; eosinophil degranulation [GO:0043308]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; natural killer cell degranulation [GO:0043320]; neutrophil degranulation [GO:0043312]; phagocytosis, engulfment [GO:0006911]; positive regulation of histamine secretion by mast cell [GO:1903595]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; vesicle fusion [GO:0006906]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] | 11840509_A G-->C transversion in a regulatory region was found to be associated with bipolar affective disorder. 11840509_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12444103_In ICF (immunodeficiency, centromeric instability, facial abnormalities) syndrome SYBL1 escapes from silencing and this correlates with altered patterns of histone methylation and acetylation. 14672948_results reported here clarify that a Staf-zinc finger family factor is the major nuclear protein bound to the synaptobrevin-like 1 (SYBL1) promoter region and is responsible for its regulation in HeLa cells 16195891_VAMP-7 is involved in the constitutive exocytosis as a slow, minor v-SNARE, but not in lysosomal transport 16430921_Data show that the insensitivity of TI-VAMP to botulinum neurotoxin B relies on at least 12 amino acid changes versus VAMP-2, which are scattered along an interface of 22 amino acid residues in length. 18042464_Our results show that VAMP-7 is a crucial component of granzyme B release and target cell killing in the NK cell line YT-Indy. 18253931_Data show that mature human mast cells express a specific pattern of SNARE and that VAMP-7 and VAMP-8, but not VAMP-2, are required for rapid degranulation. 18362137_The participation of vesicle-associated membrane protein 7 as a partner of syntaxin 7 in VacA-induced vacuole formation is reported. 18571410_Collectively, these data point to a specific role of VAMP7 in delivering MT1-MMP to sites of matrix degradation, maintaining the functional machinery required for invasion. 18775314_Study demonstrates that the clathrin-mediated endocytosis of the SNARE VAMP7 is directly mediated by Hrb, a clathrin adaptor and ArfGAP. 18819912_HRB is involved in clathrin-dependent endocytosis and recruits TI-VAMP in this process 19138172_The present results suggest that a SNARE complex containing VAMP7 and Vti1a defines a novel traffic pathway to the cell surface in both neuronal and non-neuronal cells. 19745841_show that TI-VAMP interacts with the Vps9 domain and ankyrin-repeat-containing protein Varp, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor of the small GTPase Rab21, through a specific domain herein called the interacting domain. 19781582_TI-VAMP/VAMP7 and VAMP3/cellubrevin: two v-SNARE proteins involved in specific steps of the autophagy/multivesicular body pathways. 20144992_Results highlight the role of TI-VAMP in the secretory pathway of a tetraspanin, and support a model in which CD82 allows EGFR entry in microdomains that control its clathrin-dependent endocytosis and signaling. 20378544_SNARE VAMP7/TI-VAMP adopts a closed conformation 21609427_Alternative splicing of SYBL1 by exon skipping events results in the production of a number of VAMP7 isoforms. 21805468_VAMP7 is involved in many fusion processes and thus plays a more general function in NK-cell activity than VAMP4. 22002060_The endosomal trafficking and recycling of MT1-MMP was found to be dependent upon Rab7 and VAMP7, and blocking the function of these proteins reduced cell migration and invasion. 22188132_Downregulation of VAMP7 expression inhibited the fusion of ATP-storing vesicles and ATP-mediated calcium wave propagation. 22323709_Behavioral characterization studies indicate that deletion of Vamp7 exon 7 is associated with a role for VAMP7 in higher brain functions. 22589474_These studies identify a new alpha-granule subtype expressing VAMP-7 that moves to the periphery during spreading, supporting the premise that alpha-granules are heterogeneous and demonstrating that granule exocytosis is required for platelet spreading. 22951367_In a mammalian tumor cell line a subset of VAMP7 (V-SNARE)-positive vacuoles colocalize with LC3 at the cell periphery (focal adhesions) upon starvation. 23104059_VAMP7-SNARE motif is trapped between Varp and the VAMP7 longin domain, and hence Varp kinetically inhibits the ability of VAMP7 to form SNARE complexes 23217169_Overexpression of Vamp7 inhibited the heterotypic fusion with lysosomes and the homotypic fusion between individual Coxiella phagosomes and replicative vacuoles. 23322049_hVps41 and VAMP7 are specifically involved in the fusion of trans-Golgi network-derived lysosome-associated membrane protein carriers with late endosomes. 23471971_Activation of TI-VAMP-mediated exocytosis thus relies on tyrosine phosphorylation. 23741335_CALM is able to sort VAMP4 and VAMP7, even though they have sorting signals for other clathrin adaptors. 24807903_Increased level of SNAP23-Syntaxin4-VAMP7 interaction correlates with decreased Syntaxin4 phosphorylation and trafficking of MT1-MMP to invadopodia during cellular invasion. 24880616_increased gene dosage of VAMP7, and thus higher expression levels of its protein product, enhances estrogen receptor action in male genitourinary tissues 25046114_highlight the role that VAMP3 and VAMP7 play in selection of the pathways leading to generation of ultrastructurally different LC3 compartments 25999457_VAMP-7 participates in both platelet granule secretion and spreading and suggest a mechanism whereby VAMP-7 links granule exocytosis with actin reorganization. 26279084_The pseudoautosomal region of human X and Y chromosome encoded VAMP7 protein was predicted to interact with at least 22 proteins encoded on the somatic chromosomes. 26553929_GLUT5 required an interaction cascade of Rab11, Myo5B, Slp4a, Munc18-2, and Vamp7 with Stx3. 31251111_DIPK2A promotes STX17- and VAMP7-mediated autophagosome-lysosome fusion by binding to VAMP7B. 31447853_Cytotoxic Granule Exocytosis From Human Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Is Mediated by VAMP7. 32423256_Gene Copy Number Quantification of SHOX, VAMP7, and SRY for the Detection of Sex Chromosome Aneuploidies in Neonates. 32622737_A case series of infants with increased VAMP7 gene dosage at birth and virilization defects. 33357422_Role of VAMP7-Dependent Secretion of Reticulon 3 in Neurite Growth. 33886957_A BLOC-1-AP-3 super-complex sorts a cis-SNARE complex into endosome-derived tubular transport carriers. 34042162_Organelle tethering, pore formation and SNARE compensation in the late endocytic pathway. 34088337_LINC00511 drives invasive behavior in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating exosome secretion and invadopodia formation. 35082283_The EMT-induced lncRNA NR2F1-AS1 positively modulates NR2F1 expression and drives gastric cancer via miR-29a-3p/VAMP7 axis. | 408.997116 | 1.2133563 | 0.279003222 | 0.08375690 | 11.09642390765 | 0.0008649434672239494871145981669258162582991644740104675292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00668074501354423266191728814078487630467861890792846679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 452.912903 | 23.023708 | 375.044236 | 19.319742 | |||
| ENSG00000124508 | 10385 | BTN2A2 | protein_coding | Q8WVV5 | FUNCTION: Inhibits the proliferation of CD4 and CD8 T-cells activated by anti-CD3 antibodies, T-cell metabolism and IL2 and IFNG secretion. {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Butyrophilin is the major protein associated with fat droplets in the milk. This gene is a member of the BTN2 subfamily of genes, which encode proteins belonging to the butyrophilin protein family. The gene is located in a cluster on chromosome 6, consisting of seven genes belonging to the expanding B7/butyrophilin-like group, a subset of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily. The encoded protein is a type I receptor glycoprotein involved in lipid, fatty-acid and sterol metabolism. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2010]. | hsa:10385; | external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000082]; negative regulation of activated T cell proliferation [GO:0046007]; negative regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001818]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014067]; negative regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051898]; negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050860]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014065]; positive regulation of regulatory T cell differentiation [GO:0045591]; protein kinase B signaling [GO:0043491]; regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001817]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] | 26809444_Genes encoding butyrophilin-2A2 (BTN2A2) are regulated by the class II trans-activator and regulatory factor X, two transcription factors dedicated to major histocompatibility complex class II expression, suggesting a role in T cell immunity. | ENSMUSG00000053216 | Btn2a2 | 37.158917 | 0.9709517 | -0.042528494 | 0.27665539 | 0.02351870790 | 0.8781158825807529044737975709722377359867095947265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.94623564945224336586448998787091113626956939697265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 34.348101 | 6.063725 | 35.596535 | 6.012690 | |
| ENSG00000125149 | 80262 | PHAF1 | protein_coding | Q9BSU1 | FUNCTION: Plays a regulatory role in autophagic activity. In complex with BCAS3, associates with the autophagosome formation site during both non-selective and selective autophagy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33499712}. | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome | Predicted to be involved in Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport. Located in phagophore assembly site. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:80262; | dendrite [GO:0030425]; phagophore assembly site [GO:0000407]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport [GO:0043001] | 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) | ENSMUSG00000031889 | Phaf1 | 172.364104 | 1.1772930 | 0.235473427 | 0.18186465 | 1.66908332771 | 0.1963813601451118440177623369891080074012279510498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.41061023403734292491762403187749441713094711303710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 198.313658 | 24.014255 | 169.500111 | 20.162293 | |
| ENSG00000125384 | 5732 | PTGER2 | protein_coding | P43116 | FUNCTION: Receptor for prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). The activity of this receptor is mediated by G(s) proteins that stimulate adenylate cyclase. The subsequent raise in intracellular cAMP is responsible for the relaxing effect of this receptor on smooth muscle. | 3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a receptor for prostaglandin E2, a metabolite of arachidonic acid which has different biologic activities in a wide range of tissues. Mutations in this gene are associated with aspirin-induced susceptibility to asthma. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. | hsa:5732; | plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; prostaglandin E receptor activity [GO:0004957]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus [GO:0071380]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to nematode [GO:0009624]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570] | 12051958_PGE(2) receptors and synthesis in human gastric mucosa: perturbation in cancer 12149218_effects of PGE2 on monocyte-derived dendritic cells were mediated through increased cyclic adenosine monophosphate by 2 of the known PGE2 receptors, EP2 and EP4 12228765_Activation of prostaglandin E2-receptor EP2 and EP4 pathways induces growth inhibition in human gastric carcinoma cell lines. 12466123_Data show that down-regulation of prostaglandin E(2) receptor subtype EP(2) receptors represents a potential mechanism for neoplastic progression to an invasive phenotype. 12743126_shear activates cyclooxygenase-2, via a c-Jun N-terminal kinase2/c-Jun-dependent pathway, which in turn elicits downstream prostaglandin EP2 and EP3a1 receptor mRNA synthesis 12788892_Agonists of EP(1) and EP(2) significantly increased aromatase activity levels, which were decreased by the corresponding antagonists. Generally reflective of changes in aromatase protein expression and the pattern of mRNA expression. 12933667_increased histone H3 acetylation involving the EP2 receptor, protein kinase A, CREB, and CREB binding protein is responsible for PGE(2)-induced StAR gene activation in endometriotic stromal cells. 14517215_COX-2 induction by bradykinin in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells is mediated by the cyclic AMP response element through a novel autocrine loop involving endogenous prostaglandin E2, EP2 receptor, and EP4 receptor 14562138_Human corpus cavernosum and cultured smooth muscle cells express EP1, EP2 and EP3 receptors. 14699136_role of araomatic amino acids in i2 loop in Gs coupling 15044590_elevated EP2 receptor expression may facilitate the PGE(2)-induced release of proangiogenic factors in reproductive tumor cells via intracellular cAMP-mediated transactivation of the EGFR and ERK1/2 pathways 15347673_Endothelin-1-induced prostaglandin E2-EP2 and EP4 signaling regulates vascular endothelial growth factor production and ovarian carcinoma cell invasion 15539459_PGE2, via EP2 receptor, enhances PTEN function in lung fibroblasts to inhibit directional migration 15970595_PGE2 increases VEGF transcriptionally and involves the Sp-1 binding site via a cAMP-dependent mechanism involving EP2 and EP4 receptors 16267225_a novel proinflammatory and proamyloidogenic function for the PGE2 EP2 receptor is demonstrated in a model of familial Alzheimer's disease. 16461132_significantly reduced expression of PGE(2) receptors on nasal mucosa inflammatory leukocytes in the aspirin-sensitive compared with nonaspirin-sensitive rhinosinusitis patients 16607275_Together, the results suggest that the overexpression of the human EP2 receptor plays a significant role in the protumorigenic action of PGE2 in mouse skin. 16879213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16879213_prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 polymorphisms, prostaglandin-E receptor 2 polymorphisms, and C-reactive protein concentrations may have a role in atherothrombosis 17028262_These data indicate that PGE(2) inhibits fibroblast activation in primary lung fibroblasts via binding of EP2 receptor and production of cyclic AMP; inhibition of collagen I proceeds via activation of PKA. 17078003_These results suggest that the COX-2-PGE(2) pathway may be involved in IL-8 production in gastric epithelial cells. 17290397_EP2 mRNA was significantly higher in normal colon tissue compared with tumor tissue. 17384145_Selective stimulation of the EP2 receptor subtype, leading to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) transactivation via protein kinase A 17496729_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17525067_participates in placentation through EVT invasion by up-regulating PGE2 production and PGE2 receptor expression in first trimester extravillous trophoblasts 17533365_NB cells may lose responsiveness to PTGER2-mediated growth inhibition/apoptosis through epigenetic silencing of PTGER2 and/or disruption of downstream cAMP-dependent pathway during the neuroblastomagenesis. 17555711_treatment of LS174T cells with indomethacin causes a down regulation of EP2 prostanoid receptors 17611676_Results show co-expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 receptors EP1, 2 and 4 in non-small cell lung cancer cells concomitant with the synthesis of PGE2. 17728378_Role of EP2 receptor in mediating the PGE2 effect on stimulating cyst formation may have direct pharmacological implications for the treatment of polycystic kidney disease. 17877755_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18005048_Expression of prostaglandin E(2) receptors (EP(2), EP(3), EP(4)), prostaglandin D(2) receptor (DP(2)), prostanoid thromboxane A(2) receptor (TP) and to a lesser extent EP(1) were observed in several hair follicle compartments. 18086382_herpes simplex virus type 1 infected mature monocyte-derived dendritic cells demonstrated a dramatic down-regulation of the expression of the EP2 and EP4 receptors 18254372_PGE2 receptors were expressed in both NCI-H292 and human nasal epithelial cells. 18296611_results showed that EP2 is expressed in trigeminal neurons (58% of total neurons) and is co-expressed in TRPV(1)-positive neurons (64% of TRPV(1)-positive neurons. 18319253_CCR7 and the EP2/EP4 receptor signaling pathway are down-stream targets for COX-2 to enhance the migration of breast cancer cells toward LECs and to promote lymphatic invasion 18537828_Prostaglandin E(2), via the prostanoid receptor EP2 and subsequent cAMP elevation, downregulates mRNA and protein levels of protease-activated receptor-1 in human lung fibroblasts. 18666211_PTGER2 methylation was present with greater frequency in nonsmall cell lung cancer with EGFR mutation. 18790761_A new approach for blocking E-prostanoid receptor-mediated cell signaling using a soluble chimeric EP2 fragment, is described. 18792407_findings show the G(s)-coupled EP(2) receptor closes K(Ca)3.1 in lung mast cells and attenuates both chemokine- and PGE(2)-dependent lung mast cell migration 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18829529_PGE(2) induces angiogenesis in prostate cancer through EP2 and EP4. 18989535_Common polymorphisms of cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 receptor and increased risk for acute coronary syndrome in coronary artery disease. 18989535_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19050969_Overexpression of EP2 is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 19169646_Results suggest that prostaglandin E2 mainly induces the activation of beta(1)-integrins via the EP(2) receptor in human coronary arterial endothelial cells. 19273625_PGE2 acts via prostaglandin receptor EP2- and EP4-mediated signaling and cyclic AMP pathways to up-regulate IL-23 and IL-1 receptor expression. 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19407222_EP2 and EP4 receptor inhibition induces apoptosis of human endometriotic cells through suppression of ERK1/2, AKT, NFkappaB, and beta-catenin pathways and activation of intrinsic apoptotic mechanisms 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19542367_opposite regulation of proinflammatory IL-6 and prodestructive MMP-1 by PGE(2) via EP2 in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblasts 19582788_Prostaglandin E2 inhibits the proliferation of human gingival fibroblasts via the EP2 receptor and Epac 19782748_demonstrates that co-activation of the FP and EP2 receptors results in enhanced release of cAMP via FP receptor-G alpha(q)-Ca(2+)-calmodulin pathway by activating calcium sensitive adenylyl cyclase 3 isoform. 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19808686_Phosphatase and tensin homologue on chromosome 10 (PTEN) directs prostaglandin E2-mediated fibroblast responses via regulation of E prostanoid 2 receptor expression 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20018632_PGE2 potently inhibits secretion of IFN-alpha by TLR-activated plasmacytoid dendritic cells, an effect mainly mediated by PG receptors E-prostanoid 2 and E-prostanoid 4 20086108_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20200425_Our data imply potential roles of inflammatory reaction by PTGER2 upregulation in carcinogenic process to microsatellite instability -high colorectal cancer. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20304053_analysis of expression of serum vitamin D receptor, cyclooxygenase-2, and 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase in benign and malignant ovarian tissue and 25-hydroxycholecalciferol and prostaglandin E2 in ovarian cancer patients 20347274_EP2 is a novel transcriptional target of Wnt3a in dermal papilla cells of human scalp hair follicles 20357748_Observed induction of the PG receptors EP2 and IP in atherosclerotic femoral arteries in the arterial intima, medial layer, as well as the associated atherosclerotic plaque. 20382140_The mRNA levels of EP2 implicated pathways differed significantly in gliomas according to the histological type. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20484658_EP1 and EP4 subtypes of prostaglandin E receptors (but not EP2 and EP3 receptors) may be involved in regulation of paracellular permeability in differentiated Caco-2 cell cultures. 20516073_E prostanoid (EP) 2 and EP3 have roles in cAMP/protein kinase A- and PI3-K/Akt-dependent NF-kappaB activation during shear-induced interleukin-6 synthesis in chondrocytes 20551148_Prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype EP2 and EP4 regulated gene expression profiling in ciliary smooth muscle cells. 20587336_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20705717_Data suggest that early embryonic signals may regulate fetal-maternal crosstalk in the human endometrium by inducing CXCR4 expression via the PGE-PTGER2-mediated induction of the EGFR, PI3K and ERK1/2 pathways. 20889571_Data demonstrate that down-regulation of PTGER2 and consequent PGE2 resistance are both mediated by DNA hypermethylation; increased Akt signal transduction is a novel mechanism that promotes DNA hypermethylation during fibrogenesis. 21052031_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21081469_miR-16 and miR-21 are directly regulated by the transcription factor NF-kappaB and yet nicotine-promoted cell proliferation is mediated via EP2/4 receptors. 21111772_Data show that inhibition of PGE2 receptors EP2 and EP4 suppresses expression and/or activity of MMP1, MMP2, MMP3, MMP7 and MMP9 proteins and increases expression of TIMP1, TIMP2, TIMP3, and TIMP4 proteins. 21209948_PGE2 induces IL-6 in orbital fibroblasts through EP2 receptors and increased gene promoter activity 21419570_EP2 receptor FuEP2/Ex2 may have a role in suppressing endometrial cancer cell growth 22099390_This study suggested that antipsychotics showing association with PGE2-mediated respons. 22244821_morin inhibited the production of NO and PGE(2). 22276108_Neuroblastoma express all four forms of PGE(2) receptors. 22329897_Indomethacin has a potential antagonizing effect on human EP(2) receptors. 22551900_Single nucleotide polymorphism in PTGER2 associated with multiple adenomas. 22580611_Targeted interference of EP2/EP4 signal to RalA.GTP may provide benefit to patients diagnosed with advanced kidney cancer. 22706114_This review article presents a short overview of experimental approaches aimed at manipulation of signaling via EP2 and EP4 receptors that could have therapeutic utility. 22929011_Although EP2 methylation status is inversely correlated to expression levels in established breast cancer cell lines, we could not identify that such a correlation existed in tumour-associated stroma cells. 23048027_HB9 binds to the prostaglandin E receptor 2 promoter and inhibits intracellular cAMP mobilization in leukemic cells. 23069790_The expression of the EP2 receptor and Bcl-2 was significantly increased. 23242524_Loss of function of EP2- and EP4-mediated PGE2 signaling inhibits adhesion of human endometriotic epithelial and stromal cells through integrin-mediated mechanisms. 23337716_PGE(2) coordinates control of IL-23 release in a dose-dependent manner by differential use of EP(2) and EP(4) receptors in LPS-activated MoDCs. 23786281_Although human lung mast cells may express both EP2 and EP4 receptors, the principal mechanism by which PGE2 inhibits mediator release in mast cells is by activating EP2 receptors. 23861370_Data suggest that elevated PGE2 (prostaglandin E2) in peri-implantation uterine lumen stimulates conceptus PTGER2 expression, which in turn promotes trophoblast adhesion via integrins and synthesis/secretion of embryonic signal estradiol-17. 24146253_Elastogenesis is spatially regulated by PGE-EP4 signaling in the ductus arteriosus. 24471568_The 15-PGDH gene is a MiTF-CX target gene in cervical stromal cells and is down-regulated by PGE2 through EP2 receptors. 24561081_cyclic tensile force activates ERK1/2 and p38 MAP kinase signaling pathways, and induces COX-2 expression, which is responsible for the sequential PGE2 biosynthesis and release, and mediates the increase in BMP-2 expression at the transcriptional level. 24626807_PGE2 markedly enhanced Huh-7 cell invasion and migration ability by upregulating the expression level of Snail protein, and EP2 receptor played an important role in this process. 24728410_human albumin solution infusions may be used to reduce circulating PGE2 levels, attenuating immune suppression and reducing the risk of infection in patients with acutely decompensated cirrhosis or ESLD. 24812667_In Th17 cells, RORC repressed EP2 by directly silencing PTGER2 transcription, and knock down of RORC restored EP2 expression in Th17 cells. 24827772_In adjusted models, gestations were 3.3 days longer (95%CI 0.6, 6.0) for each interquartile range of PTGER2 DNA methylation. 24883443_Overexpression of EP2 was more observed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma than in the control group. Overexpression of EP2 ESCC tissues might play an important role in carcinogenesis and the progression of ESCC. 24980222_mediates inhibitory effect of Prostaglandin E2 on nasal fibroblast migration 25059824_EP2/cAMP/protein kinase A pathway mediates the stimulatory effect of PGEs on angiogenesis essential for tissue injury healing via the induction of CREB activity and VEGF expression. 25329458_data show a protective role for the PGE2 receptors EP(2) and EP(4) following osmotic changes, through the reduction of human mast cell activity caused by calcium influx impairment and MAP kinase inhibition. 25634217_Overall, our results demonstrate that p53 is a negative regulator of aromatase in the breast and its inhibition by PGE2 provides a novel mechanism for aromatase regulation in obesity and breast cancer. 25681680_EP2 receptors exhibit more constraints to mutations than DP receptors. 25828575_Intracellular EP2 prostanoid receptor promotes cancer-related phenotypes in PC3 prostate cancer cells. 26051534_Reduced EP2 receptor expression results in resistance to the antiproliferative effects of EP2 signaling in nasal polyp fibroblasts from subjects with AERD and support a role for EP2 signaling in the aberrant growth of nasal polyp tissue. 26538827_mPGES-1 is downregulated via EGR1 and has a role in caffeine inhibition on PGE2 synthesis of HBx hepatocytes 26560040_Altered expression of EP2 in patients with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease contributes to deficient induction of IL-1RI, reducing the capacity of IL-1beta to increase COX-2 and mPGES-1 expression, which results in low PGE2 production 27012192_that the expression of ERG in prostate cancer is linked to the expression of IL-6 mediated by the prostanoid receptor EP2 27230257_PGE2 produced by mesenchymal stem cells contributes to maintenance of self-renewal capacity through EP2 in an autocrine manner, and PGE2 secretion is down-regulated by cell-to-cell contact. 27321910_EP2 receptor activation protects against endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis through down-regulation of p53. 27377703_This is the first report that PGE2 -induced uPAR expression, which stimulates invasiveness of human gastric cancer AGS cells, is mediated by the EP2 receptor-dependent Src/EGFR/JNK1/2, Erk1/2/AP-1, and Src/EGFR/JNK1/2, Erk1/2/NF-kappaB cascades. 27616330_in breast cancer cells overexpression of S1P3 and its activation by S1P has pro-inflammatory and pro-metastatic potential by inducing COX-2 expression and PGE2 signaling via EP2 and EP4. 27636113_EP2 receptors seem to be able to distinguish endogenous ligands PGD2, PGE2 or prostaglandin F2alpha better than DP receptors. 28336329_These results indicate that the ICL2 region of the EP2 receptor is its potential interaction site with Galphas, and that the aromatic side chain moiety at position 143 is a determinant for the accessibility of the ICL2 to the Galphas protein. 28630103_EP2 and EP3 receptors are involved in tolerance induction through IL-10 production by tol-DCs. 28963072_this study shows that prostaglandin E2 restrains human Treg cell differentiation via E prostanoid receptor 2-protein kinase A signaling 29401596_Prostaglandin E2 suppresses hCAP18/LL-37 expression in human macrophages via EP2/EP4: implications for treatment of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. 29491476_COLEC12 integrates H. pylori, PGE2-EP2/4 axis and innate immunity in gastric diseases 30012671_a signaling circuit involving RIPK3 and PGE2 receptors enhances accumulation and immunosuppressive activity of myeloid-derived suppressor cells 30053598_Data indicates that PGE2 suppression of TNF-alpha by human monocytic cells occurs via EP2R and EP4R expression. However EP4Rs also control their own expression and that of EP2 whereas the EP2R does not affect EP4R expression. 30103548_EP receptor levels were enhanced in human PASMCs and in lung sections from PAH patients compared to controls. Thus, EP receptors represent a novel therapeutic target for treprostinil, highlighting key pharmacological differences between prostacyclin mimetics used in pulmonary arterial hypertension. 30835912_These results suggest that PGE2 regulates human brain endothelial cell migration via cooperation of EP2, EP3, and EP4 receptors. 30890164_Altered Prostaglandin E2-EP2 augmented the excessive inflammation of innate and adaptive immune cells in response to lipopolysaccharides or E. coli in chronic hepatitis B-acute-on-chronic liver failure. 30917001_EP2 and EP4 receptors play different roles in the regulation of COX-2 expression in human amnion fibroblasts. 31217077_a role for EP2/EP4 signaling in regulating IGF-1-induced cell proliferation, in which EP2/EP4 signaling represses IGF-1-induced GGCT expression, is reported. 31980713_The prostaglandin receptor EP2 determines prognosis in EP3-negative and galectin-3-high cervical cancer cases. 32313117_Prostaglandin EP2 receptor downstream of Notch signaling inhibits differentiation of human skeletal muscle progenitors in differentiation conditions. 32438662_Concerted EP2 and EP4 Receptor Signaling Stimulates Autocrine Prostaglandin E2 Activation in Human Podocytes. 32595209_Syntenin-1 promotes colorectal cancer stem cell expansion and chemoresistance by regulating prostaglandin E2 receptor. 32851536_The role of EP-2 receptor expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. 33011635_Expression of trophoblast derived prostaglandin E2 receptor 2 (EP2) is reduced in patients with recurrent miscarriage and EP2 regulates cell proliferation and expression of inflammatory cytokines. 33545665_Polymorphisms rs2745557 in PTGS2 and rs2075797 in PTGER2 are associated with the risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease development in a Tunisian cohort. 33786738_The differential functional coupling of phosphodiesterase 4 to human DP and EP2 prostanoid receptors stimulated with PGD2 or PGE2. 34529833_Prostaglandin E2 directly inhibits the conversion of inducible regulatory T cells through EP2 and EP4 receptors via antagonizing TGF-beta signalling. 34742290_Alpha-Synuclein, cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandins-EP2 receptors as neuroinflammatory biomarkers of autism spectrum disorders: Use of combined ROC curves to increase their diagnostic values. 34822808_Prostaglandin E2 EP receptors in cardiovascular disease: An update. 34886911_Identification of ACOT13 and PTGER2 as novel candidate genes of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease through whole exome sequencing. 34914140_The EP2 agonist, omidenepag, alters the physical stiffness of 3D spheroids prepared from human corneal stroma fibroblasts differently depending on the osmotic pressure. 35543087_Increased COX-2 after ureter obstruction attenuates fibrosis and is associated with EP2 receptor upregulation in mouse and human kidney. | ENSMUSG00000037759 | Ptger2 | 42.290080 | 0.7768116 | -0.364363282 | 0.25138500 | 2.10402275252 | 0.1469121750606188769872062493959674611687660217285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.33983685800242507957236171023396309465169906616210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 35.242405 | 8.078896 | 45.585119 | 10.368798 | |
| ENSG00000125814 | 63908 | NAPB | protein_coding | Q9H115 | FUNCTION: Required for vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;ER-Golgi transport;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport | This gene encodes a member of the soluble N-ethyl-maleimide-sensitive fusion attachment protein (SNAP) family. SNAP proteins play a critical role in the docking and fusion of vesicles to target membranes as part of the 20S NSF-SNAP-SNARE complex. This gene encodes the SNAP beta isoform which has been shown to be preferentially expressed in brain tissue. The encoded protein also interacts with the GluR2 alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate (AMPA) receptor subunit C-terminus and may play a role as a chaperone in the molecular processing of the AMPA receptor. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2017]. | hsa:63908; | extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; SNARE complex [GO:0031201]; synaptobrevin 2-SNAP-25-syntaxin-1a complex [GO:0070044]; soluble NSF attachment protein activity [GO:0005483]; syntaxin binding [GO:0019905]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; regulation of synaptic vesicle priming [GO:0010807]; SNARE complex disassembly [GO:0035494]; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0035249] | 33189936_A novel NAPB splicing mutation identified by Trio-based exome sequencing is associated with early-onset epileptic encephalopathy. | ENSMUSG00000027438 | Napb | 61.053961 | 0.8064482 | -0.310346159 | 0.20090621 | 2.38840996045 | 0.1222379031848043751118382260756334289908409118652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.30405739346678956058767084869032260030508041381835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 54.408633 | 7.017625 | 67.847848 | 8.425069 | |
| ENSG00000126001 | 11190 | CEP250 | protein_coding | Q9BV73 | FUNCTION: May be involved in ciliogenesis (PubMed:28005958). Probably plays an important role in centrosome cohesion during interphase. Recruits CCDC102B to the proximal ends of centrioles (PubMed:30404835). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28005958, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30404835}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell projection;Cilium;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Coiled coil;Cone-rod dystrophy;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Deafness;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a core centrosomal protein required for centriole-centriole cohesion during interphase of the cell cycle. The encoded protein dissociates from the centrosomes when parental centrioles separate at the beginning of mitosis. The protein associates with and is phosphorylated by NIMA-related kinase 2, which is also associated with the centrosome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. | hsa:11190; | centriole [GO:0005814]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; photoreceptor inner segment [GO:0001917]; photoreceptor outer segment [GO:0001750]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; centriole-centriole cohesion [GO:0010457]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; detection of light stimulus involved in visual perception [GO:0050908]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; non-motile cilium assembly [GO:1905515]; positive regulation of protein localization to centrosome [GO:1904781]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; protein localization to centrosome [GO:0071539]; protein localization to organelle [GO:0033365]; regulation of centriole-centriole cohesion [GO:0030997] | 12140259_Data show that the dissociation of C-Nap1 from mitotic centrosomes is regulated by localized phosphorylation rather than generalized proteolysis. 18851962_CEP135 acts as a platform protein for C-NAP1 at the centriole. 20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23070519_C-NAP1 and rootletin restrain DNA damage-induced centriole splitting and facilitate ciliogenesis. 24554434_Centlein complexes with C-Nap1 and Cep68 at the proximal ends of centrioles during interphase. 24695856_multisite phosphorylation precipitates centrosome disjunction at the onset of mitosis 24780881_A homozygous nonsense CEP250 mutation, in combination with a heterozygous C2orf71 nonsense mutation, causes an atypical form of Usher syndrome, characterised by early-onset sensorineural hearing loss and a relatively mild retinitis pigmentosa. 25660448_ASPP1/2 interacted with centrosome linker protein C-Nap1. Co-depletion of ASPP1 and ASPP2 inhibited re-association of C-Nap1 with centrosome at the end of mitosis. 28100636_C-NAP1-null cells were viable and had an increased frequency of premature centriole separation, accompanied by reduced density of the centriolar satellites, with reexpression of C-NAP1 rescuing both phenotypes. Centrosome amplification induced by DNA damage or by PLK4 or CDK2 overexpression was markedly reduced in the absence of C-NAP1. 29718797_Our data indicate that mutations of CEP250 can cause mild cone-rod dystrophy (CRD) and early-onset sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) in Japanese patients. Because the ophthalmological phenotypes were very mild, high-resolution retinal imaging analysis, such as AO, will be helpful in diagnosing CEP250-associated disease. 30459346_CEP250 mutation is associated with Usher syndrome. 30998843_Study identified a nonsense mutation (c.562C>T, p.R188*) in CEP250 in a consanguineous family with nonsyndromic retinitis pigmentosa (RP). The disruption of Cep250 resulted in severe impairment of retinal function and significant retinal morphological alterations a novel Cep250 knockin mouse line. 33109182_Involvement of NEK2 and its interaction with NDC80 and CEP250 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 34223797_Expanding the clinical phenotype in patients with disease causing variants associated with atypical Usher syndrome. 35729462_Circ_0060077 Knockdown Alleviates High-Glucose-Induced Cell Apoptosis, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Fibrosis in HK-2 Cells via miR-145-5p/VASN Pathway. | ENSMUSG00000038241 | Cep250 | 393.808092 | 0.9122734 | -0.132461915 | 0.18285741 | 0.52303316521 | 0.4695506802005298130353594387997873127460479736328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.68919988611175353465654325191280804574489593505859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 349.875504 | 48.971419 | 386.175440 | 53.993890 | |
| ENSG00000126216 | 10426 | TUBGCP3 | protein_coding | Q96CW5 | FUNCTION: Gamma-tubulin complex is necessary for microtubule nucleation at the centrosome. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Microtubule;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | Enables gamma-tubulin binding activity. Predicted to be involved in meiotic cell cycle; microtubule cytoskeleton organization; and mitotic cell cycle. Located in cytoplasm and microtubule cytoskeleton. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:10426; | centriole [GO:0005814]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; equatorial microtubule organizing center [GO:0000923]; gamma-tubulin complex [GO:0000930]; gamma-tubulin small complex [GO:0008275]; membrane [GO:0016020]; polar microtubule [GO:0005827]; spindle [GO:0005819]; gamma-tubulin binding [GO:0043015]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; cytoplasmic microtubule organization [GO:0031122]; meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051321]; microtubule nucleation [GO:0007020]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; single fertilization [GO:0007338]; spindle assembly [GO:0051225] | 19299467_Stability of the small gamma-tubulin complex (gamma tubulin/GCP2/GCP3) requires HCA66, a protein of the centrosome and the nucleolus. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20858683_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23886939_Authors show genetically that GCP3/Spc98 function is fully conserved with Alp6 across species but that functional differences exist between GCP2/Spc97 and Alp4. 26079448_This study demonstrated that Overexpression and Nucleolar Localization gcp3 in glioblastoma. 28851027_NMR secondary structure and interactions of recombinant human MOZART1 protein with its binding partner, GCP3, has been presented. 34515875_CircTUBGCP3 Contributes to the Malignant Progression of Rectal Cancer. | ENSMUSG00000000759 | Tubgcp3 | 250.075637 | 0.7324765 | -0.449145692 | 0.14230956 | 9.91650277412 | 0.0016380333517103634177053406162372084509115666151046752929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.01147936398984196471051433263710350729525089263916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 205.888786 | 28.150742 | 282.241781 | 38.659295 | |
| ENSG00000126254 | 79171 | RBM42 | protein_coding | Q9BTD8 | FUNCTION: Binds (via the RRM domain) to the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of CDKN1A mRNA. {ECO:0000250}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding | Enables RNA binding activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within negative regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and nucleus. Predicted to be part of ribonucleoprotein complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:79171; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; U4/U6 x U5 tri-snRNP complex [GO:0046540]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000398]; negative regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0048025] | 19170760_hnRNP K and RBM42 have a role in the maintenance of cellular ATP level in the stress conditions possibly through protecting their target mRNAs. | ENSMUSG00000036733 | Rbm42 | 362.768410 | 0.8298036 | -0.269158233 | 0.09668289 | 7.74440413082 | 0.0053879235922397981928266830209395266138017177581787109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.03043872181270205687364516222714883042499423027038574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 334.639523 | 20.420752 | 405.030927 | 24.405847 | |
| ENSG00000128050 | 10606 | PAICS | protein_coding | P22234 | FUNCTION: Bifunctional phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase and phosphoribosylaminoimidazole succinocarboxamide synthetase catalyzing two reactions of the de novo purine biosynthetic pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17224163, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2183217, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31600779}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Decarboxylase;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Ligase;Lyase;Multifunctional enzyme;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Purine biosynthesis;Reference proteome | PATHWAY: Purine metabolism; IMP biosynthesis via de novo pathway; 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide from 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxylate: step 1/2. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:31600779}.; PATHWAY: Purine metabolism; IMP biosynthesis via de novo pathway; 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxylate from 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole (carboxylase route): step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:31600779}. | This gene encodes a bifunctional enzyme containing phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase activity in its N-terminal region and phosphoribosylaminoimidazole succinocarboxamide synthetase in its C-terminal region. It catalyzes steps 6 and 7 of purine biosynthesis. The gene is closely linked and divergently transcribed with a locus that encodes an enzyme in the same pathway, and transcription of the two genes is coordinately regulated. The human genome contains several pseudogenes of this gene. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:10606; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; 5-amino-4-imidazole carboxylate lyase activity [GO:0043727]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase activity [GO:0004638]; phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthase activity [GO:0004639]; 'de novo' AMP biosynthetic process [GO:0044208]; 'de novo' IMP biosynthetic process [GO:0006189]; 'de novo' XMP biosynthetic process [GO:0097294]; GMP biosynthetic process [GO:0006177]; purine nucleobase biosynthetic process [GO:0009113] | 19850283_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 26140362_purine biosynthetic pathway enzymes PPAT and PAICS, as well as pyruvate kinase activity are increased in lung cancer 30121007_we show that PAICS, which catalyzes a critical step in purine biosynthetic pathway, is overexpressed and plays a role in BLCA cell proliferation, colony formation, and 3D spheroid invasion, suggesting a role in oncogenesis. 30641222_PAICS is hypomethylated in the lung adenocarcinoma tissues.PAICS is highly expressed in the lung adenocarcinoma tissues. 31624245_Combinatorial targeting of MTHFD2 and PAICS in purine synthesis as a novel therapeutic strategy. 32571877_Crystal structures of human PAICS reveal substrate and product binding of an emerging cancer target. 32632107_PAICS contributes to gastric carcinogenesis and participates in DNA damage response by interacting with histone deacetylase 1/2. 34173716_PAICS is related to glioma grade and can promote glioma growth and migration. 34323174_Regulating COX10-AS1 / miR-142-5p / PAICS axis inhibits the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer. 35285625_Evidence Supporting Substrate Channeling between Domains of Human PAICS: A Time-Course Analysis of (13)C-Bicarbonate Incorporation. 35331738_Multienzyme interactions of the de novo purine biosynthetic protein PAICS facilitate purinosome formation and metabolic channeling. | ENSMUSG00000029247 | Paics | 1157.282361 | 0.9467026 | -0.079016854 | 0.09249485 | 0.72915200858 | 0.3931581936683874456406329045421443879604339599609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.62148229325724979599243624761584214866161346435546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1171.123900 | 72.095060 | 1242.962909 | 76.608775 |
| ENSG00000128928 | 3712 | IVD | protein_coding | P26440 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the conversion of isovaleryl-CoA/3-methylbutanoyl-CoA to 3-methylbut-2-enoyl-CoA as an intermediate step in the leucine (Leu) catabolic pathway (PubMed:7640268). To a lesser extent, is also able to catalyze the oxidation of other saturated short-chain acyl-CoA thioesters as pentanoyl-CoA, hexenoyl-CoA and butenoyl-CoA (PubMed:7640268). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7640268}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;FAD;Fatty acid metabolism;Flavoprotein;Lipid metabolism;Mitochondrion;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Transit peptide | PATHWAY: Amino-acid degradation; L-leucine degradation; (S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA from 3-isovaleryl-CoA: step 1/3. | Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase (IVD) is a mitochondrial matrix enzyme that catalyzes the third step in leucine catabolism. The genetic deficiency of IVD results in an accumulation of isovaleric acid, which is toxic to the central nervous system and leads to isovaleric acidemia. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. | hsa:3712; | mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity [GO:0003995]; butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase activity [GO:0004085]; flavin adenine dinucleotide binding [GO:0050660]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase activity [GO:0008470]; branched-chain amino acid catabolic process [GO:0009083]; fatty acid beta-oxidation using acyl-CoA dehydrogenase [GO:0033539]; leucine catabolic process [GO:0006552] | 16376132_Replacement of the catalytic glutamate in either short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (SCAD) or isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase (IVD)with glycine resulted in a several-fold reduction in affinity for substrate. 17576084_Mutations of isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase gene is associated with isovaleric acidemia 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20519759_A child with isovaleric acidemia was subsequently found to harbour a known missense mutation (c.A1199G [p.Y371C]) and a novel 4-bp duplication (c.1148_1151dupGCTA [p.Y355X]) in the IVD gene. The former may be a founder mutation in the Chinese population. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22350545_All were homozygous for a single c.367 G > A (p.G123R) mutation. Despite the genetic homogeneity of this South African group, the clinical presentation varied, ranging from mental handicap and episodes of metabolic derangement to an asymptomatic state 22960500_A heterogeneous mutation spectrum in the IVD gene was identified in isovaleric acidemia patients in the United Arab Emirates. 23063737_study reports the first Saudi isovaleric acidemia patients from a consanguineous family with a novel transversion (p.G362V) and briefly discuss likely phenotype-genotype correlation of the disease in the Saudi population 25450250_kinetics and ligand binding of isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase 26018748_Our results have illustrated the heterogeneous mutation spectrum and clinical presentation of IVA in the Japanese patients 27904153_Nine novel isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase mutations have been found in a Spanish cohort with isovaleric acidemia. | ENSMUSG00000027332 | Ivd | 429.219070 | 0.8341305 | -0.261655062 | 0.10379032 | 6.34440366154 | 0.0117752188352055423697928304704873880837112665176391601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.05610073605819316383547246118723705876618623733520507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 354.292001 | 26.972982 | 426.839184 | 32.652474 |
| ENSG00000128989 | 10776 | ARPP19 | protein_coding | P56211 | FUNCTION: Protein phosphatase inhibitor that specifically inhibits protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) during mitosis. When phosphorylated at Ser-62 during mitosis, specifically interacts with PPP2R2D (PR55-delta) and inhibits its activity, leading to inactivation of PP2A, an essential condition to keep cyclin-B1-CDK1 activity high during M phase. May indirectly enhance GAP-43 expression. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21164014}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cytoplasm;Mitosis;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase inhibitor;Reference proteome | The 19-kD cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein plays a role in regulating mitosis by inhibiting protein phosphatase-2A (PP2A; see MIM 176915) (summary by Gharbi-Ayachi et al., 2010 [PubMed 21164014]).[supplied by OMIM, Feb 2011]. | hsa:10776; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; phosphatase inhibitor activity [GO:0019212]; potassium channel regulator activity [GO:0015459]; protein phosphatase 2A binding [GO:0051721]; protein phosphatase inhibitor activity [GO:0004864]; protein phosphatase regulator activity [GO:0019888]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; cell division [GO:0051301]; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000086]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; negative regulation of protein dephosphorylation [GO:0035308]; positive regulation of gluconeogenesis [GO:0045722]; positive regulation of glucose import [GO:0046326] | 11771749_Decreased levels of ARPP-19 and PKA in brains of Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease. 21509594_ARPP19 gene expression is decreased in follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma. 25547487_ARPP-19 may play a role in HCC pathogenesis through regulating cell proliferation. 25736597_Data show that micrRNA miR-320a directly targets cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein 19 (ARPP-19) and estrogen-related receptor gamma protein (ERRgamma) in breast cancer cell lines. 27380244_Study showed that ARPP-19 promoted both proliferation and metastasis of human glioma cells and the expression of ARPP-19 and CD147 in high-grade glioma was significantly higher than that in the low-grade glioma. 28613156_Together, the results suggest a complex antagonistic interplay between the control of ARPP-16 by MAST3 and PKA that creates a mechanism whereby cAMP mediates PP2A disinhibition. 31943339_The cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein 19 (ARPP19) was a direct target of miR-802 and could reverse the inhibitory function of miR-802. These data suggest that the IGFL2-AS1/miR-802/ARPP19 axis plays a critical role in the progression and metastasis of gastric cancer. 32077747_Long Noncoding RNA DLX6-AS1 Promotes the Progression in Cervical Cancer by Targeting miR-16-5p/ARPP19 Axis. | 871.713942 | 1.3401844 | 0.422431498 | 0.07944030 | 28.22166605613 | 0.0000001081867579801715776148133890330327311346536589553579688072204589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000211357035003720697280697911335511918196061742492020130157470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1004.846968 | 69.899103 | 752.622792 | 52.596697 | |||
| ENSG00000129173 | 79733 | E2F8 | protein_coding | A0AVK6 | FUNCTION: Atypical E2F transcription factor that participates in various processes such as angiogenesis and polyploidization of specialized cells. Mainly acts as a transcription repressor that binds DNA independently of DP proteins and specifically recognizes the E2 recognition site 5'-TTTC[CG]CGC-3'. Directly represses transcription of classical E2F transcription factors such as E2F1: component of a feedback loop in S phase by repressing the expression of E2F1, thereby preventing p53/TP53-dependent apoptosis. Plays a key role in polyploidization of cells in placenta and liver by regulating the endocycle, probably by repressing genes promoting cytokinesis and antagonizing action of classical E2F proteins (E2F1, E2F2 and/or E2F3). Required for placental development by promoting polyploidization of trophoblast giant cells. Acts as a promoter of sprouting angiogenesis, possibly by acting as a transcription activator: associates with HIF1A, recognizes and binds the VEGFA promoter, which is different from canonical E2 recognition site, and activates expression of the VEGFA gene. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15897886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16179649, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18202719, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22903062}. | 3D-structure;Activator;Cell cycle;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation | This gene encodes a member of a family of transcription factors which regulate the expression of genes required for progression through the cell cycle. The encoded protein regulates progression from G1 to S phase by ensuring the nucleus divides at the proper time. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. | hsa:79733; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000987]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity [GO:0001217]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cell cycle comprising mitosis without cytokinesis [GO:0033301]; chorionic trophoblast cell differentiation [GO:0060718]; fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048144]; hepatocyte differentiation [GO:0070365]; negative regulation of cytokinesis [GO:0032466]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; placenta development [GO:0001890]; positive regulation of DNA endoreduplication [GO:0032877]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002040]; trophoblast giant cell differentiation [GO:0060707] | 15897886_The similarities between E2F-7 and E2F-8 define a new subgroup of the E2F family, and further imply that E2F-7 and E2F-8 may act through overlapping mechanisms in mediating cell cycle control. 16179649_E2F8 may have an important role in repressing the expression of E2F-target genes in the S-phase of the cell cycle. 18202719_E2F7 and E2F8 act upstream of E2F1, and influence the ability of cells to undergo a DNA-damage response. 20068156_Analyses indicated that E2F8 could bind to regulatory elements of cyclin D1, regulating its transcription and promoting accumulation of S-phase cells. Findings suggest that E2F8 contributes to the oncogenic potential of HCC 23064264_The results identify E2F8 as a repressor and E2F1 as an activator of a transcriptional network controlling polyploidization in mammalian cells. 25892397_transcription factor E2F8 is involved in the polyploidization during mouse and human decidualization 26089541_E2F8 is overexpressed in Lung Cancer and is required for the growth of LC cells. E2F8 knockdown reduced the expression of UHRF1. These findings implicate E2F8 as a novel therapeutic target for LC treatment. 26992224_High E2F8 expression is associated with breast cancer. 27454291_E2F8-mediated transcriptional repression is a critical tumor suppressor mechanism during postnatal liver development 27683099_Results showed that E2F8 is up-regulated in metastatic prostate cancer and associated with poor prognosis. These results indicate that E2F8 is a crucial transcription regulator controlling cell cycle and survival in prostate cancer cells. 28270228_Study provides evidence that E2F8 functions as a proliferation-related oncogene in papillary thyroid cancer progression. Moreover, miR-144 appears to be a tumor suppressor through direct inhibition of E2F8. 28605876_E2F8 can shorten cisplatin induced G2/M arrest by promoting MASTL mediated mitotic progression in ER+ breast cancer cells, conferring drug resistance. 29615147_miR-223-5p suppressed NSCLC progression through targeting E2F8. 30144184_MiR-1258 may function as a suppressive factor by negatively controlling E2F8 30951518_Authors detected the expression of hsa_circ_0002468, miR-561, and E2F8 by using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analyses. 31471336_These results demonstrate that E2F8 modulates the growth of human colon cancer cells through promoting the NF-kappaB pathway. 31733123_NONO post-transcriptionally regulates the expression of cell proliferation-related genes by binding to their mRNAs, as exemplified by S-phase-associated kinase 2 and E2F transcription factor 8. 31929759_E2F8 regulates the proliferation and invasion through epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cervical cancer. 31990034_Carcinogenesis effects of E2F transcription factor 8 (E2F8) in hepatocellular carcinoma outcomes: an integrated bioinformatic report. 31995441_Cell cycle oscillators underlying orderly proteolysis of E2F8. 32703494_E2F transcription factor 8 promotes proliferation and radioresistance in glioblastoma. 32823614_E2F8 Induces Cell Proliferation and Invasion through the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Notch Signaling Pathways in Ovarian Cancer. 36241625_Opposing functions of circadian protein DBP and atypical E2F family E2F8 in anti-tumor Th9 cell differentiation. | ENSMUSG00000046179 | E2f8 | 51.860196 | 0.9716986 | -0.041419170 | 0.22769045 | 0.03304161285 | 0.8557604656661610409429385981638915836811065673828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.93525969215793003375125636011944152414798736572265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 50.757912 | 7.215607 | 52.454568 | 7.469033 | |
| ENSG00000129219 | 5338 | PLD2 | protein_coding | O14939 | FUNCTION: Function as phospholipase selective for phosphatidylcholine (PubMed:9582313). May have a role in signal-induced cytoskeletal regulation and/or endocytosis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97813, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9582313}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Hydrolase;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat | The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidic acid and choline. The activity of the encoded enzyme is enhanced by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and ADP-ribosylation factor-1. This protein localizes to the peripheral membrane and may be involved in cytoskeletal organization, cell cycle control, transcriptional regulation, and/or regulated secretion. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. | hsa:5338; | endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine-specific phospholipase D activity [GO:0070290]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; phospholipase D activity [GO:0004630]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway involved in phagocytosis [GO:0038096]; inositol lipid-mediated signaling [GO:0048017]; phosphatidic acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006654]; phospholipid catabolic process [GO:0009395]; regulation of vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0060627]; small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0007264]; synaptic vesicle recycling [GO:0036465] | 12149127_activation of phospholipases D1 and D2 by S1P regulates the phosphorylation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase and IL-8 secretion in Beas-2B cells 12374567_localizes to the plasma membrane of mast cells; stimulated by oleic acid 12446727_PLD2 activity is directly regulated by ADP-ribosylation factor 4, and this ARF4-mediated PLD2 activation stimulates AP-1-dependent transcription in the EGF-induced cellular response 12486109_PLD is regulated py phosphoinositides through the PH domain and the polybasic motif 12519790_PLD2 may play a key role in the regulation of agonist-induced endocytosis of the mu-opioid receptor 12601529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12601529_Phospholipase D(2) gene is a susceptibility locus for colorectal cancer in Japanese individuals. 12615079_elevated PLD activity generates survival signals allowing cells to overcome default apoptosis programs 12782287_PLD isozymes stimulate cell growth by repressing expression of p21 gene 14704231_phospholipase D2 was enriched in caveolae; PLD2 could be involved in MEK/ERK signaling cascades that are induced by the VEGF/VEGFR-2/PKC-delta pathway in endothelial cells 14718562_PLD2 functions at the plasma membrane to facilitate endocytosis of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. 15052337_The phospholipase D2 possesses a PH domain, activation by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-disphosphate (PIP2) involves binding to a conserved cluster of basic residues. 15052340_Translocation of PLD2 to EGF-induced membrane ruffles has been observed in HeLa cells when coexpressed with PIP kinase Ialpha. 15210717_phospholipase D isozymes mediate EGCG-induced COX-2 expression through PKC and p38 in immortalized astroglial line and normal astrocyte cells 15282299_findings provide the first description of a mechanism for activation phospholipase D2 in a physiological setting and of a role for Fyn and Fgr in Fc epsilon RI-mediated signaling. 15548524_an increase in local membrane monomeric tubulin concentration inhibits PLD2 activity 15665518_ANP recruits a signal pathway associated with p38 MAPK, NHE-1 and PLD responsible for ROS production, suggesting a possible role for ANP as novel modulator of ROS generation in HepG2 cells 15798205_Phospholipase D2 (PLD2) enhances PKCzeta activity through direct interaction in a lipase activity-independent manner. 15919668_EWS-Fli1 may play a role in the regulation of PDGF-induced tumor proliferation-signaling enzymes via PLD2 expression in Ewing sarcoma cells 16118212_intracellular unsaturated acyl-CoA derivatives destabilize ABCA1 by activating a PLD2 signaling pathway 16341931_These results suggest that intact phosphorylation sites within the MARCKS ED are required for PLD activation and influence both membrane-cytoskeletal organization and cell viability. 16407827_Y(169) & Y(179) are in 2 consensus sites in PLD2 mediating SH2 interaction with Grb2. They are needed for recruiting Sos, but only overexpression of the PLD2 Y179F mutant resulted in more Ras activity, p44/42(Erk) phosphorylation & enhanced DNA synthesis. 16622417_PLD functions as a GTPase activating protein (GAP) through its phox homology domain (PX), which directly activates the GTPase domain of dynamin and increased epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) endocytosis at physiological EGF concentrations. 16824927_Data show that the G-->A (Gly901Asp) mutation of the human PLD2 gene results in catalytic inactivation of the encoded protein. 16873675_demonstration of the involvement of PLD1 and PLD2 and its enzymatic activity toward chemokines in the key physiologic process of leukocyte migration 16964281_gene expression is increased by EWS.Fli-1 and FLI-1 by binding to an erythroblast transformation-specific domain of the PLC2 promoter 17486115_Our findings establish a crucial role for PLD2 in the coupling of extracellular signals to Sos-mediated Ras activation, and provide new insights into the spatial coordination of this activation event. 17486117_Thus, LFA-1 acts through PLD2 to reshape the pattern of Ras activation downstream of the TCR 17627030_Plays a major role in promoting HIV-1 long terminal repeat transactivation and virus replication. 17640750_These results demonstrate for the first time that PLD1 and PLD2 isozymes enhance cobalt chlorde-induced COX-2 expression through differential signaling pathways in astroglioma cells. 17914593_Elevated phospholipase D2 is associated with colorectal carcinoma 17977756_Data suggest that recombinant human phospholipase D2 alone cannot induce apoptosis in HL-60 cells, but it can potentiate the apoptosis of HL-60 cells induced by camptothecin. 17986621_These findings indicate the involvement of phospholipase D activation in hBD-2 up-regulation in gingival epithelial cells. 18296444_Protein kinase C-epsilon regulates sphingosine 1-phosphate-mediated migration of human lung endothelial cells through activation of phospholipase D2, protein kinase C-zeta, and Rac1 18344600_depletion of phospholipase D2 inhibited motility more severely, essential for the maintenance of keratocyte-like locomotion of NBT-II cells, presumably by regulating the actin cytoskeleton. 18423386_Data suggest that PLD2 is an early player upstream of the Ras-ERK1/2-IL-2 pathway in T-cells via phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol production. 18432522_we present evidence for the presence of both PLD1 and PLD2 in platelets and indicate a role in platelet activation. 18523140_Expression of active PLD2 enhances processes favorable to lymphoma cell metastasis, whereas expression of inactive PLD2 inhibits metastasis. 18625302_The study results suggest that PLD2 is a new substrate of Cdk5 and that the phosphorylation of PLD2 by Cdk5 is involved in epidermal growth factor-dependent insulin secretion. 18694819_Phospholipase D2 is cleaved at two or three sites in the front of N-terminus and maintained anti-apoptotic potency in spite of its cleavage during apoptosis. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19366706_These results demonstrate a role of PLD in hyperoxia-mediated IQGAP1 activation through Rac1 in tyrosine phosphorylation of Src and cortactin, as well as in p47(phox) translocation and reactive oxygen species formation in human lung endothelial cells. 19519662_These findings indicate that the agonist-selective PLD2 activation plays a key role in the regulation of NADH/NADPH-mediated ROS formation by opioids. 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19666113_ARF6 protein regulates mu-opioid receptor trafficking and signaling via PLD2 activation and hence affects the development of opioid receptor desensitization and tolerance. 19707939_Inhibited PLD1&2 by siRNA and determined the activity of formyl peptide receptors. Depletion of PLD1&2 resulted in a marked reduction of formyl peptide receptor activity due to inhibited ERK1/2 phosphorylation and cAMP level reduction. 19864325_Epidermal growth factor stimulation lysophosphatidi acid production in human ovarian cancer in a manner that requires PLD2. 19896495_Data show that there is a functional relationship between phospholipases D1/2 and MAP kinases in the human HeLa carcinoma cell line. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20147969_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20176813_PLD2 activity is low in the breast cancer cell line MCF-7 because it is kept downregulated by tyrosyl phosphorylation of Y(296) by EGFR kinase. 20188462_Platelet-derived growth factor PLD2 expression via NFkappaB does not enhance the invasiveness of breast cancer cells. 20410302_IL-8 reverses an mTOR/S6K-led down-regulation of PLD2 expression and enables PLD2 to fully function as a facilitator for cell migration 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20647543_Data suggest that highly mobile cells like macrophages use all signaling machinery available to them in phospholipase D2-induced chemotaxis, which sets them apart from fibroblasts, cells normally nonmobile that rarely become migratory. 20711340_PLD isozyme acts as a novel transcriptional target and positive feedback regulator of Wnt signaling, and then promotes Wnt-driven anchorage-independent growth of colorectal cancer cells. 20733000_Thr566 of PLD2 is directly phosphorylated by PKCdelta, and PLD2 mutation in this region prevents PLD2 activation, PLD2 translocation to the edge of lamellipodia, Rac translocation, and cell spreading after integrin activation 21147981_The results of this study pointed to PLD2 as key modulators of Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. 21276418_REVIEW: aquaporin 3's role and interaction with phospholipase D2 21308979_CHDH and PLD2 as novel candidate genes, the nucleotide variants of which could be associated with the risk of tooth agenesis. 21378159_activated cells PLD2 affects Rac2 in an initial positive feedback, but as Rac2-GTP accumulates in the cell, this constitutes a 'termination signal' leading to PLD2 inactivation. 21414324_A high level of cell invasiveness of cancer cells can be explained for the first time by combined high JAK3/PLD2 phosphorylation and activity involving PLD2's Y415 residue, which might constitute a novel target to inhibit cancer cell invasion. 21440060_The PX domain of PLD2 mediates the interaction and has a GEF-like activity for RhoA, which contributes to stress fiber formation. 21760893_Host cell PLD1 and PLD2 accompanied A. fumigatus conidia during internalization. 21854185_The rhPLD2 may suppress the chronic inflammatory reaction through down-regulating PKC expression and STAT1/STAT5a activity in the lung. The rhPLD2 may be a suitable therapeutic target for asthma. 21944249_the C-terminal domain of PLD2 can regulate Casein Kinase II by accelerating Casein Kinase II beta degradation. 22094461_how PLD2 participates in cell differentiation 22504301_PLD acts as an important regulator in Bcl-2 expression by activating STAT3 involving the phosphorylation of Ser727 through the PLA(2)/G(i)/ERK1/2, RhoA/ROCK/p38 MAPK, and Rac1/p38 MAPK pathways. 23213138_FIC1 signals to FXR via a signaling pathway including PLD2 and PKCzeta 23238254_Data indicate that the invasive phenotype of MDA-MB-231 cells is mediated by phospholipase D2 (PLD2) under direct regulation of both Janus kinase 3 (JAK3) and tepidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). 23404507_analysis of the JAK-Fes-phospholipase D signaling pathway that is enhanced in highly proliferative breast cancer cells 23649737_the non-synonymous Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms (nsSNPs) of PLD2 gene and its variations in different populations to understand its role in hypertension. 23723068_Data indicate that after P2Y6 receptor stimulation both phospholipase D (PLD) and DGKzeta enzymes are responsible for producing phosphatidic acid (PA). 23752189_PLD2 has a central role in the development, metastasis and level of aggressiveness of breast cancer 24103483_PlD1 and PLD2 play roles in cell migration, invasion and metastasis. [review] 24164897_Findings indicate that phosphatidic acid (PA) production by PLD2 determines the output of ERK1/2 in cancer cell growth factor signaling. 24257753_Data indicate that phospholipase D2 (PLD2) promotes autophagy through regulation of Akt in glioblastoma cells. 24270883_the present study demonstrated the clinical significance of miR-203 in gliomas and suggested that miR-203 was able to inhibit the proliferation and invasion of glioma cells, partially at least via suppressing the protein expression of PLD2. 24618697_Phospholipase D is involved in the formation of Golgi associated clathrin coated vesicles in human parotid duct cells 24637612_Syntenin-ALIX exosome biogenesis and budding into multivesicular bodies are controlled by ARF6 and PLD2. 24650665_Inhibition of PLD2 ameliorated ABETA-induced reduction of soluble amyloid precursor protein alpha secretion. 24947526_Demonstrate a novel role for endothelial PLD2 in the survival and migration of ECs under hypoxia via the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and in pathological retinal angiogenesis and tumor angiogenesis in vivo. 24956203_PLD1 and PLD2 mutants inhibit very-low-density lipoprotein-induced aldosterone production in HAC15 cells. 24990944_Out of these myriads of functions, PLD is becoming recognized as a major player in cell migration, cell invasion, and cancer metastasis. 25064843_PLD2 downregulation causes senescence through the p53-p21(Cip1/WAF1) pathway by stimulating ROS production, which is induced by CK2 inhibition 25065577_Inhibition of PLD2 accelerated the accumulation of MxA in foci as early as 30 min postinfection. .. PLD facilitates the rapid endocytosis of influenza virus, permitting viral escape from innate immune detection 25172550_Results indicate distinctive roles of phospholipase D PLD1 and PLD2 isoforms in pathological conditions in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). 25197053_PLD2, but not PLD1, directly binds to the C terminus of TREK1 and TREK2. 25308783_A 3D model of the PLD2 by combining homology and ab initio 3 dimensional structural modeling methods, and docking conformation, is reported. 25354038_PLD2 expression regulates formation of Golgi tubules in Hela cells. 25432699_These results suggest that PLD2 expression in colon cancer cells is up-regulated via HIF1-alpha in response to hypoxic stress and underscores the crucial role of HIF1-alpha-induced PLD2 in tumor growth. 25475140_Knockdown of PLD2 induces autophagy in colorectal cancer cells. 25523098_Ectopic expression of PLD1 or PLD2 in human glioma U87 cells increased the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protein. 26124282_PLD2-mediated production of phosphatidic acid contributed to the control of EGFR exposure to ligand through a multipronged transcriptional and posttranscriptional program during the out-of-control accumulation of EGFR signaling in cancer cells. 26611735_PLD2 protein itself interacts with HIF-1alpha, prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) and VHL to promote degradation of HIF-1alpha via the proteasomal pathway independent of lipase activity. 26695710_PLD2 is involved into pathogenesis of a vast array of human diseases, and as such it can be targeted for therapy. (Review) 26781944_Slug is a positive regulator, and Snail a negative regulator, of PLD2 expression. 26818087_PLD2 functions as a key mediator in the VEGF-mediated angiogenic functions of endothelial cells. 27280401_Data suggest that elevated membrane tension acts through phospholipase D2 (PLD2) and the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2) to limit actin nucleation. 27510034_results suggest that the small GTPase RalA plays an important role in promoting invagination and trafficking of caveolae, not by potentiating the association between Cav-1 and FilA but by stimulating PLD2-mediated generation of phosphatidic acid. 28087476_Suggest PLD expression in high grade serous ovarian carcinoma may have a role in mediating progression to effusions and chemoresistance. 28656282_AQP3 siRNA and PLD2 siRNA significantly downregulated the mRNA and protein levels of AQP3 and PLD2 in the A431 cells; inhibiting proliferation and promoting apoptosis in vitro. 28831159_these findings identify a novel pathway through which the lipid signaling enzyme PLD2 regulates blood pressure, creating implications for on-going therapeutic development of PLD small molecule inhibitors. Finally, we show that the human PLD2 polymorphism does not trigger eNOS loss, but rather creates another effect, suggesting altered functioning for the allele. 29656494_High PLD2 expression is associated with atherosclerotic plaques. 29660846_Data show that phospholipase D2 (PLD2)-produced phosphatidic acid (PA) promoted cell invasion through the the expression of angiogenin (ANG) in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) cells. 30091007_High Expression of PhospholipaseD2 Induced by Hypoxia Promotes Proliferation of Colon Cancer Cells through Activating NF- kappa Bp65 Signaling Pathway. 30305726_we demonstrate that tumor cell-secreted PLD2 contributes to tumor development by modifying the microenvironment, making it a possible therapeutic target for cancer treatment. This mechanism may also explain the high levels of Wnt pathway activation in colon cancer. 30369483_Here, expressed were human PLD1 and human PLD2 in Drosophila and the study found that while reconstitution of human PLD1 is able to completely rescue retinal degeneration in a loss of function dPLD mutant, human PLD2 was less effective in its ability to mediate a rescue. 31673104_PLD2 expression correlates with increasing Gleason score to GS8. PLD2 inhibition has the potential to reduce prostate cancer (PCa) progression. 32327488_Phospholipase D2 restores endothelial barrier function by promoting PTPN14-mediated VE-cadherin dephosphorylation. 32661773_Increased phospholipase D activity contributes to tumorigenesis in prostate cancer cell models. 32687545_PLD2-PI(4,5)P2 interactions in fluid phase membranes: Structural modeling and molecular dynamics simulations. 32800947_Prostate cancer-derived exosomes promote osteoblast differentiation and activity through phospholipase D2. 33495125_Structure and regulation of human phospholipase D. 33927069_Identification and functional analysis of a novel phospholipase D2 gene mutation associated with familial systemic lupus erythematosus.', trans 'PLD2. 34471223_Phospholipase D2 is a positive regulator of sirtuin 1 and modulates p53-mediated apoptosis via sirtuin 1. 36362078_Exosome Secretion and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Ovarian Cancer Are Regulated by Phospholipase D. | ENSMUSG00000020828 | Pld2 | 73.433076 | 0.7796698 | -0.359064922 | 0.45533008 | 0.61126808552 | 0.4343107526802255646813932798977475613355636596679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.65891106496558904392912836556206457316875457763671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 62.992269 | 18.295491 | 81.450669 | 23.511398 | |
| ENSG00000129255 | 9526 | MPDU1 | protein_coding | O75352 | FUNCTION: Required for normal utilization of mannose-dolichol phosphate (Dol-P-Man) in the synthesis of N-linked and O-linked oligosaccharides and GPI anchors. {ECO:0000250}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Congenital disorder of glycosylation;Disease variant;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | This gene encodes an endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein that is required for utilization of the mannose donor mannose-P-dolichol in the synthesis of lipid-linked oligosaccharides and glycosylphosphatidylinositols. Mutations in this gene result in congenital disorder of glycosylation type If. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008]. | hsa:9526; | endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; dolichol-linked oligosaccharide biosynthetic process [GO:0006488]; oligosaccharide biosynthetic process [GO:0009312]; protein folding [GO:0006457] | 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22363504_Cystinosin, MPDU1, SWEETs and KDELR belong to a well-defined protein family with putative function of cargo receptors. 29671116_These experiments also confirmed that protein levels of CEACAM-1, which functions in cell adhesion, is dependent on LLO biosynthesis in vivo. Kato III cells and the MPDU1-rescued Kato IIIM cells therefore provide a novel model to examine the consequences of defective LLO biosynthesis both in vitro and in vivo. | ENSMUSG00000018761 | Mpdu1 | 215.358307 | 0.8885059 | -0.170546719 | 0.15182743 | 1.25826540217 | 0.2619796818287452033757745084585621953010559082031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.49046535311965983039428351730748545378446578979492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 199.247505 | 20.075534 | 225.216470 | 22.545001 | |
| ENSG00000129559 | 4738 | NEDD8 | protein_coding | Q15843 | FUNCTION: Ubiquitin-like protein which plays an important role in cell cycle control and embryogenesis via its conjugation to a limited number of cellular proteins, such as cullins or p53/TP53 (PubMed:9694792, PubMed:10318914, PubMed:10597293, PubMed:11953428, PubMed:15242646, PubMed:14690597). Attachment of NEDD8 to cullins is critical for the recruitment of E2 to the cullin-RING-based E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex, thus facilitating polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of cyclins and other regulatory proteins (PubMed:9694792, PubMed:10318914, PubMed:10597293, PubMed:11953428, PubMed:20688984). Attachment of NEDD8 to p53/TP53 inhibits p53/TP53 transcriptional activity (PubMed:15242646). Covalent attachment to its substrates requires prior activation by the E1 complex UBE1C-APPBP1 and linkage to the E2 enzyme UBE2M (PubMed:14690597). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10318914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10597293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11953428, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14690597, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15242646, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20688984, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9694792}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Direct protein sequencing;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation pathway | Enables ubiquitin protein ligase binding activity. Acts upstream of or within protein neddylation. Located in cytosol and nucleoplasm. Biomarker of Parkinson's disease and malignant astrocytoma. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:4738; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein tag [GO:0031386]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; modification-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0019941]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; protein modification process [GO:0036211]; protein neddylation [GO:0045116]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of proteolysis [GO:0030162]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] | 11953428_NEDDylation is required for conjugation and processing of p105 by SCF(beta-TrCP) following phosphorylation of the molecule 12504025_p120(CAND1) selectively binds to unneddylated CUL1 and is dissociated by CUL1 neddylation 12554766_Disruptions in the NEDD8 pathway provide a mechanism by which breast cancer cells acquire antiestrogen resistance while retaining expression of ERalpha. 12646924_structure and mutational analysis of human APPBP1-UBA3, the heterodimeric E1 enzyme for NEDD8 12740388_Conservation in the mechanism of Nedd8 activation by the AppBp1-Uba3 heterodimer. 12759363_results suggest a unique role for NEDD8-specific protease 1(DEN1) in regulating the modification of cullin 1 by Nedd8 protein 14676825_An analysis of the NEDD8 modification on beta-TrCP ubiquitin ligase was made. 14690597_Data report the structure of the quaternary complex between human APPBP1-UBA3, a heterodimeric E1, its ubl NEDD8, and ATP. 15694336_crystal structure of a complex between the C-terminal domain from NEDD8's heterodimeric E1 (APPBP1-UBA3) and the catalytic core domain of NEDD8's E2 (Ubc12) 16735510_ubiquitin ligase of EGFR, namely c-Cbl, also mediates receptor modification with the ubiquitin-like molecule Nedd8 16861300_Results describe the regulation of neddylation and deneddylation of cullin1 by Nedd8 in SCFSkp2 ubiquitin ligase by F-box protein and substrate. 16979187_Data show that NEDD8 and ubiquitin have similar conformational fluctuation in the evolutionary conserved enzyme-binding region and contain a structurally similar locally disordered conformer (I) in equilibrium with the basic folded conformer (N). 17098746_FBXO11 promotes the Neddylation (NEDD8) of p53 and inhibits its transcriptional activity 17119158_NEDD8 and ubiquitin function in a redundant manner in controlling receptor endocytic pathways. 17132228_NEDD8 modification of Cul2 has a role in the sequential activation of the ECV E3 ubiquitin ligase complex 17660949_Up-regulation of the NEDD8 conjugation is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma 17935801_A new molecular interaction between wild-type ataxin-3 and NEDD8, using in vitro and in situ approaches, is reported. 18096514_These results illustrate the regulatory mechanisms by which AICD transcriptional activity might be regulated via covalent conjugation with Nedd8. 18264111_The basis for Ubiquitin-like proteins (UBL) selection by UBL conjugating enzyme 12 (Ubc12), which is specific for the neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated protein 8 (NEDD8). 18274552_These studies identify a novel and specific role of the NEDD8 pathway in protecting a subset of ribosomal proteins from destabilization. 18323857_NEDD8 acts as a 'molecular switch' defining the functional selectivity of VHL. 18652489_X-ray crystallographic analysis of APPBP1-UBA3-NEDD8 shows that APPBP1-UBA3's preference for NEDD8's Ala72 appears to be indirect, due to proper positioning of UBA3's Arg190. 18723677_SCF may be subject to autoinhibitory regulation, in which Nedd8 conjugation acts as a molecular switch to drive the E3 into an active state by diminishing the inhibitory ECTD x ROC1 interaction 18805092_Study reports striking conformational rearrangements in the crystal structure of NEDD8~Cul5(ctd)-Rbx1 and SAXS analysis of NEDD8~Cul1(ctd)-Rbx1 relative to their unmodified counterparts. 18826954_SCCRO recruits Ubc12 approximately NEDD8 to the CAND1-Cul1-ROC1 complex but that this is not sufficient to dissociate or overcome the inhibitory effects of CAND1 on cullin neddylation 18851830_diverse effects of Nedd8 conjugation underscore the complexity of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase regulation and suggest that modification of other ubiquitin ligases with ubiquitin or ubiquitin-like proteins may likewise have major functional consequences 19245792_The mechanism of poly-NEDD8 chain formation on Cullin-1 using a complete in vitro reconstituted NEDD8 conjugation system was shown. 19281774_NEDD8 expression level is higher in the peripheral blood of HIV patients developing lipodystrophy 19713960_identify NEDD8 as a crucial regulator of L11 RP signalling to p53. A decrease in L11 NEDDylation during nucleolar stress causes relocalization of L11 from the nucleolus to the nucleoplasm. 19784069_Data show that the stability of MDM2 is regulated by NEDD8 pathway and identify NEDP1 that deneddylates MDM2, resulting in MDM2 destabilization concomitant with p53 activation. 20603103_the Nedd8 pathway plays an important role in regulating the actin cytoskeleton and cellular morphology. 20688984_CHBP is an inhibitor of the ubiquitination pathway; it deamidated Gln40 in ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like protein NEDD8 in vitro and during Burkholderia infection; Cif deamidated NEDD8, abolishing activity of neddylated Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases 20850415_EPEC Cif interacts with NEDD8 and interferes with SCF (Skp1-Cullin1-F-box protein) complex ubiquitin ligase function. 21169563_The steady-state repertoire of human SCF ubiquitin ligase complexes does not require ongoing Nedd8 conjugation 21193393_NEDD8 is an ancillary player to regulate the stability of HIF-1alpha 21316600_review the NEDD8 conjugation cascade derived from functional studies in genetic model organisms, structural insights from crystallographic studies, biochemical studies identifying a growing list of NEDD8 substrates with oncogenic implications 21399617_Study report that USP21 cleaves Ub polymers, and with reduced activity also targets ISG15, but is inactive against NEDD8. 21474709_findings suggest that TRIM40 inhibits NF-kappaB activity via neddylation of inhibitor of nuclear factor kappaB kinase subunit gamma and that TRIM40 prevents inflammation-associated carcinogenesis in the gastrointestinal tract 22004789_In cells, NEDD8 overexpression leads to this type of NEDDylation by increasing the concentration of NEDD8, whereas proteasome inhibition has the same effect by depleting free ubiquitin. 22069333_E1-E2 interactions in ubiquitin and Nedd8 ligation pathways 22081073_The studies provide insights on how nucleolar stress through L11 and NEDD8 can activate the transcriptional activity of p53. 22095636_Mdm2/NEDD8/HuR regulatory framework is essential for the malignant transformation of tumor cells. 22370482_Decrease in free ubiquitin levels under stress allows NEDD8 to be conjugated through Ube1. 22466964_These results uncover an unexpected and conserved role for NEDD8 in linking cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases ubiquitin ligase function to the p97 pathway. 22502714_High NEDD8 is associated with melanoma. 22584050_XIAP does not function as a NEDD8-E3 ligase for caspase-7 in vivo 22612509_In the present study, the proportions of intranuclear inclusion positive for NEDD8, NUB1 and SUMO-1 were significantly lower in glial cells than in neurons. 22691497_We report the crystal structures of two Cif/NEDD8 complexes, revealing a conserved molecular interface that defines enzyme/substrate recognition. 22767593_Deconjugation of Nedd8 from Cul1 is directly regulated by Skp1-F-box and substrate, and the COP9 signalosome inhibits deneddylated SCF by a noncatalytic mechanism. 22836579_NEDD8 modifies transcription factor E2F-1. 22895816_these results indicate that NAE1/APP-BP1 and NEDDylation are invovled in modulating p53 activity and regulating its role in the response of cells to ionizing radiation 23001041_Data indicate that overexpression of SENP8, a NEDD8-specific cysteine protease, resulted in deNEDDylation of E2F1 and promoted its transactivation activity at the p73 gene. 23105008_these findings suggest that once Rub1/Nedd8 is channeled into ubiquitin pathways, it is recognized essentially like ubiquitin. 23118980_a new regulatory mechanism of RCAN1 function 23175788_present a view of how a bacterial deamidase effector, cycle-inhibiting factor homolog in Burkholderia pseudomallei, recognizes its host targets, ubiquitin (Ub) and Ub-like NEDD8, and catalyzes site-specific deamidation 23209320_Neddylation is achieved via a multienzyme process wherein SENP8 enables cleavage of the Nedd8 precursor and promotes Nedd8 conjugation to the Cullin-RING ligases. 23246961_More importantly, RPS14 was specifically modified with NEDD8 and hCINAP inhibited RPS14 NEDDylation by recruiting NEDD8-specific protease 1 23290524_c-Cbl conjugates neural precursor cell-expressed, developmentally downregulated 8 (NEDD8), a ubiquitin-like protein, to TbetaRII at Lys556 and Lys567. 23300442_These studies demonstrate that disrupting host NEDD8 cascades presents a novel antiretroviral therapeutic approach enhancing the ability of the immune system to combat HIV. 23394999_histone H4 was polyneddylated in response to DNA damage, and NEDD8 was conjugated to the N-terminal lysine residues of H4 23812220_Our results suggest that NEDD8 may play an important role in the control of proliferation and differentiation of human placenta throughout pregnancy. 24019527_In coordination with the P97-UFD1-NPL4 complex (P97(UFD1/NPL4)), NUB1L promotes transfer of NEDD8 to proteasome for degradation. 24245672_Protein neddylation with NEDD8 protein plays an important role in HIV-1 and HIV-2 infection. 24634510_NEDD8 negatively regulates the DNA damage repair process through suppression of the ubiquitylation of H2A and gammaH2AX, which further blocks the recruitment of the damage response protein BRCA1. 24949976_Study reports the structure of a trapped RING E3-E2 approximately UBL-target intermediate representing RBX1-UBC12 approximately NEDD8-CUL1-DCN1, which reveals the mechanism of NEDD8 ligation and how a particular UBL and acceptor lysine are matched by a multifunctional RING E3. 25229838_E1 (NAE1 and UBA3) and E2 (UBC12) enzymes, as well as global NEDD8 conjugation, were upregulated in over 2/3 of human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma 25349211_SCCRO3 functions as a tumor suppressor by antagonizing the neddylation activity of SCCRO 25452302_a role of Nedd8 in regulating caspase-1 activation following inflammasome activation 25655932_In endothelial dysfunction, HDAC2 levels were reciprocally regulated by ectopic expression of NEDD8 and the de-NEDDylating enzyme SENP8. 25782162_we report that MLN4924 (NEDD8 enzyme inhibitor ) specifically inhibited protein neddylation, inactivated cullin-RING E3 ligase (CRL), the best-known neddylation substrate, and induced the accumulation CRL substrates in lymphoma cells. 25918018_This work sheds new light on the roles of NEDD8 lysines on neddylation cascades and provides a dominant negative mutant for the study of neddylation and its biological functions. 26003431_findings add novel evidence showing, for what we believe the first time, that NEDD8-mediated neddylation is required for normal human endometrial functions 26364603_MKK7 undergoes neddylation in human breast cancer cells 26632597_Nedd8(Q40E) cannot induce the same structural effect on Cul1-Rbx1 as wild-type Nedd8. 27086113_Neddylation of Smurf1 activates its ubiquitin ligase activity and Smurf2 exerts Nedd8 ligase activity. This study provided new clues of Smurf2 activation regulation. 27381497_NEDD8-mediated neddylation promotes stress granule assembly. 27756846_This study provides new knowledge of the CFTR biosynthetic pathway. It suggests that SYVN1 and FBXO2 represent two distinct multiprotein complexes that may degrade DeltaF508-CFTR in airway epithelia and identifies a new role for NEDD8 in regulating DeltaF508-CFTR ubiquitination. 27864145_This study identifies MyD88 as a novel substrate of NEDD8, and demonstrate that MyD88 NEDDylation antagonizes its ubiquitination. 27901050_The cellular effects of NEDD8 inhibition can be manipulated based on the p53 status. 27906189_complete blocking of CRLs at a higher inhibitor dose-induced cytotoxicity that was amplified by knockdown of CRL regulator Cand1. 28082425_CUL5 neddylation may allosterically tune polyubiquitin chain length and topology. 28169289_Nedd8 binding to Smurf plays important roles in the regulation of cell migration and the BMP and TGFbeta signaling pathways. 28475037_Furthermore, the authors characterized SENP8/DEN1 as the protease that counteracts Ubc12 auto-neddylation, and observed aberrant neddylation of Ubc12 and other NEDD8 conjugation pathway components in SENP8-deficient cells. 28535453_Here we report that high expression of neddylation components, NEDD8 and NAE1, are associated with poor survival of Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients. Blockage of neddylation by MLN4924 significantly sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine, reduced clonogenic survival, decreased invasion capacity, increased apoptosis and senescence 28536428_Data suggest that ubiquitin (Ub) and neural precursor cell expressed developmentally down-regulated 8 (NEDD8) residues 4, 12, 14, and 72 serve as the molecular determinants for specific recognition by ubiquitin specific protease 2 protein (USP2). 28569775_Downregulation of NEDD8 enhanced the susceptibility of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to cisplatin and radiation. 28592528_In conclusion, the authors revealed that E3 ligase HDM2 promotes NEDD8 NEDDylation of HBx to enhance HBx stability and chromatin localization, which in turn favors HBx-dependent transcriptional regulation, cell proliferation, and hepatitis B virus-driven tumor growth. 28831681_Impairment of NEDDylation by Ubc12 knockout enhances PCNA ubiquitination and promotes PCNA-poleta interaction, while up-regulation of NEDDylation by NEDD8 overexpression or NEDP1 deletion reduces the excessive accumulation of ubiquitinated PCNA. Moreover, Ubc12 knockout decreases cell sensitivity to H2O2-induced oxidative stress, but NEDP1 deletion aggravates this sensitivity 29301501_NEDD8 seems to inhibit the Src-mediated phosphorylation of caveolin-1 by modifying the structure of caveolin-1 protein, which blocks the migration of cancer cells. Although the neddylation process is currently regarded as an emerging target for cancer therapy, our results suggest the possibility that the inhibition of neddylation could facilitate cancer invasion or metastasis at least in some types of cancers. 30407690_NEDD8 has important roles in regulating the progression of bladder cancer (BC) cells and was associated with poor prognosis of patients; hence, it may become a potential therapeutic target of BC. 30563767_RAD18 is a target of NEDD8, an ubiquitin-like protein. 30857167_The newly identified CUBAN (Cullin binding domain associating with NEDD8) domain recognizes both ubiquitin and the ubiquitin-like NEDD8. After a slow conformational selection step, hydrophobic and then neutral and polar interactions take place, which drive the correct orientation of the CUBAN domain, leading to differences in the recognition scheme of NEDD8 and ubiquitin. 31002342_it was demonstrated that high expression of neddylation components, neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally downregulated 8 (NEDD8) and NEDD8activating enzyme 1 (NAE1), were associated with poor survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) 31208947_In this study, we found that UBC12 was overexpressed in human lung cancer, increased with disease deterioration, and positively correlated with NEDD8 expression. Moreover, targeting UBC12 effectively suppressed the malignant phenotypes of lung cancer both in vitro and in vivo 31243299_neddylation pathway promotes CCL2 transactivation and tumor-associated macrophages infiltration in lung cancer to provide a tumor-promoting microenvironment 31444342_Study shows that Cullin-RING Ligase-2 (CRL2) activates CSN5/CSN6 in a neddylation-independent manner. The presence of NEDD8 is required to activate the CSN5 active site. Synergising cryo-electron microscopy with mass spectrometry, study identified sensory regions of the COP9 signalosome that mediate its stepwise activation and provide a framework for understanding the regulatory mechanism of other Cullin family members. 31545502_The present study was designed to assess the effects of Nedd8conjugating enzyme UBE2M knockdown on intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells, and to determine the potential underlying mechanisms. UBE2M and associated protein expression levels were determined via immunohistochemistry and western blotting 31577950_The Balance between Mono- and NEDD8-Chains Controlled by NEDP1 upon DNA Damage Is a Regulatory Module of the HSP70 ATPase Activity. 31882005_We present here the first evidence that the neuroinflammatory mediator IL-1beta facilitates ubiquitin ligase parkin/NEDD8 interactions 32051583_NEDD8 nucleates a multivalent cullin-RING-UBE2D ubiquitin ligation assembly 32457294_HUWE1-dependent DNA-PKcs neddylation modulates its autophosphorylation in DNA damage response. 32819610_Neddylation promotes protein translocation between the cytoplasm and nucleus. 33097763_Neddylation blockade induces HIF-1alpha driven cancer cell migration via upregulation of ZEB1. 33268465_The Mechanism of NEDD8 Activation of CUL5 Ubiquitin E3 Ligases. 33288957_Linkage-specific ubiquitin chain formation depends on a lysine hydrocarbon ruler. 33420360_TAS4464, a NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, activates both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways via c-Myc-mediated regulation in acute myeloid leukemia. 33472076_Proteome-wide identification of NEDD8 modification sites reveals distinct proteomes for canonical and atypical NEDDylation. 33966047_Map of ubiquitin-like post-translational modifications in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Role of p53 lysine 120 NEDDylation. 34156462_The HSP70 chaperone as sensor of the NEDD8 cycle upon DNA damage. 34642328_Structural and functional consequences of NEDD8 phosphorylation. 34654435_A polydopamine nanomedicine used in photothermal therapy for liver cancer knocks down the anti-cancer target NEDD8-E3 ligase ROC1 (RBX1). 34716866_Blocking neddylation elicits antiviral effect against hepatitis B virus replication. | ENSMUSG00000010376 | Nedd8 | 364.479390 | 0.8785830 | -0.186749562 | 0.14680372 | 1.61600043659 | 0.2036503726497310429177645119125372730195522308349609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.41972320798945594866324881877517327666282653808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 325.048438 | 37.624912 | 371.795191 | 42.858985 | |
| ENSG00000129566 | 7011 | TEP1 | protein_coding | Q99973 | FUNCTION: Component of the telomerase ribonucleoprotein complex that is essential for the replication of chromosome termini (PubMed:19179534). Also a component of the ribonucleoprotein vaults particle, a multi-subunit structure involved in nucleo-cytoplasmic transport (By similarity). Responsible for the localizing and stabilizing vault RNA (vRNA) association in the vault ribonucleoprotein particle. Binds to TERC (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97499, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19179534}. | Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Chromosome;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ribonucleoprotein;RNA-binding;Telomere;WD repeat | This gene product is a component of the ribonucleoprotein complex responsible for telomerase activity which catalyzes the addition of new telomeres on the chromosome ends. The telomerase-associated proteins are conserved from ciliates to humans. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. | hsa:7011; | chromosome, telomeric region [GO:0000781]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; telomerase holoenzyme complex [GO:0005697]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; telomerase activity [GO:0003720]; telomerase RNA binding [GO:0070034]; telomere maintenance via recombination [GO:0000722] | 11942411_TP1 expression did not change after cisplatin exposure for 72 hours. 12135483_TEP1, hTR, hsp90, p23, and dyskerin remained at high and unchanged levels throughout up- or down regulation of telomerase activity. 12918126_expression of telomerase activity and its subunit level in pancreatic carcinoma significantly correlate with the clinical stage of pancreatic carcinoma 14606063_Telomerase activity and hTERT, TP-1 mRNA expression are up-regulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 17848914_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18938767_The epithelial expression of TP-1 is elevated in mildly active UC. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19329795_TEP1, TOPOIIalpha, and HSP90 interact directly with BLM in vitro and modulate its helicase activity on telomere-like DNA substrates but not on non-telomeric substrates. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19766477_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20937264_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23739867_the protein levels of MVP, TEP1 and vPARP are actually increased in the highergrade tumors suggesting existence of post-transcriptional regulation of vault component production. 24269974_8 common SNPs in telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) and telomerase-associated protein 1 (TEP1) were genotyped. 26238235_These data suggest that genetic variations in the TEP1 gene may be biomarkers for risk of PCa and BCR after RP. 27221889_TEP1 Polymorphisms are not associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Thai Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. 27305982_The current results suggested that genetic variants at TEP1 SNPs rs1760893 and rs1713423 may be associated significantly with increased risk of stomach cancer. 32584784_hsa_circ_0004018 suppresses the progression of liver fibrosis through regulating the hsa-miR-660-3p/TEP1 axis. 34543729_TEP1 is a risk gene for sporadic cerebral palsy. 34829999_MVP Expression Facilitates Tumor Cell Proliferation and Migration Supporting the Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer Cells. | ENSMUSG00000006281 | Tep1 | 577.859285 | 0.4803363 | -1.057883193 | 0.51479553 | 4.07978677236 | 0.0433991351840346886725718889010749990120530128479003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.14875449717085939549399142833863152191042900085449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 420.037055 | 121.617271 | 877.969286 | 254.155840 | |
| ENSG00000130270 | 148229 | ATP8B3 | protein_coding | O60423 | FUNCTION: P4-ATPase flippase which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled to the transport of aminophospholipids from the outer to the inner leaflet of various membranes and ensures the maintenance of asymmetric distribution of phospholipids. Phospholipid translocation seems also to be implicated in vesicle formation and in uptake of lipid signaling molecules. May be responsible for the maintenance of asymmetric distribution of phosphatidylserine (PS) in spermatozoa membranes. Involved in acrosome reactions and binding of spermatozoa to zona pellucida. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6UQ17}. | Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid transport;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of P-type cation transport ATPases, and to the subfamily of aminophospholipid-transporting ATPases. The aminophospholipid translocases transport phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine from one side of a bilayer to the other. This gene encodes member 3 of phospholipid-transporting ATPase 8B; other members of this protein family are located on chromosomes 1, 15 and 18. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. | hsa:148229; | acrosomal membrane [GO:0002080]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; phospholipid-translocating ATPase complex [GO:1990531]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity [GO:0140326]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; phosphatidylserine floppase activity [GO:0090556]; binding of sperm to zona pellucida [GO:0007339]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; phospholipid translocation [GO:0045332] | 35997042_Association of ATP8B3 gene polymorphisms with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease in asthmatics. | ENSMUSG00000003341 | Atp8b3 | 29.661403 | 0.6993129 | -0.515990070 | 0.30458424 | 2.86122163403 | 0.0907385621709924372613187415481661446392536163330078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.24799746143959403021916898524068528786301612854003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 24.568347 | 4.242206 | 35.404059 | 5.938022 | |
| ENSG00000130414 | 4705 | NDUFA10 | protein_coding | O95299 | FUNCTION: Accessory subunit of the mitochondrial membrane respiratory chain NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I), that is believed not to be involved in catalysis. Complex I functions in the transfer of electrons from NADH to the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme is believed to be ubiquinone. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27626371}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Electron transport;FAD;Flavoprotein;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Primary mitochondrial disease;Reference proteome;Respiratory chain;Transit peptide;Transport | The protein encoded by this gene is a component of 42 kDa complex I, the first enzyme complex in the electron transport chain of mitochondria. This protein has NADH dehydrogenase activity and oxidoreductase activity. It transfers electrons from NADH to the respiratory chain. A mutation in this gene was found in an individual with Leigh syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. | hsa:4705; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I [GO:0005747]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity [GO:0008137]; aerobic respiration [GO:0009060]; mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone [GO:0006120]; mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I assembly [GO:0032981]; proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis [GO:0042776] | 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19064571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22461910_NDUFA10 was found to be differentially methylated and expressed in human squamous cell carcinomas. 34124242_Identifying Mitochondrial-Related Genes NDUFA10 and NDUFV2 as Prognostic Markers for Prostate Cancer through Biclustering. 35739187_Most mitochondrial dGTP is tightly bound to respiratory complex I through the NDUFA10 subunit. | ENSMUSG00000026260 | Ndufa10 | 446.301681 | 0.9939248 | -0.008791352 | 0.08020032 | 0.01201705345 | 0.9127089070513593194178270096017513424158096313476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.96074331881068786298527584222028963267803192138671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 480.243641 | 24.178227 | 485.388590 | 24.122541 | |
| ENSG00000130511 | 170463 | SSBP4 | protein_coding | Q9BWG4 | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | Predicted to enable single-stranded DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:170463; | nucleus [GO:0005634]; single-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003697]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944] | 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) | ENSMUSG00000070003 | Ssbp4 | 766.957470 | 1.1607720 | 0.215084630 | 0.18754039 | 1.31174637993 | 0.2520787070626903103587324039835948497056961059570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.47902145827916209341879039129707962274551391601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 763.810343 | 102.657903 | 659.840378 | 88.687028 | ||
| ENSG00000130713 | 23404 | EXOSC2 | protein_coding | Q13868 | FUNCTION: Non-catalytic component of the RNA exosome complex which has 3'->5' exoribonuclease activity and participates in a multitude of cellular RNA processing and degradation events. In the nucleus, the RNA exosome complex is involved in proper maturation of stable RNA species such as rRNA, snRNA and snoRNA, in the elimination of RNA processing by-products and non-coding 'pervasive' transcripts, such as antisense RNA species and promoter-upstream transcripts (PROMPTs), and of mRNAs with processing defects, thereby limiting or excluding their export to the cytoplasm. The RNA exosome may be involved in Ig class switch recombination (CSR) and/or Ig variable region somatic hypermutation (SHM) by targeting AICDA deamination activity to transcribed dsDNA substrates. In the cytoplasm, the RNA exosome complex is involved in general mRNA turnover and specifically degrades inherently unstable mRNAs containing AU-rich elements (AREs) within their 3' untranslated regions, and in RNA surveillance pathways, preventing translation of aberrant mRNAs. It seems to be involved in degradation of histone mRNA. The catalytic inactive RNA exosome core complex of 9 subunits (Exo-9) is proposed to play a pivotal role in the binding and presentation of RNA for ribonucleolysis, and to serve as a scaffold for the association with catalytic subunits and accessory proteins or complexes. EXOSC2 as peripheral part of the Exo-9 complex stabilizes the hexameric ring of RNase PH-domain subunits through contacts with EXOSC4 and EXOSC7. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17545563}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Deafness;Disease variant;Dwarfism;Exosome;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Retinitis pigmentosa;RNA-binding;rRNA processing | Predicted to enable RNA binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of cell growth. Located in cytoplasm; nucleolus; and nucleoplasm. Part of nuclear exosome (RNase complex). [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:23404; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0000177]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0000178]; nuclear exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0000176]; nucleolar exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0101019]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; 3'-5'-exoribonuclease activity [GO:0000175]; 7S RNA binding [GO:0008312]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; CUT catabolic process [GO:0071034]; exonucleolytic catabolism of deadenylated mRNA [GO:0043928]; exonucleolytic trimming to generate mature 3'-end of 5.8S rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000467]; nuclear polyadenylation-dependent rRNA catabolic process [GO:0071035]; nuclear polyadenylation-dependent tRNA catabolic process [GO:0071038]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, exonucleolytic, 3'-5' [GO:0034427]; polyadenylation-dependent snoRNA 3'-end processing [GO:0071051]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; RNA catabolic process [GO:0006401]; RNA processing [GO:0006396]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364]; U4 snRNA 3'-end processing [GO:0034475] | 12419256_Protein-protein interactions between human exosome components support the assembly of RNase PH-type subunits into a six-membered PNPase-like ring. 17545563_Knock-down of hRrp41p or hRrp4p but not PM/Scl-100 or PM/Scl-75 leads to codepletion of other subunits. 26843489_The EXOSC2-associated phenotype shows only minimal overlap with the previously reported diseases associated with mutations. 31628467_Genetic and genomic studies of pathogenic EXOSC2 mutations in the newly described disease SHRF implicate the autophagy pathway in disease pathogenesis. 34162742_A budding yeast model for human disease mutations in the EXOSC2 cap subunit of the RNA exosome complex. 36241425_Low expression of EXOSC2 protects against clinical COVID-19 and impedes SARS-CoV-2 replication. | ENSMUSG00000039356 | Exosc2 | 233.578160 | 1.3903436 | 0.475441448 | 0.09975594 | 22.66002119041 | 0.0000019334916561763361752331481097089138643241312820464372634887695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00003042258862384093412575478132531259234383469447493553161621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 290.789536 | 19.235863 | 209.888667 | 13.754561 | |
| ENSG00000130816 | 1786 | DNMT1 | protein_coding | P26358 | FUNCTION: Methylates CpG residues. Preferentially methylates hemimethylated DNA. Associates with DNA replication sites in S phase maintaining the methylation pattern in the newly synthesized strand, that is essential for epigenetic inheritance. Associates with chromatin during G2 and M phases to maintain DNA methylation independently of replication. It is responsible for maintaining methylation patterns established in development. DNA methylation is coordinated with methylation of histones. Mediates transcriptional repression by direct binding to HDAC2. In association with DNMT3B and via the recruitment of CTCFL/BORIS, involved in activation of BAG1 gene expression by modulating dimethylation of promoter histone H3 at H3K4 and H3K9. Probably forms a corepressor complex required for activated KRAS-mediated promoter hypermethylation and transcriptional silencing of tumor suppressor genes (TSGs) or other tumor-related genes in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells (PubMed:24623306). Also required to maintain a transcriptionally repressive state of genes in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells (ESCs) (PubMed:24623306). Associates at promoter regions of tumor suppressor genes (TSGs) leading to their gene silencing (PubMed:24623306). Promotes tumor growth (PubMed:24623306). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16357870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18413740, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18754681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24623306}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Deafness;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Methylation;Methyltransferase;Neuropathy;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes an enzyme that transfers methyl groups to cytosine nucleotides of genomic DNA. This protein is the major enzyme responsible for maintaining methylation patterns following DNA replication and shows a preference for hemi-methylated DNA. Methylation of DNA is an important component of mammalian epigenetic gene regulation. Aberrant methylation patterns are found in human tumors and associated with developmental abnormalities. Variation in this gene has been associated with cerebellar ataxia, deafness, and narcolepsy, and neuropathy, hereditary sensory, type IE. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. | hsa:1786; | female germ cell nucleus [GO:0001674]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; pericentric heterochromatin [GO:0005721]; replication fork [GO:0005657]; DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase activity [GO:0003886]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-methyltransferase activity [GO:0009008]; methyl-CpG binding [GO:0008327]; promoter-specific chromatin binding [GO:1990841]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cellular response to amino acid stimulus [GO:0071230]; cellular response to bisphenol A [GO:1903926]; DNA methylation [GO:0006306]; DNA methylation involved in embryo development [GO:0043045]; DNA methylation-dependent heterochromatin formation [GO:0006346]; DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006351]; maintenance of DNA methylation [GO:0010216]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:1905460]; negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell differentiation involved in phenotypic switching [GO:1905931]; positive regulation of DNA methylation-dependent heterochromatin formation [GO:0090309]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904707]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265] | 11834837_recruited to the RARbeta2 promoter by the PML-RAR fusion protein 11932749_DNMT1 and DNMT3b cooperate to silence genes in human cancer cells 12145218_the human de novo enzymes hDNMT3a and hDNMT3b form complexes with the major maintenance enzyme hDNMT1. 12496760_DNMT1 is required to maintain CpG methylation and aberrant gene silencing in human cancer cells. 12530095_DNMT1 gene copy number does not influence susceptibility to development of malignant lymphoproliferative disease. 12538344_Human DNA methyltransferase gene DNMT1 is regulated by the APC pathway 12548018_DNA methylation is tightly coupled to replication through physical interaction of DNMT1 and core components of the replication machinery. 12576480_reduction in DNMT1 triggers intra-S-phase arrest of DNA replication proposed to protect the genome from extensive DNA demethylation. 12594811_Decrease of DNA methyltransferase 1 expression relative to cell proliferation in transitional cell carcinoma. 12637155_mutational inactivation of the DNMT1 gene that potentially causes a genome-wide alteration of DNA methylation status may be a rare event during human carcinogenesis 12738984_Over-expressed in squamous cell carcinoma of the mouth. 12789259_We investigated occupancy of ER-alpha promoter by pRb2/p130-E2F4/5-HDAC1-SUV39 H1-p300 and pRb2/p130-E2F4/5-HDAC1-SUV39H1-DNMT1 complexes, and provided a link between pRb2/p130 and chromatin-modifying enzymes in the regulation of ER-alpha transcription 12804601_structural homology model for human DNA methyltransferase 1 14559786_DNMT1 plays a key role in methylation maintenance, DNMT3b may act as an accessory to support the function in ovarian cancer cells. 14577574_gene expression as a likely mechansism in underlying causes of changes in DNA methylation in aging and tumorigenesis 14583449_Activation of p53 reduces binding and relieves transcriptional repression of the Dnmt1gene, whereas loss of p53, a frequent, early event in tumorigenesis, may significantly contribute to aberrant genomic methylation. 14684836_hypothesis that the increase of DNA-methyltransferase 1 expression in telencephalic GABAergic interneurons of schizophrenia patients causes a promoter hypermethylation of reelin and GAD(67) and perhaps of other genes expressed in these interneurons 15087453_DNA methyltransferase 1 knock down induces gene expression by a mechanism independent of DNA methylation and histone deacetylation 15220328_DNMT1 activity contributes to the preservation of the correct organization of large heterochromatic regions 15289832_inhibition of DNA methylation by DNMT1 by an antisense oligodeoxynucleotide influences cell morphology and adhesion 15340041_Expression levels of DNMT1 in tumor cells may affect the effectiveness of doxorubicin in chemotherapy. 15375672_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15526354_The average mRNA level of Dnmt1 gene from cancerous tissue was higher and that of mbd2 gene from cancerous tissue was lower than that from non-cancerous tissue 15657147_DNMT1- and p53-mediated methylation of the survivin promoter, suggesting cooperation between p53 and DNMT1 in gene silencing. 15735013_Results suggest a novel mechanism for gene silencing mediated by RUNX1/MTG8 and support the combination of HDAC and DNMT inhibitors as a novel therapeutic approach for t(8;21) AML. 15755728_DNMT1 protein levels are elevated in breast cancer tissues and in MCF-7 breast cancer cells relative to normal human mammary epithelial cells without a concomitant increase in DNMT1 mRNA or proliferative fraction. 15762053_Increased DNMT1 gene expression appears to be in lymphomas and maybe associated with oncogenesis in this group of tumors. 15799776_Unlike Dnmt1, pre-existing cytosine methylation at CpG sites or non-CpG sites does not stimulate Dnmt3a activity in vitro and in vivo. 15870198_STAT3 may transform cells by inducing epigenetic silencing of SHP-1 in cooperation with DNMT1 and histone deacetylase 1 15956212_Direct role of Dnmt1 in the restoration of epigenetic information during DNA repair. 16053511_These data suggest that increased DNMT1 protein expression participates in multistage pancreatic carcinogenesis from the precancerous stage to malignant progression of ductal carcinomas and may be a biological predictor of poor prognosis. 16227093_necessary for both class switching and somatic hypermutation in B cells 16314526_DNMT1 is necessary for proper PcG body assembly independent of DNMT-associated histone deacetylase activity. 16322686_Breast cancer cells have a prominent loss of DNA methylation accompanied by altered expression of maintenance DNA methyltransferase DNMT1. 16423997_data suggests a potential role for DNMT1 in the initiation of promoter CpG island hypermethylation in human cancer cells 16424002_human cancer cells may differ in their reliance on DNMT1 for maintaining DNA methylation 16497664_down-regulation of DNMT1 methyltransferase leads to activation and stable hypomethylation of MAGE-A1 in melanoma cells 16537562_DNMT1 protein overexpression may be responsible for aberrant DNA methylation during multistage carcinogenesis of the pancreas 16769694_In human cells maintenance of XIST methylation is controlled differently than global genomic methylation and in the absence of both DNMT1 and DNMT3B. 16801630_Inhibitors of DNMT1 may have clinical relevance for immune modulation by augmentation of cytokine effects and/or expression of tumor-associated antigens. 16861352_STAT3 binds in vitro to 2 STAT3 SIE/GAS-binding sites identified in promoter 1 and enhancer 1 of the DNMT1 gene 16897079_suppression of DNMT-1 might be related to the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis, especially in whom serum IgE level is high 16960727_study demonstrated that expression of DNMT1 is clearly regulated in both impaired spermatogenesis and development of embryonal carcinoma, while HDAC1 expression is not regulated during aberrant germ cell differentiation 16963560_Data suggest that DNMT1 might be essential for maintenance of DNA methylation, proliferation, and survival of cancer cells. 16998846_Sex-specific time windows for concomitant upregulation of DNMT1 are associated with prenatal remethylation of the human male and female germ line. 17015478_depletion of DNMT1 with either antisense or small interfering RNA (siRNA) specific to DNMT1 activates a cascade of genotoxic stress checkpoint proteins 17030625_AUF1 cell cycle variations define genomic DNA methylation by regulation of DNMT1 mRNA stability 17053888_The increased DNMT1 expression was more frequent in adenocarcinoma vs. squamous cell carcinoma (42% vs 19%). Smokers with ~65 packyears showed 4.17 times higher risk of increased DNMT1 expression compared to those who smoked 45 packyears in adenocarcinoma 17067458_DNMT1 expression was correlated to the methylation of RASSF1A, tumor grade and stage, which implied that DNMT1 may contribute to the carcinogenesis and development of adenoid cystic carcinoma. 17081533_The genes DNMT1, DNMT3A, and DNMT3B were over-expressed in the ectopic endometrium as compared with normal control subjects or the eutopic endometrium of women with endometriosis. 17085482_Direct cooperation between DNMT1 and G9a provides a mechanism of coordinated DNA and H3K9 methylation during cell division. 17093909_These findings suggested that DNMT1 was associated with the malignant phenotype, and dysregulation of DNMT1 expression was present in tumor cells of colorectal cancer. 17178861_LMP1 induces formation of a transcriptional repression complex, composed of DNMT1 and histone deacetylase, which locates on E-cadherin gene promoter. 17312023_DNMT1 is essential for the maintenance of DNA methylation patterns in human cells. 17322882_DNMT1 is required for faithfully maintaining DNA methylation patterns in human cancer cells and is essential for their proliferation and survival. 17470536_Direct interactions between HP1 and DNMT1 mediate silencing of euchromatic genes. 17492476_LAT, ZAP-70, and DNMT1 protein levels in CD4(+) T cells can be associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. 17532557_DNMT1 plays a key role in maintenance of methylation, and DNMT3B may act as an accessory DNA methyltransferase to epigenetically silence CXCL12 expression in MCF-7 and AsPC1 cells 17538945_Progressive up-regulation of the gene encoding DNMT1 was found in the colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence. 17657744_SUV39H1 is significantly associated with DNMT1, but not with euchromatic promoter methylation in colorectal cancer 17673620_data suggest that UHRF1 may help recruit DNMT1 to hemimethylated DNA to facilitate faithful maintenance of DNA methylation 17698033_mahanine can reverse an epigenetically silenced gene, RASSF1A in prostate cancer cells by inhibiting DNMT activity that in turn down-regulates a key cell cycle regulator, cyclin D1 17716861_These results suggested that PKB enhanced DNMT1 stability and maintained DNA methylation and chromatin structure, which might contribute to cancer cell growth. 17893234_DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) 1 over-expression is not a secondary result of increased cell proliferative activity but is significantly correlated with the CpG island methylator phenotype. 17931718_establish a link between HESX1 and DNMT1 and suggest a novel mechanism for the repressing properties of HESX1 17934516_The interaction of the SRA domain of ICBP90 with a novel domain of DNMT1 is involved in the regulation of VEGF gene expression. 17965595_DNMT1 expression is increased in schizophrenia (SZ) and bipolar (BP) disorder brains. [REVIEW] 17991895_reveals novel functions for DNMT1 as a component of the cellular response to DNA damage, which may help optimize patient responses to this agent in the future 18038118_mutant p53 loses its ability to suppress DNMT1 expression, and thus enhances methylation levels of the p16 ( ink4A ) promoter and subsequently down-regulates p16(ink4A )protein. 18049164_In hepatocellular carcinoma, DNMT1 is necessary to maintain the methylation of CpG islands in certain tumor-related genes. 18198215_DNMT-1 has a direct suppressive role in 15-LOX-1 transcriptional silencing that is independent of 15-LOX-1 promoter DNA methylation 18202356_Parental Dnmt1 is a modifier of transmission of alleles at an unlinked chromosomal region and perhaps has a role in the genesis of transmission ratio distortion. 18204201_The subcellular localization of DNMT1 can be altered by the addition of IL-6, and this process is greatly enhanced by phosphorylation of the DNMT1 nuclear localization signal (NLS) by PKB/AKT. 18252747_Study shows that the maintenance DNA methyltransferase Dnmt1, which preserves the patterns of CpG methylation, plays a key role in CAG repeat instability in human cells and in the male and female mouse germlines. 18253830_DNMT1 was over expressed in gastric neoplasms. 18404674_DNMT1 protein overexpression might contribute to aberrant DNA hypermethylation of specific tumor suppressor genes in endometrial cancers. 18413740_Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis of the BAG-1 promoter in DNMT1-overexpressing or DNMT3B-overexpressing colon cells show a permissive chromatin status assoscsiated with DNA binding of BORIS. 18414412_DNMT1 may play an important role in modulating NSCLC patient survival and thus be useful for identifying NSCLC patients who would benefit most from aggressive therapy. 18499700_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18499700_The association between sequence variants of DNMT1 and 3B and mutagen sensitivity induced by BPDE supports the involvement of these DNMTs in protecting the cell from DNA damage. 18505931_histone deacetylase inhibition promotes ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation of DNA methyltransferase 1 in human breast cancer cells 18563322_DNMT1 and DNMT3b will increase their biological effects and have a synergistic effect on suppressing the growth of cholangiocarcinoma 18567946_The HIV-1 responsive element resides in the 5' most 420 bp of the -1634 to +71 DNMT1 promoter; positioning of this truncated promoter proximal to a hybrid SV40-DNMT1 reporter results in HIV-1-dependent regulation 18680430_study shows endogenous DNMT1 & CFP1 interact in vivo; CFP1 interaction with Setd1A or Setd1B not required for its interaction with DNMT1; result indicates CFP1 intersects cytosine methylation machinery independently of its association with Setd1 complexes 18754681_The CXXC domain in the amino terminus region of DNMT1 cooperates with the catalytic domain for DNA methyltransferase activity. 18829110_elevated DNMT1 expression may in particular contribute to ineffective erythropoiesis in MDS. 18931722_DNMT1 and HLA-DRalpha are prognostic factors for hepatocelluar carcinoma. 19016755_Interaction between DNMT1 and DNA replication reactions in the SV40 in vitro replication system is reported. 19019634_The ratio of MBD-2/DNMT-1 might be valuable in explanation of hypomethylation and evaluation of clinical activity of systemic luopus erythematosus. 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19161160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19173286_mapped the dimerization domain to the targeting sequence TS that is located in the center of the N-terminal domain (amino acids 310-629) 19211935_miR-29b down-regulates DNMT1 indirectly by targeting Sp1. 19236003_Incorporation of 6-thioguanine into the CpG site affects the methylation of the cytosine residue by both DNMT1 and HpaII. The effect on cytosine methylation is dependent on the position of 6-thioguanine with respect to the cytosine to be methylated. 19246518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19275888_p21(WAF1)-p300-DNMT1 pathway may play a pivotal role to ensure regulated DNMT1 expression and DNA methylation in mammalian cell division. 19279403_Panobinostat treatment depletes DNMT1 levels and enhances decitabine mediated repression of JunB and loss of survival of human acute leukemia cells. 19282482_signaling through SET7 represents a means of DNMT1 enzyme turnover 19292979_DNMT1 levels in tumor cells may determine the effectiveness of doxorubicin in chemotherapy. 19339266_EBV latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A) up-regulated DNMT1, leading to an increase in methylation of the PTEN promoter in stomach cancer. 19386473_In patient with schizophrenia the DNA-methyltransferase 1 was up regulation in telencephalic GABAergic neurons. 19394279_Data showed that the CD70, perforin and KIR2DL4 promoters are demethylated in CD4(+)CD28(-) T cells, and that DNA methyltransferase 1 (Dnmt1) and Dnmt3a levels are decreased in this subset. 19399408_Silencing DNMT3b and DNMT1 could inhibit the cell growth and promote apoptosis of bladder carcinoma cells. 19399937_DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) expression was increased in hepatocellular carcinoma compared to non-neoplastic liver tissues and the incidence of DNMT1 immunoreactivity in HCCs correlated significantly with poor tumor differentiation. 19424621_Higher expression of DNMT1 and HDAC1 correlated with advanced stages of the disease and reflect the malignancy of pancreatic carcinoma. 19450230_SUMOylation significantly enhances the methylase activity of DNMT1 both in vitro and in chromatin. 19465937_the role of promoter region DNA hypermethylation as a mediator of gene silencing in glioblastoma multiforme cell line using RNAi directed against DNMT1 and DNMT3b was investigated. 19468253_Our results were not able to demonstrate a clear correlation between DNMT1 and DNMT3a immunoexpression and salivary gland neoplasms development. 19531770_Increase of DNMT1 expression is associated with multiple myeloma and plasma cell leukemias. 19539327_genetic and phenotypic consequences of silencing DNMT1 in PC3 cells are markedly different from those in colon and gastric cancers, indicating that DNMT1 preferentially targets certain gene promoters 19763880_The expression of DNMT1, DNMT2, DNMT3A and DNMT3B in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients, was investigated. 19798569_Our data suggest there is no apparent association of common DNMT-1 and DNMT-3B polymorphisms with the risk of breast cancer in Chinese women. 19896490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19932585_Our results indicate that DNMT1 plays the main role in maintenance of methylation of CXCR4 promoter, while DNMT3B may function as an accessory DNA methyltransferase to modulate CXCR4 expression in AsPC1 cells. 19936946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19957555_Downregulation of DNMT1 can inhibit cervical cancer cell proliferation and induce cell apoptosis. 20044957_The DNMT 1 is the key enzyme responsible for DNA methylation, which often occurs in CpG islands located near the regulatory regions of genes and affects transcription of specific genes. Two intron polymorphisms of DNMT1 might affect HBV clearance. 20071334_DNA methylation-mediated down-regulation of DNA methyltransferase-1 (DNMT1) is coincident with, but not essential for, global hypomethylation in human placenta 20071580_Data suggest that KSHV miRNA targets multiple pathways to maintain KHSV latency, including repression of the viral protein Rta and a cellular factor, Rbl2, and increased cellular DNMT, in regulating global epigenetic reprogramming. 20081831_DNMT1 is essential for epidermal progenitor cell function 20093774_Carcinogne-induced DNMT1 accumulation and subsequent hypermethylation of the promoter of tumor suppressor genes may lead to tumorigenesis and poor prognosis. 20147412_Hepatitis B virus-induced overexpression of DNMTs leads to viral DNA methylation and decreased viral gene expression and also leads to methylation of host CpG islands. 20192566_No association between DNMT1 and colorectal cancer in Iranian patients. 20192608_No association between DNMT1 polymorphisms and gastric cancer. 20192608_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20228804_Dnmt1 and Dnmt3a transgenes are required for synaptic plasticity, learning and memory through their overlapping roles in maintaining DNA methylation and modulating neuronal gene expression in adult central nervous system neurons. 20335008_Our results suggest that one potential mechanism by which varenicline may decrease cigarette smoking in schizophrenia is by decreasing DNMT1 mRNA. 20354000_Our results indicate that DNMT-mediated gene silencing may play a role in inflammation-associated colon tumorigenesis. 20381114_expression of DNA methyltransferase 1, 3a, and 3b showed significantly higher levels in stage IV tumors than in stage I or II tumors 20398055_DNMT1 and DNMT3b silencing sensitizes human hepatoma cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis via up-regulation of TRAIL-R2/DR5 and caspase-8. 20428781_thymine DNA glycosylase was not up-regulated in DNMT1 nor 3B knockdown cancer cells 20570896_Data provided compelling evidence that deregulation of DNMT1 is associated with gain of transcriptional activation of Sp1 and/or loss of repression of p53. 20588031_Increased expression of DNMT1 in non-neoplastic epithelium may precede or be a relatively early event in ulcerative colitis-associated tumorigenesis. 20592467_interaction between hNaa10p and DNMT1 was required for E-cadherin silencing through promoter CpG methylation, and E-cadherin repression contributed to the oncogenic effects of hNaa10p. 20593030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20613874_results reveal that the disruption of Dnmt1/PCNA/UHRF1 interactions acts as an oncogenic event and that one of its signatures (i.e. the low level of mMTase activity) is a molecular biomarker associated with a poor prognosis in GBM patients 20620135_Regulation of DNMT1 and DNMT3A by HBx promoted hypermethylation of p16(INK4A) promoter region 20840813_The expression of DNMT1 was significantly higher in lung cancer tissues than in corresponding normal lung tissues. 20875141_In MCF7 cells, ANT2 knockdown enhanced the expression and activity of DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1). 20920981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20920981_The current work shows that polymorphisms of the DNMT1 gene in exons may affect the individual intraductal carcinoma risk in women of the northeast of China. 20937307_The anti-TNFalpha biological agents do not seem to affect DNA methylation and mRNA expressions of DNMT1 and MBD2 in RA 20940144_our studies provide compelling additional evidence for DNMT1 acting as a regulator of genome integrity and as an early responder to DNA DSBs. 20951977_lower levels of DNMT1 may be related with smoking habit. significantly higher mean percentage of DNMT1 immunoreactivity in non-smokers 20970125_The mRNA of DNMT1 (DNA-methyltransferase 1) is expressed in the endometrium across the menstrual cycle. 20980350_Depletion of DNMT1 did not induce cellular invasion in MCF-7 and ZR-75-1 non-invasive breast cancer cell lines. 21042757_HPV-16 E6 may act through p53/ DNMT1 to regulate the development of cervical cancer. 21045206_a previously unknown mode of regulation of DNMT1 protein stability through the coordinated action of an array of DNMT1-associated proteins. 21078759_This study demonstrated that patients with SLE had a significantly lower level of DNA methylation than the controls, and that expression of both DNMT1 and MBD2 mRNA was significantly increased in the SLE patients compared with controls. 21151116_Modifications to DNMT1 mediated by AKT1 and SET7, affect cellular DNMT1 levels. 21163962_structure of DNMT1 composed of CXXC, tandem bromo-adjacent homology (BAH1/2), and methyltransferase domains bound to DNA-containing unmethylated CpG sites; studies identify an autoinhibitory mechanism of DNA methylation 21229291_we report significant overexpression of DNMT1 and DNMT3B in glioma 21266713_Control of DNMT1 abundance in epigenetic inheritance by acetylation, ubiquitylation, and the histone code. 21268065_Findings suggest that, by balancing Dnmt1 ubiquitination, Usp7 and Uhrf1 fine tune Dnmt1 stability. 21296890_association of Dnmt1 and alpha-synuclein might mediate aberrant subcellular localization of Dnmt1 21311766_Different binding properties and function of CXXC zinc finger domains in Dnmt1 and Tet1. 21316665_Expression level of DNMT1 is significantly higher in secretory-phase endometrium compared with proliferative endometrium and menstrual endometrium. 21321201_Mitochondrial DNMT1 appears to be responsible for mtDNA cytosine methylation. 21347439_DNA methylation recovery was mediated by the major human DNA methyltransferase, DNMT1 21353307_Results implied that IL-6 expression was regulated by promoter demethylation induced by down-regulation of DNMT activity. 21389349_the naked DNA- and polynucleosome-binding activities of Dnmt1 are inhibited by the RFTS domain, which functions by virtue of binding the catalytic domain to the exclusion of DNA 21395176_Increased expression of DNMT1 may initiate the oncogenesis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Smoking may induce expression. 21458988_Low DNMT1 expression defines a subgroup of GC patients with better outcomes following platinum/5FU-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. In vitro data support a functional relationship between DNMT1 and cisplatin sensitivity. 21459093_Study provides evidence for nuclear receptor mediated regulation of Dnmt1 expression through ERRgamma and SHP crosstalk. 21478913_These findings show an important role for p53 in the progression of serous borderline ovarian tumors to an invasive carcinoma, and suggest that downregulation of E-cadherin by DNMT1-mediated promoter methylation contributes to this process. 21523767_DNMT1 could be a significant clinical predictor for stage and treatment response of bladder cancer. 21532572_Here we show that mutations in DNMT1 cause both central and peripheral neurodegeneration in one form of hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy with dementia and hearing loss. 21539677_The proportion of cells that express DNMT1 at the mRNA and protein levels in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma clinical samples is generally higher than in paired non-cancerous tissues. 21565170_these results suggest that dysregulation of cell cycle via CDKs could induce abnormal phosphorylation of DNMT1 and lead to DNA hypermethylation often observed in cancer cells. 21565830_findings describe a new mechanism for the regulation of DNMT1 and aberrant DNA hypermethylation in colorectal cancer 21573703_DNA methylation of the BNIP3 promoter was mediated by DNMT1 via the MEK pathway 21592522_Data show that the levels of DNMT1 mRNA were significantly decreased in a depressive but not in a remissive state of MDD and BPD. 21619587_Results indicate that phosphorylation of human DNMT1 by protein kinase C is isoform-specific and provides the first evidence of cooperation between PKCzeta and DNMT1 in the control of the DNA methylation patterns of the genome. 21636528_These results offer an explanation for how and why unmethylated microsatellite repeats can be destabilized in cells with decreased DNMT1 levels and uncover a novel and important role for PARP in this process. 21735817_DNMT1 as a key enzyme in maintaing of proper methylation pattern is a attractive target in anti-tumor therapy. 21756783_PARP1 could regulate DNA methylation by inhibiting the enzyme activity of DNMT1 in bronchial epithelial cells exprosed to B(a)P. 21757290_Data show that Core inhibited p16 expression by inducing promoter hypermethylation via up-regulation of DNMT1 and DNMT3b. 21791605_Data show that trichostatin A treatment reduces global DNA methylation and the DNMT1 protein level and alters DNMT1 nuclear dynamics and interactions with chromatin. 21826395_Dnmt1 was principally expressed in the nucleus & cytoplasm of NeuN-positive neurons, but not in GFAP-positive astrocytes. Levels were significantly increased in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. 21887463_Significantly higher levels of CXCR4, DNMT3A, DNMT3B and DNMT1 transcript (p=0.0058, 0.0163, 0.0003 and | ENSMUSG00000004099 | Dnmt1 | 2110.855913 | 0.9225896 | -0.116239094 | 0.28592233 | 0.16518654258 | 0.6844255981523150733636384757119230926036834716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.83759291131697233279140846207155846059322357177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1920.126849 | 409.033634 | 2076.368465 | 442.374236 | |
| ENSG00000131051 | 9584 | RBM39 | protein_coding | Q14498 | FUNCTION: RNA-binding protein that acts as a pre-mRNA splicing factor (PubMed:15694343, PubMed:31271494, PubMed:28437394, PubMed:28302793, PubMed:24795046). Acts by promoting exon inclusion via regulation of exon cassette splicing (PubMed:31271494). Also acts as a transcriptional coactivator for steroid nuclear receptors ESR1/ER-alpha and ESR2/ER-beta, and JUN/AP-1, independently of the pre-mRNA splicing factor activity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VH51, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15694343, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24795046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28302793, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28437394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31271494}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Isopeptide bond;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes a member of the U2AF65 family of proteins. The encoded protein is found in the nucleus, where it co-localizes with core spliceosomal proteins. It has been shown to play a role in both steroid hormone receptor-mediated transcription and alternative splicing, and it is also a transcriptional coregulator of the viral oncoprotein v-Rel. Multiple transcript variants have been observed for this gene. A related pseudogene has been identified on chromosome X. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. | hsa:9584; | centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RS domain binding [GO:0050733]; mRNA processing [GO:0006397]; regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0048024]; RNA processing [GO:0006396]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380] | 11704680_This paper describes the mouse gene. 15747776_10 genes were down-regulated following treatment of the T-ALL cells with 0.15 and 1.5 microg/mL of metal ores at 72 h 18753212_this study identifies CAPERalpha (RNA binding motif protein 39) as a new transcriptional coregulator for v-Rel and reveals an important role in modulating Rel's oncogenic activity. 19342371_Analysis of human breast cancer samples revealed that CAPER is overexpressed and undergoes a cytoplasmic-to-nuclear shift during the transition from pre-malignancy to ductal carcinoma in situ 22009261_Increased VEGF(165) expression is secondary to the down-regulation of CAPER-alpha by EWS/FLI-1. CAPER-alpha mediates alternative splicing and controls the shift from VEGF(189) to VEGF(165) . 22711543_Data show that CSE1L, DIDO1 and RBM39 mRNA expression levels correlated with chromosome 20q DNA copy number status. 24621503_Knockdown of CAPER expression markedly reduced human breast cancer cell proliferation in both in vitro and in vivo settings. Mechanistically, knockdown of CAPER abrogated the activity of proliferative and protein synthesis pathways. 24643682_Our data suggest that overexpression of HCC1/CAPERalpha may increase the proliferation and migration of NSCLC cells, and HCC1/CAPERalpha could be a promising biomarker for lung cancer 24795046_identify SF3b155 as the relevant ULM-containing partner of full-length CAPERalpha in human cell extracts. 26934653_Decreased expression of CAPERalpha appears to be correlated with appearance of microvessels in hepatocellular carcinoma 27018250_mammalian c-Abl plays an important role in steroid hormone receptor-mediated transcription by regulating RBM39 27050129_This study therefore establishes a structural basis for specific UHM-ULM interactions by splicing factors such as U2AF35, U2AF65, RBM39 and SF3b155, and a platform for continued studies of intermolecular interactions governing disease-related alternative splicing in eukaryotic cells. 27354116_RBM39 is extensively involved in alternative splicing of RNA and helps regulate transcript levels. RBM39 may modulate alternative splicing similarly to U2AF65 by either directly binding to RNA or recruiting other splicing factors, such as U2AF65. 28193846_The results provide a mechanism for exon 16 3' splice site activation in which a coordinated effort among TIA1, Pcbp1, and RBM39 stabilizes or increases U2 snRNP recruitment, enhances spliceosome A complex formation, and facilitates exon definition through RBM39-mediated splicing regulation. 31271494_The splicing factors U2AF65 and CAPERalpha engage multivalent interactions through their low complexity RS domains. The resulting assemblies can bridge the U2snRNP component SF3b155 with repeated polypyrimidine tracts in introns, to promote alternative splicing. 31686031_aryl-sulfonamides neo-functionalize a shallow, non-conserved pocket on DCAF15 to selectively bind and degrade RBM39 and the closely related splicing factor RBM23 without the requirement for a high-affinity ligand 31819272_structural and mutational analysis of how indisulam mediates the DCAF15-RBM39 interaction 34077726_Inhibiting an RBM39/MLL1 epigenomic regulatory complex with dominant-negative peptides disrupts cancer cell transcription and proliferation. 34520118_Identification of a small molecule splicing inhibitor targeting UHM domains. | ENSMUSG00000027620 | Rbm39 | 1170.713711 | 0.8510405 | -0.232700321 | 0.08911895 | 6.81054831829 | 0.0090620933889257199861377856109356798697263002395629882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.04583578699664087735543560597761825192719697952270507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1081.115866 | 77.336732 | 1276.433027 | 91.029793 | |
| ENSG00000131089 | 23229 | ARHGEF9 | protein_coding | O43307 | FUNCTION: Acts as guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for CDC42. Promotes formation of GPHN clusters (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QX73, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10559246}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain;Synapse | The protein encoded by this gene is a Rho-like GTPase that switches between the active (GTP-bound) state and inactive (GDP-bound) state to regulate CDC42 and other genes. This brain-specific protein also acts as an adaptor protein for the recruitment of gephyrin and together these proteins facilitate receceptor recruitement in GABAnergic and glycinergic synapses. Defects in this gene are the cause of startle disease with epilepsy (STHEE), also known as hyperekplexia with epilepsy, as well as several other types of cognitive disability. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2017]. | hsa:23229; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; postsynaptic specialization [GO:0099572]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; regulation of postsynaptic specialization assembly [GO:0099150]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056] | 11727829_Here we identified residues critical for interaction with gephyrin in the linker region between the SH3 and the DH domains of collybistin. 15215304_translocates gephyrin to submembrane microaggregates; collybistin mutation (G55A)is found in exon 2 of the ARHGEF9 gene in a patient with clinical symptoms of both hyperekplexia and epilepsy 18208356_Results show that hPEM-2 is a target protein of Smurf1. 19911011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20622020_Study propose that the collybistin-gephyrin complex has an intimate role in the clustering of GABA(A)Rs containing the alpha2 subunit. 21633362_Data indicate that ARHGEF9 is likely to be responsible for syndromic X-linked mental retardation associated with epilepsy. 21807943_major regulator of GABAergic postsynaptic gephyrin clustering 22033413_These results reveal that G(s) and G(q) signalings regulate hPEM-2 functions through PKA and c-Src in Neuro-2a neuroblastoma cells, respectively. 22778260_Phosphorylation of gephyrin in hippocampal neurons by cyclin-dependent kinase CDK5 at Ser-270 is dependent on collybistin. 24297911_The enhancement of Cb-induced gephyrin clustering by GTP-TC10 does not depend on the guanine nucleotide exchange activity of Cb but involves an interaction that resembles reported interactions of other small GTPases with their effectors 25678704_Impairment of the membrane lipid binding activity of Collybistin R290H and a consequent defect in inhibitory synapse maturation represent a likely molecular pathomechanism of epilepsy and mental retardation in humans. 25898924_Collybistin forms a complex with mTOR and eIF3 and by sequestering these proteins downregulates mTORC1 signaling and protein synthesis potentially contributing to intellectual disability and autism. 27238888_Autism spectrum disorder patient with the smallest inactivating deletion in the collybistin gene. 29130122_Study identified a novel mutation in ARHGEF9, c.868C > T/p.R290C, which co-segregated with epileptic encephalopathy, and validated its association with epileptic encephalopathy. Further analysis revealed that all ARHGEF9 mutations were associated with intellectual disability. 31283007_Identification of TAF1, SAT1, and ARHGEF9 as DNA methylation biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. 31942680_Clinical and Molecular Characterization of Three Novel ARHGEF9 Mutations in Patients with Developmental Delay and Epilepsy. 32939676_De novo ARHGEF9 missense variants associated with neurodevelopmental disorder in females: expanding the genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of ARHGEF9 disease in females. 33600053_Loss-of-function variants in ARHGEF9 are associated with an X-linked intellectual disability dominant disorder. 35169261_Human ARHGEF9 intellectual disability syndrome is phenocopied by a mutation that disrupts collybistin binding to the GABAA receptor alpha2 subunit. 35638461_ARHGEF9 gene variant leads to developmental and epileptic encephalopathy: Genotypic phenotype analysis and treatment exploration. 35947460_LncRNA-p21 suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer by sponging miR-514b-3p and up-regulating ARHGEF9 expression. | ENSMUSG00000025656 | Arhgef9 | 197.636182 | 1.5443914 | 0.627038409 | 0.41628542 | 2.22334934838 | 0.1359378709178721555961288913749740459024906158447265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.32389077408824901160855347370670642703771591186523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 213.480363 | 106.685505 | 121.471877 | 60.675661 | |
| ENSG00000131467 | 10197 | PSME3 | protein_coding | P61289 | FUNCTION: Subunit of the 11S REG-gamma (also called PA28-gamma) proteasome regulator, a doughnut-shaped homoheptamer which associates with the proteasome. 11S REG-gamma activates the trypsin-like catalytic subunit of the proteasome but inhibits the chymotrypsin-like and postglutamyl-preferring (PGPH) subunits. Facilitates the MDM2-p53/TP53 interaction which promotes ubiquitination- and MDM2-dependent proteasomal degradation of p53/TP53, limiting its accumulation and resulting in inhibited apoptosis after DNA damage. May also be involved in cell cycle regulation. Mediates CCAR2 and CHEK2-dependent SIRT1 inhibition (PubMed:25361978). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10835274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11185562, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11432824, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15111123, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18309296, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25361978, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9325261}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cell cycle;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Host-virus interaction;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proteasome;Reference proteome | The 26S proteasome is a multicatalytic proteinase complex with a highly ordered structure composed of 2 complexes, a 20S core and a 19S regulator. The 20S core is composed of 4 rings of 28 non-identical subunits; 2 rings are composed of 7 alpha subunits and 2 rings are composed of 7 beta subunits. The 19S regulator is composed of a base, which contains 6 ATPase subunits and 2 non-ATPase subunits, and a lid, which contains up to 10 non-ATPase subunits. Proteasomes are distributed throughout eukaryotic cells at a high concentration and cleave peptides in an ATP/ubiquitin-dependent process in a non-lysosomal pathway. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides. The immunoproteasome contains an alternate regulator, referred to as the 11S regulator or PA28, that replaces the 19S regulator. Three subunits (alpha, beta and gamma) of the 11S regulator have been identified. This gene encodes the gamma subunit of the 11S regulator. Six gamma subunits combine to form a homohexameric ring. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]. | hsa:10197; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; proteasome activator complex [GO:0008537]; proteasome complex [GO:0000502]; endopeptidase activator activity [GO:0061133]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding [GO:0097371]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; positive regulation of endopeptidase activity [GO:0010950]; regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000045]; regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process [GO:0061136] | 11859414_PA28gamma is an endogenous substrate for caspase-3 and -7 12784391_Ki antigen contains multiple epitopes recognized by autoimmune sera 17088425_PA28 gamma novel regulator of Cajal body integrity in response to ultraviolet radiation. 17327906_Overexpression of the proteasome activator subunit PA28gamma recovered proteasome function in Huntington disease cells. It improved cell viability in mutant huntingtin-expressing striatal neurons exposed to pathological stressors. 18235248_REGgamma proteasome activator is involved in the maintenance of chromosomal stability. 18309296_PA28gamma, a proteasome activator that inhibits apoptosis and promotes cell cycle progression through unknown mechanisms, exerts an effect as a cofactor in the MDM2-p53 interaction. 18321762_PA28gamma/REGgamma, which specifically binds to hepatitis c virus core protein, is required for the virulence of the core protein[review] 18343811_mammalian proteasomes cannot degrade glutamine-expanded regions within pathogenic polyQ-expanded proteins, such as Huntingtin 19091860_PA28gamma specifically binds to hepatitis C virus core protein and is involved in its degradation. 19556897_these results underline a new role for REGgamma in the control and regulation of promyelocytic leukemia subnuclear structures. 19656465_Data suggest REGgamma promoting tumor growth is a process involving multiple factor mechanisms. 20467919_High REGgamma expression is associated with breast cancer and its metastatic lymph nodes. 20494959_REGgamma is present in many tissues and the highest expression is in the testis. 20683941_PA28gamma participates not only in the pathogenesis but also in the propagation of HCV by regulating the degradation of the core protein in both a ubiquitin-dependent and ubiquitin-independent manner 20719955_REGgamma-mediated p53 proteolysis contributes, as least in part, to the proviral function of REGgamma; the host REGgamma pathway is utilized and modified during CVB3 infection to promote efficient viral replication 21084564_REGgamma regulates cellular distribution of p53 by facilitating its multiple monoubiquitylation and nuclear export. 21216954_HTLV-1 p30 interacts with ATM and REGgamma to increase viral spread by facilitating cell survival 21445096_A previously unrecognized mechanism regulating the activity of the proteasome activator REGgamma, is reported. 22042974_REG-gamma associates with and modulates the abundance of nuclear activation-induced deaminase. 22134242_PA28gamma is an ATM target, being recruited to DNA damage sites where it is required for rapid accumulation of proteasomes, and the timely coordination of DNA double-strand break repair. 22938444_statistical analysisof laryngeal carcinomas revealed that there was a positive relationship between the level of REGgamma and the expression of p53 and p2; study suggests that REgamma overexpression can facilitate the growth of laryngeal cancer cells 23104922_PA28gamma acts as a co-repressor of HTLV-1 p30 to suppress virus replication and is required for the maintenance of viral latency. 23612972_the regulation of REGgamma assembly and activity, suggesting a potential venue for the intervention of the ubiquitin-independent REGgamma proteasome activity. 24113729_Expression of PA28gamma contributes to carcinogenesis and progression of colorectal cancer. 24157709_The REGgamma-proteasome pathway is regulated differentially by p53/TGF-beta signaling and mutant p53 in cancer cells. 24531141_PA28 gamma and p53 form a negative feedback loop that maintains the balance of p53 and PA28gamma in the cells. 24560667_PKA turnover by the REGgamma-proteasome modulates FoxO1 cellular activity and VEGF-induced angiogenesis. 24901344_Data suggest levels of gene expression of both PSME3 (proteasome activator subunit 3) and DUSP3 (dual specificity phosphatase 3) are associated with susceptibility to Staphylococcus aureus infection/sepsis in humans and in mouse disease model. 25361978_The results link Chk2 and REGgamma to the mechanism underlying the DBC1-dependent SIRT1 inhibition. 25482151_Increased PA28gamma sera levels were prognostic of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. 25490392_REGgamma expression is positively correlated with ERalpha status and poor clinical prognosis in ERalpha positive breast cancer patients 25511742_Our data indicate that miR-7-5p has a critical function through blocking REGgamma in breast cancer cells. 25550823_Our results suggest that the high expression of REGgamma might predict metastasis and poor prognosis in breast cancer. 25697482_Examination of EC and normal endometrium specimens confirmed the oncogenic role of REGgamma, in that REGgamma was more highly overexpressed in p53-positive specimens than in p53-negative specimens. 25908095_REGgamma acts in skin tumorigenesis mediating MAPK/p38 activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 25936920_Results show molecular cloning of a novel transcript variant encoding a truncated form of PA28G likely involved in cell cycle regulation and apoptosis. 26201457_In a p53-dominated cellular context, pro-apoptotic signaling might be overcome by PA28gamma-mediated caspase inhibition. 26425675_Surrogate Prognostic Biomarkers in OSCC: The Paradigm of PA28gamma Overexpression. 26425691_PA28gamma in OSCC tumor tissues were significantly high expression than those in normal tissues. 26944602_Study demonstrated that the gene therapy with proteasome activator, PA28gamma can improve ubiquitin-proteasome system function as well as behavioral abnormalities in Huntington's disease model mice 27511885_the ubiquitin-independent REGgamma proteasome regulates energy homeostasis 27756569_PSME3 plays an oncogenic role in pancreatic cancer by inhibiting c-Myc degradation to promote glycolysis. 28529105_that Proteasome activator subunit 3 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition with inducing the expression of CSC markers and influencing the tumor immune microenvironment in breast cancer 28605165_This study demonstrates that REGgamma is a central molecule in the development of melanoma by regulating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 29020881_Knockdown of REG-GAMMA (REGgamma) may inhibit the proliferation and migration, and promote the apoptosis of plasma cell myeloma RPMI-8226 cells possibly by downregulating NF-kappa-B (NF-kappaB) signal pathway. 29437787_REGgamma could be a master regulator during colorectal cancer development to promote YAP signaling and reinforce cross-talks between inflammation and growth pathways, and REGgamma might be a new marker for prognosis of colorectal cancer patients. 29509725_High expression of REGg seemed positively correlated with T-stage and lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma tissues. 29611800_HBx levels are upregulated via a positive feedback loop involving p53 and PA28gamma to stimulate hepatitis B virus propagation. 29702196_Study found that PA28gamma enhanced the ability of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells to promote the migration, invasion, and tube formation of HUVECs and promoted tumor-induced angiogenesis in xenograft mice models in vivo. Expression and secretion of IL-6 and CCL2 were dependent on PA28gamma expression. In addition, IL-6, CCL2 and PA28gamma expressions were correlated in a clinical OSCC cohort. 29795381_casein kinase 1epsilon (CK1epsilon) was identified as a novel target of REGgamma and knockdown of CK1epsilon effectively abolished the effect of REGgamma depletion on renal cell carcinoma cells growth. 29934401_data show that PIP30 deeply affects PA28gamma interactions with cellular proteins, including the 20S proteasome, demonstrating that it is an important regulator of PA28gamma in cells and thus a new player in the control of the multiple functions of the proteasome within the nucleus. 30602418_HCV core fragment (Core71) binds to the 20S proteasome and its activator PA28gamma. The N-terminal 1-71 fragment of Hepatitis C virus (HCV) core protein (Core71) enhances the PA28gamma-20S complex formation with reduced proteolytic activity. Fragmented HCV core can cause pathogenic dysfunction of proteasomes in the nucleus. 31243343_REGgamma ablation impedes dedifferentiation of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma and accentuates radio-therapeutic response by regulating the Smad7-TGF-beta pathway. 31282281_Expression of REGgamma in atherosclerotic plaques and promotes endothelial cells apoptosis via the cyclophilin A pathway indicates functional implications in atherogenesis. 31491459_REGgamma potentiates TGF-beta/Smad signal dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition in thyroid cancer cells. 31596196_In conclusion, the ability of hepatitis B virus X protein to upregulate human PA28gamma levels via p53 activation, in a Ser-101-dependent pathway, is critical for the stimulation of hepatitis B virus replication. 31605415_U2AF1 was significantly positively associated with PA28gamma in oral squamous cell carcinoma 31630568_PSME3 was upregulated in the colorectal cancer.PSME3 may promote proliferation, invasive and migratory potential of the colorectal cancer. 32424140_The proteasome activator REGgamma accelerates cardiac hypertrophy by declining PP2Acalpha-SOD2 pathway. 32568029_Hepatitis B virus X protein stimulates cell growth by downregulating p16 levels via PA28gamma-mediated proteasomal degradation. 33230243_Reciprocal REGgamma-mTORC1 regulation promotes glycolytic metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33262340_Conformational maps of human 20S proteasomes reveal PA28- and immuno-dependent inter-ring crosstalks. 33562807_PA28gamma: New Insights on an Ancient Proteasome Activator. 33933312_REGgamma regulates hair cycle by activating Lgr5 positive hair follicle stem cells. 34555669_Proteasomal activator 28 gamma stabilizes hepatitis B virus X protein by competitively inhibiting the Siah-1-mediated proteasomal degradation. 34913092_PA28gamma-20S proteasome is a proteolytic complex committed to degrade unfolded proteins. | ENSMUSG00000078652 | Psme3 | 883.930944 | 0.9494801 | -0.074790355 | 0.06013549 | 1.54685660978 | 0.2136000909763761390625091962647275067865848541259765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.43158140583237747378575477341655641794204711914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 875.032139 | 31.764986 | 925.754887 | 33.504247 | |
| ENSG00000131503 | 54882 | ANKHD1 | protein_coding | Q8IWZ3 | FUNCTION: May play a role as a scaffolding protein that may be associated with the abnormal phenotype of leukemia cells. Isoform 2 may possess an antiapoptotic effect and protect cells during normal cell survival through its regulation of caspases. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16098192}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding | This gene encodes a protein with multiple ankyrin repeat domains and a single KH-domain. The protein is thought to function as a scaffolding protein, and it may be involved in the regulation of caspases and thereby play an antiapoptotic role in cell survival. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, one of which generates a fusion transcript (MASK-BP3) with the downstream eIF4E-binding protein 3 (EIF4EBP3) gene, resulting in a protein comprised of the ANKHD1 sequence for the majority of the protein and a different C-terminus due to an alternate reading frame for the EIF4EBP3 segments. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010]. | hsa:404734;hsa:54882; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; innate immune response [GO:0045087] | 16098192_VBARP is a novel splice variant of ANKHD1 and may play a role in cellular apoptosis (antiapoptotic) and cell survival pathway(s 16297570_identification of new splice variant with upregulation of its mRNA considerably higher than other variants during erythroid differentiation 16956752_These findings suggest a role for ANKHD1 as a scaffolding protein that may be associated with the abnormal phenotype of leukemia cells. 23142581_These data suggest that ANKHD1 might have a role in multiple myeloma cell proliferation and cell cycle progression by regulating expression of p21. 24726915_ANKHD1 is a positive regulator of YAP1 and promotes cell growth and cell cycle progression through Cyclin A upregulation. 25483783_Data suggest an association of ANKHD1 (Ankyrin repeat and KH domain-containing protein 1) protein with p21 (WAF1/CIP1) promoter region. 25523139_ANKHD1 may be an oncogene and participate in the leukemia cell phenotype. 29695508_High ANKHD1 expression is associated with renal cancer. 30646949_we identified ANKHD1 as a co-regulator with SMYD3. We provided evidence that SMYD3 transactivates its target genes and promotes HCC cells migration and invasion through ANKHD1. 32319569_ANKHD1 promotes proliferation and invasion of nonsmallcell lung cancer cells via regulating YAP oncoprotein expression and inactivating the Hippo pathway. 32562952_ANKHD1 is an S phase protein required for histone synthesis and DNA repair in multiple myeloma cells. 32635985_Emerging functions for ANKHD1 in cancer-related signaling pathways and cellular processes. 35110552_The feedback loop of ANKHD1/lncRNA MALAT1/YAP1 strengthens the radioresistance of CRC by activating YAP1/AKT signaling. | ENSMUSG00000024483 | Ankhd1 | 204.493747 | 1.1919116 | 0.253277231 | 0.15151991 | 2.78360978161 | 0.0952333030964047366762059709799359552562236785888671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.25637479671141444326210034887481015175580978393554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 207.135985 | 31.582977 | 175.074047 | 26.835277 | |
| ENSG00000131748 | 10948 | STARD3 | protein_coding | Q14849 | FUNCTION: Sterol-binding protein that mediates cholesterol transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to endosomes (PubMed:11053434, PubMed:15930133, PubMed:22514632, PubMed:28377464). Creates contact site between the endoplasmic reticulum and late endosomes: localizes to late endosome membranes and contacts the endoplasmic reticulum via interaction with VAPA and VAPB (PubMed:24105263, PubMed:28377464). Acts as a lipid transfer protein that redirects sterol to the endosome at the expense of the cell membrane and favors membrane formation inside endosomes (PubMed:28377464). May also mediate cholesterol transport between other membranes, such as mitochondria membrane or cell membrane (PubMed:12070139, PubMed:19965586). However, such results need additional experimental evidences; probably mainly mediates cholesterol transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to endosomes (PubMed:28377464). Does not activate transcriptional cholesterol sensing (PubMed:28377464). Able to bind other lipids, such as lutein, a xanthophyll carotenoids that form the macular pigment of the retina (PubMed:21322544). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11053434, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12070139, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15930133, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19965586, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21322544, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22514632, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24105263, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28377464}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Endosome;Lipid transport;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | This gene encodes a member of a subfamily of lipid trafficking proteins that are characterized by a C-terminal steroidogenic acute regulatory domain and an N-terminal metastatic lymph node 64 domain. The encoded protein localizes to the membranes of late endosomes and may be involved in exporting cholesterol. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. | hsa:10948; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum-endosome membrane contact site [GO:0140284]; endosome [GO:0005768]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; organelle membrane contact site [GO:0044232]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; cholesterol transfer activity [GO:0120020]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; cholesterol transport [GO:0030301]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; mitochondrial transport [GO:0006839]; progesterone biosynthetic process [GO:0006701]; steroid metabolic process [GO:0008202]; vesicle tethering to endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0099044] | 12070139_role of MLN64 in cholesterol transport from lysosomes to steroidogenic mitochondria 12398991_NPC2, NPC1 and MLN64 may act in an ordered sequence to sense cholesterol, effect sterol movement, and consequently, influence the process of vesicular trafficking. 14715710_With saturating MLN64, steroidogenesis by placental mitochondria proceeds at near-maximal rate. 15010812_Oncogenomic recombination hotspot around the PPP1R1B-STARD3-TCAP-PNMT-PERLD1-ERBB2-C17orf37-GRB7 amplicon at human chromosome 17q12 is closely linked to evolutionary recombination hotspot around the GSDML-GSDM locus. 15718238_The MENTAL (MLN64 amino-terminal shared with MENTHO) domain might serve to maintain cholesterol at the membrane of late endosomes prior to its shuttle to cytoplasmic acceptor(s). 15930133_local sterol enrichment by MLN64 in the late endosomal membranes facilitates their association with actin, thereby governing actin-dependent fusion and degradative activity of late endocytic organelles 16709157_In this review, MLN64 defines discrete cholesterol-containing subdomains within the membrane of late endosomes where they may function in cholesterol transport. 16990645_three-dimensional atomic models of the StART domains of metastatic lymph node 64 (MLN64) and steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) proteins in complex with cholesterol 17117180_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18331352_provide evidence for differential cholesterol binding of the two most closely related START domain proteins STARD1 and STARD3 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19272380_Differential regulation of STARD1 and D3 reflects their distinct roles in macrophage cholesterol metabolism, and may inform anti-atherogenic strategies. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19965586_a transport pathway for endosomal cholesterol to mitochondria that requires MLN64, but not NPC1 20198306_FAK contributed to the increased adhesion in MDA-MB-231DeltaMLN64 cells. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21322544_data indicate that StARD3 is the primary lutein-binding protein in macula lutea; recombinant StARD3 selectively binds lutein with high affinity 24105263_STARD3 or STARD3NL and VAP form a novel molecular tether between late endosomes and the endoplasmic reticulum. 24276243_Findings show that PPP1R1B-STARD3 fusion transcript has a key role in subsets of gastric cancers through the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling. 24291029_Haplotype analysis indicated that combined effect of STARD3 variants (rs9972882, rs881844, rs11869286 and rs1877031) might affect the risk of GC. 25459514_Data indicate that mitochondrial proteolytic activation of START domain-containing protein 3 (STARD3) enhances steroidogenesis. 25681734_Elevated StARD3 expression may contribute to breast cancer aggressiveness by increasing membrane cholesterol and enhancing oncogenic signaling. 27055092_Study present a rare case of a 46,XY patient with CHD associated with ambiguous genitalia consisting of a clitoris-like phallus and a bifid scrotum. Exome sequencing revealed novel homozygous mutations in the FGFR1 and STARD3 genes that may be associated with the phenotype. 27068960_STARD3 or STARD3NL-mediated ER-endosome contacts, which affect endosome dynamics, are believed to be involved in cholesterol transport 27487925_Structure of the lutein-binding domain of human StARD3 at 1.74 A resolution and model of a complex with lutein has been presented. 28282615_Findings suggest that MLN64 overexpression induces an increase in mitochondrial cholesterol content and consequently a decrease in mitochondrial GSH content leading to mitochondrial dysfunction. In addition, MLN64 expression is increased in Niemann-Pick C1 deficient cells and plays a key role in cholesterol transport into the mitochondria. 28377464_Thus, STARD3 is a cholesterol transporter scaffolding endoplasmic reticulum-endosome contacts and modulating cellular cholesterol repartition by delivering cholesterol to endosomes. 35022465_Annexin A6 and NPC1 regulate LDL-inducible cell migration and distribution of focal adhesions. | ENSMUSG00000018167 | Stard3 | 371.781047 | 1.0188126 | 0.026888664 | 0.10796276 | 0.06197568803 | 0.8034001020418167771097728291351813822984695434570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.90833823370198307767253709243959747254848480224609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 379.883491 | 28.895010 | 374.616891 | 28.470515 | |
| ENSG00000132170 | 5468 | PPARG | protein_coding | P37231 | FUNCTION: Nuclear receptor that binds peroxisome proliferators such as hypolipidemic drugs and fatty acids. Once activated by a ligand, the nuclear receptor binds to DNA specific PPAR response elements (PPRE) and modulates the transcription of its target genes, such as acyl-CoA oxidase. It therefore controls the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway of fatty acids. Key regulator of adipocyte differentiation and glucose homeostasis. ARF6 acts as a key regulator of the tissue-specific adipocyte P2 (aP2) enhancer. Acts as a critical regulator of gut homeostasis by suppressing NF-kappa-B-mediated pro-inflammatory responses. Plays a role in the regulation of cardiovascular circadian rhythms by regulating the transcription of BMAL1 in the blood vessels (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P37238, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16150867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20829347, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23525231, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9065481}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Upon treatment with M.tuberculosis or its lipoprotein LpqH, phosphorylation of MAPK p38 and IL-6 production are modulated, probably via this protein. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25504154}. | 3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Biological rhythms;Cytoplasm;Diabetes mellitus;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Glycoprotein;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Obesity;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a member of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) subfamily of nuclear receptors. PPARs form heterodimers with retinoid X receptors (RXRs) and these heterodimers regulate transcription of various genes. Three subtypes of PPARs are known: PPAR-alpha, PPAR-delta, and PPAR-gamma. The protein encoded by this gene is PPAR-gamma and is a regulator of adipocyte differentiation. Additionally, PPAR-gamma has been implicated in the pathology of numerous diseases including obesity, diabetes, atherosclerosis and cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:5468; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; alpha-actinin binding [GO:0051393]; arachidonic acid binding [GO:0050544]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA binding domain binding [GO:0050692]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; double-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003690]; E-box binding [GO:0070888]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; LBD domain binding [GO:0050693]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; nuclear retinoid X receptor binding [GO:0046965]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; peptide binding [GO:0042277]; prostaglandin receptor activity [GO:0004955]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; R-SMAD binding [GO:0070412]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; STAT family protein binding [GO:0097677]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription coregulator binding [GO:0001221]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell fate commitment [GO:0045165]; cell maturation [GO:0048469]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; cellular response to low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus [GO:0071404]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; hormone-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0009755]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; lipoprotein transport [GO:0042953]; long-chain fatty acid transport [GO:0015909]; macrophage derived foam cell differentiation [GO:0010742]; monocyte differentiation [GO:0030224]; mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0042789]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration [GO:0043537]; negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030514]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress [GO:1903243]; negative regulation of cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus [GO:1903845]; negative regulation of cholesterol storage [GO:0010887]; negative regulation of connective tissue replacement involved in inflammatory response wound healing [GO:1904597]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of lipid storage [GO:0010888]; negative regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation [GO:0010745]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902894]; negative regulation of miRNA-mediated gene silencing [GO:0060965]; negative regulation of mitochondrial fission [GO:0090258]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; negative regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0060394]; negative regulation of receptor signaling pathway via STAT [GO:1904893]; negative regulation of sequestering of triglyceride [GO:0010891]; negative regulation of signaling receptor activity [GO:2000272]; negative regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060392]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048662]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; negative regulation of type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060336]; negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904706]; negative regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation [GO:1905563]; peroxisome proliferator activated receptor signaling pathway [GO:0035357]; placenta development [GO:0001890]; positive regulation of adiponectin secretion [GO:0070165]; positive regulation of adipose tissue development [GO:1904179]; positive regulation of cholesterol efflux [GO:0010875]; positive regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043388]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045600]; positive regulation of fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0045923]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of low-density lipoprotein receptor activity [GO:1905599]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060391]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:1905461]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:1900076]; regulation of cholesterol transporter activity [GO:0060694]; regulation of circadian rhythm [GO:0042752]; regulation of lipid metabolic process [GO:0019216]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to lipid [GO:0033993]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584]; retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048384]; rhythmic process [GO:0048511]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; white fat cell differentiation [GO:0050872] | 11069206_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11079814_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11242476_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11246892_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11248748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11289055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11315829_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11334419_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11402923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11409297_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11444435_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11466580_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11508283_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11511919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11522688_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11554739_The expression of the human PPARgamma gene is controlled by RORalpha1. 11554760_PPAR-gamma induces pancreatic cancer cell apoptosis 11596673_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11793024_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11809750_role in inducing cyclooxygenase-2 in monocytes 11836319_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11836575_Expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and the growth inhibitory effect of its synthetic ligands in human salivary gland cancer cell lines. 11840500_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11845236_Reduced lipolysis as possible cause for greater weight gain in subjects with the Pro12Ala polymorphism in PPARgamma2 11847231_Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists inhibit HIV-1 replication in macrophages by transcriptional and post-transcriptional effects. 11862322_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11872365_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11872365_the role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) in high-fat diet induced-obesity and insulin resistance by gene targeting and case-control study using the common PPARgamma2 polymorphism 11872366_Pharmacologic activation of PPARgamma in vascular cells may provide a novel therapeutic approach to retard diabetes-associated vascular disease. 11872377_the roles of PPARgamma and the actions of PPARgamma ligands in the cardiovascular system 11872694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11877444_T0070907, a selective ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, functions as an antagonist of biochemical and cellular activities 11884452_Activation of PPAR gamma by oxidized lipoproteins (oxLDL) promotes macrophage desensitization by reducing oxLDL-stimulated oxygen radical formation, an important determinant of the activation/deactivation balance in macrophages. 11888683_The presence of PPAR gamma in bladder cancers having characteristics of low malignancy is associated with its role in modulating expression of those angiogenic factors (e.g., bFGF and PDECGF) that may be responsible for malignancy in bladder tumor cells. 11897617_cPLA(2) plays a critical role in PPAR-mediated gene transcription in HepG2 cells 11897821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11903058_Nuclear receptor corepressor-dependent repression of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor delta-mediated transactivation 11914642_PPARgamma augments TNF-family induced apoptosis 11916624_Lack of association between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma-2 gene variants and the occurrence of coronary heart disease in patients with diabetes mellitus. 11916624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11923467_Retinoid X receptor alpha is implicated in the nuclear reorganization of PPAR gamma and suggest that PPAR gamma colocalizes with RXR alpha at specific locations within the nucleus independent of added ligand. 11924722_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11924722_PPARgamma2 pro12Ala polymorphism and insulin resistance in Japanese hypertensive patients. 11928067_Pro12Ala polymorphism of PPAR(gamma2) gene is not associated with diabetic retinopathy but is associated with dyslipidemia in male type 2 diabetic patients 11934839_activation of PPARgamma in human CD4-positive T cells limits the expression of proinflammatory cytokines, such as IFNgamma 11948400_Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma stimulates the growth arrest and DNA-damage inducible 153 gene in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. 11948965_PPAR-gamma is induced in prostate cancer; PPAR-gamma ligands may mediate its antiproliferative effect against prostate cancer cells through differentiation 11953889_Inhibition of human chondrosarcoma cell growth via apoptosis by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. 11956653_Frequent polymorphism of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma gene in colorectal cancer containing wild-type K-ras gene. 11972302_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11972302_Pro12Ala polymorphism of the gene is associated with reduced type 2 diabetes risk and increased insulin sensitivity 11979403_genes of C3, HSL, and PPARgamma may exert a modifying effect on lipid and glucose metabolism in familial combined hyperlipidemia 11980626_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11980898_differential regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in bladder cancer cells (peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, beta) 12015306_PPRE in intron 1 of the ACBP gene is a bona fide PPARgamma-response element. 12029076_findings suggest an involvement of PPARgamma in trophoblast differentiation during normal placental development; down-regulation of PPARgamma may contribute to trophoblastic diseases such as hydatidufirm mole and choriocarcinoma 12048686_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12054675_PPAR activators inhibit endothelial cell migration by targeting Akt. 12055328_adipose tissue peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma1 mRNA concentration is positively regulated by eicosapentaenoic acid 12056809_Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma inhibits osteoprotegerin gene expression in human aortic smooth muscle cells 12062858_Differential effect of variants in the development of type 2 diabetes between native Japanese and Japanese Americans. 12062858_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12065695_PPARgamma is a target for induction of apoptosis in rheumatoid synovial cells 12075579_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12077117_85kD PLA2 mediates PPARG activation in lung epithelial cells 12079854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12080321_reduces growth of esophageal cancer 12080444_obesity is associated with an inverse relationship between PPARgamma and retinoic acid receptor alpha expressions in subcutaneous adipose tissue 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12086968_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12086968_effect of polymorphism on insulin sensitivity and metabolism; interactions with birth size 12107164_Activation of endothelial PPAR-gamma has a potent anti-inflammatory role. 12118251_we describe a family in which five individuals with severe insulin resistance, but no unaffected family members, were compound heterozygous with respect to frameshift/premature stop mutations in two unlinked genes, PPARG and PPP1R3A 12145143_the Pro12Ala polymorphism in PPAR-gamma2 represents the first genetic variant with a broad impact on the risk of common type 2 diabetes 12145174_Association of the Pro12Ala polymorphism with 3-year incidence of type 2 diabetes and body weight change in the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study 12145174_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12145184_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12145184_polymorphism Pro12Ala is associated with nephropathy in type 2 diabetes 12148087_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12148087_The Pro115Gln polymorphism has no epidemiological impact on morbid obesity 12161538_Expression of PAX8-PPAR gamma 1 rearrangements in both follicular thyroid carcinomas and adenomas. 12161548_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12165097_negative regulatory function for PPARgamma on cytokine and MMP production together with inhibition of cytokine-mediated inflammatory responses in rheumatoid synovial cells 12189136_role of 13-(S)-HODE in upregulating the MAP kinase signaling pathway and subsequently downregulating PPARgamma 12193733_Nitric oxide-activated anti-inflammatory properties of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)gamma in monocytes/macrophages down-regulate p47phox and attenuate the respiratory burst. 12213872_Differential effects of adiposity on messenger ribonucleic acid expression in human adipocytes 12218380_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12218380_analysis of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma2 genotype showed that leptin levels were determined by the Pro12Ala mutation in type-2 diabetic women but not in men 12230498_melanoma cell growth may be modulated through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. 12324185_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12324185_There is no association between PPAR-gamma polymorphism and the occurence or severity of preeclampsia. 12324573_In esophageal cancer tissues, the expression of PPAR gamma was decreased compared with normal esophageal epithelium. 12354130_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12370112_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12370112_the Pro12Ala polymorphism of the PPARgamma-2 gene promotes peripheral deposition of adipose tissue and increased insulin sensitivity for a given BMI. 12395215_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12397176_mediates the proliferative action of mast-cell tryptase: possible relevance to human fibrotic disorders 12397391_mRNA levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma are not altered during fasting. 12401439_Binding of PPARG ligands (troglitazone or BRL49653) to monocyte PPARG inhibited TXA(2) production and enhanced PGE(2) production of PBMC 12404189_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12406034_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12429071_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12439219_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12439219_lack of association of codon 12 polymorphism with breast cancer and body mass 12453902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12453919_Candidate gene sequencing showed that all four affected subjects were heterozygous for a novel T-->A mutation at PPARG nucleotide 1164 in exon 5 that predicted substitution of phenylalanine at codon 388 by leucine (F388L). 12457461_Data demonstrate that Egr-1, AP1 and Smad are part components of the transforming growth factor beta signal transduction pathway that regulates PPAR gamma expression. 12468551_PPARgamma has a role in inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell growth by regulating levels of TSC-22 12485829_With RXR-alpha, forms a heterodimer involved in the regulation of human trophoblast invasion 12502512_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12502512_We investigated the phenotypic appearance of the two polymorphisms (Pro12Ala and exon 6 C-->T) in PPARgamma among elderly twins and plasma glucose and insulin profiles among MZ and DZ twins. 12502716_role of intact AF-2 domain for ligand-dependent and ligand-independent interaction and coactivation 12519876_Detection of the PAX8-PPAR gamma fusion oncogene in both follicular thyroid carcinomas and adenomas. 12535639_Results suggest that activation of peroxisome proliferative activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) may represent a novel approach for the treatment of pancreatic cancer by increasing PTEN levels and inhibiting PI3K activity. 12536206_natural mutations in human PPARgamma, associated with severe insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus, exhibit perturbations in the dynamic behavior of helix 12 12538445_activity of PPARgamma and PPARgamma ligands in cancer [review] 12544508_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12551936_that fatty acids and rosiglitazone directly stimulate transcription of the LRP gene through activation of PPARgamma and increase functional LRP expression. 12565902_Data describe the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma) co-activator 1, PPAR gamma, insulin receptor substrate-1, glucose transporter isoform-4, and mitochondrial uncoupling protein-1 in adipose tissue. 12568179_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12588773_Functional polymorphism in a STAT5B site of PPAR gamma 3 promoter region affects height and lipid homeostasis via the STAT5B pathway. 12588773_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12591919_codon 422 may be a part of a co-factor(s) interaction domain necessary for PPARgamma to induce terminal differentiation in epithelial, but not adipocyte, cell lineages 12594295_A novel anti-inflammatory pathway is revealed in human airway smooth muscle, where PPAR gamma activation by natural and synthetic ligands inhibits serum-induced cell growth and induces apoptosis. 12601634_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12601634_PPARgamma gene polymorphism is associated with exercise-mediated changes of insulin resistance in healthy men. 12601635_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12601635_conclude that the Pro12Ala polymorphism of the PPAR-gamma2 gene was associated with increased ox-LDL autoantibodies in type 2 diabetic subjects 12609711_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12609711_PPAR-gamma may play a role in prostate carcinogenesis; however, the Pro12Ala polymorphism does not appear to play a significant role in prostate cancer risk in this large cohort of male Finnish smokers. 12610044_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12615657_The activation of PPARgamma-dependent pathways induces the differentiated phenotype in proliferative VSMCs, and this induction is mediated, in part, through a GATA-6-dependent transcriptional mechanism. 12615696_PPARgamma and/or RXR activation inhibit foam cell formation through enhanced cholesterol efflux despite increased oxLDL uptake 12615821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12615821_Role for PPARgamma gene polymorphism in pathogenesis of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Presence of Ala isoform being protective against development of PCOS. 12620489_PPAR-gamma may play a role in the pathogenesis of endometriosis related to the production of IL-6 and some other cytokines. 12630956_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12630956_PPAR-gamma P12A polymorphism can modulate the association between dietary fat intake and components of the metabolic syndrome 12663371_A common A for P substitution at codon 12 in the PPARG2 was associated with reduced incidence of myocardial infarction. 12663371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12673785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12679463_common Pro12Ala polymorphism of the peoxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma2 gene has minor influence on mRNA expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma target genes in adipose tissue of obese subjects 12709137_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12714563_PPARgamma expression is reduced or lacking in all of the angiogenic plexiform lesions of pulmonary hypertensive lungs and in the vascular lesions of a rat model of severe PH (pulmonary hypertension). 12714582_Expression of PPARgamma in activated T-cells may regulate apoptosis & their immunological response in inflammation, depending on agonists released by near-by cells. 12716762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12716762_The polymorphism (Pro12Ala) of this receptor beneficially influences insulin resistance and its tracking from childhood to adulthood. 12727991_results suggest that conventional follicular thyroid carcinomas develop through at least two distinct molecular pathways initiated by either RAS point mutation or PAX8-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma rearrangement 12730300_PPARG has a role in regulating glucose and lipid uptake and oxidation and preadipocyte differentiation 12730867_commensal intestinal flora affects the expression of PPAR gamma and that PPAR gamma expression is considerably impaired in patients with ulcerative colitis 12732844_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12739018_Amino acid substistution is not associated with insulin resistance phenotype. 12746759_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12746759_The Pro115 Gln variant, but not the Pro12Ala mutation in the PPAR-gamma 2 gene, could be a rare cause of severe insulin resistance. 12763030_Transcriptional activation of hepatic scavenger receptor class B, type I is stimulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. 12765846_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12765972_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12765972_Pro12Ala of this gene is associated with lower serum insulin levels in nonobese African Americans 12767049_activity in prostate cancer cells 12776192_functional downregulation of PPARgamma is a key event in multiple types of thyroid neoplasia 12779083_Treatment of human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 with the synthetic PPARgamma ligands pioglitazone, rosiglitazone, GW7845 or its natural ligand 15-deoxy-delta 12, 14-prostaglandin J2(15d-PGJ2) led to inhibition of the invasiveness of this cell line. 12800106_Because PPARgamma(2) is mainly expressed in adipose tissue, one of the main regulatory effects of the polymorphism may well be the more efficient suppression of (possibly intra-abdominal) lipolysis. 12800106_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12800228_Troglitazone, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligand, inhibits growth of HepG2 cells and induces apoptosis. COX-2 mRNA and protein and Bcl-2 was down-regulated. Bax and Bak was up-regulated. Activity of caspase-3 was elevated. 12801525_Receptor 'C(k)'-dependent signalling pathway regulates PPAR-gamma gene transcription; a proposed molecular cross-talk pathway between Receptor-C(k) and PPAR-gamma may play a role in control of leukemogenesis. 12801610_Expression of PPARgamma was increased to greatest degree by highly-oxLDL. DNA binding activity of PPARgamma was increased only by mildly- and moderately-oxLDL. 12805087_Results suggest that granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor regulates lung homeostasis via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma-dependent pathways. 12813462_PPARgamma participates in the regulation of caveolin 1 and 2 gene expression in human carcinoma cells. 12821652_Rev-Erbalpha as a target gene of PPARgamma in adipose tissue and demonstrate a role for this nuclear receptor as a promoter of adipocyte differentiation. 12827242_Adiponectin is a genetic factor associated with insulin sensitivity. Interactions with PPARgamma2 genotypes modified this association. 12829631_Expression plays a role in energy homeostasis in obese women. 12829658_A functional variant in this protein's promoter is associated with predictors of obesity and NIDDM in Pima Indians. 12829658_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12829715_Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and ligands inhibit surfactant protein B gene expression in the lung 12829999_a novel p53-dependent mechanism in the PPARgamma ligand-mediated inhibition of cholangiocarcinoma growth and suggest a potential therapeutic role of PPARgamma ligands in the treatment of human cholangiocarcinoma. 12839938_Ligands of this receptor affect the expression of RAR beta in cancer cells 12839942_Common polymorphisms in this protein are associated with increased risk of colorectal cancer. 12839942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12861348_although activation of PPARgamma appears to have beneficial effects on atherosclerosis and heart failure, it is still largely uncertain whether PPARgamma ligands prevent the development of cardiovascular diseases-REVIEW 12866036_Down-regulation of peroxisome-proliferator activated receptor-gamma is associated with local recurrence and metastasis in breast cancer 12915690_reduced expression of PPARgamma might be an early event in colonic tumorigenesis 12923071_PPARgamma activation enhances cell surface ENaCalpha via up-regulation of SGK1 in collecting duct cells. 12923396_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12923396_significant contribution of the PPARgamma2(Pro12Ala) and eNOS(4a/b) gene polymorphisms to hypertensive risk in our population (odds ratio, 1.9 and 1.6, respectively), confirmed by multiple logistic regression analysis. 12923397_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12923397_The common Pro12Ala polymorphism in PPARgamma is associated with lower diastolic blood pressure in male subjects with type 2 diabetes. 12949056_plays an important role in the differentiation of intestinal cells 12970322_lack of the PAX8/PPAR gamma rearrangement in the anaplastic thyroid carcinoma group suggests that the tumorigenic pathway in these tumors is likely to be independent of this fusion 12974743_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14506127_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14506127_PPARG genotype is an important factor in physiological responses to dietary fat in humans. 14506281_PPARgamma and PPARdelta have roles in transcriptional activation of Spermidine/sperm-ine N1-acetyltransferase, which leads to reduced tissue polyamine contents in human colon cancer cells 14514601_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14514601_inverse association between the PPARgamma variant 12Ala allele and risk of type 2 diabetes. 14515149_15d-PGJ(2) differently upregulates MMP-1 expression in HMEC-1 through induction of oxidative stress, and inhibits uPA synthesis partly by activation of peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, gamma (PPARgamma). 14550563_non-hydrolysed, oxidised phospholipids in oxLDL activate PPARgamma as a cellular defence mechanism against macrophage death 14566836_15-hydroxy-eicosatetraenoic acid (15S-HETE), an endogenous ligand for PPARgamma, was significantly decreased in the serum of patients with colorectal cancer 14574455_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14581147_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14581147_Pro12Ala amino acid variant of the PPARgamma2 isoform is not associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes. 14581151_PPARgamma can reduce plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 production in vascular endothelial cells directly by transcriptional repression. 14581158_Japanese with the Ala12 allele had a significantly lower value of carotid artery intima-media thickness than those without it. 14581158_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14587029_phosphorylation of PPARgamma was mediated through the ciglitazone-induced activation of Erk1/2 14604894_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14616762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14616762_We report that the PPARG C161T polymorphism is associated with the survival of IgAN patients without hypertension 14627349_Treatment of gastric cancer patients with Vioxx resulted in a significant decrease in plasma and tumor contents of both progastrin and gastrin, and this was accompanied by the increment in tumor expression of COX-2, PPARy, Bax, and caspase-3. 14633865_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14633865_The presence of the Ala allele may confer protection from diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. 14657011_Transcriptional silencing via recruitment of corepressor adds to dominant-negative inhibition of wild type by P467L and V290M mutants. Introduction of artificial mutation (L318A) disrupting corepressor interaction abrogated dominant-negative activity. 14659862_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14668325_study shows that peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) agonists strongly regulate myeloperoxidase gene expression through the Alu element repeats 14671186_Higher frequency of C-->T substitution in exon 6 of PPAR-gamma gene in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). May play role in complex pathogenesis of obesity in PCOS. Pro(12)Ala polymorphism does not seem to affect body mass index in PCOS women. 14671186_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14671211_Expression of adipophilin is enhanced during trophoblast differentiation and is up-regulated by ligand-activated PPARgamma/retinoid X receptor. May contribute to fatty acid uptake by placenta. 14671555_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14677049_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14680975_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14680975_PPARgamma is a quantitative trait locus for free fatty acid and glycerol, against a background of insulin resistance for adipose tissue lipid metabolism, and therefore as a modifier gene in familial combined hyperlipidemia. 14681322_The high-level expression of PPARgamma may provide a potential molecular target for the treatment of salivary duct carcinoma using agonist ligands. 14681835_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14681835_study examined the modification by peroxisome proliferative activated receptor gamma genotype of the association between energy expenditure, dietary polyunsaturated to saturated fatty acid ratio, and fasting insulin level, a measure of insulin resistance 14686729_High-levels of PPARgamma expression is associated with glioblastoma 14702344_restoration of PPARgamma reverses the activated hepatic stellate cells to the quiescent phenotype and suppresses AP-1 activity via a physical interaction between PPARgamma and JunD 14729856_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14729856_The Pro12Ala polymorphism was more associated with plasma lipids and fasting glucose concentrations, whereas the C1431T polymorphism was related to the risk of diabetes. 14730381_Ala12 variant of PPARgamma affords protection from Type 2 diabetes, and this protection is modulated by additional common variation at the PPARG locus. 14730381_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14747257_polymorphic in metabolic syndrome phenotype in Brazil 14974928_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14981210_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14988278_Association of this gene's single nucleotide polymorphism with type 2 diabetes. 15015141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15015141_fatty acid binding protein 4 and PPARgamma work together to influence a biologic pathway affecting insulin sensitivity and body composition 15023995_mPGES-1 and Egr-1 are novel targets of PPARgamma and inhibition of mPGES-1 gene transcription may be one of the mechanisms by which PPARgamma regulates inflammatory responses 15041706_PPARgamma ligands inhibit human lung carcinoma cell growth and induce apoptosis by stimulating the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21. 15054105_PPARgamma and EGFR signalling have roles in urothelial terminal differentiation 15072437_x ray crystallography to determine binding sites 15077315_By abrogating of TGF beta-induced stimulation of collagen gene expression, myofibroblast transdifferentiation, and Smad-dependent promoter activity in normal fibroblasts, PPAR gamma may play a physiologic role in the regulation of the profibrotic response 15077315_Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor-gamma(PPAR-g) disrupts Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-b) signaling and profibrotic responses in skin fibroblasts. 15083308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15083308_Our findings argue against a significant contribution of PPARgamma variations to the genetic basis of psoriasis. 15111325_signaling through PPAR-gamma can mediate transitional differentiation of urothelial cells, modulated by growth regulatory programs 15113752_high glucose upregulates PPAR-gamma and when significantly induced demonstrates anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory effects. 15128052_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15136115_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15144586_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15144586_Peroxisome proliferative activated receptor gamma C161-T may play a important role in carotid artery arteriosclerosis. 15156314_polymorphisms of the PPARg gene are not associated with the incidence of restenosis and adverse clinical events at 30 days or 1 year after coronary artery stenting in patients with diabetes mellitus. 15161789_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15161789_Pro12Ala variant of the PPAR-gamma receptor gene did not explain the failure of patients with NIDDM to increase insulin sensitivity. 15165749_the net result of the pleiotropic effects of PPAR-gamma ligands is improvement of insulin sensitivity, although undesired side-effects limit the utility of this therapy [review] 15187150_15d-PGJ(2)-induced changes were related to functional alteration of the glucocorticoid receptor and did not require the engagement of PPARgamma 15193259_there is an in vivo crosstalk between the HER-kinase axis and PPARgamma pathways, ultimately leading to negative regulation of PPARgamma activity and tumor growth inhibition 15201543_Hypertensive subjects with low birth weight or short length at birth and the Pro12Pro variant had raised systolic blood pressure 15201543_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15202783_In Polish PPAR-gamma2 12Pro allele carriers, obesity correlated with free fatty acid tolerance in males, and insulin resistance in females. 15211802_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15217350_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15220243_Upregulated by pioglitazone in type 2 diabetes. 15236769_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15254719_both PPARgamma and its coactivator PGC-1 play important roles in the development and | ENSMUSG00000000440 | Pparg | 115.338604 | 1.5962645 | 0.674699768 | 0.17291871 | 15.19255131245 | 0.0000970856219600093158427975281732358325825771316885948181152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00100446278104778874765146134961923962691798806190490722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 141.321085 | 11.954365 | 88.899601 | 7.909598 | |
| ENSG00000132424 | 25957 | PNISR | protein_coding | Q8TF01 | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation | Enables RNA binding activity. Located in cytosol; nuclear speck; and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:25957; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; RNA binding [GO:0003723] | 28589370_results indicate that LUC7L3, PPIG, and SFRS18 are not only implicated in EDA+ fibronectin formation, but also that they could possess multiple roles in psoriasis-associated molecular abnormalities. 29512856_In our present RNA-Seq experiment, we demonstrated that the LUC7L3 and SFRS18 splicing factors contribute to the regulation of several well-known psoriasis-associated pathways, including the IFN signalling pathway, antiviral immunity and ubiquitination. | ENSMUSG00000028248 | Pnisr | 966.774417 | 0.9332389 | -0.099681663 | 0.06734090 | 2.19061528290 | 0.1388538384992937246842359400034183636307716369628906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.32828685908102073209846594181726686656475067138671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 973.556306 | 36.143995 | 1048.550504 | 38.177129 | ||
| ENSG00000133243 | 55643 | BTBD2 | protein_coding | Q9BX70 | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome | The C-terminus of the protein encoded by this gene binds topoisomerase I. The N-terminus contains a proline-rich region and a BTB/POZ domain (broad-complex, Tramtrack and bric a brac/Pox virus and Zinc finger), both of which are typically involved in protein-protein interactions. Subcellularly, the protein localizes to cytoplasmic bodies. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:55643; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; P-body [GO:0000932]; neurogenesis [GO:0022008] | 12878161_subcellular colocalization of BTBD1 and BTBD2 to cytoplasmic bodies; TRIM5delta colocalized with BTBD1/2 and appeared to serve as a scaffold for the assembly of endogenous BTBD1/2 proteins 20368557_Polymorphisms in the LIG4, BTBD2, HMGA2, and RTEL1 genes, which are involved in the double-strand break repair pathway, are associated with glioblastoma multiforme survival. 20610542_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21092135_Interaction of BTBD1 and BTBD2 with TOP1 requires TOP1 residues 236 and 237, the same residues required to enhance the infectivity of progeny virions when TOP1 is expressed in African Green Monkey producer cells. | ENSMUSG00000003344 | Btbd2 | 304.614936 | 1.2941773 | 0.372035314 | 0.27736013 | 1.78773570915 | 0.1812022877838579959508535921486327424645423889160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.38940702274576727281996113561035599559545516967773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 330.661370 | 60.640935 | 257.036770 | 46.983702 | ||
| ENSG00000133706 | 51520 | LARS1 | protein_coding | Q9P2J5 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the specific attachment of an amino acid to its cognate tRNA in a two step reaction: the amino acid (AA) is first activated by ATP to form AA-AMP and then transferred to the acceptor end of the tRNA. Exhibits a post-transfer editing activity to hydrolyze mischarged tRNAs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19426743}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Ligase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a cytosolic leucine-tRNA synthetase, a member of the class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family. The encoded enzyme catalyzes the ATP-dependent ligation of L-leucine to tRNA(Leu). It is found in the cytoplasm as part of a multisynthetase complex and interacts with the arginine tRNA synthetase through its C-terminal domain. A mutation in this gene was found in affected individuals with infantile liver failure syndrome 1. Alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. | hsa:51520; | aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase multienzyme complex [GO:0017101]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; aminoacyl-tRNA editing activity [GO:0002161]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; glutamine-tRNA ligase activity [GO:0004819]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; leucine-tRNA ligase activity [GO:0004823]; cellular response to amino acid starvation [GO:0034198]; cellular response to amino acid stimulus [GO:0071230]; cellular response to leucine [GO:0071233]; cellular response to leucine starvation [GO:1990253]; glutaminyl-tRNA aminoacylation [GO:0006425]; leucyl-tRNA aminoacylation [GO:0006429]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032008]; positive regulation of TORC1 signaling [GO:1904263]; regulation of cell size [GO:0008361]; tRNA aminoacylation for protein translation [GO:0006418] | 16055448_leucyl-tRNA synthetase requires its C-terminal domain for its interaction with arginyl-tRNA synthetase in the multi-tRNA synthetase complex 17363246_We identified a novel G3283A transition in the mitochondrial DNA tRNA(Leu (UUR)) gene in a patient with ptosis, ophthalmoparesis and hyporeflexia. 17378584_Results show that K600 in human leucyl-tRNA synthetase affects amino acid specificity and tRNA aminoacylation. 18446061_findings suggest that LARS1 may play roles in migration and growth of lung cancer cells, which suggest its potential implication in lung tumorigenesis 19426743_Study of crystal structures of the editing domain from 2 eukaryotic cytosolic LeuRS; shows a conserved structural core containing the active site for hydrolysis, with distinct bacterial, archeal, or eukaryotic peripheral insertions. 19702327_the introduction of bulky residues into the amino acid binding pocket failed to block deacylation of tRNA, indicating that the architecture of the amino acid binding pocket is different compared to that of other characterized LeuRSs 20805241_hcLeuRS can charge RNALeu with non-cognate amino acids and exclude the incorrect products by multiple editing pathways. 22424946_This work demonstrates that LRS is a key mediator for amino acid signaling to mTORC1. 22607940_Identification of a mutation in LARS as a novel cause of infantile hepatopathy 24413190_the carboxy-terminal domain of human mitochondrial (mt) leucyl-tRNA synthetase can be used to correct mt dysfunctions caused by mt-tRNA mutations. 25051973_Lack of a CP1 hairpin in LeuRS led to complete loss of aminoacylation, amino acid activation, and tRNA binding; however, the mutants retained post-transfer editing. 25817995_the KMSKS catalytic loop affects the aminoacylation and editing capacities of leucyl-tRNA synthetase 28882589_The results showed a decrease in autophagy on addition of leucine, demonstrating crosstalk between leucine sensing, LRS translocation, RagD interaction, and mTORC1 activation. 28963468_Leucyl-tRNA synthetase (LRS) is a leucine sensor of the mTORC1 pathway. 31780625_this study provides evidence for a role of leucyl-tRNA synthetase 1 (LARS1) in glucose-dependent control of leucine usage. 32232361_Molecular basis of the multifaceted functions of human leucyl-tRNA synthetase in protein synthesis and beyond. 32699352_Genotypic diversity and phenotypic spectrum of infantile liver failure syndrome type 1 due to variants in LARS1. 33300650_Severe course with lethal hepatocellular injury and skeletal muscular dysgenesis in a neonate with infantile liver failure syndrome type 1 caused by novel LARS1 mutations. 33314043_Infantile Liver Failure Syndrome 1 associated with a novel variant of the LARS1 gene: Clinical, genetic, and functional characterization. 34325132_Leucyl-tRNA synthetase 1 is required for proliferation of TSC-null cells. 35614056_O-GlcNAc modification of leucyl-tRNA synthetase 1 integrates leucine and glucose availability to regulate mTORC1 and the metabolic fate of leucine. 35962451_Identification of LARS as an essential gene for osteosarcoma proliferation through large-Scale CRISPR-Cas9 screening database and experimental verification. | ENSMUSG00000024493 | Lars | 1151.811897 | 0.9603065 | -0.058433192 | 0.05368558 | 1.18447489919 | 0.2764468743159399499731421201431658118963241577148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.50765561506666179170110808627214282751083374023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1133.326531 | 41.277626 | 1185.628905 | 42.867448 | |
| ENSG00000133961 | 8650 | NUMB | protein_coding | P49757 | FUNCTION: Regulates clathrin-mediated receptor endocytosis (PubMed:18657069). Plays a role in the process of neurogenesis (By similarity). Required throughout embryonic neurogenesis to maintain neural progenitor cells, also called radial glial cells (RGCs), by allowing their daughter cells to choose progenitor over neuronal cell fate (By similarity). Not required for the proliferation of neural progenitor cells before the onset of neurogenesis. Also involved postnatally in the subventricular zone (SVZ) neurogenesis by regulating SVZ neuroblasts survival and ependymal wall integrity (By similarity). May also mediate local repair of brain ventricular wall damage (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QZS3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18657069}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Endosome;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation | The protein encoded by this gene plays a role in the determination of cell fates during development. The encoded protein, whose degradation is induced in a proteasome-dependent manner by MDM2, is a membrane-bound protein that has been shown to associate with EPS15, LNX1, and NOTCH1. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. | hsa:8650; | apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; alpha-catenin binding [GO:0045294]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; adherens junction organization [GO:0034332]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; lateral ventricle development [GO:0021670]; negative regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903077]; neuroblast division in subventricular zone [GO:0021849]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050769]; regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor internalization [GO:0099149] | 12646252_These data strongly suggest that Mdm2 functions as the ubiquitin ligase toward hNumb and that it induces its degradation in intact cells. 15492044_the Numb/Notch biological antagonism has a role in homeostasis of the normal mammary parenchyma and its subversion contributes to human mammary carcinogenesis 16394100_These results highlight a role of Numb for dendritic spine development and synaptic functions with intersectin and EphB2. 16508311_The two distinct types of hNumb isoforms could contribute to different phases of neurogenesis in the embryonic CNS. 16865239_Epigenetic silencing, deletion and loss-of-function mutation of NUMB gene could lead to carcinogenesis through the dysregulation of the WNT - Notch signaling cycle. 17115028_Hedgehog transcription factor Gli1 is targeted by Numb for Itch-dependent ubiquitination, which suppresses Hedgehog signals, thus arresting growth and promoting cell differentiation. 17301032_significantly lower expressions of Notch1, Jagged1, Numb, and Delta-like 1 were evident in muscle biopsies from older men (60-75 years old) compared to muscle from younger men (18-25 years old). 17609107_Because Numb interacts with the aPKC binding partner PAR-3, we propose a model in which polarized Numb phosphorylation contributes to cell migration by directing integrin endocytosis to the leading edge 18172499_NUMB enters in a tricomplex with p53 and the E3 ubiquitin ligase HDM2 (also known as MDM2), thereby preventing ubiquitination and degradation of p53 18179751_Numb is implicated in aberrant differentiation programs of salivary gland carcinomas 18384513_Numb expression in astrocytomas recapitulates that of progenitor cells during neurodevelopment, and suggests a role for Numb in astrocytoma oncogenesis. 18599481_Numb endocytic adapter proteins regulate the transport and processing of the amyloid precursor protein in an isoform-dependent manner and have roles in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis 19138666_These observations demonstrate that Numb3 is an endocytic receptor for P-selectin and may be responsible for the rapid internalization of P-selectin when endothelial activation ends. 19344753_Numb promotes neuronal differentiation by a mechanism involving PTB domain-specific regulation of Ca2+ influx and MAP kinase activation. 19468255_Expression of Numb protein in Cervical squamous epithelia may be among the mechanisms involved in the genesis of cervical squamous cell carcinomas 19795205_Results indicate that loss of Numb expression is a marker of tumor aggressiveness, potentially linked to BRCA1 status and a cancer stem cell phenotype in primary breast cancer. 20818436_Numb activates the catalytic activity of Itch, releasing it from an inhibitory intramolecular interaction between its homologous to E6-AP C-terminus and WW domains. 21122105_we report the identification ofthe novel isoforms, NUMB5 and NUMB6, and propose a link between the expression of these isoforms and cancer 21486681_cell migration studies revealed NUMB isoform 1 to be involved in EVT cell migration and NUMB isoforms 2 and 4 to induce EVT apoptosis 21775625_atypical protein kinase C phosphorylates Numb to prevent its binding to p120 and alpha-adaptin, thereby attenuating E-cadherin endocytosis to maintain apicobasal polarity 21939656_NUMB is consistently expressed in glioma biopsies with predominance of NUMB2/4 isoforms as determined by isoform-specific real-time PCR and Western blotting. 22337874_analysis of MDM2 protein-mediated ubiquitination of numb protein 22455121_Numb has an important regulation in the process of colon cancer progression and may play a protective role against tumor development. 22553175_Numb regulates glioma stem cell fate and growth by altering epidermal growth factor receptor and Skp1-Cullin-F-box ubiquitin ligase activity 22593191_Dysregulation of Numb expression results in mislocalized Plk1 and poor centrosomal gamma-tubulin recruitment, potentially contributing to mitotic errors, aneuploidy, and cancer development. 22734830_This study implies that any mutations within the NUMB gene that might influence the disease course of chronic myeloid leukemia are very rare. 22784712_Down-modulation of NUMB is associated with myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia. 23140583_Numb1 interacts with TRPV6 through charged residues and inhibits its activity via the regulation of protein expression. 23233047_Expression of stem cell regulator NUMB is not associated with any prognostic significance in acute myeloid leukemia patients. 23624653_Overexpression of Numb inhibited proliferation, promoted apoptosis and enhanced sensitivity to cisplatin, and activated caspase-9 and caspase-3 through release of cytochrome c as well as downregulation of XIAP and survivin. 23706821_Data indicate the Set8-Numb-p53 signaling axis as an important regulatory pathway for apoptosis and suggests a therapeutic strategy by targeting Numb methylation. 23872314_The Numb modulates the paracellular permeability by affecting apical junctional complex (AJC) assembly and myosin light chain (MLC) phosphorylation. 23881403_The study demonstrates coordinated regulation of Numb, MDM2 and p53 on cell invasion and migration in pancreatic cancer. 24302991_miR-146a enhances the oncogenicity of oral carcinoma by concomitant targeting of the IRAK1, TRAF6 and NUMB genes. 24332178_Identify the Notch pathway regulator NUMB as a key target of these factors. 24770339_Numb up-regulation significantly correlates with cell proliferation and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. 24980814_Findings suggested NUMB-1 functions as a tumor-suppressor and serves as a prognositc biomarker for ESCC patients. 25331956_Numb specifically regulates NPC1L1-mediated cholesterol absorption both in human intestine and liver, distinct from ARH and Dab2, which selectively participate in LDLR-mediated LDL uptake. 25403733_Using LC-MS/MS, the study reports the identification of 25 serine/threonine Numb phosphorylation sites, and a single tyrosine phosphorylation site. 25480416_Taken together, our data suggest that Numb may possibly function as a tumor suppressor involved in the carcinogenesis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma 25889998_The ability of RBM10v1 to regulate alternative splicing depends, at least in part, on a structural alteration within the second RNA recognition motif domain, and correlates with preferential expression of the NUMB exon 11 inclusion variant. 26058814_Alternative splicing of Numb may provide a useful prognostic biomarker in HCC and is pharmacologically tractable 26069237_Numb/Numbl control VEGF receptor endocytosis, signaling, and recycling in endothelial cells, which promotes the angiogenic growth of blood vessels. 26074693_Report alternative splicing of NUMB in colorectal cancer. 26165304_Methylation of the Numb promoter contributed to hepatocarcinogenesis. 26174965_NANOG-NUMB-p53 signaling axis is an important regulatory pathway for tumor-initiating cells events in TIC self-renewal and liver tumorigenesis 26261495_Alternative splicing of APP, VEGFA and NUMB may play an important role in pathogenesis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 26264115_results indicated that both rs2108552 and rs17781919 in the Numb gene were associated with total cholesterol level and density lipoprotein-cholesterol level in Chinese subjects. 26307032_Notch1/Numb/Snail signal pathway plays an important role in the pathogenesis of adenomyosis. 26415596_Numb polymorphisms are associated with coronary artery disease among Han Chinese and Uighur Chinese in Xinjiang, China. 26563369_PNA-antimiR-182 reduced the levels of NICD, Hes1, HIF-1alpha, and p-Akt in both cell groups, while it augmented the intracellular content of FOXO1 and Numb suppressor proteins. In other words, PNA-antimiR-182-mediated upregulation of Numb was associated with downregulation of HIF-1alpha and Hes1. Consequently, downregulation of miR-182 might find therapeutical value for overcoming trastuzumab resistance 26944313_Dominant negative NUMB expression confers a high proliferative phenotype to chronic myeloid leukemia cells. 26987402_Numb binds to another docking regulator, Mon1b, and is required for the recruitment of cytosolic Mon1b to the early endosomes membrane. 27041567_Our evidence supports a mechanism by which Numb AS is regulated in response to oncogenic signaling pathways, and contributes to activation of downstream pathways to promote tumorigenesis. 27092875_Low NUMB expression is associated with pancreatic cancer. 27106262_HBeAg and its precursors promote HDM2-mediated degradation and impair transcriptional activity of p53 by interacting with NUMB, consequently contributing to hepatocellular carcinoma development. 27302072_this study identified a novel molecular determinant of breast cancer progression, uncovering a potential oncogenic role for the NUMB6 protein in cancer cell migration and invasion, coupled to the maintenance of mesenchymal-like cells. 27310305_Radiation sensitivity of NSCLC stem cells was enhanced with the increase of Numb expression. 27358480_Numb is a pivotal adaptor protein that mediates the subcellular localization of EAAT3 through binding the YxNxxF (where x stands for any amino acid) motif. 27383182_These findings highlight the importance of Numb and Numbl in the control of myoepithelial cell fate determination, epithelial identity, and lactogenesis 27476167_Upregulated expression of Numb is associated with reduced radiosensitivity of lung cancer. 27506933_NUMB has a role in negatively regulating the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of triple-negative breast cancer by antagonizing Notch signaling 27677287_High expression of Numb is associated with radiation resistance in pancreatic cancer. 28060745_Numb expression is not associated with favorable prognosis in small cell lung cancer. 28067668_investigations revealed that NUMB and NUMBL interacted with small GTPase Rab7 to transition ERBB2 from early to late endosome for degradation. 28095111_Study found that NUMB protein was significantly upregulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) tissues as compared with paired non-tumor samples. This rise in NUMB protein expression was an independent indicator of a poor prognosis in ESCC patients. 28153862_MAP17 overexpression activates Notch pathway by sequestering NUMB. High levels of MAP17 correlated with tumorsphere formation and Notch and Stem gene transcription. Its direct modification causes direct alteration of tumorsphere number and Notch and Stem pathway transcription 28298340_Using patient-derived xenografts, the study shows that expansion of the cancer stem cells pool, due to altered self-renewing divisions, is also a feature of Numb-deficient human breast cancers . 28437168_In the present study, we identified that the adaptor protein Numb, which is demonstrated to be a novel binding partner of NEDD4-1, plays important roles in controlling PTEN ubiquitination through regulating NEDD4-1 activity and the association between PTEN and NEDD4-1. 28531799_Data suggest that over-expression of NUMB has anti-cancer effects to prostatic cancer cells; these studies included experiments both in vitro and in vivo (xenograft experiments in nude mice). 28720501_Together, our findings revealed a novel function of Numb and its likely mechanism in regulation of autophagy events. 28751447_Numb(-/low) prostate cancer cells were smaller and quiescent, preferentially expressed Notch and Hedgehog downstream and stem-cell-associated genes, and associated with a greater resistance to androgen-deprivation therapy 29059161_Phosphorylated form of Numb by Plk1 is associated with drug-resistant Osteosarcoma. 29187638_Numb is associated with modulation of Notch-driven epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 29217616_The combination of the protein microarray screening with computer-aided prediction produced the most expansive interactome for Numb to date. 29269425_The Numb-Mdm2 interaction represents a fuzzy complex mediated by a short Numb sequence encompassing its alternatively spliced exon 3 (Ex3), which is necessary and sufficient to inhibit Mdm2 and prevent p53 degradation. 29295957_The depalmitoylating enzyme acyl-protein thioesterase 1 (APT1) directs the asymmetric localization of Numb and beta-catenin in MDA-MB-231 triple receptor-negative breast cancer cells. 29362432_activating Nrf2 antioxidant pathway suppresses Epithelial mesenchymal transition during pulmonary fibrosis via inhibiting the abnormal expression of Numb. 29398419_High NUMB expression is associated with endometriosis. 30061108_NUMB negatively controls membrane protrusions and the acquisition of mesenchymal migratory traits by modulating EFA6B-ARF6 activity. 30097225_Numb negatively regulated Notch signaling pathway in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of diabetic nephropathy (DN), implying that they had great potentials to serve as therapeutic targets or diagnostic biomarkers for DN. 30197333_The results provide new evidence of Numb and Gli1 on the clinical characteristics of Malignant pleural mesothelioma, which may be helpful in clinical diagnosis and targeted therapy. Further research with larger sample size is needed 30220706_Numb was found to be the target gene of miR-142, and its downregulation by miR-142 promoted the Notch signaling pathway and colon cancer stem cell-like traits. 30262992_Data show the expression of Zeb1 and Numb were both significantly higher in LLC-symmetric cell division than LLC-asymmetric cell division cells. 30396078_NUMB overexpression inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion in colorectal cancer cells. 30980673_Data show that member RAS oncogene family protein RAB27B (RAB27B) expression is required for the secretion of colorectal cancer stem cells (CRCSCs) exosomes, and exosomal miR-146a promotes stem-like properties and tumorigenicity by targeting endocytic adaptor protein Numb (Numb) in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells. 31023264_the results showed that Numb overexpression significantly suppressed proliferation, migration and invasion of SCC-9 and CAL-27 cells via regulating Notch1 signaling and EMT-related genes expression. 31095937_Knockdown of NUMB endocytic adaptor protein (Numb could promote the epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) of breast cancer cells via beta-catenin/RNA binding protein Lin28 (Lin28) signal pathway. 31116627_HMGA1 knockdown-induced NUMB upregulation. 31504682_NUMB enhances Notch signaling by repressing ubiquitination of NOTCH1 intracellular domain. 31898732_Cooperation of SRPK2, Numb and p53 in the malignant biology and chemosensitivity of colorectal cancer. 32146835_Numb functions as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer, and its tumor suppressor function is mediated by negative regulation of the epithelial mesenchymal transition through the Wnt signaling pathway. 32501652_Progress in the research of p53 tumour suppressor activity controlled by Numb in triple-negative breast cancer. 33120728_Musashi1 expression is negatively correlated with numb expression in brain metastases. 33394235_Different roles of Numb-p72 and Numb-p65 on the trafficking of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5. 34045601_NUMB suppression by miR-9-5P enhances CD44(+) prostate cancer stem cell growth and metastasis. 34078527_The role of NUMB/NUMB isoforms in cancer stem cells. 34315248_miR-146a-5p Promotes Chondrocyte Apoptosis and Inhibits Autophagy of Osteoarthritis by Targeting NUMB. 34667161_Loss of Numb promotes hepatic progenitor expansion and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma by enhancing Notch signaling. 34769160_miR-31-NUMB Cascade Modulates Monocarboxylate Transporters to Increase Oncogenicity and Lactate Production of Oral Carcinoma Cells. 34883044_NUMB as a Therapeutic Target for Melanoma. 34990618_Numb inhibits migration and promotes proliferation of colon cancer cells via RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway repression. 35181737_Numb exon 9 inclusion regulates Integrinbeta5 surface expression and promotes breast cancer metastasis. 35197444_Numb-PRRL promotes TGF-beta1- and EGF-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer. 35478938_Prognostic Biomarker NUMB Is Inhibited by Breast Cancer Cell Exosomes to Promote Breast Cancer Progression. 35562322_Notch, Numb and Numb-like responses to exercise-induced muscle damage in human skeletal muscle. 36200956_Aberrant phosphorylation inactivates Numb in breast cancer causing expansion of the stem cell pool. | ENSMUSG00000021224 | Numb | 746.048351 | 0.9473635 | -0.078009984 | 0.10741391 | 0.52734378373 | 0.4677257336357816819294441756937885656952857971191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.68804849880825980079634973662905395030975341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 733.388674 | 47.380911 | 777.705797 | 50.106979 | |
| ENSG00000134453 | 84991 | RBM17 | protein_coding | Q96I25 | FUNCTION: Splice factor that binds to the single-stranded 3'AG at the exon/intron border and promotes its utilization in the second catalytic step. Involved in the regulation of alternative splicing and the utilization of cryptic splice sites. Promotes the utilization of a cryptic splice site created by the beta-110 mutation in the HBB gene. The resulting frameshift leads to sickle cell anemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12015979, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17589525}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Direct protein sequencing;Isopeptide bond;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;Spliceosome;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes an RNA binding protein. The encoded protein is part of the spliceosome complex and functions in the second catalytic step of mRNA splicing. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. Related pseudogenes exist on chromosomes 9 and 15. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. | hsa:84991; | nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; spliceosomal complex [GO:0005681]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000380]; mRNA cis splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0045292]; mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000398] | 14578179_overexpression of SPF45 in HeLa, a cervical carcinoma cell line, resulted in drug resistance to doxorubicin and vincristine 16061639_Resistance to various chemotherapeutics resulting from stable transfection of RBM17 (SPF45) in A2780 ovarian carcinoma cells may be due to effects of SPF45 on transcription and splicing of ERbeta-regulated genes. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17589525_The SPF45 regulates alternative splicing of the apoptosis regulatory gene CD95; 2.1-A crystal structure of SPF45-UHM in complex with a ULM peptide from SF3b155 is reported. 17676041_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21835928_dephosphorylation of pS776-ATXN1 by PP2A regulates the interaction of ATXN1 with the splicing factors RBM17 and U2AF65 22615491_identify SPF45 as the first splicing factor regulated by multiple MAP kinase pathways and show effects of both SPF45 overexpression and phosphorylation 24858692_this work provides the structural and molecular basis of the interaction between RBM17 and the phosphorylated form of ATXN1. 30227940_Data show that RNA binding motif protein 17 (RBM17) overexpressed in glioma patients and resulted in the poor prognosis. 31002816_Also our presented results indicate that splicing factors hnRNP A1 and SPF45, previously shown to regulate Fas alternative splicing in normoxic cells, are not involved in hypoxia dependent alternative Fas pre-mRNA splicing regulation in an amount dependent manner. Our observations on hypoxia dependent alternative Fas pre-mRNA splicing regulation indicate a probable involvement of other, yet unidentified splicing factors. 32497093_Exploration of the effects of the CYCLOPS gene RBM17 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 34225773_A 5'-tRNA halve, tiRNA-Gly promotes cell proliferation and migration via binding to RBM17 and inducing alternative splicing in papillary thyroid cancer. 34389706_SPF45/RBM17-dependent, but not U2AF-dependent, splicing in a distinct subset of human short introns. 35781533_The splicing factor RBM17 drives leukemic stem cell maintenance by evading nonsense-mediated decay of pro-leukemic factors. | ENSMUSG00000037197 | Rbm17 | 165.985993 | 0.9554363 | -0.065768381 | 0.19045765 | 0.11888170030 | 0.7302505547700879340311530540930107235908508300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.86404991475309134152382739557651802897453308105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 163.804093 | 19.209500 | 172.032588 | 20.137390 | |
| ENSG00000134516 | 1794 | DOCK2 | protein_coding | Q92608 | FUNCTION: Involved in cytoskeletal rearrangements required for lymphocyte migration in response of chemokines. Activates RAC1 and RAC2, but not CDC42, by functioning as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), which exchanges bound GDP for free GTP. May also participate in IL2 transcriptional activation via the activation of RAC2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21613211}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the CDM protein family. It is specifically expressed in hematopoietic cells and is predominantly expressed in peripheral blood leukocytes. The protein is involved in remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton required for lymphocyte migration in response to chemokine signaling. It activates members of the Rho family of GTPases, for example RAC1 and RAC2, by acting as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) to exchange bound GDP for free GTP. Mutations in this gene result in immunodeficiency 40 (IMD40), a combined form of immunodeficiency that affects T cell number and function, also with variable defects in B cell and NK cell function. [provided by RefSeq, May 2018]. | hsa:1794; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; T cell receptor binding [GO:0042608]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; alpha-beta T cell proliferation [GO:0046633]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; establishment of T cell polarity [GO:0001768]; immunological synapse formation [GO:0001771]; macropinocytosis [GO:0044351]; membrane raft polarization [GO:0001766]; myeloid dendritic cell activation involved in immune response [GO:0002277]; myoblast fusion [GO:0007520]; negative thymic T cell selection [GO:0045060]; positive regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050766]; positive thymic T cell selection [GO:0045059]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0007264] | 12176041_DOCK2 mediates T cell receptor-induced activation of Rac2 and IL-2 transcription in jurkat cells 12393632_DOCK2 associates with CrkL and regulates Rac1 in human leukemia cell lines 12829596_the association of DOCK2 with ELMO1 is critical for DOCK2-mediated Rac activation, thereby suggesting that their association might be a therapeutic target for immunologic disorders caused by lymphocyte infiltration 14737186_Nef binds the DOCK2-ELMO1 complex to activate rac and inhibit lymphocyte chemotaxis 17015707_DOCK2 is needed for efficient chemokine-stimulated lymphocyte attachment to VCAM-1 under shear stress. 18056264_DOCK2 and DOCK9 specifically recognize Rac2 and Cdc42 through their switch 1 as well as beta2-beta3 regions and the mode of recognition via switch 1 appears to be conserved among diverse Rac-specific DHR-2 GEFs 18662984_PI3K and Src-ELMO-Dock2 pathways work in parallel to activate Rac2 and modulate chemotaxis in response to a CXCL8 gradient in neutrophils. 19729484_DOCK2 regulates microglial innate immunity independent of COX2 induction and DOCK2+ microglia are associated with human Alzheimer's disease pathology. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20350533_This is the first report to clarify the prominent role of DOCK2 in hematopoietic malignancy. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20412587_prostate cancer cell lines differentially express phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) catalytic subunit isoforms and dedicator of cytokinesis 2 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21645150_Our results show CXCL13-mediated PCa cell invasion requires Akt and ERK12 activation and suggests a new role for DOCK2 in proliferation of hormone-refractory CXCR5-positive PCa cells. 22331897_The C-terminal Pro-rich tail of ELMO1 winds around the Src-homology 3 domain of DOCK2 to form an intermolecular 5-helix bundle. The entire regions of both DOCK2 a& ELMO1 assemble to create a rigid structure required for the DOCK2 & ELMO1 binding. 23525077_DOCK2 mutations are associated with esophageal adenocarcinoma. 23911989_DOCK2 is required for the normal T and B cell migration and signal transduction. (Review) 24821968_findings reveal a previously unknown, nonredundant role for Elmo1 in controlling Dock2 levels and Dock2-dependent T cell migration in primary lymphocytes. 26083206_Autosomal recessive DOCK2 deficiency is a new mendelian disorder with pleiotropic defects of hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic immunity. 27748370_DOCK2 is a potential therapeutic target for novel AML treatments, as this protein regulates the survival of leukemia cells with elevated FLT3 activity and sensitizes FLT3/ITD leukemic cells to conventional antileukemic agents. 28100790_Brazilian Amerindian ancestry compared to Asian, European, and African Genomes.SNPs within or proximal to CIITA (rs6498115), SMC6 (rs1834619), and KLHL29 (rs2288697) were most differentiated in the Amerindian-specific branch. SNPs in ADAMTS9 (rs7631391), DOCK2 (rs77594147), SLC28A1 (rs28649017), ARHGAP5 (rs7151991), and CIITA (rs45601437) in the Asian comparison. 28284862_demonstrated that CPP-conjugation approach is applicable to the development of novel anti-inflammatory drugs based on DOCK2 inhibition by investigating both cellular uptake and bioactivity 29204803_this study describes DOCK2 deficiency in a patient with Hyper IgM phenotype 29678828_This study reveals that the recruitment of DOCK2 may be critical for the capacity of Wnt5a to enhance CLL proliferation, which may contribute to the observed increased tendency for disease progression in patients who have CLL cells that express high levels of ROR1. 30076747_Findings demonstrated that overexpressed DOCK2 might involve in recruiting CD8(+) T lymphocytes and serve as a novel prognostic indicator and indicated a potential therapeutic strategy by restoring DOCK2 for CRC. 30838481_this study reports DOCK2 deficiency due to novel mutation affecting cellular immunity 31630188_The DOCK2 is a Rac activator critical for migration and activation of leukocytes. 32369253_miR-16 exhibits protective function in LPS-treated cardiomyocytes by targeting DOCK2 to repress cell apoptosis and exert anti-inflammatory effect. 32651375_Structure of the DOCK2-ELMO1 complex provides insights into regulation of the auto-inhibited state. 32703426_DOCK2 couples with LEF-1 to regulate B cell metabolism and memory response. 33928462_DOCK2 Deficiency Diagnosed 18 Years After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. 34710342_DOCK2 Promotes Pleural Fibrosis by Modulating Mesothelial to Mesenchymal Transition. 35079145_DOCK2 regulates antifungal immunity by regulating RAC GTPase activity. 35584329_DOCK2 contributes to pulmonary fibrosis by promoting lung fibroblast to myofibroblast transition. 35940203_DOCK2 is involved in the host genetics and biology of severe COVID-19. 36380073_Extra-hematopoietic immunomodulatory role of the guanine-exchange factor DOCK2. | ENSMUSG00000020143 | Dock2 | 1287.181995 | 1.0054756 | 0.007878048 | 0.04322897 | 0.03320940470 | 0.8553987170415118246324936990276910364627838134765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.93518531058166898262129507202189415693283081054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1267.513610 | 38.310484 | 1266.365783 | 38.080544 | |
| ENSG00000135069 | 29968 | PSAT1 | protein_coding | Q9Y617 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the reversible conversion of 3-phosphohydroxypyruvate to phosphoserine and of 3-hydroxy-2-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutanoate to phosphohydroxythreonine. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P10658}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Amino-acid biosynthesis;Aminotransferase;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Pyridoxal phosphate;Reference proteome;Serine biosynthesis;Transferase | PATHWAY: Amino-acid biosynthesis; L-serine biosynthesis; L-serine from 3-phospho-D-glycerate: step 2/3.; PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; pyridoxine 5'-phosphate biosynthesis; pyridoxine 5'-phosphate from D-erythrose 4-phosphate: step 3/5. | This gene encodes a member of the class-V pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent aminotransferase family. The encoded protein is a phosphoserine aminotransferase and decreased expression may be associated with schizophrenia. Mutations in this gene are also associated with phosphoserine aminotransferase deficiency. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Pseudogenes of this gene have been defined on chromosomes 1, 3, and 8. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. | hsa:29968; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; O-phospho-L-serine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase activity [GO:0004648]; pyridoxal phosphate binding [GO:0030170]; L-serine biosynthetic process [GO:0006564]; pyridoxine biosynthetic process [GO:0008615] | 12633500_nucleotide sequence and enzymatic activity of two isoforms generated by alternative splicing; differential expression depending upon tissue specificity and cellular proliferation status 18221502_Overexpression of phosphoserine aminotransferase is associated with colorectal cancer development 20955740_we propose an idea that PSAT1 may be implicated in altered serine metabolism and schizophrenia spectrum conditions. 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 25142862_PSAT1 expression positively correlates with the levels of phosphorylated cyclin D1 in non-small cell lung cancer. 25152457_phosphoserine aminotransferase deficiency is associated with Neu-Laxova syndrome. 26439504_High expression of PSAT is associated with Colon Cancer. 27372650_Data suggest that phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 (PSAT1) may be a promising anticancer therapeutic target. . 28522855_PSAT1 protein and mRNA levels were significantly associated to poor outcome to tamoxifen treatment of breast cancer. 29216929_PSAT1, which is overexpressed in ER-negative breast cancers, is activated by ATF4 and promotes cell cycle progression via regulation of the GSK3beta/beta-catenin/cyclin D1 pathway. 31036704_Nf1 loss promotes Kras-driven lung adenocarcinoma and results in Psat1-mediated glutamate dependence. 31630284_Selective loss of phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 (PSAT1) suppresses migration, invasion, and experimental metastasis in triple negative breast cancer. 31903955_This study is the first description of PHGDH and PSAT1 mutations in Chinese Neu-Laxova syndrome patients, which strongly implicates them in the pathogenesis of Neu-Laxova syndrome. 31988456_Overexpression of PSAT1 promotes metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma by suppressing the IRF1-IFNgamma axis. 32077105_A yeast-based complementation assay elucidates the functional impact of 200 missense variants in human PSAT1. 32300099_Overexpression of PSAT1 regulated by G9A sustains cell proliferation in colorectal cancer. 32579715_Expanding the genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of severe serine biosynthesis disorders. 32826249_PSAT1 Upregulation Contributes to Cell Growth and Cisplatin Resistance in Cervical Cancer Cells via Regulating PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. 32901893_Long noncoding RNA MEG3 suppresses epithelialtomesenchymal transition by inhibiting the PSAT1dependent GSK3beta/Snail signaling pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 33500247_Serine Biosynthesis Is a Metabolic Vulnerability in IDH2-Driven Breast Cancer Progression. 33588715_Phosphoserine Aminotransferase has Conserved Active Site from Microbes to Higher Eukaryotes with Minor Deviations. 34089226_Adult diagnosis of congenital serine biosynthesis defect: A treatable cause of progressive neuropathy. 35045283_Lineage-specific silencing of PSAT1 induces serine auxotrophy and sensitivity to dietary serine starvation in luminal breast tumors. 35615948_Examination of the effects of microRNA-145-5p and phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 in colon cancer. 36327671_Circ_0015756 promotes ovarian cancer progression via the miR-145-5p/PSAT1 axis. | ENSMUSG00000024640 | Psat1 | 104.336391 | 1.0812624 | 0.112716709 | 0.14618434 | 0.59454055046 | 0.4406686677345033609221047754544997587800025939941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.66387434833281999679854834539582952857017517089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 108.738132 | 10.098224 | 101.061040 | 9.372352 |
| ENSG00000135090 | 51347 | TAOK3 | protein_coding | Q9H2K8 | FUNCTION: Serine/threonine-protein kinase that acts as a regulator of the p38/MAPK14 stress-activated MAPK cascade and of the MAPK8/JNK cascade. Acts as an activator of the p38/MAPK14 stress-activated MAPK cascade. In response to DNA damage, involved in the G2/M transition DNA damage checkpoint by activating the p38/MAPK14 stress-activated MAPK cascade, probably by mediating phosphorylation of upstream MAP2K3 and MAP2K6 kinases. Inhibits basal activity of MAPK8/JNK cascade and diminishes its activation in response epidermal growth factor (EGF). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10559204, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10924369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17396146}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;DNA damage;DNA repair;Kinase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase | The protein encoded by this gene is a serine/threonine protein kinase that activates the p38/MAPK14 stress-activated MAPK cascade but inhibits the basal activity of the MAPK8/JNK cascade. The encoded protein is a member of the GCK subfamily of STE20-like kinases. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. | hsa:51347; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; protein kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0004860]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; transferase activity [GO:0016740]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0007095]; negative regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046329]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of JUN kinase activity [GO:0043507]; positive regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade [GO:0032874]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043408] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26646899_Results show that three CpG loci within FYN were hypermethylated in obese individuals, while obesity was associated with lower methylation of CpG loci within PIWIL4 and TAOK3. 30031856_TAOK3 SNPs (rs1277441 and rs795484) were associated with opioid doses in advanced cancer patients receiving palliative care. The proportions of variant homozygotes (8.2% of patients) and their requirement for higher doses of opioids would appear potentially clinically important and should be validated in further studies. 30373850_TAOK3 is a positive regulator of TCR signaling by preventing premature SHP-1-mediated inactivation of LCK 32807497_TAOK3 is a MAP3K contributing to osteoblast differentiation and skeletal mineralization. 33087151_Kinase shRNA screening reveals that TAOK3 enhances microtubule-targeted drug resistance of breast cancer cells via the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. 33414172_Serine-Threonine Kinase TAO3-Mediated Trafficking of Endosomes Containing the Invadopodia Scaffold TKS5alpha Promotes Cancer Invasion and Tumor Growth. 34506849_The STE20 kinase TAOK3 controls the development of house dust mite-induced asthma in mice. 34634521_STE20-type kinase TAOK3 regulates hepatic lipid partitioning. | ENSMUSG00000061288 | Taok3 | 737.342747 | 1.0521781 | 0.073378887 | 0.05870894 | 1.56226142391 | 0.2113344113075233676735109611399821005761623382568359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.42920730477315921502778905960440170019865036010742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 744.163998 | 34.183288 | 710.688887 | 32.875549 | |
| ENSG00000135185 | 79161 | TMEM243 | protein_coding | Q9BU79 | Acetylation;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:79161; | membrane [GO:0016020] | 15556294_Data showed MGC4175 fused to the carboxy terminus of enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) was localized to the mitochondria, and its overexpression was not caused by genomic amplification or gene arrangement. 20351715_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) | ENSMUSG00000079659 | Tmem243 | 80.851792 | 1.2964587 | 0.374576267 | 0.17422806 | 4.61822433917 | 0.0316339694921760269941124477099947398528456687927246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.11825119328074780444826075154196587391197681427001953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 85.534342 | 9.381039 | 66.261408 | 7.343124 | ||
| ENSG00000135540 | 57224 | NHSL1 | protein_coding | Q5SYE7 | Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | Predicted to be involved in cell differentiation. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:57224; | cell differentiation [GO:0030154] | 34420305_Proteogenomics Integrating Novel Junction Peptide Identification Strategy Discovers Three Novel Protein Isoforms of Human NHSL1 and EEF1B2. 34584076_Nance-Horan Syndrome-like 1 protein negatively regulates Scar/WAVE-Arp2/3 activity and inhibits lamellipodia stability and cell migration. | ENSMUSG00000039835 | Nhsl1 | 104.199270 | 1.1482702 | 0.199462216 | 0.15244626 | 1.70920815745 | 0.1910881402569610532093946630993741564452648162841796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.40328016081991113761517908642417751252651214599609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 101.823995 | 11.292157 | 89.149420 | 9.525477 | ||
| ENSG00000135838 | 80896 | NPL | protein_coding | Q9BXD5 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the cleavage of N-acetylneuraminic acid (sialic acid) to form pyruvate and N-acetylmannosamine via a Schiff base intermediate (PubMed:33895133). It prevents sialic acids from being recycled and returning to the cell surface (PubMed:33895133). Involved in the N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc) degradation pathway (PubMed:22692205, PubMed:33895133). Although human is not able to catalyze formation of Neu5Gc due to the inactive CMAHP enzyme, Neu5Gc is present in food and must be degraded (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22692205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33895133, ECO:0000305|PubMed:22692205}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Carbohydrate metabolism;Cytoplasm;Lyase;Reference proteome;Schiff base | PATHWAY: Amino-sugar metabolism; N-acetylneuraminate degradation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22692205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33895133}. | This gene encodes a member of the N-acetylneuraminate lyase sub-family of (beta/alpha)(8)-barrel enzymes. N-acetylneuraminate lyases regulate cellular concentrations of N-acetyl-neuraminic acid (sialic acid) by mediating the reversible conversion of sialic acid into N-acetylmannosamine and pyruvate. A pseudogene of this gene is located on the short arm of chromosome 2. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]. | hsa:80896; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; N-acetylneuraminate lyase activity [GO:0008747]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; N-acetylneuraminate catabolic process [GO:0019262] | 16147865_an NPL splice variant is mainly expressed in human liver, kidney and peripheral blood leukocytes 19057931_3D structure model of N-acetylneuraminate lyase from human (hNAL, EC 4.1.3.3) was created and refined | ENSMUSG00000042684 | Npl | 422.970582 | 0.8918453 | -0.165134622 | 0.09482423 | 3.02977637634 | 0.0817492828640348639934742891455243807286024093627929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.23077880296712807717263160611764760687947273254394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 393.844484 | 35.772320 | 443.755508 | 40.087946 |
| ENSG00000135924 | 3300 | DNAJB2 | protein_coding | P25686 | FUNCTION: Functions as a co-chaperone, regulating the substrate binding and activating the ATPase activity of chaperones of the HSP70/heat shock protein 70 family (PubMed:7957263, PubMed:22219199). In parallel, also contributes to the ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation of misfolded proteins (PubMed:15936278, PubMed:21625540). Thereby, may regulate the aggregation and promote the functional recovery of misfolded proteins like HTT, MC4R, PRKN, RHO and SOD1 and be crucial for many biological processes (PubMed:12754272, PubMed:20889486, PubMed:21719532, PubMed:22396390, PubMed:24023695). Isoform 1 which is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum membranes may specifically function in ER-associated protein degradation of misfolded proteins (PubMed:15936278). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12754272, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15936278, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20889486, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21625540, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21719532, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22219199, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22396390, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24023695, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7957263}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Neurodegeneration;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation | This gene is almost exclusively expressed in the brain, mainly in the neuronal layers. It encodes a protein that shows sequence similarity to bacterial DnaJ protein and the yeast homologs. In bacteria, this protein is implicated in protein folding and protein complex dissociation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. | hsa:3300; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0098554]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extrinsic component of endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0042406]; inclusion body [GO:0016234]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; ATPase activator activity [GO:0001671]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; Hsp70 protein binding [GO:0030544]; polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding [GO:0031593]; proteasome binding [GO:0070628]; ubiquitin binding [GO:0043130]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; ubiquitin-dependent protein binding [GO:0140036]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; chaperone-mediated protein folding [GO:0061077]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of inclusion body assembly [GO:0090084]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091]; negative regulation of protein deubiquitination [GO:0090086]; neuron cellular homeostasis [GO:0070050]; positive regulation of ATP-dependent activity [GO:0032781]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; positive regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031398]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein refolding [GO:0042026]; regulation of chaperone-mediated protein folding [GO:1903644]; regulation of protein localization [GO:0032880]; regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031396]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433] | 12754272_data provide evidence that cytoplasmic chaperones HSJ1a and HSJ1b when targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum can influence the folding and processing of rhodopsin 15936278_HSJ1 is a neuronal shuttling factor for the sorting of chaperone clients to the proteasome. 16604191_Cystamine and cysteamine increase brain levels of BDNF in Huntington disease via HSJ1b and transglutaminase 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18321953_Damaging exercise induced the expression of capZalpha, MCIP1, CARP1, DNAJB2, c-myc, and junD, each of which are likely involved in skeletal muscle growth, remodeling, and stress management. 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20395441_Data show that DNAJB2 is expressed in skeletal muscle at the neuromuscular junction of normal fibers, in the cytoplasm and membrane of regenerating fibers, and in protein aggregates and vacuoles in protein aggregate myopathies. 22522442_a mutation causing a loss-of-function of HSJ1 is linked to a pure lower motor neuron disease, strongly suggesting that HSJ1 also plays an important and specific role in motor neurons. 24023695_HSJ1a acts on mutant SOD1 through a combination of chaperone, co-chaperone and pro-ubiquitylation activity. 25274842_The results of this study confirm that HSJ1 mutations are a rare but detectable cause of autosomal recessive dHMN and CMT2. 27449489_Study describes the identi fi cation of the fi rst deletion reported at the DNAJB2 locus, further expanding its phenotypic and genotypic spectrums as well as its disease-associated mechanisms with spinal muscular atrophy and parkinsonism. 28031292_Our results disclose a novel interplay between ubiquitin- and phosphorylation-dependent signalling, and represent the first report of a regulatory mechanism for UIM-dependent function. They also suggest that CK2 inhibitors could release the full neuroprotective potential of HSJ1, and deserve future interest as therapeutic strategies for neurodegenerative disease. 31682009_DNAJB2 expression in healthy human palatal mucosa is strongly negatively correlated with serum cotinine levels 35286755_DNAJB2-related Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2: Pathomechanism insights and phenotypic spectrum widening. | ENSMUSG00000026203 | Dnajb2 | 187.699771 | 0.7424554 | -0.429623788 | 0.15085118 | 8.10084666807 | 0.0044244586468744637533512253924072865629568696022033691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.02593852789290863186666413753300730604678392410278320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 157.307440 | 15.082001 | 212.769632 | 19.978580 | |
| ENSG00000136144 | 55213 | RCBTB1 | protein_coding | Q8NDN9 | FUNCTION: May be involved in cell cycle regulation by chromatin remodeling. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11306461}. | Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Chromatin regulator;Disease variant;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation | This gene encodes a protein with an N-terminal RCC1 domain and a C-terminal BTB (broad complex, tramtrack and bric-a-brac) domain. In rat, over-expression of this gene in vascular smooth muscle cells induced cellular hypertrophy. In rat, the C-terminus of RCBTB1 interacts with the angiotensin II receptor-1A. In humans, this gene maps to a region of chromosome 13q that is frequently deleted in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and other lymphoid malignancies. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:55213; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325] | 14565662_E4.5 gene, which maps at chromosome band 13q14.3, encodes for a 4 kb mRNA expressed in various tissues and has an open reading frame of 531 amino acids. It has a potential role in the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia [E4.5] 20085599_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20926398_Data show that the biological actions of Clld7 are consistent with those of a tumor suppressor. 24202307_Study identifies RCBTB1 as a modifier of the smoking effect on carotid intima-media thickness. 26908610_Results identified RCBTB1 as a gene associated with vitreoretinopathy and found that it plays a role in retinal angiogenesis through Norrin-induced beta-catenin signaling. 27166999_Data indicate RNA Binding Protein with Multiple Splicing (RBPMS), Regulator of Chromosome Condensation and POZ Domain Containing Protein 1 (RCBTB1), and Zinc Finger protein 608 (ZNF608) as miR-21-3p target genes. 27486781_study puts forward mutations in RCBTB1 as a cause of autosomal-recessive non-syndromic and syndromic inherited retinal dystrophies; data support a role for impaired ubiquitination in the pathogenetic mechanism of RCBTB1 mutations 33104391_Variants in RCBTB1 are Associated with Autosomal Recessive Retinitis Pigmentosa but Not Autosomal Dominant FEVR. 33624564_Deep clinical phenotyping and gene expression analysis in a patient with RCBTB1-associated retinopathy. 35057699_Novel RCBTB1 variants causing later-onset non-syndromic retinal dystrophy with macular chorioretinal atrophy. | ENSMUSG00000035469 | Rcbtb1 | 155.009806 | 1.1836670 | 0.243263218 | 0.29407009 | 0.67732018627 | 0.4105110384605737405827596830931724980473518371582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.63830907136355108377756550908088684082031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 167.720611 | 32.516414 | 141.782134 | 27.627960 | |
| ENSG00000136448 | 4836 | NMT1 | protein_coding | P30419 | FUNCTION: Adds a myristoyl group to the N-terminal glycine residue of certain cellular and viral proteins (PubMed:22865860, PubMed:25255805, PubMed:9353336, PubMed:9506952). Also able to mediate N-terminal lysine myristoylation of proteins: catalyzes myristoylation of ARF6 on both 'Gly-2' and 'Lys-3' (PubMed:32103017, PubMed:32111831). Lysine myristoylation is required to maintain ARF6 on membranes during the GTPase cycle (PubMed:32103017). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22865860, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25255805, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32103017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32111831, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9353336, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9506952}. | 3D-structure;Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase | Myristate, a rare 14-carbon saturated fatty acid, is cotranslationally attached by an amide linkage to the N-terminal glycine residue of cellular and viral proteins with diverse functions. N-myristoyltransferase (NMT; EC 2.3.1.97) catalyzes the transfer of myristate from CoA to proteins. N-myristoylation appears to be irreversible and is required for full expression of the biologic activities of several N-myristoylated proteins, including the alpha subunit of the signal-transducing guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein) GO (GNAO1; MIM 139311) (Duronio et al., 1992 [PubMed 1570339]).[supplied by OMIM, Nov 2008]. | hsa:4836; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase activity [GO:0004379]; myristoyltransferase activity [GO:0019107]; peptidyl-lysine N6-myristoyltransferase activity [GO:0018030]; cellular ketone metabolic process [GO:0042180]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; N-terminal peptidyl-glycine N-myristoylation [GO:0018008]; N-terminal protein myristoylation [GO:0006499]; positive regulation of protein insertion into mitochondrial membrane involved in apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1900740]; regulation of rhodopsin mediated signaling pathway [GO:0022400] | 12220649_In this study, we found decreases in the mRNA levels of human NMT isoforms and the NMT activities in the course of HIV-1 infection in the human T-cell line 15156568_role of HSC70 in the regulation of NMT 16123142_NMT1 and NMT2 have only partially overlapping functions; NMT1 is critical for tumor cell proliferation 17549352_Elevated N-myristoyltransferase activity is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma 18021392_N-myristoyltransferase may have a role in progression of colonic neoplasms 18089753_Nef is preferentially myristoylated by NMT2, suggesting that selective inhibition of NMT2 may provide a novel means of blocking HIV virulence. 18248763_These results strongly suggest that HIV-1 production is specifically associated with hNMT1, particularly hNMT1(L), but not with hNMT2 in vivo, contributing to the understanding of a step in HIV-1 replication. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21449607_we propose a model of the Nef:NMT complex in which only the myristoyl moiety holds the two proteins together in complex and speculate that perhaps NMT chaperones Nef to the membrane and thereby protects the myristic acid group from the cytosol 26074144_findings suggest that both NMT1 and hnRNP A2/B1 take part in the regulation of HIV-1 RNA expression through their mutual opposite effects on the viral RNA expression in HIV-1-producing cells 26603938_These observations point at a previously unrecognized contribution of calnexin to the retention of NMT1 at the ER membrane. 29038344_Genetic and pharmacologic evidence that inhibiting the N-myristoyltransferase NMT1 suppresses cell-cycle progression, proliferation, and malignant growth of prostate cancer cells. 30154572_mTOR, a downstream target of PKB/Akt, regulates NMT1 in ER positive breast cancer cells (MCF7 cells). NMT1 increased with rapamycin treatment over the period of time with a concomitant decrease in mTOR phosphorylation. 30446635_inhibition of NMT1 caused degraded proteins increase and ER stress, which cross-talked with mitochondria to produce more ROS. And both of oxidative stress and ER stress could activate JNK pathway, leading to autophagy which abrogated breast cancer progression especially triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). 30718913_Data showed that rheumatoid arthritis (RA) T cells had a defect in type I N-myristoyltransferase (NMT1) function, which prevented AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation. 34999170_N-myristoyltransferase-1 deficiency blocks myristoylation of LAMTOR1 and inhibits bladder cancer progression. 35930829_N-mytistoyltransferase 1 and 2 are potential tumor suppressors and novel targets of miR-182 in human non-small cell lung carcinomas. | ENSMUSG00000020936 | Nmt1 | 556.450189 | 0.9317857 | -0.101929899 | 0.09045804 | 1.26831229666 | 0.2600835308022335090605281493481015786528587341308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.48852536979476868239657960657496005296707153320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 591.643922 | 31.297537 | 637.470518 | 33.792074 | |
| ENSG00000137411 | 57176 | VARS2 | protein_coding | Q5ST30 | Alternative splicing;Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase;ATP-binding;Disease variant;Ligase;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Primary mitochondrial disease;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Transit peptide | This gene encodes a mitochondrial aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, which catalyzes the attachment of valine to tRNA(Val) for mitochondrial translation. Mutations in this gene cause combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency-20, and are also associated with early-onset mitochondrial encephalopathies. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2014]. | hsa:57176; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; aminoacyl-tRNA editing activity [GO:0002161]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; valine-tRNA ligase activity [GO:0004832]; valyl-tRNA aminoacylation [GO:0006438] | 18400783_Data indicate that variations in the levels of VARS2L between tissue types and patients could underlie the difference in clinical presentation between individuals homoplasmic for the 1624C>T MTTV (equivalent to mt-tRNAVal C25U) mutation. 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503108_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503108_VARS2 V552V may be considered as a prognostic factor for survival in patients with early breast cancer. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25404243_VARS2 polymorphism significantly associated with chronic hepatitis B in Korean population. 29137650_VARS2 mutation underlies a novel autosomal recessive syndrome with epilepsy, mental retardation, short stature, growth hormone deficiency, and hypogonadism. 29314548_this gene should be considered in early-onset mitochondrial encephalomyopathies or encephalocardiomyopathies. 30458719_The novel compound heterozygous pathogenic VARS2 mutations c.643 C > T (p. His215Tyr) and c.1354 A > G (p. Met452Val) has been reported in a female infant. These heterozygous mutations were carried individually by the proband's parents and elder sister. 31064326_report two additional cases of two non-related young girls from Sardinia, born from non-consanguineous and healthy parents, carrying the aforesaid homozygous VARS2 variant. At onset both the patients presented with worsening psychomotor delay, muscle hypotonia and brisk tendon reflexes 31529142_Study shows A combination of two novel VARS2 variants causes a mitochondrial disorder associated with failure to thrive and pulmonary hypertension | ENSMUSG00000038838 | Vars2 | 29.438900 | 1.0255163 | 0.036350467 | 0.41648660 | 0.00770042243 | 0.9300737485397858606006593618076294660568237304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.96883655827464543186522405449068173766136169433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 32.857467 | 12.525924 | 32.913378 | 11.856576 | ||
| ENSG00000137500 | 60492 | CCDC90B | protein_coding | Q9GZT6 | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Located in mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:60492; | mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739] | 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 30612859_Using MCUR1, the functionally characterized paralog of study the role of individual domains, results find that the conserved head domain in CCDC90B interacts directly with mitochondrial calcium uniporter and is destabilized upon Ca(2+) binding. | ENSMUSG00000030613 | Ccdc90b | 159.544467 | 1.0707384 | 0.098606082 | 0.19341479 | 0.25904759353 | 0.6107752269738506711860281939152628183364868164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.78796969162980901035808756205369718372821807861328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 163.622910 | 20.570832 | 153.650852 | 19.463460 | ||
| ENSG00000138107 | 10121 | ACTR1A | protein_coding | P61163 | FUNCTION: Component of a multi-subunit complex involved in microtubule based vesicle motility. It is associated with the centrosome. | Acetylation;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a 42.6 kD subunit of dynactin, a macromolecular complex consisting of 10-11 subunits ranging in size from 22 to 150 kD. Dynactin binds to both microtubules and cytoplasmic dynein. It is involved in a diverse array of cellular functions, including ER-to-Golgi transport, the centripetal movement of lysosomes and endosomes, spindle formation, chromosome movement, nuclear positioning, and axonogenesis. This subunit is present in 8-13 copies per dynactin molecule, and is the most abundant molecule in the dynactin complex. It is an actin-related protein, and is approximately 60% identical at the amino acid level to conventional actin. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:10121; | cell cortex region [GO:0099738]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dynactin complex [GO:0005869]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; microtubule associated complex [GO:0005875]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] | 12871323_ARP1 interacted with two regions of the FVII 5' flanking region, the hepatic nuclear factor 4 binding region and the nuclear hormone response region, indicating a role for ARP1 in transcriptional modulation of the FVII gene. 18303113_point mutation observed by transcriptome sequencing of malignant pleural mesothelioma tumors 31221720_An important role for ACTR1A in induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines.TLR2 interacts with alpha-centractin. | ENSMUSG00000025228 | Actr1a | 349.494112 | 1.2465970 | 0.317995092 | 0.10376257 | 9.37651154305 | 0.0021978340187241225851810799696295362082310020923614501953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.01473085877044227366694517655787421972490847110748291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 393.546294 | 26.336204 | 317.312165 | 21.182248 | |
| ENSG00000138363 | 471 | ATIC | protein_coding | P31939 | FUNCTION: Bifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the last two steps of purine biosynthesis (PubMed:11948179, PubMed:14756554). Acts as a transformylase that incorporates a formyl group to the AMP analog AICAR (5-amino-1-(5-phospho-beta-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide) to produce the intermediate formyl-AICAR (FAICAR) (PubMed:9378707, PubMed:11948179, PubMed:10985775). Can use both 10-formyldihydrofolate and 10-formyltetrahydrofolate as the formyl donor in this reaction (PubMed:10985775). Also catalyzes the cyclization of FAICAR to IMP (PubMed:11948179, PubMed:14756554). Is able to convert thio-AICAR to 6-mercaptopurine ribonucleotide, an inhibitor of purine biosynthesis used in the treatment of human leukemias (PubMed:10985775). Promotes insulin receptor/INSR autophosphorylation and is involved in INSR internalization (PubMed:25687571). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10985775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11948179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14756554, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25687571, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9378707}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Hydrolase;Intellectual disability;Multifunctional enzyme;Purine biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Transferase | PATHWAY: Purine metabolism; IMP biosynthesis via de novo pathway; 5-formamido-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide from 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide (10-formyl THF route): step 1/1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11948179}.; PATHWAY: Purine metabolism; IMP biosynthesis via de novo pathway; IMP from 5-formamido-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide: step 1/1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11948179}. | This gene encodes a bifunctional protein that catalyzes the last two steps of the de novo purine biosynthetic pathway. The N-terminal domain has phosphoribosylaminoimidazolecarboxamide formyltransferase activity, and the C-terminal domain has IMP cyclohydrolase activity. A mutation in this gene results in AICA-ribosiduria. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. | hsa:471; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; IMP cyclohydrolase activity [GO:0003937]; phosphoribosylaminoimidazolecarboxamide formyltransferase activity [GO:0004643]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; 'de novo' AMP biosynthetic process [GO:0044208]; 'de novo' IMP biosynthetic process [GO:0006189]; 'de novo' XMP biosynthetic process [GO:0097294]; animal organ regeneration [GO:0031100]; brainstem development [GO:0003360]; cellular response to interleukin-7 [GO:0098761]; cerebellum development [GO:0021549]; cerebral cortex development [GO:0021987]; dihydrofolate metabolic process [GO:0046452]; GMP biosynthetic process [GO:0006177]; nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process [GO:0006139]; nucleoside metabolic process [GO:0009116]; response to inorganic substance [GO:0010035]; tetrahydrofolate biosynthetic process [GO:0046654] | 11948179_The kinetic mechanism of the human bifunctional enzyme ATIC 14966129_crystal structure of ATIC 15114530_Deficiency in AICAR transformylase is associated with severe neurological defects and congenital blindness 15457444_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15457444_Polymorphisms of reduced folate carrier,aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide transformylase,and thymidylate synthase genes contribute to the therapeutic response in rheumatoid arthritis patients to methotrexate. 15677700_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16447238_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16947783_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17009228_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17181924_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17410198_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17439323_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17530705_Observational study of gene-disease association, pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17617058_AS160 is a common target of insulin, IGF-1, EGF, PMA and AICAR, these stimuli induce distinctive patterns of phosphorylation and 14-3-3 binding, mediated by at least four protein kinases. 18845790_ATIC associated with nucleophosmin-ALK, and its phosphorylation required ALK activity. ALK-mediated ATIC phosphorylation enhanced its enzymatic activity. 19016697_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19161160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19193698_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19858780_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19902562_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19936946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22180458_Results proved in cultured skin fibroblasts from patients with AICA-ribosiduria that various mutations of ATIC destabilize to various degrees purinosome assembly. 24967362_study suggests that MTHFR C677T and ATIC T675C genotyping combined with clinicopathological data may help to identify patients whom will not benefit from MTX treatment and, therefore, assist clinicians in personalizing RA treatment 25084201_MTHFR, DHFR and ATIC genetic variants can be considered as pharmacogenetic markers of outcome in RA patients under MTX monotherapy. 25240429_genotyping of ATIC rs2372536 and ITPA rs1127354 variants or measuring ITPA activity could be useful to predict methotrexate response in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 25425682_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in ATIC gene is associated with acute graft-versus-host disease. 25687571_Our data show that ATIC is in complex with insulin receptor (IR)and siRNA-mediated partial knockdown of ATIC in HEK293 cells, decreases IR tyrosine phosphorylation and regulates IR endocytosis. Insulin stimulation and ATIC knockdown readily increase level of AMPK-Thr172 phosphorylation in IR complexes.ATIC depletion delayed insulin response of Glut2 translocation in HEK293 cells and decreased AKT-Ser473 phosphorylation. 25687571_PTPLAD1 and AMPK are rapidly compartmentalized within the plasma membrane (PM) and Golgi/endosome fractions after insulin stimulation and that ATIC later accumulates in the Golgi/endosome fraction. 25823786_This study shows that polymorphisms on genes related to the metabolic pathway of pemetrexed, especially, ATIC and GGH genes, would have a therapeutic implication in pemetrexed-treated patients with lung adenocarcinoma 26799664_ATIC 347C>G gene polymorphism may be associated with the development of MTX induced gastrointestinal adverse events. 27379764_The ATIC 347 C/G polymorphism may be associated with non-responsiveness to and or toxicity of methotrexate in Caucasian rheumatoid arthritis patients. 28267080_Pediatric Osteosarcoma patients with ATIC 347C>G exhibited a good histologic response to chemotherapy 29042184_The AICARFT site is capable of independently binding both nucleotide and folate substrates with high affinity however no evidence for positive cooperativity in binding could be detected using the model ligands employed in this study. 29246230_ATIC acts as an oncogenic gene that promotes survival, proliferation and migration by targeting AMPK-mTOR-S6 K1 signaling 32557644_AICA-ribosiduria due to ATIC deficiency: Delineation of the phenotype with three novel cases, and long-term update on the first case. 33226193_Upregulation of ATIC in multiple myeloma tissues based on tissue microarray and gene microarrays. 33778066_Identification and Validation of a Prognostic Model Based on Three Autophagy-Related Genes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 33780152_Polymorphism of genes involved in methotrexate pathway: Predictors of response to methotrexate therapy in Indian rheumatoid arthritis patients. 35205374_Impact of Variants in the ATIC and ARID5B Genes on Therapeutic Failure with Imatinib in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. 35579772_CircATIC Contributes to Multiple Myeloma Progression via miR-324-5p-Dependent Regulation of HGF. | ENSMUSG00000026192 | Atic | 516.875614 | 0.8987520 | -0.154005091 | 0.13892958 | 1.22713317110 | 0.2679652933229325628694539318530587479472160339355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.49698999244247954454323235040646977722644805908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 476.464396 | 49.753535 | 532.118929 | 55.505032 |
| ENSG00000138629 | 84993 | UBL7 | protein_coding | Q96S82 | 3D-structure;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation pathway | Predicted to enable polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process. Predicted to be active in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:84993; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding [GO:0031593]; cellular response to stress [GO:0033554]; regulation of proteolysis [GO:0030162]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] | 12644319_BMSC-UbP might play roles in regulation of BMSC function or cell differentiation through an evocator- and cell-specific pattern. 16731964_the solution NMR structure of the ubiquitin-associated domain of the human BMSC-UbP protein and its complex with ubiquitin | ENSMUSG00000055720 | Ubl7 | 158.334504 | 1.1787021 | 0.237199182 | 0.13317990 | 3.16606335653 | 0.0751834603417629310229131078813225030899047851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.21841458842379643523479160194256110116839408874511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 170.715736 | 13.657706 | 145.605315 | 11.483896 | ||
| ENSG00000138777 | 27068 | PPA2 | protein_coding | Q9H2U2 | FUNCTION: Hydrolyzes inorganic pyrophosphate (PubMed:27523597). This activity is essential for correct regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential, and mitochondrial organization and function (PubMed:27523598). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27523597, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27523598}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transit peptide | The protein encoded by this gene is localized to the mitochondrion, is highly similar to members of the inorganic pyrophosphatase (PPase) family, and contains the signature sequence essential for the catalytic activity of PPase. PPases catalyze the hydrolysis of pyrophosphate to inorganic phosphate, which is important for the phosphate metabolism of cells. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:27068; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; synapse [GO:0045202]; inorganic diphosphate phosphatase activity [GO:0004427]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0004722]; diphosphate metabolic process [GO:0071344]; phosphate-containing compound metabolic process [GO:0006796]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0051881] | 16300924_No pathogenic mutations were identified in the PPA2 gene in patients with mitochondrial DNA depletion syndromes (MDS). 19067239_We think that PP2A can be one of the key components to regulate the fusion of various endocytotic compartments and /or the trafficking along the microtubules. 20332099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23241943_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in PPA2 is associated with response to antipsychotic agents in schizophrenia. 27523597_findings confirm the pathogenicity of PPA2 mutations and suggest that PPA2 is a cardiomyopathy-associated protein, which has a greater physiological importance in mitochondrial function than previously recognized 27523598_data demonstrate that PPA2 is an essential gene in yeast and that biallelic mutations in PPA2 cause a mitochondrial disease leading to sudden cardiac arrest in infants 31705601_Sudden unexpected death in asymptomatic infants due to PPA2 variants. 33036755_Structural and biochemical characterization of inorganic pyrophosphatase from Homo sapiens. 34400813_PPA2-associated sudden cardiac death: extending the clinical and allelic spectrum in 20 new families. | ENSMUSG00000028013 | Ppa2 | 202.552040 | 1.0023452 | 0.003379503 | 0.13150720 | 0.00066016450 | 0.9795016755939108810125048876216169446706771850585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.98902105945045060142462034491472877562046051025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 214.770398 | 19.819477 | 215.272999 | 19.893220 | |
| ENSG00000139618 | 675 | BRCA2 | protein_coding | P51587 | FUNCTION: Involved in double-strand break repair and/or homologous recombination. Binds RAD51 and potentiates recombinational DNA repair by promoting assembly of RAD51 onto single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). Acts by targeting RAD51 to ssDNA over double-stranded DNA, enabling RAD51 to displace replication protein-A (RPA) from ssDNA and stabilizing RAD51-ssDNA filaments by blocking ATP hydrolysis. Part of a PALB2-scaffolded HR complex containing RAD51C and which is thought to play a role in DNA repair by HR. May participate in S phase checkpoint activation. Binds selectively to ssDNA, and to ssDNA in tailed duplexes and replication fork structures. May play a role in the extension step after strand invasion at replication-dependent DNA double-strand breaks; together with PALB2 is involved in both POLH localization at collapsed replication forks and DNA polymerization activity. In concert with NPM1, regulates centrosome duplication. Interacts with the TREX-2 complex (transcription and export complex 2) subunits PCID2 and SEM1, and is required to prevent R-loop-associated DNA damage and thus transcription-associated genomic instability. Silencing of BRCA2 promotes R-loop accumulation at actively transcribed genes in replicating and non-replicating cells, suggesting that BRCA2 mediates the control of R-loop associated genomic instability, independently of its known role in homologous recombination (PubMed:24896180). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15115758, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15199141, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15671039, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18317453, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20729832, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20729858, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20729859, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21084279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21719596, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24485656, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24896180}. | 3D-structure;Cell cycle;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;DNA damage;DNA recombination;DNA repair;DNA-binding;Fanconi anemia;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Tumor suppressor;Ubl conjugation | Inherited mutations in BRCA1 and this gene, BRCA2, confer increased lifetime risk of developing breast or ovarian cancer. Both BRCA1 and BRCA2 are involved in maintenance of genome stability, specifically the homologous recombination pathway for double-strand DNA repair. The largest exon in both genes is exon 11, which harbors the most important and frequent mutations in breast cancer patients. The BRCA2 gene was found on chromosome 13q12.3 in human. The BRCA2 protein contains several copies of a 70 aa motif called the BRC motif, and these motifs mediate binding to the RAD51 recombinase which functions in DNA repair. BRCA2 is considered a tumor suppressor gene, as tumors with BRCA2 mutations generally exhibit loss of heterozygosity (LOH) of the wild-type allele. [provided by RefSeq, May 2020]. | hsa:675; | BRCA2-MAGE-D1 complex [GO:0033593]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; chromosome, telomeric region [GO:0000781]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; DNA repair complex [GO:1990391]; lateral element [GO:0000800]; nuclear ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000152]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; gamma-tubulin binding [GO:0043015]; histone H3 acetyltransferase activity [GO:0010484]; histone H4 acetyltransferase activity [GO:0010485]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; single-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003697]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cellular response to ionizing radiation [GO:0071479]; cellular senescence [GO:0090398]; centrosome duplication [GO:0051298]; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in transcription of p21 class mediator [GO:0006978]; double-strand break repair [GO:0006302]; double-strand break repair via homologous recombination [GO:0000724]; establishment of protein localization to telomere [GO:0070200]; female gonad development [GO:0008585]; hematopoietic stem cell proliferation [GO:0071425]; histone H2A monoubiquitination [GO:0035518]; histone H3 acetylation [GO:0043966]; histone H4 acetylation [GO:0043967]; inner cell mass cell proliferation [GO:0001833]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator [GO:0042771]; male meiosis I [GO:0007141]; mitotic recombination-dependent replication fork processing [GO:1990426]; negative regulation of mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0033600]; nucleotide-excision repair [GO:0006289]; oocyte maturation [GO:0001556]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0045931]; protein autoubiquitination [GO:0051865]; regulation of cytokinesis [GO:0032465]; regulation of DNA damage checkpoint [GO:2000001]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; replication fork protection [GO:0048478]; response to gamma radiation [GO:0010332]; response to UV-C [GO:0010225]; response to X-ray [GO:0010165]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; telomere maintenance via recombination [GO:0000722] | 11044354_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11062481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11063672_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11073541_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11097234_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11130383_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11149425_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11180449_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11181654_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11192759_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11207040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11207041_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11221880_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11248061_Observational study of gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11263938_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11377596_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11403219_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11410514_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11426450_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11433401_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11437399_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11448436_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11466700_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11474660_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11481082_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11493753_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11504767_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11505617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11535547_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11550168_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11556836_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11562929_Clinical trial of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11584901_Observational study of gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11668223_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11698567_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11710890_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11754111_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11786575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11786581_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11788883_Suppression of tumorigenicity of rat liver tumor cells by human chromosome 13: evidence against the involvement of pRb and BRCA2 11793480_BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations in Russian familial breast cancer 11802208_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11802209_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11807777_Germline mutation in BRCA2 associated with hypersensitivity to radiation 11807889_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11822793_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11844822_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11857015_Observational study of gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11857383_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11857748_A low frequency of recurrent BRCA2 mutations has been found in breast and ovarian cancers in Spain. 11857749_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11857749_Three Chinese cases carrying the recurrent BRCA2 mutation 3337C>T show sharing of some alleles, suggesting some degree of shared ancestry but not sufficient to demonstrate founder effect. 11870168_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11870509_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11873550_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11879560_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11883440_minor role of exon 1 among Sudanesse breast cancer patients 11890937_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11890937_mutagen sensitivity of blood lymphocytes from women carrying brca2 mutatioon 11896095_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11897832_Contribution of BRCA2 germline mutations to hereditary breast/ovarian cancer in Germany. 11920551_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11920621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11927503_BRCA2 N372H polymorphism associated with modest recessively inherited risk of breast cancer in Australian women 11927503_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11948477_somatic mutations in BRCA2 and high frequency of allelic loss occurs in sporadic male breast cancer 11950811_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11953874_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11964925_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11972384_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11977534_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11981002_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11983207_Expression of BRCA1 and BRCA2 in different tumor cell lines with various growth status 12020440_Cells from carriers of mutations in one allele of the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes have no gross defects in their ability to rejoin radiation-induced DNA breaks. 12020440_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12023992_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12036913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12039933_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12065746_cell lines derived from Fanconi anemia B and D1 patients have biallelic mutations in BRCA2 and express truncated BRCA2 proteins 12070551_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12088120_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12100744_BRCA2 exons 10 & 11 were studied by the protein truncation test, & BRCA2 exons 9, 17, 18 and 23 with the SSCP assay on genomic DNA from early-onset breast cancer patients by PCR. 2 frameshifts, 3 missense mutations, and a polymorphism were found. 12100744_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12101561_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12112655_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12112655_Results demonstrate the importance of BRCA2 in the development of ovarian cancer in this Turkish population. 12114473_The 999del5 mutation in the BRCA2 gene explains a substantial proportion of familial risk of breast cancer in Iceland. 12125210_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12145750_first BRCA2 missense mutation shown to be a predicted deleterious protein-truncating mutation and suggests a potentially useful method for determining the clinical significance of a subset of the many unclassified variants in BRCA1 and BRCA2 12181777_Contribution of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations to breast and ovarian cancer in Pakistan. 12181777_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12210341_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12215251_eight of the most common reported missense mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 occurring in patients tested for hereditary risk of breast and ovarian cancers 12220452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12228710_crystal structure of a COOH terminal BRCA2 domain bound to DSS1; demonstrate that this BRCA2 domain binds single-stranded DNA and show that BRCA2 stimulates RAD51-mediated recombination in vitro 12229875_relation of gene to various cancers, especially breast and ovarian cancers 12229876_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12237285_inactivated in ovarian cancer 12237897_Survival in prospectively ascertained familial breast cancer: analysis of a series stratified by tumour characteristics, BRCA mutations and oophorectomy 12242698_recent findings regarding BRCA2 in breast cancer - review 12376208_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12376518_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12385017_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12404104_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12431973_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12433008_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12440810_BBRCA2 gene mutation in unselected women with ovarian and early breast cancer in Mongolia predicts the genetic predisoposition to these diseases. 12442171_crystal structure of a complex between an evolutionarily conserved sequence in BRCA2 (the BRC repeat) and the RecA-homology domain of RAD51 12442273_Two BRCA2 missense variants were identified in breast cancer patients in India. 12442274_BRCA2 mutation, 7883delTTAA, was identified in breast cancer patients in China. 12442275_BRCA2 2663-2664insA and rare variants were identified in breast cancer patients in Mexico. 12453858_Germline mutations in BRCA2 account for breast neoplasms predisposition in the majority of families. 12457999_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12461697_highly recurrent BRCA2 splice site mutation (IVS16-2A>G) in three breast cancer-only families 12464649_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12470990_BRCA2 has a more specific role in DNA repair, regulating the activity of RAD51(review) 12471628_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12473589_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12474142_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12476445_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12484126_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12485194_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12491828_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12496047_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12504628_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12527904_cancer-predisposing mutation compromises interaction between BRCA2 and replication protein A 12543786_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12552570_The BRCA2 gene plays a significant role in the familial breast cancer phenotype in the Cypriot population. 12556369_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12567413_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12568865_mutation analysis of this gene in a case of familial endometriosis 12569143_Our data support an important role for BRCA2 germline mutations in a subpopulation of families with familial pancreatic cancer. 12606939_S-phase RAD51 foci form normally in CAPAN-1 cells expressing truncated BRCA2. The observed BRCA2-dependent & independent formation of RAD51 foci shows that intact BRCA2 is not required for RAD51 focus formation per se. 12611452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12618335_BRCA2 germline mutation is associated with fallopian tube cancer. 12644538_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12644778_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12655560_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12655567_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12670525_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12670525_polymorphisms in BRCA2 is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 12672886_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12673354_Changes in the topoisomerase I activity in V-C8 cells are due to the defective function of the Brca2 gene. 12677558_Average cumulative risks in BRCA2-mutation carriers by age 70 years were 45% (95% confidence interval 31%-56%) for breast cancer and 11% (2.4%-19%) for ovarian cancer 12677558_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12684407_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12691152_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12691152_germline BRCA2 mutations are not associated with an increased risk for lymphoid malignancies 12698193_Founder mutations are present within the Scottish/Northern Irish population and have implications for the organisation of molecular screening services. 12704633_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12712470_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12756300_wild-type BRCA2, but not a tumor-specific truncated mutant BRCA2, synergizes with the nuclear receptor coactivator p160 GRIP1 to enhance transcriptional activation by androgen receptor 12771943_major role of Brca2 in mediating cell survival after irradiation is in the S and G(2) phases of the cell cycle 12774040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12779088_Androgen receptor expression is absent in BRCA1-mutated breast tumors when compared to BRCA2-mutated cases, indicating that BRCA2-mutated tumors may be different. 12798717_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12815053_BRCA2 has a role in modulating M phase progression 12833555_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12845657_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12865453_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12879478_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12883740_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12911720_None of the BRCA 1 or 2 mutations were detected in the ovarian cancer patient group. 12911720_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12911837_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12917199_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12920090_Recurrent BRCA2 mutations have no role in predisposition to prostate cancer in Finland. 12927042_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12927042_The product of the BRCA2 gene has a function relating to the differentiation of epithelial tissue in the breast in response to the hormones of pregnancy. 12937835_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12938098_Eight novel BRCA2 mutations identified in breast and ovarian cancers may be deleterious cancer predisposing mutations. 12942367_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12942367_the spectrum of BRCA2 mutations in African Americans 12946038_In general, OC use, childbearing and breastfeeding do not differ between BRCA1/2 carriers and non-carriers with ovarian cancer. However, the effects of tubal ligation may differ between BRCA1 carriers and non-carriers. 12946038_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12967657_BRCA2 is epistatic to FA genes for ICL repair, but not for damage-induced modification of FANCD2 and may act downstream form FANCD2. 14507240_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14507240_study from South India, on BRCA1, BRCA2 & CHEK2 mutations in patients with a family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer and early onset breast/ovarian cancer 14517958_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14519755_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14555511_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14555518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14572939_Observational study of healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 14574155_BRCA2 mutation is associated with serous carcinoma of ovary 14576434_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14576434_risks of breast and ovarian cancer were determined for Ashkenazi Jewish women with inherited mutations in the tumor suppressor genes BRCA1 and BRCA2 14580253_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14580256_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14581427_Observational study of healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 14586320_Observational study of healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 14615451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14636569_Data report the isolation of a holoenzyme complex termed BRCC containing BRCA1, BRCA2, and RAD51, which displays increased association with p53 following DNA damage and ubiquitinates p53 in vitro. 14647210_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14647419_inactivation of the FANC-BRCA pathway is relatively common in solid tumors and may be related to tobacco and alcohol exposure 14647438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14647438_fiver germline mutations in cases of familial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma suggests role in genetic susceptibility 14648706_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14651845_The remarkable clinical overlap between sporadic EMSY amplification and familial BRCA2 deletion implicates a BRCA2 pathway in sporadic breast and ovarian cancer. 14660434_In transgenic mice, rescues embryonic lethality and mice develop normally. 14662532_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14668548_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14670928_Molecular analysis revealed biallelic BRCA2/FANCD1 mutations in a kindred with solid tumors in childhood. 14673037_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14678969_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14680495_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14709734_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14709740_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14722926_Novel germline deleterious pathogenic, protein truncating frameshift and non-sense mutations were detected in exon 11 of BRCA2 in breast-ovarian cancer families. 14722926_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14732925_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14732925_heterozygosity for germ-line mutations in BRCA2 results in development of progesterone receptor A predominance. 14735173_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14735581_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14746861_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14752193_Man with a history of clinically diagnosed right breast cancer who subsequently tested positive for the breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA2 and received a diagnosis of mammographically detected left breast cancer at screening. 14755459_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14761918_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14769635_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14973102_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14984481_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15015609_Allelic loss at the BRCA2 locus may be of use as a negative predictor for metastases-free and overall survival in breast cancer patients. 15041722_BRCA1-related breast cancers are more frequently estrogen receptor (ER) negative than are either BRCA2-related or nonhereditary breast cancers. 15041722_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15053071_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15053073_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15059511_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15067026_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15070707_identified 6 children in 5 kindreds exhibiting the co-occurrence of BRCA2 mutations, FA, and early onset acute leukemia 15073127_BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations may have a role in progression of ovarian cancer 15073127_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15082902_BRCA mutations were present in 12.7% of the high risk patients, compared with 2.8% of the unselected patients. 15082902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15083174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15084244_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15086724_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15095307_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15104281_Our results suggest that there is a field effect of early genetic events preceding morphologic changes in the mammary glands of BRCA mutation carriers. 15114373_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15115758_FANCD2 and BRCA2 can be coimmunoprecipitated from cell extracts of both human and Chinese hamster wild-type cells, thus confirming that the interaction occurs in vivo 15116316_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15117986_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15131025_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15131399_Cancer variation associated with the position of the mutation in the BRCA2 gene in 7 different neoplasms and the differences in cancer risk remain to be explored. 15131400_BRCA2 mutations could not be detected among unrelated non-Ashkenazi-Jewish high risk families in Israel. 15131400_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15131403_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15138483_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15138485_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15140370_Observational study of healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 15140371_Observational study of healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 15144764_Observational study of healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 15159322_Observational study of healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 15168169_Identification and evaluation of 55 genetic variations in the BRCA1 and the BRCA2 genes of patients from 50 Japanese breast cancer families 15170666_RAD51D polymorphism is not associated with BRCA1 or 2 genes in breast cancer. 15199141_results demonstrate that monoubiquitination of FANCD2, which is regulated by the FA pathway, promotes BRCA2 loading into chromatin complexes. These complexes appear to be required for normal homology-directed DNA repair. 15217508_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15236312_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15254695_BRCA2 germline mutations may have a role in primary cancer of the fallopian tube 15265971_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15280188_Observational study of healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 15280342_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15284715_Observational study of healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 15314155_Results suggest that BRCA2 expression levels are regulated by ubiquitination in response to DNA damage and that USP11 participates in DNA damage repair functions within the BRCA2 pathway independently of BRCA2 deubiquitination. 15317758_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15319244_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15319244_Patients with bilateral breast cancer having BRCA2 mutations are significantly younger than non-carriers. 15331870_Observational study of healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 15345109_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15365993_A novel pathogenic germline mutations,BRCA2 c.2259delT, was found in a screening of sporadic Korean breast cancer patients, along with 4 polymorphic and 8 intronic variants of unknown clinical significance. 15365993_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15367553_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15375219_results show that BRCA2 deficiency impairs the completion of cell division by cytokinesis 15519522_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15545966_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15548363_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15559734_Observational study of healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 15564800_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15571962_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15576832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15589605_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15617999_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15635067_prevalence of BRCA2 mutations in a large hospital based series of unselected breast cancer cases 15670748_Quantitative-PCR and Northern analysis confirmed down-regulation of UCRP and UBE2L6 with BRCA2 knockdown, respectively. 15671039_FANCD2 mediates double strand DNA break repair independently of BRCA2- and Rad51-associated homologous recombination 15721786_Identification of a potential novel domain in the BRCA2 protein. 15726604_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15728167_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15733268_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15733268_results reveal unique characteristics of BRCA1/2 mutation, genotype-phenotype & prognosis in moderate- & low-risk individuals of Greek ancestry; breast cancer due to mutations in BRCA1 & BRCA2 appears to be a heterogeneous syndrome in Greek population 15734731_SLUG is a negative regulator for BRCA2 gene expression 15734957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15800311_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15800615_results indicate that S3291 phosphorylation might provide a molecular switch to regulate RAD51 recombination activity, providing new insight into why BRCA2 C-terminal deletions lead to radiation sensitivity and cancer predisposition 15806175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15863145_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15880530_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15887246_BRCA1/2 mutation screening should be considered for all women diagnosed before age 41. 15887246_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15894703_No association was found for the N372H polymorphism in BRCA2 and breast cancer among Caucasian women. 15900600_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15900600_There is no significant effect of AIB1 genetic variation on breast cancer risk in BRCA2 mutation carriers. 15917310_role of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation in pre-disposition to ovarian cancer. 15930293_Expression of BRCA2 and MAGE-D1 synergistically suppresses cell proliferation independently of the p53 pathway. 15930334_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15936476_Germline mutations within breast cancer susceptibility genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 are associated with a major risk of breast cancer during lifetime. 15937124_BRCA2 BRC motifs bind distinct regions, and form stable complexes with RAD51-DNA nucleoprotein filaments. 15978801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15983021_Distribution of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations in a cohort of young women with breast cancer, compared as a function with race. 15983021_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15986445_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15986445_women with a BRCA1 protein mutation and 4 or more children had a 38% decrease in breast cancer risk compared to nulliparous women, while among BRCA2 protein carriers, increasing parity was associated with an increased risk of breast cancer 15994883_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15996267_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16003728_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16029503_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16030099_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16032702_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16042582_ells lacking the fully functional protein have consistently been found to show increased sensitivity to a variety of DNA-damaging agents. 16047333_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16049805_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16088935_analysis of Alu element insertions within the BRCA1/2 coding sequences 16118051_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16137751_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16140006_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16168118_Mutational analysis of BRCA1/2 genes in 151 high-risk patients characterized the spectrum of gene alterations and demonstrated the dominant role of the BRCA1 c.5266dupC allele in hereditary breast and ovarian cancer. 16168123_Conclusive evidence that the S384F variant of BRCA2 is not a disease causing mutation in breast cancer. 16168130_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16168130_Weight loss in early adult life (age 18 to 30) protects against early-onset BRCA2 associated breast cancers. 16176503_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16199546_large genomic deletions inactivate the BRCA2 gene in breast cancer families 16214912_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16234515_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16257105_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16257105_results of this study suggested that the polymorphism N372H in BRCA2 gene may be associated with idiopathic male infertility with azoospermia or severe oligozoospermia 16261400_BRCA2 mutations are associated with breast and ovarian cancer 16261408_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16261408_the Met1915Thr polymorphism in the BRCA2 gene may be considered as an independent marker of breast cancer 16271956_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16280055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16284991_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16284991_The frequency of hereditary ovarian carcinoma is attributed to BRCA2 gene mutation. 16324400_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16331614_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16369438_The data suggest applying an increased | ENSMUSG00000041147 | Brca2 | 161.861591 | 0.9722502 | -0.040600523 | 0.25057573 | 0.02599592830 | 0.8719102620976521000883963097294326871633529663085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.94303570294765015624705029040342196822166442871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 140.296619 | 23.776377 | 145.732655 | 24.628742 | |
| ENSG00000140474 | 25989 | ULK3 | protein_coding | Q6PHR2 | FUNCTION: Serine/threonine protein kinase that acts as a regulator of Sonic hedgehog (SHH) signaling and autophagy. Acts as a negative regulator of SHH signaling in the absence of SHH ligand: interacts with SUFU, thereby inactivating the protein kinase activity and preventing phosphorylation of GLI proteins (GLI1, GLI2 and/or GLI3). Positively regulates SHH signaling in the presence of SHH: dissociates from SUFU, autophosphorylates and mediates phosphorylation of GLI2, activating it and promoting its nuclear translocation. Phosphorylates in vitro GLI2, as well as GLI1 and GLI3, although less efficiently. Also acts as a regulator of autophagy: following cellular senescence, able to induce autophagy. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19279323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19878745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20643644}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Autophagy;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase | Enables protein serine/threonine kinase activity. Involved in several processes, including fibroblast activation; protein autophosphorylation; and regulation of smoothened signaling pathway. Located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:25989; | autophagosome [GO:0005776]; ciliary tip [GO:0097542]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; phagophore assembly site [GO:0000407]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; autophagosome organization [GO:1905037]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; cellular senescence [GO:0090398]; fibroblast activation [GO:0072537]; negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045879]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045880]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224] | 12471243_First named and identified as protein kinase of the ULK family 19141860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19430479_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19878745_serine/threonine kinase ULK3 is involved in the SHH pathway as a positive regulator of GLI proteins 20479155_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20643644_Dual function of UNC-51-like kinase 3 (Ulk3) in the Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway. 20959405_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21045733_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 26011858_Structural and biochemical studies reveal an unusually tight interaction between ULK3 and IST1, an ESCRT-III subunit required for cytokinetic abscission. 28877478_Increased ULK3 also induces autophagy, which is unlinked from GLI and CAF activation. ULK3 upregulation occurs in the CAFs of several tumor types, and ULK3 silencing suppresses the tumor-enhancing properties of these cells. 34190988_Conformational plasticity of the ULK3 kinase domain. | ENSMUSG00000032308 | Ulk3 | 325.268958 | 1.0359761 | 0.050990663 | 0.15365299 | 0.10985654045 | 0.7403075215817783716332201038312632590532302856445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.86969191331871309458279029058758169412612915039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 336.525697 | 29.820772 | 326.262338 | 28.865324 | |
| ENSG00000140598 | 79631 | EFL1 | protein_coding | Q7Z2Z2 | FUNCTION: Involved in the biogenesis of the 60S ribosomal subunit and translational activation of ribosomes. Together with SBDS, triggers the GTP-dependent release of EIF6 from 60S pre-ribosomes in the cytoplasm, thereby activating ribosomes for translation competence by allowing 80S ribosome assembly and facilitating EIF6 recycling to the nucleus, where it is required for 60S rRNA processing and nuclear export. Has low intrinsic GTPase activity. GTPase activity is increased by contact with 60S ribosome subunits. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21536732}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Elongation factor;GTP-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Ribosome biogenesis | Enables GTPase activity and ribosome binding activity. Involved in GTP metabolic process and mature ribosome assembly. Predicted to be part of ribonucleoprotein complex. Implicated in Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:79631; | ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; ribosome binding [GO:0043022]; translation elongation factor activity [GO:0003746]; cytosolic ribosome assembly [GO:0042256]; GTP metabolic process [GO:0046039] | 20966410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25015090_Downregulation of EFTUD1 induced cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gliomas by impairing ribosome biogenesis 25991726_Association of Elongation Factor-like 1 (EFL1) GTPase to SBDS did not modify the affinity for GTP but dramatically decreased that for GDP by increasing the dissociation rate of the nucleotide. 26479198_Upon EFL1 binding, SBDS is repositioned around helix 69, thus facilitating a conformational switch in EFL1 that displaces eIF6 by competing for an overlapping binding site on the 60S ribosomal subunit. 28331068_Mutations in EFL1 clinically manifest phenotypes of infantile pancytopenia, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency and skeletal anomalies. Mutant EFL1 proteins do not promote the release of yeast cytoplasmic Tif6 from the 60S subunit, likely preventing the formation of mature ribosomes. 30198570_Whole exome sequencing discloses heterozygous variants in the DNAJC21 and EFL1 genes but not in SRP54 in 6 out of 16 patients with Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome carrying biallelic SBDS mutations. 30545121_the effect of SBDS mutations on the interaction with EFL1were tested, and showed that all tested mutations disrupted the binding to EFL1. 31151987_we report biallelic mutations in EFL1 in 3 unrelated individuals with clinical features of SDS. Cellular defects in these individuals include impaired ribosomal subunit joining and attenuated global protein translation as a consequence of defective eIF6 eviction. 31838967_Exploring the role of elongation Factor-Like 1 (EFL1) in Shwachman-Diamond syndrome through molecular dynamics. 34115847_Somatic uniparental disomy mitigates the most damaging EFL1 allele combination in Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. | ENSMUSG00000038563 | Efl1 | 78.287205 | 1.2932001 | 0.370945558 | 0.21121084 | 3.07842359144 | 0.0793373889640758972463530085406091529875993728637695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.22597666398482865734997915296844439581036567687988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 88.491612 | 13.132214 | 68.724621 | 10.286945 | |
| ENSG00000141027 | 9611 | NCOR1 | protein_coding | O75376 | FUNCTION: Mediates transcriptional repression by certain nuclear receptors (PubMed:20812024). Part of a complex which promotes histone deacetylation and the formation of repressive chromatin structures which may impede the access of basal transcription factors. Participates in the transcriptional repressor activity produced by BCL6. Recruited by ZBTB7A to the androgen response elements/ARE on target genes, negatively regulates androgen receptor signaling and androgen-induced cell proliferation (PubMed:20812024). Mediates the NR1D1-dependent repression and circadian regulation of TSHB expression (By similarity). The NCOR1-HDAC3 complex regulates the circadian expression of the core clock gene ARTNL/BMAL1 and the genes involved in lipid metabolism in the liver (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q60974, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14527417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20812024}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Biological rhythms;Chromatin regulator;Coiled coil;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes a protein that mediates ligand-independent transcription repression of thyroid-hormone and retinoic-acid receptors by promoting chromatin condensation and preventing access of the transcription machinery. It is part of a complex which also includes histone deacetylases and transcriptional regulators similar to the yeast protein Sin3p. This gene is located between the Charcot-Marie-Tooth and Smith-Magenis syndrome critical regions on chromosome 17. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Pseudogenes of this gene are found on chromosomes 17 and 20.[provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. | hsa:9611; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; histone deacetylase complex [GO:0000118]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitotic spindle [GO:0072686]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription repressor complex [GO:0017053]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; nuclear receptor binding [GO:0016922]; nuclear thyroid hormone receptor binding [GO:0046966]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; locomotor rhythm [GO:0045475]; negative regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060766]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0045922]; negative regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0045820]; negative regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046329]; negative regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902894]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; spindle assembly [GO:0051225] | 9724795_This paper describes the cloning of the full-length human NCOR1 cDNA. 11903058_Nuclear receptor corepressor-dependent repression of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor delta-mediated transactivation 11931768_Results show that the N-CoR-HDAC3 complex inhibits JNK activation through the associated GPS2 subunit and thus could potentially provide an alternative mechanism for hormone-mediated antagonism of AP-1 function. 12077342_Mammalian PRP4 kinase copurifies and interacts with components of both the U5 snRNP and the N-CoR deacetylase complexes. 12089345_These results demonstrate that AR, in contrast to other SHRs, is regulated by NCoR 12150997_Exchange of N-CoR corepressor and Tip60 coactivator complexes links gene expression by NF-kappaB and beta-amyloid precursor protein. 12466959_recruited by prohibitin for transcriptional repression 12648520_N-CoR functions not merely as a repressor of basal transcription, but rather as a modulator of both basal and ligand-activated transcription of genes controlled by RAR/RXR heterodimers in a dose-dependent manner 12861000_N-CoR/histone deacetylase 3 complex is required for repression by thyroid hormone receptor 12890497_associates with CHD1 and histone deacetylase as well as with RNA splicing proteins 15377655_N-CoR utilizes repression domains I and III for interaction and co-repression with ETO 15561719_THAP7 coimmunoprecipitates with histone deacetylase 3 and the nuclear hormone receptor corepressor and represses transcription 15598662_NCoR is a physiological regulator of the AR; the N-terminal surface of the AR-mediating NCoR recruitment was distinct from tau5 and from the FXXLF motif that mediates agonist-induced N-C-terminal interaction 15695367_the DAD domain of N-CoR is singularly essential for repression by the thyroid hormone receptor 15761026_the N-CoR/HDAC3 complex has a role in regulating the expression of genes involved in circadian rhythm by functioning as corepressor for Rev-erbalpha 15802375_N-CoR and SMRT play an active role in preventing tamoxifen from stimulating proliferation in breast cancer cells through repression of a subset of target genes involved in ERalpha function and cell proliferation 16024779_N-CoR together with JMJD2A could play a role in repressing achaete scute-like homologue 2 (ASCL2) expression in various tissues. 16141343_mechanism by which the estrogen-ER complex markedly reduces the level of N-CoR through a process involving the up-regulation of Siah2 and the subsequent targeting of N-CoR for proteasomal degradation 16195251_SAFB1 was shown to interact directly with the nuclear receptor corepressor N-CoR. 16216492_N-CoR and TRbeta cooperate in the regulation of the TSHbeta gene and this ligand-dependent repression is mediated by the LXXLL motif in N-CoR 16373395_SMRT and N-CoR corepressors are involved in transcriptional regulation by both agonist- and antagonist-bound AR and regulate the magnitude of hormone response, at least in part, by competing with coactivators. 16730330_Results provide evidence to show that the N-CoR/HDAC3 co-repressor complex is involved in the aberrant transcription regulation in PML-RARalpha-expressing cells. 16849648_RB7 and butyrate induce dissociation of HDAC3 (but not HDAC1 or HDAC2) and its adaptor protein NCoR. 16914745_The repression mechanisms by the nuclear receptor corepressor (N-CoR) of steroid hormone receptor (SHR)-mediated transactivation were examined. 17073437_first report of a direct interaction between N-CoR and CBP, and suggests that the role of N-CoR in mediating transcriptional events may be more complex than previously anticipated 17630505_Data show that IKKalpha phosphorylates the homologous N-CoR corepressor in serines 2345 and 2348 creating a functional 14-3-3 binding domain (RK(p)S(2348)KSP). 17768398_Data support a role for N-CoR in erythroid differentiation and suggest that N-CoR is required for the induction of a key enzyme involved in heme synthesis. 18052923_both SMRT and N-CoR are limited in cells and knocking down either of them results in co-repressor-free TR and consequently de-repression of TR target genes 18362166_Vitamin D receptor (VDR) with the retinoid X receptor (RXR) recruits NCoR and SMRT strictly in a VDR agonist-dependent manner. 18586123_ETO family member-mediated oligomerization and repression can be distinct events and that interaction between ETO family members and hSIN3B or N-CoR may not necessarily strengthen transcriptional repression. 18632669_SMRT and NCoR have important roles in the regulation of beta-catenin-TCF4-mediated gene transcription 18637017_A point mutation (S296R) in the amino-terminal domain of the androgen receptor (AR) can decrease the ligand specificity of the AR and alter the interaction between serine296arginine and the nuclear receptor co-repressor 1 (N-coR). 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18669643_Data show that, at sufficiently high concentration, the NR corepressor (NCoR) influences the activity of the liver X receptor (LXR) even in the presence of a potent full agonist that destabilizes NCoR binding. 18832723_apoptotic cells induce PPARgamma sumoylation to attenuate the removal of NCoR, thereby blocking transactivation of NF-kappaB. 18852122_These findings show that AR antagonists can enhance corepressor recruitment by stabilizing a distinct antagonist conformation of the AR coactivator/corepressor binding site. 19048289_NCoR was expressed in the cytoplasm of colorectal carcinoma-associated myofibroblasts, but was rarely noted in myofibroblasts of normal mucosa or adenomas. 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19126649_NCOR1 is a selective regulator of nuclear receptors, notably PPARgamma and VDR, and contributes to their loss of sensitivity. 19183483_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19414341_Up-regulation of nuclear receptor corepressor is associated with progestin-induced growth suppression of endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma 19608741_NCoR1 expression is required to maintain IEC in a proliferative state, and PEDF is a novel transcriptional target for NCoR1 repressive action 19781322_NCOR1 protein expression level predicts response to endocrine therapy as first-line treatment for breast cancer patients on relapse. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19955185_hPPARalpha SUMOylation on lysine 185 down-regulates its trans-activity through the selective recruitment of NCoR 20003447_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20181716_The authors established an interaction of E8;E2C with an NCoR1/HDAC3 complex and demonstrated that this interaction requires the wild-type E8 open reading frame. 20466759_Elevated NCOR1 disrupts PPARalpha/gamma signaling and is associated with prostate cancer. 20581824_Study reports the crystal structure of a nuclear receptor-co-repressor (N-CoR) interaction domain 1 (ID1) peptide bound to truncated human Rev-erbalpha ligand-binding domain. 20587609_Amino-terminal A/B domain deletion facilitated the in vitro binding of nuclear receptor CoR with wild-type PPARG2. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20974212_These data support the hypothesis that NCoR might control a cell cycle dependent regulation of expression androgen receptor target genes in prostate cells. 21131350_Aberrant corepressor interactions implicated in PML-RAR(alpha) and PLZF-RAR(alpha) leukemogenesis reflect an altered recruitment and release of specific NCoR and SMRT splice variants. 21143702_We immunohistochemically analyzed the expression of NCOR1 and 2 as well as HDAC1, 2, and 3 on a tissue microarray comprising tumor samples from 283 astrocytic gliomas 21389087_Differential interaction of NCoR1 with TR isoforms accounted for the TR isoformdependent regulation of adipogenesis and that aberrant interaction of NCoR1 with TR could underlie the pathogenesis of lipid disorders in hypothyroidism. 21518914_data strongly support a model in which EBNA2 association with NCoR-deficient RBPJ enhances transcription and EBNALP dismisses NCoR and RBPJ repressive complexes from enhancers 21525722_ERbeta and its co-regulators p300 and NCoR are expressed in human transitional cell bladder cancer 21966475_Data suggest a possible role of misfolded N-CoR protein in the activation of oncogenic survival pathway in non-small cell lung cancer cells. 21987803_the aberrant recruitment of NCOR1 by TRbeta mutants leads to clinical resistance to thyroid hormone (RTH) 22337871_Regulated HDAC3 degradation serves as a buffering mechanism to protect independent formation of N-CoR and SMRT corepressor complexes. 22349439_PCOS rat models also showed alterations of PPARG1, NCOR1, and HDAC3 mRNA expression and methylation changes of PPARG1 and NCOR1, consistent with the results from humans. 22514634_Findings suggest that N-CoR-induced repression of Flt3 might be crucial for limiting the contribution of the Flt3 signaling pathway on the growth potential of leukemic cells. 22622808_A novel mechanism by which overexpression of estrogen receptor (ER) beta through NCoR is able to down regulate ER alpha gene expression, thus blocking ER alpha's driving role on breast cancer cell growth. 22651256_analysis of regulation of small ubiquitin-like modifier-1, nuclear receptor coreceptor, histone deacetylase 3, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in human adipose tissue 22675025_CK2alpha-NCoR cascade selectively represses the transcription of IP-10 and promotes oncogenic signaling in human esophageal cancer cells. 22944139_Corepressor molecules NCoR and SMRT are present at 1,25(OH)2D3 activated gene enhancers 23129261_These results uncover a regulatory mechanism by which PKA positively modulates NCoR function in transcriptional regulation in prostate cancer. 23295231_The aberrant cytoplasmic expression of NCoR1 in retinoblastoma appears to be associated with the proliferative and/or dedifferentiated properties of retinoblastoma. 23428870_NCOR1 and HDAC3 are instrumental in the repression of glucocorticoid receptor gene transcription. 23940660_Site directed mutagenic analysis of N-CoR identified serine 1450 as the crucial residue whose phosphorylation by Akt was essential for the misfolding and loss of N-CoR protein. 24315104_Study shows that NCoR1 is a key target of proteolysis and physically interacts with the transcription factor CREB, the genome-wide map described here ties proteolysis in mammalian cells to active enhancers and to promoters of specific gene families. 24335696_Low NCoR expression is associated with glioblastoma. 24840043_Data suggest that direct interactions of HLCS (holocarboxylase synthetase) with NCOR1 (nuclear receptor corepressor 1) and HDAC1 (histone deacetylase 1) contribute toward transcriptional repression of repeats, presumably increasing genome stability. 25823659_loss of nuclear NCoR results in upregulation of a specific cancer-related genetic signature, and is significantly associated with malignant melanoma progression. 25928846_The co-localization of AML1-ETO with the N-CoR co-repressor to be primarily on genomic regions distal to transcriptional start sites. (NcoR1) 26589942_PDCD2 and NCoR1 may act as tumor suppressors in Gastrointestinal stromal tumors cells through the Smad signaling pathway. 26663086_Data suggest that complexes of HDAC3-H1.3 with NCOR1 and NCOR2/SMRT accumulate on chromatin in synchronized HeLa cells in late G2 phase and mitosis; deacetylation activity of HDAC3 is activated via phosphorylation of Ser-424 by CK2 only in mitosis. 26729869_NCoR depletion enhances cancer cell invasion and increases tumor growth and metastatic potential. 26968201_NCOR1 function declines with prostate cancer progression. Reduction in NCOR1 levels causes bicalutamide resistance in LNCaP cells and compromises response to bicalutamide in mouse prostate in vivo 27149915_Nuclear Receptor Corepressor 1 is an important transcriptional regulator that interacts with nuclear receptors and other transcription factors. Recent results have shown the presence of inactivating mutations or deletions of the nuclear receptor corepressor 1 gene in human tumors. 27375289_verexpression of COPS5, through its isopeptidase activity, leads to ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation of NCoR, a key corepressor for ERalpha and tamoxifen-mediated suppression of ERalpha target genes. 27806339_Authors previously shown that Nuclear Receptor Corepressor 1 (NCoR) and the thyroid hormone receptor beta1 (TRbeta) inhibit tumor invasion. Here they show that these molecules repress VEGF-C and VEGF-D gene transcription in breast cancer cells, reducing lymphatic vessel density and sentinel lymph node invasion in tumor xenografts. 27880911_USP44 contributes to N-CoR functions in regulating gene expression and is required for efficient invasiveness of triple-negative breast cancer cells. 27956629_the NCOR/HDAC3 complex is a major suppressor of differentiation in rhabdomyosarcoma 29483668_19 patients with neurodevelopmental disorders harboring a rare deletion inherited from a healthy parent were investigated by whole-exome sequencing to search for SNV on the contralateral segment. This strategy allowed us to identify a candidate variant in two patients in the NUP214 and NCOR1 genes. 30117609_Survival of developing thymocytes is regulated by NCOR1. NCOR1 controls positive and negative selection of thymocytes during T cell development. HDAC3 interacts with NCOR1 corepressor complexes. Review. 30138371_Microarray analysis revealed differential expression of three vitamin D associated genes in the aortic adventitia in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and non-RA patients with coronary artery disease: while the expression of GADD45A and NCOR1 was higher, the expression of PON2 was lower in RA patients. 30485330_the presence and prognostic role of mutations in the NCOR1 gene in hormone receptor negative breast and lung adenocarcinomas 30982983_vitamin E and PIAS1-shRNA partially decreased ROS production and IKK activation induced by high glucose and PA exposure. These data indicate that ROS-IKK-PIAS1 pathway mediates PPARgamma sumoylation, leading to endothelium insulin resistance (IR) via stabilizing PPARgamma-NcoR complex. 31208445_Data suggest that the nuclear receptor co-repressor 1/2 protein NCoR-1/NCoR-2 paralogs have been subject to a mix of shared and distinct selective pressures, resulting in the pattern of divergent and convergent alternative-splicing observed in extant species. 31661545_Abnormally localized DLK1 interacts with NCOR1 in non-small cell lung cancer cell nuclear. 32034166_Exome sequencing revealed DNA variants in NCOR1, IGF2BP1, SGLT2 and NEK11 as potential novel causes of ketotic hypoglycemia in children. 33058520_NCOR1 may be a potential biomarker of a novel molecular subtype of prostate cancer. 33199837_Leukemic cells expressing NCOR1-LYN are sensitive to dasatinib in vivo in a patient-derived xenograft mouse model. 33722704_BCOR modulates transcriptional activity of a subset of glucocorticoid receptor target genes involved in cell growth and mobility. 33761934_Discovery of LAMP-2A as potential biomarkers for glioblastoma development by modulating apoptosis through N-CoR degradation. 33861372_Nuclear receptor corepressor (NCoR) is a positive prognosticator for cervical cancer. 35395674_Aberrant Nuclear Export of circNCOR1 Underlies SMAD7-Mediated Lymph Node Metastasis of Bladder Cancer. | ENSMUSG00000018501 | Ncor1 | 384.786472 | 0.8209147 | -0.284695697 | 0.19869765 | 2.04556585630 | 0.1526502150666294854719495788231142796576023101806640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.34861694127228132211726574496424291282892227172851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 288.389780 | 39.729500 | 352.965112 | 48.674520 | |
| ENSG00000141258 | 9905 | SGSM2 | protein_coding | O43147 | FUNCTION: Possesses GTPase activator activity towards RAB32, RAB33B and RAB38 (PubMed:26620560, PubMed:21808068). Regulates the trafficking of melanogenic enzymes TYR, TYRP1 and DCT/TYRP2 to melanosomes in melanocytes by inactivating RAB32 and RAB38. Inhibits RAB32 and RAB38 activation both directly by promoting their GTPase activity and indirectly by disrupting the RAB9A-HPS4 interaction which is required for RAB32/38 activation (PubMed:26620560). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21808068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26620560}. | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;GTPase activation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | The protein encoded by this gene is a GTPase activator with activity towards RAB32 and RAB33B, which are regulators of membrane trafficking. The encoded protein inactivates RAB32 and can bind RAB9A-GTP, a protein required for RAB32 activation. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. | hsa:9905; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; late endosome to Golgi transport [GO:0034499]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547] | 17509819_Identification of novel protein SGSM2 which modulate small G protein (RAP and RAB)-mediated signaling pathway 21808068_RUTBC1 is a Tre2/Bub2/Cdc16 domain-containing protein that binds to Rab9A-GTP both in vitro and in cultured cells, but is not a GTPase-activating protein for Rab9A. 26620560_Data suggest RUTBC1/SGSM2 in melanocytes functions as physiological GTPase-activating protein for Rab32/Rab38 in regulation of transport of melanogenic enzymes (tyrosinase, tyrosinase-related protein 1, dopachrome isomerase) into melanosomes. 30489189_Weighted gene co-expression network analysis identifies specific modules and hub genes related to subsyndromal symptomatic depression. 30744493_Increased expression of SGSM2 is associated with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer metastasis. 35264562_SGSM2 inhibits thyroid cancer progression by activating RAP1 and enhancing competitive RAS inhibition. | ENSMUSG00000038351 | Sgsm2 | 60.559460 | 0.5566303 | -0.845208658 | 0.37387005 | 5.01639550027 | 0.0251083838114625583493033644799652392975986003875732421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.10006155918938412774377155756155843846499919891357421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 45.085070 | 9.645705 | 81.685333 | 17.028783 | |
| ENSG00000141380 | 6760 | SS18 | protein_coding | Q15532 | FUNCTION: Appears to function synergistically with RBM14 as a transcriptional coactivator. Isoform 1 and isoform 2 function in nuclear receptor coactivation. Isoform 1 and isoform 2 function in general transcriptional coactivation. Component of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling subcomplex GBAF that carries out key enzymatic activities, changing chromatin structure by altering DNA-histone contacts within a nucleosome in an ATP-dependent manner (PubMed:29374058). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15919756, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29374058}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Nucleus;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation | Enables nuclear receptor coactivator activity. Involved in positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Part of SWI/SNF complex. Implicated in synovial sarcoma. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:6760; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; GBAF complex [GO:0140288]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; npBAF complex [GO:0071564]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; SWI/SNF complex [GO:0016514]; nuclear receptor coactivator activity [GO:0030374]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; ephrin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048013]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; negative regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045596]; neuronal stem cell population maintenance [GO:0097150]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance [GO:1902459]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410] | 11734557_The SYT protein has a unique QPGY domain, which is also present in the largest subunits, p250 and the newly identified homolog p250R, of the corresponding SNF/SWI complexes 12037676_coexistence of fusions with SSX1 and SSX2 in synovial sarcomas 15919756_SYT may function as a general coactivator 16152617_demonstrate differentially expressed genes for the 2 major gene fusion variants in SS, SS18/X breakpoint 1 sarcoma (SSX1) and SS18/SSX2, and thereby suggest that these result in different downstream effects 16227627_SYT interacts with SYT-interacting protein/co-activator activator 16247461_SYT-SSX1 induces insulin-like growth factor II expression in fibroblast cells. 16462762_SYT-SSX2 contributes to tumor development, in part through beta-catenin signaling. 16484776_SS18 and SS18L1 genes map within co-linear DNA segments that may have evolved through a relatively recent genomic duplication event. 17018603_The SS18-SSX2 fusion protein may act as a so-called transcriptional 'activator-repressor,' which induces downstream target gene deregulation through epigenetic mechanisms. 17101797_SYT-SSX1 fusion protein directly down-regulated the expression of COM1, a regulator of cell proliferation. 17667940_endogenous LHX4 binds to the CGA promoter and that LHX4-mediated CGA activation is enhanced by the SS18-SSX protein 17721327_this sarcoma showed a longer-than-expected PCR product. Direct sequencing of the product disclosed a novel SYT/SSX1 fusion transcript. 18234968_SS18-SSX1 can negatively regulate p53 tumor-suppressive function by increasing the stability of its negative regulator HDM2. 18714179_siRNA targeting of SS18-SSX1 may have therapeutic potential in the treatment of synovial sarcomas. 18992642_Findings showing a complex cryptic rearrangement that gives rise to the characteristic SYT-SSX2 fusion gene in a monophasic synovial sarcoma patient. 18997619_SYT-SSX fusion type was not correlated with survival synovial sarcoma. 19337376_provides evidence that, in the appropriate context, expression of the SYT-SSX2 oncogene leads to loss of polycomb function 19385976_SYT-SSX1 is an adverse predictor for disease-specific survival and metastasis-free survival, but has no relation to local recurrence-free survival in synovial sarcoma. 19649286_findings indicate that cytoplasmic SYT isoforms interact with actin filaments and function in the ability cells to bind and react to specific extracellular matrices 19936258_epigenetic features may define the cellular microenvironment in which SYT-SSX displays its functional effects 20198325_siRNA targeting of SS18-SSX1 has therapeutic potential for the treatment of synovial sarcoma. 20660338_Rearranged SYT wasdetected in all synovial sarcomas but not in any Ewing sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumors 21234732_the fusion gene SYT-SSX should be considered to play important role on Synovial sarcoma cell growth via ERK pathway 21996728_the initial events that likely occur when SYT-SSX2 is first expressed, and its dominant function in subverting the nuclear program of the stem cell, leading to its aberrant differentiation, as a first step toward transformation. 22442726_SS18 together with animal-specific factors defines human BAF-type SWI/SNF complexes 22594313_SYT-SSX2 was recruited to distinct loci across all chromosomes, and an overwhelming number of Polycomb-modified sites enriched with the trimethylated histone H3 on lysine 27 (H3K27me3) formed the main recruiting module for SYT-SSX2. 22976541_SS18-SSX1 and SS18-SSX2 variant translocations are associated with synovial sarcoma. 23540691_Studies show that in the 2 synovial sarcoma cell lines used, the fusion of SS18 with SSX leads to assembly of aberrant BAF complexes that become targeted to the Sox2 locus, with loss of repressive H3K27me3 marks, driving Sox2 expression and proliferation of these cells. 23716114_Knockdown of SS18-SSX1 in synovial sarcoma inhibits viability and induces apoptosis. 24022186_SS18-SSX fusion type is a significant prognostic factor for patients with synovial sarcoma. 24130893_These results suggest that the characteristic speckle localization pattern of SS18-SSX is strongly involved in the tumorigenesis through the SSX moiety of the SS18-SSX fusion protein. 24166495_SS18-SSX-induced Wnt/beta-catenin signaling appears to be of crucial biological importance in synovial sarcoma tumorigenesis and progression. 24429587_Case Report: bronchial biphasic synovial sarcoma with SS18 gene rearrangement. 24922679_SYT gene split is associated with Synovial sarcoma. 25959879_a rare variant of the SS18-SSX1 fusion transcript, which could not be identified by routine procedures for genetic diagnosis, was detected. In addition, 8 missense mutations of cancer-related genes were confirmed 26905812_Data show that SS18/SSX tightly regulates the elevated expression of the key Wnt target AXIN2 in primary synovial sarcoma. 26947017_Meta-analysis of human synovial sarcoma patient series identified two tumor-gentoype-phenotype correlations that were not modeled by the mice, namely a scarcity of male hosts and biphasic histologic features among SS18-SSX2 tumors. Re-analysis of human SS18-SSX1 and SS18-SSX2 tumor transcriptomes demonstrated very few consistent differences, but highlighted increased native SSX2 expression in SS18-SSX1 tumors. 27496426_Kidney transplant recipients' polymorphisms of genes associated with telomere length, BICD1 and chromosome 18, but not hTERT, affect kidney allograft early and long-term function after transplantation. 27572315_Data indicate that the oncogene SS18-SSX1 promotes tumorigenesis by increasing the expression of SHC SH2-domain binding protein 1 (SHCBP1), which normally acts as a tumor promoting factor. 28249647_Thirty-four patients (20 males and 14 females, mean of 31years) with SS18-SSX fusion-positive SS-HN were identified. The parapharyngeal region of the neck was the most common site 29502955_SS18-SSX1 deregulates developmental programs to drive transformation by hijacking a transcriptional repressive complex to aberrantly activate gene expression 29533464_Case Reports: identify a novel recurrent gene fusion, CRTC1-SS18, in undifferentiated small round cell sarcoma. 29893303_Synovial sarcoma (SS) is considered as high-grade tumors with a poor prognosis. Novel therapies targeted at fusion oncogene, SS18-SSX-derived peptide vaccine, epidermal growth factor receptor, and vascular endothelial growth factor are the future hope in SS. 30814111_Synovial sarcoma is a soft tissue malignancy characterized by a reciprocal t(X;18) translocation. This results into SS18-SSX fusion protein which activates YAP/TAZ signaling in synovial sarcoma. 31094920_A novel MEF2C-SS18 gene fusion and unique histologic and immunophenotypic features characterize a heretofore undefined low-grade salivary adenocarcinoma for described as a microsecretory adenocarcinoma. 32747783_The nucleosome acidic patch and H2A ubiquitination underlie mSWI/SNF recruitment in synovial sarcoma. 34091760_Correlating SS18-SSX immunohistochemistry (IHC) with SS18 fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) in synovial sarcomas: a study of 36 cases. 34215745_SS18 regulates pluripotent-somatic transition through phase separation. | ENSMUSG00000037013 | Ss18 | 563.043727 | 0.5647421 | -0.824335967 | 0.60011783 | 1.85198595599 | 0.1735525924836750222279846411765902303159236907958984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.37831598311697772762940417123900260776281356811523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 435.134486 | 148.328764 | 772.852196 | 263.513200 | |
| ENSG00000141503 | 50488 | MINK1 | protein_coding | Q8N4C8 | FUNCTION: Serine/threonine kinase which acts as a negative regulator of Ras-related Rap2-mediated signal transduction to control neuronal structure and AMPA receptor trafficking. Required for normal synaptic density, dendrite complexity, as well as surface AMPA receptor expression in hippocampal neurons. Can activate the JNK and MAPK14/p38 pathways and mediates stimulation of the stress-activated protein kinase MAPK14/p38 MAPK downstream of the Raf/ERK pathway. Phosphorylates: TANC1 upon stimulation by RAP2A, MBP and SMAD1. Has an essential function in negative selection of thymocytes, perhaps by coupling NCK1 to activation of JNK1.; FUNCTION: Isoform 4 can activate the JNK pathway. Involved in the regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization, cell-matrix adhesion, cell-cell adhesion and cell migration. | Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Golgi apparatus;Kinase;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Synapse;Transferase | This gene encodes a serine/threonine kinase belonging to the germinal center kinase (GCK) family. The protein is structurally similar to the kinases that are related to NIK and may belong to a distinct subfamily of NIK-related kinases within the GCK family. Studies of the mouse homolog indicate an up-regulation of expression in the course of postnatal mouse cerebral development and activation of the cJun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and the p38 pathways. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. | hsa:50488; | axon [GO:0030424]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; brain development [GO:0007420]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048813]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900745]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of AMPA receptor activity [GO:2000311]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022407]; regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001952]; regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043408] | 12668260_Analysis of the coding region of the NIK gene in progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) patients through single strand conformation polymorphism and direct sequencing does not support a pathogenic role of the NIK gene in PSP. 15469942_results suggest that human Misshapen/NIKs-related kinase beta (hMINK beta) plays an important role in cytoskeleton reorganization, cell adhesion, and cell motility(hMINKbeta) 16760206_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17165161_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18752142_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21048137_MINK interaction with Rap2 plays a critical role in maintaining the morphological integrity of dendrites and synaptic transmission. 22037766_MINK1 interacts with and phosphorylates PRICKLE1 and PRICKLE2. 22665485_Misshapen-like kinase 1 (MINK1) is a novel component of striatin-interacting phosphatase and kinase (STRIPAK) and is required for the completion of cytokinesis. 25747578_MINK plays a functional role in the IRES-mediated translation of EV71 viral RNA and may provide a potential target for the development of specific antiviral strategies against EV71 infection 31160382_Results find MINK1 interacting with full-length and truncated APC. Its is negatively regulated by APC independently of b-catenin. MINK1 localizes to cell-cell junctions and enhances cell adhesion and proliferation. 34529319_LncRNA SNHG14 contributes to proinflammatory cytokine production in rheumatoid arthritis via the regulation of the miR-17-5p/MINK1-JNK pathway. 35971817_The serine/threonine kinase MINK1 directly regulates the function of promigratory proteins. 36012658_Multi-Omic Investigations of a 17-19 Translocation Links MINK1 Disruption to Autism, Epilepsy and Osteoporosis. | ENSMUSG00000020827 | Mink1 | 241.561070 | 0.6223630 | -0.684171831 | 0.15089994 | 20.42503854516 | 0.0000062013115624863828772715852732932972912749391980469226837158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00008665728884721230992384255475968757309601642191410064697265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 172.828493 | 18.526053 | 277.725399 | 29.387476 | |
| ENSG00000141551 | 1453 | CSNK1D | protein_coding | P48730 | FUNCTION: Essential serine/threonine-protein kinase that regulates diverse cellular growth and survival processes including Wnt signaling, DNA repair and circadian rhythms. It can phosphorylate a large number of proteins. Casein kinases are operationally defined by their preferential utilization of acidic proteins such as caseins as substrates. Phosphorylates connexin-43/GJA1, MAP1A, SNAPIN, MAPT/TAU, TOP2A, DCK, HIF1A, EIF6, p53/TP53, DVL2, DVL3, ESR1, AIB1/NCOA3, DNMT1, PKD2, YAP1, PER1 and PER2. Central component of the circadian clock. In balance with PP1, determines the circadian period length through the regulation of the speed and rhythmicity of PER1 and PER2 phosphorylation. Controls PER1 and PER2 nuclear transport and degradation. YAP1 phosphorylation promotes its SCF(beta-TRCP) E3 ubiquitin ligase-mediated ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. DNMT1 phosphorylation reduces its DNA-binding activity. Phosphorylation of ESR1 and AIB1/NCOA3 stimulates their activity and coactivation. Phosphorylation of DVL2 and DVL3 regulates WNT3A signaling pathway that controls neurite outgrowth. Phosphorylates NEDD9/HEF1 (By similarity). EIF6 phosphorylation promotes its nuclear export. Triggers down-regulation of dopamine receptors in the forebrain. Activates DCK in vitro by phosphorylation. TOP2A phosphorylation favors DNA cleavable complex formation. May regulate the formation of the mitotic spindle apparatus in extravillous trophoblast. Modulates connexin-43/GJA1 gap junction assembly by phosphorylation. Probably involved in lymphocyte physiology. Regulates fast synaptic transmission mediated by glutamate. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9DC28, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10606744, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12270943, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14761950, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16027726, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17562708, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17962809, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19043076, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20041275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20048001, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20407760, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20637175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20696890, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20699359, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21084295, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21422228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23636092}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Biological rhythms;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Golgi apparatus;Kinase;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Wnt signaling pathway | This gene is a member of the casein kinase I (CKI) gene family whose members have been implicated in the control of cytoplasmic and nuclear processes, including DNA replication and repair. The encoded protein may also be involved in the regulation of apoptosis, circadian rhythm, microtubule dynamics, chromosome segregation, and p53-mediated effects on growth. The encoded protein is highly similar to the mouse and rat CK1 delta homologs. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2014]. | hsa:1453; | centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; spindle [GO:0005819]; spindle microtubule [GO:0005876]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; tau-protein kinase activity [GO:0050321]; cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus [GO:1990090]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; COPII vesicle coating [GO:0048208]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; microtubule nucleation [GO:0007020]; non-motile cilium assembly [GO:1905515]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:2000052]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of Wnt-mediated midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:1905426]; protein localization to centrosome [GO:0071539]; protein localization to cilium [GO:0061512]; protein localization to Golgi apparatus [GO:0034067]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of circadian rhythm [GO:0042752]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; spindle assembly [GO:0051225]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] | 11218372_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12270714_findings support a model in which sub-cellular localization at the centrosome is mediated, at least in part, through the action of CG-NAP/AKAP450 14761950_Ckidelta phosphorylates tau at sites that modulate tau/microtubule binding, and that the expression pattern of Ckidelta in Alzheimer's disease is consistent with it playing an important role in tau aggregation 15800623_identification of a missense mutation (T44A) in the human CKIdelta gene, which results in familial advanced sleep phase syndrome; CKIdelta is a central component in the mammalian clock 16027726_Inhibition of HCKID alters mitotic spindle formation and induces apoptosis in trophoblast cells. 17131344_Novel human CKIdelta mutation R324H may alter the physiological role and enhance the transforming ability of CKIdelta through a Wnt/beta-catenin independent mechanism and thereby influence colonic adenoma development. 17562708_phosphorylation sites in tau from Alzheimer brain show that casein kinase 1delta may have a role, together with glycogen synthase kinase-3beta, in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disea 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17962809_Signal transduction pathway is defined downstream of CCK2 receptor showing that CK1 delta and epsilon phosphorylate PKD2 at 3 sites, resulting in nuclear accumulation of PKD2 and phosphorylation of nuclear PKD2 substrates in human gastric cancer cells. 18228528_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18708403_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19805222_The degradation rate of PER2, which is regulated by CKIepsilon/delta-dependent phosphorylation, was temperature-insensitive in living clock cells. 19839995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20048001_identified CK1delta/epsilon as new regulators of YAP and uncovered an intricate mechanism of YAP regulation 20149345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20637175_Site-directed mutagenesis demonstrated that only Ser-74 phosphorylation was involved in deoxycytidine kinase (dCK) activation by CKI delta, strengthening the key role of this residue in the control of dCK activity. 21422228_These results provide strong evidence that the centrosomal localization of CK1delta is required for Wnt-3a-dependent neuritogenesis. 22052997_casein kinase 1-delta phosphorylation of PGC-1alpha within its arginine/serine-rich domain enhances its degradation through the proteasome system 22123863_CKIdelta-EB1 complexes contribute to the increase in microtubule growth speeds observed in polarized T cells, a mechanism that might serve to generate long-stable microtubules necessary for centrosome translocation. 22384121_Casein kinase 1 proteomics reveal prohibitin 2 function in molecular clock 22981886_These results do not support that genetic variation in CSNK1D and CSNK1E is a susceptibility factor for major psychiatric disorders in the Japanese population. 23527964_molecular docking studies to examine the effect of the S97 mutation on its ATP-binding affinity; results explained the underlying molecular mechanism behind the observed cancer associated phenotype caused by S97C mutation in CK1delta protein 23636092_decreases in CKIdelta activity can contribute to the pathogenesis of migraine. 24424021_CK1delta and CK1epsilon play a decisive role in triggering late steps of pre-40S maturation that are required for acquisition of functionality of 40S ribosomal subunits in protein translation. 24817118_role for CK1delta in controlling the cell cycle 25404202_Results indicate that changes in the expression levels of casein kinase 1 isoforms CK1delta and DK1epsilon in colorectal tumors correlate with patients' survival. 25665722_The dynamical and conformational properties for each of three isoforms of CK1 are explored through molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. 25724478_site-specific phosphorylation of adiponectin, especially at sites targeted by CK1delta in vitro, provides an additional regulatory mechanism for modulating adiponectin complex formation and function. 25744540_Inhibition of CK1delta increases lipid droplet formation and proliferation of both cancer and normal cells specifically under hypoxia and in an HIF-1alpha- and lipin-1-dependent manner. 26464264_the results suggest that CK1delta activity can be modulated by the interplay between CK1delta and CDK2/E or CDK5/p35. 26676609_CK1delta inhibition represents a promising strategy for targeted treatment in human breast cancer with Wnt/beta-catenin involvement. 26769969_Expression of truncated hyperactive form of CKIdelta causes mislocalization and aggregation of TDP-43 in cultured cells. 26803658_Protein kinase C alpha (PKCalpha) is able to phosphorylate CK1delta at its C-terminally located residues S328, T329, and S370. 28545154_Study describes a specific mechanism for the regulation of CK1delta activity by proline-directed kinases, and demonstrate the relevance of this regulation in the control of a key CK1delta substrate, the PER2 protein. 28581525_Our results reveal a new mechanism of ZNF322A oncoprotein destruction regulated by the CK1delta/GSK3beta/FBXW7a axis. Deregulation of this signaling axis results in ZNF322A overexpression and promotes cancer progression 28886336_Report temperature-compensated CKIdelta-dependent multi-site phosphorylation in mammals underlies temperature compensated phosphorylation in circadian clocks. 30177679_CK1delta phosphorylates Brg1 at Ser31/Ser35 residues to facilitate the binding of Brg1 to FBW7, leading to ubiquitination-mediated degradation. 30832206_X-ray crystallographic analysis of ligand-CK1delta complexes confirmed the expected binding mode of the 3,4-diaryl-isoxazole inhibitors. Surprisingly, the original compounds underwent spontaneous Pictet-Spengler cyclization with traces of formaldehyde during the co-crystallization process to form highly potent new ligands. 31353086_Human Rad17 is constitutively phosphorylated in vivo on a C-terminal threonine, T670. Rad17-T670 is phosphorylated by casein kinase 1delta/epsilon. 31353796_The effect of CK1delta/epsilon inhibition strongly depends on endogenous PER2 protein levels, which differs depending on both the molecular cause of the circadian disruption and the patient's lighting environment. 31376410_Structure, regulation, and (patho-)physiological functions of the stress-induced protein kinase CK1 delta (CSNK1D). 32321936_CRISPR-mediated gene targeting of CK1delta/epsilon leads to enhanced understanding of their role in endocytosis via phosphoregulation of GAPVD1. 32430484_Targeting Casein Kinase 1 Delta Sensitizes Pancreatic and Bladder Cancer Cells to Gemcitabine Treatment by Upregulating Deoxycytidine Kinase. 33420362_beta-Trcp and CK1delta-mediated degradation of LZTS2 activates PI3K/AKT signaling to drive tumorigenesis and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 34203978_CK1delta-Derived Peptides as Novel Tools Inhibiting the Interactions between CK1delta and APP695 to Modulate the Pathogenic Metabolism of APP. 34280005_Upregulation of Stress-Induced Protein Kinase CK1 Delta is associated with a Poor Prognosis for patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000025162 | Csnk1d | 1065.704815 | 0.9073624 | -0.140249249 | 0.10685619 | 1.72140416522 | 0.1895123983772216136323152113618561998009681701660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.40074065434627004211876055705943144857883453369140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 931.763482 | 70.892159 | 1031.662046 | 78.139070 | |
| ENSG00000141570 | 57332 | CBX8 | protein_coding | Q9HC52 | FUNCTION: Component of a Polycomb group (PcG) multiprotein PRC1-like complex, a complex class required to maintain the transcriptionally repressive state of many genes, including Hox genes, throughout development. PcG PRC1 complex acts via chromatin remodeling and modification of histones; it mediates monoubiquitination of histone H2A 'Lys-119', rendering chromatin heritably changed in its expressibility. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21282530}. | 3D-structure;Chromatin regulator;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation | Enables methylated histone binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in chromatin and nucleoplasm. Part of PRC1 complex. Biomarker of esophagus squamous cell carcinoma and glioblastoma. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:57332; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; heterochromatin [GO:0000792]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PcG protein complex [GO:0031519]; PRC1 complex [GO:0035102]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; methylated histone binding [GO:0035064]; single-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003727]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activator activity [GO:0097027]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; histone ubiquitination [GO:0016574]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122] | 17332741_CBX8 is an essential component of one of the polycomb repressive complexes, which directly regulate the expression of numerous target genes, including the INK4A-ARF locus, involved in cell-fate decisions. 22094252_CBX8 plays an essential role in MLL-AF9 transcriptional regulation and leukemogenesis. 23474493_CBX8 cooperated with SIRT1 for suppressing p53 acetylation induced by Sirtinol and etoposide/TSA. Upon ectopic expression, CBX8 or SIRT1 repressed the expression of p21(WAF1) by inhibiting p53 binding to the promoter. 23891621_Interaction with CBX8 precludes AF9-DOT1L binding. 24460908_The presence of CBX8-GFP in the same focus had a minor impact on BMI1 and RING1 recovery kinetics. 25197352_CBX8 might emerge as an oncogene for promoting the proliferation of tumor cells and raising the resistance of neoplasms to chemotherapy. 25360999_Low CBX8 expression was associated with distant metastasis in colorectal cancer. 25398592_IGF1 can promote the colon cancer cell line, HCT116 cell, proliferation via promoting Cbx8 expression 26718407_These data suggest that CBX8 modulates SIPS through the RB-E2F1 pathway in CML cells and provide important insight into its application in CML treatment. 26837964_The difference in the SUZ12 and CBX8 genes expression were significantly divergent between tumors and their marginal tissues. 27505670_CBX8 binds to H3K27me3 at bivalent promoters during germinal center formation, and recruits a novel PRC1-BCOR complex at BCL6 binding sites to specifically silence genes in the germinal center and promote lymphomagenesis 27555324_CBX8 plates roles in epigenetic regulation in DNA damage response. 28837252_The data suggest that high expression of CBX8 plays a critical oncogenic role in aggressiveness of urothelial carcinoma cells of the bladder through promoting cancer cell proliferation by repressing the p53 pathway, and CBX8 could be used as a novel predictor for muscle invasive bladder cancer patients. 28912889_CBX8 binds with the Snai1 promoter, represses Snai1 transcription and suppresses esophageal carcinoma metastasis. 29066512_CBX8 functions as an oncogene to upregulate EGR1 and miR-365-3p to stimulate the AKT/beta-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.CBX8 expression is increased and associated with poor outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma. 29763603_PIM1 can phosphorylate CBX8 to promote its degradation, thereby up-regulating p16, during PIM1-induced cell senescence. 30504704_Circular RNA circ_0005230 was proved to be a sponge of miR-618, and expression of miR-618 could regulate CBX8 expression via targeting the 3'UTR of CBX8. 30597065_function of the CBX8 chromodomain (CD) in vitro and in vivo; the CD is in fact a major driver of CBX8 chromatin association and this is driven by both histone and previously unrecognized DNA binding activity; characterization of the structural basis of histone and DNA binding and determine how they integrate on multiple levels 30718464_Results establish CBX8 as a critical driver of HCC stem cell-like and metastatic behaviors and characterize its role in modulating BMP4 expression. 31255735_Report shows that CBX8 is upregulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) tissues and cells and serves as an indicator of poor prognosis for ESCC patients. CBX8 knockdown inhibits cell proliferation, colony formation capability, DNA repair and promotes cell apoptosis. 31495785_Chromobox homolog 8 (CBX8) Interacts with Y-Box binding protein 1 (YBX1) to promote cellular proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 31755685_Optimization of Ligands Using Focused DNA-Encoded Libraries To Develop a Selective, Cell-Permeable CBX8 Chromodomain Inhibitor. 33417156_CBX8 acts as an independent RNA-binding protein to regulate the maturation of miR-378a-3p in colon cancer cells. 33731128_KPNA2 interaction with CBX8 contributes to the development and progression of bladder cancer by mediating the PRDM1/c-FOS pathway. 34592789_CBX8 interacts with chromatin PTEN and is involved in regulating mitotic progression. 34651663_hsamiR429 targets CBX8 to promote cell apoptosis in diffuse large Bcell lymphoma. 35681547_High Expression of a Cancer Stemness-Related Gene, Chromobox 8 (CBX8), in Normal Tissue Adjacent to the Tumor (NAT) Is Associated with Poor Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer Patients. 35894945_CBX8 Together with SET Facilitates Ovarian Carcinoma Growth and Metastasis by Suppressing the Transcription of SUSD2. | ENSMUSG00000025578 | Cbx8 | 30.098399 | 0.6809490 | -0.554381329 | 0.48615227 | 1.27421576767 | 0.2589772921147266426800115368678234517574310302734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.48740678268535225781121766885917168110609054565429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 25.145462 | 7.071817 | 37.415743 | 10.354125 | |
| ENSG00000142599 | 473 | RERE | protein_coding | Q9P2R6 | FUNCTION: Plays a role as a transcriptional repressor during development. May play a role in the control of cell survival. Overexpression of RERE recruits BAX to the nucleus particularly to POD and triggers caspase-3 activation, leading to cell death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11331249}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Coiled coil;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a member of the atrophin family of arginine-glutamic acid (RE) dipeptide repeat-containing proteins. The encoded protein co-localizes with a transcription factor in the nucleus, and its overexpression triggers apoptosis. A similar protein in mouse associates with histone deacetylase and is thought to function as a transcriptional co-repressor during embryonic development. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:473; | histone deacetylase complex [GO:0000118]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; branching morphogenesis of a nerve [GO:0048755]; cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation [GO:0021930]; cerebellar Purkinje cell layer maturation [GO:0021691]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048813]; radial glia guided migration of Purkinje cell [GO:0021942] | 14645126_The mouse ortholog of RERE is required for embryonic development 18597038_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20410501_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27087320_suggest that mutations in RERE cause a genetic syndrome and that haploinsufficiency of RERE might be sufficient to cause many of the phenotypes associated with proximal 1p36 deletions | ENSMUSG00000039852 | Rere | 460.835269 | 0.9222585 | -0.116756944 | 0.29387928 | 0.15597475160 | 0.6928898336066348084827382081130053848028182983398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.84242876944716282849867639015428721904754638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 437.819110 | 86.901038 | 474.822595 | 94.121802 | |
| ENSG00000143106 | 5686 | PSMA5 | protein_coding | P28066 | FUNCTION: Component of the 20S core proteasome complex involved in the proteolytic degradation of most intracellular proteins. This complex plays numerous essential roles within the cell by associating with different regulatory particles. Associated with two 19S regulatory particles, forms the 26S proteasome and thus participates in the ATP-dependent degradation of ubiquitinated proteins. The 26S proteasome plays a key role in the maintenance of protein homeostasis by removing misfolded or damaged proteins that could impair cellular functions, and by removing proteins whose functions are no longer required. Associated with the PA200 or PA28, the 20S proteasome mediates ubiquitin-independent protein degradation. This type of proteolysis is required in several pathways including spermatogenesis (20S-PA200 complex) or generation of a subset of MHC class I-presented antigenic peptides (20S-PA28 complex). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15244466, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27176742, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8610016}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proteasome;Reference proteome | The proteasome is a multicatalytic proteinase complex with a highly ordered ring-shaped 20S core structure. The core structure is composed of 4 rings of 28 non-identical subunits; 2 rings are composed of 7 alpha subunits and 2 rings are composed of 7 beta subunits. Proteasomes are distributed throughout eukaryotic cells at a high concentration and cleave peptides in an ATP/ubiquitin-dependent process in a non-lysosomal pathway. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides. This gene encodes a member of the peptidase T1A family, that is a 20S core alpha subunit. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding two distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. | hsa:5686; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; proteasome complex [GO:0000502]; proteasome core complex [GO:0005839]; proteasome core complex, alpha-subunit complex [GO:0019773]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; proteasomal protein catabolic process [GO:0010498]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161] | 11771738_Selective upregulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway proteins, proteasome zeta chain and isopeptidase T in fetal Down syndrome. 30738879_increased ubiquitin B mRNA expression followed by significant downregulation of proteasome subunits; 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 1, and proteasome subunit alpha-type 5 was found in pseudoexfoliation syndrome (PEXS) individuals. Decrease in chymotrypsin-like proteasome activity and increased apoptosis were also observed in PEX subjects. 30807553_PSMA5 promotes the tumorigenic process of prostate cancer and is related to bortezomib resistance. 34831298_Conserved Mitotic Phosphorylation of a Proteasome Subunit Regulates Cell Proliferation. 35605971_PSMA5 contributes to progression of lung adenocarcinoma in association with the JAK/STAT pathway. | ENSMUSG00000068749 | Psma5 | 718.161878 | 1.8764435 | 0.908000856 | 0.23433671 | 14.70092136802 | 0.0001259848596885687513173557317003314892644993960857391357421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00125992899566742502966143479881111488793976604938507080078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1007.750806 | 169.569102 | 535.057494 | 90.061741 | |
| ENSG00000143178 | 9095 | TBX19 | protein_coding | O60806 | FUNCTION: Transcriptional regulator involved in developmental processes. Can activate POMC gene expression and repress the alpha glycoprotein subunit and thyroid-stimulating hormone beta promoters. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11290323}. | Activator;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation | This gene is a member of a phylogenetically conserved family of genes that share a common DNA-binding domain, the T-box. T-box genes encode transcription factors involved in the regulation of developmental processes. Mutations in this gene were found in patients with isolated deficiency of pituitary POMC-derived ACTH, suggesting an essential role for this gene in differentiation of the pituitary POMC lineage. ACTH deficiency is characterized by adrenal insufficiency symptoms such as weight loss, lack of appetite (anorexia), weakness, nausea, vomiting, and low blood pressure. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:9095; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; cell fate specification [GO:0001708]; heart morphogenesis [GO:0003007]; mesoderm formation [GO:0001707]; pituitary gland development [GO:0021983]; regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045595]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 11916612_Review. Association of 2 mutations with an ACTH deficiency is consistent with the role of tbx19 in differentiation of POMC cells. 12651888_TPIT has a role in expression of the pro-opiomelanocortin gene and terminal differentiation of the pituitary corticotroph lineage, and its mutation causes early onset pituitary ACTH deficiency 12970370_Tpit, along with NGFI-B and SRC-2, is part of a transcription regulatory complex assembled on the POMC promoter in response to hormonal stimulation. 15476446_mutations in the TPIT gene, a T-box factor selectively expressed in developing corticotroph cells, have been found in cases of early-onset isolated ACTH deficiency 15613420_TPIT gene mutations is the principal molecular cause of neonatal congenital isolated ACTH deficiency 15666849_We report largest series of congenital ACTH deficiency and demonstrate molecular mechanism involves Tpit in majority of cases. 16390921_a new mutation (IVS4+1G>A) that affects the first nucleotide of the splice site at the 5' end of the fourth intron in isolated adrenocorticotropic hormone deviciency 16899054_Overtransmission of a haplotype GAC at the TBX19 locus was associated with increased angry/hostility scores among suicide attempters. 17652218_the M86R TPIT mutation is defining an important surface of the T domain for multiple protein interactions and for transcription 19064610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19536175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21622576_The coordinate expression of Etv1 with POMC cell differentiation and its interaction with the highly cell-restricted Tpit factor indicate that Etv1 participates in a combinatorial code for pituitary cell-specific gene expression. 22170728_Identification of nine new TPIT mutations in a large series of congenital isolated ACTH-deficiency patients. 22193973_TPIT is identified as a target autoantigen in 10.5% of patients with lymphocytic hypophysitis. 29199261_TBX19 mRNA expression was significantly increased in tumorous tissues compared to that in non-tumorous tissues, and increased TBX19 mRNA expression was associated with positive lymph node metastasis. 30747411_A new mutation in the TBX19 gene in a patient with isolated ACTH deficiency. While overgrowth is a known feature of some types of adrenal insufficiencies, including MC2R gene defects and POMC deficiency, it may be a novel feature for TPIT (T-box pituitary restricted transcription factor )deficiency, as in this patient. [review] 32344415_A Rare Cause of Adrenal Insufficiency - Isolated ACTH Deficiency Due to TBX19 Mutation. 33423260_[Analysis of TBX19 gene variant in a child with congenital isolated adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency]. 35217793_T-box transcription factor 19 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through upregulating EGFR and RAC1. 35218667_TRIM65 determines the fate of a novel subtype of pituitary neuroendocrine tumors via ubiquitination and degradation of TPIT. | ENSMUSG00000026572 | Tbx19 | 31.832793 | 1.1437482 | 0.193769414 | 0.29265134 | 0.43783408434 | 0.5081697073855071522530124639160931110382080078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.71961686597244933771833075297763571143150329589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 34.986065 | 5.888868 | 30.711089 | 5.214168 | |
| ENSG00000143198 | 4259 | MGST3 | protein_coding | O14880 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes oxydation of hydroxy-fatty acids (PubMed:9278457). Also catalyzes the conjugation of a reduced glutathione to leukotriene A4 in vitro (PubMed:9278457). May participate in the lipid metabolism (PubMed:9278457). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9278457, ECO:0000303|PubMed:9278457}. | Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid metabolism;Lipoprotein;Lyase;Membrane;Microsome;Oxidoreductase;Palmitate;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a member of the MAPEG (Membrane Associated Proteins in Eicosanoid and Glutathione metabolism) protein family. Members of this family are involved in the production of leukotrienes and prostaglandin E, important mediators of inflammation. This gene encodes an enzyme which catalyzes the conjugation of leukotriene A4 and reduced glutathione to produce leukotriene C4. This enzyme also demonstrates glutathione-dependent peroxidase activity towards lipid hydroperoxides.[provided by RefSeq, May 2011]. | hsa:4259; | endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; glutathione peroxidase activity [GO:0004602]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; leukotriene-C4 synthase activity [GO:0004464]; transferase activity [GO:0016740]; leukotriene biosynthetic process [GO:0019370]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629] | 19064610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19536175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25280473_Variants in MGST3 are associated with differences inn hippocampus size in both human brain data sets (ENIGMA MRI) and in the BXD family of mice. MGST3 is also statistically associated to genes linked to neurodegenerative disorders, including Parkinson's, Huntington's, and Alzheimer's diseases. | ENSMUSG00000026688 | Mgst3 | 197.662749 | 0.9665386 | -0.049100792 | 0.13327098 | 0.13562142177 | 0.7126733075308383513757348737271968275308609008789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.85437729051605815211445360546349547803401947021484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 199.220881 | 15.672538 | 206.885056 | 16.321117 | |
| ENSG00000143575 | 10456 | HAX1 | protein_coding | O00165 | FUNCTION: Recruits the Arp2/3 complex to the cell cortex and regulates reorganization of the cortical actin cytoskeleton via its interaction with KCNC3 and the Arp2/3 complex (PubMed:26997484). Slows down the rate of inactivation of KCNC3 channels (PubMed:26997484). Promotes GNA13-mediated cell migration. Involved in the clathrin-mediated endocytosis pathway. May be involved in internalization of ABC transporters such as ABCB11. May inhibit CASP9 and CASP3. Promotes cell survival. May regulate intracellular calcium pools. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15339924, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16857965, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17545607, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18319618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18971376, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26997484, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9058808}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sarcoplasmic reticulum | The protein encoded by this gene is known to associate with hematopoietic cell-specific Lyn substrate 1, a substrate of Src family tyrosine kinases. It also interacts with the product of the polycystic kidney disease 2 gene, mutations in which are associated with autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease, and with the F-actin-binding protein, cortactin. It was earlier thought that this gene product is mainly localized in the mitochondria, however, recent studies indicate it to be localized in the cell body. Mutations in this gene result in autosomal recessive severe congenital neutropenia, also known as Kostmann disease. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:10456; | actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cell cortex [GO:0005938]; clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; P-body [GO:0000932]; sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0016529]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; interleukin-1 binding [GO:0019966]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; cellular response to cytokine stimulus [GO:0071345]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; positive regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:2000251]; positive regulation of granulocyte differentiation [GO:0030854]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030833]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of autophagy of mitochondrion [GO:1903146]; regulation of protein targeting to mitochondrion [GO:1903214] | 12787133_In psoriasis, the epidermal differentiation could be disturbed due to the increased expression of HAX-1 and hence a prolonged resistance to terminal differentiation 15159385_HAX-1 binds bile salt export protein (BSEP), cortactin, MDR1, and MDR2. HAX-1 and cortactin regulate BSEP abundance in the apical membrane of cells. 15339924_Interacts with the alpha subunit of G protein G13 to promote cell migration. 16857965_HAX-1 is a newly identified anti-apoptotic factor and its mechanism of action is through caspase-9 inhibition. 16971486_These findings reveal that nuclear localization of pre-IL-1alpha depends on the binding to HAX-1 and that biological activities might be elicited by the binding to both HAX-1 and IL-1RII in SSc fibroblasts. 17187068_HAX1 is a major regulator of myeloid homeostasis and mutant proteins cause autosomal recessive severe congenital neutropenia. 17929250_HAX1, an anti-apoptotic protein, inhibits the HIV-1 rev function by altering is subcellular localization. 18055975_important role of HAX1 on neural development as well as myelopoiesis. 18319618_Results suggest that HAX-1, a substrate of CASP3, inhibits the apoptotic process by inhibiting CASP3 activity. 18330843_Severe congenital neutropenia caused by a homozygous mutation (R86X) in the antiapoptotic molecule HAX1. 18337561_identified 6 additional patients with HAX1 mutations carrying 4 novel mutations; mutations of transcript variants are characterized by phenotype and localization 18399350_HAX-1 deficiency or overexpression leads to hereditary or systemic diseases (Kostmann disease, lesional psoriasis, systemic sclerosis) 18472110_alternative splice variants, encoded by the chromosome 1 gene, produce a family of transcripts composed of up to eight members 18513342_neurological and neuropsychological abnormalities in the central nervous system symptoms appear to be associated with specific HAX1 mutations in Kostmann disease patients. 18611981_the R86X mutation in the HAX1 gene is an abnormality in Japanese Severe congenital neutropenia patients with HAX1 deficiency and may lead to neurodevelopmental abnormalities and severe myelopoietic defects 18971376_These findings suggest that HAX-1 may promote cell survival through modulation of SERCA2 protein levels and thus endoplasmic reticulum calcium stores. 19254774_The data indicate that Hax-1 plays a role in suppression of apoptosis and promotion of melanoma cell growth, suggesting that this Hax-1 siRNA has a therapeutic indication in control of melanoma. 19298594_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19524642_HAX-1 has been shown to bind to the 3' untranslated regions of certain mRNAs and could therefore contribute to the regulation of transport and/or stability of such transcripts. 19605487_there is an an association between HCV core and HAX-1, which promotes 5-FU mediated p53-dependent caspase-7 activation and hepatocyte growth inhibition 19679660_Data demonstrate that TPCK induces apoptosis in human B cell lines and exerts multiple effects on pro- and anti-apoptotic factors, including HAX-1. 19680265_results indicate a different function and mechanism of Hax1 in apoptosis and re-opens the question of whether mammalian PARL, in addition to apoptosis, regulates mitochondrial stress response through Omi/HtrA2 processing. 19796188_study suggests that the novel missense c.421T>C mutation in the HAX1 gene produces a milder form of severe congenital neutropenia without apparent developmental or neurological manifestations 19913549_HAX-1 is a multifaceted antiapoptotic protein localizing in the mitochondria and the sarcoplasmic reticulum of striated muscle cells 19928538_Neurological symptoms were found in HAX1-deficient patients with mutations in the HAX1 gene affecting both transcript variants, while they were not found in those affecting isoform a only. 20065084_Novel HAX1 gene mutations are associated with neurodevelopmental abnormalities in two Italian patients with severe congenital neutropenia. 20171186_HAX-1 suppresses the polyubiquitination of XIAP; formation of the HAX-1-XIAP complex inhibits apoptosis by enhancing the stability of XIAP against proteosomal degradation. 20196840_analysis of HAX-1 overexpression, splicing and cellular localization in tumors 20220065_describe congenital neutropenia patients with mutations in two candidate genes each,HAX1 and G6PC3, including 6 novel mutations 20388708_This study is the first to demonstrate GrB activity within the mitochondrion and to identify Hax-1 cleavage as a novel mechanism for GrB-mediated mitochondrial depolarization. 20406461_PELO is subcellularly localized at the actin cytoskeleton, interacts with HAX1, EIF3G and SRPX proteins and that this interaction occurs at the cytoskeleton; this interaction may facilitate PELO to detect and degrade aberrant mRNAs. 20631090_The N(pro)-HAX-1 interaction was confirmed using co-precipitation assays. 20665473_Full-length Grb7 and Hax-1 interact in mammalian cells and Grb7 is tyrosine phosphorylated. 20696135_hSpry1 and HAX1 proteins are putative candidate proteins that interact with uPAR. 21108402_identified consanguineous family with 2 patients with severe congenital neutropenia and neurological disease caused by novel, homozygous genomic deletion including exons 4-7 of the HAX1 gene; quantitative MRI showed alteration in cerebral proton density 21109726_Our resultsvindicate that HAX-1 may not be a candidate gene for psoriasis susceptibility in the Chinese Han population. 21206270_Biallelic mutations in the antiapoptotic gene HAX1 were identified in patients with autosomal recessive severe congenital neutropenia. 21301993_Data suggest that Hax-1 is a new PrP-interacting partner that may play role in cell oxidative stress and anti-apoptosis physiologically and cell damage pathologically. 21518791_Hax1 is a novel regulator of neutrophil uropod detachment and chemotaxis through RhoA 21567072_hSav1 interacts with HAX1 and attenuates its protective role against apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. 22570112_We also confirmed the interaction of HAX-1 and hSav1 in mammalian cells. 22827267_Hax-1 is a short-lived protein and that its PEST sequence dependent fast degradation by the proteasome. 23055567_These data show that HAX1 specifically interacts with influenza A virus polymerase PA in vitro and in vivo and that HAX1 interacts with the nuclear localization signal domain of PA. 23164465_HAX-1 may be involved in the regulation of expression of bound transcripts, possibly as part of the stress response. 23454784_4 ELANE mutations, 11 HAX1 mutations and 2 G6PC3 mutations have been identified in Iranian patients with severe congenital neutropenia. 23531395_HAX-1 mRNA is over-expressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and is prognostic factor for lymphatic metastasis and survival. 23975175_Genetic correction of HAX1 in induced pluripotent stem cells from a patient with severe congenital neutropenia improves defective granulopoiesis. 24057929_HAX-1 might be an important marker for tumor progression and prognosis, as well as a potential therapeutic target of Colorectal cancer 24188827_Hax1 physically interacts with TPC1/2 C-terminal domain. 24341138_Studies indicate that mutations in the gene encoding HAX1 were present in patients with the autosomal recessive form of severe congenital neutropenia. 24347163_Hax-1 is a family of anti- and proapoptotic regulators that may modulate cell survival and death through homo- or heterodimerization. 24482108_A new homozygous HAX1 deletion (exons 2-5) was found in a French Kostmann syndrome pedigree. A homozygous frameshift mutation was found in exon 3 (c.430dupG, p.Val144fs) in a 2d pedigree. Neurological retardation associated with B isoform mutations. 24910348_anti-apoptotic role of HAX-1 versus BCL-XL in cytokine-dependent bone marrow-derived cells 25275296_Authors showed that HAX1 promotes auto-ubiquitination and degradation of cIAPs by facilitating the intermolecular homodimerization of RING finger domain. 25284454_HAX1 mutation is associated with severe congenital neutropenia. 25289648_HAX-1 is involved in mRNA processing as an element of P-body interaction network. 25419709_HAX1 is a proto-oncogene in mantle cell lymphoma. 25554539_HAX-1 was significantly elevated in laryngeal carcinoma. 26062578_HAX1 knockdown significantly decreased the proliferation. In addition, the expression levels of ki67 and phosphorylatedakt were inhibited following HAX1 knockdown. 26323553_Results show that mRNA and protein levels of HAX-1 in prostate cancer cell lines were significantly higher and inhibits cell apoptosis through caspase-9 inactivation. 26339377_HAX-1 is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cell proliferation. 26869103_Results show that Grb7 and Hax1 may colocalize partially to mitochondria in EGF-treated SKBR3 cells and their interaction can affect Caspase3 cleavage of Hax1. 26871467_Oncogenic HAX-1 increases the proliferation, migration, and angiogenic activity of HUVECs. Findings provide unique insight into the pathogenesis of NPC. 26997484_Kv3.3 regulates Arp2/3-dependent cortical actin nucleation mediated by Hax-1; resulting cortical actin structures interact with the channel's gating machinery to slow its inactivation rate during sustained membrane depolarizations; a mutation that leads to late-onset spinocerebellar ataxia type 13. 27618431_results suggest that miR-223 increases the sensitivity of TNBCSCs to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by targeting HAX-1 28169428_The authors describe the first case series of patients with CN caused by HAX1 mutation who presented with HLH. They hypothesize that severe neutropenia persists after an HLH episode in children without FHLH mutations (especially infants) because these patients have CN caused by HAX1 mutations. 28347249_Study indicates that the overexpression of HAX-1 is essential in the development of chemoresistance in breast cancer. 28681255_the HAX1 gene is important for ovarian development, in which a p.Trp44X mutation may cause primary ovarian insufficiency in female patients 28751207_The overexpression of HAX-1 might contribute to the malignant progression of glioma. 28791389_HAX1 is a potential oncogene, and may promote the tumorigenesis and progression of hypopharyngeal carcinoma. 29169992_These findings reveal a role of HAX-1 in the regulation of oxidative stress and SERCA2a degradation. 29461873_Autophagy induction is involved in HAX1-induced cell protective mechanism, and AA127-180 serves as the functional autophagy-regulatory domain of this antiapoptotic protein. 29576744_data suggest that HAX-1 may be a promoting factor for AIV H9N2 replication through desensitizing PB1-F2 from its apoptotic induction in human lung epithelial cells. 29923187_high expression of HAX-1, a protein implicated in cell survival and cell migration, is associated with poor survival in MM patients, and we provide evidence that HAX-1 regulates MM cell migration, thus making HAX-1 a potentially important target for therapeutic intervention. 30698159_Increased neutrophil production in HAX1 viral vector-expressing hematopoietic cells was observed. 31047882_HAX-1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activating the NF-kappaB pathway 31321910_In Turkey, severe congenital neutropenia mostly resulted from the p W44X mutation in the HAX1 gene 31548268_This study for the first time dissects the structural architecture of HAX-1 and elucidates its role in PDZ-independent activation of HtrA2. 31644363_It was shown that HAX1 does not influence invasive potential in the breast cancer cell line, suggesting that its role in breast cancer progression may be linked instead to collective invasion of the epithelial cells but not single-cell dissemination. 31899048_miR-125b suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting HAX-1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 31943004_Frataxin deficiency in Friedreich's ataxia is associated with reduced levels of HAX-1, a regulator of cardiomyocyte death and survival. 32104694_miR-654-5p Targets HAX-1 to Regulate the Malignancy Behaviors of Colorectal Cancer Cells. 32327498_A zebrafish model for HAX1-associated congenital neutropenia. 32470650_Accumulation of HAX-1 and PARL in brainstem- and cortical-type Lewy bodies in Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. 32893878_HTLV-1 viral oncoprotein HBZ contributes to the enhancement of HAX-1 stability by impairing the ubiquitination pathway. 32926529_HAX1 enhances the survival and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through the AKT/mTOR and MDM2/p53 signaling pathway. 33000203_MicroRNA125a5p regulates liver cancer cell growth, migration and invasion and EMT by targeting HAX1. 33015771_Suppression of HAX-1 induced by miR-325 resensitizes bladder cancer cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis. 33146709_The interactome of multifunctional HAX1 protein suggests its role in the regulation of energy metabolism, de-aggregation, cytoskeleton organization and RNA-processing. 33417922_Identification of protein/mRNA network involving the PSORS1 locus gene CCHCR1 and the PSORS4 locus gene HAX1. 33560082_A Novel Intronic Mutation Reduces HAX1 Level and is Associated With Severe Congenital Neutropenia. 34075619_Sanguisorba parviflora (Maxim) Takeda alleviates cyclophosphamide-induced leukopenia via regulating the hematopoietic cell-specific protein 1-associated protein X-1 gene. 34101878_Sanguisorba parviflora (Maxim.) Takeda alleviates cyclophosphamide-induced leukopenia by regulating haematopoietic cell-specific protein 1-associated protein X-1 gene expression. 34755451_HAX1 maintains the glioma progression in hypoxia through promoting mitochondrial fission. 35015850_Hsa-miR223-3p circulating level is upregulated in Friedreich's ataxia and inversely associated with HCLS1 associated protein X-1, HAX-1. 35302298_Effect of different expression patterns of HAX-1 on the proliferation and apoptosis of human astrocyte. 35499078_HAX1-dependent control of mitochondrial proteostasis governs neutrophil granulocyte differentiation. 35524442_Extracellular vesicles rich in HAX1 promote angiogenesis by modulating ITGB6 translation. | ENSMUSG00000027944 | Hax1 | 430.091077 | 0.8802911 | -0.183947345 | 0.07206305 | 6.51946065686 | 0.0106700356442087657821149448977848805952817201614379882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.05191389864041467960831255368248093873262405395507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 398.972894 | 19.386969 | 455.398188 | 21.695596 | |
| ENSG00000143578 | 148327 | CREB3L4 | protein_coding | Q8TEY5 | FUNCTION: Transcriptional activator that may play a role in the unfolded protein response. Binds to the UPR element (UPRE) but not to CRE element. Preferentially binds DNA with to the consensus sequence 5'-T[GT]ACGT[GA][GT]-3' and has transcriptional activation activity from UPRE. Binds to NF-kappa-B site and has transcriptional activation activity from NF-kappa-B-containing regulatory elements (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16236796}. | Activator;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Unfolded protein response | This gene encodes a CREB (cAMP responsive element binding) protein with a transmembrane domain which localizes it to the ER membrane. The encoded protein is a transcriptional activator which contains a dimerization domain, and this protein may function in a number of processing pathways including protein processing. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. | hsa:148327; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cAMP response element binding [GO:0035497]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response [GO:0030968]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] | 11830526_AIbZIP, a novel bZIP gene located on chromosome 1q21.3 that is highly expressed in prostate tumors and of which the expression is up-regulated by androgens in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. 12111373_identified a novel human CREB gene (CREB4) that was 1592 bp long and encoded a protein of 395 amino acid residues 16236796_S1P cleavage of CREB4 may be suppressed by a determinant in the C-terminal region 17712038_In LNCaP cell lines that conditionally express the processed form of AIbZIP, downstream targets of AIbZIP include genes for protein processing, transcriptional regulation, small molecule transport, signal transduction, metabolism & cell homeostasis. 27853318_AIbZIP induced by the androgen receptor axis plays a crucial role in the p21 dependent proliferation of androgen-sensitive prostate cancer cells. 28338058_CREB3L4 expression is mediated by an androgen-receptor -IRE1alpha axis, but is also directly regulated by androgen-receptor-to-androgen response elements binding. 30483806_Study demonstrated that MCU1 is frequently overexpressed in breast cancer and abnormally high expression of MUC1 indicates poor prognosis. Subsequent data mining across multiple large databases demonstrated a positive association between MUC1 mRNA expression CREB3L4 in breast cancer tissues. Results indicated that MUC1 transcript expression may regulate tumor invasion and metastasis associated with CREB3L4 transcription. 32026099_The Novel Transcription Factor CREB3L4 Contributes to the Progression of Human Breast Carcinoma. 33106913_MSC-AS1 knockdown inhibits cell growth and temozolomide resistance by regulating miR-373-3p/CPEB4 axis in glioma through PI3K/Akt pathway. 33637885_CREB3L4 promotes angiogenesis and tumor progression in gastric cancer through regulating VEGFA expression. | ENSMUSG00000027938 | Creb3l4 | 47.801551 | 1.1472646 | 0.198198147 | 0.25497088 | 0.60269444702 | 0.4375518152748467670676291163545101881027221679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.66203080498264532671726101398235186934471130371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 53.303945 | 7.940254 | 46.786847 | 7.181170 | |
| ENSG00000143622 | 6016 | RIT1 | protein_coding | Q92963 | FUNCTION: Plays a crucial role in coupling NGF stimulation to the activation of both EPHB2 and MAPK14 signaling pathways and in NGF-dependent neuronal differentiation. Involved in ELK1 transactivation through the Ras-MAPK signaling cascade that mediates a wide variety of cellular functions, including cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15632082, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23791108}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;GTP-binding;Hydrolase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a member of a subfamily of Ras-related GTPases. The encoded protein is involved in regulating p38 MAPK-dependent signaling cascades related to cellular stress. This protein also cooperates with nerve growth factor to promote neuronal development and regeneration. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. | hsa:6016; | plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; G protein activity [GO:0003925]; GDP binding [GO:0019003]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 12668729_Rit plays a key role in human neuronal development and regeneration through activating both known and as yet undefined signaling pathways 14767908_Gene amplification is one of the main activating ways of RIT1 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and its amplification might be correlated with HCC carcinogenesis, while point mutation might be not. 15632082_Data suggest that Rit is involved in a novel pathway of neuronal development and regeneration by coupling specific trophic factor signals to sustained activation of the B-Raf/ERK and p38 MAP kinase cascades. 21444726_the studies establish Rit as a central regulator of a p38 MAPK-dependent signaling cascade that functions as a critical cellular survival mechanism in response to stress 23038261_the Rit-p38-MSK1/2 signaling pathway may have an important role in the stress-dependent regulation of CREB-dependent gene expression. 23123784_the present studies identify a critical role for the Rit-p38 MAPK signaling cascade in promoting hippocampal neuron survival following oxidative stress 23667514_ROC1 knockdown remarkably inhibited bladder cancer cell growth, arrested cells at the G2 phase of the cell cycle, and induced the p53-dependent cell senescence. 23765226_study demonstrates that RIT1 abnormalities, including activating mutations and locus amplifications, are novel lesions in a subgroup of patients with myeloid neoplasms, particularly frequent in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia 23770287_we highlight recent studies using transgenic and knockout animal models which have begun to elucidate the physiological roles for the Rit subfamily, including emerging roles in the regulation of neuronal morphology and cellular survival signaling 23791108_Five RIT1 alterations identified in children with Noonan syndrome enhanced ELK1 transactivation. 24469055_Data identify RIT1 as a driver oncogene in a specific subset of lung adenocarcinomas. 24939608_four additional cases of Noonan syndrome with mutations in RIT1, were identified. 25124994_Because of the relatively high frequency of mutations in RIT1 among patients with NS and its occurrence in different populations, we suggest that it should be added to the list of genes included in panels for the molecular diagnosis of NS. 25959749_Mutations in RIT1 cause Noonan syndrome. Mutations in RIT1 affect RAS-MAPK/MEK-ERK signaling. The mutant RIT1 protein may possess reduced GTPase activity or a diminished ability to interact with cellular GTPase activating proteins. 26518681_We report on a 2.5-year-old male patient with clinical signs of NS and hematologic abnormalities, in whom a novel heterozygous substitution in RIT1 with probable pathogenicity was detected. 26617739_elevated expression of RIT1 may contribute to the progression of endometrial cancer and thus may serve as a novel prognostic marker and a promising molecular target for the treatment of endometrial cancer. 26714497_A genotype-phenotype correlation analysis of available records indicated that germline RIT1 mutations cause a noonan syndrome phenotype characterized by a mild facial appearance. 26757980_Noonan patients with germline RIT1 mutations are not at high risk to developing JMML or ALL, and that RIT1 has at most a marginal role in these sporadic malignancies. 27101134_RIT1 is one of the major genes for NS. The RIT1-associated phenotype differs gradually from other NS subtypes, with a high prevalence of cardiovascular manifestations, especially hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 27109146_Our report contributes to the delineation of the phenotype associated with RIT1 mutations and underlines that lymphatic involvement is part of this spectrum 27226556_Biochemical Classification of Disease-associated Mutants of RAS-like Protein Expressed in Many Tissues (RIT1). 28347726_Congenital left main coronary artery atresia in a Noonan syndrome is associated with RIT1 variant, leading to unrescued sudden death. 29402968_The functional assessment supported the pathogenicity of the RAF1 and RIT1 variants of unknown significance (VUSs), while the significance of two VUSs in A2ML1 remained unclear. 29734338_Data show that Ras-like without CAAX 1 protein (RIT1) binds the RHO GTPases CDC42 and RAC1, both of which are crucial regulators of actin dynamics upstream of PAK1. 30348939_RIT1 displays tumor-suppressing functions in ESCC. 30872527_Pathogenic mutations affecting either RIT1 or LZTR1 resulted in incomplete degradation of RIT1. 31355539_Mek inhibitor reverses hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in RIT1 mutated Noonan syndrome. 32766847_The molecular functions of RIT1 and its contribution to human disease. 32831193_The potential oncogenic role of the RAS-like GTP-binding gene RIT1 in glioblastoma. 33517146_The RIT1 C-terminus associates with lipid bilayers via charge complementarity. 34184824_Expanding the clinical phenotype of RASopathies in 38 Turkish patients, including the rare LZTR1, RAF1, RIT1 variants, and large deletion in NF1. 34373451_Integrative oncogene-dependency mapping identifies RIT1 vulnerabilities and synergies in lung cancer. 34846918_Multiomic characterization of oncogenic signaling mediated by wild-type and mutant RIT1. 35290620_RIT1 Promotes Glioma Proliferation and Invasion via the AKT/ERK/NF-kB Signaling Pathway. | ENSMUSG00000028057 | Rit1 | 360.658189 | 0.9325744 | -0.100709293 | 0.10875676 | 0.85702016031 | 0.3545739242418420311686588775046402588486671447753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.58709517664475452392025545123033225536346435546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 376.345856 | 24.387640 | 405.306003 | 26.305729 | |
| ENSG00000143793 | 79169 | C1orf35 | protein_coding | Q9BU76 | Alternative splicing;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation | Enables RNA binding activity. Predicted to be located in extracellular region; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen; and secretory granule lumen. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:79169; | extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; RNA binding [GO:0003723] | 30633125_The study represents the first to use WES in multiplex families for preeclampsia and identifies two novel genes (QRFPR and C1orf35) not previously associated with preeclampsia and find nominal association of rs34270076 with protein levels. 32103167_C1orf35 contributes to tumorigenesis by activating c-MYC transcription in multiple myeloma. | ENSMUSG00000020441 | 2310033P09Rik | 159.143397 | 0.8172284 | -0.291188787 | 0.12999180 | 5.02035785288 | 0.0250509913281749228841643883924916735850274562835693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.09991823972013424981497564658639021217823028564453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 144.380017 | 14.772756 | 177.284688 | 17.734788 | ||
| ENSG00000144566 | 5868 | RAB5A | protein_coding | P20339 | FUNCTION: Small GTPase which cycles between active GTP-bound and inactive GDP-bound states. In its active state, binds to a variety of effector proteins to regulate cellular responses such as of intracellular membrane trafficking, from the formation of transport vesicles to their fusion with membranes. Active GTP-bound form is able to recruit to membranes different sets of downstream effectors directly responsible for vesicle formation, movement, tethering and fusion. RAB5A is required for the fusion of plasma membranes and early endosomes (PubMed:10818110, PubMed:14617813, PubMed:16410077, PubMed:15378032). Contributes to the regulation of filopodia extension (PubMed:14978216). Required for the exosomal release of SDCBP, CD63, PDCD6IP and syndecan (PubMed:22660413). Regulates maturation of apoptotic cell-containing phagosomes, probably downstream of DYN2 and PIK3C3 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9CQD1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10818110, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14617813, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14978216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15378032, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16410077, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22660413}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endocytosis;Endosome;Glycoprotein;GTP-binding;Hydrolase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phagocytosis;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport | Enables GDP binding activity; GTP binding activity; and GTPase activity. Involved in several processes, including amyloid-beta clearance by transcytosis; early endosome to late endosome transport; and regulation of exocytosis. Located in several cellular components, including cytoplasmic side of early endosome membrane; nucleoplasm; and terminal bouton. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:5868; | actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; axon [GO:0030424]; axon terminus [GO:0043679]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic side of early endosome membrane [GO:0098559]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; early phagosome [GO:0032009]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; endosome [GO:0005768]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic early endosome [GO:0098842]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; somatodendritic compartment [GO:0036477]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; terminal bouton [GO:0043195]; G protein activity [GO:0003925]; GDP binding [GO:0019003]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; amyloid-beta clearance by transcytosis [GO:0150093]; early endosome to late endosome transport [GO:0045022]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; modulation by host of viral process [GO:0044788]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; positive regulation of exocytosis [GO:0045921]; receptor internalization involved in canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:2000286]; regulation of autophagosome assembly [GO:2000785]; regulation of endocytosis [GO:0030100]; regulation of endosome size [GO:0051036]; regulation of filopodium assembly [GO:0051489]; regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity [GO:0048169]; regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis [GO:2000300]; synaptic vesicle recycling [GO:0036465] | 11792815_Expression of a GTPase-hydrolysis-defective rab5a affects lysosome biogenesis by alteration of traffic between lysosomes and endosomes. 11884531_Rab5a regulates fusion between pathogen-containing phagosomes and cytoplasmic organelles in human neutrophils 12034881_an endocytotic catalyst, a tandem regulator of thyroid hormone production 12432064_effect of SARA on rab5-mediated endocytosis 12433916_Rab5a has a P-loop backbone amide group, which is required for catalysis 12668728_dynamin2 and Rab5 have roles in endocytosis of lysophosphatidic acid-coupled LPA1/EDG-2 receptors 12761223_In Rab5 overexpressing cells, the levels of beta-cleaved amyloid precursor protein (APP) carboxyl-terminal fragments (betaCTF), the rate-limiting proteolytic intermediate in Abeta generation, were increased 14644159_increase in the concentration of copper in the medium (189 microM) rapidly induces a redistribution of the MNK protein from early sorting endosomes, positive for Rab5-myc protein, to late endosomes, containing the Rab7-myc protein 14669515_Cell cycle was lengthened by blocking or reducing expression of RAB5A G81R mutation. 15016378_identification of a pathway directly linking the small GTPase Rab5, a key regulator of endocytosis, to signal transduction and mitogenesis via APPL1 and APPL2, two Rab5 effectors 15023538_Guanine nucleotide binding state of rab5 has no bearing on the rate of EGFR endocytosis. However, expression of dominant negative rab5 affects downstream endocytic trafficking by slowing the ligand-induced disappearance of total cellular EGFR. 15328530_Rab5 regulates and coordinates different endocytic mechanisms through its effector Rabankyrin-5 15388334_These results suggest that amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2 C-terminal like (ALS2CL), a novel ALS2 homologue, modulates Rab5-mediated endosome dynamics in HeLa cells. 16554017_Taken together, these results demonstrate that Rab5 is required for insulin receptor membrane trafficking and signaling. 17173037_We show that EGF relocates to the cell centre in a dynein-dependent fashion, concomitant with the sorting away of transferrin receptor, although it remains in Rab5-positive early endosomes. 17301141_Rab5 participates in the hepatitis C virus RNA replication machinery. 17301152_Rab 5 is required for the cellular entry of dengue and West Nile viruses. 17473071_TSH controls Rab5a activity by promoting its GTP-bound state 17524504_Results suggest that Rab5 and RalA regulate P-gp trafficking between the plasma membrane and an intracellular compartment. 17581628_The crystal structures of human APPL1 N-terminal BAR-PH domain motif, is reported. 17611268_Rab5 activation via amyloid precursor protein signal pathway mediates neuronal apoptosis. 18005733_B coxsackievirus entry depends on occludin and require the activity of Rab34, Ras, and Rab5, GTPases known to regulate macropinocytosis. 18725540_SopB mediates PI(3)P production on the SCV indirectly through recruitment of Rab5 and its effector Vps34. 18957427_Rab5 is a critical regulator of syndecan-1 shedding that serves as an on-off molecular switch through its alternation between the GDP-bound and GTP-bound forms. 18974049_caspase 8 has a role as a modulator of p85alpha Rab5-GAP activity and endosomal trafficking 18982021_AdipoR1 is internalized through a clathrin- and Rab5-dependent pathway and that endocytosis may play a role in the regulation of adiponectin signaling. 19032933_Specific residues of RIN1 are required for its interaction with Rab5, binding to the endosomal membranes and subsequent regulation of the fusion reaction. 19118546_Mutations in the Vps9 domain of Rin1 lead to a loss-of-function phenotype, indicating a specific structure-function relationship between Rab5 and Rin1. 19126785_oxytocin receptors localize in vesicles containing the Rab5 and Rab4 small GTPases 19372461_Rab GTPase regulation of VEGFR2 trafficking and signaling in endothelial cells; Endothelial cell migration was increased by Rab5a depletion but decreased by Rab7a depletion 19656886_Borna Disease Virus cell entry was Rab5 dependent and exhibited rapid fusion kinetics. 19723633_suppression of Rab5A or 5B hampered the degradation of EGFR 19759177_Data report the identification of Rab22 as a binding site on early endosomes for direct recruitment of Rabex-5 and activation of Rab5, establishing a Rab22-Rab5 signaling relay to promote early endosome fusion. 19819222_The objective of the current study was to perform a detailed examination of the structural flexibility of the phosphate-binding loop (P-loop) as well as the switch I and II regions of human Rab5a upon its binding with GTP. 19830447_The Rab5(Q79L) not only induces formation of enlarged early endosomes but also causes enlargement of later endocytic profiles. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19923319_These studies identify Rab5 as a key integrator of caspase-8-mediated signal transduction downstream of integrins, regulating cell survival and migration in vivo and in vitro. 20376209_Rab5(Q79L) interacts with the carboxyl terminus of RUFY3 20412119_Rab5a promoted proliferation of ovarian cancer cells, which may be associated with the APPL1-related epidermal growth factor signaling pathway. 20457610_Data demonstrate a key role of Rab and Arf family small GTPases and intracellular trafficking in mTORC1 activation. 20472552_Rab5 and Rab7, were associated with the pathway of autophagosome formation and the fate of intracellular group A streptococcus. 20558162_Increased expression of early endosomal marker Rab5 correlates well with intracellular protein deposition in sporadic motor neuron disease. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20847427_Results indicate selective upregulation of Both rab5 and rab7 levels within basal forebrain, frontal cortex, and hippocampus in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. 20926780_These data suggest that proteasomes regulate claudin-1 localization at the plasma membrane, which changes upon proteasomal inhibition to a Rab5a-mediated endosomal localization. 21104291_Rab5a plays a role in LHR trafficking by facilitating internalization and fusion to early endosomes, increasing the degradation of internalized receptor resulting in a reduction in LHR recycling. 21203429_upon ligand activation, CysLT(1)R is tyrosine-phosphorylated and released from heterodimers with CysLT(2)R and, subsequently, internalizes from the plasma membrane to the nuclear membrane in a clathrin-, arrestin-3-, and Rab-5-dependent manner 21423773_Dmkndelta activates Rab5 function and thus is involved in the early endosomal trafficking. 21500550_RABEX-5 and RAB5 may be involved in the development of breast cancer metastasis. 21640764_results suggest that Rab5 is involved in CB2 endocytosis and that internalized receptors are recycled via a Rab11 associated pathway rather than the rapid Rab4 associated pathway. 21655223_SUN2 was redistributed to endosomes upon overexpression of Rab5, but remained on the nuclear envelope when the SUN domain was deleted. 21669283_Upregulated expression of rab4, rab5, rab7, and rab27 correlates with antemortem measures of cognitive decline in individuals with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. 21835792_Coimmunoprecipitation assay indicated that hepatitis C virus NS4B formed a complex with human Rab5 and Vps34, supporting the notion that Rab5 and Vps34 are involved in NS4B-induced autophagy. 21849022_Knockdown of Rab5a expression decreases cancer cell motility and invasion through integrin-mediated signaling pathway. 21895870_Rab5A is associated with axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients. 21987812_Rab5 forms a complex with a subset of CENP-F in mitotic cells and regulates the kinetics of release of CENP-F from the nuclear envelope and its accumulation on kinetochores. 22178872_Rab5A also binds the II-III loop of the Ca(v)2.3 calcium channel and exerts an inhibitory effect on APLP1 mediated channel internalization. 22341461_Recruitment of the inositol 5-phosphatases OCRL and Inpp5b to the Yersinia-filled prevacuoles and subsequent phosphatidylinositol 4,5-diphosphate hydrolysis required the association of the GTPase Rab5 with prevacuoles. 22547071_regulation of PI(3)P synthesis by Rab5 and Vps21 is essential for TORC1 function in both contexts. 22942286_TGF-beta1 can induce epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through reduction in SARA expression, SARA is also basally regulated by its interaction with PI3K. 23048039_Interaction of Rabex-5 with Rab5 depends on interaction of the MIU domain with the ubiquitinated L1 to drive its internalization. 23086000_These findings highlight Rab5 GTPase as a key regulator of P2X4 receptor cell surface expression and internalisation 23182941_Endoplasmic membrane protein complex subunit 6 (EMC6) interacted with both RAB5A and BECN1/Beclin 1 and colocalized with the omegasome marker ZFYVE1/DFCP1. 23291133_Rab5a and APPL1 are overexpressed in breast cancer, and are positively correlated with the HER-2 expression. 23434372_In mammalian cells, p110beta acts as a molecular sensor for growth factor availability and induces autophagy by activating a Rab5-mediated signaling cascade 23454239_Dominant negative (GDP-locked)-Rab5 and -Rab11 reproduced the effects of inhibitors of tubulin and actin, respectively, on the cycling of bradykinin B receptor. 23536683_HBV infection strongly depends on host Rab5 and Rab7 expression. 23606746_Rab5a, Rab8a and Rab14 are major regulators of MT1-MMP trafficking and invasive migration of primary human macrophages. 23687301_In silico screening for palmitoyl substrates reveals a role for DHHC1/3/10 (zDHHC1/3/11)-mediated neurochondrin palmitoylation in its targeting to Rab5-positive endosomes. 23733193_Data indicate that Rab5, Rab7 and Rab11 are involved in RGS4 traffics through plasma membrane recycling or endosome. 23813952_Rab5 activation is required to enhance cancer cell migration and invasion by promoting focal adhesion disassembly. 23815289_Rab1a and Rab5a preferentially bind to binary lipid compositions with higher stored curvature elastic energy. 23940042_clathrin interacts with Rab5 and plays a fundamental role in the entry and intracellular survival of B. abortus via interaction with lipid rafts and actin rearrangement 24466349_vinculin binds to Rab5 and is required for Staphylococcus aureus uptake in cells. 24576301_The predominant pathway mediated by Australian bat lyssavirus G envelope for internalization into HEK293T cells is clathrin-and actin-dependent also requiring Rab5. 24587345_Rab5 isoforms selectively oversee the multiple signaling and trafficking events associated with the endocytic network. 24659799_activation, which is required for cell migration is promoted by Caveolin-1 24727246_Recent studies have shown that the activation of Rab5 is a critical event for maintaining the dynamics of focal adhesions, which is fundamental in regulating not only cell migration but also tumor cell invasion 24788845_Hepatitis B virus can downregulate miR-101-3p expression by inhibiting its promoter activity and that downregulation of miR-101-3p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration by targeting Rab5a. 24848261_FGF21 has a role in promoting endothelial cell angiogenesis through a dynamin-2 and Rab5 dependent pathway 24872409_a novel mechanism by which a PKC-Rab5a-Rac1 axis regulates cytoskeleton remodeling and T-cell migration, both of which are central for the adaptive immune response. 25049275_Overexpression of the GTPase RAB5A, a master regulator of endocytosis, is predictive of aggressive behavior and metastatic ability in human breast cancers. 25152371_This process is inhibited in the presence of a Rab5 dominant-negative mutant. 25179218_TNF-alpha augments invasion of Porphyromonas gingivalis in human gingival epithelial cells through increment of ICAM-1 and activation of Rab5. 25483964_vacuolin-1 activates RAB5A to block autophagosome-lysosome fusion 25566515_Bacteria controled the localization or function of host Rab5 and Rab7, and therefore modify the maturation from early to late phagosomes.[review] 25711083_In serum-deprivated HeLa cells with low endocytic activity there two types of EEA1-vesicles: the first one carries the both EEA1 and Rab5 at high levels; the second consists of weakly decorated EEA1-vesicles that can be both Rab5-positive and -negative. 25763873_Rab5 activation as a tumor cell migration switch 26112597_Rab5a is a key mediator of LPS-induced vascular hyperpermeability. 26168723_findings suggest that Rab5 expression is required to maintain characteristics associated with cell transformation 26181205_Prelamin A/C was translocated to the nuclear membrane and formed a proper nuclear envelope. Rab5a was translocated to the early endosomes. The specific localizations of the prenylated proteins were dependent on intracellular oxygen concentration 26194181_Results indicate that persistent rab5 overactivation through beta-cleaved carboxy-terminal fragment of APP-APPL1 interactions constitutes a novel APP-dependent pathogenic pathway in Alzheimer's disease 26195760_Membrane attack complexes activate noncanonical NF-kappaB by forming a novel Akt(+)NIK(+) signalosome on Rab5(+) endosomes. 26261586_Higher expression of Rab5A was observed in colorectal cancer tissues and Rab5A may be identified as a useful predictor of metastasis and prognosis for CRC. 26344766_Data show that Rab22a- and Rab5a-driven phagosomal uptake is a crucial step in the vesicular cascade that leads to elimination of spirochetes by macrophages. 26443539_Data show that rab5 GTP-Binding Protein (Rab5a) is overexpressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and contributes to cancer cell proliferation and invasion through regulation of FAK and AKT signaling. 26473288_Low expression of RAB5A is associated with metastasis in prostate cancer. 26528697_Findings indicate the role of CMTM7 protein in the regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-AKT proto-oncogene protein signaling in tumor cells, and as a molecule related to Rab5 GTP-binding protein activation. 26582392_Results demonstrate that DRG2 is an endosomal protein and a key regulator of Rab5 deactivation and Tfn recycling. 26680696_PLD1 recovers the decrease in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) endocytosis induced by HIF-1alpha independent of lipase activity via the Rab5-mediated endosome fusion pathway. 27023526_Rab5a is involved in critical events not only at the beginning of the autophagy process with endosomal formation (initiation), but also later on, being important for autophagosome sealing and fusion with lysosomes through an interplay with Beclin 1. 27556945_results suggest a new mechanism in which Rab5 induces a change in flexibility of EEA1, generating an entropic collapse force that pulls the captured vesicle towards the target membrane to initiate docking and membrane fusion 27607061_TTBK2 down-regulates GluK2 activity by decreasing the receptor protein abundance in the cell membrane via RAB5-dependent endocytosis. 27666726_downregulated Rab5a led to slowed cell growth, decreased numbers of migrated cells, decreased numbers of cells at the G0G1 phase and a higher apoptosis rate. However, PDGF significantly rescued these phenomena caused by siRNA against Rab5a 27867015_CMTM3 decreases EGFR expression, facilitates EGFR degradation, and inhibits the EGF-mediated tumorigenicity of gastric cancer cells by enhancing Rab5 activity. 28090783_structural differences may provide an opportunity to selectively target one Rab5 state and lead to new approaches in the development of Rab5-specific therapies 28103577_High RAS-associated protein RAB5 expression correlated with the presence of lymphatic invasion and venous invasion and low E-cadherin expression. 28243729_our results show that Rab5a is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and promotes aggressive biological behavior through regulation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 28455099_Membrane localization and dynamics of geranylgeranylated Rab5 hypervariable region has been reported. 28575494_Low RAB5 expression is associated with glioma progression. 28634871_The results were indicative that rabies virus N proficiently colocalized with Rab5/EEA1 and Rab7/LAMP1 in both cell lines at 24 and 48 h post-infection, while N titers significantly decreased in early infection of rabies virus. 28650718_Ehrlichia obtains host-derived nutrients by inducing RAB5-regulated autophagy using Ehrlichia translocated factor-1 deployed by its type IV secretion system. This manipulation of RAB5 by a bacterial molecule offers a simple strategy for Ehrlichia to avoid destruction in lysosomes and obtain nutrients. 28650977_siRNA knockdown of Rab5a or overexpression of miR-494 in human macrophages significantly inhibits the survival of the parasites 28742203_The expression level of EMC-6 is significantly elevated in cervical cancer, without significant correlation with Beclin1 and Rab5a. 28834690_study elucidated a novel Malat1-miR-101-STMN1/RAB5A/ATG4D regulatory network that Malat1 activates autophagy and promotes cell proliferation by sponging miR-101 and upregulating STMN1, RAB5A and ATG4D expression in glioma cells 28849149_Rab5a is overexpressed in oral cancer tissue samples and promotes the malignant phenotype through EMT and the ERK/MMP2 signaling pathway. 28867190_In conclusion, mutant KRAS promotes endosomal degradation in PDAC cell lines, which is impaired by KRAS silencing. Moreover, KRAS silencing activates RAB5A upregulation and drives PDAC subtype-dependent modulation of endosome trafficking. 28899395_Rab5 was found abundantly localized in macrophage rich areas of human atherosclerotic lesions.Rab5 plays an important role in modulating the intracellular cholesterol of macrophages and consequently mediating the formation of foam cells. 28968219_Here the authors show that Rab5 is monoubiquitinated on K116, K140, and K165. Structural analysis combined with biochemical data revealed that interactions with downstream effectors were impeded in Rab5 monoubiquitinated at K140, whereas GDP release and GTP loading activities were altered in Rab5 monoubiquitinated at K165. 29065764_These results allow to devise a detailed structural model for the process of extraction of GG-Rab5(GDP) by GDI from the membrane and the dissociation from targeting factors and effector proteins prior to GDI binding. 29127297_Rab5 is essential for FcepsilonRI-triggered association of the SNARE protein SNAP23 with the secretory granules. 29360040_The authors demonstrate that RABGEF1, the upstream factor of the endosomal Rab GTPase cascade, is recruited to damaged mitochondria via ubiquitin binding downstream of Parkin. RABGEF1 directs the downstream Rab proteins, RAB5 and RAB7A, to damaged mitochondria, whose associations are further regulated by mitochondrial Rab-GAPs. 29361527_we demonstrate a novel role for the interaction between APPL1 and Rab5 in governing crosstalk between signaling and trafficking pathways on endosomes to affect cancer cell migration 29469808_These findings define a novel pathway whereby Alsin catalyzes the assembly of the Rab5 endocytic machinery on mitochondria. Defects in stress-sensing by endosomes could be crucial for mitochondrial quality control during the onset of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 29626103_Low RAB5A expression is associated with polycystic ovary syndrome. 29740032_several p85a mutations found in human cancers may deregulate PTEN and/or Rab5 regulated pathways to contribute to oncogenesis. We also engineered several experimental mutations within the p85a BH domain and identified L191 and V263 as important for both binding and regulation of Rab5 activity 29743547_Protease Activated Receptor2 Promotes Rab5a Mediated Generation of Pro-metastatic Microvesicles 29868450_This study showed that the RAB5A predictors of regional brain atrophy in Parkinson disease. 30333257_Overexpression of Rab5B largely rescued the miR-575-mediated impairment of angiogenesis. 30659094_results define a single, discrete Rab5-binding site in the p110beta helical domain, which may be useful for generating inhibitors to better define the physiological role of Rab5-PI3Kbeta coupling in vivo 30765602_findings show that endosomal/lysosomal RAB5 and RAB7, which regulate mitophagy, are essential for the survival of colon cancer stem cells 31221728_The study reveals an evolutionarily conserved role for the early endocytic marker Rab5 in cytokinetic abscission. 31337623_sorting nexin SNX3 is transported with Rab5a vesicles and that its PX domain enables vesicle-phagosome contact by binding to PI(3)P in the phagosomal coat. Moreover, the C-terminal region of SNX3 recruits galectin-9, a lectin implicated in protein and membrane recycling, which we identify as a further regulator of phagosome compaction. 31358736_The findings suggest that SPIN90, as an adaptor protein, simultaneously binds inactive Rab5 and Gapex5, thereby altering their spatial proximity and facilitating Rab5 activation. 31558725_Data suggest a mechanism whereby flotillins mediate T cell receptor (TCR) sorting into rab5 GTP-binding protein (Rab5) and ras-related protein Rab-11A (Rab11) endosomes. 31705388_EGFR signaling augments TLR4 cell surface expression and function in macrophages via regulation of Rab5a activation. 31811856_Study data indicate that GRK2 and RAB5 play key roles in alpha1B-adrenergic receptor phosphorylation, internalization, and desensitization. The possibility that RAB5 might form part of a signaling complex is suggested, as well as that GDP-Rab5 might interfere with the ability of GRK2 to catalyze alpha1B-adrenergic receptor phosphorylation. 32304339_Protein diaphanous homolog 1 (Diaph1) promotes myofibroblastic activation of hepatic stellate cells by regulating Rab5a activity and TGFbeta receptor endocytosis. 32560826_Rac1-dependent endocytosis and Rab5-dependent intracellular trafficking are required by Enterovirus A71 and Coxsackievirus A10 to establish infections. 33092247_Rab GTPase Mediating Regulation of NALP3 in Colorectal Cancer. 33137306_The G-Protein Rab5A Activates VPS34 Complex II, a Class III PI3K, by a Dual Regulatory Mechanism. 33341673_RAB5A promotes the formation of filopodia in pancreatic cancer cells via the activation of cdc42 and beta1-integrin. 33416169_Long noncoding RNA CASC19 promotes glioma progression by modulating the miR4543p/RAB5A axis and is associated with unfavorable MRI features. 33692360_Structural basis for VPS34 kinase activation by Rab1 and Rab5 on membranes. 33831402_RAB5A effect on metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell line via altering the pro-invasive content of exosomes. 34129971_Propofol Represses Cell Growth and Metastasis by Modulating the Circular RNA Non-SMC Condensin I Complex Subunit G/MicroRNA-200a-3p/RAB5A Axis in Glioma. 34281589_CMTM7 as a novel molecule of ATG14L-Beclin1-VPS34 complex enhances autophagy by Rab5 to regulate tumorigenicity. 34383013_Who's in control? Principles of Rab GTPase activation in endolysosomal membrane trafficking and beyond. 34826799_Nectin stabilization at adherens junctions is counteracted by Rab5a-dependent endocytosis. 35017116_lncRNA HITT inhibits metastasis by attenuating Rab5-mediated endocytosis in lung adenocarcinoma. 36438897_Identification of Key Genes and miRNAs Affecting Osteosarcoma Based on Bioinformatics. | ENSMUSG00000017831 | Rab5a | 413.031603 | 1.2507297 | 0.322770066 | 0.09213184 | 12.26501388441 | 0.0004615297842244815967188698024870063818525522947311401367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00390319142789120193670626690618519205600023269653320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 437.658962 | 26.273443 | 351.550568 | 21.343513 | |
| ENSG00000144677 | 10217 | CTDSPL | protein_coding | O15194 | FUNCTION: Recruited by REST to neuronal genes that contain RE-1 elements, leading to neuronal gene silencing in non-neuronal cells (By similarity). Preferentially catalyzes the dephosphorylation of 'Ser-5' within the tandem 7 residue repeats in the C-terminal domain (CTD) of the largest RNA polymerase II subunit POLR2A. Negatively regulates RNA polymerase II transcription, possibly by controlling the transition from initiation/capping to processive transcript elongation. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12721286}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome | Predicted to enable RNA polymerase II CTD heptapeptide repeat phosphatase activity. Predicted to be involved in protein dephosphorylation. Predicted to act upstream of or within negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle and negative regulation of protein phosphorylation. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:10217; | extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; myosin phosphatase activity [GO:0017018]; phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0004721]; RNA polymerase II CTD heptapeptide repeat phosphatase activity [GO:0008420]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933] | 15051889_analysis of RBSP3/HYA22located in the AP20 region, and evidence for tumor suppressor function 17085434_SCP3 acts as a phosphatase for regulatory phosphorylations in the linker regions of Smad1 and Smad2. 19016758_Frequent alterations of RBSP3 at chromosomal 3p22.3 region in early and late-onset breast carcinoma are reported with reference to clinical and prognostic significance. 19047128_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19140316_Down-regulation of RBSP3/CTDSPL, NPRL2/G21, RASSF1A, ITGA9, HYAL1 and HYAL2 genes in non-small cell lung cancer 19478941_This is the first report of high frequencies of somatic mutations in RASSF1 and RBSP3 in different cancers suggesting it may underlay the mutator phenotype of cancer. 19885927_In cervical intraepithelial neoplasms and uterine cervical carinoma, RBSP3 is oftne deletd, compared with other genes. 20193080_tumor suppressor genes RBSP3/CTDSPL, NPRL2/G21 and RASSF1A are downregulated in primary non-small cell lung cancer 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20412120_dysregulation of hMLH1, ITGA9, and RBSP3 associated multiple cellular pathways are needed for the development of early dysplastic lesions of the head and neck. 21643017_identified RBSP3, a phosphatase-like tumor suppressor, as a bona fide target of miR-100 and validated that RBSP3 was involved in cell differentiation and survival in acute myeloid leukemia 27414789_CTDSPL and Rb directly interact and can be involved in the common mechanism of cell cycle regulation. 27458253_data suggest that overexpression of p-RB1 in basal-parabasal layers of normal cervical epithelium was due to methylation/low functional-linked non-synonimous SNPs of P16 and RBSP3. This pattern was maintained during cervical carcinogenesis by additional deletion/mutation 29382357_we have presented herein the novel finding that miR-181b contributes to cell cycle progression through depressing the expression of CTDSPL, which in turn activates the downstream effector E2F1 and promotes S-phase entry. 29672635_our data also suggests the importance ofLIMD1 and CDC25A in conjunction with HPV for use as diagnostic and prognostic markers of HNSCC, whereas RBSP3 as a prognostic marker only. 31774910_Tumor suppressor properties of the small C-terminal domain phosphatases in non-small cell lung cancer. | ENSMUSG00000047409 | Ctdspl | 85.730453 | 1.1844170 | 0.244177147 | 0.25286935 | 0.92248976798 | 0.3368220886034769545602785001392476260662078857421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.56929281964541278426850112737156450748443603515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 87.515427 | 16.732435 | 73.546368 | 14.054576 | |
| ENSG00000145391 | 80854 | SETD7 | protein_coding | Q8WTS6 | FUNCTION: Histone methyltransferase that specifically monomethylates 'Lys-4' of histone H3 (PubMed:11779497, PubMed:11850410, PubMed:12588998, PubMed:12540855, PubMed:16141209). H3 'Lys-4' methylation represents a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional activation (PubMed:12588998, PubMed:12540855, PubMed:16141209). Plays a central role in the transcriptional activation of genes such as collagenase or insulin (PubMed:16141209, PubMed:12588998). Recruited by IPF1/PDX-1 to the insulin promoter, leading to activate transcription (PubMed:16141209). Has also methyltransferase activity toward non-histone proteins such as CGAS, p53/TP53, TAF10, and possibly TAF7 by recognizing and binding the [KR]-[STA]-K in substrate proteins (PubMed:15099517, PubMed:35210392, PubMed:15525938, PubMed:16415881). Monomethylates 'Lys-189' of TAF10, leading to increase the affinity of TAF10 for RNA polymerase II (PubMed:15099517, PubMed:16415881). Monomethylates 'Lys-372' of p53/TP53, stabilizing p53/TP53 and increasing p53/TP53-mediated transcriptional activation (PubMed:17108971, PubMed:15525938, PubMed:16415881). Monomethylates 'Lys-491' of CGAS, promoting interaction between SGF29 and CGAS (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VHL1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11779497, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11850410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12540855, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12588998, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15099517, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15525938, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16141209, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16415881, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17108971, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35210392}. | 3D-structure;Activator;Chromatin regulator;Chromosome;Direct protein sequencing;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase | Enables histone-lysine N-methyltransferase activity and p53 binding activity. Involved in peptidyl-lysine dimethylation and peptidyl-lysine monomethylation. Acts upstream of or within cellular response to DNA damage stimulus and heterochromatin organization. Located in chromosome and nucleolus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:80854; | chromosome [GO:0005694]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; histone lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0018024]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0016279]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; heterochromatin organization [GO:0070828]; histone lysine methylation [GO:0034968]; peptidyl-lysine dimethylation [GO:0018027]; peptidyl-lysine monomethylation [GO:0018026]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of histone H3-K9 methylation [GO:0051570] | 11779497_purification and functional characterization of a histone H3-lysine 4-specific methyltransferase 12372304_crystal structure of human SET7/9 shows residues essential for catalytic activity with histone H3 12540855_Crystal structure and catalytic mechanism of the human histone methyltransferase SET7/9 12670868_This enzyme and human Sin3 deacetylase are tethered together selectively by the cell-proliferation factor HCF-1. 16415881_SET7/9 recognizes a conserved K/R-S/T/A motif preceding the lysine substrate and has a propensity to bind aspartates and asparagines on the C-terminal side of the lysine target 17573780_RBP2 associates with MRG15 complex to maintain reduced H3K4 methylation at transcribed regions, which may ensure the transcriptional elongation state 17646389_Results suggest that the cross talk between lysine methylation and acetylation is critical for p53 activation in response to DNA damage and that Set7/9 may play an important role in tumor suppression. 18471979_Results show that estrogen receptor alpha is directly methylated at lysine 302 (K302) by the SET7 methyltransferase. 18474616_This report shows that H3K9 monomethylation is dependent upon the PR-Set7 H4K20 monomethyltransferase but independent of its catalytic function, indicating that PR-Set7 recruits an H3K9 monomethyltransferase to establish the trans-tail histone code. 18650421_a novel role for SET7/9 in inflammation and diabetes. 19262565_Data show that lysine methyltransferase Set9 physically associates with RelA in vitro and in vivo in response to TNF-alpha. 19282482_signaling through SET7 represents a means of DNMT1 enzyme turnover 19351588_These data may lead to a new insight into PCAF functions and provide additional information to identify unknown targets of Set9. 19752191_the binding of two SET domain-containing proteins, ALL1 and SET7, to chromatin substrates was studied. 20227666_Set7/9-KMT7 associates with the HIV promoter in vivo and monomethylates lysine 51, a highly conserved residue located in the RNA-binding domain of Tat. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20675860_SET7/9 catalytic mutants reveal the role of active site water molecules in lysine multiple methylation 21098664_Data show that STAT3 binds to the SOCS3 promoter, and S727 is then phosphorylated, followed by the coincident binding of SET9 and dimethylation of K140, and lastly by the binding of LSD1. 21245319_results reveal that Set7/9 is a critical regulator of the SIRT1-p53 interaction and suggest that Set7/9 can modulate p53 function indirectly in addition to acting through a methylation-dependent mechanism 21273441_Set9 directly acts on AR at the amino acid level. Chromatin recruitment of Set9 to AREs is suggestive of its additional role as a transcriptional coactivator. 21454678_Direct evidence for methyl group coordination by carbon-oxygen hydrogen bonds in the lysine methyltransferase SET7/9. 21896933_genetic association studies in a Finnish population with type I diabetes: No associations were found between SNPs in SETD7 and the diabetic complications studied. 22242964_simulations show that while the wild-type SET7/9 is a monomethylase, the Y245-->A mutation increases the ability of the enzyme to add more methyl groups on the target lysine 22403242_The response to hyperglycemia in vascular endothelial cells involves Set7 mediated changes in chromatin remodeling and gene expression. 22406368_H3K4me3 level defines unrecognized subsets of heptaocellular carcinoma patients with distinct epigenetic phenotype and clinical outcome and can thus be a novel predictor for poor prognosis of heptaocellular carcinoma patients 22820736_The methyltransferase Set9 directly methylates FoxO3 in vitro and in cells. The modulation of FoxO3 stability and activity by methylation may be critical for fine-tuning cellular responses to stress stimuli. 23509280_Methylation of SUV39H1 by SET7/9 results in heterochromatin relaxation and genome instability. 23519668_The crystal structures presented here provide information about the binding of both AdoMet-analogue inhibitors and peptides by the SET domain of SET7/9. 23873758_study indicates that Set7/9 prevents the histone deacetylase activity of SirT1, potentiating euchromatin formation on the promoter site of COL2A1 and resulting in morphology-dependent COL2A1 gene transactivation. 24129573_Vesicular stomatitis virus and influenza A virus increased IFITM3-K88me1 levels by promoting the interaction between IFITM3 and SET7, suggesting that this pathway could be hijacked to support infection; conversely, IFN-alpha reduced IFITM3-K88me1 levels. 24875254_Set7-dependent gene expression changes that occurred independent of H3K4m1 may involve transcription factor lysine methylation events. 25042802_Results show Set7 efficiently monomethylates Sox2 at K119 residue controling its stability. 25124555_Set7/9 is a potential biomarker in tumour cells and is associated with overexpressed E2F1 activity. 25472959_Set7-induced epigenetic changes contribute to vascular dysfunction in patients with T2DM. 25637186_SET9 enriches at hypoxia response elements sites of HIF-1 responsive glycolytic genes and stabilizes HIF-1alpha at these sites in hypoxia. 25681344_Results show that histone-lysine N-methyltransferase Set7 facilitates hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication through the attenuation of interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) signaling pathways and IFN-related effectors. 25954928_Based on our results miR-153 inhibits proliferation and suppresses EMT and the invasive potential of ovarian cancer cells through downregulation of SET7 and ZEB2, supporting the pursuit of miR-153 as a potential target for ovarian cancer intervention. 26116705_Findings indicate the regulation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and the role of SET domain-containing protein 7/9 (SET7/9) in cancer cells. 26317544_Unleashed expression of Mdm2 in cancer patients with diminished expression of Set7/9 is associated with poor survival outcome. 26435321_Lysine methylation by SETD7 is important for the fine-tuning of reactive oxygen species signaling through its regulation on pro-inflammatory responses. 26701885_Reduced expression of SET7 is associated with gastric cancer progression. 26713889_These results demonstrate that S...O chalcogen bonds contribute to AdoMet recognition and can enable methyltransferases to distinguish between substrate and product. 26779630_High SET7 expression is associated with breast cancer. 26848522_SET7 was required for GATA1-induced breast tumor angiogenesis and growth in nude mice. GATA1 and SET7 are independent poor prognostic factors in breast cancer. 26861389_study identified a novel locus associated with serum lycopene concentrations and results raise a number of possibilities regarding the nature of the relationship between SETD7 and lycopene, both independently associated with prostate cancer. 26890252_Knock-down of SETD7 causes differentiation defects in human embryonic stem cell including delay in both the silencing of pluripotency-related genes and the induction of differentiation genes. 26902152_SET7/SET9-mediated YY1 methylation was shown to be involved in YY1-regulated gene transcription and cell proliferation. 27132511_SET9 expression levels were significantly higher in samples from patients with pathological complete remission than in samples from patients with disease recurrence, which indicates that SET9 acts as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer and that its expression may serve as a prognostic marker for malignancy. 27146893_Methylation at K436 and K595 respectively by Set7 increases the stability and DNA binding ability of Gli3, resulting in an enhancement of Shh signaling activation. 27183310_SETD7 plays a critical role in HCC, and its immunohistochemistry signature provides potential clinical significance for personalized prediction of HCC prognosis. 27235396_These findings underscore the role of KMT7 as an important monomethyltransferase regulating HIV transcription through Tat. 27292644_the methyltransferase Set9 potentiates TGF-beta signaling by targeting Smad7, an inhibitory downstream effector. 28417976_Revealing inhibition difference between PFI-2 enantiomers against SETD7 by molecular dynamics simulations, binding free energy calculations and unbinding pathway analysis. 29222115_SET9 is broadly required for the effects of TGFB1 in diseased primary renal fibroblasts; SET9 promotes fibroblast migration into wounds, expression of extracellular matrix proteins, collagen contractility and myofibroblast differentiation. SET9 is recruited to the alpha-smooth muscle actin gene in response to TGFB1, providing a mechanism by which SET9 regulates myofibroblast contractility and differentiation. 29383876_Setd7 knockdown decreases Nrf2 and Nrf2-target genes expression, and phenethyl isothiocyanate and ursolic acid induce Setd7 expression, which activates the Nrf2/antioxidant response element signaling pathway and protects DNA from oxidative damage. 29499155_these results reveal how SETD7 acts at sequential steps in cardiac lineage commitment. 29684621_Setd7 plays an positive role in osteogenic differentiation 29723250_SET7/9 expression in nonadherent cells isolated from the effluent of peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients. SET7/9 expression was elevated in nonadherent cells isolated from the effluent of PD patients. SET7/9 expression was positively correlated with dialysate/plasma ratio of creatinine in PD patients. 30106440_High SET7 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma progression. 30357346_SET7-mediated UHRF1 methylation is also shown to be essential for cell viability against DNA damage. Our data revealed the regulatory mechanism underlying the UHRF1 methylation status by SET7 and LSD1 in double-strand break repair pathway 30361067_data indicate that SETD7 could serve as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. 30396921_Setd7 KD impacted a larger set of genes and caused a higher fold change compared to PEITC treatment. This study offers new insights into the mechanisms of action of the epigenetic modifier Setd7 and the effects of PEITC treatment in PCa cells and enhances our understanding of the potential cancer preventive/treatment effects of isothiocyanate compounds such as PEITC in PCa. 30674889_Paper uncovers a molecular mechanism of ISL1 promoting metastasis of GC through binding to the ZEB1 promoter together with co-factor SETD7. 31035088_Our findings demonstrate that the inhibition of SETD7 restricts TNF-alpha-induced airway smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by blocking the NF-kappaB/CD38 signaling axis. These results highlight a potential relevance of the SETD7/NF-kappaB/CD38 axis in the pathogenesis of asthma. 31324717_The SET domain-containing 7 histone lysine methyltransferase (SETD7) uses its N-terminal membrane occupation and recognition nexus (MORN) repeats to dock its substrates and subsequently juxtapose their Lys methylation motif for efficient and specific methylation by the catalytic SET domain. 31751593_The N-terminal MORN domain of SET7/9 is essential for its interaction with eL42 and methylates eL42 at three different lysines - Lys53, Lys80 and Lys100 through site-directed mutagenesis. 31863092_Methylation of PLK1 by SET7/9 ensures accurate kinetochore-microtubule dynamics. 32120841_Isoform-Specific Lysine Methylation of RORalpha2 by SETD7 Is Required for Association of the TIP60 Coactivator Complex in Prostate Cancer Progression. 32126149_METTL3/YTHDF2 m(6) A axis promotes tumorigenesis by degrading SETD7 and KLF4 mRNAs in bladder cancer. 32178870_KMT Set7/9 is a new regulator of Sam68 STAR-protein. 32320649_The Set7 Lysine Methyltransferase Regulates Plasticity in Oxidative Phosphorylation Necessary for Trained Immunity Induced by beta-Glucan. 32323737_Downregulation of SETD7 promotes migration and invasion of lung cancer cells via JAK2/STAT3 pathway. 33336743_SET7/9 promotes H3K4me3 at lncRNA DRAIC promoter to modulate growth and metastasis of glioma. 33564100_SRF is a nonhistone methylation target of KDM2B and SET7 in the regulation of skeletal muscle differentiation. 34252487_lncRNA SNHG6 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by interacting with HNRNPL/PTBP1 to facilitate SETD7/LZTFL1 mRNA destabilization. 34343833_Set7/9 controls proliferation and genotoxic drug resistance of NSCLC cells. 34856916_Non-histone Methylation of SET7/9 and its Biological Functions. 35137483_Melatonin regulates trophoblast pyroptosis, invasion and migration in preeclampsia by inhibiting HtrA1 transcription through the microRNA-520c-3p/SETD7 axis. | ENSMUSG00000037111 | Setd7 | 451.161011 | 1.6116236 | 0.688514802 | 0.08266458 | 69.30697278412 | 0.0000000000000000842711354319146620109093920015702080435232606452425341281298187823267653584480285644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000000000000471513856968648912110831753540064205304163528001404337430813029641285538673400878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 528.166592 | 60.439787 | 327.718013 | 37.712709 | |
| ENSG00000146463 | 9202 | ZMYM4 | protein_coding | Q5VZL5 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in the regulation of cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21834987}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Predicted to enable DNA binding activity. Involved in cytoskeleton organization and regulation of cell morphogenesis. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:9202; | DNA binding [GO:0003677]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; regulation of cell morphogenesis [GO:0022604] | 12356764_regulates apoptosis by altering mRNA turnover and CDIR inhibits apoptosis by acting as a competitive inhibitor of AUF1, preventing AUF1 from binding to its targets 32439918_Characterization of the zinc finger proteins ZMYM2 and ZMYM4 as novel B-MYB binding proteins. 33938481_Expression and Mutation Alterations of ZMYM4 Gene in Gastric and Colonic Cancers. | ENSMUSG00000042446 | Zmym4 | 457.839437 | 0.9953792 | -0.006681927 | 0.11950619 | 0.00312090159 | 0.9554493292288831485237210472405422478914260864257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.97982589569308053967233718140050768852233886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 435.417248 | 33.962306 | 438.780592 | 34.320163 | |
| ENSG00000146826 | 55262 | TRAPPC14 | protein_coding | Q8WVR3 | FUNCTION: Specific subunit of the TRAPP (transport protein particle) II complex, a highly conserved vesicle tethering complex that functions in late Golgi trafficking as a membrane tether (PubMed:31467083, PubMed:30715179). TRAPP II complex has also GEF activity toward RAB1A (By similarity). TRAPPC14 is dispensable for TRAPPII complex integrity but mediates RAB3IP preciliary vesicle trafficking to the mother centriole during ciliogenesis (PubMed:31467083). Modulates YAP1 activity as transcriptional regulator (PubMed:30447097). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3TLI0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30447097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30715179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31467083}. | Alternative splicing;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Primary microcephaly;Reference proteome | Enables alpha-tubulin binding activity. Involved in cilium assembly and regulation of cell population proliferation. Located in several cellular components, including microtubule cytoskeleton; midbody; and plasma membrane. Part of TRAPPII protein complex. Implicated in primary autosomal recessive microcephaly. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:55262; | centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; midbody [GO:0030496]; mitotic spindle [GO:0072686]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; TRAPPII protein complex [GO:1990071]; alpha-tubulin binding [GO:0043014]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127] | 31467083_C7orf43 directly binds to Rabin8 and that C7orf43 knockdown diminishes Rabin8 preciliary centrosome accumulation. | ENSMUSG00000036948 | Trappc14 | 148.506079 | 0.7187222 | -0.476493747 | 0.21803408 | 4.74930627720 | 0.0293101082426099925071216745209312648512423038482666015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.11168340890700860501549840364532428793609142303466796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 113.703576 | 15.362412 | 159.164822 | 21.207584 | |
| ENSG00000147130 | 9203 | ZMYM3 | protein_coding | Q14202 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in the regulation of cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21834987}. | Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene is located on the X chromosome and is subject to X inactivation. It is highly conserved in vertebrates and most abundantly expressed in the brain. The encoded protein is a component of histone deacetylase-containing multiprotein complexes that function through modifying chromatin structure to keep genes silent. A chromosomal translocation (X;13) involving this gene is associated with X-linked cognitive disability. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010]. | hsa:9203; | nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; regulation of cell morphogenesis [GO:0022604] | 29332164_Data found skewing of the genetic architecture at the ZMYM3 short tandem repeats (STR) in schizophrenia. Further, results found a bell-shaped distribution of alleles and selection against alleles at the extreme ends of this STR. 30889214_AGS mutations in this cluster impair the interaction of RNase H2 with several members of the CoREST chromatin-silencing complex that include the histone deacetylase HDAC2 and the demethylase KDM1A, the transcriptional regulators RCOR1 and GTFII-I as well as ZMYM3, an MYM-type zinc finger protein. 30909162_The ZMYM3 'exceptionally long' 5' UTR STR findings may alter our perspective of disease pathogenesis in psychiatric disorders, and set an example in which the low frequency alleles at the extreme short and long ends of the human STRs are, at least in part, a result of natural selection against these alleles and their unambiguous link to major human disorders. 33173136_Evolving evidence on a link between the ZMYM3 exceptionally long GA-STR and human cognition. | ENSMUSG00000031310 | Zmym3 | 185.088347 | 0.5583647 | -0.840720302 | 0.11530706 | 53.34223982109 | 0.0000000000002802159887707193075071725807477878342189279992080486181293963454663753509521484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000000001088794791923561527984570867979164515704226801062759477645158767700195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 131.826738 | 10.500192 | 236.957170 | 18.063994 | |
| ENSG00000147475 | 11160 | ERLIN2 | protein_coding | O94905 | FUNCTION: Component of the ERLIN1/ERLIN2 complex which mediates the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors (IP3Rs) such as ITPR1 (PubMed:19240031, PubMed:17502376). Promotes sterol-accelerated ERAD of HMGCR probably implicating an AMFR/gp78-containing ubiquitin ligase complex (PubMed:21343306). Involved in regulation of cellular cholesterol homeostasis by regulation the SREBP signaling pathway. May promote ER retention of the SCAP-SREBF complex (PubMed:24217618). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17502376, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19240031, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21343306, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24217618}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cholesterol metabolism;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Steroid metabolism;Sterol metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a member of the SPFH domain-containing family of lipid raft-associated proteins. The encoded protein is localized to lipid rafts of the endoplasmic reticulum and plays a critical role in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) signaling by mediating ER-associated degradation of activated IP3 receptors. Mutations in this gene are a cause of spastic paraplegia-18 (SPG18). Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. | hsa:11160; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; negative regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0045541]; negative regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0045717]; regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0045540]; SREBP signaling pathway [GO:0032933]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433] | 16835267_Erlin-1 and erlin-2 are novel members of the prohibitin family of proteins that define lipid-raft-like domains of the ER. 17502376_SPFH2 as a key endoplasmic reticulum associated degradation pathway component and suggest that it may act as a substrate recognition factor. 19240031_Results suggest that this novel SPFH1/2 complex is a recognition factor that targets IP(3)Rs and perhaps other substrates for ERAD. 19751772_m3 receptor-expressing HeLa cells are a valuable system for studying IP(3) receptor ERAD, and suggest that the SPFH1/2 complex is a factor that selectively mediates the ERAD of activated IP(3) receptors. 21330303_The gene encodes endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lipid raft-associated protein 2 that mediates the ER-associated degradation of activated inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors and other substrates. 21796390_study describes an extended consanguineous Saudi family in which hereditary spastic paraplegia is linked to SPG18, an autosomal recessive locus, and show it is associated with a nullimorphic deletion of ERLIN2 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 22681620_ERLIN2 may confer a selective growth advantage for breast cancer cells by facilitating a cytoprotective response to various cellular stresses associated with oncogenesis. 22690709_a novel role for ERLIN2 in supporting cancer cell growth by promoting the activation of the key lipogenic regulator SREBP1c and the production of cytosolic lipid droplets. 22771797_a novel brain gamma-secretase associated protein , erlin-2, that resides in detergent resistant membranes and affects amyloid beta-peptide production. 23085305_ERLIN2 was found to be responsible for causing hereditary spastic paraplegia in a Saudi family. 23109145_ERLIN2 loss on cell growth may advance understanding of the mechanism behind motor neuron degeneration in primary lateral sclerosis 24217618_Erlin-2 and the related erlin-1 were found to negatively regulate cholesterol and fatty acid biosynthesis in cultured cell models when the proteins were depleted by RNAi. The proteins also selectively bound cholesterol. 24217618_Here we show that the multimeric ER proteins erlins-1 and -2 are additional sterol regulatory element binding protein regulators. 27824013_Novel Mutations in Endoplasmic Reticulum Lipid Raft-associated Protein 2 Gene Cause Pure Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Type 18 29453415_Here we suggest that ERLIN1 variants, previously shown in juvenile hereditary spastic paraplegia cases, may also be the cause of a slowly progressive early-onset Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) , starting with upper motor neuron features and developing into classical ALS with the addition of lower motor neuron dysfunction. 29528531_Biallelic variants in ERLIN2 are known to cause recessive HSP type SPG18. Here, the first two families with an autosomal dominant, pure form of HSP caused by a novel ERLIN2 heterozygous missense variant are described. These findings expand the mutational and inheritance spectrum of SPG18. 32094424_An autosomal dominant ERLIN2 mutation leads to a pure HSP phenotype distinct from the autosomal recessive ERLIN2 mutations (SPG18). 32147972_Expansion of the genetic landscape of ERLIN2-related disorders. 33424830_Molecular and Immune Characteristics for Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients With ERLIN2 Overexpression. | ENSMUSG00000031483 | Erlin2 | 1320.254486 | 1.0867533 | 0.120024462 | 0.05492960 | 4.77328960194 | 0.0289045454516844296799504832051752600818872451782226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.11068584731134460674706332383721019141376018524169921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1353.803710 | 51.545933 | 1251.555764 | 47.832144 | |
| ENSG00000147526 | 6867 | TACC1 | protein_coding | O75410 | FUNCTION: Involved in transcription regulation induced by nuclear receptors, including in T3 thyroid hormone and all-trans retinoic acid pathways (PubMed:20078863). Might promote the nuclear localization of the receptors (PubMed:20078863). Likely involved in the processes that promote cell division prior to the formation of differentiated tissues. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20078863}. | Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat | This locus may represent a breast cancer candidate gene. It is located close to FGFR1 on a region of chromosome 8 that is amplified in some breast cancers. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2017]. | hsa:6867; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; midbody [GO:0030496]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; nuclear estrogen receptor binding [GO:0030331]; nuclear glucocorticoid receptor binding [GO:0035259]; nuclear receptor binding [GO:0016922]; nuclear receptor coactivator activity [GO:0030374]; nuclear retinoic acid receptor binding [GO:0042974]; nuclear retinoid X receptor binding [GO:0046965]; nuclear thyroid hormone receptor binding [GO:0046966]; peroxisome proliferator activated receptor binding [GO:0042975]; cell division [GO:0051301]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cerebral cortex development [GO:0021987]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; mitotic spindle organization [GO:0007052] | 11903063_Interaction of the transforming acidic coiled-coil 1 (TACC1) protein with ch-TOG and GAS41/NuBI1 suggests multiple TACC1-containing protein complexes in human cells 12165861_Down regulation of tacc1 controls mrna homeostasis in polarized cells and participates in oncogenic processes in human cancers 12389629_REVIEW: genetics, expression, gene expression regulation, and function studies 12547166_Splicing pattern of its mRNA is altered in stomach cancer 15064709_TACC1 and the mitotic kinase Aurora B belong to the same complex during cytokinesis. 16496324_Splice variants can be localized to different subcellular compartments in a cell-and tissue-specific manner. 18984771_TACC1 and a three-gene expression signature (TACC1, NOV, and PTTG1) were identified as independent prognostic markers. 20078863_TACC1 depletion in the cell led to decreased RARalpha and TRalpha ligand-dependent transcriptional activity and to delocalization of TR from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. 20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21531210_the study demonstrated that TACC1 localizes at the midbody during cytokinesis and interacts with and is a substrate of Aurora-C, which warrant further investigation in order to elucidate the functional significance of this interaction. 22837387_study reports that a small subset of glioblastoma multiforme tumors harbors oncogenic chromosomal translocations that fuse in-frame the tyrosine kinase coding domains of fibroblast growth factor receptor genes(FGFR1 or FGFR3) to the transforming acidic coiled-coil coding domains of TACC1 or TACC3; the FGFR-TACC fusion protein displays oncogenic activity 23354013_These findings provide proof and the foundation for the molecular and biological relationships of ErbB-2 and TACC1 in breast cancer. 24358147_TFF3 and TACC1 over-expression in epithelial cells of surgically resected gastric cancer tissues was an independent predictor of short survival in gastric cancer patients. 25297519_The correlation between TACC1 expression and HER-2-positive status indicates synergistic regulation of these two prognostic markers in gastric carcinoma patients. 33481389_Neurofibrosarcoma Revisited: An Institutional Case Series of Uterine Sarcomas Harboring Kinase-related Fusions With Report of a Novel FGFR1-TACC1 Fusion. 35307914_LINC01140 inhibits nonsmall cell lung cancer progression and cisplatin resistance through the miR-4742-5p/TACC1 axis. | ENSMUSG00000065954 | Tacc1 | 3691.932365 | 1.1284069 | 0.174287443 | 0.04485753 | 15.08955242802 | 0.0001025291677893075474288855919446916686865733936429023742675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00105376781707335336231434741449675129842944443225860595703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 3888.775937 | 126.626346 | 3462.430907 | 113.067248 | |
| ENSG00000147813 | 93100 | NAPRT | protein_coding | Q6XQN6 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the first step in the biosynthesis of NAD from nicotinic acid, the ATP-dependent synthesis of beta-nicotinate D-ribonucleotide from nicotinate and 5-phospho-D-ribose 1-phosphate (PubMed:17604275, PubMed:21742010, PubMed:26042198). Helps prevent cellular oxidative stress via its role in NAD biosynthesis (PubMed:17604275). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17604275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21742010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26042198}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Ligase;Magnesium;Manganese;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Pyridine nucleotide biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Transferase | PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; NAD(+) biosynthesis; nicotinate D-ribonucleotide from nicotinate: step 1/1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17604275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21742010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26042198}. | Nicotinic acid (NA; niacin) is converted by nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase (NAPRT; EC 2.4.2.11) to NA mononucleotide (NaMN), which is then converted to NA adenine dinucleotide (NaAD), and finally to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), which serves as a coenzyme in cellular redox reactions and is an essential component of a variety of processes in cellular metabolism including response to stress (Hara et al., 2007).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:93100; | azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase activity [GO:0004516]; transferase activity [GO:0016740]; NAD salvage [GO:0034355]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979] | 17604275_NA elevates cellular NAD levels through NAPRT function and, thus, protects the cells against stress, partly due to lack of feedback inhibition of NAPRT but not NamPRT by NAD 21492230_NAPRT expression was varied in lymphomas with 30-50% low expression except for Hodgkin's lymphoma where 85% displayed low expression 22570471_Inhibition of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) activity by small molecule GMX1778 regulates reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated cytotoxicity in a p53- and nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase1 (NAPRT1)-dependent manner 24097869_Tumor-specific promoter hypermethylation of NAPRT1 inactivates one of two NAD salvage pathways, resulting in synthetic lethality with the coadministration of a NAMPT inhibitor. 26675378_High NAPRTase expression is associated with neoplasms. 28416276_Synthesis and Degradation of Adenosine 5'-Tetraphosphate by Nicotinamide and Nicotinate Phosphoribosyltransferases 28860121_No correlation between IDH1/2 mutation status and sensitivity for NAMPT inhibitors was observed. Strikingly, higher methylation of the NAPRT promoter was observed in high-grade versus low-grade chondrosarcomas. In conclusion, this study identified NAMPT as a potential target for treatment of chondrosarcoma 31268507_Association of Schizophrenia Risk With Disordered Niacin Metabolism in an Indian Genome-wide Association Study. 31439867_Study demonstrated that PPM1D mutant astrocytes and patient-derived PPM1D mutant diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma lines are particularly sensitive to treatment with NAMPT inhibitors. Mutant PPM1D-induced NAMPT inhibitor sensitivity is driven by hypermethylation of CpG islands throughout the genome and the epigenetic silencing of NAPRT, a key gene involved in NAD biosynthesis. 31511522_these data identify NAPRT as a endogenous ligand for TLR4 and a mediator of inflammation. 34946971_NAPRT Expression Regulation Mechanisms: Novel Functions Predicted by a Bioinformatics Approach. 36432602_NAPRT, but Not NAMPT, Provides Additional Support for NAD Synthesis in Esophageal Precancerous Lesions. | ENSMUSG00000022574 | Naprt | 495.873714 | 1.1197622 | 0.163192342 | 0.08620817 | 3.58202520151 | 0.0584079039781491907157295884189807111397385597229003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.18289898384740338466158959818130824714899063110351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 511.285469 | 26.323100 | 458.657165 | 23.918837 |
| ENSG00000149269 | 5058 | PAK1 | protein_coding | Q13153 | FUNCTION: Protein kinase involved in intracellular signaling pathways downstream of integrins and receptor-type kinases that plays an important role in cytoskeleton dynamics, in cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, apoptosis, mitosis, and in vesicle-mediated transport processes (PubMed:11896197, PubMed:30290153). Can directly phosphorylate BAD and protects cells against apoptosis. Activated by interaction with CDC42 and RAC1. Functions as GTPase effector that links the Rho-related GTPases CDC42 and RAC1 to the JNK MAP kinase pathway. Phosphorylates and activates MAP2K1, and thereby mediates activation of downstream MAP kinases. Involved in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, actin stress fibers and of focal adhesion complexes. Phosphorylates the tubulin chaperone TBCB and thereby plays a role in the regulation of microtubule biogenesis and organization of the tubulin cytoskeleton. Plays a role in the regulation of insulin secretion in response to elevated glucose levels. Part of a ternary complex that contains PAK1, DVL1 and MUSK that is important for MUSK-dependent regulation of AChR clustering during the formation of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). Activity is inhibited in cells undergoing apoptosis, potentially due to binding of CDC2L1 and CDC2L2. Phosphorylates MYL9/MLC2. Phosphorylates RAF1 at 'Ser-338' and 'Ser-339' resulting in: activation of RAF1, stimulation of RAF1 translocation to mitochondria, phosphorylation of BAD by RAF1, and RAF1 binding to BCL2. Phosphorylates SNAI1 at 'Ser-246' promoting its transcriptional repressor activity by increasing its accumulation in the nucleus. In podocytes, promotes NR3C2 nuclear localization. Required for atypical chemokine receptor ACKR2-induced phosphorylation of LIMK1 and cofilin (CFL1) and for the up-regulation of ACKR2 from endosomal compartment to cell membrane, increasing its efficiency in chemokine uptake and degradation. In synapses, seems to mediate the regulation of F-actin cluster formation performed by SHANK3, maybe through CFL1 phosphorylation and inactivation. Plays a role in RUFY3-mediated facilitating gastric cancer cells migration and invasion (PubMed:25766321). In response to DNA damage, phosphorylates MORC2 which activates its ATPase activity and facilitates chromatin remodeling (PubMed:23260667). In neurons, plays a crucial role in regulating GABA(A) receptor synaptic stability and hence GABAergic inhibitory synaptic transmission through its role in F-actin stabilization (By similarity). In hippocampal neurons, necessary for the formation of dendritic spines and excitatory synapses; this function is dependent on kinase activity and may be exerted by the regulation of actomyosin contractility through the phosphorylation of myosin II regulatory light chain (MLC) (By similarity). Along with GIT1, positively regulates microtubule nucleation during interphase (PubMed:27012601). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O88643, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P35465, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10551809, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11733498, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11896197, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12624090, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12876277, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14585966, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15611088, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15831477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15833848, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17726028, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17989089, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22669945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23260667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23633677, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25766321, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27012601, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30290153, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8805275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9032240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9395435, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9528787}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Allosteric enzyme;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;ATP-binding;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Chromosome;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Exocytosis;Intellectual disability;Kinase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase | This gene encodes a family member of serine/threonine p21-activating kinases, known as PAK proteins. These proteins are critical effectors that link RhoGTPases to cytoskeleton reorganization and nuclear signaling, and they serve as targets for the small GTP binding proteins Cdc42 and Rac. This specific family member regulates cell motility and morphology. Mutations in this gene have been associated with macrocephaly, seizures, and speech delay. Overexpression of this gene is also reported in many cancer types, and particularly in breast cancer. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. | hsa:5058; | actin filament [GO:0005884]; axon [GO:0030424]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; chromosome [GO:0005694]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; intercalated disc [GO:0014704]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; gamma-tubulin binding [GO:0043015]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; molecular function inhibitor activity [GO:0140678]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube [GO:0048754]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; ephrin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048013]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway involved in phagocytosis [GO:0038096]; hepatocyte growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048012]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; localization [GO:0051179]; negative regulation of cell proliferation involved in contact inhibition [GO:0060244]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0033148]; positive regulation of JUN kinase activity [GO:0043507]; positive regulation of microtubule nucleation [GO:0090063]; positive regulation of microtubule polymerization [GO:0031116]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of axonogenesis [GO:0050770]; regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043408]; stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002223]; wound healing [GO:0042060] | 11804587_Pak1 forms homodimers in vivo and its dimerization is regulated by the intracellular level of GTP-Cdc42 or GTP-Rac1 11948406_PAK1 primes MEK1 for phosphorylation by Raf-1 kinase during cross-cascade activation of the ERK pathway. 12011045_binding of the Rho family member Cdc42 to PLD1 and the subsequent stimulation of its enzymatic activity are distinct events 12151336_Pak1 interacts with and phosphorylates histone H3 and may thus influence the Pak1-histone H3 pathway, which in turn may influence mitotic events in breast cancer cells 12198493_FLNa may be essential for Pak1-induced cytoskeletal reorganization 12453877_Cdc42/Rac1-dependent activation of PAK may trigger early platelet shape change, at least in part through the regulation of cortactin binding to PAK. 12522133_p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) interacts with the Grb2 adapter protein to couple to growth factor signaling 12531429_phorbol ester induced cell migration is accompanied by selective and transient down-regulation of PAK1, which coincided with the formation of stress fibres. 12551923_role in phosphorylating Raf-1 regulates Raf-1 autoinhibition 12560069_results identify a novel signaling pathway linking estrogen action to Pak1 signaling, and Pak1 to FKHR, suggesting that Pak1 is an important mediator of estrogen's cell survival functions 12887916_Activated Cdc42 at the leading edge of a neutrophil in culture helps orient the cell's axis in a signaling complex with G beta gamma, PAK1, and PIXalpha. 12887923_G beta gamma binds PAK1 and, via PAK-associated PIX alpha, activates Cdc42 which, in turn, activates PAK1. In this pathway, PAK1 is not only an effector for Cdc42, but it also functions as a scaffold protein required for Cdc42 activation. 12912914_PAK1 regulates contact inhibition during epithelial wound healing. 12937139_PAK1 copy number gains were observed in 30% of ovarian carcinomas and PAK1 protein was expressed in 85% of tumors. PAK1 gains were associated with high grade. 14530270_Pak1 regulation of cyclin D1 expression might involve an NF-kappaB-dependent pathway; Pak1 is up-regulated in breast tumors 14607331_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14694110_Tat induces actin cytoskeletal rearrangements through PAK1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells 14749719_Phosphorylation of p41-ARC protein by p21-activated kinase 1. 15047871_PAK2 is constitutively activated in certain breast cancer cell lines and that this active PAK is mislocalized to atypical focal adhesions in the absence of high levels of activated Rho GTPases. 15059930_Src- & ROS-dependent PDK1 activation leads to site-specific PAK1 phosphorylation. This is critically important for PDGF-induced VSMC migration, a process integral to the vascular response to injury that leads to vessel occlusion & plaque formation. 15161701_Pak-1 has a role in human colorectal tumor invasiveness and motility 15225553_These results support a role for Pak1-mediated RhoGDI phosphorylation as a mechanism for Cdc42-mediated Rac activation, and suggest the possibility of Rac-induced positive feed-forward regulation of Rac activity. 15333633_PAK is a central regulator of endothelial permeability induced by multiple growth factors and cytokines via an effect on cell contractility 15378030_cell signaling kinase Pak1 is a novel regulator of glucose metabolism through its phosphorylation and regulation of PGM activity. 15561713_NF-kappaB- and C/EBPbeta-driven interleukin-1beta gene expression and PAK1-mediated caspase-1 activation play essential roles in interleukin-1beta release from Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages 15611088_epithelial cell motility is modulated by integrin engagment through RhoA/ROCK and PAK1 15684429_PAK1 negatively regulates the activity of NET1 15749698_These findings define the nuclear localization signals (NLSs) of Pak1, its association with chromatin, and the resulting modulation of transcription, thus opening new avenues to further the search for nuclear Pak1 functions. 15824732_Pak1-SHARP interaction plays an essential role in enhancing the corepressor functions of SHARP, thereby modulating Notch1 signaling in human cancer cells. 15831477_PAK1 phosphorylation of tubulin cofactor B (TCoB)is essential for the polymerization of new microtubules. 15833848_The regulation of phosphorylation and function of Snail by Pak1 represents a novel mechanism by which a signaling kinase might contribute to the process of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 15849194_Pak1-dependent Raf-1 phosphorylation regulates its mitochondrial localization, phosphorylation of BAD, and Bcl-2 association 15864311_PAK1 recruitment to the T cell-antigen-presenting cell interface required interaction with PIX. 15893667_1.8 A resolution structure for the free PAK1 kinase domain was determined. 16002401_Data suggest that nischarin, in addition to regulating the p21-activated kinase (PAK) strand of Rac1 signaling, can also regulate other links in the web of Rac1 signaling pathways. 16026643_p21-activated kinase 1 has a role in the suppression of anoikis in breast cancer cells 16407834_the SH3 domain of betaPix specifically interacts with a proline-arginine motif (PxxxPR) present within the ubiquitin ligase Cbl and Pak1 kinase. Cbl and Pak1 compete for binding to betaPix. 16449192_Results show that PAK1 cooperate with different Rho effectors to regulate matrix contraction. 16490785_PI3K through p21-activated kinase 1 regulates FRA-1 proto-oncogene induction by cigarette smoke and the subsequent activation of the Elk1 and cAMP-response element-binding protein transcription factors 16611744_Myosin II-B resides in a complex with p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) and atypical protein kinase C (PKC) zeta (aPKCzeta) and the interaction between these proteins is EGF-dependent. 16705121_Our data support a role for Pak1, particular Pak1 localized to the nucleus, in ERalpha signaling and in tamoxifen resistance. 16800003_Phosphorylation of caldesmon by PAK is a dynamic process required to regulate actin dynamics and membrane protrusions in wound-induced cell migration. 16845324_Increased p21-activated kinase-1 expression is associated with invasive potential in uveal melanoma 17012749_Akt1 and Akt2 have opposing roles in Rac/Pak signaling and cell migration 17018616_TGF-ss, via PI3K, recruits the actin cytoskeleton to HER2, which colocalizes with Vav2, activated Rac1, & its effector Pak1 at lamellipodia, leading to prolonged Rac1 activation, enhanced cell motility & survival. Dominant-negative Pak1 abrogates this. 17255101_p70 S6 kinase activates PAK1 and contributes to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase- and ERK-mediated regulation of HCV RNA replication 17355222_Results demonstrate a novel mechanism of signal termination mediated by the Rho-family GTPases Chp and Cdc42, which results in ubiquitin-mediated degradation of one of their direct effectors, Pak1. 17420447_PAK1 is a physiological upstream kinase for integrin-linked kinase (ILK); PAK1 depletion dramatically increases the nuclear and focal point accumulation of ILK. 17486065_Amplification of PAK1 is associated with recurrence and tamoxifen resistance in postmenopausal breast cancer 17491012_ESE-1 functions are coordinately regulated by Pak1 phosphorylation and beta-TrCP-dependent ubiquitin-proteasome pathways. 17609315_we present a model for Pak1 signaling that provides a mechanism for specifically affecting cardiac cellular processes--REVIEW 17621631_point to Pak1 as an exciting target for therapy of renal cancer, which remains highly refractory to existing treatments 17911169_study reports that elevated (alpha6)beta4 integrin-dependent Rac-Pak1 signaling supports resistance to apoptosis in mammary acini by permitting stress-dependent activation of the p65 subunit of NF-kappaB through Pak1 17981134_Rac1/Pak1/LIMK1 signaling pathway controls cofilin activity within the lamellipodium. 18006851_16k PRL inhibits cell migration by blocking the Ras-Tiam1-Rac1-Pak1 signaling pathway in endothelial cells 18065495_Pak1 overexpression enhanced htt toxicity in cell models and neurons in parallel with its ability to promote aggregation, while Pak1 knockdown suppressed both aggregation and toxicity 18160398_a VAV1-Rac1-PAK1 signaling axis in mononuclear phagocytes regulating superoxide production in a stimulus-dependent manner. 18314909_In an ovarian carcinoma cohort, RSF1 was amplified in 15% of the cases. It was correlated with serous histology. The 11q13 amplicon in ovarian cancer is likely driven by a cassette of genes rather than by a single oncogene. 18319303_The data indicate that PAK1 is at the interface between junction destabilization and increased motility during morphogenetic events. 18344974_Clathrin-independent endocytosis used by the IL-2 receptor is regulated by Rac1, Pak1 and Pak2. 18347024_p21-activated kinase-aberrant activation and translocation may have a role in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis 18354494_These results provide an insight into the molecular mechanisms of CtBP1/BARS activation in membrane fissioning, and extend the relevance of CtBP1/BARS-induced fission to human viral infection. 18392133_Overexpression of p21-activated kinase 1 may be a key coordinator of aberrant cell survival and proteolysis in breast cancer progression. 18411304_Pak1 and Pak2 mediate tumor cell invasion through distinct signaling mechanisms 18448666_alpha2beta1 integrin clustering defines its own entry pathway that is Pak1 dependent but clathrin and caveolin independent and that is able to sort cargo to caveosomes 18586681_1) PAK plays a required role in hyperosmotic signaling through the PI3K/pTEN/Cdc42/PP2Calpha/p38 pathway, and 2) PAK and PP2Calpha modulate the effects of this pathway on focal adhesion dynamics. 18656238_In Cox analysis, higher p21-activated kinase-1 staining extent independently correlated with longer progression-free survival (P = .016) and shorter overall survival (.049) in primary diagnosis and disease recurrence effusions. 18676874_PAK1-specific paxillin phosphorylation at Ser(273) is critically involved in positive-feedback regulation. 18787380_Data examine possible allelic imbalance in papillary thyroid cancer at EMSY, CAPN5, and PAK1, as candidate genes within 11q13.5-q14 region using a single nucleotide polymorphism-based analysis. 18922890_Pak1 is a target of miR-7 and that HoxD10 plays a regulatory role in modifying the expression of miR-7. 18923061_Expression of active p21-activated kinase-1 induces Ca2+ flux modification with altered regulatory protein phosphorylation in cardiac myocytes. 19136554_TH1 interacts with PAK1 and specifically restricts the activation of MAPK modules through the upstream region of the MAPK pathway, thereby influencing cell migration. 19162178_Pak1 protein plays a critical role in Hepatocyte Growth Factor-induced WASF2 protein transport and lamellipodia formation by directing Pak1 protein-WASF2 protein-kinesin complex. 19165420_Pak protein kinases have a role in cancer [review] 19296259_Overexpression of PAK1 protein is closely associated with the malignant histological and invasive phenotype of colorectal carcinoma. 19298660_We identified a novel mechanism for MMP-9 expression in response to injury signals, which is mediated by PAK1 activation 19520772_study identified p21 activated kinase 1 (PAK1) as a new CDK11(p58) substrate; mapped a new phosphorylation site of Ser174 on PAK1; results indicated PAK1 may serve as a downstream effector of CDK11(p58) during mitosis progression 19557173_LC8 facilitates nuclear import of Pak1 and this function is indispensable during vertebrate development 19574218_a model for the complex and accurate regulation of PAK1 kinase in vivo at cell protrusions. 19610058_Overexpression of Pak1 was associated with progression, metastasis and prognosis of gastric cancer. 19628037_Knockdown of PAK1 inhibits Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) stimulated migration and loss of cell-cell junctions in DU145 prostate carcinoma cells. In PC3 prostate carcinoma cells, knockdown of PAK1 reduces HGF-stimulated migration. 19747561_Basic properties of group I Paks are summarized discuss recently uncovered roles for these kinases in immune function and in viral infection are discussed. 19819966_Data identify a novel signaling pathway in the endocrine L cell, whereby Cdc42 regulates actin remodeling, activation of the cannonical 1/2-ERK1/2 pathway and PAK1, and GLP-1 secretion in response to insulin. 20001745_PAK-1 and its activator Rac1 are novel HIF-1 targets that may constitute a positive-feedback loop for induction of HIF-1alpha by thrombin and ROS, thus explaining elevated levels of PAK-1, Rac1, and HIF-1alpha in remodeled pulmonary vessels. 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20079895_A possible role of Pak1 in the establishment of adenomyosis. 20083228_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20131316_Our studies suggest that Rac1 --> Pak1/Pak2 --> NFkappaB is a separate pathway that contributes to the expression of COX-2 in HPV-induced papillomas, independently of the previously described Rac1 --> p38 --> COX-2 pathway. 20179234_Our results suggest that patients with tumors expressing Pak1 and pERalpha(ser305) in combination are a group in which tamoxifen treatment is insufficient 20213082_PKA-induced phosphorylation of ERalpha at serine 305 and high PAK1 levels is associated with sensitivity to tamoxifen in ER-positive breast cancer. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20400510_PAK1 is a direct downstream target of LKB1 and plays an essential role in LKB1-induced suppression of cell migration 20413688_Data reveal the involvement of p21-Activated kinase 1 in the pathogenesis and clinical progress of gestational trophoblastic disease. 20417602_A functional requirement for PAK1 binding to the KH(2) domain of the fragile X protein- related FXR1 is reported. 20426825_Suggest that Rac1 activity and Pak1 are involved in lymphovascular invasion and lymph node metastasis of urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract , and may be prognostic markers for this disease. 20457839_Pak1-induced branching morphogenesis in 3D MDCK cell culture requires PIX binding and beta1-integrin signaling. 20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20523167_Rac1/Cdc42/PAK pathway controls actin reorganization that is necessary for microvesicle shedding 20526801_Rac1/Pak1 signaling is critical to MB cell migration and is functionally dependent on PDGFRbeta/ERK activity 20591216_Expression of PAK1 is an early molecular event in the tumorigenesis of gastric carcinoma. It is also closely correlated the development of gastric carcinoma and the patients' prognosis. 20595063_P21-activated kinase 1 stimulates colon cancer cell growth and migration/invasion via ERK- and AKT-dependent pathways. 20729389_Data show that the protective effects of atrial natriuretic peptide against lipopolysaccharide-induced vascular leak are mediated at least in part by PAK1-dependent signaling leading to endothelial cell barrier enhancement. 20811717_Results suggest that activated Pak1 regulates colorectal cancer metastasis requiring an ERK-dependent phosphorylation of FAK at Ser-910. 21070974_These findings expand the role of phosphoinositides in kinase signaling and suggest how altered phosphoinositide metabolism may upregulate Pak1 activity in cancer cells. 21209852_the PI3K/PAK1/ERK signaling pathway has a role in LPA-stimulated breast cancer cell migration 21310649_The importance of PIK3K/PAK in neoplasm transformation and progression, their disregulation detected in oral squamous cell carcer may provide early diagnosis and aid in the design of new therapies. 21653999_Contribution of the PAK family member, PAK1, in growth factor signaling and tumorigenesis. 21719533_Adapter protein Nck sequesters PAK1 in the cytoplasm and that coexpression of both PAK1 and Nck inhibits the amplifying effect of PRL-induced PAK1 on cyclin D1 promoter activity. 21722895_Interleukin-1beta up-regulates Pak1 expression in endometrial stromal cells and Pak1 immunoreactivity is increased in endometriotic cysts. 21727092_increased activation of associated PAK1 can contribute to enhanced Cx43 dephosphorylation and impaired intercellular coupling that may underlie slow conduction in heart failure 21748785_results suggest that CIB1 positively regulates cell migration and is necessary for the recruitment of FAK to the focal adhesions. Furthermore, CIB1-induced cell migration is dependent on MAP kinase signaling and its function is attenuated by PAK1 21822311_a Rac1/PAK1 cascade controls beta-catenin S675 phosphorylation and full activation in colon cancer cells 21969371_Inhibition or ablation of p21-activated kinase (PAK1) disrupts glucose homeostatic mechanisms in vivo. 21982772_These results provide evidence for the importance of PAK1 activation during influenza virus infection and its association with ERK in regulating virus replication. 22096607_Findings demonstrate that Pak1 phosphorylates BAD directly at S111, but phosphorylated S112 through Raf-1. 22100495_In colorectal neoplasms p-21 activated kinase 1 knockdown inhibits beta-catenin signalling and blocks cell proliferation and migration. 22105346_A Rac-PAK1-Ajuba feedback loop integrates spatiotemporal signaling with actin remodeling at cell-cell contacts and stabilizes preassembled cadherin complexes. 22105362_PAK1 as a breast cancer oncogene that coordinately regulates multiple signaling pathways 22130069_Smad4 suppresses the PAK1, which promotes the PUMA destabilization 22153498_crystal structures of the phosphorylated and unphosphorylated PAK1 kinase domain. 22252525_Data suggest that targeting P21-activated protein kinase1 (PAK1) may represent a novel treatment strategy for developing novel chemotherapeutic agents. 22293972_Pak1 is overexpressed in gastric cancer and plays an important role in the metastasis of gastric cancer. The mechanism by which Pak1 induces cancer metastasis may involve activation of ERK and JNK. 22369945_these results provide evidence that PAK1 specifically phosphorylates beta-catenin at S663 and that this phosphorylation is essential for the PAK1-mediated transcriptional activation of beta-catenin. 22416254_PAK1 plays an important role in regulating the migration, invasion and production and activity of MMPs in RA FLS, which is mediated by the JNK pathway. 22458949_In both anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), study found a reduction of Duo expression and PAK1 phosphorylation in schizophrenia. Cdc42 protein expression was decreased in ACC but not in DLPFC 22493453_results show that a STRADalpha-rac1-PAK1 pathway regulates cell polarity and invasion in LKB1-null cells. It also suggests that while the function of LKB1 and STRADalpha undoubtedly overlap, they may also have mutually exclusive roles 22845716_PI3K, Rac1 and PAK1 may play important roles in the pathogenesis of EMPD. 22848689_the role of PAK1 in the promotion of cell motility, cell invasiveness and the down regulation of p120-catenin through CRK serine 41 phosphorylation in NSCLC cells 22983922_Results show a strong positive correlation between advanced stage and grade and PAK1 expression in skin cnacer. 23017497_Phosphoproteome analyses reveal specific implications of Hcls1, p21-activated kinase 1 and Ezrin in proliferation of a myeloid progenitor cell line downstream of wild-type and ITD mutant Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 receptors. 23019370_Pak-1 interacts with Wnt signaling to regulate tissue polarity and gene expression. 23038262_PAK1 negatively regulates the expression of TFPI and additionally contributes to increased TF activity. 23055517_PAK1 phosphorylates MCAK and regulates both its localization and function. 23233484_Results support a role for the PAK4 and PAK1 in the proliferation of mutant KRAS-driven colorectal carcinoma cells via pathways not involving RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling. 23246867_data suggest that glucose-mediated activation of Cdc42 leads to activation of PAK1 and prompts activation of its downstream targets Raf-1, MEK1/2 and ERK1/2 to elicit F-actin remodeling and recruitment of insulin granules to the plasma membrane 23258534_Gene array data revealed reduced expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 with the ablation of either Pak1 or Pak6 gene expression in PC3 cells. 23298303_Positive rates of Rac1, Pak1 and Rock1 expression in normal tissue, dysplasia and gastric carcinoma show an increasing trend and are correlated with tumor lymph node metastasis and TNM stage. 23300274_High expression of the PAK1 gene was significantly associated with resistance to all three PI3K inhibitors in lymphomas. 23321640_Data suggest that regulation of PAK-PIX interactions controls neurite outgrowth by influencing the activity of several important mediators of actin filament polymerization and retrograde flow, as well as integrin-dependent adhesion to laminin. 23333386_these findings demonstrate that miR-221 affects the MEK/ERK pathway by targeting PAK1 to inhibit the proliferation ofendothelial progenitor cells. 23338047_These results suggest that Pak1 plays important roles at multiple stages of EC progression. 23340249_PAK1 phosphorylates serine (Ser) 2152 of the actin-binding protein filamin A to a greater extent when PAK1 is tyrosyl phosphorylated by JAK2. 23393142_analysis of synergistic activation of p21-activated kinase 1 by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and Rho GTPases 23499762_Cytokine-induced migration correlated with phosphorylation of PAK1 in primary myeloma cells & cell lines. Downregulation of PAK1 with siRNA in INA-6 cells resulted in decreased cytokine-driven migration. 23516476_Klotho endows hepatoma cells with resistance to anoikis via VEGFR2/PAK1 activation in hepatocellular carcinoma. 23535073_Taken together, our results provide evidence for a functional role of PAK1 in BRAF wild-type melanoma and therapeutic use of PAK inhibitors in this indication. 23576562_Data indicate a signaling pathway from ErbB2 to p21-Activated kinase-1 (Pak1) to beta-catenin that is required for efficient transformation of mammary epithelial cells. 23613712_no significant change in PAK1 level detected in the schizophrenia subjects 23622267_Group I p21-activated kinases augment Tax-mediated transcriptional activation of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeats in a kinase-independent manner. 23653349_PAK1 can stimulate MEK activity in a kinase-independent manner, probably by serving as a scaffold to facilitate interaction of C-RAF. 23737530_Data indicate that depletion of NFATc1, cyclin D1, CDK6, or CDK4 levels attenuated MCP1-induced Pak1 phosphorylation/activation and resulted in decreased aortic smooth muscle cells (HASMCs) F-actin stress fiber formation, migration, and proliferation. 23744893_These data illustrate the complex interaction between the substratum and PRL/PAK1 signaling in human breast cancer cells and suggest a pivotal role for PRL-dependent PAK1 tyrosyl phosphorylation in MMP secretion. 23811286_PAK1 stimulates colorectal cancer cell survival by up-regulation of HIF-1alpha. 23811795_The results identified Mgat5-mediated beta-1-6-GlcNAc branched N-glycosylation and following activation of EGFR as a potential novel upstream molecular event for PAK1-induced anoikis resistance in hepatoma cells. 23885116_These findings identify CK2 as an upstream activating kinase of PAK1, providing a novel mechanism for PAK1 activation. 24236193_PAK1 is overexpressed during tumorigenic progression and its upregulation correlates with malignant properties mainly relevant to invasion and metastasis. 24347489_blocking PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by LY294002 or Akt siRNA could remarkably inhibit the PAK1 activation and cell invasion 24561527_identified fibronectin, a component of the extracellular matrix and a mesenchymal marker, as a transcriptional target of Pak1 signaling 24634274_PAK1 is associated with the aggressive tumor behavior and poor prognosis of head and neck cancer. 24811999_Review of the role of PAK1 in gastrointestinal inflammation and progression to cancer. 24859002_Describe here an invadopodia disassembly model, where a signalling axis involving TrioGEF, Rac1, Pak1, and phosphorylation of cortactin, causes invadopodia dissolution. 24935174_Amplified PAK1, as well as KRAS amplification/mutation, may represent unique opportunities for developing targeted therapeutics for the treatment of gastric cancer. 24954107_Data indicate that p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) is a target of miR-145. 25019394_PAK1 and Snail1 are involved in the formation of estrogen-independent phenotype of breast cancer cells showing the potential role of both proteins as markers of hormone resistance of breast tumors. 25074413_results provide evidence for a functional role of MET/PAK1 signalling in pancreatic adenocarcinoma 25125660_findings offered evidence that JAK2 phosphorylates and stabilizes functions of PAK1 that promote EMT and radioresistance in lung cancer cells 25159681_high PAK1 expression in PTs is predictive of node metastasis and can be easily integrated in the clinical decision process for personalized therapeutics of GEJA. 25182632_PAK1 is a novel prognostic marker for pathologically confirmed human pancreatic cancer. Reduced expression of PAK1 correlates with poor histological differentiation in pancreatic cancer. 25215948_PAK1 is an essential controller of inflammatory macrophage polarization, regulating immune responses against pathogenic stimuli. 25228413_Increased p21-activated kinase is associated with invasive papillary thyroid cancers. 25388666_Provide first evidence for existence of a previously unknown Erk5/KLF2/PAK1 axis, which may limit undesired cell migration in unperturbed endothelium and lower its sensitivity for migratory cues that promote vascular diseases including atherosclerosis. 25412958_we demonstrated that the overexpression of PAK1 is closely associated with the clinicopathological features of BC, suggesting that PAK1 may play an important role in the development and progression of Bladder cancer 25415869_Studies indicate a p21-activated kinase PAK1 inhibitor series were discovered. 25416031_PAK1 role in cardiac physiology such as egulation of cardiac excitability and contractility has been identified. 25447917_miR-221-3p has an effect on PAK1 gene expressions in breast cancer cell lines 25456130_These results reveal a leukemic pathway involving FAK/Tiam1/Rac1/PAK1 and demonstrate an essential role for these signaling molecules in regulating the nuclear translocation of Stat5 in leukemogenesis. 25466889_High Phosphorylation of tyrosine 285 of PAK1 protein is associated with breast cancer. 25472536_A pivotal role for PRL/PAK1 signaling in breast cancer metastasis.[review] 25569743_Overexpression of PAK1 promotes cell survival in inflammatory bowel diseases and colitis-associated cancer. 25596744_Data show that group I p21-activated kinases (Paks) Pak1 and Pak2 were much more abundant than Pak3 in meningioma. 25675297_results unraveled that oncogenic activation of PAK1 defines an important mechanism for maintaining stem-like phenotype and sunitinib resistance through NF-kappaB/IL-6 activation in RCC. 25746720_TGFbeta1 induces apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells via activation of P38-MAPK and Rac1/Pak1 respectively. 25766321_these findings provide important evidence that PAK1 can positively regulate RUFY3 expression, which contribute to the metastatic potential of gastric cancer cells 25791829_PAK1 and PAK4 expression were associated with colorectal cancer metastasis and infiltration 25888627_PAK1-mediated MORC2 phosphorylation promotes gastric tumorigenesis 25956913_Studied the role of PAK1/Crk axis in transduction of the oncogenic KRAS signal in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). 25981171_This study showed that PAK1 messenger RNA levels were significantly downregulated specifically in deep layer 3 pyramidal cells in patient with schizophrenia. 26004135_Rich1 negatively regulates the epithelial cell cycle, proliferation and adhesion by CDC42/RAC1-PAK1-Erk1/2 pathway. 26023713_Study indicates that PAK1 is important in metastasis and progression of primary esophageal small cell carcinoma. The contribution of PAK1 to clinical outcomes may be involved in regulating DNA damage pathway. 26036343_PAK1 overexpression and activation in inflammation and colitis-associated cancer promote NF-kappaB activity via suppression of PPARgamma in intestinal epithelial cells. 26078008_Pak1 and Pak2 counteract centrosome separation in a kinase-dependent manner. 26104863_Pak1 is an important factor in the initiation and progression of atherogenesis. 26160174_There is a major role of the CK2alpha-interacting protein CKIP-1 in activation of PAK1 for neoplastic prostate cells transformation. 26218748_Pak1 promote endometrial cancer cell proliferation. 26255026_Cx43 increases serum induced filopodia formation via activation of p21-activated protein kinase 1. 26257058_These findings suggest that small-molecule inhibitors of Pak1 may have a therapeutic role in the ~25% of ovarian cancers characterized by PAK1 gene amplification. 26324182_p120 participates in the progress of gastric cancer through regulating Rac1 and Pak1. 26377044_These findings indicate that genetic variants in PAK1 gene may contribute to susceptibility to lung cancer in the Chinese population. 26379399_beta-elemene enhances radiosensitivity of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting Pak1 signaling. 26423403_overexpression of PAK1, NEK6, AURKA, and AURKB genes in patients with Colorectal adenomatous polyp and colorectal cancer in the Turkish population. 26547035_Data indicate that NOTCH1 receptor intracellular domain (NOTCH1-IC) physically interacts with serine-threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 (PAK1) in intact cells. 26774265_Combination of a PAK1 inhibitor such as FRAX597 with cytotoxic chemotherapy deserves further study as a novel therapeutic approach to pancreatic cancer treatment. 26809475_Formation of filopodia by membrane glycoprotein M6a (Gpm6a) requires actin regulator coronin-1a (Coro1a), known to regulate plasma membrane localization and activation of Rac1 and its downstream effector Pak1. 26884861_PAK-1 overexpression may be involved in colorectal carcinoma progression and could be considered an independent predictor of disease recurrence. 26898755_Our results from clinical samples also suggest that Threonine 209 phosphorylation by Pak1 could be a potential therapeutic target and of great clinical relevance with implications for Runx3 inactivation in cancer cells where Runx3 is known to be oncogenic. The findings presented in this study provide evidence of Runx3-Threonine 209 phosphorylation as a molecular switch in dictating the tissue-specific dualistic functions 26918678_PAK1-cofilin phosphorylation mechanism to mediate lung adenocarcinoma cells migration promoted by apelin-13 26944939_these data strongly support a critical interplay between prolactin and estrogen via PAK1 and suggest that ligand-independent activation of ERalpha through prolactin/PAK1 may impart resistance to anti-estrogen therapies. 27003261_PAK1 nuclear translocation is ligand-dependent: only PRL but not E2 stimulated PAK1 nuclear translocation 27012601_Data show association of G protein-coupled receptor kinase-interacting protein 1 (GIT1), p21-activated kinase interacting exchange factor (betaPIX), and p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) with centrosomes. 27027431_Studies indicate that PAK1 expression may be a predictive marker of overall survival and disease-specific survival in patients with solid tumors. 27044328_VEGF-induced angiogenesis and vascular permeability are inhibited by BET bromodomain suppression through blocking of VEGFR2-mediated activation of PAK1 and eNOS 27056567_Pak1 expression is not associated with breast cancer recurrence and resistance to tamoxifen. 27060895_High p21-activated kinase 1 and cell division control protein 42 homolog expressions are closely related to the clinicopathological features and poor prognosis of cervical carcinoma, serving as unfavorable prognostic factors. 27117533_To our knowledge, this is the first study illustrating the mechanistic role of Pak1 in causing gemcitabine resistance via multiple signaling crosstalks, and hence Pak1-specific inhibitors will prove to be a bet | ENSMUSG00000030774 | Pak1 | 538.513773 | 0.7370654 | -0.440135442 | 0.12402520 | 12.55555892201 | 0.0003950294292951032925666210449122672798694111406803131103515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00341935127288360432920577558491004310781136155128479003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 442.944471 | 39.870851 | 603.597877 | 53.774196 | |
| ENSG00000149541 | 26229 | B3GAT3 | protein_coding | O94766 | FUNCTION: Glycosaminoglycans biosynthesis (PubMed:25893793). Involved in forming the linkage tetrasaccharide present in heparan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate. Transfers a glucuronic acid moiety from the uridine diphosphate-glucuronic acid (UDP-GlcUA) to the common linkage region trisaccharide Gal-beta-1,3-Gal-beta-1,4-Xyl covalently bound to a Ser residue at the glycosaminylglycan attachment site of proteoglycans. Can also play a role in the biosynthesis of l2/HNK-1 carbohydrate epitope on glycoproteins. Shows strict specificity for Gal-beta-1,3-Gal-beta-1,4-Xyl, exhibiting negligible incorporation into other galactoside substrates including Galbeta1-3Gal beta1-O-benzyl, Galbeta1-4GlcNAc and Galbeta1-4Glc. Stimulates 2-phosphoxylose phosphatase activity of PXYLP1 in presence of uridine diphosphate-glucuronic acid (UDP-GlcUA) during completion of linkage region formation (PubMed:24425863). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24425863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25893793}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the glucuronyltransferase gene family, enzymes that exhibit strict acceptor specificity, recognizing nonreducing terminal sugars and their anomeric linkages. This gene product catalyzes the formation of the glycosaminoglycan-protein linkage by way of a glucuronyl transfer reaction in the final step of the biosynthesis of the linkage region of proteoglycans. A pseudogene of this gene has been identified on chromosome 3. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2013]. | hsa:26229; | cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; galactosylgalactosylxylosylprotein 3-beta-glucuronosyltransferase activity [GO:0015018]; glucuronosyltransferase activity [GO:0015020]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein phosphatase activator activity [GO:0072542]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0050650]; dermatan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0050651]; glycosaminoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0006024]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0015012]; positive regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0043085]; positive regulation of intracellular protein transport [GO:0090316]; protein glycosylation [GO:0006486] | 12794088_functional glycosyltransferase signature sequence of the human beta 1,3-glucuronosyltransferase is a XDD motif 15522873_we evaluated the consequences of C-4/C-6 sulfation of Galbeta1-3Gal (Gal2-Gal1) on the activity and specificity of beta1,3-glucuronosyltransferase I 15601778_GlcAT-I has a role in controlling and reversing articular cartilage defects 17567734_A comparison of substrate specificity of beta1,3-glucuronosyltransferases revealed that GlcAT-I was selective toward Galbeta1,3Gal, whereas GlcAT-P presented a broader profile. 18400750_2-o-phosphorylation of xylose and 6-o-sulfation of galactose in the protein linkage region of glycosaminoglycans influence the glucuronyltransferase-I activity involved in the linkage region synthesis 21763480_Reduced GlcAT-I activity impairs skeletal as well as heart development and results in variable combinations of heart malformations. 25893793_Since the phenotype of the Nias patients differs from the Larsen-like syndrome described for patients with mutation p.(Arg277Gln), we suggest mutation B3GAT3:p.(Pro140Leu) to cause a different type of GAG linkeropathy showing no involvement of the heart. 28771243_We identified a novel B3GAT3-related disorder with craniosynostosis and bone fragility, due to a unique homozygous mutation in B3GAT3. This syndrome should be considered in the prenatal period in light of the severe outcome and as an alternative diagnosis to Antley-Bixler or Shprintzen-Goldberg syndrome. 31988067_Pseudodiastrophic dysplasia expands the known phenotypic spectrum of defects in proteoglycan biosynthesis. | ENSMUSG00000071649 | B3gat3 | 441.099223 | 0.8876483 | -0.171939921 | 0.07464531 | 5.30902142758 | 0.0212152695758874403064719871281340601854026317596435546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.08785055974763573971575425503033329732716083526611328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 417.555374 | 19.928010 | 472.635244 | 21.894415 |
| ENSG00000150756 | 134145 | ATPSCKMT | protein_coding | Q6P4H8 | FUNCTION: Mitochondrial protein-lysine N-methyltransferase that trimethylates ATP synthase subunit C, ATP5MC1 and ATP5MC2. Trimethylation is required for proper incorporation of the C subunit into the ATP synthase complex and mitochondrial respiration (PubMed:29444090, PubMed:30530489). Promotes chronic pain (PubMed:29444090). Involved in persistent inflammatory and neuropathic pain: methyltransferase activity in the mitochondria of sensory neurons promotes chronic pain via a pathway that depends on the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and on the engagement of spinal cord microglia (PubMed:29444090). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29444090, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30530489}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Membrane;Methyltransferase;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Enables protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity. Involved in peptidyl-lysine trimethylation; positive regulation of sensory perception of pain; and regulation of proton transport. Located in mitochondrial crista. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:134145; | mitochondrial crista [GO:0030061]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0016279]; peptidyl-lysine methylation [GO:0018022]; peptidyl-lysine trimethylation [GO:0018023]; positive regulation of proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism [GO:1905273]; positive regulation of sensory perception of pain [GO:1904058]; regulation of mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled proton transport [GO:1905706] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21802380_Genetic alteration of JS-2 was found to be related to location, pathological subtypes and staging of colorectal cancer. 29444090_we uncover a role for methyltransferase activity of FAM173B in the neurobiology of pain. These results also highlight FAM173B methyltransferase activity as a potential therapeutic target to treat debilitating chronic pain conditions 30530489_It has been identified FAM173B as the long-sought KMT responsible for methylation of ATP synthase c-subunit (ATPSc), a key protein in cellular ATP production, and have demonstrated functional significance of ATPSc methylation. 33067627_Expression of mitochondrial TSPO and FAM173B is associated with inflammation and symptoms in patients with painful knee osteoarthritis. | ENSMUSG00000039065 | Atpsckmt | 102.401251 | 0.8112191 | -0.301836490 | 0.17979511 | 2.81238311206 | 0.0935393270338272520003641830044216476380825042724609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.25317881318675999890999150920833926647901535034179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 87.417929 | 12.789725 | 108.355125 | 15.824463 | |
| ENSG00000151348 | 2132 | EXT2 | protein_coding | Q93063 | FUNCTION: Glycosyltransferase required for the biosynthesis of heparan-sulfate. The EXT1/EXT2 complex possesses substantially higher glycosyltransferase activity than EXT1 or EXT2 alone. Appears to be a tumor suppressor. Required for the exosomal release of SDCBP, CD63 and syndecan (PubMed:22660413). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22660413}. | Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Epilepsy;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Hereditary multiple exostoses;Intellectual disability;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tumor suppressor | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. | This gene encodes one of two glycosyltransferases involved in the chain elongation step of heparan sulfate biosynthesis. Mutations in this gene cause the type II form of multiple exostoses. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:2132; | endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transferase complex [GO:0043541]; glucuronosyl-N-acetylglucosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0050508]; glucuronosyltransferase activity [GO:0015020]; glycosyltransferase activity [GO:0016757]; heparan sulfate N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0042328]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; N-acetylglucosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-glucuronosyltransferase activity [GO:0050509]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; cellular polysaccharide biosynthetic process [GO:0033692]; cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus [GO:0044344]; chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0002062]; endochondral bone morphogenesis [GO:0060350]; fluid transport [GO:0042044]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; glycosaminoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0006024]; heart contraction [GO:0060047]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0015012]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process, polysaccharide chain biosynthetic process [GO:0015014]; heparin biosynthetic process [GO:0030210]; mesoderm formation [GO:0001707]; multicellular organismal water homeostasis [GO:0050891]; ossification [GO:0001503]; protein N-linked glycosylation [GO:0006487]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; sodium ion homeostasis [GO:0055078]; sulfation [GO:0051923]; vasodilation [GO:0042311] | 12907669_the EXT1/2 heterocomplex can act as heparan sulfate polymerases in vitro without the addition of additional auxiliary proteins 14654969_112delAT causes multiple exostoses, indicating full penetrance since relatives with isolated exotoses lacked this deletion. 15586175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15586175_Variations in EXT2 gene is associated with multiple osteochondromas 15796962_Promoter methylation was not detected in any of the chondrosarcoma cases in EXT2. 16088908_analysis of multiple osteochondroma-related mutations in EXT1 and EXT2 16283885_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16638657_We found three novel mutations (S277X in the EXT1 gene, and G194X and 939+1G>A in the EXT2 gene) and a known mutation (Q172X in the EXT2 gene)in hereditary multiple exostoses 17293876_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17301954_Detection of mutations in EXT2 gene can significantly improve the identification of both point-mutations and mid-size rearrangemements in osteochrondromas. 17589361_Hereditary multiple exostosis patients with mutations in EXT1 gene have more anatomic abnormality and burden than those with EXT2 mutations. 17676624_Compared to EXT2-linkage, female individuals with EXT1-linkage were smaller in stature. 17761672_capacity of wild type EXT2 to enhance heparan sulfate chain length together with EXT1 was not shared by the EXT2-Y419X mutant 17786204_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17928989_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18210030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18294062_A novel mutation, c505 G > T, in the EXT2 gene was identified in two unrelated Chinese families with hereditary multiple exostoses. 18373409_found EXT1 to be responsible in seven families (19 affected members) and EXT2 in four families (17 affected members) with multiple osteochondromas 18544707_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18597214_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18633108_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18666861_A novel mutation in EXT2 gene in a Chinese family with hereditary exostoses is reported. 19008344_Data show that SNPs in EXT2 did not confer a significant risk for type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians. 19008344_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19179614_The tumor suppressor gene EXT2 is involved in the formation of multiple osteochondromas, which can progress to become secondary peripheral chondrosarcomas. 19309273_A previously unreported stop mutation, the substitution c.817C>T, was observed in the EXT2 gene in an Indian pedigree of hereditary multiple exostoses families. 19336475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19344451_Novel mutations have been identified in the EXT1 and the EXT2 gene in 17 Multiple Osteochondromas patients. 19380854_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19839753_Two novel EXT1 gene mutations and two novel EXT2 gene mutations were identified in two and three hereditary multiple exostoses pedigrees, respectively. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19933996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20140877_The nonsens mutation 536G>A in the EXT2 is the disease-causing mutation in a family with hereditary multiple exostoses. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20418910_results clearly indicate that, in most cases, biallelic inactivation of EXT genes does not account for osteochondromas formation; this mechanism should be regarded as a common feature for hereditary osteochondromas transformation 20571754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20580033_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20813973_Loss of heterozygosity for EXT2 is associated with multiple osteochondromas. 20872591_primary defect in EXT2 mRNA level can produce profound effect on the synthesis of HS chains in cartilage, the consequence of which impacts on the regulation of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. 20879858_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21039224_8 novel mutations of EXT1 and EXT2 genes among families and sporadic cases with multiple exostoses were identified. 21499719_Fifteen mutations and large deletions, of which nine are new, were detected in the EXT1 and EXT2 gene by sequence analysis, FISH and MLPA analysis. 21510814_Association of genetic variations in EXT2 with Type 2 diabetes mellitus in Tunisia 21703028_Molecular characterization of EXT1- and EXT2-deletion breakpoints in multiple osteochondroma indicates that non-allelic homologous recombination between Alu-sequences as well as NHEJ are causal and that the majority of these deletions are nonrecurring. 22040554_Two novel EXT1 gene mutations were identified and no mutation was found in EXT2 gene in two families with multiple osteochodromas. 22820392_analysis of novel pathogenic mutations in EXT1 and EXT2 that may have roles in multiple osteochondroma in Chinese patients 23052945_A meta analysis indicates variation in the EXT2 locus appears to be associated with a small increase in the risk of type 2 diabetes. 23262345_20 novel EXT1/EXT2 mutations and one large EXT2 deletion identified in the largest Southern Italy cohort of patients affected by hereditary multiple exostosis. 23439489_we found a mutation in EXT1 or in EXT2 in 95% of the Spanish patients. Eighteen of the mutations were novel. 23450490_No mutations have been found among all exons of the EXT1 and EXT2 genes in this family. Linkage analysis is necessary for identifying the cause of this disease. 23629877_Novel and recurrent mutations occur in the EXT1 and EXT2 genes in Chinese kindreds with multiple osteochondromas. 23871501_This study demonstrated no association of rs1113132, rs3740878 and rs11037909 EXT2 variants with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 24120389_these findings are useful for extending the mutational spectrum in EXT1 and EXT2 and understanding the genetic basis of multiple osteochondromas in Chinese patients. 24532482_EXT1 and EXT2 heterozygous mutations in 18 (54.6 %) and ten (30.3 %) probands respectively, which represents a total of 28 (84.9 %) index cases. 24728384_The heterozygous mutation c.743+1G>A in the EXT2 gene causes HME as a result of abnormal splicing, mRNA decay, and the resulting haploinsufficiency of EXT2. 25207843_EXT2 gene might not have a major role in the development of type 2 diabetes in the Chinese population. 25230886_EXT2 mutation is associated with multiple osteochondromatosis. 25449079_The second exon of EXT2. A c.244delG mutation is associated with hereditary multiple exostosis. 25468659_Heterozygous loss of function of EXT1 and EXT2 results in a decreased arteriolar endothelial glycocalyx but improved flow mediated vasodilation. 25541963_loss of function of EXT2 subjects with hereditary multiple exostoses affects pancreatic insulin secretion capacity and development. 25591329_We report the discovery of a non-sense mutation in EXT2 in an 11-y-old boy diagnosed with multiple osteochondroma. 25744876_Analysis of microsatellite polymorphic markers in the 11p region harboring the EXT2 gene did not reveal any loss of heterozygosity 26246518_Authors identified two homozygous mutations p.Met87Arg and p.Arg95 Cys in exostosin 2, EXT2, a ubiquitously expressed gene that encodes a glycosyltransferase. In patient cells, diminished expression and function was observed. 26690531_identification of mutations in EXT1 and EXT2 in Cypriot patients with a clinical diagnosis of hereditary multiple osteochondromas (HMO); five patients, representing the first report of genetic screening of HMO affected individuals in the Cypriot population are described 26961984_We found that the prevalence of EXT1 mutations was greater than that of EXT2 mutations in Japanese multiple osteochondromas families. 27636706_Germline EXT2 mutation is associated with chondrosarcoma. 27650265_Let-7b-mediated suppression of initiation codon depends on the length of 5'-UTR of EXT2 mRNA and its suppression is inhibited in the presence of polyamines. 27748933_The mutation results in deletion of exon 5 in the mRNA, producing a frameshift that leads to a premature termination codon. The present study extends the mutational spectrum of EXT2. 28690282_The nine mutations identified by targeted next-generation sequencing include two missense mutations (EXT1: c.1088G>A and c.2120C>T), one splicing mutation (EXT2: c.744-1G>T) 28849184_the present study identified a novel missense mutation (c.1385G>A) in exon 8 and a splicing mutation (c.725+1G>C) in intron 3 of the EXT2 gene, which are responsible for MO in certain Chinese patients. The findings are useful for expanding the database of known EXT2 mutations and understanding the genetic basis of MO in Chinese patients, which may improve genetic counseling and the prenatal diagnosis of MO. 29104277_RT-PCR analysis showed that the overall transcriptional activity of the main Heparan Sulfate biosynthesis-involved genes (EXT1, EXT2, NDST1, NDST2, GLCE, HS2ST1, HS3ST1, HS3ST2, HS6ST1, HS6ST2, SULF1, SULF2, HPSE) was decreased by 1.5-2-fold in Grade II-III glioma. 29529714_Exons and flanking regions of the EXT1 and EXT2 genes were analyzed from the genomic DNA of 153 patients in 114 families with multiple osteochondromas. We identified 33 variants in EXT1 (13 frameshift, 11 nonsense, 5 missense, 2 splice site mutation, and 2 large deletions) in and 17 (6 frameshift, 6 splice site mutation, 3 nonsense, 1 missense, and 1 large deletion) in EXT2 gene. Of all 50 variants, 31 (62%) were novel. 30075207_A novel EXT2 mutation was identified in a family with severe developmental delay, microcephaly, seizures, feeding difficulties, and osteopenia. 30288735_AREXT2 (autosomal recessive EXT2-related syndrome) can be considered as a multiorgan Congenital Disorder of Glycosylation caused by a significant, but non-lethal, decrease in EXT2 expression, thereby affecting the synthesis of the heparan sulfate proteoglycans, which is relevant in many physiological processes. 30334991_The present study identified pathogenic mutations in 93% (68/73) of unrelated hereditary multiple osteochondromasprobands from 73 pedigrees. Mutations in EXT1 and EXT2 were identified in 53% (39/73) and 40% (29/73) of families. 30730578_a novel frameshift mutation in EXT2 is identified in a fourth-generation Korean family with multiple osteochondromas 31030431_Mutations of the EXT1 and EXT2 genes probably underlie the hereditary multiple exostosis in both pedigrees 31400121_a heterozygous missense variation in the exon 1 and a heterozygous frameshift variation in exon 6 of EXT1 are associated with hereditary multiple exostosis 32293802_Identification of Novel EXT Mutations in Patients with Hereditary Multiple Exostoses Using Whole-Exome Sequencing. 33478971_In Patients with Membranous Lupus Nephritis, Exostosin-Positivity and Exostosin-Negativity Represent Two Different Phenotypes. 33596140_Identification of Novel Mutations in the EXT1 and EXT2 Genes of Chinese Patients with Hereditary Multiple Osteochondromas. 33632255_Mutation spectrum of EXT1 and EXT2 in the Saudi patients with hereditary multiple exostoses. 34280007_A Novel Intronic Splicing Mutation in the EXT2 Gene of a Chinese Family with Multiple Osteochondroma. 34302213_Immunopathological analysis of the expression of glomerular exostosin 1 and exostosin 2 in Japanese patients with lupus nephritis. 34403521_Identification of a novel EXT2 frameshift mutation in a family with hereditary multiple exostoses by whole-exome sequencing. 35194125_Prevalence of neural epidermal growth factor-like 1- and exostosin 1/exostosin 2-associated membranous nephropathy: a single-center retrospective study in Japan. 35211766_Clinical survey of a pedigree with hereditary multiple exostoses and identification of EXT2 gene deletion mutation. | ENSMUSG00000027198 | Ext2 | 501.332189 | 1.5456237 | 0.628189101 | 0.16457407 | 14.45751958382 | 0.0001433563746327086180915033608584963076282292604446411132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00141216124532558308379837086476982221938669681549072265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 659.221018 | 73.719829 | 428.593815 | 47.916637 |
| ENSG00000151718 | 80014 | WWC2 | protein_coding | Q6AWC2 | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat | This gene encodes a member of the WW-and-C2-domain-containing family of proteins. Members of this family have two N-terminal WW domains that mediate binding to target proteins harboring L/PPxY motifs, an internal C2 domain for membrane association, and C-terminal alpha protein kinase C binding sites and class III PDZ domain-interaction motifs. Proteins of this family are able to form homo- and heterodimers and to modulate hippo pathway signaling. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. | hsa:80014; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; negative regulation of hippo signaling [GO:0035331]; negative regulation of organ growth [GO:0046621]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of hippo signaling [GO:0035330] | 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 28815883_WWC2 functions as a tumor suppressor by negatively regulating the Hippo signaling pathway and may serve as a prognostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. 32623387_miR-21-5p promotes lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion via targeting WWC2. | ENSMUSG00000031563 | Wwc2 | 508.838226 | 1.3373697 | 0.419398385 | 0.11771750 | 12.65516534654 | 0.0003745294701343304102567066671269913058495149016380310058593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00326453440524596908561827390826692862901836633682250976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 611.285382 | 47.530924 | 459.083708 | 35.922051 | ||
| ENSG00000151743 | 196394 | AMN1 | protein_coding | Q8IY45 | Alternative splicing;Reference proteome | Predicted to be involved in SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process. Predicted to be part of SCF ubiquitin ligase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:196394; | microvillus membrane [GO:0031528]; SCF ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0019005]; SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0031146] | Mouse_homologues 17971504_C730024G19Rik is most abundantly expressed in tissues rich in highly ciliated cells, such as olfactory sensory neurons, and is predicted to be important to cilia. | ENSMUSG00000068250 | Amn1 | 97.590365 | 1.1297034 | 0.175944090 | 0.17932644 | 0.96112451032 | 0.3269037207623364804653931514621945098042488098144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.55942436783800064681315689085749909281730651855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 114.711851 | 13.899492 | 102.027406 | 12.596439 | ||
| ENSG00000152332 | 127933 | UHMK1 | protein_coding | Q8TAS1 | FUNCTION: Upon serum stimulation, phosphorylates CDKN1B/p27Kip1, thus controlling CDKN1B subcellular location and cell cycle progression in G1 phase. May be involved in trafficking and/or processing of RNA (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase | The gene encodes a serine/threonine protein kinase that promotes cell cycle progression through G1 by phosphorylation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (p27Kip1), which causes nuclear export and degradation. The encoded protein is also thought to function in the adult nervous system and the gene has been associated with schizophrenia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. | hsa:127933; | axon [GO:0030424]; dendrite cytoplasm [GO:0032839]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; neuronal ribonucleoprotein granule [GO:0071598]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; ribonucleoprotein complex binding [GO:0043021]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; splicing factor binding [GO:1990935]; transferase activity [GO:0016740]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; positive regulation of translational initiation [GO:0045948]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of protein export from nucleus [GO:0046825] | 12093740_We identify the kinase responsible for S10 phosphorylation as human kinase interacting stathmin (hKIS) and show that it regulates cell cycle progression in response to mitogens. 12782393_KIS gene was overexpressed in NF1-associated plexiform neurofibromas and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs) as compared to dermal neurofibroma which suggests a possible implication of KIS in the genesis of NF1-associated tumors. 16978587_Evidence indicating that UHMK1 may be a candidate susceptibility gene for Schizophrenia in the British population. UHMK1 is situated between previously implicated genes RGS4 and NOS1AP. 16978587_These results provide preliminary evidence that the UHMK1 gene increases susceptibility to schizophrenia. Further confirmation in adequately powered samples is needed. 17726090_KIS promoter is activated by serum-responsive GABP binding to Ets-binding sites which leads to KIS gene expression, cell migration, and cell cycle progression 17984092_Results show that KIS is a direct transcriptional target of FoxM1. 18384876_Overexpression of KIS protein kinase is associated with acute myelogenous leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome and acute lymphoblastic leukemia 18414510_A follow up article showing further association between markers in UHMK1 and schizophrenia in a London based sample. Association replicated in an independent Scottish sample. 18414510_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18414510_The association between UHMK1 and schizophrenia is confirmed. 19747464_KIS is expressed in neurons, and its encoded protein is localised to the nucleus and cytoplasm. No difference in KIS expression was found between schizophrenics and controls or in the lymphoblast cell lines. 19747464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21399567_The contribution of UHMK1 gene in schizophrenia susceptibility, was explored. 23419774_Moreover, we showed that CATS and KIS antagonize the transactivation capacity of CALM/AF10.In summary, our results show that CATS interacts with and is a substrate for KIS, suggesting that KIS regulates CATS function 27424934_genome-wide association study identified the UHMK1 gene as a novel bone mineral density locus specific to East Asians. 29307747_UHMK1 plays a role in hematopoietic cell differentiation and suppression of autonomous clonal growth of leukemia cells. 30936457_provide a model by which YAP supports cell proliferation through the induction of important cell cycle regulators in a UHMK1- and MYBL2-dependent manner 31975428_UHMK1 promotes gastric cancer progression through reprogramming nucleotide metabolism. 35151311_UHMK1-dependent phosphorylation of Cajal body protein coilin alters 5-FU sensitivity in colon cancer cells. 35501324_UHMK1 aids colorectal cancer cell proliferation and chemoresistance through augmenting IL-6/STAT3 signaling. | ENSMUSG00000026667 | Uhmk1 | 1742.358191 | 1.1429998 | 0.192825198 | 0.04208809 | 20.98884335340 | 0.0000046196569781277821249904948219811018361724563874304294586181640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00006703294793573797978429584798476525975274853408336639404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1858.319343 | 48.782414 | 1633.538820 | 43.128842 | |
| ENSG00000152683 | 55676 | SLC30A6 | protein_coding | Q6NXT4 | FUNCTION: Has probably no intrinsic transporter activity but together with SLC30A5 forms a functional zinc ion:proton antiporter heterodimer, mediating zinc entry into the lumen of organelles along the secretory pathway (PubMed:15994300, PubMed:19366695, PubMed:19759014). As part of that zinc ion:proton antiporter, contributes to zinc ion homeostasis within the early secretory pathway and regulates the activation and folding of enzymes like alkaline phosphatases and enzymes involved in phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis (PubMed:15994300, PubMed:19759014, PubMed:35525268). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15994300, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19366695, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19759014, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35525268}. | Alternative splicing;Antiport;Golgi apparatus;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Zinc;Zinc transport | This gene encodes a member of a family of proteins that function as zinc transporters. This protein can regulate subcellular levels of zinc in the Golgi and vesicles. Expression of this gene is altered in the Alzheimer's disease brain plaques. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. | hsa:55676; | Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; zinc ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005385]; cellular zinc ion homeostasis [GO:0006882]; insulin processing [GO:0030070]; regulation of zinc ion transport [GO:0071579]; zinc ion import into Golgi lumen [GO:1904257]; zinc ion import into organelle [GO:0062111]; zinc ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071577]; zinc ion transport [GO:0006829] | 16580781_Our results show that Zn transporter-4 and Zn transporter-6 are significantly (P | ENSMUSG00000024069 | Slc30a6 | 311.350922 | 1.1404580 | 0.189613315 | 0.09178815 | 4.26613953857 | 0.0388791640990277728717749994302721461281180381774902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.13736846360626434049301280992949614301323890686035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 326.820074 | 20.339951 | 288.058869 | 18.077025 | |
| ENSG00000154642 | 54149 | C21orf91 | protein_coding | Q9NYK6 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in cortical progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation. Promotes dendritic spine development of post-migratory cortical projection neurons by modulating the beta-catenin signaling pathway. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9D7G4}. | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Differentiation;Neurogenesis;Reference proteome | Predicted to be involved in cerebral cortex neuron differentiation and positive regulation of dendritic spine development. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:54149; | cerebral cortex neuron differentiation [GO:0021895]; positive regulation of dendritic spine development [GO:0060999] | 12815627_Authors demonstrate that human AL109761 is in fact the human ortholog of chicken EURL (GeneID: 395489) 22039568_Two complementary techniques identified C21orf91 as a gene of interest for susceptibility to herpes simplex labialis. 27404227_EURL is an important new player in neuronal development that is likely to impact on the neuropathogenesis of HSA21-related disorders including Down Syndrome. | ENSMUSG00000022864 | D16Ertd472e | 142.598399 | 0.6305220 | -0.665381324 | 0.13445041 | 24.51548955029 | 0.0000007371484784619510083000532701946738711740181315690279006958007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00001248333282896582471430384914112821093112870585173368453979492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 113.150261 | 13.003041 | 180.213098 | 20.385326 | |
| ENSG00000155100 | 51633 | OTUD6B | protein_coding | Q8N6M0 | FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Deubiquitinating enzyme that may play a role in the ubiquitin-dependent regulation of protein synthesis, downstream of mTORC1 (PubMed:21267069, PubMed:27864334). May associate with the protein synthesis initiation complex and modify its ubiquitination to repress translation (PubMed:27864334). May also repress DNA synthesis and modify different cellular targets thereby regulating cell growth and proliferation (PubMed:27864334). May also play a role in proteasome assembly and function (PubMed:28343629). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21267069, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27864334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28343629}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Stimulates protein synthesis. Influences the expression of CCND1/cyclin D1 by promoting its translation and regulates MYC/c-Myc protein stability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27864334}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Hydrolase;Intellectual disability;Protease;Reference proteome;Thiol protease;Ubl conjugation pathway | This gene encodes a member of the ovarian tumor domain (OTU)-containing subfamily of deubiquitinating enzymes. Deubiquitinating enzymes are primarily involved in removing ubiquitin from proteins targeted for degradation. This protein may function as a negative regulator of the cell cycle in B cells. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2013]. | hsa:51633; | cysteine-type deubiquitinase activity [GO:0004843]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; negative regulation of translation [GO:0017148]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727]; proteasome assembly [GO:0043248]; protein deubiquitination [GO:0016579] | 21267069_down-regulation of Otud-6b expression after prolonged cytokine stimulation may be required for cell proliferation in B lymphocytes 27864334_The global OTUD6B expression level does not change significantly between nonneoplastic and malignant tissues, suggesting that modifications of splicing factors during the process of transformation are responsible for this isoform switch. 28343629_OTUD6B encodes a deubiquitinating enzyme; study reports biallelic pathogenic variants in OTUD6B in 12 individuals from 6 families with intellectual disability syndrome associated with seizures & dysmorphic features; other features include developmental delay, microcephaly, absent speech, hypotonia, growth retardation, feeding difficulties, structural brain abnormalities, malformations of heart & musculoskeleton. 31156645_OTUD6B-AS1 Might Be a Novel Regulator of Apoptosis in Systemic Sclerosis. 32323143_DUB-independent regulation of pVHL by OTUD6B suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma. 34354232_OTUD6B-associated intellectual disability: novel variants and genetic exclusion of retinal degeneration as part of a refined phenotype. 34680978_Compound Heterozygote of Point Mutation and Chromosomal Microdeletion Involving OTUD6B Coinciding with ZMIZ1 Variant in Syndromic Intellectual Disability. 35110537_Deubiquitylase OTUD6B stabilizes the mutated pVHL and suppresses cell migration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 35430327_Novel biallelic variants affecting the OTU domain of the gene OTUD6B associate with severe intellectual disability syndrome and molecular dynamics simulations. 36059274_The OTUD6B-LIN28B-MYC axis determines the proliferative state in multiple myeloma. | ENSMUSG00000040550 | Otud6b | 161.856217 | 1.2575512 | 0.330617133 | 0.12032660 | 7.55359792243 | 0.0059890377185838269968876090842968551442027091979980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.03324391254267879819428443965989572461694478988647460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 180.564765 | 13.714437 | 144.259066 | 11.192699 | |
| ENSG00000155256 | 118813 | ZFYVE27 | protein_coding | Q5T4F4 | FUNCTION: Key regulator of RAB11-dependent vesicular trafficking during neurite extension through polarized membrane transport (PubMed:17082457). Promotes axonal elongation and contributes to the establishment of neuronal cell polarity (By similarity). Involved in nerve growth factor-induced neurite formation in VAPA-dependent manner (PubMed:19289470). Contributes to both the formation and stabilization of the tubular ER network (PubMed:24668814). Involved in ER morphogenesis by regulating the sheet-to-tubule balance and possibly the density of tubule interconnections (PubMed:23969831). Acts as an adapter protein and facilitates the interaction of KIF5A with VAPA, VAPB, SURF4, RAB11A, RAB11B and RTN3 and the ZFYVE27-KIF5A complex contributes to the transport of these proteins in neurons. Can induce formation of neurite-like membrane protrusions in non-neuronal cells in a KIF5A/B-dependent manner (PubMed:21976701). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3TXX3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17082457, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19289470, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21976701, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23969831, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24668814}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Membrane;Metal-binding;Neurodegeneration;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a protein with several transmembrane domains, a Rab11-binding domain and a lipid-binding FYVE finger domain. The encoded protein appears to promote neurite formation. A mutation in this gene has been reported to be associated with hereditary spastic paraplegia, however the pathogenicity of the mutation, which may simply represent a polymorphism, is unclear. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. | hsa:118813; | axon [GO:0030424]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum tubular network [GO:0071782]; growth cone membrane [GO:0032584]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; endoplasmic reticulum tubular network formation [GO:0071787]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048011]; positive regulation of axon extension [GO:0045773]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] | 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16826525_Mutation affects neuronal intracellular trafficking in the corticospinal tract, which is consistent with the pathology of hereditary spastic paraplegia. 17082457_protrudin regulates Rab11-dependent membrane recycling to promote the directional membrane trafficking required for neurite formation [protrudin] 18606302_The role of ZFYVE27/protrudin in hereditary spastic paraplegia is reported. 19289470_VAP-A is an important regulator both of the subcellular localization of protrudin and of its ability to stimulate neurite outgrowth. 21976701_Protrudin-KIF5 complex contributes to the vesicular transport in neurons. 22573551_findings indicate that protrudin interacts with spastin and induces axon formation through its N-terminal domain. Moreover, protrudin and spastin may work together to play an indispensable role in motor axon outg 23969831_SPG33 protein protrudin contains hydrophobic, intramembrane hairpin domains, interacts with tubular ER proteins, and functions in ER morphogenesis by regulating the sheet-to-tubule balance and possibly the density of tubule interconnections. 31772151_Protrudin modulates seizure activity through GABAA receptor regulation. 32479595_Protrudin-mediated ER-endosome contact sites promote MT1-MMP exocytosis and cell invasion. 32917905_Protrudin and PDZD8 contribute to neuronal integrity by promoting lipid extraction required for endosome maturation. 33154382_Protrudin functions from the endoplasmic reticulum to support axon regeneration in the adult CNS. | ENSMUSG00000018820 | Zfyve27 | 156.366305 | 0.7394063 | -0.435560709 | 0.16060488 | 7.33906500237 | 0.0067471924802635406884232516233623755397275090217590332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.03636983753908532013277010719320969656109809875488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 122.010462 | 11.607995 | 165.798602 | 15.268147 | |
| ENSG00000155975 | 137492 | VPS37A | protein_coding | Q8NEZ2 | FUNCTION: Component of the ESCRT-I complex, a regulator of vesicular trafficking process. Required for the sorting of endocytic ubiquitinated cargos into multivesicular bodies. May be involved in cell growth and differentiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15240819}. | Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Endosome;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport | This gene belongs to the VPS37 family, and encodes a component of the ESCRT-I (endosomal sorting complex required for transport I) protein complex, required for the sorting of ubiquitinated transmembrane proteins into internal vesicles of multivesicular bodies. Expression of this gene is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, and mutations in this gene are associated with autosomal recessive spastic paraplegia-53. A related pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 5. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2012]. | hsa:137492; | centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; ESCRT I complex [GO:0000813]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; macroautophagy [GO:0016236]; membrane fission [GO:0090148]; multivesicular body assembly [GO:0036258]; protein targeting to membrane [GO:0006612]; protein targeting to vacuole [GO:0006623]; protein transport to vacuole involved in ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the multivesicular body sorting pathway [GO:0043328]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the multivesicular body sorting pathway [GO:0043162]; viral budding via host ESCRT complex [GO:0039702] | 14623289_Our results strongly suggest that HCRP1 might be a growth inhibitory protein and associated with decreasing the invasion of HCC cells 15240819_HCRP1 is a subunit of mammalian ESCRT-I, and its function is essential for lysosomal sorting of EGF receptors. 22016507_Data show hVps37A mRNA downregulation in ovarian cancer. 22717650_The missense mutation c.1146A>T in Vps37A causes autosomal recessive complex hereditary spastic paraparesis. 22891969_Low HCRP1 expression was found to be of adverse prognostic significance in patients with oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma who received preoperative chemoradiotherapy 27311861_The present data indicate that HCRP1 inhibits breast cancer metastasis through downregulating EGFR phosphorylation. 28458158_HCRP1 is a negative regulator in prostate cancer progression, metastasis and multi-drug resistance. 28963677_this study identifies HCRP1 downregulation correlates with tumor stage, nodal metastasis, and poor patient survival in human gastric cancer 30518879_HCRP-1 regulates EGFR-AKT-BIM-mediated anoikis resistance and serves as a prognostic marker in human colon cancer. 31519728_The VPS37A coordinates the recruitment of a unique set of ESCRT machinery components for phagophore closure in mammalian cells. | ENSMUSG00000031600 | Vps37a | 375.871561 | 1.4955500 | 0.580676149 | 0.15128594 | 14.63507556723 | 0.0001304636412941534017069511453001950940233655273914337158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00129887929852143626553717670191190336481668055057525634765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 452.958967 | 57.379145 | 303.961283 | 38.595288 | |
| ENSG00000156398 | 118980 | SFXN2 | protein_coding | Q96NB2 | FUNCTION: Mitochondrial amino-acid transporter that mediates transport of serine into mitochondria (PubMed:30442778). Involved in mitochondrial iron homeostasis by regulating heme biosynthesis (PubMed:30570704). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30442778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30570704}. | Acetylation;Amino-acid transport;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | Predicted to enable serine transmembrane transporter activity. Involved in mitochondrial transmembrane transport. Located in mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:118980; | mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; serine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022889]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; mitochondrial transmembrane transport [GO:1990542]; serine import into mitochondrion [GO:0140300] | 12670026_molecular cloning of SFXN2 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 30570704_SFXN2 functions in mitochondrial iron metabolism by regulating heme biosynthesis. 36163342_Elevated SFXN2 limits mitochondrial autophagy and increases iron-mediated energy production to promote multiple myeloma cell proliferation. | ENSMUSG00000025036 | Sfxn2 | 30.603125 | 1.4251150 | 0.511078359 | 0.30383175 | 2.80854652930 | 0.0937632924785831434189020683334092609584331512451171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.25349071031898356975986530414957087486982345581054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 47.501184 | 9.251078 | 33.513774 | 6.426350 | |
| ENSG00000157045 | 123803 | NTAN1 | protein_coding | Q96AB6 | FUNCTION: N-terminal asparagine deamidase that mediates deamidation of N-terminal asparagine residues to aspartate. Required for the ubiquitin-dependent turnover of intracellular proteins that initiate with Met-Asn. These proteins are acetylated on the retained initiator methionine and can subsequently be modified by the removal of N-acetyl methionine by acylaminoacid hydrolase (AAH). Conversion of the resulting N-terminal asparagine to aspartate by NTAN1/PNAD renders the protein susceptible to arginylation, polyubiquitination and degradation as specified by the N-end rule. This enzyme does not act on substrates with internal or C-terminal asparagines and does not act on glutamine residues in any position, nor on acetylated N-terminal peptidyl Asn. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21375249}. | 3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Reference proteome | The protein encoded by this gene functions in a step-wise process of protein degradation through the N-end rule pathway. This protein acts as a tertiary destabilizing enzyme that deamidates N-terminal L-Asn residues on proteins to produce N-terminal L-Asp. L-Asp substrates are subsequently conjugated to L-Arg, which is recognized by specific E3 ubiquitin ligases and targeted to the proteasome. Pseudogenes of this gene are located on the long arms of chromosomes 8, 10 and 12. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2012]. | hsa:123803; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-N-terminal asparagine amidohydrolase activity [GO:0008418]; adult locomotory behavior [GO:0008344]; memory [GO:0007613]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] | 18496130_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21375249_Results indicate that hNTAN1 is highly selective for the hydrolysis of N-terminal peptidyl L-Asn. | ENSMUSG00000022681 | Ntan1 | 147.051834 | 0.9124757 | -0.132141963 | 0.17901531 | 0.54293971670 | 0.4612169595945476707754551171092316508293151855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.68269871225487122057273836617241613566875457763671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 150.089290 | 16.963865 | 165.610200 | 18.891165 | |
| ENSG00000157895 | 64897 | C12orf43 | protein_coding | Q96C57 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in the regulation of Wnt signaling pathway during early development. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A9C3N6}. | Developmental protein;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Wnt signaling pathway | Predicted to be involved in Spemann organizer formation and negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway. Predicted to be located in nuclear envelope. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:64897; | nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030178]; Spemann organizer formation [GO:0060061]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] | 19198612_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27263109_Study provides evidence that C12orf43/rs2258287 was associated with the risk of coronary artery disease in the studied Pakistani cohort. | ENSMUSG00000029559 | 2210016L21Rik | 98.261562 | 0.9192320 | -0.121499010 | 0.15399305 | 0.62248780192 | 0.4301243028951742264354152212035842239856719970703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.65547213736765408409468136596842668950557708740234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 95.698599 | 9.914884 | 104.599253 | 10.604200 | |
| ENSG00000158473 | 912 | CD1D | protein_coding | P15813 | FUNCTION: Antigen-presenting protein that binds self and non-self glycolipids and presents them to T-cell receptors on natural killer T-cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17475845}. | 3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Innate immunity;Lysosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA | This gene encodes a divergent member of the CD1 family of transmembrane glycoproteins, which are structurally related to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins and form heterodimers with beta-2-microglobulin. The CD1 proteins mediate the presentation of primarily lipid and glycolipid antigens of self or microbial origin to T cells. The human genome contains five CD1 family genes organized in a cluster on chromosome 1. The CD1 family members are thought to differ in their cellular localization and specificity for particular lipid ligands. The protein encoded by this gene localizes to late endosomes and lysosomes via a tyrosine-based motif in the cytoplasmic tail. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. | hsa:912; | basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; beta-2-microglobulin binding [GO:0030881]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; endogenous lipid antigen binding [GO:0030883]; exogenous lipid antigen binding [GO:0030884]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; lipid antigen binding [GO:0030882]; lipopeptide binding [GO:0071723]; antigen processing and presentation, endogenous lipid antigen via MHC class Ib [GO:0048006]; antigen processing and presentation, exogenous lipid antigen via MHC class Ib [GO:0048007]; detection of bacterium [GO:0016045]; heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034113]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; positive regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045089]; positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001916]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; T cell selection [GO:0045058] | 9374463_CD1d presents lipid and glycolipid antigens to T cells 11580851_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12239218_Data show that CD1d associates in the ER with both calnexin and calreticulin and with the thiol oxidoreductase ERp57 in a manner dependent on glucose trimming of its N-linked glycans. 12368486_CD1d ligand at the human maternal-fetal interface 12454749_B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells significantly down-regulated transcripts from CD1c and CD1d genes, permitting cells to evade the immune response 12618910_the CD1d alpha1-alpha2 domains of both rhesus monkeys and humans are highly homologous (95.6%) 12730881_CD1d is expressed functionally on IECs with a polarity of presentation (basal > apical) predicting a role in presentation of mucosal glycolipid antigens to local CD1d-restricted T cells. 12952923_a novel autocrine pathway of CD1d regulation by Hsp110. 14551186_CD1d proteins sre strong binders of small hydrophobic probes such as 1-anilinonaphthalene-8-sulfonic acid and 4,4'-dianilino-1,1'-naphthyl-5,5'-disulfonic acid. 14716312_saposins mobilize monomeric lipids from lysosomal membranes and facilitate their association with CD1d 15100293_Investigation of the 5' upstream region of human CD1D reveals multiple transcription initiation sites and TATA boxless dual promoters located within 700 base pairs 5' upstream of the coding region. 15128771_Transgenic overexpression of CD1d within pancreatic islets of nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice protects them from autoimmune diabetes through activation of NKT cells and improvement of IL-4 secretion at the site of autoimmunity (i.e., peripheral lymph nodes). 15187105_CD1d can inhibit NK cell-mediated cytolysis; the putative inhibitory receptor does not recognize CD1d molecules loaded with alpha-GalCer 15243159_Data show that phosphatidylinositol mannoside represents a mycobacterial antigen recognized by T cells in the context of CD1d. 15265953_Hepatic inflammatory cells & biliary cells near portal tract fibrotic areas of HCV-infected donors specifically up-regulate CD1d. CD1d presentation of liver Ag may be beneficial in acute viral clearance, but in chronic infection could add to liver injury. 15345586_The ability of CD1d-unrestricted natural killer T cells to recruit innate immune system cells might play a role in cancer cell eradication and contribute to inflammatory diseases. 15654963_TGFbeta produced by keratinocytes contribute to selectively downregulate CD1d expression on intraepidermal-resident Langerhans cells 15665086_CD1d-dimer staining revealed human natural killer T cells reactivity toward Sphingomonas glycosphingolipids. 15916790_ability of Nef to alter the cell surface expression of human CD1d. In cells co-expressing CD1d and Nef, a reduction in the cell surface level of CD1d was observed. 16007090_analysis of the crystal structure of human CD1d in complex with synthetic alpha-galactosylceramide at a resolution of 3.0 A 16091469_CD1d ligation alone, in the absence of iNKT, could rapidly (within 24 h) stimulate production of bioactive IL-12p70 by CD1d+ human peripheral blood monocytes as well as immature dendritic cells 16148122_CD1d continues to play a role in late-stage NKT cell development and, in particular, during the functionally significant acquisition of NK1.1 that is indicative of NKT cell maturity 16178273_CD1d has a role in intrahepatic T-cell recognition in hepatocytes 16456021_Time-course studies of CD1d gene expression indicated that keratinocytes slowly increased gene expression with CaCl(2)-induced terminal differentiation 16517731_These results highlight the variation in Ag recognition among CD1d-restricted Receptors, Antigen, T-Cell (TCRs) and suggest that TCR alpha-chain elements contribute to alpha-linked glycosphingolipid specificity [CD1d] 16675349_CD1d-restricted gamma delta T cells specific for phospholipids can represent a key mucosal regulatory subset for the control of early host reactivity against tree pollens. 16818729_This review highlights the role of the CD1d antigen processing pathway and the immunopotentiating effects of the ligands that can be presented by CD1d to natural killer (NK)T cells or other CD1d-restricted T cells during cancer and infections. 16820217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17015708_Schwann cells activated iNKT cells in a CD1d-dependent manner in the presence of alpha-galactosylceramide 17071498_CD1d has a role in cytolysis of lymphoblastic lymphoma cells 17071611_One of the N-linked glycans (at position asparagine-42) exists mainly in a form that is sensitive to endoglycosidase H. Deletion of Asn-42 affects stability of the CD1d heavy chain beta 2-microglobulin heterodimer. 17363727_CD4 potentiates human iNKT cell activation by engaging CD1d molecules. These results indicate that the CD4 coreceptors may contribute to the fine tuning of iNKT cells reactivity. 17372201_saposin B may facilitate lipid binding to CD1d molecules throughout the endocytic pathway 17475845_Cotrafficking with major histocompatibility class II molecules and the invariant chain (Ii) selectively enhances CD1d-mediated presentation of exogenous antigens. 17476670_CD1d-restricted NKT cells have roles in the intestine and in inflammatory bowel diseases [review] 17581592_The structure provides a basis for the interaction between the highly conserved NKT TCR alpha-chain and the CD1d-antigen complex 17726154_These results indicate that CD4 can contribute to natural killer cell activation independently of the presence of a CD4-ligand on antigen presenting cells and suggest that it preferentially modulates cytokine and proliferative responses. 18068183_Used a lentiviral system to generate stable cell lines producing beta2m-CD1d single chain protein which was used to form CD1d tetramer. 18253929_Data indicate that viral danger signals trigger NKT cell activation by enhancing CD1d de novo synthesis through increasing the abundance of CD1D mRNA in human myeloid dendritic cells. 18337560_monocyte-derived DCs cultured in an immunoglobulin-rich milieu expressed CD1d but not CD1a, CD1b, and CD1c, whereas DCs cultured in the presence of low levels of immunoglobulins had an opposite CD1 profile 18378792_An alanine scanning mutagenesis approach was undertook to define the energetic basis of this interaction between the natural killer cell T cell receptors and CD1d. 18385757_PKCzeta is an important transduction molecule downstream of TNF-alpha signaling and is associated with increased expression of CD1d that may enhance CD1d-natural killer T cell interactions in psoriasis lesions. 18433720_Trophoblast differentiation is characterized by TGF-beta1-mediated decreases in trophoblast cell CD1d expression. 18458073_CD1D expression and ligand induced cytokine production in mucosal epithelial cells from lower reproductive tract is tissue specific and CD1d-mediated cytokine production in penile urethral cells was abrogated by C. trachomatis infection. 18535199_a distinct population of human CD1d-restricted T cells specific for inflammation-associated lysolipids suggest a novel mechanism for inflammation mediated immune regulation in human cancer 18684921_Protection from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis afforded by the enrichment of natural killer T cells is independent of extrathymic CD1d transgene expression. 18713998_Although the allogeneic activation of iNKT cells is invariant TCR-CD1d interaction-dependent, glycosphingolipid (GSL) profiling suggests it does not involve the recognition of disparate CD1d/GSL complexes 19056691_A novel function of CD1d in the regulation of cell death with tumor survival and progression in humans. 19124746_CD1d overlaps with Ig-like transcript 4 (ILT4) both at the cell surface and in the cytoplasm; its interaction with ILT4 provides insights into the regulation of natural killer T cell-mediated immunity. 19415116_CD1d molecules bind a surprising diversity of lipid structures within the secretory pathway 19446558_Report ex vivo induction and expansion of natural killer T cells by CD1d1-Ig coated artificial antigen presenting cells. 19454494_infiltrating NKT cells are mainly observed in CD1d nodules 19592659_C/EBP-beta binds to the CCAAT box in the CD1d promoter, required for its expression in keratinocytes 19637196_Data suggest that IL-18-mediated activation and subsequent dysregulation of the CD1d-restricted iNKT-cells plays a role in the pathogenesis of AE. 19651460_Uncoupling between CD1d upregulation induced by retinoic acid and conduritol-B-epoxide and iNKT cell responsiveness. 19724888_The amount of sCD1d proteins in plasma was significantly decreased in rheumatoid arthritis patients compared with healthy donors. Plasma sCD1d protein levels correlated with the number of NKT cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. 19734232_Preferential stimulatory activities of two alpha-galactosylceramide C-glycoside analogues against human vs mouse invariant natural killer (NK)T cells are due to the differences between human vs mouse CD1d molecules. 19757161_A novel, high-level amplicon at 1q22-23.1 occurs in both hepatocellular carcinoma cell line and tissues. 19830742_Studies indicate that during bacterial infections, NKT cells can be activated either indirectly by DC or directly by bacterial lipid antigens presented by CD1d. 20080535_show that the mouse and human CD1d present glycolipids having different fatty acids, based in part upon a difference at a single amino acid position that is involved in positioning the sugar epitope. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20368272_A heretofore unknown tyrosine-based signal is demonstrated in the cytoplasmic tail of CD1d that may have relevance to other type I integral membrane proteins that traverse through the endocytic pathway. 20520738_These data indicate that bone marrow-dendritic cells express an endogenous CD1d ligand and B7-H1 to ihibit type II but not type I natural killer T cells. 20530791_Data show that the Vpu protein interacts with CD1d and suppresses its recycling from endosomal compartments to the cell surface by retaining CD1d in early endosomes. 20810727_CD1d is downregulated by the HPV16 E5 and HPV6 E5 protein. 20861015_Calreticulin controls the rate of assembly of CD1d molecules in the endoplasmic reticulum. 21095162_Studies indicate that NKTs can suppress tumor growth indirectly by targeting CD1d-positive elements of tumor-supportive stroma such as tumor-associated macrophages. 21185200_Studies indicate that iNKT cells, CD1d dependent natural killer T cells are a unique population of T cells. 21198755_Myeloid dendritic cells did not change their numbers or CD1d-expression during treatment 21258883_CD1d gene polymorphisms are associated with breast, colorectal and lung cancers. 21451111_both CD1d and CD1c are upregulated by retinoic acid receptor alpha signaling in human B cells 21454514_Binding strength and dynamics of invariant natural killer cell T cell receptor/CD1d-glycosphingolipid interaction on living cells by single molecule force spectroscopy. 21557213_Data show that CD1d knock-out mice, which are deficient in NKT cells and resistant to ConA-induced hepatitis, no longer expressed IL-33 in hepatocytes following ConA administration. 21632718_Although zinc finger protein PLZF is known to direct the effector program of natural killer (NK)T cells, this study shows that CD1d naive-like cells express it at a significantly lower amount than NKT cells. 21646050_Studies indicate that CD1d-restricted T-cells can rapidly produce large amounts of Th1 and/or Th2//Treg/Th17-type cytokines, thereby regulating immunity. 21653669_identified gB and US3 as two viral factors that together downregulate CD1d surface expression; results suggest that HSV-1 uses gB and US3 to rapidly inhibit NKT cell function in the initial antiviral response 21695190_Breast cancer cells, through downregulation of CD1d and subsequent evasion of natural killer T-mediated antitumor immunity, gain increased potential for metastatic tumor progression. 21846915_CD1d can differentiate chronic lymphocytic leukemia from other B-cell chronic lymphoproliferative disorders with high accuracy. 21853044_These findings provide the basis for investigations into a role for CD1d in lung mucosal immunity. 21900247_Identification of self-lipids presented by CD1c and CD1d proteins. 21925141_these results suggest that antigen presentation by CD1d is largely unaffected by the multiple immune-modulating functions of human cytomegalovirus. 21956730_The serine-containing variant showed the strongest CD1d binding, offering an explanation for its predominance in vivo. 21980475_CD1d appears to modulate some metabolic functions through an iNKT-independent mechanism 21987790_phenyl glycolipids showed greater binding avidity and stability for iNKT T-cell receptor when complexed with CD1d 22395072_These findings provide insight into how lysophospholipids are presented by human CD1d molecules and how this complex is recognized by some, but not all, human Invariant Natural Killer T cells. 22406267_Defective B cell-mediated stimulation of iNKT cells in SLE patients was associated with altered CD1d recycling. 22407918_Enhancing immunostimulatory function of human embryonic stem cell-derived dendritic cells by CD1d overexpression. 22419072_The binding of Sp1 to CD1d promoter and histone H3 acetylation on Sp1 sites were increased by histone deacetylase inhibitors. 22829134_Recombinant Vdelta1 TCRs from different individuals were shown to bind recombinant CD1d-sulfatide complexes in a sulfatide-specific manner. 22888216_Data suggest that when CD1c is up-regulated, ILT4 is recruited to CD1c, thus reducing the inhibitory effect of immunoglobulin-like transcript 4 (ILT4) on CD1d recognition. 22995911_Human and mouse type I natural killer T cell antigen receptors exhibit different fine specificities for CD1d-antigen complex 23049754_A correlation between CD1d expression (a negative prognostic marker) and the soluble CTLA-4 in B-ALL patients was observed. 23109910_crystallographic and biophysical analyses of alpha-galactosylceramide (alpha-GalCer) recognition by a human CD1d-restricted TCR 23171451_Antigen presentation of keratinocyte to invariant killer cells show that these cells do not activate the cytotoxicity effector genes in resting iNKT-cells, but had the capacity to serve as targets for activated iNKT-cells dependent on CD1d expression. 23265858_Total CD1d levels are upregulated in pollen lipid-treated dendritic cells, which are then able to activate invariant natural killer (NK)T cells through a CD1d-dependent pathway. 23280365_CD1d protein structure determines species-selective antigenicity of isoglobotrihexosylceramide (iGb3) to invariant NKT cells. 23347583_Downregulation of both CD1c and CD1d expression through a Vpu-dependent and Nef-independent mechanism, and the concomitant HIV-1-induced production of host cholesterol decreased the extent of CD1c and CD1d modulation. 23372165_A novel, autoreactive, CD1d-restricted, GPI-specific T-cell population, enriched in an invariant TCRalpha chain, is expanded in paroxysmal noctural hemoglobinuria and may be responsible for bone marrow failure. 23468111_Type II NKT cells are absolutely dependent on CD1d expression in the thymus for their selection. CD1d trafficks between the cell surface & endosomes. It plays a role in presentating lipid antigens & mycobacterial antigens. Review. 23668820_Data indictate variable expression of CD1d on chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)lymphocytes and an association between high expression of CD1d with shorter time to treatment and overall survival of patients. 23677998_for isoforms CD1b through CD1e, our simulations show the near-complete collapse of the hydrophobic cavities in the absence of the antigen. This event results from the spontaneous closure of the binding domain entrance, flanked by two alpha-helices. 23710894_our findings strongly suggest that T322 and S323 form a dual residue motif that can regulate the functional expression of CD1d during a viral infection. 23808994_CD1d was found selectively expressed on the surface of hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis C, but not those subjects with history of alcohol usage or resolved chronic hepatitis C. 24009709_MHC class I physically associates with CD1d and regulates its functional expression on the cell surface. 24076636_The gamma-delta TCR docked orthogonally, over the A' pocket of CD1d, in which the Vdelta1-chain, and the germ line-encoded CDR1d loop, dominated interactions with CD1d. 24104458_We suggest that unique set of interactions between CEACAM5, CD1d, and CD8 render CD1d more class I-like molecule, facilitating antigen presentation and activation of CD8(+)-suppressor regulatory T cells. 24213674_results showed the interaction between endoplasmic reticulum (ER)- lumenal domain of HCMV US2 and alpha3 domain of hCD1d was observed within ER; these results show the function of HCMV US2 in immune evasive mechanisms against anti-viral immunity of invariant NKT cells 24307737_these results provide new insight into the control of CD1d gene expression, and they have implications for the evolution of CD1d and type I NKT cells. 24418751_Relationship between high CD1d expression and shorter time to treatment and overall survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. CD1d expression in individual patients significantly changed over time. 24513807_CXCL16, iNKT cell-associated cell marker Valpha24, and CD1d were significantly upregulated in esophageal biopsies from EoE patients and correlated with the expression of inflammatory mediators associated with allergy. 24556395_[review] Humans express both Group 1 (CD1a, CD1b and CD1c) and Group 2 (CD1d) CD1 molecules with nonredundant functions in response to the presentation of endogenous lipids. 25115738_High CD1d expression is associated with medulloblastomas. 25381357_Expression of CD1d on B cells is suggestive of the ability of these cells to present antigens to, and form cognate interactions with, invariant natural killer T-Cells. (Review) 25390653_simplexide, apart from activating iNKT cells, induces the production of cytokines and chemokines from human monocytes by direct interaction with CD1d 25452463_These findings highlight how components from alphabeta and gammadeltaTCR gene loci can recombine to confer antigenic specificity. 25477528_CD1d expression in renal cell carcinoma correlated with aggressive disease and poorer clinical outcomes. 25618030_CD1d acts as a cell surface receptor that recognizes and binds oxysterols and initializes a pathway connecting oxysterol binding to PPARgamma activation 25649790_Using diffraction-based dotReadytrade mark immunoassays, the present study showed that staphylococcal enterotoxin B directly and specifically conjugated to CD1d. 25878107_Ablation of this phosphorylation abolished herpes simplex virus 1 US3-mediated downregulation of CD1d expression, suggesting that phosphorylation of KIF3A is the primary mechanism of viral suppression of CD1d expression. 25929465_our results demonstrate that both Ets1 and miR-155 can directly regulate the expression of CD1d on B-cells 26041373_This suggests that CD1D is more polymorphic than previously assumed 26119195_both membrane-bound (V4) and soluble (V5) isoforms of CD1d were over-expressed in gastric tumor tissues, suggesting that they are involved in anti-tumor immune responses. 26260288_by controlling a fundamental step in CD1d-mediated lipid antigen presentation, STAT3 signalling promotes innate immune responses driven by CD1d 26798067_the spatiotemporal distribution of CD1d molecules on the surface of antigen-presenting cells (APCs) modulates activation of Invariant natural killer T cells. 26969612_Data suggest that CD1d antigen-restricted B lymphocytes (Bc) presentation of NGcGM3 drives effective invariant natural killer T cells (iNKT) activation. 27069116_CD1d-restricted peripheral T cell lymphoma in mice and humans 27327902_These findings suggest that VP22 is required (but not sufficient) for the inhibition of CD1d-mediated antigen presentation in herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. 27368347_Importantly, among the analyzed molecules, only CD1d expression showed an association with the activation of double-negative T cells, as well as with worse ventricular function in patients with Chagas disease. 27385215_CD1D has a role in disease progression and survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and may interact with CD161 27513300_BCR-ABL-dependent ROCK, but not TK, is involved in CD1d downregulation. We propose that ROCK, which is most likely activated by the DH/PH domain of BCR-ABL, mediates iNKT-cell immune subversion in chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) patients by downregulating CD1d expression on CML mDCs. 28338767_The expression of CD1d showed a significantly negative correlation with CD86 level in B cells from imiquimod (IMQ)-treated mice, B6.MRLlpr mice, and lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. 28505514_FasL expression in splenic CD5(+)CD1d(hi) B cells was decreased compared to the control group after TLR4 ligation. 28633979_We have studied the relation of CD1d expression in various breast cancer cell lines to their viability and progression. We observed a novel phenomenon that CD1d expression level increases with the progressive stage of the cancer. 29108995_CD1d-expressing cells isolated from peripheral blood of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients showed the suppressive activity of T cell proliferation and higher expression of MyD88 and IDO compared with CD1d(-) cells. 29509047_It provides the additional data of adipocyte CD1d-dependent regulation of adipose iNKT cell responses as well as systemic insulin sensitivity. In addition, we discuss how the interaction between adipocytes and iNKT cells would be regulated with the progression of obesity. 29643189_The increased CD1d expression in HBV-infected liver. 30210497_Role of CD1d- and MR1-Restricted T Cells in Asthma. 30864713_In samples from lung cancer patients, the antitumor activities of all the T cells were enhanced with the increase of CD1D+DCs. Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas data revealed that high levels of CD1D indicated better outcomes for patients. Collectively, CD1D enhanced DCbased antitumor immunity, not only by targeting NKT, but also by activating CD4+T and CD8+T cells. 31050367_Expression of CD1d by astrocytes corresponds with relative activity in multiple sclerosis lesions. 31354710_Invariant NKT Cells From Donor Lymphocyte Infusions (DLI-iNKTs) Promote ex vivo Lysis of Leukemic Blasts in a CD1d-Dependent Manner. 31560833_Increased cytoplasmatic expression of cancer immune surveillance receptor CD1d in anaplastic thyroid carcinomas. 32244759_Structural Dynamics of the Lipid Antigen-Binding Site of CD1d Protein. 32512511_Low oxygen saturation during sleep reduces CD1D and RAB20 expressions that are reversed by CPAP therapy. 33128583_CD1d expression in glioblastoma is a promising target for NKT cell-based cancer immunotherapy. | ENSMUSG00000028076+ENSMUSG00000041750 | Cd1d1+Cd1d2 | 163.173676 | 1.2239189 | 0.291508015 | 0.15146050 | 3.69924013556 | 0.0544372539284899009670581904174468945711851119995117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.17416932935766624157558624119701562449336051940917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 176.539436 | 12.929774 | 145.156549 | 10.946000 |
| ENSG00000158517 | 653361 | NCF1 | protein_coding | P14598 | FUNCTION: NCF2, NCF1, and a membrane bound cytochrome b558 are required for activation of the latent NADPH oxidase (necessary for superoxide production). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19801500, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2547247, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2550933}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chronic granulomatous disease;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain | The protein encoded by this gene is a 47 kDa cytosolic subunit of neutrophil NADPH oxidase. This oxidase is a multicomponent enzyme that is activated to produce superoxide anion. Mutations in this gene have been associated with chronic granulomatous disease. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:653361; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; NADPH oxidase complex [GO:0043020]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; phagolysosome [GO:0032010]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; rough endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005791]; electron transfer activity [GO:0009055]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding [GO:0043325]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; superoxide-generating NAD(P)H oxidase activity [GO:0016175]; superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase activator activity [GO:0016176]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; cellular response to cadmium ion [GO:0071276]; cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0071333]; cellular response to reactive oxygen species [GO:0034614]; cellular response to testosterone stimulus [GO:0071394]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epidermal growth factor-activated receptor activity [GO:0045741]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900745]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; protein targeting to membrane [GO:0006612]; reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process [GO:1903409]; regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response [GO:0060264]; respiratory burst [GO:0045730]; superoxide anion generation [GO:0042554]; superoxide metabolic process [GO:0006801] | 16326715_the C-terminal alpha-helical region of the p22phox peptide increases the binding affinity for the tandem SH3 domains of p47phox more than 10-fold 16608528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16778989_Data show that GM-CSF and TNF-alpha induce phosphorylation of Ser345 on p47phox, a cytosolic component of NADPH oxidase, in human neutrophils. 17150107_The phox homology (PX) domain of p47phox localizes to the plasma membrane in human neutrophils, but is not translocated to the membrane of mature phagosomes. 17217339_Thr133, Ser288 and Thr356, targets for IRAK-4 phosphorylation in vitro, are also phosphorylated in endogenous p47phox after LPS stimulation and regulates NADPH oxidase activation. 17438039_These results indicate that a functional NADPH oxidase and the generation of oxidants in the neutrophil phagosome prevent the activation of the cytoplasmic caspase cascade. 17478731_Increased expression of NAD(P)H oxidase-p47phox and nuclear factor-kappaB p65 may contribute to endothelial oxidative stress with aging in humans. 17586618_Homocysteine increased intracellular reactive oxygen species by NAD(P)H oxidase activation, as shown by the membrane translocation of its p47(phox) subunit. 17651608_There is an increased expression of NADPH oxidase p47(-PHOX) and p67(-PHOX) factor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. 17922419_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17925180_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18004884_the cytosolic regulatory subunit p47phox modulates the conformation of Cyt b (in addition to serving as an adapter protein) during oxidase activation. 18028450_these results indicate that activation of the ASK1/p38 MAPK/p47phox cascade plays a central role in PPD/TLR2-induced ROS generation and suggests the existence of a 'ROS/ASK1' inflammatory amplification feedback loop in monocytes/macrophages. 18045865_CD95L-induced endosomal acidification, ceramide formation, and downstream events, such as p47(phox) phosphorylation, ROS formation, CD95 activation, and apoptosis. 18070887_Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent membrane recruitment of Rac-1 and p47phox is critical for alpha-platelet-derived growth factor receptor-induced production of reactive oxygen species. 18287880_nox1, nox2, and p47 have distinct roles in NADPH oxidase activity in human veins. 18390927_The kinetics of p47phox activation was investigated by comparing neutrophils from diabetic and healthy subjects, and the mechanism of hyperglycemia-induced changes was studied by using neutrophil-like HL-60 cells as a model. 18424721_As(2)O(3) induced phosphorylation and membrane translocation of the NADPH oxidase subunit p47(phox) and it also increased translocation of Rac1 and p67(phox). 18523147_NF-kappaB is necessary for CYBB and NCF1 gene expression and activation of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase normal and anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia leukocytes. 18546332_mutations in CYBB, NCF1, CYBA or NCF2 may play a role in chronic granulomatous disease 18765662_Ile67 of the cPLA2-C2 domain is identified as a critical, centrally positioned residue in a hydrophobic interaction in the p47phox-PX domain 18983267_The direct interaction of PI3Kgamma with PKCalpha forms a discrete regulatory module of N-formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-dependent reactive oxygen species production in neutrophils. 19077231_NCF1DeltaGT/GTGT ratios were correlated with clinical parameters and ROI (reactive oxygen intermediates) production during Plasmodium falciparum malaria and with susceptibility to the autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis (MS) 19077231_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19130504_Nef regulates the NADPH oxidase p47(phox)activity through the activation of the Src kinases and PI3K 19192478_Conformational changes in p47(phox) upon activation highlighted by mass spectrometry coupled to hydrogen/deuterium exchange and limited proteolysis are reported. 19329991_Mutation in NCF1 in Chronic granulomatous disease patient is associated with liver abscess. 19366706_These results demonstrate a role of PLD in hyperoxia-mediated IQGAP1 activation through Rac1 in tyrosine phosphorylation of Src and cortactin, as well as in p47(phox) translocation and reactive oxygen species formation in human lung endothelial cells. 19410294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19632255_NADPH oxidase and lipid raft-associated redox signaling are required for PCB153-induced upregulation of cell adhesion molecules in human brain endothelial cells. 19717732_Conclude that acute exercise increases intracellular NO in endothelial progenitor cells through an NADPH oxidase-inhibition mechanism in sedentary men. 19833721_These results suggest that hyperoxia induces caveolin-1-dependent, c-Abl-mediated dynamin 2 phosphorylation required for recruitment of p47(phox) to caveolin-enriched microdomains and subsequent ROS production in lung endothelium. 19929442_Expression of the p47phox subunit and NOX activity was evaluated in affected (superior and middle temporal gyri) and unaffected (cerebellum) brain regions from a longitudinally followed group of patients with varying degrees of cognitive impairment. 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20167518_All mutations and some polymorphisms identified in the NCF1 gene in the autosomal forms of chronic granulomatous disease are listed. Review. 20407811_granulomatous disease in Iran is predominantly due to mutations in p47-phox, while the number of mutations in p22-phox is roughly equal to that in gp91-phox, indicating that the genetics of CGD are ethnically variable 20495074_Loss of p47phox is associated with inflammasome activation resulting in chronic granulomatous disease. 20592030_p47phox molecular activation for assembly of the neutrophil NADPH oxidase complex. 20817944_a differential and agonist-dependent role of the p47(phox) PX domain for neutrophil NADPH oxidase activation. 21506107_Direct contact of solid tumor cells and ECs activates endothelial NAD(P)H oxidase-mediated superoxide production. The oxidative stress contributes to EC apoptosis which in turn facilitates tumor cell extravasation. 21518975_Results demonstrate that PBEF can prime for PMN respiratory burst activity by promoting p40 and p47 translocation to the membrane. 21566280_There is no correlation between C923T(Ala308Val)polymorphism and cerebral hemorrhage in Han people in Hunan province. 21728841_an increased copy number of NCF1 can be protective against developing RA and add support to previous findings of a role of NCF1 and the phagocyte NADPH oxidase complex in RA pathogenesis. 21789723_autosomal recessive mutational defects are the predominant subtype in Iranian patients with chronic granulomatous disease 21791598_tein disulfide isomerase redox-dependent association with p47(phox): evidence for an organizer role in leukocyte NADPH oxidase activation. 21813271_Resveratrol decreases hyperglycemic induced superoxide production via up-regulation of SIRT1, induction of FOXO3a and inhibition of p47phox in monocytes. 21911753_Data implicate p47phox as one of the sources of oxidative stress in diabetic islets or beta cells during hyperglycemia; evidence supports accelerated Rac1-Nox-ROS-JNK1/2 signaling pathway leading to mitochondrial dysregulation. 21956105_cooperation of p40(phox) with p47(phox) for Nox2-based NADPH oxidase activation during Fcgamma receptor (FcgammaR)-mediated phagocytosis 22219181_MLCK is essential for the translocation and association of cortactin and p47phox. 22460559_Phosphorylation of p47(phox) at different serine sites plays distinct roles in endothelial cell response to TNFalpha stimulation. 22493288_The low affinity and selectivity of the atypical phosphoinositide-binding site on the p47(phox) PX domain suggest that different types of phosphoinositides sequentially bind to the p47(phox) PX domain 22690528_A diffuse cytosolic distribution of p47-phox was observed in neutrophils from HIV-infected patients. 23216310_Patients with p47(phox) hereditary deficiency have intermediate flow mediated dilation and oxidative stress compared to healthy subjects and patients with NOX2 deficiency. 23386289_this study identified a 10 % incidence of diabetes in p47 (phox) deficient chronic granulomatous disease (CGD), but none in X-linked CGD. 23393912_Defining p47-phox deficient Chronic Granulomatous Disease in a Malay family. 23671702_Data show that curcumin-loaded polyvinylpyrrolidone nanoparticles (CURN) decreased the expression of ICAM-1, inhibited NADPH oxidase (NOX)-derived ROS generation, and reduced MAPKs and AP-1 transcription factor binding activities. 23688784_three different cross-over points exist within the NCF1 gene cluster, indicating that autosomal p47(phox)-deficient CGD is genetically heterogeneous but can be dissected in detail by MLPA 23870057_p47(phox) and Rac2 accumulate only transiently at the phagosome at the onset of NADPH activity and detach from the phagosome before the end of reactive oxygen species production. 23975181_There was an increase in p47-phox phosphorylation in neutrophils from myeloproliferative disorder patients with the JAK2 (V617F) mutation. 24081483_Two novel mutations are identified in Greek patients with chronic granulomatous disease: one in NCF1 and one in cytochrome CYBB. 24126171_Williams syndrome patients are at risk for increased aortic stiffness. This vascular stiffness is caused by elastin insufficiency and is modified by NCF1 copy number. 24596025_Four novel mutations in the NCF1, NCF2, and CYBB genees have been identified in chronic granulomatous disease patients in Morocco. 24967690_Suggest eupafolin attenuated COX-2 expression leading to reduced production of prostaglandin E2 by blocking Nox2/p47(phox) pathway. 25239440_Reduced carotid but not coronary artery atherosclerosis in patients with chronic granulomatous disease despite the high prevalence of traditional risk factors raises questions about the role of NADPH oxidase in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. 25761062_Results identifies p47phox-dependent NADPH oxidase activity as a critical component of Angpt-1-mediated endothelial barrier defense against classic inflammatory permeability factors. 25877926_TLR8, but not TLR7, is involved in priming of human neutrophil reactive oxygen species production by inducing the phosphorylation of p47phox and p38 MAPK. 25981738_DCLRE1C and NCF1 mutations have been found by whole-genome sequencing to cause primary immunodeficiency in unrelated patients. 26317224_increased levels of gp91phox, p47phox and p22phox likely account for the interferon-gamma mediated enhancement of dimethyl sulfoxide-induced Nox2 activity. 26460255_A rare mutation in NCF1 encoding p47phox of the leukocyte NADPH oxidase causes lack of superoxide generation, leads to chronic granulomatous disease and was recently (1200-2300 years ago) introduced into the Kavkazi Jewish population 26728380_Data show that diphenylene iodonium (DPI) and apocynin can reduce hyperoxia-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production by decreasing the translocation and level of NADPH Oxidase p47phox. 26760964_Overexpression of p47phox is associated with increased migration/metastasis rate in melanoma. 27040869_Study provides evidence for a novel PKC-zeta to p47phox interaction that is required for cell transformation from blebbishields and ROS production in cancer cells. 27343196_A novel role for Spns2 and S1P1&2 in the activation of p47(phox) and production of reactive oxygen species involved in hyperoxia-mediated lung injury. 27531930_Lysophosphatidylcholines prime polymorphonuclear neutrophil through Hck-dependent activation of PKCdelta, which stimulates PKCgamma, resulting in translocation of phosphorylated p47(phox). 27723093_patients with hereditary p47phox deficiency show reduced platelet activation suggesting a role for this Nox cytosolic subunit in platelet activation. 27765769_Skeletal muscle protein expression of the NADPH oxidase subunits p22(phox), p47(phox), and p67(phox) was increased in obese relative to lean subjects, where p22(phox) and p67(phox) expression was attenuated by exercise training in obese subjects. 28135245_Decreased and increased copy numbers of NCF1 predispose to and protect against SLE. 28240310_IL-27 enhances the potential of reactive oxygen species generation from monocyte-derived macrophages and dendritic cells by induction of p47(phox). 28606963_There was an increased frequency of the NCF1-339 T allele in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. The NCF1-339 T allele reduced extracellular ROS production in neutrophils and led to an increase expression of type 1 interferon-regulated genes. 28939422_p47phox, but not p67phox or p40phox, binds to and activates Nrf2, enhancing the function of Nrf2 in suppressing inflammation. 29195919_p47phox S-glutathionylation plays an essential key role in the sustained ROS generation by human neutrophils. 29311151_Tyrosine kinase substrate (Tks) proteins, analogous to the related proteins p47(phox), p40(phox) and NoxO1, also facilitate local generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which aid in signaling at invadopodia and/or podosomes to promote their activity. As their name suggests, Tks adaptor proteins are substrates for tyrosine kinases, especially Src. [review] 29331982_In six additional Ashkenazi carriers of the NCF1 c.579G>A mutation, we found five individuals with three complete NCF1 genes of which one was mutated (like the parents), and one individual with in addition a fusion gene of NCF1 with a pseudogene 29360265_Our findings in experiments on activated human retinal endothelial cells provide translational corroboration of studies in experimental models of retinal vasculopathy and support the therapeutic application of Nox4 inhibition by GKT136901 and GKT137831 in patients with retinal vascular diseases. 29411231_Correlation between genotype and phenotype is unpredictable, although clinically, the Kavkazi patients were more severely affected than other patients with p47phox deficiency. 30078213_we discovered the existence of p47(phox) /Hyal2 complex. LSS induced the dissociation of p47(phox) /Hyal2 complex, which was inhibited by LKB1 overexpression and AICAR. Furthermore, knockdown of Hyal2 performed a positive feedback on LKB1 activity 30323221_Activation of PAD4 by membranolytic insults that result in high levels of intracellular calcium (higher than physiological neutrophil activation) leads to rapid citrullination of p47(phox)/NCF1 and p67(phox)/NCF2, as well as their dissociation from PAD4 30465301_NCF1, a critical gene in the ROS system, was upregulated in THP-1 cell and monocytes under lipopolysaccharides stimulation. Moreover, we identified the upregulation of NCF1 in a sepsis model. 30470980_of the total molecularly characterized Indian patients with chronic granulomatous disease (n = 90), 56% of the patients had a mutation in the NCF1 gene 30580571_we identify specific cysteine residues of protein disulfide isomerase and p47phox necessary for the direct interaction of these proteins, the assembly of the Nox1 complex and subsequent activation of Nox1 in vascular disease. 30651282_flow cytometry for p47(phox) expression quickly identifies patients and carriers of p47(phox) CGD, and genomic ddPCR identifies patients and carriers of DeltaGT NCF1, the most common mutation in p47(phox) CGD. 30963593_this study shows genetic and molecular findings of 38 Iranian patients with chronic granulomatous disease caused by p47-phox defect 31492810_Data showed that proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) associated with neutrophil cytosolic factor 1 (p47phox), a key subunit of NADPH oxidase in neutrophils and that this association regulated reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. 31704719_Polymorphism NCF1-339, rs201802880 mediated decreased NADPH oxidase function, is associated with high interferon activity and impaired formation of neutrophil extracellular traps in systemic lupus erythematosus, allowing dependence on mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS). Also a striking connection between the ROS deficient NCF1-339 genotypes and the presence of phospholipid antibodies and antiphospholipid syndrome 31705128_Association of NCF1 polymorphism with systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis but not with ANCA-associated vasculitis in a Japanese population. 31973815_P-Tyr42 RhoA GTPase amplifies superoxide formation through p47phox, phosphorylated by ROCK. 33596590_Neutrophil Cytosolic Factor-1 Genotyping in Acne Vulgaris. 33903979_Whole genome sequencing identifies variants associated with sarcoidosis in a family with a high prevalence of sarcoidosis. 34556485_Human SLE variant NCF1-R90H promotes kidney damage and murine lupus through enhanced Tfh2 responses induced by defective efferocytosis of macrophages. 34708124_NCF1/2/4 Are Prognostic Biomarkers Related to the Immune Infiltration of Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma. 35108370_Impaired p47phox phosphorylation in neutrophils from patients with p67phox-deficient chronic granulomatous disease. | ENSMUSG00000015950 | Ncf1 | 557.016644 | 0.8671802 | -0.205596207 | 0.07000488 | 8.62810736320 | 0.0033101530653845594523443374157523066969588398933410644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.02047756872908898170826397233668103581294417381286621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 521.821507 | 27.341049 | 604.563842 | 31.155113 | |
| ENSG00000158615 | 84919 | PPP1R15B | protein_coding | Q5SWA1 | FUNCTION: Maintains low levels of EIF2S1 phosphorylation in unstressed cells by promoting its dephosphorylation by PP1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26159176, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26307080}. | 3D-structure;Diabetes mellitus;Disease variant;Dwarfism;Intellectual disability;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Translation regulation | This gene encodes a protein phosphatase I-interacting protein that promotes the dephosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2A to regulate translation under conditions of cellular stress. The transcribed messenger RNA contains two upstream open reading frames (ORFs) that repress translation of the main protein coding ORF under normal conditions, while the protein coding ORF is expressed at high levels in response to stress. Continual translation of the mRNA under conditions of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2A inactivation is thought to create a feedback loop for reactivation of the gene during recovery from stress. In addition, it has been shown that this protein plays a role in membrane traffic that is independent of translation and that it is required for exocytosis from erythroleukemia cells. Allelic variants of this gene are associated with microcephaly, short stature, and impaired glucose metabolism. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. | Mouse_homologues mmu:108954; | endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; protein phosphatase type 1 complex [GO:0000164]; protein phosphatase regulator activity [GO:0019888]; ER overload response [GO:0006983]; negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced eIF2 alpha phosphorylation [GO:1903912]; negative regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response [GO:1903898]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; peptidyl-serine dephosphorylation [GO:0070262]; positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0032516]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976]; response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0042542] | 22915583_the mammalian traffic machinery co-opts p-eIF2alpha and CReP, regulators of translation initiation. 25325377_CIP2A regulates cancer metabolism and CREB phosphorylation in non-small cell lung cancer 26159176_the first homozygous mutation in the PPP1R15B gene encoding the regulatory subunit of an eIF2alpha-specific phosphatase in two siblings affected by a novel syndrome of diabetes of youth with short stature, intellectual disability, and microcephaly 26307080_Whole-exome sequencing identified a homozygous missense mutation, c.1972G>A; p.Arg658Cys, in protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 15b (PPP1R15B) 29599191_p97-mediated degradation, together with a reduction in CReP synthesis, is essential for timely stress-induced reduction of CReP levels and, consequently, for robust eIF2alpha phosphorylation to enforce the stress response. 34847777_Substrate recognition determinants of human eIF2alpha phosphatases. | ENSMUSG00000046062 | Ppp1r15b | 1236.658115 | 1.1030961 | 0.141558545 | 0.04530906 | 9.75896775348 | 0.0017845007990209536298531478593076826655305922031402587890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.01231455213453630861963894460586743662133812904357910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1297.028742 | 38.427501 | 1181.129405 | 35.031821 | |
| ENSG00000158863 | 64760 | FHIP2B | protein_coding | Q86V87 | FUNCTION: Able to activate MAPK/ERK and TGFB signaling pathways (PubMed:22971576). May regulate the activity of genes involved in intestinal barrier function and immunoprotective inflammation (By similarity). May play a role in cell proliferation (PubMed:22971576). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80YR2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22971576}. | Reference proteome | hsa:64760; | 22971576_Retinoic acid induced 16 enhances tumorigenesis and serves as a novel tumor marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. 25900241_RAI16 interacted with the type II regulatory subunit of protein kinase A(PKA-RIIalpha), acting as a novel protein kinase A anchoring protein (AKAP). In addition, RAI16 also interacted with heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) and 14-3-3theta;. 31353455_FAM160B1 deficit associated with microcephaly, severe intellectual disability, ataxia, behavioral abnormalities and speech problems. 31862898_Retinoid acid induced 16 deficiency aggravates colitis and colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice. 32014455_Identification of retinoid acid induced 16 as a novel androgen receptor target in prostate cancer cells. | ENSMUSG00000022095 | Fhip2b | 299.881033 | 0.5801843 | -0.785416751 | 0.11593188 | 45.73018523255 | 0.0000000000135715248175144826354367800090892437828160588253467722097411751747131347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000000044458662563792176250870568848870371947423763003826024942100048065185546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 217.726826 | 18.121680 | 376.965875 | 30.692527 | |||
| ENSG00000159199 | 516 | ATP5MC1 | protein_coding | P05496 | FUNCTION: Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F(1)F(0) ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F(1) - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core and F(0) - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F(1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Part of the complex F(0) domain. A homomeric c-ring of probably 10 subunits is part of the complex rotary element. | CF(0);Hydrogen ion transport;Ion transport;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Methylation;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | This gene encodes a subunit of mitochondrial ATP synthase. Mitochondrial ATP synthase catalyzes ATP synthesis, utilizing an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane during oxidative phosphorylation. ATP synthase is composed of two linked multi-subunit complexes: the soluble catalytic core, F1, and the membrane-spanning component, Fo, comprising the proton channel. The catalytic portion of mitochondrial ATP synthase consists of 5 different subunits (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon) assembled with a stoichiometry of 3 alpha, 3 beta, and a single representative of the other 3. The proton channel seems to have nine subunits (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, F6 and 8). This gene is one of three genes that encode subunit c of the proton channel. Each of the three genes have distinct mitochondrial import sequences but encode the identical mature protein. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:516; | mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex [GO:0005753]; mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, coupling factor F(o) [GO:0000276]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, coupling factor F(o) [GO:0045263]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; proton transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015078]; proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis [GO:0015986] | 19889836_The subunit c isoforms are nonredundant, because they differ functionally by their targeting peptides, which, in addition to mediating mitochondrial protein import, play a yet undiscovered role in respiratory chain maintenance. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27563065_ATP5G1 turnover increases upon depletion of ZC3H14, double knockdown of ZC3H14 and the nonsense-mediated decay factor, UPF1, rescues ATP5G1 transcript levels. Furthermore, fractionation reveals an increase in the amount of ATP5G1 pre-mRNA that reaches the cytoplasm when ZC3H14 is depleted and that ZC3H14 binds to ATP5G1 pre-mRNA in the nucleus. 28289229_ATP5G1, ATP5G2, and ATP5G3 of the ATP synthase are not involved in forming the permeability transition pore. 33852870_A naturally occurring mutation in ATP synthase subunit c is associated with increased damage following hypoxia/reoxygenation in STEMI patients. | 263.073915 | 0.8543171 | -0.227156380 | 0.15781868 | 2.06791844726 | 0.1504267096596032249333774188926327042281627655029296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.34539868921840610749285360725480131804943084716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 250.645890 | 26.853949 | 294.626732 | 31.457074 | |||
| ENSG00000160211 | 2539 | G6PD | protein_coding | P11413 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the rate-limiting step of the oxidative pentose-phosphate pathway, which represents a route for the dissimilation of carbohydrates besides glycolysis. The main function of this enzyme is to provide reducing power (NADPH) and pentose phosphates for fatty acid and nucleic acid synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15858258, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24769394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26479991, ECO:0000269|PubMed:743300}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Carbohydrate metabolism;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Glucose metabolism;Hereditary hemolytic anemia;Hydroxylation;Membrane;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | PATHWAY: Carbohydrate degradation; pentose phosphate pathway; D-ribulose 5-phosphate from D-glucose 6-phosphate (oxidative stage): step 1/3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15858258, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24769394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26479991, ECO:0000269|PubMed:743300}. | This gene encodes glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. This protein is a cytosolic enzyme encoded by a housekeeping X-linked gene whose main function is to produce NADPH, a key electron donor in the defense against oxidizing agents and in reductive biosynthetic reactions. G6PD is remarkable for its genetic diversity. Many variants of G6PD, mostly produced from missense mutations, have been described with wide ranging levels of enzyme activity and associated clinical symptoms. G6PD deficiency may cause neonatal jaundice, acute hemolysis, or severe chronic non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:2539; | centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; glucose binding [GO:0005536]; glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity [GO:0004345]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; NADP binding [GO:0050661]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0006695]; erythrocyte maturation [GO:0043249]; glucose 6-phosphate metabolic process [GO:0051156]; glucose metabolic process [GO:0006006]; glutathione metabolic process [GO:0006749]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; NADP metabolic process [GO:0006739]; NADPH regeneration [GO:0006740]; negative regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0061052]; negative regulation of protein glutathionylation [GO:0010734]; negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000378]; pentose biosynthetic process [GO:0019322]; pentose-phosphate shunt [GO:0006098]; pentose-phosphate shunt, oxidative branch [GO:0009051]; positive regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel [GO:1904879]; regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043523]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to food [GO:0032094]; response to iron(III) ion [GO:0010041]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; ribose phosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0046390]; substantia nigra development [GO:0021762] | 11024211_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11042039_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11499668_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11793482_DNA mutational analysis in Thailand: G6PD Viangchan (871G>A) is the most common deficiency variant in the Thai population 11793482_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11852882_A single mutation 202G>A in the human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (G6PD) can cause acute hemolysis by itself. 11874436_a candidate gene for diabetes 11876979_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11877026_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11920200_31 alleles carrying the betaS mutation, 6 beta-thalassaemic alleles & 17 G6PD alleles, were studied from a group of carriers or affected subjects. Allele frequencies were 3% for haemoglobin S, 1% for beta-thalassaemia trait and 9.5% for G6PD deficiency. 12130518_Deletion of leucine 61 in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase leads to chronic nonspherocytic anemia, granulocyte dysfunction, and increased susceptibility to infections. 12135480_Recombinant human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase uses a rapid-equilibrium random-order mechanism for substrate binding. 12378426_nucleotide diversity across a 5.2-kb region of G6PD in a sample of 160 Africans and 56 non-Africans, to determine how selection has shaped patterns of DNA variation at this gene 12380870_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12439228_Observational study of gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12497642_Mutational analysis of G6PD variants in Malaysian Malays with G6PD deficiency. 12497642_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12524354_Nucleotide variability at G6pd and the signature of malarial selection in humans. 12588050_Significant difference in distribution of G6PD activities as grouped by an increment of 100 U/10(12) red blood cells (RBCs) was observed between diabetic patients and healthy subjects. 12616531_HPRT and G6PD origins of replication that are functional in the active X chromosome are utilized even when the two genes are transcriptionally silent in the inactive X chromosome. 12641410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12680285_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12696079_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12737938_the association of G6PD Sumare and G6PD A- in a compound heterozygote gave rise to a very mild chronic hemolysis, and the red cell population containing G6PD A- is probably enough to protect against severe chronic hemolysis 12737940_Molecular characterization of G6PD Insuli--a novel 989 CGC --> CAC (330 Arg --> His) mutation in exon 9 in the Indian population with normal enzyme activity 12737943_This study suggests that the metabolic consequences of a combined deficiency of GPI and G6PD might be responsible for a different clinical outcome, severe congenital hemolytic anemia, than predicted for either defect in isolation. 12768444_G6PD deficiency was studied in Nepalese males. 12850494_screening a Mexican population identified new mutations located at cDNA nt 376 A --> T (126 Asn --> Tyr), nt 770 G --> T (257 Arg --> Leu), nt 1094 G --> A (365 Arg --> His), and nt 1285 A --> G (429 Lys --> Glu) 12921788_glycolaldehyde inactivates glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, and Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase, suppresses cell growth, and induces apoptosis. 12972027_4% of males in the Kuwaiti population have G6PD deficiency coexisting with low activity of the UDPGT1 promoter 12972027_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14614139_distribution of erythrocyte G6PD activity in human populations reveals a selective pressure for maintaining high activity 14757424_identified two de novo missense mutations in patients with severe G6PD deficiency as sites Pro409 and Val431, located on different subunits, that interact directly across the subunit interface and perturb formation of the G6PD dimer upon mutation 14757426_gene 1226 C-->G mutation in a chronic nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia patient causes significant differences in Km values and enzyme stability, by changing tetramer interactions and disturbing the binding of structural NADP+ 15223006_determined the frequency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency in Cyprus; one previously undescribed mutation in exon 3, 148C-->T (Pro50Ser), was found 15282679_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15307413_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15315792_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15315792_genetic diversity of enzyme forms in GPD deficiency in India. 15330559_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15466166_uncommon splice site mutation causes enzyme deficiency 15476167_G6PD cDNA 1388 (G-->A), 1376 (G-->T), 95(A--> G), 392 (G-->T), 1024 (C-->T) and 1311 (C-->T) accompanied with intron 11 (93 T-->C) are the common mutations in Chinese population. 15506519_Review. Nearly 150 different G6PD variants have been described. The recent determination of its 3-dimensional structure explains the mechanisms of G6PD deficiency in terms of structure-function relationship. 15558953_Observational study of gene-environment interaction, pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15598086_Based on the increased susceptibility of G6PD-deficient patients to oxidative stress, an increase in Se-GSH-Px activity can facilitate the detoxification of reactive oxygen species. 15622766_G6PD mutation from G6PD deficient patients were analyzed. 15659240_We have shown two distinct CREB-responsive sites in the glucose-6-phosphatase gene promoter that are responding to a constitutively active CREB or elevated concentrations of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in the nucleus. 15718915_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15727905_G6PD Viangchan and Mahidol are common Southeast Asian variants and support the theory of genetic drifts throughout Southeast Asia. 15727905_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15748456_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15766741_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15864125_UGT1A1, OATP2 and G6PD genes have roles in genetic predisposition to unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia 15906717_G6PD Viangchan and G6PD Mediterranean account for the main variants in G6PD deficiency among the Malay population in Malaysia. 15906719_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15914531_G6PD deficiency alone is not causative of diabetic ketosis and alterations in genes controlling both insulin secretion and G6PD-mediated antioxidant defenses may contribute to the predisposition in West Africans 15914531_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15957246_Mediterranean mutation at nt 563(C-->T) is predominant in the Iran's Golestan province (69%) and 26.7% of patients have Chatham mutation at nt 1003(G-->A) 16059744_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16088936_analysis of disease phenotype in two human glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase mutants, G6PD(Union) and G6PD(Andalus) 16136268_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16137669_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16143877_A novel variant, named G6PD Split, is caused by a nucleotide change 1442 C-->G leading to the amino acid substitution 481 Pro-->Arg and is characterized by moderate enzyme deficiency (class III variant). 16155737_G6PD Viangchan (871G>A) is the most common G6PD-deficient variant in the Cambodian population. 16155737_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16255851_G-6-PD deficiency coexists with G71R or A388G mutation in some individuals with neonatal jaundice in Guangxi region. 16255851_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16272653_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16331553_Data show that 34 heterozygous females with from patients with G6PD deficiency variants was identified by denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography. 16331553_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16356170_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16461316_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16483869_Microtubule motor proteins colocalize with G6PDase; microtubule motor proteins participate in hexose monophosphate shunt enzyme transport within leukocytes. 16532971_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16569302_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16607506_Arg459 and Arg463 play important roles in anchoring NADP+ to the catalytic domain, sequence from codon 459 to the carboxyl terminal is essential for the enzymatic function. 16637741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16792831_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16859949_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16927025_analysis of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase variants in Flores Island, eastern Indonesia 16934959_These results, together with structural information, suggest that the instability of the R393H protein, enhanced by the weakened binding of 'structural' NADP+, is the likely cause of the severe clinical manifestation observed for G6PD(Nashville). 16944148_Novel missense mutation in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene causing chronic nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia. 17007653_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17018380_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17077204_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17264545_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17499234_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17499234_Three different major polymorphic variants were found in Iran: G6PD Mediterranean 75.4% (187 out of 248), G6PD Chatham 19.76% (49 out of 248), G6PD Cosenza 2.02% (5 out of 248) and 7 samples out of 248 remained unknown. 17524386_A novel genetic mutation (G130A) in the third exon was found in a case of an asymptomatic young subject affected by severe deficiency of Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) activity. 17557555_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17557555_results do not confirm an association either positive or negative between the G6PD polymorphism and lymphoma risk. 17587269_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17587269_study found that the nucleotide substitutions associated with G6PD deficiency in Chinese subjects are distinctly different from those associated with G6PD deficiency in other ethnic groups 17611006_biochemical and clinical effect of variants and discussion of the relationship between genotype and phenotype [review] 17637841_G6PD variants have been compared with mutants from germany and other countries. 17653668_prevalence of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency and its gene mutations were studied in the Achang population of Southwestern China; a new polymorphism IVS5-612 (G>C), which combined into a novel haplotype, was identified 17660836_In hematopoietic stem cell transplantationfemale donors heterozygous for X-linked recessive disorders, altered G6PD may cause clinical diseases in the recipients. 17877203_Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase G1376T and G1388A are the most common mutations in the populations of the Han and Li nationalities in Hainan. 17959407_Purification and detailed study of two clinically different human glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase variants, G6PD(Plymouth) and G6PD(Mahidol). 18043863_Mutation in the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene is associated with Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency 18046504_glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase mutations in Mon and Burmese males of southern Myanmar who migrated to Thailand in Samutsakhon province. G 18056001_investigation of mutations and G6PD locus haplotype diversity in Portuguese G6PD-deficient individuals 18066402_Three novel mutations in the G6PD gene are presented, andt the changes they cause in the 3-dimensional structure of the enzyme are discussed. 18086567_A symptomatic baby is affected by severe deficiency of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity due to a novel de novo genetic mutation that may have occurred in a very early stage of embryogenesis or in the mother's germ cell lines. 18164966_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18164966_Whereas the frequency of beta-thalassemia minor among Moslems is higher than in the Jews in Shiraz, the frequency of G6PD deficiency was not significantly different in the two populations. 18173836_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18215251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18226470_Screening of 79 Tunisian G6PD deficiency patients revealed a newly described silent mutation in exon 12 associated with the polymorphism in the intron 11 93 TC in one subject and 2 single intronic base deletions: IVS V 17 (-C) & IVS VIII 43 (-G). 18302154_G6PD activity was intensely elevated in tumor tissues. 18376107_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18458302_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18493020_Data show that G6PD thus forms active dimer without structural NADP+. Apparently, the true role of the second, tightly bound NADP+ is to secure long-term stability. 18494377_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18558634_Gene polymorphisms of G6PD were detected in children with hereditary hyperbilirubinemia; degree of genetic heterogeneity and variant coexpression across G6PD gene points to polygenic nature of this disease. 18558634_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18677765_glucose-6-phosphate Dehydrogenase exon mutation is associated with hemolytic anemia with Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. 18985093_Nine different glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) variants in a Malaysian population with Malay, Chinese, Indian and Orang Asli (aboriginal Malaysian) backgrounds were detected in G6PD-deficient cases. 19219640_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19219640_Our finding indicate the prevalence of factor V Leiden, prothrombin G20210A and MTHFR C677T in G6PD deficiency is not statistically different compared to normal subjects and is not associated with these thrombophilic mutations in Western Iran. 19223928_G6PD-deficient male hemizygotes and female heterozygotes are protected from severe malaria. 19223928_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19224086_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19272180_Results show that ectopic expression of hTERT stimulates telomerase activity and prevents accelerated senescence in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase -deficient cells. 19317913_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19323016_Both clinical and hematological phenotypes of simple homozygous HbE did not differ from those who also inherited alpha-thalassemia and/or G6PD deficiency. 19336475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19359662_Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase is regulated through c-Src-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation in endothelial cells. 19419973_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19422023_A prolonged neonatal jaundice associated with a rare G6PD mutation. 19465117_Results suggest that impaired binding of 'structural' NADP(+) can hinder folding as well as cause instability of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase clinical mutant enzymes in the fully folded state. 19497363_G6PD confers protection against oxidant-induced cytotoxicity through effective glutathione regeneration. 19589177_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19589177_This study confirmed that G6PD deficiency is strongly associated with haemoglobinuria 19594365_G6PD Mediterranean S188F codon mutation is common among Saudi sickle cell patients and increases the risk of stroke. 19594365_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19632868_This is the second documented observation of a class-III variant, we named G6PD Pyrgos, found in a Greek family. A 3-dimensional structure model for the enzyme shows that the region modified by the substitution is identical to that modified in G6PD A(-) 19640310_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19811411_The decline in the activities of G6PD and b5Rm would indicate a decrease in the antioxidant response associated with RBC aging. 19858149_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19858149_coexpression of the G6PD African A- mutation with UGT1A1 and/or SLCO1B1 variants was seen more frequently in neonatal hyperbilirubinemia 19896395_the most frequent mutations of G6PD in diagnosed deficient patients in Panama Children's Hospital 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19941843_A concomitant response of G6PD activities and RBC fragility towards the oxidative stress was established. 19996424_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20007901_effect of G6Pd-Mahidol(487A) variant in Southeast Asia on survival in vivax & falciparum malaria; results show positive selection has targeted Mahidol variant over past 1500 years; the variant reduces vivax but not falciparum parasite density 20017397_The regulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and glycogen synthase activities by insulin superfamily peptides in myometrium of pregnant women and its impairments under different types of diabetes mellitus 20032314_High-glucose-mediated decrease in G6PD activity may provide a mechanistic explanation for the gradual loss of beta cells in patients with diabetes. 20113600_G-6-PD gene mutations alone may not contribute to the development of acute bilirubin encephalopathy and the changes of peak bilirubin concentration 72 hrs after birth. 20113600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20118060_Low glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase is associated with severe hemolysis. 20200584_This is the first report of a G6PD-deficient Chinese patient in the category of class I 20203002_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20236109_determined the frequency and spectrum of G6PD mutations in Saudi patients 20447239_frequency of G6PD gene mutations in G6PD deficient cases in Saudi Arabia; 2 mutations were resolved in exon 6- Mediterranean and Sibari; no mutation was detected in exon 7; frequency of exon 6 mutations responsible for G6PD deficiency was 50.1% 20459687_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20507315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20514852_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20520804_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20528626_haplotypes linked to G6PD genotypes in India defined by studying intragenic RFLPs in G6PD deficient and normal chromosomes;only 4 haplotypes were observed, indicating linkage disequilibrium; all G6PD deficient mutations associated with haplotype I or VII 20582980_A novel missense mutation (G473A), predicting a Cys-to-Tyr substitution at codon 158, was identified in a male infant patient and confirmed in his mother 20602793_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20621077_three families carrying G6PD mutations unusual for Italian population 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20684792_Results of the survey indicate that G6PD deficiency is prevalent in Isabel Province 20713184_in Indian population, study identified 1 new exonic variant predicted to result in G6PD deficiency; results provide indication of weak negative selection and reveal signals of recent positive selection for Orissa and Coimbra mutation bearing haplotypes 20927393_Plasmodium falciparum induced its own G6PD gene in G6PD-deficient erythrocytes. 20949590_Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase mutation is associated with severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia and cholestasis. 21125776_The interaction effect of G-6-PD deficiency with sickle cell gene (trait) in lowering the red cell indices was more marked in females than in males 21180140_G6PD contributes to replenish intracellular GSH and is a critical factor regulating GSH levels during oxidative stress. 21205543_G6PD(C563T) Mediterranean mutation accounted for 65.6% of favism in Jordan. There is likely to be another G6PD deficiency variant in acute hemolytic crisis (favism). 21302115_Data report two families with novel mutations of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase causing chronic nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia. 21376116_erythrocytes from the common African variant G6PD A- were used to analyze by redox proteomics the major oxidative changes occurring in host membrane proteins during intraerythrocytic development of Plasmodium falciparum, the most lethal malaria parasite 21376267_Data suggest that HIV-positive G6PD-deficient subjects due to reduced intracellular GSH levels may be more prone to the development of AIDS. 21397531_Molecular studies revealed heterozygosity for an in-frame 18-bp deletion, mapping to exon 10 leading to a deletion of 6 residues, 362-367 (LNERKA), which is a novel G6PD class 1 variant, G6PD Tondela 21507164_The frequency of G6PD deficiency is higher among the Negrito Orang Asli than other Malaysian races and might be a result of genetic drift within this isolated group. 21507207_Data show that 563C-T was the commonest G6PD variant, while 1003A-G and 131C-G were less-frequent genetic variants of G6PD in Pakistani population. 21549219_G6PD A- carriers had a lower increase of IgG3 levels to plasmodium falciparum MSP2 antigen during the transmission season than the noncarriers 22012600_overexpression of G6PD is closely related to progression of gastric cancer, and might be regarded as an independent predictor of poor prognosis for gastric cancer. 22117603_analysis of mutations in homozygous sickle cell anemia and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency [case report] 22139979_Novel mutations in the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene isoforms have been described among ethnically diverse French patients with the glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. 22165289_Enzyme kinetics and molecular modeling studies of G6PD(Mahidol) associated with acute hemolytic anemia 22307442_Case Report: novel GLA mutation in mother/daughter/son with Fabry disease and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. 22364808_The Mediterranean mutation c.563T, while common among G6PD deficient Gaza Strip Palestinians and closely linked with the G6PD c.1311T polymorphism, does not account for most of the G6PD mutations in Gaza Strip population. 22431005_G6PD is under complex regulatory control and of central importance to many cellular processes. [Review] 22537951_UGT1A1 Gly71Arg and G6PD gene mutations may be involved in the development of neonatal unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. 22552160_Using PCR-SSCP of coding regions followed by direct sequencing of abnormal pattern, three new mutations were detected in G6PD in Tunisian population. 22768742_Deficiencies of erythrocytic G6PD in Uzbekistan are marked with diverse pathological phenotypes. 22770933_G6PD Beverly Hills(c.1160A) mutation, and a novel G6PD missense mutation c.536G>A (Ser179Asn), G6PD 'Gaza' have been found in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene in Gaza Strip Palestinian children. 22848499_G6PD activity antagonizes the cytotoxicity of 8-substituted adenosine analogues and suggests that administration of these agents to patients with B-cell malignancies exhibiting normal levels of G6PD expression may be particularly efficacious. 22906047_Infants with G6PD c.563C > T variant developed jaundice earlier than infants with normal G6PD enzyme levels. Compared to G6PD normal infants, G6PD c.563C > T carrying infants had significantly low G6PD activity. 22906837_This is the first report of G6PD Santamaria and Cairo among our Jordanian population. 22958163_Intracranial vasculopathy was observed in a minority of children with sickle cell anaemia (SCA), and when present, was associated with G6PD status in males and Silent cerebral infarct (SCI). 22963789_2 novel missense class III variants were identified (c.920A>C: p.307Gln>Pro and c.968T>C: p.323 Leu>Pro)& designated G6PD Tunis & G6PD Nefza. 14 other genotypes were found among 293 Tunisian G6PD deficiency patients. 23023104_The most potent hG6PD inhibitors presented IC(50) values of T, is common in many ethnic groups in Afghanistan, indicating that screening for G6PD deficiency is required in all individuals before radical treatment of P. vivax with primaquine. 24615128_Our results support the protective effect in G6PD A- heterozygous females and suggest that homozygotes might be more susceptible to severe malaria attacks. 24636884_The G6PD-deficient erythrocytes were severely compromised in their ability to recycle oxidized Prx2. 24769394_Regulation of G6PD acetylation by SIRT2 and KAT9 modulates NADPH homeostasis and cell survival during oxidative stress. 24805191_We show that HDAC inhibitors selectively enhance transcription of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase 24853873_No G6PD deficiency was observed using phenotypic- or genetic-based tests in individuals residing in vivax malaria endemic regions in the ROK. 24958328_Heterozygotes with hypermethylation of specific CpG sites in the G6PD promoter and preferential X-inactivation of the wild-type allele were at risk of enzyme deficiency. 24994855_G6PD may be a novel target in future treatment of HBV-associated cancer of the liver. 25015414_53 G6PD polymorphisms, including 202/376, were genotyped across the 712 samples from Dogon and Fulani people. Association of these polymorphisms and mild malaria was assessed in both ethnic groups using genotypic and haplotypic statistical tests. 25169987_The G6PD A- mutation (G202A and A376G) does not appear to have a role in G6PD deficiency. 25189226_A novel G6PD mutation named Mexico DF(193A>G) (rs199474830), which probably results in a damaging functional effect in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. 25201310_c.376A>G (rs1050829) augments 202AG heterozygote risk for deficiency trait by two-fold. 25246627_G6PD-deficient neonates had a higher risk of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia compared to controls. 25261071_Adequate hemodialysis in correcting anemia had a benificial effect by enhancing the erythrocyte G6PD activity in patients. 25261933_The main African form of G6PD deficiency reduces the risk of cerebral malaria but increases the risk of severe malarial anemia. 25297600_Studies suggest that the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency genetic screening should be performed prior to assisted reproduction. 25407525_These results show that the location of the mutation affects the catalytic properties, stability and structure of G6PD and that these changes are closely associated with the clinical presentation of its deficiency. 25536053_The population from Myanmar living in the study area has a high frequency of G6PD deficiency ranging from 9% to 18%. 25616277_G6PD expressions in the HR-HPV + human CC tissues and cell lines play an important role in tumor growth and proliferation. 25633909_Proteomics results showed that G6PD was highly expressed in cervical cancer cells and its down regulation reduced reduced the capacity of HeLa cells to migrate and invade in vitro. 25671784_Our study also demonstrates that the much-needed large-scale studies of severe malaria and G6PD enzymatic function across African populations require the identification and analysis of the full repertoire of G6PD genetic markers. 25818003_G6PD, GGCT, IDH1, isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (NADP+,mitochondrial) (IDH2) and glutathione S-transferase pi 1(GSTP1), five of the critical components of GSH pathway, contribute to chemoresistance. 25885177_Studied G6PD mutations present in a Sri Lankan population and their association with uncomplicated malaria. 25979194_differential expression in children with allergic asthma 26004559_To understand the sporadic Alzheimer's disease, the writer of this paper thinks that, looking into a crystal ball might not yield much of a benefit but glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency could effortlessly give some clues. 26139767_G6PD deficiency is an example of balanced polymorphism, in which high rate of mortality caused by this disorder is offset by the protection that it offers against Plasmodium falciparum malaria 26250461_G6PD may function as an important regulator in development and progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by manipulating STAT3 signaling pathway 26399441_G6PD glycosylation is increased in human lung cancers. Glycosylation activates G6PD activity and increases glucose flux through the PPP, thereby providing precursors for nucle | ENSMUSG00000031400+ENSMUSG00000089992 | G6pdx+G6pd2 | 371.529226 | 0.7158565 | -0.482257698 | 0.08544083 | 31.93551970393 | 0.0000000159376014511544361129084264707203577593475074536399915814399719238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000035612646820886302433562409924805436389760870952159166336059570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 299.778808 | 20.221474 | 420.373965 | 27.443464 |
| ENSG00000160691 | 6464 | SHC1 | protein_coding | P29353 | FUNCTION: Signaling adapter that couples activated growth factor receptors to signaling pathways. Participates in a signaling cascade initiated by activated KIT and KITLG/SCF. Isoform p46Shc and isoform p52Shc, once phosphorylated, couple activated receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras via the recruitment of the GRB2/SOS complex and are implicated in the cytoplasmic propagation of mitogenic signals. Isoform p46Shc and isoform p52Shc may thus function as initiators of the Ras signaling cascade in various non-neuronal systems. Isoform p66Shc does not mediate Ras activation, but is involved in signal transduction pathways that regulate the cellular response to oxidative stress and life span. Isoform p66Shc acts as a downstream target of the tumor suppressor p53 and is indispensable for the ability of stress-activated p53 to induce elevation of intracellular oxidants, cytochrome c release and apoptosis. The expression of isoform p66Shc has been correlated with life span (By similarity). Participates in signaling downstream of the angiopoietin receptor TEK/TIE2, and plays a role in the regulation of endothelial cell migration and sprouting angiogenesis. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14665640}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Cytoplasm;Growth regulation;Host-virus interaction;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain | This gene encodes three main isoforms that differ in activities and subcellular location. While all three are adapter proteins in signal transduction pathways, the longest (p66Shc) may be involved in regulating life span and the effects of reactive oxygen species. The other two isoforms, p52Shc and p46Shc, link activated receptor tyrosine kinases to the Ras pathway by recruitment of the GRB2/SOS complex. p66Shc is not involved in Ras activation. Unlike the other two isoforms, p46Shc is targeted to the mitochondrial matrix. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. | hsa:6464; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; Shc-EGFR complex [GO:0070435]; ephrin receptor binding [GO:0046875]; epidermal growth factor binding [GO:0048408]; epidermal growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005154]; insulin receptor binding [GO:0005158]; insulin-like growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005159]; neurotrophin TRKA receptor binding [GO:0005168]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity [GO:0043539]; receptor tyrosine kinase binding [GO:0030971]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase adaptor activity [GO:0005068]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007173]; heart development [GO:0007507]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048009]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cell proliferation in bone marrow [GO:0071864]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; regulation of epidermal growth factor-activated receptor activity [GO:0007176]; regulation of superoxide metabolic process [GO:0090322]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] | 11877420_Tyrosine phosphorylation of the beta-amyloid precursor protein cytoplasmic tail promotes interaction with Shc. 11903040_Isoform-specific knockdown and expression of adaptor protein ShcA using small interfering RNA 11948181_The p66Shc longevity gene is silenced through epigenetic modifications of an alternative promoter 12586295_Among ten hepatocellular carcinoma cases with amplicon 1q21-q22, significant gene expression level of JTB, SHC1, CCT3 and COPA in the tumors than the paired adjacent non-malignant liver tissues. 12589038_shc phosphorylation is regulated by protein kinase C-dependent phosphorylations of Lck in T-lymphocytes 14530863_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14530863_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in SHC1 have no impact on longevity for Japanese centenarians. 14665640_there is a novel interaction between Tie2 with the adapter molecule ShcA that may play a role in the regulation of migration and three-dimensional organization of endothelial cells induced by angiopoietin-1 14749389_novel interplay between p66Shc and p52Shc in the control of T-cell fate 14764897_Shc and IGF-1R serve as key elements in the translocation of ERalpha to the cell membrane and in the facilitation of ERalpha-mediated rapid E2 action 14983012_Shc is a critical angiogenic switch for VEGF production downstream from the HGF and ErbB2 RTKs. 14990987_Y317 of p52(Shc) serves as an important regulatory site that allows tyrosine phosphorylation pathways to moderate androgen sensitivity in human prostate cancer cells. 15036421_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15094067_MK2 is activated with p66(ShcA) co-expression and p66(ShcA) is an in vitro substrate for MK2, further demonstrating their association and suggesting a biological role for p66(Shc) in MK2 activation 15226408_CD9 activates the p46 Shc isoform in tumor cells and leads to apoptosis 15308584_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15308584_polymorphisms in SHC1 is associated with breast cancer 15316024_insulin receptor substrate-4 and ShcA have roles in signaling by the fibroblast growth factor receptor 15485499_NCAM activates FGFR signaling in a manner distinct from FGF2 stimulation, and regulates ShcA phosphorylation by the concerted efforts of the NCAM/FGFR as well as the NCAM/Fyn signaling pathway. 15562031_Type 2 diabetes induces p66(shc) gene expression in circulating peripheral blood mononuclear cells. 15688026_p52Shc couples tyrosine kinase receptors to Ras by recruiting Grb2. 15705774_conclude that the expression of p66Shc protein is regulated by signaling through the thyrotropin receptor in proliferating thyroid cells 15753984_p46 Shc expressed in the nucleus may play an important role in gastric carcinogenesis 15888547_SHPS-1 functions as an anchor protein that recruits both Shc and SHP-2, whose recruitment is necessary for IGF-I-dependent Shc phosphorylation 15992607_p66shc may have a complex role in mammalian longevity: it is highly expressed in fibroblasts from centenarians 16170380_Expression of p66SHC protein correlates with proliferation of prostate cancer cells. 16186108_DDR2 autophosphorylation generates cytosolic domain phosphotyrosines that promote the formation of DDR2 cytosolic domain-Shc signaling complexes. 16257509_The data show that Shc is connected to the activated TCR via direct interaction with Lck. 16481327_p66(shc) regulates mitochondrial oxidative capacity and may extend life span by repartitioning metabolic energy conversion away from oxidative and toward glycolytic pathways 16487929_p66Shc overexpression plays a pro-apoptotic role in human cell lines that is independent from the presence of a functional form of p53. 16519809_Important variations in the p66Shc gene may be extremely rare and probably this gene is not involved in the genetic susceptibility to coronary artery disease. 16756945_present study identifies ShcA as a mediator of the anti-apoptotic activity of venous malformation -mutant Tie2 16825188_Upon IGF-I stimulation, a complex assembles on SHPS-1 that contains SHP-2, c-Src, and Shc wherein Src phosphorylates Shc, a signaling step that is necessary for an optimal mitogenic response 16934220_CpG methylation has a role in the control of p66Shc gene expression and Ca2+ signaling may lead to epigenetic modifications in nondividing cells 17081113_report novel investigations into the role of the mitochondrial import machinery on p66(Shc) activation, which highlight the energetic status of mitochondria as a crucial determinant of p66(Shc) function 17158237_Since p66Shc is an aging-regulating gene, we envision that these data may help in understanding the relationship among aging, cancer, and stem cells. 17167775_p66Shc may play an important role in downstream hypoxic signaling, involving HIF-1alpha protein accumulation and cell death in T lymphocytes. 17380301_PTX3 and p66((ShcA)) mRNA levels are significantly more elevated in WBCs and in adipose tissue samples of patients with high levels of LDL compared to those with low levels. 17906149_the adaptors Nck and ShcA influenced adherence of S. Typhimurium to non-phagocytic cells. 17908971_p66 Shc may have a role in progression of colon cancer 17938255_IL-15 but not IL-21 caused an increased phosphorylation of Shc and ERK1/2. 17998013_Up-regulation of muscle p66(ShcA) relates to proteolysis rate, suggesting an involvement of this gene in muscle catabolic response in hypercatabolic traumatized patients. 18032526_Suggest new pathway for the induction of oxidative stress by AGEs involving FKHRL1 inactivation and MnSOD suppression via Ser-36 phosphorylation of p66(shc) in human kidney cells. 18067454_demonstrated that 8-isoprostane has a significant influence on p66Shc promoter methylation. In the control group and in patients with ESRD, increasing 8-isoprostane levels were linked to an elevated promoter methylation 18093973_Protein-tyrosine phosphatase epsilon regulates Shc signaling in a kinase-specific manner: increasing coherence in tyrosine phosphatase signaling 18279888_Shc has an intrinsic phosphorylation-dependent gating mechanism where the SH2 domain adopts an open conformation only when tyrosine phosphorylation has occurred. 18385518_These results identify p66Shc and FOXO3a as novel partners of beta(1)Pix and represent the first direct evidence of beta(1)Pix in cell proliferation via Erk/p66Shc-dependent and Akt-independent mechanisms. 18420583_in VSMCs exposed to hyperglycemia, IGF-I stimulation of Shc facilitates the transfer of Grb2 to p85 resulting in enhanced PI3K activation and AKT phosphorylation leading to enhanced cell proliferation and migration 18480379_Thyroid cancers are characterized by APP upregulation, increased membrane targeting of the APP ectodomain and significantly increased mRNA levels of the APP scaffold proteins JIP1, ShcA and Fe65. 18504439_A novel role for p66Shc-ROS pathway in androgen-induced prostate cancer cell proliferation and a role in early prostate carcinogenesis. 18611262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18840094_The recruitment of Shc protein to FGFR2 via an indirect mechanism provides new insight into the regulation of protein assembly and activation of various signalling pathways. 19055724_In human endometriosis, the PI3K-Akt and MAPK signaling pathways may be activated via overexpression of AXL and SHC1, respectively. 19229850_The interaction processes of the SH2 domain with CD247 and phosphorylated CD247, respectively, was analysed. 19383602_inhibition of p66ShcA redox activity prevents generation of HIV-1 stress signals and activation of podocyte apoptosis program 19696221_These findings illustrate a novel mechanism by which p66shc promotes cellular oxidative stress, through suppression of MEF2A expression and consequent repression of KLF2 transcription. 19826412_Data identify a novel function for Shc as a regulator of apoptosis and drug resistance in mammary epithelial cells. 19828641_A critical role for the Shc transgene is demonstrated in early B lymphopoiesis with a requirement in early B cell survival. 19889638_Oscillatory shear stress induces osteoblast-like cell proliferation through activation of alpha(v)beta(3) and beta(1) integrins and synergistic interactions of FAK and Shc with PI3K, leading to the modulation of ERK and Akt/mTOR/p70S6K pathways. 19889727_Hypoxic T cells may contribute to the onset of angiogenesis through a novel VEGF-mediated mechanism, where p66Shc acts as a positive regulator. 20061561_Loss of p66Shc expression is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 20111892_p66Shc might be a useful biomarker for the prognosis of prostate cancer and serve as an effective target for its cancer treatment. 20226758_relationships between the extent of p66Shc phosphorylation at Ser36, mitochondrial dysfunctions and an antioxidant defense reactions in fibroblasts derived from five patients with various mitochondrial disorders 20354186_p66(Shc) has a critical role in regulation of PEITC-induced apoptotic cell death in prostate cancer 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20534722_The increase in p66shc that occurs in response to hyperglycemia is functioning to inhibit IGF-I-stimulated signaling and that the incremental increase in SMC sensitivity to IGF-I. 20624904_a critical role for SHC1 in early C. trachomatis-induced cell survival 20637729_The phosphorylation of p66(Shc) at Ser36 is significantly increased in PINK1 deficient cell lines under normal tissue culture conditions, further still in the presence of compounds which elicit oxidative stress. 20667496_the epigenetic enhancement of p66Shc is associated with the specifically increased histone acetylation and methylation, which may contribute to cellular replicative senescence or premature senescence. 20676142_Data show that p66(Shc) coordinates Ras-dependent control of proliferation and anchorage sensation. 20739287_Integrin {beta}3 phosphorylation dictates its complex with the Shc phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain. 20842738_The researchers found an association between p66(shc)gene expression in peripheral blood monocytes and the risk of coronary artery disease in Japanese subjects. 21206972_Migration of renal tumor cells depends on dephosphorylation of Shc by PTEN. 21264241_functional steroid receptors are required in steroid up-regulation of p66Shc protein levels in prostate and ovarian cancer cells, correlating with cell proliferation 21439852_Increased p66(shc) gene expression correlates with TNF-alpha mRNA and with levels of markers of oxidative stress in Hemodialysis. 21612602_acts as an immune-regulator for the LPS-stimulated maturation of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells 21616139_diallyl trisulfide-induced G2/M arrest is abrogated in prostate cancer cells expressing mutant protein 21778425_Inactivation of p66Shc adaptor protein confers resistance to oxidative stress and protects mice from aging-associated vascular diseases. 21817106_p66(Shc) silencing blunted oxidized LDL-induced O(2)(-.) production, underscoring the critical role of p66(Shc) in oxidized LDL-induced oxidative stress in endothelial cells 21828072_p66Shc activation by mutSOD1 causes a strong decrease in the activity of the small GTPase Rac1 through a redox-sensitive regulation. 21933910_Homocysteine up-regulates human p66shc expression via hypomethylation of specific CpG dinucleotides in the p66shc promoter, and this mechanism is important in homocysteine-induced endothelial cell dysfunction. 21983898_increases in Ca(2+) lead to CaMKII activation and subsequent Lck-dependent p66Shc phosphorylation on Serine 36. This event causes both mitochondrial dysfunction and impaired Ca(2+) homeostasis, which synergize in promoting Jurkat T-cell apoptosis. 22020565_Expression of SHC1 mutant protects PC-3 cells against Diallyl trisulfide induced death. 22039050_mp53 disrupts the role of ShcA in balancing the Smad-dependent and -independent signaling activity of TGF-beta and ShcA/ERK signaling is a major pathway regulating the tumor-promoting activity of TGF-beta 22096252_Data show that adaptor protein Shc is required for angiogenesis in zebrafish, mice, and human vascular endothelial cell-culture models. 22100252_Suggest an involvement of p66Shc in the transition of a stable coronary artery disease to an acute coronary syndrome patient. 22101521_These studies uncover a novel role of p66Shc as a positive regulator for ROS-dependent VEGFR2 signaling linked to angiogenesis in endothelial cells. 22561705_Elevated p66Shc expression enhances prostate cancer tumorigenicity. 22641095_our analysis of human samples demonstrated that enhanced p53/p66Shc signaling plays an important role in the progression of human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. 22661506_These findings indicate that LDL cholesterol upregulates human endothelial p66shc expression via hypomethylation of CpG dinucleotides in the p66shc promoter. 23033271_S1P1 expression is controlled by the pro-oxidant activity of p66Shc and is impaired in B-CLL patients with unfavorable prognosis. 23277357_Distinct phosphotyrosine-dependent functions of the ShcA adaptor protein are required for transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta)-induced breast cancer cell migration, invasion, and metastasis 23524280_p66(Shc) is a good candidate molecule to address the mechanisms underlying healthy aging and to be targeted for the development of novel pharmacological tools for the prevention or cure of age-related pathologies. 23529764_DNA methylation of the p66Shc promoter was significantly decreased in the intrauterine growth restricted compared with the appropriate for gestational age infants groups. 23584453_The Shc-Erk complex restricts Erk nuclear translocation, restraining Erk-dependent transcription of genes, including those responsible for oncogenic growth. 23606925_The p66Shc protein (SHC1 protein) is very important for the regulation of the intracellular redox balance and oxidative stress levels. 23689140_Knock-down of p66(Shc) leads to a positive feedback upregulation of Nrf2 expression and accordingly, Nrf2 is found to be highly expressed in tumors with low p66(Shc) expression 23815759_Shc plays a pivotal role in coordinately regulating autophagy process and apoptotic resistance in lung adenocarcinoma cells under nutrient-limited conditions. 23832324_Arg-II promotes mitochondrial dysfunction leading to VSMC senescence/apoptosis through complex positive crosstalk among S6K1-JNK, ERK, p66Shc, and p53, contributing to atherosclerotic vulnerability phenotype. 23990909_different domains in SOCS5 contribute to two distinct mechanisms for regulation of cytokine and growth factor signaling with JAK1 and SHC-1 23993977_Salvianolic acid A induced SIRT1 plays an anti-apoptotic role in concanavalin A induced hepatitis by inhibiting p66Shc expression. 24085465_Serine phosphorylation of p66shc is carried out by active MKK6.beta-Amyloid-induced ROS production and apoptosis increased in the presence of MKK6 and p66shc, which directly associate. 24165399_repression of Shc expression by let-7a delays senescence of human diploid fibroblasts. 24349153_TNFalpha signals via p66(Shc) to induce E-Selectin, promote leukocyte transmigration and enhance permeability in human endothelial cells. 24395385_Results show elevated level of p66Shc protein reveal in ovarian cancer cells (OCa) indicating a functional role of the protein in regulating the proliferation of OCa cells. 24407288_a central role for adaptor proteins p66Shc and Grb2 in the regulation of ARF1 and ARF6 activation in invasive breast cancer cells. 24550542_unlike the other isoforms of Shc1, p66Shc appears to antagonize insulin and mTOR signaling, which limits glucose uptake and metabolism. 24599562_High p66Shc expression is associated with malignant gastrointestinal lesions. 24618848_the p66shc-dependant ROS production during oxidative stress has mitochondrial origin in human normal and cancer cells. 24676406_p66shc expression in coronary heart disease patients was significantly higher compared with the control group 24708867_these results identify Grb2 and Shc as central signaling effectors of Met-driven progression of intestinal epithelial-derived cancers. Notably, they suggest that Grb2 may represent a promising target for the design of novel colorectal cancer therapies. 24722289_PKCbeta2 inhibition protects mice from gut ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing the adaptor p66(Shc)-mediated oxidative stress and subsequent apoptosis. 24766279_Although H2S failed to affect the activities of these two proteins, it disrupted their association. Cysteine-59 resides in proximity to serine-36, the phosphorylation site of p66Shc. 24807908_p66Shc is a bifunctional protein involved in cellular oxidative stress response and differentiation. 24823637_In lung cancer tissues and single cells, p66(Shc) expression inversely correlates with that of Aiolos. 24837366_demonstrate that ShcA-dependent activation of AKT, but not the RAS/MAPK pathway, induces VEGF production by bolstering VEGF mRNA translation 24842918_Exposure of human aortic endothelial cells to stretch led to stretch- and time-dependent p66(Shc) phosphorylation downstream of integrin alpha5beta1 and JNK kinase. In parallel, NADP oxidase and reactive oxygen species increased, and NO bioavailability decreased 24845561_study concludes hypercholesterolemia stimulates p66Shc expression in platelets, promoting platelet oxidative stress, hyperreactivity and hyperaggregation via p66Shc 24906005_CRIF1 knockdown partially induces endothelial activation via increased ROS production and phosphorylation of p66shc 25071152_Study identifies p66ShcA as one of the first prognostic biomarkers for the identification of more aggressive tumors with mesenchymal properties, regardless of molecular subtype. 25147340_p66(Shc) plays a vital part in canonical Wnt signaling in the endothelium and mediates Wnt3a-stimulated endothelial oxidative stress and dysfunction. 25217205_Data show that ouabain-induced glioblastoma cells apoptosis and increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in extracellular signal-related kinases ERK1/2-Shc signaling adaptor protein p66SHC-dependent pathway. 25680868_p66ShcA was upregulated in hearts of patients with ischemic heart disease without heart failure 25810038_p53-dependent augmentation of p66(Shc) expression and function represents a key signalling response contributing to beta cell apoptosis under conditions of lipotoxicity 25815500_Hyperoxia can increase the expression of PKCbeta in alveolar epithelial cells and production of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and decrease mitochondrial membrane potential. 25961473_These data demonstrate that the p52Shc phosphorylation level is altered by the solution environment without affecting the fraction of active c-Src. 26122877_In mice and humans, reduced p66Shc levels protect from obesity, but not from ectopic fat accumulation, glucose intolerance and insulin resistance. 26464652_The silence of p66(Shc) in HCT8 cells reduced the proliferation and accelerated the apoptosis, in addition, the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins caspase-3, caspase-9, Bax was enhanced and the expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 was declined. 26551075_Finally, a crystal structure of EGFR in complex with a primed Shc1 peptide reveals the structural basis for EGFR substrate specificity. 26643258_regulates the alternative splicing of XAF1 in extracellular matrix-detachment induced autophagy to coordinate with the anoikic cell death 26680585_Data suggest SHC1 (SH2 domain protein C1) expression down-regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition by repressing TGFB-induced SMAD2/3 activation through differential partitioning of receptors at cell surface of mammocytes/keratinocytes. 27048591_Data identify, for the first time, a novel non-canonical dynamic mode of interaction between Met and the p66 protein isoform of Shc and its effects on rewiring binding effector complexes according to the activation state of the receptor. 27377870_A positive relationship between the p66Shc expression and oxidative stress was found. p66Shc and oxidative stress were significant predictors of the degree of tubular damage. 27475256_miR-5582-5p induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in cancer cells, but not in normal cells. GAB1, SHC1, and CDK2 were identified as direct targets of miR-5582-5p. 27494881_STAT4 is a novel transcriptional regulator of p66Shc in normal and chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells 27530145_Adeno-X Adenoviral System 3 can be used to efficiently construct recombinant adenovirus containing p66Shc gene, and the Adeno-X can inhibit the proliferation of MCF-7 cells by inducing cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase 27605668_Isoform b of DDR1 is responsible for collagen I-induced up-regulation of N-cadherin and tyrosine 513 of DDR1b is necessary. 27624939_Taken together, these data argue for a complex mechanism of PKC-beta-dependent regulation of SHCA (p66) activation involving Ser(139) and a motif surrounding Ser(213). 28424170_Nox4-derived H2O2 in part activates Nox2 to increase mitochondrial ROS via pSer36-p66Shc, thereby enhancing VEGFR2 signaling and angiogenesis in endothelial cells. 28690151_The results show that the interaction between STS-1 and ShcA is regulated in response to EGF receptor activation. 28739512_Characterization of bioenergetic parameters and reactive oxygen species production showed that the cellular model of Leigh syndrome is described by increased intracellular oxidative stress and oxidative damage to DNA and proteins, which correlate with increased p66Shc phosphorylation at Ser36. 28739690_NIC exacerbated AZA-dependent injury via augmenting p66shc transcription. While RES suppressed NIC+AZA-mediated injury, -surprisingly-it further enhanced activity of the p66shc promoter. RES protected cells via the cytoplasmic p66shc/Nrf2/heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) axis 28831120_Using multiple -omics approach, study validated key molecules, such as CAP1, SHC1 and PRCP, that might play a significant role in IgA nephropathy pathogenesis. 29018139_Our results suggest that increases in ShcA perturb nephrin phosphosignaling dynamics, leading to aberrant nephrin turnover and slit diaphragm disassembly. 29208567_Data suggest that up-regulation of SHC threonine phosphorylation is responsible for elevated Akt-signaling and Erk-signaling in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines. 29326436_Identification of p66Shc as a regulator of CXCR4/CCR7 recycling in B cells; this underscores the relevance of its deficiency to Chronic lymphocytic leukemia pathogenesis and provides new clues to the mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of ibrutinib. 29343271_p66Shc expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells was not associated with prevalent diabetic complications but predicted new onset of complications, especially macroangiopathy. 29462661_p66Shc increases prostate cancer migratory activity through generation of ROS for activation or inhibition of ROS-sensitive proteins. 29509254_In B cell lymphoma cells, reactive oxygen species production promoted p66shc expression, induced DNA damage, and facilitated cell apoptosis. 29930100_These data demonstrate that metabolic reprogramming is a key component of ShcA signaling and serves an unappreciated yet vital role during breast cancer initiation and progression. These data further unravel a novel interplay between ShcA and PGC-1alpha in the coordination of metabolic reprogramming and demonstrate the sensitivity of breast tumors to drugs targeting oxidative phosphorylation 30105917_p66Shc has dual role in the development of diabetic retinopathy; its regulation in the early stages of the disease should impede Rac1-ROS production and, in the later stages, prevent mitochondrial damage and initiation of a futile cycle of free radicals. 30109811_p66SHC is a novel regulator of autophagy and mitophagy in B cells and mediates coordination of autophagy and apoptosis in B cell survival and differentiation. 30189773_The positive rate of ShcA was significantly higher in lupus nephritis (LN) class V, while it was negative in primary membranous nephropathy (MN) and other secondary MN, suggesting that ShcA might be used to distinguish membranous LN from primary and other secondary MN. 31100478_p66Shc (SHC1) protein through a redox mechanism enhances the progression of prostate cancer cells towards castration-resistance. 31398350_High p66Shc expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) predicts a worse prognosis for survival. Furthermore, p66Shc may serve as a novel candidate target for HCC therapy. 31536807_P66Shc Deletion Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Cardiac Dysfunction in Pressure Overload-Induced Heart Failure. 31605605_PTRF/CAVIN1, regulated by SHC1 through the EGFR pathway, is found in urine exosomes as a potential biomarker of ccRCC. 31610708_Physical activity may drive healthy microvascular ageing via downregulation of p66(Shc). 31806365_CRIF1 deficiency induced mitophagy via p66shc-regulated ROS in endothelial cells. 31941526_p66ShcA functions as a contextual promoter of breast cancer metastasis. 31974654_A SYK/SHC1 pathway regulates the amount of CFTR in the plasma membrane. 32308389_SHC1 was highly expressed in cartilage from osteoarthritis patients. 33203836_DEPDC1B is a tumor promotor in development of bladder cancer through targeting SHC1. 33759377_Human SHC-transforming protein 1 and its isoforms p66shc: A novel marker for prediabetes. 34117717_The increased expression and aberrant methylation of SHC1 in non-small cell lung cancer: Integrative analysis of clinical and bioinformatics databases. 34260260_p52Shc regulates the sustainability of ERK activation in a RAF-independent manner. 34529688_Lower p66Shc promoter methylation in subjects with chronic renal failure. 34719845_Genistein suppresses ox-LDL-elicited oxidative stress and senescence in HUVECs through the SIRT1-p66shc-Foxo3a pathways. 35042950_The E3 ubiquitin ligase SOCS-7 reverses immunosuppression via Shc1 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. 35612429_The p66Shc Protein Mediates Insulin Resistance and Secretory Dysfunction in Pancreatic beta-Cells Under Lipotoxic Conditions. | ENSMUSG00000042626 | Shc1 | 581.703431 | 1.0088913 | 0.012770784 | 0.10589167 | 0.01451969997 | 0.9040888874895863791536498865752946585416793823242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.95694789750082942525466478400630876421928405761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 575.635348 | 39.474786 | 572.514189 | 39.241788 | |
| ENSG00000160746 | 55129 | ANO10 | protein_coding | Q9NW15 | FUNCTION: Does not exhibit calcium-activated chloride channel (CaCC) activity. Can inhibit the activity of ANO1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20056604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22946059}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The transmembrane protein encoded by this gene belongs to the anoctamin family of calcium-activated chloride channels, also known as the transmembrane 16 family. The encoded protein contains eight transmembrane domains with cytosolic N- and C-termini. Defects in this gene may cause autosomal recessive spinocerebellar ataxia-10. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. | hsa:55129; | intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium activated cation channel activity [GO:0005227]; intracellular calcium activated chloride channel activity [GO:0005229]; cation transport [GO:0006812]; chloride transport [GO:0006821]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] | 22008874_This study report Gypsy family with autosomal recessive ataxia caused by the same truncating ANO10 defect. 22527681_New DNA sequencing technologies are enabling us to investigate the whole or large targeted proportions of the genome in a rapid, affordable, and comprehensive way. Exome and targeted sequencing ANO10 genes causing ataxia. 24275721_Whole-exome and targeted sequencing have defined the genetic basis of dizziness including new genes causing ataxia: GBA2, TGM6, ANO10 and SYT14 25089919_An ANO10 mutation is responsible for autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia that is mainly characterized by cerebellar atrophy and lack of peripheral neuropathy. 25182700_The detection of mutations in ANO10 indicate that ANO10 defects cause secondary low coenzyme Q10. 25730773_ANO10 has a central role in innate immune defense against Borrelia infection. 27045840_results suggest that executive and attentional disorders are impaired in ANO10 mutation 27787937_This study describe 2 Romani families from Serbia presenting with seemingly dominant (multiple affected individuals in successive generations) cerebellar ataxia, both harboring the same homozygous (recessive) mutation in ANO10, identified by whole-exome sequencing. 27838374_mutations in ANO10 cause cellular defects and genetic disorders through deranged local Ca(2+) signaling. 30515630_ANO10 mutations cause recessive ataxias. 31423897_Cognitive impairment seems to be a characteristic of the SCAR10 produced by an ANO10 gene mutation, with a range from mild impairment, especially involving prefrontal systems, to a severe cognitive impairment suggesting widespread cerebral involvement. 31477691_Data show that transmembrane protein 16K (TMEM16K) is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident lipid scramblase with a requirement for short chain lipids and calcium for robust activity. 32620747_TMEM16K is an interorganelle regulator of endosomal sorting. | ENSMUSG00000037949 | Ano10 | 111.118716 | 1.0733671 | 0.102143574 | 0.21095874 | 0.23374747675 | 0.6287589462110277915840583773388061672449111938476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.80130103312680911464838118263287469744682312011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 112.501602 | 14.149124 | 105.273141 | 13.170167 | |
| ENSG00000161013 | 11282 | MGAT4B | protein_coding | Q9UQ53 | FUNCTION: Glycosyltransferase that catalyze the transfer of GlcNAc from UDP-GlcNAc to the GlcNAcbeta1-2Manalpha1-3 arm of the core structure of N-linked glycans through a beta1-4 linkage and participates in the production of tri- and tetra-antennary N-linked sugar chains (PubMed:17006639, PubMed:10372966). Prefers complex-type N-glycans over hybrid-types (PubMed:17006639). Has lower affinities for donors or acceptors than MGAT4A, suggesting that, under physiological conditions, it is not the main contributor in N-glycan biosynthesis (PubMed:17006639). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10372966, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17006639}. | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17006639}. | This gene encodes a key glycosyltransferase that regulates the formation of tri- and multiantennary branching structures in the Golgi apparatus. The encoded protein, in addition to the related isoenzyme A, catalyzes the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) from UDP-GlcNAc in a beta-1,4 linkage to the Man-alpha-1,3-Man-beta-1,4-GlcNAc arm of R-Man-alpha-1,6(GlcNAc-beta-1,2-Man-alpha-1,3)Man-beta-1, 4-GlcNAc-beta-1,4-GlcNAc-beta-1-Asn. The encoded protein may play a role in regulating the availability of serum glycoproteins, oncogenesis, and differentiation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:11282; | endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment [GO:0005793]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; Golgi stack [GO:0005795]; acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008375]; alpha-1,3-mannosylglycoprotein 4-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008454]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; N-glycan processing [GO:0006491]; protein glycosylation [GO:0006486]; protein N-linked glycosylation [GO:0006487]; viral protein processing [GO:0019082] | 16434023_analysis of expression of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-IVa and IVb (GnT-IVa and b) in pancreatic cancer 17006639_GnT-IVa is more active than GnT-IVb under physiological conditions and it primarily contributes to the biosynthesis of N-glycans. 17488527_We investigated mRNA levels of glycosyltransferases, namely, N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase a (GnT)-IVb, and found that (GnT)-IVb expression was increased in HLE-cells Epirubicin resistant. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 25944901_UDP-galactose (SLC35A2) and UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (SLC35A3) Transporters Form Glycosylation-related Complexes with Mannoside Acetylglucosaminyltransferases (Mgats). | ENSMUSG00000036620 | Mgat4b | 582.869690 | 0.7775784 | -0.362940008 | 0.07617133 | 22.69078268166 | 0.0000019027842120972619628324097595939434768297360278666019439697265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00003000692847668151187604836105382588584689074195921421051025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 500.203861 | 21.243113 | 646.128910 | 26.887032 |
| ENSG00000161642 | 25946 | ZNF385A | protein_coding | Q96PM9 | FUNCTION: RNA-binding protein that affects the localization and the translation of a subset of mRNA. May play a role in adipogenesis through binding to the 3'-UTR of CEBPA mRNA and regulation of its translation. Targets ITPR1 mRNA to dendrites in Purkinje cells, and may regulate its activity-dependent translation. With ELAVL1, binds the 3'-UTR of p53/TP53 mRNAs to control their nuclear export induced by CDKN2A. Hence, may regulate p53/TP53 expression and mediate in part the CDKN2A anti-proliferative activity. May also bind CCNB1 mRNA. Alternatively, may also regulate p53/TP53 activity through direct protein-protein interaction. Interacts with p53/TP53 and promotes cell-cycle arrest over apoptosis enhancing preferentially the DNA binding and transactivation of p53/TP53 on cell-cycle arrest target genes over proapoptotic target genes. May also regulate the ubiquitination and stability of CDKN1A promoting DNA damage-induced cell cycle arrest. Also plays a role in megakaryocytes differentiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17719541}. | Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;DNA damage;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Translation regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Zinc finger proteins, such as ZNF385A, are regulatory proteins that act as transcription factors, bind single- or double-stranded RNA, or interact with other proteins (Sharma et al., 2004 [PubMed 15527981]).[supplied by OMIM, Oct 2008]. | hsa:25946; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; hemostasis [GO:0007599]; learning or memory [GO:0007611]; locomotory behavior [GO:0007626]; megakaryocyte development [GO:0035855]; mRNA localization resulting in post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression [GO:0010609]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator [GO:1902166]; platelet alpha granule organization [GO:0070889]; platelet formation [GO:0030220]; positive regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in transcription of p21 class mediator [GO:1902164]; positive regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045600]; regulation of cytoplasmic translation [GO:2000765] | 15527981_Results suggest that RZF is a shuttling regulatory protein expressed in photoreceptors of the human retina that may be involved in mRNA or protein regulation of photoreceptor-specific genes and therefore have role in retinal disease mechanisms. 29084334_Brain gene expression of PADI2, ZNF385A, PSD2, and A2ML1 and DNA methylation dysregulations are implicated in the alteration of brain tissue properties associated with late-life cognitive decline above and beyond the influence of common neuropathologic conditions. | ENSMUSG00000000552 | Zfp385a | 222.363088 | 0.8494496 | -0.235399680 | 0.15625456 | 2.26588075974 | 0.1322510053146423170122858437025570310652256011962890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.31884299592230552766736195735575165599584579467773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 197.326193 | 20.303128 | 233.219175 | 23.706298 | |
| ENSG00000161692 | 80174 | DBF4B | protein_coding | Q8NFT6 | FUNCTION: Regulatory subunit for CDC7 which activates its kinase activity thereby playing a central role in DNA replication and cell proliferation. Required for progression of S and M phases. The complex CDC7-DBF4B selectively phosphorylates MCM2 subunit at 'Ser-40' and then is involved in regulating the initiation of DNA replication during cell cycle. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12065429, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15668232, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17062569}. | Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a regulator of the cell division cycle 7 homolog (S. cerevisiae) protein, a serine-threonine kinase which links cell cycle regulation to genome duplication. This protein localizes to the nucleus and, in complex with the cell division cycle 7 homolog (S. cerevisiae) protein, may facilitate M phase progression. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010]. | hsa:80174; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; Dbf4-dependent protein kinase complex [GO:0031431]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; protein kinase activator activity [GO:0030295]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity [GO:0043539]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0010971]; positive regulation of nuclear cell cycle DNA replication [GO:0010571]; regulation of cell cycle phase transition [GO:1901987] | 12065429_Results describe a novel human protein, Drf1, related to both human and yeast Dbf4. Drf1 is a nuclear cell cycle-regulated protein which binds to Cdc7 and activates the kinase. 15668232_ASKL1 in a complex with Cdc7 may play a role in normal progression of both S and M phases 19111665_These results indicate that Ddk functions as an upstream regulator to monitor S-phase checkpoint signaling. 29262322_Knockdown of the exon6-containing isoform (DBF4B-FL) significantly inhibits the tumorigenic potential of colon cancer. Overexpression of DBF4B-FL protects against DNA damage induced by SRSF1 knockdown. | 115.668003 | 2.1107744 | 1.077772415 | 0.45031582 | 5.53703216415 | 0.0186181312824927128191099257037421921268105506896972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.07933022370324720184964206737276981584727764129638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 139.458590 | 47.709557 | 63.962172 | 21.785573 | |||
| ENSG00000161813 | 113251 | LARP4 | protein_coding | Q71RC2 | FUNCTION: RNA binding protein that binds to the poly-A tract of mRNA molecules (PubMed:21098120). Associates with the 40S ribosomal subunit and with polysomes (PubMed:21098120). Plays a role in the regulation of mRNA translation (PubMed:21098120). Plays a role in the regulation of cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization (PubMed:21834987, PubMed:27615744). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21098120, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21834987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27615744}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome;RNA-binding | Enables mRNA 3'-UTR binding activity and poly(A) binding activity. Involved in cytoskeleton organization; positive regulation of translation; and regulation of cell morphogenesis. Located in cytosol. Colocalizes with cytoplasmic stress granule; cytosolic small ribosomal subunit; and polysome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:113251; | cytoplasmic stress granule [GO:0010494]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; poly(A) binding [GO:0008143]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727]; post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression [GO:0010608]; regulation of cell morphogenesis [GO:0022604]; translation [GO:0006412] | 15572213_The c-MPL protein altered expression provide an opportunity to diagnose and identify subpopulations of MPD patients. 16682284_FISH study showed no cytogenetic abnormalities in any of the analyzed cases. 21098120_LARP4 activity is integrated with other PAM2 protein activities by PABP as part of mRNA homeostasis. 23887937_The results demonstrate that the La modules of the human LARP4 is also active in tRNA-mediated suppression, even in the absence of stable UUU-3'OH trailer protection. 26644407_Involvement of LARP4 as a target of TNF-alpha-TTP regulation provides a clue as to how its functional activity may be used in a physiologic pathway. 27615744_LARP4 inhibits migration and invasion of cancer cells, and that some cancer-associated mutations stimulate these effects of LARP4. 28782243_A cytoplasmic isoform of La protein as well as LARPs 6, 4, and 1 function in mRNA metabolism and translation in distinct but similar ways, sometimes with the poly(A)-binding protein, and in some cases by direct binding to poly(A)-RNA. 28893265_The expression of circLARP4 was downregulated in GC tissues and represented an independent prognostic factor for overall survival of GC patients. 28895529_The results indicate that LARP4 is a posttranscriptional regulator of ribosomal protein production in mammalian cells and suggest that this activity can be controlled by tRNA levels. 30468459_These results indicated that circLARP4 expression was lower and highlighted that circLARP4 was identified as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis. 30520539_The role of circLARP4/miR-761/RUNX3/p53/p21 signaling in HCC progression, providing a potential survival predictor and therapeutic candidate for HCC. 30686809_LARP4 could suppress motility and metastatic potential of ovarian cancer cells. 30820564_LARP4A recognizes polyA RNA via a novel binding mechanism mediated by disordered regions and involving the PAM2w motif, revealing interplay between PABP, LARP4A and mRNA. 31642110_Circular RNA LARP4 correlates with decreased Enneking stage, better histological response, and prolonged survival profiles, and it elevates chemosensitivity to cisplatin and doxorubicin via sponging microRNA-424 in osteosarcoma. 31897898_Circular RNA_LARP4 Sponges miR-1323 and Hampers Progression of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Through Modulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT Pathway. 32141555_Circular RNA_LARP4 inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by regulating the expression of SMAD7. 32187743_Circular RNA La-related RNA-binding protein 4 correlates with reduced tumor stage, as well as better prognosis, and promotes chemosensitivity to doxorubicin in breast cancer. 32495863_Circular RNA_LARP4 inhibits cell migration and invasion of prostate cancer by targeting FOXO3A. 32744499_Single molecule poly(A) tail-seq shows LARP4 opposes deadenylation throughout mRNA lifespan with most impact on short tails. | ENSMUSG00000023025 | Larp4 | 296.710983 | 1.0457208 | 0.064497716 | 0.15123298 | 0.18175555735 | 0.6698688630914042541064645774895325303077697753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.83024327989744484135314905870473012328147888183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 305.950230 | 30.322435 | 293.895461 | 29.252566 | |
| ENSG00000161999 | 339123 | JMJD8 | protein_coding | Q96S16 | FUNCTION: Functions as a positive regulator of TNF-induced NF-kappa-B signaling (PubMed:27671354). Regulates angiogenesis and cellular metabolism through interaction with PKM (PubMed:27199445). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27199445, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27671354}. | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal | Involved in several processes, including positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling; positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis; and regulation of glycolytic process. Located in endoplasmic reticulum lumen and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:339123; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903672]; regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0006110]; regulation of pyruvate kinase activity [GO:1903302] | 27199445_Jmjd8 is upregulated during endothelial differentiation and regulates endothelial sprouting and metabolism by interacting with pyruvate kinase M2. 29133832_Study demonstrated that JMJD8 is the first JmjC domain-containing protein found in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum that may function in protein complex assembly and protein folding. 31473257_The research provided data to establish the role of JMJD8 in regulating tumor cell proliferation and their sensitivity to ionizing irradiation or chemo-therapy drug, and the AKT/NF-kappaB/COX-2 signaling mediated expression of Ku70/Ku80 was involved. 32879443_Aberrant JmjC domain-containing protein 8 (JMJD8) expression promotes activation of AKT and tumor epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 35898493_JMJD8 Is an M2 Macrophage Biomarker, and It Associates With DNA Damage Repair to Facilitate Stemness Maintenance, Chemoresistance, and Immunosuppression in Pan-Cancer. | ENSMUSG00000025736 | Jmjd8 | 174.388562 | 0.7909427 | -0.338354842 | 0.13706817 | 6.09079554143 | 0.0135887888843210929978866374767676461488008499145507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.06254688348597678415607958868349669501185417175292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 154.724684 | 12.735093 | 196.415993 | 15.849169 | |
| ENSG00000162191 | 51035 | UBXN1 | protein_coding | Q04323 | FUNCTION: Ubiquitin-binding protein that plays a role in the modulation of innate immune response. Blocks both the RIG-I-like receptors (RLR) and NF-kappa-B pathways. Following viral infection, UBXN1 is induced and recruited to the RLR component MAVS. In turn, interferes with MAVS oligomerization, and disrupts the MAVS/TRAF3/TRAF6 signalosome. This function probably serves as a brake to prevent excessive RLR signaling (PubMed:23545497). Interferes with the TNFalpha-triggered NF-kappa-B pathway by interacting with cellular inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (cIAPs) and thereby inhibiting their recruitment to TNFR1 (PubMed:25681446). Prevents also the activation of NF-kappa-B by associating with CUL1 and thus inhibiting NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha/NFKBIA degradation that remains bound to NF-kappa-B (PubMed:28152074). Interacts with the BRCA1-BARD1 heterodimer and regulates its activity. Specifically binds 'Lys-6'-linked polyubiquitin chains. Interaction with autoubiquitinated BRCA1 leads to the inhibition of the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity of the BRCA1-BARD1 heterodimer (PubMed:20351172). Component of a complex required to couple deglycosylation and proteasome-mediated degradation of misfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum that are retrotranslocated in the cytosol. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20351172, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23545497, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25681446, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28152074}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Host-virus interaction;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | Enables several functions, including enzyme binding activity; polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding activity; and proteasome regulatory particle binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of cellular protein metabolic process. Located in cytosol; endoplasmic reticulum; and nucleoplasm. Part of VCP-NPL4-UFD1 AAA ATPase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:51035; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; VCP-NPL4-UFD1 AAA ATPase complex [GO:0034098]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; K48-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding [GO:0036435]; K6-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding [GO:0071796]; polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding [GO:0031593]; proteasome regulatory particle binding [GO:1904855]; ubiquitin binding [GO:0043130]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; negative regulation of ERAD pathway [GO:1904293]; negative regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032435]; negative regulation of protein K48-linked deubiquitination [GO:1903094]; negative regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031397]; negative regulation of ubiquitin-specific protease activity [GO:2000157]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161] | 15944415_Specific interaction of rat protein 2B28 with rat Homer2 may play a role in regulation of protein degradation by ubiquitin-proteasome systems and that this function may be specific to Homer2 proteins among Homer family proteins. 20351172_Data suggest that UBXN1 regulates the enzymatic function of BRCA1 in a manner that is dependent on its ubiquitination status. 21135095_SAKS1 inhibits protein degradation mediated by p97 complexes in the cytosol with a component of the mechanism being the ability to shield polyubiquitin chains from ubiquitin-processing factors. 23545497_UBXN1 is induced and recruited to MAVS after virus infection, serving as a brake to prevent excessive RLR signaling, most likely at a late stage of infection. 25681446_UBXN1 is a negative regulator of NF-kappaB signaling. 27785701_p47 promotes, whereas SASK1 delays the degradation of a single ERAD substrate, alpha-TCR. Additionally, we found that SAKS1 selectively inhibits the degradation of ERAD substrates without affecting cytosolic proteasomal substrates. 28152074_The ability of UBXN1 and other family members to negatively regulate the NFkappaB pathway may be important for dampening the host immune response in disease processes and also re-activating quiescent HIV from latent viral reservoirs in chronically infected individuals 29685906_Our results identify how VCP is specifically targeted to ubiquitylated substrates in the BAG6 triage pathway and suggest that the degradation of ubiquitylated clients by the proteasome is reliant on the association of UBXN1 with ubiquitylated substrates and the catalytic activity of VCP. 33754075_LncRNA PRADX-mediated recruitment of PRC2/DDX5 complex suppresses UBXN1 expression and activates NF-kappaB activity, promoting tumorigenesis. 34246306_YTHDF2 facilitates UBXN1 mRNA decay by recognizing METTL3-mediated m(6)A modification to activate NF-kappaB and promote the malignant progression of glioma. | ENSMUSG00000071655 | Ubxn1 | 352.961009 | 0.9064424 | -0.141712688 | 0.12412936 | 1.30234552285 | 0.2537852309807061002011607797612668946385383605957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.48091270483350939679567659368331078439950942993164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 337.833016 | 31.865433 | 374.360226 | 35.251406 | |
| ENSG00000162735 | 5824 | PEX19 | protein_coding | P40855 | FUNCTION: Necessary for early peroxisomal biogenesis. Acts both as a cytosolic chaperone and as an import receptor for peroxisomal membrane proteins (PMPs). Binds and stabilizes newly synthesized PMPs in the cytoplasm by interacting with their hydrophobic membrane-spanning domains, and targets them to the peroxisome membrane by binding to the integral membrane protein PEX3. Excludes CDKN2A from the nucleus and prevents its interaction with MDM2, which results in active degradation of TP53. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10051604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10704444, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11259404, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11883941, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14709540, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15007061}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Peroxisome;Peroxisome biogenesis;Peroxisome biogenesis disorder;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Reference proteome;Zellweger syndrome | This gene is necessary for early peroxisomal biogenesis. It acts both as a cytosolic chaperone and as an import receptor for peroxisomal membrane proteins (PMPs). Peroxins (PEXs) are proteins that are essential for the assembly of functional peroxisomes. The peroxisome biogenesis disorders (PBDs) are a group of genetically heterogeneous autosomal recessive, lethal diseases characterized by multiple defects in peroxisome function. These disorders have at least 14 complementation groups, with more than one phenotype being observed for some complementation groups. Although the clinical features of PBD patients vary, cells from all PBD patients exhibit a defect in the import of one or more classes of peroxisomal matrix proteins into the organelle. Defects in this gene are a cause of Zellweger syndrome (ZWS), as well as peroxisome biogenesis disorder complementation group 14 (PBD-CG14), which is also known as PBD-CGJ. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2010]. | hsa:5824; | brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; peroxisomal membrane [GO:0005778]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; peroxisome membrane class-1 targeting sequence binding [GO:0036105]; peroxisome membrane targeting sequence binding [GO:0033328]; protein carrier chaperone [GO:0140597]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; chaperone-mediated protein folding [GO:0061077]; establishment of protein localization to peroxisome [GO:0072663]; negative regulation of lipid binding [GO:1900131]; peroxisome fission [GO:0016559]; peroxisome membrane biogenesis [GO:0016557]; peroxisome organization [GO:0007031]; protein import into peroxisome membrane [GO:0045046]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; protein targeting to peroxisome [GO:0006625] | 10777694_LDRP (ABCD2) interacts with both farnesylated wild-type and farnesylation-deficient mutant PEX19. This interaction is mediated by amino acids 1-218 of ALDRP. 10777694_MP70 (ABCD3) interacts with both farnesylated wild-type and farnesylation-deficient mutant PEX19. 11883941_ALDRP interacts with PEX19 splice variants PEX19-delta-E2 and PEX19-delta-E8. 11883941_MP70 interacts with PEX19 splice variants PEX19-delta-E2 and PEX19p-delta-E8. 11883941_a considerable functional diversity of the proteins encoded by two PEX19 splice variants and thereby provide first experimental evidence for specific biological functions of the different predicted domains of the PEX19 protein. 14709540_PEX19 binds and stabilizes newly synthesized PMPs in the cytosol, binds to multiple PMP targeting signals (mPTSs), interacts with the hydrophobic domains of PMP targeting signals, and is essential for PMP targeting and import. 14713233_Interaction of PEX3 and PEX19 visualized by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). 14715663_Pex19p has a role in assembly of PTS-receptor docking complexes 15007061_Results suggest that PEX3 plays a selective, essential, and direct role in class I peroxisomal membrane protein import as a docking factor for PEX19. 15252024_human Pex19p domain architecture and activity 15781447_analysis of the PEX19-binding site of human adrenoleukodystrophy protein 16280322_Pex19p translocates the membrane peroxins from the cytosol to peroxisomes in an ATP- and Pex3p-dependent manner and then shuttles back to the cytosol 16344115_Pex19p binds to PMP70 co-translationally and keeps PMP70 in a proper conformation for the localization to peroxisome. 16791427_Nonfarnesylated and farnesylated human Pex19p display a similar affinity towards a select set of peroxisomal membrane proteins. 16895967_Data suggest that Pex19p probably functions as a chaperone for membrane proteins and transports them to peroxisomes by anchoring to Pex3p using residues 12-73 and 40-131. 18174172_either one or two tryptophan residues of Pex3p (Trp-104 and Trp-224) are directly involved in binding to Pex19p. 18782765_targeting of hFis1 to peroxisomes and mitochondria are independent events and support a direct, Pex19p-dependent targeting of peroxisomal tail-anchored proteins. 19197237_N-terminal domain of Pex14, Pex14(N), adopts a three-helical fold. Pex5 and Pex19 ligand helices bind competitively to the same surface in Pex14(N) albeit with opposite directionality. 20531392_data indicate a divided N-terminal and C-terminal structural arrangement in Pex19p, which is reminiscent of a similar division in the Pex5p receptor, to allow separation of cargo-targeting signal recognition and additional functions. 20554521_The crystal structure of the cytosolic domain of PEX3 in complex with a PEX19-derived peptide. PEX3 adopts a novel fold that is best described as a large helical bundle. 21102411_The Pex19p peptide contains a characteristic motif, consisting of the leucine triad (Leu18, Leu21, Leu22), and Phe29, which are critical for the Pex3p binding and peroxisome biogenesis. 22624858_PEX3-PEX19 interaction is crucial for de novo formation of peroxisomes in peroxisome-deficient cells. 23460677_PEX19 formed a complex with the peroxisomal tail anchored protein PEX26 in the cytosol and translocated it directly to peroxisomes by a TRC40-independent class I pathway. 25062251_Thus within the cell, PEX3 is stabilized by PEX19 preventing PEX3 aggregation. 26018079_suggest a novel regulatory mechanism for peroxisome biogenesis through the interaction between Pex19p and PLA/AT-3 27295553_that newly synthesized UBXD8 is post-translationally inserted into discrete ER subdomains by a mechanism requiring cytosolic PEX19 and membrane-integrated PEX3, proteins hitherto exclusively implicated in peroxisome biogenesis 28281558_The results demonstrate an allosteric mechanism for the modulation of PEX19 function by farnesylation. 29282281_Hnf4-induced lipotoxicity and accumulation of free fatty acids is the cause for mitochondrial damage in consequence of peroxisome loss in Pex19 mutants 29396426_Thus, PEX19 and PEX3 peroxisome biogenesis factors provide an alternative posttranslational route for membrane insertion of the reticulon homology domain-containing proteins, implying that endoplasmic reticulum membrane shaping and peroxisome biogenesis may be coordinated. 29500918_The summarize recent insights into the biogenesis and function of Lipid droplets and peroxisomes with emphasis on the role of PEX19 in these processes. 30776093_studies indicate that Pex3 and Pex19 can also facilitate sorting of certain membrane proteins to other cellular organelles, including the endoplasmic reticulum, lipid droplets, and mitochondria 34108265_Viperin interacts with PEX19 to mediate peroxisomal augmentation of the innate antiviral response. 35215846_Dengue and Zika Virus Capsid Proteins Contain a Common PEX19-Binding Motif. | ENSMUSG00000003464 | Pex19 | 400.718030 | 0.8057783 | -0.311545183 | 0.14974410 | 4.31500415286 | 0.0377776787863060153904726234941335860639810562133789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.13456434195641672757481899225240340456366539001464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 385.363985 | 46.883097 | 480.741305 | 58.531474 | |
| ENSG00000162819 | 148362 | BROX | protein_coding | Q5VW32 | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Prenylation;Reference proteome | Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:148362; | extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020] | 18190528_Results revealed that Strep-Brox(WT) exhibited accumulation in the perinuclear area suggested physiological significance of farnesylation of Brox in its subcellular distribution and efficient interaction with CHMP4s in vivo. 22162750_structural analysis of the Bro1 domain protein BROX and functional analyses of the ALIX Bro1 domain in HIV-1 budding 26866605_homologous domain of human Bro1 domain-containing proteins, Alix and Brox, binds CHMP4B but not STAM2, despite their high structural similarity 32385852_BROX haploinsufficiency in familial nonmedullary thyroid cancer. | ENSMUSG00000046836 | Brox | 813.711778 | 1.2431419 | 0.313990981 | 0.09063188 | 11.98801036792 | 0.0005354392612457096025171954245536198868649080395698547363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00445022245175578489567724815856308850925415754318237304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 879.869408 | 52.586096 | 711.090110 | 42.828852 | ||
| ENSG00000162910 | 128308 | MRPL55 | protein_coding | Q7Z7F7 | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ribonucleoprotein;Ribosomal protein;Transit peptide | Mammalian mitochondrial ribosomal proteins are encoded by nuclear genes and help in protein synthesis within the mitochondrion. Mitochondrial ribosomes (mitoribosomes) consist of a small 28S subunit and a large 39S subunit. They have an estimated 75% protein to rRNA composition compared to prokaryotic ribosomes, where this ratio is reversed. Another difference between mammalian mitoribosomes and prokaryotic ribosomes is that the latter contain a 5S rRNA. Among different species, the proteins comprising the mitoribosome differ greatly in sequence, and sometimes in biochemical properties, which prevents easy recognition by sequence homology. This gene encodes a 39S subunit protein. Multiple transcript variants encoding two different isoforms were identified through sequence analysis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:128308; | mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial large ribosomal subunit [GO:0005762]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; synapse [GO:0045202]; structural constituent of ribosome [GO:0003735]; mitochondrial translation [GO:0032543]; translation [GO:0006412] | 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) | ENSMUSG00000036860 | Mrpl55 | 129.082165 | 0.8673753 | -0.205271758 | 0.15032761 | 1.86402577961 | 0.1721608857345413579054138608626089990139007568359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.37650105224076563237289860808232333511114120483398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 113.842581 | 21.144961 | 132.084895 | 24.357134 | ||
| ENSG00000163110 | 10611 | PDLIM5 | protein_coding | Q96HC4 | FUNCTION: May play an important role in the heart development by scaffolding PKC to the Z-disk region. May play a role in the regulation of cardiomyocyte expansion. Isoforms lacking the LIM domains may negatively modulate the scaffolding activity of isoform 1. Overexpression promotes the development of heart hypertrophy. Contributes to the regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis in neurons. May be required to restrain postsynaptic growth of excitatory synapses. Isoform 1, but not isoform 2, expression favors spine thinning and elongation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62920}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Isopeptide bond;LIM domain;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Ubl conjugation;Zinc | This gene encodes a member of a family of proteins that possess a 100-amino acid PDZ domain at the N terminus and one to three LIM domains at the C-terminus. This family member functions as a scaffold protein that tethers protein kinases to the Z-disk in striated muscles. It is thought to function in cardiomyocyte expansion and in restraining postsynaptic growth of excitatory synapses. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. | hsa:10611; | actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; adherens junction [GO:0005912]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; filamentous actin [GO:0031941]; membrane [GO:0016020]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; stress fiber [GO:0001725]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; actinin binding [GO:0042805]; cadherin binding involved in cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098641]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; muscle alpha-actinin binding [GO:0051371]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0061049]; heart development [GO:0007507]; muscle structure development [GO:0061061]; regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis [GO:0061001]; regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051963] | 14743183_Altered expression of LIM was found in brains and lymphoblastoid cells from patients with bipolar disorder. 15362566_It is confirmed a decreased expression of LIM in the lymphoblastoid cell lines from patients with bipolar I disorder and schizophrenia. 15555569_Western blot studies of muscle tissues revealed that ENH4 is present only in skeletal muscle and there is a specific distribution of ENH members between skeletal and cardiac muscles, which is different in human and mouse. 16044170_Genetic association study revealed the association of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)1 (rs10008257) with bipolar disorder. 16044170_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16213469_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16549780_ENH is a restraining factor of the oncogenic activity of inhibitor of DNA binding 2 proteins in neural tumors 16595163_Our investigation indicates that the lower expression levels of LIM mRNA in the peripheral leukocytes are associated with the depressive state and that its recovery after treatment may be an adaptive change induced by the antidepressant. 17287082_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17287082_We suggest that the higher expression levels of the PDLIM5 mRNA in the peripheral leukocytes may be a candidate marker for medication-free schizophrenic patients. 18021463_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18021463_our results provide further evidence to support PDLIM5 as a potential susceptible gene for schizophrenia 18197271_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18197271_PDLIM5 gene is associated with recurrent major depressive disorder. 18456508_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18456508_tested for an association between three single nucleotide polymorphisms at the PDLIM5 gene and lithium prophylaxis in a Sardinian sample comprised of 155 bipolar patients treated with lithium 18496208_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18496208_PDLIM5 may have a minor effect on susceptibility to bipolar disorder in Caucasians. 18496210_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18496210_The aim of this study was to investigate the association between PDLIM5 single nucleotide polymorphisms and bipolar disorder in a case-control sample. 19328558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19448850_Our results suggest that PDLIM5 might play a role in susceptibility to bipolar disorder among the Chinese Han population. 19767753_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20564319_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20878950_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21266195_LIM domains have a novel molecular function: the regulation of PKC activities in a PKC isoform-specific manner. 22741436_PDLIM5 (rs17021918,T), SLC22A3 (rs9364554,C) and NKX3-1 (rs1512268,A) SNPs might not be associated with prostate cancer in Chinese men. 23031404_The significant difference in expression of PDLIM5 mRNA in the peripheral blood leukocytes of treatment-naive bipolar (BPD) patients versus that of healthy control subjects suggests that it may be a good biological marker for BPD. 24064681_It can be deduced that the nonsynonymous rs7690296 polymorphism of PDLIM5 could play an important role in the pathophysiology of both bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. 27350677_The study provides evidence of several genetic variants within the PDLIM5 gene and interactions between PDLIM5 and steroid use influencing cancer. 27693979_Findings provide evidence of shared genetic variants in PDLIM5 gene influencing alcohol dependence, type 2 diabetes, and hypertension. 28045035_this study shows functional importance of PDLIM5 for proper kAE1 membrane residency, as a crucial linker between kidneyAE1 and actin cytoskeleton-associated proteins in polarized cells 28139119_PDLIM5 was strongly up-regulated during cardiomyogenesis and novel stage-specific isoforms were detected for PDLIM5 29574154_PDLIM5 promotes papillary thyroid carcinoma via activation of the Ras-ERK pathway. 30404826_Forces acting on integrins recruit Enigma family proteins (PDLIM5 AND PDLIM7) to trigger YAP activation during mechanotransduction. 31424159_Novel polymorphisms in PDLIM3 and PDLIM5 gene encoding Z-line proteins increase risk of idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. 31880413_Mutations in PDLIM5 are rare in dilated cardiomyopathy but are emerging as potential disease modifiers. 32737199_PDLIM5 inhibits STUB1-mediated degradation of SMAD3 and promotes the migration and invasion of lung cancer cells. 34069539_Mechanical Sensing Element PDLIM5 Promotes Osteogenesis of Human Fibroblasts by Affecting the Activity of Microfilaments. | ENSMUSG00000028273 | Pdlim5 | 1023.956490 | 1.0964367 | 0.132822530 | 0.09527767 | 1.94169279120 | 0.1634848513110632728384530309995170682668685913085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.36439924951071400727187210577540099620819091796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1097.201392 | 81.422216 | 1004.001671 | 74.761715 | |
| ENSG00000163166 | 55677 | IWS1 | protein_coding | Q96ST2 | FUNCTION: Transcription factor which plays a key role in defining the composition of the RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) elongation complex and in modulating the production of mature mRNA transcripts. Acts as an assembly factor to recruit various factors to the RNAPII elongation complex and is recruited to the complex via binding to the transcription elongation factor SUPT6H bound to the C-terminal domain (CTD) of the RNAPII subunit RPB1 (POLR2A). The SUPT6H:IWS1:CTD complex recruits mRNA export factors (ALYREF/THOC4, EXOSC10) as well as histone modifying enzymes (such as SETD2) to ensure proper mRNA splicing, efficient mRNA export and elongation-coupled H3K36 methylation, a signature chromatin mark of active transcription. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17184735, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17234882, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19141475}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;mRNA transport;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transport | Involved in regulation of histone modification; regulation of mRNA export from nucleus; and regulation of mRNA processing. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:55677; | nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; mRNA processing [GO:0006397]; poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus [GO:0016973]; regulation of histone H3-K36 trimethylation [GO:2001253]; regulation of histone H4 acetylation [GO:0090239]; regulation of mRNA export from nucleus [GO:0010793]; regulation of mRNA processing [GO:0050684]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380] | 17184735_Here we report that the human homolog of Iws1, hIws1, physically interacts with protein arginine methyltransferases PRMT5 which methylates elongation factor Spt5 and regulates its interaction with RNA polymerase II. 17234882_binding of Spt6 to Ser2-P RNAPII provides a cotranscriptional mechanism to recruit Iws1, REF1/Aly, and associated mRNA processing, surveillance, and export factors to responsive genes. 19141475_recombinant Spt6 binds selectively to a stretch of uninterrupted consensus repeats located in the N-terminal half of the CTD and recruits Iws1 24462114_IWS1, an RNA processing regulator, is phosphorylated by Akt3 and Akt1 at Ser720/Thr721 in lung cancer 25590759_Altogether, these results indicate that a complex containing LEDGF/p75, Iws1, and Spt6 participates in regulating postintegration steps of HIV latency. 26245978_common LEDGF/p75 interaction interface shared by JPO2, PogZ, MLL1, IWS1 and HIV IN 34822292_A ubiquitous disordered protein interaction module orchestrates transcription elongation. | ENSMUSG00000024384 | Iws1 | 324.890728 | 1.0423124 | 0.059787736 | 0.09857341 | 0.36770259921 | 0.5442592192600625988774254437885247170925140380859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.74545201746596756464668942498974502086639404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 325.918655 | 20.122747 | 314.083151 | 19.477175 | |
| ENSG00000163219 | 9938 | ARHGAP25 | protein_coding | P42331 | FUNCTION: GTPase activator for the Rho-type GTPases by converting them to an inactive GDP-bound state. {ECO:0000250}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;GTPase activation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | ARHGAPs, such as ARHGAP25, encode negative regulators of Rho GTPases (see ARHA; MIM 165390), which are implicated in actin remodeling, cell polarity, and cell migration (Katoh and Katoh, 2004 [PubMed 15254788]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:9938; | phagocytic cup [GO:0001891]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; negative regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051058]; phagocytosis, engulfment [GO:0006911]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 19911011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 31228451_ARHGAP25 negatively regulates the metastatic potential of CRC cells via the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway 33994864_ARHGAP25 Inhibits Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Growth by Suppressing Glycolysis via AKT/mTOR Pathway. 36190314_A novel BRET-Based GAP assay reveals phosphorylation-dependent regulation of the RAC-specific GTPase activating protein ARHGAP25. 36207695_Relationship between the expression of ARHGAP25 and RhoA in non-small cell lung cancer and vasculogenic mimicry. | ENSMUSG00000030047 | Arhgap25 | 357.718259 | 1.4628559 | 0.548787617 | 0.09894877 | 30.73067315322 | 0.0000000296441756768304315361014020365967858161582171305781230330467224121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000064189276991873690520872680620456662836659234017133712768554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 421.432623 | 23.232979 | 289.365474 | 16.446705 | |
| ENSG00000163359 | 1293 | COL6A3 | protein_coding | P12111 | FUNCTION: Collagen VI acts as a cell-binding protein. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Collagen;Congenital muscular dystrophy;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dystonia;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Phosphoprotein;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Serine protease inhibitor;Signal | This gene encodes the alpha-3 chain, one of the three alpha chains of type VI collagen, a beaded filament collagen found in most connective tissues. The alpha-3 chain of type VI collagen is much larger than the alpha-1 and -2 chains. This difference in size is largely due to an increase in the number of subdomains, similar to von Willebrand Factor type A domains, that are found in the amino terminal globular domain of all the alpha chains. These domains have been shown to bind extracellular matrix proteins, an interaction that explains the importance of this collagen in organizing matrix components. Mutations in the type VI collagen genes are associated with Bethlem myopathy, a rare autosomal dominant proximal myopathy with early childhood onset. Mutations in this gene are also a cause of Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy, also referred to as Ullrich scleroatonic muscular dystrophy, an autosomal recessive congenital myopathy that is more severe than Bethlem myopathy. Multiple transcript variants have been identified, but the full-length nature of only some of these variants has been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2009]. | hsa:1293; | collagen type VI trimer [GO:0005589]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular vesicle [GO:1903561]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring tensile strength [GO:0030020]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517] | 11785962_Postranslational processing of type VI collagen in articular cartilage was investigated: alpha3(VI) collagen C5 domain is initially incorporated into the newly formed type VI fibrils, but after secretion is cut and not in the mature pericellular matrix 11992252_Mutations in COL6A3 cause severe and mild phenotypes of Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy. 12011280_Haplotype analysis clearly suggested linkage of Ullrich muscular dystrophy to the COL6A1/2 locus in two cases and to the COL6A3 loci in the third case. In the remaining nine patients, primary collagen VI involvement was excluded 12077460_The C-terminal Kunitz-type domain from the alpha3 chain of human type VI collagen (C5), a single amino-acid residue chain with three disulfide bridges, was refined at 0.9 A resolution in a monoclinic form 15563506_dominant mutations are common in Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD). 15965965_These results suggest that different alpha3(VI) chain isoforms, containing also domains of the N10-N7 region, are required for assembling a proper collagen VI network in the extracellular matrix. 16613849_the alpha3(VI) C5 domain is present in the extracellular matrix of SaOS-2 N6-C5 expressing cells and fibroblasts, which demonstrates that processing of the C-terminal region of the alpha3(VI) chain is not essential for microfibril formation 17918257_Col6A3 fusion with colony-stimulating factor-1 gene is associated with tenosynovial giant cell tumors. 18366090_Study reports 10 unrelated patients with a Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy clinical phenotype and de novo dominant negative heterozygous splice mutations in COL6A1, COL6A2 and COL6A3. 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19837927_in humans increased COL6A3 mRNA is associated with adipose tissue macrophage chemotaxis and inflammation and that weight gain 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23818951_Data indicate that the aberrantly methylated and expressed genes in cancer process including IRS1 and collagen-related genes COL4A1, COL4A2 and COL6A3. 24443028_Mutations in each of the three collagen VI genes, COL6A1, COL6A2 and COL6A3, cause four types of muscle disorders: Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy, Bethlem myopathy, limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, and autosomal recessive myosclerosis. (Review) 24647224_Data indicate that endotrophin (COL6alpha3) levels are higher in diabetic patients. 24719315_Increased adipocyte COL6A3 expression associates with insulin resistance; COL6A3 mRNA associates with small adipocyte size 24801232_In UCMD, 1 mutation was indentified in Chinese patients. 25204870_Parental mosaicism was confirmed in the four families through quantitative analysis of the ratio of mutant versus wild-type allele (COL6A1, COL6A2, and COL6A3) in genomic DNA from various tissues; consistent with somatic mosaicism, parental samples had lower ratios of mutant versus wild-type allele compared with the fully heterozygote offspring. 25337653_This study showed that COL6A3 expression appeared to be lowered in obesity, whereas diet- and surgery-induced weight loss increased COL6A3 expression. 25449070_The heterozygous c.3353A>C mutation in exon 8 of the COL6A3 gene is associated with the Bethlem myopathy with autosomal dominant inheritance. 25635128_COL6A mutations were identified in eight cases having clinical phenotypes of Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) or Bethlem myopathy (BM). 26004199_Recessive mutations in the alpha3 (VI) collagen gene COL6A3 cause early-onset isolated dystonia. 26338966_Data indicate that circulating plasma COL6A3 in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients was upregulated significantly comparing with healthy peoples. 26687111_COL6A3-associated dystonia represents a newly identified autosomal-recessive entity characterized clinically by an early symptom onset with variable distribution. 26872670_In conjunction with the relatively high frequency of homozygous carriers of reported mutations in publically available databases, our data call a causal role for variants in COL6A3 in isolated dystonia into question. 27729337_Overexpression of endotrophin led to a fibrotic program in white adipose tissue (WAT) adipocytes, a proinflammatory program in (WAT) macrophages, and upregulation of both profibrotic and proinflammatory genes in the stromal vascular fraction isolated from WAT. 28403201_Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) are at increased risk of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and early mortality. Serum endotrophin, a COL6A3 cleavage product was significantly associated with progression to ESRD. 29066004_Altered white matter structure especially in various parts of the cerebello-thalamo-cortical network in dystonia patients with COL6A3 mutations. 29465610_COL6A mutation Congenital Muscular Dystrophy showed the muscle weakness and poor respiratory function. 29620224_Study found COL6A3 expression to be downregulated and associated with poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer (CRC). In silico analysis of cell typespecific gene expression and COL6A3 knockout experiments indicated the clinical relevance of COL6A3 in the development of CRC. 29894794_two compound heterozygous mutations in COL6A3 gene lead to myopathy from Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy and Bethlem myopathy spectrum. 30014607_The morphology and immunophenotype of all 6 cases was analogous to those with the canonical COL1A1-PDGFB fusion; none of the cases showed fibrosarcomatous transformation. This study illustrates that the COL6A3-PDGFD fusion product is rare in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and associated with an apparent predilection for breast 30066698_COL6A3 could influence the viability and angiogenesis of bladder cancer cells. COL6A3 may have a certain relationship with the TGF-beta/Smad-induced EMT process. 30695889_two patients were diagnosed as spontaneous collagen type -related myopathy and carried different variants of COL6A3 gene 30706156_The most frequent mutation in a series of 16 Bethlem myopathy patients was the COL6A3 variant c.7447A>G, p.Lys2486Glu, with either an homozygous or compound heterozygous presentation. Five new mutations were found in COL6A1 gene and other two in COL6A3 gene, all of them with a dominant heritability pattern. 30896449_Human endotrophin as a driver of malignant tumor growth. 31122696_overexpressed circCOL6A3 promoted cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis of gastric cancer through rescission of miR-3064-5p-induced inhibitory effect on COL6A3; study will furnish theoretical grounds for future clinical diagnosis and treatment of GC patients 31286980_An association was determined between COL6A3 polymorphisms and lung cancer risk in a Chinese population. 31425922_study found that COL6A3 variants were associated with risk of esophageal cancer in the Chinese population 32037012_COL6A3 mutation associated early-onset isolated dystonia (DYT)-27: Report of a new case and review of published literature. 32245981_A Fragment of Collagen Type VI alpha-3 chain is Elevated in Serum from Patients with Gastrointestinal Disorders. 32389683_Coexistence of digenic mutations in the collagen VI genes (COL6A1 and COL6A3) leads to Bethlem myopathy. 32448721_Collagen VI-related limb-girdle syndrome caused by frequent mutation in COL6A3 gene with conflicting reports of pathogenicity. 32640306_Single cell sequencing revealed the underlying pathogenesis of the development of osteoarthritis. 32719005_Structure of a collagen VI alpha3 chain VWA domain array: adaptability and functional implications of myopathy causing mutations. 32934754_Identification of Key Prognostic Biomarker and Its Correlation with Immune Infiltrates in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. 33214660_COL6A3 expression in adipose tissue cells is associated with levels of the homeobox transcription factor PRRX1. 33749658_Clinical and Molecular Spectrum Associated with COL6A3 c.7447A>G p.(Lys2483Glu) Variant: Elucidating its Role in Collagen VI-related Myopathies. 33964895_Study of the collagen type VI alpha 3 (COL6A3) gene in Parkinson's disease. | ENSMUSG00000048126 | Col6a3 | 293.221315 | 2.7812063 | 1.475710777 | 0.92921235 | 2.40862845347 | 0.1206680473358095750935348178245476447045803070068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.30168200395077182651704106319812126457691192626953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 529.040395 | 304.233328 | 192.365315 | 110.431356 | |
| ENSG00000163681 | 7871 | SLMAP | protein_coding | Q14BN4 | FUNCTION: May play a role during myoblast fusion. {ECO:0000250}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a component of a conserved striatin-interacting phosphatase and kinase complex. Striatin family complexes participate in a variety of cellular processes including signaling, cell cycle control, cell migration, Golgi assembly, and apoptosis. The protein encoded by this gene is a coiled-coil, tail-anchored membrane protein with a single C-terminal transmembrane domain that is posttranslationally inserted into membranes. Mutations in this gene are associated with Brugada syndrome, a cardiac channelopathy. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015]. | hsa:7871; | microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; smooth endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005790]; muscle contraction [GO:0006936]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; regulation of membrane depolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:1900825]; regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1902305]; regulation of voltage-gated sodium channel activity [GO:1905150] | 23064965_Mutations in SLMAP may cause Brugada syndrome via modulating the intracellular trafficking of hNav1.5 channel. 25880194_The data suggests the potential role of SLMAP single nucleotide polymorphism as a risk factor for the susceptibility of diabetic retinopathy among type 2 diabetes patients in the Qatari population. 29063833_Here, the authors discover SAV1-mediated inhibition of the PP2A complex STRIPAK(SLMAP) as a key mechanism of MST1/2 activation. | ENSMUSG00000021870 | Slmap | 274.665915 | 1.1789740 | 0.237531912 | 0.09101143 | 6.80534577745 | 0.0090885351713683032448543031023291405290365219116210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.04589546208559560497297624692691897507756948471069335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 298.157842 | 17.787324 | 254.162752 | 15.131988 | |
| ENSG00000163703 | 78987 | CRELD1 | protein_coding | Q96HD1 | FUNCTION: Protein disulfide isomerase (By similarity). Promotes the localization of acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) to the plasma membrane (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91XD7, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9CYA0}. | Alternative splicing;Calcium;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Isomerase;Membrane;Redox-active center;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a member of a subfamily of epidermal growth factor-related proteins. The encoded protein is characterized by a cysteine-rich with epidermal growth factor-like domain. This protein may function as a cell adhesion molecule. Mutations in this gene are the cause of atrioventricular septal defect. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Apr 2010]. | hsa:78987; | collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; membrane [GO:0016020]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; protein disulfide isomerase activity [GO:0003756]; cardiac septum development [GO:0003279]; endocardial cushion development [GO:0003197] | 12632326_Missense mutations in this protein are associated with cardiac atrioventricular septal defects. 18076106_Mutations in CRELD1,are infrequently found in patients with congenital cardiac septal defects 19521671_CRELD1 could partly change the localization of RTN3 from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane and modulate the apoptotic activity of RTN3 through binding with it. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21080147_CRELD1 is likely to be an AVSD-susceptibility gene and CRELD1 mutations may increase the risk of developing a heart defect rather than being a direct causative mutation 21080147_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21413875_SNP c.985 C>T of CRELD1 is involved in causing congenital heart disease in patients of Mysore, South India. 22740159_study indicates that deleterious CRELD1 missense mutations are specifically associated with AVSD and are not correlated with other aspects of the heterotaxy phenotype 22987595_we identified two CRELD1 haplotypes associated with AVSD phenotype among DS and euploid individuals. 24927998_Mutation of the CRELD1 gene increased the risk for atrioventricular septal defect. 25524324_Germline mutations in the NKX2-5, GATA4, and CRELD1 genes do not appear to be associated with CHD in Mexican DS patients. 29054759_The CRELD1 gene is likely to have a major role in causation of AVSD phenotype in selected DS patients. | ENSMUSG00000030284 | Creld1 | 190.358633 | 0.8340966 | -0.261713538 | 0.13900732 | 3.53861736790 | 0.0599554193377107927376279405962122837081551551818847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.18624392753628660202025457692798227071762084960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 177.186672 | 13.810397 | 213.068389 | 16.100558 | |
| ENSG00000163795 | 130557 | ZNF513 | protein_coding | Q8N8E2 | FUNCTION: Transcriptional regulator that plays a role in retinal development and maintenance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20797688}. | Alternative splicing;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Retinitis pigmentosa;Sensory transduction;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Vision;Zinc;Zinc-finger | The protein encoded by this gene is a possible transcriptional regulator involved in retinal development. Defects in this gene can be a cause of autosomal-recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2011]. | hsa:130557; | nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; response to stimulus [GO:0050896]; retina development in camera-type eye [GO:0060041]; visual perception [GO:0007601] | 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20797688_These results suggest that the ZNF513 p.C339R mutation is responsible for retinitis pigmentosa and that ZNF513 plays a key role in the regulation of photoreceptor-specific genes in retinal development and photoreceptor maintenance. | ENSMUSG00000043059 | Zfp513 | 136.838250 | 0.9331288 | -0.099851866 | 0.12950924 | 0.59458558843 | 0.4406513583316861160099620065011549741029739379882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.66387434833281999679854834539582952857017517089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 134.155865 | 11.704055 | 144.448809 | 12.339252 | |
| ENSG00000163803 | 151056 | PLB1 | protein_coding | Q6P1J6 | FUNCTION: Calcium-independent membrane-associated phospholipase that catalyzes complete diacylation of phospholipids by hydrolyzing both sn-1 and sn-2 fatty acyl chains attached to the glycerol backbone (phospholipase B activity) (By similarity). Has dual phospholipase and lysophospholipase activities toward diacylphospholipids. Preferentially cleaves sn-2 ester bonds over sn-1 bonds. Acts as a lipase toward glycerolipid substrates (By similarity). Hydrolyzes fatty acyl chains of diacylglycerols with preference for the sn-2 position and of triacylglycerols with not positional selectivity (By similarity). May also hydrolyze long chain retinyl esters such as retinyl palmitate (By similarity). May contribute to digestion of dietary phospholipids, glycerolipids and retinoids, facilitating lipid absorption at the brush border (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O54728, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q05017}. | Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Phospholipid metabolism;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a membrane-associated phospholipase that displays lysophospholipase and phospholipase A2 activities through removal of sn-1 and sn-2 fatty acids of glycerophospholipids. In addition, it displays lipase and retinyl ester hydrolase activities. The encoded protein is highly conserved and is composed of a large, glycosylated extracellular domain composed of four tandem homologous domains, followed by a hydrophobic segment that anchors the enzyme to the membrane and a short C-terminal cytoplasmic tail. This gene has been identified as a candidate rheumatoid arthritis risk gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. | hsa:151056; | apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium-independent phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0047499]; lysophospholipase activity [GO:0004622]; phosphatidyl phospholipase B activity [GO:0102545]; phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0004623]; phospholipase activity [GO:0004620]; retinyl-palmitate esterase activity [GO:0050253]; triglyceride lipase activity [GO:0004806]; diacylglycerol catabolic process [GO:0046340]; phosphatidylcholine acyl-chain remodeling [GO:0036151]; phosphatidylcholine catabolic process [GO:0034638]; phosphatidylethanolamine catabolic process [GO:0046338]; phosphatidylglycerol catabolic process [GO:0034478]; phospholipid metabolic process [GO:0006644]; positive regulation of acrosome reaction [GO:2000344]; retinoid metabolic process [GO:0001523]; triglyceride catabolic process [GO:0019433] | 12150957_identification of epidermis as a site of expression 24520335_PLB1 is a candidate risk gene for rheumatoid arthritis. 28104536_rs117512489 in gene phospholipase B1 gene is associated with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. | ENSMUSG00000029134 | Plb1 | 66.631295 | 3.9428950 | 1.979255303 | 1.52939678 | 1.15533674172 | 0.2824347628431740919729975303198443725705146789550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.51448072179324377817266622514580376446247100830078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 114.513298 | 118.001074 | 19.875380 | 20.494920 | |
| ENSG00000163874 | 80149 | ZC3H12A | protein_coding | Q5D1E8 | FUNCTION: Endoribonuclease involved in various biological functions such as cellular inflammatory response and immune homeostasis, glial differentiation of neuroprogenitor cells, cell death of cardiomyocytes, adipogenesis and angiogenesis. Functions as an endoribonuclease involved in mRNA decay (PubMed:19909337). Modulates the inflammatory response by promoting the degradation of a set of translationally active cytokine-induced inflammation-related mRNAs, such as IL6 and IL12B, during the early phase of inflammation (PubMed:26320658). Prevents aberrant T-cell-mediated immune reaction by degradation of multiple mRNAs controlling T-cell activation, such as those encoding cytokines (IL6 and IL2), cell surface receptors (ICOS, TNFRSF4 and TNFR2) and transcription factor (REL) (By similarity). Inhibits cooperatively with ZC3H12A the differentiation of helper T cells Th17 in lungs. They repress target mRNA encoding the Th17 cell-promoting factors IL6, ICOS, REL, IRF4, NFKBID and NFKBIZ. The cooperation requires RNA-binding by RC3H1 and the nuclease activity of ZC3H12A (By similarity). Together with RC3H1, destabilizes TNFRSF4/OX40 mRNA by binding to the conserved stem loop structure in its 3'UTR (By similarity). Self regulates by destabilizing its own mRNA (By similarity). Cleaves mRNA harboring a stem-loop (SL), often located in their 3'-UTRs, during the early phase of inflammation in a helicase UPF1-dependent manner (PubMed:19909337, PubMed:26320658, PubMed:26134560, PubMed:22561375). Plays a role in the inhibition of microRNAs (miRNAs) biogenesis (PubMed:22055188). Cleaves the terminal loop of a set of precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs) important for the regulation of the inflammatory response leading to their degradation, and thus preventing the biosynthesis of mature miRNAs (PubMed:22055188). Also plays a role in promoting angiogenesis in response to inflammatory cytokines by inhibiting the production of antiangiogenic microRNAs via its anti-dicer RNase activity (PubMed:24048733). Affects the overall ubiquitination of cellular proteins (By similarity). Positively regulates deubiquitinase activity promoting the cleavage at 'Lys-48'- and 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains on TNF receptor-associated factors (TRAFs), preventing JNK and NF-kappa-B signaling pathway activation, and hence negatively regulating macrophage-mediated inflammatory response and immune homeostasis (By similarity). Induces also deubiquitination of the transcription factor HIF1A, probably leading to its stabilization and nuclear import, thereby positively regulating the expression of proangiogenic HIF1A-targeted genes (PubMed:24048733). Involved in a TANK-dependent negative feedback response to attenuate NF-kappaB activation through the deubiquitination of IKBKG or TRAF6 in response to interleukin-1-beta (IL1B) stimulation or upon DNA damage (PubMed:25861989). Prevents stress granule (SGs) formation and promotes macrophage apoptosis under stress conditions, including arsenite-induced oxidative stress, heat shock and energy deprivation (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of macrophage polarization; promotes IL4-induced polarization of macrophages M1 into anti-inflammatory M2 state (By similarity). May also act as a transcription factor that regulates the expression of multiple genes involved in inflammatory response, angiogenesis, adipogenesis and apoptosis (PubMed:16574901, PubMed:18364357). Functions as a positive regulator of glial differentiation of neuroprogenitor cells through an amyloid precursor protein (APP)-dependent signaling pathway (PubMed:19185603). Attenuates septic myocardial contractile dysfunction in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) by reducing I-kappa-B-kinase (IKK)-mediated NF-kappa-B activation, and hence myocardial pro-inflammatory cytokine production (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q5D1E7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16574901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18364357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19185603, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19909337, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22055188, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22561375, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24048733, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25861989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26134560, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26320658}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Binds to Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) and Dengue virus (DEN) RNAs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23355615}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Exhibits antiviral activity against HIV-1 in lymphocytes by decreasing the abundance of HIV-1 viral RNA species. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24191027}. | 3D-structure;Angiogenesis;Antiviral defense;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;DNA damage;DNA-binding;Endonuclease;Endoplasmic reticulum;Host-virus interaction;Hydrolase;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Neurogenesis;Nuclease;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;RNA-binding;Stress response;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | ZC3H12A is an MCP1 (CCL2; MIM 158105)-induced protein that acts as a transcriptional activator and causes cell death of cardiomyocytes, possibly via induction of genes associated with apoptosis.[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:80149; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule [GO:0036464]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; extrinsic component of endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0042406]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; P-body [GO:0000932]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; rough endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005791]; rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0030867]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; endoribonuclease activity [GO:0004521]; exoribonuclease activity [GO:0004532]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; miRNA binding [GO:0035198]; mRNA 3'-UTR AU-rich region binding [GO:0035925]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; ribonuclease activity [GO:0004540]; ribosome binding [GO:0043022]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA stem-loop binding [GO:0035613]; 3'-UTR-mediated mRNA destabilization [GO:0061158]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to chemokine [GO:1990869]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cellular response to glucose starvation [GO:0042149]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to ionomycin [GO:1904637]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; cellular response to sodium arsenite [GO:1903936]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; immune response-activating signaling pathway [GO:0002757]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; miRNA catabolic process [GO:0010587]; negative regulation by host of viral genome replication [GO:0044828]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle contraction [GO:0055118]; negative regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900016]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043124]; negative regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032691]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of macrophage activation [GO:0043031]; negative regulation of muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010656]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; negative regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901223]; negative regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045019]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; negative regulation of T-helper 17 cell differentiation [GO:2000320]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; negative regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032689]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, endonucleolytic cleavage-dependent decay [GO:0000294]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of cell death [GO:0010942]; positive regulation of defense response to virus by host [GO:0002230]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; positive regulation of execution phase of apoptosis [GO:1900119]; positive regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045600]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of lipid storage [GO:0010884]; positive regulation of miRNA catabolic process [GO:2000627]; positive regulation of mRNA catabolic process [GO:0061014]; positive regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900745]; positive regulation of protein deubiquitination [GO:1903003]; positive regulation of protein import into nucleus [GO:0042307]; positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000379]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein complex oligomerization [GO:0051259]; protein deubiquitination [GO:0016579]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; RNA phosphodiester bond hydrolysis [GO:0090501]; RNA phosphodiester bond hydrolysis, endonucleolytic [GO:0090502]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] | 16574901_May cause cell death and plays important role in development of ischemic heart disease. Could be a potential target for therapeutic intervention. 18178554_MCPIP1, 2, 3, and 4, encoded by four genes, Zc3h12a, Zc3h12b, Zc3h12c, and Zc3h12d, respectively, regulates macrophage activation. 18364357_MCP-1-induced angiogenesis is mediated via MCPIP, at least in part through transcriptional activation of cdh12 and cdh19 19185603_data demonstrate the role amyloid precursor protein (APP) has in glial differentiation of NT2 cells through MCP-1(MCP-1)/MCP-1-induced protein (MCPIP) signaling 19747262_Observations provide evidence for a novel negative feedback loop in the activation of NF-kappaB and point to potential significance of MCPIP in the treatment of pathological states that involve disturbances in the functioning of the NF-kappaB system. 20807520_REVIEW: Understanding ZC3H12A gives a comprehensive panorama that promises to improve our understanding of processes in which this gene is involved including autoimmune, infectious and cardiovascular diseases. 21971051_MCPIP1 coordinates SG formation and apoptosis during cellular stress and may play a critical role in immune homeostasis and resolution of macrophage inflammation. 22055188_MCPIP1 ribonuclease antagonizes dicer and terminates microRNA biogenesis through precursor microRNA degradation. 22132693_Our data suggest that Zc3h12a is a novel IL-6 regulator in fibroblast-like synovial cells, which may be involved in the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. 22196138_Data indicate that absence of MCPIP1 exacerbates ischemic brain damage by upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines and that MCPIP1 participates in LPS-induced ischemic stroke tolerance. 22820500_MCPIP-induces differentiation via induction of oxidative stress that leads to ER stress that causes autophagy involved in tube formation. 23185455_Taken together, these data demonstrate that MCPIP1 down-regulates via an ARE-independent pathway 23355615_MCPIP1 can act as a host innate defense via RNase activity for targeting and degrading viral RNA. 23658019_MCPIP1 is regulated by IL-17 and IL-1 24008336_These results demonstrate that MCPIP may be an important regulator of inflammatory angiogenesis and provide novel mechanistic insights into the link between MCP-1 and cardiovascular diseases. 24048733_The present results show for the first time that the antidicer RNase activity of MCPIP1 is critical in mediating the angiogenic function of MCPIP. 24191027_MCPIP1 acts as an RNase to limit HIV-1 production in resting CD4+ T cells. 24270572_MCPIP1-associated USP10 is essential for negative regulation of NF-kappaB activation. 25187114_Data show that regulator of G protein signaling 2 (RGS2) was stabilized by deubiquitinase monocyte chemotactic protein-induced protein 1 (MCPIP1). 25225661_MCPIP1 may suppress hepatitis C virus replication and hepatitis C virus-mediated proinflammatory responses with infection, which might contribute to the regulation of host defense against the infection and virus-induced inflammation. 25955820_In this review we summarize current progress regarding the specific characteristics of sequences and structures in the 3' untranslated regions of mRNAs that are recognized by tristetraproline, Roquins, and Regnase-1. 26134560_MCPIP1 and MCPIP4 form a complex but they act independently in regulation of IL-6 mRNA degradation. 26308737_expression of miR-3613-3p might be regulated by MCPIP1 by cleavage of its precursor form. 26315540_In white blood cells from patients with SLE, MCPIP1 expression was elevated, and its expression correlated positively with the IFN score and negatively with the miR-146a transcript level. 26329288_Findings show increased MCP1P expression in a model of Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury (I/R) and suggest a vital role for MCPIP1 in cell migration and apoptosis, resulting in increased angiogenesis and apoptosis during the late stages of I/R. 26399696_demonstrated induction of MCPIP1 in human fibroblasts embedded in the stress-released 3-D collagen matrix, which occurred through activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases, phosphoinositide 3-kinase, and NF-kappaB 26450708_miR-139-mediated downregulation of MCPIP1 promotes IL-6 expression in osteoarthritis. 26617772_Suggest that MCPIP1 may play an important role in cholesterol induced damage in endothelial cells. 27044405_Regnase-1 can be induced by HMGB1 in microglia and negatively regulates HMGB1-mediated neuroinflammation and neuronal toxicity 27075251_both human and cynomolgus monkey MCPIP1 restrict simian immunodeficiency virus replication. Unlike SAMHD1, MCPIP1-mediated HIV-1 restriction cannot be overcome by SIV Vpx. 27180111_IL-17A-mediated induction of MCPIP1 is involved in the regulation of local altered gene expression in suprabasal epidermal layers in psoriasis 27322373_These data revealed that influenza A virus-induced expression of miR-9 negatively regulated MCPIP1 expression and partially acts as a brake on host MCPIP1-mediated antiviral effect. 27404795_SAHA-mediated suppression of the IL-6 expression is achieved through increased recruitment of CEBPalpha to the MCPIP1 promoter and by relieving the miR-9-mediated inhibition of MCPIP1 expression in OA chondrocytes. 27494113_The human conserved stem-loop structure is not sufficient for ZC3H12A-dependent degradation. 27513529_this study uncovered a novel IL-8-dependent mechanism via which MCPIP-1 maintains epithelial homeostasis 27782836_findings provide novel insight into the potential targeting of MCPIP1 or autophagy in the development of potential therapeutic strategies for silicosis 27866190_These findings reveal a new potential function of MCPIP1, suggesting a possible mechanism of fibrosis in pulmonary silicosis. 27893764_propose that KSHV infection inhibits a negative regulator of miRNA biogenesis (MCPIP1) and up-regulates critical miRNA processing components to evade host mechanisms that inhibit expression of viral miRNAs 27920272_MCPIP1 is a potent negative regulator of psoriatic skin inflammation through IL-17A and IL-17C 27935099_data extend knowledge on roles of MCPIP1 in our model and link the protein to regulation of expression and stability of MYCN through decrease of signaling via Akt/mTOR pathway. 28194024_A comprehensive update on the function, regulation and molecular mechanisms of Regnase-1 is provided. Authors propose that Regnase-1 may function as a master rapid response gene for cellular adaption triggered by microenvironmental changes. [Review] 28197812_MCPIP1 contributes to the clear cell renal cell carcinoma development. 28328949_MCPIP1 recognizes regions of the 3'UTR of C/EBPbeta mRNA. 28377026_MCPIP1 contributes to the UVB response of keratinocytes by altering metabolic and apoptotic processes and the release of inflammatory mediators. 28475459_Regnase-1 controls the magnitude of innate and adaptive immune responses, and thereby dysfunction of this protein in mice leads to the development of spontaneous systemic inflammation. 28716897_Loss of MCPIP1 expression is associated with Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma metastasis. 28892164_Conclusively, these data demonstrate the MCPIP1 contributes to attenuate influenza A virus-induced host antiviral response by suppressing RIG-I expression. 28939056_MCPIP1 overexpression results in modulated levels of 58 miRNAs in adipocytes on day 2 of differentiation. Among them, 30 miRNAs showed significantly reduced levels and 28 showed increased levels in comparison to control. Approximately one third of the modulated miRNAs were not previously reported to be involved in adipocytes differentiation. 29054363_Zc3h12a may be a key factor for the aberrant increase in IL-6 after neonate infection. 29103983_The activation of p38 in response to low doses of ultraviolet radiation was postulated to be protective for p53-inactive cells. Therefore, MCPIP1 may favor the survival of p53-defective HaCaT cells by sustaining the activation of p38. 29379093_Based on these findings, ischemia/reperfusion-induced MCPIP1 expression regulates the migration and apoptosis of human vascular endothelial cells via HMGB1 and CaSR, respectively. 29471506_Evidence that MCPIP1 takes part not only in the destabilizing effect but also in translational silencing exerted by the NFKBIZ translational silencing element. 29545178_MCPIP1 is an important positive regulator of IFNs antiviral activity. 29551769_Low MCPIP1 expression is associated with breast neoplasms. 29742804_protective factor in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury 29743536_Substrate specificity of human MCPIP1 endoribonuclease was studied using RNA cleavage assays and affinity determination assays. 29913212_MALT1 paracaspase also targets MCPIP1 and degrade MCPIP1 protein in endothelial cells. 29920243_Data indicate a mechanism used by monocyte chemotactic protein-inducing protein 1 (MCPIP1) to negatively regulated type I IFN interferon-beta antiviral defense. 30096769_Although interleukin-6 (IL-6) mRNA level was higher in 3D-culured cells, its secretion levels were higher in 2D-cultured cells. In addition, the levels of mRNA and protein expression of regnase-1, regulatory RNase of inflammatory cytokine, significantly increased in 3D culture, suggesting post-translational modification of IL-6 mRNA via regnase-1. 30631045_MCPIP1 is a novel, powerful cytokine-induced protein in beta-cells that regulates beta-cell cytokine susceptibility by affecting a number of cytokine-sensitive pathways. 30842549_Study reveals that Regnase-1-mediated post-transcriptional regulation is required for hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell maintenance and suggest that it represents a leukemia tumor suppressor. 31185306_MCPIP1 overexpression in HepG2 cells treated with oleate induces the level and activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma). 31530713_The authors show that n transient transfection, MCPIP1 expression potently degraded the mRNA from exogenously transfected vectors and expression of MCPIP1 suppressed replication of Zika virus in infected cells. 31611552_CCL2 promotes macrophages-associated chemoresistance via MCPIP1 dual catalytic activities in multiple myeloma. 31651935_Up-regulated MCPIP1 in abdominal aortic aneurysm is associated with vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis and MMPs production. 31816951_MCP-1 and MCPIP potentially reduce the IL-1beta-mediated oncogenic effect in Renal Cell Carcinoma. 31893310_Integrative genomics reveal a role for MCPIP1 in adipogenesis and adipocyte metabolism. 31919874_MCPIP1 overexpression in human neuroblastoma cell lines causes cell-cycle arrest by G1/S checkpoint block. 31926181_MCPIP1 inhibits Hepatitis B virus replication by destabilizing viral RNA and negatively regulates the virus-induced innate inflammatory responses. 32548715_How are MCPIP1 and cytokines mutually regulated in cancer-related immunity? 32615986_Increased expression of CDKN1A/p21 in HIV-1 controllers is correlated with upregulation of ZC3H12A/MCPIP1. 32757706_MCPIP1 ribonuclease can bind and cleave AURKA mRNA in MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma cells. 32971087_The anti-inflammatory protein MCPIP1 inhibits the development of ccRCC by maintaining high levels of tumour suppressors. 33003343_MCPIP1 RNase and Its Multifaceted Role. 33007332_Loss of keratinocyte Mcpip1 abruptly activates the IL-23/Th17 and Stat3 pathways in skin inflammation. 33191882_Multifunctional RNase MCPIP1 and its Role in Cardiovascular Diseases. 33544962_MCPIP1 expression positively correlates with melanoma-specific survival of patients, and its overexpression affects vital intracellular pathways of human melanoma cells. 33756228_Elevated linc00936 or silenced microRNA-425-3p inhibits immune escape of gastric cancer cells via elevation of ZC3H12A. 33823555_Monocyte chemoattractant protein-induced protein 1 directly degrades viral miRNAs with a specific motif and inhibits KSHV infection. 33824311_MCPIP1-mediated NFIC alternative splicing inhibits proliferation of triple-negative breast cancer via cyclin D1-Rb-E2F1 axis. 34144091_MCPIP1 is a novel link between diabetogenic conditions and impaired insulin secretory capacity. 34298861_MCPIP1/Regnase-1 Expression in Keratinocytes of Patients with Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Preliminary Results. 34657130_MCPIP1 inhibits Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway activity and modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition during clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression by targeting miRNAs. 34659213_Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-Induced Protein 1 (MCPIP-1): A Key Player of Host Defense and Immune Regulation. 35082795_Dynamic Regulation of the Nexus Between Stress Granules, Roquin, and Regnase-1 Underlies the Molecular Pathogenesis of Warfare Vesicants. 35257717_MCPIP1 regulates focal adhesion kinase and Rho GTPase-dependent migration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 35752346_MCPIP1 promotes cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis of glioma via VEGFA-mediated ERK pathway. 36138026_Resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors promotes renal cancer progression through MCPIP1 tumor-suppressor downregulation and c-Met activation. 36165203_MCP-Induced Protein 1 Participates in Macrophage-Dependent Endotoxin Tolerance. 36272359_MCPIP1 alleviates inflammatory response through inducing autophagy in Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis. | ENSMUSG00000042677 | Zc3h12a | 1190.438508 | 0.6615445 | -0.596089995 | 0.05493507 | 117.77451881887 | 0.0000000000000000000000000019426307062898601524923231483785196750765388508932604373405447763557965046646303086674834048608317971229553222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000000000000000000000019002460363344449579728981469938780179211820294602876613272754397843469775786218178836861625313758850097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 969.868189 | 47.916868 | 1472.840995 | 71.317622 | |
| ENSG00000164466 | 94081 | SFXN1 | protein_coding | Q9H9B4 | FUNCTION: Amino acid transporter importing serine, an essential substrate of the mitochondrial branch of the one-carbon pathway, into mitochondria. Mitochondrial serine is then converted to glycine and formate, which exits to the cytosol where it is used to generate the charged folates that serve as one-carbon donors (PubMed:30442778). May also transport other amino acids including alanine and cysteine (PubMed:30442778). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30442778}. | Acetylation;Amino-acid transport;Direct protein sequencing;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;One-carbon metabolism;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | Enables D-serine transmembrane transporter activity and L-serine transmembrane transporter activity. Involved in D-serine transport; L-serine transport; and serine import into mitochondrion. Located in mitochondrion. Is integral component of mitochondrial inner membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:94081; | mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; L-alanine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015180]; L-serine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015194]; serine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022889]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0030218]; iron ion transport [GO:0006826]; L-alanine transport [GO:0015808]; L-serine transport [GO:0015825]; mitochondrial transmembrane transport [GO:1990542]; one-carbon metabolic process [GO:0006730]; serine import into mitochondrion [GO:0140300] | 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 30442778_SFXN1 functions as a mitochondrial serine transporter in one-carbon metabolism. 32950919_CircSFXN1 regulates the behaviour of trophoblasts and likely mediates preeclampsia. 33730581_The mitochondrial carrier SFXN1 is critical for complex III integrity and cellular metabolism. 35878532_Overexpression of SFXN1 indicates poor prognosis and promotes tumor progression in lung adenocarcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000021474 | Sfxn1 | 283.307072 | 1.1012176 | 0.139099531 | 0.15853852 | 0.76713233541 | 0.3811056518724731390079796256031841039657592773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.61231643089098797272384899770258925855159759521484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 328.663611 | 38.335858 | 299.556045 | 34.840627 | |
| ENSG00000164758 | 90390 | MED30 | protein_coding | Q96HR3 | FUNCTION: Component of the Mediator complex, a coactivator involved in the regulated transcription of nearly all RNA polymerase II-dependent genes. Mediator functions as a bridge to convey information from gene-specific regulatory proteins to the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. Mediator is recruited to promoters by direct interactions with regulatory proteins and serves as a scaffold for the assembly of a functional preinitiation complex with RNA polymerase II and the general transcription factors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11909976, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16595664}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation | The multiprotein TRAP/Mediator complex facilitates gene expression through a wide variety of transcriptional activators. MED30 is a component of this complex that appears to be metazoan specific (Baek et al., 2002 [PubMed 11909976]).[supplied by OMIM, Nov 2010]. | hsa:90390; | core mediator complex [GO:0070847]; mediator complex [GO:0016592]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000151]; nuclear receptor coactivator activity [GO:0030374]; nuclear thyroid hormone receptor binding [GO:0046966]; nuclear vitamin D receptor binding [GO:0042809]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0032968]; positive regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0060261]; RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex assembly [GO:0051123]; somatic stem cell population maintenance [GO:0035019] | 11909976_Requirement of TRAP/mediator for both activator-independent and activator-dependent transcription in conjunction with TFIID-associated TAF(II)s. 20493979_analysis of a novel transcript of MED30, termed MED30 short (MED30s) generated by alternative splicing 29187445_Knockdown of MED30 led to reduction of the tumour parameters proliferation, migration, and invasion in the bladder cancer (BCa) cell lines. 29661722_MED30 seems to be involved in the progression of the renal cell carcinoma (RCC). 32705436_HIF1alpha and p53 Regulated MED30, a Mediator Complex Subunit, is Involved in Regulation of Glioblastoma Pathogenesis and Temozolomide Resistance. | ENSMUSG00000038622 | Med30 | 94.641529 | 1.1139995 | 0.155748591 | 0.16169031 | 0.92795007233 | 0.3353961646138625685154011080157943069934844970703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.56797502472859739963695346887107007205486297607421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 99.890198 | 9.942548 | 89.937335 | 8.995749 | |
| ENSG00000164897 | 83590 | TMUB1 | protein_coding | Q9BVT8 | FUNCTION: Involved in sterol-regulated ubiquitination and degradation of HMG-CoA reductase HMGCR (PubMed:21343306). Involved in positive regulation of AMPA-selective glutamate receptor GRIA2 recycling to the cell surface (By similarity). Acts as negative regulator of hepatocyte growth during regeneration (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q53AQ4, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JMG3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21343306}.; FUNCTION: [iHOPS]: May contribute to the regulation of translation during cell-cycle progression. May contribute to the regulation of cell proliferation (By similarity). May be involved in centrosome assembly. Modulates stabilization and nucleolar localization of tumor suppressor CDKN2A and enhances association between CDKN2A and NPM1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JMG3}. | Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Endosome;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Reference proteome;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Involved in ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway. Predicted to be located in several cellular components, including nucleolus; postsynaptic membrane; and recycling endosome. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:83590; | microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433] | 19254477_a novel ubiquitin-like molecule DULP from human dendritic cells was identified. 31827061_TMUB1 promoted the expression of STAT1, and suppressed the expression of CCND1 in HCC cells. TMUB1 negatively regulates hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation via regulating STAT1. 32860479_The Ins and Outs of HOPS/TMUB1 in biology and pathology. 35928927_TMUB1 Correlated with Immune Infiltration Is a Prognostic Marker for Colorectal Cancer. 36376293_Promoting anti-tumor immunity by targeting TMUB1 to modulate PD-L1 polyubiquitination and glycosylation. | ENSMUSG00000028958 | Tmub1 | 244.178740 | 0.8958638 | -0.158648627 | 0.09926737 | 2.55578510712 | 0.1098912117015382466922446269563806708902120590209960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.28323922452525940318679431584314443171024322509765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 229.944391 | 14.829433 | 258.047389 | 16.128638 | |
| ENSG00000165283 | 30968 | STOML2 | protein_coding | Q9UJZ1 | FUNCTION: Mitochondrial protein that probably regulates the biogenesis and the activity of mitochondria. Stimulates cardiolipin biosynthesis, binds cardiolipin-enriched membranes where it recruits and stabilizes some proteins including prohibitin and may therefore act in the organization of functional microdomains in mitochondrial membranes. Through regulation of the mitochondrial function may play a role into several biological processes including cell migration, cell proliferation, T-cell activation, calcium homeostasis and cellular response to stress. May play a role in calcium homeostasis through negative regulation of calcium efflux from mitochondria. Required for mitochondrial hyperfusion a pro-survival cellular response to stress which results in increased ATP production by mitochondria. May also regulate the organization of functional domains at the plasma membrane and play a role in T-cell activation through association with the T-cell receptor signaling complex and its regulation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17121834, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18641330, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19597348, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19944461, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21746876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22623988}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Lipid-binding;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transit peptide | Enables GTPase binding activity and cardiolipin binding activity. Involved in several processes, including inorganic cation transmembrane transport; positive regulation of cardiolipin metabolic process; and positive regulation of mitochondrial DNA replication. Located in membrane raft; mitochondrial inner membrane; and mitochondrial intermembrane space. Is extrinsic component of plasma membrane. Colocalizes with several cellular components, including COP9 signalosome; T cell receptor complex; and immunological synapse. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:30968; | cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; extrinsic component of plasma membrane [GO:0019897]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cardiolipin binding [GO:1901612]; GTPase binding [GO:0051020]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation [GO:0035710]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; lipid localization [GO:0010876]; mitochondrial calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0006851]; mitochondrial protein processing [GO:0034982]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; positive regulation of cardiolipin metabolic process [GO:1900210]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; positive regulation of mitochondrial DNA replication [GO:0090297]; positive regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0010918]; protein complex oligomerization [GO:0051259]; proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis [GO:0042776]; stress-induced mitochondrial fusion [GO:1990046]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] | 16533792_overexpression of stomatin-like protein 2 is associated with neoplasms 16671055_SLP-2 is a high abundance protein in several tissues and cells and may play an important biological role; this study uses mass spectrometry to analyze its primary structure 17342323_SLP-2 was overexpressed in endometrial adenocarcinoma compared with their normal counterparts. 17709317_High-level SLP-2 expression was associated with decreased overall survival (P = .011) and was more often found in patients with tumors larger than 20 mm, lymph node metastasis, advanced clinical stage, distant metastasis 18267007_Endosymbiotic origin of paraslipin from an alphaprotoebacterial ancestor (SLP-2) 18641330_SLP-2 is an important player in T cell activation by ensuring sustained TCR signaling 19767238_Familial MGUS and multiple myeloma were associated with a dominant inheritance of hyperphosphorylated paratarg-7 19839737_SLP-2 overexpression is associated with tumour distant metastasis and poor prognosis in pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma. 19944461_negatively modulates mitochondrial sodium-calcium exchange 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21209152_plasma concentrations of stomatin (EPB72)-like 2 in early-stage colorectal cancer patients were elevated as compared with those of healthy individuals 21220746_The dominant inheritance of hyperphosphorylated paratarg-7 explains cases of familial IgM monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia 21501885_[review] Stomatin family member STOML2 is oligomeric; it localizes mostly to membrane domains and has been shown to modulate ion channel activity. 21746876_We propose that the function of SLP-2 is to recruit prohibitins to cardiolipin to form cardiolipin-enriched microdomains in which electron transport complexes are optimally assembled. 22081131_SLP-2 and HER2/neu can play a role in lymph node/distant metastases of breast cancers 22158085_investigation of biomarkers for early diagnosis of endometriosis: Data suggest that SLP2, tropomyosin 3, and tropomodulin 3 are autoantigens present in blood of women with endometriosis; immunodominant epitopes were identified. 22623988_SLP-2 facilitates the compartmentalization not only of mitochondrial membranes but also of the plasma membrane into functional microdomains. 23028053_SLP-2 deficiency in T-lymphocytes is associated with abnormal cardiolipin compartmentalization in mitochondrial membranes, defects associated with altered mitochondrial respiration that is increasingly uncoupled from ATP production. 23371255_Increased levels of SLP-2 correlate with lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer. 23667687_Expression of SLP-2 is associated with invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 23918306_SLP-2 may play an important role in human GBC tumorigenesis, and SLP-2 might serve as a novel prognostic marker in human GBC. 24190591_SLP-2 was upregulated by TGF-beta1, indicating a possible role of SLP-2 in Papillary thyroid cancer tumorigenesis. 24258357_STOML2 may have a role in progression of gastric adenocarcinoma 25695396_Our study showed that STOML-2 was negatively regulated by miR1207-5p in esophageal carcinoma 25973071_STOML2 was correlated to progression in cervical cancer, and implicated it as a potential predictive factor for the prognosis of cervical cancer. 26487491_Stomatin-like protein 2 is overexpressed in epithelial ovarian cancer and predicts poor patient survival 26750533_The significant association of SLP-2 overexpression with unfavorable clinicopathological characteristics and BRAFV600E mutation indicates that SLP-2 may have a role in aggressiveness of BRAF-mutated papillary thyroid carcinoma. 26932604_The expression of STOML2, a gene that plays a key role in mitochondrial function and T-cell activation, is associated with both IL-6 signaling and asthma risk. 27737933_results reveal an important role of SLP2 membrane scaffolds for the spatial organization of inner membrane proteases regulating mitochondrial dynamics, quality control, and cell survival. 27986413_Slp2 is involved in endometrial stromal cell proliferation and differentiation during decidualization in mice and humans 29364474_The downregulation of SLP-2 by siRNA inhibited cell proliferation, elevated caspase3 activity, and decreased CCBE1 expression 29516570_Data show that SLP-2 is upregulated by high cisplatin concentrations, leading to increased protein turnover. Overexpression of SLP-2 activates the MEK/ERK signaling pathway, and suppresses the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway, indicating that SLP-2 inhibits apoptosis by activating the MEK/ERK pathway and inhibiting the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway in cervical cancer cells. 29556045_SLP-2 promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation by enhancing survivin expression mediated through the TCF4/beta-catenin pathway. 29951933_TROP-2, SLP-2 and CD56 were effective diagnostic markers for PTC, especially when they were combined to use. 30359340_The knockdown of STOML2 significantly repressed the viability, migration, and invasion of LM3 cells. Authors observed that silencing STOML2 markedly downregulated the expression levels of MMP-2, MMP-9,MTA1, and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB), and upregulated levels of E-cadherin, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 2 (TIMP2), and the inhibitor of kappa B (IkappaB). 30389319_that SLP-2 may predict a poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients as a novel marker 30555578_These findings demonstrated a positive feedback loop of SLP2 which leads to acceleration of tumor progression and poor survival of gastric cancer patients. This finding also provided evidence for the reason of SLP2 elevation. 30888245_Hyperphosphorylated paratarg-7 carrier state is a strong molecularly defined risk factor for the development of Waldenstrom's macroglobulinaemia. 32141532_Clinical significance of SLP-2 in epithelial ovarian cancer and its regulatory effect on the Notch signaling pathway. 32814233_Stomatin-like protein 2 (SLP2) regulates the proliferation and invasion of trophoblast cells by modulating mitochondrial functions. 33412331_Characterization of the interactome of c-Src within the mitochondrial matrix by proximity-dependent biotin identification. 33446239_STOML2 potentiates metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting PINK1-mediated mitophagy and regulates sensitivity to lenvatinib. 33846782_Stomatinlike protein 2 induces metastasis by regulating the expression of a ratelimiting enzyme of the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway in pancreatic cancer. 34088631_Stomatin-Like Protein-2: A Potential Target to Treat Mitochondrial Cardiomyopathy. 35656794_CHCHD10 and SLP2 control the stability of the PHB complex: a key factor for motor neuron viability. | ENSMUSG00000028455 | Stoml2 | 318.482221 | 0.9427143 | -0.085107508 | 0.09979708 | 0.72704440584 | 0.3938428923787196112016317783854901790618896484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.62221305382804725780943044810555875301361083984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 305.378125 | 20.323287 | 325.355169 | 21.501904 | |
| ENSG00000165637 | 7417 | VDAC2 | protein_coding | P45880 | FUNCTION: Forms a channel through the mitochondrial outer membrane that allows diffusion of small hydrophilic molecules (By similarity). The channel adopts an open conformation at low or zero membrane potential and a closed conformation at potentials above 30-40 mV (By similarity). The open state has a weak anion selectivity whereas the closed state is cation-selective (By similarity). Binds various lipids, including the sphingolipid ceramide, the phospholipid phosphatidylcholine, and the sterol cholesterol (PubMed:31015432). Binding of ceramide promotes the mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) apoptotic pathway (PubMed:31015432). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P21796, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31015432}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Ion transport;Isopeptide bond;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;NAD;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Porin;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane beta strand;Transport;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes a member of the voltage-dependent anion channel pore-forming family of proteins that are considered the main pathway for metabolite diffusion across the mitochondrial outer membrane. The encoded protein is also thought to be involved in the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway via regulation of BCL2-antagonist/killer 1 protein activity. Pseudogenes have been identified on chromosomes 1, 2, 12 and 21, and alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. | hsa:7417; | acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; mitochondrial nucleoid [GO:0042645]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; pore complex [GO:0046930]; sperm midpiece [GO:0097225]; ceramide binding [GO:0097001]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; nucleotide binding [GO:0000166]; phosphatidylcholine binding [GO:0031210]; porin activity [GO:0015288]; voltage-gated anion channel activity [GO:0008308]; anion transport [GO:0006820]; binding of sperm to zona pellucida [GO:0007339]; mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization [GO:0097345]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001243]; negative regulation of protein polymerization [GO:0032272] | 14739283_VDAC2 and VDAC3 might have an alternative structural organization and different functions in outer dense fibers than in mitochondria 15757910_VDAC-2 inhibits the Bak-mediated apoptotic response via Bax 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18278581_Results identify VDAC2 and aldolase A as membrane proteins of K562 cells with increased expression under iron deprivation. 20809416_The high abundance of VDAC2 mRNA seemed to have a positive correlation with low sperm motility in male infertility with idiopathic asthenozoospermia. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21241999_VDAC2 may facilitate mitochondrial Ca(2+) uptake and restrict Ca(2+) spark expansion without regulating activations of sparks under resting conditions. 21347391_distribution and function of VDAC2 in human spermatozoa 22114330_VP5-induced apoptosis during IBDV infection is mediated by interacting with VDAC2, a protein that appears to restrict viral replication via induction of cell death 22119777_The reconstitution of functional VDAC-2 in lauryldimethylamine-oxide (LDAO) detergent micelles and 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DMPC) lipid bilayer nanodiscs, is reported. 22842492_Binding of VDAC2 enhances eNOS activity in the pulmonary circulation. 23060438_VDAC 1, 2, and 3 recruit Parkin to defective mitochondria to promote mitochondrial autophagy. 23873934_minor conformational variations in local residues are sufficient to define the membrane protein dynamics in hVDAC-2. 24642864_Cysteine residues impact the stability and micelle interaction dynamics of the human mitochondrial beta-barrel anion channel VDAC-2. 25187518_GSK-3beta translocates from the cytosol to mitochondria in a kinase activity- and VDAC2-dependent manner in which an N-terminal domain of GSK-3beta may function as a mitochondrial targeting sequence 25341036_These data suggest that an interaction between Mcl-1 and VDAC promotes lung cancer cell migration by a mechanism that involves Ca(2+)-dependent reactive oxygen species production. 25583988_RACK1 plays an antiapoptotic role during IBDV infection via interaction with VDAC2 and VP5. 25617717_Results show that in thyroid tumours and cell lines, VDAC2 is upregulated and BAK1 downregulated. Also, transient knockdown of VDAC2 promoted upregulation of the BAK1 expression, and increased susceptibility to sorafenib treatment. 26417093_Motifs of VDAC2 required for mitochondrial Bak import and tBid-induced apoptosis. 26487717_The evolutionary demand for the NTE in the presence of cysteines clearly emerges from our biochemical and functional studies, providing insight into factors that functionally demarcate hVDAC-2 from the other VDACs. 26947058_The works available on VDAC cysteines support the notion that VDAC1, VDAC2, and VDAC3 proteins are paralogs with a similar pore-function and slightly different, but important, ancillary biological functions. (Review) 27620692_VDAC2 ensures mitochondria-specific membrane association of Bax and in the absence of VDAC2 Bax localizes towards other cell compartments. Bax retrotranslocation is also regulated by nucleotides and calcium ions, suggesting a potential role of the transport of these ions through VDAC2 in Bax retrotranslocation. 27806320_Chinese men carrying VDAC2 variants may have a decreased or increased risk of abnormal semen parameters associated with male infertility. 27892527_High methylation of the VDAC2 promoter CpGs in men with asthenospermia 30250190_VDAC2 is a new glycolytic regulator controlling the phenotype transition between glioma stem cells and non-stem cells and may serves as a new prognostic indicator and a potential therapeutic target for glioma patients. 30503532_VDAC plasticity and stability in the mitochondrial outer membrane are modulated by physical properties of the bilayer 31015432_Study data support a role of VDAC2 as direct effector of ceramide-mediated cell death, providing a molecular framework for how ceramides exert their anti-neoplastic activity. 31285435_mitochondrial targeting domain peptide induces necrotic cell death by interaction with the VDAC2 protein. 31974380_VDAC2 role in the melanoma drug resistance to erastin.Erastin-induced resistance mediated by FOXM1-Nedd4-VDAC2/VDAC3 negative feedback loop in melanoma.Nedd4 ubiquitinates and degrades VDAC2. 31981967_Structure-based modeling of turnover of Bcl-2 family proteins bound to voltage-dependent anion channel 2 (VDAC2): Implications for the mechanisms of proapoptotic activation of Bak and Bax in vivo. 32098132_A High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Study Reveals the Potential of Disulfide Formation in Human Mitochondrial Voltage-Dependent Anion Selective Channel Isoforms (hVDACs). 32641986_Inflammatory IFIT3 renders chemotherapy resistance by regulating post-translational modification of VDAC2 in pancreatic cancer. 32829673_Expression of voltage-dependent anion channels in endometrial cancer and its potential prognostic significance. 33046783_Bisindolylpyrrole triggers transient mitochondrial permeability transitions to cause apoptosis in a VDAC1/2 and cyclophilin D-dependent manner via the ANT-associated pore. 33067255_Palmitoylated CKAP4 regulates mitochondrial functions through an interaction with VDAC2 at ER-mitochondria contact sites. 33067418_BioID-based proteomic analysis of the Bid interactome identifies novel proteins involved in cell-cycle-dependent apoptotic priming. 33386501_Protein mass spectrometry reveals lycorine exerting anti-multiple-myeloma effect by acting on VDAC2 and causing mitochondrial abnormalities. | ENSMUSG00000021771 | Vdac2 | 437.930999 | 0.9121105 | -0.132719535 | 0.08569406 | 2.39819937503 | 0.1214750002061998346292170936067122966051101684570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.30296930543583999728696198872057721018791198730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 422.661988 | 26.962838 | 465.565959 | 29.493094 | |
| ENSG00000165732 | 9188 | DDX21 | protein_coding | Q9NR30 | FUNCTION: RNA helicase that acts as a sensor of the transcriptional status of both RNA polymerase (Pol) I and II: promotes ribosomal RNA (rRNA) processing and transcription from polymerase II (Pol II) (PubMed:25470060, PubMed:28790157). Binds various RNAs, such as rRNAs, snoRNAs, 7SK and, at lower extent, mRNAs (PubMed:25470060). In the nucleolus, localizes to rDNA locus, where it directly binds rRNAs and snoRNAs, and promotes rRNA transcription, processing and modification. Required for rRNA 2'-O-methylation, possibly by promoting the recruitment of late-acting snoRNAs SNORD56 and SNORD58 with pre-ribosomal complexes (PubMed:25470060, PubMed:25477391). In the nucleoplasm, binds 7SK RNA and is recruited to the promoters of Pol II-transcribed genes: acts by facilitating the release of P-TEFb from inhibitory 7SK snRNP in a manner that is dependent on its helicase activity, thereby promoting transcription of its target genes (PubMed:25470060). Functions as cofactor for JUN-activated transcription: required for phosphorylation of JUN at 'Ser-77' (PubMed:11823437, PubMed:25260534). Can unwind double-stranded RNA (helicase) and can fold or introduce a secondary structure to a single-stranded RNA (foldase) (PubMed:9461305). Together with SIRT7, required to prevent R-loop-associated DNA damage and transcription-associated genomic instability: deacetylation by SIRT7 activates the helicase activity, thereby overcoming R-loop-mediated stalling of RNA polymerases (PubMed:28790157). Involved in rRNA processing (PubMed:14559904, PubMed:18180292). May bind to specific miRNA hairpins (PubMed:28431233). Component of a multi-helicase-TICAM1 complex that acts as a cytoplasmic sensor of viral double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and plays a role in the activation of a cascade of antiviral responses including the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines via the adapter molecule TICAM1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JIK5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11823437, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14559904, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18180292, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25260534, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25470060, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25477391, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28431233, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28790157, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9461305}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Helicase;Hydrolase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Isopeptide bond;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;rRNA processing;Transcription;Ubl conjugation | DEAD box proteins, characterized by the conserved motif Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD), are putative RNA helicases. They are implicated in a number of cellular processes involving alteration of RNA secondary structure such as translation initiation, nuclear and mitochondrial splicing, and ribosome and spliceosome assembly. Based on their distribution patterns, some members of this family are believed to be involved in embryogenesis, spermatogenesis, and cellular growth and division. This gene encodes a DEAD box protein, which is an antigen recognized by autoimmune antibodies from a patient with watermelon stomach disease. This protein unwinds double-stranded RNA, folds single-stranded RNA, and may play important roles in ribosomal RNA biogenesis, RNA editing, RNA transport, and general transcription. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:9188; | B-WICH complex [GO:0110016]; chromosome [GO:0005694]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; 7SK snRNA binding [GO:0097322]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; miRNA binding [GO:0035198]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA helicase activity [GO:0003724]; rRNA binding [GO:0019843]; snoRNA binding [GO:0030515]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of histone acetylation [GO:0035066]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of myeloid dendritic cell cytokine production [GO:0002735]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I [GO:0045943]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0045945]; R-loop disassembly [GO:0062176]; response to exogenous dsRNA [GO:0043330]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] | 14559904_RNA helicase II/Gualpha silencing inhibits mammalian ribosomal RNA production 16045751_the function of Gu(alpha)in rRNA processing is at least partially dependent on its ability to interact with ribosomal protein L4. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18180292_in addition to its transcriptional effects, c-Jun regulates rRNA processing and nucleolar compartmentalization of the rRNA processing protein DDX21 20873769_Studies indicated that DDX21, HNRNPC, and RCC2 were isolated from Ku86 multicomponent complex in response to DNA damage. 23419719_Data indicate that DDX21, a nucleolar protein, was confirmed to associate with SET8. 24721576_As sequential interaction of PB1 and NS1 with DDX21 leads to temporal regulation of viral gene expression, influenza A virus likely uses the DDX21-NS1 interaction not only to overcome restriction, but also to regulate the viral life cycle. 25260534_DDX21 expression in breast cancer cells can promote AP-1 activity and rRNA processing, and thus, promote tumorigenesis by two independent mechanisms. 25470060_results uncover the multifaceted role of DDX21 in multiple steps of ribosome biogenesis, and provide evidence implicating a mammalian RNA helicase in RNA modification and Pol II elongation control 25477391_Identification of several late-acting snoRNAs that bind pre-40S particles in human cells and show that their association and function in pre-40S complexes is regulated by the RNA helicase DDX21. 27033607_In dengue virus infected cells, DDX21 translocates from nucleus to cytoplasm to active the innate immune response and thus inhibits DENV replication in the early stages of infection. 28472472_DDX21 can suppress the expression of proteins with G4 qudruplexes in the 3 UTR of its mRNA. 28475895_Results report the biogenesis and function of a box H/ACA snoRNA-ended sno-lncRNA, referred to SLERT (snoRNA-ended lncRNA enhances pre-ribosomal RNA transcription). SLERT is different from Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS) sno-lncRNAs and plays a crucial role in rRNA biogenesis by dislodging a previously unknown clamp of DDX21 ring-shaped arrangements on Pol I complexes, thereby liberating Pol I for active rRNA transcription. 28705764_DDX21 is both an ATP-dependent and ATP-independent helicase, and both ATPase and ATP-dependent helicase activities are inhibited by Rev in a dose-dependent manner, although ATP-independent helicase activity is not. A conserved binding interaction between DDX protein's DEAD domain and Rev was identified, with Rev's nuclear diffusion inhibitory signal motif playing a significant role in binding. 28790157_Knockdown of SIRT7 leads to the same phenotype as depletion of DDX21 (i.e., increased formation of R loops and DNA double-strand breaks), indicating that SIRT7 and DDX21 cooperate to prevent R-loop accumulation, thus safeguarding genome integrity. 29906500_can drastically reduce DDX21's affinity for quadruplex, indicating that the recognition of quadruplex and specificity for telomeric repeat containing RNA quadruplex is mediated by interactions with the 2'OH of loop nucleotides 30165191_Data indicate that DEAD-box helicase 21 (DDX21) regulated Snail transcription factors (Snail) expression independent of its helicase activity. 30322617_DDX21 induced gastric cancer cell growth by up-regulating levels of Cyclin D1 and CDK2. 31251802_The findings revealed that enhancer-mediated enrichment of novel JMJD3-DDX21 interaction at ENPP2 locus is necessary for nascent transcript synthesis via the resolution of aberrant R-loops formation in response to inflammatory stimulus. 31351877_Activation of PARP-1 by snoRNAs Controls Ribosome Biogenesis and Cell Growth via the RNA Helicase DDX21. 31554690_DDX21 knockdown prevented viral late gene transcription and consequently impaired HCMV replication. 31653714_Our work identifies the role of DDX21 in regulation at the translational level through biologically relevant RNA G-quadruplex (rG4) and shows that MAGED2 protein levels are regulated, at least in part, by the potential to form rG4 in their 5'-UTRs. 32231306_RNA helicase DDX21 mediates nucleotide stress responses in neural crest and melanoma cells. 32652076_PRL3-DDX21 Transcriptional Control of Endolysosomal Genes Restricts Melanocyte Stem Cell Differentiation. 33328538_DEAD-box RNA helicase protein DDX21 as a prognosis marker for early stage colorectal cancer with microsatellite instability. 33497018_The RNA-helicase DDX21 upregulates CEP55 expression and promotes neuroblastoma. 33604619_DDX21 interacts with nuclear AGO2 and regulates the alternative splicing of SMN2. 33754909_Identification of Prognostic RBPs in Osteosarcoma. 34125604_Caspase-Dependent Cleavage of DDX21 Suppresses Host Innate Immunity. 34326237_lncRNA SLERT controls phase separation of FC/DFCs to facilitate Pol I transcription. 34578346_DDX21, a Host Restriction Factor of FMDV IRES-Dependent Translation and Replication. 34688145_Identification of MDM2, YTHDF2 and DDX21 as potential biomarkers and targets for treatment of type 2 diabetes. 34903139_Downregulation of DEAD-box helicase 21 (DDX21) inhibits proliferation, cell cycle, and tumor growth in colorectal cancer via targeting cell division cycle 5-like (CDC5L). 34987058_The Roles of RNA Helicases in DNA Damage Repair and Tumorigenesis Reveal Precision Therapeutic Strategies. | ENSMUSG00000020075 | Ddx21 | 986.579273 | 1.1265884 | 0.171960533 | 0.04907573 | 12.27864153572 | 0.0004581717592706795335287528470047391238040290772914886474609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00388418579919894927515722216071480943355709314346313476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1054.763003 | 40.340086 | 940.697865 | 36.140520 | |
| ENSG00000166165 | 1152 | CKB | protein_coding | P12277 | FUNCTION: Reversibly catalyzes the transfer of phosphate between ATP and various phosphogens (e.g. creatine phosphate) (PubMed:8186255). Creatine kinase isoenzymes play a central role in energy transduction in tissues with large, fluctuating energy demands, such as skeletal muscle, heart, brain and spermatozoa (Probable). Acts as a key regulator of adaptive thermogenesis as part of the futile creatine cycle: localizes to the mitochondria of thermogenic fat cells and acts by mediating phosphorylation of creatine to initiate a futile cycle of creatine phosphorylation and dephosphorylation (By similarity). During the futile creatine cycle, creatine and N-phosphocreatine are in a futile cycle, which dissipates the high energy charge of N-phosphocreatine as heat without performing any mechanical or chemical work (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q04447, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8186255, ECO:0000305}. | 3D-structure;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Kinase;Mitochondrion;Nitration;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase | The protein encoded by this gene is a cytoplasmic enzyme involved in energy homeostasis. The encoded protein reversibly catalyzes the transfer of phosphate between ATP and various phosphogens such as creatine phosphate. It acts as a homodimer in brain as well as in other tissues, and as a heterodimer with a similar muscle isozyme in heart. The encoded protein is a member of the ATP:guanido phosphotransferase protein family. A pseudogene of this gene has been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:1152; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; creatine kinase activity [GO:0004111]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; cellular chloride ion homeostasis [GO:0030644]; cellular response to estrogen stimulus [GO:0071391]; cellular response to wortmannin [GO:1904568]; cerebellum development [GO:0021549]; phosphocreatine biosynthetic process [GO:0046314]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; substantia nigra development [GO:0021762] | 12160938_2D fingerprinting & mass spectrometry reveal specific targets of protein oxidation in Alzheimer's disease brain, including creatine kinase BB, suggesting involvement of oxidatively modified proteins in neurodegeneration. 15996648_Expression of CKB mRNA and CK-B sometimes occurred in blastic transformation of the hematopoietic system 16384981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16424007_CKB was expressed in 78% of colon tumors 17036164_GM130 and BB-CK co-localize specifically in a transient fashion during early prophase of mitosis, when GM130 plays an important role in Golgi fragmentation that starts also at early prophase. 18309274_The asymmetric unit contained two molecules of CKB, giving a crystal volume per protein mass (Vm) of 1.80 A3 Da-1 and a solvent content of 31.6%. 18552983_Autoantibodies to EsteD and BB-CK produced in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis -induced mice were also detected in some endogenous uveitis patients, suggesting that these proteins might be autoantigens. 18566107_Using a yeast 2-hybrid it was discovered that the C-terminal domain of KCC3, that is lost in most hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy with agenesis of the corpus callosum-causing mutations, directly interacts with brain-specific creatine kinase. 18682038_The Tat-CK fusion protein markedly increased endogenous CK activity levels within PC12 cells. 18793185_Data show that dose-response inactivation by 4HNE (4-hydroxynonenal) of hBAT (human bile acid CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase) and CKBB (cytosolic brain isoform of creatine kinase) is associated with site-specific modifications. 18977227_Three structural aspects of human-brain-type-creatine-kinase were identified by X-ray crystallography: the ligand-free-form at 2.2A; the ADP-Mg2+, nitrate, and creatine complex (transition-state-analogue complex; TSAC); and the ADP-Mg2+-complex at 2.0A. 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19337554_Report the effects of prior calcium channel blocker therapy on creatine kinase-MB (myocardial form) levels after percutaneous coronary interventions. 19405953_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the Wernicke's Area from patients with schizophrenia. 20460152_The correlation of CK-BB as a disease biomarker in both CNS and peripheral tissues from Huntington's disease mice and patients may provide a powerful means to assess disease progression and prognosis. 20520825_Phosphocreatine metabolism in the normal appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis is impaired due to decreased CK-B levels. 20588136_A single troponin I value at 3 days from symptom onset is a better predictor of infarct size compared to peak values and CK-MB. 20721618_CKB was up-regulated in women older than 38 years, and its expression in cumulus cells was associated with embryo quality 20923681_These observations suggested that the ability to generate the oxidized form could protect BBCK against the intracellular oxidative stress. 21308735_Data demonstrate that the downregulation of CKB may play an important role in colon cancer progression by promoting EMT. 21931810_The results suggested that the intra- and inter-subunit domain interactions modified the behavior of kinetic refolding. 21980054_Cigarette smoke induced carbonylation and subsequent degradation of creatine kinase B are involved in the regulation of senescence in bronchial epithelial cells. 22088263_de-methylated CKB gene is inherited that leads to high CKB expression levels in myeloic precursor cells in the bone marrow 22418839_His103 and Phe107 in hASB9-2 are essential for binding to CKB. 22623148_study found promoter SNPs of CKB and TPI1 were weakly associated with schizophrenia;in addition, IFNG polymorphisms were associated with schizophrenia; results suggest that IFNG and proteins affected by IFNG may play a role in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia 22885020_effects of osmolytes on human brain-type creatine kinase folding 23049898_analysis of SNPs and their effect on creatine kinase structure and function 23876027_Estimation of CK and its CK isoenzyme fractions can aid in quick and accurate diagnosis of tubal ectopic pregnancy. 23882694_We found that most patients with macular telangiectasia-2 possess retinal autoantibodies, the most prevalent of which were directed against AGL, RBP3, and CK-B. 24518563_increased serum Ckbb reflects failure of osteoclasts or suppression of osteoclasts in children with osteogenesis imperfecta during neridronate treatment 25141318_CK-MB levels were higher after ERCP in non-ischemic patients compared with a myocardial ischemia group. Creatine phosphokinase levels did not differ significantly between groups. 25538032_CK-B catalytic activity also helps in the formation of protrusive ruffle structures which are actin-dependent and abundant on the surface of both unstimulated and LPS-activated macrophages. 26460485_SRC, LYN and CKB expression or DNA methylation could be useful markers for predicting tumor progression. 27318991_membrane localization of BCK seems to be an important and regulated feature for the fueling of membrane-located, ATP-dependent processes, stressing again the importance of local rather than global ATP concentrations. 28364583_The data revealed a varying but significant increase of CK activity in CKBE individuals as compared to controls, reaching an almost 800-fold increase in two CKBE individuals which also had increased erythrocyte creatine. 28806770_These findings support increased CK activity as protection against ischaemia-reperfusion injury, in particular, protection via CKMT2 in a cardiac-relevant cell line, which merits further investigation in vivo. 29227081_Association and oligomerization of Prx II could take part in recovery and protection of the CK BB enzyme activity from inactivation during heat-induced stress. 33485312_Clinical impact of creatine phosphokinase and c-reactive protein as predictors of postgastrectomy complications in patients with gastric cancer. 33597756_Creatine kinase B controls futile creatine cycling in thermogenic fat. 34706306_CKB inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and prostate cancer progression by sequestering and inhibiting AKT activation. | ENSMUSG00000001270 | Ckb | 265.290793 | 0.6555246 | -0.609278181 | 0.12195401 | 24.94755685194 | 0.0000005891113687790933329361544278091056270341141498647630214691162109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00001019862602287370836309701033206565057298575993627309799194335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 178.006376 | 22.615957 | 272.724250 | 34.011889 | |
| ENSG00000166197 | 9221 | NOLC1 | protein_coding | Q14978 | FUNCTION: Nucleolar protein that acts as a regulator of RNA polymerase I by connecting RNA polymerase I with enzymes responsible for ribosomal processing and modification (PubMed:10567578, PubMed:26399832). Required for neural crest specification: following monoubiquitination by the BCR(KBTBD8) complex, associates with TCOF1 and acts as a platform to connect RNA polymerase I with enzymes responsible for ribosomal processing and modification, leading to remodel the translational program of differentiating cells in favor of neural crest specification (PubMed:26399832). Involved in nucleologenesis, possibly by playing a role in the maintenance of the fundamental structure of the fibrillar center and dense fibrillar component in the nucleolus (PubMed:9016786). It has intrinsic GTPase and ATPase activities (PubMed:9016786). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10567578, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26399832, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9016786}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;GTP-binding;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation | Enables protein heterodimerization activity and protein-macromolecule adaptor activity. Involved in neural crest cell development; neural crest formation; and regulation of translation. Located in fibrillar center. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:9221; | box C/D RNP complex [GO:0031428]; box H/ACA snoRNP complex [GO:0031429]; Cajal body [GO:0015030]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; box C/D RNA binding [GO:0034512]; box C/D snoRNP complex binding [GO:0062064]; box H/ACA snoRNA binding [GO:0034513]; box H/ACA snoRNP complex binding [GO:0062065]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; molecular function inhibitor activity [GO:0140678]; nuclear localization sequence binding [GO:0008139]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; TFIIB-class transcription factor binding [GO:0001093]; box H/ACA RNA metabolic process [GO:0033979]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; neural crest cell development [GO:0014032]; neural crest formation [GO:0014029]; nucleolus organization [GO:0007000]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; regulation of protein import into nucleus [GO:0042306]; regulation of translation [GO:0006417]; response to osmotic stress [GO:0006970]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364] | 12167624_NOPP140 is involved in a PKA signaling pathway that leads to agp activation 12446766_These data show that Nopp140 reversibly associates with snoRNPs in a phosphorylation-dependent manner, but this association has no effect on pseudouridylation of rRNA. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17001309_Hypoxia induces substantial p130 dephosphorylation and nuclear accumulation, leading to the formation of E2F4/p130 complexes and increased occupancy of E2F4 and p130 at the RAD51 and BRCA1 promoters. 17038328_hNopp140 serves as a negative regulator of CK2 and InsP(6) stimulates the activity of CK2 by blocking the interaction between hNopp140 and CK2 17531812_Evolutionarily conserved multisubunit protein complex that contains p130 and E2F4 mediates the repression of cell cycle-dependent genes in quiescence. 18253863_hNopp140, a scaffold protein, is involved in the nucleolar assembly, fusion, and maintenance 18790693_InsP(6) specifically binds to CK2alpha and disrupts the interaction between CK2alpha and Nopp140 with an IC(50) value of 25 microM, thereby attenuating the Nopp140-mediated repression of CK2 activity. 19129172_The functional deficiency in spinal muscular atrophy cells is associated with decreased localization of the snoRNP chaperone Nopp140 in Cajal bodies that correlates with disease severity. 19381672_Nopp140 could be a component implicated in the early steps of pre-rRNA processing. 19541936_both NOLC1 and tumor protein 53 work together synergistically to activate the MDM2 promoter in NPC cells. 21266110_The regulation of NOCL1 protein is a critical role for the transcription NF-kB and cAMP response element-bing protein 22906532_Structural disorder and local order of hNopp140 23188192_H5N1 viral NS1 interacts with host NOLC1 protein. 23970161_our study demonstrated that DNA methylation is a key mechanism of silenced NOLC1 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells, and NOLC1 gene hypermethylation of the four CpG dinucleotides is a potential biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. 24218616_A Nopp140 fragment (residues 568-596) and inositol hexakisphosphate competitively bind to the catalytic subunit of CK2 (CK2alpha), and phospho-Ser574 of Nopp140 significantly enhances its interaction with CK2alpha. 25205458_pRb2/p130 cytoplasmic delocalization can lead to cell cycle deregulation 25645906_D120 and R195 of H5N1 influenza virus NS1 were crucial for the binding to host NOLC1. 27297113_In this study, the disordered feature of Nopp140 and the effect of CK2alpha on the structure of Nopp140 were examined using single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer (smFRET) and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR). 29725012_Nucleolar TRF2 attenuated nucleolus stress-induced hepatocellular carcinoma cell-cycle arrest by altering rRNA synthesis via interaction with NOLC1. 30505321_Identification and validation of NOLC1 might be a promising therapeutic strategy for the management of multidrug resistance of non-small cell lung cancer patients. 31664887_This study suggests that the dynamic distribution of telomerase between Cajal bodies and nucleoplasm uniquely impacts telomere length maintenance and identifies Nopp140 as a novel player in telomere biology. 33323972_Pten-NOLC1 fusion promotes cancers involving MET and EGFR signalings. 36265288_NOLC1 knockdown suppresses prostate cancer progressions by reducing AKT phosphorylation and beta-catenin accumulation. | ENSMUSG00000015176 | Nolc1 | 402.010516 | 1.0932925 | 0.128679430 | 0.07674366 | 2.81060396354 | 0.0936431146863184599160589982602687086910009384155273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.25336168050913393523515537708590272814035415649414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 418.114786 | 21.931269 | 384.207970 | 20.108459 | |
| ENSG00000166337 | 6881 | TAF10 | protein_coding | Q12962 | FUNCTION: The TFIID basal transcription factor complex plays a major role in the initiation of RNA polymerase II (Pol II)-dependent transcription (PubMed:33795473). TFIID recognizes and binds promoters with or without a TATA box via its subunit TBP, a TATA-box-binding protein, and promotes assembly of the pre-initiation complex (PIC) (PubMed:33795473). The TFIID complex consists of TBP and TBP-associated factors (TAFs), including TAF1, TAF2, TAF3, TAF4, TAF5, TAF6, TAF7, TAF8, TAF9, TAF10, TAF11, TAF12 and TAF13 (PubMed:33795473). TAF10 is also component of the PCAF histone acetylase complex, the TATA-binding protein-free TAF complex (TFTC) and the STAGA transcription coactivator-HAT complex (PubMed:18206972, PubMed:11564863, PubMed:9885574, PubMed:10373431, PubMed:12601814). May regulate cyclin E expression (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K0H5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10373431, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11564863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12601814, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18206972, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33795473, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9885574}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Direct protein sequencing;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation | Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II requires the activities of more than 70 polypeptides. The protein that coordinates these activities is transcription factor IID (TFIID), which binds to the core promoter to position the polymerase properly, serves as the scaffold for assembly of the remainder of the transcription complex, and acts as a channel for regulatory signals. TFIID is composed of the TATA-binding protein (TBP) and a group of evolutionarily conserved proteins known as TBP-associated factors or TAFs. TAFs may participate in basal transcription, serve as coactivators, function in promoter recognition or modify general transcription factors (GTFs) to facilitate complex assembly and transcription initiation. This gene encodes one of the small subunits of TFIID that is associated with a subset of TFIID complexes. Studies with human and mammalian cells have shown that this subunit is required for transcriptional activation by the estrogen receptor, for progression through the cell cycle, and may also be required for certain cellular differentiation programs. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:6881; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; male germ cell nucleus [GO:0001673]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; SAGA complex [GO:0000124]; transcription factor TFIID complex [GO:0005669]; transcription factor TFTC complex [GO:0033276]; transcription preinitiation complex [GO:0097550]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; nuclear estrogen receptor binding [GO:0030331]; promoter-specific chromatin binding [GO:1990841]; RNA polymerase binding [GO:0070063]; RNA polymerase II general transcription initiation factor activity [GO:0016251]; allantois development [GO:1905069]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; DNA-templated transcription initiation [GO:0006352]; embryonic placenta development [GO:0001892]; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000082]; hepatocyte differentiation [GO:0070365]; histone acetylation [GO:0016573]; histone H3 acetylation [GO:0043966]; lateral mesodermal cell differentiation [GO:0048371]; limb development [GO:0060173]; monoubiquitinated histone deubiquitination [GO:0035521]; monoubiquitinated histone H2A deubiquitination [GO:0035522]; mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0042789]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0060261]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of DNA binding [GO:0051101]; regulation of DNA repair [GO:0006282]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of RNA splicing [GO:0043484]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex assembly [GO:0051123]; SAGA complex assembly [GO:0036285]; somitogenesis [GO:0001756]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter [GO:0006367] | 15099517_TAF10 can be monomethylated by SET9-mediated methylation. 15870280_novel role of three mammalian interacting partners in the nuclear localization of TAF10 17599049_TAFII30 was required for optimal P4 promoter activity and for the repressive association of estrogen receptor. 20106982_CDKN1C negatively regulates RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphorylation in an E2F1-dependent manner 20457598_The carboxyl-terminal domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (pol II) comprises multiple tandem repeats of a heptapeptide. 25586196_the TAF2-TAF8-TAF10 complex demonstrates that there is a stepwise assembly pathway of nuclear holo-TFIID, regulated by nuclear import of preformed cytoplasmic submodules 25959397_Lysine oxidation of the transcription factor TAF10 by LOXL2 is a controlled protein modification and demonstrates a role for protein oxidation in regulating pluripotency genes. | ENSMUSG00000043866 | Taf10 | 436.020274 | 0.9625938 | -0.055000898 | 0.10307479 | 0.28445893236 | 0.5937934568628341347462651356181595474481582641601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.77706237710022718623292803385993465781211853027343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 443.077068 | 27.963451 | 462.055714 | 28.906980 | |
| ENSG00000166783 | 9665 | MARF1 | protein_coding | Q9Y4F3 | FUNCTION: Essential regulator of oogenesis required for female meiotic progression to repress transposable elements and preventing their mobilization, which is essential for the germline integrity. Probably acts via some RNA metabolic process, equivalent to the piRNA system in males, which mediates the repression of transposable elements during meiosis by forming complexes composed of RNAs and governs the methylation and subsequent repression of transposons. Also required to protect from DNA double-strand breaks (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Differentiation;Meiosis;Oogenesis;Peroxisome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding | This gene encodes a putative peroxisomal protein that appears to be conserved across Euteleostomi. In humans, it may be autoantigenic. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. | hsa:9665; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; CCR4-NOT complex binding [GO:1905762]; mRNA base-pairing translational repressor activity [GO:1903231]; ribonuclease activity [GO:0004540]; double-strand break repair [GO:0006302]; female meiotic nuclear division [GO:0007143]; oogenesis [GO:0048477]; post-transcriptional gene silencing [GO:0016441]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468] | 24755989_LMKB is the first protein identified to date that interacts with this portion of Ge-1. LMKB was expressed in human B and T lymphocyte cell lines; depletion of LMKB increased expression of IFI44L. 30364987_Human MARF1 is an endoribonuclease that interacts with the DCP1:DCP2 decapping complex and degrades target mRNAs. 32510323_A non-canonical role for the EDC4 decapping factor in regulating MARF1-mediated mRNA decay. 35801873_P-bodies directly regulate MARF1-mediated mRNA decay in human cells. | ENSMUSG00000060657 | Marf1 | 436.028874 | 1.2118972 | 0.277267333 | 0.10718172 | 6.68245953195 | 0.0097366186038002795755108564890178968198597431182861328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.04846826371172893721528396326903020963072776794433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 466.218611 | 26.675400 | 386.724413 | 22.262895 | |
| ENSG00000166913 | 7529 | YWHAB | protein_coding | P31946 | FUNCTION: Adapter protein implicated in the regulation of a large spectrum of both general and specialized signaling pathways. Binds to a large number of partners, usually by recognition of a phosphoserine or phosphothreonine motif. Binding generally results in the modulation of the activity of the binding partner. Negative regulator of osteogenesis. Blocks the nuclear translocation of the phosphorylated form (by AKT1) of SRPK2 and antagonizes its stimulatory effect on cyclin D1 expression resulting in blockage of neuronal apoptosis elicited by SRPK2. Negative regulator of signaling cascades that mediate activation of MAP kinases via AKAP13. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17717073, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19592491, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21224381}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative initiation;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Nitration;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation;Vacuole | This gene encodes a protein belonging to the 14-3-3 family of proteins, members of which mediate signal transduction by binding to phosphoserine-containing proteins. This highly conserved protein family is found in both plants and mammals. The encoded protein has been shown to interact with RAF1 and CDC25 phosphatases, suggesting that it may play a role in linking mitogenic signaling and the cell cycle machinery. Two transcript variants, which encode the same protein, have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:7529; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; vacuolar membrane [GO:0005774]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phosphoprotein binding [GO:0051219]; phosphoserine residue binding [GO:0050815]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0004860]; cytoplasmic sequestering of protein [GO:0051220]; negative regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045744]; negative regulation of protein dephosphorylation [GO:0035308]; positive regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0043085]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; protein targeting [GO:0006605]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 11996670_Results show that three 14-3-3 isoforms, beta, gamma and eta, are DAL-1/Protein 4.1B-binding proteins. 12364343_TSC2 associates with 14-3-3 in vivo 12437930_KCNK3 potassium channels are shown to bear two cytoplasmic trafficking motifs: an N-terminal dibasic site that binds beta-COP to hold channels in ER and a C-terminal 'release' site that binds the ubiquitous intracellular regulator 14-3-3beta 12468542_14-3-3 beta interacts with the TSC1-TSC2 complex and negatively regulates the function of the TSC proteins 12482592_14-3-3 binds to the IGF-1 receptor after IGF1R's serine autophosphorylation 12582162_MK2 phosphorylates TSC2, which creates a 14-3-3 binding site and thus regulates the cellular function of the TSC2 tumor suppressor protein 12618428_14-3-3beta is a p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) isoform 1-binding protein that negatively regulates RSK kinase activity 12669242_Immunoexpression of 14-3-3 proteins in glial cytoplasmic inclusions of multiple system atrophy. 14680818_These findings suggest that deregulation of 14-3-3 protein amounts might contribute to the development of tumors in tuberous sclerosis patients. 15022330_HS1 with EPEP insertion polymorphism transmits accelerated signals from B cell receptor and is involved in pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. 15389601_novel binding site on 14-3-3 for integrin beta1 and a functional amphipathic groove, rather than its interaction with integrin beta1, is required for 14-3-3 regulation of cell spreading and migration. 15726117_decreased expression of selected 14-3-3 genes is a common feature of schizophrenia 16166738_Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan S-monooxygenase activation protein, beta polypeptide is decreased during acute lung injury more in mice deficient in metallothionein 1/2 17098443_These data show a novel interaction for 14-3-3 with NFL mRNA, and suggests that 14-3-3 may play a role in regulating NFL mRNA stability. 17229891_14-3-3beta binds DYRK1A 17531190_PBF is a new cellular factor mediating the effects of PI3K/Akt signaling and 14-3-3 on cell growth 17717073_Ror2 induces osteogenic differentiation, at least in part, through a release of the 14-3-3beta-mediated inhibition 18094049_A new regulatory mechanism of myosin light-chain phosphatase via the interaction between 14-3-3 and MYPT1, is reported. 19173300_changes in the expression of five 14-3-3 isoforms (beta, gamma, epsilon, tau, and zeta) during the apoptosis of JURL-MK1 and K562 cells. 19360691_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19558434_14-3-3beta, 14-3-3gamma, 14-3-3epsilon, 14-3-3eta and 14-3-3theta isoforms interact with the GPIb-IX complex in platelets 19821490_Study identified an overrepresentation of focal amplifications of known (FGFR3, CCND1, MYC, MDM2) and novel candidate genes (MYBL2, YWHAB and SDC4) in stage Ta bladder carcinoma. 20070120_Show that viral infection activates 14-3-3 protein mediated signaling pathways in human keratinocytes. 20381070_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the anterior cingulate cortex from patients with schizophrenia 20388496_14-3-3 eta, beta, gamma and sigma isoforms were negatively expressed in meningioma 21147917_protein within PIV5-infected cells is phosphorylated at residue S369, binds the 14-3-3 protein, and is held away from sites of virus budding. 21262972_14-3-3beta interacts with human Dapper1, attenuating the ability of hDpr1 to promote Dishevelled (Dvl) degradation, thus enhancing Wnt signaling 21396404_Studies indicate that Akt phosphorylates acetylated-FoxO and then phosphorylated FoxO interacts with 14-3-3 proteins in the nucleus, which in turn results in cytoplasmic retention of FoxO. 21416292_Data indicate that gene analysis revealed an up-regulation of all four 14-3-3 isoforms beta, eta, gamma, and sigma. 21553213_The expression levels of 14-3-3 protein beta/alpha were higher in urine samples from patients with renal cell carcinoma than in samples from healthy volunteers. 21598387_14-3-3beta protein has the potential to be used as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in gastric cancer. 21708191_Studies indictet that the mammalian FoxO family consists of FoxO1, 3, 4 and 6 and are regulated by by AKT and 14-3-3 proteins. 21935479_Analyses show that high cytoplasmic levels of 14-3-3beta and epsilon independently correlate with poor disease-specific survival in vulvar squamous cell carcinoma cases. 21948273_Modulation of matrix metalloproteinase 1 by 14-3beta/alpha, may be important in the alteration of collagenase production associated with airway remodelling in obstructive lung diseases 21972092_In glioblastoma PTPIP51 expression increases with the grade of malignancy and PTPIP51 interacts in situ with 14-3-3ss and PTP1B. 22125622_Data identified 14-3-3beta as a prognostic biomarker. 22278744_14-3-3beta binding to phosphorylated CFTR augments its biogenesis by reducing retrograde retrieval of CFTR to the endoplasmic reticulum. This mechanism permits cAMP/PKA stimulation to make more CFTR available for anion secretion. 23053962_These results indicate that the six YWHAB polymorphisms are not associated with the genetic susceptibility to sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. 24038028_Using gene reporter assays, we show that promoter variations in 11 intrinsic apoptosis genes, including ADPRT, APAF1, BCL2, BAD, BID, MCL1, BIRC4, BCL2L1, ENDOG, YWHAB, and YWHAQ, influence promoter activity in an allele-specific manner. 24269229_Data identified three classes of 14-3-3 targets that all have two binding sites, but displayed synergistic interaction between converging signalling pathways for different ranges of parameter values. 24555778_Data suggest that serum 14-3-3beta concentrations may constitute a useful marker for blood brain barrier damage severity and follow up in patients with eosinophilic meningitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. 24636949_Crystal structure of Myo1c/14-3-3beta complex, which has been implicated in the exocytosis of glucose transporter 4 storage vesicles during insulin-stimulated glucose uptake. 25228695_miR-152 controls both the expression of 14-3-3beta and HLA-G and exerts a dual role in tumor cells by both altering the immunogenicity and the tumorigenicity 26260846_These findings indicate that 14-3-3beta and gamma are novel PPARgamma2 regulators and are involved in hepatic lipid metabolism. 14-3-3b and gamma can be therapeutic target molecules to treat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. 26730736_Data show that 14-3-3beta protein augmented the expression of matrix metalloproteinasea MMP2 and MMP9 through PI3 kinase/Akt protein/NF-kappaappa B pathway, thereby enhancing the invasiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. 28116547_Our results indicate that 14-3-3beta negatively regulates senescence in glioblastoma cells via the ERK/SKP2/p27 pathway. 29772231_14-3-3 beta and gamma function as positive regulators of GR transactivation and glucocorticoid-mediated hepatic gluconeogenesis. 30224724_14-3-3beta protein activates Pseudomonas exotoxin-S and exotoxin-T ADP-ribosyltransferase domains by chaperoning their hydrophobic surfaces independently of the amphipathic C-terminal segment. 30317584_YWHAB was identified and validated in association with pulmonary arterial hypertension progression, which might serve as a biomarker and/or therapeutic target for pulmonary arterial hypertension. 30617183_findings advance our understanding of how phosphorylation of lipin 1beta phosphatidate phosphatase regulates its interaction with 14-3-3beta protein and intracellular localization and uncover a mechanism by which CKII regulates cellular physiology. 30653408_YWHA/14-3-3 proteins recognize phosphorylated TFEB by a noncanonical mode for controlling TFEB cytoplasmic localization and its activity. 31202814_the interaction of lncRNA RP11-732M18.3 with 14-3-3beta/alpha increases the degradation of the p21 protein. lncRNA RP11-732M18.3 promoted the recruitment of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 E1 to 14-3-3beta/alpha and the binding of 14-3-3beta/alpha with ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 E1 (UBE2E1) promoted the degradation of p21. 31811090_The regulatory protein 14-3-3beta binds to the IQ motifs of myosin-IC independent of phosphorylation. 33588586_Circ SMARCA5 Inhibited Tumor Metastasis by Interacting with SND1 and Downregulating the YWHAB Gene in Cervical Cancer. 34379822_14-3-3beta isoform is specifically acetylated at Lys51 during differentiation to the osteogenic lineage. 34638679_Compensatory Protection of Thioredoxin-Deficient Cells from Etoposide-Induced Cell Death by Selenoprotein W via Interaction with 14-3-3. | ENSMUSG00000018326 | Ywhab | 2914.347979 | 1.0885251 | 0.122374739 | 0.02900666 | 17.79813944519 | 0.0000245623311938834683267225689196067150987801142036914825439453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00029850381298005381272564484618214919464662671089172363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 3073.676297 | 53.285348 | 2837.065478 | 49.258400 | |
| ENSG00000166946 | 23582 | CCNDBP1 | protein_coding | O95273 | FUNCTION: May negatively regulate cell cycle progression. May act at least in part via inhibition of the cyclin-D1/CDK4 complex, thereby preventing phosphorylation of RB1 and blocking E2F-dependent transcription. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10801854}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene was identified by the interaction of its gene product with Grap2, a leukocyte-specific adaptor protein important for immune cell signaling. The protein encoded by this gene was shown to interact with cyclin D. Transfection of this gene in cells was reported to reduce the phosphorylation of Rb gene product by cyclin D-dependent protein kinase, and inhibit E2F1-mediated transcription activity. This protein was also found to interact with helix-loop-helix protein E12 and is thought to be a negative regulator of liver-specific gene expression. Several alternatively spliced variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009]. | hsa:23582; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726] | 16501603_In transgenic mice, GCIP functions as a transcriptional suppressor, regulates cyclin D1 expression, inhibits cell growth and colony formation in human HepG2 cells, suggesting GCIP plays a significant role in tumor initiation and development. 17532760_CT847 interacts with mammalian Grap2 cyclin D-interacting protein 17621266_P0 overexpression may cause tumorigenesis in breast and liver tissues at least in part by inhibiting GCIP-mediated tumor suppression. 18923419_Data suggest that HHM/Maid regulates a subset of TGF-beta target genes including the Olig1-Smad synexpression group. 18983464_decreased expression of GCIP in vivo is present in human breast carcinoma. 19153449_Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of GCIP/HHM transcriptional regulator 20460530_It is proposed for the first time that Rad may promote carcinogenesis at least in part by inhibiting GCIP-mediated tumor suppression. 22453338_The first structure of a free-standing human dominant-negative helix-loop-helix protein (DIP1) was reported. DIP1 adopts a V-shaped conformation, with N-terminal and C-terminal five-helix bundles connected by the HLH region. 24970809_Data indicate that grap2 and cyclin D1 interacting protein (GCIP) and inhibitor of of DNA binding/differentiation 1 (Id1) are inversely expressed in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines and specimens. 26002959_Data suggest MAID/CCNDBP1 inhibits cell migration induced by TGFB1 (transforming growth factor-beta1) but not by BMP4 (bone morphogenetic protein-4); MAID does not alter cell proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, or TGFB3-induced apoptosis. 26107195_GCIP underexpression is associated with Osteosarcoma. 31907980_MEK2 is a critical modulating mechanism to down-regulate GCIP stability and function in cancer cells. 33576455_Grap2 cyclin D interacting protein negatively regulates CREBbinding protein, inhibiting fibroblastlike synoviocyte growth. | ENSMUSG00000023572 | Ccndbp1 | 227.816333 | 1.1719615 | 0.228925220 | 0.12203425 | 3.51504769453 | 0.0608139064936061499166974897434556623920798301696777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.18804663007173544331251946459815371781587600708007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 272.748726 | 24.267161 | 233.767161 | 20.837531 | |
| ENSG00000166949 | 4088 | SMAD3 | protein_coding | P84022 | FUNCTION: Receptor-regulated SMAD (R-SMAD) that is an intracellular signal transducer and transcriptional modulator activated by TGF-beta (transforming growth factor) and activin type 1 receptor kinases. Binds the TRE element in the promoter region of many genes that are regulated by TGF-beta and, on formation of the SMAD3/SMAD4 complex, activates transcription. Also can form a SMAD3/SMAD4/JUN/FOS complex at the AP-1/SMAD site to regulate TGF-beta-mediated transcription. Has an inhibitory effect on wound healing probably by modulating both growth and migration of primary keratinocytes and by altering the TGF-mediated chemotaxis of monocytes. This effect on wound healing appears to be hormone-sensitive. Regulator of chondrogenesis and osteogenesis and inhibits early healing of bone fractures. Positively regulates PDPK1 kinase activity by stimulating its dissociation from the 14-3-3 protein YWHAQ which acts as a negative regulator. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10995748, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15241418, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15588252, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16156666, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16751101, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16862174, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17327236, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19218245, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19289081, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9732876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9892009}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;ADP-ribosylation;Alternative splicing;Aortic aneurysm;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc | The SMAD family of proteins are a group of intracellular signal transducer proteins similar to the gene products of the Drosophila gene 'mothers against decapentaplegic' (Mad) and the C. elegans gene Sma. The SMAD3 protein functions in the transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway, and transmits signals from the cell surface to the nucleus, regulating gene activity and cell proliferation. This protein forms a complex with other SMAD proteins and binds DNA, functioning both as a transcription factor and tumor suppressor. Mutations in this gene are associated with aneurysms-osteoarthritis syndrome and Loeys-Dietz Syndrome 3. [provided by RefSeq, May 2022]. | hsa:4088; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; heteromeric SMAD protein complex [GO:0071144]; nuclear inner membrane [GO:0005637]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; SMAD protein complex [GO:0071141]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; bHLH transcription factor binding [GO:0043425]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000987]; co-SMAD binding [GO:0070410]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; DEAD/H-box RNA helicase binding [GO:0017151]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity [GO:0001217]; I-SMAD binding [GO:0070411]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; nuclear glucocorticoid receptor binding [GO:0035259]; nuclear mineralocorticoid receptor binding [GO:0031962]; nuclear receptor binding [GO:0016922]; phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; promoter-specific chromatin binding [GO:1990841]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; R-SMAD binding [GO:0070412]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sterol response element binding [GO:0032810]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription coactivator binding [GO:0001223]; transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0005160]; ubiquitin binding [GO:0043130]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097296]; activin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0032924]; adrenal gland development [GO:0030325]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell-cell junction organization [GO:0045216]; cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus [GO:0071560]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; developmental growth [GO:0048589]; embryonic cranial skeleton morphogenesis [GO:0048701]; embryonic foregut morphogenesis [GO:0048617]; embryonic pattern specification [GO:0009880]; endoderm development [GO:0007492]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; immune response [GO:0006955]; immune system development [GO:0002520]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; lens fiber cell differentiation [GO:0070306]; liver development [GO:0001889]; mesoderm formation [GO:0001707]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress [GO:1903243]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0051481]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of lung blood pressure [GO:0061767]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; negative regulation of osteoblast proliferation [GO:0033689]; negative regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0042177]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of wound healing [GO:0061045]; nodal signaling pathway [GO:0038092]; osteoblast development [GO:0002076]; paraxial mesoderm morphogenesis [GO:0048340]; pericardium development [GO:0060039]; positive regulation of alkaline phosphatase activity [GO:0010694]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0032332]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of extracellular matrix assembly [GO:1901203]; positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051894]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; positive regulation of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050927]; positive regulation of protein import into nucleus [GO:0042307]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta3 production [GO:0032916]; primary miRNA processing [GO:0031053]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of binding [GO:0051098]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050678]; regulation of immune response [GO:0050776]; regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902893]; regulation of striated muscle tissue development [GO:0016202]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0017015]; regulation of transforming growth factor beta2 production [GO:0032909]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; signal transduction involved in regulation of gene expression [GO:0023019]; SMAD protein complex assembly [GO:0007183]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395]; somitogenesis [GO:0001756]; T cell activation [GO:0042110]; thyroid gland development [GO:0030878]; transdifferentiation [GO:0060290]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; ureteric bud development [GO:0001657]; wound healing [GO:0042060] | 12023901_repression of transactivating activity by association with a novel splice variant of CCAAT-binding factor C subunit 12097320_HTLV-1 tax represses Smad-mediated TGF-beta signaling. 12154125_Smad3 trimerization, induced by phosphorylation, activates the TGF-beta signal by driving Smad3 dissociation from SARA & sets up the negative feedback mechanism by Ski. 12161428_Data suggest that SMAD3 interactions with the positive regulators NKX2.1 and HNF-3 underlie the molecular basis for TGF-beta-induced repression of surfactant protein B gene transcription. 12161532_Smad3 is unlikely to function as a classical tumor suppressor gene in the pathogenesis of sporadic parathyroid or enteropancreatic endocrine tumors. 12191474_Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of Smads 2, 3, and 4 permits sensing of TGF-beta receptor activity. 12202987_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12226080_interactions between AR, Smad3, and Smad4 may result in the differential regulation of the AR transactivation, which further strengthens their roles in the prostate cancer progression 12270924_adenovirally-expressed Smad3 augmented the TGF-beta-elicited induction of MMP-13 expression 12393416_Levels of phosphorylated Smad2/3 are sensors of the interplay between effects of retinoic acid and TGF-beta or vitamin D3 on monocytic and granulocytic differentiation of HL-60 cells. 12393612_HTLV1 Tax inhibits TGF-beta1 signaling by reducing the Smad3 DNA binding activity 12411310_autocrine regulation of TGF-beta2 production in endothelial cell hypoxia may involve cross-talk between Smad3 and hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha signaling pathways 12531695_Phenotypic and functional changes associated with TGF-beta1-induced fibroblast terminal differentiation are differentially regulated by Smad2, Smad3, and Smad4. 12615364_TGF-beta1 inhibited IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha-induced TARC production in HaCaT cells via Smad2/3. Modulation of TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway may be beneficial for treatment of atopic dermatitis. 12618756_In SMAD4-negative cell lines, TGF-beta caused Smad3 to move to the nucleus in a Smad4-independent fashion. Nuclear translocation of Smad3 was not sufficient to activate reporters for TGF-beta-induced transcriptional responses. 12631740_Results suggest that the transcriptional cross talk between the TGFbeta-regulated Smads 3 and 4 and hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 is mediated by specific functional domains in the two types of transcription factors. 12758167_stimulates basal and Tat-mediated transcription of MCP-1 in human astrocytic cells 12759229_Mediation of tumor growth factor beta-1 induced collagen I expression in glomerular mesangial cells. 12760775_Down-regulation of Smad 3 expression by TGF-beta(1) at later stage is involved in negative modulation of TGF-beta(1) signaling. 12815042_SMAD3 has a role in regulating TGF-beta expression along with PIASy 12847691_Protein and mRNA levels of SMAD3, but not of SMAD4 or SMAD7, were variably elevated in scleroderma fibroblasts 12917407_A surface hydrophobic corridor within the MH2 domain of Smad3 is critical for association with CAN/Nup214 and nuclear import; Smad3 and Smad4 have different susceptibility to inhibition of import by cytoplasmic retention factor SARA 12917425_smad3 interacts directly with YB1 during TGFbeta signal inhibition by interferon gamma 12939660_Smad3 gene mutations could be associated with the pathogenesis of human osteoarthritis 14531804_a signal transduction cascade of the TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway, which is activated in the GEC, appears to be involved in the development of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis 14555988_Smad2, Smad3 and Smad4 contribute to the regulation of TGF-beta responses to varying extents, and exhibit distinct roles in different cell types 14630914_SMAD3 and SMAD4 activate gadd45beta through its third intron to facilitate G2 progression following TGFbeta treatment 14633126_TGF-beta and Smad3 mediate beta-hydroxybutyrate(HB)-induced cell cycle-dependent growth inhibition while Smad3 mediates beta-HB-induced collagen production and p21WAF1/p27kip1 protein expression in human proximal tubule (HK-2) cells. 14647420_Smad3 expression may have a critical role in tumor suppression in the early stages of gastric carcinogenesis. 14691252_PIAS3 and Smad3 interact with each other at the endogenous protein level in mammalian cells and also in vitro, and the association occurs through the C-terminal domain of Smad3. 14727154_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15001984_a novel, functional binding element in the proximal region of the TN-C promoter mediating responsiveness to TGF-beta involving Smad3/4, Sp1, Ets1, and CBP/p300 15044214_Analysis of the human SMAD3 promoter demonstrates that isoprenoid regulation of SMAD3 expression is dependent on Sp1/Sp3 activity 15066998_Tuberin (TSC2) interact with smad2/smad3 during TGF-beta1 growth regulation. 15107418_Smad3 has a role in Activin receptor-like kinase-7 induces apoptosis through activation of MAPKs 15150273_menin and TGF-beta/Smad3 negatively regulate the BMP-2/Smad1/5- and Runx2-induced transcriptional activities leading to inhibition of cell differentiation 15166010_The most transcriptionally active splice variants of Smad3 are made in macrophages (but not SMCs) of fibrofatty lesions and are upregulated after cell differentiation from monocytes. Cyclin inhibitors are induced by Smads. Fibrous plaque SMCs make Smad3. 15198928_Gly-BSA increases DNA binding activity of Smad3 and that it stimulates PAI-1 transcription through Smad-binding CAGA sequences in the PAI-1 promoter in human mesangial cells 15240101_Our findings suggest that BAMBI transcription is regulated by TGF-beta signaling through direct binding of SMAD3 and SMAD4 to the BAMBI promoter. 15247277_sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors and the transforming growth factor beta-type I receptor serine/threonine kinase are essential for activation of Smad3 by lysophospholipids 15308665_Smad2/3 is activated in undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells and required for the expression of genes controlling Nodal signaling 15334054_HCV viral proteins interact with the TGF-beta signaling mediator Smad3 and differentially impair TGF-beta/Smad3-mediated transactivation and growth inhibition. 15494412_TGF-beta-stimulation of transcription of PAI-1 is inhibited by VEGF, and TGF-beta phosphorylation of Smad2/3, an obligatory step of intracellular TGF-beta signaling, is suppressed by VEGF 15520018_p38 MAP kinase and Rho/ROCK pathways together with Smad2 and Smad3 are necessary for TGF-beta-mediated growth inhibition 15623506_Smad3 induces chondrogenesis through the activation of SOX9 via CREB-binding protein/p300 recruitment 15629128_Transforming growth factor-beta1 stimulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production by fibroblasts is regulated by Smad3 but not by Smad2 signaling 15665291_c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase tended to induce the phosphorylation of Smad2/3L in human colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence. 15735739_TGFbeta1/Smad3 suppresses BRCA1-dependent DNA repair in response to a DNA damaging agent 15799969_TGF-beta signaling suppresses nuclear export of Smad4 by chromosome region maintenance 1 and targets Smad4 into the nucleus; mutations in Smad4 that affect its interaction with Smad2 or Smad3 impair nuclear accumulation of Smad4 in response to TGF-beta 15845540_TGF-beta/Smad3 signaling is required for hypoxia-mediated inhibition of adipocyte differentiation in marrow stromal cells 15881652_Tsc-22 binds to and modulate the transcriptional activity of Smad3 and Smad4 15907489_lysine residues of Smad3 MH2 domain play important roles in the transcriptional regulation of TGF-beta signals through TbetaR-I 15917296_interleukin-1beta and its downstream mediator mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 inhibit SMAD3-mediated TGFbeta target gene activation 16187293_TGF-beta1 and bleomycin intracellular signaling through autocrine regulation of Smad 3 binding to the proximal promoter of the Smad 7 gene 16223572_deletion constructs of the promoter and mutational deletion of specific transcription factor binding sites indicated that Smad3/4 and AP-1 binding sites mediated the TGF-beta1 response on LTBP-3 16253118_Distinct roles for Smad2 and Smad3 in TGFbeta1-induced CTGF expression and markers of EMT in human PTECs are reported. 16403803_TGF-beta1 acts on adjacent stromal cells to turn on Smad3 signalling that could lead to stromal decidualization. 16413503_These observations, together with the finding that CILP protein binds and inhibits TGF-beta1, suggest that CILP and TGF-beta1 may form a functional feedback loop that controls chondrocyte metabolism. 16449645_A short peptide representing the minimal interaction domain in Smad3 effectively competes with Smad3 association to exportin 4 and blocks nuclear export of Smad3 in vivo. 16528675_summary of the recent understanding of Smad3 phosphoisoform-mediated signaling, particularly 'cross-talk' between Smad3 and JNK pathways that cooperatively promote oncogenic activities in colorectal carcinogenesis [review] 16543220_role in nuclear translocation of beta-catenin 16556868_Activation of Smad3 but not Smad2 is a key mechanism by which Angioteinsin ii mediates artriosclerosis. 16754688_One mechanism for positive regulation of TLR2 induction involves functional cooperation between the TGF-betaR-Smad3/4 pathway and NF-kappaB pathway. Another involves (MKP-1)-dependent inhibition of p38 MAPK, a known negative regulator for TLR2 induction 16785237_TGFbeta suppresses TERT by Smad3 interactions with c-Myc and the hTERT gene 16828225_a novel mutation was found to result in the inhibition of translocation of Smad3 protein to the nucleus and a reduction in the activity of Smad3 during TGF-beta-induced transcriptional activation 16849317_These results suggest that RACK1 modulates transcription of alpha2(I) collagen by TGF-beta1 through interference with Smad3 binding to the gene promoter. 16886151_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16924420_These results suggest that p38 affects the phosphorylation of Smad2 and Smad3 differentially during TGF-beta signaling in human dental pulp cells and ERK1/2 might be involved in the process. 17035229_identified the small C-terminal domain phosphatase 1 (SCP1) as a specific phosphatase for Smad2/3 dephosphorylation in the linker and N terminus 17053951_mRNA expressed in human granulosa-luteal cells at oocyte retrieval. 17074765_SHP is a novel co-regulator of Smad3 that regulates TGF-beta signaling 17142261_Leptin and TGF-beta1 synergistically augmented activation of signalling components of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), STAT3 and Smad but did not modulate the expression of LEPR-B. 17197157_These data lead to the conclusion that MEK1 is an important regulator of SMAD3 expression. 17230494_Smad3 appears to be important in colonic inflammation. 17264880_These results suggest that TGFbeta Smad3-dependent signalling is perturbed in Barrett's carcinogenesis, resulting in failure of growth-arrest. 17279001_Neurofibrillary tangles sequester pSmad3, preventing its translocation into the nucleus and the induction of gene transcription. Interference with the Smad signaling may adversely affect survival of tangle-bearing neurons in AD. 17471513_The TGFB/SMAD3 signaling pathway is involved in butyrate-mediated vitamin D receptor expression. 17476473_examined the possible deterioration in the pathway in human squamous cancer cell lines, focusing on intracellular localization of S100C/A11 and its functional partners Smad3 and Smad4- 17591695_Results show that Arkadia specifically activates transcription via Smad3/Smad4 binding sites by inducing degradation of the transcriptional repressor SnoN. 17591701_Results define Erbin as a novel negative modulator of Smad2/Smad3 functions and expand the physiological role of Erbin to the regulation of TGFbeta signaling. 17623674_Inhibition of beta-catenin resulted in increased TGF-beta1-dependent Smad3 phosphorylation and restoration of TGF-beta1 anti-proliferative effects. 17638910_transforming growth factor-beta has a role in Smad3-dependent activation of Gli2 and Gli1 expression 17653079_findings suggest that CEA (CEACAM5) and CEACAM6 are major target genes for Smad3-mediated TGF-beta signaling. 17657819_ALK5-dependent Smad3 signaling is the responsible pathway inducing CTGF expression. 17786540_SMAD3 dependent inactivation of CYP17 promoter activity and repression of SF-1 expression. 17875924_Mutant p53 attenuates TGF-beta1 signaling. This was exhibited by a reduction in SMAD2/3 phosphorylation and an inhibition of both the formation of SMAD2/SMAD4 complexes and the translocation of SMAD4 to the cell nucleus. 17908958_Smad3, through regulating angiogenic molecule expression in tumor cells, is critical for progression of prostate cancer 17920062_TGFbeta1 represses CYP7A1 gene transcription in human hepatocytes by a mechanism involving Smad3-dependent inhibition of HNF4alpha and histone deacetylase remodeling of CYP7A1 chromatin. 17927854_The expression of Smad2/3 in cervical cancer had no correlation to clinical stage, pathologic classification, histological grade, and lymph node involvement, but was positively correlated to HPV16 E7 infection. 17934056_Recent studies highlighted in this review suggest that TGF-beta suppresses neoplastic cell development by employing Smad3 protein to repress the human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene. 17994767_functional characterization of a tumorigenic mutation in Smad4(E330A); findings show this mutant & a Smad3 mutant (Smad3 E239A) failed to activate transcription in response to TGFbeta stimulation because of defects in oligomerization 18055455_SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein interacts with Smad3 and modulates transforming growth factor-beta signaling 18078810_Thus, SMCX is a novel Smad3 corepressor that may antagonize the tumor suppressing activity of the TGF-beta/Smad3 signaling pathway and thereby contribute to tumorigenesis. 18082619_These findings suggest that CLU regulates TGF-beta signaling pathway by modulating the stability of Smad2/3 proteins. 18095113_sequencing of exon 2 of the Smad3 gene disclosed single nucleotide polymorphism 18095154_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18166170_Activin A increased and follistatin decreased phosphorylation of SMAD2/3 in vitro, and activin increased SMAD2 and decreased KITLG mRNA expression. 18174158_TGF-beta(1) regulates proliferation through Smad3 signaling in both fibroblast populations; however, it is the levels of HA generated by the cells that influence the outcome of this response. 18174246_TGF-beta-mediated activation of the ALK5-Smad 3 pathway plays a role in SHH promoted motility and invasiveness of gastric cancer cells 18203713_myostatin enhanced nuclear translocation of beta-catenin and formation of the Smad3-beta-catenin-TCF4 complex, together with the altered expression of a number of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway genes in hMSCs 18210139_increased TGF-beta-Smad signaling in sporadic and familial ALS and impaired TGF-beta signal transduction in neurons of sporadic ALS patients, presumably at the step of pSmad2/3 translocation into the nucleus 18223258_TGF-beta mediates its effects on proteoglycan synthesis in VSMCs via the ALK5/Smad2/3 phosphorylation pathway as well as via the p38 MAP kinase signaling cascade. 18245174_tagln is a novel target of TGF-beta/Smad3-dependent gene expression in alveolar epithelial type II cells 18250161_AMPK inhibits TGFbeta-induced transcription downstream of Smad3 COOH-terminal phosphorylation and nuclear translocation 18263591_interaction between RAP250, Smad2, and Smad3 constitutes an important bridging mechanism linking LXR and TGF-beta signaling pathways. 18333754_both ALK1 and ALK5 are needed for TGF-beta-induced phosphorylation of intracellular mediators Smad1/5, whereas only ALK5 is essential for TGF-beta1-induced phosphorylation of Smad3 18384750_Coexpression of Smad3 with PIASy and SUMO1 stimulated the nuclear export of Smad3. 18393632_SMAD 2/3 signaling directly supports NANOG expression, while SMAD 1/5/8 activation moderately represses SOX2. 18445023_A case-control study in Afro-Caribbeans found SMAD3 SNPs were not strongly associated with increased risk of developing keloids. 18445023_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18482992_PTEN abrogates TGF-beta-induced Smad2/3 phosphorylation. This study establishes a novel role for nuclear PTEN in the stabilization of PPM1A. 18505915_the TGF-beta1-2-3/Smad3 pathway has a role in mediating ovarian oncogenesis by enhancing metastatic potential 18568018_Data demonstrate that in response to TGFbeta stimulation the transcriptional regulator TAZ binds heteromeric Smad2/3-4 complexes and is recruited to TGFbeta response elements. 18729074_a number of putative novel Smad2 and Smad3 associated proteins in TGF-beta1 signaling were identified that have functions in cell proliferation, apoptosis, actin cytoskeleton regulation, cell motility, transcription, and Ras or insulin signaling 18768831_SMAD3 is one important transcription factor mediating transforming growth factor beta's- inhibitory effects on IFN-gamma production and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity following CD16 activation of natural killer cells. 18776948_TGF-beta1 and SMAD3 may be involved in the pathology of corneal diseases associated with herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. 18791848_Galectin-1 decreases Smad3-complex from binding to the SBE, down-regulating transcription of COL1A2 in TGF-beta1-stimulated renal epithelial cells. 18794808_Ligand-dependent ubiquitination of Smad3 is regulated by CK1g2, an inhibitor of TGF-beta signaling. 18826955_Activin stimulates endogenous inhibin alpha- and betaB-subunit mRNA, protein, and proteolytic processing. Simultaneously, activin stimulated the proconvertase furin through a Smad2/3-dependent process. 18955504_Binding elements for ETS and transcription factor AP-2 (TFAP2) were significantly enriched in Smad2/3 binding sites, and knockdown of either ETS1 or TFAP2A resulted in overall alteration of TGF-beta-induced transcription. 19013433_Arginine 279, glutamic acid 246 in Smad3 and glutamic acid 1321 in Erbin are important for these proteins binding. 19041414_Smad3 stimulated the Sox9-mediated transcription in a TGF-beta-dependent manner. 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19066393_Single nucleotide polymorphism in SMAD3 gene is associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 19101551_These data indicate that the intracellular glutathione redox status regulates TGF-beta-induced fibrogenic effects through Smad3 activation. 19106105_FoxL2 and Smad3 coordinately regulate follistatin gene transcription.( 19122240_Pin1 negatively regulates TGF-beta signaling by down-regulating Smad2/3 protein levels via induction of Smurf2-mediated ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation. 19129849_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19129849_part of the variance in SMAD3 expression was gender related as women expressed lower levels of SMAD3 transcripts than men. 19211612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19218245_TGF-beta-induced phosphorylation of Smad3 linker sites inhibits its antiproliferative activity 19247629_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19252133_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19255064_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19263472_Hepatitis B virus X protein shifts hepatocytic TGF-beta signaling from the tumor-suppressive pSmad3C pathway to the oncogenic pSmad3L pathway in early carcinogenic process. 19265200_TGF-beta/Smad3 signaling as an important regulator of insulin gene transcription and beta-cell function and suggest that components of the TGF-beta signaling pathway may be dysregulated in diabetes. 19289081_RanBP3 directly recognizes dephosphorylated Smad2/3, which results from the activity of nuclear Smad phosphatases, and mediates nuclear export of Smad2/3 in a Ran-dependent manner. 19336575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19351817_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19375841_Sustained co-cultivation with human placenta-derived MSCs enhances SMAD3 signaling in human breast epithelial cells, leading to EMT and differentiation. 19394554_Characterization of primary and restenotic atherosclerotic plaque from the superficial femoral artery: Potential role of Smad3 in regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation. 19421146_Results show that targeted disruption of the cell surface Cripto/GRP78 complex precludes Cripto activation of MAPK/PI3K and Smad2/3 pathways. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19458083_Transforming growth factor-beta induces phosphorylation at three sites in the Smad3 linker region in addition to the two C-terminal residues, and glycogen synthase kinase 3 is responsible for phosphorylation at one of these sites, namely Ser-204. 19461048_(PPAR)delta regulates extracellular matrix synthesis and degradation through transforming growth factor-beta1 and its effector, Smad3 19468687_Data suggest that Smad3 can regulate acetylcholinesterase transcriptional activation following calcium-induced nuclear accumulation. 19589780_Akt, activated downstream from ERK 1/2, was required for TGF-beta1-induced ZEBRA expression and enabled Smad3, a mediator of TGF-beta1 signaling, to be acetylated by direct interaction with the co-activator CREB-binding protein 19595713_Data show that inhibition of TACE activity or expression enhanced the cell surface TbetaRI levels and TGF-beta-induced Smad3 and Akt activation. 19616922_genetic variation in SMAD3 alters the susceptibility of an individual to atopic dermatitis. 19620243_SARA has a role in regulating cell phenotype and its effects are mediated through modification of the balance between Smad2 and Smad3 signaling 19693466_Smad signaling pathway plays in important role in the progress of glomerular sclerosis, renal tubular injury and interstitial fibrosis in children with IGA nephropathy. 19751112_Myostatin or 20 ng/mL BMP-11 maintain the colony and cellular morphology of undifferentiated hESC, maintain POU5f1, NANOG, TRA-1-60, and SSEA4 expression, and display increased SMAD2/3 phosphorylation 19768112_loss or reduction of BRCA1 alters TGF-beta growth inhibiting activity via Smad3 during oxidative stress responses 19819941_Data suggest that the SMAD family, possibly through disruption of SMAD1/5 or activation of SMAD2/3 may contribute to the pathogenesis of JGCT in humans. 19822523_p130Cas is required for mammary tumor growth and transforming growth factor-beta-mediated metastasis through regulation of Smad2/3 activity 19917253_Results identify Nedd4L as the ubiquitin ligase in TGF-beta induced phosphorylation of the transcription factors Smad2 and Smad3. 19951945_Data show that upon hypoxia, the TGF-beta-induced phosphorylation of Smad3 was inhibited, although Smad2 remained phosphorylated, and Smad3 was dephosphorylated by PP2A. 19959123_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20010874_TGF-beta induction of key target genes involved in bone metastasis, were found to be dependent on Smad3 but not Smad2. 20037158_High levels of Smad3 are required for the tumor suppressor activities of TGF-beta, whereas lower levels are sufficient for the tumor promoting functions. 20070253_Data show that S100A4 binds to Smad3 in a Ca2+-dependent manner, potentiates transcriptional activity of Smad3 and the related Smad2, and increases TGF-beta-induced MMP-9 expression. 20093492_BMP-7 prevents TGF-beta-mediated loss of the transcriptional repressor SnoN and hence specifically limits Smad3 DNA binding. 20097766_Smad3 prevents beta-catenin degradation and facilitates beta-catenin nuclear translocation in chondrocytes 20102559_Smad3 is involved in fibrogenic TGF-ss signaling; its expression is reduced in monocytes, programmable cells of monocytic origin, and neohepatocytes from alcoholic liver disease patients and controls. 20142324_JNK/Smad3 pathway plays a critical role in TGF-beta1-induced FXII expression in human lung fibroblasts 20222112_This study is the first to show that TGF-beta induces CTGF expression through activation of Smad3 and activator protein 1 (AP-1) signaling pathways in nucleus pulposus cells. 20346360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20463300_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20463300_These data show that the rs28683050 polymorphism of the Smad3 gene may be associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 20506137_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20506137_genetic variation in the SMAD3 gene is involved in the risk of both hip and knee osteoarthritis in European populations 20547485_Smad3 regulates RhoA activation and cytoskeletal reorganization by controlling NET1 in TGF-beta1-induced ARPE-19 cells. 20599907_These results uncovered a novel mechanism for the GSK3beta negative regulation of TGF-beta1/Smad3 and Angiotensin II/ Smad3-mediated transcription and apoptosis by the identification of a crosstalk between GSK3beta and Smad3 signal pathway. 20602465_Oncogenic Smad3 signaling induced by chronic inflammation is an early event in ulcerative colitis-associated carcinogenesis. 20607798_The Smad2/3 pathway is the predominant TGFbeta1 signaling pathway inducing Il6 and inhibiting Il8 release in bronchial epithelial cells. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20694560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20736297_Smad3 phosphorylation releases cyclin D1-regulated blockade of Smad3 transcriptional activity and recovered cell cycle arrest in breast cancer cells. 20738937_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20739403_Data suggest that deregulated/enhanced expression and activation of AR in prostate carcinomas may intercept the tumor suppressor function of TGF-beta through transcriptional suppression of Smad3. 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20860503_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20945383_Smad2/3 and p38 MAPK differentially regulate TGFB1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary epithelial cells. 21042764_GDF-9 can promote the motile and adhesive capacity of PC-3 prostate cancer cells by up-regulating expression of FAK and paxillin in a Smad dependent manner, suggesting a pro-tumourigenic role for GDF-9 in prostate cancer. 21068203_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21081648_These findings indicate that IKKalpha contributes to the tumor-promoting function of the TGFbeta-SMAD signaling pathway in particular cancers. 21095583_PARP-1 dissociates Smad complexes from DNA by ADP-ribosylating Smad3 and Smad4, which attenuates Smad-specific gene responses and TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 21114847_study provides evidence SMAD3 gene, which encodes a key regulatory protein in transforming growth factor beta signalling pathway and is known to interact directly with BRCA2, may contribute to increased risk of breast cancer in BRCA2 mutation carriers 21150326_Data show that cyclin E-mediated inhibition of Smad3 is regulated by CDK2 phosphorylation of the Smad3 protein in MCF7 cells. 21159608_Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-gamma) inhibits transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta)-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells and prevents metastasis by antagonizing Smad3 function. 21217753_SMAD3 mutations in the TGF-beta pathway cause a syndromic form of aortic aneurysms and dissections with early-onset osteoarthritis 21258410_Data show that the WWP2-N isoform interacts with Smad2 and Smad3, whereas WWP2-C interacts only with Smad7. 21307346_Data demonstrate that RGC-32 interacts with Smad3 to mediate the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human renal proximal tubular cells. 21345218_TGFbeta1 induced MAD1 expression by recruitment C/EBPalpha/beta heterodimers, SP1, and SMAD3 binding to promoter of the MAD1. 21377836_Activin A-ACVRIB/ALK4-Smad-dependent collagen production was augmented in SSc fibroblasts, suggesting the involvement of this signaling mechanism in systemic sclerosis. 21624123_In malignant cells with a functional TGF-beta signalling pathway Rac1 antagonizes the TGF-beta1 growth inhibitory response and enhances cell migration by antagonistically regulating Smad2 and Smad3 activation 21625455_Identification of global targets and molecular pathways and networks associated with TGFbeta1/SMAD3 signaling allow for a better understanding of the mechanisms that determine epithelial cell phenotypes in fibrogenesis and carcinogenesis 21646355_l type-specific target selection by combinatorial binding of Smad2/3 proteins and hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha in HepG2 cells. 21749466_In middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced activation of Smad-binding elements (SBEs), a downstream target of Smad 2/3 transcription factors regulates expression of the luciferase reporter. 21778426_The causative mutation in a large family with autosomal dominant inheritance of thoracic aortic aneurysms leading to acute aortic dissections with intracranial and abdominal aortic aneurysms is identified by exome sequencing. 21798735_TGF-beta1-induced activation of Smad3 is the critical step for the uPA upregulation and E-cadherin downregulation 21828274_HEB and E2A-bind the SCA motif at regions overlapping SMAD2/3 and FOXH1 21835029_in breast cancer cases SMAD3 was significantly over-expressed 21883378_we describe TGF-beta signalling through Smad2/3 and the importance of the linker region in the regulation and expression of genes induced by TGF-beta--{REVIEW} 21896644_the TRB3-SMAD3 interaction promoted the nuclear localization of SMAD3 because of the interaction of TRB3 with the MH2 domain of SMAD3 21924870_Androgen receptor transactivity is potentiated by TGF-beta1 through Smad3 but checked by its coactivator Hic-5/ARA55 in balding dermal papilla cells. 21947082_USP15 is a deubiquitylating enzyme for receptor-activated SMAD3. 21960005_Protein phosphatase PPM1A regulates the nuclear export of Smad2/3 through targeting nuclear exporter RanBP3. 22020340_Study concludes that Smad3 regulates, at the transcriptional level, miR-200 family members, which themselves regulate ZEB1 and ZEB2, known transcriptional repressors of E-cadherin, at the posttranscriptional level in a TGF-beta-independent manner. 22034170_we provide evidences that induction of TGF-beta1 production and Smad3 phosphorylation by Ox-LDL is mediated by Ras/ERK/PLTP pathway in human alveolar epithelial cells. 22110135_Functional blockade of the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 mediates reversion of T effector to central memory lymphocytes through SMAD3/p21cip1 signaling. 22161558_human umbilical cord blood-derived stromal cells which secrete a high level of TGF-beta1, modulate the Foxp3 expression of Treg cells through the TGF-beta1/Smad3 pathway to regulate graft-versus-host disease 22167769_Five novel SMAD3 mutations (one nonsense, two missense and two frame-shift mutations) were identified in five new aneurysms-osteoarthritis syndrome families 22228025_Enhanced TGF-beta1-induced Smad2 and -3 signaling in prostate cancer cells may correlate with tumor suppressive activity. 22232600_Low Smad3 is associated with lung cancer. 22251470_Smad3 and its phosphoisoforms are prognostic predictors of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative hepatectomy. 22278155_Data suggest that TGF-beta, TGF-betaR1, TGF-betaR2, Smad4, pSmad2/3, and E-cadherin are closely related to tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage of colorectal cancer (CRC). 22382019_These findings suggest that Smad3 and Snail have circadian rhythm in vitro and vivo, | ENSMUSG00000032402 | Smad3 | 308.323026 | 0.9649745 | -0.051437241 | 0.25361030 | 0.04102751764 | 0.8394848151980270900551772683684248477220535278320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.92783767343473477762216816699947230517864227294921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 314.475107 | 50.128365 | 327.292303 | 52.100261 | |
| ENSG00000167302 | 146705 | TEPSIN | protein_coding | Q96N21 | FUNCTION: Associates with the adapter-like complex 4 (AP-4) and may therefore play a role in vesicular trafficking of proteins at the trans-Golgi network. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:22472443, ECO:0000305|PubMed:26542808}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | Located in coated vesicle membrane; nucleus; and trans-Golgi network membrane. Is extrinsic component of organelle membrane. Colocalizes with AP-4 adaptor complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:146705; | coated vesicle membrane [GO:0030662]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extrinsic component of organelle membrane [GO:0031312]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588] | 26542808_The bivalency of the interactions contributes to a higher avidity of tepsin for AP-4. | ENSMUSG00000025377 | Tepsin | 159.383480 | 0.9047270 | -0.144445560 | 0.18128335 | 0.63291386608 | 0.4262884989205938390810501914529595524072647094726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.65197064540796700882197001192253082990646362304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 149.757337 | 16.271222 | 166.453149 | 17.626872 | |
| ENSG00000167397 | 79001 | VKORC1 | protein_coding | Q9BQB6 | FUNCTION: Involved in vitamin K metabolism. Catalytic subunit of the vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR) complex which reduces inactive vitamin K 2,3-epoxide to active vitamin K. Vitamin K is required for the gamma-carboxylation of various proteins, including clotting factors, and is required for normal blood coagulation, but also for normal bone development. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14765194, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14765195, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15879509, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16270630, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20978134, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22923610, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33154105}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Oxidoreductase;Quinone;Redox-active center;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes the catalytic subunit of the vitamin K epoxide reductase complex, which is responsible for the reduction of inactive vitamin K 2,3-epoxide to active vitamin K in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Vitamin K is a required co-factor for carboxylation of glutamic acid residues by vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase in blood-clotting enzymes. Allelic variation in this gene is associated with vitamin k-dependent clotting factors combined deficiency of 2, and increased resistance or sensitivity to warfarin, an inhibitor of vitamin K epoxide reductase. Pseudogenes of this gene are located on chromosomes 1 and X. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015]. | hsa:79001; | endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; quinone binding [GO:0048038]; vitamin-K-epoxide reductase (warfarin-insensitive) activity [GO:0047058]; vitamin-K-epoxide reductase (warfarin-sensitive) activity [GO:0047057]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; bone development [GO:0060348]; peptidyl-glutamic acid carboxylation [GO:0017187]; positive regulation of coagulation [GO:0050820]; regulation of blood coagulation [GO:0030193]; response to antibiotic [GO:0046677]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; response to organonitrogen compound [GO:0010243]; vitamin K metabolic process [GO:0042373]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805] | 14765194_using a positional cloning approach that integrated mapping information from three species, the gene VKORC1 that is mutated in combined deficiency of vitamin-K-dependent clotting factors type 2 and warfarin resistance was identified 14765195_identification of the gene for VKOR based on specific inhibition of VKOR activity by a single siRNA pool 15358623_Genetic variants of the VKORC1 gene locus modulate the mean daily dose of drug prescribed to acquire the target anticoagulation intensity. 15358623_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15630486_association between a nucleotide transition in VKORC1 and pharmacodynamic warfarin resistance supports the hypothesis that VKORC1 is the site of action of warfarin and indicates thatVKORC1 sequence is an important determinant of the warfarin dose response 15790782_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15790782_The simple genotyping of 2 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), VKORC1 -1639G>A or 1173C>T and the CYP2C9*3 polymorphisms, could thus predict a high risk of overdose before initiation of anticoagulation with acenocoumarol 15883587_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15883587_VKORC1 single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated significantly with warfarin dose, and explain 29-30% of variance in dose. 15888487_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15930419_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15930419_VKORC1 haplotypes can be used to stratify patients into low-, intermediate-, and high-dose warfarin groups and may explain differences in dose requirements among patients of different ancestries. 15947090_CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotype have roles in determining response to warfarin therapy and therefore in blood coagulation 15947090_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15972850_VKOR is involved in angiogenesis. 15978113_a VKORC1 mutation is described in a patient with vitamin K antagonist resistance [case report] 16030016_Overexpression of VKORC1 can be utilized for increased cellular production of recombinant vitamin K-dependent proteins. 16141794_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16201835_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16270629_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16270630_the C132-X-X-C135 motif in VKORC1 comprises part of the redox active site that catalyzes VKO reduction and also suggest a crucial role for the hydrophobic Thr-Tyr-Ala motif in coumarin binding 16420583_Population variation in VKORC1 haplotype structure. 16424822_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16424822_VKORC1 and CYP2C9 polymorphisms contribute to inter-population difference in warfarin doses among Japanese, Caucasians and African-Americans 16432637_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16513444_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16549638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16549638_subjects with the CC and CT genotypes had lower levels of undercarboxylated osteocalcin, and lower levels of protein induced in vitamin K absence or antagonism than those with TT genotypes 16580898_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16611310_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16611750_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16611750_The association between single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in VKORC1 and CYP2C9 and average weekly warfarin dose was tested. 16634640_These data indicate that the effect of VKOR overexpression is limited in vivo, possibly because a carboxylation component like the redox protein becomes saturated or because another step is now rate-limiting. 16676068_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16677080_VKORC1 is the key protein of the vitamin K cycle [review] 16700826_VKORC1 1173C>T could be responsible, atleast in part, for the higher sensitivity of Asian people to oral anticoagulants. 16815313_Observational study of gene-gene interaction and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16847429_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16879214_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16879214_VKORC1*2 is the most important haplotype for warfarin dosage in the Swedish population 16890578_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17015052_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17031720_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17048007_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17049586_In addition to polymorphisms in VKORC1 and CYP2C9, we identified GGCX 8016G>A, resulting in the missense mutation R325Q, as a genetic determinant of warfarin maintenance dose in Japanese patients. 17049586_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17110455_Asp36Tyr is a new marker of the high end of the warfarin dosing range 17110455_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17111199_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17164330_Purified vitamin K epoxide reductase alone is sufficient for conversion of vitamin K epoxide to vitamin K and vitamin K to vitamin KH2. 17189218_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17192772_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17192772_Results suggest that knowledge of both VKORC1 and CYP2C9 genotypes could contribute to a safer treatment with along acting anticoagulant phenprocoumom. 17301738_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17325732_Observational study of gene-gene interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17329985_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17391071_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17413769_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17413769_VKORC1 haplotypes possibly are linked to some unidentified factors involved in the metabolic clearance of warfarin enantiomers 17510308_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17549303_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17549303_study examined the potential association between the functional SNP rs9923231 & early-onset coronary heart disease (CHD)in Northern Germans; no evidence for a significant association was detected between VKORC1 genotype & CHD phenotype 17596133_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17653141_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17653141_VKORC1 genotype did not confer a significant increase in risk for hemorrhage in patients on warfarin. 17666014_VKORC1 gene variation may not have a role in venous thrombosis [commentary] 17721328_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17721328_VKORC1 (-1639) G/A genotyping might be necessary for patients with Factor V Leiden and/or prothrombin G2021A mutation before warfarin anticoagulant therapy. 17764537_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17849045_Mutations and single nucleotide polymorphisms within the translated and non-translated regions of the VKORC1 gene have been shown to cause coumarin resistance and sensitivity, respectively. 17883698_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17883698_the VKORCI polymorphism may have a role in the pathogenesis of venous thromboembolism 17883699_VKORC1 variants are not associated with arterial or venous thrombosis 17899045_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17961434_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17989110_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17995970_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17995970_Warfarin dose requirements in Asian patients homozygous for VKORC1 H1 haplotype are significantly lower compared with patients homozygous for the H7 haplotype. 18030307_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18034618_VKORC1 protein genotype was not associated with warfarin dose requirements in the African-Americans population. 18034619_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18034619_T allele of VKORC1 1173C>T SNP (tag-SNP of H1-H2 haplotypes) is highly associated with low mean weekly warfarin dose. 18183038_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18218987_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18218987_Persons with at least one 1173C>T-allele had a statistically significant 19% (95% CI 2 to 40%) risk increase of calcification of the aortic far wall compared to CC homozygous persons, adjusted for age and gender. 18240904_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18240904_Single nucleotide polymorphisms show significant differences between ethnic groups and are associated with warfarin dose requirements for achieving a recommended International Normalized Ratio range in Japanese cardiovascular surgery patients. 18252229_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18281915_Observational study of pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18305455_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18322281_Initial variability in the INR response to warfarin was more strongly associated with genetic variability in the pharmacologic target of warfarin, VKORC1, than with CYP2C9. 18322281_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18370846_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18449434_No clear link waqs found between VKORC1 genetic polymorphism and the risk of venous thrombosis or peripheral arterial disease. 18466099_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18466315_Observational study and clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18466315_effect of VKORC1 genotype on vitamin K-induced alterations in the anticoagulation response 18480003_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18516070_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18523153_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18523153_SNPs to -1639G>A and 1173CA, and the tightly linked intron1 SNP 1173C>T, predict warfarin dose more accurately than intron 2 SNP 1542G>C in blacks.Increased warfarin dose requirement in blacks was accounted for by lower frequency of the -1639 A allele 18532998_Multiple genetic alterations in vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 gene (VKORC1) can explain the high dose requirement during oral anticoagulation. 18535201_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18535201_Warfarin dosing is correlated with polymorphisms in VKORC1 and the CYP2C9 genes 18542936_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18542936_VKORC1 polymorphisms are associated with warfarin dose requirements in Turkish patients. 18559094_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18574025_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18629445_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18680536_Mutations associated with warfarin resistance do not cause a discernible defect in VKORC1 reductase function 18680536_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18680736_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18690342_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18690342_genetic variation in VKORC1 appears to have a different influence than CYP2C9 on anticoagulation-related outcomes such as bleeding events and time in therapeutic range of warfarin 18698879_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18754001_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18781852_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18805772_Mutations in the VKORC1 gene affect the sensitivity of the epoxy reductase enzyme for warfarin. The three main haplotypes of VKORC1 gene, *2, *3, *4, explain most of the genetic variability in warfarin dose among Caucasians. 18805772_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18813101_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18813101_VKORC1 haplotypes may play a role in the long-term renal allograft function but these findings need to be replicated in prospective clinical studies. 18826394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18826394_study in European patients with CHD and CVD did not show any association between SNP +2255 in VKORC1 and cardiovascular disease, as opposed to findings in a Chinese population and a French study in patients with venous thromboembolism 18841283_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18841283_Our data do not confirm the association between polymorphism in the VKORC1 gene and stroke in the German population 18848323_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18855533_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18855533_VKORC1 polymorphisms, haplotypes and haplotype groups on warfarin dose among African Americans and European Americans are reported. 18950464_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18950464_The risk of gastrointestinal bleeding during acenocoumarol therapy in carriers of any of the studied polymorphisms is severely increased with exposure to weekly doses of acenocoumarol higher than 15 mg or the use of amiodarone or aspirin. 19018718_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19018719_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19025725_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19025725_results show that the inverse association between dietary vitamin K intake and serum ucOC depends on a functionally relevant allelic variant of the VKORC1 gene. 19034590_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19034590_Preoperative screening for the VKORC-1 genotype could identify joint replacement arthroplasty patients with a greater potential for being a hyperresponder or hyporesponder to warfarin 19056482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19074728_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19074728_much of the information provided by CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotypes during warfarin initiation is captured by the early international normalized ratio response 19077919_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19099951_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19117406_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19124480_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19124480_VKORC1 +2255 genotype revealed stronger inverse associations between dietary intake of methaquinones and risk of prostate cancer in homo- and heterozygous carriers of the A allele compared with GG carriers. 19135231_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19135231_The VKORC1 polymorphism, body weight, age, and serum albumin were found to affect the inter-individual variability. The dosing algorithm of warfarin maintenance dose was investigated by multivariate linear regression. 19139476_VKORC1 single nucleotide polymorphism(SNP)s have been identified that influence warfarin metabolism and sensitivity, including SNP variants in VKORC1 which influence individual sensitivity to a given dose of warfarin. 19172700_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19177029_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19181737_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19207028_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19225451_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19225451_The risk of severe overanticoagulation is increased in individuals with a genetic variation of VKORC1 that contain additional T-alleles. 19233910_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19297219_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19300499_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19300499_warfarin dose variance is explained by single nucleotide polymorphisms in VKORC1, CYP2C9, and CYP4F2 19319511_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19319511_The data suggest a fundamental role of VKORC1 haplotypes in the anticoagulation property of phenprocoumon. 19320825_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19324988_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19376320_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19376320_VKORC1 genotype is associated with cardiovascular events in patients with DES implantation, suggesting the role of coagulation system. 19387626_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19436136_VKORC1 rs8050894 GG homozygotes had significantly higher measures of plasma phylloquinone than carriers of the CG or CC genotypes and carriers of VKORC1 rs7294 AA or AG had significantly lower plasma phylloquinone concentrations 19530970_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19530970_VKORC1 haplotypes in healthy Hungarian and Roma population samples are reported. 19538716_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19545555_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19567378_A stepwise multivariate linear regression analysis showed that 38.2% of the warfarin dose response variance was accounted for by a model involving age (20.9%), VKORC1-1639G/A (11.3%), and CYP2C9*1, *2, and *3 variants (7.1%) 19578179_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19652895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19652895_Polymorphisms in VKORC1 and GGCX are not major genetic determinants of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factor activity in Western Germans. 19663669_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19738376_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19745563_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19780415_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19780415_VKORC1 polymorphism influenced anticoagulants dose and predicted individuals predisposed to unstable anticoagulation. 19781295_VKORC1 polymorphisms are associated with differences in the initial response to warfarin when given at fixed doses, without affecting, as expected, its plasma concentration. 19794411_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19842934_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19842934_VKORC1 haplotypes in five East-Asian populations and Indians are reported. 19874474_Although CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotypes were significant independent predictors of therapeutic dose at each weekly interval, the magnitude of their predictive ability diminished over time. 19874474_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19875892_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19875892_VKORC1 -1639 G>A gene polymorphism may explain at least in part the low responsiveness to acenocoumarol. 19941044_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19942260_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19958090_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20020283_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20043560_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20043560_There was a high prevalence of the VKORC1 haplotype AA and AB in a group of Thai patients with heart valve disease who took warfarin. 20072124_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20073138_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20075209_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20121287_Genotyping of four SNPs for VKORC1 and CYP2C9 polymorphisms is useful in predicting a high probability of the occurrence of DAH in patients receiving oral anticoagulants. 20149073_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20163834_The study shows the occupancy of human RNA polymerase II and c-Myc on VKORC1 promoter, studied by ChIP-qPCR using antibodies against these proteins. 20193673_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20193673_Subtle polymorphisms, including those in GGCX, NQO1, and VKORC1 genes, influence individual susceptibility to the development of atherosclerotic stroke. 20203262_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20203262_Single VKORC1 polymorphism is associated with dose across 3 racial groups. 20204461_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20210733_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20226775_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20228265_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20339191_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20339978_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20339978_VKORC1 genotype and CYP2C9 polymorphism affect daily dose requirements and time to therapeutic INR in Turkish patients receiving warfarin for anticoagulation. 20354686_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20359285_Review and summary comparison of values of the Michaelis-Menten constant, maximal velocity and intrinsic clearance for 84 substrates reportedly mediated by major variants of CYP2C9 call for standardization in assessment of enzyme kinetics. 20376629_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20381283_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20386359_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20421126_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20434758_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20434758_VKORC1 c.-1639G > A variant is not likely to be associated with hepatic or portal vein thrombosis. 20442691_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20459419_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20488169_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20499136_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20499136_Significant associations with warfarin dose were seen for VKORC1 -1639, CYP2C9*2 and *3, the CYP4F2 SNP, and VKORC1 3730 20504253_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20532885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20553802_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20555338_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20555338_four genetic polymorphisms known to influence warfarin dosing (VKORC1 rs9923231, CYP2C9 rs1799853, CYP2C9 rs1057910 and CYP4F2 rs2108622) 20569971_Letter: Algorithms using clinical and genetic data (CYP2C9, VKORC1) are relevant to predict warfarin dose in patients with different INR targets. 20569971_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20575749_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20579077_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20581661_Carriers of AA genotype were more likely to be overanticoagulated during follow-up after initiation of VKA when compared with carriers of the GA and GG genotypes 20581661_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20585445_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20585834_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20597268_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20615525_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20615525_The presence of the rare VKORC1 V66M in two warfarin high dose outlier patients implies that this variant may be more frequent among African Brazilians and has implications for future warfarin studies in other populations of African descent. 20621035_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20621035_These findings suggested that polymorphisms of VKORC1 may play a role in osteoporosis. 20637959_CYP2C9, and VKORC1 had significant effects on warfarin maintenance dose requirements. 20637959_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20653674_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20653676_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20696932_VKOR employs the same electron transfer pathway as its bacterial homologs and VKORs generally prefer membrane-bound thioredoxin-like redox partners 20709439_Decreased kidney function was associated with lower warfarin dose requirements independently of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotype and clinical factors. 20709439_Observational study of gene-disease association, g | ENSMUSG00000096145 | Vkorc1 | 248.769564 | 0.7940320 | -0.332730948 | 0.12103619 | 7.55762951725 | 0.0059756541633716820163813032706912053981795907020568847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.03318279096357407143003115379542578011751174926757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 220.516712 | 15.216830 | 278.983636 | 18.711181 | |
| ENSG00000167470 | 90007 | MIDN | protein_coding | Q504T8 | FUNCTION: Facilitates ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation of polycomb protein CBX4. Plays a role in inhibiting the activity of glucokinase GCK and both glucose-induced and basal insulin secretion. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:D4AE48, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3TPJ7}. | Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Reference proteome | Predicted to enable kinase binding activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of glucokinase activity and negative regulation of insulin secretion. Located in cytoplasm and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:90007; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; negative regulation of glucokinase activity [GO:0033132]; negative regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0046676] | 24187134_midnolin plays a role in cellular signaling of adult tissues and regulates glucokinase enzyme activity in pancreatic beta cells 28724963_MIDN promotes the expression of parkin E3 ubiquitin ligase, and that MIDN loss can trigger Parkinson's disease-related pathogenic mechanisms. 31588691_Midnolin is a confirmed genetic risk factor for Parkinson's disease. | ENSMUSG00000035621 | Midn | 726.502389 | 0.8618260 | -0.214531478 | 0.05824248 | 13.57361128428 | 0.0002293876336503986761768819624407456103654112666845321655273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00213059377124952004783908776630596548784524202346801757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 679.025815 | 27.803123 | 791.720507 | 31.776013 | |
| ENSG00000167522 | 29123 | ANKRD11 | protein_coding | Q6UB99 | FUNCTION: Chromatin regulator which modulates histone acetylation and gene expression in neural precursor cells (By similarity). May recruit histone deacetylases (HDACs) to the p160 coactivators/nuclear receptor complex to inhibit ligand-dependent transactivation (PubMed:15184363). Has a role in proliferation and development of cortical neural precursors (PubMed:25556659). May also regulate bone homeostasis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:E9Q4F7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15184363, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25556659}. | ANK repeat;Disease variant;Dwarfism;Intellectual disability;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat | This locus encodes an ankryin repeat domain-containing protein. The encoded protein inhibits ligand-dependent activation of transcription. Mutations in this gene have been associated with KBG syndrome, which is characterized by macrodontia, distinctive craniofacial features, short stature, skeletal anomalies, global developmental delay, seizures and intellectual disability. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. Related pseudogenes exist on chromosomes 2 and X. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. | hsa:29123; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; face morphogenesis [GO:0060325]; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042475]; skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048705] | 17521611_Together, these results indicate that the transcriptional potential of ANCO-1 may be modulated by a combination of repression and activation signals. 18840648_ANKRD11 has a role as a p53 coactivator and may be involved in a regulatory feedback loop with p53 19920853_ANKRD11 is a candidate gene for autism and variable cognitive impairment in the novel 16q24.3 microdeletion syndrome. 21782149_Mutations in ANKRD11 cause KBG syndrome and outline a fundamental role of ANKRD11 in craniofacial, dental, skeletal, and central nervous system development and function. 22538187_aberrant DNA methylation of three CpGs in a 19 bp region within the ANKRD11 promoter may be responsible for its down-regulation in breast cancer. 23184435_The complete neurological and psychiatric features observed in two patients with KBG syndrome due to ANKRD11 mutations, are reported. 23494856_Partial deletion of ANKRD11 results in the KBG phenotype distinct from the 16q24.3 microdeletion syndrome. 24678732_AIB1, AIB1-delta4 and ANCO1 are important determinants of endocrine and growth factor responsiveness in breast cancer. 25413698_ANKRD11 C-terminus plays an important role in regulating the abundance of the protein, and a disturbance of the protein abundance due to the mutations leads to KBG syndrome. 25424714_Further delineation of the KBG syndrome phenotype on large patients cohort caused by ANKRD11 aberrations has been presented. 25464108_we conclude that severe short stature, intellectual disability, and macrodontia are the main characteristics in KBG syndrome related to ANKRD11 mutation 25652421_These findings point out the importance of screening ANKRD11 in young CdLS patients who were found to be negative for mutations in the five known CdLS genes. 27605097_Here we report a large series of 39 patients with KBG syndrome; these patients harbored ANKRD11 mutations (20 cases) or deletions (19 cases). All the mutations were found by targeted molecular analysis on patients with clinical features suggestive of KBG. 27900361_exome sequencing identified a novel de novo heterozygous single base pair duplication (c.6015dupA) in ANKRD11, which is predicted to lead to a premature stop codon and loss of function in ANKRD11, thereby implicating it as contributing to the molecular diagnosis of KBG syndrome. 28250421_ANKRD11 variants cause variable clinical features associated with KBG syndrome and Coffin-Siris-like syndrome. 28422132_Twelve novel cases of haploinsufficiency for ANKRD11-flanking genes make the difference between KBG and 16q24.3 microdeletion syndromes. 28566769_ANKRD11 variants cause KBG syndrome and Coffin-Siris-like syndrome. 30642272_Novel ANKRD11 gene mutation in an individual with a mild phenotype of KBG syndrome associated to a GEFS+ phenotypic spectrum. 31788936_Loss of ANCO1 repression at AIB1/YAP targets drives breast cancer progression. 32124548_KBG syndrome: Common and uncommon clinical features based on 31 new patients. 32222090_KBG syndrome in two patients from Egypt. 32476269_Pathogenic variants in EP300 and ANKRD11 in patients with phenotypes overlapping Cornelia de Lange syndrome. 32820523_[Analysis of ANKRD11 gene variant in a family affected with KBG syndrome]. 33354850_Two loss-of-function ANKRD11 variants in Chinese patients with short stature and a possible molecular pathway. 33955014_ANKRD11 variants: KBG syndrome and beyond. 34247373_[Gender difference in clinical manifestations of KBG syndrome due to variants of ANKRD11 gene]. 34440431_Wide Fontanels, Delayed Speech Development and Hoarse Voice as Useful Signs in the Diagnosis of KBG Syndrome: A Clinical Description of 23 Cases with Pathogenic Variants Involving the ANKRD11 Gene or Submicroscopic Chromosomal Rearrangements of 16q24.3. 34547584_Abnormal frontal gyrification pattern and uncinate development in patients with KBG syndrome caused by ANKRD11 aberrations. 34704418_Clinical and genetic characteristics of Keishi-Bukuryo-Gan syndrome: an analysis of 5 cases. 35598261_[Analysis of three patients with KBG syndrome and epileptic seizures due to variants of ANKRD11 gene]. 35682590_Expanding the Molecular Spectrum of ANKRD11 Gene Defects in 33 Patients with a Clinical Presentation of KBG Syndrome. 35833929_Missense variants in ANKRD11 cause KBG syndrome by impairment of stability or transcriptional activity of the encoded protein. | ENSMUSG00000035569 | Ankrd11 | 1695.595837 | 0.5979935 | -0.741798257 | 0.50232667 | 2.14866826960 | 0.1426936131547032471367231210024328902363777160644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.33411420502309824298592388913675677031278610229492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1392.178643 | 393.774265 | 2335.543987 | 660.721925 | |
| ENSG00000167548 | 8085 | KMT2D | protein_coding | O14686 | FUNCTION: Histone methyltransferase that catalyzes methyl group transfer from S-adenosyl-L-methionine to the epsilon-amino group of 'Lys-4' of histone H3 (H3K4) (PubMed:25561738). Part of chromatin remodeling machinery predominantly forms H3K4me1 methylation marks at active chromatin sites where transcription and DNA repair take place (PubMed:25561738, PubMed:17500065). Acts as a coactivator for estrogen receptor by being recruited by ESR1, thereby activating transcription (PubMed:16603732). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16603732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17500065, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25561738}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Coiled coil;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Methylation;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | The protein encoded by this gene is a histone methyltransferase that methylates the Lys-4 position of histone H3. The encoded protein is part of a large protein complex called ASCOM, which has been shown to be a transcriptional regulator of the beta-globin and estrogen receptor genes. Mutations in this gene have been shown to be a cause of Kabuki syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2010]. | hsa:8085; | MLL3/4 complex [GO:0044666]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; histone H3K4 methyltransferase activity [GO:0042800]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; beta-catenin-TCF complex assembly [GO:1904837]; heterochromatin formation [GO:0031507]; histone H3-K4 dimethylation [GO:0044648]; histone H3-K4 methylation [GO:0051568]; histone H3-K4 monomethylation [GO:0097692]; histone H3-K4 trimethylation [GO:0080182]; oocyte growth [GO:0001555]; oogenesis [GO:0048477]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0033148]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627] | 16603732_suggests a central role for the MLL2 complex in the growth of ERalpha-positive cancer cells 17178841_Knockdown of MLL2 reveals ALR target genes and leads to alterations in cell adhesion and growth. 18082152_CGBP interacts with MLL1, MLL2 as well as Set1 H3-Lysine 4 (H3K4) specific methyl-transferases and plays critical roles in regulations of MLL target genes. 19219072_A molecular mechanism by which the recruitment of a H3K4 histone methyltransferase complex on the promoter of a NF-kappaB-dependent gene induces its expression. 19221051_Study show that the C-terminal SET domain of MLL3 and MLL4 directly interacts with INI1, an integral subunit of Swi/Snf. 19556342_ASCOM-MLL3 and ASCOM-MLL4 play redundant but essential roles in FXR transactivation via their histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation activity. 20711175_Mutations in MLL2 are major cause of Kabuki syndrome. 20937768_Data show that Pygo2 associates with MLL2 histone methyltransferase and STAGA histone acetyltransferase to facilitate their interaction with beta-catenin and Wnt1-induced, TCF/LEF-dependent transactivation in breast cancer cells. 21280141_Direct sequencing of all 54 exons of the MLL2 gene in 45 clinically well-defined Kabuki Syndrome patients identified 34 (75.6%) different mutations. One mutation has been described previously, all others are novel. 21447625_The trimethylation of histone H3 at Lys 4 by the MLL2/MLL3 subunits of ASCOM, enhanced by the hormone-induced displacement of the H3K4 demethylase KDM5B, stabilizes NURF binding. 21658225_a large spectrum of MLL2 mutations in patients with Kabuki syndrome 21671394_MLL2 mutations were found in 81/110 (74%) of Kabuki syndrome families 21683083_These studies demonstrated that HOXC6 is an estrogen-responsive gene, and that histone methylases MLL2 and MLL3, in coordination with ERalpha and ERbeta, transcriptionally regulate HOXC6 in an estrogen-dependent manner. 21796119_32% of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and 89% of follicular lymphoma cases had somatic mutations in MLL2, and 11.4% and 13.4% of DLBCL and FL cases, respectively, had mutations in MEF2B 22126750_phenotypic variability of Kabuki syndrome suggests that MLL2 testing should be considered even in atypical patients. 22183980_No somatic mutations were identified in the PTCH1, MLL2, and MLL3 genes in our cohort of hepatoblastoma samples 22829784_we defined a role for Trithorax proteins WDR5 and MLL2 in activating the differentiation gene program in epidermal progenitor cells 22840376_Microdeletions and microduplications have not been identified in the MLL2 and KDM6A genes of a large cohort of patients with Kabuki syndrome. 22901312_This study expands the known genetic basis of Kabuki syndrome (KS) by showing mosaic mutations and large intragenic deletions and duplications of MLL2 in patients with KS. 23045699_results present a genome-wide integrative analysis of the MLL2 target loci and suggest potential mechanisms underlying tumorigenesis driven by MLL2 alterations 23129768_the second PHD finger (PHD2) of MLL1 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase in the presence of the E2-conjugating enzyme CDC34. This activity is conserved in the second PHD finger of MLL4, the closest homolog to MLL1 but not in MLL2 or MLL3. 23130995_Studies suggest the KMT2D (MLL2) nomenclature as H3K4 methyltransferases. 23131014_Studies indicate that mutation screening confirmed KMT2D (MLL2) as the major causative gene for Kabuki syndrome (KS). 23184418_MLL2 mutations occur in a subgroup-independent manner. 23192982_MLL1 and MLL2 bind to SR-B1 promoter in an E2-dependent manner and control the assembly of transcription pre-initiation complex and RNA polymerase II recruitment. 23320472_MLL2 mutation positive patients have a more severe and typical Kabuki phenotype than the MLL2 mutation negative group. 23754336_these results indicate that the suppression of MLL genes, especially MLL2 and MLL5, take part in modulating breast carcinogenesis. 23913813_The identification of novel MLL2 mutations in patients with Kabuki syndrome. 23995757_Ectopic AKAP95 stimulates expression of a chromosomal reporter gene in synergy with MLL1 or MLL2, whereas AKAP95 depletion impairs retinoic acid-mediated gene induction in embryonic stem cells 24081332_MLL3 and MLL4 function in the regulation of enhancer activity. 24240169_Study supports that KMT2D has distinct roles in neoplastic cells, as opposed to normal cells. 24323028_Data indicate that seven genes showed statistical enrichment for mutation: TP53, RB1, PTEN, NFE2L2, KEAP1, MLL2, and PIK3CA. 24368734_Identify MLL4 as a major mammalian H3K4 mono- and di-methyltransferase essential for enhancer activation during cell differentiation. 24368734_MLL4 (KMT2D) is a major H3K4 mono- and di-methyltransferase with partial functional redundancy with MLL3 (KMT2C) in mouse and human cells. MLL4 is enriched on enhancers and is required for enhancer activation, cell-type-specific gene expression and cell differentiation. 24368734_MLL4 (KMT2D) is a major H3K4 mono- and di-methyltransferase with partial functional redundancy with MLL3 (KMT2C) in mouse and human cells. MLL4 is enriched on enhancers and is required for enhancer activation, cell-type-specific gene expression and cell differentiation. 24491801_High levels of UTX or MLL4 are associated with poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer. 24705355_Like KMT2D, CHD7 interacts with members of the WAR complex, namely WDR5, ASH2L and RbBP5. We therefore propose that CHD7 and KMT2D function in the same chromatin modification machinery. 24739679_10 out of the 11 mutations found in patients with Kabuki syndrome were novel. KMT2D mutations included four small deletions or insertions and four nonsense and two missense mutations. 25112956_Reduced or lost expression of MLL2 was commonly observed in tumor tissues as compared with paired adjacent non-tumor tissues regardless of mutation status. 25123191_Data identified mutations in epigenetic modifiers such as KMT2D as potential early driving events in lymphomagenesis and immune escape alterations as relapse-associated events in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 25281733_Mutations in KMT2D gene were identified in 10/16 (62%) of the patients, whereas none of the patients had KDM6A mutations. 25355294_Results from targeted sequencing in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia identified KMT2D and KIF1B as novel putative driver genes and a putative regulatory non-coding variant that coincided with overexpression of the growth factor MDK. 25944076_We have reported a female Kabuki syndrome patient with typical dysmorphic features and developmental delay and a novel KMT2D mutation. 25972376_Our results provide further support for the similar roles of KMT2D and KDM6A in the etiology of KS by using a vertebrate model organism to provide direct evidence of their roles in the development of organs and tissues affected in KS patients. 26032282_KMT2D represents a recurrently mutated gene with potential implication for pheochromocytoma development. 26049589_Kabuki syndrome may be caused by mutations in one of two histone methyltransferase genes: KMT2D and KDM6A. 26138514_Mutations in MLL2 are present in approximately 27% of urothelial carcinoma cases . 26194542_In patients with Kabuki Syndrome, autosomal dominant KMT2D mutations are associated with dysregulation of terminal B-cell differentiation, leading to humoral immune deficiency and, in some cases, autoimmunity. 26290144_The results do not support our hypothesis that common germline genetic variants in the MLL2 genes is associated with the risk of developing medulloblastoma. 26303934_Data suggest that lysine methyltransferase 2D (KMT2D) mutations are rare in abdominal paraganglioma (PGLs). 26366710_KMT2D mutations may promote malignant outgrowth by perturbing the expression of tumor suppressor genes that control B cell-activating pathways 26366712_findings suggest that KMT2D acts as a tumor suppressor gene whose early loss facilitates lymphomagenesis by remodeling the epigenetic landscape of the cancer precursor cells 26551667_Mutations in KMT2D gene is associated with cutaneous T cell lymphoma and Sezary syndrome. 26711341_Whereas Set1 targets are largely associated with the maintenance of the stem cell population, MLL1/2 targets are specifically enriched for genes involved in ciliogenesis. 26722499_Our data suggest that MLL2 protein is overexpressed in primary gastrointestinal diffuse large B cell lymphoma and appears as a prognostic factor 26757828_Mutation in the MLL2 gene is associated with Kabuki Syndrome. 26841698_high proportion of recurrent somatic DICER1 and KMT2D mutations in this series of sporadic IO-MEPL points to their likely important roles in the molecular pathogenesis of these rare embryonal tumors 26841933_Pathogenic variants in KMT2D resulting in protein truncation in 43% (6/14; of which 3 are novel) of all cases were detected, while analysis of KDM6A was negative. MLPA analysis was negative in all instances. 26898171_Mutations of the epigenetic genes KMT2D and KDM6A cause dysregulation of certain developmental genes and account for the multiple congenital anomalies of the syndrome 26902498_Pygo2 functions as a prognostic factor for glioma due to its up-regulation of H3K4me3 and promotion of MLL1/MLL2 complex recruitment. 27280393_we demonstrate that low KMT2C and KMT2D expression in biopsies defines better outcome groups in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma 27302555_Study reports mutation screening in patients with Kabuki Syndrome Subtype 2 (KS2), in which 12 novel KDM6A mutations are identified. These results confirm that female patients with KS2 may have a rather mild manifestation of KS and may even develop normally with regard to cognitive function. 27387124_Mutations of ARID1A, GPRC5A and MLL2 grant bladder cancer non-stem cells the capability of self-renewal. 27530205_A possible correlation between the position of the KMT2D premature termination codon caused by the mutation and height SDS was assessed, but a significant difference could not be observed for the Kabuki syndrome patients 27566587_analysis of highly recurrent genetic lesions in components of the NF-kappaB pathway, of NOTCH1 and NOTCH2 as well as KMT2D that may have a role in ocular adnexal MALT-type marginal zone lymphomas 27632392_We identify three mosaic missense and likely-gene disrupting mutations in genes previously implicated in ASD (KMT2C, NCKAP1, and MYH10) in probands but none in siblings. We find a strong ascertainment bias for mosaic mutations in probands relative to their unaffected siblings 27698142_Although enhancer priming by MLL4/KMT2D is dispensable for cell-identity maintenance in mouse, it controls cell fate transition by orchestrating p300-mediated enhancer activation 27749841_KMT2D Mutation is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 27991736_KMT2D p.Gln3575His segregated with disease status in the family, and is associated with a unique and conserved phenotype in the affected family members, with features overlapping with Kabuki and CHARGE syndromes. Our findings further support the potential etiological link between these two classically distinct conditions. 28007623_KMT2D mutation is associated with small Cell Lung Cancer. 28013028_The enzymatic activity of H3K4 methyltransferase MLL4 is required for its protein stability. 28157506_Study shows the contribution of MLL2's methyltransferase and CXXC domain in the trimethylation of H3K4 in embryonic stem cells and find that while it trimethylates H3K4 at both bivalent gene promoters and non-TSS elements, it regulates transcription at a limited number of genes including those required for primordial germ cell specification. 28256057_Two patients' presentation of Kabuki syndrome has been described caused by different KMT2D mutations, both including an interrupted/bipartite clavicle. 28336670_data support akey role forKMT2D in modulating the chromatin competence necessary for the assembly of the ER-FOXA1-PBX1 transcriptional regulatory network in breast cancer. 28390392_Results highlight the emerging role of mutations in epigenetic regulators, particularly MLL2, in cervical carcinogenesis, which suggests a potential disruption of histone modifications. 28475860_Our findings provide evidence that CHARGE and Kabuki syndromes result from dysregulatrion of CHD7 and KMT2D genes involved embryonal development that are expressed in a tissue-specific manner. 28590022_The uniqueness of our case is the sporadic co-occurrence of two genetic disorders, that is, a de novo frameshift variant in the KMT2D gene and a de novo 3.2 Mbp 10q22.3q23.1 deletion. 28609655_MLL1 and MLL2 collaborate to regulate gene expression and leukemia maintenance not through redundancy, but through distinct pathways. 28805986_Three of four cases of histiocytic sarcoma had alterations in the KMT2D gene. 28884922_a congenital heart defects (CHD)is detected in 70% of patients with KMT2D (MLL2) pathogenic variants, most commonly left-sided obstructive lesions, including multiple left-sided obstructions similar to those observed in the spectrum of the Shone complex, and septal defects. 29265349_The results suggest therefore that KMT2D mutations may help to diagnose CAD and better distinguish it from lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. 29269867_KMT2D epigenetically activates PI3K/Akt pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting LIFR and KLF4 and thus serves as a putative epigenetic-based target for treating Prostate cancer. 29283410_Clinical and neurobehavioral features of three novel Kabuki Syndrome unrelated patients with mosaic KMT2D mutations have been described. 29305415_enhancing the interaction of KMT2D with the transcription factor PU.1, thereby inactivating the H3K4me-associated signaling pathway MAPK, which is constitutively activated in T-cell lymphoma 29440247_results reveal a critical role for KMT2D in the control of epithelial enhancers and p63 target gene expression, including the requirement of KMT2D for the maintenance of epithelial progenitor gene expression and the coordination of proper terminal differentiation. 29532228_Results indicate that overexpression of MLL2 predicts poor clinical outcomes and facilitates ESCC tumor progression, and it may exert oncogenic role via activation of EMT. 29627316_The KMT2D mutation was associated with reduced survival in non-small-cell lung cancer but not in small cell lung cancer 29807113_mutations in KMT2D, which are common in many cancers, correlate with drug sensitivity in two independent datasets 29907798_we retrospectively evaluated 100 infants with HI lacking a genetic diagnosis, for causative variants in KS genes. Molecular diagnoses of KS were established by identification of pathogenic variants in KMT2D (n = 5) and KDM6A (n = 4). 29914387_This is a case of a mutation in the KMT2D gene in a girl with Kabuki syndrome. 29950560_Study findings identify KMT2D inactivation as a novel driver event in adult-type granulosa cell tumors of the ovary and suggest that mutation of this gene may increase the risk of disease recurrence. 30107592_The mutation pattern of KMT2D and KDM6A in a cohort of 505 patients clinically diagnosed as Kabuki syndrome was reported. The functional role of a subset of KMT2D missense mutations in impairing the protein enzymatic activity was demonstrated. 30177394_KMT2D modulates proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer 30213761_A novel loss-of-function mutation was identified in a patient with Kabuki syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus. 30459467_KMT2D missense mutation is associated with Kabuki syndrome and cancers. 30556359_Three of the 27 children had a KDM6A mutation and had thesame hypermobility as the KMT2D subjects. Only one of the Kabuki syndrome chil-dren had a patellar luxation in here previous history and was not con-sidered hypermobile using both scores. 30984543_Comparison of the mRNA and miRNA expression profiles of mutated and wild-type KMT2D suggested that two signaling pathways (FOX1-miR-1224-5p-DLK1 and HIF/GATA5-miR-133a-3p-DRD5) may mediate the tumor suppressive effect of the KMT2D mutation. 30990809_This work describes epigenetic modulating genes which are found to be mutated in breast cancer. Identified is the histone methyltransferase KMT2D, which is mutated in 6% of triple negative tumors and linked with poor survival. 31123786_The most frequently mutated driver genes in our cohort were TP53 (involved in cell cycle control), FAT1 (Wnt signalling, cell-cell contacts, migration) and KMT2D.However, somatic mutations in FAT1 and smaller primary tumour volumes were associated with reduced radiomic intra-tumour heterogeneity. 31127101_Nuclear magnetic resonance study identifies the PHD6 finger of MLL4 (MLL4-PHD6) as histone reader that exhibits high selectivity toward H4K16ac. 31232159_Knockdown of KMT2D sensitized cells to DNA damage through the disturbance of antioxidative gene expression. 31311407_Somatic mutations in KMT2D and TET2 associated with worse prognosis in Epstein-Barr virus-associated T or natural killer-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. 31465303_Precocious neuronal differentiation and disrupted oxygen responses in Kabuki syndrome. 31529049_we show that the nuclear PASK associates with the mammalian H3K4 MLL2 methyltransferase complex and enhances H3K4 di- and tri-methylation. We also show that PASK is a histone kinase that phosphorylates H3 at T3, T6, S10 and T11. 31537689_KMT2D mutations and TP53 disruptions are poor prognostic biomarkers in mantle cell lymphoma receiving high-dose therapy: a FIL study. 31547991_MiRNA-217 accelerates proliferative and migratory abilities in bladder cancer via inhibiting the level of tumor suppressor KMT2D, thereafter leading to the poor prognosis in bladder cancer patients 31654559_Prenatal and perinatal history in Kabuki Syndrome. 31676369_MLL2 promotes cancer cell lymph node metastasis by interacting with RelA and facilitating STC1 transcription. 31846209_Holoprosencephaly in Kabuki syndrome. 31876365_Growth charts in Kabuki syndrome 1. 31883305_The phenotypic spectrum of Kabuki syndrome in patients of Chinese descent: A case series. 31924266_KMT2C/D COMPASS complex-associated diseases [KCDCOM-ADs]: an emerging class of congenital regulopathies. 31935506_This study expands the number of naturally occurring KMT2D and KDM6A variants. The discovery of novel pathogenic variants will add to the knowledge on disease-causing variants and the relevance of missense variants in Kabuki syndrome. 31949313_A restricted spectrum of missense KMT2D variants cause a multiple malformations disorder distinct from Kabuki syndrome. 32024448_Thyroid Carcinomas That Occur in Familial Adenomatous Polyposis Patients Recurrently Harbor Somatic Variants in APC, BRAF, and KTM2D. 32064880_KMT2D and TP53 mutation status improve the prognostic value of the International Prognostic Index (IPI) stratification in ENKTL patients. 32083401_Phenotypic expansion of KMT2D-related disorder: Beyond Kabuki syndrome. 32139118_MLL2 regulates glucocorticoid receptor-mediated transcription of ENACalpha in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. 32243837_KMT2D Deficiency Impairs Super-Enhancers to Confer a Glycolytic Vulnerability in Lung Cancer. 32350066_FBXW7 Triggers Degradation of KMT2D to Favor Growth of Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Cells. 32525229_Kabuki syndrome with midgut malrotation and hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia: A rare co-occurrence from Thailand. 32668765_Loss of Function of the Gene Encoding the Histone Methyltransferase KMT2D Leads to Deregulation of Mitochondrial Respiration. 32697937_Crystal Structure of MLL2 Complex Guides the Identification of a Methylation Site on P53 Catalyzed by KMT2 Family Methyltransferases. 32738303_Identification of novel candidate genes in heterotaxy syndrome patients with congenital heart diseases by whole exome sequencing. 32803813_Update of the genotype and phenotype of KMT2D and KDM6A by genetic screening of 100 patients with clinically suspected Kabuki syndrome. 32878339_Merkel Cell Polyomavirus in Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Integration Sites and Involvement of the KMT2D Tumor Suppressor Gene. 32988919_Predictive Role of TP53, PIK3CA and MLL2 in ER+ HER2+ Breast Bancer: Biomarker Analysis of Neo-ALL-IN [NCT 01275859]. 33110216_Inhibition of Drp1 SUMOylation by ALR protects the liver from ischemia-reperfusion injury. 33169020_MLL4-associated condensates counterbalance Polycomb-mediated nuclear mechanical stress in Kabuki syndrome. 33314698_Clinical and molecular characterization study of Chinese Kabuki syndrome in Hong Kong. 33402515_Low MLL2 Protein Expression Is Associated With Fibrosis in Early Stage Gastric Cancer. 33483618_High incidence of MYD88 and KMT2D mutations in Chinese with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 33793001_KMT2D promotes proliferation of gastric cancer cells: evidence from ctDNA sequencing. 34156443_The MLL3/4 H3K4 methyltransferase complex in establishing an active enhancer landscape. 34369642_Neuroimaging in Kabuki syndrome and another KMT2D-related disorder. 34613626_Lysine methyltransferase 2D regulates muscle fiber size and muscle cell differentiation. 34645806_Cancer gene mutation frequencies for the U.S. population. 34933446_GRWD1-WDR5-MLL2 Epigenetic Complex Mediates H3K4me3 Mark and Is Essential for Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Induced Cellular Transformation. 35060672_Refining the clinical phenotype associated with missense variants in exons 38 and 39 of KMT2D. 35073341_Mutually exclusive mutation profiles define functionally related genes in muscle invasive bladder cancer. 35411950_USP7 sustains an active epigenetic program via stabilizing MLL2 and WDR5 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 35506254_Comparison of methylation episignatures in KMT2B- and KMT2D-related human disorders. 35640156_Kabuki syndrome stem cell models reveal locus specificity of histone methyltransferase 2D (KMT2D/MLL4). | ENSMUSG00000048154 | Kmt2d | 251.127028 | 1.4686516 | 0.554492223 | 0.29363045 | 3.51826631250 | 0.0606959064382782270685723347014572937041521072387695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.18783503080943272922631592791731236502528190612792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 291.840659 | 89.554475 | 199.799470 | 61.239237 | |
| ENSG00000168685 | 3575 | IL7R | protein_coding | P16871 | FUNCTION: Receptor for interleukin-7. Also acts as a receptor for thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP). | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;SCID;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor for interleukin 7 (IL7). The function of this receptor requires the interleukin 2 receptor, gamma chain (IL2RG), which is a common gamma chain shared by the receptors of various cytokines, including interleukins 2, 4, 7, 9, and 15. This protein has been shown to play a critical role in V(D)J recombination during lymphocyte development. Defects in this gene may be associated with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. | hsa:3575; | clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; antigen binding [GO:0003823]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; interleukin-7 receptor activity [GO:0004917]; B cell homeostasis [GO:0001782]; B cell proliferation [GO:0042100]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; immune response [GO:0006955]; lymph node development [GO:0048535]; negative regulation of T cell apoptotic process [GO:0070233]; negative regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001915]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via STAT [GO:1904894]; positive regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033089]; regulation of cell size [GO:0008361]; regulation of DNA recombination [GO:0000018]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033077]; T cell homeostasis [GO:0043029]; T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001913] | 12149213_IL-7 may function to regulate the milieu of the microenvironment by modulating IL-6 secretion by the IL-7R-expressing stromal elements 12354940_IL-2 signaling can diminish IL-7Ralpha expression via a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent mechanism. 12792903_IL-7R has a role in some human solid malignancies [review] 14607751_Interaction between IL-7 and its receptor has the major role in modulating T-ALL survival within the microenvironment generated by the T-ALL/TEC interaction. 14726805_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, genetic testing, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 15674389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15728501_Expansion of CD8 positive, CD127 negative effector-like T cells is identified as a novel feature of HIV-associated immune perturbation. 15879083_Maturation of memory CD4 and CD8 T cells is associated with a CD127high phenotype and the expression of CD127 serves as a predictor of the functional quality of antiviral T cells. 15947093_Virus-specific IL-7Ralpha+ cells proliferated vigorously in response to IL-7, IL-15, or peptide, whereas IL-7Ralpha- cells required both peptide and helper-cell activation or IL-2 or IL-15 for optimal expansion 16004964_Altogether, we show that gamma(c) is the target of an ubiquitination mechanism and its expression level can be regulated through the activities of a couple of ubiquitin-ligase/ubiquitin-hydrolase enzymes, namely c-Cbl/DUB-2. 16075257_The T cell proliferation gene IL7R (CD127) was also underexpressed in PPMS, but was up-regulated in SPMS compared to the controls. 16357322_Aging affects IL-7Ralpha expression by T cells, leading to impaired signaling and survival responses to IL-7. 16435014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16614257_HIV infection produces the Tat protein, which in turn may up-regulate IL-7R in a paracrine manner, which ultimately promotes early events in HIV replication. 16709829_Transcription of the IL-7R alpha subunit is suppressed in both naive and memory T cells following IL-7 stimulation. 16818676_Cell surface expression of CD127 therefore allows accurate estimation of regulatory T cell numbers and isolation of pure populations for in vitro studies and should contribute to our understanding of regulatory abnormalities in immunopathic diseases. 16818678_CD127 can be used to quantitate regulatory T (Treg) cell subsets in individuals with type 1 diabetes supporting the use of CD127 as a biomarker for human Treg cells. 16837861_CD127 expression on T cells remains low in HIV-infected patients despite antiretroviral therapy 16951331_IL-7 receptor and Notch1 pathways cooperate to synchronize cell proliferation and suppression of non-T lineage choices in primitive intrathymic progenitors. 17045841_CD127 uniquely enables the purification of FOXP3+ Treg cells and, potentially, also 'adaptive' regulatory T-cell subsets from the CD4+CD25- T-cell population. 17079288_A large fraction of peripheral HCV-specific CD8+ T cells were CD127+ and KLRG1-. Intrahepatic virus-specific CD8+ T cells displayed significantly reduced levels of CD127 expression but similar levels of KLRG1 expression compared to the peripheral blood. 17173927_CD4+ regulatory T-cells exhibiting suppressive activity in vitro display distinctly lower surface expression of CD127, irrespective of their level of CD25 expression. 17363735_results confirm that signal transduction via the IL-15R, and hence NK ontogeny, is preferentially retained relative to the IL-7R as gammac expression becomes limiting. 17442928_These findings suggest that DNA methylation is involved in regulating IL-7Ralpha expression in T cells via affecting IL-7Ralpha gene promoter activity. 17504502_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17504502_gene encoding the IL-7Ralpha chain is polymorphic, and investigation of inhalation allergic patients compared with controls showed significant association with two alleles at position +1237 and +2087 17579041_A subset of naive CD8-positive cells characterized by low interleukin-7 receptor alpha message and protein expression may encompass cells that have recently received homeostatic signals. 17591854_CD4(+)CD25(+)CD45RO(+)IL-7Ralpha(high) cell population contained allospecific CD4 T cells and secreted effector cytokines. 17609371_Increased constitutive interleukin-7 receptor alpha expression has minimal effects on the numbers or function of effector and memory CD8 T cells formed. 17660530_Alleles of IL2RA and IL7RA and those in the HLA locus are identified as heritable risk factors for multiple sclerosis. 17660530_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17660816_Results provide compelling evidence that polymorphisms in IL7R, which encodes the interleukin 7 receptor alpha chain (IL7Ralpha), indeed contribute to the non-HLA genetic risk in multiple sclerosis. 17660817_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17660817_Results show allelic association of a polymorphism in interleukin 7 receptor alpha chain (IL7R) as a significant risk factor for multiple sclerosis in four independent family-based or case-control data sets. 17894415_Immunolocalization of IL-7, IL-7Ralpha, SDF-1alpha, and CXCR4 resulted in a diffuse but specific labeling. RT-PCR analysis confirmed the expression of the above-mentioned transcripts. 17909291_Stimulation of the IL-7 pathway begins with IL-7 binding to unglycosylated and glycosylated forms of its alpha-receptor, IL-7 receptor alpha. 17928869_Haplotypes of the IL7R gene are correlated with altered expression in whole blood cells in multiple sclerosis. 17956896_IL-7 reduced CD127-surface expression and shedding by CD8+ T cells; results support a role for IL-7 in the down-regulation of CD127 expression and impairment of CTL function observed in HIV infection 18025189_We report that loss of CD127 defines terminally differentiated B cell-helping effector T cells in human tonsils. 18272905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18272905_The association between rs6897932 and multiple sclerosis in the Olmsted County collection appeared to be much stronger than anticipated on the basis of recent studies 18292507_Expression of transgenic IL-7 receptor alpha by itself does not support increased survival of effector antigen-specific CD4 or CD8 T cells into the memory phase following infection with Listeria monocytogenes. 18354419_IL2RA and IL7RA genes confer susceptibility for multiple sclerosis in two independent European populations. 18354419_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18390701_IL-7- and TCR/CD28-mediated signaling data show that differentially regulate IL-7Ralpha expression on human T cells with a transient and chronic effect, respectively. 18390743_during HIV infection, specific changes in the fraction of CD4(+) T cells expressing CD25 and/or CD127 are associated with disease progression 18563381_Independent replication of the association between the CAPSL and IL7R locus and type 1 diabetes, especially for early-onset type 1 diabetes patients. 18563381_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18633131_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18687755_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18721276_Association studies between IL7RA rs6897932 and multiple sclerosis. 18721276_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18774388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18847371_Down-regulation of CD127 was mainly associated with T cell activation and reverted only partially after suppression of detectable plasma HIV RNA with HAART 19011158_This suggests a role for gamma(C) cytokines in the pathogenesis of diseases in which CD127 expression is altered on CD8+ T cells such as in progressive viral infections and cancer. 19096522_CD8+ T-cell CD127 expression is significantly higher in children with better HIV disease control, and may have a role as an immunologic indicator of disease status. 19141282_The SCID mutations of IL-7Ralpha locate outside the binding interface with IL-7, suggesting that the expressed mutations cause protein folding defects in IL-7Ralpha 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19231135_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19231135_confirm involvement of polymorphisms in the IL7RA and IL2RA genes in multiple sclerosis pathogenesis 19239367_HIV infection results in impaired IL-7 responsiveness, especially in memory CD4+ T cells, and this defect is likely compounded by aging. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19253027_No significant differences were observed between the genotypic distributions of IL-7alphaR polymorphisms and incidence of acute or chronic graft versus host disease. 19253027_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19349467_Notch1 controls early T cell development, in part by regulating the stage- and lineage-specific expression of IL-7Ralpha. 19494261_sIL-7Ralpha mRNA is constitutively present among peripheral T lymphocytes and is down-modulated in vitro by IL-7 19505916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19506219_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19523791_Letter: Analysis of variation in the IL7RA and IL2RA genes in atopic dermatitis. 19525955_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19605492_following the antigen-driven downregulation of IL-7Ralpha seen on all populations in acute IM, in every case, the TLD-specific population recovered expression unusually quickly post-IM 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19626041_Combined analysis of 663 individuals with sarcoidosis and 586 controls provided strong statistical support for a genuine association of IL7R with the risk of sarcoidosis 19626041_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19667968_Quantification of CD127( expression in t4 cells is a significant tool for monitoring the outcome course of renal transplant patients. 19690616_This is the first report on the quantification of plasma sCD127 in a population of healthy adults. Soluble CD127 plasma concentrations remained stable over time in a given individual and sCD127 immunoreactivity was resistant to repeated freeze-thaw cycles 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19714586_Enhanced expression of IL-7Ralpha and IL-7 in rheumatoid arthritis patients contributes significantly to the joint inflammation by activating T cells, B cells, and macrophages. 19744146_A role of rs6897932 in predisposition to chronic inflammatory arthropathies. 19744146_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19798683_Data show that bound CD4+ T cells had high proliferative activity and increased CD25 and FoxP3 expression, and also expressed CD127. 19834503_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19834503_Studies indicate that five SNPs showed genome-wide significant association with MS: HLA-DRA, IL7R, IL2RA, CD58 and CLEC16A. 19865102_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19866484_The IL-7Ralpha(high)CD25(+)CD45RO(+)CD4(+)FoxP3(-) T cell population is expanded after liver transplantation. A preexisting HCV infection negatively influences the expansion of this population. 19874827_a marker for regulatory T cell in patients with malignant glioma treated with autologous dendritic cell vaccination 19879194_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19940860_CD127(low/-) and FoxP3(+) expression levels characterize different regulatory T-cell populations in human peripheral blood 20035760_Demonstrate that sCD127 is detectable at various levels in the plasma of healthy humans. IL-7 treatment has no impact on sCD127 plasma concentration in patients infected by HIV. 20060740_These findings support a role for the IL-7/IL-7R system in B-cell oncogenesis. 20072139_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20072142_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20072142_findings suggest that IL-7Ralpha polymorphisms can influence T cell development and homeostasis, and thereby contribute to the altered immune regulation associated with disease development in patients with multiple sclerosis 20097866_Data suggest that IL-7Ralpha haplotype difference is likely to affect the immunophenotype and disease pathogenesis. 20112030_The association with rs6897932[T244I] in the interleukin-7 receptor alpha chain (IL7RA) gene suggest this variant is likely to be causative rather than a surrogate proxy in Multiple Sclerosis. 20187771_gene polymorphism influences multiple sclerosis susceptibility and response to interferon-beta 20190194_IL-7 triggers rapid IL-7Ralpha endocytosis, which is required for IL-7-mediated signaling and subsequent receptor degradation. 20194581_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20194581_We found no significant difference in genotype or allele frequencies interleukin 7 receptor alpha rs6897932 between controls and patients with multiple sclerosis 20219786_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20226540_The IL-7 transcript, lacking exon 4, and not the full length IL-7 represents the dominant IL-7 RNA transcript in human PBMCs and a novel IL-7R splice variant lacking exons 5, 6 and 7. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20304824_Recombinant and native sources of soluble CD127 significantly inhibit interleukin (IL)-7-mediated signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)5 and Akt phosphorylation in CD8(+) T cells. 20368992_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20378664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20450971_Studies indicate that SNP in IL7RA, IL2RA, CD58 and CLEC16A genes has been consistently associated with MS. 20466416_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20539016_Circulating CD4+CD25hiCD127lo Treg-cell levels are not significantly associated with the extent of severity of carotid/coronary atherosclerosis. 20638239_increased expression by CD8-positive Treg populations from primary biliary cirrhosis patients 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20812848_IL-7Ralpha haplotype 2 HIV-infected patients with IL-7Ralpha haplotype 2 had significantly lower soluble IL-7Ralpha levels compared with those of patients without haplotype 2 20812848_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20815339_A large favorable entropy change, a global favorable electrostatic component, and glycosylation of the receptor, albeit not at the interface, contribute significantly to the interaction between IL-7 and the IL-7R subunit alpha extracellular domain. 20952689_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20962850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21129157_sIL-7R is induced by pro-inflammatory cytokines in Rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells 21131424_Activation and proliferation of CD127-positive T regulatory cells (Tregs) is inhibited by a hypocalcemic vitamin D analog TX527, which has immunoregulatory properties. 21159243_The high expression of IL-7 and IL-7R is highly positie correlated with clinic stage, lymph node metastasis, VEGF-D, LVD and poor prognosis in Non-small cell lung cancer. 21161391_The IL7R T244I polymorphism was associated with susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. 21190413_Considering allele, genotype and haplotype frequencies, no significant association was observed between multiple sclerosis and IL7Ra polymorphisms 21209878_immunological nonresponders to HIV therapy display elevated BM IL-7/IL-7Ralpha expression but impaired T-cell responsiveness to IL-7, suggesting the activity of a central compensatory pathway targeted to replenish the CD4+ compartment 21211217_The frequency of IL-7R rs6897932 C allele in idiopathic demyelinating optic neuritis patients was significantly greater than in controls. 21287555_screened for multiple sclerosis-associated IL-7RA gene polymorphism rs6897932 21300823_When isolated from multiple sclerosis patients, both nonmature and effector subsets of memory CD127(low) regulatory T cells exhibit kinetically distinct defects in suppression that are evident with CD2 pathway costimulation. 21326139_an association between severe acute graft versus host disease and donor IL-7R[alpha] single nucleotide polymorphism genotypes. 21481848_During chronic HCV infection non-reactive HCV-specific CD8(+) cells targeting the virus are PD-1(+)/CD127(-)/Bim(+) and, blocking apoptosis and PD-1/PD-L1 pathway on them enhances in vitro reactivity. 21536738_Gain-of-function mutations in interleukin-7 receptor-alpha (IL7R) in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemias. 21543551_Homozygosity for the IL7R exon 6 rs6897932 C allele is associated with a higher risk for multiple sclerosis in our Dutch population 21562156_Dominant HIV clonotypes are characterized by higher PD-1 expression and lower C127 expression compared with subdominant clonotypes, and TCR avidity positively correlates with PD-1 expression 21625022_IL7R and RAG1/2 genes mutations/polymorphisms in patients with SCID. 21670443_Data reveal a significant association of the SNP rs6897932 of the interleukin-7 receptor alpha gene with non-NMO multiple sclerosis in Japanese populations. 21680796_relationship between CD127 expression, IL-7 signaling and Ig gene rearrangement in pre-B cells 21740271_Infection of PBMCs with HIV in vitro results in the downregulation of CD127 surface expression on CD8(+) T cells. 21757642_Demonstrate an increase in the proportion of CD4+CD25highIL-7Ralphahigh activated T cells in kidney transplant recipients, regardless of the immunosuppressive regimen. 21839739_Results show a downregulation of CD127 expression on T cells including Tregs in patients early post-SCT. 21863001_[review] CD127 has an important role in HIV immunopathogenesis 21892159_IL7R mutational activation is involved in human T-cell leukemogenesis. 21904560_Our data strongly support superiority of combined CD127 and FOXP3 analysis in comparison to CD25 and FOXP3 assessment for further quantification of T(reg) cells in malignant diseases. 21920046_HIV infection of thymocytes did not affect CD127 expression on either total thymocytes or on single positive CD4 or single positive CD8 subsets. 21938017_we did not demonstrate a significant association between IL-7Ralpha haplotype 2 and faster CD4 T-cell recovery in Africans. The IL-7Ralpha SNPs associated with CD4 T-cell recovery following cART differ in African and Caucasian cohorts. 22021616_Though dispensable for autophagy induction, transgenic Vps34 is a critical regulator of naive T cell homeostasis, modulating interleukin (IL)-7 receptor alpha trafficking, signaling, and recycling. 22247488_No difference was found between patients with Vogt Koyanagi-Harada disease and normal controls in the expression of IL-7Ralpha on CD4(+) T cells. 22262655_multiple sclerosis is associated with increased expression of IL-7R-alpha on most CD8+ T cell subsets and with higher frequencies of CD8 effector memory cells coexpressing IL-7R-alpha 22302060_IL-7 and IL-7Ralpha+ T cells were both found to be increased in exocrine glands of Sjogren syndrome patients indicating that IL-7 could contribute to glandular inflammation. 22310831_CD127 expression was significantly reduced in T cells from HIV infected subject. 22312161_IL-7(R)-dependent T cell-driven immune activation plays an important role in inflammation in Sjogren syndrome. 22329520_our comprehensive genetic study revealed three SNPs and a risk of haplotype associated with rapid progression to AIDS in the IL7RA gene and more widely, its role in CD4+ T cell homeostasis. 22425228_The genetic association of IL-7R varients with diseases is discussed in a review. 22471460_Polymorphisms of IL-7R is not associated with Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma. 22640659_Letter: report increased frequency of CD127/CD215 co-expressing CD4(+) T cells in Wegener's granulomatosis. 22661557_IL-7Ralphalow memory CD8+ T cells are significantly elevated in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. 22695916_Notch1 controls T-cell development, in part by regulating the stage- and lineage-specific expression of IL-7R. (Review) 22824721_Data indicate that the mean number of CD4(+)CD25(+)CD127(lo) regulatory T cells per mul of whole blood was 48+/-16.9with a range of 18 - 79. 22914435_The soluble IL-7Ralpha levels correlate with the rs6897932 [C] risk allele carriership. 23069254_IL7R mutations may contribute to the development of diverse types of acute leukemias. 23151878_CPSF1 was identified among protein-binding candidates. A consensus polyadenylation signal AAUAAA is present in intron 6 of IL7 receptor directly downstream from the 5' splice site. Mutations to this site and CPSF1 knockdown increased exon 6 inclusion. 23157741_IL-7/IL-7R promotes c-Fos/c-Jun expression and activity in non-small cell lung cancer which further facilitates cyclin D1 expression, and accelerates proliferation of cells and VEGF-D-induced lymphovascular formation. 23207282_IL-7 induces the initial reduction in cell-surface CD127 protein independent of transcriptional suppression, which is delayed by 40-60 min. 23282736_The percentage of CD4+CD25+CD127low/- Treg and Foxp3 in portal hypertension and hypersplenism was significantly increased, suggesting that they may take part in the regulation of immune function and be related to the change of T lymphocyte subsets. 23301543_A low Mcl-1 expression and Bim upregulation after antigen encounter are involved in CD127(low) HCV-specific cytotoxic T cell hyporeactivity during chronic infection. 23329834_Activated IL-7 receptors embedded in membrane microdomains induce actin-microfilament meshwork formation, anchoring microtubules that grow radially from rafted receptors to the nuclear membrane. 23454692_genetic, immunologic, and metabolic factors contribute to a dysregulation of the IL-7/IL-7 receptor pathway in type 1 diabetes and identify a novel hyperglycemia-mediated interference of immune regulatory networks. 23462217_results suggest an association between the IL7Ralpha, rs6897932, T-allele and increased mortality among untreated HIV-infected, Zimbabwean individuals 23610432_IL7Ralpha has a role in potentiating IL-7 bioactivity and in promoting autoimmunity 23628622_Data indicate that both CgammaCR-CD127(+)composed of Interleukin-7 (IL-7) tethered to IL-7Ralpha/CD127, and CgammaCR-CD122(+) CD8(+) T((E/CM)) engraft in mice and persist in an absence of exogenous cytokine administration. 23692589_The rs1494555GG and rs1494558TT IL-7Ralpha genotypes of the donor were associated with the acute and chronic graft versus host disease in the univariate analysis. 23841696_Data indicate that HCV-infected patients with fibrosis presented with a higher proportion of CD4+ T cells expressing CD127 compared with HCV-infected patients without fibrosis. 23888080_In the cord blood of children with respiratory syncytial virus disease there was downregulation of interleukin 7 receptor and chemokine receptor 7, and in the severe disease subcategory, downregulation of Toll-like receptor 4. 23965471_CD127 is downregulated at a transcriptional level in memory CD8 T cells in association with upregulation of Eomes expression in HIV infected patients. 23985573_The findings indicate that genetic variants of IL7RA result in haplotype-associated differential responsiveness to immunological stimuli that influence multiple sclerosis susceptibility not exclusively by varying levels of soluble IL-7RA. 24130709_The IL7R, TNFRSF1A, and GPC5 polymorphisms tended to be associated with having a second event of Multiple sclerosis within a year. 24130718_The IL7R polymorphism was associated with reduced odds of multiple sclerosis attacks involving the brainstem/cerebellum as were the TNFRSF1A and IL12A polymorphisms. 24242875_Il7 receptor SNP rs6897932 may be associated with increased systemic lupus erythematosus risk in Chinese populations. 24337176_the results indicate that the genetic variation of IL7R may be associated with inflammatory demyelinating diseases such as Multiple sclerosis (MS) and neuromyelitis optica (NMO) in the population studied. 24348676_CD127 expression is differentially modulated on CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells in the course of T1D. 24465587_CD8 positive T lymphocytes expressing CD127 exhibit increased distribution frequency and distinct functional characteristics that correlate with clinicopathological status in oral neoplasms. 24572742_The IL2RA and IL7RA variants had univariate association in MS and T1D, whereas the MGAT1 and CTLA-4 variants associated with only MS or T1D, respectively. 24678068_Our analysis revealed that none of these 35 samples carried an IL7R mutation in exon 6. Whether differences in the genetic makeup of adult and childhood T-ALL explain the differential response to therapy remains to be determined 24695377_These results strongly suggest that IL-7/IL-7R prevents apoptosis by upregulating the expression of bcl-2 and by downregulating the expression of bax 24708420_Newborns have a higher proportion of circulating thymically derived Helios(+) Treg cells than adults and that S. aureus possess an ability to convert neonatal conventional CD4(+) T cells into FOXP3(+) CD25(+) CD127(low) Treg cells via the PD-1/PD-L1 axis. 24723426_data suggest that lnc-IL7R contributes another layer of complexity in regulation of the inflammatory response 24759676_Early Omenn syndrome can be observed in patients with IL7R mutations, and autoimmune cytopenias could also complicate the clinical course of SCID babies with this type of defect. 24787007_we report noncysteine in-frame mutations in IL7R and CRLF2 located in a region of the transmembrane domain closer to the cytosolic domain in acute lymphoblastic leukemias 24820104_Low-level transient antigenic stimuli during cART were not associated with changes in the thymic function or the IL-7/CD127 system. 24946690_Measurement of the sIL-7R/IL-7 axis will help in guided immune monitoring after HSCT and guided interference with sIL-7R may be explored in GVHD management. 25007250_Sustained virological response correlates with higher expression of CD127, lower T cell exhaustion status and better HIV and HCV proliferative responses at baseline. 25033393_This study then provides evidence that soluble factor(s) are responsible for low CD127 expression on circulating CD8 T-cells in HIV+ individuals and further implicates Tat in suppressing this receptor essential to CD8 T-cell proliferation and function. 25231631_CD127(hi) effluxer CD8(+) T cells represent a novel population of early memory T cells resident in BM with properties required for long-lived memory 25333710_In view of the important role IL-7 plays in lymphocyte proliferation, homeostasis and survival, down regulation of CD127 by Tat likely plays a central role in immune dysregulation and CD4 T-cell decline 25352021_the influence of IL-7 receptor alpha-chain (IL-7Ralpha) gene haplotypes in donors on the outcome of haematopoietic cell transplantation, was investigated. 25366767_Data indicate that individuals carrying the interleukin-7 receptor A/A genotype were more susceptible to diarrhea. 25421942_rs6897932 allele of interleukin-7 receptor alpha is not associated with general inflammation, and reported associations between T-allele in rs6897932 with several autoimmune diseases may be mediated through effects on restricted part of the immune system 25539460_CD4+CD45RO+CD25-/lowCD127+: CD4+CD45RO+CD25hiCD127-/low ratio in peripheral blood indicates heart transplant recipients at risk for cardiac allograft vasculopathy. 25769928_The present study highlights perturbed IL-7/IL-7R T cell signaling through STAT5 as a potential mechanism of T cell exhaustion in chronic T. cruzi infection. 25903732_This study demonstrated that rs6897932 in IL7Ra gene is associated with the progression of multiple sclerosis in Central European Slovak population. 25986373_Substitution of the first 10 Nterminal residues or deletion of residues 17-21 prevented Tat from interacting with and down regulating CD127 from the cell surface. 26100671_Findings indicate that IL7 receptor (IL7R) and c-myc expression as intrinsic biomarkers that can predict the fate of CD8+ T effector cells after adoptive transfer. 26123418_A girl with severe combined immunodeficiency was a compound heterozygote for 2 new frameshift mutations, c.589_598del10 p.P197fsX44 and c.993delA p.Q331fsX2. Each parent carried one of these. 26272555_this study shows that in human CD8 T cells that IL-7 binding to its receptor induces CD127 internalization via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, transport of the receptor from early to late endosomes and ultimately degradation of CD127 by the proteasome. 26333292_A decrease of CD4(+) CD25(+) CD127(low) FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells with impaired suppressive function had been found in untreated ulcerative colitis patients. 26408663_cooperation between IL-7R and alpha2beta1 integrin can represent an important pathogenic pathway in Th17-osteoclast function associated with inflammatory diseases 26425877_Pretransplant recipient circulating CD4+CD127lo/-TNFR2+ Treg cell is potentially a simpler alternative to Treg cell function as a pretransplant recipient immune marker for acute kidney injury. 26499378_Data suggest that the lack of IL-7 receptor alpha chain (IL7Ralpha) expression, associated with hypermethylation of the IL7R promoter, in T cells restricts T-cell development in Schimke immuno-osseous dysplasia (SIOD) patients. 26608987_the variant of IL-7RA (rs6897932) was associated with NMO especially NMO-IgG positive patients while the variant of IL-7 (rs1520333) with MS patients. 26852660_Immunophenotyping with CD135 and CD117 predicts the FLT3, IL-7R and TLX3 gene mutations in childhood T-cell acute leukemia. 26974155_results suggest that LNK suppresses IL-7R/JAK/STAT signaling to restrict pro-/pre-B progenitor expansion and leukemia development, providing a pathogenic mechanism and a potential therapeutic approach for B-ALLs with LNK mutations. 26999524_IL7Ralpha level was higher in asthmatic than in nonasthmatic children. 27105585_CD127 is a useful surface marker to isolate donor-antigen-specific-Tregs in operational tolerance after liver transplantation 27188999_This study suggested that the IL7R C allele was associated with an increased risk of MS and larger-scale studies of populations are needed to explore the roles played by the IL7R T244I polymorphism during the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. 27268088_The interleukin-7 receptor alpha (IL-7Ralpha) signaling pathways are prime therapeutic targets because these pathways harbor genetic aberrations in both T-cell ALL and B-cell precursor ALL. Therapeutic targeting of the IL-7Ralpha signaling pathways may lead to improved outcomes in a subset of patients. 27315061_Therefore, generalized CD8+ T-cell impairment in HCV infection is characterized, in part, by impaired IL-7-mediated signalling and survival, independent of CD127 expression. This impairment is more pronounced in the liver and may be associated with an increased potential for apoptosis. This generalized CD8+ T-cell impairment represents an important immune dysfunction in chronic HCV infection that may alter patient health. 27322554_indicate that IL7RhighSH2B3low expression distinguishes a novel subset of high-risk B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia associated with Ikaros dysfunction 27325567_These studies provide in vivo evidence that IL-7Ralpha signals positively regulate normal human B-cell production and proliferation beyond the fetal period and suggest that TSLP can replace IL-7 in providing these signals. 27456877_ | ENSMUSG00000003882 | Il7r | 258.376311 | 1.3813012 | 0.466027923 | 0.09863173 | 22.34235133242 | 0.0000022811979476699989679698999528456582197577517945319414138793945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00003533709511850271182834340444323117935709888115525245666503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 295.127693 | 15.944502 | 214.727433 | 12.108807 | |
| ENSG00000168781 | 9677 | PPIP5K1 | protein_coding | Q6PFW1 | FUNCTION: Bifunctional inositol kinase that acts in concert with the IP6K kinases IP6K1, IP6K2 and IP6K3 to synthesize the diphosphate group-containing inositol pyrophosphates diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate, PP-InsP5, and bis-diphosphoinositol tetrakisphosphate, (PP)2-InsP4. PP-InsP5 and (PP)2-InsP4, also respectively called InsP7 and InsP8, regulate a variety of cellular processes, including apoptosis, vesicle trafficking, cytoskeletal dynamics, exocytosis, insulin signaling and neutrophil activation. Phosphorylates inositol hexakisphosphate (InsP6) at position 1 to produce PP-InsP5 which is in turn phosphorylated by IP6Ks to produce (PP)2-InsP4. Alternatively, phosphorylates PP-InsP5 at position 1, produced by IP6Ks from InsP6, to produce (PP)2-InsP4. Activated when cells are exposed to hyperosmotic stress. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17690096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17702752}. | Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase | This gene encodes a dual functional inositol kinase. The encoded enzyme converts inositol hexakisphosphate to diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate and diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate to bis-diphosphoinositol tetrakisphosphate. This protein may be important for intracellular signaling pathways. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome 15.[provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. | hsa:9677; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; diphosphoinositol-pentakisphosphate kinase activity [GO:0033857]; inositol heptakisphosphate kinase activity [GO:0000829]; inositol hexakisphosphate 1-kinase activity [GO:0052723]; inositol hexakisphosphate 3-kinase activity [GO:0052724]; inositol hexakisphosphate 5-kinase activity [GO:0000832]; inositol hexakisphosphate kinase activity [GO:0000828]; inositol-1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate kinase activity [GO:0000827]; inositol metabolic process [GO:0006020]; inositol phosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0032958]; inositol phosphate metabolic process [GO:0043647]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310] | 21222653_Upon activation of the appropriate cell-surface receptors to stimulate PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 synthesis, human PPIP5K1 translocates from the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. 26854614_results suggest that PPIP5K1 might play an important role in regulating function of exocyst complex in establishing cellular polarity and directional migration of cells 27776974_PPIP5K is a rare example of a single protein that catalyzes a kinase/phosphatase futile cycle. (Review) 28126903_This study characterized kinetic properties of the bifunctional inositol pyrophosphate 5-diphosphoinositol 1,2,3,4,6-pentakisphosphatekinase/inositol pyrophosphate, 1,5-bisdiphosphoinositol 2,3,4,6-tetrakisphosphate phosphatase activities of full-length diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate kinase 1 and 2. | ENSMUSG00000033526 | Ppip5k1 | 187.912205 | 0.9176676 | -0.123956416 | 0.13398302 | 0.85474231334 | 0.3552142128607292392850069973064819350838661193847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.58787700065024617313014232422574423253536224365234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 155.925653 | 37.667734 | 170.864866 | 41.180927 | |
| ENSG00000168876 | 54851 | ANKRD49 | protein_coding | Q8WVL7 | FUNCTION: Induces HBG1 expression (PubMed:16131492, PubMed:11162141). May have a role in spermatogenesis where it promotes autophagy in response to serum starvation, via the NF-kappaB pathway (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VE42, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11162141, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16131492}. | ANK repeat;Differentiation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Spermatogenesis | Involved in positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Predicted to be located in nucleus. Predicted to be active in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:54851; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] | 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 28694302_The research findings implicate that ANKRD49 promotes the proliferation of human malignant glioma cells. 29865034_The results of the present study highlighted an important role of the ANKRD49 protein in the progression of gastric cancer. The ANKRD49 protein could act as a potential biomarker for prognosis evaluation of gastric cancer and may be used as a molecular target for gastric cancer treatment. 30798416_these results suggest that ANKRD49 plays an important role in reducing intrinsic apoptosis of GC-1 cells by modulating the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. | ENSMUSG00000031931 | Ankrd49 | 99.395510 | 0.8777098 | -0.188184062 | 0.19320793 | 0.94775918495 | 0.3302903340978263768690226243052165955305099487304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.56307370288896430032821172062540426850318908691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 96.160610 | 11.983089 | 110.000090 | 13.620580 | |
| ENSG00000169019 | 54951 | COMMD8 | protein_coding | Q9NX08 | FUNCTION: May modulate activity of cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase (CRL) complexes (PubMed:21778237). May down-regulate activation of NF-kappa-B (PubMed:15799966). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15799966, ECO:0000305|PubMed:21778237}. | Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation | The protein encoded by this gene binds coiled-coil domain-containing protein 22 (CCDC22), and this complex can regulate the turnover of I-kappa-B and the activation of NF-kappa-B. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. | hsa:54951; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 30982576_MNX1-AS1 promoted COMMD8 expression through sponging miR-218-5p. MNX1-AS1 promoted hepatocellular carcinoma progression through activating COMMD8. 31088898_complex determines GRK6 specificity for chemoattractant receptors 31566716_Long noncoding RNA LINC00657 induced by SP1 contributes to the non-small cell lung cancer progression through targeting miR-26b-5p/COMMD8 axis. | ENSMUSG00000029213 | Commd8 | 168.397283 | 1.2927624 | 0.370457188 | 0.14289736 | 6.71868225067 | 0.0095408095231461244323245551868239999748766422271728515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.04766315843205999602805178483322379179298877716064453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 190.816823 | 15.967087 | 148.277259 | 12.670229 | |
| ENSG00000169032 | 5604 | MAP2K1 | protein_coding | Q02750 | FUNCTION: Dual specificity protein kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. Binding of extracellular ligands such as growth factors, cytokines and hormones to their cell-surface receptors activates RAS and this initiates RAF1 activation. RAF1 then further activates the dual-specificity protein kinases MAP2K1/MEK1 and MAP2K2/MEK2. Both MAP2K1/MEK1 and MAP2K2/MEK2 function specifically in the MAPK/ERK cascade, and catalyze the concomitant phosphorylation of a threonine and a tyrosine residue in a Thr-Glu-Tyr sequence located in the extracellular signal-regulated kinases MAPK3/ERK1 and MAPK1/ERK2, leading to their activation and further transduction of the signal within the MAPK/ERK cascade. Activates BRAF in a KSR1 or KSR2-dependent manner; by binding to KSR1 or KSR2 releases the inhibitory intramolecular interaction between KSR1 or KSR2 protein kinase and N-terminal domains which promotes KSR1 or KSR2-BRAF dimerization and BRAF activation (PubMed:29433126). Depending on the cellular context, this pathway mediates diverse biological functions such as cell growth, adhesion, survival and differentiation, predominantly through the regulation of transcription, metabolism and cytoskeletal rearrangements. One target of the MAPK/ERK cascade is peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG), a nuclear receptor that promotes differentiation and apoptosis. MAP2K1/MEK1 has been shown to export PPARG from the nucleus. The MAPK/ERK cascade is also involved in the regulation of endosomal dynamics, including lysosome processing and endosome cycling through the perinuclear recycling compartment (PNRC), as well as in the fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14737111, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17101779, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29433126}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cardiomyopathy;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Ectodermal dysplasia;Intellectual disability;Kinase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Tyrosine-protein kinase | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the dual specificity protein kinase family, which acts as a mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase. MAP kinases, also known as extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals. This protein kinase lies upstream of MAP kinases and stimulates the enzymatic activity of MAP kinases upon wide variety of extra- and intracellular signals. As an essential component of MAP kinase signal transduction pathway, this kinase is involved in many cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:5604; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; MAP kinase kinase activity [GO:0004708]; MAP-kinase scaffold activity [GO:0005078]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; protein kinase activator activity [GO:0030295]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity [GO:0043539]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004712]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; Bergmann glial cell differentiation [GO:0060020]; cell motility [GO:0048870]; cellular senescence [GO:0090398]; cerebellar cortex formation [GO:0021697]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; endodermal cell differentiation [GO:0035987]; epithelial cell proliferation involved in lung morphogenesis [GO:0060502]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; face development [GO:0060324]; heart development [GO:0007507]; insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048009]; keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0030216]; labyrinthine layer development [GO:0060711]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; placenta blood vessel development [GO:0060674]; positive regulation of axonogenesis [GO:0050772]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of endodermal cell differentiation [GO:1903226]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071902]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of axon regeneration [GO:0048679]; regulation of early endosome to late endosome transport [GO:2000641]; regulation of Golgi inheritance [GO:0090170]; regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade [GO:0032872]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; thymus development [GO:0048538]; thyroid gland development [GO:0030878]; trachea formation [GO:0060440]; type B pancreatic cell proliferation [GO:0044342] | 8621729_A-Raf interacts with MEK1 and activates MEK1 by phosphorylation. 8621729_MEK1 interacts with B-Raf. 8621729_c-Raf interacts with MEK1 and activates MEK1 by phosphorylation. 11134045_MEK1 interacts with ERK1. This interaction is mediated via a conserved N-terminal docking site in MEK1. 11134045_MEK1 interacts with and phosphorylates ERK2. This interaction is mediated via a conserved N-terminal docking site in MEK1. Note that this interaction was demonstrated using rat ERK2. 11891225_Laminin-10/11 and fibronectin differentially prevent apoptosis induced by serum removal via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt- and MEK1/ERK-dependent pathways (Laminin 10; separate entry for Laminin 11). 11948406_PAK1 primes MEK1 for phosphorylation by Raf-1 kinase during cross-cascade activation of the ERK pathway 12032872_MEK1 activity ad dual-phosphorylation were undetectable in expanding and self-renewing hematopoietic progenitors (HP). Adding IL-3, inducing maturation and cell death in HP, led to sustained high levels of MEK1 activity and dual-phosphorylation. 12063167_Activation of a Src-dependent Raf-MEK1/2-ERK signaling pathway is required for IL-1alpha-induced upregulation of beta-defensin 2 in human middle ear epithelial cells. 12370306_MEK1 has an activation domain that forms a hydrophobic binding pocket for enzyme inhibitor PD184352 12456688_Ubiquitylation of MEKK1 inhibits its phosphorylation of MKK1 and MKK4 and activation of the ERK1/2 and JNK pathways 12522135_the NH(2)-terminal end of MEK is important not only for substrate interaction but also for catalytic activity 12531514_Data show that p-MEK1/2 and p-ERK1/2 are present in neurons in the initial stages of neurofibrillary degeneration in Alzheimer's disease, before deposition of beta-amyloid. 12609978_the dramatic activation of an endomembrane-associated MEK1 without the corresponding activation of the MEK substrate ERK during normal G(2)/M 12612059_Inhibition of either phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K) or Mek1/2 signaling pathways completely abrogated the IGF-I-induced increase in VEGF secretion and promoter activity 12663662_serum stimulation of fibroblasts in floating matrices does not result in ERK translocation to the nucleus. In addition, there was decreased serum activation of upstream members of the ERK signaling pathway, MEK and Raf 12682854_The 1,25(OH)(2)D3-responsive element in cystatin A gene is identical to TRE, T2 (-272 to -278). Suppression of Raf-1/MEK1/ERK1,2 signaling pathway increases cystatin A expression of normal human keratinocytes. 12689928_Inhibition of the upstream MAPK kinase inhibited the phosphorylation of ERK; modulated the levels of Bcl-2, Mcl-1, and cFLIP; and induced G2M cell-cycle arrest or apoptosis 12807433_Distribution of total MEK1 between Alzheimer disease[AD] and age-matched control cases was similar but increased levels of activated phospho-MEK1 were specifically localized to neuronal intracytoplasmic granular structures in severe AD 12839928_results show that p38-mediated dephosphorylation of MEK1,2 mediates initiation of apoptosis 12917419_constituitively activated in choroidal melanoma cell lines, independent of Ras, and regulated by B-RafV599E 14581471_RhoA binds to the amino terminus of MEKK1 and regulates its kinase activity. 14656894_MEK1,2 response element that mediates angiotensin II-stimulated PAI-1 promoter activation and shows that activation of this element requires Sp1 and AP-1 co-activation. 14672918_Stress-related signaling pathways in epithelial cells are modulated by hypoxia and confer protection from reoxygenation, since hypoxia and chemical inhibition of p38mapk and MEK1/2 similarly increase cytolysis resulting from O2-. 15020233_Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta is tyrosine-phosphorylated by mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 in fibroblasts. 15021912_Plk3 may be a key protein kinase mediating MEK1 function in the Golgi fragmentation pathway during cell division. 15069060_in non-transformed human colonocytes, MEK activation following flagellin/TLR5 engagement is a key modulator for NFkappaB-independent, IL-8 and MIP3alpha expression. 15284233_Has distinct ways to contribute to a regulated ERK activity and cell cycle progression. 15292274_Molecular cross-talk between MEK1/2 and mTOR signaling during recovery of 293 cells from hypertonic stress. 15297310_Detailed pathway analysis revealed that BM stromal cells stimulate STAT3 via the IL-6R, and MEK1/ERK1 pathways, via IL-6R-independent mechanisms 15538402_Arsenic trioxide and inhibitors of this enzyme my be combined as anticancer agents for acute promyelocytic leukemia. 15543157_X-ray structures of human MEK1 and MEK2, each determined as a ternary complex with MgATP and an inhibitor to a resolution of 2.4 A and 3.2 A, respectively 15557124_Integrin alphav controls melanoma cell survival in 3D-collagen through a pathway involving p53 regulation of MEK1 signaling. 15572374_MEK1 facilitates ligand-initiated transcriptional activation while targeting the Ah receptor for degradation 15615716_Blockade of MEK1 by PD98059 suppresses c-Fos and Fra-1 expression and, thus, affects two counteractive signals for IL-8 mRNA. 15657353_Selesctive inhibitors potentiate apoptosis induction by sulindac sulfide, an NSAID, suggesting a novel strategy for the prevention or treatment of colorectal cancer. 15657590_The induction of the raf-1/MEK1 pathway blocks IGF-1-mediated intracellular neuroendocrine hormone regulation. This pathway may be a therapeutic target in gastrointestinal carcinoid tumor therapy. 15665520_whereas MAPKK-1 signaling is required for VEGF synthesis only and PI3K activation activity was lowered in hypoxia. 15757891_RAS-MEK-ERK1/2 signaling pathway can sensitize cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by up-regulating DR4 and DR5 15888452_Cdc2 inhibits growth factor receptor-mediated ERK activation during mitosis by primarily targeting signaling proteins that are upstream of MEK1 15979847_The ability of constitutively-active human MEK1 to stimulate ERK phosphorylation and to induce the neoplastic transformation of NIH 3T3 cells required the integrity of the D-site was found. 16086581_results suggest that activated JNK can, in turn, activate not only jun but also raf that, in turn, activates MEK that can then cross-activate JNK in a positive feedback loop 16239230_PP2A ABalphaC and ABdeltaC holoenzymes function as positive regulators of Raf1-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 signaling by targeting Raf1 16439621_findings demonstrate that heterogeneous de novo missense mutations in three genes within the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, BRAF, MEK1 and MEK2 cause cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome 16820947_Results describe the roles of MEK1/ERK and AKT/PKB pathways on the effects of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and M-CSF on tumor progression of lung cancer. 16861903_REVIEW. surprises yielded by the analysis of the role of B-Raf and Raf-1 and of their downstream effectors using conditional knockouts 16957420_Taxotere and MEK1/2 inhibitors have the potential to suppress mammary tumor growth in vivo. 17038630_Inhibition of overactive ras-MEK-ERK pathway in HepG2 cells can correct the defect in VLDL assembly leading to the secretion of VLDL-sized particles, similar to primary hepatocytes, implicating the MEK-ERK cascade in VLDL assembly in the HepG2 model. 17054908_Our data suggest that overexpression of TNFalpha leads to topical GC insensitivity by reducing GR nuclear translocation in keratinocytes. 17101779_MEK1 exports PPARgamma from the nucleus, and this finding was supported by small interfering RNA knockdown of MEK1 and use of a cell-permeable interaction-blocking peptide, which prevented tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate-induced export of PPARgamma. 17182854_MEK1 plays an in vivo role in Golgi reorganization, which regulates cell cycle progression. 17197157_Further studies confirm that promoter activity correlates with protein expression by demonstrating reduced SMAD3 protein expression in A549 cells and airway smooth muscle cells after treatment with MEK1 inhibitors. 17260965_allosteric inhibitors have a dynamic range in the type of MEK1 activation states and nucleotide complexes that they can bind. 17366577_mutational analysis of KRAS, BRAF, and MAP2K1/2 in 56 patients with CFC syndrome; comparison of the genotype-phenotype correlation of CFC with that of Costello syndrome suggest a significant clinical overlap but not genotype overlap. 17419998_Mek1/2 are functionally redundant in the epidermis, where they act as a linear relay in the MAPK pathway to mediate development and homeostasis. 17461449_These results indicated that the activation of CXCR4 and its signaling pathways (MEK1/2 and Akt) are essential for CXCL12-induced cholangiocarcinoma cell invasion. 17490600_analysis of the ATPase activity of phospho-MEK-1 uncoupled from downstream ERK phosphorylation 17667937_WNK2 is involved in the modulation of growth factor-induced cancer cell proliferation through the MEK1/ERK1/2 pathway. 17704260_3 novel mutations for MEK1 (E44G, T55P, D67N) were found in cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome. A novel mutation in exon 2 was found in Noonan syndrome. 17951252_modulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/GSK3beta signaling cascades can be beneficial for protecting or facilitating recovery from cellular LeTx intoxication in cells that depend on basal MEK1 activity for proliferation. 17981815_study reports data concerning the biochemical functions of novel MEK1 and MEK2 mutants found in patients with cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome, as well as the roles of these genes in the MAPK signaling cascade 18042262_the results of HRAS, BRAF and MAP2K1/2 mutation screening in a large cohort of patients with CS and CFC 18060073_BRAF and MEK1/2 mutations may be more common than anticipated in ovarian cancer which could have important implications for treatment of patients with this disease and suggests potential new therapeutic avenues 18192500_Has a role in epithelial cell proliferation and lung remodeling after toxic injury. 18390968_Phase I trial of MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 in tumor patients. 18413255_study describes the biochemical characterization of novel BRAF and MEK germline mutations in cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome 18424438_the induction of inflammatory genes by farnesol is mediated by the activation of the NF-kappaB pathway and involves MEK1/2-ERK1/2-MSK1-dependent phosphorylation of p65/RelA(Ser(276)) 18434598_MEK1/ERK regulation of GRASP55-mediated Golgi linking is a control point in cell cycle progression 18533112_MEK1 is the critical isoform regulating tumor cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. 18593598_WNK2 controls a RhoA-mediated cross-talk mechanism that regulates the efficiency with which MEK1 can activate ERK1/2 upon growth factor stimulation. 18617556_Esophageal cells from GERD patients with Barrett's esophagus have elevated MEK1 phosphorylation and decreased MEK1/MEK2 activity. 18632602_analysis of the MEK1 mutation in lung adenocarcinoma 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19001375_the molecular interactions of arrestin2 and arrestin3 and their individual domains with the components of the two MAPK cascades, ASK1-MKK4-JNK3 and c-Raf-1-MEK1-ERK2 19014680_MEK1 & MEK2 isoforms have similar transforming properties & are able to induce formation of metastatic intestinal tumors in mice; results suggest MEK2 plays a more important role than MEK1 in sustaining proliferation of human colorectal cancer cells 19133693_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19153083_MEK1 binds directly to betaarrestin1, influencing both its phosphorylation by ERK and the timing of its isoprenaline-stimulated internalization 19156172_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19156172_Spectrum of MEK1 gene mutations in cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome and genotype-phenotype correlations 19164283_MEK1/2 phosphorylates ERK1/2, which phosphorylates Sp1 and AP-1 that in turn bind to their respective binding sites to regulate the expression of human VIL2 in ESCC cells. 19206169_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19261809_TNF-alpha abrogated TGFbeta1-induced SMalphaA gene expression at the level of transcription without disrupting phosphorylation of regulatory Smads. 19342664_activation of MEK1 selectively down-regulates human rhinovirus-induced expression of CXCL10 via modulation of IFN regulatory factor-1 interactions with the gene promoter in human airway epithelial cells 19411838_One MAP kinase kinase 1 mutation is found in 1 of 37 melanoma tumor samples and another MEK1 mutation in 1 of 45 colon cancer samples. 19447520_SGK1 expression during liver regeneration is a part of a signaling pathway that is necessary for enhancing ERK signaling activation through modulating the MEK/ERK complex formation. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19500021_Different mutations in the MAPK pathway play distinct roles in the growth and invasion of thyroid cancer cells 19567590_Data provide a basis for rational combination of MEK and PI3K inhibitors in basal-like cancers with both intact and deleted PTEN. 19625741_Meaasurement of ERK 1/2 in csf from patients iwht neuropsychiatric disorders and evidence for the presence of the activated form. 19681119_Investigated the prevalence of PTPN11, HRAS, KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, MEK1, and MEK2 mutations in a relatively large cohort of primary embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) tumors. No mutation was observed in BRAF and MEK genes. 19802003_Data show that in hypoxic conditions or coexpressed with a constitutively active form of HIF-1alpha, c-Kit mutants activate the Ras/Raf/Mek/Erk pathway, stimulate proliferation and transform melanocytes. 19816936_Data show that oncogenic level of ERK1/2 phosphorylation appears to be MEK1 and MEK2 dependent in basal condition. 19835659_In suicide brain, the interaction of MEK1 with ERK1 and ERK2 is increased along with decreased phosphorylation and catalytic activity of ERK1/2. 19858308_This study demonstrated that H. pylori LPS may be a pathogenic factor causing gastric tumors by enhancing cell proliferation and inflammation via the MAPK cascade in gastric epithelial cells. 20007706_Data show that the FGF2-induced ERK MAP kinase strongly increased the Runx2 protein level through an increase in acetylation and a decrease in ubiquitination. 20056645_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20172001_These results demonstrate that MEK1 and MEK2 act differently and that herpes simplex virus type 2 hijacks host MEK1 for its own amplification. 20179161_Pin1 plays an important role in the overexpression of HER-2 through Pin1-MEK1-activator protein-2alpha signaling in breast cancer. 20299489_results show that PMA activates the MEK-ERK pathway and strongly induces miRNA-34a expression, which in turn inhibits cell proliferation by repressing the expression of MEK1 20302979_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20354455_MEK1 mutations exclusive with EGFR, K-ras, and B-raf mutations at kinase domain is associated with lung cancer. 20354455_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20512084_SH3GL2 participates in the regulation of apoptosis through the MEK-ERK signal pathway by adjusting EGFR in the laryngeal carcinoma cell line Hep2 20610816_The C-terminal ILLHPWF motif that is well conserved among Trib family proteins is required for MEK1 binding, enhancement of ERK phosphorylation, enhanced self-renewal activity of bone marrow cells and leukemogenic activity by Trib1. 20676060_Here, the authors show that an MEK-cofilin signalling module has an important function for the migration of human T cells in 3D environments. 20885957_Apoptosis induction by MEK1/2 inhibition in human lung cancer cells is mediated by Bim. 20926789_We have uncovered an IL-2- and IL-4-driven MEK1 induction mechanism that results in heightened ERK1/2 activation in asthmatic T cells 20956560_Nek10 physically associated with Raf-1 and MEK1 in a Raf-1-dependent manner, and the formation of this complex was necessary for Nek10-mediated MEK1 activation. 21131601_Data suggest a novel mechanism for MEK1 in regulating the sensitivity to TGF-beta signaling by stabilizing TbetaRII. 21179471_decreased mir-424 expression and increased levels of MEK1 or cyclin E1 in senile hemangioma may cause abnormal cell proliferation in the tumor 21336309_oncogenic Ras efficiently activates the ERK pathway both by activating Raf and by inhibiting MEK SUMOylation, thereby inducing carcinogenesis 21383288_Thus, MEK1(C121S) or functionally similar mutations are predicted to confer drug resistance of neoplasms to combined MEK/RAF inhibition. 21447798_Amplification of the driving oncogene, KRAS or BRAF, underpins acquired resistance to MEK1/2 inhibitors in colorectal cancer cells. 21458501_Data show that mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases direct mitochondrial biogenesis by selectively inducing PGC-1beta expression. 21621846_These results suggest the regulatory role of MEK in TIM-3 transcription by human CD4+ T cells and mast cells 21705440_In an isogenic cell system that extended these findings into other cancer cell lines, the MEK1(F129L) mutant exhibited higher intrinsic kinase activity than wild-type MEK1 [MEK1(WT)], leading to potent activation of ERK and downstream targets 21707777_These findings suggest that the upregulation of PGRN via the p38MAPK and MEK1/2 signaling pathway in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells may contribute to the carcinogenic process. 21713404_TGF-beta1 undergo a switch into mesenchymal cells and PI3K/Akt and MAPK/Erk1/2 signaling pathways serve to regulate TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of A549 cells. 21835307_The BRAF/MEK/ERK pathway is upregulated in progressive retinal arterial macroaneurysm patients, caused by mutation in IGFBP7. 21965271_conclude that graded increases in the MEK1 signaling module are correlated with M1-MMP expression, renal epithelial cell tumor phenotype, invasive activity and nuclear grade 22037177_the activation of PI3K and MEK pathways is not the only mechanism of EGFR-resistance 22052387_LPS increased IL-8 and IL-6 and decreased EVT invasion through activation of MEK1/2 MAPK signaling 22180573_Our data suggest that the miR-1826 plays an important role as a tumor suppressor by downregulating beta-catenin and MEK1 in von Hippel-Lindau-inactivated renal cancers. 22188669_These results indicate that activation of MAPK may play a significant role in aberrant expression of miRNAs and their associated phenotypes in pancreatic cancer. 22197931_Screening a cohort of individuals with melanoma revealed the presence of recurring somatic MAP2K1 and MAP2K2 mutations, which occurred at an overall frequency of 8%. 22241220_The induction of CDK1, cyclin B1 mRNA and protein were shown to be dependent on the activation of MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling. 22298595_Findings indicate that Ras-induced nuclear accumulation of activated MEK1/2 was reliant on downregulation of the spatial regulator Sef. 22327936_A total of six (3.5%) activating mutations in MAP2K1 were thus identified among 172 of specimens or cell lines for human epithelial tumors. 22357202_Inhibition of extracellular signal regulated kinase 1/2 and c-jun N-terminal kinases increases, but that inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase decreases M. tuberculosis-induced CD44 surface expression in THP-1 human monocytes. 22495818_These data indicate that MED28 regulates cellular migration in a MEK1-dependent manner in human breast cancer cells, reinforcing the important cellular roles of MED28. 22546605_These results suggest that EGF is secreted from A549 cells by MMP and increases claudin-2 expression mediated via the activation of an EGFR/MEK/ERK pathway. 22588879_Activating MEK1 exon 3 mutations identified herein and concurrent with V600E/KBRAF do not cause BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma. 22707717_observed that, although MEK1 negatively regulates TLR2 signaling in EC, MEK1 promotes TLR2 signaling in monocytes 22752157_VRK2A can form a high molecular size complex with both MEK1 and KSR1; the KSR1 complex assembled and retained by VRK2A in the endoplasmic reticulum can have a modulatory effect on the signal mediated by MAPK,locally affecting the magnitude of its responses 22773810_Lung cancers with acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors occasionally harbor BRAF gene mutations but lack mutations in KRAS, NRAS, or MEK1. 22791812_a Ras-Raf-MEK1, but not MEK2, signaling cascade is necessary and sufficient for Erk2 nuclear localization that works in concert with TGF-beta to promote EMT. 22805291_Define the maximum tolerated dose and recommended phase 2 dose of MEK1/2 inhibitor trametinib and to assess its safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and response rate in individuals with advanced solid tumours. 22805292_Data show substantial clinical activity of MEK1/2 inhibitor trametinib in melanoma and suggest that MEK is a valid therapeutic target. 22833572_C-MYC as a key driver of cell proliferation downstream of RAF-->MEK1/2-->ERK signaling. 22902540_IL1beta treatment reduces SHBG production in HepG2 cells by the down-regulation of HNF-4A via the MAPK kinase (MEK)-1/2 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) MAPK signaling pathways. 22935974_osteosarcoma patients whose tumors expressed pMEK1 had a poorer clinical outcome than those whose tumors did not. 22946047_integrin-triggered, RIAM-dependent MEK activation represents a key feedback event required for efficient focal adhesion disassembly. 22946697_Data indicate that of the 32 cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome (CFC) patients, 28 (88%) had a known mutation in a gene that is causative for CFC, including BRAF (n = 21), MEK1 (n = 2), MEK2 (n = 4), and KRAS (n = 1). 23001481_These data show that the MAPK-ERK pathway plays an important role in the regulation of hepatitis C virus gene expression and replication. 23157514_DiRas3 interacts with C-RAF and downregulates MEK1 activity to restrict cell migration. 23225884_A novel nuclear function of MEK1 triggers a complex pattern of early T cell activation, followed by a late inhibition through its interaction with silencing mediator of retinoid and thyroid hormone receptor (SMRT). 23237773_JTP-74057 is a novel MEK1/2 inhibitor able to sustain MEK in an unphosphorylated form resulting in pronounced suppression of the downstream signaling pathways involved in cellular proliferation. 23241949_Myt1 is inactivated by MEK1 mediated phosphorylation to fragment the Golgi complex in G2 and for the entry of cells into mitosis. 23360980_The ability of MEK to activate C-Raf was only partially dependent on MEK kinase activity but required MEK binding to C-Raf, suggesting that the binding results in a conformational change that increases C-Raf susceptibility to phosphorylation 23423222_Gene expression changes due to neurofibromin modulation but independent of NRAS and MEK1/2 regulation in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor cells indicated bone morphogenetic protein 2 (Bmp2) signaling as a key pathway. 23524336_MEK1 is a novel outcome for signalling through the canonical MAPK pathway that is a naturally occurring,pathway regulated dominant negative to block signalling to ERK-p90RSK 23684925_Report a synthetic lethal interaction between PI3K/mTOR and MEK inhibitors in rhabdomyosarcoma. 23698055_Substituted 3-benzylcoumarins as allosteric MEK1 inhibitors: design, synthesis and biological evaluation as antiviral agents. 23698777_Data show that hepatitis C virus NS5A-transactivated protein 9 (NS5ATP9) knockdown activated mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/extracellular signal regulated kinases 1/2 signaling under C virus nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) expression. 23727904_genetic association study in Han population in China: Data suggest that SNPs in MEK1 (rs28730804) and in RSK3 (rs2229712) demonstrate gene-gene interaction that affects antidepressant drug outcome in female patients with major depressive disorder. 23746211_Authors demonstrate that HIV-1 Nef expression mediates phosphorylation of Mek1 on serine298 and Pak2 on serine192/197 in T cell lines as well as primary human T cells. 23852369_inhibition of MEK partially inhibited MTOR in a cell-type-dependent manner 23923067_activation of RAF1-MEK1-ERK/AKT axis may determine the resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cell lines bearing wild type EGFR to erlotinib 24011934_Data indicate that dual targeted inhibitors of PI3K/mTOR in combination with inhibitors of RAS/ERK signalling as a potentially effective approach to treating ovarian cancer. 24091658_Phosphorylated-FAKSer732 was barely detectable during interphase while its levels strongly increased in mitotic cells upon activation of the EGFR/MEK/ERK/CDK5 axis in an integrin-independent manner. 24132923_Combined therapy targeting both MEK and STAT3, but not either single pathway, resulted in complete regression of selumetinib-resistant tumors 24211253_MEK1-YAP interaction is critical for liver cancer cell proliferation and maintenance of transformed phenotypes both in vitro and in vivo. 24241536_high frequency of MAP2K1 mutations in variant and IGHV4-34-expressing hairy-cell leukemias. 24419498_Studies suggest that MAP Kinase Kinase 1 (MEK1) inhibitors represent a new treatment option in BRAF and NRAS mutated melanoma. 24445144_Activated MEK1 is associated with chordoma. 24501087_our data emphasizes the importance of the translational regulation of p21 by the MEK1/2-ERK1/2-p70S6K pathway to negatively control the cell cycle progression. 24681949_Treatment of cells with sirtuin inhibitors, or siRNA knockdown of SIRT1 or SIRT2 proteins, increases MEK1 acetylation and subsequent phosphorylation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase. 24709918_Findings support the hypothesis that BDNF and MEK1 mRNA expression levels are more obviously decreased in patients with treatment-resistant depression. 24909280_Data indicate that combined PI3K inhibitor LY294002 and mitogen activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitor AZD6244 showed synergistic effect on inhibition of SKOV3/DDP cell growth by inducing apoptosis and blocking cell cycle. 24982505_This is the first report of MAP2K1 mutations in Langerhans cell histiocytosis(LCH) that occur in 50% of BRAF wild-type cases. The mutually exclusive nature of MAP2K1 and BRAF mutations implicates a critical role of oncogenic MAPK signaling in LCH. 25155755_X-ray crystallography reveals a regulatory role for BRAF in the MAPK pathway independent of its kinase activity but dependent on interaction with MEK. 25188412_Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes extravillous trophoblast cell invasion by activating MEK/ERK/MMP-2 signaling pathways via S1P/S1PR1 axis activation. 25194980_MAP2K1 missense mutations were found in 2 of 11 patients with cadiofaciocutaneous syndrome: Pro124Gln and Asp67Asn. 25202140_33% of Langerhans cell histiocytosis cases with wild-type BRAF and none with BRAFV600E harbored somatic mutations in MAP2K1 (6 in-frame deletions and 1 missense mutation) that induced extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation in vitro. 25351745_MEK1 mutations define a distinct subset of lung cancers ( approximately 1%) with potential sensitivity to MEK inhibitors. Mutations are predominantly transversions, in keeping with a strong association with smoking. 25370473_our data indicate that preexisting MEK1(P124) mutations are associated with a reduced response to BRAF inhibitor therapy and identify a subset of patients with BRAF-mutant melanoma likely to benefit from combination therapies 25408231_MEK1 is associated with carboplatin resistance and is a prognostic biomarker in epithelial ovarian cancer. 25425646_CCR7 can also promote survival of mDCs through a novel MEK1/2-ERK1/2-AMPK signaling axis. 25463315_We documented three novel mutations in the BRAF gene in cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome patients and correlated clinical findings with causative mutations in the BRAF or MEK1/MEK2 genes 25534823_Findings establish that the convergence of 2 distinct Ras effector pathways on mammalian target of rapamycin signaling maintains neurofibromatosis type 1 mouse optic glioma growth. 25541062_MEK1/2 inhibitor potentiated the anti-tumor effects of cisplatin in KRAS-dependent lung cancer cells and an animal model through inhibition of BIM degradation 25710724_Data show that licochalcone A (LicoA) suppresses solar UV-induced cyclooxygenase (COX-2) expression by acting as a potent inhibitor of enzymes PI3K, MEK1, and B-Raf. 25713071_Data indicate that cyclic AMP signaling reduces the expression of sirtuin 6 deacetylase via inhibition of the c-Raf-MEK1-ERK1/2 pathway. 25722381_MEK1/2 inhibitor trametinib showed similar PFS and a response rate as docetaxel in patients with previously treated KRAS-mutant-positive non-small cell lung carcinoma. 25729732_The MAP2K1 mutation analysis of three hairy cell leukemia cases, one hairy cell leukemia-variant case, and three splenic marginal zone lymphoma cases revealed negative results. 25899310_Langerhans cell histiocytosis cells can harbor additional genetic alterations in the RAS-RAF-MEK pathway which, in the case of MAP2K1, may be responsible for ERK activation in a wild type BRAF setting. 26034353_SGK1 inhibits intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis and promotes proliferation via the MEK/ERK/p53 pathway in colitis. 26143635_Studies indicate that concurrent inhibition of proto-oncogene protein B-raf (BRAF) and Map kinase kinase (MEK) improved the most effective therapeutic modality as compared as single BRAF or MEK inhibition for patients with metastatic melanoma (MM). 26155939_at clinically relevant concentrations, cDDP binds to and inhibits MEK1/2 and both the binding and inhibitory activity are related to its interaction with Cu bound to MEK1/2 26163823_MEK1 levels are upregulated at transcriptional level whereas MEK2 levels are downregulated at posttranslational level. 26208478_Findings suggest that triple therapy directed against BRAF/MEK/ErbB3 may be able to provide durable control of BRAF mutated metastatic melanoma. 26324360_MEK1 Mutations are associated with Low-grade Serous Ovarian Cancer. 26358373_Data show that src kinases (SRC) and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 (MEK) co-inhibition by saracatinib and PD0325901 respectively can be broadly effective in tumor growth control of a wide panel of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines. 26384399_Our data demonstrate that MEK inhibitors can inhibit breast cancer stem cells and may have clinical potential for the prevention of metastasis in certain cases in which tumors are MAPK dependent. 26426381_NOTCH1, TP53, and MAP2K1 mutations in splenic diffuse red pulp small B-cell lymphoma are associated with progressive disease. 26544513_Data show that Ba/F3 cells transformed with mutant HRAS protien indicated equal sensitivity towards Map kinase kinase (MEK) and mTOR serine-threonine kinase (mTOR) inhibition. 26625317_Data show that mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases MEK1/2 inhibitor pimasertib (MEKI) sensitized the cells to apoptosis through its ability to promote a G1 cell cycle arrest. 26825960_Specific inhibition of BRAF oncogene, MEK or p38 signaling was associated with decreases in DIO3 expression in papillary thyroid cancer cells 26858456_Endocytosis separates EGF receptors from endogenous fluorescently labeled HRas and diminishes receptor signaling to MAP kinases in endosomes. 26860843_MEK1 mutation is associated with central nervous system metastases of non-small cell lung cancer. 26967560_High MEK1 expression is associated with liver cancer. 26980021_There was no statistically significant association between BRAF or MAP2K1 mutation and anatomic site, unifocal versus multifocal presentation, or clinical outcome in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. 27098723_the purpose of this paper was to investigate MAPK downstream signalling molecules in Natural killer cell phenotypes from Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis patients. 27169363_MEK1 is constitutively and mainly phosphorylated at the Thr-292, Ser-298, Thr-386, and Thr-388 residues in vivo, and combinations of phosphorylations at these four residues produce at least six phosphorylated variants of MEK1. The phosphorylation statuses of Thr-292, Ser-298, Thr-386, and Thr-388 residues vary widely during activation and deactivation of the MAPK pathway. 27241017_Data indicate two atypical hairy ce | ENSMUSG00000004936 | Map2k1 | 943.215261 | 1.0218166 | 0.031136282 | 0.05420409 | 0.32988049414 | 0.5657294659241506318281267340353224426507949829101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.75861050571931798458535922691226005554199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 951.673336 | 35.639143 | 935.443821 | 34.788956 | |
| ENSG00000169439 | 6383 | SDC2 | protein_coding | P34741 | FUNCTION: Cell surface proteoglycan that bears heparan sulfate. Regulates dendritic arbor morphogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. | 3D-structure;Differentiation;Glycoprotein;Heparan sulfate;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Proteoglycan;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is a transmembrane (type I) heparan sulfate proteoglycan and is a member of the syndecan proteoglycan family. The syndecans mediate cell binding, cell signaling, and cytoskeletal organization and syndecan receptors are required for internalization of the HIV-1 tat protein. The syndecan-2 protein functions as an integral membrane protein and participates in cell proliferation, cell migration and cell-matrix interactions via its receptor for extracellular matrix proteins. Altered syndecan-2 expression has been detected in several different tumor types. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:6383; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048813]; regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048814] | 12036876_Identification of integrin alpha(M)beta(2) as an adhesion receptor on human peripheral blood monocytes for Cyr61 and connective tissue growth factor: immediate-early gene products expressed in atherosclerotic lesions.(integrin alpha(M)beta(2)) 12055189_role in mediating adhesion and proliferation of colon carcinoma cells 12708751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12860416_Ezrin N-terminal domain binds to the syndecan-2 cytoplasmic domain with an estimated K(D) of 0.71 microM and without the requirement of other proteins 12860968_Mechanisms for the regulation of HSPG have been studied. 14527339_Interleukin-8 binds to syndecan-2 on vascular endothelial cells. 14674716_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14674716_the HSPG T allele is a risk factor for the development of severe diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic patients 15936998_Syndecan-2 induces osteoblastic cell apoptosis through the JNK/Bax apoptotic pathway and the cytoplasmic domain of syndecan-2 is required for this action. 16253987_the transmembrane domains are sufficient for inducing dimerization and transmembrane domain-induced oligomerization is crucial for syndecan-2 and syndecan-4 functions 16440330_PKCdelta acts as a pro-survival kinase and that SYND2 inhibits the anti-apoptotic action of PKCdelta in osteoblast. 16997272_molecular complex most likely to obstruct RACK1 for functional attachment at syndecan-2, as revealed in cells transfected with oncogenic ras 17035092_HSPGs are expressed on the membrane of myeloid leukemic cell lineages. 17261577_heparanase-1 expression and heparan sulphate proteoglycan degradation are induced by estradiol in human endometrium 17457918_these data suggested that both HSPG and CD81 are important for HCV entry. 17516498_HSPG modulation of BMP signaling in myositis ossificans cells is reported. 17623663_syndecan-2 acts as a suppressor for MMP-2 activation, causing suppression of metastasis 18032547_There are pronounced tubulointerstitial HSPG alterations in primary kidney disease, which may affect the inflammatory response. 18093920_syndecan TMD homodimerization and heterodimerization can be mediated by GxxxG motifs and modulated by sequence context 18342939_This study provides evidence for the up-regulation of syndecan-2 and -4 in human primary CD4 T cells during in vitro activation and suggest an inhibitory role for these syndecans in CD4 T cells. 18599487_pleiotrophin (PTN) and syndecan-2 and -3 as direct binding partners of Y-P30. 18716610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19073173_A pivotal role of this heparan sulphate proteoglycan in the formation of new blood vessels. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19179614_HSPGs and HSPG-dependent signaling are affected in both central and peripheral chondrosarcomas. 19288017_SDC2 and CYR61 expression affect the severity of cancer, and the survival of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). 19383343_estradiol affects the expression of syndecan-2, but not of syndecan-4, through ERalpha 19450993_changes in the pattern expression of syndecan-1 and -2 indicate that both molecules may be involved in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and tumor progression of prostate cancer. 19641225_Syndecan-2 plays a crucial role in the migratory potential of melanoma cells. 19786981_Study results supported the potential role of SDC2 in prostatic carcinogenesis and cancer progression. 19822079_Data report that the bFGF, FGFR1/2 and syndecan 1-4 expressions are altered in bladder tumours. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19962968_these results suggest that syndecan-2 regulates cell migration of colon carcinoma cells through Tiam1-dependent Rac activation in colon cancer cells. 20006588_syndecan's interactions with both CASK and neurofibromin are dependent on syndecan homodimerization. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20683009_Results support a potential role for syndecan-2 in pancreatic carcinogenesis and cancer progression. Expression of syndecan-2 might serve as a prognostic marker. 20929862_RGD-independent cell adhesion via a tissue transglutaminase 2-fibronectin matrix promotes fibronectin fibril deposition and requires syndecan-4/2 and {alpha}5{beta}1 integrin co-signaling. 21036168_syndecan-2 and syndecan-4 regulate the compensatory effect of TG-FN on osteoblast cell adhesion and actin cytoskeletal formation in the presence of RGD peptides. 21148276_These results demonstrate that syndecan-1 and syndecan-2 gene silencing by RNA interference reduces HSV-1 entry, plaque formation and facilitates cell survival. 21289173_The findings demonstrate that LRP1 and HSPG function in a cooperative manner to mediate cellular Abeta uptake and define a major pathway through which Abeta gains entry to neuronal cells. 21317913_syndecan-2 was expressed preferentially in basal cells in benign tissue. In prostate cancer samples, syndecan 2 was expressed in granular-cytoplasmic localisation. 21482826_HIV-1 p17 matrix protein interacts with heparan sulfate side chain of CD44v3, syndecan-2, and syndecan-4 proteoglycans expressed on human activated CD4+ T cells affecting tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 2 production. 21569759_the cytoplasmic domain of syndecan-2 regulates colon cancer cell migration via interaction with syntenin-1. 21813734_Here the protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor CD148 is shown to be a key intermediary in cell adhesion to syndecan-2 extracellular domain, with downstream beta1 integrin-mediated adhesion and cytoskeletal organization. 22170634_a specific glycochain is a receptor for dengue virus strain DEN2 16681 22227189_the data suggest that MMP-7 directly mediates shedding of syndecan-2 from colon cancer cells. 22238310_Syndecan 1 and syndecan 2 are cellular molecules responsible for susceptibility to HTLV-1. 22437834_Notch receptors control their own activity by inducing the expression of syndecan-2, which then acts to propagate Notch signaling by direct receptor interaction. 22471946_SDC-2 is a novel (perineural) invasion-associated gene in PDAC which cooperates with K-ras to induce a more invasive phenotype. 22493442_MC1R regulates melanoma cell migration via inhibition of syndecan-2 expression. 22550000_The repression of syndecan-2 by Wnt/beta-catenin/TCF signaling contributes to the resistance of osteosarcoma cells to doxorubicin. 22745764_Report demonstrates that syndecan-1 enhances malignancy of a mesenchymal tumour cell line, via induction of syndecan-2 expression. 22881146_lower TCR/CD3 surface levels caused by syndecan-2 led to reduced TCR/CD3 responsiveness 23297089_SDC-2 modulates TGFbeta2 transcriptional regulation via Smad2 signaling to facilitate fibrosarcoma cell adhesion. 23333331_Taken together, these results suggest that the extracellular domain of syndecan-2 regulates the interaction of HCT116 human colon carcinoma cells with fibronectin. 23736812_DNA from 4 HPV positive and 4 HPV negative fresh frozen primary HNSCC were subject to comprehensive genome-wide methylation profiling.Pathway analysis of 1168 methylated genes showed 8 signal transduction pathways (SDC2) of which 62% are hypermethylated. 23747112_Clinical validation of SDC2 methylation in serum DNA by quantitative methylation-specific PCR demonstrated a high sensitivity of 87.0% (95% CI, 80.0% to 92.3%) in detecting cancers. 23975428_RKIP, LOX and SDC2 are coordinately regulated and collectively encompass a prognostic signature for metastasis-free survival in ER-negative breast cancer patients 24424718_syndecan 2 shows no changes associated to histological grade of Prostate cancer 24442880_SDC2 is overexpressed in Leri's pleonosteosis. The minor allele of a missense SDC2 variant, p.Ser71Thr, could confer protection against systemic sclerosis. 24447566_RhoA, but not RhoC was shown to be essential for the anchored phenotype of breast carcinoma cells that accompanied siRNA-mediated loss of syndecan-2. 24472179_SDC2 expression was higher in skin melnaoma cells. It enhanced tyrosinase activity by increasing the membrane and melanosome localization of protein kinase CbetaII. UVB-induced up-regulation was required for UVB-induced melanin synthesis. 24613844_Taken together, these data suggest that IL-1alpha regulates extracellular domain shedding of syndecan-2 through regulation of the MAP kinase-mediated MMP-7 expression in colon cancer cells. 24662262_The results demonstrate the importance of PDZ-binding domain of syndecan-2 for controlling LFA-1 affinity and cell adhesion. 24736615_HIV matrix protein p17 is pro-fibrogenic through its interactions both with CXCR2 and syndecan-2 on activated HSCs 24804215_Extracellular matrix proteins expression profiling in chemoresistant variants of the A2780 ovarian cancer cell line. 24956062_Data indicate that the extracellular and cytoplasmic domains of syndecans 1/2/3/4 are intrinsically disordered regions. 25916113_In this review we considered the function of syndecan-2, the structure of syndecan-2 and its role in the formation of amyloid plaques. 27270030_data suggest that syndecan-2 induces extracellular shedding of E-cadherin and supports the acquisition of a fibroblast-like morphology by regulating MMP-7 expression in a colon cancer cell line 28753106_Methylation of SFRP1, SFRP2, SDC2, and PRIMA1 promoter sequences was observed in 85.1%, 72.3%, 89.4%, and 80.9% of plasma samples from patients with Colorectal cancer and 89.2%, 83.8%, 81.1% and 70.3% from adenoma patients, respectively. 28940845_Emerging roles of SDC2 in epithelial and mesenchymal cancer progression has been summarized. (Review) 30562054_SDC2 plays an important role in the invasive properties of lung adenocarcinoma cells. 31311305_Acute inflammation induces syndecan-2 expression predominantly in the proximal colon. 31707342_Syndecan-2 in colorectal cancer plays oncogenic role via epithelial-mesenchymal transition and MAPK pathway. 31930596_LMP1 upregulates SDC2 and SYTL4. 31962098_A novel plasma based early colorectal cancer screening assay base on methylated SDC2 and SFRP2. 32902825_Circular RNA circNFATC3 acts as a miR-9-5p sponge to promote cervical cancer development by upregulating SDC2. 33126908_Robust performance of a novel stool DNA test of methylated SDC2 for colorectal cancer detection: a multicenter clinical study. 33152121_Targeting stromal cell Syndecan-2 reduces breast tumour growth, metastasis and limits immune evasion. 33393623_Stool DNA test targeting methylated syndecan-2 (SDC2) as a noninvasive screening method for colorectal cancer. 34355516_Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived syndecan-2 regulates the immune response during sepsis to foster bacterial clearance and resolution of inflammation. 34360683_Syndecan Transmembrane Domain Specifically Regulates Downstream Signaling Events of the Transmembrane Receptor Cytoplasmic Domain. 34596215_Syndecan-2, negatively regulated by miR-20b-5p, contributes to 5-fluorouracil resistance of colorectal cancer cells via the JNK/ERK signaling pathway. 34769248_Bacteroides fragilis Enterotoxin Upregulates Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 Expression through MAPK and AP-1 Activation in Intestinal Epithelial Cells, Leading to Syndecan-2 Release. 35227195_The methylation of SDC2 and TFPI2 defined three methylator phenotypes of colorectal cancer. 35499710_Evaluation of combined detection of multigene mutation and SDC2/SFRP2 methylation in stool specimens for colorectal cancer early diagnosis. 35569509_Plasma membrane proteoglycans syndecan-2 and syndecan-4 engage with EGFR and RON kinase to sustain carcinoma cell cycle progression. | ENSMUSG00000022261 | Sdc2 | 14819.826720 | 1.0527572 | 0.074172762 | 0.02182454 | 11.54789124578 | 0.0006782614204797506171282228670804670400684699416160583496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00547462247528606588131694365984003525227308273315429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 15416.906922 | 253.359067 | 14712.877583 | 242.062752 | |
| ENSG00000170085 | 375484 | SIMC1 | protein_coding | Q8NDZ2 | FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Inhibits the protease activity of CAPN3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23707407}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 5]: Inhibits the protease activity of CAPN3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23707407}. | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome | Enables SUMO polymer binding activity and peptidase inhibitor activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of peptidase activity. Located in sarcomere. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:375484; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; sarcomere [GO:0030017]; peptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0030414]; SUMO polymer binding [GO:0032184]; negative regulation of peptidase activity [GO:0010466] | 23707407_Authors found that PLEIAD also interacts with CTBP1 (C-terminal binding protein 1), a transcriptional co-regulator, and CTBP1 is proteolyzed in COS7 cells expressing CAPN3. | ENSMUSG00000043183 | Simc1 | 75.941553 | 0.8619702 | -0.214290088 | 0.23931525 | 0.79958293151 | 0.3712180953968325924918758573767263442277908325195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.60287921959954648976065527676837518811225891113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 69.747076 | 8.721335 | 81.215741 | 10.139627 | |
| ENSG00000170296 | 11337 | GABARAP | protein_coding | O95166 | FUNCTION: Ubiquitin-like modifier that plays a role in intracellular transport of GABA(A) receptors and its interaction with the cytoskeleton (PubMed:9892355). Involved in autophagy: while LC3s are involved in elongation of the phagophore membrane, the GABARAP/GATE-16 subfamily is essential for a later stage in autophagosome maturation (PubMed:15169837, PubMed:20562859, PubMed:22948227). Through its interaction with the reticulophagy receptor TEX264, participates in the remodeling of subdomains of the endoplasmic reticulum into autophagosomes upon nutrient stress, which then fuse with lysosomes for endoplasmic reticulum turnover (PubMed:31006538). Also required for the local activation of the CUL3(KBTBD6/7) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, regulating ubiquitination and degradation of TIAM1, a guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) that activates RAC1 and downstream signal transduction (PubMed:25684205). Thereby, regulates different biological processes including the organization of the cytoskeleton, cell migration and proliferation (PubMed:25684205). Involved in apoptosis (PubMed:15977068). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15169837, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15977068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20562859, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22948227, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25684205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31006538, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9892355}. | 3D-structure;Apoptosis;Autophagy;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Cytoskeleton;Golgi apparatus;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Microtubule;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport | Gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptors [GABA(A) receptors] are ligand-gated chloride channels that mediate inhibitory neurotransmission. This gene encodes GABA(A) receptor-associated protein, which is highly positively charged in its N-terminus and shares sequence similarity with light chain-3 of microtubule-associated proteins 1A and 1B. This protein clusters neurotransmitter receptors by mediating interaction with the cytoskeleton. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:11337; | actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; autophagosome [GO:0005776]; autophagosome membrane [GO:0000421]; axoneme [GO:0005930]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule associated complex [GO:0005875]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; smooth endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005790]; sperm midpiece [GO:0097225]; synapse [GO:0045202]; beta-tubulin binding [GO:0048487]; GABA receptor binding [GO:0050811]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; autophagosome assembly [GO:0000045]; autophagy of mitochondrion [GO:0000422]; cellular response to nitrogen starvation [GO:0006995]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:0008625]; macroautophagy [GO:0016236]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; positive regulation of protein K48-linked ubiquitination [GO:1902524]; protein targeting [GO:0006605]; regulation of Rac protein signal transduction [GO:0035020] | 11727985_Sequence-specific 1H, 13C and 15N resonance assignments of human GABA receptor associated protein. 11727986_Backbone 1H, 13C, and 15N resonance assignments for a 14 kD protein, GABA(A) receptor associated protein (GABARAP). 11729197_We present the three-dimensional structure of GABARAP obtained by x-ray diffraction at 1.75 A resolution 11825910_Human Apg3p/Aut1p homologue is an authentic E2 enzyme for multiple substrates, GATE-16, GABARAP, and MAP-LC3, and facilitates the conjugation of hApg12p to hApg5p 11875056_Solution structure of human GABA(A) receptor-associated protein GABARAP: implications for biolgoical funcrion and its regulation 14625090_Gec1/GABARAPL1 was more expressed than GABARAP in the central nervous system (CNS), while GABARAP was more expressed in endocrine glands. 15695379_GABARAP mRNA expression and protein expression were significantly down-regulated in invasive ductal and invasive lobular carcinomas; GABARAP acts via a vesicle transport mechanism as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer. 15977068_GABARAP and DDX 47 are involved in the apoptotic process 16303767_Phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine are targets of the mammalian Atg8 modifiers, LC3, GABARAP, and GATE-16 16339017_GABARAP does not alter receptor kinetics directly, but by facilitating surface expression of alphabetagamma receptors. 16874098_Results suggest that lysosomal turnover of GABARAP-PL is activated during the differentiation of C2C12 cells to myotubes without inactivation of the mTor kinase-signaling pathway. 17164261_GABARAP and DLG4 genes are involved in the etiology of nicotine dependence in European-American smokers. 17164261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17581966_The association of structurally altered GABARAP protein together with GABA(A) receptor downstream of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CAMKII) activation is essential for long-term potentiation. 18638487_The X-ray structure of the soluble form of human GABA(A) receptor-associated protein complexed with a high-affinity synthetic peptide at 1.3 A resolution, is presented. 19154346_Molecular modeling of a complex containing full-length calreticulin suggests a novel mode of substrate interaction, which may have functional implications for the calreticulin/calnexin family in general. 19363302_The proapoptotic protein Nix/Bnip3L was found to be a potential GABARAP ligand. 19533740_analysis of human NSF possible binding mode to GABARAP and GATE-16 20111057_DLG4/PSD95 and GABARAP were analyzed using zebrafish embryos with morpholino knockdown system as a model organism. 20665069_Used diffusion-ordered nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to study the temperature and concentration dependence of the diffusion properties of GABARAP. 20820800_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21376781_Evidence suggests that changes in the expression and function of GABA(A) receptors are involved in the pathogenesis of epilepsy (review) 21684337_The level of GABARAPs is decreased in Lewy body disease. 23545901_Taken together, our results indicate that GABARBP can regulate the pro-apoptotic activity of cisplatin via the upregulation of p53 expression. 24240096_These results support the regulatory role of Bcl-2 in autophagy and define GABARAP as a novel interaction partner involved in this intricate connection. 24582747_knockdown of LC3B but not GABARAPs resulted in significant accumulation of p62/Sqstm1, one of the selective substrates for autophagy 24686084_GABARBP dramatically inhibited VEGF-induced endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation, as well as VEGFR-2 phosphorylation in vitro. 25126726_The FLCN-GABARAP association is modulated by the presence of either folliculin-interacting protein (FNIP)-1 or FNIP2 and further regulated by ULK1. 25126728_A functional complementation of an lgg-1 null mutant with human GABARAP, its closer homolog showed that it localizes to autophagosomes and can rescue LGG-1 functions in the early embryo. 25224329_The interaction of GABARAP with Mulan-Ube2E3 supports the role of Mulan as an important regulator of mitophagy. 25498145_PLEKHM1 regulates autophagosome-lysosome fusion through homotypic fusion and protein sorting complex and LC3/GABARAP proteins. 25684205_KBTBD6 and KBTBD7 specifically bind to GABARAP proteins.GABARAP proteins mediate localized ubiquitylation of TIAM1 by CUL3. 26687599_Data show that WAC directly binds to GM130 and that this binding is required for autophagosome formation through interacting with GABARAP regulating its subcellular localization. 27221053_GABRP plays an important role in placentation and this pathway may be a promising molecular target for the development of novel therapeutic strategies for preeclampsia. 27764541_Cardiolipin interaction with various Atg8 human orthologs, namely LC3B, GABARAPL2 and GABARAP, was investigated. 27864321_Although neither GABARAPs nor LC3s are required for autophagosome biogenesis, loss of all Atg8s yields smaller autophagosomes and a slowed initial rate of autophagosome formation. 28320742_Development of LC3/GABARAP sensors containing a LIR and a hydrophobic domain to monitor autophagy. 28497576_GABAergic synapse is proposed as a focus of aging. (Review) 28729737_GABARAPs are identified as the first known direct interaction partners of Nef that are essential for its plasma membrane localization. 28990689_The centrosome and centriolar satellites regulate autophagosome formation by delivery of an ATG8-family member, GABARAP, to the forming autophagosome membrane, the phagophore. Its proposed that GABARAP regulates phagophore expansion by activating the ULK complex. [review] 29142222_We have also observed membrane aggregation induced by ATG3 in vitro, which could point to a more complex function of this protein in AP biogenesis. Moreover, in vitro GABARAP lipidation assays suggest that ATG3-membrane interaction could facilitate the lipidation of ATG8 homologues. 29792687_These results indicate that GABARAP and PI4K2A interact tightly. Although lipidation of GABARAP is essential for its role in autophagy, here we show that its lipidation is not required for the interaction of GABARAP and PI4K2A. 30218067_GABARAP regulates overall cellular levels of Fn14. Fn14 accumulates in the ERGIC in absence of GABARAP but within endosomes in the vicinity of autophagic membranes in absence of GATE-16. 30258106_Two isoforms of ATG7 are expressed in various tissues. ATG7(2) does not bind LC3B. ATG7(2) is unable to lipidate LC3/GABARAP. 30504823_Ankyrin-G regulates forebrain connectivity and network synchronization via interaction with GABARAP. 30767700_PIK3C3, BECN1 and ATG14 contain functional LIR motifs and interact with the Atg8-family proteins with a preference for GABARAP and GABARAPL1. 30773365_ATL3 functions as a receptor for endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-phagy, promoting tubular ER degradation upon starvation. ATL3 specifically binds to GABARAP, but not LC3, subfamily proteins via 2 GABARAP interaction motifs (GIMs). ATL3-GABARAP interaction is essential for ATL3 to function in ER-phagy. 30982432_Human LC3 and GABARAP subfamily members achieve functional specificity via specific structural modulations. 30990354_An atypical LIR motif within UBA5 (ubiquitin like modifier activating enzyme 5) interacts with GABARAP proteins and mediates membrane localization of UBA5. 31208283_GABARAPs and LC3s have opposite roles in regulating ULK1 for autophagy induction. 31315929_Autophagy-related 4 cysteine peptidase (ATG4) proteases process inactive pro-LC3/GABARAP before lipidation, and the same proteases can also deconjugate LC3/GABARAP from lipids. 32009292_A conserved ATG2-GABARAP family interaction is critical for phagophore formation. 32272685_A Conserved LIR Motif in Connexins Mediates Ubiquitin-Independent Binding to LC3/GABARAP Proteins. 32456010_Deficiency of GABARAP but not its Paralogs Causes Enhanced EGF-induced EGFR Degradation. 32685993_Differential expression and prognostic relevance of autophagy-related markers ATG4B, GABARAP, and LC3B in breast cancer. 33374830_Lack of GABARAP-Type Proteins Is Accompanied by Altered Golgi Morphology and Surfaceome Composition. 33591943_GABARAP suppresses EMT and breast cancer progression via the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. | ENSMUSG00000018567 | Gabarap | 97.350249 | 0.6269105 | -0.673668705 | 0.23956782 | 7.83107472785 | 0.0051355555214577554290489302957212203182280063629150390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.02927308501799147713584581254053773591294884681701660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 71.330609 | 13.120487 | 112.239691 | 20.306343 | |
| ENSG00000170364 | 6419 | SETMAR | protein_coding | Q53H47 | FUNCTION: Protein derived from the fusion of a methylase with the transposase of an Hsmar1 transposon that plays a role in DNA double-strand break repair, stalled replication fork restart and DNA integration. DNA-binding protein, it is indirectly recruited to sites of DNA damage through protein-protein interactions. Has also kept a sequence-specific DNA-binding activity recognizing the 19-mer core of the 5'-terminal inverted repeats (TIRs) of the Hsmar1 element and displays a DNA nicking and end joining activity (PubMed:16332963, PubMed:16672366, PubMed:17877369, PubMed:17403897, PubMed:18263876, PubMed:22231448, PubMed:24573677, PubMed:20521842). In parallel, has a histone methyltransferase activity and methylates 'Lys-4' and 'Lys-36' of histone H3. Specifically mediates dimethylation of H3 'Lys-36' at sites of DNA double-strand break and may recruit proteins required for efficient DSB repair through non-homologous end-joining (PubMed:16332963, PubMed:21187428, PubMed:22231448). Also regulates replication fork processing, promoting replication fork restart and regulating DNA decatenation through stimulation of the topoisomerase activity of TOP2A (PubMed:18790802, PubMed:20457750). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16332963, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16672366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17403897, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17877369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18790802, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20457750, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20521842, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21187428, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22231448, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24573677, ECO:0000303|PubMed:18263876}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Chromosome;DNA damage;DNA repair;DNA-binding;Endonuclease;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Methylation;Methyltransferase;Multifunctional enzyme;Nuclease;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase;Zinc | This gene encodes a fusion protein that contains an N-terminal histone-lysine N-methyltransferase domain and a C-terminal mariner transposase domain. The encoded protein binds DNA and functions in DNA repair activities including non-homologous end joining and double strand break repair. The SET domain portion of this protein specifically methylates histone H3 lysines 4 and 36. This gene exists as a fusion gene only in anthropoid primates, other organisms lack mariner transposase domain. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]. | hsa:6419; | nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; site of double-strand break [GO:0035861]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA topoisomerase binding [GO:0044547]; double-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003690]; endonuclease activity [GO:0004519]; histone H3K36 methyltransferase activity [GO:0046975]; histone H3K4 methyltransferase activity [GO:0042800]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; single-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003697]; single-stranded DNA endodeoxyribonuclease activity [GO:0000014]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; DNA catabolic process, endonucleolytic [GO:0000737]; DNA double-strand break processing [GO:0000729]; DNA integration [GO:0015074]; double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining [GO:0006303]; histone H3-K36 dimethylation [GO:0097676]; histone H3-K4 methylation [GO:0051568]; mitotic DNA integrity checkpoint signaling [GO:0044774]; negative regulation of chromosome organization [GO:2001251]; nucleic acid phosphodiester bond hydrolysis [GO:0090305]; positive regulation of DNA topoisomerase (ATP-hydrolyzing) activity [GO:2000373]; positive regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining [GO:2001034]; replication fork processing [GO:0031297] | 16332963_Metnase is a nonhomologous end-joining repair protein that regulates genomic integration of exogenous DNA and establishes a relationship among histone modification, DNA repair, and integration. 16989604_These data suggest that vectors based on the Himar1 transposable element, in conjunction with the hyperactive mutant transposase C9, may be suitable vectors for gene therapy applications. 17130240_SETMAR is unlikely to catalyze transposition in the human genome, although the nicking activity may have a role in the DNA repair phenotype. 17403897_The activities of the SETMAR protein on transposon ends are described. 17877369_Results suggest that Metnase's DNA cleavage activity, unlike those of other eukaryotic transposases, is not coupled to its sequence-specific DNA binding. 18263876_hPso4 is necessary to bring Metnase to the DSB sites for its function(s) in DNA repair 18790802_Metnase physically interacts and co-localizes with Topoisomerase IIalpha, the key chromosome decatenating enzyme. 19458360_myeloid leukemia cells fail to arrest at the mitotic decatenation checkpoint, and their progression through this checkpoint is regulated by the DNA repair component Metnase (also termed SETMAR) 20416268_hPso4, once it forms a complex with Metnase, negatively regulates Metnase's TIR binding activity 20457750_results establish Metnase as a key factor that promotes restart of stalled replication forks, and implicate Metnase in the repair of collapsed forks. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21124928_Data show that DBN1, SETMAR and HIG2 are direct transcriptional targets of the SOX11 protein. 21187428_DNA repair protein Metnase (also SETMAR), which has a SET histone methylase domain, localized to an induced DSB and directly mediated the formation of H3K36me2 near the induced DSB 21491884_a role for Metnase's endonuclease activity in promoting the joining of noncompatible ends 22231448_phosphorylation of Metnase S495 differentiates between these two functions, enhancing DSB repair and repressing replication fork restart. 24573677_a single mutation DDN(610) --> DDD(610), which restores the ancestral catalytic site, results in loss of function in Metnase 24607956_found known and novel SETMAR splice variants to be significantly increased in acute myeloid leukemia 24655462_293 T transfected with Metnase revealed a large number of rescued plasmids. 25333365_Metnase may possess an important role in DNA repair, topoisomerase II function, and the maintenance of stemness during colon cancer development. 25795785_methylation of snRNP70 by SETMAR regulates constitutive and/or alternative splicing 26437079_The SET domain is needed for the 5' end of ss-overhang cleavage with fork and non-fork DNA without affecting the Metnase-DNA interaction. This domain has a positive role in restart of replication fork and the 5' end of ss-overhang cleavage. 27974460_These results suggest that Metnase enhances Exo1-mediated exonuclease activity on the lagging strand DNA by facilitating Exo1 loading onto a single strand gap at the stalled replication fork. 28038463_Various SETMAR proteins can be synthesized in human glioblastoma that may each have specific biophysical and/or biochemical properties and characteristics. 30329085_ur data is consistent with a model in which SETMAR is part of an anthropoid primate-specific regulatory network centered on the subset of genes containing a transposon end. 31238295_The roles of the human SETMAR protein in illegitimate DNA recombination and non-homologous end joining repair were studied. Contrary to previous reports, it was found that wild type SETMAR had little to no effect on the rate of cell division, DNA integration into the genome or non-homologous end joining. 33621919_Mutation and expression alterations of histone methylation-related NSD2, KDM2B and SETMAR genes in colon cancers. 33812898_Two repeated motifs enriched within some enhancers and origins of replication are bound by SETMAR isoforms in human colon cells. 35378129_Structural and genome-wide analyses suggest that transposon-derived protein SETMAR alters transcription and splicing. | 47.601119 | 0.9109384 | -0.134574602 | 0.22334430 | 0.36272002691 | 0.5469994692704335248478741959843318909406661987304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.74721119623928466957352156896376982331275939941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 45.070908 | 6.129444 | 49.676490 | 6.685751 | |||
| ENSG00000170949 | 90338 | ZNF160 | protein_coding | Q9HCG1 | FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. | Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | The protein encoded by this gene is a Kruppel-related zinc finger protein which is characterized by the presence of an N-terminal repressor domain, the Kruppel-associated box (KRAB). The KRAB domain is a potent repressor of transcription; thus this protein may function in transcription regulation. Multiple transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. | hsa:90338; | nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 19846881_TLR4 gene transcription was repressed by epigenetic regulations, which were, at least in part, dependent on ZNF160. | ENSMUSG00000067942 | Zfp160 | 187.163338 | 0.9010974 | -0.150245020 | 0.11788219 | 1.62410682494 | 0.2025200989987922806090381300236913375556468963623046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.41831824347240198491704177286010235548019409179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 168.345155 | 19.054044 | 187.574872 | 21.107102 | |
| ENSG00000171169 | 203245 | NAIF1 | protein_coding | Q69YI7 | FUNCTION: Induces apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16378748}. | Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Nucleus;Reference proteome | Involved in negative regulation of cell growth and regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability involved in apoptotic process. Located in cytosol; nucleoplasm; and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:203245; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability involved in apoptotic process [GO:1902108] | 16378748_NAIF1 (C9orf90)is a nuclear protein that induces apoptosis when overexpressed 18339812_The functions of two transposon-derived human proteins: HARBI1, a domesticated transposase-derived protein, and NAIF1, which contains a trihelix motif similar to that described in the Myb-like protein, was investigated. 21286669_NAIF1 is down-regulated in gastric cancer. 25432142_NAIF1 plays a role in regulating cellular migration and invasion through the MAPK pathways and may function as a tumor suppressor in the progression of gastric carcinoma. 25725584_MiR-24 acted as an oncomir, at least partially through regulation of its functional target NAIF1 in non-small cell lung cancer. 32506303_MicroRNA-351 Promotes the Proliferation and Invasion of Glioma Cells through Downregulation of NAIF1. 34607512_Long noncoding RNA SRY-box transcription factor 2 overlapping transcript participates in Parkinson's disease by regulating the microRNA-942-5p/nuclear apoptosis-inducing factor 1 axis. | ENSMUSG00000039164 | Naif1 | 65.360500 | 0.8055232 | -0.312002019 | 0.22134285 | 1.97792803160 | 0.1596088545979871820001960713852895423769950866699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.35876725986126384304597536356595810502767562866210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 56.683403 | 7.101518 | 70.438512 | 8.773456 | |
| ENSG00000171307 | 84287 | ZDHHC16 | protein_coding | Q969W1 | FUNCTION: Palmitoyl acyltransferase that mediates palmitoylation of proteins such as PLN and ZDHHC6 (PubMed:28826475). Required during embryonic heart development and cardiac function, possibly by mediating palmitoylation of PLN, thereby affecting PLN phosphorylation and homooligomerization (By similarity). Also required for eye development (By similarity). Palmitoylates ZDHHC6, affecting the quaternary assembly of ZDHHC6, its localization, stability and function (PubMed:28826475). May play a role in DNA damage response (By similarity). May be involved in apoptosis regulation (By similarity). Involved in the proliferation of neural stem cells by regulating the FGF/ERK pathway (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:B8A4F0, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ESG8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28826475}. | Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;DNA damage;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Enables palmitoyltransferase activity. Involved in protein palmitoylation. Predicted to be located in endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in Golgi apparatus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:84287; | endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; palmitoyltransferase activity [GO:0016409]; protein-cysteine S-palmitoyltransferase activity [GO:0019706]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; eye development [GO:0001654]; heart development [GO:0007507]; protein palmitoylation [GO:0018345]; telencephalon development [GO:0021537] | 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17123647_APH2 contains a zf-DHHC domain (148-210aa), which is involved in protein-protein or protein-DNA interaction. 28826475_human ZDHHC6, which modifies key proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum, is controlled by an upstream palmitoyltransferase, ZDHHC16, revealing the first palmitoylation cascade. 35192890_SETD2 Palmitoylation Mediated by ZDHHC16 in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Glioblastoma Promotes Ionizing Radiation-Induced DNA Damage. | ENSMUSG00000025157 | Zdhhc16 | 108.272772 | 0.9604575 | -0.058206379 | 0.15647129 | 0.13836875265 | 0.7099081083279923376494480180554091930389404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.85245039224757124252107587381033226847648620605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 103.409562 | 10.361424 | 108.111293 | 10.694457 | |
| ENSG00000171311 | 51013 | EXOSC1 | protein_coding | Q9Y3B2 | FUNCTION: Non-catalytic component of the RNA exosome complex which has 3'->5' exoribonuclease activity and participates in a multitude of cellular RNA processing and degradation events. In the nucleus, the RNA exosome complex is involved in proper maturation of stable RNA species such as rRNA, snRNA and snoRNA, in the elimination of RNA processing by-products and non-coding 'pervasive' transcripts, such as antisense RNA species and promoter-upstream transcripts (PROMPTs), and of mRNAs with processing defects, thereby limiting or excluding their export to the cytoplasm. The RNA exosome may be involved in Ig class switch recombination (CSR) and/or Ig variable region somatic hypermutation (SHM) by targeting AICDA deamination activity to transcribed dsDNA substrates. In the cytoplasm, the RNA exosome complex is involved in general mRNA turnover and specifically degrades inherently unstable mRNAs containing AU-rich elements (AREs) within their 3' untranslated regions, and in RNA surveillance pathways, preventing translation of aberrant mRNAs. It seems to be involved in degradation of histone mRNA. The catalytic inactive RNA exosome core complex of 9 subunits (Exo-9) is proposed to play a pivotal role in the binding and presentation of RNA for ribonucleolysis, and to serve as a scaffold for the association with catalytic subunits and accessory proteins or complexes. EXOSC1 as peripheral part of the Exo-9 complex stabilizes the hexameric ring of RNase PH-domain subunits through contacts with EXOSC6 and EXOSC8. | 3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Exosome;Neurodegeneration;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;rRNA processing | This gene encodes a core component of the exosome. The mammalian exosome is required for rapid degradation of AU rich element-containing RNAs but not for poly(A) shortening. The association of this protein with the exosome is mediated by protein-protein interactions with ribosomal RNA-processing protein 42 and ribosomal RNA-processing protein 46. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. | hsa:51013; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0000177]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0000178]; nuclear exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0000176]; nucleolar exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0101019]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA catabolic process [GO:0006401]; RNA processing [GO:0006396]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364] | 11812149_association of hCsl4p with the exosome is mediated by protein-protein interactions with hRrp42p and hRrp46p 12419256_Protein-protein interactions between human exosome components support the assembly of RNase PH-type subunits into a six-membered PNPase-like ring. 22068837_Human exosome hCsl4p participates in RNA degradation. 28144684_The combined p16- and p53-expression status in cervical metastases of CUP may represent a simple method for risk stratification. Further validation of these biomarkers in large prospective trials is essential to design rational trials for CUP treatment optimization. 33119769_Post-transcriptional control of cellular differentiation by the RNA exosome complex. 33463720_Bi-allelic missense variant, p.Ser35Leu in EXOSC1 is associated with pontocerebellar hypoplasia. | ENSMUSG00000034321 | Exosc1 | 56.407003 | 1.3647833 | 0.448671908 | 0.23266872 | 3.70359383235 | 0.0542954030910187332437111251692840596660971641540527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.17379498820072541986903047472878824919462203979492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 67.815198 | 9.362971 | 49.812121 | 6.858530 | |
| ENSG00000171456 | 171023 | ASXL1 | protein_coding | Q8IXJ9 | FUNCTION: Probable Polycomb group (PcG) protein involved in transcriptional regulation mediated by ligand-bound nuclear hormone receptors, such as retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG) (PubMed:16606617). Acts as coactivator of RARA and RXRA through association with NCOA1 (PubMed:16606617). Acts as corepressor for PPARG and suppresses its adipocyte differentiation-inducing activity (By similarity). Non-catalytic component of the PR-DUB complex, a complex that specifically mediates deubiquitination of histone H2A monoubiquitinated at 'Lys-119' (H2AK119ub1) (PubMed:20436459). Acts as a sensor of N(6)-methyladenosine methylation on DNA (m6A): recognizes and binds m6A DNA, leading to its ubiquitination and degradation by TRIP12, thereby inactivating the PR-DUB complex and regulating Polycomb silencing (PubMed:30982744). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P59598, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16606617, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20436459, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30982744}. | Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Craniosynostosis;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene is similar to the Drosophila additional sex combs gene, which encodes a chromatin-binding protein required for normal determination of segment identity in the developing embryo. The protein is a member of the Polycomb group of proteins, which are necessary for the maintenance of stable repression of homeotic and other loci. The protein is thought to disrupt chromatin in localized areas, enhancing transcription of certain genes while repressing the transcription of other genes. The protein encoded by this gene functions as a ligand-dependent co-activator for retinoic acid receptor in cooperation with nuclear receptor coactivator 1. Mutations in this gene are associated with myelodysplastic syndromes and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. | hsa:171023; | nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; PR-DUB complex [GO:0035517]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; nuclear retinoic acid receptor binding [GO:0042974]; peroxisome proliferator activated receptor binding [GO:0042975]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; bone marrow development [GO:0048539]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; heart morphogenesis [GO:0003007]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; homeostasis of number of cells [GO:0048872]; lung saccule development [GO:0060430]; monoubiquitinated histone H2A deubiquitination [GO:0035522]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599]; negative regulation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor signaling pathway [GO:0035359]; podocyte development [GO:0072015]; positive regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048386]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of kidney size [GO:0035564]; response to retinoic acid [GO:0032526]; thymus development [GO:0048538] | 19388938_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19586940_Data show that sequences 3' of PAX5 disrupting ASXL1, and ZCCHC7 disrupted by sequences 3' of FRG1B and LOC1499503. 19609284_ASXL1 haploinsufficiency plays a role in leukemogenesis 19609284_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19865112_ASXL1 mutations were mutually exclusive with NPM1 alterations in acute myeloid leukemias. 19865112_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20182461_Mutations of the polycomb-associated gene ASXL1 is associated with myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia. 20182461_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20334914_ASXL1 mutations are associated with refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis. 20408841_2 novel heterozygous (nonsense and frameshift) mutations in exon 12 of ASLX1 in 49 juvenile myelomonocytic leukaemia patients 20410925_ASXL1 gene mutation is associated with chronic myeloid leukemia. 20596031_the 8 mononucleotide guanine repeat sequence in the reference sequence for ASXL1 in this region may confound delimitation of the true repeat number in this region 20678218_Mutations in ASXL1 were frequent in refractory anemia with excess of blasts. 20678218_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20693432_Acute myeloid leukemia bearing ASXL1 mutations showed distinct clinical and biological features. 20880116_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21307773_Studies indicate that additional mutations in genes which appear to affect the epigenome of MPN patients have been discovered including mutations in TET2, IDH1/ 2, EZH2, and ASXL1. 21346257_ASXL1 mutation is asssociated with chronic myelogenous leukemia. 21455215_9 new missense mutations were found in myelofibrosis, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and blast-phase myeloproliferative disorders. 21576631_results suggest that ASXL1 mutations are frequent molecular aberrations in myelodysplastic syndrome that predict an adverse prognostic outcome 21706002_Nonsense mutations in ASXL1 cause Bohring-Opitz syndrome. 21712540_ASXL1 haploinsufficiency is associated with a myelofibrosis phenotype in the context of other known and unknown lesions, and disruption of ASXL1 function may contribute to the disease pathogenesis of myelofibrosis. 21904853_Data show that TET2 and ASXL1 pathogenic mutations are found in 8% of myeloproliferative neoplasms lacking JAK2 and MPL mutations, whereas IDH1, IDH2, and c-CBL mutations are not detected in this subset of patients. 21923651_ASXL1 mutations were already seen at diagnosis in most patients with primary or secondary myelofibrosis. They were associated with progression from the chronic phase of a previous polycythemia vera or essential thrombocythemia. 22031865_Results indicate that demonstrates that ASXL1-mutated older patients have unfavorable outcomes and may be candidates for experimental treatment approaches. 22058207_ASXL1 mutations are common mutations in acute myeloid leukemia and indicate a poor therapy outcome. 22271902_Germline GATA2 mutations predispose to familial myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukemia; monosomy 7 and ASXL1 mutations may be recurrent secondary genetic abnormalities triggering overt malignancy. 22419483_study reports on 2 novel cases of Bohring-Opitz syndrome (BOS) carrying two previously undescribed ASXL1 mutations (c.2407_2411del5 [p.Q803TfsX17] and c.2893C>T [p.R965X]); these new data further support ASXL1 as cause of BOS 22436456_A systematic determination of ASXL1 mutational status in myeloid malignancies should help in prognosis assessment. 22489043_We found a high incidence of ASXL1 mutation in myelofibrosis patients (20%) and a low incidence in polycythemia vera (7%) and essential thrombocythemia (4%) patients. 22535592_genetic association studies in a French population: Data suggest that acute myeloid leukemia with myelodysplasia-related changes is associated with higher frequency of ASXL1 mutations in intergenic DNA regions. 22542624_ASXL1 may be a direct target of SOX2 and may play a role in maintaining the pluripotency of stem cells. 22897849_ASXL1 associates with the PRC2 and loss of ASXL1 in vivo collaborates with NRASG12D to promote myeloid leukemogenesis. 22905207_TET2, DNMT3A, CBL and ASXL1 mutations are present in mastocytosis and these mutations may affect prognosis, as demonstrated by worse OS in mutated patients 22915647_Mutations in ASXL1 is associated with worse response to therapy in acute myeloid leukemia. 22929312_Patients with ASXL1 mutations did not harbor IDH1, FLT3, or CEBPA mutations, and a combination of ASXL1 and IDH2 mutations was found only in one patient with acute myeloid leukemia. 23009937_ASXL1 mutations are associated with the pathogenesis of myeloproliferative neoplasms. 23018865_ASXL1 exon 12 mutations are frequent in acute myeloid leukemia. 23065512_Data show that myelodysplastic chronic myelomonocytic leukemias are characterized by mutations in transcription/epigenetic regulators ASXL1, RUNX1, TET2 and SRSF2. 23099237_ASXL1 mutations might results in dominance of the mutant clone in Chinese with myelodysplastic syndromes. 23294243_ASXL1 knockdown perturbs human granulomonocytic differentiation. 23365461_Data indicate there were two patients carried ASXL1 mutations, both with t(8;21), 2 had DNMT3A mutations, 2 had IDH1 mutations, 1 had IDH2 mutation, and 3 had TET2 mutations. 23531518_We evaluated the prognostic relevance of several clinical and laboratory parameters in 226 Mayo Clinic patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and spliceosome component (P=0.4) and ASXL1 mutations (P=0.37) had no impact survival. 23690417_A new prognostic score including ASXL1 status, age, hemoglobin, WBC, and platelet counts defines three groups of CMML patients with distinct outcomes. This score appears more discriminative than those based solely on clinical parameters. 23704076_duplication of ASXL1 contributes to the metopic ridging/trigonocephaly phenotype in patients with 20q11.2 duplication syndrome 23952244_The low incidence of mutations in younger patients with primary disease and the lack of significance indicate that there is a limited role for screening at diagnosis for ASXL1 mutations for the purpose of prognostic stratification. 24077845_Acquired ASXL1 mutations are common in patients with inherited GATA2 mutations and correlate with myeloid transformation. 24115220_IDH mutations were closely associated with mutations of DNMT3A, ASXL1, and SRSF2, suggesting the interaction of IDH mutations with these gene aberrations may play a role in the development of MDS. 24216483_Although loss-of-function ASXL1 mutations promote myeloid transformation, a large subset of ASXL1 mutations is thought to result in stable truncation of ASXL1. 24465546_ASXL1 but not TET2 mutations adversely impact overall survival of patients suffering systemic mastocytosis with associated clonal hematologic non-mast-cell diseases. 24496303_These observations signify immediate clinical relevance and warrant i) CALR and ASXL1 mutation determination in all patients with PMF and ii) molecular revision of DIPSS-plus. 24695057_The current study confirms the independent prognostic value of nonsense/frameshift ASXL1 mutations in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and signifies its added value to the Mayo prognostic model. 25005031_Data indicate that 8 of 190 patients with essential thrombocythemia with calreticulin (CALR) mutation had an additional Sex Comb-Like 1 protein (ASXL1) mutation. 25239264_Mutations in ASXL1 gene is associated with chronic neutrophilic leukemia, atypical chronic myeloid leukemia, and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. 25306901_SETBP1 mutations are critical drivers of ASXL1-mutated myelodysplastic syndrome. 25308295_Data show that additional sex combs like 1 (Drosophila) protein (ASXL1) mutational status can improve the risk stratification of patients with acute myeloid leukemia in the setting of integrated mutational profiling. 25322686_The expression of ASXL1 and CALR predicts the survival and momelotinib drug response in myelofibrosis patients. 25592059_ASXL1 mutations are associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 25596262_study identified TET2 and ASXL1 mutations in Chinese patients with aplastic anemia 25596267_ASXL1 mutation, particularly in the context of a coexisting RUNX1 mutation, constitutes a strong adverse prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia. 25835095_ASXL1, ASXL2 and ASXL3 are epigenetic scaffold proteins that are involved in the pathogenesis of non-cancerous diseases and cancers. [Review] 25836587_USP7 demonstrated that USP7 bound to both ASXL1-WT and ASXL1-MT 25850813_The SETBP1 and ASXL1 mutations have pathogenetic roles in CSF3R-mutated chronic neutrophilic leukemia. 25860933_ASXL1 and TP53 mutations identify two molecular subgroups among AML-MRCs, with specific poor prognosis. This could be useful for future diagnostic and prognostic classifications. 25921057_Somatic mutations in ASXL1 are associated with myeloid malignancies. 26095772_ASXL1 truncation mutations confer gain-of-function on the ASXL-BAP1 complex. 26234322_identified significant ASXL1 SNPs in Chinese patients with acquired aplastic anemia (AA); results showed 8.2% had the recurrent conjoined rs62206933, rs117901891 and rs74638057 genotype (WT1), which was closely associated with poor prognosis in patients with nonsevere AA and had a greater risk of transformation to myelodysplastic syndrome 26286068_ASXL1 germline missense substitution is associated with hematological malignancies. 26364555_Frameshift mutation in the ASXL1 gene is associated with Bohring-Opitz syndrome. 26470845_Tumor suppressor ASXL1 is essential for the activation of INK4B expression in response to oncogene activity and anti-proliferative signals 26508027_Mutations in ASXL1, U2AF1, and SF3B1 are common in Chinese patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. 26623729_Correction of ASXL1 driver mutation in leukemia cells using CRISPR/Cas increases survival in vivo in mice. 26628266_Patients harbouring ASXL1 and/or CBL mutations (n = 8, 8 deaths, median OS = 11 months) had a significantly worse OS as compared to those without either mutation (n = 11, 4 deaths, median OS = 84 months) (P = 0.0002) (Fig 1a). 26700326_the present results indicate that the truncating ASXL1 mutant is indeed expressed in MDS cells and may play a role in MDS pathogenesis not previously considered. 26714837_This study showed ASXL1 exon 12 mutations in 16 of 70 (23%) patients with myelofibrosis, with 11 different mutations found in these patients. 26739236_This study showed that the BAP1 C-terminal extension is important for H2A deubiquitination but needs to be activated by the DEUBAD domains of ASXL1 or its relatives. 26768331_De novo mutation in ASXL1 gene is associated with Bohring-Opitz syndrome. 26771811_We confirm the negative prognostic impact imparted by ASXL1 mutations and suggest a favorable impact from TET2 mutations in the absence of ASXL1 mutations. 26848006_Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia has an inherent tendency to transform to acute myeloid leukemia. Gene mutations involving ASXL1 are frequent and identified to have an independent negative prognostic effect on overall survival. 27129146_Hypermethylation of the CTNNA1 promoter was associated with unfavorable karyotype, and possessed the higher frequency of coexisting with ASXL1 and RUNX1 mutations. 27352931_Evidence of a key role for ASXL1 in erythropoiesis, ASXL1 loss hinders erythroid development/maturation. 27385790_Mutation in ASXL1 gene is associated with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. 27416984_mutations in the SRSF2/ASXL1/RUNX1 gene panel identified as significant prognostic markers in systemic mastocytosis 27616637_We conclude that ASXL1 is essential for erythroid development and differentiation and that the aberrant differentiation is, at least in part, facilitated via PRC2. 27640403_Demonstration of ASXL1 mutation, a putative tumor suppressor gene, represents an important molecular abnormality in CML. Authors also showed that concomitant detection of BCR-ABL and JAK2V617F mutations has a relatively high incidence in Iranian patients. 27736271_Data indicate that additional Sex Comb-Like 1 protein (ASXL1)-mut were associated with poor prognosis in de novo AML with trisomy 8 as the sole aberration. 27736885_ASXL1 Circular RNA is Produced by Splicing from its pre-mRNA. 27984641_CSF3R T618I, ASXL1 G942 fs and STAT5B N642H trimutation co-contribute to a rare chronic neutrophilic leukaemia manifested by rapidly progressive leucocytosis, severe infections, persistent fever and deep venous thrombosis. 28027687_Studied ASXL1 mutations in myeloid neoplasms, and their association with survival and clinical outcomes in patients with myeloid neoplasms. 28063196_ASXL1 mutation is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 28218607_TET2, ASXL1, IDH1, and IDH2 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Turkish Patients with Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. 28229513_We examined all ASXL1 truncating variants in the ExAC database and determined most are likely somatic. Failure to consider somatic mosaicism may lead to the inaccurate assumption that conditions like BOS have reduced penetrance, or the misclassification of potentially pathogenic variants. 28424161_It was found that the absence of mutations in the SRSF2, ASXL1, and/or RUNX1gene panel at baseline and a reduction of the KIT D816V allele burden more than 25% at month 6 are the most favorable predictors for improved survival in midostaurin-treated advanced systemic mastocytosis patients. 28452984_Patients with mutations 6 showed higher rate of achieving major molecular response than those | ENSMUSG00000042548 | Asxl1 | 383.077937 | 0.9245304 | -0.113207269 | 0.16337708 | 0.47911316653 | 0.4888242905542273253338692029501544311642646789550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.70440652892474830970570565114030614495277404785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 358.880620 | 34.959192 | 389.966130 | 37.823770 | |
| ENSG00000171522 | 5734 | PTGER4 | protein_coding | P35408 | FUNCTION: Receptor for prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). The activity of this receptor is mediated by G(s) proteins that stimulate adenylate cyclase. Has a relaxing effect on smooth muscle. May play an important role in regulating renal hemodynamics, intestinal epithelial transport, adrenal aldosterone secretion, and uterine function. | 3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the G-protein coupled receptor family. This protein is one of four receptors identified for prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). This receptor can activate T-cell factor signaling. It has been shown to mediate PGE2 induced expression of early growth response 1 (EGR1), regulate the level and stability of cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA, and lead to the phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Knockout studies in mice suggest that this receptor may be involved in the neonatal adaptation of circulatory system, osteoporosis, as well as initiation of skin immune responses. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:5734; | membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; prostaglandin E receptor activity [GO:0004957]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007188]; bone development [GO:0060348]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus [GO:0071380]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; negative regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001818]; negative regulation of eosinophil extravasation [GO:2000420]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of integrin activation [GO:0033624]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; regulation of ossification [GO:0030278]; regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051492]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to nematode [GO:0009624]; T-helper cell differentiation [GO:0042093] | 11782353_Involvement of prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP(4) in colon carcinogenesis. 11876748_Placentally derived prostaglandin E2 acts via the EP4 receptor to inhibit IL-2-dependent proliferation of CTLL-2 T cells. 11948128_Increased PGE(2) synthesis in the adjacent stroma and its biological effect via EP(4) on the carcinoma cells may contribute to tumor growth and progression of gallbladder carcinoma. 12149218_effects of PGE2 on monocyte-derived dendritic cells were mediated through increased cyclic adenosine monophosphate by 2 of the known PGE2 receptors, EP2 and EP4 12215436_endogenous PGE(2) may modulate inflammation during atherogenesis and other inflammatory diseases by suppressing macrophage-derived chemokine production via the EP4 receptor 12228765_Activation of prostaglandin E2-receptor EP2 and EP4 pathways induces growth inhibition in human gastric carcinoma cell lines. 12566441_activation of PI3K/ERK signaling by the EP(4) receptors induces the functional expression of early growth response factor-1 (EGR-1). 14517215_COX-2 induction by bradykinin in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells is mediated by the cyclic AMP response element through a novel autocrine loop involving endogenous prostaglandin E2, EP2 receptor, and EP4 receptor 14709160_both beta-arrestin1 recruitment and the presence of Ser/Thr residues in the distal half of the C-terminal domain were necessary for maximal agonist-induced internalization 15100359_Vascular COX-2 was colocalized with prostaglandin E(2) EP4 receptors but not with EP2 receptors in kidney 15290741_EP3 and EP4 mediate different actions of PGE2 on mature human osteoclasts. Activation of EP4 receptors inhibits actin ring formation and activation of EP3 receptors increases number of lamellipodia. 15347673_Endothelin-1-induced prostaglandin E2-EP2 and EP4 signaling regulates vascular endothelial growth factor production and ovarian carcinoma cell invasion 15528329_Prostaglandin (PG)E2 induces an increase in intracellular cyclic AMP concentration in the T-leukemic cell line Jurkat via the E-prostanoid (EP)3 receptor. 15970595_PGE2 increases VEGF transcriptionally and involves the Sp-1 binding site via a cAMP-dependent mechanism involving EP2 and EP4 receptors 16020747_EP4 overexpression is associated with enhanced inflammatory reaction in atherosclerotic plaques 16428339_We concluded that PGE2 stimulates the BNP promoter mainly via EP4, PKA, Rap, and p42/44 MAPK. 16574793_seminal plasma and PGE(2) can promote the expression of tumorigenic and angiogenic factors, in cervical adenocarcinoma cells via the EP4 receptor, EGFR, and ERK1/2 signaling pathways 16857763_Presumably plays a key role for active patency of the human ductus arteriosus in the third trimester. 17046175_The EP4 receptor mediates IL-1 beta-induced catabolic metabolism via the p38 MAP kinase pathway in human tendon fibroblasts and may play a major role in the tendon's degenerative changes often seen in the later stages of tendinopathy. 17130837_Elevated activity in colorectal cancer cells increases resistance to spontaneous apoptosis and promotes anchorage-independent growth, but has no effect on proliferation. 17290397_EP4 mRNA was significantly higher in normal colon tissue compared with tumor tissue. 17447842_Genetic variants associated with Crohn disease risk in a locus modulating cis-acting regulatory elements of PTGER4. 17496729_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17525067_participates in placentation through EVT invasion by up-regulating PGE2 production and PGE2 receptor expression in first trimester extravillous trophoblasts 17611676_Results show co-expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 receptors EP1, 2 and 4 in non-small cell lung cancer cells concomitant with the synthesis of PGE2. 17631291_Results reveal that egr-1 is a target gene of PGE(2) in HCA-7 cells and is regulated via the newly identified EP4/ERK/CREB pathway. 17877755_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18005048_Expression of prostaglandin E(2) receptors (EP(2), EP(3), EP(4)), prostaglandin D(2) receptor (DP(2)), prostanoid thromboxane A(2) receptor (TP) and to a lesser extent EP(1) were observed in several hair follicle compartments. 18086382_herpes simplex virus type 1 infected mature monocyte-derived dendritic cells demonstrated a dramatic down-regulation of the expression of the EP2 and EP4 receptors 18254372_mRNA expressions of EP4 receptors observed in NCI-H292 cells and human nasal epithelial cells. 18270204_PGE(2)-EP4 signaling augments NF-kappaB1 p105 protein stability through EPRAP after proinflammatory stimulation, limiting macrophage activation. 18319253_CCR7 and the EP2/EP4 receptor signaling pathway are down-stream targets for COX-2 to enhance the migration of breast cancer cells toward LECs and to promote lymphatic invasion 18516068_Of the 4 EP receptor subtypes, smooth muscle cells in the human pulmonary vein express the EP4 and EP1 receptor subtypes. The relaxations induced by PGE2 in this vessel result from the activation of the EP4 receptor. 18797183_level of exptression in nasal polyps reversely correlates with chronic rhinosinusitis associated with bronchial asthma 18802112_The catabolic effects of prostaglandin E2 in osteoarthritis (OA) are specifically mediated via engagement of the EP4 receptor; of the four PGE2 receptors, only EP4 is up-regulated in OA vs normal cartilage. 18829529_PGE(2) induces angiogenesis in prostate cancer through EP2 and EP4. 19227010_EP4 is directly involved in regulation of proliferation and invasion of inflammatory breast cancer cells 19273625_PGE2 acts via prostaglandin receptor EP2- and EP4-mediated signaling and cyclic AMP pathways to up-regulate IL-23 and IL-1 receptor expression. 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19407222_EP2 and EP4 receptor inhibition induces apoptosis of human endometriotic cells through suppression of ERK1/2, AKT, NFkappaB, and beta-catenin pathways and activation of intrinsic apoptotic mechanisms 19407341_PGE(2)-stimulated production of Abeta involves EP(4) receptor-mediated endocytosis of PS-1 followed by activation of the gamma-secretase, as well as EP(2) receptor-dependent activation of adenylate cyclase and PKA 19444759_These results suggest that IL-1beta induces EP4 receptor expression in chondrocytes by an autocrine mechanism that increases PGE2 production, whereas it reduces the expression of EP1 and EP2 via direct action. 19445930_The EP4 agonist PF-04475270 is a novel ocular hypotensive compound which is bioavailable following topical dosing and effectively lowers intraocular pressure. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19558693_PGE2 expression is mediated by EP4 receptor and may have a role in colorectal cancer 19760754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19879194_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20014019_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20018632_PGE2 potently inhibits secretion of IFN-alpha by TLR-activated plasmacytoid dendritic cells, an effect mainly mediated by PG receptors E-prostanoid 2 and E-prostanoid 4 20086108_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20145136_EP4 overexpression, via AR activation, supports an important mechanism for castration-resistant progression of prostate cancer. 20222910_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20353998_Increased expression of PGE2 in the lung tumor microenvironment may initiate a mitogenic signaling cascade composed of EP4, betaArrestin1, and c-Src which mediates cancer cell migration. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20484658_EP1 and EP4 subtypes of prostaglandin E receptors (but not EP2 and EP3 receptors) may be involved in regulation of paracellular permeability in differentiated Caco-2 cell cultures. 20503412_regulate activities exhibited by IBC cells that have been associated with the aggressive phenotype. ep4 regulate invasion 20549515_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20551148_Prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype EP2 and EP4 regulated gene expression profiling in ciliary smooth muscle cells. 20561984_Data seem to rule out a major influence of these polymorphisms on UC or RA predisposition. 20587336_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20846217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20962850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20970516_chronic activation of the EP receptor is associated with increased production of mediators likely to increase the pro-inflammatory milieu of airway epithelial cells. 21052031_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21071691_Results are suggestive of platelet EP4 receptor activation as a novel antithrombotic strategy. 21072187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21081469_miR-16 and miR-21 are directly regulated by the transcription factor NF-kappaB and yet nicotine-promoted cell proliferation is mediated via EP2/4 receptors. 21111772_Data show that inhibition of PGE2 receptors EP2 and EP4 suppresses expression and/or activity of MMP1, MMP2, MMP3, MMP7 and MMP9 proteins and increases expression of TIMP1, TIMP2, TIMP3, and TIMP4 proteins. 21365278_EP4 receptors are expressed by human eosinophils, and are also present on infiltrating leukocytes in inflamed human nasal mucosa. 21424266_The role of PGE(2) in human atherosclerotic plaque on platelet EP(3) and EP(4) receptor activation and platelet function in whole blood. 21589857_found that PGE(2) and hypoxia independently induce expression of PTGER4 indicating two independent pathways regulating prostanoid receptor expression 21600299_Prostaglandin EP4 receptor enhances BCR-induced apoptosis of immature B cells 21681739_Data suggest that PGE(2) -EP4 signaling might be protective against allergic responses by inhibiting the interaction of eosinophils with the endothelium and might hence be a useful therapeutic option for controlling inappropriate eosinophil infiltration. 21683675_Prostaglandin E2 produced by Entamoeba histolytica signals via EP4 receptor and alters claudin-4 to increase ion permeability of tight junctions 21723865_findings indicate early divergence in the signaling pathways stimulated by strain and establish PGE2/EP4 as the pathway used by strain to regulate Sost expression. 21832044_Human kidney cells evidence increased EP4 and decreased Rap1GAP expression levels in the malignant compared with benign samples. 22037551_We identified new susceptibility loci for non-cardia gastric cancer at 5p13.1: rs13361707 in the region including PTGER4 and PRKAA1 22080750_PGE(2) enhances IL-8 production via EP4 receptor coupled to G(s) protein in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells 22276108_Neuroblastoma express all four forms of PGE(2) receptors. 22353936_EP-4 receptor expression is modulated at the post-transcriptional level by miR-101. 22362924_With HO as a model oxidant stress, stimulation of CFTR seems to involve PGE production and likely EP receptor activation in Calu-3 airway epithelial cells. 22580611_Targeted interference of EP2/EP4 signal to RalA.GTP may provide benefit to patients diagnosed with advanced kidney cancer. 22695889_The PTGER4 -1254 G allele demonstrated a higher frequency in aspirin-intolerant chronic urticaria (AICU)patients and lower promoter activity with decreased expression of PTGER4 and contributes to the development of AICU. 22704539_Activation of E-type prostanoid (EP) 4 receptor by PGE(2) or an EP4-selective agonist (ONO AE1-329) enhanced the barrier function of human microvascular lung endothelial cells. 22706114_This review article presents a short overview of experimental approaches aimed at manipulation of signaling via EP2 and EP4 receptors that could have therapeutic utility. 22732652_different EP receptors (EP(1-4)) to PGE(2)-induced anion secretion in human and mouse colon mucosa 22924768_PGE(2) -mediated NF-kappaB activation by simultaneous stimulation of EP(1) and EP(4) receptors induces maximal IL-8 promoter activation and IL-8 mRNA and protein induction 23090667_Data indicate that PGE2 regulates pancreatic stellate cell profibrotic activities via EP4 receptor, thus suggesting EP4 receptor as useful therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer to reduce desmoplasia. 23242524_Loss of function of EP2- and EP4-mediated PGE2 signaling inhibits adhesion of human endometriotic epithelial and stromal cells through integrin-mediated mechanisms. 23300802_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the PTGER4 gene regulatory sequences are strongly associated with Crohn's disease susceptibility. 23337716_PGE(2) coordinates control of IL-23 release in a dose-dependent manner by differential use of EP(2) and EP(4) receptors in LPS-activated MoDCs. 23364535_Human prostate cancer is associated with EP4 and EP2 overexpression and reduced EP3 expression. 23613969_This is the first report to demonstrate that Lymphocytic colitis is associated with increased TNF-alpha, INF-gamma and IL-8 concurrent with a marked up-regulation of EP4. 23619266_PGE2 induces MUC2 and MUC5AC expression in intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells via EP4-p38MAPK signaling. 23759445_PGE2 production induced by pathogen recognition receptors/p38 MAPK signaling is up-regulated by EP4-triggered signaling to maintain an effective PGE2 concentration. 24069348_JARID1A, JMY, and PTGER4 polymorphisms are related to ankylosing spondylitis in Chinese Han patients. 24133193_potential relevance of the COX-2/mPGES-1/EP-4 axis in the AAA-associated hypervascularization 24146253_Elastogenesis is spatially regulated by PGE-EP4 signaling in the ductus arteriosus. 24467603_Four single nucleotide polymorphisms in two genes in the PGE2 family, PTGES2 and PTGER4, were significantly associated with primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation. 24793213_The PTGER4 modulating variant rs7720838 increases susceptibility for Crohn's disease and might resemble a risk factor for stricturing disease behavior. 24876670_the microsomal PGE2-synthase-1/PGE-receptor-4 axis is increased by smoking in human abdominal aortic aneurysms 24980222_mediates inhibitory effect of Prostaglandin E2 on nasal fibroblast migration 25109834_PGE2 upregulates c-myc in hepatocellular carcinoma via PTGER4 signaling. 25329458_data show a protective role for the PGE2 receptors EP(2) and EP(4) following osmotic changes, through the reduction of human mast cell activity caused by calcium influx impairment and MAP kinase inhibition. 25531811_Altered inhibitory function of the EP4R in eosinophils and monocytes from aspirin-intolerant patients 25670004_Gene expression analysis revealed that three gene BACH2, PTGER4 and ZFP36L1, are down-regulated in MS patients' blood cells compared to healthy subjects. 25690101_TGF-beta2 therefore promotes the adhesion and invasiveness of virulent macrophages by modulating COX2, EP4, and PKIG transcription to initiate a prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)-driven autostimulatory loop that augments PKA and EPAC activities. 25733698_miRNA 526b is a COX-2 upregulated, oncogenic miRNA promoting stem-like cells, the expression of which follows EP4 receptor-mediated signaling. 26188701_IP and EP4 receptors have a role in prostanoid regulation of angiogeneis 26538147_The PTGER4 gene is a candidate risk factor for radiological progression in rheumatoid arthritis 26689593_The cross-talk between SP1 and p65, and the positive feedback regulatory loop of PI3-K/Akt signaling by EP4 contribute to the overall responses of solamargine in this process 27010855_GW627368X therefore effectively inhibits cervical cancer survival, motility, proliferation and angiogenesis by blocking EP4/EGFR interactive signaling. 27230680_Findings suggest SUMO-1 protein and PGE2 receptor subtype 4 (EP4) as two potential targets for new therapeutic or prevention strategies for endometrial cancers. 27450806_These results indicate that the blockage of PGE2-EP4 signaling prevents the bone destruction required for prostate cancer metastases, and that this is, in part due to the abrogation of bone cell responses. The study provides further evidence that an EP4 antagonist is a candidate for the treatment of prostate cancer in the blockade of bone metastasis. 27506158_Reprogramming of mammary epithelial cells can result from EP4 -mediated stem cell property transfer by extracellular vesicles/exosomes containing caveolae-associated proteins, between mammary basal and luminal epithelial cells. 27544059_High PTGER4 methylation is associated with Lung cancer. 27616330_in breast cancer cells overexpression of S1P3 and its activation by S1P has pro-inflammatory and pro-metastatic potential by inducing COX-2 expression and PGE2 signaling via EP2 and EP4. 27869171_EP4 expression can promote the development of resistance to aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast cancer 28094049_The results show that stimulation with the selective EP4 agonist CAY10598 or PGE2 promotes invadopodia-mediated degradation of the ECM, as well as the invasion of breast cancer cells in in vitro models. 28108433_Case Report: elevated EP4 expression in pulmonary hypertension patient with dissecting pulmonary aneurysm. 28432343_Collectively, these results indicate that COX-1/PGE2/EP4 upregulates the beta-arr1 mediated Akt signaling pathway to provide mucosal protection in colitis. 28899736_discovery of recurrent PTGER4 amplification implies a potential of exploring targeting therapy to the prostaglandin synthesis pathways in a subset of these tumors 29401596_results indicate that PGE2 inhibits hCAP18/LL-37 expression, especially VD3-induced cathelicidin and autophagy, which may reduce host defense against Mtb. Accordingly, antagonists of EP4 may constitute a novel adjunctive therapy in Mtb infection. 29491476_COLEC12 integrates H. pylori, PGE2-EP2/4 axis and innate immunity in gastric diseases 29658109_High EP4 expression is associated with chemoresistant breast carcinoma. 30053598_Data indicates that PGE2 suppression of TNF-alpha by human monocytic cells occurs via EP2R and EP4R expression. However EP4Rs also control their own expression and that of EP2 whereas the EP2R does not affect EP4R expression. This implies that EP4 receptors have an important master role in controlling inflammatory responses. 30191681_Data imply an upregulated expression of PTGER4 and PSCA as well as a downregulated expression of MBOAT7 in gastric tissue as risk-conferring gastric cancer patho-mechanisms. 30455960_Study demonstrated that the expression of EP4 receptors was up-regulated by c-Myc by binding to Sp-1 under low cellular density conditions but was down-regulated under high cellular density conditions via the increase in the expression levels of HIF-1alpha protein, which may pull out c-Myc and Sp-1 from DNA-binding. 30835912_These results suggest that PGE2 regulates human brain endothelial cell migration via cooperation of EP2, EP3, and EP4 receptors. 30917001_EP2 and EP4 receptors play different roles in the regulation of COX-2 expression in human amnion fibroblasts. 30980797_butyrate uptake reduces expressions of prostanoid EP4 receptors and their mediation of cyclooxygenase-2 induction in HCA-7 human colon cancer cells 31167696_SHOX2 and PTGER4 methylation detection in blood plasma has certain value in the early diagnosis of lung cancer 31217077_a role for EP2/EP4 signaling in regulating IGF-1-induced cell proliferation, in which EP2/EP4 signaling represses IGF-1-induced GGCT expression, is reported. 31253169_Prostaglandin receptor EP4 expression by Th17 cells is associated with high disease activity in ankylosing spondylitis. 31455205_This work has generated a set of novel homology models of the rEP4 and hEP4 receptors. 32321307_Dysregulated prostaglandin E receptor 4 overexpression in vascular smooth muscle cells promotes inflammatory monocyte/macrophage infiltration leading to abdominal aortic aneurysm exacerbation. 32438662_Concerted EP2 and EP4 Receptor Signaling Stimulates Autocrine Prostaglandin E2 Activation in Human Podocytes. 32464244_3 SNPs were found to be significantly associated with CD/UC/IBD: IRF5 rs4728142 (UC: OR = 1.21, 95% CI = 1.09-1.35, P = 0.0003; OR = 1.30, 95% CI = 1.08-1.57, P = 0.006 in Asian), PTGER4 rs4613763 (CD: the overall OR = 1.28, 95% CI = 1.01-1.64, P = 0.04; IBD: OR = 1.31, 95% CI = 1.04-1.65, P = 0.02), IL12B rs6887695 (CD: the overall OR = 1.17, 95% CI = 1.06-1.30, P = 0.002; UC: the overall OR = 1.13, 95% CI = 1.01-1.26. 32846747_Association between PTGER4 polymorphisms and inflammatory bowel disease risk in Caucasian: A meta-analysis. 33038299_Prostaglandin D2 strengthens human endothelial barrier by activation of E-type receptor 4. 33053354_Prostaglandin E2-EP4 Axis Promotes Lipolysis and Fibrosis in Adipose Tissue Leading to Ectopic Fat Deposition and Insulin Resistance. 33158942_Prostanoid Receptors of the EP4-Subtype Mediate Gene Expression Changes in Human Airway Epithelial Cells with Potential Anti-Inflammatory Activity. 33264604_Cryo-EM Structure of the Prostaglandin E Receptor EP4 Coupled to G Protein. 33600772_Whole-genome sequencing of African Americans implicates differential genetic architecture in inflammatory bowel disease. 33662689_DNA methylation of PTGER4 in peripheral blood plasma helps to distinguish between lung cancer, benign pulmonary nodules and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. 34262017_CD147 receptor is essential for TFF3-mediated signaling regulating colorectal cancer progression. 34475053_Pathological Roles of Prostaglandin E2-specific E-type Prostanoid Receptors in Hormone-sensitive and Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. 34502044_Prostaglandin E2 Receptor 4 (EP4) Affects Trophoblast Functions via Activating the cAMP-PKA-pCREB Signaling Pathway at the Maternal-Fetal Interface in Unexplained Recurrent Miscarriage. 34529833_Prostaglandin E2 directly inhibits the conversion of inducible regulatory T cells through EP2 and EP4 receptors via antagonizing TGF-beta signalling. 34740924_Single-Cell Analysis Reveals EP4 as a Target for Restoring T-Cell Infiltration and Sensitizing Prostate Cancer to Immunotherapy. 35549670_Nanomolar EP4 receptor potency and expression of eicosanoid-related enzymes in normal appearing colonic mucosa from patients with colorectal neoplasia. 35914351_PARP14 regulates EP4 receptor expression in human colon cancer HCA-7 cells. 36078128_The Prostaglandin E2 Receptor EP4 Promotes Vascular Neointimal Hyperplasia through Translational Control of Tenascin C via the cAPM/PKA/mTORC1/rpS6 Pathway. | ENSMUSG00000039942 | Ptger4 | 1428.054428 | 1.0633738 | 0.088648782 | 0.04077264 | 4.72665319986 | 0.0296986207975360912147966274687860277481377124786376953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.11291772430441283925350859362879418767988681793212890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1467.081043 | 55.964296 | 1386.301970 | 52.710891 | |
| ENSG00000171606 | 10782 | ZNF274 | protein_coding | Q96GC6 | FUNCTION: Probable transcription repressor. Specifically binds to the 3'-end of zinc-finger coding genes and recruiting chromatin-modifying proteins such as SETDB1 and TRIM28/KAP1, leading to transcription repression. The SETDB1-TRIM28-ZNF274 complex may play a role in recruiting ATRX to the 3'-exons of zinc-finger coding genes with atypical chromatin signatures to establish or maintain/protect H3K9me3 at these transcriptionally active regions (PubMed:27029610). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10777669, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27029610}. | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA | This gene encodes a zinc finger protein containing five C2H2-type zinc finger domains, one or two Kruppel-associated box A (KRAB A) domains, and a leucine-rich domain. The encoded protein has been suggested to be a transcriptional repressor. It localizes predominantly to the nucleolus. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms exist. These variants utilize alternative polyadenylation signals. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:10782; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of histone H3-K9 trimethylation [GO:1900112]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 16954381_KAP1 functions to coordinate activities that dynamically regulate changes in histone modifications and deposition of HP1 to establish a de novo microenvironment of heterochromatin, which is required for repression of gene transcription by KRAB-zfps. 21170338_analysis of a KRAB domain-containing ZNF (ZNF274) that is involved in recruitment of the KAP1 and SETDB1 to specific regions of the human genome 24128372_A proximal promoter construct for the MAS gene was repressed by the SOX [SRY (sex-determining region on the Y chromosome) box] proteins SRY, SOX2, SOX3 and SOX14, of which SRY is known to interact with the KRAB domain. 32977341_Specific ZNF274 binding interference at SNORD116 activates the maternal transcripts in Prader-Willi syndrome neurons. | ENSMUSG00000058638+ENSMUSG00000021514 | Zfp110+Zfp369 | 204.489819 | 0.8750179 | -0.192615602 | 0.11391076 | 2.86122713676 | 0.0907382517828886764332807501887145917862653732299804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.24799746143959403021916898524068528786301612854003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 191.491120 | 15.465345 | 219.474929 | 17.382103 |
| ENSG00000172183 | 3669 | ISG20 | protein_coding | Q96AZ6 | FUNCTION: Interferon-induced antiviral exoribonuclease that acts on single-stranded RNA and also has minor activity towards single-stranded DNA. Exhibits antiviral activity against RNA viruses including hepatitis C virus (HCV), hepatitis A virus (HAV) and yellow fever virus (YFV) in an exonuclease-dependent manner. May also play additional roles in the maturation of snRNAs and rRNAs, and in ribosome biogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11401564, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12594219, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16033969, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21036379}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;Exonuclease;Hydrolase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Manganese;Metal-binding;Nuclease;Nucleus;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;rRNA processing | Enables 3'-5' exonuclease activity and RNA binding activity. Involved in defense response to virus; negative regulation of viral genome replication; and nucleobase-containing compound catabolic process. Located in cytoplasm and nuclear lumen. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:3669; | Cajal body [GO:0015030]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PML body [GO:0016605]; 3'-5'-exoribonuclease activity [GO:0000175]; exonuclease activity [GO:0004527]; exoribonuclease II activity [GO:0008859]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; single-stranded DNA 3'-5' exodeoxyribonuclease activity [GO:0008310]; U1 snRNA binding [GO:0030619]; U2 snRNA binding [GO:0030620]; U3 snoRNA binding [GO:0034511]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; DNA catabolic process, exonucleolytic [GO:0000738]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045071]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; RNA catabolic process [GO:0006401]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364] | 15527770_ISG20has distinctive residues, Met14 and Arg53, to accommodate hydrogen bonds with the 2'-OH group of the UMP ribose, and these residues may be responsible for the preference of ISG20 for RNA substrates 18278447_ISG20 has a role in reducing the synthesis of HBV proteins 21036379_ISG20 inhibited infections by hepatitis C virus, bovine viral diarrhea virus and hepatitis A virus. Moreover, ISG20 demonstrated cell-type specific antiviral activity against yellow fever virus, a classical flavivirus. 23830076_The results suggest that hantavirus infection interferes with DAXX-mediated apoptosis, and expression of interferon-activated Sp100 and ISG-20 proteins may indicate intracellular intrinsic antiviral attempts. 27342813_these data provide a detailed explanation for the specific antiviral action of ISG20 and suggest that ISG20 may act as a promising antiviral drug candidate against IAV. 27626689_Interferon-stimulated gene of 20 kDa protein (ISG20) acts as an innate anti-HBV effector that selectively degrades hepatitis B virus (HBV) RNA and blocks replication of infectious HBV particles. 27764096_We discovered two genome-wide significant SNPs. The first was novel and near ISG20. The second was in TRIOBP, a gene previously associated with prelingual nonsyndromic hearing loss. Motivated by our TRIOBP results, we also looked at exons in known hearing loss genes, and identified two additional SNPs, rs2877561 in ILDR1 and rs9493672 in EYA4 (at a significance threshold adjusted for number of SNPs in those regions). 28521375_Variation at rs12913965 may affect the risk for shoulder dislocation by affecting the activity of either TICRR or ISG20. 29195126_we have identified a novel mechanism involving ISG20 induction by T3 via the IL-8/p-JAK2/p-STAT3 signaling pathway to promote tumor angiogenesis in HCC. 29899085_In conclusion, the authors identified that the influenza A virus-upregulated Long noncoding RNA lnc-ISG20 is a novel interferon-stimulated gene that elicits its inhibitory effect on influenza A virus replication by enhancing ISG20 expression. They demonstrated that lnc-ISG20 functions as a competitive endogenous RNA to bind miR-326 to reduce its inhibition of ISG20 translation. 33147372_ISG20 and nuclear exosome promote destabilization of nascent transcripts for spliceosomal U snRNAs and U1 variants. 33830434_Host Interferon-Stimulated Gene 20 Inhibits Pseudorabies Virus Proliferation. 33896836_High expression of ISG20 predicts a poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. 33969602_Interferon-induced degradation of the persistent hepatitis B virus cccDNA form depends on ISG20. 34405956_Placenta-derived interferon-stimulated gene 20 controls ZIKA virus infection. 36177004_The regulation of ISG20 expression on SARS-CoV-2 infection in cancer patients and healthy individuals. | ENSMUSG00000039236 | Isg20 | 172.080498 | 1.3711907 | 0.455429222 | 0.41279776 | 1.18625869757 | 0.2760855223752637921386110519961221143603324890136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.50720833819085764382350589585257694125175476074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 228.819273 | 60.711804 | 168.340421 | 44.822371 | |
| ENSG00000172613 | 5883 | RAD9A | protein_coding | Q99638 | FUNCTION: Component of the 9-1-1 cell-cycle checkpoint response complex that plays a major role in DNA repair. The 9-1-1 complex is recruited to DNA lesion upon damage by the RAD17-replication factor C (RFC) clamp loader complex. Acts then as a sliding clamp platform on DNA for several proteins involved in long-patch base excision repair (LP-BER). The 9-1-1 complex stimulates DNA polymerase beta (POLB) activity by increasing its affinity for the 3'-OH end of the primer-template and stabilizes POLB to those sites where LP-BER proceeds; endonuclease FEN1 cleavage activity on substrates with double, nick, or gap flaps of distinct sequences and lengths; and DNA ligase I (LIG1) on long-patch base excision repair substrates. The 9-1-1 complex is necessary for the recruitment of RHNO1 to sites of double-stranded breaks (DSB) occurring during the S phase. RAD9A possesses 3'->5' double stranded DNA exonuclease activity. Its phosphorylation by PRKCD may be required for the formation of the 9-1-1 complex. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10713044, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21659603}. | 3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;DNA damage;Exonuclease;Hydrolase;Nuclease;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene product is highly similar to Schizosaccharomyces pombe rad9, a cell cycle checkpoint protein required for cell cycle arrest and DNA damage repair. This protein possesses 3' to 5' exonuclease activity, which may contribute to its role in sensing and repairing DNA damage. It forms a checkpoint protein complex with RAD1 and HUS1. This complex is recruited by checkpoint protein RAD17 to the sites of DNA damage, which is thought to be important for triggering the checkpoint-signaling cascade. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. | hsa:5883; | checkpoint clamp complex [GO:0030896]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; 3'-5' exonuclease activity [GO:0008408]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; exodeoxyribonuclease III activity [GO:0008853]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cellular response to ionizing radiation [GO:0071479]; DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0000077]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; DNA replication checkpoint signaling [GO:0000076]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage [GO:0008630]; mitotic intra-S DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0031573]; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage [GO:1902231] | 11971963_These findings indicate that Rad9 is regulated by a c-Abl-dependent mechanism in the apoptotic response to genotoxic stress. (c-abl protein) 11994305_role of C-terminal region in nuclear transport of the hRad9 checkpoint complex 12228248_Rad9, Hus1, and Rad1 heterotrimeric complex chromatin binding is a proximal event in the checkpoint signaling cascade 12628935_Protein kinase C-delta is responsible for constitutive and DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of this protein. 12709442_the Rad9 phospho-tail is a key participant in the transduction of downstream checkpoint signals 12734188_Characterization of nonphosphorylatable mutants has revealed that Rad9 phosphorylation plays a critical role in checkpoint signaling. 12941802_hRad9/hHus1/hRad1 complex acts as a checkpoint sensor during S phase by rapidly localizing to sites of DNA damage and transducing checkpoint responses by facilitating proper localization of downstream checkpoint proteins, including TopBP1. 14500360_HRAD9 and Mrad9 are part of a gene family and reveal a new genetic element encoding a product that interacts with multiple, known cell cycle checkpoint control proteins. 14966297_Data report the identification of Rad9, a key member of the checkpoint Rad protein family, as a coregulator to suppress androgen-androgen receptor transactivation in prostate cancer cells. 14988409_results suggest that the predominant role of Rad9 in embryonic stem cells is to promote survival after replicative stress and topoisomerase-mediated DNA damage 15314187_The human Rad9/Rad1/Hus1 complex interacts with and stimulates DNA polymerase beta activity. 15326225_Rad9 stimulates the carbamoyl phosphate synthetase activity of the multifunctional protein CAD. 15556996_complex with rad1 and hus1 is a damage-specific activator of flap endonuclease 1 15558813_Rad9 expression may play an important role in cell cycle control in NSCLC cells and may influence NSCLC cell phenotype 15773892_Rad9 plays critical role in the activation of S-phase checkpoint and the maintenance of chromosome stability. 15871698_The long-patch base excision machinery is an important target of the Rad9-Rad1-Hus1 complex, thus enhancing the quality control of DNA. 16365875_The encoded mammalian proteins participate in promoting resistance to DNA damage, cell cycle checkpoint control, DNA repair, and apoptosis. 16479004_role for Rad9 in telomere stability and homologous recombinational repair as a mechanism for promoting cell survival after ionizing radiation exposure 16731526_human DNA ligase I is stimulated by the Rad9-rad1-Hus1 checkpoint complex 16814252_These data provide in vivo evidence that the human 9-1-1 complex participates in DNA repair in addition to its previously described role in DNA damage sensing. 17395641_Human NEIL1 DNA glycosylase activity is significantly stimulated by hRad9 and by the Rad9/Rad1/Hus1 heterotrimer. 17493829_we report successful tri-cistronic cloning, overexpression and purification of a three-protein complex of Rad9, Rad1 and Hus1 using a single hexa-histidine tag. 17511890_Rad9 modulates the P21WAF1 pathway by direct association with p53. 18156970_Rad9 expression correlated closely to significance only with the apoptotic and mitotic indices in epithelial ovarian tumors 18215141_elements found in the aquaporin-5 and the Rad9 (radiation-sensitive 9) genes showed selective AR versus GR binding in band-shift assays and a strong activity and selectivity in functional assays, both as isolated elements and in their original contexts 18316588_Rad9 levels are high in prostate cancer cells due at least in part to aberrant methylation or gene amplification 18616832_up-regulated in breast cancer; mRNA up-regulation correlates with tumor size and local recurrenc;hyperphosphorylated forms of the protein inthe nucleus of the cancer cells 18842633_Disruption of the Rad9-MLH1 interaction by a single-point mutation in Rad9 leads to significantly reduced DNA mismatch repair activity. 18936170_Data show that the basic cleft of the RPA70 N-terminal OB-fold domain binds multiple checkpoint proteins, including RAD9, to promote ATR signaling. 19411845_Rad9 foci were predominately formed in G1 and S phase after UV light, while treatment of cells with ionizing radiation (IR) resulted in accumulation of Rad9 into foci in S and G2. 19523882_The DNA binding domain (DBD) within the hLigI catalytic fragment interacts with both PCNA and the heterotrimeric cell-cycle checkpoint clamp, hRad9-hRad1-hHus1 (9-1-1). 19535328_The interdomain connecting loops (IDC loop) of hRad9, hHus1, and hRad1 are largely divergent and unique structural features of the 9-1-1 complex that are proposed to contribute to DNA damage recognition. 19536092_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19615952_Rad9-Rad1-Hus1 complex enhances in vitro activity of 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20081369_Rad9A-mediated Claspin localization is a vital step during checkpoint activation. 20188637_9-1-1 complex is a component of the mismatch repair involved in MNNG-induced damage response. 20305300_results emphasize the importance of Rad9A in preserving genomic integrity in the presence of catenated chromosomes and all types of DNA aberrations 20545769_When over-expressed in HeLa cells, a mutant Rad9 harboring phospho-deficient substitutions at both Ser-341 and Ser-387 residues causes hypersensitivity to UV and methyl methane sulfonate. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21858012_Data indicate that association of RAD18 with DSBs through ubiquitylated H2A and other ubiquitylated chromatin components allows recruitment of RAD9. 21978893_The RAD9 is loaded to damaged sites where it serves as a platform for the selective recruitment of checkpoint and repair proteins. 21991345_Modulation of RAD9A and other cell cycle arrest and DNA repair proteins contribute to the risk of developing a second malignancy in childhood cancer patients. 22034047_A review of the many activities assigned to Rad9, and speculation as to which influence its function in tumor development. 22586102_Data show models for the ternary PCNA/FEN1/DNA and Rad9-Rad1-Hus1 (9-1-1 complex)/FEN1/DNA assemblies. 22925454_the affinity of Rad9 to TopBP1 correlates with the activation of the cellular DNA damage response and survival after DNA damage in HeLa cells. 23028682_cyclin A-Cdk2 regulates apoptosis through a mechanism that involves Rad9phosphorylation 23066031_Rad9 contributes to prostate tumorigenesis by increasing not only tumor proliferation and survival but also tumor migration and invasion, anoikis resistance, and anchorage-independent growth 23383325_Rad9, Rad17, TopBP1 and claspin play essential roles in heat-induced activation of ATR kinase and heat tolerance. 23433811_Loss of Rad9 alters expression of nucleotide excision repair factors. 24376897_Tousled-like kinase-dependent phosphorylation of Rad9 plays a role in cell cycle progression and G2/M checkpoint exit. 24403312_Loss of hrad9 expression is associated with breast and lung cancer. 24971543_These data suggest that v-Src attenuates ATR-Chk1 signaling through the inhibition of Rad17-Rad9 interaction. 25111005_Downregulation of RAD9 when combined with ionizing radiation results in reduction of ITGB1 protein levels in prostate cancer cells, and increased lethality. 25127721_These data reveal that human Rad9 interacts directly with N-terminal region of human MYH. 25234738_we found that H1299 cells with reduced RAD9 protein levels showed a higher frequency of radiation induced bystander micronuclei formation 25485590_The role of Rad9 in homologous recombination is independent of its function in checkpoint activation, and this function is important for preventing alternative non-homologous end joining. 26088138_Intramolecular binding of the rad9 C-terminus in the checkpoint clamp Rad9-Hus1-Rad1 is closely linked with its DNA binding. 26658951_these results demonstrate a positive feedback loop involving Rad9A-dependend activation of Chk1. 26667770_RAD9 has a prominent role in the ATR-Chk1 pathway that is necessary for successful formation of the damage-sensing complex and DNA damage checkpoint signaling. 26860083_TLK1B mediated phosphorylation of Rad9 regulates its nuclear/cytoplasmic localization and cell cycle checkpoint 29254517_The authors show that human Cyclin-Dependent-Kinases (CDKs) target the RAD9 subunit of the 9-1-1 checkpoint clamp on Thr292, to modulate DNA damage checkpoint activation. Thr292 phosphorylation on RAD9 creates a binding site for Polo-Like-Kinase1 (PLK1), which phosphorylates RAD9 on Thr313. 30295739_RAD9A drives metastasis by controlling AGR2 abundance. 31310624_breast and lung tumor suppressive activities of resveratrol are, at least in part, mediated by the upregulation of Rad9 in a DNA damage response pathway involving reactive oxygen species 32576832_Rad9/53BP1 promotes DNA repair via crossover recombination by limiting the Sgs1 and Mph1 helicases. 32780107_DNMT1 and DNMT3B regulate tumorigenicity of human prostate cancer cells by controlling RAD9 expression through targeted methylation. | ENSMUSG00000024824 | Rad9a | 93.529245 | 0.7642529 | -0.387877979 | 0.15690743 | 6.11588001607 | 0.0133972696388443470588702766121969034429639577865600585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.06197123270772312425558325799102021846920251846313476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 80.455022 | 8.263898 | 105.875086 | 10.614803 | |
| ENSG00000172890 | 55191 | NADSYN1 | protein_coding | Q6IA69 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the final step of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) de novo synthesis pathway, the ATP-dependent amidation of deamido-NAD using L-glutamine as a nitrogen source. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12547821, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31883644}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Disease variant;Ligase;NAD;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome | PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; NAD(+) biosynthesis; NAD(+) from deamido-NAD(+) (L-Gln route): step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:12547821}. | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme in metabolic redox reactions, a precursor for several cell signaling molecules, and a substrate for protein posttranslational modifications. NAD synthetase (EC 6.3.5.1) catalyzes the final step in the biosynthesis of NAD from nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide (NaAD).[supplied by OMIM, Apr 2004]. | hsa:55191; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; glutaminase activity [GO:0004359]; NAD+ synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing) activity [GO:0003952]; 'de novo' NAD biosynthetic process [GO:0034627]; NAD biosynthetic process [GO:0009435] | 19724895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20418485_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22390397_several SNPs related to calcium metabolism are associated with height, in particular rs3829251 at the DHCR7/NADSYN1 gene. 22785457_findings suggest that VDR, NADSYN1, and GC polymorphisms may be linked to the manifestation of vitamin D deficiency in Japanese children 23636220_Data indicate that SNPs in the DHCR7/NADSYN1 locus showed evidence of positive association with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). 24642724_NADSYN1/DHCR7 locus (rs12785878 and rs1790349) polymorphisms have an effect on plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and coronary artery disease incidence 26149120_Polymorphisms in CYP2R1-rs10766197 and DHCR7/NADSYN1-rs12785878 are associated with vitamin D deficiency in Uygur and Kazak ethnic populations 31883644_Bi-allelic Mutations in NADSYN1 Cause Multiple Organ Defects and Expand the Genotypic Spectrum of Congenital NAD Deficiency Disorders. 31911602_Homo sapiens NAD(+) synthetase (hsNadE) lacks substrate specificity for glutamine over ammonia. 32938288_Genetic variants of vitamin D metabolism-related DHCR7/NADSYN1 locus and CYP2R1 gene are associated with clinical features of Parkinson's disease. 34681008_Disruptive NADSYN1 Variants Implicated in Congenital Vertebral Malformations. 35491967_Further description of two patients with biallelic variants in NADSYN1 in association with cardiac and vertebral anomalies. | ENSMUSG00000031090 | Nadsyn1 | 395.313860 | 0.6152233 | -0.700818002 | 0.23829314 | 8.43250724470 | 0.0036857179035898915246682872037808920140378177165985107421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.02238637517820903435894486221968691097572445869445800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 250.199248 | 57.100748 | 406.765049 | 92.713710 |
| ENSG00000173039 | 5970 | RELA | protein_coding | Q04206 | FUNCTION: NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52. The heterodimeric RELA-NFKB1 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. The NF-kappa-B heterodimeric RELA-NFKB1 and RELA-REL complexes, for instance, function as transcriptional activators. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. The inhibitory effect of I-kappa-B on NF-kappa-B through retention in the cytoplasm is exerted primarily through the interaction with RELA. RELA shows a weak DNA-binding site which could contribute directly to DNA binding in the NF-kappa-B complex. Beside its activity as a direct transcriptional activator, it is also able to modulate promoters accessibility to transcription factors and thereby indirectly regulate gene expression. Associates with chromatin at the NF-kappa-B promoter region via association with DDX1. Essential for cytokine gene expression in T-cells (PubMed:15790681). The NF-kappa-B homodimeric RELA-RELA complex appears to be involved in invasin-mediated activation of IL-8 expression. Key transcription factor regulating the IFN response during SARS-CoV-2 infection (PubMed:33440148). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10928981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12748188, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15790681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17000776, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17620405, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19058135, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19103749, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20547752, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33440148}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-nitrosylation;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation | NF-kappa-B is a ubiquitous transcription factor involved in several biological processes. It is held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state by specific inhibitors. Upon degradation of the inhibitor, NF-kappa-B moves to the nucleus and activates transcription of specific genes. NF-kappa-B is composed of NFKB1 or NFKB2 bound to either REL, RELA, or RELB. The most abundant form of NF-kappa-B is NFKB1 complexed with the product of this gene, RELA. Four transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. | hsa:5970; | chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; NF-kappaB complex [GO:0071159]; NF-kappaB p50/p65 complex [GO:0035525]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; actinin binding [GO:0042805]; ankyrin repeat binding [GO:0071532]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; general transcription initiation factor binding [GO:0140296]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; NF-kappaB binding [GO:0051059]; peptide binding [GO:0042277]; phosphate ion binding [GO:0042301]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000979]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription coactivator binding [GO:0001223]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; cellular response to angiotensin [GO:1904385]; cellular response to hepatocyte growth factor stimulus [GO:0035729]; cellular response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0070301]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to interleukin-6 [GO:0071354]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to lipoteichoic acid [GO:0071223]; cellular response to nicotine [GO:0071316]; cellular response to peptidoglycan [GO:0071224]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; defense response to tumor cell [GO:0002357]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; hair follicle development [GO:0001942]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070498]; liver development [GO:0001889]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902894]; negative regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901223]; negative regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0042177]; negative regulation of protein sumoylation [GO:0033234]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuropeptide signaling pathway [GO:0007218]; NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0038061]; nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 signaling pathway [GO:0070431]; positive regulation of amyloid-beta formation [GO:1902004]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of leukocyte adhesion to vascular endothelial cell [GO:1904996]; positive regulation of miRNA metabolic process [GO:2000630]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050862]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter involved in cellular response to chemical stimulus [GO:1901522]; postsynapse to nucleus signaling pathway [GO:0099527]; protein catabolic process [GO:0030163]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription in response to stress [GO:0043620]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901222]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to cytokine [GO:0034097]; response to interleukin-1 [GO:0070555]; response to muramyl dipeptide [GO:0032495]; response to muscle stretch [GO:0035994]; response to organic substance [GO:0010033]; response to UV-B [GO:0010224]; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033209] | 11813986_Physical exercise induces activation of NF-kappaB in human peripheral blood lymphocytes 11922866_Respiratory syncytial virus induction of chemokine gene expression involves a redox-sensitive NF-kappaB1 signaling mechanism that differs from that mediated by TNF alpha in that it involves predominantly the RelA subunit of NF-kappaB. 11953203_activation and expression of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) and effects of anti-inflammatory treatment on NF-kappaB in the intestinal mucosa of patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) 11964305_MDM2 can induce expression of the p65 subunit of NF-kappaB 11980335_NF-KB could be considered as a coordinating element in the body's response to stress, infection or inflammation, and it may be a good therapeutic target. 12027803_A novel form is induced by and forms a complex with the proto-oncogene c-Myc 12067985_NFkB is associated with antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer 12080470_C-Rel can both induce and inhibit apoptosis in HeLa cells by upregulation of MnSOD 12213807_NF-kappaB is regulated by the redox factor Ref-1 in the nucleus 12350227_Data show that interleukin-1 induces nuclear transport of RelA. 12377934_cross-linking FcgammaRI and -RII but not FcgammaRIII activates transcription factor NF-kappaB(p65) 12419806_acetylation of p65 plays a key role in IkappaBetaalpha-mediated attenuation of NF-kappaBeta transcriptional activity which is an important process that restores the latent state in post-induced cells 12419817_The NF-kappa B activation in lymphotoxin beta receptor signaling depends on the phosphorylation of p65 at serine 536. 12429528_B-oligomer of pertussis toxin inhibits HIV-1 LTR-driven transcription through suppression of NF-kappaB p65 subunit activity 12493764_Protein kinase C delta-NF-kappaB signaling regulates VCAM1 stimulation by thrombin in endothelial cells 12509469_RelA expression is regulated by replication factor C (p140) 12517770_mediates tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced nuclear translocation of telomerase reverse transcriptase protein 12559944_S276 is the major phosphorylation site of p65 and its phosphorylation is essential for p65-dependent cellular responses 12589049_IkappaBalpha and p65 have roles in regulating the cytoplasmic shuttling of nuclear corepressors 12606945_The translocation of RelA/p65 was investigated using Western blotting and immunocytochemistry. the COX-2 inhibitor SC236 worked directly through suppressing nuclear translocation of RelA/p65. 12606947_Adenosine selectively suppresses TNF-induced NF-kappaB activation, which may contribute to its role in suppression of inflammation and of the immune system. 12618762_Inhibiting constitutive NF-kappa B activity by expressing I kappa B alpha M suppressed the tumorigenicity of a nonmetastatic human pancreatic cancer cell line, PANC-1, in an orthotopic nude mouse model. 12651903_Data show that increased expression of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kB) in amnion during labor is associated with an increase in the expression of NF-kBp65 and the NF-kB binding proteins IkBa, IkBb-1 and IkBb-2. 12673201_NF-kappa B induced proinflammatory & antiapoptotic genes in epithelial and mesenchymal cells of human skin. In keratinocytes, not fibroblasts, it induced p21(CIP1). GIF levls increased by NF-kappa B in both, but inhibited growth only in keratinocytes. 12690099_NF-kappaB has a role in the migration and the organ-specific homing of metastatic breast cancer cells 12700228_p65/RelA, one of the two subunits of the transcription factor NF-kappaB, binds to the BRCA1 protein. 12736262_SINK specifically interacted with the NF-kappaB transactivator p65 and inhibited p65 phosphorylation 12748188_RING finger protein AO7 supports NF-kappaB-mediated transcription by interacting with the transactivation domain of the p65 subunit. 12767057_Mitogenic and antiapoptotic role of constitutive NF-kappaB/Rel activity in pancreatic cancer. 12820969_During dendritic cell maturation, rapidly activated dimers (e.g.,RelA) bound to a subset of target promoters are gradually replaced by slowly activated dimers (e.g., RelB). 12829026_Primary CML blasts showed constitutive p65/RelA NF-kappaB/Rel DNA binding activity 12842894_IkappaB and NF-kappaB are substrates for the IKK complex in the activation of NF-kappaB 12972607_NFkB confers estrogen-independent growth on breast cancer 14576841_NFkB is part of a gene network impliceted in estrogen receptor signaling 14587029_Ciglitazone induced phosphorylation of PPARgamma through the MAP kinase pathway provides a potential regulatory mechanism for PPARgamma's physical interaction with p65 14593105_STAT3/NF-kappaB p65 cross-talk activated by IL-1 via TRAF6. 14600158_TGF-beta1 is a negative regulator of NF-kappaB p65 activation in the gut 14623898_overexpression of TNF-alpha downstream signaling targets, nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB)-inducing kinase (NIK) and p65 nuclear factor NF-kappaB, lowers PTEN expression 14688382_RelA blunts IL-4 induction in T cells during the relapse in patients with minimal change nephrotic syndrome. 14690596_Data show that NF-kappaB function is regulated by Pin1-mediated prolyl isomerization and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of its p65/RelA subunit. 14711835_the p65 peptide that can selectively inhibit NF-kappaB activation induced by various inflammatory stimuli, down-regulate NF-kappaB-mediated gene expression, and up-regulate apoptosis 14716817_NF-kappaBp65 and hTERT expressions are upregulated at the early stage of gastric carcinogenesis. 14966904_Intestinal type gastric carcinoma is strongly associated with high expression of c-myc, cyclinD1 and bcl-xl through NF-kappaB/p65 activated by H pylori cagA 14970236_NF-kappaB positively regulates the NR1 promoter during neuronal differentiation via interacting mainly with Sp1/Sp3 15016307_RelA expression is altered in metastatic melanoma cells and has a role in deregulated NFkappaB signaling 15073167_NF-kappaB p65 Thr dephosphorylation is activated by protein phosphatase 4 15073170_NF-kappaB activation is induced by p53 by an IkappaB kinase-independent mechanism involving phosphorylation of p65 by ribosomal S6 kinase 1 15079071_transcription of CD28-induced genes is mediated by the specific recruitment of RelA and p52 NF-kappaB subunits to target promoters 15128824_Jurkat T cell costimulation-induced phosphorylation sites have been systematically mapped within the carboxyl-terminal half of the strongly trans-activating NF-kappa B p65 subunit; serine 536 is identified as the main phosphorylation site. 15130920_Ang II stimulates IL-6 and IL-8 production and release from human adipocytes by a NF-kappaB-dependent pathway. Ang II increases p50/p65 heterodimer translocation to the nucleus in adipocytes. 15140884_the transcriptional activity of p65 is suppressed by PIAS3 15155458_unique mechanism for p53 regulation by the p65/RelA subunit of NF-kappaB. 15167972_IVIG inhibits NF-kappaB activation induced by TNF-alpha in cultured endothelial cells of coronary arteries, thereby possibly modulating IL-6 production and E-selectin expression 15200413_The decrease of NF-kappaB p65 subunit and up-regulation of IL-2 are potential mechanism of glucocorticoid resistance in steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. 15226358_These results indicate that proteasomal degradation of p65/RelA does not merely regulate its stability and abundance, but also actively promotes transcriptional termination. 15231833_mitochondrial recruitment of NF-kappaB observed following ANT1 overexpression has an important role in ANT1 proapoptotic activity 15246972_cAMP concentration in endothelial cells prevents thrombin-induced ICAM-1 expression by inhibiting p38 MAPK activation, which in turn prevents phosphorylation of RelA/p65 and transcriptional activity of the bound NF-kappaB. 15256061_NF-kappaB/p65 is constitutively activated in human prostate adenocarcinoma and is related to tumor progression. 15484295_increased expression of RelA/nuclear factor-kappaB plays an important role in the pathogenesis of colorectal carcinoma. 15489227_IL-1-inducible phosphorylation of p65 NFkB is mediated by multiple protein kinases including IKKalpha, IKKbeta, IKKepsilon, TBK1, and an unknown kinase and couples p65 to TAFII31-mediated IL-8 transcription 15498932_TRAIL effects on mitochondrial NF-kappaB-DNA binding 15499023_transcription of target genes depended on oscillation persistence, involving cycles of RelA phosphorylation and dephosphorylation 15543947_a signal-specific transcriptional repression appears to selectively inhibit stimuli that transiently activate p65-p50 complexes 15556937_the p65-dependent repression and the E1A-mediated attenuation of repression require the Brg1-dependent chromatin remodeling function and p300/CBP-dependent complex formation at a promoter assembled within chromatin 15599399_data demonstrate, for the first time to our knowledge, that the RAGE-NF-kappaB axis operates in diabetic neuropathy, by mediating functional sensory deficits, and that its inhibition may provide new therapeutic approaches 15657351_Inhibition of NFkB restores sensitivity to antiestrogens 15671037_Plk3 is a RelA-NF-kappaB-regulated gene that induces apoptosis in both p53-dependent and -independent signaling pathways 15682491_NF-kappaB RelA (p65) activation was related with increased heparanase gene expression and correlated with poor clinicopathological characteristics in gastric cancers 15718492_Shear stress inhibited the smooth muscle cell coculture-induced NF-kappaB activation in endothelial cells and monocytic THP-1 cell adhesion to ECs. 15746428_caspase-8 deficiency specifically abolishes activation of NF-kappaB after stimulation in T, B & NK cells; recruitment of the IKKalpha, beta complex, its activation & the nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB require activity of full-length caspase-8 15845545_inactivation of NF-kappaB function by proteolytic cleavage of p65-RelA is the common mechanism by which picornaviruses suppress the innate immune response 15849198_transactivation and phosphorylation on serine 536 is mediated by bruton's tyrosine kinase 15885892_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15905616_the constitutive activation and the protein expression of NF-kappaB are different in gastric cancer cell lines 15913553_whereas wild type p16INK4a strongly inhibits NF-kappaB transcriptional activity, a subset of melanoma-associated p16INK4a mutants show reduced NF-kappaB inhibitory function 15917220_FBI-1 enhances transcription of the NF-kappaB-responsive E-selectin gene by nuclear localization of the p65 subunit of NF-kappaB 15935276_data support the notion that PKCzeta is essential for LPS-induced NF-kB p65 subunit nuclear translocation in human myometrial cells 15975999_NF-kappaB may regulate Fas-mediated apoptosis in HIVAN by controlling the expression of Fas ligand in renal epithelium 15988014_The nucleolar accumulation of RelA is paralleled by a decrease in basal levels of NF-kappaB transcriptional activity and by apoptosis. 16034126_Upon neutrophil activation, RelA becomes phosphorylated in both cell nucleus and cytoplasm 16046471_IKKbeta phosphorylates multiple p65 sites, as well as in an IkappaB-p65 complex, and S468 phosphorylation slightly reduces TNF-alpha- and IL-1beta-induced NF-kappaB activation 16052512_Data show that stimulation of PAR1 results in increased DNA binding of the NFkappaB p65 subunit, and that activation of PAR1 attenuates docetaxel induced apoptosis through the upregulation of Bcl-xL. 16081638_RelA did not bind directly to the Galphas promoter. Expression of a coactivator protein, cAMP response element binding protein binding protein, relieved RelA-induced down-regulation of Galphas. expression. 16105840_p65 phosphorylated on serine 536 is not associated with or regulated by IkappaBalpha, but it has a distinct set of target genes and may represent a noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway that is independent of IkappaBalpha regulation 16135789_Acetylation of RelA at lysine 310 is importantly regulated by prior phosphorylation of serines 276 and 536. 16186799_study provides the first example of a gene (SH#BGRL) that is downregulated in v-Rel-expressing cells that also plays a role in v-Rel transformation 16243805_The expression of NF-kappaB p65 was related with tumor angiogenesis. 16285952_The activation of p50 and p65 by tumor necrosis factor alpha suppresses the expression of the alpha1C subunit of Cav1.2 channels in human colonic circular smooth muscle cells 16322332_In parathyroid tumors, p65 phosphorylation is dramatically increased. 16329838_Expression of NF-kappaB p65 was related to microvessel density in adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary glands. 16407283_Data raise the possibility of a positive feedback loop in which NF-kappaB activation by oxidative stress leads to further radical production via NADPH oxidase subunit gp91(phox). 16408727_Activation of P50 and P65 subunits of NF-kappaB might be one of the mechanisms for induction of IL-6 and IL-8 expression in chronic sinusitis. 16410078_NFkB has a role in VEGF signaling in endothelial cell survival 16477006_The critical IRAK1 role in LMP1-induced NF-kappaB activation is in mediating p65/RelA S536 phosphorylation through an effect on p38 or other p65 S536 kinases. 16497702_curcumin-mediated activation of JNK or induction of apoptosis does not require inhibition of p65 16524505_LPS treatment resulted in an increase in upregulation and nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB p65 protein, which was inhibited bt CCK8. 16573520_These data support the significance of COMMD protein-protein interactions and provide new mechanistic insight into the function of this protein family in NF-kappaB signalling. 16584809_NF-kappaB movement through the cytoplasm to the nucleus is independent of the cytoskeleton. NF-kappaB p65 is not associated with the dynein/dynactin molecular motor complex. 16608838_NF-kappaB p65 directly interacted with the DNA-binding domain of RXRalpha and may prevent its binding to the consensus DNA sequences, thus inhibiting the transactivation by the PXR.RXRalpha complex. 16723503_LRRC4 plays a major role in suppressing U251 cell proliferation by regulating the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/Akt/NF-kappaBp65, STAT3, and JNK2/c-Jun pathways. 16728495_results indicate that inflammatory signals regulate iodothyronine deiodinase type II expression predominantly via the nuclear factor-kappa B pathway in a direct transcriptional manner 16735506_siRNA knockdown of p65 inhibits proteasome inhibitor-induced NF-kappaB transcriptional activity 16785565_C/EBP beta association with NF-kappa B subunit p65/RelA blocks phosphorylation of p65, causing inhibition of NF-kappa B-mediated transcription in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-tolerant cells. 16829531_DEK functions to negatively regulate transcription of RelA/p65 16931600_Results indicate that 14-3-3 proteins facilitate the nuclear export of IkappaBalpha-p65 complexes and are required for the appropriate regulation of NFkappaB signaling. 16940169_findings show NFKB translocation is stimulated by the L. pneumophila virulence system & is required to support bacterial intracellular growth in macrophages 16966488_Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 led to an activation of NFkB, and increased mRNA levels of the antioxidant enzyme manganese-superoxide dismutase (MnSOD). 16982623_COX-2 induction by nickel compounds occurs via an IKKbeta/p65 NF-kappaB-dependent but IKKalpha- and p50-independent pathway and plays a crucial role in antagonizing nickel-induced cell apoptosis in Beas-2B cells 16998237_CDDO and CDDO-Me directly block IKKbeta activity and thereby the NF-kappaB pathway by interacting with Cys-179 in the IKKbeta activation loop 17003035_Novel interactions reveal a hitherto unknown function of IKKepsilon in the regulation of the alternative NF-kappaB activation pathway involving p52 and p65 are reported. 17012367_These data implicate an important role of c-Src in phosphorylating RelA/p65 to promote the transcriptional activity of NF-kappaB and thereby ICAM-1 expression in endothelial cells. 17041012_These data show that SIRT1 regulates cigarette smoke-mediated proinflammatory mediator release via NF-kappaB, implicating a role of SIRT1 in sustained inflammation and aging of the lungs. 17054067_T lymphocytes from patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) had significantly decreased expression of CD3zeta & absence of the p65/p50 heterodimer of NF- kappa B; findings provide a novel mechanism for the T cell dysfunction in patients with PTB 17070014_Antigens CD3/CD28 activation induces the transactivation activity of both p65/RelA and c-Rel in T cells. 17079333_Together, these studies reveal that phosphorylation of the SIMPL protein plays a critical role in SIMPL regulation by affecting both SIMPL subcellular localization and the p65 coactivator function of SIMPL. 17085785_TNF-alpha enhances the binding of p65 to the promoter/enhancer regions of the MnSOD gene, which primes neuronal cells to develop resistance against subsequent exposure to beta-amyloid and FeSO(4). 17136479_These data reveals for the first time that PDK1 and PKB may differentially activate NF-kappaB, and that TPCK may subserve a useful anti-inflammatory function by inhibiting IKKbeta. 17158457_RelA/p65 associates with actin, accumulates in the nucleus, and induces ICAM-1 expression after thrombin stimulation of endothelial cells. 17167080_Deficiency of RelA reduces cerebral infarct size in RelA transgenic mice. 17196614_These results indicate that MYBBP1a is a novel NF-kappaB co-repressor of transcription that competes with p300 and may function to regulate cell type specific genes. 17207971_the p38 MAPK/NF-kappaB/cyclin D1 signaling pathway might participate in the oncogenesis of extramammary Paget's disease 17242904_Unequal alterations in the levels of activated NF-kappaB subunits p50 and p65 might provide insights into the mechanisms of NF-kappaB action and anti-TNF-alpha therapy in AS. 17255956_two kappaB-binding sites were identified upstream from the start codon in the IL-20 gene 17258784_Taken together, these results illustrate a role for p65 in regulating the ERVWE1 promoter and in TNFalpha-mediated induction of syncytin-1 in multiple sclerosis. 17301240_Chlamydiae have the ability to interfere with the NF-kappaB pathway of host inflammatory response. 17317104_These results indicate that the reactive oxygen species-mediated TNF-alpha-induced IL-8 transcription is regulated by NF-kappaB/RelA phosphorylation at the critical Ser(276) residue by PKAc, resulting in stable enhanceosome formation on target genes. 17362989_The physical interaction between Daxx and p65 provides a functional framework for the inhibition of p65 acetylation by p300/CBP and subsequent repression of NF-kappaB transcriptional activity. 17374495_These data suggest that nitric oxide as an inhibitor or activator of NF-kappaB p65 may depend on the state of activation of vascular endothelial cells in which it contacts. 17403902_Data suggest that Twist-1 and -2 play an important role in NF-kappaB-dependent chemoresistance. 17439942_Results indicate that antitumor and anti-inflammatory activities previously assigned to butein may be mediated in part through the direct inhibition of IKK, leading to the suppression of the NF-kappaB activation pathway. 17452529_Inhibition of NFkappaB at G2-M diminished mitosis induced by constitutive activation of ERK5, providing a direct link between ERK5, NFkappaB, and regulation of G2-M progression. 17468103_GRx-dependent S-glutathionylation of p65-NFkappaB is most likely responsible for NAC-mediated NFkappaB inactivation and enhanced hypoxic apoptosis 17478731_Increased expression of NAD(P)H oxidase-p47phox and nuclear factor-kappaB p65 may contribute to endothelial oxidative stress with aging in humans. 17493236_Frequent osteopontin expression is typical of, but not specific for malignant pleural mesothelioma, whereas it appears to select pulmonary adenocarcinoma cases with p65 and MMP-9 expression, suggesting a link with EGFR signalling pathways. 17521736_These findings provide evidence for the involvement of the nuclear hormone receptors PPAR gamma and VDR in butyrate-mediated inhibition of inducible NF kappa B activation dependent on the stimulated signalling pathway. 17525529_Review. In cells with mutant RelA lacking the nucleolar targeting domain treated with CDK4 inhibitor, RelA translocated from the cytoplasm to the nucleoplasm, but was excluded from the nucleolus. CDK4 inhibition did not induce apoptosis in these cells. 17530443_increased apoptosis by dual knockdown of p65 and p50 may prove advantageous in preventing invasiveness and destructiveness of hyperplastic synoviocytes 17537731_nuclear IKKalpha is required for p65 DNA binding in a gene-specific manner 17586618_Pathophysiologically relevant homocysteine concentrations induce VCAM-1 expression through a prooxidant mechanism involving NF-kappaB. 17590503_U2-OS cells were used to study direct interactions between fluorescent fusion proteins of ERalpha and the NF-kappaB subunits p50 and p65. 17611696_calyculin A elicits phosphorylation of NF-kappaB on serine 536 in MG63 cells, resulting in the translocation of phospho-NF-kappaB to the nucleus, thereby promoting transcriptional activity of NF-kappaB-related genes 17622249_High expression of RelA/p65 is correlated to an activation of the NF-kappaB pathway and indicates poor patient survival. 17626072_Bortezomib reduced the levels of the p50 and p65 components of the canonical NF-kappaB pathway and reduced the level of p52 in the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway, which is induced by EBV LMP1. 17631635_The study demonstrates that CT441 is a tail-specific protease that is capable of interfering with the NF-kappaB pathway of host antimicrobial and inflammatory responses. 17660862_Selective suppression of RELA in hepatitis virus-infected pregnant women manifesting severe liver damage and high mortality. 17675239_These data support an unsuspected role for HLA-G in innate immunity by activating classical NF-kappaB pathway in natural killer cells. 17707233_NF-kappaB recruits E2F1 to fully activate the transcription of NF-kappaB target genes. 17708800_NF-kappaB P65 protein is expressed in cells of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 17715045_Heparanase and NF-kappaB p65 proteins were found in 30 (62.5%) and 22 (45.9%) tumor specimens, respectively, a rate significantly higher than that in the adjacent tissues. 17720813_NOS2 regulates cytokine-induced S-nitrosylation of p65, resulting in decreased NF-kappaB binding to the NOS2 promoter, thereby inhibiting further NOS2 expression. 17889033_In summary, pulse therapy resulted in a decreased level of activated p65 NF-kappaB subunits leading to decreased levels of transcriptionally active pro-inflammatory NF-kappaB. 17889859_Activation of nuclear factor-kappa B p65 subunit is increased in peritoneal macrophages from patients with endometriosis. 17904523_Results show that gankyrin directly binds to RelA. 17911169_study reports that elevated (alpha6)beta4 integrin-dependent Rac-Pak1 signaling supports resistance to apoptosis in mammary acini by permitting stress-dependent activation of the p65 subunit of NF-kappaB through Pak1 17947640_both IKKalpha and IKKbeta as well as NF-kappaB-inducing kinase are indispensable for lactoferrin-induced p65 phosphorylation 17956668_The expression of P-gp and mdr1 were positively correlated with NF-kappaB/p65. 17959673_Tumorigenic adenovirus type 12 E1A inhibits phosphorylation of NF-kappaB by PKAc, causing loss of DNA binding and transactivation. 17962362_RelA was decreased in PBMC from patients with chronic pancreatitis. 17969521_Positive expression of NF-kappaB p65 correlated with the development of distant metastasis in laryngeal carcinoma. 17982102_a novel regulatory role of p38 during neuroinflammation where this MAP kinase controls acetylation of NF-kappaB p65 by regulating acetyltransferase activity of coactivator p300. 18021261_p65 induces transcriptional activation of several human & mouse hair keratin genes. It is co-expressed with HKs and may mediate the NF-kappaB pathway's activity. Binding sites for Ha5 were found. 18024283_There was a positive correlation between TRAF2 and cyclin D1 expressions and the expression NF-kappaBp65 in the epithelial cells and lymphocytes in oral lichen planus. 18025803_demonstrated that HCCs almost universally overexpress Bcl-3 and preferentially express nuclear p52 and p50, with little evidence of p65 activation 18034190_findings identify RelA/NF-kappaB as a critical regulator of T-cell survival by affecting the balance of Bcl-2 family members. 18035048_Our data suggest a crucial role of Ki-Ras:Akt1 complex in NF-kappaB transcriptional activation and enhancement of cell survival. 18036607_Present immunofluorescence microscopy method to follow NF-kappaB nuclear translocation in primary human macrophages stimulated with LPS. 18037904_ternary complex consisting of PPARdelta, p65/RelA, and HDAC1 in keratinocytes PPARdelta repression 18040287_These results suggest that overexpression of p28(GANK) prevents the nuclear localization and inhibits the activity of NF-kappaB/RelA. 18045535_RPS3 is an essential but previously unknown subunit of NF-kappaB involved in the regulation of key genes in rapid cellular activation responses. 18059344_The proapoptotic effects of sulindac, sulindac sulfone and indomethacin are mediated by nucleolar translocation of the RelA(p65) subunit of NF-kappaB 18061975_TNF-alpha stimulated tenascin-C expression through NF-kappaB signaling with RelA activation in cultured OA chondrocytes, suggesting involvement of tenascin-C in OA cartilage remodeling. 18095109_The expression of constitutively activated RelA/NF-kappaB is associated with malignancy potential in astrocytic tumors and may play a critical role in the regulation of u-PA expression and invasiveness in gliomas. 18163488_High levels of TNFRI at the cell surface in patients with the C73R mutation hypersensitizes cells to stimulation by TNF, leading to increased NF-kappaB p65 subunit activation and an exaggerated proinflammatory response 18163503_up-regulation of Smad7 by IL-1beta is mediated through the NF-kappaB pathway, especially the p65 subunit in chondrocytes 18172215_analysis of a cross-talk between AP-1 and NF-kappaB 18174252_the activation of NF-kappaB in human cancer cell lines and Min mice is inhibited by NO-donating aspirin 18178962_AKIP1 colocalized with p65 within the cells and appeared to retain p65 in nucleus. 18188593_Results show that nuclear p65/RelA expression was positively associated with tumour grade and T-category. 18201972_phosphorylation of Ser-468 was indispensable for the physical interaction between RelA/p65 and GSK3beta. 18212740_copine-I regulates the half-life of NF-kappaB transcriptional responses through a novel mechanism that involves endoproteolysis of the p65 protein 18215193_RelA,was observed as increased expression in non-small cell lung cancer tissues 18215660_p65 and p50 subunits of NF-kappaB can bind to alpha-actinin; the alpha-actinin-4 is important for the NF-kappaB nuclear translocation and its functions inside the nucleus. 18227347_DNA binding of p50, Rel A, and c-Rel in primary CLL cells, and Rel A DNA binding was associated with in vitro survival, with high white cell count, and shorter lymphocyte doubling time 18241676_RelA/p65 represses ARE-dependent gene transcription by depriving CBP from Nrf2 and facilitating recruitment of HDAC3 to MafK. 18294642_in conditions of hyperglycemia C-peptide reduces proliferation of VSMCs and NF-kappaB nuclear translocation 18314621_Demonstration of a deregulation of the classical NF-kappaB rrelA pathway in ovarian cancer. 18362147_Syk signals downstream of PKC-delta to mediate thrombin induced ICAM-1 expression in endothelial cells by increasing transcriptional capacity of NF-kappaB via a mechanism that relies on tyrosine phosphorylation of RelA/p65 18362169_Promoter induction by RelA are controlled by a phosphorylation code influencing its interactions with coactivators and transcriptional elongation factors. 18422166_NF-kappaB p65 was strongly expressed in the cytoplasm of nasal mucosa cells in allergic rhinitis. 18424071_These novel data demonstrate an IKK2-dependent, predominantly G-protein-independent pathway involved in PAR-2 regulation of NFkappaB phosphorylation in keratinocytes. 18424438_the induction of inflammatory genes by farnesol is mediated by the activation of the NF-kappaB pathway and involves MEK1/2-ERK1/2-MSK1-dependent phosphorylation of p65/RelA(Ser(276)) 18434448_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18439422_Cot was identified as a novel p65 interacting protein kinase. 18461473_p50 and p65 subunits of NF-kappaB involved in the production of Wnt-1 by HepG2 cells 18466468_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18541671_These results provide insight into a glutamate-induced regulatory pathway distinct from that described for cytokine-induced NF-kappaB activation and have important implications with regard to both normal glial cell physiology and pathogenesis. 18550535_RIG-1 - MAVS interacts with cytoplasmic 100-kDa NF-kappa B2 complexes via a novel retinoic acid-inducible gene-I - NF- kappa B-inducing kinase signaling pathway 18598236_down-regulation of the NF-kappaB p65 subunit by RNA interference led to a reduction in cathepsin B expression in mitochondrial DNA-depleted osteosarcoma cells 18600306_Data demonstrated that the NF-kappaB pathway components, p65 and IKK-2, are expressed in hMSCs. The data provide evidence that this signal transduction pathway is implicated in TNF-alpha-mediated invasion and proliferation of hMSCs. 18607537_IL-8 and p53 protein expression is regulated through inverse activation of the p38 MAPK and the JNK pathways and the NF-kappaB p65 expression 18652316_siRNA targeting NF-kappaBp65 has significant inhibition effects on the proliferation of Hep-2 cells. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18701591_Results show that the p65 NF-kappaB host signaling pathway can differentially regulate influenza virus RNA synthesis. 18703796_C/EBPbeta was found to have an important role in epithelial cell ICAM-1 regulation, while the adjacent NF-kappaB sequence binds the RelA/p65 and NF-kappaB1/p50 members of the NF-kappaB family to induce ICAM-1 expression in response to H. influenzae. 18714023_protein kinase C betaII augments NF-kappaB-mediated TNF-alpha-induced transcription of the target gene CCL11, promoting p65 association with the CCL11 promoter, in human airway smooth muscle cells by phosphorylating p300/CBP-associated factor 18720533_NF-kappaB p65 is activated in gastric carcinoma tissue, and is related to overall survival after chemotherapy. 18798274_intraperitoneal administration of NF-kappaB p65 siRNA and paclitaxel may provide a breakthrough in the treatment of peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer 18823280_TGF-beta1 synergistically enhances TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB DNA binding activity via induction of RelA acetylation 18947494_Hyperoxia combined with LPS induced a more prolonged duration of NF-kappaB activation. 18952281_NFKB signal transduction is altered in premature rupture of fetal membranes 18981184_tumor suppressor protein SMAR1 can modulate NF-kappaB transactivation and inhibit tumorigenesis by regulating NF-kappaB target genes 18983609_expression of P-p65 is involved in NF-kappaB activation in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma 18990707_thrombin-induced p65/RelA, AMPK, and PKCdelta activation were markedly reduced by knockdown of the TRPC isoform TRPC1 expressed in human endothelial cells and in endothelial cells obtained from Trpc4 knock-out mice. 18991026_Blockage of the NF-kappaB pathway with the RNAi adenovirus substantially protected HUVECs from decreased proliferation and reduced cellular apoptosis in HG conditions. 19019440_c-mip inhibits the degradation of I-kappaBalpha and impedes the dissociation of the NF-kappaB/I-kappaBalpha complexes. 19038492_p27Kip1 is regulated by serine 276 phosphorylation of the p65 subunit of NF-kappaB 19043589_effect of fhaB on the NFKB pathway in human monocytes, macrophages,epithelial cells; nuclear translocation of RelA, degradation of cytosolic IkappaB alpha, activation of the NF-kappaB pathway. 19046417_These data suggest a mechanism for maintaining NF-kappaB activity in human T cells through the binding of the Caspase-3-generated carboxy-terminal fragment of p65/RelA to IkappaBalpha in order to protect wild-type p65/ | ENSMUSG00000024927 | Rela | 439.377423 | 0.6788663 | -0.558800698 | 0.14963204 | 13.86538552167 | 0.0001963823102849252672224417137769592045515310019254684448242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00186489868042466694700309837173790583619847893714904785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 307.663639 | 99.352149 | 444.355381 | 143.523049 | |
| ENSG00000173137 | 203054 | ADCK5 | protein_coding | Q3MIX3 | FUNCTION: The function of this protein is not yet clear. It is not known if it has protein kinase activity and what type of substrate it would phosphorylate (Ser, Thr or Tyr). | Kinase;Membrane;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Predicted to enable protein serine/threonine kinase activity. Predicted to be involved in protein phosphorylation. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:203054; | membrane [GO:0016020]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310] | 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 32277958_aarF domain containing kinase 5 gene promotes invasion and migration of lung cancer cells through ADCK5-SOX9-PTTG1 pathway. | ENSMUSG00000022550 | Adck5 | 114.702404 | 0.8926932 | -0.163763727 | 0.13911426 | 1.38710925603 | 0.2388938842730543854475655507485498674213886260986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.46334515300119316627558418986154720187187194824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 108.318110 | 9.688408 | 121.911116 | 10.440619 | |
| ENSG00000173214 | 91749 | MFSD4B | protein_coding | Q5TF39 | FUNCTION: May function as a sodium-dependent glucose transporter. Potential channels for urea in the inner medulla of kidney. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80T22}. | Cell membrane;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sodium;Sodium transport;Sugar transport;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA | Predicted to enable glucose transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in glucose transmembrane transport and sodium ion transport. Predicted to be located in apical plasma membrane. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:91749; | apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; glucose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005355]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; sodium ion transport [GO:0006814] | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA | ENSMUSG00000096687+ENSMUSG00000038522+ENSMUSG00000038528 | Mfsd4b4+Mfsd4b1+Mfsd4b5 | 324.748700 | 1.2855968 | 0.362438210 | 0.23882407 | 2.29286205079 | 0.1299700639684348846270012245440739206969738006591796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.31559429620545814687559982303355354815721511840820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 387.998334 | 80.184460 | 302.176321 | 62.465056 |
| ENSG00000173473 | 6599 | SMARCC1 | protein_coding | Q92922 | FUNCTION: Involved in transcriptional activation and repression of select genes by chromatin remodeling (alteration of DNA-nucleosome topology). Component of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes that carry out key enzymatic activities, changing chromatin structure by altering DNA-histone contacts within a nucleosome in an ATP-dependent manner. May stimulate the ATPase activity of the catalytic subunit of the complex (PubMed:10078207, PubMed:29374058). Belongs to the neural progenitors-specific chromatin remodeling complex (npBAF complex) and the neuron-specific chromatin remodeling complex (nBAF complex). During neural development a switch from a stem/progenitor to a postmitotic chromatin remodeling mechanism occurs as neurons exit the cell cycle and become committed to their adult state. The transition from proliferating neural stem/progenitor cells to postmitotic neurons requires a switch in subunit composition of the npBAF and nBAF complexes. As neural progenitors exit mitosis and differentiate into neurons, npBAF complexes which contain ACTL6A/BAF53A and PHF10/BAF45A, are exchanged for homologous alternative ACTL6B/BAF53B and DPF1/BAF45B or DPF3/BAF45C subunits in neuron-specific complexes (nBAF). The npBAF complex is essential for the self-renewal/proliferative capacity of the multipotent neural stem cells. The nBAF complex along with CREST plays a role regulating the activity of genes essential for dendrite growth (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97496, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10078207, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11018012, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29374058, ECO:0000303|PubMed:22952240, ECO:0000303|PubMed:26601204}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Chromatin regulator;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the SWI/SNF family of proteins, whose members display helicase and ATPase activities and which are thought to regulate transcription of certain genes by altering the chromatin structure around those genes. The encoded protein is part of the large ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complex SNF/SWI and contains a predicted leucine zipper motif typical of many transcription factors. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:6599; | brahma complex [GO:0035060]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; GBAF complex [GO:0140288]; kinetochore [GO:0000776]; male germ cell nucleus [GO:0001673]; nBAF complex [GO:0071565]; npBAF complex [GO:0071564]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; RSC-type complex [GO:0016586]; SWI/SNF complex [GO:0016514]; XY body [GO:0001741]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; negative regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045596]; negative regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032435]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; nucleosome disassembly [GO:0006337]; positive regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045597]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of double-strand break repair [GO:2000781]; positive regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045663]; positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance [GO:1902459]; positive regulation of T cell differentiation [GO:0045582]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of G0 to G1 transition [GO:0070316]; regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000045]; regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition [GO:0030071]; regulation of nucleotide-excision repair [GO:2000819]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 16199878_protein levels of BAF155/170 dictate the maximum cellular amount of BAF57 16568092_BAF155 and potentially INI1 are substrates for Akt phosphorylation 17513758_Constitutive expression of SRG3 inhibits positive selection processes in T-cell receptor transgenic mice. 18581278_An increased expression of SMARCC1 protein was found in prostate cancer positively correlated with tumour dedifferentiation, progression, metastasis and time to recurrence. 19156145_patients with tumours displaying high levels of CBFB and SMARCC1 proteins had a significantly better overall survival rate than patients with low levels 19367581_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20829358_Data show that the mechanism of BAF155-mediated stabilization of BAF57 involves blocking its ubiquitination by preventing interaction with TRIP12. 22139574_loss of BAF155 expression represents another mechanism for inactivation of SWI/SNF complex activity in the development in human cancer. 23799850_miR-320c regulates the resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine through SMARCC1. 23996527_Results show the secondary structure of SWIRM domain of BAF155 consists of five alpha-helices forming a typical histone fold for DNA interactions. 24365151_Wwp2 acts as a ubiquitin ligase of SRG3. 24434208_we identify BAF155 as a substrate for arginine methyltransferase CARM1. 26257059_NKX6.1 directly enhances the mRNA level of E-cadherin by recruiting BAF155 coactivator and represses that of vimentin and N-cadherin by recruiting RBBP7 (retinoblastoma binding protein 7) corepressor. 27190130_our data showed that Swi3 strongly affects haem/oxygen-dependent activation of respiration gene promoters whereas Swi2 affects only the basal, haem-independent activities of these promoters. using computational analysis and RNAi knockdown, we showed that the mammalian Swi3 BAF155 and BAF170 regulate respiration in HeLa cells. 28438634_Here, the authors first confirmed that SWIRM domain of BAF155 is responsible for its interaction with BAF47 and then narrowed down the SWIRM-binding region in BAF47 to the Repeat 1 (RPT1) domain. 30144500_Study found SMARCC1 as a direct target of miR-202-5p and promoted the growth and metastasis of colorectal carcinoma (CRC) cells. Furthermore, SMARCC1 could reverse the inhibitory effect of miR-202-5p on growth and metastasis of CRC cells. 31533543_BAF155 plays important roles in ubiquitin-independent degradation of hepatitis B virus X protein 32244797_A Coil-to-Helix Transition Serves as a Binding Motif for hSNF5 and BAF155 Interaction. 33931740_Multiple interactions of the oncoprotein transcription factor MYC with the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeler. 33953332_SWI/SNF subunit BAF155 N-terminus structure informs the impact of cancer-associated mutations and reveals a potential drug binding site. 35158202_Assembly and interaction of core subunits of BAF complexes and crystal study of the SMARCC1/SMARCE1 binary complex. | ENSMUSG00000032481 | Smarcc1 | 953.546419 | 1.1458803 | 0.196456399 | 0.08581705 | 5.23364127534 | 0.0221541063493981109366881554478823090903460979461669921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.09085067124461471133045620263146702200174331665039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 999.830789 | 82.176939 | 875.796401 | 72.092026 | |
| ENSG00000173581 | 29903 | CCDC106 | protein_coding | Q9BWC9 | FUNCTION: Promotes the degradation of p53/TP53 protein and inhibits its transactivity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20159018}. | Coiled coil;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | Located in cytosol and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:29903; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] | 20159018_CCDC106 promotes the degradation of p53 protein and inhibits its transactivity. 28460455_Our studies revealed that CCDC106 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer progression and unfavorable prognosis. CCDC106 enhanced Cyclin A2 and Cyclin B1 expression and promoted A549 and H1299 cell proliferation, which depended on AKT signaling. These results suggest that CCDC106 may be a novel target for lung cancer treatment. 30885251_Study revealed a CK2/CCDC106/p53 signaling axis in the progression of breast and cervical cancers. 33023834_HPV-CCDC106 integration alters local chromosome architecture and hijacks an enhancer by three-dimensional genome structure remodeling in cervical cancer. 35484984_CCDC106 promotes the proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells by suppressing p21 transcription through a p53-independent pathway. | ENSMUSG00000035228 | Ccdc106 | 36.685724 | 1.0040438 | 0.005822145 | 0.27817903 | 0.00043752454 | 0.9833117959255917028826843306887894868850708007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.99017820181464089035472397881676442921161651611328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 36.445476 | 5.560695 | 36.307182 | 5.395563 | |
| ENSG00000174652 | 10781 | ZNF266 | protein_coding | Q14584 | FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. | DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a protein containing many tandem zinc-finger motifs. Zinc fingers are protein or nucleic acid-binding domains, and may be involved in a variety of functions, including regulation of transcription. This gene is located in a cluster of similar genes encoding zinc finger proteins on chromosome 19. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2012]. | hsa:10781; | nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 20601676_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) | ENSMUSG00000060510 | Zfp266 | 130.423434 | 0.8843690 | -0.177279715 | 0.14569601 | 1.47927995493 | 0.2238872140171052904644710679349373094737529754638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.44409165480307272177995514539361465722322463989257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 123.644046 | 10.475517 | 140.457995 | 11.916627 | |
| ENSG00000174928 | 285315 | C3orf33 | protein_coding | Q6P1S2 | FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Secreted protein may play a role in transcription regulation via the MAPK3/MAPK1 pathway through an unidentified receptor on the plasma membrane. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Secreted;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Involved in negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade and regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity. Located in extracellular space. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:285315; | extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051090] | 18487146_The preliminary results showed that AC3-33 is an important novel gene related to supress AP-1 activity. 20680465_AC3-33 is a novel member of the secretory family and inhibits Elk1 transcriptional activity via ERK1/2 MAP | ENSMUSG00000048581 | E130311K13Rik | 18.873964 | 1.0945307 | 0.130312373 | 0.35732891 | 0.13299058871 | 0.7153512248633235870443058956880122423171997070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.85553462152771631021863640853553079068660736083984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 20.200160 | 5.080591 | 18.523651 | 4.545683 | |
| ENSG00000175106 | 201158 | TVP23C | protein_coding | Q96ET8 | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Predicted to be involved in protein secretion and vesicle-mediated transport. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be integral component of Golgi membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:100533496;hsa:201158; | Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; protein secretion [GO:0009306]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] | 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) | ENSMUSG00000014177 | Tvp23b | 19.920171 | 3.0250619 | 1.596964674 | 0.68193327 | 5.01348719746 | 0.0251505958319246762655563287580662290565669536590576171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.10019107950070310630863446021976415067911148071289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 39.721421 | 18.469066 | 12.218733 | 5.818388 | ||
| ENSG00000175198 | 5095 | PCCA | protein_coding | P05165 | FUNCTION: This is one of the 2 subunits of the biotin-dependent propionyl-CoA carboxylase (PCC), a mitochondrial enzyme involved in the catabolism of odd chain fatty acids, branched-chain amino acids isoleucine, threonine, methionine, and valine and other metabolites (PubMed:8434582, PubMed:6765947). Propionyl-CoA carboxylase catalyzes the carboxylation of propionyl-CoA/propanoyl-CoA to D-methylmalonyl-CoA/(S)-methylmalonyl-CoA (PubMed:8434582, PubMed:6765947, PubMed:10101253). Within the holoenzyme, the alpha subunit catalyzes the ATP-dependent carboxylation of the biotin carried by the biotin carboxyl carrier (BCC) domain, while the beta subunit then transfers the carboxyl group from carboxylated biotin to propionyl-CoA (By similarity). Propionyl-CoA carboxylase also significantly acts on butyryl-CoA/butanoyl-CoA, which is converted to ethylmalonyl-CoA/(2S)-ethylmalonyl-CoA at a much lower rate (PubMed:6765947). Other alternative minor substrates include (2E)-butenoyl-CoA/crotonoyl-CoA (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P0DTA4, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q5LUF3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10101253, ECO:0000269|PubMed:6765947, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8434582}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Biotin;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Ligase;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Magnesium;Manganese;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transit peptide | PATHWAY: Metabolic intermediate metabolism; propanoyl-CoA degradation; succinyl-CoA from propanoyl-CoA: step 1/3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:6765947, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8434582}. | The protein encoded by this gene is the alpha subunit of the heterodimeric mitochondrial enzyme Propionyl-CoA carboxylase. PCCA encodes the biotin-binding region of this enzyme. Mutations in either PCCA or PCCB (encoding the beta subunit) lead to an enzyme deficiency resulting in propionic acidemia. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. | hsa:5095; | catalytic complex [GO:1902494]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; biotin binding [GO:0009374]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; propionyl-CoA carboxylase activity [GO:0004658]; branched-chain amino acid metabolic process [GO:0009081]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; short-chain fatty acid catabolic process [GO:0019626] | 12385775_pathogenicity of 11 mutations by expression studies and correlation of genotype-phenotype in PCCA-deficient propionic acidemia patients. 12559849_Data reported 9 novel PCCA gene mutations and represents an extensive update of the mutational study of propionic acidemia providing important information about the worldwide distribution of PA mutations. 15890657_analysis of propionyl-CoA carboxylase containing pathogenic mutations in the beta subunit (R165W, E168K, and R410W) and one PCCB polymorphism (A497V) and their structural and functional effects 17051315_analysis of PCCA and PCCB mutations in propionic acidemia 17966092_propionyl CoA carboxylase alpha polypeptide intronic variations causing aberrantly spliced messenger RNA is associated with propionic and methylmalonic acidemia. 19157943_This work describes for the first time the high frequency of large genomic deletions in the PCCA gene, which could be due to the characteristics of the PCCA gene structure and its abundance in intronic repetitive elements. 19296078_Activities of propionyl-CoA carboxylase were not significantly different in pancreatic islets of patients with type 2 diabetes from those of the control. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20725044_cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) reconstruction at 15-A resolution 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22156789_Thsi study presented that Propionic acidemia(PCCA mutation) associated with visual hallucinations 24464666_Mutation analysis of the PCCA gene identified homozygous c.1284+1G>A in patient 1, c.230G>A (p.R77Q) and c.1855C>T (p.R619X) in patient 2, homozygous c.2125T>C (p.S709P) in patient 3, and only one mutant allele, c.231+1G>T in patient 4. 24863100_Two PCCA mutations, c.229C-->T (p.R77W) and c.1262A-->C (p.Q421P), were identified in a PCCA-deficient patient. 25636094_Ten propionic acidemia mutations were confirmed, including 8 affecting the PCCA gene and 2 affecting the PCCB gene 27227689_The majority of patients had mutations in the PCCA gene (18/25). A total of 26 mutations were noted: 20 in the PCCA gene and 6 in PCCB gene. Seventeen mutations were novel (14 in PCCA and 3 in PCCB). The SNP c.937C>T (p.Arg313Ter), was noted in 9/36 (25%) alleles in the PCCA gene 27468871_The data indicate that amino acid/nucleotide metabolism-related genes OGDH, PPAT and PCCA acquire somatic mutations in microsatellite instability-high gastric cancers and colorectal cancers and that mutational intratumoral heterogeneity may occur in at least some of these tumors. 30274917_his work represents a large-scale update on pathogenic mutations in the PCCA and PCCB genes causing Propionic acidemia (PA), and confirms previous reports indicating a major causative role of mutation-induced protein destabilization 33741272_A novel small molecule approach for the treatment of propionic and methylmalonic acidemias. 33881965_Differentially expressed genes PCCA, ECHS1, and HADH are potential prognostic biomarkers for gastric cancer. 33923806_Functional Analysis of the PCCA and PCCB Gene Variants Predicted to Affect Splicing. | ENSMUSG00000041650 | Pcca | 103.460178 | 1.0704320 | 0.098193162 | 0.33588982 | 0.08480287677 | 0.7708912235490549269556481704057659953832626342773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.88941161621611519727537142898654565215110778808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 101.332474 | 24.197300 | 94.994294 | 22.747062 |
| ENSG00000175550 | 10589 | DRAP1 | protein_coding | Q14919 | FUNCTION: The association of the DR1/DRAP1 heterodimer with TBP results in a functional repression of both activated and basal transcription of class II genes. This interaction precludes the formation of a transcription-competent complex by inhibiting the association of TFIIA and/or TFIIB with TBP. Can bind to DNA on its own. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8608938, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8670811}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation | Transcriptional repression is a general mechanism for regulating transcriptional initiation in organisms ranging from yeast to humans. Accurate initiation of transcription from eukaryotic protein-encoding genes requires the assembly of a large multiprotein complex consisting of RNA polymerase II and general transcription factors such as TFIIA, TFIIB, and TFIID. DR1 is a repressor that interacts with the TATA-binding protein (TBP) of TFIID and prevents the formation of an active transcription complex by precluding the entry of TFIIA and/or TFIIB into the preinitiation complex. The protein encoded by this gene is a corepressor of transcription that interacts with DR1 to enhance DR1-mediated repression. The interaction between this corepressor and DR1 is required for corepressor function and appears to stabilize the TBP-DR1-DNA complex. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:10589; | negative cofactor 2 complex [GO:0017054]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0001046]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; RNA polymerase II general transcription initiation factor activity [GO:0016251]; RNA polymerase II general transcription initiation factor binding [GO:0001091]; TBP-class protein binding [GO:0017025]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] | 12477712_Hypoxia actively represses transcription by inducing this protein and blocking preinitiation complex assembly. 15509807_physical cooperation between BTAF1 and NC2alpha in TBP regulation 17548813_The global distribution of DRAP1 on promoters was determined. 17994103_provide evidence that negative cofactor-2 (NC2) induces dynamic conformational changes in the TBP-DNA complex that allow it to escape and return to TATA-binding mode 19204005_heterodimerization with NC2alpha masks the nuclear localization signal in NC2beta, which prevents nuclear export of the NC2 complex | ENSMUSG00000024914 | Drap1 | 370.975722 | 0.7519733 | -0.411246577 | 0.08339791 | 24.36720069809 | 0.0000007961269443848577852330451222473417516312110819853842258453369140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00001338488425247042219582739586147823729334049858152866363525390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 317.496387 | 18.016819 | 423.990693 | 23.194061 | |
| ENSG00000175792 | 8607 | RUVBL1 | protein_coding | Q9Y265 | FUNCTION: Possesses single-stranded DNA-stimulated ATPase and ATP-dependent DNA helicase (3' to 5') activity; hexamerization is thought to be critical for ATP hydrolysis and adjacent subunits in the ring-like structure contribute to the ATPase activity (PubMed:17157868, PubMed:33205750). Component of the NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex which is involved in transcriptional activation of select genes principally by acetylation of nucleosomal histones H4 and H2A (PubMed:14966270). This modification may both alter nucleosome-DNA interactions and promote interaction of the modified histones with other proteins which positively regulate transcription (PubMed:14966270). This complex may be required for the activation of transcriptional programs associated with oncogene and proto-oncogene mediated growth induction, tumor suppressor mediated growth arrest and replicative senescence, apoptosis, and DNA repair (PubMed:14966270). The NuA4 complex ATPase and helicase activities seem to be, at least in part, contributed by the association of RUVBL1 and RUVBL2 with EP400. NuA4 may also play a direct role in DNA repair when recruited to sites of DNA damage (PubMed:14966270). Component of a SWR1-like complex that specifically mediates the removal of histone H2A.Z/H2AZ1 from the nucleosome (PubMed:24463511). Proposed core component of the chromatin remodeling INO80 complex which exhibits DNA- and nucleosome-activated ATPase activity and catalyzes ATP-dependent nucleosome sliding (PubMed:16230350, PubMed:21303910). Plays an essential role in oncogenic transformation by MYC and also modulates transcriptional activation by the LEF1/TCF1-CTNNB1 complex (PubMed:10882073, PubMed:16014379). Essential for cell proliferation (PubMed:14506706). May be able to bind plasminogen at cell surface and enhance plasminogen activation (PubMed:11027681). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10882073, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11027681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14506706, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14966270, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16014379, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16230350, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17157868, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21303910, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24463511, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33205750}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell cycle;Cell division;Chromatin regulator;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;DNA damage;DNA recombination;DNA repair;Growth regulation;Helicase;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Mitosis;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes a protein that has both DNA-dependent ATPase and DNA helicase activities and belongs to the ATPases associated with diverse cellular activities (AAA+) protein family. The encoded protein associates with several multisubunit transcriptional complexes and with protein complexes involved in both ATP-dependent remodeling and histone modification. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. | hsa:8607; | chaperone complex [GO:0101031]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dynein axonemal particle [GO:0120293]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Ino80 complex [GO:0031011]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; MLL1 complex [GO:0071339]; NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex [GO:0035267]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleosome [GO:0000786]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; R2TP complex [GO:0097255]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; RPAP3/R2TP/prefoldin-like complex [GO:1990062]; Swr1 complex [GO:0000812]; ADP binding [GO:0043531]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; DNA helicase activity [GO:0003678]; TBP-class protein binding [GO:0017025]; TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding [GO:0001094]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; box C/D snoRNP assembly [GO:0000492]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell division [GO:0051301]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; DNA recombination [GO:0006310]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; histone acetylation [GO:0016573]; histone H2A acetylation [GO:0043968]; histone H4 acetylation [GO:0043967]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of DNA repair [GO:0045739]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination [GO:1905168]; positive regulation of telomerase RNA localization to Cajal body [GO:1904874]; positive regulation of telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage [GO:1904507]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of chromosome organization [GO:0033044]; regulation of DNA repair [GO:0006282]; regulation of DNA replication [GO:0006275]; regulation of DNA strand elongation [GO:0060382]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of double-strand break repair [GO:2000779]; regulation of embryonic development [GO:0045995]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; telomere maintenance [GO:0000723] | 14675489_Pontin52/TIP49a promotes COX-2 expression in tissue culture and is overexpressed in colon cancer tissue, co-localizing with COX-2 expression in transformed tissue, relative to paired normal tissue 14695187_TIP49 is an important cofactor in beta-catenin/TCF gene regulation in normal and neoplastic cells, likely functioning in chromatin remodeling. 16230350_similar to the yeast INO80 complex, the hINO80 complex of Tip49a and Tip49b exhibits DNA- and nucleosome-activated ATPase activity and catalyzes ATP-dependent nucleosome sliding 17060327_structure of the RuvBL1.ADP complex, combined with our biochemical results, suggest that although RuvBL1 has all the structural characteristics of a molecular motor, even of an ATP-driven helicase 17157868_The results point to biochemical differences between TIP48 and TIP49, which may explain the structural differences between the two hexameric rings and could be significant for specialised functions that the proteins perform individually. 18087039_pontin is a component of chromatin-remodeling complexes that is SUMO-modified, which has a role in transcriptional regulation of pontin on androgen-receptor target genes in prostate cancer cells 18285460_Rvb1 is critical for the dephosphorylation of phospho-H2AX due to the role of Rvb1 in maintaining the histone acetyltransferase activity of Tip60/NuA4 18358808_Study identifies the ATPases pontin and reptin as telomerase components through affinity purification of TERT from human cells. 18463163_Pontin has a mitosis-specific function in regulating microtubule assembly 18548265_Pontin was found to associate with RNA polymerase I and to interact in a complex with c-Myc with rDNA sequences indicating that Pontin is involved in the c-Myc-dependent regulation of rRNA synthesis. 18765919_Crystal structure has been solved and the solutions obtained show that the RuvBL1-RuvBL2 complex forms a dodecamer. 18834951_The results suggest that as a constituent of chromatin modification complexes TIP49 may facilitate the access of the repair machinery to the sites of DNA damage. 19048121_Phorbol ester enhances KAI1 transcription by recruiting Tip60/Pontin complexes 19270026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19450687_Is part of an RNA polymerase II-associated complex with possible chaperone activity. 19524533_RVB1 and RVB2 function within multiple protein complexes is reviewed. 19620283_snoRNP assembly factor NUFIP can regulate the interactions between TIP48 and TIP49 and the core box C/D proteins. 19877184_Reptin and Pontin protein levels are strictly controlled by a posttranslational mechanism involving proteasomal degradation of newly synthesized proteins. 20130364_S100A9 and NMP238 expression is associated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy sensitivity in cervical carcinoma. 20371770_RUVBL1 and RUVBL2 control the abundance of Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-related protein kinases (PIKKs), and stimulate the formation of PIKK-containing molecular complexes, such as those involved in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. 20412048_Several experimental approaches were used to investigate the molecular architecture of the RuvBL1-RuvBL2 complex and the role of the ATPase-insert domain (domain II) for its assembly and stability. 20635389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21617703_These results indicate that EHF-mediated RUVBL1 expression allows colon tumour cells to avoid p53-mediated apoptosis. 21825155_Pontin is methylated by G9a/GLP methyltransferases in hypoxic condition and potentiates HIF-1alpha-mediated activation by increasing the recruitment of p300 coactivator to a subset of HIF-1alpha target promoters. 21933716_DNA unwinding of the human RuvBL proteins can be auto-inhibited by domain II, which is not present in the homologous bacterial helicase RuvB. 22895545_Pontin-positivity seems to be a negative predictor for response to adjuvant therapy in colorectal cancer patients and may help to identify patients with adverse outcome in advanced tumor stages. 22923768_First insight into the mechanism of action of pontin and reptin in the assembly of macromolecular complexes. 23002137_Two coexisting conformations, compact and stretched, are revealed by analysis of cryo-electron microscopy structures of the RuvBL1-RuvBL2 complex. 23878400_Data indicate that the RVB1/2 chromatin-remodeling complex is required for efficient Pol II recruitment and initiation at IFN-alpha-stimulated genes (ISGs) promoters and is recruited through interaction with the STAT2 transactivation domain. 24023044_Anti-RuvBL1/2 antibody is a novel systemic scleroderma-related autoantibody associated with a unique combination of clinical features, including myositis overlap and diffuse cutaneous involvement. 24342949_Upregulation of PONTIN by AML1-ETO participate in the oncogenic growth of t(8;21) leukemia cells. 24728183_Results showed RUVBL1 promoting concentration of G-actin subunits and polymerization of actin filaments via its direct binding to F-actin in cell protrusions and results in increased invasive properties of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. 24990942_these findings suggest that YY1-RuvBL1-RuvBL2 complexes could contribute to functions beyond transcription, and we show that YY1 and the ATPase activity of RuvBL2 are required for RAD51 foci formation during homologous recombination. 25336637_Reptin and Pontin oligomerization and activity are modulated through histone H3 N-terminal tail interaction. 25428364_The results suggests that a potential mechanism for the role of RuvBL1-RuvBL2 in maintaining genome integrity is through controlling the cellular abundance of Fanconi anaemia core complex. 25751257_Study showed that pontin is up-regulated in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and high cytoplasmic pontin expression was associated with poor survival of RCC patients. 25857266_Results highlight an important role and mechanism for Pontin, a new mutp53 partner, in promoting mutp53 GOF in tumorigenesis. 26201077_data thus demonstrate that RUVBL1 is essential for efficient mitosis and proliferation. 26303906_RuvbL1 and RuvbL2 enhance aggresome formation and disaggregate amyloid fibrils. 26711270_The interaction of ECD with RUVBL1, and its CK2-mediated phosphorylation, independent of its interaction with PIH1D1, are important for its cell cycle regulatory function. 26863765_by means of molecular docking approaches we first modeled the structures of hetero-hexameric TIP49 ( TIP49a and TIP49b )complexes with short ds-DNA fragments (20 base pairs with different GC content) within the central channel of hexameric ring 28028178_association of c-FLIPL and TIP49 provided an additional mechanism involved in c-FLIPL-mediated functions, including Wnt activation 28122980_Adenovirus E1A was found to bind to RuvBL1 via the C terminus of E1A, and this interaction was important for suppression of interferon-stimulated gene transcriptional activation and recruitment of E1A to interferon-regulated promoters. 28238654_Methylation of RUVBL1 by the arginine methyltransferase PRMT5 is required for homologous recombination-mediated double-strand break repair by promoting TIP60-mediated histone H4K16 acetylation. 28341484_The interaction between RUVBL1 and ITFG1 is required for breast cancer cell collective invasion and progression. 28561026_The interaction between RUVBL1/RUVBL2 and the U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein is mostly mediated by the previously uncharacterized factor ZNHIT2. 29228333_DNAAF1 links heart laterality with the AAA+ ATPase RUVBL1 and ciliary intraflagellar transport 29323271_the INO80 complex, including Ino80 and actin-related proteins, is assembled around a single RUVBL1 (Tip49a) and RUVBL2 (Tip49b) AAA+ heterohexamer 29545175_RUVBL1 could activate the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway by inhibiting phosphorylation of the C-RAF protein at serine 259, to promote lung cancer progression. 29862278_the present study suggested that Pontin could act as a potential prognostic predictor, which might be a new valuable molecular candidate for the prevention and treatment of Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma. 29873033_These results suggest a role of Reptin and Pontin in Salivary gland cancer tumor progression and/or patient survival. 31018511_We identify RUVBL1 and RUVBL2 as novel interactors of Ebola virus NP and EBOV NP recruitment of the R2TP complex, which may provide novel targets for broad-acting anti-EBOV therapeutics. 31083717_Genetic variant of RUVBL1 is associated with epithelial ovarian cancer. 31721195_Liver haploinsufficiency of RuvBL1 causes hepatic insulin resistance and enhances hepatocellular carcinoma progression. 32745900_RUVBL1 is an amplified epigenetic factor promoting proliferation and inhibiting differentiation program in head and neck squamous cancers. 32846207_Deregulated levels of RUVBL1 induce transcription-dependent replication stress. 33205750_Regulation of RUVBL1-RUVBL2 AAA-ATPases by the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay factor DHX34, as evidenced by Cryo-EM. 33355144_Assembly of the asymmetric human gamma-tubulin ring complex by RUVBL1-RUVBL2 AAA ATPase. 33367824_NOPCHAP1 is a PAQosome cofactor that helps loading NOP58 on RUVBL1/2 during box C/D snoRNP biogenesis. 33542204_The ATPase Pontin is a key cell cycle regulator by amplifying E2F1 transcription response in glioma. 33894417_HEATR1, a novel interactor of Pontin/Reptin, stabilizes Pontin/Reptin and promotes cell proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 34880314_A proteomics study identifying interactors of the FSHD2 gene product SMCHD1 reveals RUVBL1-dependent DUX4 repression. 35078195_The Expression of the RUVBL1 Component of the R2TP Complex Correlates with Poor Prognosis in DLBCL. 35493294_Involvement of RUVBL1 in WNT/beta-Catenin Signaling in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 35508542_RUVBL1 promotes enzalutamide resistance of prostate tumors through the PLXNA1-CRAF-MAPK pathway. 36153326_Recruitment of LEF1 by Pontin chromatin modifier amplifies TGFBR2 transcription and activates TGFbeta/SMAD signalling during gliomagenesis. 36438486_Hippocalcin-Like 1 blunts liver lipid metabolism to suppress tumorigenesis via directly targeting RUVBL1-mTOR signaling. | ENSMUSG00000030079 | Ruvbl1 | 236.318574 | 0.9695404 | -0.044627107 | 0.10544402 | 0.17907323771 | 0.6721708979931710903343855534330941736698150634765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.83176986209558356755167096707737073302268981933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 227.898262 | 17.745897 | 236.137440 | 18.263396 | |
| ENSG00000178761 | 57184 | FAM219B | protein_coding | Q5XKK7 | Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | hsa:57184; | ENSMUSG00000032305 | Fam219b | 385.191048 | 1.0725065 | 0.100986446 | 0.11030222 | 0.83754489300 | 0.3600998779443823627488541205821093171834945678710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.59243444002512057888765184543444775044918060302734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 393.458669 | 29.222427 | 368.584778 | 27.300637 | |||||
| ENSG00000178922 | 81888 | HYI | protein_coding | Q5T013 | FUNCTION: Catalyzes the reversible isomerization between hydroxypyruvate and 2-hydroxy-3-oxopropanoate (also termed tartronate semialdehyde). {ECO:0000250}. | Alternative splicing;Isomerase;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a putative hydroxypyruvate isomerase, which likely catalyzes the conversion of hydroxypyruvate to 2-hydroxy-3-oxopropanoate, and may be involved in carbohydrate transport and metabolism. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. | hsa:81888; | hydroxypyruvate isomerase activity [GO:0008903]; glyoxylate metabolic process [GO:0046487] | 22490543_Protein HYI may closely bind with protein P311 by an alpha helix in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. | 69.456111 | 0.7875957 | -0.344472934 | 0.27891144 | 1.51761938987 | 0.2179801062817245116409736738205538131296634674072265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.43702246333220040597211664135102182626724243164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 75.606488 | 11.703477 | 96.925098 | 14.405327 | |||
| ENSG00000179029 | 84314 | TMEM107 | protein_coding | Q6UX40 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in cilia formation and embryonic patterning. Requires for normal Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling in the neural tube and acts in combination with GLI2 and GLI3 to pattern ventral and intermediate neuronal cell types (By similarity). During ciliogenesis regulates the ciliary transition zone localization of some MKS complex proteins (PubMed:26518474). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9CPV0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26518474}. | Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Meckel syndrome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a transmembrane protein and component of the primary cilia transition zone. The encoded protein regulates ciliogenesis and ciliary protein composition. Human fibroblasts expressing a mutant allele of this gene exhibit reduced numbers of cilia, altered cilia length, and impaired sonic hedgehog signaling. In human patients, different mutations in this gene cause different ciliopathies, including Meckel-Gruber syndrome and orofaciodigital syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, May 2017]. | hsa:84314; | ciliary transition zone [GO:0035869]; membrane [GO:0016020]; MKS complex [GO:0036038]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; craniofacial suture morphogenesis [GO:0097094]; detection of nodal flow [GO:0003127]; embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:0042733]; neural tube patterning [GO:0021532]; non-motile cilium assembly [GO:1905515]; protein localization to ciliary transition zone [GO:1904491]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021] | 19727342_TMEM107 (2810049P21Rik) is a strong candidate gene for central areolar choroidal dystrophy, CACD (human 17p13). Conclusion is based on a massive expression data set for mouse (103 strains in GeneNetwork.org) and joint analysis of RetNet database. 26123494_This study shows that known MKS loci account for the overwhelming majority of MKS cases but additional loci exist including MKS13 caused by TMEM107 mutation. | ENSMUSG00000020895 | Tmem107 | 24.299202 | 1.3301388 | 0.411576779 | 0.32628485 | 1.57898029612 | 0.2089076347569919223090550985943991690874099731445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.42659853941325592829869606248394120484590530395507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 30.964602 | 7.758510 | 23.141242 | 5.868829 | |
| ENSG00000179115 | 2193 | FARSA | protein_coding | Q9Y285 | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Ligase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome | Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are a class of enzymes that charge tRNAs with their cognate amino acids. This gene encodes a product which is similar to the catalytic subunit of prokaryotic and Saccharomyces cerevisiae phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetases (PheRS). This gene product has been shown to be expressed in a tumor-selective and cell cycle stage- and differentiation-dependent manner, the first member of the tRNA synthetase gene family shown to exhibit this type of regulated expression [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:2193; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; phenylalanine-tRNA ligase complex [GO:0009328]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; phenylalanine-tRNA ligase activity [GO:0004826]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; tRNA binding [GO:0000049]; phenylalanyl-tRNA aminoacylation [GO:0006432]; protein heterotetramerization [GO:0051290] | 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 29573043_Expression studies using fibroblasts isolated from the proband revealed a severe depletion of both FARSB and FARSA protein levels. These data indicate that the FARSB variants destabilize total phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase levels, thus causing a loss-of-function effect. 31355908_FARSA mutations mimic phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase deficiency caused by FARSB defects. | ENSMUSG00000003808 | Farsa | 500.868355 | 0.8740626 | -0.194191505 | 0.07191286 | 7.29397464106 | 0.0069186243804789330363869126472309289965778589248657226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.03712769209897370803474814238143153488636016845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 468.083595 | 23.419520 | 538.072598 | 26.460228 | ||
| ENSG00000179542 | 139065 | SLITRK4 | protein_coding | Q8IW52 | FUNCTION: It is involved in synaptogenesis and promotes synapse differentiation (PubMed:27812321). Suppresses neurite outgrowth (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q810B8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27812321}. | Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a transmembrane protein belonging to the the SLITRK family. These family members include two N-terminal leucine-rich repeat domains similar to those found in the axonal growth-controlling protein SLIT, as well as C-terminal regions similar to neurotrophin receptors. Studies of an homologous protein in mouse suggest that this family member functions to suppress neurite outgrowth. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. | hsa:139065; | glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; regulation of presynapse assembly [GO:1905606]; regulation of synapse organization [GO:0050807] | 35292404_Aberrant overexpression of HOTAIR inhibits abdominal adipogenesis through remodelling of genome-wide DNA methylation and transcription. | ENSMUSG00000046699 | Slitrk4 | 619.671992 | 1.1577800 | 0.211361190 | 0.07389519 | 8.17657829105 | 0.0042434730503850427024703506617697712499648332595825195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.02502432589746457838875137724699015961959958076477050781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 701.379971 | 30.353238 | 608.904351 | 26.575359 | |
| ENSG00000180011 | 284273 | PTGR3 | protein_coding | Q8N4Q0 | FUNCTION: Functions as 15-oxo-prostaglandin 13-reductase and acts on 15-keto-PGE1, 15-keto-PGE2, 15-keto-PGE1-alpha and 15-keto-PGE2-alpha with highest efficiency towards 15-keto-PGE2-alpha. Overexpression represses transcriptional activity of PPARG and inhibits adipocyte differentiation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BGC4}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Lipid metabolism;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Peroxisome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | Predicted to enable 13-prostaglandin reductase activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of fat cell differentiation. Predicted to be located in peroxisome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:284273; | peroxisome [GO:0005777]; 13-prostaglandin reductase activity [GO:0036132]; 15-oxoprostaglandin 13-oxidase activity [GO:0047522]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599] | 19690890_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 30372681_In patients with late-onset Alzheimer disease, a number of differentially methylated postitions were hypomethylated in ZADH2 compared with controls. 34143546_Thermal proteome profiling identifies PIP4K2A and ZADH2 as off-targets of Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor volasertib. 36224673_[Mechanism of miRNA-3679 Inhibiting Downstream ZADH2-Target Genes to Promote Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Proliferation]. | ENSMUSG00000049090 | Zadh2 | 173.912429 | 0.7781801 | -0.361823922 | 0.18710990 | 3.72576006870 | 0.0535792373336300559172329371904197614639997482299804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.17209331155518189926389993615885032340884208679199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 168.322375 | 20.342431 | 217.143971 | 26.175127 | |
| ENSG00000180448 | 23526 | ARHGAP45 | protein_coding | Q92619 | FUNCTION: Contains a GTPase activator for the Rho-type GTPases (RhoGAP) domain that would be able to negatively regulate the actin cytoskeleton as well as cell spreading. However, also contains N-terminally a BAR-domin which is able to play an autoinhibitory effect on this RhoGAP activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24086303}.; FUNCTION: Precursor of the histocompatibility antigen HA-1. More generally, minor histocompatibility antigens (mHags) refer to immunogenic peptide which, when complexed with MHC, can generate an immune response after recognition by specific T-cells. The peptides are derived from polymorphic intracellular proteins, which are cleaved by normal pathways of antigen processing. The binding of these peptides to MHC class I or class II molecules and its expression on the cell surface can stimulate T-cell responses and thereby trigger graft rejection or graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from HLA-identical sibling donor. GVHD is a frequent complication after bone marrow transplantation (BMT), due to mismatch of minor histocompatibility antigen in HLA-matched sibling marrow transplants. Specifically, mismatching for mHag HA-1 which is recognized as immunodominant, is shown to be associated with the development of severe GVHD after HLA-identical BMT. HA-1 is presented to the cell surface by MHC class I HLA-A*0201, but also by other HLA-A alleles. This complex specifically elicits donor-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) reactivity against hematologic malignancies after treatment by HLA-identical allogenic BMT. It induces cell recognition and lysis by CTL. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12601144, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8260714, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8532022, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9798702}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;GTPase activation;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Predicted to enable GTPase activator activity. Predicted to be involved in activation of GTPase activity. Located in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:23526; | azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 11920221_The intensity of the tetramer-staining of the HA-1/HA-2-specific cytotoxic T cells strongly correlates with their capability to recognize mHag positive target cells. 12091347_HA-1-specific CTLs restricted by nonself HLA-A2 molecules can be generated in an HLA-A2-mismatched setting. 15350465_In bone marrow transplant recipients and their genetically HLA-identical siblings, the presence of different alleles of two minor histocompatibility antigen genes is studied. 15498856_Pre-existing HA-1-specific T cells are observed in cord blood samples. Both circulating and ex vivo-generated HA-1-specific T cells show specific and hematopoietic restricted lysis of HLA-A2+/HA-1+ target cells, including leukemic cells. 15593299_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15593299_the incidence of the HA-1 168His allele is significantly lower in Sjogren's syndrome patients than in controls 16984283_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17580157_There was no difference in acute rejection rates between the HA-1-matched and -mismatched groups in kidney transplantation. 18093280_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18414982_targeting mHags encoded not only by HMHA1, whose aberrant expression in solid tumors has been reported, but also BCL2A1 may bring about beneficial selective graft-versus-tumor effects 19234124_study examined antigenic presentation & T-cell recognition of HA-1, a prototypic autosomal mHag derived from single nucleotide dimorphism (HA-1(H) versus HA-1(R)) in the HMHA1 gene; results define the molecular mechanisms governing immunogenicity of HA-1 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20509834_the information on allele and genotype frequencies of HA-1 and HA-2 in a Taiwanese population 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 24086303_study shows that HMHA1 acts as a RhoGAP to regulate GTPase activity, cytoskeletal remodeling and cell spreading, which are crucial functions in normal hematopoietic and cancer cells 26095815_Placental HA-1 expression is regulated by oxygen and is increased in the syncytial nuclear aggregates and syncytiotrophoblast of preeclamptic as compared to control placentas. 28939173_HMHA1 significantly promotes melanoma cells proliferation, invasion and migration, and prevents cell apoptosis. 29174013_ArhGAP45 acts as a Rac-GAP contributing to the balance between formation and disruption of endothelial junctions, which is required for the dynamic regulation of vascular permeability. | ENSMUSG00000035697 | Arhgap45 | 2013.065154 | 0.9927319 | -0.010523876 | 0.06227212 | 0.02854873571 | 0.8658251852066668474705579683359246701002120971679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.94081485134184494878439863896346651017665863037109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1940.411729 | 98.374641 | 1961.824264 | 99.250850 | |
| ENSG00000181061 | 25994 | HIGD1A | protein_coding | Q9Y241 | FUNCTION: Proposed subunit of cytochrome c oxidase (COX, complex IV), which is the terminal component of the mitochondrial respiratory chain that catalyzes the reduction of oxygen to water. May play a role in the assembly of respiratory supercomplexes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22342701}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Electron transport;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Respiratory chain;Stress response;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | Acts upstream of or within negative regulation of apoptotic process. Located in mitochondrion and nucleoplasm. Part of protein-containing complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:25994; | mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; respirasome [GO:0070469]; mitochondrial respirasome assembly [GO:0097250]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066] | 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22355194_depletion of HIG1 increased gamma-secretase activation and enhanced hypoxia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction 23646141_Nuclear localization of the mitochondrial factor HIGD1A during metabolic stress. 23878241_Data indicate that hypoxia-induced gene domain protein-1a (Higd-1a) inhibits Optic atrophy 1 (Opa1) cleavage and is required for mitochondrial fusion by virtue of its interaction with Opa1. 31089410_Higd1a plays positive roles in protecting cells from oxidative stress, and reactive oxygen species could induce Higd1a expression by upregulating PGC-1a and HIF-1a expressions. 31310799_High Higd-1a expression is associated with proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells through a pERK/p27/pRB pathway. 31914602_Higd1a, or its mimic, provides therapeutic options for the treatment of mitochondrial diseases. 32375044_Distinct Roles of Mitochondrial HIGD1A and HIGD2A in Respiratory Complex and Supercomplex Biogenesis. 34787061_HIG1 domain family member 1A disrupts proliferation, migration, and invasion of colon adenocarcinoma cells. | ENSMUSG00000038412 | Higd1a | 423.000237 | 1.1147538 | 0.156725163 | 0.09236731 | 2.87669306513 | 0.0898704125761190936172440046902920585125684738159179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.24634672371443347427266701288317563012242317199707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 460.980631 | 32.711577 | 415.242416 | 29.485899 | |
| ENSG00000181513 | 79777 | ACBD4 | protein_coding | Q8NC06 | FUNCTION: Binds medium- and long-chain acyl-CoA esters and may function as an intracellular carrier of acyl-CoA esters. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Lipid-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a member of the acyl-coenzyme A binding domain containing protein family. All family members contain the conserved acyl-Coenzyme A binding domain, which binds acyl-CoA thiol esters. They are thought to play roles in acyl-CoA dependent lipid metabolism. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. | hsa:79777; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; fatty-acyl-CoA binding [GO:0000062]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631] | 21045733_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 28463579_acyl-CoA binding domain protein 4 (ACBD4) as a tail-anchored peroxisomal membrane protein which interacts with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) protein, vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein-B (VAPB) to promote peroxisome-ER associations. | ENSMUSG00000056938 | Acbd4 | 26.136506 | 0.7136804 | -0.486649902 | 0.31556575 | 2.36955772789 | 0.1237220987924185222617268209432950243353843688964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.30589833368136071234388850825780536979436874389648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 22.157270 | 3.584008 | 31.576257 | 4.571178 | |
| ENSG00000182173 | 283989 | TSEN54 | protein_coding | Q7Z6J9 | FUNCTION: Non-catalytic subunit of the tRNA-splicing endonuclease complex, a complex responsible for identification and cleavage of the splice sites in pre-tRNA. It cleaves pre-tRNA at the 5' and 3' splice sites to release the intron. The products are an intron and two tRNA half-molecules bearing 2',3' cyclic phosphate and 5'-OH termini. There are no conserved sequences at the splice sites, but the intron is invariably located at the same site in the gene, placing the splice sites an invariant distance from the constant structural features of the tRNA body. The tRNA splicing endonuclease is also involved in mRNA processing via its association with pre-mRNA 3'-end processing factors, establishing a link between pre-tRNA splicing and pre-mRNA 3'-end formation, suggesting that the endonuclease subunits function in multiple RNA-processing events. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15109492}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Methylation;mRNA processing;Neurodegeneration;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Pontocerebellar hypoplasia;Reference proteome;tRNA processing | This gene encodes a subunit of the tRNA splicing endonuclease complex, which catalyzes the removal of introns from precursor tRNAs. The complex is also implicated in pre-mRNA 3-prime end processing. Mutations in this gene result in pontocerebellar hypoplasia type 2.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. | hsa:283989; | nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; tRNA-intron endonuclease complex [GO:0000214]; mRNA processing [GO:0006397]; tRNA splicing, via endonucleolytic cleavage and ligation [GO:0006388]; tRNA-type intron splice site recognition and cleavage [GO:0000379] | 18711368_In two subtypes, PCH2 and PCH4, we identified mutations in three of the four different subunits of the tRNA-splicing endonuclease complex. 20956791_We confirm that the common p.A307S mutation in TSEN54 is responsible for most of the patients with a PCH2 phenotype. 21383226_The results demonistrated that not all cases of clinically defined pontocerebellar hypoplasia-4 result from mutations in TSEN54. 21468723_TSEN54 mutation causes a severe form of pontocerebellar hypoplasia type 1 in a family. 24938831_A novel heterozygous mutation was found in the TSEN54 gene by c.254A > T(+) (p.E85V), which may be a new subtype of hereditary ataxia 26701950_TSEN54 gene-related pontocerebellar hypoplasia type 2 presented with exaggerated startle response in cousins. 32697043_A homozygote variant in the tRNA splicing endonuclease subunit 54 causes pontocerebellar hypoplasia in a consanguineous Iranian family. | ENSMUSG00000020781 | Tsen54 | 172.447093 | 0.6710345 | -0.575541209 | 0.15861443 | 13.13037787972 | 0.0002905461669903412389413810412719385567470453679561614990234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00261360757804559055636484110607398179126903414726257324218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 141.367562 | 15.615469 | 211.973460 | 22.712790 | |
| ENSG00000182446 | 55666 | NPLOC4 | protein_coding | Q8TAT6 | FUNCTION: The ternary complex containing UFD1, VCP and NPLOC4 binds ubiquitinated proteins and is necessary for the export of misfolded proteins from the ER to the cytoplasm, where they are degraded by the proteasome. The NPLOC4-UFD1-VCP complex regulates spindle disassembly at the end of mitosis and is necessary for the formation of a closed nuclear envelope (By similarity). Acts as a negative regulator of type I interferon production via the complex formed with VCP and UFD1, which binds to RIGI and recruits RNF125 to promote ubiquitination and degradation of RIGI (PubMed:26471729). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ES54, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26471729}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger | PATHWAY: Protein degradation; proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent pathway. | Predicted to enable ATPase binding activity; ubiquitin binding activity; and ubiquitin protein ligase binding activity. Predicted to contribute to K48-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding activity and K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of RIG-I signaling pathway; negative regulation of type I interferon production; and proteolysis involved in cellular protein catabolic process. Located in nucleus. Part of UFD1-NPL4 complex and VCP-NPL4-UFD1 AAA ATPase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:55666; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; nuclear outer membrane-endoplasmic reticulum membrane network [GO:0042175]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; UFD1-NPL4 complex [GO:0036501]; VCP-NPL4-UFD1 AAA ATPase complex [GO:0034098]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; K48-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding [GO:0036435]; K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding [GO:0070530]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; ubiquitin binding [GO:0043130]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; negative regulation of RIG-I signaling pathway [GO:0039536]; negative regulation of type I interferon production [GO:0032480]; retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol [GO:0030970]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] | 17331469_Ufd1-Npl4 is a negative regulator of retrotranslocation, delaying the retrotranslocation of endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation substrates independently of its association with VCP 18586029_This favors the model where the Ufd1-Npl4 dimer forms a regulatory gate at the exit from the retrotranslocone, rather than actively promoting retrotranslocation like the p97VCP ATPase. 20702414_Data suggest that the human cytomegalovirus dislocation reaction in US2 cells is independent of the p97 cofactor Ufd1-Npl4, and different retrotranslocation mechanisms can employ distinct p97 ATPase complexes to dislocate substrates. 21486945_Data establish Cdc48/p97-Ufd1-Npl4 as a crucial negative regulator of Aurora B early in mitosis of human somatic cells and suggest that the activity of Aurora B on chromosomes needs to be restrained to ensure faithful chromosome segregation. 23293021_Data indicate that Npl4-Ufd1 heterodimer is required for VCP-FAF1 interaction. 24019527_In coordination with the P97-UFD1-NPL4 complex (P97(UFD1/NPL4)), NUB1L promotes transfer of NEDD8 to proteasome for degradation. 24248593_Data indicate that the p97-UFD1L-NPL4 protein complex specifically associates with ubiquitinated IkappaBalpha via the interactions between p97 and the SCF(beta-TRCP) ubiquitin ligase. 24429874_p97-Ufd1-Npl4 is an integral part of G2/M checkpoint signaling and thereby suppresses chromosome instability. 26112410_The study revealed a regulatory role of the p97-Npl4-Ufd1 complex in regulating a partial degradation of the NF-kappaB subunit p100. 28512218_We demonstrate that WT p97 can unfold proteins and that this activity is dependent on the p97 adaptor NPLOC4-UFD1L, ATP hydrolysis, and substrate ubiquitination, with branched chains providing maximal stimulation. 31623962_Multisystem proteinopathy mutations in VCP/p97 increase NPLOC4-UFD1L binding and substrate processing. 32667929_Targeting NPL4 via drug repositioning using disulfiram for the treatment of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 33402676_Seesaw conformations of Npl4 in the human p97 complex and the inhibitory mechanism of a disulfiram derivative. 35920641_Multiple UBX proteins reduce the ubiquitin threshold of the mammalian p97-UFD1-NPL4 unfoldase. 36087575_Structural basis for the interaction between human Npl4 and Npl4-binding motif of human Ufd1. | ENSMUSG00000039703 | Nploc4 | 894.156769 | 0.9326542 | -0.100585880 | 0.08946188 | 1.26367672698 | 0.2609562820628684165491506519174436107277870178222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.48955369489318406595046440088481176644563674926757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 866.473022 | 74.710700 | 933.588101 | 80.284903 |
| ENSG00000182534 | 439921 | MXRA7 | protein_coding | P84157 | Alternative splicing;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Located in endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:439921; | collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; membrane [GO:0016020] | 29781547_MXRA7 gene might function as a negative modulator in psoriasis development when propsoriatic factors attack, presumably via expression alteration or redistribution of MXRA7 proteins in keratinocytes. | 228.073388 | 0.8937136 | -0.162115489 | 0.14411873 | 1.26391261280 | 0.2609117836918211641439313552837120369076728820800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.48955369489318406595046440088481176644563674926757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 226.867087 | 20.872493 | 255.101136 | 23.110995 | ||||
| ENSG00000182552 | 201965 | RWDD4 | protein_coding | Q6NW29 | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Reference proteome | hsa:201965; | ENSMUSG00000031568 | Rwdd4a | 217.209400 | 1.0232744 | 0.033193062 | 0.24556117 | 0.01820114701 | 0.8926817468500218843985294370213523507118225097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.95277819483948855694421808948391117155551910400390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 231.746543 | 37.852541 | 227.096321 | 37.185411 | |||||
| ENSG00000182718 | 302 | ANXA2 | protein_coding | P07355 | FUNCTION: Calcium-regulated membrane-binding protein whose affinity for calcium is greatly enhanced by anionic phospholipids. It binds two calcium ions with high affinity. May be involved in heat-stress response. Inhibits PCSK9-enhanced LDLR degradation, probably reduces PCSK9 protein levels via a translational mechanism but also competes with LDLR for binding with PCSK9 (PubMed:18799458, PubMed:24808179, PubMed:22848640). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18799458, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22848640, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24808179}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Binds M.pneumoniae CARDS toxin, probably serves as one receptor for this pathogen. When ANXA2 is down-regulated by siRNA, less toxin binds to human cells and less vacuolization (a symptom of M.pneumoniae infection) is seen. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25139904}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Annexin;Basement membrane;Calcium;Calcium/phospholipid-binding;Direct protein sequencing;Extracellular matrix;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;Secreted;Ubl conjugation | This gene encodes a member of the annexin family. Members of this calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein family play a role in the regulation of cellular growth and in signal transduction pathways. This protein functions as an autocrine factor which heightens osteoclast formation and bone resorption. This gene has three pseudogenes located on chromosomes 4, 9 and 10, respectively. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Annexin A2 expression has been found to correlate with resistance to treatment against various cancer forms. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2019]. | hsa:302; | adherens junction [GO:0005912]; AnxA2-p11 complex [GO:1990665]; azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; basement membrane [GO:0005604]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cornified envelope [GO:0001533]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; midbody [GO:0030496]; myelin sheath adaxonal region [GO:0035749]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PCSK9-AnxA2 complex [GO:1990667]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; plasma membrane protein complex [GO:0098797]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; Schmidt-Lanterman incisure [GO:0043220]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; cadherin binding involved in cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098641]; calcium channel activity [GO:0005262]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306]; cytoskeletal protein binding [GO:0008092]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; phospholipase A2 inhibitor activity [GO:0019834]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; S100 protein binding [GO:0044548]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; virion binding [GO:0046790]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; fibrinolysis [GO:0042730]; membrane raft assembly [GO:0001765]; mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0042789]; negative regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle receptor catabolic process [GO:0032804]; negative regulation of receptor internalization [GO:0002091]; osteoclast development [GO:0036035]; positive regulation of exocytosis [GO:0045921]; positive regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle clearance [GO:1905581]; positive regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding [GO:1905597]; positive regulation of low-density lipoprotein receptor activity [GO:1905599]; positive regulation of plasma membrane repair [GO:1905686]; positive regulation of plasminogen activation [GO:0010756]; positive regulation of receptor recycling [GO:0001921]; positive regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis involved in cholesterol transport [GO:1905602]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of vacuole organization [GO:0044090]; positive regulation of vesicle fusion [GO:0031340]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; vesicle budding from membrane [GO:0006900] | 11781322_identification of a hetereotetramer as a plasmin reductase 12468550_amino acids critical for tissue-type plasminogen activator-annexin A2 interaction 12629510_results suggest that annexin II, and, likely, annexin I, may be endogenous suppressors of prostate cancer cell migration and their reduced or lost expression may contribute to prostate cancer development and progression 12699894_virtual Northern blots to analyze expression of NACA and ANX2 in progenitor cultures of nine children with Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia and five healthy individuals 12730231_analysis of annexin A2 interaction with tissue plasminogen activator, plasminogen, and plasmin 13679511_annexin 2/S100A10 complex functions in the intracellular positioning of recycling endosomes and that both subunits are required for this activity 14504107_annexin II-mediated assembly of plasminogen and t-PA on monocyte/macrophages contributes to plasmin generation, matrix remodeling, and directed migration 14522961_annexin II binds to CEACAM1 in breast neoplasms 14613585_possible mechanistic and regulatory role of Anx-II in prostate cancer progression 14672933_ANXA2 is a Ca(2+)-dependent RNA-binding protein that interacts with the mRNA of the nuclear oncogene, c-myc 14991775_AII does not bind 1,25-D(3) in a physiologically relevant manner 14995994_Western blotting of endothelial cell surface of a number of sites showed higher amounts of tissue plasminogen activator annexin II on cerebral endothelial cell. In contrast, expression of u-PA receptor was the same for all ECs 15051937_Lipocortin II may be a marker or contribute to asthma exacerbation. 15064349_Annexin I serves as both ligand and receptor in promoting phagocytosis. 15070701_E2A-HLF induces annexin II by substituting for cytokines that activate downstream pathways of Ras 15211578_Reduced Annexin 2 expression is associated with osteosarcoma metastases 15226372_Experiments using individual subunits identify annexin 2 as a PtdIns(4,5)P(2)-binding entity 15257287_siRNA-mediated downregulation of annexin A2/S100A10 and disruption of the complex by microinjection of peptide competitors result in a marked reduction in von Willebrand Factor 15302870_Temperature stress-induced annexin 2 translocation is dependent on both expression of protein p11 tyrosine phosphorylation of annexin 2. 15471954_observations suggest a novel pathway for endothelial activation induced by APLA/anti-beta2GPI antibodies that is initiated by cross-linking or clustering of annexin A2 on the endothelial surface 15526283_Human colon adenocarcinoma cell differentiation is associated with an up-regulation of AnxA1, AnxA2, and AnxA5 and with a subcellular relocation of these proteins 15567461_investigation undertaken to identify the significance of annexin II expression and regulation in leukaemia do not fully support the concept of the coagulopathy associated with APL being caused by hyperfibrinolysis alone 15574370_S100A10 and annexin A2 play an important role in plasmin regulation and in cancer cell invasiveness and metastasis [review] 15784727_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15784727_several single nucleotide polymorphisms in bone morphogenic protein 6, annexin A2, and klotho were associated with sickle cell osteonecrosis 15788416_S100A4 protein alone or in a complex with annexin II accelerated tissue plasminogen activator-mediated plasminogen activation in solution and on the endothelial cell surface 15849182_complex with S100A10 is a substrate of thioredoxin 15940368_AX-II, in addition to inducing GM-CSF expression, increases membrane-bound RANKL synthesis by marrow stromal cells through MAPK-dependent pathway. 15944914_Results show that progression from prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia to prostate cancer is characterized by a reduction of ANX2 and suggest that downregulation of these proteins could represent an important event in prostate carcinogenesis. 16100712_annexin A1 and A2 may have roles in dysferlin deficiency and in muscular dystrophies 16177123_Annexin A2 is part of the putative cell surface vitamin D binding protein binding site complex and functions to mediate the chemotactic cofactor effect. 16230353_analysis of the structural determinant of the PtdIns(4,5)P2 selectivity of A2t (annexin II-p11 heterotetramer), which may be involved in the regulation of PtdIns(4,5)P2 clustering in the cell 16331566_The experimental data suggest that the ANNEXIN A2 gene may relate to cellular apoptosis induced by p53 gene. 16493010_anti-A2 antibodies contribute to the prothrombotic diathesis in antiphospholipid syndrome 16501079_novel gag-binding protein essential for the proper assembly of HIV in monocyte-derived macrophages. 16524621_annexin 2 mediated fibrinolysis on the transitional cell carcinoma cells may play a role in inducing hemorrhagic disorder in vascular intimal carcinomatosis 16643892_Annexin II-dependent localized plasmin generation is associated with angiogenesis and metastasis in breast cancer 16709165_Review discusses a role for annexin 2 in the regulation of ecto-5'-nucleotidase activity, which is dependent upon the stability of the membrane rafts. 16797773_Real-time RT-PCR confirmed up-regulation of IL-8, osteopontin, and TNFRSF14 and down-regulation of SAMeS and CD209 in AH. 16882661_analysis of calcium-dependent heparin binding to annexin A2 16963080_Results describe the design, production, biophysical characterization and binding properties of a soluble mutant form of annexin A2 domain IV that adopts a partially folded conformation. 16984913_that Annexin2 is required for strong binding of S100A10 to the C-terminal domain of the protein Ahnak. 16989986_we further showed that LMP1 increased the serine, but not tyrosine, phosphorylation of annexin A2 by activating a novel signaling pathway, the protein kinase C (PKC) signaling pathway. 17065584_The median of anti-annexin A2 IgM titer from preterm infants who were delivered with high-grade chorioamnionitis (CAM) was significantly higher than those from preterm infants without CAM and with low-grade CAM. 17239928_demonstration of an angiostatin receptor (ANX2) in vascular endothelial tumors including angiosarcoma; diffuse and strong reactivity signified the absence of any down-regulation of ANX2 in both benign and malignant tumors 17441315_Cellular DNA synthesis is significantly reduced in small interference RNa transfected a prostatic cancer cell line. 17513451_following injury, N-glycosylation events and AII presentation on the cell surface of airway epithelial cells are important mediators in repair 17581860_The anx 2-S100A10/CFTR complex is important for CFTR function across epithelia. 17626749_Elevated or reduced expression of Annexin II may be correlated to reverse or progression of carcinogenesis, respectively. 17709546_uPA plays a major role in inducing MMP-1 production in activated human monocytes, which is mediated by a plasmin-dependent mechanism involving signaling through the annexin A2 heterotetramer. 17711622_The increase of annexin II and its expression levels, and the increase of core-fucosylation might all be related to HCC metastatic ability. 17824845_analysis of the pH-induced membrane binding of annexins A6 and A2-S100A10 17971878_p11/S100A10 light chain of annexin A2 is dispensable for annexin A2 association to endosomes and functions in endosomal transport 17999956_the annexin II-S100A10 complex, which regulates exocytosis, forms a ternary complex with TrpRS. 18008140_These results suggested that Annexin A2 may play roles in p53 induced apoptosis and it is also involved in regulation of cell proliferation. 18084608_IRF-1 silencing with siRNA produced upmodulation of the Annexin-II protein in THP-1 cells. 18164291_analysis of translocation and assembly at the plasma membrane; heterogeneous assembly formation was shown between annexins A5 and A2 18174463_it is proposed that annexin 2 acts as a receptor for factor Xa on the surface of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and that annexin 2 facilitates factor Xa activation of PAR-1 but does not enhance coagulant function of factor Xa 18211896_The findings suggest annexin 2 externalization is coupled to lipid efflux in prostate epithelium and that IFNgamma induces down-regulation of the protease-binding anx2(t) scaffold at the cell surface. 18262347_Annexin A2 localizes to the basal epithelial layer and is down-regulated in dysplasia and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 18289715_The effect of alcohol on fibrinolysis and plasmin is mediated in part by ANXA2. Alcohol directly influences hepatic pathways of fibrinolysis that may contribute to ALD. 18332131_Rab14 also co-localized in part with annexin A2 and lamellar bodies in alveolar type II cells 18384219_Annexin II and beta(2)-tubulin down-regulation is important in nasopharyngeal carcinoma formation and may represent potential targets for further investigations. 18389276_annexin-2 is required for cAMP-induced AQP2 exocytosis in renal cells 18434302_Within the endothelial cell, p11 is required for Src kinase-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of A2, which signals translocation of both proteins to the cell surface. 18494762_annexin II is a novel HSP27-interacted protein which is involved in UVC resistance in human cells 18502476_Expression of ANAX2 in human atheroslerotic abdominal aortic aneurysms is reported. 18565825_a tyrosine phosphorylation switch in annexin A2 is an important event in triggering Rho/ROCK-dependent and actin-mediated changes in cell morphology associated with the control of cell adhesion 18636554_annexin II and its receptor axis play a central role in prostate cancer metastasis, and prostate cancer utilizes the hematopoietic stem cell homing mechanisms to gain access to the niche. 18712570_Annexin II overexpression may induce gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer resulting in rapid recurrence. 18799458_identification of the minimal inhibitory sequence of AnxA2 should pave the way toward the development of PCSK9 inhibitory lead molecules for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia 18924133_Annexin A2 has a role in malignant phenotype and secretion of IL-6 in DU145 prostate cancer cells 18990701_phosphorylation of Tyr-23 is essential for proper endosomal association and function of AnxA2, perhaps because it stabilizes membrane-associated protein via a conformational change. 19016789_EspL2 of E. coli O157:H7 Sakai bound F-actin-aggregating annexin 2 directly, increasing its activity.[EspL2] 19020748_Annexin A2 expression and phosphorylation are up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma. 19022301_These observations are consistent with a role for annexin A2 as an actin nucleator on PI(4,5)P2-enriched membranes. 19176991_Via its receptor annexin II on endothelial surface, tPA regulates intravascular fibrin deposition. Review. 19289089_actin patches are nucleated on early endosomes via annexin A2 and Spire1, and these patches control endosome biogenesis, presumably by driving the membrane remodeling process 19325895_Anx2, by interacting with Gag at the membranes that support viral assembly, functions in the late stages of HIV-1 replication 19339807_fatty acid-binding protein-5, squamous cell carcinoma antigens 2, alpha-enolase, annexin II, apolipoprotein A-I and albumin were detected at a high level in Atopic dermatitis skin lesions, but scarcely in the normal controls 19380152_This study found that patients with Posttraumatic stress disorder had lower levels of p11 mRNA than control subjects, while those with major depression disorder, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia had significantly higher p11 levels than the controls. 19513064_ANX2 expression in the primary kidney tumours showed significant associations with a higher stage, a higher nuclear grade. ANX2 expression is an independent predictor for metastasis. 19549357_Annexin II participates in invasion and infiltration of hematologic malignancies probably through enhancing the degradation of extracellular matrix by cells of hematologic malignancies. 19556289_Annexin A2 is associated with receptivity in the human endometrium. 19585213_AnxA2 is overexpressed in MM patients and myeloma cell lines U266 and RPMI8226, and AnxA2 overexpression appeared to affect the proliferation, apoptosis, invasive potential and production of pro-angiogenic factors 19605586_In this study, rabbit vesivirus (RaV) virions were shown to bind annexin A2 (ANXA2) in a membrane protein fraction from HEK293T cells. 19642359_Abnormally high levels of Annexin II and u-PAR expression in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells may contribute to the increased production of plasmin, leading to primary hyperfibrinolysis. 19656851_Studies show that GSK-3 and Omi/HtrA2 synergistically cause annexin A2 cleavage and then cell cycle inhibition or apoptosis. 19724273_S100A6 binds to annexin 2 in pancreatic cancer cells and promotes pancreatic cancer cell motility. 19764771_Results showed that expression of Anxa2 is enhanced when cancer cells acquire drug resistance and it plays an essential role in MDR-induced tumor invasion. 19823170_Inducible ANXA2 expression in cholangiocytes may play a compensatory role for the impaired anion exchanger activity of cholangiocytes in primary biliary cirrhosis. 19885616_A sandwich ELISA system for ANXA2 was developed for the detection of ANXA2 in human samples. The serum ANXA2 concentrations of the patients with hepatocellular carcinoma were significantly elevated when compared with those of normal individuals. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19951950_Data show that identification of annexin-II as one of the fH ligands on apoptotic cells together with the fact that autoantibodies against annexin-II are found in systemic lupus erythematosus provides further insight in the pathogenesis of this disease. 19954599_Thalidomide can inhibit the expression of AnxA2 mRNA and protein in RPMI8226 and HMEC-1 cells. 20015551_the upregulated expression of annexin A2 by SARS-associated cytokines and the cross-reactivity of anti-SARS-CoV S2 antibodies to annexin A2 may have implications in SARS disease pathogenesis. 20018898_Study identify annexin A2 as a novel binding partner for TM601 in multiple human tumor cell lines and human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC). 20047591_annexin II promotes the invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro, and annexin II and HAb18G/CD147 interact with each other in the same signal transduction pathway working as a functional complex in tumor progression. 20079732_Annexin II may be an attractive target for therapeutic strategies aimed to inhibit angiogenesis and breast cancer. 20093721_CFTR function by annexin A2-S100A10 complex has roles in health and disease [review] 20093722_endothelial annexin A2 has a role in vascular fibrinolysis [review] 20121258_the interaction of AnxA2 with STAT6 20225235_This study identified 22 differentially expressed proteins related to liver fibrosis, and verified a potential biomarker (ANXA2) for non-invasive diagnosis of immune liver fibrosis. 20229030_Levels of anti-A2 autoantibody are higher in antiphospholipid patients and systemic lupus erythematosus patients with thrombosis, which may be helpful in identifying potential cases of antiphospholipid syndrome. 20335258_identify ANXA2 as a novel host factor contributing, with NS5A, to the formation of infectious HCV particles. NS5A specifically recruits ANXA2 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20407807_Shear stress especially induced sustained increases in the expression of Annexin A2 and GAPDH in a comparative proteome analysis of effect of shear stress on HMSCs. 20493868_The metabolism of annexin A2 in for Opisthorchis viverrini-associated cholangiocarcinoma is reported; its use as a neoplasm marker is discussed. 20540360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20561442_Bortezomib may down-regulate the expression of VEGF in endothelial cells through regulating the activity of HIF-1alpha and the expression of Annexin A2. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20702651_These results indicate that plasminogen promotes influenza A virus replication in an annexin 2-dependent fashion in the absence of viral neuraminidase. 20826156_Annexin A2 expression is required for the biologic effects of progastrin in vivo and in vitro. 20847146_Annexin II mediates the binding of anti-dsDNA antibodies to mesangial cells, contributing to the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. 20947498_annexin 2 regulates endothelial morphogenesis through an adherens junction-mediated pathway upstream of Akt. 20970165_Annexin A2 expression is reduced in intestinal-type sinonasal adenocarcinoma, and this loss of expression is associated to the more aggressive histopathological types. 21033036_Expression of ANXA2 was high in glioma samples and was correlated with pathological grades. 21122411_The benign lesions with positive ANXA1 and/or ANXA2 expression showed mild to severe atypical hyperplasia of the gallbladder epithelium. The positive rates of ANXA1 and/or ANXA2 were significantly lower in the well-differentiated adenocarcinoma. 21132403_results suggest that annexin-1, annexin-2, and annexin-3 are identified as potential biomarkers associated with lymph node metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma 21146216_High annexin II is associated with acute promyelocytic leukemia. 21193750_Anti-annexin A2 autoantibodies are significantly associated with cerebral venous thrombosis. 21237296_ANXA2 plays a role in regulating proliferation in dasatinib-sensitive WM-115 cells and could potentially play a role in sensitivity to dasatinib in melanoma cells. 21330046_altered expression levels of proteins involved in brush border formation, such as ezrin and keratin 19 support the notion that annexin II is a key player in cell differentiation and an indispensable element of apical membrane domain. 21491466_MBD1-containing chromatin associated factor 2, epithelial malignancy-related vimentin and exocytosis-related annexin A2 were changed upon exposure to airborne nanoparticle PM(0.056). 21572519_Data show that ANXA2 is part of a novel molecular pathway underlying PDA metastases and a new target for development of PDA therapeutics. 21603851_Aberrant expression of Annexin A2 and Cdc42 play a role in carcinogenesis, differentiation and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. 21645192_Data suggest that although annexin A2 is not an exclusive marker of APPL1/2 endosomes, it has an important function in membrane recruitment of APPL proteins, acting in parallel to Rab5. 21809360_results suggest that the interaction of HAb18G/CD147 with annexin II is involved in the interconversion between mesenchymal and amoeboid movement of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 21817168_this study identified a novel osteoporosis susceptibility gene ANXA2, and suggested a novel pathophysiological mechanism, mediated by ANXA2, for osteoporosis in humans 21849434_Both the annexin A2 and p11 subunits of calpactin I coimmunoprecipitate with human papillomavirus type 16 E5 in COS cells and in human epithelial cell lines, and an intact E5 C terminus is required for binding. 21886777_Cochlin interacts with TREK-1 and annexin A2. 21900167_In this study, the authors showed that human annexin II (Anx2) protein could bind to the enterovirus type 71 virion via the capsid protein VP1. 21908427_The role of the annexin A2 heterotetramer in vascular fibrinolysis. 21918681_Results suggest that ANXA2 is a cellular RBP that can modulate the frameshifting efficiency of viral RNA, enabling it to act as an anti-viral cellular protein, and hinting at roles in RNA metabolism for other cellular mRNAs. 21928315_Interferon-gamma stimulates p11-dependent surface expression of annexin A2 in lung epithelial cells to enhance phagocytosis. 21976520_The levels of expression of annexin A2 in human glioma samples correlate with their degree of malignancy. 22044461_Selective disruption of the fibrinolytic activity of ANX II may provide a novel strategy for specific inhibition of neoangiogenesis in human breast cancer. 22141411_Bcl-xL to Bax protein ratios, an index of survival activity in cells exposed to lethal stresses, were increased in the cells that had been precultured in rANX II for 24 h prior to UVC irradiation 22223826_Results show that AXII and AXIIR play important roles in multiple myeloma (MM) and that targeting the AXII/AXIIR axis may be a novel therapeutic approach for MM. 22230505_Overexpression of AnnexinII in the Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma(ccRCC) is closely correlated with the ccRCC development. 22235123_a novel interaction involving K17 and AnxA2 and identify AnxA2 as a potential regulator of keratin filaments. 22301157_Anxa2 recruits HCV NS proteins and enriches them on the lipid raft to form the HCV replication complex. 22452176_This review retraces the current state of knowledge on Annexin A2 and A5 functions causing thrombophilia. [review] 22452352_Anxa2 might influence proliferation, migration and invasion of MCF-7 cells by increasing expression of c-myc and cyclin D1 via activation of Erk1/2 signalling pathways. 22493182_ANXA2 has a dual role in the pathogenesis of human adenomyosis through conferring endometrial cells both metastatic potential and proangiogenic capacity. 22587461_AnxA2 and NHERF2 form a scaffold complex that links adjacent Tir molecules at the plasma membrane forming a lattice that could be involved in retention and dissemination of other effectors at the bacterial attachment site. 22645245_ANXA2 may act upstream of the RhoA/ROCK pathway by regulating F-actin remodeling and is a key factor in human endometrial adhesiveness 22679123_the M2 haplotype of the ANXA5 gene confers a risk of delivering small-for-gestational age babies 22681645_Upregulated expression of annexin II is associated with gastric cancer. 22705595_ANXA2 exemplifies an interesting class of targetable bone-remodeling factors expressed by normal and malignant plasma cells and the BM microenvironment that have a significant impact on survival of myeloma patients. 22792315_Depletion of annexin A1 or A2 alters the retrograde transport of shiga toxin but not ricin, without affecting toxin binding or internalization. 22822523_presenting application of the PCR-RFLP technique for determination of the ANXA2 gene single nucleotide polymorphism frequency and their clinical association among Indian sickle cell patients 22830395_Annexin A2 anchors S100A10 to the cell surface and, in doing so, allows S100A10 to play a prominent role in the activation of plasminogen in angiogenesis and oncogenesis. 22848640_AnxA2 acts as an endogenous regulator of PCSK9-induced LDLR degradation 22859294_a novel role for ANXA2 in NSCLC cell proliferation by facilitating the cell cycle partly through the regulation of p53 via JNK/c-Jun. 22879587_Annexin A2 and A5 serve as new ligands for C1q on apoptotic cells 22913982_Protein expression analysis found downregulation of annexin II in human coronary artery endothelial cells 22917188_Results suggest that abnormal ubiquitination and/or degradation of annexin A2 may lead to presence of annexin A2 at high level, which may further promote metastasis and infiltration of the breast cancer cells. 22939813_the ANXA2 N-terminal domain does not appear to be the target antigen for anti-ANXA2 antibodies in antiphospholipid syndrome. 22940583_The AHNAK peptide adopts a coil conformation that arches across the heterotetramer contacting both annexin A2 and S100A10 protomers with tight affinity. 22957061_AnxA2 has a role in EGFR-Src membrane bound signaling complex and ligand induced activation of downstream signaling pathways 23091277_N-terminal acetylation of AnxA2 is required for S100A10 binding 23091278_AnxA2 has an inhibitory effect on actin polymerization, and a modification with WithfA significantly increases this inhibitory role of AnxA2 23131771_Partial knockdown of Annexin A2 and PSF showed decrease in p53 IRES activity and reduced levels of both the p53 isoforms. 23139605_The characteristics and distribution of ANXA2 expression has good diagnostic potential for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis. 23148505_an annexin A2 niche in cell fate regulation 23174572_Up-regulated expression of ANXA2 is closely related to the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis. 23188673_Annexin A2 may serve as a discriminative serological marker for HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. 23226323_nuclear translocation of annexin A2 in response to genotoxic agents and its role in mitigating DNA damage 23275167_Binding of AHNAK peptide to the surface of AnxA2 is governed by several hydrophobic interactions between side chains of AHNAK and pockets on S100A10. 23334362_shRNA-mediated knockdown of either ANXA2, FYN, LCK or S100A10, all led to inhibition of annexin A2 phosphorylation and resulted in marked sensitization to prednisolone 23391921_Annexin II is involved in fibroblast resistance to UV B light. 23494179_Annexin II up-regulation was associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 23522334_ANXA2 deletion in caco2 cells induced the pseudopodia shorted and spared, non-stained areas increased, mitochondria decreased, and the expression and polymerization of F-actin and beta-tubulin changed. 23529818_Elevated expression of annexin II was associated with lymph node metastatic lung cancers. 23558678_an important role of AnxA2 in controlling dynamics of beta1 integrin at the cell surface that in turn is required for the active turnover of cell-matrix associations, cell migration, and wound closure. 23572070_annexin A2 has a role in preventing hyperglycemia-induced loss of human endothelial cell surface fibrinolytic activity 23637395_Annexin A2 and S100A10 regulate human papillomavirus type 16 entry and intracellular trafficking in human keratinocytes. 23696646_extracellular C-1-P, acting through the extracellular annexin a2-p11 heterotetrameric protein, can mediate vascular endothelial cell invasion. 23713052_Perfomed proteomic analysis on a transgenic mouse model of severe cardiac hypertrophy; compared data to dataset of heart failure found MYH7, IGFBP7, ANXA2, and DESM to be biomarker candidates for heart failure. 23721211_Plasminogen stimulates autocrine cytokine production in human airway smooth muscle cells in a manner mediated by plasmin and annexin A2. 23757730_complex formation of AnxA2 with S100A10 is a central regulatory mechanism in the acute release of VWF in response to cAMP-elevating agonists 23792445_data provide evidence for AnxA2 as a mediator of EGFR endocytosis and signaling in breast cancer via regulation of cofilin activation 23840117_Annexin A2 silencing inhibits invasion, migration, and tumorigenic potential of hepatoma cells. 23861394_annexins such as AnxA2 can efficiently induce membrane deformations after lipid segregation, a mechanism possibly underlying annexin functions in membrane trafficking. 23886630_The regulation of S100A4, S100A6 and ANXA2 in primary human thyrocytes, was investigated. 23931152_Authors show here that AnxA2, p11 and AHNAK are required for type 3 secretion system-mediated Salmonella invasion of cultured epithelial cells. 23950866_ANXA2 enhances the migration and invasion potential of HCC cells in vitro by regulating the trafficking of CD147-harboring membrane microvesicles. 23994525_an annexin A2-S100A10 molecular bridge participates in cell-cell interactions, revealing a hitherto unexplored function of this protein interaction 24019232_Studied secreted protein biomarkers in invasive breast cancer; identified annexin II as a novel secretory biomarker candidate for invasive breast cancer, especially estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. 24111848_Plasminogen stimulates airway smooth muscle cell proliferation in a manner mediated by urokinase and annexin A2. 24239898_By associating with P-glycoprotein, Anxa2 promotes invasion of multidrug resistant breast cancer cells. 24402284_annexin A2 may participate in keloid formation by inhibiting keloid fibroblast proliferation. 24591759_With some cancers, ANXA2 can be used for the detection and diagnosis of cancer and for monitoring cancer progression. [Review] 24626613_the present study demonstrated that ANXA2 and SOD2 are potential target genes of HOXA13 and their coexpression predicts the poor prognosis of Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. 24668792_Annexin A2 was identified as down-regulated in the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissues after 2-DE Gel coupled with MALDI-TOF-MS identification. 24719459_HPV16 suppresses LC maturation through an interaction with A2t, revealing a novel role for this protein. 24806074_metastatic cancer cells have elevated rate of cell injury and they rely on the S100A11-ANXA2 complex to enable cell membrane repair. S100A11 in a complex with Annexin A2 helps reseal the plasma membrane. 24808179_data revealed a plausible new role of AnxA2 in the reduction of PCSK9 protein levels via a translational mechanism. 24819400_Annexin A2 is a key molecule in the DDR-2/annexin A2/MMP-13 loop, the activation of which contributes to joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis, mainly through promoting invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. 24884814_Urinary calreticulin, annexin A2, and annexin A3 are very likely a panel of biomarkers with potential value for upper tract urothelial carcinoma diagnosis. 24968947_Data suggest that S100A4 and Annexin A2 proteins could be useful prognostic markers to predict tumor progression and prognosis in urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder. 25034653_This study shows that ANXA2 and GAL3 deregulated expression was associated with an invasive phenotype in gastric cancer cell lines and may contribute to metastasis in gastric cancer patients. 25139904_CARDS toxin binds selectively to annexin A2; it serves as a distinct receptor for CARDS toxin binding and internalization and enhances CARDS toxin-induced vacuolization in mammalian cells 25150310_ANXA2 is involved in gastric cancer multi-drug-resistance (MDR) through regulating p38MAPK and AKT pathways as well as certain MDR factors 25219463_ANXA2 effectively predicted those endometrioid endometrial carcinomas that finally recurred. 25233429_Data suggest that calcium-dependent phosphatidylinositol 4,5-diphosphate- (PI(4,5)P2-) binding proteins (such as ANXA2, PRKCA [protein kinase C alpha], and SYT1 [synaptotagmin I]) interactions with membrane microdomains are tightly regulated. [REVIEW] 25284003_Study points out the regulatory function of Anxa2 in RCC cell motility and provides a molecular-based mechanism of Anxa2 positivity in the progression of RCC. 25287627_findings indicate a significant decrease in Anx A2 expression in colon cancer patients compared to healthy controls and in parallel with tumor progression 25290763_These data indicate a novel functional role of AnxA2 in the negative post-transcriptional regulation of type I collagen synthesis in human fibroblasts. 25303710_Annexin A2 complexes with S100 proteins: structure, function and pharmacological manipulation 25344575_Results show the transcriptional repression of ANXA2 by ERG in prostate epithelial cells plays a critical role in abrogating differentiation, promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and in the inverse correlation of expression seen in prostate tumor. 25347736_Data indicate that annexin A2 overexpression in microsatellite instability (MIN) cells induces disassembly and colocalization of coilin with centromeres. 25355205_Our results support a model whereby AnxA2 limits the availability of TRPA1 channels to regulate nociceptive signaling in vertebrates. 25362534_HE4 and annexin II binding interaction promoted ovarian cancer cell invasion. 25402728_annexin A2 (ANXA2) on nasopharygeal carcinoma cells is a ligand for DC-SIGN on dendritic cells 25416440_Consistently, double-labeling immunofluorescence experiments illustrated co-localization of ANXA2 and Lewis y antigen within the same area. In conclusions, ANXA2 contains Lewis y antigen. 25418092_Results reveal that AnxA2 and its derivatives bind cooperatively to membranes containing cholesterol, phosphatidylserine, and/or phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate, thus providing a mechanistic model for the lipid clustering activity of AnxA2 25476478_The present meta-analysis results indicated that ANXA2 overexpression might be associated with poor outcomes in patients with malignant tumors. 25500542_Mir206 targets ANXA2 a | ENSMUSG00000032231 | Anxa2 | 3798.238908 | 1.0017745 | 0.002557761 | 0.03379387 | 0.00572853620 | 0.9396680440446442128532567039655987173318862915039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.97309219192718876545455941595719195902347564697265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 3831.458967 | 121.459861 | 3842.799608 | 121.368630 | |
| ENSG00000182979 | 9112 | MTA1 | protein_coding | Q13330 | FUNCTION: Transcriptional coregulator which can act as both a transcriptional corepressor and coactivator. As a part of the histone-deacetylase multiprotein complex (NuRD), regulates transcription of its targets by modifying the acetylation status of the target chromatin and cofactor accessibility to the target DNA. In conjunction with other components of NuRD, acts as a transcriptional corepressor of BRCA1, ESR1, TFF1 and CDKN1A. Acts as a transcriptional coactivator of BCAS3, PAX5 and SUMO2, independent of the NuRD complex. Stimulates the expression of WNT1 by inhibiting the expression of its transcriptional corepressor SIX3. Regulates p53-dependent and -independent DNA repair processes following genotoxic stress. Regulates the stability and function of p53/TP53 by inhibiting its ubiquitination by COP1 and MDM2 thereby regulating the p53-dependent DNA repair. Plays an important role in tumorigenesis, tumor invasion, and metastasis. Involved in the epigenetic regulation of ESR1 expression in breast cancer in a TFAP2C, IFI16 and HDAC4/5/6-dependent manner. Plays a role in the regulation of the circadian clock and is essential for the generation and maintenance of circadian rhythms under constant light and for normal entrainment of behavior to light-dark (LD) cycles. Positively regulates the CLOCK-BMAL1 heterodimer mediated transcriptional activation of its own transcription and the transcription of CRY1. Regulates deacetylation of BMAL1 by regulating SIRT1 expression, resulting in derepressing CRY1-mediated transcription repression. Isoform Short binds to ESR1 and sequesters it in the cytoplasm and enhances its non-genomic responses. With TFCP2L1, promotes establishment and maintenance of pluripotency in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and inhibits endoderm differentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K4B0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16617102, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17671180, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17922032, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19837670, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21965678, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24413532}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Biological rhythms;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a protein that was identified in a screen for genes expressed in metastatic cells, specifically, mammary adenocarcinoma cell lines. Expression of this gene has been correlated with the metastatic potential of at least two types of carcinomas although it is also expressed in many normal tissues. The role it plays in metastasis is unclear. It was initially thought to be the 70kD component of a nucleosome remodeling deacetylase complex, NuRD, but it is more likely that this component is a different but very similar protein. These two proteins are so closely related, though, that they share the same types of domains. These domains include two DNA binding domains, a dimerization domain, and a domain commonly found in proteins that methylate DNA. The profile and activity of this gene product suggest that it is involved in regulating transcription and that this may be accomplished by chromatin remodeling. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. | hsa:9112; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; NuRD complex [GO:0016581]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; double-strand break repair [GO:0006302]; entrainment of circadian clock by photoperiod [GO:0043153]; epigenetic regulation of gene expression [GO:0040029]; histone deacetylation [GO:0016575]; locomotor rhythm [GO:0045475]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of protein autoubiquitination [GO:1902499]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; regulation of cell fate specification [GO:0042659]; regulation of stem cell differentiation [GO:2000736]; response to ionizing radiation [GO:0010212]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 11804687_expression is closely related to invasiveness and metastasis in non-small-cell lung carcinoma 11948399_metastasis-associated protein (MTA)1 enhances migration, invasion, and anchorage-independent survival of immortalized human keratinocytes 12167865_naturally occurring short form that contains a previously unknown sequence of 33 amino acids with an ER-binding motif, Leu-Arg-Ile-Leu-Leu (LRILL); MTA1s localizes in the cytoplasm, sequesters ER in the cytoplasm, and enhances non-genomic responses of ER 12431981_MTA1 binds to the MMP-9 promoter, thereby repressing expression of this type IV collagenase via histone-dependent and independent mechanisms 12527756_interaction with MAT1 and regulation of estrogen receptor transactivation functions 12650603_The results suggest that the MTA1 protein may serve multiple functions in cellular signaling, chromosome remodeling and transcription processes that are important in the progression, invasion and growth of metastatic epithelial cells. 12684630_High expression of the MTA1 gene is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma 12920132_MTA1 and MTA2 repress transcription specifically, are located in the nucleus, and contain associated histone deacetylase activity; MTA1 associates with a different set of transcription factors from MTA2 14735193_enhanced expression of MTA1 promotes the acquisition of an invasive, metastatic phenotype, and thus enhances the malignancy of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells by modulation of the cytoskeleton 14871807_This study identified an association of MTA1 expression and prostate cancer progression. 15077195_MTA1s interacts with CKI-gamma2 in vitro and in vivo and colocalizes in the cytoplasm 15095300_overexpression of MTA1 protein and acetylation level of histone H4 protein are closely related 15254226_Metastasis-associated protein 1 interacts with NRIF3, an estrogen-inducible nuclear receptor coregulator 16172399_MTA1 is one of the first downstream targets of c-MYC function that are essential for the transformation potential of c-MYC. 16244788_MTA1 overexpression is associated with high recurrence of breast cancer 16502042_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16617102_role for MTA1-BCAS3 pathway in promoting cancerous phenotypes in breast tumor cells 16646402_Overexpression of the MTA1 gene correlates with lymph node metastasis of carcinomas of the larynx. 16807247_structure and antiestrogenic activity of the unique C-terminal, NR-box motif-containing region of MTA1 16831056_These studies demonstrate that MTA1 is expressed in both benign and malignant neoplasms. While its expression is associated with tissue invasion it may not be sufficient for the progression of neoplasms to metastatic stages. 16855396_BCAS3 overexpression in hormone receptor-positive premenopausal breast cancer seemed to be associated with impaired responses to tamoxifen 16969516_MTA1 enhances angiogenesis by stabilization of the HIF-1alpha protein, which is closely related to the increased metastatic potential of cancer cells with high MTA1 expression 17666527_role for the MTA1 as an upstream modifier of Six3 and indicate that Six3 is a direct stimulator of rhodopsin expression. 17868030_Results suggest that MTA1 promotes the metastatic ability of B16F10 cancer cells. 17922032_These findings strongly implicate MTA1 in the transcriptional repression of BRCA1 leading to abnormal centrosome number and chromosomal instability. 17922035_study shows HSF1 binds to MTA1 in vitro & in breast carcinoma; repression of estrogen-dependent transcription may contribute to role of HSF1 in cancer 18196870_MTA1 expression was significantly higher in noninvasive breast cancer cell lines than in invasive ones. 18306220_MTA1 is closely associated with microvascular invasion, frequent postoperative recurrence, and poor survival of HCC patients, especially in those with HBV-associated HCC. 18362831_HIF-1alpha expression may be regulated through HDAC1/MTA1, which is associated with a poor prognosis for pancreatic carcinoma 18640824_Histologically, MTA1 protein production was strongly associated with cancer cell invasion, and clinically there was a correlation between lymph node metastasis and MTA1 protein production. 18719363_MTA1 is up-regulated in advanced ovarian cancer, represses ERbeta, and enhances expression of GRO. 18769059_This study was undertaken to explore the potential role of MTA1 in mouse liver. 19363681_the high expression level of MTA proteins in human chorionic cells might facilitate trophoblast cell migration and neoangiogenesis 19366061_ezrin and metastatic tumor antigen positivity can be additional prognostic markers in osteosarcoma of the jaw. 19377441_Metastasis-associated gene 1 expression is significantly associated with malignant behavior in pancreatic endocrine tumors. 19403384_MTA1 may promote lung carcinogenesis by enhancing HIF-1alpha protein activity. 19584269_Results suggest that miR-661 be further investigated for therapeutic use in down-regulating the expression of MTA1 in cancer cells. 19805145_MTA1 is required for optimum DNA double-strand break repair after ionizing radiation. 20071335_there is a p53-independent function of MTA1 in DNA damage response via modulation of the p21 WAF1-proliferating cell nuclear antigen pathway 20427275_Findings suggest that, in addition to its role in the repair of double strand breaks caused by ionizing radiation, MTA1 also participates in the UV-induced ATR-mediated DNA damage checkpoint pathway. 20547755_identify MTA1, a subunit of the NuRD complex, as a new HIC1 corepressor. 20619094_Expression of Mta-1 expression and VEGF is positively associated with the development of endometrial cancer. 20651739_Data show that induced levels of metastasis-associated protein 1 (MTA1) are sufficient to transform Rat1 fibroblasts and that the transforming potential of MTA1 is dependent on its acetylation at Lys626. 20661085_High metastasis-associated protein 1 nuclear expression is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 20697987_Increased expression of MTA1 is associated with invasive ductal breast carcinoma. 20717904_MTA1 pro-angiogenic and pro-invasive functions create permissive environment for prostate tumor growth and likely support metastasis. 20935042_Mta1 protein overexpression is an independent prognostic factor for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. 21047798_RbAp48 interacts with the NuRD subunit MTA-1 via a surface that is distinct from its FOG-binding pocket, providing a first glimpse into the way in which NuRD assembly facilitates interactions with cofactors 21240515_There was a significant correlation between the expression of MTA1 and lymph node metastasis in tonsil cancer. 21258411_findings suggest that TGF-beta1 regulates EMT via stimulating expression of MTA1, which in turn, induces FosB to repress E-cadherin expression and thus, revealed an inherent function of MTA1 as a target and effector of TGF-beta1 signaling in epithelial cells 21290196_Overexpression of metastasis-associated protein 1 is significantly correlated with tumor angiogenesis in patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. 21336715_MTA1 plays an important role in the migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells. 21445634_in ileal neuroendocrine cancer, HER-2/neu overexpression plays a role in the carcinogenetic process and by triggering the altered expression of c-Met and MTA-1, may activate the molecular pathway(s) promoting tumor progression and metastasis development. 21448429_Data suggest that MTA1, as a regulator of tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis, promotes lymphangiogenesis in colorectal cancer by mediating the VEGF-C expression. 21555589_MTA1-mediated activation of ARF and ARF-mediated functional inhibition of MTA1 represent a p53-independent bidirectional autoregulatory mechanism in which these two opposites act in concert to regulate cell homeostasis and oncogenesis 21595884_Silencing effect of MTA1 could efficiently inhibit the invasion and proliferation in MDA-MB-231 cells. 21617866_HDAC1 and MTA1 expression levels are potential prognostic indicators for colon cancer. 21661415_Barrett's esophagus (BE) with HDAC-1 and MTA-1 expression is considered to be a precancerous lesion re quiring curative treatment. 21725997_immunohistochemical analysis of approximately 300 liver tissue cores from confirmed cases of Opisthorchis viverrini-induced cholangiocarcinoma showed that MTA1 expression was elevated in >80% of the specimens 21813470_The data suggest that EIF5A2 plays an important oncogenic role in CRC aggressiveness by the upregulation of MTA1 to induce EMT. 21835429_Metastasis tumor antigen 1 overexpression can be used as a predictor of clinical outcome in patients with ovarian cancer and therefore may represent a new prognostic marker. 21837953_MTA1 siRNA can inhibit the anchorage-independent growth of prostate cancer cells by inducing anoikis. 21892752_MTA1may play an important role in the smoked-related progress of non-small cell lung cancer 21949998_Aberrant expression of MTA1 and RECK gene may be involved in the invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 21965678_SUMOylation and SUMO-interacting motif (SIM) of metastasis tumor antigen 1 (MTA1) synergistically regulate its transcriptional repressor function 22022494_The fine coordination between MTA1 and p53 in pachytene spermatocytes upon hyperthermal stimulation, was investigated. 22098246_The genetic polymorphism IVS4-81G/A in MTA1 were correlated with MTA1 overexpression and may be an important risk factor for the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. 22139444_MiR-30c was directly bound to the 3'-untranslated regions of MTA1. 22176993_MTA1 may play a role in promoting cervical cancer cell invasion, migration, adhesion, as well as cell growth and colony formation. 22253283_Study reveals several new physiologic functions of MTA1 related to DNA damage, inflammatory responses, and infection, in which MTA1 functions as a permissive 'gate keeper' for cancer-causing parasites. 22270359_Leptin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells requires beta-catenin activation via Akt/GSK3- and MTA1/Wnt1 protein-dependent pathways. 22270988_High expression of MTA1 protein is closely associated with esophageal tumor progression, increased tumor angiogenesis, and poor survival. 22286760_the MTA1 gene is a target of p53-mediated transrepression 22537306_results of this study suggest that nuclear overexpression of MTA1 correlates significantly with poorer disease free survival and poorer overall survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma 22547301_MTA1 gene overexpression can be used as a molecular biological marker to predict the prognosis of middle esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 22575258_Metastasis-associated protein 1 staining is not ideal for investigating the possible malignant nature of smaller metastases because of the relatively low concordance between the primary tumor and metastases. 22576802_MTA1 functions in regulating the invasive phenotype of lung cancer cells and this regulation may be through altered miRNA expression 22700976_Metastasis-associated protein 1/histone deacetylase 4-nucleosome remodeling and deacetylase complex regulates phosphatase and tensin homolog gene expression and function. 22844865_The conversely abnormal expression levels of MTA1 and RECK may be collectively involved in progression of malignancies and may serve as molecular predictors for metastasis, recurrence, and prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 22864797_Overexpression of MTA1 is associated with Breast Cancer. 23227138_results demonstrate that MTA1 plays an important role in controlling the malignant transformation of prostate cancer cells through the p-AKT/E-cadherin pathway 23283219_MTA1 overexpression is frequently observed in node-negative gastric cancer patients and is significantly associated with increased angiogenesis and poor prognosis. 23343746_These findings demonstrate that MTA1 protein plays important roles in regulating the migration, invasion, and angiogenesis potentials of 95D cells. 23352453_MTA1 possesses an inherent histone amplifier activity with an instructive role in impacting the epigenetic landscape. 23371285_High MTA-1 expression is associated with metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. 23592142_These results demonstrated that MTA1 played an important role in the cell metastasis in ovarian cancer. 23618874_we have demonstrated a critical role of MTA1 in regulating NPC metastasis. This kind of role is associated with its influence on cytoskeleton organization. Rho GTPases and Hedgehog signaling are involved in MTA1-mediated metastasis promotion. 23718732_MTA1 and miR-125b have antagonistic effects on the migration and invasion of NSCLC cells. 23791785_The structure of HDAC1 in complex with MTA1 from the NuRD complex is reported. 23831020_MTA1 acts as a potent corepressor of the nuclear receptor NR4A1 transcription by interacting with HDAC2 and may serve as a novel DTX-resistance promoter in PC-3 cells 23866297_Metastasis-associated protein 1 is a novel marker predicting survival and lymph nodes metastasis in cervical cancer. 23900262_We concluded that MTA1 nuclear overexpression may be a prognostic indicator and a future therapeutic target for aggressive PCa in African American men 23941622_MTA1 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation via enhancing G1 to S phase transition, leading to increased tumor growth. 24089055_MTA1 has an important role in the maintenance of circadian rhythmicity. 24214543_MTA1 gene plays an important role in progressiona and metastasis of ovarian cancers. 24265228_Crosstalk between VEGF and MTA1 signaling pathways contribute to aggressiveness of breast carcinoma. 24413532_MTA1-TFAP2C or the MTA1-IFI16 complex may contribute to the epigenetic regulation of ESR1 expression. 24424621_These results demonstrate a novel role for MTA1 in the regulation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma invasion and provide insight into the mechanisms involved in this process. 24920672_RbAp48 recognizes MTA1 using the same site that it uses to bind histone H4, showing that assembly into NuRD modulates RbAp46/48 interactions with histones. 25205035_MTA1 drove a global decondensation of chromatin structure, it changed the expression of only a small proportion of genes. 25245523_MTA1 plays a critical role in promoting cisplatin resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by regulating cancer stem cell properties via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 25301048_High expression of the MTA1 protein was seen in oral squamous cell carcinoma, and was closely associated with tumor progression and increased tumor angiogenesis. 25315816_In this review, we will briefly discuss the researches for the identification and characterization of the mta1 gene, its human counterpart MTA1, and their protein products 25315817_In this review, we described various molecular studies of osteosarcoma, especially associated with MTA1. 25319202_This review focuses on the current knowledge about the function and regulation of MTA1 and MTA3 proteins in gynecological cancer, including ovarian, endometrial, and cervical tumors. 25332143_MTA1 is involved in prostate tumor angiogenesis by regulating several pro-angiogenic factors. Evidence for MTA1 as a prognostic marker for aggressive prostate cancer and disease recurrence has been described. 25332144_Therefore, targeting MTA1 would not only suppress tumor progression but also greatly sensitize cancer cells to DNA damage-based radio- and chemotherapies 25332145_propose that MTA1 is a stress response protein that is upregulated in various stress-related situations such as heat shock, hypoxia, and ironic radiation. 25332146_Recent studies demonstrating the bi-regulatory nature of MTA1 challenged the conventional paradigm of MTA function and raised many questions in fully understanding their roles in cancer progression 25344802_the concept of the dynamic nature of corepressor versus coactivator complexes and the MTA1 proteome as a function of time to signal is likely to be generally applicable to other multiprotein regulatory complexes in living systems. 25352341_In this review, we summarise the structure and function of the four domains of MTA1 and discuss the possible functions of less well-characterised regions of the protein. 25359583_This review gives a brief account on the existing biological and molecular data in the context of head and neck cancer invasion and metastasis in relation to MTA1. 25374266_Taken together, current literature suggests that MTA proteins, especially MTA1, act as a master co-regulatory molecule involved in the carcinogenesis and progression of various malignant tumors 25416046_MTA1 expression was significantly associated with poor metastasis-free survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. 25501238_Results show that MTA1 promotes the proliferation of epithelial ovarian cancer cells by enhancing DNA repair. 25502548_MTA1 plays a critical role in regulating the malignant behaviors of small cell lung cancer 25688501_MTA1 might be important biological marker involved in the carcinogenesis, metastasis, and invasion of gallbladder adenocarcinoma, and MTA1 is an independent factor of prognosis. 25797255_protein abundance of YB-1 and MTA1, irrespective of DNA or mRNA status, can predict for prostate cancer relapse and uncover a vast underappreciated repository of biomarkers regulated at the level of protein expression. 25977170_MTA1 is associated with the aggressive nature of pituitary tumors and may be a potential therapeutic target in this tumor type. 25998575_report demonstrates that miR-125a-3p inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of NSCLC cells through down-regulation of MTA1 26168722_MTA1 dysregulation in a subset of salivary gland cancer might promote aggressive phenotypes by compromising the tumor suppressor activity of ERbeta 26503703_Inhibition of MTA1 by ERalpha contributes to protection hepatocellular carcinoma from tumor proliferation and metastasis 26543080_MTA1 is up-regulated in CRC; its expression is inversely associated with lymphatic metastases and the expression of VEGFC, VEGFD and VEGFR3 26689197_MTA1 plays an important role in Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) to promote metastasis via suppressing E-cadherin expression, resulting in a poor prognosis in MPM. MTA1 is a novel biomarker and indicative of a poor prognosis in MPM patients 26698569_We revealed a new molecular mechanism of MTA1-mediated invasion and metastasis in lung cancer through downstream target EpCAM, and interfering with EpCAM function may be a novel therapeutic strategy for treatment of MTA1-overexpressing lung carcinoma 26728277_the augmentation of endogenous MTA1 expression during neuronal ischemic injury acts additionally to an endocrinous cascade orchestrating intimate interactions between ERalpha and BCL2 pathways. 26797758_High MTA1 expression is associated with osteosarcoma progression. 26943043_Findings highlight MTA1 as a key upstream regulator of prostate tumorigenesis and cancer progression. 26968810_Data show that KRAS, MTA1 and HMGA2 are direct targets of miR-543. 27026268_show that AR might be an additional marker for endocrine responsiveness in ER(+) cancers and suggests that blocking MTA1 might be an effective way to inhibit AR/HER2 signaling in ER(-) breast cancer 27035126_There is no interaction between IGFBP3 and MTA1 in ESCC, and they are not independent risk factors for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma prognosis. 27044752_Results show that metastasis-associated protein 1 (MTA1) and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) levels were significantly down-regulated in Parkinson disease (PD) samples as compared with normal brain tissue. 27048111_RNAi aiming at MTA1 can effectively inhibit the expression of MTA1 in endometrial carcinoma Ishikawa cells 27052252_Results showed that in the development of colon cancer, MTA1 is linked to certain signal pathways, such as Wnt/Notch/nucleotide excision repair pathways. The findings also suggested that MTA1 demonstrates the closest relationship in a coregulation process with the key molecules AKT1, EP300, CREBBP, SMARCA4, RHOA, and CAD. 27098840_The crystal structure reveals an extensive interface between MTA1 and RBBP4. 27144666_The MTA1 subunit of the nucleosome remodeling and deacetylase complex can recruit two copies of RBBP4/RBBP7. 27320813_MTA1 expression is upregulated in tumours compared to normal colon cancer samples. 27323185_the significance of MTA1 expression in the invasion and metastasis of medulloblastoma 27506865_Metastasis-associated protein-1 expression levels in HPV-infected non-small cell lung cancer tissues correlated positively with tumor stage and nodal metastasis. 27574100_elevated expression of MTA1 was significantly correlated with recurrence, and was an independent risk factor for lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer 27583980_Suppression of breast cancer metastasis occurs following miR-421 inhibition of MTA1 expression. 27603575_Data show that metastasis associated 1 (MTA1) represses neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) expression upon oxygen glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced oxidative stress. 28231399_Data indicate a positive correlation between metastasis-associated protein 1 (MTA1) and microRNA miR-22, supporting their inhibitory effect on E-cadherin expression. 28288133_Downregulation of miR-30e can increase levels of MTA1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma, and furthermore promote cell invasion and metastasis by promoting ErbB2. 28393842_Together findings presented here recognize an inherent role of MTA1 as a modifier of DNMT3a and IGFBP3 expression, and consequently, the role of MTA1-DNMT3a-IGFBP3 axis in breast cancer progression. 28418915_High Expressions of MTA1 is associated with epithelial to mesenchymal transition and metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer. 28443468_our studies indicate that Curcumin increases the sensitivity of Paclitaxel-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer cells to Paclitaxel through microRNA-30c-mediated MTA1 reduction. Curcumin might be a potential adjuvant for non-small-cell lung cancer patients during Paclitaxel treatment. 28504714_Findings illustrate how cancer cells utilize a chromatin remodeling factor to engage a core survival pathway to support its cancerous phenotypes, and reveal new facets of MTA1-SGK1 axis by a physiologic signal in cancer progression. 28506766_Our findings revealed that miR-183 upregulation and MTA1 gene silence significantly repressed the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion of human pancreatic cancer cells. 28570554_In subgroup analyses based on study quality and tumor type, MTA1 overexpression was obviously related to clinical parameters, such as lymph node metastasis and TNM stage, and was also associated with prognosis of patients with gastrointestinal or esophageal cancer 28589145_MTA1 contributed to neovascularization of residual tumors. Cellular experiments further revealed that MTA1 increased the stability and the expression of HIF-1alpha, and overexpression of MTA1 enhanced tube formation and neovessels of chick embryos. 28631568_In this study, we aimed to analyze the expression of miR-183 and MTA1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissues and cells; explore the role of miR-183 in NPC cell proliferation, invasion, as well as DDP-induced apoptosis; and investigate the relationship between miR-183 and MTA1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. 28635511_MTA 1 protein may constitute an important prognostic marker in pancreatic cancer and could improve prognosis and treatment. 28686969_Inhibit the metastasis and EMT via MTA1. 28739699_MTA1 expression was positively correlated with LAT1 (p=0.013) and CD34 (p=0.034) expression, but not with Ki-67 (p=0.078). MTA1 shows promise as a diagnostic and prognostic marker in esophageal cancer, and we anticipate that the gene will also prove to be a good therapeutic target. 28861931_TRIM25 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting MTA1. 28901313_MiR-30c and MTA1 abnormally expressed in ovarian cancer (OC), which may be related to metastasis of OC. In MiR-30c as a tumor suppressor gene, its expression in OC could lead to reduced expression of MTA1, which may be one of the mechanisms of metastasis of OC cells. 29061215_Overexpression of MTA1 could be a marker of poor prognosis in Chinese NSCLC patients, but not in lung cancer or small cell lung cancer. 29125886_MTA1 participates in Nasopharyngeal carcinoma malignant transformation via regulating IQGAP1 expression and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 29130361_MTA1 induces AMPK activation and subsequent autophagy that could contribute to tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. 29465084_Data found that MTA1 is a PKD1-interacting substrate, and that PKD1 phosphorylates MTA1, supports its nucleus-to-cytoplasmic redistribution and utilises its N-terminal and kinase domains to effectively inhibit the levels of MTA1 via polyubiquitin-dependent proteosomal degradation. 29573865_MTA1 immunopositivity was significantly associated with progression of gastric cancer, and may be helpful in gastric cancer prognosis. 29654742_data indicate that suppression of TRIM25 expression by high levels of miR-873 dictates MTA1 protein upregulation in hepatocellular carcinoma 30013189_High expression of FMNL1, resulted from decreased miR-16 and/or MTA1 amplification. 30027683_MTA1 promotes prostate tumor growth and formation of bone metastasis by positively regulating CTSB expression in the primary tumor cells. MTA1 is an attractive target for the treatment of prostate cancer and prevention of bone metastasis. 30118695_It has been shown that TRIM25 ubiquitinates MTA-1 at lysine 98 and degrades it normal liver cells. 30170442_MTA1 is closely associated with the occurrence and development of endometriosis. Thus, MTA1 level may be used as a new indicator to predict the progression of endometriosis 30268463_this study shows relationship between MTA1 and spread through air space and their joint influence on prognosis of patients with stage I-III lung adenocarcinoma 30313027_Meta-analysis demonstrated that increased MTA1 expression was an effective predictor of a worse prognosis in solid tumor patients. 30314706_The circ-UBAP2 was mainly observed in the cytoplasm and was capable of sponging miRNA-661 to increase the expression of the oncogene MTA1. 30327463_MTA1 binding to PWWP2A during recruitment of the entire MHR complex . 30396299_These results indicated that MTA1 potentially promoted pancreatic cancer metastasis via HIF-alpha/VEGF pathway. This research supplies a new molecular mechanism for MTA1 in the pancreatic cancer progression and metastasis. MTA1 may be an effective therapy target in pancreatic cancer. 30610787_High MTA1 expression is associated with proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer. 30631898_Upregulation of MTA1 expression by human papillomavirus infection promotes cisplatin resistance in cervical cancer cells via modulation of NF-kappaB/APOBEC3B cascade 30642362_MTA1 and MTA2 play opposing roles in the metastasis of ZR-75-30 luminal B breast cancer cells in vitro. 30651530_MTA1 silencing with si-RNA significantly reduced the tumor growth rate in nude mice (p | ENSMUSG00000021144 | Mta1 | 539.119785 | 0.6486162 | -0.624563019 | 0.07019720 | 79.35819042071 | 0.0000000000000000005181100929952707083154266849871061024203851675050912489045584763402985117863863706588745117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000000000000003339780636321588576333293455263918687479692139858863941803690522647229954600334167480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 426.764873 | 28.170364 | 659.923907 | 42.562024 | |
| ENSG00000183208 | 390637 | GDPGP1 | protein_coding | Q6ZNW5 | FUNCTION: Specific and highly efficient GDP-D-glucose phosphorylase regulating the levels of GDP-D-glucose in cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21507950}. | Cytoplasm;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Hydrolase;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleotidyltransferase;Reference proteome;Transferase | Enables GDP-D-glucose phosphorylase activity. Involved in glucose metabolic process. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:390637; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; GDP-D-glucose phosphorylase activity [GO:0080048]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787]; nucleotide binding [GO:0000166]; glucose metabolic process [GO:0006006] | 21507950_C15orf58 in humans and C10F3.4 in C. elegans display GDP-hexose phosphorylase activity but the major reaction catalyzed by these enzymes is the phosphorolysis of GDP-D-glucose to GDP and D-glucose 1-phosphate | ENSMUSG00000050973 | Gdpgp1 | 18.960355 | 0.9800705 | -0.029042614 | 0.43250440 | 0.00448067470 | 0.9466311869970344128333294975163880735635757446289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.97579049695759156879404372375574894249439239501953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 19.144764 | 4.255928 | 19.403523 | 4.227740 | |
| ENSG00000183735 | 29110 | TBK1 | protein_coding | Q9UHD2 | FUNCTION: Serine/threonine kinase that plays an essential role in regulating inflammatory responses to foreign agents (PubMed:12692549, PubMed:14703513, PubMed:18583960, PubMed:12702806, PubMed:15367631, PubMed:10581243, PubMed:11839743, PubMed:15485837, PubMed:21138416, PubMed:25636800, PubMed:23453971, PubMed:23453972, PubMed:23746807, PubMed:26611359, PubMed:32404352). Following activation of toll-like receptors by viral or bacterial components, associates with TRAF3 and TANK and phosphorylates interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) IRF3 and IRF7 as well as DDX3X (PubMed:12692549, PubMed:14703513, PubMed:18583960, PubMed:12702806, PubMed:15367631, PubMed:25636800). This activity allows subsequent homodimerization and nuclear translocation of the IRFs leading to transcriptional activation of pro-inflammatory and antiviral genes including IFNA and IFNB (PubMed:12702806, PubMed:15367631, PubMed:25636800, PubMed:32972995). In order to establish such an antiviral state, TBK1 form several different complexes whose composition depends on the type of cell and cellular stimuli (PubMed:23453971, PubMed:23453972, PubMed:23746807). Plays a key role in IRF3 activation: acts by first phosphorylating innate adapter proteins MAVS, STING1 and TICAM1 on their pLxIS motif, leading to recruitment of IRF3, thereby licensing IRF3 for phosphorylation by TBK1 (PubMed:25636800, PubMed:30842653). Phosphorylated IRF3 dissociates from the adapter proteins, dimerizes, and then enters the nucleus to induce expression of interferons (PubMed:25636800). Thus, several scaffolding molecules including FADD, TRADD, MAVS, AZI2, TANK or TBKBP1/SINTBAD can be recruited to the TBK1-containing-complexes (PubMed:21931631). Under particular conditions, functions as a NF-kappa-B effector by phosphorylating NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha/NFKBIA, IKBKB or RELA to translocate NF-Kappa-B to the nucleus (PubMed:10783893, PubMed:15489227). Restricts bacterial proliferation by phosphorylating the autophagy receptor OPTN/Optineurin on 'Ser-177', thus enhancing LC3 binding affinity and antibacterial autophagy (PubMed:21617041). Phosphorylates SMCR8 component of the C9orf72-SMCR8 complex, promoting autophagosome maturation (PubMed:27103069). Phosphorylates ATG8 proteins MAP1LC3C and GABARAPL2, thereby preventing their delipidation and premature removal from nascent autophagosomes (PubMed:31709703). Phosphorylates and activates AKT1 (PubMed:21464307). Seems to play a role in energy balance regulation by sustaining a state of chronic, low-grade inflammation in obesity, wich leads to a negative impact on insulin sensitivity (By similarity). Attenuates retroviral budding by phosphorylating the endosomal sorting complex required for transport-I (ESCRT-I) subunit VPS37C (PubMed:21270402). Phosphorylates Borna disease virus (BDV) P protein (PubMed:16155125). Plays an essential role in the TLR3- and IFN-dependent control of herpes virus HSV-1 and HSV-2 infections in the central nervous system (PubMed:22851595). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WUN2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10581243, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10783893, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11839743, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12692549, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12702806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14703513, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15367631, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15485837, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15489227, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16155125, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18583960, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21138416, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21270402, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21464307, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21617041, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21931631, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22851595, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23453971, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23453972, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23746807, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25636800, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26611359, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27103069, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30842653, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31709703, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32972995}. | 3D-structure;Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;Antiviral defense;ATP-binding;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Glaucoma;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Innate immunity;Isopeptide bond;Kinase;Neurodegeneration;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Ubl conjugation | The NF-kappa-B (NFKB) complex of proteins is inhibited by I-kappa-B (IKB) proteins, which inactivate NFKB by trapping it in the cytoplasm. Phosphorylation of serine residues on the IKB proteins by IKB kinases marks them for destruction via the ubiquitination pathway, thereby allowing activation and nuclear translocation of the NFKB complex. The protein encoded by this gene is similar to IKB kinases and can mediate NFKB activation in response to certain growth factors. The protein is also an important kinase for antiviral innate immunity response. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2021]. | hsa:29110; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; serine/threonine protein kinase complex [GO:1902554]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; phosphoprotein binding [GO:0051219]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein phosphatase binding [GO:0019903]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; activation of innate immune response [GO:0002218]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; dendritic cell proliferation [GO:0044565]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0018107]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of interferon-alpha production [GO:0032727]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; positive regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016239]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of type I interferon production [GO:0032481]; positive regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060340]; positive regulation of xenophagy [GO:1904417]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of neuron death [GO:1901214]; regulation of type I interferon production [GO:0032479]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060337] | 11839743_IKK-i and TBK-1 are enzymatically distinct from the homologous enzyme IKK-2: comparative analysis of recombinant human IKK-i, TBK-1, and IKK-2. 12133833_Association of the adaptor TANK with the I kappa B kinase (IKK) regulator connects IKK complexes with IKK epsilon and TBK1 kinases 12692549_IKKepsilon and TBK1 have a pivotal role in coordinating the activation of IRF3 and NF-kappaB in the innate immune response. 15367631_data suggest that intracellular RNP formation contributes to the early recognition of vesicular stomatitis virus infection, activates the catalytic activity of TBK1, and induces transcriptional upregulation of IKKepsilon in epithelial cells 15485837_NAK is a component of the TNFalpha.TNFR1 signaling complex and has a physiological role in the TNFalpha-mediated response 15489227_IL-1-inducible phosphorylation of p65 NFkB is mediated by multiple protein kinases including IKKalpha, IKKbeta, IKKepsilon, TBK1, and an unknown kinase and couples p65 to TAFII31-mediated IL-8 transcription 15619605_TBK1 has a role in human cytomegalovirus-infected vascular smooth muscle cells 15841462_HCV NS3 protein interacts directly with TBK1, and that this binding results in the inhibition of the association between TBK1 and IRF-3, which leads to the inhibition of IRF-3 activation 16223731_studies define one important mechanism of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK) regulation and the central role of NIK stabilization in the induction of NF-kappaB2 precursor protein p100 processing 16380379_interferon-A promoter organization differentially affects virus-induced expression and responsiveness to TBK1 and IKKepsilon 16394098_The present study identified a specific interaction between IRF3 and chaperone heat-shock protein of 90 kDa (Hsp90).In addition, TBK1 is found to be a client protein of Hsp90 in vivo. 16537515_TBK1 is important for vascularization and subsequent tumor growth 16888014_TBK1 and IKK epsilon directly phosphorylate the C-terminal domain of cRel in vitro and in vivo and regulate nuclear accumulation of cRel. 16973572_Interferon Regulatory Factor-3 is a direct target of TBK-1 phosphorylation 17018283_These observations define the mechanistic contribution of RalGTPases to cancer cell survival and reveal the RalB/Sec5 effector complex as a component of TBK1-dependent innate immune signaling. 17327220_TANK may be a critical adaptor that regulates the assembly of the TANK-binding kinase 1-inducible IkappaB kinase complex with upstream signaling molecules in multiple antiviral pathways 17526488_analysis of a two-step phosphorylation model for IRF-3 activation mediated by TBK1 17568778_results suggest that efficient signal transduction upon viral infection requires SINTBAD, TANK and NAP1 because they link TBK1 and IKKi to virus-activated signalling cascades 17823124_Lipopolysaccharide-mediated interferon regulatory factor activation involves TBK1-IKKepsilon-dependent Lys(63)-linked polyubiquitination and phosphorylation of TANK/I-TRAF. 18307994_The OPTN[E50K] mutant associated with Primary Open Angle Glaucoma (POAG) displayed strikingly enhanced binding to TBK1, suggesting that this interaction may contribute to familial POAG caused by this mutation. 18353649_distinct scaffold proteins assemble IKK, and potentially TBK1 and IKK-epsilon subcomplexes, in a stimulus-specific manner, which might be a mechanism to achieve specificity [review] 18508731_The TBK-1 pathway may be an important cross-link between angiogenesis and inflammation representing a possible target for anti-tumor therapy. 18583960_DDX3X is a critical effector of TBK1 that is necessary for type I IFN induction. 18614628_These findings indicate that the Hantavirus NY-1V Gn cytoplasmic tail forms a complex with TRAF3 which disrupts the formation of TBK1-TRAF3 complexes and downstream signaling responses required for IFN-beta transcription. 18977754_Upon Sendai virus (SeV) infection, TBK1s is induced in both human and mouse cells and binds to RIG-1, disrupting the interaction between RIG-I and VISA 19017982_a novel TLR-independent pathogen-sensing mechanism in immune and nonimmune cells that converges on TBK1 and IFN regulatory factor 3 for activation of IFN-beta gene expression. 19153231_These data suggest that VP35 exerts its interferon-antagonist function, at least in part, by blocking necessary interactions between the kinases IKKepsilon and TBK-1 and their normal interaction partners, including their substrates, IRF-3 and IRF-7. 19307177_the phosphorylation of Ser-172 and the activation of TBK1 and IKKepsilon are catalyzed by a distinct protein kinase(s) in vivo 19380831_Major outer protein of Treponema lecithinolyticum (Msp) induces interferon-beta expression and subsequent up-regulation of IP-10 and RANTES via TBK1 and interferon regulatory factor-3 signaling secondary to lipid raft activation. 19847166_Suppression of TBK1 induced apoptosis specifically in human cancer cell lines that depend on oncogenic KRAS expression 19955181_Activation of IRF3 and IRF3-dependent gene expressions was dependent on TAK1 and TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1). 19958770_Data suggest that TBK1 may play a role in the hepatitis B viral X protein -mediated activation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway and the development of hepatocellular carcinoma . 20304918_results demonstrate TBK1-IKKi to be novel substrates for A20 and further identify a novel mechanism whereby A20 and TAX1BP1 restrict antiviral signaling by disrupting a TRAF3-TBK1-IKKi signaling complex 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20588308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21270402_TBK1 directly interacts with VPS37C, a subunit of endosomal sorting complex required for transport-I (ESCRT-I) in the multivesicular body (MVB) pathway, without affecting the ultrastructure or general function of MVB. 21332394_NF-kB p65 binds to 27 of the mutant p53-bound promoters, indicating that mutant p53 could influence the transcriptional output of these NF-kB target genes. 21364999_PLP2(papain-like protease domain 2 (PLP2), a catalytic domain of the nonstructural protein 3 (nsp3) of MHV-A59) may also target TANK-binding kinase-1 (TBK1), the upstream kinase of IRF3 in the IFN signaling pathway. 21447600_Extra copies of the encompassed TBK1 gene is likely responsible for cases of normal tension glaucoma. 21464307_IkappaB kinase epsilon and TANK-binding kinase 1 activate AKT by direct phosphorylation. 21492457_inhibition of signaling reduces growth of medulloblastoma 21813773_Mechanistically, the tetratrico-peptide repeat motif (E164/E165) of IFIT3 interacts with the N terminus (K38) of TBK1, thus bridging TBK1 to MAVS on the mitochondrion 21868362_TBK1 mediates crosstalk between the innate immune response and autophagy. 21931631_TBK1 activation was strictly dependent on the integrity of the TBK1/TANK interaction 21939555_NF-kappaB and Notch1 signaling contribute to lymph nodes metastasis and tumor-induced lymphangiogenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), and reveal that up-regulation of NF-kappaB is associated with down-regulation of Notch1 in tumor tissue. 22127978_Patients with SLE display enhanced IL-23p19 expression as a result of hyperactivation of TBK-1, resulting in increased binding of IRF-3 to the promoter. 22306015_This is the first confirmation that chromosome 12q14 duplications which encompass the TBK1 gene are associated with (normal tension glaucoma) NTG. 22388039_Our results provide molecular insight into the mechanisms by which NLRP4-DTX4 targets TBK1 for degradation. 22394562_results suggest that STING functions as a scaffold protein to specify and promote the phosphorylation of IRF3 by TBK1. 22610919_The crystal structure of the ULD of human TBK1, is reported. 22619329_TBK1 autoactivation and substrate specificity are likely driven by signal-dependent colocalization events 22787218_phosphorylation of IRF7 on Ser477 and Ser479 by IKKepsilon or TBK1 is inhibited by KSHV ORF45 22851595_TBK1 is essential for the TLR3- and IFN-dependent control of HSV-1 in the central nervous system 23096996_These experiments demonstrated direct physical interactions of the IKKepsilon and TBK1 kinases with hepatitis C virus NS2. 23157677_we summarize the roles of IKKepsilon and TBK1 in different diseases and outline therapeutic options for modulation of these kinases. 23209807_Data propose that TBK1-dependent mechanism for NF-kappaB signalling contributes to autophagy addiction in K-Ras driven NSCLC. 23286385_Studies show that three proteins expressed in HEK-293T cells (NAP1, TANK and TBKBP1) interact with TBK1. 23395611_TBK1 mediates the activation of interferon regulatory factor (IRF) 3, leading to the induction of type I IFNs (IFN-a/b) following viral infections. (Review) 23395801_Studies suggest that both substrate selection and activation processes rely on TBK1 subcellular localization. 23421332_Expression of TBK1 in human retinal ganglion cells compared to the widespread pattern of expression of neighboring genes provides additional evidence that TBK1 is the glaucoma gene in the chromosome 12q14 duplication within the GLC1P locus. 23542348_Mechanistic studies indicated that NS4B disrupts the interactions between STING/MITA and TBK1, an additional mechanism for HCV evasion of host interferon responses. 23649622_Data indicate that suppressor of IKKepsilon (SIKE) inhibits TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1)-mediated phosphorylation of interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3), which is essential to type I interferon production. 23675467_TRIM11 negatively regulates IFN-beta production and antiviral activity by targeting TBK1. 23836654_results collectively revealed TBK1 as a mitosis regulator through activation of PLK1 and also suggested metadherin as a putative TBK1 downstream effector involved in lung cancer cell survival 24027431_TBK1 interacts with mTOR and inhibits its function. mTOR inhibition induces the cell cycle arrest of prostate cancer cells and enhances chemotherapeutic resistance of PCa cells. 24062311_The loss of TBK1 expression parallels the loss of ERalpha expression, in turn helping drive an aggressive breast cancer phenotype. 24335286_Through interaction with TBK1, phlebovirus nonstructural protein sequester the IKKepsilon and IRF3 into viral inclusion bodies. 24349538_data elucidated the cell type-specific subcellular localization of p-TBK1 and a cell type-specific role of IPS-1 in TBK1 activation in response to cytoplasmic viral DNA. 24449872_TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1), is a crucial determinant of resistance to tamoxifen therapies. 24468793_TBK1 signaling regulates radiation-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by controlling GSK-3beta phosphorylation and ZEB1 expression. 24549848_Collectively, these findings indicate that the Andes virus N inhibits interferon signaling responses by interfering with TBK1 activation, upstream of IRF3 phosphorylation and NF-kappaB activation. 24696485_Murine gammaherpesvirus 68 ORF11 targets TANK binding kinase 1 to negatively regulate the host interferon beta. 24699864_Duplication of the TBK1 gene is a rare cause of NTG. The identification of another case of NTG attributed to TBK1 gene duplication strengthens the case that this mutation causes glaucoma. 24722368_The results highlight the importance of the C-terminal region in the functional activity of IKKepsilon in innate immune response.Interestingly, corresponding region and residues are not required for activation of downstream signaling by TBK1. 24807708_Authors found that RIOK3 physically interacts with TBK1 and IRF3 and bridges the functions between TBK1 and IRF3 in the activation of type I interferon pathway. 24872591_This binding sequesters the association between TBK1 and IRF3. 24962318_TBK1 promotes the malignant properties of NRAS-mutant melanoma and its targeting. 25070846_findings demonstrated that USP2b deubiquitinates K63-linked polyubiquitin chains from TBK1 to terminate TBK1 activation and negatively regulate IFN-beta signaling and antiviral immune response. 25142606_The DLAIS motif in MAVS was found to be critical for MIB2 binding, the ligation of K63-linked ubiquitin to TANK-binding kinase 1, and phosphorylation-mediated IRF3/7 activation. 25284765_results confirm TBK1 to be an important cause of normal-tension glaucoma, but do not suggest common involvement in high-tension glaucoma 25297994_The cGAS/STING/TBK1/IRF3 cascade was not a direct target of viral antihost strategies, and authors found no evidence that adenovirus stimulation of the cGAS/STING DNA response had an impact on viral replication efficiency. 25531185_HTLV-1 Tax is recruited into the TBK1/IKKvarepsilon complexes as a scaffolding-adaptor protein that enhances IFN-beta gene expression. 25606824_TBK1 has a role in regulating T-cell activation and migration 25700176_TBK1 (the gene encoding TANK-binding kinase 1) was identified as an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis gene. 25780039_A role for APPL1 in TLR3/4-dependent TBK1 and IKKepsilon activation in macrophages. 25803835_The mutations co-segregating with ALS and FTD result in impairment of the optineurin-binding CCD2 domain of TBK1. 25815785_findings demonstrate a novel regulatory circuit in which STING and TBK1 reciprocally regulate each other to enable efficient antiviral signaling activation, and PPM1A dephosphorylates STING and TBK1 25855743_HIV-1 Vpr and Vif were shown to bind to TBK1 and inhibit its autophosphorylation by binding of these proteins leading to a block in type I and III interferon induction. 25923723_Data suggest OPTN (optineurin) is involved in up-regulation of innate immunity in mitosis; mechanism involves phosphorylation/mitochondrial translocation of TBK1 and phosphorylation/nuclear translocation of CYLD (cylindromatosis protein). 25939384_Data indicate that suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) knockdown markedly increases the abundance of TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1). 25943890_Loss-of-function variants in OPTN and TBK1 are associated with clinical and pathological frontotemporal dementia without motor neuron disease; TBK1 mutations are common cause of frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TAR DNA-binding protein 43 inclusions 25972374_Optineurin and TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) are transiently recruited to the polyubiquitinated mitochondria, and the activated TBK1 phosphorylates p62 at S403 26350399_Its frame-shift mutation results in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis of Chinese origin. 26476236_TBK1 should thus also be sequenced, after exclusion of C9orf72 mutation, in patients presenting frontotemporal dementia, particularly in cases secondarily associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 26581300_TBK1 loss of function mutations are the third most frequent cause of clinical frontotemporal dementia in a Belgian cohort. 26611359_Autoubiquitination of TRIM26 links TBK1 to NEMO in RLR-mediated innate antiviral immune response 26656453_The expression of TBK1 in mammalian cell mitosis is reported, including localization of the protein during division and its binding properties. 26674655_TBK1 carriers with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis had shorter disease duration than carriers with frontotemporal dementia in a Belgian cohort. 26804609_Mutations in the TBK1 gene were identified to cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) 26915459_TRIM9s undergoes Lys-63-linked auto-polyubiquitination and serves as a platform to bridge GSK3beta to TBK1, leading to the activation of IRF3 signaling. 26976762_Given the critical roles of TBK1, important regulatory mechanisms are required to regulate its activity. Among these, Optineurin (Optn) was shown to negatively regulate the interferon response, in addition to its important role in membrane trafficking, protein secretion, autophagy and cell division. 27035970_In combination with phosphorylation of S177 and S513, this posttranslational modification promotes recruitment and retention of OPTN/TBK1 on ubiquitinated, damaged mitochondria 27086836_Report establishes optineurin as a positive regulator TBK1 via a bipartite interaction between these molecules. 27123832_demonstrate a key role of TBK1/IKKepsilon in the survival and proliferation of HTLV-1-transformed T cells 27145266_Data suggest that changes in inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase subunit epsilon (IKKepsilon) and TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) expression may be involved in the development of intestinal-type gastric cancer. 27156075_Mutations in the TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) gene were identified as a cause for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) with or without comorbid frontotemporal dementia. 27211305_review of the role of TBK1 in the seemingly unrelated, yet allelic diseases amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), frontotemporal dementia (FTD), normal tension glaucoma (NTG) and childhood herpes simplex encephalitis and discuss the role of TBK1 in neuroinflammatory diseases 27234299_Human herpesvirus 1 ICP27 interacted with TBK1 and STING in a manner that was dependent on TBK1 activity and the RGG motif in ICP27 and inhibited type I IFN induction through the cGAS-STING-TBK1 pathway in human macrophages. 27247382_ALS-linked mutations in OPTN and TBK1 can interfere with mitophagy, suggesting that inefficient turnover of damaged mitochondria may represent a key pathophysiological mechanism contributing to neurodegenerative disease. 27260353_The results of this study proposed that TBK1 is not a frequent causal gene in Chinese ALS patients. 27350692_TBK1 duplication is found in normal tension and not in high tension open-angle glaucoma patients of Indian origin. 27355837_We report a five-generation pedigree with a complex pattern of primary open angle glaucoma(POAG) inheritance; familial clustering of POAG in this pedigree is consistent with dominant inheritance of a glaucoma-causing gene, mutations were not detected in genes previously associated with autosomal dominant glaucoma, suggesting the involvement of a novel disease-causing gene in this pedigree. 27370208_Here the authors show that recruitment of WIPI2, itself essential for anti-bacterial autophagy, is dependent on the localization of catalytically active TBK1 to the vicinity of cytosolic bacteria. 27538435_Our results highlight an unexpected role of the Golgi apparatus in innate immunity as a key subcellular gateway for TBK1 activation after RNA virus infection. 27568284_ZIKV infection of neuroepithelial stem cells and radial glial cells causes centrosomal depletion and mitochondrial sequestration of phospho-TBK1 during mitosis. 27570907_The occurrence of TBK1 mutations in FTD and ALS underlines the fact that FTD and ALS are part of the same disease spectrum. For future therapeutic trials, characterization of TBK1 mutation carriers in presymptomatic cohorts, such as the genetic frontotemporal dementia initiative (GENFI), is of great importance. 27620379_This study describes the crystal structures of optineurin/TBK1 complex and the related NAP1/TBK1 complex, uncovering the detailed molecular mechanism governing the optineurin and TBK1 interaction, and revealing a general binding mode between TBK1 and its associated adaptor proteins. 27705791_YPEL5 silencing enhanced the induction of IFNB1 by pattern recognition receptors and phosphorylation of TBK1/IKBKE kinases, whereas co-immunoprecipitation experiments revealed that YPEL5 interacted physically with IKBKE. 27881886_A broader phenotypic range may be associated with TBK1 copy-number variations, although mutations in this gene are most often detected in patients with normal-tension glaucoma. 27892983_This review suggested that haploinsufficiency of TBK1 is causative for ALS and FTD regardless of the type of mutation. 27939697_Pathogenic variants in TBK1 are rare but could be responsible for sALS in a small number of Korean patients. 28008748_we investigated a large European study population of 2,538 European FTD-ALS spectrum patients to get a deeper appreciation of the mutation frequency, mutation spectrum, and the genotype-phenotype profile of TBK1 patient carriers. 28025332_High TBK1 expression is associated with normal tension glaucoma. 28119118_Human T-lymphotropic virus 1 Tax protein impairs K63-linked ubiquitination of STING and disrupted the interactions between STING and TBK1 to evade host innate immunity. 28159912_TBK1 complexes required for the phosphorylation of IRF3 and the production of interferon-beta have been identified. 28188292_Upon cytosolic DNA stimulation, STAT3 Ser(754) is directly phosphorylated by TBK1 in a STING-dependent manner. Moreover, Ser(754) phosphorylation inhibits cytosolic DNA-induced STAT3 transcriptional activity and selectively reduces STAT3 target genes that are up-regulated in response to cytosolic DNA 28282485_Enrichment of qualifying variants toward glaucoma was present in all genes except WDR36, in which controls harbored more variants, and TBK1, in which no qualifying variants were detected in cases or controls. 28346439_YAP/TAZ act as natural inhibitors of TBK1 and are vital for antiviral physiology. 28365590_The study links the Arg573Gly TBK1 mutation with an autosomal dominant primary lateral sclerosis/dementia phenotype. 28487378_Data suggest that Encephalomyocarditis virus 3C protease cleaves TANK and disrupts the TANK-TBK1-IKKepsilon-IRF3 complex, resulting in reduction in IRF3 phosphorylation and type I interferon production. (TANK = TRAF family member associated NFKB activator; TBK1 = TANK binding kinase 1; IKKepsilon = inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase subunit epsilon; IRF3 = interferon regulatory factor 3) 28716898_High TBK1 expression is associated with Lung cancer. 28822984_We identified novel genomic TBK1 variants including two loss-of-function (LoF) (p.Leu59Phefs*16 and c.358+5G>A), two missense (p.Asp118Asn and p.Ile397Thr) and one intronic variant (c.1644-5_1644-2delAATA). 28848048_these data suggest that HNSs, an antagonist of host innate immunity, interacts with TBK1 and thereby hinders the association of TBK1 with its substrate IRF3, thus blocking IRF3 activation and transcriptional induction of the cellular antiviral responses. 28871090_work identifies the TRIM23-TBK1-p62 axis as a key component of selective autophagy and further reveals a role for K27-linked ubiquitination in GTPase-dependent TBK1 activation 28954889_HERP Binds TBK1 To Activate Innate Immunity and Repress Virus Replication in Response to Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress 28984711_we detected no statistical difference in age at diagnosis or maximum IOP when we compared patients with a TBK1 gene duplication and patients with a TBK1 gene triplication. 29103041_This study supports the implication of TBK1 in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Cognitive Decline pathogenesis in Italy. 29137817_TBK1 is not only a recurrent cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD), but a cause of other neurodegenerative disorders like progressive cerebellar ataxia and cerebellar ataxia. 29138248_These results outline a novel mechanism for the control of TBK1 activity and suggest USP1-UAF1 complex as a potential target for the prevention of viral diseases. 29146049_TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) loss-of-function (LoF) mutations are risk of Alzheimer's disease. 29251827_Study identified TTC4 as a TBK1 interactor and positive regulator of Sendai virus-induced innate immunity. 29349657_Two-stage meta-analysis to investigate the frequency of TBK1 mutations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/frontotemporal dementia (ALS/FTD) patients and the association between the mutations and risk of ALS/FTD spectrum showed that TBK1 loss of function and missense mutations are not frequently found in ALS/FTD patients, and both of them are associated with an increased risk for ALS/FTD spectrum. 29394115_these findings expand our knowledge on the molecular mechanism of ubiquitin- decorated autophagic substrates recognition by OPTN as well as the mutual regulation between OPTN and TBK1 in selective autophagy. 29398122_It contributes to the etiology of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Japanese patients. 29559975_this review describes TBK1-dependent response in health and autoimmunity 29653159_Phosphorylation thus introduces subtle changes in long-range contacts that might lead to significant conformational change of TBK-1. 29673738_this study shows that TBK1 is a key regulator and potential treatment target for interferon positive Sjogren's syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis 29743353_Low TBK1 expression is associated with RNA virus infections. 29743370_Loss of TBK1 by Us11 promotes HSV-1 infection through Formation of the Us11-Hsp90 Complex. 29797567_Our data suggest that MKP1 expression can be differentially regulated by p38, JNK, and the TBK1-JAK2-STAT3 pathway after activation of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) 29886477_Of the whole cohort of patients with Motor Neuron Disease and Frontotemporal Dementia, 2 patients harboured a mutation in the TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1). 30021902_Cdc25A negatively regulates the antiviral immune response by inhibiting TBK1 activity. 30033073_Study shows that amyotrophic lateral sclerosis associated missense and nonsense TANK binding kinase 1 mutations can both cause loss of kinase function. 30082428_Installation of a tetrazole carboxylic acid bioisostere improved potency to 200 and 400 nM toward IKKepsilon and TBK1, respectively. 30183071_The NLRP2-TBK1 axis may serve as an additional signaling cascade to maintain immune homeostasis in response to viral infection. 30196251_The patient had rapidly progressive ALS, with a novel frameshift mutation at codon 700 of the TBK1 gene in the optineurin binding site. Genetic testing identified a heterozygous two base pair deletion in the TBK1 gene (NM_013254.3: c.2099_2100del; p.(Val700Glyfs*2) 30296527_this study shows that TBK1 is required for early autophagy induction upon herpes simplex virus 1 infection 30349097_Collectively, these data reveal an evolutionarily conserved and critical role of TBK1/IKKepsilon suppression in expanding functional beta-cell mass. 30404831_Authors extensively studied the dynamics of this response using both live-cell imaging and correlative light-electron microscopy, and found that it correlates with lysosomal damage and is characterised by the recruitment of the selective autophagy-associated proteins TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and optineurin (OPTN) to ubiquitylated lysosomes. 30420664_TANK-binding kinase 1 protein (TBK1) and IKK-epsilon protein (IKKepsilon) phosphorylate the kinase receptor (TNFRSF)-interacting serine-threonine kinase 1 (RIPK1) and prevent RIPK1-dependent cell death. 30504235_IKBKE/TBK1-sensitive AML cells typically possess an MYC oncogenic signature. Consistent with this finding, the MYC oncoprotein was significantly downregulated upon IKBKE/TBK1 inhibition. 30530224_Activation of TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) is inhibited by Zika virus NS5 protein. The interaction between ubiquitin-like domain of TBK1 and NS5 results in less complex of TBK1 and TNF (tumor necrosis factor) receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6), leading to dampened TBK1 activation and IRF3 phosphorylation. 30627666_data reveal a novel function for TBK1 in mitophagy 30672142_TBK1 mutation p.Ile334Thr was identified as a pathogenic variant in frontotemporal dementia. 30769920_THOC7 negatively regulates type I IFN production by promoting TBK1 proteasomal degradation in Sendai virus infection 30827897_Stx17 knockout diminished LC3 response and reduced sequestration of the prototypical bulk autophagy cargo lactate dehydrogenase. We conclude that Stx17 is a TBK1 substrate and that together they orchestrate assembly of mammalian pre-autophagosomal structure 30842653_mutational analyses validate the interaction mode between TBK1 and STING and support a model in which high-order oligomerization of STING and TBK1, induced by cGAMP, leads to STING phosphorylation by TBK1 30853401_The capability of NDP52 to induce mitophagy is dependent on its interaction with the FIP200/ULK1 complex, which is facilitated by TBK1. Ectopically tethering ULK1 to cargo bypasses the requirement for autophagy receptors and TBK1. 30912981_Coculture of 2 mammary carcinoma cell lines, Ep5 from mice and MCF10A(MII) from humans, with isolated platelets induced morphologic as well as molecular changes characteristic of EMT, which was paralleled with activation of TBK1.TBK1 depletion using small interfering RNA impaired platelet-induced EMT in MCF10A(MII) cells. 30995277_RalA and RalB both relocalize to mitochondria following depolarization in a process dependent on clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Furthermore, both genetic and pharmacologic inhibition of RalA and RalB leads to an increase in the activity of the atypical IkappaB kinase TBK1 both basally and in response to mitochondrial depolarization. 31113902_Here, HSV-1 tegument protein UL46 was demonstrated to downregulate TBK1-dependent antiviral innate immunity. UL46 interacted with TBK1 and reduced TBK1 activation and its downstream signaling. 31114588_NOD2 and TLR2 Signal via TBK1 and PI31 to Direct Cross-Presentation and CD8 T Cell Responses. 31118511_a conserved PLPLRT/SD motif within the C-terminal tail of STING mediates the recruitment and activation of TBK1 31189704_HSV-1 US11 downregulates TRIM23 and TBK1 protein abundance in virus-infected cells. Furthermore, Us11 protein binds to the C-terminal ARF domain of TRIM23 and thereby prevents TBK1 binding to TRIM23, which inhibits autophagy. 31235549_We identified human nucleus accumbens-associated 1 (NAC1), a member of the BTB/POZ family, as a bridge for MAVS and TBK1 that positively regulates the RIG-I-like receptors-mediated induction of type I IFN 31256920_Leading to proinflammatory cytokine secretion through the adaptor protein STING and the TBK1 kinase. 31498468_Neuropathological characterization of a novel TANK binding kinase (TBK1) gene loss of function mutation associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 31509299_Our study identifies that RNF144B interaction with TBK1 is sufficient to inactivate TBK1 and delineates a previously unrecognized role for RNF144B in innate immune responses. 31577952_PINK1/Parkin Influences Cell Cycle by Sequestering TBK1 at Damaged Mitochondria, Inhibiting Mitosis. 31662325_Rab7, a recently identified substrate of PTEN phosphatase activity, is also a substrate of the innate immune signaling kinases TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1)/IkappaB kinase epsilon (IKKepsilon) on the same serine-72 site. TBK1/IKKepsilon mediated phosphorylation of this site as a key regulator of Rab7 mislocalization, which sustains levels of the upstream TBK1 adaptor STING, and thus promotes hyperactive innate immune si... 31709703_TBK1-mediated phosphorylation of LC3C and GABARAP-L2 controls autophagosome shedding by ATG4 protease. 31748271_Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-associated TBK1 missense mutations affect kinase activity and the phosphorylation of autophagy receptors. 31792381_The TBK1-TBKBP1 axis facilitates tumour-mediated immunosuppression. 31810986_TBK1 Is a Synthetic Lethal Target in Cancer with VHL Loss. 31818880_Priming phosphorylation of TBK1 by IKKbeta is required to surpass the threshold to induce signaling, thereby activating IRF-3.Kinase activity of TBK1 is required for the association of TRIF and IRF-3. 31987900_We provide the first report of the clinical features and long-term clinical course in a family of normal tension glaucoma (NTG) patients with TBK1 gene duplications. TBK1-associated glaucoma exhibits classic features of NTG. Patients present with severe disease at a relatively early age and most (67%) have slow-to-moderate progression of their visual field defects. 32034138_TBC1D9 controls TBK1 activation during xenophagy and mitophagy through Ca(2+)-dependent ubiquitin-recognition.TBC1D9 is involved in TBK1 phosphorylation. 32079994_Genomic Characterization of TBK1 Duplication in Korean Normal-tension Glaucoma Patients. 32159970_TBK1 regulates YAP/TAZ and fibrogenic fibroblast activation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 32238587_Human Cytomegalovirus Protein UL94 Targets MITA to Evade the Antiviral Immune Response. 32268090_TBK1 and IKKepsilon Act Redundantly to Mediate STING-Induced NF-kappaB Responses in Myeloid Cells. 32284536_The cGAS/STING/TBK1/IRF3 innate immunity pathway maintains chromosomal stability through regulation of p21 levels. 32298923_E3 ubiquitin ligase ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 8(ASB8) interacted with TBK1/IKKi and phosphorylation modification of | ENSMUSG00000020115 | Tbk1 | 350.576963 | 0.7215550 | -0.470818699 | 0.31960106 | 2.10779309740 | 0.1465505325070225184358463366152136586606502532958984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.33922701451402131889167890221870038658380508422851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 230.022924 | 81.094433 | 328.395781 | 115.796131 | |
| ENSG00000183763 | 10293 | TRAIP | protein_coding | Q9BWF2 | FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin ligase required to protect genome stability in response to replication stress (PubMed:25335891, PubMed:26781088, PubMed:27462463, PubMed:26711499, PubMed:26595769, PubMed:31545170). Acts as a key regulator of interstrand cross-link repair, which takes place when both strands of duplex DNA are covalently tethered together, thereby blocking replication and transcription (By similarity). Controls the choice between the two pathways of replication-coupled interstrand-cross-link repair by mediating ubiquitination of MCM7 subunit of the CMG helicase complex (By similarity). Short ubiquitin chains on MCM7 promote recruitment of DNA glycosylase NEIL3 (By similarity). If the interstrand cross-link cannot be cleaved by NEIL3, the ubiquitin chains continue to grow on MCM7, promoting the unloading of the CMG helicase complex by the VCP/p97 ATPase, enabling the Fanconi anemia DNA repair pathway (By similarity). Only catalyzes ubiquitination of MCM7 when forks converge (By similarity). Also involved in the repair of covalent DNA-protein cross-links (DPCs) during DNA synthesis: promotes ubiquitination of DPCs, leading to their degradation by the proteasome (By similarity). Has also been proposed to play a role in promoting translesion synthesis by mediating the assembly of 'Lys-63'-linked poly-ubiquitin chains on the Y-family polymerase POLN in order to facilitate bypass of DNA lesions and preserve genomic integrity (PubMed:24553286). The function in translesion synthesis is however controversial (PubMed:26595769). Acts as a regulator of the spindle assembly checkpoint (PubMed:25335891). Also acts as a negative regulator of innate immune signaling by inhibiting activation of NF-kappa-B mediated by TNF (PubMed:22945920). Negatively regulates TLR3/4- and RIG-I-mediated IRF3 activation and subsequent IFNB1 production and cellular antiviral response by promoting 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitination of TNK1 leading to its proteasomal degradation (PubMed:22945920). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6NRV0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22945920, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24553286, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25335891, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26595769, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26711499, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26781088, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27462463, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31545170}. | 3D-structure;Chromosome;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;DNA damage;DNA repair;Dwarfism;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17544371, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22945920}. | This gene encodes a protein that contains an N-terminal RING finger motif and a putative coiled-coil domain. A similar murine protein interacts with TNFR-associated factor 1 (TRAF1), TNFR-associated factor 2 (TRAF2), and cylindromatosis. The interaction with TRAF2 inhibits TRAF2-mediated nuclear factor kappa-B, subunit 1 activation that is required for cell activation and protection against apoptosis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:10293; | nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; site of DNA damage [GO:0090734]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; negative regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032688]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0010804]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; protein-DNA covalent cross-linking repair [GO:0106300]; replication fork processing [GO:0031297]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] | 14676304_CYLD interacts with TRIP and regulates negatively nuclear factor kappaB activation by tumor necrosis factor. 18200509_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19151749_The overexpression of TRIP sensitizes cells to TNF-induced apoptosis, an effect that can be reversed by the coexpression of Syk. 20307617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21068752_The TRAF-interacting protein (TRIP) is a regulator of keratinocyte proliferation. 24553286_observed enhanced ubiquitylation of Poleta by TRIP E3 ligase and show that TRIP promotes Poleta localization to nuclear foci 25335891_The TRAIP ubiquitin ligase activity is functionally required for the spindle assembly checkpoint control. 25716317_Data indicate that TRAF interacting protein TRIP negatively regulates the TNFR-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) ubiquitin-dependent pathway by modulating the TRAF2-sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) interaction. 26093298_a number of TRAIP mutants were used to define the TRAIP molecular domains responsible for its homo-dimerization. A co-immunoprecipitation assay indicated that the TRAIP forms homo-dimerization through the CC domain 26369285_cell cycle-dependent transcription of the TRAIP gene by E2F1, E2F2, and E2F4 and rapid protein degradation leads to cell cycle-dependent expression with a maximum in G2/M 26595769_TRAIP is a component of the DNA damage response to replication-blocking DNA lesions.TRAIP promotes DNA damage response during genome replication and is mutated in primordial dwarfism. 26711499_These findings establish TRAIP as a PCNA-binding ubiquitin ligase with an important role in protecting genome integrity after obstacles to DNA replication. 26781088_TRAIP/RNF206 is required for recruitment of RAP80 to sites of DNA damage.( 26820530_Taken together, these findings improve the understanding clinical implication of TRAIP in various diseases including primordial dwarfism and cancers. 27847407_TRIP interacts with transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) and promotes K48-linked polyubiquitination of TAK1 in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-Like synoviocytes 30127245_The TRAIP coiled-coil domain altered its stoichiometry between dimer and trimer in a concentration-dependent manner. Additionally, the TRAIP RING domain induced even higher-ordered assembly, which was necessary for interacting with the TRAF-N domain of TRAF2 but not TRAF1. 30165463_Nucleolar residence of the Seckel syndrome protein TRAIP is coupled to ribosomal DNA transcription. 30842657_present results, together with other recent findings, establish TRAIP as a master regulator of DNA helicase CMG unloading and the response of the replisome to obstacles 30942468_hese results suggest that TRAIP is a novel regulator of H2B monoubiquitination in DNA damage response and cancer development in lung adenocarcinoma. 31972358_TRAIP promotes malignant behaviors and correlates with poor prognosis in liver cancer. 31980815_TRAIP is important for the recruitment of NEIL3 but not FANCD2, and knockdown of TRAIP promotes FA/BRCA pathway activation. Interestingly, TRAIP is non-epistatic with both NEIL3 and FA pathways in psoralen-ICL repair, suggesting that TRAIP may function upstream of the two pathways. 32640040_TRIP suppresses cell proliferation and invasion in choroidal melanoma via promoting the proteasomal degradation of Twist1. 33317933_The Ubiquitin Ligase TRAIP: Double-Edged Sword at the Replisome. 34349117_TRAIP modulates the IGFBP3/AKT pathway to enhance the invasion and proliferation of osteosarcoma by promoting KANK1 degradation. | ENSMUSG00000032586 | Traip | 45.291768 | 0.9977886 | -0.003193868 | 0.24398033 | 0.00017093028 | 0.9895687299910083112308711861260235309600830078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.99340790819145818879576381732476875185966491699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 36.420626 | 15.928174 | 34.974597 | 15.152913 |
| ENSG00000184787 | 7327 | UBE2G2 | protein_coding | P60604 | FUNCTION: Accepts ubiquitin from the E1 complex and catalyzes its covalent attachment to other proteins (PubMed:20061386). In vitro catalyzes 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitination (PubMed:20061386). Involved in endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) (PubMed:22607976). Required for sterol-induced ubiquitination of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase and its subsequent proteasomal degradation (PubMed:23223569). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20061386, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22607976, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23223569}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid droplet;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transferase;Ubl conjugation pathway | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00388}. | The modification of proteins with ubiquitin is an important cellular mechanism for targeting abnormal or short-lived proteins for degradation. Ubiquitination involves at least three classes of enzymes: ubiquitin-activating enzymes, or E1s, ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, or E2s, and ubiquitin-protein ligases, or E3s. This gene encodes a member of the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family. The encoded protein shares 100% sequence identity with the mouse counterpart. This gene is ubiquitously expressed, with high expression seen in adult muscle. Three alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]. | hsa:7327; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity [GO:0061631]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; cellular response to interferon-beta [GO:0035458]; negative regulation of retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol [GO:1904153]; protein K48-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070936]; protein polyubiquitination [GO:0000209]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] | 12869571_Ubc7 mediates inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor ubiquitination and is a component of the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation pathway 16407162_interrupting a specific E2-E3 interaction can selectively inhibit endoplasmic reticulum -associated degradation 16582478_Structural comparison of human UBE2G2 with yeast Ubc7 indicated that the overall structures are similar except for the long loop region and the C-terminal helix. 20014027_Results report the solution structure and backbone dynamics of Ube2g2 solved by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. 21098018_Lys-48-linked polyubiquitin chains may be designed to bind certain proteins like Ube2g2 such that the terminal ubiquitin subunit carrying the reactive Lys-48 side chain can be positioned properly for chain elongation regardless of chain length. 21127063_The presence of the AUP1-Ube2g2 complex at LDs provides a direct molecular link between LDs and the cellular ubiquitination machinery. 24366945_These results reveal an unanticipated mode of Ube2g2 self-association that allows Ube2g2 to effectively engage two ubiquitins to specifically synthesize Lys48-linked ubiquitin chains. 27067047_Further study discovered that the gp78 CUE domain works as a proofreading machine during the growth of K48-linked polyubiquitin chains to ensure the linkage specificity. Together, our studies uncover a novel mechanism underlying the linkage specificity determination of longer polyubiquitin chains. 28743740_UBE2G2 was crucial for the degradation of various immunoreceptors. UBE2J2, on the other hand, counteracted US2-induced endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation by downregulating TRC8 expression. 34879065_A structurally conserved site in AUP1 binds the E2 enzyme UBE2G2 and is essential for ER-associated degradation. | ENSMUSG00000009293 | Ube2g2 | 853.323739 | 0.8982695 | -0.154779769 | 0.09495808 | 2.65481117703 | 0.1032370152354080278245263002645515371114015579223632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.27086035495113902626940216578077524900436401367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 814.369739 | 46.350148 | 911.137164 | 51.701478 |
| ENSG00000185043 | 10519 | CIB1 | protein_coding | Q99828 | FUNCTION: Calcium-binding protein that plays a role in the regulation of numerous cellular processes, such as cell differentiation, cell division, cell proliferation, cell migration, thrombosis, angiogenesis, cardiac hypertrophy and apoptosis. Involved in bone marrow megakaryocyte differentiation by negatively regulating thrombopoietin-mediated signaling pathway. Participates in the endomitotic cell cycle of megakaryocyte, a form of mitosis in which both karyokinesis and cytokinesis are interrupted. Plays a role in integrin signaling by negatively regulating alpha-IIb/beta3 activation in thrombin-stimulated megakaryocytes preventing platelet aggregation. Up-regulates PTK2/FAK1 activity, and is also needed for the recruitment of PTK2/FAK1 to focal adhesions; it thus appears to play an important role in focal adhesion formation. Positively regulates cell migration on fibronectin in a CDC42-dependent manner, the effect being negatively regulated by PAK1. Functions as a negative regulator of stress activated MAP kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways. Down-regulates inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-dependent calcium signaling. Involved in sphingosine kinase SPHK1 translocation to the plasma membrane in a N-myristoylation-dependent manner preventing TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis. Regulates serine/threonine-protein kinase PLK3 activity for proper completion of cell division progression. Plays a role in microtubule (MT) dynamics during neuronal development; disrupts the MT depolymerization activity of STMN2 attenuating NGF-induced neurite outgrowth and the MT reorganization at the edge of lamellipodia. Promotes cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via activation of the calcineurin/NFAT signaling pathway. Stimulates calcineurin PPP3R1 activity by mediating its anchoring to the sarcolemma. In ischemia-induced (pathological or adaptive) angiogenesis, stimulates endothelial cell proliferation, migration and microvessel formation by activating the PAK1 and ERK1/ERK2 signaling pathway. Promotes also cancer cell survival and proliferation. May regulate cell cycle and differentiation of spermatogenic germ cells, and/or differentiation of supporting Sertoli cells.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Plays a regulatory role in angiogenesis and tumor growth by mediating PKD/PRKD2-induced vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) secretion. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23503467}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Involved in keratinocyte-intrinsic immunity to human beta-papillomaviruses (HPVs). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30068544}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Apoptosis;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Differentiation;Golgi apparatus;Lipoprotein;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Myristate;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Spermatogenesis | This gene encodes a member of the EF-hand domain-containing calcium-binding superfamily. The encoded protein interacts with many other proteins, including the platelet integrin alpha-IIb-beta-3, DNA-dependent protein kinase, presenilin-2, focal adhesion kinase, p21 activated kinase, and protein kinase D. The encoded protein may be involved in cell survival and proliferation, and is associated with several disease states including cancer and Alzheimer's disease. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2013]. | hsa:10519; | apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; axon [GO:0030424]; cell periphery [GO:0071944]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; filopodium tip [GO:0032433]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent protein kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0008427]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0030291]; protein-membrane adaptor activity [GO:0043495]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell division [GO:0051301]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus [GO:1990090]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cytoplasmic microtubule organization [GO:0031122]; double-strand break repair [GO:0006302]; endomitotic cell cycle [GO:0007113]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation [GO:0045653]; negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization [GO:0007026]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; negative regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051898]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; platelet formation [GO:0030220]; positive regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade [GO:0070886]; positive regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0043085]; positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033630]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090050]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001954]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of male germ cell proliferation [GO:2000256]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903078]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071902]; positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane [GO:0090314]; positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900026]; regulation of cell division [GO:0051302]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; spermatid development [GO:0007286]; thrombopoietin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038163] | 11856312_NBR1 interacts with fasciculation and elongation protein zeta-1 (FEZ1) and calcium and integrin binding protein (CIB) and shows developmentally restricted expression in the neural tube. 12023286_describes regions within CIB and alpha(IIb) that interact with one another 12714504_An association between GPIIb/IIIa and calcium- and integrin-binding protein (CIB) is required for the process of platelet spreading. 12881299_CIB regulates platelet spreading through the regulation of FAK activation. 14992593_CIB may exist in multiple structural and metal ion-bound states in vivo which may play a role in its regulation of target proteins such as platelet integrin. 15190070_KIP has a role in telomere length maintenance and regulation 15574431_crystallographic structure of CIP1, an EF-hand-containing protein 15885068_calmyrin may be involved in the pathogenesis of AD. 15933764_Data indicate that although calmyrin forms stable covalent dimers in vitro, it most probably functions as a monomer in vivo. 16061695_CIB1 as a key regulator of PAK1 activation and signaling. 16418530_CIB1 appears to inhibit integrin activation by competing with talin for binding to alphaIIbbeta3, thus providing a model for tightly controlled regulation of alphaIIbbeta3 activation. 16723353_CIB1 is a ubiquitously expressed activating and inhibiting protein ligand of the InsP(3)R 16825200_Data report the structural characteristics of calcium- and integrin-binding protein 1 in solution and the mechanistic details of its interaction with a synthetic peptide derived from the alphaIIb integrin cytoplasmic domain. 17516631_communication between the paired EF-hand domains as well as between the N- and C-lobes of CIB1 is distinct from the ancestral proteins calmodulin and troponin C, which might be important for the unique function of CIB1 in numerous biological processes 18627437_The function of CIB1 on InsP3-evoked Ca2+ release from the ER is most likely mediated by its interaction with the InsP3 receptor. Thus, CIB1 seems to be an inhibitor of InsP3-dependent Ca2+ release in vivo. 18989529_Characterization of calcium- and integrin-binding protein 1 (CIB1) knockout platelets: potential compensation by CIB family members. 19388079_data identify low affinity (K(d), 10(-2)M) Ca(2+) binding events that influence the structures of the N- and C-terminal extensions of CIB1 under high (300 mM) Ca(2+) crystallization conditions 19854831_CIB1 interacts with SK1 in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner at the previously identified 'calmodulin-binding site' of SK1. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19923078_content of DNA-PKcs was significantly higher in A549 cells than in H1299 cells 20473878_CIB1 may be a potential biomarker and target for therapeutic intervention of breast cancer. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20951827_Calcium- and integrin-binding protein 1 regulates microtubule organization and centrosome segregation through polo like kinase 3 during cell cycle progression. 21215777_CaMy1 via SCG10 couples Ca(2+) signals with the dynamics of microtubules during neuronal outgrowth in the developing brain. 21388953_analysis of Ca2+-CIB1 and Mg2+-CIB1 and their interactions with the platelet integrin alphaIIb cytoplasmic domain 21748785_results suggest that CIB1 positively regulates cell migration and is necessary for the recruitment of FAK to the focal adhesions. Furthermore, CIB1-induced cell migration is dependent on MAP kinase signaling and its function is attenuated by PAK1 21857112_CIB1 may be used as a novel prognostic factor and possibly an attractive therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. 22547769_The CIB1 and calcineurin expression was increased in AF atrial tissue and was related to the type of AF. This finding suggests that CIB1 may be involved in the pathogenesis of AF in VHD patients. 22964641_Results indicate that CIB1 is uniquely positioned to regulate PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK signaling and that simultaneous disruption of these pathways synergistically induces a nuclear GAPDH-dependent cell death. 23503467_CIB1a is a novel mediator of PKD2-driven carcinogenesis. 24011356_we present data that show that CIB1 binds to seven additional alpha-integrin CT peptides, bringing the total number of alpha-integrins that can associate with CIB1 to eight. 24464679_mRNA and protein expression levels of CIB1 were decreased in the oligoasthenozoospermia patients.CIB1 may be involved in the pathogenesis of oligoasthenozoospermia by the CDK1 signaling pathway. 24550731_these studies suggested that Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus utilizes CIB1 as one of the key molecule(s) to coordinate and sustain the EphA2 mediated signaling involved in its entry 24585405_High serum CIB1 levels are associated with pancreatic cancer.s 25012820_KIP binding to TRF2 enhances the telomere-binding activity of TRF2, suggesting that KIP acts as a positive regulator of TRF2 function. 26105795_a large subset of TNBCs depend on CIB1 for cell survival and tumor growth, independent of CIB1 expression levels. 27489023_this study identifies CIB1 and CIB2 as host helper factors for HIV-1 replication that are required for optimal receptor-mediated viral entry 27941888_we found that ectopic expression of oncogenic KRas and HRas in cells resulted in elevated CIB1 expression. We previously described the Ca(2+)-myristoyl switch function of CIB1, and its ability to facilitate agonist-induced plasma membrane localisation of sphingosine kinase 1 (SK1), a location where SK1 is known to elicit oncogenic signalling. 28542214_Results suggest that interaction of CIB1 with alphaIIb is one of the early events occurring during outside-in signaling. Furthermore, CIB1 recruits FAK to the alphaIIbbeta3 complex at the filopodia where FAK is activated, which in turn activates c-Src, resulting in propagation of outside-in signaling leading to platelet spreading. 28939911_Study in human dopaminergic neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells revealed that CIB1 physically associates with ASK1, and thereby prevents ASK1 activation induced by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyrinidium (MPP+). CIB1 binds to the region containing amino acid residues 378-648 of ASK1. CIB1 depletion by RNA interference potentiates MPP+-induced dopaminergic neuronal death. 29017172_In summary, as a multifunctional protein, CIB1 serving not only as a Ca2+ modulating protein, most surprisingly, but also as an important potential tumor promoting factor. [review] 29028109_In patients with chronic stable ischemic heart failure, the diagnostic value of urine CIB1 outperforms that of serum pro-BNP 29125118_CIB1 may regulate tumor biological processes that range from adhesion, migration, cell survival, proliferation, and angiogenesis [review] 30068544_these findings suggest that the disruption of CIB1-EVER1-EVER2-dependent keratinocyte-intrinsic immunity underlies the selective susceptibility to beta-HPVs of epidermodysplasia verruciformis patients. 31530712_these results suggest that in resting platelets ASK1 is bound to CIB1 at low Ca2+ concentrations. Agonist-induced platelet activation causes an increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration that leads to the dissociation of CIB1 from ASK1, allowing for proper dimerization through ASK1 N-terminal coiled-coil (NCC) domains. 32307772_Identification of calcium and integrin-binding protein 1 as a novel regulator of production of amyloid beta peptide using CRISPR/Cas9-based screening system. 32917726_Expression of a TMC6-TMC8-CIB1 heterotrimeric complex in lymphocytes is regulated by each of the components. 32917957_Gene expression is stable in a complete CIB1 knockout keratinocyte model. 33082516_CHIP-mediated CIB1 ubiquitination regulated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. 34349085_Calcium and integrin binding protein 1 (CIB1) induces myocardial fibrosis in myocardial infarction via regulating the PI3K/Akt pathway. 34794407_Expression of CIB1 correlates with colorectal liver metastases but not with peritoneal carcinomatosis. | ENSMUSG00000030538 | Cib1 | 279.921082 | 1.6910694 | 0.757935870 | 0.52950282 | 2.01149063364 | 0.1561118653327582261880479563842527568340301513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.35357233564167628303565038550004828721284866333007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 381.673169 | 151.219135 | 228.401448 | 90.537601 | |
| ENSG00000185164 | 283820 | NOMO2 | protein_coding | Q5JPE7 | FUNCTION: Component of a ribosome-associated endoplasmic reticulum (ER) translocon complex involved in multi-pass membrane protein transport into the ER membrane and biogenesis (PubMed:32820719). May antagonize Nodal signaling and subsequent organization of axial structures during mesodermal patterning, via its interaction with NCLN/Nicalin (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6NZ07, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32820719}. | Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | This gene encodes a protein originally thought to be related to the collagenase gene family. This gene is one of three highly similar genes in a region of duplication located on the p arm of chromosome 16. These three genes encode closely related proteins that may have the same function. The protein encoded by one of these genes has been identified as part of a protein complex that participates in the Nodal signaling pathway during vertebrate development. Mutations in ABCC6, which is located nearby, rather than mutations in this gene are associated with pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Two transcripts encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:283820; | endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; ribosome binding [GO:0043022] | Mouse_homologues 25576386_NOMO1 gene knockdown inhibits the differentiation of P19 cells into cardiomyocytes, which highlights a potential role for NOMO1 in early cardiogenesis. | ENSMUSG00000030835 | Nomo1 | 2496.506953 | 0.7526700 | -0.409910676 | 0.05188218 | 62.29238747784 | 0.0000000000000029606733756205832959451841977226998554809241862711965964649607485625892877578735351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000000000014280654889027834232631774767045891474763485984311728316242806613445281982421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 2075.343469 | 101.544246 | 2768.609632 | 134.760629 | |
| ENSG00000185201 | 10581 | IFITM2 | protein_coding | Q01629 | FUNCTION: IFN-induced antiviral protein which inhibits the entry of viruses to the host cell cytoplasm, permitting endocytosis, but preventing subsequent viral fusion and release of viral contents into the cytosol (PubMed:33563656, PubMed:26354436). Active against multiple viruses, including influenza A virus, SARS coronaviruses (SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2), Marburg virus (MARV), Ebola virus (EBOV), Dengue virus (DNV), West Nile virus (WNV), human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), hepatitis C virus (HCV) and vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) (PubMed:33563656, PubMed:26354436, PubMed:33270927, PubMed:33239446). Can inhibit: influenza virus hemagglutinin protein-mediated viral entry, MARV and EBOV GP1,2-mediated viral entry, SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 S protein-mediated viral entry and VSV G protein-mediated viral entry (PubMed:33563656). Induces cell cycle arrest and mediates apoptosis by caspase activation and in p53-independent manner. In hepatocytes, IFITM proteins act in a coordinated manner to restrict HCV infection by targeting the endocytosed HCV virion for lysosomal degradation (PubMed:26354436). IFITM2 and IFITM3 display anti-HCV activity that may complement the anti-HCV activity of IFITM1 by inhibiting the late stages of HCV entry, possibly in a coordinated manner by trapping the virion in the endosomal pathway and targeting it for degradation at the lysosome (PubMed:26354436). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19544527, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20064371, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20534863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20943977, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21177806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21253575, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22479637, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26354436, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33239446, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33270927, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33563656}. | Acetylation;Antiviral defense;Cell membrane;Endosome;Immunity;Innate immunity;Lipoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA | Interferon-induced transmembrane (IFITM) proteins are a family of interferon induced antiviral proteins. The family contains five members, including IFITM1, IFITM2 and IFITM3 and belong to the CD225 superfamily. The protein encoded by this gene restricts cellular entry by diverse viral pathogens, such as influenza A virus, Ebola virus and Sars-CoV-2. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2021]. | hsa:10581; | cell junction [GO:0030054]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; cellular response to interferon-beta [GO:0035458]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; immune response [GO:0006955]; negative regulation of viral entry into host cell [GO:0046597]; negative regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045071]; response to interferon-alpha [GO:0035455]; response to interferon-beta [GO:0035456]; response to type II interferon [GO:0034341]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060337] | 19544527_Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in 1-8D is associated with neoplasms. 20534863_IFITM2 and IFITM3, disrupted early steps (entry and/or uncoating) of the viral infection, viperin, ISG20, and double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase, inhibited steps in west nile virus and dengue virus viral proteins and/or RNA biosynthesis. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21177806_IFITM1, IFITM2, and IFITM3 inhibit HIV-1 replication through interfering with virus entry. 23376165_Although their inhibitory activities were modest when compared to that of tetherin, IFITMs, but not tetherin, directly reduced the expression of HIV-1 proteins including Gag, Vif and Nef. 23720721_Authors show that interferon-induced transmembrane protein 1 (IFITM-1), IFITM-2, and IFITM-3 exhibit a broad spectrum of antiviral activity against several members of the Bunyaviridae family. 24992036_G3BP1, G3BP2 and CAPRIN1 are required for translation of interferon stimulated mRNAs and are targeted by a dengue virus non-coding RNA. 25422070_In virus-producing cells, IFITMs coalesce with forming virions and are incorporated into HIV-1 viral particles. 25464829_Incorporation of IFITM1, IFITM2 and IFITM3 into HIV-1 virions impair viral fusion and spread. 25552713_Host IFITM3,IFITM2 and IFITM1 facilitate morphogenesis of the human cytomegalovirus assembly. 26354436_propose that the IFITM proteins act in a coordinated manner to restrict HCV infection by targeting the endocytosed HCV virion for lysosomal degradation and demonstrate that the actions of the IFITM proteins are indeed virus and cell-type specific 26387945_IFITM2 and IFITM3 specifically antagonize the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein (Env), thereby inhibiting viral infection. 27219333_These results indicate that IFITM2 protein can restrict alphavirus infection by inhibiting viral fusion with cellular membranes. 28223169_IFITM2 promotes gastric cancer growth and metastasis via IGF1/IGF1R/STAT3 signaling pathway. 28356532_findings show that the sensitivity of influenza A viruses to the IFN-induced antiviral state and IFITM2 and IFITM3 proteins depends on the pH value at which the viral HA undergoes a conformational transition and mediates membrane fusion 28511927_The transcriptional regulation of IFITM1, 2 and 3 expression. 28630320_Delta20 IFITM2 may serve as a major contributor to the gatekeeping mechanism that explains restriction of X4 viruses in the early stage of HIV-1 infection 30087232_overexpression of IFITM1, 2 and 3 suppressed entry of CXCR4 and CCR5 tropic viruses; entry of transmitted founder HIV-1 in U87 cells is more sensitive to inhibition by IFITM2 and IFITM3 than by IFITM1 30266929_These studies identify a novel role for IFITM1, 2, and 3 in inhibiting HIV replication at the level of translation. 31735710_IFITM2 knockdowns in BeWo trophoblasts increased their spontaneous fusion and allowed fusion in the presence of IFN while also making the cells more susceptible to virus infection. 31792954_IFITM1-IFITM3 are expressed by T cells and are directly involved in adaptive immunity; they regulate CD4+ T helper cell differentiation in a T-cell-intrinsic manner. (Review) 33270927_Opposing activities of IFITM proteins in SARS-CoV-2 infection. 33308825_Predicative value of IFITM2 in renal clear cell carcinoma: IFITM2 is associated with lymphatic metastasis and poor clinical outcome. 34319159_IFITM Proteins That Restrict the Early Stages of Respiratory Virus Infection Do Not Influence Late-Stage Replication. 34321474_IFITM proteins promote SARS-CoV-2 infection and are targets for virus inhibition in vitro. 34933450_Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Proteins Inhibit Infection by the Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus and the Related Rhesus Monkey Rhadinovirus in a Cell-Specific Manner. 35543509_SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Hijack IFITM2 for Efficient Replication in Human Lung Cells. | ENSMUSG00000025492+ENSMUSG00000060591+ENSMUSG00000025491+ENSMUSG00000065968 | Ifitm3+Ifitm2+Ifitm1+Ifitm7 | 85.299764 | 0.7985683 | -0.324512246 | 0.19573396 | 2.73609839227 | 0.0981040286131966005056526114458392839878797531127929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.26149145740749890620691076037473976612091064453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 80.763912 | 9.769832 | 101.714103 | 12.124428 |
| ENSG00000185215 | 7127 | TNFAIP2 | protein_coding | Q03169 | FUNCTION: May play a role as a mediator of inflammation and angiogenesis. | Angiogenesis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Reference proteome | This gene was identified as a gene whose expression can be induced by the tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) in umbilical vein endothelial cells. The expression of this gene was shown to be induced by retinoic acid in a cell line expressing a oncogenic version of the retinoic acid receptor alpha fusion protein, which suggested that this gene may be a retinoic acid target gene in acute promyelocytic leukemia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:7127; | exocyst [GO:0000145]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; exocyst localization [GO:0051601]; exocytosis [GO:0006887] | 19339270_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20157331_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21057457_TNFAIP2 is a cell migration-promoting protein and its expression predicts distant metastasis. Our data suggest that TNFAIP2 may serve as an independent prognostic indicator for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 21555518_TNFAIP2 is a target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq analysis in HEK 293 cells. 21921781_TNFAIP2 may serve as a useful new marker of dendritic and histiocytic sarcomas. 21934093_A functional variant at the miR-184 binding site in TNFAIP2 is associated with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. 23724109_The TNFAIP2 miRNA binding site rs8126 T>C single nucleotide polymorphism may be a marker for susceptibility to gastric cancer. 23975427_the regulation of TNFAIP2 and its role in promoting NPC tumor progression 25383966_A functional TNFAIP2 3'-UTR rs8126 genetic polymorphism contributes to risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 26189798_findings collectively suggest that TNFAIP2 is a direct KLF5 target gene, and both KLF5 and TNFAIP2 promote breast cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion through Rac1 and Cdc42 26347487_data suggest that TNFAIP2 is a novel inhibitor of NF-kappa-B that acts as an autoinhibitor of the TNFalpha response during septic shock. 26701136_A polarized secretion assay suggested that the silencing of endothelial myeloid-secretory impairs T effector transendothelial migration by reducing the preferential secretion of endothelial-produced CCL2. 27130431_Taken together, genome-wide chromatin analysis of Legionella pneumophila-infected macrophages demonstrated induction of TNFAIP2, a NF-kappaB-dependent factor relevant for bacterial replication. 28393234_Data indicate that TNFAIP2 overexpression may facilitate proliferation and metastasis via activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 29596155_Study investigates the role of miR-221 in the inflammatory response and neuronal apoptosis following spinal cord I/R and the potential participation of TNFAIP2 signaling in oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD)-stressed neuronal cell lines. TNFAIP2 overexpression reversed the inflammatory response and cell apoptosis induced by miR-221 under OGD stress. 30145807_The expression of TNFAIP2 is frequently abnormal in human cancers and in infectious diseases. Due to its significant functions in cell proliferation, angiogenesis, migration and invasion, TNFAIP2 could be a potential diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for cancer. 30877198_ERp29-MSec interaction appeared to require the presence of other bridging protein(s), perhaps triggered by post-translational modification of ERp29 31263157_Knockdown of TNFAIP2 resulted in upregulation of E-cadherin expression and downregulation of TWIST1 expression, which decreased motile function in platinum-resistant urothelial cancer cells. 31392347_we establish TNFAIP2 as a novel target of uORF-mediated translational regulation. Furthermore, our findings suggest that during macrophage differentiation a major uORF-dependent translational switch occurs. 32650782_M-Sec facilitates intercellular transmission of HIV-1 through multiple mechanisms. 33109108_Genetic polymorphisms of PGF and TNFAIP2 genes related to cervical cancer risk among Uygur females from China. 34112215_STAT1 epigenetically regulates LCP2 and TNFAIP2 by recruiting EP300 to contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. 36243694_Pan-cancer analysis of oncogenic TNFAIP2 identifying its prognostic value and immunological function in acute myeloid leukemia. | ENSMUSG00000021281 | Tnfaip2 | 939.321613 | 0.7308862 | -0.452281313 | 0.10270372 | 19.32101602099 | 0.0000110483586418103650660191977772583982186915818601846694946289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00014511215087478253208189138412365082331234589219093322753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 783.438166 | 57.084159 | 1077.622524 | 77.808291 | |
| ENSG00000185658 | 54014 | BRWD1 | protein_coding | Q9NSI6 | FUNCTION: May be a transcriptional activator. May be involved in chromatin remodeling (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization. Required in the control of cell shape. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21834987}. | 3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Bromodomain;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;WD repeat | This gene encodes a member of the WD repeat protein family. WD repeats are minimally conserved regions of approximately 40 amino acids typically bracketed by gly-his and trp-asp (GH-WD) residues which may facilitate formation of heterotrimeric or multiprotein complexes. Members of this family are involved in a variety of cellular processes including cell cycle progression, signal transduction, apoptosis, and gene regulation. This protein contains 2 bromodomains and multiple WD repeats. This gene is located within the Down syndrome region-2 on chromosome 21. Alternative splicing of this gene generates multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. In mouse, this gene encodes a nuclear protein that has a polyglutamine-containing region that functions as a transcriptional activation domain which may regulate chromatin remodelling and associates with a component of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling complex.[provided by RefSeq, Jun 2011]. | hsa:54014; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 12359327_isolation and characterization of the gene located in the Down Syndrome critical region-2 of chromosome 21 20014019_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 27100087_RNA-seq evidence of biallelic expression of BRWD1 and 10 neighboring genes in at least one primary human tissue tested indicates that the expression of BRWD1 is uncoupled from the control of the maternally inherited 5mCpG imprints at the WRB differentially methylated region (DMR) in disomic controls or trisomy (Down syndrome) individuals. 30250168_Study data indicate that, in both mice and humans, BRWD1 is a master orchestrator of enhancer accessibility that cooperates with transcription factor networks to drive late B-cell development. 33389130_Bi-allelic BRWD1 variants cause male infertility with asthenoteratozoospermia and likely primary ciliary dyskinesia. | 368.772208 | 1.1842557 | 0.243980559 | 0.14044923 | 3.01203455902 | 0.0826484929069994794792464176680368836969137191772460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.23261310237084684149344582237972645089030265808105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 425.275551 | 36.758748 | 360.835622 | 31.342218 | |||
| ENSG00000185864 | 440345 | NPIPB4 | protein_coding | C9JG80 | Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] | 167.841306 | 0.5233177 | -0.934241104 | 0.17380761 | 28.61146765592 | 0.0000000884567681867738235245579450985453640043942868942394852638244628906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000175757567243834141899948113330065524451129022054374217987060546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 113.737047 | 12.686513 | 217.766914 | 23.309030 | ||||||
| ENSG00000186001 | 84859 | LRCH3 | protein_coding | Q96II8 | FUNCTION: As part of the DISP complex, may regulate the association of septins with actin and thereby regulate the actin cytoskeleton. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29467281}. | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Leucine-rich repeat;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat | Involved in septin cytoskeleton organization. Located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:84859; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; septin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032185] | Mouse_homologues 17971504_Lrch3 is most abundantly expressed in tissues rich in highly ciliated cells, such as olfactory sensory neurons, and is predicted to be important to cilia. | ENSMUSG00000022801 | Lrch3 | 255.756965 | 0.6307151 | -0.664939658 | 0.17180943 | 14.87097833996 | 0.0001151205537314401854695825044849755158793414011597633361816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00116499145434891654936337967995996223180554807186126708984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 191.449089 | 20.513554 | 304.770876 | 32.481057 | |
| ENSG00000186141 | 10623 | POLR3C | protein_coding | Q9BUI4 | FUNCTION: DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Specific core component of RNA polymerase III which synthesizes small RNAs, such as 5S rRNA and tRNAs. May direct with other members of the subcomplex RNA Pol III binding to the TFIIIB-DNA complex via the interactions between TFIIIB and POLR3F. May be involved either in the recruitment and stabilization of the subcomplex within RNA polymerase III, or in stimulating catalytic functions of other subunits during initiation. Plays a key role in sensing and limiting infection by intracellular bacteria and DNA viruses. Acts as nuclear and cytosolic DNA sensor involved in innate immune response. Can sense non-self dsDNA that serves as template for transcription into dsRNA. The non-self RNA polymerase III transcripts, such as Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNAs (EBERs) induce type I interferon and NF- Kappa-B through the RIG-I pathway. Preferentially binds single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) in a sequence-independent manner (PubMed:21358628). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19609254, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19631370, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21358628}. | 3D-structure;Antiviral defense;DNA-binding;DNA-directed RNA polymerase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription | Enables single-stranded DNA binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of innate immune response and positive regulation of interferon-beta production. Located in nucleoplasm. Part of RNA polymerase III complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:10623; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; RNA polymerase III complex [GO:0005666]; DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity [GO:0003899]; single-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003697]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006351]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; positive regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045089]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0006359] | 20970119_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21358628_The study reports the crystal structure of RPC62. 28783042_monogenic or digenic POLR3A and POLR3C deficiencies confer increased susceptibility to severe VZV disease in otherwise healthy children, providing evidence for an essential role of a DNA sensor in human immunity 31529052_the eWH domain of hTFIIEalpha can replace the first eWH (eWH1) domain of hRPC62 in ATPase and DNA unwinding assays. Our results identify intrinsic enzymatic activities in hRPC62 and hTFIIEalpha. 32600152_From Rare Copy Number Variants to Biological Processes in ADHD. | ENSMUSG00000028099 | Polr3c | 375.836034 | 1.1628403 | 0.217652930 | 0.08375904 | 6.74706126073 | 0.0093902224896360488720636894299786945339292287826538085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.04711278055417111171321309370796370785683393478393554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 408.863313 | 28.165481 | 353.107121 | 24.329118 | |
| ENSG00000186615 | 100129075 | KTN1-AS1 | lncRNA | 32267161_Long noncoding RNA KTN1-AS1 promotes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting miR-153-3p. 32396871_STAT1-induced upregulation of lncRNA KTN1-AS1 predicts poor prognosis and facilitates non-small cell lung cancer progression via miR-23b/DEPDC1 axis. 32820252_LncRNA KTN1-AS1 promotes the progression of non-small cell lung cancer via sponging of miR-130a-5p and activation of PDPK1. 33125151_lncRNA KTN1AS1 promotes glioma cell proliferation and invasion by negatively regulating miR5053p. 33480975_The long noncoding RNA KTN1-AS1 promotes bladder cancer tumorigenesis via KTN1 cis-activation and the consequent initiation of Rho GTPase-mediated signaling. 33491970_Long noncoding RNA KTN1 antisense RNA 1exerts an oncogenic function in lung adenocarcinoma by regulating DEP domain containing 1 expression via activating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 35381130_IncRNA KTN1-AS1 Silencing Inhibits Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation and KTN1-AS1 Expression Predicts Survival. | 9.284792 | 1.0964146 | 0.132793390 | 0.50195018 | 0.06888131932 | 0.7929725948881368724485696475312579423189163208007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.90183688169972764381299157321336679160594940185546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 9.363277 | 3.412107 | 8.711880 | 2.904815 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000186665 | 284018 | C17orf58 | protein_coding | Q2M2W7 | Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Reference proteome;Signal | Part of collagen-containing extracellular matrix. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:284018; | collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023] | ENSMUSG00000078607 | 1810010H24Rik | 25.777867 | 1.3139287 | 0.393886938 | 0.29476074 | 1.78897814376 | 0.1810507155136814039231296646903501823544502258300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.38925627102029281001449589894036762416362762451171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 29.885226 | 4.606328 | 22.883638 | 3.670428 | |||
| ENSG00000187815 | 339559 | ZFP69 | protein_coding | Q49AA0 | FUNCTION: Putative transcription factor that appears to regulate lipid metabolism. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A2A761}. | DNA-binding;Lipid metabolism;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II and regulation of lipid metabolic process. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:339559; | nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of lipid metabolic process [GO:0019216]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 19578398_Zfp69 is the most likely candidate for the diabetogenic effect of Nidd/SJL locus. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) | ENSMUSG00000064141 | Zfp69 | 709.124735 | 0.9915189 | -0.012287781 | 0.09316490 | 0.01738805506 | 0.8950920420201199378951173457608092576265335083007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.95358320516202876859779280493967235088348388671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 687.607385 | 46.604967 | 696.145176 | 46.929930 | |
| ENSG00000188186 | 389541 | LAMTOR4 | protein_coding | Q0VGL1 | FUNCTION: As part of the Ragulator complex it is involved in amino acid sensing and activation of mTORC1, a signaling complex promoting cell growth in response to growth factors, energy levels, and amino acids. Activated by amino acids through a mechanism involving the lysosomal V-ATPase, the Ragulator functions as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor activating the small GTPases Rag. Activated Ragulator and Rag GTPases function as a scaffold recruiting mTORC1 to lysosomes where it is in turn activated. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22980980}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Lysosome;Reference proteome | Contributes to guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity and molecular adaptor activity. Involved in several processes, including cellular response to amino acid stimulus; positive regulation of TOR signaling; and protein localization to lysosome. Located in lysosome. Part of Ragulator complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:389541; | intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; Ragulator complex [GO:0071986]; cellular response to amino acid stimulus [GO:0071230]; positive regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032008]; protein localization to lysosome [GO:0061462]; regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0050790]; regulation of cell size [GO:0008361]; TORC1 signaling [GO:0038202] | 22980980_Study identified HBXIP and C7orf59 as two additional Ragulator components that are required for mTORC1 activation by amino acids. 31314152_The C7orf59 was phosphorylated by protein kinase A (PKA) in vitro and mutation of the conserved Ser67 residue to aspartate prevented phosphorylation and negatively affected the C7orf59 interaction with p18 both in cell culture and in vitro. | ENSMUSG00000050552 | Lamtor4 | 203.459177 | 1.0418531 | 0.059151839 | 0.11509016 | 0.26400375509 | 0.6073827679351904151872076909057796001434326171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.78587273683076896979571301926625892519950866699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 211.818203 | 13.372832 | 204.223686 | 12.804571 | |
| ENSG00000189223 | 654433 | PAX8-AS1 | lncRNA | 27225188_Study suggested that PAX8 eQTLs SNPs (rs4848320 and rs1110839) located in lncRNA PAX8-AS1 might predict decreased risk of cervical cancer. 29693272_results demonstrated that PAX8-AS1-N activation mediated the anti-cancer effects of baicalein via regulating miR-17-5p, and suggested that baicalein and enhancing PAX8-AS1-N would be potential therapeutic strategies against breast cancer. 30720110_Expression levels of PAX8AS1:28 and PAX8 were lower in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) tissue and PTC cells than those in healthy tissue and cells. Expression level of MYC was higher in PTC cells than that in normal cells. PAX8AS1:28 silencing reduced the expression level of PAX8 and promoted tumor cell growth, while PAX8AS1:28 overexpression increased the expression level of PAX8 and inhibited tumor cell growth. 32633379_Inhibition of lncRNA-PAX8-AS1-N directly associated with VEGF/TGF-beta1/8-OhdG enhances podocyte apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy. 34145460_PAX8/PAX8-AS1 DNA methylation levels are associated with objective sleep duration in persons with unexplained hypersomnolence using a deep phenotyping approach. 35938744_Association between PAX8AS1 (rs4848320 C > T, rs1110839 G > T, and rs6726151 T > G) and MEG3 (rs7158663) gene polymorphisms and non-Hodgkin lymphoma risk. | 54.230502 | 0.9826586 | -0.025237794 | 0.38031806 | 0.00434966136 | 0.9474160704835021817871165694668889045715332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.97631177205858454826170600426848977804183959960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 54.056375 | 13.045878 | 55.051530 | 13.520853 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000196465 | 140465 | MYL6B | protein_coding | P14649 | FUNCTION: Regulatory light chain of myosin. Does not bind calcium. | 3D-structure;Motor protein;Muscle protein;Myosin;Reference proteome;Repeat | Myosin is a hexameric ATPase cellular motor protein. It is composed of two heavy chains, two nonphosphorylatable alkali light chains, and two phosphorylatable regulatory light chains. This gene encodes a myosin alkali light chain expressed in both slow-twitch skeletal muscle and in nonmuscle tissue. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. | hsa:140465; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; muscle myosin complex [GO:0005859]; myosin complex [GO:0016459]; myosin II complex [GO:0016460]; unconventional myosin complex [GO:0016461]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; cytoskeletal motor activity [GO:0003774]; structural constituent of muscle [GO:0008307]; muscle contraction [GO:0006936]; muscle filament sliding [GO:0030049]; skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0007519] | 18587628_Only the first IQ motif of IQGAP1 interacts with MYL6B. The first and second IQ motifs of IQGAP1 interact with S100B in the presence of calcium ions. 29439719_our results demonstrate that MYL6B is a putative tumor driver gene in HCC which could promote the degradation of p53 by enhancing its' MDM2-mediated ubiquitination. | ENSMUSG00000039824 | Myl6b | 254.042314 | 1.2459911 | 0.317293774 | 0.11002252 | 8.30658343518 | 0.0039501628386036926818269954253537434851750731468200683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.02360310883656063785096534957119729369878768920898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 272.755748 | 20.635905 | 219.881495 | 16.509782 | |
| ENSG00000196639 | 3269 | HRH1 | protein_coding | P35367 | FUNCTION: In peripheral tissues, the H1 subclass of histamine receptors mediates the contraction of smooth muscles, increase in capillary permeability due to contraction of terminal venules, and catecholamine release from adrenal medulla, as well as mediating neurotransmission in the central nervous system. | 3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Histamine is a ubiquitous messenger molecule released from mast cells, enterochromaffin-like cells, and neurons. Its various actions are mediated by histamine receptors H1, H2, H3 and H4. The protein encoded by this gene is an integral membrane protein and belongs to the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. It mediates the contraction of smooth muscles, the increase in capillary permeability due to contraction of terminal venules, the release of catecholamine from adrenal medulla, and neurotransmission in the central nervous system. It has been associated with multiple processes, including memory and learning, circadian rhythm, and thermoregulation. It is also known to contribute to the pathophysiology of allergic diseases such as atopic dermatitis, asthma, anaphylaxis and allergic rhinitis. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]. | hsa:3269; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; G protein-coupled serotonin receptor activity [GO:0004993]; histamine receptor activity [GO:0004969]; neurotransmitter receptor activity [GO:0030594]; cellular response to histamine [GO:0071420]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; eosinophil chemotaxis [GO:0048245]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger [GO:0007187]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; inositol phosphate-mediated signaling [GO:0048016]; memory [GO:0007613]; phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007200]; positive regulation of inositol trisphosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0032962]; positive regulation of vasoconstriction [GO:0045907]; regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0048167]; regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043114]; visual learning [GO:0008542] | 11603849_could be detected at the feto-maternal interface of human 11898002_expressed on monocyte-derived dendritic cells 12218662_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12218662_genetic variant of this protein and body weight change during clozapine treatment in schizophrenia 12429384_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12680587_markedly different potency for activation of multiple signaling pathways by H1- and H2-HRs 12755404_there are three mechanisms for h1 receptor down regulation: phosphorylation of thr-140 or ser-398 or five sites 12757445_No significant differences in H1R or H2R mRNA levels between seasonal allergic rhinitic and nonrhinitic subjects in-season, despite observed differences in H reactivity. 15328002_Thr140 and Ser398 mainly contributed to downregulation, and Thr142 or Ser396 had a slight inhibitory effect on Thr140- or Ser398-mediated process, respectively 15542600_rapid termination of H1HR signaling is mediated by both the kinase activity and RGS function of GRK2 15820830_expression of the histamine (H) receptors 1 (H1) and 2 (H2) by germinal, interstitial, and peritubular cells in the testes of fertile and infertile patients 15928828_gene expression regulation of HRH1 gene by HRH1 15928843_expression in chondrocytes of osteoarthritic cartilage 15953854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16027157_analysis of agonist binding to histamine H(1) receptor 16408006_characterization of important steps in the activation of the human histamine H1 receptor 16484687_These data suggest the use of alternative promoters directing human H1 receptor gene expression, both within and between cell types. 16491014_The H1R-PKC-ERK pathway may play crucial roles in eliciting cytokine production from bronchial epithelial cells stimulated by histamine, leading to airway inflammation 16547808_results exclude the participation of histamine receptors other than the H1 subtype in the control of human intestinal motility by oxogenous histamine 16705383_histamine stimulates integrin alpha-V beta-3 expression in cultured trophoblast cells; the H1 receptor is implicated 16760260_Ascorbate enhancement of seven-transmembrane-spanning membrane receptor activity occurs in both adrenergic and histaminergic receptors. These receptors may play a significant role in maintaining extracellular ascorbate in a reduced state. 16888049_These data suggest postexercise skeletal muscle hyperemia exists in endurance trained men and women. 17122961_Histamine stimulates IL-6 release from SW982 cells by binding to the H1 receptor and this is coupled to the PI/PKC signal transduction pathway. 17243823_The data suggest a global functional analogy between H1 receptor activation and the meta I/meta II charge/discharge equilibrium in rhodopsin. 17517105_Cytokine-induced endothelial intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expressionwas inhibited by tecastemazole in a manner independent of H1 receptor antagonism. 17547532_roles of dermatopontin and histamine receptor H1 genes as downstream targets for the VDR were confirmed by gel electromotility shift and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays that showed the presence of VDR complex binding sequences 17627982_Histamine excites human enteric neurones and this effect involves histamine H1-4 receptors. 17637176_M3R was involved in the up-regulation of H1R by activating H1R gene transcription through a PKC-dependent process. 18258331_a dramatic alteration in the distribution of histamine receptors in colon cancer 18345497_Results describe the molecular interactions between histamine and the human H1 receptor that influence phospholipase C and cyclic AMP signaling. 18366640_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18366640_These results indicate that the polymorphisms analyzed are not a major risk factor for Parkinson disease, although the HRH1Leu449Ser amino acid substitution might be related to PD 18446005_Internalization-mediated changes in the binding properties of H1-receptor antagonists were well correlated with their sedative and non-sedative behaviors. 18498711_results indicate that the beta2AR is involved in the down-regulation of human H1R by inhibiting H1R gene transcription through a PKA-dependent process 18511496_Histamine stimulates phospholipase C-signaling in myometrial smooth muscle cells through H(1) histamine receptors and that GRK2 recruitment is a key mechanism in the regulation of H(1) histamine receptor signaling in human uterine smooth muscle. 18548114_Histamine upregulates keratinocyte MMP-9 production via the histamine H1 receptor 18682391_Histamine-induced Egr-1 expression is dependent on the activation of the H1 receptor, and rapidly and transiently activates PKCdelta, ERK1/2, p38 kinase, and JNK prior to Egr-1 induction. 18814859_anorexia nervosa patients may have higher expression of H1R in the limbic brain, particularly in the amygdala 19156168_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19193342_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19271144_Results compare the correlation between H1-receptor expression and SLPI levels within cultured amniotic epithelial cells derived from chorioamnionitis-complicated and normal pregnancies. 19443731_Human salivary gland cells express histamine H1 receptors and histamine-synthesizing enzymes, revealing the cellular mechanism of antihistamine-induced xerostomia. 19913013_Functional coupling of the H1R to Gq-PLC leads to the activation of RhoA and Rac small GTPases and suggest distinct roles for Rho GTPases in the control of cell proliferation by histamine. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21255012_Results demonstrate that LPS, through TLR4 activation, up-regulates the expression and function of H1R and amplifies histamine-induced inflammatory responses in HCAEC. 21433074_Measurement of H1R occupancy is a sensitive and absolute method to characterize the non-sedating property of drugs with H1 antagonistic activity. 21686228_H1 and PAR2 receptors enhance delivery of immune-competent cells and molecules by interrupting E-cadherin adhesion in lung epithelial cells. 21697825_crystal structure of the H(1)R complex with doxepin, a first-generation H(1)R antagonist 21730054_the PKCdelta/ERK/poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 signaling pathway is involved in histamine- or PMA-induced up-regulation of H1R gene expression in HeLa cells 21937795_The glu349asp polymorphism of histamine-1 receptor is not associated with antipsychotic induced weight gain. 22169095_evidence supports the involvement of histaminergic and gamma-aminobutyric acidergic mechanisms in the etiology of TS and show an overlap of rare CNVs in TS and autism spectrum disorder. 22860191_[review] The H1, H2, and H3 receptors are all involved in recovery of neurological function when extracellular histamine is gradually increasing, after cerebral ischemia. 23132961_Study revealed that epithelial cells and vascular endothelial cells showed intense immunoreactivity for histamine H1 receptor inperennial allergic rhinitis. 23225320_Histamine was able to synergistically augment bFGF-induced angiogenesis, and this action was linked to VEGF production through H1-receptor. 23414213_Our observations point to a close histamine-/HR-mediated activation of dermal macrophages, leading to modified cell differentiation and responsiveness via H1R, which might contribute to the aggravation of allergic skin inflammation in AD. 23609395_our study does not support the contribution of histamine H1HR gene variants to antipsychotic induced weight gain nor differences in distribution between healthy volunteers and patients with schizophrenia 23677734_In this review, we focus on the role of histamine and its receptors in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. 23900020_Histamine demonstrably inhibited ACh-induced sweating in both mice and humans via H1R-mediated signaling. 23962049_Overexpression of H1R further increases the oxidative output of Duox-expressing HEK-293 cells. 24236486_But carriers of one or three copies of HRH1 (5% of individuals), HRH2 (1.1%) and HRH4 genes (0.9%) were also identified. 24535227_The relationship between the expression of HRH1 and prognosis was found to vary in different types of cancers, even in the same cancer from different databases. 25293806_HRH1 transcript was significantly down-modulated in multiple sclerose compared with health control. 25582918_multiple signaling pathways contribute to histamine-induced endothelial barrier dysfunction via the H1 receptor. 25664905_Thus, the results in the initial study were due to the degradation of histamine in skeletal muscle by ascorbate, because the histaminergic vasodilatation was unaffected by N-acetylcysteine. 25682263_Study suggests that both MAPK p44/p42 and PKC pathways appear to be involved in histamine-upregulated matrix metalloproteinase-9 release via histamine H1 receptors in astrocytes. 25909280_HRH1-17 TT and HNMT-1639 TT genotypes were associated with the allergic asthma phenotype among African-American children and that the ABP 4107 GG genotype was associated with nonallergic asthma among white children. 26635083_Activation of the H1R by its full agonists resulted in a composite potentiating effect. Intriguingly, inactivation of the Gaq-PLC pathway by H1R inverse agonists resulted also in a potentiation of GR activity. 26752109_HRH1-mediated sensitization of TRPV1 is involved in IBS. Ebastine, an antagonist of HRH1, reduced visceral hypersensitivity, symptoms, and abdominal pain in patients with IBS. 27468652_Antihistamines displayed similar kinetic signatures on antagonizing histamine-induced beta-arrestin2 recruitment as compared to displacing radioligand binding from the H1R. 27871651_that histamine H1 receptor activation mediates MAPK activation through PLCbeta, Src, PKCdelta and MEK pathway, but does not lead to nuclear relocalization of phospho-ERK (pERK), classically associated with pro-proliferative changes. 28391980_H1R and H4R are useful biomarkers of allergic inflammation on the ocular surface. Most notably, H4R expressed on eosinophils is useful as a biomarker of eosinophilic inflammation of the ocular surface. 28400155_This study demonstrated that HRH1 gene polymorphisms associated with sedation in clozapine-treated patient with schizophrenia. 29063596_Human H1 receptors in Chinese hamster ovary cells are apparently down-regulated by a sustained increase in intracellular Ca(2+) concentrations with no process of endocytosis and lysosomal/proteasomal degradation of receptors. 29548821_Study identified HRH1 as a receptor frequently overexpressed in basal and HER2-targeted therapy-resistant breast cancer (BC) cells, demonstrating that HRH1 inhibition culminates in apoptotic death and hampers tumor growth. ERK activation was identified as the mechanism through which HRH1 blockade signals to promote death in basal BC cells. 30168182_HRH1 gene polymorphisms may correlate with oral H1-antihistamine efficacy for the treatment of patients with allergic rhinitis, which can be used as a biological indicator of the prediction of therapeutic efficacy of patients with allergic rhinitis. 31406237_Human H1 receptor (HRH1) gene polymorphism is associated with the severity of side effects after desloratadine treatment in Chinese patients with chronic spontaneous uticaria. 31740780_Upregulation of histamine receptor H1 promotes tumor progression and contributes to poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33080103_Histamine receptor 1 is expressed in leukaemic cells and affects differentiation sensitivity. 33918180_Analysis of Missense Variants in the Human Histamine Receptor Family Reveals Increased Constitutive Activity of E410(6.30x30)K Variant in the Histamine H1 Receptor. 34595742_Molecular Signaling and Transcriptional Regulation of Histamine H1 Receptor Gene. 34638832_P2X4 Receptors Mediate Ca(2+) Release from Lysosomes in Response to Stimulation of P2X7 and H1 Histamine Receptors. 35031480_Epigallocatechin gallate stimulated histamine production and downregulated histamine H1 receptor in oral cancer cell lines expressing histidine decarboxylase. | ENSMUSG00000053004 | Hrh1 | 162.321313 | 0.9761869 | -0.034770659 | 0.12254050 | 0.08054114628 | 0.7765654013588709769777551628067158162593841552734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.89241687409557590715536434800014831125736236572265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 160.138473 | 13.920983 | 164.823523 | 14.197057 | |
| ENSG00000197021 | 541578 | EOLA2 | protein_coding | Q96DE9 | Mouse_homologues FUNCTION: May play a role in cell protection during the inflammatory response. In epithelial cells, negatively regulates IL6 production and apoptosis through the regulation of MT2A expression. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8TE69}. | Reference proteome | hsa:541578; | ENSMUSG00000045237 | Eola1 | 128.130394 | 0.8348470 | -0.260416331 | 0.13635932 | 3.64859286096 | 0.0561166037610212539710197177100781118497252464294433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.17799525020615994397310544172796653583645820617675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 117.380887 | 10.269201 | 141.348227 | 12.063438 | ||||
| ENSG00000197170 | 5718 | PSMD12 | protein_coding | O00232 | FUNCTION: Component of the 26S proteasome, a multiprotein complex involved in the ATP-dependent degradation of ubiquitinated proteins. This complex plays a key role in the maintenance of protein homeostasis by removing misfolded or damaged proteins, which could impair cellular functions, and by removing proteins whose functions are no longer required. Therefore, the proteasome participates in numerous cellular processes, including cell cycle progression, apoptosis, or DNA damage repair. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1317798}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Proteasome;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation | The 26S proteasome is a multicatalytic proteinase complex with a highly ordered structure composed of 2 complexes, a 20S core and a 19S regulator. The 20S core is composed of 4 rings of 28 non-identical subunits; 2 rings are composed of 7 alpha subunits and 2 rings are composed of 7 beta subunits. The 19S regulator is composed of a base, which contains 6 ATPase subunits and 2 non-ATPase subunits, and a lid, which contains up to 10 non-ATPase subunits. Proteasomes are distributed throughout eukaryotic cells at a high concentration and cleave peptides in an ATP/ubiquitin-dependent process in a non-lysosomal pathway. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides. This gene encodes a non-ATPase subunit of the 19S regulator. A pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 3. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2015]. | hsa:5718; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear proteasome complex [GO:0031595]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; proteasome accessory complex [GO:0022624]; proteasome complex [GO:0000502]; proteasome regulatory particle [GO:0005838]; proteasome regulatory particle, lid subcomplex [GO:0008541]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161] | 28132691_we identified six de novo genomic deletions and four de novo point mutations in unrelated individuals with intellectual disability, congenital malformations, ophthalmologic anomalies, feeding difficulties, deafness, and subtle dysmorphic facial features 30421579_We performed WES on six affected siblings from a multiplex family with ID and autistic features. We identified an inherited heterozygous nonsense mutation in PSMD12 (NM_002816: c.367C>T: p.R123X) in the multiplex family and a de novo nonsense mutation in the same gene (NM_002816: c.601C>T: p.R201X) in the simplex family. 32222279_PSMD12 promotes breast cancer growth via inhibiting the expression of pro-apoptotic genes. 35080150_Haploinsufficiency of PSMD12 Causes Proteasome Dysfunction and Subclinical Autoinflammation. 36137220_PSMD12 promotes the activation of the MEK-ERK pathway by upregulating KIF15 to promote the malignant progression of liver cancer. | ENSMUSG00000020720 | Psmd12 | 497.356405 | 1.0494256 | 0.069599919 | 0.09631413 | 0.52202500964 | 0.4699791465380656063643982633948326110839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.68942714121481574185423824019380845129489898681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 555.132842 | 35.530252 | 531.204511 | 34.104788 | |
| ENSG00000197323 | 51592 | TRIM33 | protein_coding | Q9UPN9 | FUNCTION: Acts as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase. Promotes SMAD4 ubiquitination, nuclear exclusion and degradation via the ubiquitin proteasome pathway. According to PubMed:16751102, does not promote a decrease in the level of endogenous SMAD4. May act as a transcriptional repressor. Inhibits the transcriptional response to TGF-beta/BMP signaling cascade. Plays a role in the control of cell proliferation. Its association with SMAD2 and SMAD3 stimulates erythroid differentiation of hematopoietic stem/progenitor (By similarity). Monoubiquitinates SMAD4 and acts as an inhibitor of SMAD4-dependent TGF-beta/BMP signaling cascade (Monoubiquitination of SMAD4 hampers its ability to form a stable complex with activated SMAD2/3 resulting in inhibition of TGF-beta/BMP signaling cascade). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10022127, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15820681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16751102, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19135894}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Bromodomain;Chromosomal rearrangement;Coiled coil;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. | The protein encoded by this gene is thought to be a transcriptional corepressor. However, molecules that interact with this protein have not yet been identified. The protein is a member of the tripartite motif family. This motif includes three zinc-binding domains, a RING, a B-box type 1 and a B-box type 2, and a coiled-coil region. Three alternatively spliced transcript variants for this gene have been described, however, the full-length nature of one variant has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:51592; | nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; co-SMAD binding [GO:0070410]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; R-SMAD binding [GO:0070412]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030514]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0017015] | 12096914_TIF1alpha interacts with TIF1gamma and the coiled-coil region of TIF1gamma is necessary for this interaction. 16751102_Thus, Smad2/3-TIF1gamma and Smad2/3-Smad4 function as complementary effector arms in the control of hematopoietic cell fate by the TGFbeta/Smad pathway. 19629168_Study reports that TIF1gamma expression is markedly down-regulated in human pancreatic tumors by quantitative RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry. 20158380_Hyperthermia incurred platelet glycoprotein Ibalpha ectodomain shedding. 20447379_These studies are consistent with a model in which TIF1gamma acts to ubiquitinate LDB1 leading to degradation of LDB1 and changes in transcription of LDB1-dependent promoters. 20603019_Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays in human CD34(+) cells supported a TIF1gamma-dependent recruitment of positive elongation factors to erythroid genes to promote transcription elongation by counteracting Pol II pausing. 21474105_regulation of adult hematopoiesis through TIF1gamma-mediated transcriptional repression of TAL1 and PU.1 target genes. 21537084_TIF1gamma was almost undetectable in leukemic cells of 35% of CMML patients. This downregulation was related to the hypermethylation of CpG sequences and specific histone modifications in the gene promoter. 21597466_TIF1gamma binds to and represses the plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 promoter, demonstrating a direct role of TIF1gamma in TGF-beta-dependent gene expression 21726812_TIF1gamma dictates the residence time of activated Smad complexes at promoters of TGF-beta superfamily target genes. 22046087_Data suggest that over-expression of TIF1gamma occurs in early stages of colorectal carcinogenesis, is inversely related with Smad4 loss, and may be a prognostic indicator for poor outcome. 22123502_These results suggest that E4-ORF3 targets proteins for relocalization through a loosely homologous sequence dependent on accessibility. 22196728_Study reports an essential role for TRIM33 in the activation of Gsc and Mixl1 by nodal signals, and delineate how Smads gain access to poised promoters of master regulators under the command of nodal TGF-beta signals. 22205733_Adenovirus E4orf3 targets TIF1 gamma for proteasome-dependent degradation during infection. 22461896_Data suggest that the formation of transient TIF1gamma-Smad2-Smad4 ternary complexes is the only one that can account for TGF-beta signaling. 23154409_Tif1gamma transgene is essential for the terminal differentiation of mammary alveolar epithelial cells at the end of pregnancy and to ensure lactation. 23160376_TIF1gamma is an APC/C-interacting protein that regulates APC/C function. It is not a substrate for APC/C-dependent ubiquitylation but associates specifically with the APC/C holoenzyme & Cdc20 to affect APC/C activity & progression through mitosis. 23407650_Case Report: suggest that TIF1gamma expression in neoplasms not only determines the tumour activity but also causes dermatomyositis. 23676978_mutation and methylation in the promoter region of TIF1gamma in non-small cell lung cancer 23788427_Results identify a new TGFbeta regulatory layer, whereby sumoylation strengthens the TIF1gamma repressive action on canonical TGFbeta signaling. 23926104_TRIM33 plays a role in PARP-dependent DNA damage response and regulates ALC1 activity by promoting its timely removal from sites of DNA damage. 24037894_These studies demonstrate that anti-NXP-2 and anti-TIF-1gamma antibodies are frequent DM specificities (found in 55% of patients) and are present in most patients with cancer-associated dermatomyositis. 24189344_Study suggests TRIM33 and NRAS-CSDE1 as candidate genes for autism, and may provide a novel insight into the etiology of autism 24954480_regulates tumor growth and metastasis through inhibition of TGF-beta/Smad signaling and may serve as a novel prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma 25059663_Data indicate that tripartite motif containing 33 protein TIF1gamma promotes sumoylation of SKI-like proto-oncogene protein SnoN1 and regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). 25172487_The ubiquitination of DHX33 by TRIM33 is lysine 63 specific and is required for the formation of the DHX33-NLRP3 inflammasome complex. 25186009_The dermatomyositis autoantigen TIF1gamma is markedly up-regulated during muscle regeneration in human and mouse muscle cells. 25381221_Results show that TRIM33 is significantly downregulated in clear renal cell carcinoma tissues which seems to correlate with pathologic stages and grades. 25639486_Tumour suppressor TRIM33 targets nuclear beta-catenin degradation 25961934_our findings reveal a new mechanism by which SOX2-mediated transcription repression of TIF1gamma promotes TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small-cell lung cancer 26282171_our work indicates that TIF1gamma exerts its tumor-suppressive functions in part by promoting chromosomal stability. 27247387_The adenovirus E4-ORF3 protein functions as a SUMO E3 ligase for TIF-1gamma sumoylation and poly-SUMO chain elongation. 27430247_suggest that SnoN suppresses TGF-betainduced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion of bladder cancer cells in a TIF1gammadependent manner 27432991_Data show that tripartite motif-containing protein 33 (TRIM33) silencing attenuates down-regulation of MYC and TGF-beta signaling in response to bromodomain and extraterminal domain protein inhibitors (BETi). 28704599_Anti-TIF1gamma antibodies are rarely present in patients with solid cancers or paraneoplastic rheumatic syndromes. This finding strengthens the approach to using anti-TIF1gamma IgG as a marker for cancer-associated dermatomyositis. 29149307_Tumors from paraneoplastic anti-TIF1gamma-positive cancer-associated myositis patients showed an increased number of genetic alterations, such as mutations and loss of heterozygosity, in TIF1 genes. 29745874_Not only did anti-TIF1gamma antibodies correlate strongly with malignancy in dermatomyositis patients, but cancers were also significantly more advanced in anti-TIF1gamma-positive DM patients than in anti-TIF1gamma-negative patients. 30177833_These results suggest that nuclear c-Abl-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of TIF1gamma has a desuppressive role in TGF-beta-Smad2/3 signaling. 30261900_Our findings show that circPTK2 (hsa_circ_0008305) inhibits TGF-beta-induced EMT and metastasis by controlling TIF1gamma in NSCLC, revealing a novel mechanism by which circRNA regulates TGF-beta-induced EMT and tumor metastasis, and suggesting that circPTK2 overexpression could provide a therapeutic strategy for advanced NSCLC. 30398003_The expression of TIF1gamma in the muscle of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies was related to the positivity for serum anti-TIF1gamma antibody and presence of tubuloreticular bodies in the muscle biopsies. 30804369_TRIM33 acts as a cellular factor restricting HIV-1 infection by preventing provirus formation. 30896800_These findings support the potential of using measurements of Tif1gamma plasma levels to guide breast cancer therapy and monitoring. Further studies are required to validate Tif1gamma as an easily detectable, noninvasive prognostic biomarker for breast cancer. 31130476_we have shown that TRIM33 deficiency in myeloid cells during colitis is associated with increased production of blood monocytes, a defect in monocytes recruitment and differentiation into functional macrophages leading to failure to resolve intestinal inflammation. 32184320_TRIM33 prevents pulmonary fibrosis by impairing TGF-beta1 signalling. 32267915_Hepatic stellate cell-specific knockout of transcriptional intermediary factor 1gamma aggravates liver fibrosis. 32770107_PIAS1 and TIF1gamma collaborate to promote SnoN SUMOylation and suppression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 32908919_TRIM33 Overexpression Inhibits the Progression of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma In Vivo and In Vitro. 32932986_Trim24 and Trim33 Play a Role in Epigenetic Silencing of Retroviruses in Embryonic Stem Cells. 33053171_Direct measurement of protein-protein interactions by FLIM-FRET at UV laser-induced DNA damage sites in living cells. 33481220_Alteration of TRIM33 Expression at Transcriptional and Translational Levels is Correlated with Autism Symptoms. 33764396_TRIM33 gene somatic mutations identified by next generation sequencing in neoplasms of patients with anti-TIF1gamma positive cancer-associated dermatomyositis. 34101965_TRIM33 protects osteoblasts from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in osteoporosis by inhibiting FOXO3a ubiquitylation and degradation. 34392614_KAT6A Acetylation of SMAD3 Regulates Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Recruitment, Metastasis, and Immunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. 35785414_TRIM33 drives prostate tumor growth by stabilizing androgen receptor from Skp2-mediated degradation. 35929141_Downregulation of TRIM33 Promotes Survival and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Gastric Cancer. 36096861_E3 ubiquitin ligase Trim33 ubiquitylates Annexin A2 to promote NF-kappaB induced skin inflammation in psoriasis. | ENSMUSG00000033014 | Trim33 | 511.090916 | 1.4172588 | 0.503103207 | 0.16102867 | 9.70985771830 | 0.0018328220381789008062295431855659444408956915140151977539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.01261068109692398651888733951409449218772351741790771484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 574.817197 | 85.727622 | 407.077997 | 60.751783 |
| ENSG00000197774 | 197342 | EME2 | protein_coding | A4GXA9 | FUNCTION: Interacts with MUS81 to form a DNA structure-specific endonuclease which cleaves substrates such as 3'-flap structures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17289582}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;DNA damage;DNA recombination;DNA repair;Endonuclease;Hydrolase;Nuclease;Nucleus;Reference proteome | EME2 forms a heterodimer with MUS81 (MIM 606591) that functions as an XPF (MIM 278760)-type flap/fork endonuclease in DNA repair (Ciccia et al., 2007 [PubMed 17289582]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:197342; | endodeoxyribonuclease complex [GO:1905347]; Holliday junction resolvase complex [GO:0048476]; nuclear replication fork [GO:0043596]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; endonuclease activity [GO:0004519]; double-strand break repair [GO:0006302]; mitotic intra-S DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0031573]; replication fork processing [GO:0031297]; resolution of meiotic recombination intermediates [GO:0000712] | 24371268_The results indicate that MUS81-EME2 is a more active endonuclease than MUS81-EME1 and exhibits broader substrate specificity. 24692662_The presence of a 5' phosphate terminus at nicks and gaps rendered DNA significantly less susceptible to the cleavage by MUS81-EME2 than its absence. 24813886_Results define distinct and temporal roles for MUS81-EME1 and MUS81-EME2 in the maintenance of genome stability. 26804904_Avoiding damage formation through invalidation of Mus81-Eme2 and Mre11, or preventing damage signaling by turning off the ATM pathway, suppresses the replication phenotypes of Chk1-deficient cells. 35290797_Crystal structure of the human MUS81-EME2 complex. | ENSMUSG00000073436 | Eme2 | 213.474107 | 0.5290947 | -0.918402149 | 0.18421488 | 24.55301850477 | 0.0000007229300546764889642280846153432616318923464859835803508758544921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00001230212360683056810816641407635430027767142746597528457641601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 148.823092 | 21.454351 | 282.068881 | 39.884365 | |
| ENSG00000197858 | 8733 | GPAA1 | protein_coding | O43292 | FUNCTION: Essential for GPI-anchoring of precursor proteins but not for GPI synthesis. Acts before or during formation of the carbonyl intermediate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29100095, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9468317}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor biosynthesis;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | PATHWAY: Glycolipid biosynthesis; glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchor biosynthesis. | Posttranslational glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor attachment serves as a general mechanism for linking proteins to the cell surface membrane. The protein encoded by this gene presumably functions in GPI anchoring at the GPI transfer step. The mRNA transcript is ubiquitously expressed in both fetal and adult tissues. The anchor attachment protein 1 contains an N-terminal signal sequence, 1 cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation site, 1 leucine zipper pattern, 2 potential N-glycosylation sites, and 8 putative transmembrane domains. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:8733; | centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; GPI-anchor transamidase complex [GO:0042765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; tubulin binding [GO:0015631]; attachment of GPI anchor to protein [GO:0016255]; protein retention in ER lumen [GO:0006621]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003] | 14660601_a conserved proline in the last transmembrane segment of Gaa1 is required for glycosylphosphatidylinositol recognition by GPI transamidase 15713669_passively retained in the ER by a signalless mechanism 16642471_Increased expression of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor attachment protein 1 is associated with gene amplification in hepatocellular carcinoma 18028549_Results show an increased expression level and elevated copy number for GAA1 in head and neck squamous carcinoma, suggesting a role for this GPI anchor subunit in HNSCC. 24743167_the lumenal domain of GAA1/GPAA1 has a 3D structure similar to that of an M28-type aminopeptidase. GAA1/GPAA1 is a candidate for the enzyme that catalyzes the peptide bond formation between the omega-site and a phosphoethanolamine group of GPI lipid anchor. 29100095_The splicing mutation was found to decrease GPAA1 mRNA. 31118109_Mechanistically, GPAA1 enhanced the levels of metastasis-associated GPI-anchored proteins to increase tumour metastasis and intensified lipid raft formation, which consequently promoted the interaction between EGFR and ERBB2 as well as downstream pro-proliferative signalling. 32432756_GPAA1 promotes progression of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia through regulating c-myc. 32533362_A novel variant in GPAA1, encoding a GPI transamidase complex protein, causes inherited vascular anomalies with various phenotypes. 32993792_Structural modelling of the lumenal domain of human GPAA1, the metallo-peptide synthetase subunit of the transamidase complex, reveals zinc-binding mode and two flaps surrounding the active site. 33496978_Subunits of the GPI transamidase complex localize to the endoplasmic reticulum and nuclear envelope in Drosophila. | ENSMUSG00000022561 | Gpaa1 | 1548.618000 | 0.8820773 | -0.181022942 | 0.04155456 | 18.98630705057 | 0.0000131659906552150179442862640288858244730363367125391960144042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00016927010779884895958630197654315452382434159517288208007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1455.191854 | 36.945200 | 1657.561933 | 40.968606 |
| ENSG00000197912 | 6687 | SPG7 | protein_coding | Q9UQ90 | FUNCTION: ATP-dependent zinc metalloprotease. Plays a role in the formation and regulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) and its proteolytic activity is dispensable for this function (PubMed:26387735). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26387735, ECO:0000305}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Disease variant;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Neurodegeneration;Nitration;Nucleotide-binding;Osteogenesis imperfecta;Protease;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc | This gene encodes a mitochondrial metalloprotease protein that is a member of the AAA family. Members of this protein family share an ATPase domain and have roles in diverse cellular processes including membrane trafficking, intracellular motility, organelle biogenesis, protein folding, and proteolysis. Mutations in this gene cause autosomal recessive spastic paraplegia 7. Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014]. | hsa:6687; | axon cytoplasm [GO:1904115]; m-AAA complex [GO:0005745]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial permeability transition pore complex [GO:0005757]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATP-dependent peptidase activity [GO:0004176]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; anterograde axonal transport [GO:0008089]; mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in programmed cell death [GO:1902686]; mitochondrial protein processing [GO:0034982]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability [GO:0046902] | 14506940_mutation in spastin and paraplegin genes does not appear to cause motor neuron disease 16357941_Adenoassociated virus-mediated intramuscular delivery of paraplegin halted the progression of neuropathological changes and rescued mitochondrial morphology in the peripheral nerves of paraplegin-deficient mice. 16534102_Cerebellar signs or cerebellar atrophy on brain imaging were the most frequent additional features in patients with SPG7 hereditary spastic paraplegia. 17420921_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17646629_The new SPG7 gene mutation leads to a novel complicated autosomal recessive hereditary spastic paraparesis phenotype that widens the spectrum of different brain systems that are optionally affected in hereditary spastic paraplegia. 18200586_identification of six novel point mutations and one large intragenic deletion in hereditary spastic paraplegia 18563470_This study identified a novel paraplegin mutation, c.1047insC, in a non-consanguineous Norwegian family with ARHSP. 18799786_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18799786_Results suggest that paraplegin mutations are a frequent cause of sporadic spastic paraparesis. 19748354_An intersubunit signaling network coordinates ATP hydrolysis by m-AAA protease paraplegin. 19841671_structural analysis of the ATPase domain of the human AAA+ protein paraplegin/SPG7 20108356_The novel mutation is the first splice site mutation found in the SPG7 gene. It removes part of the AAA domain of paraplegin protein, probably leading to a loss-of-function of the paraplegin-AFG3L2 complex in the mitochondrial inner membrane. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22563492_Studies indicate that both mouse and human SPG7 ESTs containing alternative first exons. 22571692_Data suggest a pathogenic role for this SPG7 p.A510V variant. 22964162_SPG7 mutations correlate with spastic paraplegia phenotypes. 23065789_SPG7 mutations are a frequent cause of middle-aged onset of spastic gait when strict inclusion criteria are applied and should, therefore, be tested in autosomal recessive or sporadic hereditary spastic paraplegia. 23269439_This study showed that the p.Ala510Val mutation is prevalent amongst severe hereditary spastic paraparesis patients of UK. 23857099_A Japanese patient is reported with an SPG7 mutation for a slowly progressive form of autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia and spastic paraplegia. 24727571_Using an unbiased exome sequencing approach we identified pathogenic compound heterozygous SPG7 mutations in patients with PEO and multiple mitochondrial DNA deletions in skeletal muscle 24767997_The SPG7 Q866 variant is efficiently processed independent of phosphorylation of AFG3L2 at Y179, which inhibits processing of SPG7. 25681447_In unexplained ataxia, there was a significant number of patients with SPG7 mutations. 26260707_a novel homozygous frameshift deletion in the SPG7 gene was identifies as the genetic cause of hereditary spastic paraplegia in a Greek family. 26387735_Data indicates that SPG7 is essential for the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (PTP) complex formation, interacts with CypD and VDAC and determines C terminus of SPG7 and CsA-binding region of CypD as necessary for PTP formation. 26506339_this case shows that the spectrum of pathologies in SPG7 can include neuron loss of the dentate nucleus and the inferior olivary nucleus as well as neuritic pathology. 26626314_Compound heterozygous variants in SPG7 identified in 22 French Canadian patients with spastic ataxia. 26756429_A Norwegian founder mutation p.H701P is a major cause of SPG7 in Norway. 27084228_The results of this study showed that the most frequently detected variant in this cohort was the SPG7 p.Leu78. 28444220_CACNA1A and SPG7 are major ataxia genes. 30098094_SPG7 mutants accounted for 2.3% of cerebellar ataxia cases in Italy, suggesting that this variant should be considered as a priority test in the presence of late-onset pure ataxia 30252181_Data report here co-occurrence of a heterozygous de novo AFG3L2 missense mutation (p.R468C) and a maternally inherited heterozygous intragenic deletion of SPG7 in a patient with a complex ataxic and extrapyramidal phenotype with early-onset optic atrophy. 30747022_we identified novel variants of SPG7 in two patients with late onset hereditary spastic paraplegias 31044621_study provides evidence for two novel candidate genes, SPG7 and RASGEF1B, associating with white coat effect 31068484_This is the largest spastic paraplegia 7 cohort study to date and shows a spasticity-predominant phenotype of loss-of-function variants and more frequent cerebellar ataxia and later onset in patients carrying at least 1 Ala510Val variant. 31117107_This finding of a missense mutation of SPG7 gene in a primary lateral sclerosis family expands the spectrum of known SPG7 mutations 32002796_Novel homozygous SPG7 missense mutation in a Chinese hereditary spastic paraplegia family. 32447552_SPG7 mutations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a genetic link to hereditary spastic paraplegia. 33045469_Impaired flickering of the permeability transition pore causes SPG7 spastic paraplegia. 33774748_Neurophysiological and ophthalmological findings of SPG7-related spastic ataxia: a phenotype study in an Irish cohort. 34500365_Clinical and genetic characteristics of 21 Spanish patients with biallelic pathogenic SPG7 mutations. 35637455_A novel compound heterozygous SPG7 variant is associated with progressive spastic ataxia and persecutory delusions found in Chinese patients: two case reports. | ENSMUSG00000000738 | Spg7 | 720.745461 | 0.8478327 | -0.238148511 | 0.08129634 | 8.57241683675 | 0.0034129381793127988933833627527292264858260750770568847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.02103091597014424343758953739325079368427395820617675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 672.607435 | 61.961224 | 797.239614 | 73.052948 | |
| ENSG00000197965 | 9019 | MPZL1 | protein_coding | O95297 | FUNCTION: Cell surface receptor, which is involved in signal transduction processes. Recruits PTPN11/SHP-2 to the cell membrane and is a putative substrate of PTPN11/SHP-2. Is a major receptor for concanavalin-A (ConA) and is involved in cellular signaling induced by ConA, which probably includes Src family tyrosine-protein kinases. Isoform 3 seems to have a dominant negative role; it blocks tyrosine phosphorylation of MPZL1 induced by ConA. Isoform 1, but not isoform 2 and isoform 3, may be involved in regulation of integrin-mediated cell motility. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11751924, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12410637}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | Predicted to enable structural molecule activity. Predicted to be involved in cell-cell signaling and transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. Predicted to act upstream of or within positive regulation of cell migration. Located in cell surface and focal adhesion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:9019; | cell surface [GO:0009986]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] | 11751924_PZR is a major receptor of ConA and has an important role in cell signaling via c-Src. Considering the various biological activities of ConA, the study of PZR may have major therapeutic implications 12684038_Characterization of PZR1b, an alternative spliced isoform of PZR. 16702974_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16702974_the MPZL1/PZR gene may be important in the predisposition to schizophrenia among Han Chinese 18568953_Phosphorylation and localization of PZR in cultured endothelial cells is reported. 19064610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19536175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19629567_Clinico-electrophysiological features and MRI findings are described in leg musculature from three patients belonging to a CMT2J pedigree due to MPZ Thr124Met mutation. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24296779_MPZL1 is a target gene within the 1q24.1-24.2 amplicon that plays a pivotal role in HCC cell migration and tumor metastasis, and a novel MPZL1/Src/cortactin signaling cascade. 28912526_These data demonstrate that the formation of this MPZL1-PTPN11-GRB2 complex is triggered by the attachment of HER2+ breast cancer cells to fibronectin. 30392906_dimerization of MPZL1 participates in control of its signal transmission in cell adhesion. 30877754_Data indicate that myelin protein zero-like 1 (PZR) may promote the invasion and migration of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells through increasing the phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and protooncogene SRC (Src). 31233194_High MPZL1 expression is associated with proliferation and metastasis of ovarian cancer. 31322261_The present study showed that the expression and protein levels of MPZL1 were significantly higher in gallbladder carcinoma tissues, especially in patients diagnosed with advanced tumor stages. 35637954_LncRNA TNFRSF10A-AS1 promotes gastric cancer by directly binding to oncogenic MPZL1 and is associated with patient outcome. 35727197_MPZL1 upregulation promotes tumor metastasis and correlates with unfavorable prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. | ENSMUSG00000026566 | Mpzl1 | 272.110635 | 0.9961930 | -0.005502867 | 0.11204148 | 0.00240903897 | 0.9608539785233335406289256752643268555402755737304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.98178414979067707424320587961119599640369415283203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 290.391806 | 26.348312 | 292.756203 | 26.438529 | |
| ENSG00000198324 | 144717 | PHETA1 | protein_coding | Q8N4B1 | FUNCTION: Plays a role in endocytic trafficking. Required for receptor recycling from endosomes, both to the trans-Golgi network and the plasma membrane. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21233288}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | This gene encodes a protein that localizes to the endosome and interacts with the enzyme, inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase OCRL-1. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. | hsa:144717; | clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; endosome organization [GO:0007032]; receptor recycling [GO:0001881]; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi [GO:0042147] | 20133602_Two closely related endocytic proteins, Ses1 and Ses2, which interact with OCRL, were identified. The interaction is mediated by a short amino acid motif similar to that used by the rab-5 effector APPL1. 21233288_Two novel OCRL1-binding proteins, termed inositol polyphosphate phosphatase interacting protein of 27 kDa (IPIP27)A and B (also known as Ses1 and 2), that also bind the related 5-phosphatase Inpp5b, were identified. 32152089_Deficiency in the endocytic adaptor proteins PHETA1/2 impairs renal and craniofacial development. | ENSMUSG00000044134 | Pheta1 | 502.531353 | 0.8556724 | -0.224869551 | 0.10795114 | 4.33450537500 | 0.0373472657869135110653147080483904574066400527954101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.13347305923028773833038940210826694965362548828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 467.407763 | 35.248915 | 548.909398 | 41.057914 | |
| ENSG00000198598 | 4326 | MMP17 | protein_coding | Q9ULZ9 | FUNCTION: Endopeptidase that degrades various components of the extracellular matrix, such as fibrin. May be involved in the activation of membrane-bound precursors of growth factors or inflammatory mediators, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha. May also be involved in tumoral process. Cleaves pro-TNF-alpha at the '74-Ala-|-Gln-75' site. Not obvious if able to proteolytically activate progelatinase A. Does not hydrolyze collagen types I, II, III, IV and V, gelatin, fibronectin, laminin, decorin nor alpha1-antitrypsin. | Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Hydrolase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen | This gene encodes a member of the peptidase M10 family and membrane-type subfamily of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Proteins in this family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Members of this subfamily contain a transmembrane domain suggesting that these proteins are expressed at the cell surface rather than secreted. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protease. This protein is unique among the membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases in that it is anchored to the cell membrane via a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor. Elevated expression of the encoded protein has been observed in osteoarthritis and multiple human cancers. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. | hsa:4326; | extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; enzyme activator activity [GO:0008047]; metalloaminopeptidase activity [GO:0070006]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; drinking behavior [GO:0042756]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] | 12661033_down-regulation of most MT-MMPs is typical for prostate carcinoma; seems to occur mainly in epithelial cells 12962706_Data show that eosinophils constitutively express membrane type-4 matrix metalloproteinase (MT4-MMP), which is increased upon stimulation with tumor necrosis factor-alpha. 14701864_MT4-MMP and the proteoglycan form of syndecan-1 have roles in ADAMTS-4 activation on the cell surface 16686598_MT1-MT4-MMP chimaeras do not undergo normal trafficking and are not correctly processed to their fully active forms and, as a consequence, they are unable to activate pro-MMP-2 at the cell surface. 19426156_MT4-MMP promotes lung metastasis by disturbing the tumour vessel integrity and thereby facilitating tumour cell intravasation 20019845_Studies suggest a model of hypoxia induced metastasis through expression of HIF-1alpha, and SLUG regulation of MT4-MMP transcription. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21828052_The data presented here provide a new insight into the characteristics of MT4-MMP and highlight the common and distinct properties of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane type-matrix metalloproteinases. 22262494_It identifies MT4-MMP as a key intrinsic tumor cell determinant that contributes to the elaboration of a permissive microenvironment for metastatic dissemination. 22674854_CAV1 when found in lipid rafts does not allow the metalloproteinase MT4-MMP to localize into the lipid rafts, affecting its expression in the cell and probably its activity which is translated into the metastasis-associated activities of these cells. 25320013_A functional link between MT4-MMP and the growth factor receptor EGFR. 25963716_Screening of patients with inherited thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections identified a missense mutation (R373H) in the MMP17 gene that prevented the expression of the protease in human transfected cells. 26663028_The MT4-MMP is internalized by the clathrin-independent carriers/GPI-enriched early endosomal compartments pathway, a mechanism that differs from that responsible for the internalization of other membrane-type MMP members. 28196064_Low MT4-MMP expression is associated with erlotinib resistance in breast cancer. 28531887_Three forms of MT4-MMP with molecular masses of 45 kDa, 58 kDa and 69 kDa were detected. Further, we demonstrate that the 58 kDa form is the mature protein in the cell membrane, while the 69 kDa form is its precursor found in intracellular compartments. 29500407_MT4-MMP targeting may constitute a novel strategy to boost patrolling monocyte activity in early inflammation. 30792164_In breast cancer cells, the overexpression of MT4-MMP modulates the expression of microRNAs involved in several biological processes associated with tumor formation and progression and with clinical relevance. 31813546_MT4-MMP promotes invadopodia formation and cell motility in FaDu head and neck cancer cells. 36042626_Increased expression of MMP17 predicts poor clinical outcomes in epithelial ovarian cancer patients. | ENSMUSG00000029436 | Mmp17 | 309.245870 | 0.8933489 | -0.162704298 | 0.09524127 | 2.91959805027 | 0.0875096600540829078207494262642285320907831192016601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.24181847586655705328873011694668093696236610412597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 306.768038 | 16.149998 | 344.919853 | 17.604670 | |
| ENSG00000198945 | 84456 | L3MBTL3 | protein_coding | Q96JM7 | FUNCTION: Putative Polycomb group (PcG) protein. PcG proteins maintain the transcriptionally repressive state of genes, probably via a modification of chromatin, rendering it heritably changed in its expressibility. Required for normal maturation of myeloid progenitor cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BLB7}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a member of the malignant brain tumor (MBT) family of chromatin interacting transcriptional repressors. Members of this family function as methyl-lysine readers, which recognize methylated lysine residues on histone protein tails, and are associated with the repression of gene expression. The encoded protein may regulate hematopoiesis. Homozygous deletion of this gene has been observed in human patients with medulloblastoma. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. | hsa:84456; | nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; erythrocyte maturation [GO:0043249]; granulocyte differentiation [GO:0030851]; macrophage differentiation [GO:0030225]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; regulation of DNA methylation-dependent heterochromatin formation [GO:0090308] | 15889154_The mouse MBT-1 protein influences myelopoiesis by transiently enhancing p57(KIP2) expression levels. 27841877_Mutation in L3MBTL3 gene is associated with insulin-resistant cardiometabolic disease. 29030483_RBPJ interacts with L3MBTL3 to promote repression of Notch signaling via histone demethylase KDM1A. 30442713_The direct binding of L3MBTL3 to the methylated SOX2 protein leads to the recruitment of the CRL4(DCAF5) ubiquitin E3 ligase to target SOX2 protein for ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. 30456721_L3MBTL3 rs4364506 was found neither as a predisposing nor a protective variant against multiple sclerosis 34373992_Effect of L3MBTL3/PTPN9 polymorphisms on risk to alcohol-induced ONFH in Chinese Han population. 35088080_Identification of the genetic mechanism that associates L3MBTL3 to multiple sclerosis. | ENSMUSG00000039089 | L3mbtl3 | 191.010444 | 0.7438334 | -0.426948610 | 0.16777275 | 6.44971778346 | 0.0110969968046342216949629033706514746882021427154541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.05356272991829657409423859348862606566399335861206054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 170.986127 | 23.676779 | 231.041282 | 32.001312 | |
| ENSG00000198964 | 259230 | SGMS1 | protein_coding | Q86VZ5 | FUNCTION: Major sphingomyelin synthase at the Golgi apparatus (PubMed:17449912, PubMed:14685263). Catalyzes the reversible transfer of phosphocholine moiety in sphingomyelin biosynthesis: in the forward reaction transfers phosphocholine head group of phosphatidylcholine (PC) on to ceramide (CER) to form ceramide phosphocholine (sphingomyelin, SM) and diacylglycerol (DAG) as by-product, and in the reverse reaction transfers phosphocholine from SM to DAG to form PC and CER. The direction of the reaction depends on the levels of CER and DAG in Golgi membranes (PubMed:14685263, PubMed:17449912, PubMed:14976195, PubMed:17982138, PubMed:19454763). Does not use free phosphorylcholine or CDP-choline as donor (PubMed:14976195, PubMed:14685263). Regulates receptor-mediated signal transduction via mitogenic DAG and proapoptotic CER, as well as via SM, a structural component of membrane rafts that serve as platforms for signal transduction and protein sorting (PubMed:14976195, PubMed:17449912, PubMed:17982138). Plays a role in secretory transport via regulation of DAG pool at the Golgi apparatus and its downstream effects on PRKD1 (PubMed:18370930, PubMed:21980337). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14685263, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14976195, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17449912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17982138, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18370930, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19454763, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21980337}. | Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Golgi apparatus;Kinase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sphingolipid metabolism;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | PATHWAY: Sphingolipid metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17982138}. | The protein encoded by this gene is predicted to be a five-pass transmembrane protein. This gene may be predominately expressed in brain. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:259230; | endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; Golgi trans cisterna [GO:0000138]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ceramide cholinephosphotransferase activity [GO:0047493]; ceramide phosphoethanolamine synthase activity [GO:0002950]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; sphingomyelin synthase activity [GO:0033188]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; ceramide biosynthetic process [GO:0046513]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001242]; sphingolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0030148]; sphingomyelin biosynthetic process [GO:0006686] | 11841947_The 1.6 kb Hmob33 clone obtained from the medulla oblongata cDNA library and mapped to the human chromosome 10 was examined to find the coding region(MOB) 14976195_SMS1 is responsible for SM synthase activity in mammalian cells and plays a critical role in cell growth of lymphoid cells. 15315829_MOB gene activity is believed to be controlled at least at the transcriptional and the posttranscriptional levels, strictly regulating the amount of the encoded protein product. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16508036_Adenovirus-mediated SMS1 overexpression increased lipoprotein atherogenic potential. 17449912_Data show that sphingomyelin synthases SMS1 and SMS2 are co-expressed in a variety of cell types and function as the key Golgi- and plasma membrane-associated SM synthases in human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells, respectively. 17467659_Overexpression of SMS1 is associated with suppressed ceramide response and apoptotic resistance after photodamage. 17616479_Results indicate that both synthase (SMS)1 and 2 contribute to sphingomyelin (SM) de novo synthesis and control SM levels in the cells and on the cell membrane including plasma membrane. 17982138_SMS1 and SMS2 are key factors in the control of sphingomyelin and diacylglycerol metabolism within the cell, and thus they influence apoptosis. 18370930_SMS1 regulates subcellular pools of diacylglycerol-binding proteins in the Golgi apparatus. 18694848_Both SMS1 and SMS2 contain two histidines and one aspartic acid which are conserved within the lipid phosphate phosphatase superfamily. Site-directed mutagenesis of these amino acids abolished SMS activity without altering cellular distribution. 18820264_Impaired TCR signaling through dysfunction of lipid rafts in SMS1-knockdown T cells 19506037_Results establish the sphingomyelin synthase (SMS1)-related enzyme SMSr as a key regulator of ceramide homeostasis that seems to operate as a sensor rather than a converter of ceramides in the endoplasmic reticulum. 19779494_Altogether, our data show that SMS1 is a novel caspase target that is functionally involved in the regulation of FasL-induced apoptosis. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21203393_sphingomyelin synthase has a role in controlling the antimicrobial activity of neutrophils against Cryptococcus neoformans 21418611_Cellular sphingomyelin levels are positively related to cellular cholesterol levels and sphingomyelin synthase overexpression-mediated cellular sphingomyelin content changes are related to cellular Apo A-I content and secretion 21549185_Our results indicate that the regulation of SMS1 expression is complex and occurs at the transcriptional, post-transcriptional and translational levels. 21856749_SMS1-mediated SM synthesis directs Tf-TfR to undergo clathrin-dependent endocytosis and recycling, promoting the proliferation of lymphoma cells. 21980337_SMS1 and SMS2 are capable of regulating TGN-mediated protein trafficking and secretion 22106271_Data indicate that the increased sphingomyelin mass was due to a rapid and highly specific activation of sphingomyelin synthases SMS1 and SMS2. 23160178_Findings indicate that Sms1 is a downstream target of Bcr-abl, involved in sustaining cell proliferation of Bcr-abl-positive cells. 23977395_SGMS activity impacts on amyloid precursor protein processing to produce amyloid-beta (Abeta) and it could be a contributing factor in Abeta pathology associated with Alzheimer's disease. 24062078_The amount of SMS1 transcripts varies considerably between different human tissues. 24960545_We found upregulation of specific sphingolipid enzymes, namely sphingomyelin synthase 1 (SMS1), sphingomyelinase 3 (SMPD3), and glucosylceramide synthase (GCS) in the endometrium of endometriotic women. 25912551_A study of the expression of the full-length SMS1 protein and the sum of the alternative transcripts encoding this protein in human tissues. 26065260_The structural organization of 5'-UTR variants of SGMS1 transcripts, directed by alternative promoters, is substantially different; this can provide regulation of the gene functioning on post-transcriptional level. 27194473_Sphingomyelin synthase 1 positively regulates KCNQ1/KCNE1 channel density in a protein kinase D-dependent manner. 27394416_SMS regulates the expression and function of drug transporters P-gp and MRP2. 27927984_findings suggest that the C-terminal tails of SMSs are involved in homodimer formation, which is required for efficient transport from the ER. 28087695_HepG2 cells stably transfected with SMS1 (HepG2-SMS1) exhibit elevated enzyme activity in vitro and increased sphingomyelin content (mainly C22:0- and C24:0-sphingomyelin) but lower hexosylceramide (Hex-Cer) levels. 29128370_The inhibition of SMS 1 activity induced CD cells to lose their epithelial phenotype and to undergo an epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process. 29454087_the SGMS1 gene exhibits a complex regulation at the post-transcriptional level 29533737_An oncogene-Bcr-Abl-has been demonstrated to drive such a mechanism that up-regulates the expression of a functionally important target gene, SMS1. 30191692_PECULIARITIES OF THE STRUCTURE AND EXPRESSION OF HUMAN SPHINGOMYELIN SYNTHASE 1 GENE (SGMS1). 30242129_findings suggest that complex formation between SMS1 and GCS is part of a critical mechanism controlling the metabolic fate of Cer in the Golgi. 30535436_SMS1 could inhibit EMT and the migration and invasion of MDAMB231 cells via TGFbeta/Smad signaling pathway. 31164434_Differential lung tissue gene expression in males and females: implications for the susceptibility to develop COPD. 31262710_optively transferred wide-type B cells partially recovered B-cell activation and autoantibody production in SMS1 deficient bm12-induced lupus mice. Moreover, the SMS1 mRNA level in B cells of SLE patients was increased and positively correlated with the serum anti-dsDNA level, IgG and globulin titers. 31596951_Chlamydia trachomatis-infected human cells convert ceramide to sphingomyelin without sphingomyelin synthases 1 and 2. 31980461_Diacylglycerol kinase delta and sphingomyelin synthase-related protein functionally interact via their sterile alpha motif domains. 33037626_Regulation of human sphingomyelin synthase 1 translation through its 5'-untranslated region. 33226447_Overriding sorafenib resistance via blocking lipid metabolism and Ras by sphingomyelin synthase 1 inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33500344_Sphingomyelin Biosynthesis Is Essential for Phagocytic Signaling during Mycobacterium tuberculosis Host Cell Entry. | ENSMUSG00000040451 | Sgms1 | 74.564817 | 2.0757861 | 1.053657754 | 0.52132425 | 3.95262720181 | 0.0467982512086755134128601696374971652403473854064941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.15679375758250374550684114183241035789251327514648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 79.839776 | 28.406499 | 38.127668 | 13.550566 |
| ENSG00000204120 | 26058 | GIGYF2 | protein_coding | Q6Y7W6 | FUNCTION: Key component of the 4EHP-GYF2 complex, a multiprotein complex that acts as a repressor of translation initiation (PubMed:22751931, PubMed:31439631). In the 4EHP-GYF2 complex, acts as a factor that bridges EIF4E2 to ZFP36/TTP, linking translation repression with mRNA decay (PubMed:31439631). Also recruits and bridges the association of the 4EHP complex with the decapping effector protein DDX6, which is required for the ZFP36/TTP-mediated down-regulation of AU-rich mRNA (PubMed:31439631). May act cooperatively with GRB10 to regulate tyrosine kinase receptor signaling, including IGF1 and insulin receptors (PubMed:12771153). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12771153, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22751931, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31439631}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Neurodegeneration;Parkinson disease;Parkinsonism;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation | This gene contains CAG trinucleotide repeats and encodes a protein containing several stretches of polyglutamine residues. The encoded protein may be involved in the regulation of tyrosine kinase receptor signaling. This gene is located in a chromosomal region that was genetically linked to Parkinson disease type 11, and mutations in this gene were thought to be causative for this disease. However, more recent studies in different populations have been unable to replicate this association. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. | hsa:26058; | cytoplasmic stress granule [GO:0010494]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endosome [GO:0005768]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; proximal dendrite [GO:1990635]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; proline-rich region binding [GO:0070064]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; adult locomotory behavior [GO:0008344]; feeding behavior [GO:0007631]; homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue [GO:0048873]; insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048009]; mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0031571]; mRNA destabilization [GO:0061157]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; musculoskeletal movement [GO:0050881]; negative regulation of translation [GO:0017148]; neuromuscular process controlling balance [GO:0050885]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; post-transcriptional gene silencing [GO:0016441]; protein metabolic process [GO:0019538]; spinal cord motor neuron differentiation [GO:0021522] | 18358451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18358451_These data strongly support GIGYF2 as a PARK11 gene with a causal role in familial Parkinson disease. 18923002_Mutations in GIGYF2 are not strongly related to the development of the Parkinson's disease in Portuguese and North American populations. 18923002_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19117363_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19133664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19133664_This study suggested that reported mutations in GIGYF2 are not a common cause of Parkinson's disease in Norway and United States. 19250854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19250854_The results of this study concluded that neither of Asn56Ser and Asn457Thr variants plays a major role in the pathogenesis of parkinson disease. 19279319_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19279319_We believe that variation in a gene other than GIGYF2 accounts for the previously reported linkage finding on chromosome 2q36-37. 19321232_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19321232_The results of this study did not support a role for GIGYF2 in the genetic etiology of Belgian Parkinson disease. 19348706_The current genetic evidence suggestes that GIGYF2 is not a common cause od parkinson disease in several Caucasian. 19429085_GIGYF2 Asn56Ser and Asn457Thr mutations are a rare cause of PD in North American Caucasian population 19429085_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19449032_analysis of GIGYF2 variants in Parkinson's disease from two Asian populations 19482505_GIGYF2 mutations are not a frequent cause of Parkinson's disease 19482505_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19562763_This letter suggested that GIGYF2 is neither responsible for PARK11 nor a gene implicated in Parkinson disease. 19638301_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19638301_The GIGYF2 Asn56Ser mutation is rare in Chinese PD patients. 19845746_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19845746_our findings suggest that GIGYF2 variants are not a frequent cause of Parkinson's disease in the Spanish population, since we found no clearly segregating GIGYF2 variants 20004041_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20004041_The results of this study do not support a major role of GIGYF2 in parkinson disease. 20044296_GIGYF2 variants are not associated with Parkinson's disease in the mainland Chinese Population. 20044296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20060621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20060621_These data, together with those recently reported by other groups, suggest that GIGYF2 is unlikely to be the PARK11 gene. 20178831_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20178831_We identified nine novel variants in GIGYF2 gene, which might be associated with PD in the Chinese population. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20641165_GIGYF2 is unlikely to play a major role in PD in Japanese patients, similar to other populations. 20816920_No clearly pathogenic mutations are identified in GIGYF2 and ATP13A2 in Brazilian patients with early-onset Parkinson's disease. 20816920_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22115759_within the Chinese population, the c.297T>C p.Ala99Ala polymorphism of the GIGYF2 gene may be associated with an increased risk of developing Parkinson disease. 22503729_Our result indicated that SCNA, LRRK2, UCHL1, HtrA2 and GIGYF2 genes' mutations might not be a main reason for Chinese Autosomal dorminant Parkinson's disease 22751931_GIGYF2 and the zinc finger protein 598 (ZNF598) are identified as components of the 4EHP complex. 26134514_required, this finding may shed light on the GIGYF2-associated mechanisms that lead to PD and suggests insulin dysregulation as a disease-specific mechanism for both PD and cognitive dysfunction. 26152800_Results suggest that the N56S and N457T of GIGYF2 are risk factors for Parkinson's disease in Caucasians, but not in Asians 27157137_Full-length GIGYF2 coimmunoprecipitates with AGO2 in human cells, and upon tethering to a reporter mRNA, GIGYF2 exhibits strong, dose-dependent silencing activity, involving both mRNA destabilization and translational repression. 28873462_genetic analyses of indel loci in ACE, DJ-1, and GIGYF2 genes, was performed to explore the potential contribution of insertion (I)/deletion (D) polymorphisms (indels) to the risk of PD in a Chinese population. 29554310_GIGYF2 has two distinct mechanisms of repression: one depends on 4EHP binding and mainly affects translation; the other is 4EHP-independent and involves the CCR4/NOT complex and its deadenylation activity. 32726578_GIGYF2 and 4EHP Inhibit Translation Initiation of Defective Messenger RNAs to Assist Ribosome-Associated Quality Control. 33053355_4EHP and GIGYF1/2 Mediate Translation-Coupled Messenger RNA Decay. 33239198_Association study of DNAJC13, UCHL1, HTRA2, GIGYF2, and EIF4G1 with Parkinson's disease. 34665823_Translational repression of NMD targets by GIGYF2 and EIF4E2. | ENSMUSG00000048000 | Gigyf2 | 704.618231 | 1.5118297 | 0.596295622 | 0.24009192 | 6.10845022979 | 0.0134537047529135530415933530434813292231410741806030273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.06210905019265833965080858547480602283030748367309570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 863.518563 | 268.196390 | 553.422455 | 171.948790 | |
| ENSG00000204348 | 1797 | DXO | protein_coding | O77932 | FUNCTION: Decapping enzyme for NAD-capped RNAs: specifically hydrolyzes the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) cap from a subset of RNAs by removing the entire NAD moiety from the 5'-end of an NAD-capped RNA (PubMed:28283058). The NAD-cap is present at the 5'-end of some RNAs and snoRNAs (PubMed:28283058). In contrast to the canonical 5'-end N7 methylguanosine (m7G) cap, the NAD cap promotes mRNA decay (PubMed:28283058). Preferentially acts on NAD-capped transcripts in response to environmental stress (PubMed:31101919). Also acts as a non-canonical decapping enzyme that removes the entire cap structure of m7G capped or incompletely capped RNAs and mediates their subsequent degradation (By similarity). Specifically degrades pre-mRNAs with a defective 5'-end m7G cap and is part of a pre-mRNA capping quality control (By similarity). Has decapping activity toward incomplete 5'-end m7G cap mRNAs such as unmethylated 5'-end-capped RNA (cap0), while it has no activity toward 2'-O-ribose methylated m7G cap (cap1) (PubMed:29601584). In contrast to canonical decapping enzymes DCP2 and NUDT16, which cleave the cap within the triphosphate linkage, the decapping activity releases the entire cap structure GpppN and a 5'-end monophosphate RNA (By similarity). Also has 5'-3' exoribonuclease activities: The 5'-end monophosphate RNA is then degraded by the 5'-3' exoribonuclease activity, enabling this enzyme to decap and degrade incompletely capped mRNAs (PubMed:29601584). Also possesses RNA 5'-pyrophosphohydrolase activity by hydrolyzing the 5'-end triphosphate to release pyrophosphates (By similarity). Exhibits decapping activity towards FAD-capped RNAs (PubMed:32374864). Exhibits decapping activity towards dpCoA-capped RNAs in vitro (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O70348, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28283058, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29601584, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31101919, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32374864}. | Exonuclease;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nuclease;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding | This gene localizes to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class III region on chromosome 6. The function of its protein product is unknown, but its ubiquitous expression and conservation in both simple and complex eukaryotes suggests that this may be a housekeeping gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:1797; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; 5'-3' exonuclease activity [GO:0008409]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; mRNA 5'-diphosphatase activity [GO:0034353]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; nucleotide binding [GO:0000166]; RNA NAD-cap (NAD-forming) hydrolase activity [GO:0110152]; mRNA catabolic process [GO:0006402]; NAD-cap decapping [GO:0110155]; nuclear mRNA surveillance [GO:0071028]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process [GO:0000956]; nucleic acid phosphodiester bond hydrolysis [GO:0090305]; RNA destabilization [GO:0050779] | 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 29601584_Study showed that DXO is a multifunctional enzyme that possesses both decapping and 5'-3' exoribonuclease activities toward non-2'-O-methylated RNA transcripts. DXO is directly involved in the mRNA quality control mechanism by degrading mRNAs with abnormal cap structures. 29672716_DOM3Z limits both miR-122-dependent and miR-122-independent Hepatitis C RNA accumulation. | ENSMUSG00000040482 | Dxo | 91.977317 | 0.8561458 | -0.224071602 | 0.21394071 | 1.09281495352 | 0.2958483467749647988220829120109556242823600769042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.52880445588862268202490213298005983233451843261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 85.975683 | 11.966484 | 100.286917 | 13.565325 | |
| ENSG00000204463 | 7917 | BAG6 | protein_coding | P46379 | FUNCTION: ATP-independent molecular chaperone preventing the aggregation of misfolded and hydrophobic patches-containing proteins (PubMed:21636303). Functions as part of a cytosolic protein quality control complex, the BAG6/BAT3 complex, which maintains these client proteins in a soluble state and participates in their proper delivery to the endoplasmic reticulum or alternatively can promote their sorting to the proteasome where they undergo degradation (PubMed:20516149, PubMed:21636303, PubMed:21743475, PubMed:28104892). The BAG6/BAT3 complex is involved in the post-translational delivery of tail-anchored/type II transmembrane proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Recruited to ribosomes, it interacts with the transmembrane region of newly synthesized tail-anchored proteins and together with SGTA and ASNA1 mediates their delivery to the endoplasmic reticulum (PubMed:20516149, PubMed:20676083, PubMed:28104892, PubMed:25535373). Client proteins that cannot be properly delivered to the endoplasmic reticulum are ubiquitinated by RNF126, an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase associated with BAG6 and are sorted to the proteasome (PubMed:24981174, PubMed:28104892, PubMed:27193484). SGTA which prevents the recruitment of RNF126 to BAG6 may negatively regulate the ubiquitination and the proteasomal degradation of client proteins (PubMed:23129660, PubMed:25179605, PubMed:27193484). Similarly, the BAG6/BAT3 complex also functions as a sorting platform for proteins of the secretory pathway that are mislocalized to the cytosol either delivering them to the proteasome for degradation or to the endoplasmic reticulum (PubMed:21743475). The BAG6/BAT3 complex also plays a role in the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD), a quality control mechanism that eliminates unwanted proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum through their retrotranslocation to the cytosol and their targeting to the proteasome. It maintains these retrotranslocated proteins in an unfolded yet soluble state condition in the cytosol to ensure their proper delivery to the proteasome (PubMed:21636303). BAG6 is also required for selective ubiquitin-mediated degradation of defective nascent chain polypeptides by the proteasome. In this context, it may participate in the production of antigenic peptides and play a role in antigen presentation in immune response (By similarity). BAG6 is also involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced pre-emptive quality control, a mechanism that selectively attenuates the translocation of newly synthesized proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum and reroutes them to the cytosol for proteasomal degradation. BAG6 may ensure the proper degradation of these proteins and thereby protects the endoplasmic reticulum from protein overload upon stress (PubMed:26565908). By inhibiting the polyubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of HSPA2 it may also play a role in the assembly of the synaptonemal complex during spermatogenesis (By similarity). Also positively regulates apoptosis by interacting with and stabilizing the proapoptotic factor AIFM1 (By similarity). By controlling the steady-state expression of the IGF1R receptor, indirectly regulates the insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway (PubMed:26692333). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z1R2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20516149, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20676083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21636303, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21743475, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23129660, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24981174, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25179605, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26565908, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26692333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27193484, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28104892}.; FUNCTION: Involved in DNA damage-induced apoptosis: following DNA damage, accumulates in the nucleus and forms a complex with p300/EP300, enhancing p300/EP300-mediated p53/TP53 acetylation leading to increase p53/TP53 transcriptional activity (PubMed:17403783). When nuclear, may also act as a component of some chromatin regulator complex that regulates histone 3 'Lys-4' dimethylation (H3K4me2) (PubMed:18765639). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17403783, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18765639}.; FUNCTION: Released extracellularly via exosomes, it is a ligand of the natural killer/NK cells receptor NCR3 and stimulates NK cells cytotoxicity. It may thereby trigger NK cells cytotoxicity against neighboring tumor cells and immature myeloid dendritic cells (DC). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18055229, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18852879}.; FUNCTION: Mediates ricin-induced apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14960581}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Chaperone;Chromatin regulator;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;Immunity;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Spermatogenesis;Transport;Ubl conjugation | This gene was first characterized as part of a cluster of genes located within the human major histocompatibility complex class III region. This gene encodes a nuclear protein that is cleaved by caspase 3 and is implicated in the control of apoptosis. In addition, the protein forms a complex with E1A binding protein p300 and is required for the acetylation of p53 in response to DNA damage. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:7917; | BAT3 complex [GO:0071818]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; Hsp70 protein binding [GO:0030544]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; misfolded protein binding [GO:0051787]; polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding [GO:0031593]; proteasome binding [GO:0070628]; ribosome binding [GO:0043022]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; ubiquitin-specific protease binding [GO:1990381]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced pre-emptive quality control [GO:0061857]; ER-associated misfolded protein catabolic process [GO:0071712]; immune response-activating cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002429]; internal peptidyl-lysine acetylation [GO:0018393]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator [GO:0042771]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0070059]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; lung development [GO:0030324]; maintenance of unfolded protein involved in ERAD pathway [GO:1904378]; natural killer cell activation [GO:0030101]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032435]; negative regulation of proteolysis [GO:0045861]; positive regulation of ERAD pathway [GO:1904294]; post-translational protein targeting to endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0006620]; proteasomal protein catabolic process [GO:0010498]; protein localization to cytosolic proteasome complex involved in ERAD pathway [GO:1904379]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of embryonic development [GO:0045995]; regulation of protein stability [GO:0031647]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; synaptonemal complex assembly [GO:0007130]; tail-anchored membrane protein insertion into ER membrane [GO:0071816]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] | 14960581_Evidence indicates that casp3 activated by ricin acts on BAT3 at the caspase cleavage site, DEQD(1001) to release a C-terminal fragment designated CTF-131, which induces phosphatidylserine exposure, cell rounding, and chromatin condensation as ricin does 16777091_Interaction of hSGT with Hsc70, Hsp70 or Bag-6/Bat-3/Scythe was demonstrated in prometaphase, thereby suggesting a possible role for complexes containing hSGT and distinct (co)-chaperones during mitosis. 16954377_MRK phosphorylates Scythe at T1080 in vitro as determined by site-directed mutagenesis and mass spectrometry, supporting the consensus and suggesting Scythe as a physiological substrate for MRK. 17403783_Bat3 is a novel and essential regulator of p53-mediated responses to genotoxic stress, and that Bat3 controls DNA damage-induced acetylation of p53. 17672918_occurrence of an unusual TG 3' splice site in intron 6 18055229_HLA-B-associated transcript 3 (BAT3) was released from tumor cells, bound directly to NKp30, and engaged NKp30 on NK cells. BAT3 triggered NKp30-mediated cytotoxicity and was necessary for tumor rejection in a multiple myeloma model. 18056262_Scythe regulates apoptosis-inducing factor stability during endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis 18757527_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18765639_BORIS acts as a platform upon which BAT3 and SET1A assemble and exert effects upon chromatin structure and gene expression. 18835879_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18852879_NKp30-mediated NK cells/dendritic cells cross talk resulting either in iDC killing or maturation was BAT3-dependent 18978787_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19018758_colocalization of PBF and Scythe/BAT3 in the nucleus might be an important factor for survival of osteosarcoma cells. 19115949_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19242354_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19357808_The HSP70-driven degradation of BAG6, following the BAG6-dependent accumulation of HSP70, could allow the protein-refolding activity of HSP70 and limit the extent of its induction. 19837266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19955392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20098615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20106900_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20385987_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20626023_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20626023_Results suggest BAT2 -8671, BAT3 8854, and BAT5 22655, 9569 SNPs as well as BAT haplotypes (ATTGTG and ATCATG) might be associated with higher Kawasaki disease susceptibility and coronary artery aneurysm formation. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20713601_Data suggest that BAG-6 is necessary for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of newly synthesized defective polypeptides. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21940994_We present a mechanism explaining how parallel IFNgamma-mediated regulation of CIITA and of its chaperone BAT3 controls the level of components of the HLA class II processing pathway. 22174835_BAT3, a cytosolic chaperone, is recruited to the site of dislocation through its interaction with Derlin2. 22285488_Data show that cleavage of Scythe by caspase-3 occurs after activation of both the extrinsic (i.e. Fas/APO-1-mediated) and the intrinsic (i.e. staurosporine-induced) apoptosis pathway. 22373577_These findings identify a novel role for Bat3 in regulating DOT1L function, which plays a critical role in DNA damage response. 22558287_Cell type-specific subcellular expression of BAT3 suggests distinct functions in the cytosol and in the nucleus. 22641691_Aberrant enhancement of YWK-II/APLP2 by nuclear export of Bat3 may play a role in cancer development by inhibiting cell apoptosis. 22863785_Bat3 promotes T cell responses and autoimmunity by repressing Tim-3-mediated cell death and exhaustion. 23077592_our results suggest an essential role for AIF and its binding partner Scythe in the pathway leading to apoptotic corpse clearance. 23129660_A BAG6/SGTA cycle operates during protein maturation and quality control in the cytosol. 23246001_SGTA recognizes a noncanonical ubiquitin-like domain in the Bag6-Ubl4A-Trc35 complex to promote endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation. 23665563_Data indicate that the Bag6-Ubl4A-Trc35 complex is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane to regulate ER-associated degradation (ERAD). 23723067_Data indicate that BCL2-associated athanogene 6 (BAG6) appears to be the central component for the process, as depletion of BAG6 leads to the loss of both UBL4A and GET4 proteins and resistance to cell killing by DNA-damaging agents. 23900548_Bag6, a protein in the TRC pathway that is also responsible for the degradation of mislocalized proteins, is not only involved in core particle assembly but also has a key role in efficient regulatory particle assembly. 24133212_we show for the first time that BAG-6(686-936) comprises a subdomain of BAG-6, which is sufficient for receptor docking and inhibition of NKp30-dependent NK cell cytotoxicity as part of a tumor immune escape mechanism 24594942_show that endogenous dislocation clients are captured specifically in association with the cytosolic chaperone BAG6, or retrieved en masse via their glycan handle 24625963_VNTR in the coding region of the FAM46A gene, FAM46A rs11040 SNP and BAG6 rs3117582 SNP are associated with susceptibility to tuberculosis 24806960_Exogenous BAG6 perturbs the function of the BAG6 complex at a stage subsequent to substrate recognition and polyubiquitylation, most likely the BAG6-dependent delivery of OpD to the proteasome. 24981174_RNF126 is recruited to the N-terminal Ubl domain of Bag6 and preferentially ubiquitinates juxtahydrophobic lysine residues on Bag6-associated clients. 24989925_This meta-analysis suggested that BAT3 polymorphisms contributed the development of lung cancer. 25091272_Tim-3/Gal-9 interaction favors apoptosis of MBP-specific T lymphocytes in benign multiple sclerosis; this process is reduced in PPMS by the up-regulation of Bat3 25111513_The BAT2/BAT3 polymorphisms and specifically the A/C haplotype may represent a novel immunogenetic factor associated with graft rejection in patients undergoing allo-HSCT. 25231575_Susceptibility to large-joint osteoarthritis (hip and knee) is associated with BAG6 rs3117582 SNP and the VNTR polymorphism in the second exon of the FAM46A gene on chromosome 6. 25415308_Data show that molecular chaperone BAG6_ubiquitin-like domain (UBL) and ubiquitin-like 4A UBL4A_UBL compete for the same binding site on N-terminal dimerisation domain of SGTA protein (SGTA_NT). 25430685_This meta-analysis suggested that HLA-B-associated transcript 3 polymorphisms are risk factors for lung cancer. 25535373_Both TRC35 and Ubl4A have distinct C-terminal binding sites on Bag6 defining a minimal Bag6 complex. 25884493_BAG6 rs3117582 SNP was associated with non small cell lung cancer in the Norwegian subjects and the combined Croatian-Norwegian subjects corroborating the earlier finding that BAG6 rs3117582 SNP was associated with lung cancer in Europeans. 26153132_BAG6 co-localizes with HSPA2 in huinan testicular germ cells and epididymal spermatozoa, moving from the equator to the anterior head during capacitation and stably interacting with HSPA2. In zona pellucida binding defect infertility, BAG6 is lacking. 26598275_we found BAG6 to be dispensable in antigen processing 26663859_The observations suggest a mechanism whereby the BAG6 ubiquitin-linked domain provides a platform for discriminating substrates with shorter hydrophobicity stretches as a signal for defective proteins. 29685906_Our results identify how VCP is specifically targeted to ubiquitylated substrates in the BAG6 triage pathway and suggest that the degradation of ubiquitylated clients by the proteasome is reliant on the association of UBXN1 with ubiquitylated substrates and the catalytic activity of VCP. 29706626_Mechanistically, Lnc-Tim3 specifically binds to Tim-3 and blocks its interaction with Bat3, thus suppressing downstream Lck/ NFAT1/AP-1 signaling, leading to nuclear localization of Bat3, and enhancing p300-dependent p53 and RelA transcriptional activation of anti-apoptosis genes including MDM2 and Bcl-2. 30635083_The SGTA is a co-chaperone that, in collaboration with the complex of BAG6, facilitates the biogenesis and quality control of hydrophobic proteins, protecting them from the aqueous cytosolic environment. 30804014_we suggest that Rab proteins represent a novel set of substrates for BAG6, and the BAG6-mediated pathway is associated with the regulation of membrane vesicle trafficking events in mammalian cells. 31371451_We conclude that the RNF126/BAG6 complex contributes to G0S2 degradation and that interventions to prevent G0S2 degradation may offer a therapeutic strategy for managing ischemic diseases. 31534536_Exosome-dependent immune surveillance at the metastatic niche requires BAG6 and CBP/p300-dependent acetylation of p53. 31647545_HLA-B-associated transcript 3 (Bat3) stabilizes and activates p53 in a HAUSP-dependent manner. 31838060_BAG6 is a novel microtubule-binding protein that regulates ciliogenesis by modulating the cell cycle and interacting with gamma-tubulin. 31904842_PAQR9 binds to the DUF3538 domain within the proline-rich stretch of BAG6. PAQR9 reduces the binding of MLPs to BAG6 in a DUF3538 domain-dependent manner. Taken together, our results indicate that PAQR9 plays a role in the regulation of protein quality control of MLPs via affecting the interaction of BAG6 with membrane proteins. 32696179_BAG3 and BAG6 differentially affect the dynamics of stress granules by targeting distinct subsets of defective polypeptides released from ribosomes. 32986360_Expression Analysis of Fyn and Bat3 Signal Transduction Molecules in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. 32991875_The cleft palate candidate gene BAG6 supports FoxO1 acetylation topromote FasL-mediated apoptosis during palate fusion. 33522017_BAG6 promotes PINK1 signaling pathway and is essential for mitophagy. 33539267_Association Between eNOS, MMP-9, BAG-6 Gene Polymorphisms and Risk of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy in the Northern Chinese Population. 33671836_Secreted Ligands of the NK Cell Receptor NKp30: B7-H6 Is in Contrast to BAG6 Only Marginally Released via Extracellular Vesicles. 34704338_GET4 is a novel driver gene in colorectal cancer that regulates the localization of BAG6, a nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein. 35543156_Mitochondrial antiviral-signalling protein is a client of the BAG6 protein quality control complex. | ENSMUSG00000024392 | Bag6 | 2046.381974 | 0.9093460 | -0.137098746 | 0.07913331 | 2.99998672109 | 0.0832651991155044235437543420630390755832195281982421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.23373742830176114093632122603594325482845306396484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 1800.831292 | 88.407624 | 1989.885805 | 97.423518 | |
| ENSG00000204673 | 84335 | AKT1S1 | protein_coding | Q96B36 | FUNCTION: Subunit of mTORC1, which regulates cell growth and survival in response to nutrient and hormonal signals. mTORC1 is activated in response to growth factors or amino acids. Growth factor-stimulated mTORC1 activation involves a AKT1-mediated phosphorylation of TSC1-TSC2, which leads to the activation of the RHEB GTPase that potently activates the protein kinase activity of mTORC1. Amino acid-signaling to mTORC1 requires its relocalization to the lysosomes mediated by the Ragulator complex and the Rag GTPases. Activated mTORC1 up-regulates protein synthesis by phosphorylating key regulators of mRNA translation and ribosome synthesis. mTORC1 phosphorylates EIF4EBP1 and releases it from inhibiting the elongation initiation factor 4E (eiF4E). mTORC1 phosphorylates and activates S6K1 at 'Thr-389', which then promotes protein synthesis by phosphorylating PDCD4 and targeting it for degradation. Within mTORC1, AKT1S1 negatively regulates mTOR activity in a manner that is dependent on its phosphorylation state and binding to 14-3-3 proteins. Inhibits RHEB-GTP-dependent mTORC1 activation. Substrate for AKT1 phosphorylation, but can also be activated by AKT1-independent mechanisms. May also play a role in nerve growth factor-mediated neuroprotection. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16174443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17277771, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17386266}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | AKT1S1 is a proline-rich substrate of AKT (MIM 164730) that binds 14-3-3 protein (see YWHAH, MIM 113508) when phosphorylated (Kovacina et al., 2003 [PubMed 12524439]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:84335; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; negative regulation of cell size [GO:0045792]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; negative regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032007]; neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048011]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043523] | 17277771_PRAS40 is an important regulator of insulin sensitivity of the Akt-mTOR pathway and a potential target for the treatment of cancers, insulin resistance and hamartoma syndromes. 17386266_PRAS40 inhibits cell growth, S6K1 phosphorylation, and rheb-induced activation of the mTORC1 pathway 17510057_PRAS40 regulates mTORC1 kinase activity by functioning as a direct inhibitor of substrate binding. 17604271_PRAS40 acts downstream of mTORC1 but upstream of its effectors, such as S6K1 and 4E-BP1 18215133_activation of mTORC1 signalling by phorbol esters does not require PRAS40 to be phosphorylated at Thr(246), bind to 14-3-3 or be released from mTORC1. 18372248_after mTORC1 kinase activation by upstream regulators, PRAS40 is phosphorylated directly by mTOR, thus contributing to the relief of PRAS40-mediated substrate competition. 21886838_phosphorylation of PRAS40 is critical for the activation of mTOR in CNI-induced VEGF overexpression and renal cancer progression. 21906675_PRAS40 is known for its ability to regulate the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 kinase activity, possessing a key regulatory role at the cross point of signal transduction pathways activated by growth factor receptors 21910584_PIM1-activated pPRAS40, AKT-activated pFOXO3a, and their complex formation with 14-3-3 could be key regulators of the radiation-induced radioresistance in NSCLC cells 21914810_dissociation of PRAS40 from insulin-stimulated 4E-BP protein binding to mTORC1 and enhanced mTORC1 substrate binding results from Akt and mTORC1 activation and makes little or no contribution to mTORC1 signaling 22090422_study found tuberin and PRAS40 to be potent anti-apoptotic gatekeepers in early stem-cell differentiation; data allow new insights into the regulation of early stem-cell maintenance and differentiation and identify a new role of the tumor suppressor tuberin and the oncogenic protein PRAS40 22241085_our findings suggest that PRAS40 promotes the development of ESFT 22354785_This review summarizes the regulation and potential function(s) of PRAS40 in the complex Akt- and mTOR-signaling network in health and disease--{REVIEW} 22873724_WISP1 governs PRAS40 by sequestering PRAS40 intracellularly through post-translational phosphorylation. 23460019_Data suggest that PRAS40 modulates insulin action in skeletal muscle; knockdown of PRAS40 inhibits insulin action in cultured myotubes and is associated with up-regulation of IRS1 (insulin receptor substrate 1) degradation via proteasome proteolysis. 23712034_PRAS40 contains a functional nuclear export signal. Furthermore, enforced nuclear accumulation of PRAS40 impairs insulin action, thereby substantiating the function of this protein in the regulation of insulin sensitivity. 24576065_PRAS40 as a regulator of insulin sensitivity in hSkMC 24704832_Findings indicate that dual phosphorylation of PRAS40 by Akt and mTORC1 promotes formation of a nuclear-specific PRAS40- and RPL11-containing complex distinct from mTORC1 that inhibits the RPL11-HDM2-p53 pathway. 25531317_Supporting this idea, we identified a downstream target of the TGFb-miR-96 signaling pathway to be AKT1S1 mRNA, whose translated protein is a negative regulator of mTOR kinase. 25648575_The frameshift mutation detected in the current study would result in a premature stop of amino-acid synthesis in AKT1S1 protein and hence resembles a typical loss-of-function mutation. 26003731_This review discusses the role of PRAS40 and possible feedback mechanisms, and alterations in AKT/PRAS40/mTOR signaling that have been implicated in the pathogenesis of tumor progression. [review] 26876154_Phosphorylation of S202/203 of AKT1S1 by PKM2 released AKT1S1 from raptor and facilitated its binding to 14-3-3, resulted in hormonal- and nutrient-signals independent activation of mTORC1 signaling and led accelerated oncogenic growth and autophagy inhibition in cancer cells. 27431378_PRAS40 was downregulated in the DU145 cells following MYO6 knockdown. 28484006_The Akt-PRAS40 pathway is activated by uric acid, which inhibits autophagy and recapitulates the uric acid-induced proinflammatory cytokine phenotype. 28674187_Study found that activated PRAS40 acts not only as a regulator of TGFA-triggered exosome secretion but also as a common regulator of distinct microenvironmental and oncogenic signal-triggered exosome secretion in both normal and tumor cell types. PRAS40 is the first regulator identified for stress-induced exosome secretion. 29236692_crystal structures of RAPTOR-TOS motif complexes that define the determinants of TOS recognition, of an mTOR FKBP12-rapamycin-binding (FRB) domain-substrate complex that establishes a second substrate-recruitment mechanism, and of a truncated mTOR-PRAS40 complex that reveals PRAS40 inhibits both substrate-recruitment sites 31210839_ROS act in concert with BLM to facilitate Prostate cancer (PC) oncogenesis, potentially via further enhancing AKT signaling and downregulating PTEN expression. Importantly, inhibiting the BLM-AKT-PRAS40 axis induced PC cell apoptosis. 31692069_M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophages promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition via activation of the AKT3/PRAS40 signaling pathway in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 31728028_PRAS40 suppresses atherogenesis through inhibition of mTORC1-dependent pro-inflammatory signaling in endothelial cells. 31740404_This study, for the first time, links PF4's anti-RNV function to an intracellular signaling molecule PRAS40 and its phosphorylation. 31813279_MELK is Upregulated in Advanced Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma and Promotes Disease Progression by Phosphorylating PRAS40. 31901857_PRAS40 hyperexpression promotes hepatocarcinogenesis. 32467173_PRAS40 Phosphorylation Correlates with Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Receptor-Induced Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition in Head and Neck Cancer Cells. 33804169_Dual Specificity Kinase DYRK3 Promotes Aggressiveness of Glioblastoma by Altering Mitochondrial Morphology and Function. 35058442_PGK1 represses autophagy-mediated cell death to promote the proliferation of liver cancer cells by phosphorylating PRAS40. | ENSMUSG00000011096 | Akt1s1 | 523.772519 | 0.6901418 | -0.535035245 | 0.07221729 | 55.08451241073 | 0.0000000000001154570941966681990234106558780900185251939299435619545874942559748888015747070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000000000470849514175800186884811675796736949155957274726347350224386900663375854492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 416.189576 | 22.264517 | 606.088700 | 30.889472 | |
| ENSG00000213672 | 51517 | NCKIPSD | protein_coding | Q9NZQ3 | FUNCTION: Has an important role in stress fiber formation induced by active diaphanous protein homolog 1 (DRF1). Induces microspike formation, in vivo (By similarity). In vitro, stimulates N-WASP-induced ARP2/3 complex activation in the absence of CDC42 (By similarity). May play an important role in the maintenance of sarcomeres and/or in the assembly of myofibrils into sarcomeres. Implicated in regulation of actin polymerization and cell adhesion. Plays a role in angiogenesis. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22419821}. | 3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;SH3 domain;SH3-binding | The protein encoded by this gene contains a nuclear localization signal. It plays a role in signal transduction, and may function in the maintenance of sarcomeres and in the assembly of myofibrils into sarcomeres. It also plays an important role in stress fiber formation This protein is involved in the formation and maintenance of dendritic spines, and modulates synaptic activity in neurons. The gene is involved in therapy-related leukemia by a chromosomal translocation t(3;11)(p21;q23) that involves this gene and the myeloid/lymphoid leukemia gene. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2019]. | hsa:51517; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; intermediate filament [GO:0005882]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; Arp2/3 complex binding [GO:0071933]; cytoskeletal protein binding [GO:0008092]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976] | 14559906_the interaction of the betaPIX.WASP.SPIN90 complex with Nck is crucial for stable cell adhesion and can be dynamically modulated by SPIN90 phosphorylation that is dependent on cell adhesion and ERK activation 16253999_SPIN90 participates in reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and in actin-based cell motility 17398099_DIP binds to and inhibits actin assembly by the FH2 domain of the formin mDia2 17398099_These observations point to a pivotal role for DIP in the control of nonbranched and branched actin-filament assembly that is mediated by Diaphanous-related formins and activators of Arp2/3, respectively. 17537434_The interplay between palladin, SPIN90 and Src and characterized the role of palladin and SPIN90 in platelet derived growth factor and Src-induced cytoskeletal remodeling, was analyzed. 19460367_SPIN90 and IRSp53 positively cooperated to mediate Rac activation, and co-expression of SPIN90 and IRSp53 in COS-7 cells led to the complex formation of SPIN90-IRSp53 in the leading edge of cells 23024796_Dia2 and DIP co-tether to nascent blebs and this linkage is required for bleb formation. 23342115_Findings show that SPIN90 modulates synaptic activity in neurons as a result of its phosphorylation. 23765104_SPIN90 dephosphorylation is a prerequisite step for releasing cofilin so that cofilin can adequately sever actin filaments into monomeric form. 24340049_findings suggest that SPIN90 contributes to the formation and movement of endosomal vesicles, and modulates the stability of EGFR protein, which affects cell cycle progression 28652253_Low SPIN90 expression is associated with Breast Cancer. 30322896_Structure of the nucleation-promoting factor SPIN90 bound to the actin filament nucleator Arp2/3 complex. 31358736_The findings suggest that SPIN90, as an adaptor protein, simultaneously binds inactive Rab5 and Gapex5, thereby altering their spatial proximity and facilitating Rab5 activation. | ENSMUSG00000032598 | Nckipsd | 165.546263 | 1.1423098 | 0.191953977 | 0.13702055 | 1.95968516075 | 0.1615469939580786440380677504435880109667778015136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.36167083090358581598522391686856281012296676635742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 166.787013 | 12.123056 | 146.517956 | 10.470592 | |
| ENSG00000213983 | 8906 | AP1G2 | protein_coding | O75843 | FUNCTION: May function in protein sorting in late endosomes or multivesucular bodies (MVBs). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9733768}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Involved in MVB-assisted maturation of hepatitis B virus (HBV). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16867982, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17553870}. | 3D-structure;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport | Adaptins are important components of clathrin-coated vesicles transporting ligand-receptor complexes from the plasma membrane or from the trans-Golgi network to lysosomes. The adaptin family of proteins is composed of four classes of molecules named alpha, beta-, beta prime- and gamma- adaptins. Adaptins, together with medium and small subunits, form a heterotetrameric complex called an adaptor, whose role is to promote the formation of clathrin-coated pits and vesicles. The protein encoded by this gene is a gamma-adaptin protein and it belongs to the adaptor complexes large subunits family. This protein along with the complex is thought to function at some trafficking step in the complex pathways between the trans-Golgi network and the cell surface. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. | hsa:8906; | AP-1 adaptor complex [GO:0030121]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; Golgi-associated vesicle [GO:0005798]; membrane [GO:0016020]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; cargo adaptor activity [GO:0140312]; clathrin adaptor activity [GO:0035615]; Golgi to vacuole transport [GO:0006896]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] | 17553870_These results demonstrate that HBV exploits the multivesicular bodies machinery with the aid of gamma 2-adaptin. 18772139_gamma2-adaptin's ubiquitin-interacting motif mediates a specific physical interaction with the ubiquitin ligase Nedd4 and promotes ubiquitination of gamma2-adaptin 20708039_Data show that gamma2-adaptin in MVB sorting specifically interacts with the ESCRT subunits Vps28 and CHMP2A. 27909244_Depletion of the gamma2 or mu1A (AP1M1) subunits of AP-1, but not of gamma1 (AP1G1), precludes Nef-mediated lysosomal degradation of CD4. | ENSMUSG00000040701 | Ap1g2 | 237.239100 | 0.6556705 | -0.608957013 | 0.28387071 | 4.51557013576 | 0.0335876900867580555076763459965150104835629463195800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.12380095097063811837578839458728907629847526550292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 179.840893 | 33.030421 | 274.189104 | 50.013973 | |
| ENSG00000214253 | 51024 | FIS1 | protein_coding | Q9Y3D6 | FUNCTION: Involved in the fragmentation of the mitochondrial network and its perinuclear clustering. Plays a minor role in the recruitment and association of the fission mediator dynamin-related protein 1 (DNM1L) to the mitochondrial surface and mitochondrial fission. Can induce cytochrome c release from the mitochondrion to the cytosol, ultimately leading to apoptosis. Also mediates peroxisomal fission. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12783892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12861026, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14996942, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16107562, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16118244, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23283981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23530241}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;Apoptosis;Direct protein sequencing;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Peroxisome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;TPR repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation | The balance between fission and fusion regulates the morphology of mitochondria. TTC11 is a component of a mitochondrial complex that promotes mitochondrial fission (James et al., 2003 [PubMed 12783892]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. | hsa:51024; | cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; peroxisomal membrane [GO:0005778]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; autophagy of mitochondrion [GO:0000422]; calcium-mediated signaling using intracellular calcium source [GO:0035584]; mitochondrial fission [GO:0000266]; mitochondrial fragmentation involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043653]; mitochondrial fusion [GO:0008053]; mitochondrion morphogenesis [GO:0070584]; negative regulation of ATP metabolic process [GO:1903579]; negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion concentration [GO:0032471]; negative regulation of fatty acid transport [GO:2000192]; peroxisome fission [GO:0016559]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043280]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001244]; positive regulation of mitochondrial calcium ion concentration [GO:0051561]; positive regulation of mitochondrial fission [GO:0090141]; positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane [GO:0090314]; protein targeting to mitochondrion [GO:0006626]; regulation of mitochondrion organization [GO:0010821]; release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0001836] | 12783892_hFis1 is part of the mammalian fission machinery and regulation of the fission processes might be involved in apoptotic mechanisms 12861026_regulates mitochondrial fission in mammalian cells through an interaction with the dynamin-like protein DLP1 14705031_Cytosolic domain of fis1 adopts a tetratricopeptide repeat domain fold. 14996942_the level of Fis1 at the mitochondrial surface influences mitochondrial fission events and hence overall mitochondrial morphology within the cell 15024001_hFis1 induces mitochondrial fragmentation and perinuclear clustering in a state of calcium homeostasis 15356267_Fis1, Drp1, and Opa1 have roles in apoptosis 16010987_Fis1 together with dynamin-related protein (Drp1) antogonizes Bcl-2. 16107562_These findings provide the first evidence for a role of Fis1 in peroxisomal fission and suggest that the fission machinery of mitochondria and peroxisomes shares common components. 16118244_TPR region of hFis1 participates in the interaction with DLP1 or DLP1-containing complex and that the first helix (alpha1) of hFis1 is required for mitochondrial fission presumably by regulating DLP1-hFis1 interaction. 16883569_Direct induction of mitochondrial elongation by blocking mitochondrial fission process with Fis1-DeltaTM or Drp1-K38A was sufficient to develop senescent phenotypes with increased Reactive oxygen species production. 16914522_hFis1 is a bifunctional protein that independently regulates mitochondrial fragmentation and endoplasmic reticulum-mediated apoptosis. 17408615_Fis1 plays important roles in peroxisome division and maintenance of peroxisome morphology in mammalian cells, possibly in a concerted manner with Pex11pbeta and DLP1. 17545159_hFis1 and OPA1 modulate cellular senescence 17884824_the concave surface of the Fis1 tetratricopeptide repeat-like domain is evolutionarily conserved to bind the dynamin-like GTPase Dnm1 and not Mdv1 as previously predicted 18515060_Changes correlate with mitochondrial dysfunction rather than with fragmentation, as substantiated by Fis1 mutants with different effects on organelle shape and function 18782765_targeting of hFis1 to peroxisomes and mitochondria are independent events and support a direct, Pex19p-dependent targeting of peroxisomal tail-anchored proteins. 18832378_Fis1 and Mfn1 activities influence mitochondrial signal generation thereby insulin exocytosis. 18845145_oligomerization of hFis1 in the mitochondrial outer membrane plays a role in mitochondrial fission, potentially through participating in fission factor recruitment. 19864424_hFis1 can bind to multiple amino acid sequences selectively, and the tetratricopeptide repeat constitutes the main binding region of hFis1. 20179104_There is a Drp1- and Fis1-induced, and PINK1-mediated protection mechanism in senescent cells. 20428767_we observed interactions between Drp1 and Fis1 in mitochondrial fragmentation induced by increasing mitochondrial calcium 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21183955_The mitochondrial fission protein Fission 1 homologue (Fis1) conveys an apoptosis signal from the mitochondria to the ER by interacting with Bap31 at the ER and facilitating its cleavage into the pro-apoptotic p20Bap31. 22340708_Fis1 and dynamin-related protein (Drp)1 levels are remarkably increased in peripheral blood lymphocytes of Alzheimer's disease patients. 22595523_PEX11 proteins attract both Mff and human Fis1 (hFis1) to their site of action. 22789569_Fis1 activity depends on its ability to interconvert between monomer and dimer species 23077178_Fis1 acts as a mitochondrial recruitment factor for TBC1D15 that is involved in regulation of mitochondrial morphology. 23713734_Fis1 expression is significantly increased in spinal cord in a transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 23907611_Overexpression of FoxM1 and Plk1 in Fis1-depleted cells restores mitotic entry. 23921378_MiD49 and MiD51 can act independently of Mff and Fis1 in Drp1 recruitment and suggest that they provide specificity to the division of mitochondria. 24416201_PDCD7, Ang2 and FIS1 may indicate a more aggressive form and poor prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia. 25822260_Results show that Fis1 is significantly overexpressed in malignant oncocytomas. 25843291_Study revealed that a novel mitochondrial fission pathway composed of miR-483-5p and FIS1 regulates cisplatin sensitivity. 27497958_Fis1 depletion in osteoarthritis impairs chondrocyte survival and peroxisomal and lysosomal function. 29335339_inhibition of Drp1/Fis1 interaction by a selective peptide inhibitor, P110, led to a significant reduction in reactive oxygen species levels, and to improvement in mitochondrial structure and functions. 29910151_data suggest a model in which leukemia stem cells co-opt AMPK/FIS1-mediated mitophagy as a means to maintain stem cell properties that may be otherwise compromised by the stresses induced by oncogenic transformation 30404157_we found that differential expression of BAK1, FIS1, and SFN were altered across the Barrett's disease sequence and manipulation of these genes elicited significant effects on mitochondrial membrane potential. 30555023_FIS1 and PDCD7 expression are considered independent risk factors and should be integrated into the current acute myeloid leukemia stratification system 30566949_Glomerular overproduction of Drp1, phospho-Drp1 (Ser 616) and Fis1 occurred mainly in children with membranous nephropathy. 31053718_Study demonstrated that the STX17 initiates mitophagy upon depletion of outer mitochondrial membrane protein Fis1. Fis1 loss results in aberrant STX17 accumulation on mitochondria, which exposes the N terminus and promotes self-oligomerization to trigger mitophagy. Findings uncover a PINK1/Parkin-independent mitophagic mechanism in which outer mitochondrial membrane protein Fis1 regulates mitochondrial quality control. 31482366_In human EPCs, down-regulation of Fis1 is involved in mitochondrial dysfunction and contributes to the impaired activity of EPCs during the senescence process. Enhanced expression of Fis1 in senescent EPCs restores the youthful phenotype. 31843624_Genome-wide synthetic lethal CRISPR screen identifies FIS1 as a genetic interactor of ALS-linked C9ORF72. 33258025_Human skeletal muscle mitochondrial dynamics in relation to oxidative capacity and insulin sensitivity. 33841340_Mitochondrial Fission Protein 1: Emerging Roles in Organellar Form and Function in Health and Disease. 33890233_FIS1 Overexpression Is Correlated with Tumor Metastasis in Gastric Adenocarcinoma. 34848680_Fis1 phosphorylation by Met promotes mitochondrial fission and hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. 35275026_Iron chelation promotes mitophagy through SENP3-mediated deSUMOylation of FIS1. 35290083_DNA-PKcs interacts with and phosphorylates Fis1 to induce mitochondrial fragmentation in tubular cells during acute kidney injury. 35678336_PEX11beta and FIS1 cooperate in peroxisome division independently of mitochondrial fission factor. 36044022_Mid51/Fis1 mitochondrial oligomerization complex drives lysosomal untethering and network dynamics. | ENSMUSG00000019054 | Fis1 | 203.730032 | 0.8827619 | -0.179903760 | 0.15168523 | 1.40496137748 | 0.2358946374651103849995337213840684853494167327880859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.45970858040407536204696725690155290067195892333984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 191.602800 | 19.176023 | 217.699384 | 21.708725 | |
| ENSG00000214655 | 23053 | ZSWIM8 | protein_coding | A7E2V4 | FUNCTION: Substrate recognition component of a SCF-like E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex that promotes target-directed microRNA degradation (TDMD), a process that mediates degradation of microRNAs (miRNAs) (PubMed:33184234, PubMed:33184237). The SCF-like E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex acts by catalyzing ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of AGO proteins (AGO1, AGO2, AGO3 and/or AGO4), thereby exposing miRNAs for degradation (PubMed:33184234, PubMed:33184237). Specifically recognizes and binds AGO proteins when they are engaged with a TDMD target (PubMed:33184234). May also act as a regulator of axon guidance: specifically recognizes misfolded ROBO3 and promotes its ubiquitination and subsequent degradation (PubMed:24012004). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24012004, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33184234, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33184237}. | Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger | PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33184234, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33184237}. | Enables ubiquitin ligase-substrate adaptor activity. Involved in positive regulation of miRNA catabolic process; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; and protein ubiquitination. Part of Cul3-RING ubiquitin ligase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:23053; | Cul2-RING ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0031462]; Cul3-RING ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0031463]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; ubiquitin ligase-substrate adaptor activity [GO:1990756]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; positive regulation of miRNA catabolic process [GO:2000627]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] | 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 33184234_A ubiquitin ligase mediates target-directed microRNA decay independently of tailing and trimming. 33184237_The ZSWIM8 ubiquitin ligase mediates target-directed microRNA degradation. 34686700_ZSWIM8 is a myogenic protein that partly prevents C2C12 differentiation. 35940847_The conserved Pelado/ZSWIM8 protein regulates actin dynamics by promoting linear actin filament polymerization. | ENSMUSG00000021819 | Zswim8 | 298.704588 | 1.1292272 | 0.175335837 | 0.25577254 | 0.46680363075 | 0.4944613347104243605834028585377382114529609680175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.70870287104044082937548409972805529832839965820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 302.396588 | 48.709001 | 269.283901 | 43.252999 |
| ENSG00000219626 | 375190 | FAM228B | protein_coding | P0C875 | Reference proteome | hsa:375190; | ENSMUSG00000050545 | Fam228b | 66.426052 | 0.4964474 | -1.010287285 | 1.01248135 | 0.88755896596 | 0.3461396632856236221797985308512579649686813354492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.57801186253117087243680316532845608890056610107421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 47.524932 | 25.360804 | 93.341038 | 49.774911 | |||||
| ENSG00000221978 | 81669 | CCNL2 | protein_coding | Q96S94 | FUNCTION: Involved in pre-mRNA splicing. May induce cell death, possibly by acting on the transcription and RNA processing of apoptosis-related factors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14684736, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18216018}. | Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cyclin;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the cyclin family. Through its interaction with several proteins, such as RNA polymerase II, splicing factors, and cyclin-dependent kinases, this protein functions as a regulator of the pre-mRNA splicing process, as well as in inducing apoptosis by modulating the expression of apoptotic and antiapoptotic proteins. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. | hsa:81669; | cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex [GO:0000307]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity [GO:0016538]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of centrosome cycle [GO:0046605]; regulation of RNA splicing [GO:0043484]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] | 14623875_characterize cyclin L2 as a highly mobile component of nuclear speckles and suggest that DYRK1A may regulate splicing by phosphorylation of cyclin L2 17494991_Data show that a green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion protein of cyclin L1, in contrast to cyclin L2, was not mobile within the nucleus of living COS7 cells. 18216018_CDK11(p110) interacts physically and functionally with cyclin Lalpha and -beta isoforms and SR proteins to regulate splicing. 24218572_CDK10/cyclin M is a protein kinase that controls ETS2 degradation and is deficient in STAR syndrome. 25532805_Therefore, cyclin L2-mediated control of SAMHD1 levels in macrophages supports HIV-1 replication. 31852782_The Dual-Specificity Kinase DYRK1A Modulates the Levels of Cyclin L2 To Control HIV Replication in Macrophages. 33849617_CLK1/SRSF5 pathway induces aberrant exon skipping of METTL14 and Cyclin L2 and promotes growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer. 34937039_Exosome miR-23a-3p from Osteoblast Alleviates Spinal Cord Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Down-Regulating KLF3-Activated CCNL2 Transcription. | ENSMUSG00000029068 | Ccnl2 | 973.438886 | 0.7819331 | -0.354882869 | 0.10277588 | 11.89612445457 | 0.0005625086000855583677829341304743593354942277073860168457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00464484669303234440351779710454138694331049919128417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 853.902851 | 51.133998 | 1097.691406 | 65.034785 | |
| ENSG00000233384 | CNIH3-AS2 | lncRNA | 23.090354 | 0.5097137 | -0.972241020 | 0.42402297 | 5.06838417883 | 0.0243660861141348460134903319840304902754724025726318359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.09777189115448027545429710016833269037306308746337890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 17.768124 | 4.210815 | 33.818026 | 8.297740 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000233461 | 122526782 | lncRNA | 26.391277 | 1.8548554 | 0.891306751 | 0.29660431 | 9.06321978402 | 0.0026080232450416511447155443192968959920108318328857421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.01685035988528527442498194943709677318111062049865722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 35.358367 | 6.031562 | 19.165135 | 3.492888 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000234127 | 7726 | TRIM26 | protein_coding | Q12899 | FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase which regulates the IFN-beta production and antiviral response downstream of various DNA-encoded pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs). Promotes nuclear IRF3 ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Bridges together TBK1 and NEMO during the innate response to viral infection leading to the activation of TBK1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25763818, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26611359}. | Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Immunity;Innate immunity;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the tripartite motif (TRIM) family. The TRIM motif includes three zinc-binding domains, a RING, a B-box type 1 and a B-box type 2, and a coiled-coil region. The protein localizes to cytoplasmic bodies. Although the function of the protein is unknown, the RING domain suggests that the protein may have DNA-binding activity. The gene localizes to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I region on chromosome 6. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2011]. | hsa:7726; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of viral entry into host cell [GO:0046597]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; suppression of viral release by host [GO:0044790] | 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20593013_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22294275_The study reports no associations between polymorphisms in TRIM26 and the risk of aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease in both logistic and regression analyses. 22433715_In addition to confirming one of the top findings in the meta-analysis, TRIM26, RNF5 and HLA-DRB3 have been identified as potential candidate genes for schizophrenia. 26043685_Down-regulation of TRIM26 is associated with worse prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 26611359_Autoubiquitination of TRIM26 links TBK1 to NEMO in RLR-mediated innate antiviral immune response 29610152_This paper demonstrates the importance of TRIM26 in regulating the cellular levels of NTH1, particularly under conditions of oxidative stress. 29956500_We have identified a novel gene TRIM26 and a novel SNP rs117565607_A associated with NPC risk by regulating transcriptional process and established a new functional link between TRIM26 downregulation and low immune response in NPC. 30927273_TRIM26 overexpression inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in Papillary thyroid carcinoma cells. TRIM26 overexpression also suppressed the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition process. 32052576_Overexpression of tripartite motif containing 26 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell growth by suppressing PI3K/AKT signaling. 33305515_Inhibition of tripartite motif containing 26 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell growth. 33419081_TRIM26 Facilitates HSV-2 Infection by Downregulating Antiviral Responses through the IRF3 Pathway. 33549581_Knockdown of TRIM26 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells through the Akt/GSK3beta/beta-catenin pathway. 34732716_Competitive binding of E3 ligases TRIM26 and WWP2 controls SOX2 in glioblastoma. 35617983_Comprehensive analysis of expression profiles and prognosis of TRIM genes in human kidney clear cell carcinoma. | ENSMUSG00000024457 | Trim26 | 144.642557 | 0.7471238 | -0.420580787 | 0.17381329 | 5.84498337238 | 0.0156215215690456744879188732966213137842714786529541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.06932545802912783161620069449782022275030612945556640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 125.635138 | 16.356084 | 168.758907 | 21.567680 | |
| ENSG00000235173 | 51236 | HGH1 | protein_coding | Q9BTY7 | Acetylation;Direct protein sequencing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | hsa:51236; | ENSMUSG00000022554 | Hgh1 | 235.677778 | 0.9180761 | -0.123314316 | 0.10685336 | 1.33219889493 | 0.2484144085549509495258746483159484341740608215332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.47496182980681433960512549674604088068008422851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 226.969574 | 17.173046 | 248.333850 | 18.482706 | |||||
| ENSG00000237187 | 441094 | NR2F1-AS1 | lncRNA | 29602203_results conclude that NR2F1-AS1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) oxaliplatin resistance through targeting miR-363-ABCC1 pathway, providing a vital theoretic mechanism and therapeutic target for HCC chemoresistance. 31109400_Results demonstrated that NR2F1-AS1 was highly expressed in EC, which involved in the proliferation and migration of EC cells through downregulation of miR-363 to target SOX4 and regulating PI3K/AKT/GSK-3(beta) pathway. 31692033_NR2F1-AS1 regulated miR-423-5p/SOX12 to promote proliferation and invasion of papillary thyroid carcinoma. 32329844_LncRNA NR2F1-AS1 promotes proliferation and metastasis of ESCC cells via regulating EMT. 32392629_Long non-coding NR2F1-AS1 is associated with tumor recurrence in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers. 32407174_LncRNA NR2F1-AS1 Regulates miR-371a-3p/TOB1 Axis to Suppress Proliferation of Colorectal Cancer Cells. 32548873_lncRNA NR2F1-AS1 promotes breast cancer angiogenesis through activating IGF-1/IGF-1R/ERK pathway. 32945459_Long noncoding RNA NR2F1AS1 facilitates the osteosarcoma cell malignant phenotype via the miR4855p/miR2185p/BIRC5 axis. 33378023_Long non-coding RNA NR2F1-AS1 promoted neuroblastoma progression through miR-493-5p/TRIM2 axis. 33822440_STAT3 activates the transcription of lncRNA NR2F1-AS1 to promote the progression of melanoma via regulating the miR-493-5p/GOLM1 axis. 34475402_Long non-coding RNA NR2F1-AS1 induces breast cancer lung metastatic dormancy by regulating NR2F1 and DeltaNp63. 35082283_The EMT-induced lncRNA NR2F1-AS1 positively modulates NR2F1 expression and drives gastric cancer via miR-29a-3p/VAMP7 axis. 35083026_NR2F1-AS1 Acts as an Oncogene in Breast Cancer by Competitively Binding with miR-641. 35094651_LncRNA nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group F member 1 antisense RNA 1 (NR2F1-AS1) aggravates nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation. 35283481_Hypoxia-induced long noncoding RNA NR2F1-AS1 maintains pancreatic cancer proliferation, migration, and invasion by activating the NR2F1/AKT/mTOR axis. | 21.257750 | 0.6928533 | -0.529378135 | 0.43118560 | 1.43792442242 | 0.2304755095061130909517288500865106470882892608642578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.45285734330264221236816979399009142071008682250976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 20.783299 | 8.461507 | 26.700679 | 10.268883 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000237491 | LINC01409 | lncRNA | 17.087333 | 0.6973598 | -0.520024959 | 0.77673111 | 0.41319368641 | 0.5203529510915926303837863997614476829767227172851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.72852538082966655785810417000902816653251647949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 9.715159 | 5.485771 | 14.409047 | 7.851678 | |||||||||||
| ENSG00000242086 | 727956 | MUC20-OT1 | lncRNA | 195.106458 | 0.5947912 | -0.749544677 | 0.15180740 | 24.28046379769 | 0.0000008327944956089469493446452927343237604418391129001975059509277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00001393436531648080037694772959078193252935307100415229797363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 142.073357 | 12.886313 | 239.796238 | 21.049744 | ||||||||||
| ENSG00000243927 | 64968 | MRPS6 | protein_coding | P82932 | 3D-structure;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;Ribonucleoprotein;Ribosomal protein | Mammalian mitochondrial ribosomal proteins are encoded by nuclear genes and help in protein synthesis within the mitochondrion. Mitochondrial ribosomes (mitoribosomes) consist of a small 28S subunit and a large 39S subunit. They have an estimated 75% protein to rRNA composition compared to prokaryotic ribosomes, where this ratio is reversed. Another difference between mammalian mitoribosomes and prokaryotic ribosomes is that the latter contain a 5S rRNA. Among different species, the proteins comprising the mitoribosome differ greatly in sequence, and sometimes in biochemical properties, which prevents easy recognition by sequence homology. This gene encodes a 28S subunit protein that belongs to the ribosomal protein S6P family. Pseudogenes corresponding to this gene are found on chromosomes 1p and 12q. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. | hsa:64968; | mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial small ribosomal subunit [GO:0005763]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; small ribosomal subunit [GO:0015935]; small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding [GO:0070181]; structural constituent of ribosome [GO:0003735]; mitochondrial translation [GO:0032543]; translation [GO:0006412] | 19198609_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20738937_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20971364_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 33964376_Mitochondrial ribosomal small subunit proteins (MRPS) MRPS6 and MRPS23 show dysregulation in breast cancer affecting tumorigenic cellular processes. | ENSMUSG00000039680 | Mrps6 | 296.402213 | 0.9216965 | -0.117636370 | 0.09109503 | 1.66833337756 | 0.1964819135623509793742158535678754560649394989013671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.41069769977737080601798425050219520926475524902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 286.590953 | 16.940623 | 312.461561 | 18.108215 | ||
| ENSG00000247774 | 100233209 | PCED1B-AS1 | lncRNA | 31680313_LncRNA PCED1B-AS1 activates the proliferation and restricts the apoptosis of glioma through cooperating with miR-194-5p/PCED1B axis. 34036383_Long noncoding RNA PCED1BAS1 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression by regulating the miR4113p/HIF1alpha axis. 34516330_Long non-coding RNA PCED1B antisense RNA 1 promotes gastric cancer progression via modulating microRNA-215-3p / C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 1 axis. 35997114_LncRNA PCED1B-AS1 Upregulation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Regulation of the miR-10a/BCL6 Axis to Promote Cell Proliferation. 36274134_LncRNA PCED1B-AS1 knockdown inhibits osteosarcoma via methylation-mediated miR-10a downregulation. 36418980_Upregulation of PCED1B-AS1 in proliferative diabetic retinopathy and its involvement in retinal vascular endothelial cell proliferation. | 66.849475 | 0.7910876 | -0.338090584 | 0.26036293 | 1.67713311371 | 0.1953058301964629428493225304919178597629070281982421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.40970875116798494142145159457868430763483047485351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 61.514085 | 8.922670 | 78.204014 | 11.289925 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000248323 | 100505994 | LUCAT1 | lncRNA | 23672216_these results identify a novel and intriguing new noncoding RNA that may act downstream of NRF2 to regulate gene expression and mediate oxidative stress protection in airway epithelial cells. 28423699_lncRNA LUCAT1 expression is significantly up-regulated in NSCLC tissues and cell lines. Its abnormal expression can predict a poor prognosis of NSCLC patients, and it may be an independent prognostic marker. 29089067_lncRNA LUCAT1 could act as an oncogenic lncRNA that promotes glioma tumorigenesis via regulating miR-375. 29170124_Rescue experiments confirmed the combined role of LUCAT1, miR-200c and ABCB1 on osteosarcoma proliferation, invasion and methotrexate resistance. Overall, results indicate the vital role of LUCAT1 in the methotrexate resistance regulation through miR-200c/ABCB1 pathway, providing a novel insight and treatment strategy for osteosarcoma drug resistance. 29247823_Data show that long noncoding RNA LUCAT1 activated DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1), a major DNA methylation protein, to repress the expression of tumor-suppressor genes, leading to the development and progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). 29932248_Results indicate that highly expressed LUCAT1 acts as an oncogenic lncRNA that promotes the tumorigenesis and progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) through the miR-495-3p-SATB1 axis, indicating that LUCAT1 could be a useful marker for ccRCC. 30032137_LUCAT1 promoted proliferation and invasion in ccRCC cells partly through inducing the phosphorylation of AKT and suppressing the phosphorylation of GSK-3beta. 30479162_it was found that LUCAT1 was activated by STAT3 and promoted cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in HB through modulation of the miR-301b/STAT3 axis. 30588744_LUCAT1 inhibited the phosphorylation of Annexin A2 (ANXA2) to reduce the degradation of ANXA2-S100A10 heterotetramer (AIIt). 30690837_our findings indicate that suppression of LUCAT1 induces CRC cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by binding UBA52 and activating the RPL40-MDM2-p53 pathway. These results implicate LUCAT1 as a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for CRC. 30831032_SP1-induced up-regulation of lncRNA LUCAT1 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of cervical cancer by sponging miR-181a 31300015_LUCAT1 might be a significant biomarker to evaluate prognosis in breast cancer survivors. LUCAT1 increased BCCs stem-like properties and BCSCs stemness by competitively binding miR-5582-3p with TCF7L2 and enhancing the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 31399501_LncRNA LUCAT1 facilitates tumorigenesis and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer through modulating miR-5702. 31577719_Up-regulation of LUCAT1 was significantly related to worse overall survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma 31591432_LncRNA LUCAT1 as a novel prognostic biomarker for patients with papillary thyroid cancer. 31635802_the expression of lnc-LUCAT1 was highly up-regulated in breast cancer tissues and cell lines. Over-expression of lnc-LUCAT1 enhanced cell proliferation, migration and invasion in breast cancer cell lines. 31646588_Knockdown of long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 reverses high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte injury via targeting CYP11B2. 31769911_LUCAT1 contributes to MYRF-dependent smooth muscle cell apoptosis and may facilitate aneurysm formation via the sequestration of miR-199a-5p. 31789465_LncRNA LUCAT1 contributes to cell proliferation and migration in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via sponging miR-539. 31957853_Downregulated long noncoding RNA LUCAT1 inhibited proliferation and promoted apoptosis of cardiomyocyte via miR-612/HOXA13 pathway in chronic heart failure. 31964396_Hypoxia induced LUCAT1/PTBP1 axis modulates cancer cell viability and chemotherapy response. 31968402_ELF1-mediated LUCAT1 promotes choroidal melanoma by modulating RBX1 expression. 32141534_LncRNA LUCAT1 promotes proliferation of ovarian cancer cells by regulating miR-199a-5p expression. 32812490_Long Noncoding RNA LUCAT1 Promotes Multiple Myeloma Cell Growth by Regulating the TGF-beta Signaling Pathway. 32844284_Serum LUCAT1 implicates the pathogenesis of muscle-invasive bladder cancer via targeting miR-199a-5p and miR-199b-5p. 32945379_Long noncoding RNA LUCAT1 contributes to cisplatin resistance by regulating the miR514a3p/ULK1 axis in human nonsmall cell lung cancer. 32998707_LncRNA LUCAT1/miR-181a-5p axis promotes proliferation and invasion of breast cancer via targeting KLF6 and KLF15. 33097685_The long noncoding RNA LUCAT1 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation by antagonizing Nucleolin to regulate MYC expression. 33215214_Lung cancerassociated transcript 1 facilitates tumorigenesis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma through the targeted inhibition of miR493. 33282949_Downregulation of Long Noncoding RNA LUCAT1 Suppresses the Migration and Invasion of Bladder Cancer by Targeting miR-181c-5p. 33311506_The long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 is a negative feedback regulator of interferon responses in humans. 33426083_Knockdown of the Long Noncoding RNA LUCAT1 Inhibits High-Glucose-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through the miR-199a-5p-ZEB1 Axis in Human Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. 33541136_MiR-133b inhibits colorectal cancer metastasis via lncRNA-LUCAT1. 33577028_The progression of pancreatic cancer cells is promoted by a long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 by activating AKT phosphorylation. 33787082_LUCAT1 as an oncogene in tongue squamous cell carcinoma by targeting miR-375 expression. 34125980_Expression of long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its potential functions in regulating cigarette smoke extract-induced 16HBE cell proliferation and apoptosis. 34272987_Knockdown of lncRNA LUCAT1 attenuates sepsisinduced myocardial cell injury by sponging miR-642a. 34383427_IncRNA LUCAT1 acts as a Potential Biomarker and Demonstrates Malignant Biological Behaviors in Gastric Cancer. 34414854_Long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 inhibits myocardial oxidative stress and apoptosis after myocardial infarction via targeting microRNA-181a-5p. 34526564_Concomitant and decoupled effects of cigarette smoke and SCAL1 upregulation on oncogenic phenotypes and ROS detoxification in lung adenocarcinoma cells. 35441392_LncRNA PVT1 is increased in renal cell carcinoma and affects viability and migration in vitro. 35711895_lncRNA LUCAT1/ELAVL1/LIN28B/SOX2 Positive Feedback Loop Promotes Cell Stemness in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. | 574.935324 | 0.6425182 | -0.638190790 | 0.15708273 | 16.37531699328 | 0.0000519574597641572985822107366704614150876295752823352813720703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00057498492656727240735642370239588672120589762926101684570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 493.094274 | 68.760955 | 768.988467 | 106.694193 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000250479 | 400916 | CHCHD10 | protein_coding | Q8WYQ3 | FUNCTION: May be involved in the maintenance of mitochondrial organization and mitochondrial cristae structure. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24934289}. | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Mitochondrion;Neurodegeneration;Reference proteome;Transit peptide | This gene encodes a mitochondrial protein that is enriched at cristae junctions in the intermembrane space. It may play a role in cristae morphology maintenance or oxidative phosphorylation. Mutations in this gene cause frontotemporal dementia and/or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-2. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. Related pseudogenes have been identified on chromosomes 7 and 19. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2014]. | hsa:400916; | MICOS complex [GO:0061617]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; maintenance of protein location in nucleus [GO:0051457]; maintenance of synapse structure [GO:0099558]; mitochondria-nucleus signaling pathway [GO:0031930]; mitochondrial nucleoid organization [GO:0090144]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; oxidative phosphorylation [GO:0006119]; positive regulation of cristae formation [GO:1903852]; positive regulation of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1901030]; positive regulation of mitochondrial transcription [GO:1903109]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; stabilization of membrane potential [GO:0030322] | 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20888800_CHCHD10 and GBAS are involved in oxidative phosphorylation; CHCHD10 plays role in complex IV activity. 20888800_Functional annotation of CHCHD10 as mitochondrial protein with function related to cytochrome-c-oxidase (complex IV) activity. 24934289_Mitochondrial disease (CHCHD10 mutation) may be at the origins of some frontotemporal dementia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis phenotypes. 25155093_CHCHD10 encodes a protein located in the mitochondrial intermembrane space and is likely involved in mitochondrial genome stability and maintenance of cristae junctions. 25193783_findings identify a novel gene causing mitochondrial myopathy, thereby expanding the spectrum of mitochondrial myopathies caused by nuclear genes. Our findings also suggest a role for CHCHD10 in the morphologic remodeling of the mitochondria. 25428574_The results of this study support this estimation, and suggest that the real prevalence of CHCHD10-related disease in Finland is probably much higher. 25726362_CHCHD10 mutations account for approximately 1% of Italian ALS patients and are a cause of disease in subjects without dementia or other atypical clinical signs. 26224640_Even within the same family, the p.Gly66Val variant can cause variable phenotypes ranging from CMT2-type axonal neuropathy to spinal muscular atrophy, which may also present as an ALS-like disease. 26344877_CHCHD10 P34S variant is not associated with ALS in a UK cohort of familial and sporadic patients. 26362910_CHCHD10 was found to not be a highly penetrant pathogenic variant for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. 26666268_Disassembly of the mitochondrial contact site and cristae organizing system complex secondary to CHCHD10 mutations leads to mitochondrial dysfunction including inhibition of apoptosis. 27056076_CHCHD10 gene mutation appears to be an uncommon cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Chinese populations. 27077676_No mutations were identified in CHCHD10 in ALS cases of Chinese ancestry. 27095681_CHCHD10 is not a primary cause of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in France. 27578015_that CHCHD10 mutation was presented in different types of dementia 27810918_In Finnish cohorts with motor neuron disease, heterozygous mutation c.197G>T p.G66V in CHCHD10 was detected in 23 patients. In two siblings with a cramping disorder and mitochondrial pathology, heterozygous c.100C>T p.P34S was detected. 28069311_Its mutations were seen in patients with ALS and frontotemporal dementia. 28108040_Its mutation is not arelevant cause of Parkinson's disease in Italian population. 28318595_Its mutations are found in Chinese patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 28462717_Screening of MAPT, GRN and CHCHD10 genes in Chinese patients with frontotemporal dementia (FTD) identified about 4.9% mutation carriers. Among the known FTD causative genes tested, MAPT and CHCHD10 play the most important roles in Chinese patients with sporadic FTD. 28585542_CHCHD10 mutations have a role in cytoplasmic TDP-43 accumulation and synaptic integrity 29112723_Evidence obtained from in vitro and in vivo studies suggest that CHCHD10 mutants cause disease through a gain of toxic function mechanism, rather than a loss of function. 29121267_Results indicate that CHCHD10-CHCHD2 complexes are necessary for efficient mitochondrial respiration, and support a role for mitochondrial dysfunction in some patients with ALS. 29249678_This studt did not found statistical differences in genotypic distribution between Parkinson's disease cases and control individuals for these variants in CHCHD10. 29315381_Data show that the CHCHD10 mutations p.R15L and p.G66V cause motoneuron disease primarily based on haploinsufficiency of CHCHD10. 29519717_Homozygous Pro96Thr mutation in CHCHD10 might be pathogenic to mitochondrial myopathy. 29540477_results reveal that CHCHD10 positively regulates mitochondrial respiration and contributes to transcriptional repression of ORE-containing genes in the nucleus, and that genetic CHCHD10 variants are impaired in these activities. 29789341_A novel CHCHD10 mutation is linked with mitochondrial import deficit in ALS. 30014597_This study shows that routine testing for CHCHD10 mutations in pure ALS is not recommended and illustrates the importance of sufficient genetic and functional evidence in establishing pathogenicity of genetic variants 30084972_these findings demonstrate that differences in the stability and mutual affinity of CHCHD2 and CHCHD10 regulate their heterodimerization in response to mitochondrial distress, revealing an unanticipated link between Parkinson Disease and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis/Frontotemporal Dementia pathogenesis. 31690696_genetic variation is not a common cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia in Australia, but neuron-specific role and a loss of function may be 32369233_CHCHD10-regulated OPA1-mitofilin complex mediates TDP-43-induced mitochondrial phenotypes associated with frontotemporal dementia. 32437855_ALS and Parkinson's disease genes CHCHD10 and CHCHD2 modify synaptic transcriptomes in human iPSC-derived motor neurons. 32651855_Meta-analysis of the association between CHCHD10 Pro34Ser variant and the risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 33749723_Multi-OMICS study of a CHCHD10 variant causing ALS demonstrates metabolic rewiring and activation of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial unfolded protein responses. 35349255_Structures of the Wild-Type and S59L Mutant CHCHD10 Proteins Important in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis-Frontotemporal Dementia. 35656794_CHCHD10 and SLP2 control the stability of the PHB complex: a key factor for motor neuron viability. 35709007_CHCHD10 Modulates Thermogenesis of Adipocytes by Regulating Lipolysis. 35787294_Modulation of synaptic plasticity, motor unit physiology, and TDP-43 pathology by CHCHD10. | ENSMUSG00000049422 | Chchd10 | 80.762525 | 0.8812203 | -0.182425287 | 0.20757247 | 0.76971048841 | 0.3803066299510958758745005070522893220186233520507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.61174438129667996211225045044557191431522369384765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 75.612986 | 10.174638 | 85.771006 | 11.424185 | |
| ENSG00000253853 | lncRNA | 10.459958 | 1.6681374 | 0.738238117 | 0.44687192 | 2.69682834331 | 0.1005480894154651694272217810066649690270423889160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.26563356354580447415969501889776438474655151367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 12.932924 | 4.445099 | 7.727651 | 2.566731 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000254873 | lncRNA | 165.017084 | 1.2089278 | 0.273728077 | 0.16227732 | 2.84004970905 | 0.0919413695473881298347862411901587620377540588378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.25006336325663330866220235293440055102109909057617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 179.281713 | 20.360299 | 148.823832 | 17.160063 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000254996 | 404734 | ANKHD1-EIF4EBP3 | protein_coding | H7C0V5 | Reference proteome | The ANKHD1-EIF4EBP3 mRNA is an infrequent but naturally occurring readthrough transcript of the neighboring ANKHD1 and EIF4EBP3 genes. This readthrough transcript encodes a protein composed mostly of the multiple ankyrin repeats, single KH-domain protein, with its C-terminus encoded in a different reading frame from the shared portion of the EIF4EBP3 gene. The significance of this readthrough mRNA and the function of its protein product have not yet been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. | 674.781145 | 1.0561112 | 0.078761746 | 0.07180099 | 1.20291369939 | 0.2727401004360009983962243040878092870116233825683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.50291174860252862988119204601389355957508087158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 683.936787 | 29.357332 | 650.536297 | 27.826655 | |||||||
| ENSG00000257923 | 1523 | CUX1 | protein_coding | Q13948 | FUNCTION: May be involved in intra-Golgi retrograde transport. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15718469}. | Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Disulfide bond;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the homeodomain family of DNA binding proteins. It may regulate gene expression, morphogenesis, and differentiation and it may also play a role in the cell cycle progession. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. | hsa:1523; | Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; intra-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006891] | 11953010_Transfection of keratinocytes with plasmid DNA leads to the loss of detectable DNA-binding activity of CCAAT displacement protein. 12193717_Analysis of flanking sequences of IgH and Ig kappa V region genes show extensive heterogeneity in frequency and location of CDP binding sites and capability of CDP to bind to the nuclear matrix. 12429822_Data report the characterization of a mammalian coiled-coil protein, CASP, a Golgi protein that shares with giantin a conserved histidine in its transmembrane domain. 12522000_Lack of LF expression in the acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line NB4 is associated with the persistent binding of the silencer CCAAT displacement protein (CDP/cut) to the LF promoter in these cells. 12665598_correlation between binding of CDP/Cux to the DNA pol alpha promoter and the stimulation of gene expression 12743282_CDP, in conjunction with one or more viral proteins, binds to the packaging sequences of Adenovirus type 5 to initiate the encapsidation process 12766905_our data suggested that somatic mutations in CDP gene were rare in unselected uterine leiomyomas 15269344_interaction of G9a with a sequence-specific transcription factor that regulates gene repression through CDP/cut. 15950902_CUTL1 plays a central role in coordinating a gene expression program associated with cell motility and tumor progression. 16529788_Binding of E2 at the binding sites play an important role in overcoming inhibition of E1 complex formation caused by the binding of CDP to the origin of replication. 16574653_PKA-induced phosphorylation results in decreased DNA binding affinity of CUTL1 and diminished CUTL1-mediated cell cycle progression and cell motility. 17140660_Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in CUTL1 is associated with myeloid neoplasias 17227781_CUTL1 transcriptionally up-regulates WNT5A on RNA, protein and promoter level. 17369846_Src plays a crucial role in CUTL1-induced tumor cell migration 17496784_CDP inhibits cytokine-induced NF-kappaB-regulated chemokine transcription in melanoma cells 17681953_CUX1 C-terminal proteolytic processing by a caspase enables transcriptional activation in proliferating cells 17682059_Data show that in renal cell carcinoma, the Cut-like homeodomain protein is involved in FIH-1 transcriptional regulation and is controlled by a specific signaling event involving protein kinase C zeta. 17957475_The data strongly suggest that CDP acts as a major suppressor for Human papillomavirus type 16 P670 transcription by binding to the promoter region in the undifferentiated cells 18347061_Genome-wide location analysis revealed that targets common to p110 CUX1 and E2F1 included many genes involved in cell cycle, DNA replication, and DNA repair. 18403643_This result revealed a negative feedback loop whereby CUX1 shuts down the expression of the protease that cleaves it. 18614194_CUX1 showed evidence of association with the HCMV major immediate early regulatory region and inhibited the capacity of the virus to express ie1 and ie2 transcripts, suggesting that this cellular factor regulates MIE gene expression following virus entry. 19015243_study reports that mitotic complex genes Ect2, RacGAP, and MKLP1 are coordinately induced in S phase in proliferating T lymphocytes as well as in epithelial cells, depending upon activity of the CUX1 and E2F1 transcription factors 19361498_Activation of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway by EBV in epithelial cells suggests a novel mechanism of epithelial mesenchymal transition via CUX1 signaling. 19590514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19635798_role of p110 CUX1 in cell motility involves its functions in both activation and repression of transcription 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20442202_data indicate that CUX1 represents an important survival factor downstream of PI3K/Akt, which orchestrates a transcriptional programme mediating resistance to apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. 20689760_GRIA3 plays a role as a mediator of tumor progression in pancreatic cancer downstream CUX1. 20842632_findings show that CUTL1 expression is gradually silenced at the posttranscriptional level during liver development; overexpression and knockdown studies that miR-122 repressed CUTL1 protein expression in HCC cell lines 20848487_Elevated levels of cux1 are associated with inflammatory bowel disease. 21245318_Transcriptional targets of CUX1 involved in DNA replication and bipolar mitosis defined a gene expression signature that, across 12 breast cancer gene expression datasets, was associated with poor clinical outcome. 21330321_we identified a novel CUX1-FGFR1 fusion oncogene in a patient with the 8p11 myeloproliferative syndrome and demonstrated its transforming potential in the Ba/F3 cell line. 21471005_modifications of CUX1 expression lead to aberrant expression of type I collagen, which may provide a molecular basis for fibrogenesis 21674579_screening for mutations in CUX1 using 15 secondary acute myeloid leukemia cases with preceding myeloproliferative neoplasms or loss-of-heterozygosity on chromosome 7q (collaborative study in several countries) 22180456_The data demonstrates that the autism spectrum disorder-associated A-C intronic haplotype of the ENGRAILED2 gene is a transcriptional activator, and both CUX1 and NFIB mediate this activity. 22306263_cux1 is associated with cell functions and human disease. 22438831_we find repression of apoptosis regulators by Cux1 in human cancer cells. 22584459_Our results provide the first evidence that polymorphisms of the CUX1 gene may be associated with response to antidepressant treatment in Japanese patients with MDD. 22965931_Authors found that both chromosomal inversions target the cut-like homeobox 1 (CUX1) gene on chromosomal band 7q22.1 in a way which is functionally equivalent to the more frequently observed del(7q) cases. 23085261_Cutl1 played transcriptional level mediated by signal transduction, translational level mediated by miR122, posttranslational level such as phosphorylation, de-phosphorylation, acetylation and proteolytic cleavage. 23212519_Data indicate CUX1 as a conserved, haploinsufficient tumor suppressor frequently deleted in myeloid neoplasms. 23255599_overexpression of active CUTL1 significantly resulted in increased cancer tissue response to chemotherapy and therefore inhibited growth, whereas knockdown of CUTL1 conferred resistance to chemotherapy. 23590133_p110 CUX1 can mediate transcriptional repression or activation of specific genes when bound at variable distances from the transcription start site. 24316979_Cux1 is a tumor suppressor and inactivating CUX1 mutations promote tumorigenesis. 24336331_Authors identified CUX1 as an important modulator of the TAMs phenotype and function by modulating NF-kappaB-dependent cytokines. 24429498_Loss of CUX1 is associated with myeloid neoplasms. 24686420_Suggest that CUTL1 may regulate the proliferation of malignant melanoma by modulating the expression of cell cycle-related proteins. 25096634_Results show that Cux1 is expressed in cerebellar granule cell precursors and downregulated as they terminally differentiate; coexpression analysis in human medulloblastomas suggests another function related to DNA integrity and stability 25124494_This is a novel gene implicated in atrial fibrillation 25159843_CASP is specifically cleaved by granzymeB. 25190083_CUX1 expression is associated with tumour progression and tumor burden. [Review] 25248790_High CUX1 expression is associated with metastasis in pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. 27956696_a positive feedback loop between Snail-nuclear Cat L-CUX1 drives epithelial mesenchymal transition, is reprted. 28147323_our results have uncovered the requirement for CUX1 expression in cancer cells with elevated reactive oxygen species levels 28369554_CUX1 is enriched at sites of DNA looping, as determined by Hi-C analysis, and these loops connect CUX1 to the promoters of regulated genes. 28405678_Study found are higher CUTL1 expression level in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tissues and showed that CUTL1 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in NSCLC. 28698143_Therefore, we show for the first time that the nuclear localization of Cat L and its substrate Cux1can be positively regulated by Snail NLS and importin beta1, suggesting that Snail, Cat L and Cux1 all utilize importin beta1 for nuclear import. 29036362_High CUX1 expression is associated with resistance of glioblastoma cells to temozolomide. 29246726_the findings demonstrated that mutated K-ras promotes cathepsin L expression and plays a pivotal role in EMT of human lung cancer. The regulatory effect of IR-induced cathepsin L on lung cancer invasion and migration was partially attributed to the Cathepsin L /CUX1-mediated EMT signaling pathway 29363918_Our data indicate that there exist frameshift mutations of CUX1 and SIRT1 genes as well as intratumoral heterogeneity of CUX1 frameshift mutation in high microsatellite instability cancers, which together might play a role in tumorigenesis of gastric cancer and colorectal cancer with high microsatellite instability 30014507_Haploinsufficiency of CUX1, causes an isolated phenotype of developmental delay or intellectual disability with possible catch-up development. 30964885_CUX1 activated by Snail-Cat L signaling may contribute to TNBC via ER-alpha repression. 31320321_These functional findings may explain why samples with either CUX1 (MT) or low CUX1 expression coincided with significantly higher numbers of somatic hits by whole-exome sequencing. Our findings implicate the DNA repair dysfunction resulting from CUX1 lesions in the pathogenesis of MNs, in which they lead to a mutator phenotype. 32079724_In fibroblasts, IL-17A response depends on CUX1 and IkappaBzeta to engage the NF-kappaB complex to produce chemoattractants for neutrophil and monocyte recruitment. 32271392_Regulation of Janus Kinase 2 by an Inflammatory Bowel Disease Causal Non-coding Single Nucleotide Polymorphism. 33542188_Overexpressed P75CUX1 promotes EMT in glioma infiltration by activating beta-catenin. 33741902_N6-methyladenosine modification of circCUX1 confers radioresistance of hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma through caspase1 pathway. 33931647_Cut-like homeobox 1 (CUX1) tumor suppressor gene haploinsufficiency induces apoptosis evasion to sustain myeloid leukemia. 34579723_p113 isoform encoded by CUX1 circular RNA drives tumor progression via facilitating ZRF1/BRD4 transactivation. 34661647_Clinically Significant CUX1 Mutations Are Frequently Subclonal and Common in Myeloid Disorders With a High Number of Co-mutated Genes and Dysplastic Features. 34997000_Genomic studies controvert the existence of the CUX1 p75 isoform. | ENSMUSG00000029705 | Cux1 | 368.261061 | 0.9494553 | -0.074828016 | 0.08564381 | 0.76328701642 | 0.3823018128406653337592047137150075286626815795898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.61305029898145446676238634609035216271877288818359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 348.159924 | 16.298799 | 368.259012 | 17.280067 | |
| ENSG00000260537 | 55308 | protein_coding | H3BN59 | ATP-binding;Helicase;Hydrolase;Nucleotide-binding;Proteomics identification;Reference proteome | ATP binding [GO:0005524]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; RNA helicase activity [GO:0003724] | 167.286807 | 0.8341768 | -0.261574842 | 0.14503103 | 3.25243626719 | 0.0713173812909626142486629873928904999047517776489257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.21050591464401458008381951003684662282466888427734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 154.112638 | 19.195249 | 185.294015 | 22.827611 | ||||||||
| ENSG00000266714 | 80022 | MYO15B | protein_coding | Q96JP2 | FUNCTION: Unknown, due to the absence of a functional motor domain. | 3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome;SH3 domain | Predicted to enable ATP binding activity; actin binding activity; and cytoskeletal motor activity. Predicted to be located in brush border; cytoplasm; and cytoskeleton. Predicted to be part of myosin complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | hsa:80022; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; myosin complex [GO:0016459]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cytoskeletal motor activity [GO:0003774] | 11964073_myosin XVBP is a transcribed pseudogene (myosin XVBP=MYO15BP) | ENSMUSG00000034427 | Myo15b | 509.983614 | 0.5655756 | -0.822208205 | 0.15355317 | 28.28602874172 | 0.0000001046485728436855611890165130423158146300011139828711748123168945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.00000204730662508737575622252448381832579116235137917101383209228515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 367.259128 | 39.710012 | 654.604068 | 69.912027 | |
| ENSG00000269556 | 84548 | TMEM185A | protein_coding | Q8NFB2 | Cell projection;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix | The protein encoded by this gene is predicted to be a transmembrane protein. This gene is best known for localizing to the CpG island of the fragile site FRAXF. The 5' untranslated region of this gene contains a CGG trinucleotide repeat sequence that normally consists of 7-40 tandem CGG repeats but which can expand to greater than 300 repeats. Methylation of the CpG island leads to transcriptional silencing of this gene, but neither the silencing nor an expanded repeat region appear to manifest itself in a clear phenotypic manner. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. A pseudogene of this gene has been defined on the X chromosome. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013]. | hsa:84548; | dendrite [GO:0030425]; membrane [GO:0016020] | 12404111_Transcriptionally silenced in a normal individual with a FRAXF CGG full mutation (fragile site). 12806492_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15525354_The mouse ee3 is an orphan G-protein-coupled receptor with potential connections to erythropoietin and 5HT2a receptor signalling. ee3_2, a similar gene, is also described, along with human orthologs. | ENSMUSG00000073139 | Tmem185a | 148.913813 | 1.1492897 | 0.200742550 | 0.14136356 | 2.01337156658 | 0.1559184775421501023551229536678874865174293518066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.35325358987035887503580511292966548353433609008789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 162.160933 | 14.951741 | 141.760260 | 12.934410 | ||
| ENSG00000270647 | 8148 | TAF15 | protein_coding | Q92804 | FUNCTION: RNA and ssDNA-binding protein that may play specific roles during transcription initiation at distinct promoters. Can enter the preinitiation complex together with the RNA polymerase II (Pol II). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19124016}. | 3D-structure;Acetylation;ADP-ribosylation;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger | This gene encodes a member of the TET family of RNA-binding proteins. The encoded protein plays a role in RNA polymerase II gene transcription as a component of a distinct subset of multi-subunit transcription initiation factor TFIID complexes. Translocations involving this gene play a role in acute leukemia and extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma, and mutations in this gene may play a role in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]. | hsa:8148; | cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; mRNA stabilization [GO:0048255]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380] | 12359745_The transcription factor gene CIZ/NMP4 is recurrently involved in acute leukemia through fusion with either EWSR1 or TAF15. 15094065_hTAF(II)68-mediated transactivation is linked to the cytoplasmic Src signal transduction pathway. The hTAF(II)68 protein can associate with the SH3 domains of several cell signaling proteins, including v-Src. 18330902_The oncogenic effect of the t(9;17) translocation may be due to the hTAF(II)68-TEC chimeric protein and that fusion of the hTAF(II)68 NTD to the TEC protein produces a gain of function chimeric product. 18620564_FUS, EWS and TAF15 proto-oncoproteins were targeted to stress granules induced by heat shock and oxidative stress 19124016_Data demonstrate that arginine methylation of TAF15 by PRMT1 is a crucial event determining its proper localization and gene regulatory function. 19282884_Data show that a fraction of human U1 snRNA specifically associates with the nuclear RNA-binding protein TBP-associated factor 15 (TAF15). 19426707_These results suggest that caspase-mediated degradation may represent a novel regulatory mechanism that controls TAF15 and TAF15-CIZ/NMP4 activities. 20048082_Our findings define a role for a tumor-specific TAF15 antigen in malignant processes. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21344536_Elevated TAF15 mRNA levels did not translate to strongly elevated protein levels, consistent with its infrequent occurrence as translocation partner in tumors. 21438137_These results suggest that additional studies are needed to determine whether mutations in the TAF15 gene represent a cause of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 21504714_Rare translocation t(12;17)(p13;q12), this translocation has been reported in 25 cases and its putative molecular consequence, the formation of a TAF15-ZNF384 fusion gene, in only six cases. 21856723_REsults suggest the possibility that alterations of TAF15 and EWS might also be involved in the pathogenesis of FUS proteinopathies such as ALS and FTLD. 22019700_The existence of a functionally discrete subset of U1 snRNP in association with TAF15 was suggested and provided further support for the involvement of U1 snRNP components in early steps of coordinated gene expression. 22065782_Missense mutations of TAF-15, an RNA-binding protein, were found in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and gene conferred neurodegeneration when expressend in Drosophila. 22771914_TAF15 plays a role in RNA transport and/or local RNA translation 23049996_Data show that FUS and TAF15 locate to cellular stress granules to a larger extend than EWS. FET-protein stress granule association most likely is a downstream response to cellular stress. 23128393_TAF15 depletion inhibits growth & increases apoptosis. Its knockdown affects many genes involved in cell cycle & cell death. Among these, targets of microRNAs generated from the onco-miR-17 locus were overrepresented. 24055347_Data indicate that distinct differences in proteins becoming Poly(ADP-ribose) PARylated upon various genotoxic insults are observed, exemplified by the PARylation of RNA-processing factors THRAP3 and TAF15 under oxidative stress. 24474660_our data suggest that TAF15 and TLS/FUS operate within similar but not identical hnRNP M-TET protein complexes to influence the transcriptional or post-transcriptional output of a particular cell type. 26612539_RNA binding by TAF-15 is dependent upon structural elements in the RNA rather than sequence. 27311318_Aggregation of FET proteins FUS, EWSR1, and TAF15 mediate a pathological change in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. (Review) 27378374_In human stem cell-derived motor neurons, the RNA profile associated with concomitant loss of both TAF15 and FUS resembles that observed in the presence of the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)-associated mutation FUS R521G, but contrasts with late-stage sporadic ALS patients. 27415968_Studies provide evidence that FUS/TLS, EWS and TAF15 proteins play a major role in neurodegenerative disorders. (review). 27903134_O-GlcNAc glycosylation stoichiometry of TAF15 28291257_In a cohort of youth at risk for bipolar disorder, pathway analysis showed an enrichment of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) pathway with the genes MED1, HSPA1L, GTF2A1 and TAF15, which might underlie the previously reported role of stress response in the risk for bipolar disorder in vulnerable populations. 28945358_weak, multivalent interactions between TAF15 fibrils and heptads throughout RNA pol II CTD collectively mediate complex formation. 29193371_Results find that the Asp residue in TAF15 YGGDR(S/G)G repeats confers poor binding to PRMT1 indicating that YGGDR(S/G)G repeats may contribute to TAF15 specialization by enabling differential interactions with PRMT1 and reduced overall levels of TAF15 methylation compared with other FET proteins. 30398641_FUS, EWSR1, TAF15 and MATR3 within the RNAP II/U1 snRNP machinery play distinct roles in the development of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and spinal muscular atrophy that are more intimately tied to one another than previously thought. 31020999_NR4A3 fusion proteins trigger an axon guidance switch that marks the difference between EWSR1 and TAF15 translocated extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcomas cells. 31887411_TRPM2-AS promotes cancer cell proliferation through control of TAF15. 32871048_LncRNA PITPNA-AS1 boosts the proliferation and migration of lung squamous cell carcinoma cells by recruiting TAF15 to stabilize HMGB3 mRNA. 32915460_SCF-Slimb is critical for Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta-mediated suppression of TAF15-induced neurotoxicity in Drosophila. 33674598_Loci-specific phase separation of FET fusion oncoproteins promotes gene transcription. 33875793_LncRNA GAS5 activates the HIF1A/VEGF pathway by binding to TAF15 to promote wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers. 35228660_LncRNA LINC00649 recruits TAF15 and enhances MAPK6 expression to promote the development of lung squamous cell carcinoma via activating MAPK signaling pathway. 35643629_The SGYS motif of TAF15 prion-like domain is critical to amyloid fibril formation. | ENSMUSG00000020680 | Taf15 | 992.442750 | 0.9362671 | -0.095007921 | 0.06383564 | 2.21378967588 | 0.1367822964371341876166354722954565659165382385253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.32517178153681730590207621389708947390317916870117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 973.823737 | 42.514773 | 1044.676170 | 45.033173 | |
| ENSG00000284308 | 388963 | C2orf81 | protein_coding | A6NN90 | Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome | Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] | Mouse_homologues 17971504_1700003E16Rik is most abundantly expressed in tissues rich in highly ciliated cells, such as olfactory sensory neurons, and is predicted to be important to cilia. | ENSMUSG00000030030 | 1700003E16Rik | 15.911421 | 1.0736942 | 0.102583173 | 0.41172452 | 0.06216846047 | 0.8031008561113516242002674516697879880666732788085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.90822012897449977408825816382886841893196105957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 17.628120 | 4.167076 | 16.526757 | 3.859143 | ||||
| ENSG00000288612 | lncRNA | 14.487434 | 0.8149208 | -0.295268225 | 0.40354048 | 0.53619894962 | 0.4640122880846615505134877821546979248523712158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.68460479307028465623119473093538545072078704833984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 12.717920 | 3.211324 | 15.614344 | 3.756356 | ||||||||||||
| ENSG00000291150 | 645166 | LSP1P5 | lncRNA | 33717069_Down-Regulation of LOC645166 in T Cells of Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Promotes the NF-kappaB Signaling via Decreasingly Blocking Recruitment of the IKK Complex to K63-Linked Polyubiquitin Chains. | 15.128986 | 0.7607231 | -0.394556586 | 0.52580770 | 0.55375267653 | 0.4567883937119533444004559896711725741624832153320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.67879278839240730913928700829274021089076995849609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 14.179109 | 5.056547 | 18.819704 | 6.563225 | |||||||||
| ENSG00000291152 | 155370 | SBDSP1 | lncRNA | 133.663876 | 0.9804477 | -0.028487383 | 0.13646701 | 0.04355872778 | 0.8346767584447178922602006423403508961200714111328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | 0.92530475415585589082922979287104681134223937988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 | No | Yes | 131.521432 | 13.596550 | 134.598667 | 13.772994 |
- Note:
- The spreadsheet above contains the non-differential expressed genes but with significantly changes in alternative splicing (q < 0.05 and dIf > 0.05). Please Click HERE to check all mapped genes in a Microsoft .excel file.
Gene Biotype
| Biotype | Amount of Genes |
|---|---|
| lncRNA | 14 |
| protein_coding | 348 |
MA plot
PCA plot
Co-expression Analysis
The co-expression pattern was determined using weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) through WGCNA R software.
Choosing the soft-thresholding power: analysis of network topology
Quantifying module-trait associations
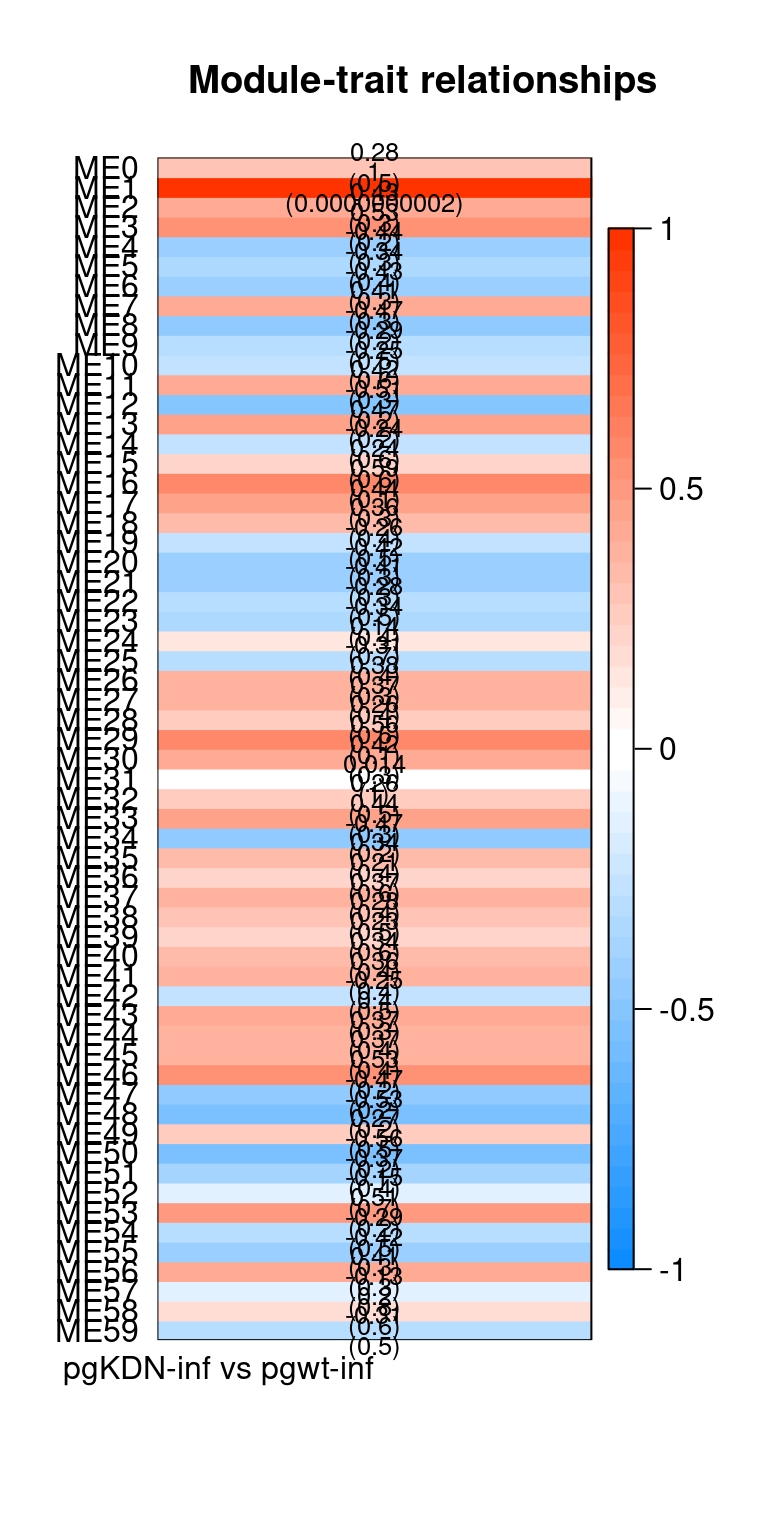
In the above figure, each cell contains the corresponding correlation (upper) and p-value (lower). ME, Module Eigengene.
Spreadsheet
| Cluster ID | Correlation | P-value | DEGs ID | DEGs Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ME0 | 0.28197276 | 0.4986567209901274 | ||
| ME1 | 0.99958644 | 0.0000000001767811 | ENSG00000000971||ENSG00000001617||ENSG00000005059||ENSG00000006837||ENSG00000008086||ENSG00000013619||ENSG00000015568||ENSG00000019102||ENSG00000025434||ENSG00000025708||ENSG00000027869||ENSG00000047597||ENSG00000057704||ENSG00000064547||ENSG00000065534||ENSG00000066056||ENSG00000067840||ENSG00000069493||ENSG00000070018||ENSG00000074181||ENSG00000075790||ENSG00000077984||ENSG00000078487||ENSG00000081923||ENSG00000082458||ENSG00000085514||ENSG00000088179||ENSG00000088827||ENSG00000088882||ENSG00000092068||ENSG00000092445||ENSG00000092929||ENSG00000099985||ENSG00000100154||ENSG00000100522||ENSG00000100628||ENSG00000100784||ENSG00000101152||ENSG00000101654||ENSG00000101901||ENSG00000102271||ENSG00000102890||ENSG00000102931||ENSG00000102962||ENSG00000103269||ENSG00000103742||ENSG00000104140||ENSG00000104219||ENSG00000104888||ENSG00000104936||ENSG00000105419||ENSG00000105877||ENSG00000107317||ENSG00000108679||ENSG00000109107||ENSG00000109158||ENSG00000109339||ENSG00000109787||ENSG00000110944||ENSG00000111335||ENSG00000111344||ENSG00000111732||ENSG00000111817||ENSG00000111913||ENSG00000112715||ENSG00000113205||ENSG00000113263||ENSG00000114812||ENSG00000115008||ENSG00000115590||ENSG00000116396||ENSG00000116497||ENSG00000116701||ENSG00000116833||ENSG00000117091||ENSG00000117115||ENSG00000117152||ENSG00000117298||ENSG00000117318||ENSG00000118162||ENSG00000119283||ENSG00000119508||ENSG00000119866||ENSG00000119917||ENSG00000119922||ENSG00000120162||ENSG00000120262||ENSG00000120337||ENSG00000120885||ENSG00000121068||ENSG00000121858||ENSG00000121864||ENSG00000123689||ENSG00000124191||ENSG00000124731||ENSG00000125730||ENSG00000125863||ENSG00000125954||ENSG00000126353||ENSG00000126709||ENSG00000127586||ENSG00000128342||ENSG00000128594||ENSG00000128965||ENSG00000130368||ENSG00000130477||ENSG00000130590||ENSG00000130714||ENSG00000131203||ENSG00000131355||ENSG00000131370||ENSG00000132274||ENSG00000132361||ENSG00000132530||ENSG00000132688||ENSG00000133019||ENSG00000133106||ENSG00000133250||ENSG00000133561||ENSG00000133574||ENSG00000133816||ENSG00000134107||ENSG00000134256||ENSG00000134321||ENSG00000134326||ENSG00000134815_ENSG00000134830||ENSG00000135074||ENSG00000135114||ENSG00000135253||ENSG00000135454||ENSG00000135547||ENSG00000135636||ENSG00000136122||ENSG00000136244||ENSG00000136305||ENSG00000136688||ENSG00000136689||ENSG00000136717||ENSG00000136869||ENSG00000137177||ENSG00000137203||ENSG00000137474||ENSG00000137673||ENSG00000137745||ENSG00000137766||ENSG00000137936||ENSG00000137959||ENSG00000137965||ENSG00000138185||ENSG00000138378||ENSG00000138411||ENSG00000138646||ENSG00000138759||ENSG00000139160||ENSG00000140563||ENSG00000140950||ENSG00000144161||ENSG00000144339||ENSG00000145331||ENSG00000145723||ENSG00000146067||ENSG00000146070||ENSG00000146192||ENSG00000146281||ENSG00000147364||ENSG00000148677||ENSG00000148824||ENSG00000149564_ENSG00000019102||ENSG00000151012||ENSG00000151617||ENSG00000151651||ENSG00000152192||ENSG00000153162||ENSG00000153234||ENSG00000153982||ENSG00000153993||ENSG00000154358||ENSG00000154645||ENSG00000156265||ENSG00000156500||ENSG00000156509||ENSG00000157570||ENSG00000157601||ENSG00000157613||ENSG00000157873||ENSG00000158747||ENSG00000158859||ENSG00000160145||ENSG00000160654||ENSG00000160932||ENSG00000161640||ENSG00000161835||ENSG00000162591||ENSG00000163395||ENSG00000163406||ENSG00000163605_ENSG00000255423||ENSG00000163739||ENSG00000164125||ENSG00000165300||ENSG00000165698||ENSG00000166068||ENSG00000166104||ENSG00000166396||ENSG00000166523||ENSG00000166548||ENSG00000167103||ENSG00000167123||ENSG00000167244||ENSG00000167680||ENSG00000168237_ENSG00000114841||ENSG00000169245||ENSG00000169248||ENSG00000169403||ENSG00000169964||ENSG00000170054||ENSG00000170190||ENSG00000170745||ENSG00000170989||ENSG00000171757||ENSG00000171951||ENSG00000172399||ENSG00000172803||ENSG00000173083||ENSG00000173918||ENSG00000174837||ENSG00000174945||ENSG00000176049||ENSG00000176155||ENSG00000177943||ENSG00000178685||ENSG00000179388||ENSG00000179528||ENSG00000179532||ENSG00000179813||ENSG00000180616||ENSG00000180953||ENSG00000181577||ENSG00000181804||ENSG00000182132||ENSG00000182185||ENSG00000182389||ENSG00000182667||ENSG00000183023||ENSG00000183631||ENSG00000184371||ENSG00000184445||ENSG00000184557||ENSG00000185507||ENSG00000185614||ENSG00000185745||ENSG00000185885||ENSG00000186439||ENSG00000186810||ENSG00000186891||ENSG00000187186||ENSG00000187210||ENSG00000187608||ENSG00000187775||ENSG00000188290||ENSG00000196562||ENSG00000196664||ENSG00000196684||ENSG00000196814||ENSG00000197506||ENSG00000197594||ENSG00000197893||ENSG00000198270||ENSG00000198467||ENSG00000198719||ENSG00000198720||ENSG00000198796||ENSG00000198825||ENSG00000198829||ENSG00000203799||ENSG00000204044||ENSG00000204287||ENSG00000204305_ENSG00000204304||ENSG00000204564||ENSG00000204577_ENSG00000131042||ENSG00000204642||ENSG00000204650||ENSG00000204745||ENSG00000204791||ENSG00000205086||ENSG00000205560||ENSG00000205795||ENSG00000213928||ENSG00000214193||ENSG00000215041||ENSG00000215817||ENSG00000224186||ENSG00000224578||ENSG00000224596||ENSG00000225434||ENSG00000228477||ENSG00000229314||ENSG00000229953||ENSG00000230107||ENSG00000230724||ENSG00000231877_ENSG00000234464||ENSG00000232648||ENSG00000233143||ENSG00000233429||ENSG00000233695||ENSG00000234409||ENSG00000234464||ENSG00000235027||ENSG00000235703||ENSG00000237541||ENSG00000237973||ENSG00000238035||ENSG00000238045||ENSG00000239440||ENSG00000239445||ENSG00000240053||ENSG00000240583||ENSG00000240990||ENSG00000242948||ENSG00000243302||ENSG00000244242||ENSG00000244479||ENSG00000244482||ENSG00000247095||ENSG00000249395||ENSG00000250091||ENSG00000251301||ENSG00000254102||ENSG00000254870||ENSG00000255031||ENSG00000257258||ENSG00000258017||ENSG00000258623||ENSG00000259066||ENSG00000259081||ENSG00000259878_ENSG00000291297||ENSG00000260428||ENSG00000261732||ENSG00000262468||ENSG00000267512||ENSG00000269378||ENSG00000269720||ENSG00000270580||ENSG00000271216||ENSG00000271270||ENSG00000271857||ENSG00000272068||ENSG00000272405||ENSG00000274272||ENSG00000274386||ENSG00000275131||ENSG00000275888||ENSG00000275993||ENSG00000276231||ENSG00000278996||ENSG00000280061||ENSG00000280195||ENSG00000283208||ENSG00000283787||ENSG00000284095||ENSG00000284690||ENSG00000287097||ENSG00000287255||ENSG00000287562||ENSG00000287721||ENSG00000287823||ENSG00000288931||ENSG00000289623||ENSG00000289757||ENSG00000291006||ENSG00000291010||ENSG00000291088||ENSG00000291092||ENSG00000291092_ENSG00000272391 | CFH||SEMA3F||MCUB||CDKL3||CDKL5||MAMLD1||RGPD5||VSIG2||NR1H3||TYMP||SH2D2A||XK||TMCC3||LPAR2||MYLK||TIE1||PDZD4||CLEC2D||LRP6||NOTCH3||BCAP29||CST7||ZCWPW1||ATP8B1||DLG3||PILRA||PTPN4||SIGLEC1||CPXM1||SLC7A8||TYRO3||UNC13D||OSM||TTC28||GNPNAT1||ASB2||RPS6KA5||DNAJC5||RNMT||ALG13||KLHL4||ELMO3||ARL2BP||CCL22||RHBDL1||IGDCC4||RHOV||ZDHHC2||SLC17A7||DMPK||MEIS3||DNAH11||PTGDS||LGALS3BP||ALDOC||GABRA4||MAPK10||KLF3||IL23A||OAS2||RASAL1||AICDA||DSE||RIPOR2||VEGFA||PCDHB3||ITK||VIPR1||IL1A||IL1R2||KCNC4||S100PBP||NCF2||NR5A2||CD48||PADI2||RGS4||ECE1||ID3||KPTN||TRIM67||NR4A3||BCL11A||IFIT3||IFIT2||MOB3B||CCDC170||TNFSF18||CLU||TBX2||TNFSF10||ZNF639||G0S2||TOX2||TREM1||C3||MKKS||CHURC1-FNTB||CCR7||IFI6||CHTF18||LIF||LRRC4||CHAC1||MAS1||UNC13A||SAMD10||POMT1||IDO1||ADGRE3||SH3BP5||TRIM22||CLUH||XAF1||NES||CHRM3||EPSTI1||ZNF414||GIMAP6||GIMAP4||MICAL2||BHLHE40||CD101||RSAD2||CMPK2||ENSG00000134815_ENSG00000134830||ADAM19||OASL||KCP||B4GALNT1||HEY2||DYSF||BORA||IL6||CIDEB||IL36G||IL1RN||BIN1||TLR4||KIF13A||TFAP2A||MYO7A||MMP7||MMP13||UNC13C||BCAR3||IFI44L||IFI44||ENTPD1||STAT4||HECW2||HERC5||FRAS1||ETFBKMT||MCTP2||MEAK7||ZC3H8||TMEFF2||TRMT10A||GIN1||FAM193B||PLA2G7||FGD2||PM20D2||FBXO25||ANKRD1||MTG1||ENSG00000149564_ENSG00000019102||SLC7A11||EDNRA||ADAM8||POU4F1||BMP6||NR4A2||GDPD1||SEMA3D||OBSCN||CHODL||MAP3K7CL||PABIR3||FBXO43||TSPAN18||MX1||CREB3L1||TNFRSF14||NBL1||ADAMTS4||KALRN||CD3G||LY6E||SIGLEC11||TAMALIN||MEGF6||IGFN1||SLC15A2||ENSG00000163605_ENSG00000255423||CXCL1||GASK1B||SLITRK5||SPACA9||SPRED1||ENSG00000166104||SERPINB7||CLEC4E||TK2||PIP5KL1||CERCAM||IGF2||SEMA6B||ENSG00000168237_ENSG00000114841||CXCL10||CXCL11||PTAFR||TMEM42||SERPINA9||SLC16A5||KCNS3||S1PR1||LRRC34||SCG2||MYOZ2||SNX32||HPSE||C1QTNF1||ADGRE1||AMZ1||JAKMIP2||CCDC57||MAMDC4||PARP10||EGR3||LBX2||DNHD1||FAM216B||SSTR2||ST20||C6orf223||SLC9A9||KCNIP1||RAD51B||CACNB4||NTM||SLC8A1||PRR32||CSF1||KNTC1||SOCS3||IRF7||INKA1||IFIT1||IFITM1||TRDN||CXCR3||TNFRSF18||ENSG00000187186||GCNT1||ISG15||DNAH17||HES4||SULF2||TLR7||HSH2D||MVB12B||SLC28A3||ENPP1||NRAP||TMEM116||TPM2||DLL1||ANKRD13B||ALPK2||INPP5F||SUCNR1||CCDC162P||SLC12A5-AS1||HLA-DRA||ENSG00000204305_ENSG00000204304||C6orf136||ENSG00000204577_ENSG00000131042||HLA-F||LINC02210||ENSG00000204745||ENSG00000204791||LINC02898||CPT1B||CYS1||IRF9||SH3D21||NEURL4||ZC3H11B||PITX1-AS1||HNRNPA1L3||ZMIZ1-AS1||LINC01504||ENSG00000228477||ORM1||ENSG00000229953||ENSG00000230107||ENSG00000230724||ENSG00000231877_ENSG00000234464||ENSG00000232648||ENSG00000233143||HOTAIRM1||ENSG00000233695||CCDC188||ENSG00000234464||ENSG00000235027||EOLA2-DT||HLA-DQA2||MTCO1P12||ENSG00000238035||ENSG00000238045||LINC02008||ENSG00000239445||LY6G5B||AQP1||HOXA11-AS||ENSG00000242948||ENSG00000243302||IFITM10||ENSG00000244479||LILRA6||MIR210HG||CASC9||ENSG00000250091||ENSG00000251301||BHLHE22-AS1||ATP6V1G2-DDX39B||ENSG00000255031||ENSG00000257258||ENSG00000258017||ENSG00000258623||ENSG00000259066||ENSG00000259081||ENSG00000259878_ENSG00000291297||SCX||ENSG00000261732||ENSG00000262468||ENSG00000267512||ENSG00000269378||CCDC194||PKD1P6-NPIPP1||ENSG00000271216||TMCC1-DT||ENSG00000271857||ENSG00000272068||ENSG00000272405||ENSG00000274272||TMEM269||ENSG00000275131||ENSG00000275888||ENSG00000275993||PIK3R6||ENSG00000278996||ENSG00000280061||ENSG00000280195||ENSG00000283208||PRR33||ENSG00000284095||CD300H||ENSG00000287097||ENSG00000287255||ENSG00000287562||ENSG00000287721||ENSG00000287823||ENSG00000288931||ENSG00000289623||ENSG00000289757||ENSG00000291006||MRPS31P5||NPEPPSP1||PMS2P3||ENSG00000291092_ENSG00000272391 |
| ME2 | 0.42990894 | 0.2877343861999994 | ENSG00000143971||ENSG00000145147||ENSG00000151474||ENSG00000172380||ENSG00000215769_ENSG00000266820_ENSG00000291117||ENSG00000251364 | ETAA1||SLIT2||FRMD4A||GNG12||ENSG00000215769_ENSG00000266820_ENSG00000291117||SYT9-AS1 |
| ME3 | 0.52920580 | 0.1774348583867341 | ENSG00000001084||ENSG00000079387||ENSG00000148143||ENSG00000163617||ENSG00000172339||ENSG00000197989 | GCLC||SENP1||ZNF462||CCDC191||ALG14||SNHG12 |
| ME4 | -0.43700302 | 0.2789617230197438 | ENSG00000113356||ENSG00000124225||ENSG00000138794 | POLR3G||PMEPA1||CASP6 |
| ME5 | -0.34024963 | 0.4095601391816628 | ENSG00000074660||ENSG00000197646 | SCARF1||PDCD1LG2 |
| ME6 | -0.43161197 | 0.2856162744619309 | ENSG00000135678||ENSG00000213809||ENSG00000249319 | CPM||KLRK1||ENSG00000249319 |
| ME7 | 0.40894525 | 0.3144267185599993 | ENSG00000158301||ENSG00000241489 | GPRASP2||ENSG00000241489 |
| ME8 | -0.47284971 | 0.2366961622015915 | ENSG00000080573||ENSG00000085999||ENSG00000181634 | COL5A3||RAD54L||TNFSF15 |
| ME9 | -0.28677235 | 0.4910541521440401 | ||
| ME10 | -0.24588701 | 0.5572078339698863 | ||
| ME11 | 0.41979228 | 0.3004733169677800 | ENSG00000184949||ENSG00000250506 | FAM227A||CDK3 |
| ME12 | -0.51372634 | 0.1928199798343628 | ENSG00000106415||ENSG00000111788||ENSG00000206384 | GLCCI1||ENSG00000111788||COL6A6 |
| ME13 | 0.46647610 | 0.2439559686602284 | ||
| ME14 | -0.24098111 | 0.5653484522385990 | ||
| ME15 | 0.23565880 | 0.5742263505305478 | ||
| ME16 | 0.59178112 | 0.1222494206951692 | ENSG00000092969||ENSG00000152409||ENSG00000157110||ENSG00000171115_ENSG00000242258 | TGFB2||JMY||RBPMS||ENSG00000171115_ENSG00000242258 |
| ME17 | 0.44386422 | 0.2706039813052853 | ENSG00000145743||ENSG00000160229||ENSG00000176681||ENSG00000180008||ENSG00000186300||ENSG00000257242 | FBXL17||ZNF66||LRRC37A||SOCS4||ZNF555||LINC01619 |
| ME18 | 0.35599179 | 0.3867649813380841 | ENSG00000261150 | EPPK1 |
| ME19 | -0.26107246 | 0.5322773078026515 | ||
| ME20 | -0.41931054 | 0.3010865835966871 | ||
| ME21 | -0.41386682 | 0.3080581856904490 | ENSG00000161647 | MPP3 |
| ME22 | -0.28185733 | 0.4988401064431366 | ||
| ME23 | -0.33758200 | 0.4134788793725601 | ||
| ME24 | 0.13798733 | 0.7445391743981240 | ENSG00000186026 | ZNF284 |
| ME25 | -0.31395837 | 0.4488676870913042 | ENSG00000198691 | ABCA4 |
| ME26 | 0.38423186 | 0.3473319346355980 | ENSG00000289740 | TALAM1 |
| ME27 | 0.37360358 | 0.3619480861155965 | ||
| ME28 | 0.25592481 | 0.5406823115698527 | ||
| ME29 | 0.56278096 | 0.1464220165933499 | ENSG00000134815_ENSG00000288827 | ENSG00000134815_ENSG00000288827 |
| ME30 | 0.42359452 | 0.2956541967662894 | ENSG00000124782||ENSG00000289444 | RREB1||ENSG00000289444 |
| ME31 | 0.01355284 | 0.9745915317006594 | ||
| ME32 | 0.25760313 | 0.5379367126769219 | ENSG00000213366_ENSG00000168765 | ENSG00000213366_ENSG00000168765 |
| ME33 | 0.44056641 | 0.2746054629154511 | ||
| ME34 | -0.47122917 | 0.2385314432678345 | ENSG00000113494 | PRLR |
| ME35 | 0.33506120 | 0.4171965982025563 | ENSG00000154529 | CNTNAP3B |
| ME36 | 0.21148776 | 0.6151258290802524 | ||
| ME37 | 0.36750251 | 0.3704617182395107 | ||
| ME38 | 0.28198485 | 0.4986375090202482 | ||
| ME39 | 0.23086012 | 0.5822713742227059 | ||
| ME40 | 0.33993123 | 0.4100270338638827 | ||
| ME41 | 0.36034234 | 0.3805663615447790 | ||
| ME42 | -0.25444794 | 0.5431025455687229 | ||
| ME43 | 0.40316679 | 0.3219829904959369 | ||
| ME44 | 0.37039673 | 0.3664119041460804 | ||
| ME45 | 0.37145562 | 0.3649352287495113 | ||
| ME46 | 0.52777129 | 0.1788319080847587 | ||
| ME47 | -0.46593133 | 0.2445816423465784 | ENSG00000206127 | GOLGA8O |
| ME48 | -0.52867610 | 0.1779500433608002 | ENSG00000137812||ENSG00000148297_ENSG00000148296||ENSG00000156886 | KNL1||ENSG00000148297_ENSG00000148296||ITGAD |
| ME49 | 0.27399274 | 0.5113960269175533 | ||
| ME50 | -0.55637065 | 0.1520926940656255 | ENSG00000233024||ENSG00000272030_ENSG00000189171 | NPIPA9||ENSG00000272030_ENSG00000189171 |
| ME51 | -0.36720330 | 0.3708815309497931 | ||
| ME52 | -0.15295360 | 0.7176535126256467 | ||
| ME53 | 0.51462577 | 0.1919073848673306 | ||
| ME54 | -0.29086186 | 0.4846122191406524 | ||
| ME55 | -0.42471161 | 0.2942455080551821 | ||
| ME56 | 0.40860711 | 0.3148665487764654 | ||
| ME57 | -0.13428334 | 0.7512291141117240 | ||
| ME58 | 0.19886564 | 0.6368410954720514 | ||
| ME59 | -0.30548692 | 0.4618502477373794 |
2. Functional Enrichment Analysis
2-1. Spreadsheet
GSEA
Please Click HERE to download a Microsoft .excel that contains all GSEA results.
GO: BP
| ID | Description | setSize | enrichmentScore | NES | pvalue | p.adjust | qvalues | rank | leading_edge | core_enrichment | No-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgKDN-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgwt-inf_Log2MeanTPM | log2TPM_No-inf_1 | log2TPM_No-inf_2 | log2TPM_No-inf_3 | log2TPM_No-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0071222 | cellular response to lipopolysaccharide | 147 | -0.5328937 | -1.760375 | 0.00004854886 | 0.02831542 | 0.02793343 | 1964 | tags=30%, list=14%, signal=26% | CXCL8||IL18||CD40||KMO||BPI||CCL2||CASP1||RELA||NOD2||CD274||ZC3H12A||CCL3||ADAMTS13||CXCL2||CEBPB||PDE4B||CXCL3||CD68||MEF2C||CXCL13||IL1B||PPARD||WNT5A||SRC||HCK||AXL||CSF2||CCL5||MALT1||CD86||CXCL1||CMPK2||NR1H3||BMP6||ANKRD1||PTAFR||IL1A||CXCL11||CXCL10||IL36G||PTPN22||IL6||NOS2||PDCD1LG2 | 5.602065 | 6.377258 | 6.668393 | 5.611467 | 5.588703 | 5.617768 | 5.590093 | 6.386363 | 6.356848 | 6.388852 | 6.376751 | 6.679675 | 6.668113 | 6.671684 | 6.653981 |
| GO:0002181 | cytoplasmic translation | 142 | 0.4429409 | 1.777677 | 0.00010069801 | 0.03984764 | 0.03931008 | 5265 | tags=61%, list=38%, signal=39% | CPEB3||RPS15A||RPL5||EIF3H||RPS3A||RPL26||DHX29||RPS17||RPS21||RWDD1||RPL27||RPS7||RPS6||RPL31||EIF4A2||RPL34||RPS25||EIF3C||RPS27A||MTOR||YTHDF2||RPS18||RPL38||RPL15||EIF3E||RPL9||RPL39||RPL6||RPS24||RPS8||RPS27||RPL17||RPS12||RPL35A||EIF3J||DENR||DHX36||EIF3L||RPL29||RPL4||FTSJ1||RPL21||ZC3H15||RPS4X||RPS13||EIF3F||RPL19||RPL27A||RPL7||RPS10||EIF3I||RPL24||EIF3M||EIF2S2||RPS29||RPS20||RPL23||DPH3||RPS11||RPL11||RPS14||CNBP||RPS5||EIF5||RPL23A||DPH5||EIF3K||RPL37||RPL18A||RPL36A||CPEB1||EIF4B||CPEB4||RPL32||DRG2||DRG1||RPL37A||RPL10||RPS26||RPL12||YBX3||RPS16||RPL3||RPL18||RPLP1||GSPT2||TMA7 | 10.071216 | 10.099047 | 9.905364 | 10.075395 | 10.072678 | 10.071051 | 10.065722 | 10.103440 | 10.103363 | 10.103968 | 10.085328 | 9.904311 | 9.905468 | 9.904156 | 9.907520 |
| GO:0048245 | eosinophil chemotaxis | 10 | -0.8753953 | -1.835662 | 0.00040254606 | 0.09384696 | 0.09258092 | 1636 | tags=80%, list=12%, signal=71% | CCL2||CCL3||CCL4||CCL4L2||DAPK2||CCL5||CCL1||SCG2 | 4.202412 | 7.373362 | 8.097188 | 4.128794 | 4.200950 | 4.249881 | 4.227172 | 7.395902 | 7.409602 | 7.368607 | 7.317632 | 8.062513 | 8.118189 | 8.092768 | 8.114602 |
| GO:0002577 | regulation of antigen processing and presentation | 14 | -0.8133644 | -1.837461 | 0.00059172682 | 0.11707738 | 0.11549796 | 1522 | tags=57%, list=11%, signal=51% | NOD2||CD74||TAPBPL||CD68||CCL19||SLC11A1||CCR7||NOD1 | 5.958454 | 5.618073 | 6.036820 | 5.889958 | 5.959109 | 5.941059 | 6.039654 | 5.690731 | 5.591565 | 5.625891 | 5.560861 | 6.049192 | 6.023071 | 6.043127 | 6.031747 |
| GO:0045071 | negative regulation of viral genome replication | 45 | -0.6521019 | -1.837501 | 0.00079226244 | 0.12286428 | 0.12120679 | 1679 | tags=38%, list=12%, signal=33% | N4BP1||PLSCR1||BST2||OAS1||IFITM3||CCL5||OAS3||PARP10||OAS2||ISG15||AICDA||IFIT1||IFITM1||IFIT5||MX1||RSAD2||OASL | 5.757779 | 6.079732 | 6.570917 | 5.753978 | 5.749926 | 5.824677 | 5.699782 | 6.081680 | 6.074060 | 6.102637 | 6.060226 | 6.529888 | 6.594232 | 6.548119 | 6.609949 |
| GO:0002468 | dendritic cell antigen processing and presentation | 11 | -0.8396173 | -1.801388 | 0.00122318199 | 0.14117559 | 0.13927107 | 1978 | tags=82%, list=14%, signal=70% | HLA-DRB1||NOD2||CD74||CD68||CCL19||SLC11A1||HLA-DRA||CCR7||NOD1 | 5.160835 | 5.539716 | 6.162471 | 5.022226 | 5.199160 | 5.107806 | 5.299352 | 5.584281 | 5.510518 | 5.558857 | 5.503642 | 6.212503 | 6.131797 | 6.158566 | 6.145716 |
| GO:0070098 | chemokine-mediated signaling pathway | 41 | -0.6401349 | -1.773769 | 0.00239099859 | 0.24083877 | 0.23758975 | 2038 | tags=56%, list=15%, signal=48% | CCL20||CXCL8||CXCR4||CCL2||CCL3||CXCL2||CXCL3||CCL4||CCL4L2||ACKR3||CCL3L3||CCL19||CCR1||CXCL13||CCL5||CCL1||CXCL1||CXCR3||PADI2||CCR7||CCL22||CXCL11||CXCL10 | 4.942244 | 6.645200 | 7.142348 | 4.944161 | 4.952342 | 5.057979 | 4.803196 | 6.636484 | 6.670499 | 6.651517 | 6.621847 | 7.167052 | 7.146340 | 7.126767 | 7.128866 |
| GO:0030593 | neutrophil chemotaxis | 67 | -0.5739134 | -1.725463 | 0.00315374507 | 0.27317036 | 0.26948518 | 1636 | tags=40%, list=12%, signal=36% | CCL2||ITGA1||NOD2||CD74||CCL3||CXCL2||PDE4B||CXCL3||CCL4||CCL4L2||PIP5K1C||CCL3L3||CCL19||MDK||CXCL13||DAPK2||CCL5||CCL1||TREM1||CXCL1||S100A8||RIPOR2||CD300H||CCR7||CCL22||CXCL11||CXCL10 | 7.613547 | 7.929617 | 8.079746 | 7.633389 | 7.614432 | 7.609215 | 7.596911 | 7.935661 | 7.920295 | 7.928298 | 7.934164 | 8.071592 | 8.084285 | 8.078248 | 8.084819 |
| GO:0006892 | post-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport | 96 | 0.4336506 | 1.644280 | 0.00325213141 | 0.27317036 | 0.26948518 | 2656 | tags=38%, list=19%, signal=31% | KIF13A||EXOC2||ANKFY1||DOP1A||VTI1A||AP3S2||VPS13A||CCDC91||EPS15||EXOC5||PKDCC||LYPLA1||BLZF1||SORL1||PREPL||RP2||MON2||MACF1||KLHL20||CNST||SORT1||SCFD1||GOLGA7||SCAMP1||EXOC4||RAB10||DOP1B||KIF16B||CCDC93||GOLPH3L||RBSN||ARL3||COMMD1||SORCS1||GOLPH3||SPTBN1 | 6.284775 | 6.354789 | 6.281763 | 6.298179 | 6.282928 | 6.277301 | 6.280603 | 6.340870 | 6.357878 | 6.354274 | 6.366019 | 6.311074 | 6.292692 | 6.244881 | 6.277590 |
| GO:0002690 | positive regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis | 64 | -0.5722643 | -1.707164 | 0.00344325255 | 0.27645825 | 0.27272871 | 1540 | tags=31%, list=11%, signal=28% | VEGFB||CD74||CCL3||CCL4||CCL19||CCR1||MDK||CXCL13||WNT5A||DAPK2||CCL5||CCL1||CSF1||PLA2G7||RIPOR2||VEGFA||CCR7||SLAMF1||CXCL10||IL6 | 6.272371 | 7.033161 | 7.322300 | 6.268483 | 6.267044 | 6.284230 | 6.269661 | 7.039208 | 7.034702 | 7.038458 | 7.020195 | 7.323246 | 7.330962 | 7.324932 | 7.309977 |
| GO:0035456 | response to interferon-beta | 24 | -0.6923362 | -1.752819 | 0.00460008903 | 0.29981757 | 0.29577291 | 2344 | tags=50%, list=17%, signal=42% | TREX1||SHFL||STAT1||PLSCR1||HTRA2||BST2||OAS1||IFITM3||IRF1||AIM2||XAF1||IFITM1 | 6.342222 | 6.025942 | 6.299906 | 6.332319 | 6.394615 | 6.333625 | 6.306876 | 6.052162 | 6.022565 | 6.040214 | 5.988019 | 6.258982 | 6.315207 | 6.365883 | 6.256724 |
| GO:1901379 | regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport | 45 | 0.5144642 | 1.709457 | 0.00553759652 | 0.33574571 | 0.33121636 | 1963 | tags=33%, list=14%, signal=29% | KCNIP1||BIN1||RGS4||FLNA||KCNIP2||KLHL24||NETO2||KCNQ1||KCNN2||AMIGO1||STK39||CRBN||ALG10B||FHL1||ATP1B1 | 6.366091 | 6.669085 | 6.672497 | 6.349819 | 6.364830 | 6.371448 | 6.378114 | 6.681195 | 6.661721 | 6.669900 | 6.663443 | 6.653230 | 6.725881 | 6.634019 | 6.675216 |
| GO:0061844 | antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide | 21 | -0.7050257 | -1.732602 | 0.00590461771 | 0.34799555 | 0.34330095 | 1964 | tags=52%, list=14%, signal=45% | CXCL8||HMGN2||CXCL14||NOD2||GNLY||CXCL2||CXCL3||CXCL13||CXCL1||CXCL11||CXCL10 | 8.671430 | 8.984973 | 8.994156 | 8.685353 | 8.665157 | 8.659837 | 8.675240 | 8.955079 | 8.995496 | 8.997118 | 8.991785 | 9.005581 | 8.982451 | 9.019825 | 8.968213 |
| GO:0050829 | defense response to Gram-negative bacterium | 30 | -0.6541682 | -1.720106 | 0.00633640553 | 0.36554599 | 0.36061463 | 1649 | tags=37%, list=12%, signal=32% | BPI||CASP1||AZU1||SLC11A1||DROSHA||TREM1||AQP1||TNFRSF14||IL23A||IL6||NOS2 | 7.531399 | 7.503267 | 7.518604 | 7.537081 | 7.514659 | 7.542634 | 7.531071 | 7.471199 | 7.520783 | 7.516633 | 7.503929 | 7.518629 | 7.507151 | 7.542760 | 7.505570 |
| GO:0032740 | positive regulation of interleukin-17 production | 17 | -0.7370050 | -1.733415 | 0.00668844299 | 0.37053974 | 0.36554101 | 2093 | tags=53%, list=15%, signal=45% | SPHK1||CARD9||IL18||NOD2||SLC7A5||CCL1||OSM||IL23A||IL6 | 5.073505 | 6.265223 | 6.707285 | 4.991289 | 5.027139 | 5.107469 | 5.161920 | 6.278903 | 6.224967 | 6.296521 | 6.259528 | 6.710021 | 6.725694 | 6.717207 | 6.675718 |
| GO:0099068 | postsynapse assembly | 16 | -0.7409612 | -1.717590 | 0.00692695214 | 0.37622858 | 0.37115310 | 1048 | tags=38%, list=7%, signal=35% | CDH2||ABI3||WNT5A||EPHB2||PTPRS||NLGN2 | 3.623392 | 3.526807 | 3.628121 | 3.631502 | 3.640027 | 3.649678 | 3.571065 | 3.737242 | 3.378924 | 3.441089 | 3.524026 | 3.727902 | 3.625317 | 3.523506 | 3.628522 |
| GO:0042402 | cellular biogenic amine catabolic process | 16 | -0.7376544 | -1.709924 | 0.00802896725 | 0.41134419 | 0.40579499 | 1800 | tags=50%, list=13%, signal=44% | HAAO||SAT1||KMO||SULT1A3||IL4I1||LRRC51||IDO1||SULT1A4 | 4.905262 | 6.101012 | 6.384023 | 4.957059 | 4.884504 | 4.833139 | 4.942986 | 6.136557 | 6.076818 | 6.048510 | 6.140044 | 6.354115 | 6.414618 | 6.378858 | 6.387852 |
| GO:0002544 | chronic inflammatory response | 11 | -0.8008068 | -1.718121 | 0.00809323406 | 0.41134419 | 0.40579499 | 976 | tags=45%, list=7%, signal=42% | CXCL13||CCL5||S100A8||UNC13D||VNN1 | 4.851007 | 6.965034 | 7.660180 | 4.700208 | 4.791260 | 5.027323 | 4.865108 | 6.972084 | 6.993929 | 6.937405 | 6.956117 | 7.643445 | 7.652344 | 7.627372 | 7.715979 |
| GO:0140374 | antiviral innate immune response | 13 | -0.7732441 | -1.721215 | 0.00817307692 | 0.41162587 | 0.40607287 | 1879 | tags=46%, list=13%, signal=40% | ZDHHC1||OAS1||DDX58||IFIT1||MX1||CXCL10 | 4.900979 | 5.046972 | 5.124223 | 4.795822 | 4.864043 | 4.908701 | 5.025581 | 5.128284 | 4.950729 | 4.995045 | 5.106199 | 5.077400 | 5.182885 | 5.091020 | 5.143121 |
| GO:0051457 | maintenance of protein location in nucleus | 22 | 0.6359327 | 1.791467 | 0.00896057348 | 0.44210782 | 0.43614360 | 442 | tags=14%, list=3%, signal=13% | BARD1||ARL2BP||SYNE1 | 6.408228 | 6.530815 | 6.468365 | 6.392719 | 6.431420 | 6.370901 | 6.436838 | 6.460910 | 6.499898 | 6.619244 | 6.538426 | 6.452163 | 6.463064 | 6.505437 | 6.452124 |
| GO:0010225 | response to UV-C | 15 | -0.7458819 | -1.709375 | 0.00969023034 | 0.44348383 | 0.43750105 | 2251 | tags=33%, list=16%, signal=28% | BCL3||WRN||TP53||ST20||POLH | 5.455437 | 5.314489 | 5.636324 | 5.253999 | 5.223908 | 5.495493 | 5.777863 | 5.345736 | 5.273984 | 5.282160 | 5.354260 | 5.834772 | 5.545310 | 5.577746 | 5.567574 |
| GO:0061003 | positive regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis | 14 | -0.7548535 | -1.705280 | 0.00971801816 | 0.44348383 | 0.43750105 | 59 | tags=21%, list=0%, signal=21% | LRP8||CUX2||GPRASP2 | 6.075985 | 6.189976 | 6.034493 | 6.030962 | 6.113980 | 5.937034 | 6.208048 | 6.184003 | 6.211883 | 6.153265 | 6.209971 | 6.082252 | 6.011455 | 5.997207 | 6.045555 |
| GO:0006607 | NLS-bearing protein import into nucleus | 16 | -0.7270352 | -1.685308 | 0.01007556675 | 0.44348383 | 0.43750105 | 10 | tags=12%, list=0%, signal=13% | RGPD2||RGPD5 | 4.996688 | 5.100778 | 5.353413 | 5.494355 | 4.712053 | 4.768949 | 4.865611 | 5.118606 | 5.058210 | 5.077843 | 5.146798 | 5.421843 | 4.960603 | 5.427554 | 5.538703 |
| GO:0090317 | negative regulation of intracellular protein transport | 32 | 0.5533529 | 1.694025 | 0.01034367701 | 0.45121237 | 0.44512533 | 2548 | tags=31%, list=18%, signal=26% | BARD1||ANGPT1||LRRK2||UBE2J1||CD36||SVIP||YOD1||SUFU||BAG4||SUMO1 | 5.930211 | 6.120897 | 6.049548 | 5.954214 | 5.954947 | 5.901275 | 5.909559 | 6.134745 | 6.110614 | 6.146031 | 6.091578 | 6.028614 | 6.073251 | 6.052162 | 6.043805 |
| GO:1903861 | positive regulation of dendrite extension | 18 | -0.7105121 | -1.693438 | 0.01079580506 | 0.46363380 | 0.45737919 | 1038 | tags=44%, list=7%, signal=41% | CXCR4||SYT3||SYT4||NEDD4L||RIMS2||SYT2||UNC13A||RASAL1 | 4.111397 | 3.524411 | 3.726524 | 4.027506 | 4.394276 | 3.907265 | 4.070141 | 3.432185 | 3.709664 | 3.483486 | 3.454773 | 3.527354 | 3.540637 | 3.841653 | 3.949041 |
| GO:0006953 | acute-phase response | 25 | -0.6575983 | -1.676312 | 0.01121936817 | 0.47811769 | 0.47166769 | 2498 | tags=48%, list=18%, signal=39% | CD163||APOL2||TNFSF11||PLSCR1||CEBPB||TNFRSF11A||PTGS2||IL1B||ORM1||IL1A||ITIH4||IL6 | 4.477817 | 6.283921 | 6.888269 | 4.487096 | 4.554332 | 4.435619 | 4.430753 | 6.264953 | 6.262098 | 6.279962 | 6.327707 | 6.895921 | 6.878363 | 6.897119 | 6.881575 |
| GO:0048791 | calcium ion-regulated exocytosis of neurotransmitter | 10 | -0.7980672 | -1.673508 | 0.01172197457 | 0.49572320 | 0.48903569 | 496 | tags=40%, list=4%, signal=39% | RIMS2||SYT2||UNC13A||UNC13C | 4.247731 | 4.494508 | 4.592804 | 4.274309 | 4.238411 | 4.256067 | 4.221602 | 4.412503 | 4.618486 | 4.553281 | 4.380381 | 4.564744 | 4.557995 | 4.599260 | 4.647467 |
| GO:0045589 | regulation of regulatory T cell differentiation | 17 | -0.7164431 | -1.685054 | 0.01182143413 | 0.49614201 | 0.48944885 | 1978 | tags=65%, list=14%, signal=56% | FANCA||DUSP10||HLA-DRB1||KAT2A||IL4I1||SOCS1||MDK||LILRB4||DROSHA||IRF1||HLA-DRA | 5.843576 | 6.118296 | 6.383853 | 5.819108 | 5.848577 | 5.827077 | 5.878799 | 6.137078 | 6.103454 | 6.105622 | 6.126752 | 6.343406 | 6.346365 | 6.516853 | 6.320029 |
| GO:0042104 | positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation | 17 | -0.7149746 | -1.681600 | 0.01213252450 | 0.50159840 | 0.49483164 | 1875 | tags=41%, list=13%, signal=36% | IL18||ICOSLG||IL12RB1||TNFSF9||IGF2||IL23A||SLAMF1 | 7.432329 | 7.614432 | 7.605994 | 7.419812 | 7.447136 | 7.425538 | 7.436678 | 7.624616 | 7.602278 | 7.630778 | 7.599803 | 7.594091 | 7.631608 | 7.597116 | 7.600848 |
| GO:0001832 | blastocyst growth | 18 | 0.6569287 | 1.768106 | 0.01250710631 | 0.50576182 | 0.49893889 | 1088 | tags=17%, list=8%, signal=15% | RAD51B||ACVR1C||COPS2 | 4.236284 | 4.543136 | 4.322980 | 4.218266 | 4.160807 | 4.192523 | 4.364920 | 4.724642 | 4.366457 | 4.588546 | 4.467950 | 4.313662 | 4.319188 | 4.371547 | 4.286198 |
| GO:0002548 | monocyte chemotaxis | 38 | -0.5930421 | -1.625653 | 0.01314301865 | 0.52008802 | 0.51307183 | 2104 | tags=45%, list=15%, signal=38% | TNFSF11||CCL20||CCL2||CCL3||CCL4||CCL4L2||TNFRSF11A||CCL3L3||CCL19||CCR1||CCL5||CCL1||PLA2G7||NBL1||CCL22||CXCL10||IL6 | 6.015285 | 7.089481 | 7.407922 | 6.029063 | 5.976965 | 6.024432 | 6.030003 | 7.075836 | 7.122358 | 7.084625 | 7.074580 | 7.394666 | 7.415928 | 7.428812 | 7.391958 |
| GO:0021602 | cranial nerve morphogenesis | 17 | -0.7096209 | -1.669009 | 0.01415461191 | 0.54422800 | 0.53688614 | 1536 | tags=53%, list=11%, signal=47% | GLI3||SEMA3A||PLXNA3||EPHB2||TIFAB||HOXB3||TFAP2A||SEMA3F||ATP8B1 | 5.772104 | 5.528216 | 5.450904 | 5.740605 | 5.742866 | 5.742486 | 5.858859 | 5.564805 | 5.523246 | 5.505467 | 5.518659 | 5.412006 | 5.295725 | 5.576371 | 5.504323 |
| GO:0046718 | viral entry into host cell | 106 | -0.4687914 | -1.495270 | 0.01456250771 | 0.54422800 | 0.53688614 | 2922 | tags=35%, list=21%, signal=28% | SLC1A5||IFITM2||SLC52A2||NPC1||ITGB7||TPCN2||CXADR||ANPEP||TRIM26||CD209||TRIM14||HLA-DRB1||HSPA1A||CXCR4||CTSL||PLSCR1||CD74||TPCN1||HS3ST5||SELPLG||CTSB||SLC3A2||EFNB2||CLEC5A||IFITM3||AXL||PTX3||NCAM1||ITGB3||CD86||TNFRSF14||TRIM22||LY6E||TYRO3||SLAMF1||IFITM1||SIGLEC1 | 7.009564 | 7.548432 | 7.729019 | 6.990850 | 7.020449 | 7.007320 | 7.019440 | 7.543839 | 7.524789 | 7.557716 | 7.567034 | 7.702282 | 7.736501 | 7.747486 | 7.729424 |
| GO:0032689 | negative regulation of interferon-gamma production | 22 | -0.6639635 | -1.650546 | 0.01472798317 | 0.54422800 | 0.53688614 | 2227 | tags=50%, list=16%, signal=42% | RARA||DDIT3||HLA-DRB1||NOD2||CD274||ZC3H12A||LILRB4||AXL||INHBA||SLAMF1||PDCD1LG2 | 7.103056 | 7.416003 | 7.404429 | 7.095650 | 7.099211 | 7.117107 | 7.100160 | 7.429482 | 7.405034 | 7.406554 | 7.422791 | 7.399709 | 7.410679 | 7.421906 | 7.385165 |
| GO:0001947 | heart looping | 34 | -0.6042695 | -1.627510 | 0.01477062917 | 0.54422800 | 0.53688614 | 1130 | tags=29%, list=8%, signal=27% | MEF2C||WNT5A||TBX3||TBX2||ASB2||DLL1||MICAL2||BBS7||SETDB2||MKKS | 5.926671 | 5.484374 | 5.611538 | 6.018006 | 5.740141 | 5.845296 | 6.078235 | 5.401453 | 5.400669 | 5.451636 | 5.666635 | 5.833975 | 5.375363 | 5.543513 | 5.654687 |
| GO:0040018 | positive regulation of multicellular organism growth | 13 | -0.7517939 | -1.673468 | 0.01506410256 | 0.54481459 | 0.53746482 | 579 | tags=23%, list=4%, signal=22% | CSF1||IGF2||MKKS | 6.628846 | 6.373293 | 6.551139 | 6.662429 | 6.477204 | 6.654720 | 6.710360 | 6.303844 | 6.329563 | 6.278529 | 6.562869 | 6.587956 | 6.532087 | 6.418305 | 6.655787 |
| GO:0001960 | negative regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway | 49 | -0.5560949 | -1.589682 | 0.01584915972 | 0.56082048 | 0.55325478 | 1784 | tags=31%, list=13%, signal=27% | USP18||STAT2||NOL3||NLRC5||OAS1||IRAK3||PIAS4||CCL5||OAS3||NR1H3||ISG15||IL1R2||IL1RN||PADI2||IL6 | 5.669144 | 5.952244 | 6.322585 | 5.666857 | 5.651667 | 5.695160 | 5.662533 | 5.941380 | 5.997181 | 5.911598 | 5.957491 | 6.303233 | 6.350566 | 6.291838 | 6.343819 |
| GO:0051447 | negative regulation of meiotic cell cycle | 11 | -0.7728065 | -1.658046 | 0.01748138556 | 0.59139509 | 0.58341694 | 227 | tags=18%, list=2%, signal=18% | LIF||FBXO43 | 4.643743 | 4.744738 | 4.691910 | 4.621967 | 4.594194 | 4.830335 | 4.508743 | 4.784420 | 4.667871 | 4.794679 | 4.728453 | 4.549656 | 4.753018 | 4.637353 | 4.813243 |
| GO:0002726 | positive regulation of T cell cytokine production | 21 | -0.6650822 | -1.634441 | 0.01907645723 | 0.61036122 | 0.60212720 | 1262 | tags=33%, list=9%, signal=30% | IL18||SASH3||IL1B||MALT1||SLAMF1||RSAD2||IL6 | 8.513535 | 8.485796 | 8.678677 | 8.525804 | 8.501076 | 8.511088 | 8.516063 | 8.494988 | 8.485017 | 8.474899 | 8.488205 | 8.675948 | 8.677864 | 8.678342 | 8.682545 |
| GO:0035066 | positive regulation of histone acetylation | 21 | -0.6647832 | -1.633706 | 0.01907645723 | 0.61036122 | 0.60212720 | 1527 | tags=29%, list=11%, signal=25% | KAT2A||SPHK2||MUC1||IL1B||LIF||RPS6KA5 | 5.086219 | 6.607498 | 7.179867 | 5.050960 | 5.195141 | 5.006793 | 5.085190 | 6.620769 | 6.565526 | 6.624672 | 6.618215 | 7.162734 | 7.195393 | 7.176444 | 7.184701 |
| GO:0046007 | negative regulation of activated T cell proliferation | 10 | -0.7815492 | -1.638871 | 0.01915139508 | 0.61036122 | 0.60212720 | 1475 | tags=40%, list=11%, signal=36% | CD274||SCRIB||LILRB4||PDCD1LG2 | 5.847677 | 5.759677 | 5.765917 | 5.910337 | 5.758254 | 5.868327 | 5.849544 | 5.851510 | 5.704609 | 5.772451 | 5.705036 | 5.694826 | 5.773284 | 5.913080 | 5.669842 |
| GO:0032729 | positive regulation of interferon-gamma production | 51 | -0.5410557 | -1.556087 | 0.01918106380 | 0.61036122 | 0.60212720 | 1485 | tags=29%, list=11%, signal=26% | IL12RB1||SCRIB||PDE4B||ZP3||SASH3||PDE4D||IL1B||WNT5A||SLC7A5||SLC11A1||ISG15||CD226||IL23A||SLAMF1||PTPN22 | 5.061710 | 6.360359 | 6.771145 | 5.027389 | 5.037053 | 5.063294 | 5.117400 | 6.367267 | 6.364964 | 6.359347 | 6.349795 | 6.767682 | 6.767082 | 6.775032 | 6.774764 |
| GO:0051216 | cartilage development | 109 | -0.4574516 | -1.464227 | 0.01928036350 | 0.61036122 | 0.60212720 | 1959 | tags=27%, list=14%, signal=23% | ANXA6||TIMP1||THRA||POR||GLI3||SNAI1||WNT5B||KAT2A||BMP1||PITX1||COL27A1||LNPK||CHI3L1||ADAMTS7||EVC||SFRP2||MEF2C||MDK||CTSK||WNT5A||CCN2||TRIP11||LTBP3||SCX||HOXB3||SULF2||BMP6||MKKS||COL11A2 | 6.275789 | 6.191794 | 6.459648 | 6.293646 | 6.224413 | 6.295572 | 6.288317 | 6.178573 | 6.164048 | 6.191941 | 6.231731 | 6.494818 | 6.444249 | 6.431797 | 6.466929 |
| GO:0098586 | cellular response to virus | 65 | -0.5103682 | -1.526476 | 0.01955602537 | 0.61557034 | 0.60726605 | 1431 | tags=18%, list=10%, signal=17% | ZC3H12A||OAS1||DDX58||CCL19||DDX60||CCL5||OAS3||IRF7||IFI6||OASL||CXCL10||IL6 | 6.015945 | 6.418838 | 6.713349 | 6.018593 | 5.992639 | 5.996828 | 6.054875 | 6.433678 | 6.408662 | 6.415064 | 6.417829 | 6.689992 | 6.716508 | 6.698090 | 6.748112 |
| GO:2000047 | regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin | 13 | -0.7383392 | -1.643518 | 0.01987179487 | 0.62013074 | 0.61176493 | 1842 | tags=46%, list=13%, signal=40% | MAD2L2||NOTCH4||WNT5A||ADAM19||BMP6||VEGFA | 5.024370 | 5.064677 | 5.299132 | 5.080467 | 4.930406 | 5.012998 | 5.068776 | 5.056304 | 4.998871 | 5.114176 | 5.086826 | 5.327222 | 5.302820 | 5.263137 | 5.302621 |
| GO:0030540 | female genitalia development | 10 | -0.7753488 | -1.625869 | 0.02063727918 | 0.62013074 | 0.61176493 | 899 | tags=40%, list=6%, signal=37% | WNT5A||AXL||TBX3||TYRO3 | 4.073644 | 4.197452 | 4.251028 | 4.168093 | 4.005688 | 4.054065 | 4.061814 | 4.255141 | 4.207155 | 4.153611 | 4.171813 | 4.155062 | 4.314462 | 4.231240 | 4.297905 |
| GO:0070528 | protein kinase C signaling | 17 | -0.6921132 | -1.627831 | 0.02068750972 | 0.62013074 | 0.61176493 | 1786 | tags=47%, list=13%, signal=41% | CD40||AZU1||SPHK2||WNT5A||MC1R||ANKRD1||VEGFA||MAS1 | 5.026988 | 4.274420 | 4.594142 | 4.995793 | 4.972939 | 5.041678 | 5.094528 | 4.252055 | 4.247629 | 4.252134 | 4.343587 | 4.642341 | 4.636973 | 4.553533 | 4.540722 |
| GO:0046823 | negative regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport | 18 | 0.6278008 | 1.689709 | 0.02103467879 | 0.62013074 | 0.61176493 | 2548 | tags=28%, list=18%, signal=23% | BARD1||ANGPT1||CD36||SUFU||SUMO1 | 5.899309 | 6.099733 | 5.993943 | 5.872820 | 5.916242 | 5.907725 | 5.900082 | 6.085390 | 6.046698 | 6.187515 | 6.075366 | 5.973943 | 6.011472 | 6.009016 | 5.980961 |
| GO:0016339 | calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules | 19 | 0.6119525 | 1.665494 | 0.02165752238 | 0.62013074 | 0.61176493 | 1623 | tags=47%, list=12%, signal=42% | PCDHB3||PCDHB9||PCDHGB4||PCDH12||PCDHB5||AJUBA||PCDHB2||PCDHB13||PCDHB10 | 5.167494 | 4.647021 | 4.607629 | 5.174368 | 5.194727 | 5.139023 | 5.161289 | 4.751733 | 4.629256 | 4.549382 | 4.650474 | 4.644445 | 4.631222 | 4.601767 | 4.551316 |
| GO:0002501 | peptide antigen assembly with MHC protein complex | 10 | -0.7728449 | -1.620618 | 0.02179296682 | 0.62013074 | 0.61176493 | 1978 | tags=70%, list=14%, signal=60% | HLA-DRB1||HLA-DMA||HLA-DQB1||TAPBPL||HLA-DQA1||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA2 | 9.595804 | 9.234129 | 9.291826 | 9.610318 | 9.585192 | 9.591428 | 9.596159 | 9.249391 | 9.231955 | 9.212447 | 9.242453 | 9.293412 | 9.294732 | 9.288342 | 9.290810 |
| GO:0035459 | vesicle cargo loading | 20 | 0.6038802 | 1.658383 | 0.02182770664 | 0.62013074 | 0.61176493 | 15 | tags=5%, list=0%, signal=5% | KIF13A | 5.702846 | 6.171889 | 6.084227 | 5.680224 | 5.650561 | 5.676197 | 5.799717 | 6.190472 | 6.141915 | 6.177819 | 6.176899 | 6.079152 | 6.088618 | 6.062704 | 6.106094 |
| GO:0090308 | regulation of DNA methylation-dependent heterochromatin assembly | 12 | -0.7440815 | -1.626030 | 0.02247009376 | 0.62870868 | 0.62022715 | 301 | tags=25%, list=2%, signal=24% | TRIM28||AICDA||SETDB2 | 6.224960 | 6.056379 | 6.274191 | 6.377107 | 6.064641 | 6.144614 | 6.292764 | 5.839932 | 6.193466 | 6.042057 | 6.126101 | 6.259820 | 6.233783 | 6.341809 | 6.259033 |
| GO:1901616 | organic hydroxy compound catabolic process | 43 | -0.5573390 | -1.558491 | 0.02311333890 | 0.63906118 | 0.63043999 | 2508 | tags=37%, list=18%, signal=31% | PDXP||SYNJ1||ALDH1B1||GPD2||ALDH3B1||FAH||APOE||SULT1A3||CYP27A1||CYP27B1||INPP5E||HSD17B6||ALDH2||LRRC51||SCARF1||SULT1A4 | 4.752985 | 4.716370 | 4.793028 | 4.786667 | 4.685022 | 4.820111 | 4.716115 | 4.714948 | 4.733698 | 4.684820 | 4.731487 | 4.778177 | 4.890277 | 4.714877 | 4.783242 |
| GO:1905330 | regulation of morphogenesis of an epithelium | 31 | -0.5984700 | -1.584171 | 0.02369668246 | 0.64120370 | 0.63255361 | 1036 | tags=29%, list=7%, signal=27% | WNT5B||ITGAX||MDK||WNT5A||TBX2||VEGFA||LIF||LBX2||CXCL10 | 5.583208 | 5.656009 | 5.793122 | 5.590278 | 5.571918 | 5.627294 | 5.542018 | 5.639111 | 5.579289 | 5.668841 | 5.732568 | 5.774253 | 5.801390 | 5.782519 | 5.813987 |
| GO:0006085 | acetyl-CoA biosynthetic process | 16 | 0.6383949 | 1.675116 | 0.02465753425 | 0.64120370 | 0.63255361 | 3827 | tags=62%, list=27%, signal=45% | MLYCD||PDK2||PDK3||ACAT1||ACSS2||PDHX||DLAT||ACSS1||PPCS||MPC2 | 5.187207 | 5.088063 | 4.916485 | 5.187405 | 5.167990 | 5.216616 | 5.176345 | 5.073290 | 5.046575 | 5.155839 | 5.074196 | 4.954277 | 4.944155 | 4.905791 | 4.859812 |
| GO:0050796 | regulation of insulin secretion | 104 | -0.4545800 | -1.446688 | 0.02477393782 | 0.64120370 | 0.63255361 | 2014 | tags=23%, list=14%, signal=20% | SIDT2||STX1A||HLA-DRB1||CDK16||NADK||STXBP4||ZBED6||SLC8B1||LRP1||IL1B||VSNL1||PPARD||EFNA5||SNAP25||OXCT1||IRS1||TRPM2||CCL5||NLGN2||LRP5||KLF7||GIPR||IL6||NOS2 | 5.587320 | 6.257123 | 6.564618 | 5.575260 | 5.553550 | 5.579699 | 5.639360 | 6.277235 | 6.255048 | 6.240779 | 6.255194 | 6.572544 | 6.577142 | 6.554052 | 6.554584 |
| GO:0032693 | negative regulation of interleukin-10 production | 13 | -0.7252931 | -1.614478 | 0.02500000000 | 0.64120370 | 0.63255361 | 1475 | tags=38%, list=11%, signal=34% | CD274||LILRB4||DLL1||IL23A||PDCD1LG2 | 7.247273 | 7.426243 | 7.442423 | 7.279060 | 7.210797 | 7.264159 | 7.234106 | 7.422633 | 7.451315 | 7.426749 | 7.403876 | 7.438272 | 7.440611 | 7.434680 | 7.456037 |
| GO:0071346 | cellular response to interferon-gamma | 83 | -0.4728460 | -1.465918 | 0.02566722002 | 0.64322115 | 0.63454383 | 2118 | tags=35%, list=15%, signal=30% | GBP5||MYO1C||SLC26A6||CCL20||STAT1||GBP1||CCL2||CASP1||TP53||IL12RB1||NLRC5||CCL3||STXBP4||ADAMTS13||SOCS1||CCL4||CCL4L2||CCL3L3||CCL19||WNT5A||PARP9||HCK||IRF1||CCL5||CCL1||CDC42EP2||NR1H3||CCL22||NOS2 | 7.064393 | 7.498321 | 7.582831 | 7.071703 | 7.051266 | 7.059501 | 7.074975 | 7.492450 | 7.503014 | 7.501554 | 7.496239 | 7.564915 | 7.593909 | 7.598698 | 7.573530 |
| GO:0030210 | heparin biosynthetic process | 10 | 0.7238492 | 1.681018 | 0.02585551331 | 0.64322115 | 0.63454383 | 737 | tags=50%, list=5%, signal=47% | SLC10A7||ANGPT1||ENSG00000272916||XYLT2||EXT2 | 3.661279 | 3.881649 | 3.422097 | 3.729292 | 3.554567 | 3.572410 | 3.775999 | 3.673751 | 3.557930 | 3.998849 | 4.204232 | 3.388236 | 3.391303 | 3.420657 | 3.486033 |
| GO:0002230 | positive regulation of defense response to virus by host | 26 | -0.6149083 | -1.582709 | 0.02589233470 | 0.64322115 | 0.63454383 | 1879 | tags=35%, list=13%, signal=30% | ZDHHC1||STAT1||IL12RB1||ZC3H12A||DDX58||PARP9||AIM2||IL23A||PTPN22 | 5.529088 | 5.687898 | 5.779208 | 5.493843 | 5.526934 | 5.497232 | 5.595990 | 5.750185 | 5.655923 | 5.666179 | 5.677389 | 5.787379 | 5.767369 | 5.754404 | 5.807125 |
| GO:0043277 | apoptotic cell clearance | 41 | -0.5581671 | -1.546642 | 0.02658227848 | 0.64723922 | 0.63850770 | 2344 | tags=39%, list=17%, signal=33% | TREX1||RARA||RHOH||CCL2||MARCO||TGM2||JMJD6||LRP1||ABCA7||AXL||ITGB3||RHOBTB1||C3||NR1H3||TYRO3||XKR6 | 6.728644 | 6.604731 | 6.504254 | 6.738927 | 6.700993 | 6.750185 | 6.724000 | 6.590213 | 6.633551 | 6.635277 | 6.558462 | 6.480038 | 6.534849 | 6.492706 | 6.508838 |
| GO:0099170 | postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission | 10 | 0.7177300 | 1.666807 | 0.02661596958 | 0.64723922 | 0.63850770 | 2784 | tags=60%, list=20%, signal=48% | PLCB1||NRGN||CYFIP1||RNF19A||GHRL||EIF4E | 7.536598 | 6.314280 | 5.978151 | 7.504574 | 7.535887 | 7.611810 | 7.491061 | 6.240615 | 6.370356 | 6.290215 | 6.352275 | 6.015560 | 5.965545 | 5.968520 | 5.962314 |
| GO:0050427 | 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate metabolic process | 15 | -0.7002000 | -1.604684 | 0.02668784750 | 0.64723922 | 0.63850770 | 1750 | tags=27%, list=13%, signal=23% | SLC26A1||SULT1A3||ENPP1||SULT1A4 | 4.836897 | 4.908847 | 4.842507 | 4.861397 | 4.863681 | 4.780259 | 4.840689 | 4.901871 | 4.923166 | 4.906805 | 4.903446 | 4.877678 | 4.843539 | 4.782857 | 4.864140 |
| GO:0060337 | type I interferon signaling pathway | 45 | -0.5423257 | -1.528172 | 0.02712427346 | 0.65051288 | 0.64173720 | 3437 | tags=47%, list=25%, signal=35% | SAMHD1||IRF3||PTPN1||CACTIN||IFITM2||PTPN6||TYK2||TREX1||TBK1||USP18||STAT1||STAT2||NLRC5||OAS1||IFITM3||WNT5A||OAS3||IRF7||OAS2||ISG15||IFITM1 | 6.237278 | 6.348637 | 6.435985 | 6.298176 | 6.215299 | 6.248825 | 6.184335 | 6.339735 | 6.349227 | 6.366194 | 6.339225 | 6.409050 | 6.471871 | 6.430557 | 6.431744 |
| GO:1904646 | cellular response to amyloid-beta | 31 | 0.5105419 | 1.555594 | 0.02796972688 | 0.66492089 | 0.65595084 | 2275 | tags=45%, list=16%, signal=38% | TLR4||GSK3B||IGF1R||ADRB2||BCL2L11||NGFR||ITGA4||CD36||FOXO3||TLR6||PARP1||AGER||CACNB1||SNX6 | 5.857272 | 5.790503 | 5.677037 | 5.844758 | 5.886525 | 5.860998 | 5.836297 | 5.917752 | 5.839530 | 5.724875 | 5.666589 | 5.767598 | 5.649883 | 5.628643 | 5.657940 |
| GO:0090713 | immunological memory process | 13 | -0.7181678 | -1.598617 | 0.02820512821 | 0.66492089 | 0.65595084 | 1978 | tags=38%, list=14%, signal=33% | HLA-DRB1||IL12RB1||TNFRSF14||HLA-DRA||IL23A | 6.654950 | 6.912957 | 7.120824 | 6.669059 | 6.666988 | 6.631105 | 6.652330 | 6.903098 | 6.902138 | 6.933766 | 6.912602 | 7.119586 | 7.103230 | 7.113514 | 7.146609 |
| GO:0042755 | eating behavior | 13 | 0.6711952 | 1.663677 | 0.02870813397 | 0.66792284 | 0.65891229 | 3134 | tags=85%, list=22%, signal=66% | P2RY1||SLC24A4||BBS12||OPRL1||NAPEPLD||STAT3||CPT1A||GHRL||BBIP1||MTOR||GDF15 | 4.268717 | 4.620288 | 4.328254 | 4.174764 | 4.257275 | 4.546384 | 4.048966 | 4.528809 | 4.768967 | 4.616621 | 4.554500 | 4.299488 | 4.463644 | 4.313263 | 4.226177 |
| GO:1903557 | positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor superfamily cytokine production | 84 | -0.4665092 | -1.449787 | 0.02989821883 | 0.67843622 | 0.66928384 | 1587 | tags=24%, list=11%, signal=21% | AZU1||NOD2||CCL3||OAS1||SASH3||SPHK2||DDX58||CCL19||WNT5A||EPHB2||OAS3||CD86||ADAM8||ORM1||OAS2||PTAFR||IL1A||IL23A||NOD1||IL6 | 6.945545 | 6.969009 | 6.967670 | 6.934640 | 6.951059 | 6.946531 | 6.949890 | 6.977096 | 6.969071 | 6.977675 | 6.952044 | 6.964348 | 6.975949 | 6.967790 | 6.962555 |
| GO:0019886 | antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II | 20 | -0.6489288 | -1.583317 | 0.03000304599 | 0.67843622 | 0.66928384 | 2478 | tags=55%, list=18%, signal=45% | LGMN||HLA-DRB1||CTSL||HLA-DMA||HLA-DQB1||CD74||IFI30||CTSD||HLA-DQA1||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA2 | 9.552787 | 9.590244 | 9.748362 | 9.564375 | 9.554671 | 9.547663 | 9.544358 | 9.586791 | 9.589386 | 9.584616 | 9.600132 | 9.735384 | 9.755223 | 9.745078 | 9.757654 |
| GO:0002675 | positive regulation of acute inflammatory response | 21 | -0.6397668 | -1.572228 | 0.03133989402 | 0.68744586 | 0.67817194 | 1268 | tags=43%, list=9%, signal=39% | ZP3||TNFRSF11A||PTGS2||IL1B||ADAM8||C3||OSM||CCR7||IL6 | 5.273196 | 7.293729 | 7.731690 | 5.262571 | 5.236677 | 5.286657 | 5.305942 | 7.297693 | 7.280986 | 7.277485 | 7.318385 | 7.728485 | 7.726545 | 7.743463 | 7.728200 |
| GO:0051904 | pigment granule transport | 20 | -0.6464476 | -1.577263 | 0.03137374353 | 0.68744586 | 0.67817194 | 1999 | tags=30%, list=14%, signal=26% | RAB17||BLOC1S3||RAB27A||BBS7||MYO7A||MKKS | 5.111898 | 4.785770 | 5.027363 | 5.269465 | 4.610605 | 5.020748 | 5.421479 | 4.647623 | 4.664442 | 4.597649 | 5.157859 | 5.162003 | 4.813096 | 4.759427 | 5.302000 |
| GO:0042509 | regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | 49 | -0.5247364 | -1.500039 | 0.03156168876 | 0.68744586 | 0.67817194 | 1875 | tags=31%, list=13%, signal=27% | IL18||CLCF1||CD40||SOCS1||CRLF1||PARP9||CSF2||CCL5||SOCS3||OSM||TNFRSF18||LIF||IL23A||IL6||INPP5F | 5.369853 | 6.178940 | 6.489370 | 5.328404 | 5.309394 | 5.497311 | 5.336278 | 6.143899 | 6.229540 | 6.166586 | 6.174354 | 6.460776 | 6.512806 | 6.493595 | 6.489824 |
| GO:0001768 | establishment of T cell polarity | 10 | -0.7553435 | -1.583919 | 0.03169886082 | 0.68744586 | 0.67817194 | 1424 | tags=40%, list=10%, signal=36% | SCRIB||CCL19||RIPOR2||CCR7 | 6.845278 | 6.622525 | 6.714633 | 6.851050 | 6.904095 | 6.808720 | 6.815249 | 6.654775 | 6.593157 | 6.612120 | 6.629333 | 6.707692 | 6.696857 | 6.681901 | 6.770494 |
| GO:0034162 | toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway | 15 | -0.6874439 | -1.575450 | 0.03208895949 | 0.68744586 | 0.67817194 | 483 | tags=27%, list=3%, signal=26% | EPG5||PTPRS||RSAD2||PTPN22 | 6.295277 | 6.440738 | 6.342425 | 6.308994 | 6.265295 | 6.286077 | 6.320123 | 6.464326 | 6.399709 | 6.435549 | 6.462424 | 6.330184 | 6.349060 | 6.371494 | 6.318400 |
| GO:0060042 | retina morphogenesis in camera-type eye | 21 | -0.6363721 | -1.563886 | 0.03255109765 | 0.68744586 | 0.67817194 | 1738 | tags=29%, list=12%, signal=25% | SDK1||MFSD2A||DLL1||TFAP2A||LRP5||IGFN1 | 4.714610 | 5.297449 | 5.756285 | 4.608783 | 4.649712 | 4.649710 | 4.927121 | 5.245697 | 5.340457 | 5.362179 | 5.237184 | 5.746755 | 5.794535 | 5.718749 | 5.764052 |
| GO:0010862 | positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation | 29 | 0.5136752 | 1.540749 | 0.03256268317 | 0.68744586 | 0.67817194 | 1380 | tags=34%, list=10%, signal=31% | RBPMS||TGFB2||GDF7||PPARG||DAB2||BMP10||BMP8B||BMP4||BMP2||BMPR2 | 6.012736 | 6.118374 | 6.006134 | 6.036983 | 6.002929 | 5.998132 | 6.012589 | 6.137328 | 6.096792 | 6.131957 | 6.107025 | 6.033158 | 6.021711 | 6.011366 | 5.957130 |
| GO:0035455 | response to interferon-alpha | 19 | -0.6534337 | -1.576726 | 0.03272671662 | 0.68744586 | 0.67817194 | 1463 | tags=42%, list=10%, signal=38% | BST2||IFITM3||MX2||LAMP3||AXL||IFIT3||IFIT2||IFITM1 | 5.821106 | 5.578908 | 5.883922 | 5.807601 | 5.850533 | 5.874784 | 5.748323 | 5.623158 | 5.542690 | 5.613245 | 5.534310 | 5.881404 | 5.939070 | 5.838244 | 5.875156 |
| GO:0032494 | response to peptidoglycan | 11 | -0.7334386 | -1.573583 | 0.03285853027 | 0.68744586 | 0.67817194 | 1946 | tags=45%, list=14%, signal=39% | CARD9||RELA||NOD2||IRAK3||IL6 | 5.990291 | 6.090473 | 6.285618 | 6.233650 | 5.864780 | 5.957013 | 5.873721 | 6.116872 | 6.080795 | 6.085164 | 6.078729 | 6.233616 | 6.337289 | 6.289306 | 6.280386 |
| GO:0003184 | pulmonary valve morphogenesis | 12 | 0.6703884 | 1.634486 | 0.03406708595 | 0.70422260 | 0.69472235 | 1083 | tags=33%, list=8%, signal=31% | SLIT2||HEY2||TGFB2||BMP4 | 4.232616 | 4.706080 | 4.796837 | 4.210548 | 4.371543 | 4.185157 | 4.153224 | 4.690082 | 4.653038 | 4.733839 | 4.745497 | 4.823770 | 4.891129 | 4.701730 | 4.763877 |
| GO:0043029 | T cell homeostasis | 27 | 0.5324583 | 1.569272 | 0.03456000000 | 0.70735711 | 0.69781458 | 2356 | tags=37%, list=17%, signal=31% | FAS||ZC3H8||BCL2L11||BCL2||SPNS2||CASP3||PPP2R3C||NCKAP1L||PMAIP1||RPS6 | 7.671918 | 7.805117 | 7.669573 | 7.671764 | 7.670623 | 7.680143 | 7.665102 | 7.803371 | 7.808535 | 7.799286 | 7.809252 | 7.664266 | 7.656575 | 7.684692 | 7.672606 |
| GO:0002830 | positive regulation of type 2 immune response | 13 | -0.7034776 | -1.565917 | 0.03493589744 | 0.70735711 | 0.69781458 | 2227 | tags=54%, list=16%, signal=45% | RARA||IL18||NOD2||CD74||CD86||RSAD2||IL6 | 6.588866 | 6.853889 | 6.989710 | 6.597722 | 6.594987 | 6.576562 | 6.586096 | 6.841908 | 6.861320 | 6.870537 | 6.841574 | 6.986491 | 6.968001 | 6.994973 | 7.009068 |
| GO:0050872 | white fat cell differentiation | 11 | 0.6863164 | 1.629058 | 0.03530334728 | 0.70735711 | 0.69781458 | 643 | tags=36%, list=5%, signal=35% | PDGFRA||FABP4||CTBP2||PPARG | 5.874633 | 4.177129 | 3.972494 | 5.857298 | 5.885283 | 5.910068 | 5.844999 | 4.227054 | 4.251337 | 4.072105 | 4.151241 | 4.027595 | 3.904922 | 3.957614 | 3.996937 |
| GO:0046496 | nicotinamide nucleotide metabolic process | 23 | -0.6181744 | -1.550537 | 0.03536785554 | 0.70735711 | 0.69781458 | 1800 | tags=35%, list=13%, signal=30% | HAAO||NADK||KMO||NADSYN1||NUDT17||PARP9||PARP10||IDO1 | 5.311845 | 5.029503 | 5.187925 | 5.419453 | 5.272553 | 5.221762 | 5.326140 | 5.064221 | 5.089956 | 4.985796 | 4.974648 | 5.206519 | 5.177726 | 5.137849 | 5.228027 |
| GO:1900120 | regulation of receptor binding | 14 | -0.6905174 | -1.559939 | 0.03648239605 | 0.71697571 | 0.70730341 | 1122 | tags=29%, list=8%, signal=26% | ATP2A3||MMP9||PTPRF||PLCL1 | 8.862317 | 9.262859 | 9.620660 | 8.875010 | 8.856205 | 8.854805 | 8.863160 | 9.264784 | 9.267200 | 9.248698 | 9.270655 | 9.608363 | 9.620716 | 9.625195 | 9.628287 |
| GO:0045840 | positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division | 28 | -0.5904343 | -1.535673 | 0.03655352480 | 0.71697571 | 0.70730341 | 1023 | tags=32%, list=7%, signal=30% | SPHK1||INSR||ESPL1||EREG||IL1B||LRP5||IL1A||IGF2||PDGFRB | 5.261987 | 6.392799 | 6.881502 | 5.271220 | 5.227941 | 5.296528 | 5.251376 | 6.395563 | 6.401692 | 6.375507 | 6.398291 | 6.869153 | 6.863491 | 6.908618 | 6.884324 |
| GO:0035743 | CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell cytokine production | 11 | -0.7270986 | -1.559981 | 0.03658141793 | 0.71697571 | 0.70730341 | 964 | tags=45%, list=7%, signal=42% | IL18||IL1B||SLAMF1||RSAD2||IL6 | 6.600709 | 7.922506 | 8.388983 | 6.626701 | 6.599524 | 6.585678 | 6.590584 | 7.918833 | 7.917185 | 7.927209 | 7.926770 | 8.383505 | 8.381310 | 8.396979 | 8.394078 |
| GO:0062013 | positive regulation of small molecule metabolic process | 89 | -0.4536419 | -1.416438 | 0.03697115995 | 0.71697571 | 0.70730341 | 2095 | tags=27%, list=15%, signal=23% | MT-CO2||TWIST1||PPARA||GUCA1B||INSR||POR||KAT2A||CD74||ENTPD5||CES1||PTGS2||IL1B||SLC25A12||PPARD||ZBTB20||SRC||IRS1||NR1H3||NR4A3||BMP6||PTAFR||IGF2||MAS1||NOS2 | 8.108726 | 8.209219 | 8.383735 | 8.112826 | 8.109354 | 8.102207 | 8.110494 | 8.216754 | 8.199770 | 8.208709 | 8.211591 | 8.384591 | 8.383623 | 8.393581 | 8.373071 |
| GO:0030502 | negative regulation of bone mineralization | 11 | -0.7246455 | -1.554718 | 0.03771447070 | 0.71697571 | 0.70730341 | 1430 | tags=36%, list=10%, signal=33% | CCL3||CCR1||ENPP1||LTBP3 | 6.227861 | 6.698509 | 6.971040 | 6.256669 | 6.255639 | 6.203819 | 6.194170 | 6.681554 | 6.751598 | 6.709457 | 6.649472 | 6.973834 | 6.987450 | 6.977402 | 6.945134 |
| GO:0030198 | extracellular matrix organization | 163 | -0.4058992 | -1.353273 | 0.03771827707 | 0.71697571 | 0.70730341 | 1500 | tags=23%, list=11%, signal=21% | BMP1||MMP3||COL27A1||NFKB2||ADAMTS13||APLP1||ADAMTS7||COLGALT2||MMP16||SFRP2||SPINT1||SH3PXD2B||COL9A2||COL8A1||LRP1||CTSK||PAPLN||MMP9||EMILIN1||COL15A1||COL19A1||CCN2||TPSAB1||PTX3||ADAM8||CREB3L1||LTBP3||TIE1||MMP7||SCX||SULF2||COL5A3||MMP19||PHLDB1||COL11A2||IL6||COL6A6 | 5.865514 | 6.452022 | 6.689373 | 5.872118 | 5.857190 | 5.879513 | 5.853075 | 6.454535 | 6.441630 | 6.457438 | 6.454432 | 6.674094 | 6.708282 | 6.692937 | 6.681951 |
| GO:1903307 | positive regulation of regulated secretory pathway | 33 | -0.5633720 | -1.510443 | 0.03898690950 | 0.72538272 | 0.71559701 | 1268 | tags=24%, list=9%, signal=22% | ZP3||SPHK2||RAB27A||SYT4||UNC13D||PTAFR||HLA-F||SLC4A8 | 7.417680 | 7.167955 | 7.289319 | 7.406565 | 7.425838 | 7.418980 | 7.419270 | 7.159061 | 7.153311 | 7.186791 | 7.172425 | 7.277023 | 7.285496 | 7.316582 | 7.277812 |
| GO:0010575 | positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production | 18 | -0.6513680 | -1.552474 | 0.03901912400 | 0.72538272 | 0.71559701 | 1114 | tags=33%, list=8%, signal=31% | PTGS2||IL1B||C3||SULF2||IL1A||IL6 | 5.703219 | 7.368466 | 7.853234 | 5.666546 | 5.678995 | 5.687635 | 5.777032 | 7.370343 | 7.351860 | 7.380938 | 7.370572 | 7.850991 | 7.857488 | 7.859208 | 7.845206 |
| GO:0010818 | T cell chemotaxis | 19 | -0.6429985 | -1.551546 | 0.03914971708 | 0.72538272 | 0.71559701 | 1430 | tags=42%, list=10%, signal=38% | PLEC||CCL3||CXCL13||WNT5A||CCL5||CXCR3||CXCL11||CXCL10 | 4.907867 | 6.594400 | 7.177205 | 4.909270 | 4.844420 | 4.944955 | 4.930782 | 6.608934 | 6.606323 | 6.586649 | 6.575426 | 7.155445 | 7.196697 | 7.163180 | 7.193047 |
| GO:0007213 | G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway | 11 | 0.6729033 | 1.597220 | 0.03948744770 | 0.72677894 | 0.71697440 | 890 | tags=27%, list=6%, signal=26% | CHRM3||PLCB1||GNAQ | 6.580873 | 6.475390 | 6.459657 | 6.570114 | 6.546453 | 6.629342 | 6.576306 | 6.481895 | 6.504016 | 6.434976 | 6.479806 | 6.488619 | 6.463550 | 6.439297 | 6.446662 |
| GO:0001916 | positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity | 22 | -0.6167644 | -1.533214 | 0.03967538323 | 0.72781994 | 0.71800136 | 1978 | tags=50%, list=14%, signal=43% | IL12B||HLA-B||CD1E||HLA-DRB1||CD1B||IL12RB1||CD1C||CD1A||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||IL23A | 8.482814 | 8.180112 | 8.259281 | 8.486891 | 8.471313 | 8.487194 | 8.485799 | 8.187655 | 8.182029 | 8.168210 | 8.182480 | 8.255091 | 8.260914 | 8.251131 | 8.269919 |
| GO:1905668 | positive regulation of protein localization to endosome | 10 | 0.6926261 | 1.608508 | 0.04005069708 | 0.73146633 | 0.72159855 | 1824 | tags=40%, list=13%, signal=35% | ABHD17C||ROCK2||SORL1||ABHD17B | 6.528154 | 6.648058 | 6.499869 | 6.521452 | 6.549011 | 6.525065 | 6.516874 | 6.653958 | 6.646768 | 6.658673 | 6.632698 | 6.479730 | 6.502109 | 6.526333 | 6.490889 |
| GO:0010460 | positive regulation of heart rate | 13 | 0.6414289 | 1.589896 | 0.04013822435 | 0.73146633 | 0.72159855 | 1887 | tags=54%, list=13%, signal=47% | HEY2||RGS4||EDN1||ADRB1||ADA||KCNQ1||GCH1 | 5.697794 | 5.657925 | 5.556025 | 5.695800 | 5.679907 | 5.730312 | 5.684616 | 5.631005 | 5.699075 | 5.637010 | 5.663606 | 5.516304 | 5.573468 | 5.564969 | 5.568627 |
| GO:0043410 | positive regulation of MAPK cascade | 294 | -0.3674452 | -1.283748 | 0.04050279330 | 0.73569008 | 0.72576532 | 2144 | tags=22%, list=15%, signal=19% | PAK1||MAPK8IP3||TNFSF11||SPHK1||CCL20||HLA-DRB1||PIK3R5||BANK1||CARD9||NRG1||SEMA7A||CD40||INSR||ALKAL1||PLCE1||SHC2||GPNMB||CCL2||APOE||NOD2||CD74||ZC3H12A||CCL3||CHI3L1||SEMA3A||MARCO||CCL4||CCL4L2||TNFRSF11A||MINK1||MID1||PRKD2||ACKR3||LRP1||CCL3L3||CCL19||CDH2||CCR1||GADD45G||ABCA7||IL1B||KSR1||WNT5A||SRC||CCN2||CCL5||CCL1||AVPI1||WWC1||ADAM8||FGD2||OSM||DENND2B||BCAR3||VEGFA||CCR7||C1QTNF1||IGF2||LIF||SLAMF1||PDGFRB||NOD1||CCL22||PIK3R6||PTPN22||IL6 | 6.155625 | 6.612169 | 6.770089 | 6.138974 | 6.154607 | 6.170347 | 6.158400 | 6.627727 | 6.592329 | 6.610567 | 6.617820 | 6.768754 | 6.778636 | 6.769732 | 6.763191 |
| GO:0032720 | negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production | 44 | -0.5261952 | -1.478608 | 0.04106548280 | 0.74347312 | 0.73344337 | 2251 | tags=32%, list=16%, signal=27% | BCL3||RARA||TWIST1||GPNMB||BPI||NOD2||ZC3H12A||IRAK3||AXL||ORM1||ACP5||MC1R||SLAMF1||PTPN22 | 5.778937 | 5.895945 | 5.963821 | 5.726875 | 5.766602 | 5.830032 | 5.790296 | 5.945824 | 5.888700 | 5.868194 | 5.879816 | 5.942601 | 5.972298 | 5.950618 | 5.989302 |
| GO:0010996 | response to auditory stimulus | 10 | -0.7409150 | -1.553663 | 0.04127455836 | 0.74482428 | 0.73477630 | 2527 | tags=60%, list=18%, signal=49% | ABHD12||SLC1A3||HTT||MDK||TIFAB||CXCL10 | 4.689960 | 4.702375 | 5.045967 | 4.625365 | 4.679347 | 4.709900 | 4.742653 | 4.576248 | 4.861619 | 4.620424 | 4.734097 | 4.938003 | 4.995218 | 5.159427 | 5.081378 |
| GO:0002639 | positive regulation of immunoglobulin production | 34 | -0.5566073 | -1.499139 | 0.04246555887 | 0.75890063 | 0.74866276 | 2290 | tags=35%, list=16%, signal=30% | TP53BP1||STAT6||XBP1||KMT5C||MAD2L2||CLCF1||CD40||SASH3||TNFSF13||EPHB2||CD86||IL6 | 5.544809 | 6.074248 | 6.158021 | 5.511684 | 5.467331 | 5.625192 | 5.570105 | 6.055142 | 6.054995 | 6.098047 | 6.088289 | 6.150438 | 6.167331 | 6.155687 | 6.158578 |
| GO:0006359 | regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III | 21 | 0.5595316 | 1.560026 | 0.04327347660 | 0.76978870 | 0.75940393 | 637 | tags=14%, list=5%, signal=14% | POLR3G||ZC3H8||RPTOR | 4.913519 | 4.816326 | 4.599466 | 4.885296 | 4.974016 | 4.908182 | 4.884727 | 4.665943 | 4.888425 | 4.767575 | 4.928656 | 4.529771 | 4.588951 | 4.713987 | 4.558207 |
| GO:0006575 | cellular modified amino acid metabolic process | 119 | -0.4243760 | -1.371571 | 0.04341481211 | 0.76978870 | 0.75940393 | 2926 | tags=28%, list=21%, signal=22% | PEMT||SERINC5||LPCAT4||GSTM4||NA||GGACT||ABHD12||GCLM||PLOD3||PTDSS2||OSBPL5||MMACHC||G6PD||GGT7||POR||PLSCR1||MFSD2A||CKB||PLOD2||OPLAH||KYAT1||CTSB||SLC16A10||CLIC2||CTSK||SLC22A4||CHAC1||GCLC||SLC7A11||CPT1B||GSTA4||CROT||VNN1 | 6.111899 | 6.307851 | 6.351181 | 6.092208 | 6.122760 | 6.131397 | 6.100881 | 6.307045 | 6.304798 | 6.302268 | 6.317247 | 6.355647 | 6.317517 | 6.362955 | 6.368062 |
| GO:0006925 | inflammatory cell apoptotic process | 18 | -0.6428191 | -1.532099 | 0.04349167181 | 0.76978870 | 0.75940393 | 1633 | tags=33%, list=12%, signal=29% | CTSL||NOD2||MEF2C||SLC7A11||IRF7||IL6 | 6.694620 | 7.364915 | 7.612106 | 6.685404 | 6.674196 | 6.728043 | 6.690268 | 7.378116 | 7.357581 | 7.324267 | 7.398651 | 7.680239 | 7.567477 | 7.595039 | 7.603223 |
| GO:0009072 | aromatic amino acid family metabolic process | 17 | -0.6530969 | -1.536066 | 0.04386374242 | 0.77390170 | 0.76346145 | 2309 | tags=53%, list=17%, signal=44% | KYNU||TDO2||QDPR||HPDL||HAAO||KMO||FAH||IL4I1||IDO1 | 4.853828 | 5.959237 | 6.234664 | 4.889652 | 4.864293 | 4.838225 | 4.822228 | 5.974854 | 5.927057 | 5.944518 | 5.989682 | 6.240993 | 6.235742 | 6.244365 | 6.217406 |
| GO:0048679 | regulation of axon regeneration | 17 | -0.6522985 | -1.534188 | 0.04495255872 | 0.78050155 | 0.76997227 | 1082 | tags=29%, list=8%, signal=27% | LRP1||PTPRF||PTPRS||SCARF1||INPP5F | 9.031149 | 9.684207 | 9.680920 | 9.025821 | 9.034504 | 9.046150 | 9.017969 | 9.694678 | 9.672942 | 9.683639 | 9.685485 | 9.679528 | 9.687037 | 9.672045 | 9.685025 |
| GO:2000108 | positive regulation of leukocyte apoptotic process | 19 | -0.6338477 | -1.529466 | 0.04496100321 | 0.78050155 | 0.76997227 | 1507 | tags=37%, list=11%, signal=33% | TP53||CD274||MEF2C||WNT5A||CCL5||ADAM8||IDO1 | 5.726494 | 6.686068 | 7.156592 | 5.754002 | 5.689027 | 5.723925 | 5.738223 | 6.718949 | 6.709617 | 6.642206 | 6.672203 | 7.220066 | 7.144848 | 7.103615 | 7.155412 |
| GO:0043372 | positive regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation | 28 | -0.5788902 | -1.505648 | 0.04511169133 | 0.78050155 | 0.76997227 | 2227 | tags=43%, list=16%, signal=36% | RARA||HLA-DRB1||IL18||IL12RB1||NFKBID||SASH3||SOCS1||CCL19||MALT1||CD86||HLA-DRA||IL23A | 5.175984 | 5.428989 | 5.668758 | 5.153993 | 5.123587 | 5.242145 | 5.181551 | 5.456144 | 5.439001 | 5.430655 | 5.389323 | 5.705431 | 5.677827 | 5.636852 | 5.653997 |
| GO:0070498 | interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway | 25 | -0.5941782 | -1.514645 | 0.04546796575 | 0.78050155 | 0.76997227 | 1979 | tags=32%, list=14%, signal=28% | EGR1||RELA||IRAK3||IL1B||IL1R2||IL1RN||RPS6KA5||IL6 | 4.740669 | 6.436546 | 7.068193 | 5.033984 | 4.593082 | 4.640330 | 4.649826 | 6.419250 | 6.409836 | 6.473960 | 6.442287 | 7.053658 | 7.086068 | 7.071143 | 7.061699 |
| GO:0002446 | neutrophil mediated immunity | 22 | -0.6101710 | -1.516823 | 0.04568680493 | 0.78050155 | 0.76997227 | 612 | tags=27%, list=4%, signal=26% | CARD9||AZU1||TREM1||PTAFR||KMT2E||IL6 | 7.756670 | 7.455149 | 7.634470 | 7.764936 | 7.759732 | 7.753660 | 7.748296 | 7.446537 | 7.455955 | 7.460575 | 7.457492 | 7.661153 | 7.636089 | 7.630109 | 7.610069 |
| GO:0072525 | pyridine-containing compound biosynthetic process | 24 | -0.5973349 | -1.512300 | 0.04689123015 | 0.78050155 | 0.76997227 | 1800 | tags=33%, list=13%, signal=29% | HAAO||NADK||KMO||PDXK||NADSYN1||PARP9||PARP10||IDO1 | 5.309907 | 5.145190 | 5.348850 | 5.432832 | 5.277535 | 5.209487 | 5.310609 | 5.127652 | 5.222441 | 5.122002 | 5.105732 | 5.380042 | 5.326660 | 5.301180 | 5.385755 |
| GO:0001779 | natural killer cell differentiation | 18 | -0.6390646 | -1.523150 | 0.04734731647 | 0.78050155 | 0.76997227 | 808 | tags=17%, list=6%, signal=16% | AXL||TYRO3||SLAMF1 | 4.610598 | 4.929910 | 4.776986 | 4.654704 | 4.586971 | 4.607121 | 4.592606 | 4.925509 | 4.917393 | 4.924591 | 4.951908 | 4.818235 | 4.739516 | 4.764500 | 4.784542 |
| GO:0060391 | positive regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction | 16 | 0.5973671 | 1.567461 | 0.04739726027 | 0.78050155 | 0.76997227 | 1696 | tags=50%, list=12%, signal=44% | RBPMS||PPARG||DAB2||BMP4||BMP2||BMPR2||JAK2||PARP1 | 6.007202 | 6.109621 | 6.060456 | 6.060298 | 6.007106 | 5.950803 | 6.008523 | 6.172907 | 6.041369 | 6.118754 | 6.102410 | 6.089384 | 6.108317 | 6.033531 | 6.008318 |
| GO:0030879 | mammary gland development | 94 | -0.4414789 | -1.387353 | 0.04747512908 | 0.78050155 | 0.76997227 | 3508 | tags=39%, list=25%, signal=30% | ORAI1||APRT||AREG||ERBB4||STAT6||XBP1||PAM||FASN||IQGAP3||CAD||BTRC||NCOR2||PML||ARHGAP5||MGMT||TNFSF11||MT-CO2||NRG1||WNT3||GLI3||STAT5A||SCRIB||CEBPB||TNFRSF11A||HK2||NOTCH4||NEURL1||WNT5A||SRC||TBX3||CSF1||TBX2||OAS2||LRP5||VEGFA||PRLR||RREB1 | 7.316976 | 7.185490 | 7.468988 | 7.319311 | 7.312261 | 7.323865 | 7.312435 | 7.185449 | 7.171859 | 7.186188 | 7.198344 | 7.469390 | 7.473526 | 7.475637 | 7.457330 |
| GO:0060412 | ventricular septum morphogenesis | 29 | 0.4966802 | 1.489773 | 0.04754151742 | 0.78050155 | 0.76997227 | 1380 | tags=31%, list=10%, signal=28% | SLIT2||HEY2||TGFB2||TGFBR2||SOX4||SAV1||CITED2||BMP4||BMPR2 | 5.453584 | 4.964032 | 4.764651 | 5.449670 | 5.457141 | 5.460966 | 5.446513 | 4.964295 | 4.935784 | 4.990981 | 4.964538 | 4.776924 | 4.807251 | 4.737586 | 4.735611 |
| GO:2000406 | positive regulation of T cell migration | 22 | -0.6065217 | -1.507752 | 0.04854223024 | 0.79226465 | 0.78157668 | 976 | tags=27%, list=7%, signal=25% | CXCL13||WNT5A||CCL5||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10 | 6.333148 | 6.905518 | 7.250680 | 6.343683 | 6.304218 | 6.350565 | 6.333693 | 6.938336 | 6.897007 | 6.888448 | 6.897756 | 7.241508 | 7.265664 | 7.217649 | 7.277173 |
| GO:0001921 | positive regulation of receptor recycling | 11 | -0.7108603 | -1.525142 | 0.04872126902 | 0.79226465 | 0.78157668 | 1424 | tags=36%, list=10%, signal=33% | SCRIB||ARAP1||ECE1||INPP5F | 5.947446 | 6.708350 | 6.924641 | 5.954703 | 5.878501 | 6.040934 | 5.910440 | 6.688817 | 6.792812 | 6.618533 | 6.727716 | 7.013368 | 6.803827 | 6.937055 | 6.936505 |
| GO:0022038 | corpus callosum development | 12 | -0.6957009 | -1.520304 | 0.04881991594 | 0.79226465 | 0.78157668 | 889 | tags=33%, list=6%, signal=31% | SZT2||EPHB2||EPHB3||PTPRS | 5.077779 | 4.724154 | 4.728814 | 5.080370 | 5.038213 | 5.052951 | 5.137573 | 4.731265 | 4.704716 | 4.781964 | 4.676574 | 4.773318 | 4.674358 | 4.836152 | 4.621749 |
| GO:0032963 | collagen metabolic process | 66 | -0.4728020 | -1.419614 | 0.04890875625 | 0.79226465 | 0.78157668 | 2044 | tags=32%, list=15%, signal=27% | PLOD3||LARP6||ADAMTS2||CTSL||CBX8||MMP3||MMP16||CTSB||TNS2||CTSK||PPARD||MMP9||EMILIN1||CCN2||CREB3L1||MMP7||SCX||MMP19||PDGFRB||SERPINB7||IL6 | 6.831889 | 7.581084 | 7.951351 | 6.832448 | 6.827435 | 6.842825 | 6.824782 | 7.566473 | 7.575126 | 7.596756 | 7.585804 | 7.941078 | 7.967024 | 7.954720 | 7.942429 |
| GO:0018206 | peptidyl-methionine modification | 11 | 0.6575885 | 1.560869 | 0.04916317992 | 0.79406419 | 0.78335194 | 3909 | tags=55%, list=28%, signal=39% | NAA35||NAA20||METAP1||PDF||NAA30||NAA16 | 5.288581 | 4.998974 | 4.792359 | 5.274942 | 5.352056 | 5.289603 | 5.235270 | 4.986478 | 5.024726 | 4.999606 | 4.984732 | 4.746313 | 4.891603 | 4.757085 | 4.769607 |
| GO:0032816 | positive regulation of natural killer cell activation | 17 | -0.6447167 | -1.516356 | 0.04946336911 | 0.79492385 | 0.78420000 | 1974 | tags=29%, list=14%, signal=25% | BLOC1S3||IL18||AXL||HLA-F||IL23A | 7.162674 | 7.161341 | 7.101896 | 7.188458 | 7.123869 | 7.178257 | 7.159276 | 7.159650 | 7.185661 | 7.160644 | 7.139030 | 7.104312 | 7.120606 | 7.065666 | 7.116350 |
| GO:2000785 | regulation of autophagosome assembly | 37 | 0.4599160 | 1.463301 | 0.04964297858 | 0.79492385 | 0.78420000 | 4272 | tags=49%, list=31%, signal=34% | LRRK2||MTM1||MTMR3||FEZ2||ADPRH||RALB||TBC1D14||SCFD1||RAB5A||PINK1||SH3GLB1||PIKFYVE||PIP4K2A||FEZ1||IFT20||IFT88||RNF5||PIP4K2C | 5.188090 | 5.146167 | 4.985282 | 5.187098 | 5.210880 | 5.176875 | 5.177243 | 5.158212 | 5.132351 | 5.165821 | 5.127918 | 4.961389 | 4.984438 | 4.985754 | 5.009152 |
| GO:0048843 | negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance | 19 | -0.6281387 | -1.515690 | 0.04970178926 | 0.79492385 | 0.78420000 | 1899 | tags=63%, list=14%, signal=55% | SEMA7A||SEMA4F||WNT3||SEMA3A||SEMA4A||PLXNA3||SEMA4D||WNT5A||SEMA3C||SEMA6A||SEMA3F||SEMA6B | 3.512774 | 4.317263 | 4.629599 | 3.490920 | 3.610737 | 3.517096 | 3.426223 | 4.233298 | 4.324978 | 4.269763 | 4.433049 | 4.772307 | 4.481396 | 4.729512 | 4.512347 |
| GO:0002021 | response to dietary excess | 12 | 0.6399151 | 1.560188 | 0.04979035639 | 0.79492385 | 0.78420000 | 1365 | tags=42%, list=10%, signal=38% | APPL2||ACVR1C||ADRB2||ADRB1||SORL1 | 5.172262 | 5.065617 | 5.004974 | 5.153039 | 5.191439 | 5.144566 | 5.199232 | 5.053272 | 5.109111 | 5.019349 | 5.079223 | 4.992434 | 5.004985 | 5.003949 | 5.018409 |
GO: MF
| ID | Description | setSize | enrichmentScore | NES | pvalue | p.adjust | qvalues | rank | leading_edge | core_enrichment | No-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgKDN-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgwt-inf_Log2MeanTPM | log2TPM_No-inf_1 | log2TPM_No-inf_2 | log2TPM_No-inf_3 | log2TPM_No-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0008009 | chemokine activity | 22 | -0.8329889 | -2.054336 | 0.000006177463 | 0.001235493 | 0.001235493 | 2038 | tags=82%, list=15%, signal=70% | CCL20||CXCL8||CXCL14||CCL2||CCL3||CXCL2||CXCL3||CCL4||CCL4L2||CCL3L3||CCL19||CXCL13||CCL5||CCL1||CXCL1||CCL22||CXCL11||CXCL10 | 4.661476 | 7.336671 | 7.908591 | 4.742723 | 4.658529 | 4.658808 | 4.581323 | 7.367746 | 7.337433 | 7.330670 | 7.310246 | 7.893723 | 7.922333 | 7.914025 | 7.904122 |
| GO:0008266 | poly(U) RNA binding | 18 | -0.7897814 | -1.875585 | 0.000561649718 | 0.080235674 | 0.080235674 | 180 | tags=28%, list=1%, signal=27% | HNRNPH1||DIS3L2||IFIT5||RBMS2||ATXN1 | 8.241239 | 8.348124 | 8.260658 | 8.251975 | 8.309096 | 8.169413 | 8.231015 | 8.326284 | 8.409682 | 8.303361 | 8.350981 | 8.276334 | 8.236265 | 8.247795 | 8.281734 |
| GO:0008083 | growth factor activity | 62 | -0.5765797 | -1.698781 | 0.002508913244 | 0.250891324 | 0.250891324 | 1947 | tags=39%, list=14%, signal=33% | GDF11||NRG1||TIMP1||MACC1||CLCF1||JAG2||VEGFB||BMP1||ADA2||MDK||EREG||INHBA||CSF2||CCN2||CXCL1||CSF1||OSGIN1||OSM||BMP6||VEGFA||IGF2||LIF||TYMP||IL6 | 6.564895 | 6.333211 | 6.513167 | 6.571109 | 6.564066 | 6.567302 | 6.557068 | 6.331334 | 6.304736 | 6.348731 | 6.347606 | 6.509150 | 6.517083 | 6.508832 | 6.517579 |
| GO:0043495 | protein-membrane adaptor activity | 13 | 0.7429374 | 1.861668 | 0.005920344456 | 0.493362038 | 0.493362038 | 1416 | tags=46%, list=10%, signal=42% | SYNE1||CIB1||SYNE3||SLC9A3R2||SLC9A3R1||JUP | 6.451564 | 6.490908 | 6.347715 | 6.392071 | 6.559907 | 6.556443 | 6.278578 | 6.464812 | 6.576469 | 6.500316 | 6.417339 | 6.510723 | 6.318121 | 6.267750 | 6.280690 |
| GO:0015459 | potassium channel regulator activity | 27 | 0.5866704 | 1.749552 | 0.009232728430 | 0.710209879 | 0.710209879 | 1553 | tags=33%, list=11%, signal=30% | KCNIP1||KCNS3||FLNA||ADRB2||RASA1||KCNIP2||ARPP19||PRKCZ||AMIGO1 | 6.075316 | 6.004015 | 5.923688 | 6.087481 | 6.077667 | 6.049208 | 6.086575 | 6.059735 | 5.956815 | 5.998955 | 5.998684 | 5.943618 | 5.915755 | 5.906449 | 5.928659 |
| GO:0140375 | immune receptor activity | 71 | -0.5167235 | -1.554103 | 0.012024825446 | 0.831012686 | 0.831012686 | 2418 | tags=37%, list=17%, signal=30% | GPR35||EBI3||F3||CSF2RA||IFNLR1||IL11RA||HLA-DRB1||CXCR4||IL18RAP||HLA-DQB1||CD74||IL12RB1||HLA-DQA1||CRLF1||ACKR3||CCR1||IL2RB||IL3RA||CXCR3||LILRB3||IL1R2||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA2||CCR7||LILRA6||PRLR | 6.766883 | 6.999792 | 6.945789 | 6.786634 | 6.780244 | 6.753646 | 6.746608 | 7.004616 | 6.991503 | 6.997668 | 7.005337 | 6.936372 | 6.944951 | 6.944303 | 6.957451 |
| GO:0004252 | serine-type endopeptidase activity | 58 | -0.5390216 | -1.577473 | 0.012465190293 | 0.831012686 | 0.831012686 | 2741 | tags=41%, list=20%, signal=33% | MMP8||RHBDD3||PRSS23||HTRA3||F3||OVCH1||IMMP1L||AZU1||HTRA2||BMP1||MMP3||MASP2||CTSK||C1RL||MMP9||PCSK5||TPSAB1||TPSD1||TPSB2||ADAM8||MMP7||MMP19||RHBDL1||PRSS36 | 6.617631 | 7.300255 | 7.617588 | 6.622282 | 6.619892 | 6.621755 | 6.606539 | 7.287131 | 7.296754 | 7.313348 | 7.303661 | 7.601840 | 7.638192 | 7.620527 | 7.609535 |
| GO:0042056 | chemoattractant activity | 16 | -0.7175139 | -1.661480 | 0.013431204123 | 0.839450258 | 0.839450258 | 2054 | tags=56%, list=15%, signal=48% | ALKBH1||GPNMB||VEGFB||CCL3||WNT5A||CCL5||SCG2||VEGFA||CXCL10 | 6.337513 | 7.322712 | 7.809817 | 6.350566 | 6.353775 | 6.319545 | 6.325858 | 7.360046 | 7.308144 | 7.311095 | 7.310908 | 7.790920 | 7.848302 | 7.792629 | 7.806669 |
| GO:0030291 | protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity | 27 | 0.5530886 | 1.649405 | 0.017828716969 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 1805 | tags=37%, list=13%, signal=32% | INKA1||SPRED1||CIB1||RPTOR||SPRY2||CDKN1B||INKA2||PRKAR2B||KAT2B||CASP3 | 6.554962 | 6.429224 | 6.297552 | 6.536837 | 6.581593 | 6.630691 | 6.465632 | 6.407190 | 6.467057 | 6.417981 | 6.423947 | 6.367290 | 6.251955 | 6.280772 | 6.287634 |
| GO:0140103 | catalytic activity, acting on a glycoprotein | 16 | 0.6476510 | 1.706076 | 0.018060572381 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 2120 | tags=38%, list=15%, signal=32% | GCNT1||MGAT5B||MGAT4A||MGAT5||C1GALT1C1||MGAT2 | 5.254938 | 5.299605 | 5.239881 | 5.396670 | 5.145687 | 5.165018 | 5.297760 | 5.345770 | 5.257161 | 5.277468 | 5.316388 | 5.274035 | 5.243854 | 5.242254 | 5.198373 |
| GO:0008375 | acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity | 32 | 0.5241392 | 1.625949 | 0.019478375702 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 1065 | tags=22%, list=8%, signal=20% | GCNT1||ALG13||MGAT5B||MGAT4A||EXT2||MGAT5||B3GNT5 | 5.906773 | 5.327096 | 5.284337 | 5.898202 | 5.991789 | 5.809504 | 5.921731 | 5.308056 | 5.301925 | 5.276856 | 5.417449 | 5.332514 | 5.295231 | 5.263151 | 5.244910 |
| GO:0048020 | CCR chemokine receptor binding | 18 | -0.6796637 | -1.614076 | 0.020820575628 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 2038 | tags=67%, list=15%, signal=57% | CCL20||STAT1||CCL2||CCL3||CCL4||CCL4L2||CCL3L3||CCL19||CXCL13||CCL5||CCL1||CCL22 | 4.812116 | 7.050551 | 7.654508 | 4.844328 | 4.816820 | 4.772621 | 4.813788 | 7.052317 | 7.065864 | 7.055213 | 7.028552 | 7.630726 | 7.674425 | 7.651965 | 7.660568 |
| GO:0005521 | lamin binding | 14 | 0.6518917 | 1.668935 | 0.024741707450 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 2530 | tags=50%, list=18%, signal=41% | PLCB1||MLIP||SYNE1||LBR||TOR1AIP1||NARF||PPP1CC | 5.830642 | 5.835089 | 5.600719 | 5.759644 | 5.839001 | 5.839079 | 5.882145 | 5.780767 | 5.758898 | 5.962935 | 5.828923 | 5.505471 | 5.644877 | 5.642925 | 5.605215 |
| GO:0019003 | GDP binding | 63 | 0.4124039 | 1.462584 | 0.025041736227 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 4869 | tags=67%, list=35%, signal=44% | DIRAS2||RAB9B||GEM||RAB28||RAB9A||RAB27B||RAP1A||RHOB||RALB||RAB4A||RAB21||RAB5A||RAB10||DYNC1LI1||ARL3||RRAGC||TRIM23||RAP2B||NRAS||GNAI3||RAP1B||DIRAS1||RAB8A||RAB14||RAB2A||RRAGD||MIEF1||RAB29||RAB12||RHOA||RHEB||RAB31||SRP54||RAB5C||ARF6||RAB5B||NME2||RRAS2||RRAS||RAB18||RAP2C||RAB7A | 6.201983 | 6.377565 | 6.211573 | 6.158328 | 6.207477 | 6.226809 | 6.214385 | 6.392390 | 6.378622 | 6.359366 | 6.379691 | 6.208383 | 6.206926 | 6.214057 | 6.216901 |
| GO:0003697 | single-stranded DNA binding | 115 | 0.3517842 | 1.383492 | 0.025906735751 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 3274 | tags=28%, list=23%, signal=21% | RAD51B||MCM8||POU4F1||DMC1||CTC1||RADX||RBBP8||TSNAX||RNF138||RAD51AP1||ERCC4||ZRANB3||SSBP2||MEIOB||PMS2||RPA3||POLA1||TERF1||SWSAP1||MSH3||ANXA1||SMC4||NEIL3||LRPPRC||RAD18||MCM9||TSN||POLR3C||SSBP4||HMGB1||RBMS1||DHX36 | 6.753420 | 6.931809 | 6.857866 | 6.756381 | 6.725083 | 6.795195 | 6.736027 | 6.918652 | 6.958061 | 6.927357 | 6.922831 | 6.837986 | 6.860247 | 6.883487 | 6.849351 |
| GO:0005164 | tumor necrosis factor receptor binding | 25 | -0.6162340 | -1.558622 | 0.031019202363 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 2104 | tags=32%, list=15%, signal=27% | TNFSF11||TNFSF13B||STAT1||LTB||TNFSF13||TNFSF9||TNFSF10||TNFSF15 | 4.230779 | 4.591644 | 4.757208 | 4.226068 | 4.216421 | 4.244704 | 4.235767 | 4.559952 | 4.567510 | 4.714942 | 4.516269 | 4.751293 | 4.715998 | 4.734531 | 4.824638 |
| GO:0098960 | postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor activity | 10 | 0.7010882 | 1.638128 | 0.032723524865 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 1036 | tags=50%, list=7%, signal=46% | GABRR2||CHRM3||GABRA4||ADRB1||GLRB | 3.310628 | 2.905699 | 1.724926 | 3.220936 | 3.380974 | 3.174030 | 3.448977 | 3.033733 | 3.380132 | 1.853361 | 2.956218 | 1.433998 | 1.354223 | 1.307753 | 2.456394 |
| GO:0015301 | anion:anion antiporter activity | 13 | -0.6993633 | -1.553629 | 0.036907413299 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 2071 | tags=38%, list=15%, signal=33% | SLC26A6||SLC26A1||SLC26A11||SLC4A8||SLC4A11 | 6.174908 | 6.244537 | 6.174024 | 6.152470 | 6.177103 | 6.189913 | 6.179882 | 6.229958 | 6.205041 | 6.299045 | 6.242449 | 6.141509 | 6.185078 | 6.205324 | 6.163399 |
| GO:0030145 | manganese ion binding | 52 | 0.4241425 | 1.454567 | 0.042528735632 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 3144 | tags=37%, list=22%, signal=28% | MGAT5B||XYLT2||GALNT3||MGAT5||PEPD||NEK4||ATP13A2||GALNT4||PAPOLA||MTPAP||DYRK2||PPM1A||MGAT2||MRE11||GALNT1||IMPA1||DCP2||PPM1B||MPPE1 | 5.155137 | 5.075123 | 4.948715 | 5.201879 | 5.139903 | 5.086529 | 5.189375 | 5.068103 | 5.046616 | 5.037715 | 5.145537 | 4.935215 | 4.956579 | 4.945315 | 4.957636 |
| GO:0003953 | NAD+ nucleosidase activity | 18 | 0.5723891 | 1.554633 | 0.043227665706 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 1960 | tags=33%, list=14%, signal=29% | TLR4||TLR7||TICAM2||TLR6||TLR1||TIRAP | 4.017484 | 4.118424 | 3.955228 | 3.946638 | 4.144276 | 4.055495 | 3.911794 | 4.153356 | 4.097295 | 4.129744 | 4.092442 | 3.965690 | 3.930462 | 3.984087 | 3.940053 |
| GO:0008656 | cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process | 14 | -0.6776313 | -1.529218 | 0.043327008223 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 1612 | tags=29%, list=12%, signal=25% | CASP1||ATP2A3||NOD1||ST20 | 7.031925 | 7.267023 | 7.375633 | 7.003920 | 7.025921 | 7.043003 | 7.054354 | 7.267353 | 7.259109 | 7.253478 | 7.287913 | 7.411854 | 7.391793 | 7.352593 | 7.345241 |
| GO:0015101 | organic cation transmembrane transporter activity | 17 | 0.5799621 | 1.556103 | 0.044494508589 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 760 | tags=29%, list=5%, signal=28% | SLC7A8||SLC29A4||SLC44A5||SLC25A20||SLC22A16 | 4.216695 | 4.468719 | 4.274749 | 4.239203 | 4.164748 | 4.194480 | 4.266218 | 4.476370 | 4.478894 | 4.476138 | 4.443176 | 4.269448 | 4.277491 | 4.237769 | 4.313287 |
| GO:1901611 | phosphatidylglycerol binding | 11 | -0.7102753 | -1.523399 | 0.044809800129 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 33 | tags=36%, list=0%, signal=36% | GSDMD||GSDME||PITPNA||ATP8B1 | 4.969685 | 4.368273 | 4.627782 | 4.701052 | 4.929183 | 5.065614 | 5.144504 | 4.370394 | 4.431564 | 4.407111 | 4.257973 | 4.498834 | 4.469704 | 4.600531 | 4.900395 |
| GO:0023023 | MHC protein complex binding | 21 | -0.6193468 | -1.514057 | 0.046287947099 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 1978 | tags=38%, list=14%, signal=33% | HLA-DRB1||HLA-DMA||HLA-DQB1||CD74||TAPBPL||HLA-DQA1||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA2 | 8.870843 | 9.025429 | 9.030122 | 8.877093 | 8.866719 | 8.865286 | 8.874242 | 9.032058 | 9.032883 | 9.012852 | 9.023836 | 9.023335 | 9.037910 | 9.025379 | 9.033815 |
| GO:0030507 | spectrin binding | 17 | -0.6497347 | -1.519334 | 0.047434506278 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 3385 | tags=59%, list=24%, signal=45% | ADD2||MYO10||KIF3A||SPTBN5||ANK2||EPB41L2||GBP1||ANK3||CAMSAP3||MYO7A | 4.972971 | 5.241894 | 5.200794 | 4.897210 | 5.078390 | 4.934692 | 4.975186 | 5.234218 | 5.156795 | 5.338178 | 5.232586 | 5.307002 | 5.098485 | 5.260927 | 5.126038 |
| GO:0008201 | heparin binding | 65 | -0.4794270 | -1.424359 | 0.049529534762 | 1.000000000 | 1.000000000 | 2938 | tags=40%, list=21%, signal=32% | APP||ANOS1||HBEGF||ADAMTSL5||FGFRL1||ADAMTS3||EFEMP2||LTBP2||GPNMB||TGFBR3||AZU1||APOE||VEGFB||APLP1||ADA2||MDK||CXCL13||CCN2||PTPRF||CFH||MMP7||PTPRS||COL5A3||VEGFA||CXCL11||CXCL10 | 6.508431 | 6.299913 | 6.294777 | 6.517174 | 6.523999 | 6.495402 | 6.496935 | 6.326440 | 6.293638 | 6.275829 | 6.303280 | 6.301488 | 6.301536 | 6.283628 | 6.292378 |
GO: CC
| ID | Description | setSize | enrichmentScore | NES | pvalue | p.adjust | qvalues | rank | leading_edge | core_enrichment | No-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgKDN-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgwt-inf_Log2MeanTPM | log2TPM_No-inf_1 | log2TPM_No-inf_2 | log2TPM_No-inf_3 | log2TPM_No-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0042611 | MHC protein complex | 15 | -0.7699826 | -1.752355 | 0.00375881 | 1 | 1 | 1978 | tags=73%, list=14%, signal=63% | HLA-DRB5||HLA-B||HLA-DRB1||HLA-C||HLA-DMA||HLA-DQB1||CD74||HLA-DQA1||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA2||HLA-F | 9.077183 | 8.722957 | 8.821423 | 9.080381 | 9.068647 | 9.077090 | 9.082575 | 8.733852 | 8.726947 | 8.708850 | 8.722063 | 8.818601 | 8.826116 | 8.809867 | 8.831020 |
| GO:0022625 | cytosolic large ribosomal subunit | 54 | 0.4861443 | 1.661908 | 0.01126214 | 1 | 1 | 5576 | tags=74%, list=40%, signal=45% | RPL5||RPL26||RPL27||RPL31||RPL34||RPL38||RPL15||RPL9||RPL39||RPL6||ZCCHC17||RPL17||RPL35A||RPL39L||RPL29||RPL4||RPL21||RPL19||RPL27A||RPL7||RPL24||RPL23||RPL11||RPL23A||RPL37||RPL18A||MRPL1||RPL36A||RPL32||RPL37A||RPL10||RPL12||RPL3||RPL18||RPLP1||RPL7A||RPLP0||RPL10A||RPL30||RPL14 | 10.553769 | 10.537681 | 10.362050 | 10.561284 | 10.563567 | 10.545026 | 10.545095 | 10.547934 | 10.546611 | 10.543239 | 10.512650 | 10.365044 | 10.356449 | 10.363205 | 10.363486 |
| GO:0005581 | collagen trimer | 32 | -0.6203156 | -1.642698 | 0.01299072 | 1 | 1 | 1570 | tags=47%, list=11%, signal=42% | COL6A1||COL27A1||COL7A1||MARCO||COL9A2||COL8A1||COL6A2||EMILIN1||COL15A1||COL19A1||C1QTNF6||COL5A3||C1QTNF1||COL11A2||COL6A6 | 4.830647 | 5.362918 | 5.448989 | 4.889776 | 4.871389 | 4.797096 | 4.760450 | 5.327498 | 5.351093 | 5.275119 | 5.489173 | 5.458959 | 5.480470 | 5.446400 | 5.409199 |
| GO:0030877 | beta-catenin destruction complex | 10 | 0.7442661 | 1.721438 | 0.01694045 | 1 | 1 | 2182 | tags=60%, list=16%, signal=51% | GSK3B||APC||CACYBP||APC2||GSK3A||CSNK1A1 | 6.361660 | 6.744256 | 6.338917 | 6.436830 | 6.284362 | 6.321901 | 6.398505 | 6.967602 | 6.678175 | 6.724798 | 6.577314 | 6.374823 | 6.285579 | 6.504676 | 6.169726 |
| GO:0034702 | ion channel complex | 93 | 0.3835436 | 1.440697 | 0.02123457 | 1 | 1 | 1424 | tags=20%, list=10%, signal=18% | KCNIP1||GABRR2||MCUB||KCNQ5||DLG3||CACNB4||KCNS3||GABRA4||KCNMA1||LRRC8C||OLFM3||STXBP5||KCNIP2||PACC1||GLRB||HCN2||CLIC6||KCNQ1||MICU2 | 5.385716 | 5.454007 | 5.408961 | 5.374404 | 5.402208 | 5.402324 | 5.363524 | 5.482086 | 5.468705 | 5.434987 | 5.429571 | 5.408709 | 5.391078 | 5.410424 | 5.425426 |
| GO:0032421 | stereocilium bundle | 27 | -0.6090370 | -1.562659 | 0.02915027 | 1 | 1 | 476 | tags=22%, list=3%, signal=22% | CDH23||KPTN||RIPOR2||MYO7A||MKKS||ATP8B1 | 5.253838 | 4.713979 | 4.699130 | 5.311518 | 5.034454 | 5.221536 | 5.420448 | 4.599918 | 4.566129 | 4.619373 | 5.020700 | 4.723474 | 4.487282 | 4.539488 | 4.991093 |
| GO:0045334 | clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle | 59 | -0.5080105 | -1.487288 | 0.02956126 | 1 | 1 | 1562 | tags=22%, list=11%, signal=20% | HLA-DQB1||APOE||CD74||HLA-DQA1||EREG||TF||WNT5A||EPN2||SYT2||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA2||INPP5F||CLTCL1 | 6.082557 | 6.325955 | 6.296110 | 6.061494 | 6.072303 | 6.128926 | 6.066472 | 6.320732 | 6.324733 | 6.320310 | 6.337974 | 6.270093 | 6.308298 | 6.272120 | 6.332972 |
| GO:0005666 | RNA polymerase III complex | 18 | 0.6179904 | 1.651503 | 0.03036437 | 1 | 1 | 13 | tags=6%, list=0%, signal=6% | POLR3G | 5.504477 | 5.727224 | 5.609978 | 5.504058 | 5.490945 | 5.448105 | 5.572041 | 5.676358 | 5.849775 | 5.715335 | 5.659576 | 5.616151 | 5.613765 | 5.598367 | 5.611561 |
| GO:0042405 | nuclear inclusion body | 12 | -0.7224240 | -1.570123 | 0.03408545 | 1 | 1 | 55 | tags=33%, list=0%, signal=33% | NXF1||ATXN3||PABPN1||ATXN1 | 5.779918 | 5.428313 | 5.513502 | 5.721608 | 5.748793 | 5.983384 | 5.643052 | 5.392586 | 5.426862 | 5.477042 | 5.415434 | 5.688637 | 5.468529 | 5.501225 | 5.377592 |
| GO:0071556 | integral component of lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane | 21 | -0.6299699 | -1.534261 | 0.03797468 | 1 | 1 | 3540 | tags=57%, list=25%, signal=43% | HM13||HLA-DRB5||HLA-B||SPPL2B||HLA-DRB1||HLA-C||HLA-DQB1||CD74||HLA-DQA1||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA2||HLA-F | 7.694330 | 7.804025 | 8.001993 | 7.689557 | 7.695998 | 7.696451 | 7.695303 | 7.799263 | 7.805500 | 7.814852 | 7.796415 | 7.997161 | 8.008844 | 7.999056 | 8.002884 |
| GO:0098982 | GABA-ergic synapse | 34 | 0.4905955 | 1.538019 | 0.03930871 | 1 | 1 | 1345 | tags=29%, list=10%, signal=27% | GABRR2||PLCB1||GABRA4||SLITRK2||CTBP2||PCLO||PTPRO||LRFN5||GLRB||BSN | 4.388230 | 5.074232 | 5.103915 | 4.357018 | 4.380725 | 4.415076 | 4.399451 | 5.084865 | 5.062811 | 4.992708 | 5.152061 | 5.073843 | 5.090975 | 5.132222 | 5.117901 |
| GO:0031012 | extracellular matrix | 242 | -0.3787428 | -1.305304 | 0.03949691 | 1 | 1 | 2764 | tags=36%, list=20%, signal=29% | AGRN||MMP8||LTBP1||LAMB3||ADAMTSL5||BCAM||HSPG2||ADAMTS3||IGFBP7||SPON2||SDC3||ELFN1||F3||ANXA8||TGFBI||OLFML2A||MST1||COL4A1||SBSPON||EFEMP2||PLOD3||LTBP4||ANXA6||SEMA7A||TIMP1||LTBP2||TGFB1I1||ADAMTS2||THSD4||ADAMDEC1||CTSL||TGFBR3||WNT3||COL6A1||APOE||WNT5B||PLSCR1||MMP3||COL27A1||CHI3L1||COL7A1||ADAMTS13||APLP1||ADAMTS7||MMP16||ZP3||CTSD||TGM2||SFRP2||COL9A2||ANGPTL6||CTSB||COL8A1||TFPI2||L1CAM||CDH2||COL6A2||MDK||PAPLN||WNT5A||MMP9||EMILIN1||COL15A1||POMZP3||COL19A1||CCN2||LAMA5||TPSAB1||PTX3||NCAM1||TPSB2||LTBP3||ORM1||LGALS3BP||MMP7||FBN2||S100A8||COL5A3||ADAM19||MMP19||LAMA3||SSPOP||VEGFA||ITIH4||COL11A2||COL6A6 | 6.819459 | 7.403236 | 7.639426 | 6.802364 | 6.821953 | 6.821636 | 6.831725 | 7.401588 | 7.383113 | 7.407331 | 7.420661 | 7.627685 | 7.653911 | 7.642790 | 7.633182 |
| GO:0097440 | apical dendrite | 12 | 0.6511413 | 1.579570 | 0.04822808 | 1 | 1 | 528 | tags=42%, list=4%, signal=40% | CLU||ITSN1||MAP2||CPEB3||FLNA | 5.885275 | 5.659875 | 5.404924 | 6.023336 | 5.831579 | 5.712134 | 5.954567 | 5.841292 | 5.453151 | 5.933814 | 5.320521 | 5.141914 | 5.513443 | 5.722334 | 5.157572 |
KEGG
| ID | Description | setSize | enrichmentScore | NES | pvalue | p.adjust | qvalues | rank | leading_edge | core_enrichment | No-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgKDN-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgwt-inf_Log2MeanTPM | log2TPM_No-inf_1 | log2TPM_No-inf_2 | log2TPM_No-inf_3 | log2TPM_No-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa04060 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | 132 | -0.5941242 | -2.035918 | 0.00000003905041 | 0.000004490797 | 0.000003987252 | 1680 | tags=45%, list=13%, signal=39% | TNFSF11||CSF2RA||IFNLR1||IL11RA||CCL20||TNFSF13B||CXCL8||GDF11||CXCR4||IL18RAP||IL18||CXCL14||CLCF1||CD40||CCL2||TNFRSF12A||LTB||IL12RB1||CCL3||CXCL2||CXCL3||CCL4||CCL4L2||TNFRSF11A||TNFSF13||TNFSF9||ACKR3||CCL3L3||CCL19||CCR1||CXCL13||IL2RB||IL1B||IL3RA||INHBA||CSF2||CCL5||CCL1||CXCL1||CXCR3||CSF1||TNFSF10||TNFRSF14||OSM||IL1R2||BMP6||IL1RN||TNFRSF18||IL1A||CCR7||LIF||IL23A||CCL22||TNFSF15||CXCL11||CXCL10||PRLR||IL36G||IL6 | 5.086895 | 6.202895 | 6.595424 | 5.076743 | 5.101743 | 5.074889 | 5.094023 | 6.217429 | 6.181225 | 6.212603 | 6.200054 | 6.586842 | 6.593162 | 6.583248 | 6.618186 |
| hsa04625 | C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | 89 | -0.5711092 | -1.862956 | 0.00003017962962 | 0.001735328703 | 0.001540749512 | 1807 | tags=30%, list=14%, signal=26% | BCL3||PAK1||CD209||CARD9||STAT1||STAT2||CASP1||LSP1||RELA||CALML4||NFKB2||MAP3K14||PTGS2||ITPR1||ITPR3||IL1B||KSR1||SRC||IRF1||MALT1||EGR3||MAPK10||IRF9||CLEC4E||IL23A||CCL22||IL6 | 6.660317 | 6.874663 | 6.963941 | 6.688233 | 6.675412 | 6.641058 | 6.635878 | 6.880213 | 6.846659 | 6.865132 | 6.905995 | 6.942256 | 6.949467 | 6.973618 | 6.989921 |
| hsa03010 | Ribosome | 131 | 0.4200147 | 1.728177 | 0.00005463599916 | 0.002094379968 | 0.001859541024 | 4728 | tags=56%, list=38%, signal=36% | RPS10-NUDT3||RPS15A||RPL5||RPS3A||RPL17-C18orf32||RPL26||MRPL13||MRPS10||RPS17||RPS21||RPL27||RPS7||RPS6||MRPL32||RSL24D1||RPL31||RPL34||RPS25||RPS27A||RPS18||RPL38||RPL15||RPL9||RPL39||RPL6||RPS24||MRPL19||RPS8||RPS27||RPL17||MRPL35||RPS12||RPL35A||RPS27L||RPL29||RPL4||RPL21||RPS4X||RPS13||RPL19||RPL27A||MRPL10||RPL7||RPS10||RPL24||MRPS11||RPS29||RPS20||RPL23||RPS11||RPL11||RPS14||RPS5||RPL23A||MRPL3||FAU||MRPL33||RPL37||RPL18A||MRPL1||RPL36A||RPS4Y1||RPL32||RPL37A||RPL10||RPS26||MRPL18||RPL12||MRPL9||MRPS15||RPS16||RPL3||RPL18||RPLP1 | 10.154761 | 10.168441 | 9.970174 | 10.158744 | 10.157492 | 10.153396 | 10.149391 | 10.172131 | 10.173135 | 10.173394 | 10.155023 | 9.969250 | 9.968621 | 9.970920 | 9.971903 |
| hsa04668 | TNF signaling pathway | 99 | -0.5358986 | -1.770879 | 0.00014111134488 | 0.004056951165 | 0.003602052751 | 1284 | tags=25%, list=10%, signal=23% | CCL2||RELA||NOD2||MMP3||MAP3K14||CXCL2||CEBPB||CXCL3||PTGS2||IL1B||MMP9||IRF1||CSF2||CCL5||MLKL||CREB3L1||CXCL1||SOCS3||CSF1||MAPK10||CREB5||LIF||CXCL10||RPS6KA5||IL6 | 5.672874 | 6.796137 | 7.307626 | 5.689898 | 5.688634 | 5.659989 | 5.652590 | 6.792082 | 6.790702 | 6.805525 | 6.796191 | 7.285020 | 7.314741 | 7.320371 | 7.310122 |
| hsa05164 | Influenza A | 127 | -0.5020519 | -1.711603 | 0.00023460670011 | 0.005395954102 | 0.004790915771 | 1574 | tags=24%, list=13%, signal=22% | HLA-DRB1||CXCL8||TBK1||IL18||STAT1||STAT2||CCL2||CASP1||HLA-DMA||RELA||HLA-DQB1||OAS1||IL1B||MX2||TPSAB1||CCL5||CREBBP||OAS3||TPSD1||TPSB2||SOCS3||TNFSF10||IRF7||IRF9||OAS2||HLA-DRA||IL1A||MX1||RSAD2||CXCL10||IL6 | 6.876102 | 7.191024 | 7.321240 | 6.899589 | 6.869638 | 6.870578 | 6.864337 | 7.200377 | 7.187613 | 7.197474 | 7.178529 | 7.325638 | 7.331922 | 7.315561 | 7.311752 |
| hsa05152 | Tuberculosis | 135 | -0.4707084 | -1.618139 | 0.00086056917483 | 0.016494242517 | 0.014644773677 | 1671 | tags=24%, list=13%, signal=21% | SPHK1||CD209||HLA-DRB1||CARD9||IL18||STAT1||HLA-DMA||LSP1||RELA||HLA-DQB1||NOD2||CD74||CALML4||CEBPB||CTSD||SPHK2||ITGAX||IL1B||KSR1||SRC||CYP27B1||MALT1||CREBBP||C3||MAPK10||CAMK2A||HLA-DRA||CLEC4E||IL1A||IL23A||IL6||NOS2 | 7.287533 | 7.426140 | 7.541544 | 7.301719 | 7.296681 | 7.278032 | 7.273501 | 7.426307 | 7.410039 | 7.423270 | 7.444730 | 7.525855 | 7.545638 | 7.540690 | 7.553850 |
| hsa04514 | Cell adhesion molecules | 80 | -0.5162252 | -1.658535 | 0.00354423733263 | 0.057440706368 | 0.050999986432 | 1661 | tags=32%, list=13%, signal=28% | ITGA6||HLA-DRB1||HLA-C||CLDN23||CD40||HLA-DMA||HLA-DQB1||ICOSLG||CLDN15||CD274||SELPLG||L1CAM||CDH2||MPZ||CLDN7||NCAM1||PTPRF||CD86||NRCAM||PTPRS||CD226||NLGN2||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||SIGLEC1||PDCD1LG2 | 6.712245 | 6.768462 | 6.883147 | 6.708076 | 6.721809 | 6.718045 | 6.700955 | 6.766351 | 6.765418 | 6.781290 | 6.760705 | 6.885242 | 6.896058 | 6.882683 | 6.868473 |
| hsa04630 | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | 90 | -0.4963287 | -1.622665 | 0.00399587522557 | 0.057440706368 | 0.050999986432 | 1658 | tags=28%, list=13%, signal=24% | CSF2RA||IFNLR1||IL11RA||CLCF1||STAT1||STAT2||STAT5A||IL12RB1||SOCS1||CISH||STAM2||IL2RB||PIAS4||IL3RA||CSF2||CREBBP||SOCS3||IRF9||OSM||LIF||IL23A||PDGFRB||STAT4||PRLR||IL6 | 5.798479 | 5.855192 | 5.789364 | 5.809397 | 5.811975 | 5.780190 | 5.792120 | 5.834596 | 5.876643 | 5.859921 | 5.849279 | 5.774185 | 5.786034 | 5.759564 | 5.836503 |
| hsa04062 | Chemokine signaling pathway | 134 | -0.4368873 | -1.500204 | 0.00812712275594 | 0.103846568548 | 0.092202445301 | 1717 | tags=26%, list=14%, signal=23% | PAK1||CCL20||PIK3R5||CXCL8||CXCR4||CXCL14||GRK4||SHC2||STAT1||STAT2||CCL2||RELA||CCL3||ADCY1||CXCL2||BCAR1||CXCL3||CCL4||CCL4L2||CCL3L3||CCL19||CCR1||CXCL13||SRC||HCK||CCL5||CCL1||CXCL1||CXCR3||ITK||CCR7||CCL22||CXCL11||CXCL10||PIK3R6 | 5.744445 | 6.272208 | 6.473053 | 5.766626 | 5.746681 | 5.725173 | 5.738988 | 6.282292 | 6.289842 | 6.285769 | 6.230113 | 6.454515 | 6.490275 | 6.496459 | 6.450373 |
| hsa04931 | Insulin resistance | 89 | -0.4642698 | -1.514446 | 0.01294163323411 | 0.144247999044 | 0.128073738282 | 2391 | tags=30%, list=19%, signal=25% | PCK2||NFKB1||GYS1||RPS6KB2||CREB3L2||SLC27A2||MLXIP||PPARA||OGT||PPP1R3B||INSR||SLC2A1||RELA||CRTC2||PRKAG1||GFPT2||SLC27A3||ACACB||IRS1||PTPRF||CREB3L1||SOCS3||MAPK10||NR1H3||CPT1B||CREB5||IL6 | 5.325164 | 5.342827 | 5.398927 | 5.359087 | 5.335342 | 5.277837 | 5.327184 | 5.429146 | 5.387219 | 5.295675 | 5.252404 | 5.472379 | 5.464855 | 5.335105 | 5.316218 |
| hsa05160 | Hepatitis C | 114 | -0.4367256 | -1.470855 | 0.01426445050856 | 0.144247999044 | 0.128073738282 | 1631 | tags=19%, list=13%, signal=17% | PPARA||TBK1||CLDN23||STAT1||STAT2||RELA||CLDN15||TP53||OAS1||PPP2R1B||MX2||CLDN7||OAS3||SOCS3||IRF7||IRF9||OAS2||NR1H3||IFIT1||MX1||RSAD2||CXCL10 | 5.986245 | 6.230674 | 6.181634 | 6.020419 | 5.970485 | 5.994002 | 5.959309 | 6.265731 | 6.235998 | 6.216332 | 6.203877 | 6.185915 | 6.175414 | 6.174209 | 6.190931 |
| hsa05167 | Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection | 150 | -0.4142025 | -1.442738 | 0.01505196511767 | 0.144247999044 | 0.128073738282 | 1570 | tags=19%, list=12%, signal=17% | PIK3R5||CXCL8||TBK1||HLA-C||STAT1||STAT2||RELA||TP53||CALML4||CXCL2||CXCL3||PTGS2||ITPR1||CCR1||ITPR3||SRC||HCK||CSF2||CREBBP||CD86||C3||CXCL1||MAPK10||IRF7||IRF9||HLA-F||VEGFA||PIK3R6||IL6 | 6.652857 | 6.720990 | 6.687743 | 6.659124 | 6.656846 | 6.656189 | 6.639180 | 6.736921 | 6.712207 | 6.726891 | 6.707755 | 6.705342 | 6.688463 | 6.673428 | 6.683554 |
| hsa04620 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 80 | -0.4665870 | -1.499056 | 0.01798372276188 | 0.159086778278 | 0.141248672705 | 1564 | tags=22%, list=12%, signal=20% | CXCL8||TBK1||CD40||STAT1||RELA||CCL3||CCL4||CCL4L2||CCL3L3||IL1B||CTSK||CCL5||CD86||MAPK10||IRF7||CXCL11||CXCL10||IL6 | 6.857067 | 7.864424 | 8.031730 | 6.900834 | 6.841592 | 6.849210 | 6.835700 | 7.871990 | 7.853207 | 7.867530 | 7.864901 | 8.028003 | 8.039847 | 8.027727 | 8.031310 |
| hsa04810 | Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | 164 | 0.3089857 | 1.308653 | 0.02585649644473 | 0.212392649367 | 0.188577455274 | 1883 | tags=18%, list=15%, signal=16% | ITGAD||F2R||VAV2||CHRM3||GNG12||MYLK||PDGFRA||PDGFD||VAV3||ACTR3B||ITGAE||APC||SCIN||ITGA4||DIAPH2||PDGFC||ROCK2||FGD3||APC2||PIK3CA||WASL||CRK||BDKRB2||PAK2||ITGA2||NCKAP1L||SOS2||CYFIP1||MYH10||PTK2 | 7.866547 | 7.950069 | 7.913257 | 7.868572 | 7.867043 | 7.865551 | 7.865020 | 7.956705 | 7.941088 | 7.954331 | 7.948099 | 7.910862 | 7.912793 | 7.917322 | 7.912045 |
| hsa04151 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 222 | -0.3680763 | -1.329503 | 0.03270655270655 | 0.250750237417 | 0.222634078073 | 1268 | tags=15%, list=10%, signal=14% | MET||COL6A1||RELA||VEGFB||ITGA1||TP53||PPP2R1B||CRTC2||FLT3LG||COL9A2||PPP2R3B||DDIT4||COL6A2||EREG||IL2RB||IL3RA||EFNA5||IRS1||LAMA5||ITGB3||CREB3L1||CSF1||CREB5||OSM||LPAR2||LAMA3||NR4A1||VEGFA||IGF2||PDGFRB||PRLR||PIK3R6||IL6||COL6A6 | 6.682235 | 7.106428 | 7.061342 | 6.692412 | 6.679574 | 6.677568 | 6.679339 | 7.112024 | 7.103687 | 7.101792 | 7.108187 | 7.064362 | 7.057127 | 7.064505 | 7.059359 |
| hsa04380 | Osteoclast differentiation | 107 | -0.4187613 | -1.399812 | 0.03631354871024 | 0.261003631355 | 0.231737777954 | 1316 | tags=21%, list=10%, signal=19% | STAT1||STAT2||RELA||NFKB2||MAP3K14||SOCS1||OSCAR||TNFRSF11A||SIRPG||IL1B||LILRB4||CTSK||FHL2||ITGB3||SOCS3||CSF1||LILRB3||MAPK10||IRF9||ACP5||NCF2||IL1A||LILRA6 | 6.586307 | 6.815743 | 6.924388 | 6.590097 | 6.588715 | 6.585986 | 6.580411 | 6.816030 | 6.812978 | 6.833909 | 6.799852 | 6.920005 | 6.933660 | 6.912408 | 6.931375 |
| hsa04621 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 143 | -0.3907912 | -1.353227 | 0.04293961991821 | 0.275805280032 | 0.244879745200 | 1564 | tags=22%, list=12%, signal=20% | CXCL8||TBK1||CARD9||TRPV2||IL18||PSTPIP1||STAT1||STAT2||GBP1||CCL2||CASP1||RELA||NOD2||OAS1||CXCL2||CXCL3||GABARAP||CTSB||ITPR1||ITPR3||IL1B||TRPM2||CCL5||OAS3||CXCL1||AIM2||MAPK10||IRF7||IRF9||OAS2||NOD1||IL6 | 6.251026 | 6.673795 | 6.903518 | 6.256704 | 6.230573 | 6.253792 | 6.262828 | 6.675522 | 6.663632 | 6.680139 | 6.675837 | 6.887584 | 6.928398 | 6.903037 | 6.894722 |
| hsa05165 | Human papillomavirus infection | 238 | -0.3585895 | -1.303728 | 0.04316952209197 | 0.275805280032 | 0.244879745200 | 1316 | tags=16%, list=10%, signal=14% | STAT1||STAT2||PARD6G||TUBG2||WNT3||RFNG||COL6A1||RELA||ITGA1||WNT5B||TP53||SCRIB||PPP2R1B||COL9A2||PPP2R3B||PTGS2||NOTCH4||COL6A2||MX2||WNT5A||IRF1||LAMA5||CREBBP||ITGB3||CREB3L1||IRF9||ISG15||CREB5||LAMA3||HLA-F||VEGFA||HES4||PDGFRB||MX1||OASL||NOTCH3||COL6A6 | 6.488302 | 6.944573 | 6.974719 | 6.509168 | 6.479664 | 6.487422 | 6.476731 | 6.951878 | 6.938578 | 6.943178 | 6.944627 | 6.973654 | 6.984916 | 6.974091 | 6.966152 |
ORA: All DEGs
Please Click HERE to download a Microsoft .excel that contains all of the “ORT: All DEGs” results.
GO: BP
| ID | Description | GeneRatio | BgRatio | pvalue | p.adjust | qvalue | geneID | Count | No-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgKDN-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgwt-inf_Log2MeanTPM | log2TPM_No-inf_1 | log2TPM_No-inf_2 | log2TPM_No-inf_3 | log2TPM_No-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0030595 | leukocyte chemotaxis | 22/301 | 268/20870 | 0.00000000005835123 | 0.0000002252941 | 0.0000001880138 | TGFB2||CCL22||RIPOR2||VEGFA||PADI2||TNFSF18||TREM1||CCR7||IL6||SLIT2||PLA2G7||ADAM8||NBL1||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||S1PR1||SCG2||CSF1||CXCR3||KLRK1||CD300H | 22 | 7.083536 | 7.379525 | 7.502467 | 7.090422 | 7.081914 | 7.077300 | 7.084476 | 7.376976 | 7.376392 | 7.376521 | 7.388176 | 7.496692 | 7.516555 | 7.504886 | 7.491614 |
| GO:0050900 | leukocyte migration | 27/301 | 428/20870 | 0.00000000015617758 | 0.0000003015008 | 0.0000002516103 | TGFB2||ASB2||CCL22||RIPOR2||VEGFA||PADI2||TNFSF18||TREM1||CCR7||IL6||SLIT2||PLA2G7||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||NBL1||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||PTAFR||S1PR1||SCG2||CSF1||CXCR3||TNFRSF18||GCNT1||KLRK1||CD300H | 27 | 6.964052 | 7.305350 | 7.475330 | 6.970243 | 6.965686 | 6.958039 | 6.962212 | 7.304248 | 7.301741 | 7.306149 | 7.309253 | 7.466529 | 7.487203 | 7.478769 | 7.468725 |
| GO:0051607 | defense response to virus | 22/301 | 306/20870 | 0.00000000073844924 | 0.0000007127881 | 0.0000005948403 | UNC13D||IL23A||OAS2||AICDA||POLR3G||IFIT3||IFIT2||IFI6||TRIM22||RSAD2||OASL||IL6||IFI44L||HERC5||MX1||CXCL10||IRF7||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15||TLR7||IRF9 | 22 | 5.560236 | 5.626557 | 5.751936 | 5.591743 | 5.556254 | 5.557421 | 5.534953 | 5.625001 | 5.617580 | 5.653544 | 5.609725 | 5.736605 | 5.757706 | 5.763703 | 5.749587 |
| GO:0140546 | defense response to symbiont | 22/301 | 306/20870 | 0.00000000073844924 | 0.0000007127881 | 0.0000005948403 | UNC13D||IL23A||OAS2||AICDA||POLR3G||IFIT3||IFIT2||IFI6||TRIM22||RSAD2||OASL||IL6||IFI44L||HERC5||MX1||CXCL10||IRF7||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15||TLR7||IRF9 | 22 | 5.560236 | 5.626557 | 5.751936 | 5.591743 | 5.556254 | 5.557421 | 5.534953 | 5.625001 | 5.617580 | 5.653544 | 5.609725 | 5.736605 | 5.757706 | 5.763703 | 5.749587 |
| GO:0009615 | response to virus | 25/301 | 420/20870 | 0.00000000252805778 | 0.0000019013263 | 0.0000015867064 | UNC13D||CCL22||IL23A||OAS2||AICDA||POLR3G||IFIT3||IFIT2||CLU||IFI6||TRIM22||RSAD2||OASL||IL6||IFI44L||IFI44||HERC5||MX1||CXCL10||IRF7||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15||TLR7||IRF9 | 25 | 6.641763 | 6.626694 | 6.615414 | 6.651325 | 6.644070 | 6.633737 | 6.637860 | 6.625735 | 6.620015 | 6.635351 | 6.625631 | 6.600811 | 6.619182 | 6.620456 | 6.621107 |
| GO:0060326 | cell chemotaxis | 23/301 | 360/20870 | 0.00000000295466408 | 0.0000019013263 | 0.0000015867064 | TGFB2||CCL22||RIPOR2||VEGFA||PADI2||TNFSF18||TREM1||CCR7||IL6||SLIT2||PLA2G7||ADAM8||NBL1||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||S1PR1||SCG2||EGR3||CSF1||CXCR3||KLRK1||CD300H | 23 | 7.420946 | 7.632148 | 7.698801 | 7.423195 | 7.417902 | 7.420298 | 7.422383 | 7.636151 | 7.625448 | 7.630074 | 7.636888 | 7.692880 | 7.705452 | 7.703822 | 7.693002 |
| GO:0071674 | mononuclear cell migration | 18/301 | 242/20870 | 0.00000001592306422 | 0.0000087827073 | 0.0000073293984 | ASB2||CCL22||RIPOR2||PADI2||TNFSF18||CCR7||IL6||SLIT2||PLA2G7||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||NBL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||S1PR1||CSF1||CXCR3||KLRK1 | 18 | 6.373474 | 6.821085 | 6.973271 | 6.357472 | 6.375267 | 6.368280 | 6.392648 | 6.830046 | 6.825929 | 6.813798 | 6.814497 | 6.962104 | 6.996159 | 6.976565 | 6.957947 |
| GO:0050920 | regulation of chemotaxis | 18/301 | 255/20870 | 0.00000003569872364 | 0.0000162610690 | 0.0000135702865 | SEMA3F||RIPOR2||VEGFA||PADI2||TNFSF18||CCR7||IL6||SLIT2||PLA2G7||SEMA3D||NBL1||SEMA6B||CXCL10||S1PR1||SCG2||CSF1||SUCNR1||KLRK1 | 18 | 6.966195 | 7.294631 | 7.384699 | 6.957606 | 6.962347 | 6.976834 | 6.967920 | 7.303045 | 7.289229 | 7.291965 | 7.294247 | 7.386540 | 7.384670 | 7.392520 | 7.375009 |
| GO:0097529 | myeloid leukocyte migration | 18/301 | 256/20870 | 0.00000003790458979 | 0.0000162610690 | 0.0000135702865 | TGFB2||CCL22||RIPOR2||VEGFA||TNFSF18||TREM1||CCR7||IL6||SLIT2||PLA2G7||ADAM8||NBL1||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||SCG2||CSF1||CD300H | 18 | 7.248137 | 7.517777 | 7.632278 | 7.260379 | 7.250545 | 7.245304 | 7.236213 | 7.516295 | 7.511541 | 7.521235 | 7.522015 | 7.625159 | 7.637097 | 7.637789 | 7.629028 |
| GO:0097530 | granulocyte migration | 14/301 | 164/20870 | 0.00000011851417110 | 0.0000423020543 | 0.0000353021683 | TGFB2||CCL22||RIPOR2||TNFSF18||TREM1||CCR7||SLIT2||ADAM8||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||SCG2||CSF1||CD300H | 14 | 7.293974 | 7.623455 | 7.756631 | 7.312537 | 7.298990 | 7.289358 | 7.274750 | 7.626991 | 7.616015 | 7.622286 | 7.628496 | 7.751006 | 7.760856 | 7.753954 | 7.760682 |
| GO:0071621 | granulocyte chemotaxis | 13/301 | 140/20870 | 0.00000012600344333 | 0.0000423020543 | 0.0000353021683 | TGFB2||CCL22||RIPOR2||TNFSF18||TREM1||CCR7||SLIT2||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||SCG2||CSF1||CD300H | 13 | 7.424814 | 7.762995 | 7.909668 | 7.443832 | 7.427076 | 7.419814 | 7.408304 | 7.768665 | 7.753959 | 7.762184 | 7.767128 | 7.902981 | 7.913695 | 7.907341 | 7.914625 |
| GO:0002685 | regulation of leukocyte migration | 17/301 | 248/20870 | 0.00000013147491621 | 0.0000423020543 | 0.0000353021683 | RIPOR2||VEGFA||PADI2||TNFSF18||CCR7||IL6||SLIT2||PLA2G7||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||NBL1||CXCL10||PTAFR||CSF1||CXCR3||TNFRSF18||KLRK1 | 17 | 6.529385 | 6.937917 | 7.103903 | 6.528496 | 6.534993 | 6.527518 | 6.526518 | 6.945217 | 6.929019 | 6.940867 | 6.936517 | 7.097605 | 7.116149 | 7.108173 | 7.093577 |
| GO:0045071 | negative regulation of viral genome replication | 9/301 | 65/20870 | 0.00000037744135663 | 0.0001121000829 | 0.0000935504447 | OAS2||AICDA||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||PARP10||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 9 | 5.757779 | 6.079732 | 6.570917 | 5.753978 | 5.749926 | 5.824677 | 5.699782 | 6.081680 | 6.074060 | 6.102637 | 6.060226 | 6.529888 | 6.594232 | 6.548119 | 6.609949 |
| GO:0045069 | regulation of viral genome replication | 10/301 | 94/20870 | 0.00000104165781900 | 0.0002746154394 | 0.0002291737510 | OAS2||AICDA||NR5A2||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||PARP10||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 10 | 7.015155 | 7.333250 | 7.500881 | 6.848251 | 6.923270 | 7.096989 | 7.169076 | 7.330894 | 7.386915 | 7.275220 | 7.337798 | 7.516515 | 7.459509 | 7.506431 | 7.520255 |
| GO:0002688 | regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis | 12/301 | 142/20870 | 0.00000106688204906 | 0.0002746154394 | 0.0002291737510 | RIPOR2||VEGFA||PADI2||TNFSF18||CCR7||IL6||SLIT2||PLA2G7||NBL1||CXCL10||CSF1||KLRK1 | 12 | 6.076542 | 6.859043 | 7.116823 | 6.076534 | 6.074316 | 6.082915 | 6.072378 | 6.865076 | 6.850966 | 6.859792 | 6.860302 | 7.117342 | 7.129369 | 7.120158 | 7.100271 |
| GO:0071675 | regulation of mononuclear cell migration | 12/301 | 143/20870 | 0.00000114979868107 | 0.0002774607942 | 0.0002315482739 | RIPOR2||PADI2||TNFSF18||CCR7||SLIT2||PLA2G7||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||NBL1||CXCL10||CSF1||KLRK1 | 12 | 6.306448 | 6.836272 | 7.029916 | 6.293792 | 6.312521 | 6.310631 | 6.308773 | 6.855976 | 6.829151 | 6.827363 | 6.832411 | 7.018807 | 7.044757 | 7.033000 | 7.022960 |
| GO:0018108 | peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | 20/301 | 415/20870 | 0.00000286155360712 | 0.0006481945522 | 0.0005409352702 | TIE1||DLG3||TYRO3||OSM||ARL2BP||IL23A||VEGFA||ITK||PRLR||TNFSF18||LIF||SH3BP5||IL6||BMP6||TNFRSF14||IGF2||SOCS4||SOCS3||TNFRSF18||INPP5F | 20 | 5.987589 | 6.181374 | 6.314010 | 5.971469 | 5.978780 | 6.007471 | 5.992376 | 6.173270 | 6.180880 | 6.188769 | 6.182535 | 6.301529 | 6.331648 | 6.320809 | 6.301823 |
| GO:0007517 | muscle organ development | 18/301 | 345/20870 | 0.00000302339388401 | 0.0006481945522 | 0.0005409352702 | MYLK||TGFB2||ASB2||RIPOR2||ID3||LIF||HEY2||ANKRD1||POU4F1||CHODL||LY6E||IGF2||CXCL10||S1PR1||MYOZ2||EGR3||DLL1||SCX | 18 | 6.097461 | 5.908065 | 5.860493 | 5.987651 | 6.043297 | 6.130406 | 6.217864 | 5.916200 | 5.962478 | 5.837111 | 5.913683 | 5.911265 | 5.805662 | 5.834083 | 5.888516 |
| GO:0018212 | peptidyl-tyrosine modification | 20/301 | 418/20870 | 0.00000318976858127 | 0.0006481945522 | 0.0005409352702 | TIE1||DLG3||TYRO3||OSM||ARL2BP||IL23A||VEGFA||ITK||PRLR||TNFSF18||LIF||SH3BP5||IL6||BMP6||TNFRSF14||IGF2||SOCS4||SOCS3||TNFRSF18||INPP5F | 20 | 5.985509 | 6.183163 | 6.312752 | 5.970084 | 5.976266 | 6.005153 | 5.990279 | 6.175220 | 6.183022 | 6.190207 | 6.184161 | 6.300541 | 6.330266 | 6.319296 | 6.300683 |
| GO:0003007 | heart morphogenesis | 15/301 | 251/20870 | 0.00000400805743104 | 0.0007737554871 | 0.0006457191472 | TGFB2||ASB2||DNAH11||VEGFA||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||HEY2||SLIT2||ANKRD1||POU4F1||LY6E||S1PR1||DLL1||ALPK2 | 15 | 5.463710 | 5.405228 | 5.436223 | 5.506568 | 5.413688 | 5.422336 | 5.509429 | 5.410453 | 5.338387 | 5.427200 | 5.442679 | 5.474634 | 5.393899 | 5.443675 | 5.431528 |
| GO:1990266 | neutrophil migration | 11/301 | 138/20870 | 0.00000531089736008 | 0.0008956248450 | 0.0007474223069 | TGFB2||CCL22||RIPOR2||TREM1||CCR7||SLIT2||ADAM8||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||CD300H | 11 | 7.466107 | 7.769987 | 7.906780 | 7.485791 | 7.469490 | 7.461899 | 7.446977 | 7.774027 | 7.762321 | 7.768201 | 7.775362 | 7.899851 | 7.911220 | 7.904569 | 7.911449 |
| GO:0002687 | positive regulation of leukocyte migration | 12/301 | 166/20870 | 0.00000548715563345 | 0.0008956248450 | 0.0007474223069 | RIPOR2||VEGFA||TNFSF18||CCR7||IL6||PLA2G7||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10||PTAFR||CSF1||TNFRSF18 | 12 | 6.700125 | 7.126714 | 7.342652 | 6.692622 | 6.700521 | 6.709761 | 6.697543 | 7.136872 | 7.119055 | 7.134460 | 7.116353 | 7.337292 | 7.355210 | 7.343590 | 7.334428 |
| GO:0050921 | positive regulation of chemotaxis | 12/301 | 166/20870 | 0.00000548715563345 | 0.0008956248450 | 0.0007474223069 | RIPOR2||VEGFA||TNFSF18||CCR7||IL6||SLIT2||PLA2G7||CXCL10||S1PR1||SCG2||CSF1||SUCNR1 | 12 | 7.456660 | 7.768956 | 7.868716 | 7.459116 | 7.454369 | 7.457555 | 7.455594 | 7.785538 | 7.757483 | 7.768973 | 7.763681 | 7.868117 | 7.869256 | 7.875686 | 7.861769 |
| GO:0050730 | regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | 16/301 | 291/20870 | 0.00000556720960371 | 0.0008956248450 | 0.0007474223069 | DLG3||OSM||ARL2BP||IL23A||VEGFA||TNFSF18||LIF||SH3BP5||IL6||BMP6||TNFRSF14||IGF2||SOCS4||SOCS3||TNFRSF18||INPP5F | 16 | 6.316631 | 6.553299 | 6.700355 | 6.305630 | 6.306290 | 6.336436 | 6.317951 | 6.543305 | 6.553231 | 6.558849 | 6.557758 | 6.688453 | 6.718361 | 6.707917 | 6.686440 |
| GO:1903900 | regulation of viral life cycle | 13/301 | 198/20870 | 0.00000643605869607 | 0.0009939849050 | 0.0008295063439 | TYRO3||OAS2||AICDA||NR5A2||TRIM22||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||LY6E||PARP10||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 13 | 7.017875 | 7.565773 | 7.729136 | 6.888556 | 6.978128 | 7.058979 | 7.134253 | 7.563604 | 7.568045 | 7.544530 | 7.586601 | 7.715019 | 7.708984 | 7.744274 | 7.747855 |
| GO:0072676 | lymphocyte migration | 11/301 | 144/20870 | 0.00000799664516267 | 0.0011845483353 | 0.0009885364998 | CCL22||RIPOR2||PADI2||CCR7||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10||CXCL11||S1PR1||CXCR3||KLRK1 | 11 | 6.183495 | 6.609464 | 6.861102 | 6.177270 | 6.206504 | 6.185118 | 6.164768 | 6.633184 | 6.611576 | 6.593453 | 6.599319 | 6.851927 | 6.874761 | 6.855241 | 6.862375 |
| GO:0030593 | neutrophil chemotaxis | 10/301 | 118/20870 | 0.00000828355479243 | 0.0011845483353 | 0.0009885364998 | TGFB2||CCL22||RIPOR2||TREM1||CCR7||SLIT2||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||CD300H | 10 | 7.613547 | 7.929617 | 8.079746 | 7.633389 | 7.614432 | 7.609215 | 7.596911 | 7.935661 | 7.920295 | 7.928298 | 7.934164 | 8.071592 | 8.084285 | 8.078248 | 8.084819 |
| GO:0055001 | muscle cell development | 13/301 | 204/20870 | 0.00000889208825327 | 0.0012261554552 | 0.0010232587272 | ASB2||RIPOR2||VEGFA||RGS4||HEY2||DYSF||BIN1||ANKRD1||OBSCN||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP||ALPK2 | 13 | 6.420787 | 6.557195 | 6.527652 | 6.429272 | 6.410019 | 6.426920 | 6.416855 | 6.556308 | 6.549533 | 6.571219 | 6.551618 | 6.485159 | 6.545349 | 6.542804 | 6.536461 |
| GO:0042509 | regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | 9/301 | 96/20870 | 0.00001036147894714 | 0.0013795058695 | 0.0011512336500 | OSM||ARL2BP||IL23A||TNFSF18||LIF||IL6||SOCS3||TNFRSF18||INPP5F | 9 | 5.369853 | 6.178940 | 6.489370 | 5.328404 | 5.309394 | 5.497311 | 5.336278 | 6.143899 | 6.229540 | 6.166586 | 6.174354 | 6.460776 | 6.512806 | 6.493595 | 6.489824 |
| GO:0042692 | muscle cell differentiation | 19/301 | 416/20870 | 0.00001090018590702 | 0.0014028539262 | 0.0011707182127 | ASB2||DMPK||RIPOR2||VEGFA||RGS4||TBX2||HEY2||DYSF||BIN1||ANKRD1||OBSCN||IGF2||CXCL10||MYOZ2||LBX2||SLC8A1||NRAP||DLL1||ALPK2 | 19 | 6.738567 | 6.895861 | 6.878914 | 6.746115 | 6.740953 | 6.738072 | 6.729074 | 6.891816 | 6.896176 | 6.891990 | 6.903433 | 6.866854 | 6.888438 | 6.876309 | 6.883962 |
| GO:0007260 | tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | 9/301 | 99/20870 | 0.00001332187366177 | 0.0016592178777 | 0.0013846606207 | OSM||ARL2BP||IL23A||TNFSF18||LIF||IL6||SOCS3||TNFRSF18||INPP5F | 9 | 5.344823 | 6.153502 | 6.462323 | 5.301251 | 5.282661 | 5.470930 | 5.316527 | 6.116720 | 6.202408 | 6.146338 | 6.147207 | 6.433296 | 6.485402 | 6.467647 | 6.462461 |
| GO:0050792 | regulation of viral process | 13/301 | 214/20870 | 0.00001484601621166 | 0.0017614574263 | 0.0014699821922 | TYRO3||OAS2||AICDA||NR5A2||TRIM22||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||LY6E||PARP10||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 13 | 6.927273 | 7.454784 | 7.611930 | 6.807328 | 6.889759 | 6.966385 | 7.035581 | 7.451268 | 7.458534 | 7.434163 | 7.474873 | 7.599560 | 7.592454 | 7.626699 | 7.628649 |
| GO:0048638 | regulation of developmental growth | 17/301 | 351/20870 | 0.00001505519167797 | 0.0017614574263 | 0.0014699821922 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||RASAL1||VEGFA||RGS4||BCL11A||TBX2||MKKS||UNC13A||HEY2||SEMA3D||IGF2||SEMA6B||CSF1||DLL1||EPPK1 | 17 | 6.357096 | 6.788540 | 6.800863 | 6.354830 | 6.359589 | 6.364061 | 6.349865 | 6.795691 | 6.779266 | 6.784518 | 6.794619 | 6.819812 | 6.796535 | 6.792004 | 6.794930 |
| GO:0048644 | muscle organ morphogenesis | 8/301 | 78/20870 | 0.00001667247288392 | 0.0018933064060 | 0.0015800136067 | MYLK||TGFB2||LIF||HEY2||ANKRD1||POU4F1||LY6E||S1PR1 | 8 | 5.132797 | 5.309763 | 5.435590 | 5.108064 | 5.102638 | 5.103870 | 5.213506 | 5.331057 | 5.294131 | 5.327240 | 5.286083 | 5.439355 | 5.466459 | 5.421010 | 5.414979 |
| GO:0060537 | muscle tissue development | 19/301 | 432/20870 | 0.00001843839233278 | 0.0020340180799 | 0.0016974411708 | MYLK||TGFB2||ASB2||RIPOR2||VEGFA||RGS4||TBX2||HEY2||ANKRD1||POU4F1||LY6E||IGF2||S1PR1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP||DLL1||ALPK2||SCX | 19 | 6.237649 | 6.207868 | 6.183220 | 6.157958 | 6.211851 | 6.265188 | 6.311046 | 6.227633 | 6.234946 | 6.167794 | 6.200135 | 6.194990 | 6.152260 | 6.174392 | 6.210572 |
| GO:0048738 | cardiac muscle tissue development | 14/301 | 254/20870 | 0.00002090112798299 | 0.0022416459762 | 0.0018707120689 | TGFB2||ASB2||VEGFA||RGS4||TBX2||HEY2||ANKRD1||POU4F1||LY6E||S1PR1||SLC8A1||NRAP||DLL1||ALPK2 | 14 | 5.985579 | 6.073793 | 6.097059 | 5.989234 | 6.003624 | 5.982907 | 5.966304 | 6.101736 | 6.053971 | 6.080963 | 6.057990 | 6.097368 | 6.092846 | 6.096002 | 6.102004 |
| GO:0071260 | cellular response to mechanical stimulus | 8/301 | 83/20870 | 0.00002635487823431 | 0.0027501671585 | 0.0022950862667 | GCLC||TLR4||MMP7||ANKRD1||BMP6||TLR7||AQP1||SCX | 8 | 6.230437 | 6.758638 | 7.021425 | 6.211382 | 6.258688 | 6.225537 | 6.225721 | 6.774458 | 6.786468 | 6.737634 | 6.735292 | 7.024497 | 7.064101 | 7.010771 | 6.985200 |
| GO:0048525 | negative regulation of viral process | 10/301 | 136/20870 | 0.00002877360954750 | 0.0029235501701 | 0.0024397789148 | OAS2||AICDA||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||LY6E||PARP10||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 10 | 6.035323 | 6.193514 | 6.493518 | 6.024200 | 6.029903 | 6.046859 | 6.040222 | 6.207102 | 6.166709 | 6.205415 | 6.194466 | 6.459978 | 6.502713 | 6.476658 | 6.533644 |
| GO:0071676 | negative regulation of mononuclear cell migration | 5/301 | 26/20870 | 0.00003096665590802 | 0.0030656989349 | 0.0025584057688 | RIPOR2||PADI2||SLIT2||NBL1||KLRK1 | 5 | 4.676758 | 5.186923 | 5.170907 | 4.536051 | 4.695201 | 4.626895 | 4.832547 | 5.205356 | 5.122000 | 5.087299 | 5.321626 | 5.137248 | 5.218877 | 5.178128 | 5.147978 |
| GO:0014706 | striated muscle tissue development | 18/301 | 412/20870 | 0.00003341148469388 | 0.0030748418218 | 0.0025660357465 | TGFB2||ASB2||RIPOR2||VEGFA||RGS4||TBX2||HEY2||ANKRD1||POU4F1||LY6E||IGF2||S1PR1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP||DLL1||ALPK2||SCX | 18 | 6.260378 | 6.232633 | 6.214179 | 6.178880 | 6.233292 | 6.288843 | 6.335703 | 6.254565 | 6.261037 | 6.191347 | 6.222512 | 6.225862 | 6.182874 | 6.206607 | 6.240723 |
| GO:1990868 | response to chemokine | 9/301 | 111/20870 | 0.00003344816278559 | 0.0030748418218 | 0.0025660357465 | CCL22||RIPOR2||PADI2||CCR7||SLIT2||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||CXCR3 | 9 | 5.397966 | 6.654542 | 7.075181 | 5.397572 | 5.402568 | 5.469729 | 5.317995 | 6.655483 | 6.672483 | 6.653831 | 6.636143 | 7.095145 | 7.077760 | 7.060078 | 7.067502 |
| GO:1990869 | cellular response to chemokine | 9/301 | 111/20870 | 0.00003344816278559 | 0.0030748418218 | 0.0025660357465 | CCL22||RIPOR2||PADI2||CCR7||SLIT2||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||CXCR3 | 9 | 5.397966 | 6.654542 | 7.075181 | 5.397572 | 5.402568 | 5.469729 | 5.317995 | 6.655483 | 6.672483 | 6.653831 | 6.636143 | 7.095145 | 7.077760 | 7.060078 | 7.067502 |
| GO:0006939 | smooth muscle contraction | 9/301 | 112/20870 | 0.00003591731157749 | 0.0032250404651 | 0.0026913804342 | MYLK||TBX2||MKKS||CHRM3||EDNRA||PTAFR||SSTR2||SLC8A1||SULF2 | 9 | 5.189384 | 5.098388 | 5.046867 | 5.215527 | 5.081595 | 5.228004 | 5.227220 | 5.057299 | 5.051013 | 5.083644 | 5.196740 | 5.061834 | 5.042258 | 4.964162 | 5.115161 |
| GO:0019079 | viral genome replication | 10/301 | 143/20870 | 0.00004425171976263 | 0.0038830884092 | 0.0032405386171 | OAS2||AICDA||NR5A2||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||PARP10||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 10 | 6.920573 | 7.227896 | 7.334749 | 6.832214 | 6.856751 | 6.968867 | 7.016349 | 7.225237 | 7.277339 | 7.181354 | 7.226052 | 7.347382 | 7.299879 | 7.342903 | 7.348270 |
| GO:0051146 | striated muscle cell differentiation | 15/301 | 311/20870 | 0.00005012274000220 | 0.0043005310922 | 0.0035889054303 | ASB2||DMPK||RIPOR2||VEGFA||RGS4||HEY2||ANKRD1||OBSCN||IGF2||CXCL10||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP||DLL1||ALPK2 | 15 | 6.972553 | 7.131860 | 7.118249 | 6.977810 | 6.973775 | 6.971540 | 6.967065 | 7.139389 | 7.120579 | 7.131006 | 7.136394 | 7.108150 | 7.124123 | 7.118417 | 7.122251 |
| GO:0010575 | positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production | 5/301 | 29/20870 | 0.00005395904333517 | 0.0045290405721 | 0.0037796025549 | IL1A||C3||IL6||HPSE||SULF2 | 5 | 5.703219 | 7.368466 | 7.853234 | 5.666546 | 5.678995 | 5.687635 | 5.777032 | 7.370343 | 7.351860 | 7.380938 | 7.370572 | 7.850991 | 7.857488 | 7.859208 | 7.845206 |
| GO:0019058 | viral life cycle | 17/301 | 390/20870 | 0.00005678308793038 | 0.0046395393480 | 0.0038718166671 | SIGLEC1||TYRO3||OAS2||AICDA||NR5A2||ZNF639||TRIM22||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||TNFRSF14||LY6E||PARP10||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15||MVB12B | 17 | 6.869392 | 7.291442 | 7.420550 | 6.819818 | 6.847786 | 6.890617 | 6.917380 | 7.286220 | 7.302263 | 7.275597 | 7.301516 | 7.410232 | 7.409469 | 7.434755 | 7.427576 |
| GO:0050729 | positive regulation of inflammatory response | 11/301 | 178/20870 | 0.00005767881085281 | 0.0046395393480 | 0.0038718166671 | OSM||IL23A||TNFSF18||C3||CCR7||IL6||TLR4||PLA2G7||ADAM8||TLR7||SUCNR1 | 11 | 6.793309 | 7.009496 | 7.176289 | 6.789639 | 6.782989 | 6.791134 | 6.809343 | 7.015028 | 7.013241 | 7.005118 | 7.004568 | 7.176094 | 7.170422 | 7.194368 | 7.164097 |
| GO:0032728 | positive regulation of interferon-beta production | 6/301 | 48/20870 | 0.00006314048757620 | 0.0049752127047 | 0.0041519448436 | OAS2||POLR3G||TLR4||IRF7||ISG15||TLR7 | 6 | 5.923571 | 5.867557 | 5.780233 | 6.001191 | 5.893480 | 5.916145 | 5.880373 | 5.858144 | 5.885684 | 5.824393 | 5.900836 | 5.750266 | 5.757130 | 5.878066 | 5.730746 |
| GO:0050731 | positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | 12/301 | 213/20870 | 0.00006573263171804 | 0.0050758738213 | 0.0042359491724 | DLG3||OSM||ARL2BP||IL23A||VEGFA||TNFSF18||LIF||IL6||BMP6||TNFRSF14||IGF2||TNFRSF18 | 12 | 5.838362 | 6.322641 | 6.532059 | 5.823351 | 5.834913 | 5.845496 | 5.849543 | 6.320142 | 6.308163 | 6.331898 | 6.330237 | 6.530388 | 6.539696 | 6.538069 | 6.519999 |
| GO:0060415 | muscle tissue morphogenesis | 7/301 | 71/20870 | 0.00007311361116257 | 0.0055351304451 | 0.0046192108105 | MYLK||TGFB2||HEY2||ANKRD1||POU4F1||LY6E||S1PR1 | 7 | 5.136792 | 5.345375 | 5.480612 | 5.136975 | 5.127562 | 5.129204 | 5.153284 | 5.371145 | 5.326653 | 5.361982 | 5.321068 | 5.487305 | 5.506067 | 5.465273 | 5.463378 |
| GO:0007259 | receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT | 11/301 | 184/20870 | 0.00007778190584836 | 0.0057753065092 | 0.0048196440041 | OSM||ARL2BP||IL23A||PRLR||TNFSF18||LIF||IL6||STAT4||SOCS3||TNFRSF18||INPP5F | 11 | 5.589713 | 6.053650 | 6.164930 | 5.547856 | 5.685969 | 5.566337 | 5.554183 | 5.937499 | 6.044536 | 6.107077 | 6.118430 | 6.137024 | 6.160410 | 6.229970 | 6.130139 |
| GO:1901214 | regulation of neuron death | 17/301 | 401/20870 | 0.00007983710153792 | 0.0058160575290 | 0.0048536517936 | GCLC||TYRO3||TGFB2||DNAJC5||NR4A3||CLU||NES||TLR4||TFAP2A||MEAK7||SLC7A11||ADAM8||POU4F1||NR4A2||GPRASP2||CSF1||HLA-F | 17 | 6.798750 | 6.788936 | 6.861117 | 6.807417 | 6.797212 | 6.784975 | 6.805288 | 6.804616 | 6.797819 | 6.786815 | 6.766201 | 6.857545 | 6.869633 | 6.861318 | 6.855933 |
| GO:0060560 | developmental growth involved in morphogenesis | 13/301 | 253/20870 | 0.00008419775636414 | 0.0060201395800 | 0.0050239635912 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||RASAL1||VEGFA||BCL11A||TBX2||UNC13A||SLIT2||SEMA3D||SEMA6B||S1PR1||CSF1 | 13 | 6.482581 | 7.027302 | 7.018547 | 6.476873 | 6.488104 | 6.494033 | 6.471202 | 7.040377 | 7.025811 | 7.016528 | 7.026393 | 7.030795 | 7.024533 | 7.007574 | 7.011161 |
| GO:0071222 | cellular response to lipopolysaccharide | 13/301 | 258/20870 | 0.00010249679292469 | 0.0071952748633 | 0.0060046446534 | NR1H3||IL1A||CMPK2||IL6||IL36G||TLR4||ANKRD1||BMP6||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||PTAFR||PDCD1LG2 | 13 | 5.602065 | 6.377258 | 6.668393 | 5.611467 | 5.588703 | 5.617768 | 5.590093 | 6.386363 | 6.356848 | 6.388852 | 6.376751 | 6.679675 | 6.668113 | 6.671684 | 6.653981 |
| GO:1903131 | mononuclear cell differentiation | 19/301 | 494/20870 | 0.00011122122514135 | 0.0076683062548 | 0.0063994016947 | TYRO3||IL23A||AICDA||VEGFA||ITK||IL1A||TNFSF18||CCR7||RSAD2||IL6||ZC3H8||ADAM8||CD3G||EGR3||CSF1||IRF7||DLL1||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 19 | 6.875889 | 7.116099 | 7.185286 | 6.875768 | 6.879741 | 6.864678 | 6.883302 | 7.123233 | 7.097082 | 7.115901 | 7.127988 | 7.162259 | 7.190503 | 7.203323 | 7.184755 |
| GO:0070098 | chemokine-mediated signaling pathway | 8/301 | 102/20870 | 0.00011571753483220 | 0.0078383403857 | 0.0065412996144 | CCL22||PADI2||CCR7||SLIT2||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||CXCR3 | 8 | 4.942244 | 6.645200 | 7.142348 | 4.944161 | 4.952342 | 5.057979 | 4.803196 | 6.636484 | 6.670499 | 6.651517 | 6.621847 | 7.167052 | 7.146340 | 7.126767 | 7.128866 |
| GO:0097696 | receptor signaling pathway via STAT | 11/301 | 195/20870 | 0.00013040364597805 | 0.0085776079356 | 0.0071582376780 | OSM||ARL2BP||IL23A||PRLR||TNFSF18||LIF||IL6||STAT4||SOCS3||TNFRSF18||INPP5F | 11 | 5.657043 | 6.123086 | 6.232478 | 5.612609 | 5.744271 | 5.635968 | 5.631580 | 6.019147 | 6.108569 | 6.176352 | 6.182320 | 6.209691 | 6.230804 | 6.291405 | 6.196161 |
| GO:0042531 | positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | 7/301 | 78/20870 | 0.00013329616061542 | 0.0085776079356 | 0.0071582376780 | OSM||ARL2BP||IL23A||TNFSF18||LIF||IL6||TNFRSF18 | 7 | 5.242150 | 6.198981 | 6.616334 | 5.219377 | 5.261998 | 5.259830 | 5.226891 | 6.178163 | 6.201619 | 6.203829 | 6.212094 | 6.600526 | 6.627838 | 6.619485 | 6.617350 |
| GO:0050922 | negative regulation of chemotaxis | 7/301 | 78/20870 | 0.00013329616061542 | 0.0085776079356 | 0.0071582376780 | SEMA3F||PADI2||SLIT2||SEMA3D||NBL1||SEMA6B||KLRK1 | 7 | 5.201034 | 5.754280 | 5.821285 | 5.074499 | 5.176163 | 5.309193 | 5.234136 | 5.707682 | 5.787820 | 5.744532 | 5.775754 | 5.852782 | 5.819427 | 5.813701 | 5.798685 |
| GO:1903557 | positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor superfamily cytokine production | 9/301 | 134/20870 | 0.00014474713030386 | 0.0091617814771 | 0.0076457457439 | IL23A||OAS2||IL1A||CLU||IL6||TLR4||ADAM8||PTAFR||ORM1 | 9 | 6.945545 | 6.969009 | 6.967670 | 6.934640 | 6.951059 | 6.946531 | 6.949890 | 6.977096 | 6.969071 | 6.977675 | 6.952044 | 6.964348 | 6.975949 | 6.967790 | 6.962555 |
| GO:0045860 | positive regulation of protein kinase activity | 17/301 | 423/20870 | 0.00015176659250436 | 0.0094511421558 | 0.0078872247819 | DLG3||TGFB2||IL23A||VEGFA||PRLR||CLU||CCR7||MAS1||BORA||TLR4||ETAA1||FGD2||ADAM8||IGF2||TNFSF15||CSF1||PIK3R6 | 17 | 6.274199 | 6.602494 | 6.691660 | 6.255130 | 6.281147 | 6.282518 | 6.277831 | 6.606546 | 6.600187 | 6.607268 | 6.595944 | 6.695335 | 6.694364 | 6.681821 | 6.695074 |
| GO:0072678 | T cell migration | 7/301 | 80/20870 | 0.00015640002606743 | 0.0095151896631 | 0.0079406740983 | RIPOR2||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10||CXCL11||S1PR1||CXCR3 | 7 | 6.385685 | 6.833325 | 7.076395 | 6.388676 | 6.389117 | 6.396296 | 6.368501 | 6.851643 | 6.835841 | 6.830466 | 6.815115 | 7.075563 | 7.090227 | 7.057311 | 7.082273 |
| GO:0090025 | regulation of monocyte chemotaxis | 5/301 | 36/20870 | 0.00015772394157970 | 0.0095151896631 | 0.0079406740983 | TNFSF18||SLIT2||PLA2G7||NBL1||CXCL10 | 5 | 5.346606 | 6.610486 | 7.089980 | 5.322819 | 5.340878 | 5.373943 | 5.348315 | 6.637457 | 6.626141 | 6.587109 | 6.590571 | 7.053950 | 7.120402 | 7.092342 | 7.092453 |
| GO:0071219 | cellular response to molecule of bacterial origin | 13/301 | 271/20870 | 0.00016696126220753 | 0.0097453044171 | 0.0081327108660 | NR1H3||IL1A||CMPK2||IL6||IL36G||TLR4||ANKRD1||BMP6||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||PTAFR||PDCD1LG2 | 13 | 5.657281 | 6.366285 | 6.642598 | 5.664427 | 5.645436 | 5.673761 | 5.645290 | 6.375781 | 6.346713 | 6.375987 | 6.366461 | 6.653174 | 6.642004 | 6.645670 | 6.629441 |
| GO:1901215 | negative regulation of neuron death | 13/301 | 271/20870 | 0.00016696126220753 | 0.0097453044171 | 0.0081327108660 | GCLC||TYRO3||DNAJC5||NR4A3||NES||MEAK7||SLC7A11||ADAM8||POU4F1||NR4A2||GPRASP2||CSF1||HLA-F | 13 | 6.660277 | 6.647098 | 6.666824 | 6.657500 | 6.671901 | 6.657017 | 6.654625 | 6.664565 | 6.662085 | 6.630941 | 6.630431 | 6.690614 | 6.647747 | 6.665139 | 6.663467 |
| GO:0048247 | lymphocyte chemotaxis | 7/301 | 81/20870 | 0.00016911043666123 | 0.0097453044171 | 0.0081327108660 | CCL22||PADI2||ADAM8||CXCL10||CXCL11||CXCR3||KLRK1 | 7 | 5.169438 | 6.501941 | 6.991191 | 5.178518 | 5.199111 | 5.183710 | 5.114990 | 6.516897 | 6.502618 | 6.484426 | 6.503640 | 6.972994 | 7.002812 | 6.992502 | 6.996287 |
| GO:0002690 | positive regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis | 8/301 | 111/20870 | 0.00020838693333561 | 0.0118320874942 | 0.0098741858040 | RIPOR2||VEGFA||TNFSF18||CCR7||IL6||PLA2G7||CXCL10||CSF1 | 8 | 6.272371 | 7.033161 | 7.322300 | 6.268483 | 6.267044 | 6.284230 | 6.269661 | 7.039208 | 7.034702 | 7.038458 | 7.020195 | 7.323246 | 7.330962 | 7.324932 | 7.309977 |
| GO:0035051 | cardiocyte differentiation | 10/301 | 173/20870 | 0.00021549591865464 | 0.0120134503119 | 0.0100255378085 | TGFB2||ASB2||VEGFA||RGS4||TBX2||HEY2||SLC8A1||NRAP||DLL1||ALPK2 | 10 | 6.170644 | 6.297204 | 6.341258 | 6.167455 | 6.183230 | 6.172871 | 6.158914 | 6.330029 | 6.269110 | 6.300944 | 6.288053 | 6.342822 | 6.338910 | 6.339986 | 6.343309 |
| GO:0003012 | muscle system process | 18/301 | 478/20870 | 0.00021780407195960 | 0.0120134503119 | 0.0100255378085 | MYLK||DMPK||RGS4||NR4A3||TBX2||MKKS||CHRM3||HEY2||BIN1||EDNRA||PTAFR||MYOZ2||SSTR2||SLC8A1||TRDN||SULF2||TPM2||INPP5F | 18 | 6.197495 | 6.441757 | 6.510739 | 6.186866 | 6.189210 | 6.206639 | 6.207142 | 6.438655 | 6.432809 | 6.455249 | 6.440222 | 6.495510 | 6.526803 | 6.488041 | 6.532097 |
| GO:0050767 | regulation of neurogenesis | 16/301 | 398/20870 | 0.00023565947660274 | 0.0128152287206 | 0.0106946428151 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||LIF||BHLHE40||HEY2||IL6||BIN1||SLIT2||POU4F1||SEMA3D||CHODL||GPRASP2||SEMA6B||DLL1 | 16 | 6.699334 | 6.976764 | 7.013124 | 6.699380 | 6.690117 | 6.709653 | 6.698122 | 6.979491 | 6.972709 | 6.969557 | 6.985248 | 7.019339 | 7.019133 | 7.008736 | 7.005234 |
| GO:0051960 | regulation of nervous system development | 18/301 | 482/20870 | 0.00024097488138485 | 0.0128249892899 | 0.0107027882650 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||TYMP||CST7||VEGFA||LIF||BHLHE40||HEY2||IL6||BIN1||SLIT2||POU4F1||SEMA3D||CHODL||GPRASP2||SEMA6B||DLL1 | 18 | 6.577894 | 6.809045 | 6.837024 | 6.576770 | 6.570407 | 6.590360 | 6.573960 | 6.812935 | 6.805163 | 6.801111 | 6.816917 | 6.842026 | 6.842129 | 6.833468 | 6.830436 |
| GO:0055008 | cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis | 6/301 | 61/20870 | 0.00024424292076462 | 0.0128249892899 | 0.0107027882650 | TGFB2||HEY2||ANKRD1||POU4F1||LY6E||S1PR1 | 6 | 5.058301 | 5.439267 | 5.604533 | 5.063918 | 5.048990 | 5.049971 | 5.070211 | 5.458373 | 5.412763 | 5.465666 | 5.419521 | 5.617371 | 5.622961 | 5.587772 | 5.589679 |
| GO:0001960 | negative regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway | 7/301 | 86/20870 | 0.00024580399053510 | 0.0128249892899 | 0.0107027882650 | NR1H3||IL1R2||PADI2||IL6||IL1RN||SLIT2||ISG15 | 7 | 5.669144 | 5.952244 | 6.322585 | 5.666857 | 5.651667 | 5.695160 | 5.662533 | 5.941380 | 5.997181 | 5.911598 | 5.957491 | 6.303233 | 6.350566 | 6.291838 | 6.343819 |
| GO:0070997 | neuron death | 17/301 | 442/20870 | 0.00025431081539316 | 0.0130919207764 | 0.0109255495568 | GCLC||TYRO3||TGFB2||DNAJC5||NR4A3||CLU||NES||TLR4||TFAP2A||MEAK7||SLC7A11||ADAM8||POU4F1||NR4A2||GPRASP2||CSF1||HLA-F | 17 | 6.786417 | 6.797651 | 6.862524 | 6.793626 | 6.785303 | 6.773363 | 6.793281 | 6.810926 | 6.806311 | 6.792834 | 6.780333 | 6.858997 | 6.870636 | 6.861435 | 6.858997 |
| GO:0048846 | axon extension involved in axon guidance | 5/301 | 40/20870 | 0.00026263352132835 | 0.0131691951409 | 0.0109900370306 | SEMA3F||VEGFA||SLIT2||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 5 | 3.987081 | 4.985164 | 5.259509 | 3.987477 | 4.051329 | 3.977565 | 3.929330 | 4.935403 | 4.978454 | 4.973460 | 5.050906 | 5.342861 | 5.198263 | 5.285411 | 5.206571 |
| GO:1902284 | neuron projection extension involved in neuron projection guidance | 5/301 | 40/20870 | 0.00026263352132835 | 0.0131691951409 | 0.0109900370306 | SEMA3F||VEGFA||SLIT2||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 5 | 3.987081 | 4.985164 | 5.259509 | 3.987477 | 4.051329 | 3.977565 | 3.929330 | 4.935403 | 4.978454 | 4.973460 | 5.050906 | 5.342861 | 5.198263 | 5.285411 | 5.206571 |
| GO:0034340 | response to type I interferon | 6/301 | 62/20870 | 0.00026717633961776 | 0.0132252288111 | 0.0110367985907 | OAS2||MX1||IRF7||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 6 | 6.109724 | 6.209027 | 6.304528 | 6.164978 | 6.087404 | 6.121653 | 6.062812 | 6.206713 | 6.207351 | 6.219084 | 6.202910 | 6.276904 | 6.343399 | 6.297391 | 6.299601 |
| GO:1903037 | regulation of leukocyte cell-cell adhesion | 18/301 | 490/20870 | 0.00029384987640672 | 0.0142429199679 | 0.0118860884205 | IL23A||RIPOR2||IL1A||NR4A3||TNFSF18||CCR7||IL6||ZC3H8||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||IGF2||PTAFR||EGR3||PDCD1LG2||HLA-DRA||KLRK1||HLA-DQA2||PIK3R6 | 18 | 6.936365 | 7.303898 | 7.444103 | 6.932850 | 6.943994 | 6.930473 | 6.938105 | 7.310322 | 7.286927 | 7.304984 | 7.313213 | 7.423541 | 7.448678 | 7.461237 | 7.442700 |
| GO:0002675 | positive regulation of acute inflammatory response | 5/301 | 41/20870 | 0.00029561344766119 | 0.0142429199679 | 0.0118860884205 | OSM||C3||CCR7||IL6||ADAM8 | 5 | 5.273196 | 7.293729 | 7.731690 | 5.262571 | 5.236677 | 5.286657 | 5.305942 | 7.297693 | 7.280986 | 7.277485 | 7.318385 | 7.728485 | 7.726545 | 7.743463 | 7.728200 |
| GO:0071887 | leukocyte apoptotic process | 8/301 | 117/20870 | 0.00029880251680971 | 0.0142429199679 | 0.0118860884205 | CCR7||IDO1||IL6||ZC3H8||SLC7A11||ADAM8||CD3G||IRF7 | 8 | 6.518892 | 6.817712 | 6.915426 | 6.517505 | 6.505317 | 6.533467 | 6.519139 | 6.820596 | 6.829244 | 6.800531 | 6.820326 | 6.924253 | 6.901047 | 6.916621 | 6.919678 |
| GO:0016032 | viral process | 18/301 | 495/20870 | 0.00033179945339757 | 0.0156228986533 | 0.0130377166476 | SIGLEC1||TYRO3||OAS2||AICDA||NR5A2||ZNF639||TRIM22||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||TNFRSF14||LY6E||PARP10||IRF7||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15||MVB12B | 18 | 6.733532 | 7.133900 | 7.242622 | 6.695006 | 6.716146 | 6.751977 | 6.769809 | 7.131411 | 7.149174 | 7.116366 | 7.138452 | 7.235311 | 7.233209 | 7.255327 | 7.246533 |
| GO:0060761 | negative regulation of response to cytokine stimulus | 7/301 | 91/20870 | 0.00034830700397743 | 0.0160096826471 | 0.0133604979846 | NR1H3||IL1R2||PADI2||IL6||IL1RN||SLIT2||ISG15 | 7 | 5.680620 | 5.905343 | 6.251259 | 5.669947 | 5.673035 | 5.707293 | 5.671873 | 5.893734 | 5.950267 | 5.867514 | 5.908609 | 6.234732 | 6.272570 | 6.224982 | 6.272109 |
| GO:2000106 | regulation of leukocyte apoptotic process | 7/301 | 91/20870 | 0.00034830700397743 | 0.0160096826471 | 0.0133604979846 | CCR7||IDO1||ZC3H8||SLC7A11||ADAM8||CD3G||IRF7 | 7 | 5.558441 | 5.968834 | 6.255261 | 5.539445 | 5.545848 | 5.599333 | 5.548339 | 5.982514 | 5.989858 | 5.943547 | 5.958943 | 6.279237 | 6.238724 | 6.251816 | 6.250961 |
| GO:0002689 | negative regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis | 4/301 | 24/20870 | 0.00035886614793475 | 0.0163009670256 | 0.0136035824004 | PADI2||SLIT2||NBL1||KLRK1 | 4 | 5.337415 | 6.362109 | 6.417702 | 5.385567 | 5.332261 | 5.301012 | 5.329521 | 6.374623 | 6.273780 | 6.342872 | 6.451500 | 6.431345 | 6.452768 | 6.393225 | 6.392549 |
| GO:0060759 | regulation of response to cytokine stimulus | 10/301 | 185/20870 | 0.00036873966309760 | 0.0165546958049 | 0.0138153256884 | NR1H3||IL1R2||PADI2||IL6||IL1RN||TLR4||SLIT2||CSF1||IRF7||ISG15 | 10 | 6.098369 | 6.343913 | 6.491184 | 6.115623 | 6.078461 | 6.098809 | 6.100341 | 6.335759 | 6.351400 | 6.343531 | 6.344921 | 6.480960 | 6.504025 | 6.485259 | 6.494383 |
| GO:0030278 | regulation of ossification | 8/301 | 121/20870 | 0.00037520956364684 | 0.0166515416694 | 0.0138961460898 | TGFB2||TFAP2A||BMP6||S1PR1||SLC8A1||CSF1||ISG15||ENPP1 | 8 | 5.476861 | 5.907544 | 6.012849 | 5.477983 | 5.478199 | 5.462590 | 5.488553 | 5.908816 | 5.895155 | 5.899927 | 5.926083 | 6.108199 | 5.985694 | 5.973039 | 5.980073 |
| GO:0071216 | cellular response to biotic stimulus | 13/301 | 296/20870 | 0.00039184383035789 | 0.0170066789329 | 0.0141925174044 | NR1H3||IL1A||CMPK2||IL6||IL36G||TLR4||ANKRD1||BMP6||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||PTAFR||PDCD1LG2 | 13 | 5.794434 | 6.426580 | 6.644484 | 5.799828 | 5.791211 | 5.805826 | 5.780749 | 6.447456 | 6.421047 | 6.421054 | 6.416554 | 6.660395 | 6.639708 | 6.644972 | 6.632718 |
| GO:0002548 | monocyte chemotaxis | 7/301 | 93/20870 | 0.00039783279734831 | 0.0170066789329 | 0.0141925174044 | CCL22||TNFSF18||IL6||SLIT2||PLA2G7||NBL1||CXCL10 | 7 | 6.015285 | 7.089481 | 7.407922 | 6.029063 | 5.976965 | 6.024432 | 6.030003 | 7.075836 | 7.122358 | 7.084625 | 7.074580 | 7.394666 | 7.415928 | 7.428812 | 7.391958 |
| GO:1903039 | positive regulation of leukocyte cell-cell adhesion | 15/301 | 376/20870 | 0.00039804245351539 | 0.0170066789329 | 0.0141925174044 | IL23A||IL1A||NR4A3||CCR7||IL6||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||IGF2||PTAFR||EGR3||PDCD1LG2||HLA-DRA||KLRK1||HLA-DQA2||PIK3R6 | 15 | 7.134261 | 7.528899 | 7.683683 | 7.128002 | 7.140414 | 7.129619 | 7.138964 | 7.531380 | 7.506780 | 7.534895 | 7.542296 | 7.663628 | 7.687476 | 7.695529 | 7.687901 |
| GO:0030217 | T cell differentiation | 13/301 | 297/20870 | 0.00040458789055999 | 0.0170066789329 | 0.0141925174044 | IL23A||ITK||IL1A||TNFSF18||CCR7||RSAD2||IL6||ZC3H8||ADAM8||CD3G||EGR3||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 13 | 7.003079 | 7.104962 | 7.138221 | 7.019186 | 7.003417 | 6.996776 | 6.992796 | 7.115935 | 7.098678 | 7.096434 | 7.108717 | 7.128401 | 7.132917 | 7.151941 | 7.139517 |
| GO:0030098 | lymphocyte differentiation | 16/301 | 418/20870 | 0.00040523555084834 | 0.0170066789329 | 0.0141925174044 | TYRO3||IL23A||AICDA||ITK||IL1A||TNFSF18||CCR7||RSAD2||IL6||ZC3H8||ADAM8||CD3G||EGR3||DLL1||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 16 | 6.937395 | 7.197329 | 7.255879 | 6.939574 | 6.942872 | 6.928987 | 6.938109 | 7.204619 | 7.176714 | 7.196633 | 7.211119 | 7.234240 | 7.254569 | 7.277203 | 7.257184 |
| GO:0009612 | response to mechanical stimulus | 11/301 | 223/20870 | 0.00041518607124643 | 0.0172369185063 | 0.0143846583371 | GCLC||MKKS||TLR4||MMP7||ANKRD1||BMP6||CXCL10||SLC8A1||TLR7||AQP1||SCX | 11 | 6.655237 | 6.745157 | 6.970231 | 6.666085 | 6.641408 | 6.654020 | 6.659321 | 6.741952 | 6.755465 | 6.732665 | 6.750443 | 6.958360 | 6.992760 | 6.959574 | 6.969966 |
| GO:1990138 | neuron projection extension | 10/301 | 189/20870 | 0.00043661288336564 | 0.0179037103521 | 0.0149411135342 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||RASAL1||VEGFA||BCL11A||UNC13A||SLIT2||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 10 | 5.638871 | 5.883867 | 5.871944 | 5.630839 | 5.640238 | 5.670590 | 5.613214 | 5.902922 | 5.893765 | 5.860380 | 5.878037 | 5.908730 | 5.873230 | 5.855632 | 5.849444 |
| GO:0048880 | sensory system development | 16/301 | 422/20870 | 0.00044954090896309 | 0.0179037103521 | 0.0149411135342 | TGFB2||SLC17A7||MEIS3||VEGFA||TBX2||C3||NES||TFAP2A||MYO7A||BCAR3||SLC7A11||POU4F1||BMP6||IGFN1||SPRED1||DLL1 | 16 | 5.574649 | 5.634690 | 5.660676 | 5.574735 | 5.569061 | 5.568460 | 5.586269 | 5.650799 | 5.576628 | 5.696528 | 5.612041 | 5.672276 | 5.656021 | 5.668505 | 5.645749 |
| GO:0014820 | tonic smooth muscle contraction | 3/301 | 11/20870 | 0.00044979536497022 | 0.0179037103521 | 0.0149411135342 | MYLK||MKKS||EDNRA | 3 | 5.720665 | 4.611351 | 5.134876 | 6.004231 | 4.903833 | 5.644211 | 6.061771 | 4.063136 | 4.076069 | 3.961246 | 5.603306 | 5.250248 | 4.799330 | 4.416075 | 5.735773 |
| GO:2000659 | regulation of interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway | 3/301 | 11/20870 | 0.00044979536497022 | 0.0179037103521 | 0.0149411135342 | IL1R2||IL6||IL1RN | 3 | 3.234978 | 4.777036 | 5.770857 | 3.225098 | 3.244225 | 3.152400 | 3.313622 | 4.791825 | 4.858920 | 4.713185 | 4.739902 | 5.766636 | 5.797825 | 5.750789 | 5.767777 |
| GO:0032608 | interferon-beta production | 6/301 | 69/20870 | 0.00047894373895274 | 0.0186788058192 | 0.0155879509297 | OAS2||POLR3G||TLR4||IRF7||ISG15||TLR7 | 6 | 5.699115 | 5.620393 | 5.547004 | 5.784642 | 5.655594 | 5.687674 | 5.664866 | 5.617127 | 5.630948 | 5.591712 | 5.641305 | 5.527149 | 5.524719 | 5.627528 | 5.505431 |
| GO:0032648 | regulation of interferon-beta production | 6/301 | 69/20870 | 0.00047894373895274 | 0.0186788058192 | 0.0155879509297 | OAS2||POLR3G||TLR4||IRF7||ISG15||TLR7 | 6 | 5.699115 | 5.620393 | 5.547004 | 5.784642 | 5.655594 | 5.687674 | 5.664866 | 5.617127 | 5.630948 | 5.591712 | 5.641305 | 5.527149 | 5.524719 | 5.627528 | 5.505431 |
| GO:0014829 | vascular associated smooth muscle contraction | 4/301 | 26/20870 | 0.00049357072174141 | 0.0188872280830 | 0.0157618847482 | MKKS||CHRM3||EDNRA||SLC8A1 | 4 | 6.009656 | 6.025296 | 6.055758 | 6.087553 | 5.843585 | 5.981768 | 6.110497 | 6.000249 | 5.918640 | 5.937114 | 6.224125 | 6.097685 | 6.001633 | 5.916596 | 6.192327 |
| GO:0048639 | positive regulation of developmental growth | 10/301 | 192/20870 | 0.00049407149349507 | 0.0188872280830 | 0.0157618847482 | CDKL5||RASAL1||VEGFA||TBX2||MKKS||UNC13A||HEY2||IGF2||CSF1||DLL1 | 10 | 5.723141 | 5.696969 | 5.794108 | 5.747433 | 5.687361 | 5.742920 | 5.714038 | 5.673784 | 5.697045 | 5.644597 | 5.769473 | 5.865573 | 5.780096 | 5.707169 | 5.818944 |
| GO:0055013 | cardiac muscle cell development | 7/301 | 98/20870 | 0.00054654593686099 | 0.0206883711982 | 0.0172649856835 | ASB2||VEGFA||RGS4||HEY2||SLC8A1||NRAP||ALPK2 | 7 | 5.945223 | 6.258170 | 6.307760 | 5.964091 | 5.934841 | 5.953567 | 5.928106 | 6.285736 | 6.251448 | 6.277588 | 6.216912 | 6.221514 | 6.339425 | 6.333967 | 6.332797 |
| GO:1903203 | regulation of oxidative stress-induced neuron death | 4/301 | 27/20870 | 0.00057287725341504 | 0.0213758562678 | 0.0178387099158 | NR4A3||TLR4||MEAK7||SLC7A11 | 4 | 7.159159 | 7.063772 | 7.004184 | 7.123006 | 7.155292 | 7.113820 | 7.240995 | 7.075713 | 7.057194 | 7.035909 | 7.085771 | 6.968164 | 7.092505 | 6.996210 | 6.955830 |
| GO:0002526 | acute inflammatory response | 8/301 | 129/20870 | 0.00057578064020959 | 0.0213758562678 | 0.0178387099158 | OSM||IL1A||TREM1||C3||CCR7||IL6||ADAM8||ORM1 | 8 | 5.093333 | 6.183311 | 6.528774 | 5.088652 | 5.120144 | 5.090694 | 5.073447 | 6.190058 | 6.177013 | 6.174808 | 6.191286 | 6.535760 | 6.519521 | 6.523342 | 6.536397 |
| GO:0002274 | myeloid leukocyte activation | 12/301 | 270/20870 | 0.00058623986034710 | 0.0214101154705 | 0.0178673001146 | NR1H3||CST7||UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3||CLU||DYSF||IL6||TLR4||PTAFR||CSF1||SUCNR1 | 12 | 7.156141 | 7.253265 | 7.302597 | 7.160392 | 7.159133 | 7.159988 | 7.144991 | 7.263031 | 7.238600 | 7.256622 | 7.254695 | 7.303072 | 7.303569 | 7.299709 | 7.304035 |
| GO:0016188 | synaptic vesicle maturation | 3/301 | 12/20870 | 0.00059333912337348 | 0.0214101154705 | 0.0178673001146 | ZDHHC2||UNC13A||UNC13C | 3 | 4.908614 | 4.639784 | 4.287201 | 5.122540 | 4.865178 | 4.756257 | 4.864728 | 4.489816 | 4.575248 | 4.987353 | 4.438974 | 4.343697 | 4.240954 | 4.364620 | 4.192524 |
| GO:0021559 | trigeminal nerve development | 3/301 | 12/20870 | 0.00059333912337348 | 0.0214101154705 | 0.0178673001146 | SEMA3F||TFAP2A||POU4F1 | 3 | 3.428781 | 4.669453 | 5.076681 | 3.524273 | 3.280369 | 3.557952 | 3.332843 | 4.563748 | 4.772439 | 4.660441 | 4.673606 | 5.148156 | 4.829537 | 5.391023 | 4.864456 |
| GO:0032760 | positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production | 8/301 | 130/20870 | 0.00060600531550173 | 0.0216646900292 | 0.0180797492276 | IL23A||OAS2||IL1A||CLU||IL6||TLR4||PTAFR||ORM1 | 8 | 6.994096 | 7.017190 | 7.014912 | 6.982806 | 6.999592 | 6.995382 | 6.998544 | 7.025849 | 7.017466 | 7.025846 | 6.999438 | 7.011258 | 7.022897 | 7.015287 | 7.010171 |
| GO:0048608 | reproductive structure development | 16/301 | 435/20870 | 0.00062350209131026 | 0.0220815826128 | 0.0184276569686 | MAMLD1||TYRO3||TGFB2||VEGFA||TNFSF10||C3||MKKS||LIF||MAS1||ADAM19||HEY2||SLIT2||BMP6||IGF2||SOCS3||SCX | 16 | 6.580551 | 6.867529 | 6.858255 | 6.584500 | 6.574636 | 6.579344 | 6.583703 | 6.856055 | 6.861273 | 6.871650 | 6.881011 | 6.856086 | 6.860630 | 6.852650 | 6.863632 |
| GO:0031349 | positive regulation of defense response | 15/301 | 393/20870 | 0.00062910491774436 | 0.0220815826128 | 0.0184276569686 | OSM||IL23A||POLR3G||TNFSF18||C3||CCR7||IL6||TLR4||PLA2G7||ADAM8||IRF7||TLR7||SUCNR1||HLA-F||KLRK1 | 15 | 6.666897 | 6.862931 | 6.986268 | 6.669884 | 6.655852 | 6.670364 | 6.671431 | 6.864474 | 6.870248 | 6.859265 | 6.857704 | 6.993580 | 6.986632 | 6.985856 | 6.978968 |
| GO:0061458 | reproductive system development | 16/301 | 438/20870 | 0.00067096725551652 | 0.0233387799419 | 0.0194768209496 | MAMLD1||TYRO3||TGFB2||VEGFA||TNFSF10||C3||MKKS||LIF||MAS1||ADAM19||HEY2||SLIT2||BMP6||IGF2||SOCS3||SCX | 16 | 6.580987 | 6.863292 | 6.855412 | 6.587091 | 6.574751 | 6.575495 | 6.586562 | 6.851415 | 6.856561 | 6.868235 | 6.876822 | 6.851425 | 6.856951 | 6.852335 | 6.860917 |
| GO:0001503 | ossification | 16/301 | 440/20870 | 0.00070429888469376 | 0.0242794463732 | 0.0202618316358 | BCAP29||TGFB2||ID3||IL6||TFAP2A||MMP13||BMP6||CREB3L1||IGF2||S1PR1||SLC8A1||CSF1||IFITM1||ISG15||ENPP1||SCX | 16 | 6.712685 | 7.184369 | 7.294757 | 6.676108 | 6.691892 | 6.725123 | 6.756290 | 7.180044 | 7.200688 | 7.168587 | 7.187967 | 7.300947 | 7.282735 | 7.292662 | 7.302599 |
| GO:0002366 | leukocyte activation involved in immune response | 13/301 | 316/20870 | 0.00072278095005126 | 0.0246050200256 | 0.0205335313454 | UNC13D||PTGDS||IL23A||NR4A3||TNFSF18||DYSF||IL6||TLR4||PTAFR||DLL1||SUCNR1||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 13 | 7.202099 | 7.465457 | 7.488595 | 7.195496 | 7.208659 | 7.200276 | 7.203932 | 7.462114 | 7.448913 | 7.476119 | 7.474515 | 7.474166 | 7.491117 | 7.499973 | 7.489006 |
| GO:0070167 | regulation of biomineral tissue development | 7/301 | 103/20870 | 0.00073643768214793 | 0.0246050200256 | 0.0205335313454 | HEY2||TFAP2A||BMP6||S1PR1||SLC8A1||ISG15||ENPP1 | 7 | 5.646468 | 6.123353 | 6.249280 | 5.653459 | 5.636137 | 5.633277 | 5.662791 | 6.121930 | 6.110899 | 6.119527 | 6.140891 | 6.347994 | 6.223707 | 6.206922 | 6.213765 |
| GO:0022409 | positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion | 16/301 | 442/20870 | 0.00073903502518243 | 0.0246050200256 | 0.0205335313454 | IL23A||IL1A||NR4A3||CCR7||ADAM19||IL6||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||IGF2||PTAFR||EGR3||PDCD1LG2||HLA-DRA||KLRK1||HLA-DQA2||PIK3R6 | 16 | 7.045654 | 7.430617 | 7.584441 | 7.039326 | 7.049736 | 7.041211 | 7.052303 | 7.431501 | 7.410633 | 7.435991 | 7.444132 | 7.565485 | 7.589960 | 7.594064 | 7.588083 |
| GO:0032481 | positive regulation of type I interferon production | 6/301 | 75/20870 | 0.00074858068267469 | 0.0246050200256 | 0.0205335313454 | OAS2||POLR3G||TLR4||IRF7||ISG15||TLR7 | 6 | 6.149076 | 6.440955 | 6.415428 | 6.196729 | 6.147805 | 6.133283 | 6.117257 | 6.423921 | 6.440046 | 6.457462 | 6.442195 | 6.387141 | 6.408484 | 6.473429 | 6.390976 |
| GO:2000401 | regulation of lymphocyte migration | 6/301 | 75/20870 | 0.00074858068267469 | 0.0246050200256 | 0.0205335313454 | RIPOR2||PADI2||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10||KLRK1 | 6 | 6.294099 | 6.806183 | 7.081653 | 6.286496 | 6.295707 | 6.292113 | 6.302036 | 6.826790 | 6.807991 | 6.785054 | 6.804592 | 7.067437 | 7.102129 | 7.071048 | 7.085740 |
| GO:0045778 | positive regulation of ossification | 5/301 | 50/20870 | 0.00075197937400029 | 0.0246050200256 | 0.0205335313454 | TGFB2||TFAP2A||BMP6||SLC8A1||ISG15 | 5 | 5.216938 | 5.671167 | 5.812508 | 5.186478 | 5.175406 | 5.189679 | 5.311830 | 5.664976 | 5.625390 | 5.652354 | 5.739454 | 6.026046 | 5.733032 | 5.723540 | 5.744379 |
| GO:0055006 | cardiac cell development | 7/301 | 104/20870 | 0.00078001454125868 | 0.0253078667546 | 0.0211200752834 | ASB2||VEGFA||RGS4||HEY2||SLC8A1||NRAP||ALPK2 | 7 | 5.878818 | 6.209550 | 6.262842 | 5.894643 | 5.871785 | 5.885605 | 5.863032 | 6.235121 | 6.202495 | 6.227293 | 6.172461 | 6.179771 | 6.292754 | 6.286859 | 6.288889 |
| GO:0002263 | cell activation involved in immune response | 13/301 | 320/20870 | 0.00081148496672538 | 0.0261095288044 | 0.0217890831855 | UNC13D||PTGDS||IL23A||NR4A3||TNFSF18||DYSF||IL6||TLR4||PTAFR||DLL1||SUCNR1||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 13 | 7.190609 | 7.454633 | 7.480262 | 7.187405 | 7.194502 | 7.189759 | 7.190760 | 7.448742 | 7.439798 | 7.463402 | 7.466425 | 7.466895 | 7.481588 | 7.488833 | 7.483638 |
| GO:0110149 | regulation of biomineralization | 7/301 | 105/20870 | 0.00082560464822826 | 0.0263442937753 | 0.0219850006805 | HEY2||TFAP2A||BMP6||S1PR1||SLC8A1||ISG15||ENPP1 | 7 | 5.646468 | 6.123353 | 6.249280 | 5.653459 | 5.636137 | 5.633277 | 5.662791 | 6.121930 | 6.110899 | 6.119527 | 6.140891 | 6.347994 | 6.223707 | 6.206922 | 6.213765 |
| GO:0032496 | response to lipopolysaccharide | 15/301 | 405/20870 | 0.00085391577571180 | 0.0270243345084 | 0.0225525124198 | NR1H3||IL1A||CCR7||CMPK2||IL6||IL36G||TLR4||ANKRD1||BMP6||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||PTAFR||GNG12||PDCD1LG2 | 15 | 5.566540 | 6.198817 | 6.422688 | 5.565015 | 5.559973 | 5.577813 | 5.563298 | 6.204943 | 6.175767 | 6.211016 | 6.203288 | 6.431125 | 6.420027 | 6.427059 | 6.412472 |
| GO:0045058 | T cell selection | 5/301 | 52/20870 | 0.00090104386035130 | 0.0279909123404 | 0.0233591468461 | IL23A||TNFSF18||CCR7||IL6||CD3G | 5 | 6.107984 | 6.495746 | 6.753945 | 6.117611 | 6.114680 | 6.093755 | 6.105772 | 6.496879 | 6.535857 | 6.469469 | 6.479891 | 6.747602 | 6.761850 | 6.738915 | 6.767238 |
| GO:0071622 | regulation of granulocyte chemotaxis | 5/301 | 52/20870 | 0.00090104386035130 | 0.0279909123404 | 0.0233591468461 | RIPOR2||TNFSF18||CCR7||SLIT2||CSF1 | 5 | 5.614424 | 7.047197 | 7.399781 | 5.597395 | 5.627873 | 5.627832 | 5.604334 | 7.054750 | 7.049132 | 7.054644 | 7.030122 | 7.397294 | 7.408564 | 7.393420 | 7.399803 |
| GO:0001959 | regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway | 9/301 | 172/20870 | 0.00090620669322874 | 0.0279909123404 | 0.0233591468461 | NR1H3||IL1R2||PADI2||IL6||IL1RN||SLIT2||CSF1||IRF7||ISG15 | 9 | 6.143792 | 6.408319 | 6.567647 | 6.165788 | 6.118197 | 6.144452 | 6.146335 | 6.400884 | 6.414432 | 6.407992 | 6.409934 | 6.555778 | 6.585737 | 6.558324 | 6.570553 |
| GO:0050727 | regulation of inflammatory response | 16/301 | 451/20870 | 0.00091402962643174 | 0.0280084792671 | 0.0233738069048 | NR1H3||CST7||TYRO3||OSM||IL23A||TNFSF18||C3||CCR7||MAS1||IL6||TLR4||PLA2G7||ADAM8||SOCS3||TLR7||SUCNR1 | 16 | 6.961617 | 7.265227 | 7.431958 | 6.968246 | 6.953033 | 6.959322 | 6.965819 | 7.266837 | 7.266331 | 7.261073 | 7.266661 | 7.424592 | 7.429126 | 7.447251 | 7.426750 |
| GO:0150063 | visual system development | 15/301 | 409/20870 | 0.00094258490573604 | 0.0285458175681 | 0.0238222297403 | TGFB2||SLC17A7||MEIS3||VEGFA||TBX2||C3||NES||TFAP2A||MYO7A||BCAR3||SLC7A11||BMP6||IGFN1||SPRED1||DLL1 | 15 | 5.587874 | 5.647851 | 5.673829 | 5.587981 | 5.582263 | 5.581722 | 5.599459 | 5.663903 | 5.589786 | 5.709747 | 5.625201 | 5.685402 | 5.669156 | 5.681667 | 5.658938 |
| GO:0016322 | neuron remodeling | 3/301 | 14/20870 | 0.00096092633505869 | 0.0285458175681 | 0.0238222297403 | SCARF1||BCL11A||C3 | 3 | 5.157256 | 5.238382 | 5.628451 | 5.129045 | 5.203289 | 5.163032 | 5.132417 | 5.144691 | 5.263294 | 5.323261 | 5.216374 | 5.585647 | 5.638377 | 5.643342 | 5.645596 |
| GO:0072540 | T-helper 17 cell lineage commitment | 3/301 | 14/20870 | 0.00096092633505869 | 0.0285458175681 | 0.0238222297403 | IL23A||TNFSF18||IL6 | 3 | 4.674476 | 4.538319 | 5.240682 | 4.653474 | 4.768468 | 4.664098 | 4.606990 | 4.528096 | 4.529847 | 4.649054 | 4.438484 | 5.246967 | 5.213392 | 5.216386 | 5.284828 |
| GO:0045927 | positive regulation of growth | 12/301 | 286/20870 | 0.00096845134324715 | 0.0285458175681 | 0.0238222297403 | CDKL5||TGFB2||RASAL1||VEGFA||TBX2||ZNF639||MKKS||UNC13A||HEY2||IGF2||CSF1||DLL1 | 12 | 6.505582 | 6.565097 | 6.621309 | 6.504711 | 6.487772 | 6.530368 | 6.499140 | 6.536409 | 6.571365 | 6.557081 | 6.594902 | 6.650268 | 6.616818 | 6.587276 | 6.630150 |
| GO:0036475 | neuron death in response to oxidative stress | 4/301 | 31/20870 | 0.00098161399695243 | 0.0285458175681 | 0.0238222297403 | NR4A3||TLR4||MEAK7||SLC7A11 | 4 | 7.030682 | 6.963978 | 6.907817 | 6.993185 | 7.025891 | 6.988656 | 7.111588 | 6.977667 | 6.955835 | 6.937140 | 6.984781 | 6.872430 | 6.992624 | 6.902024 | 6.860435 |
| GO:0070498 | interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway | 4/301 | 31/20870 | 0.00098161399695243 | 0.0285458175681 | 0.0238222297403 | RPS6KA5||IL1R2||IL6||IL1RN | 4 | 4.740669 | 6.436546 | 7.068193 | 5.033984 | 4.593082 | 4.640330 | 4.649826 | 6.419250 | 6.409836 | 6.473960 | 6.442287 | 7.053658 | 7.086068 | 7.071143 | 7.061699 |
| GO:0002686 | negative regulation of leukocyte migration | 5/301 | 53/20870 | 0.00098331876108590 | 0.0285458175681 | 0.0238222297403 | RIPOR2||PADI2||SLIT2||NBL1||KLRK1 | 5 | 5.243829 | 5.921022 | 5.972915 | 5.234779 | 5.247548 | 5.197981 | 5.293395 | 5.939672 | 5.875789 | 5.882870 | 5.983082 | 5.968219 | 6.009292 | 5.972744 | 5.940574 |
| GO:0055007 | cardiac muscle cell differentiation | 8/301 | 141/20870 | 0.00103113569726059 | 0.0297105591576 | 0.0247942369938 | ASB2||VEGFA||RGS4||HEY2||SLC8A1||NRAP||DLL1||ALPK2 | 8 | 6.239376 | 6.455472 | 6.522829 | 6.243461 | 6.248645 | 6.244930 | 6.220294 | 6.487416 | 6.429362 | 6.455785 | 6.448717 | 6.521595 | 6.522963 | 6.522675 | 6.524082 |
| GO:0033077 | T cell differentiation in thymus | 6/301 | 80/20870 | 0.00105216082689794 | 0.0300917996493 | 0.0251123921336 | IL1A||CCR7||ZC3H8||ADAM8||CD3G||EGR3 | 6 | 7.747139 | 7.764042 | 7.784824 | 7.764975 | 7.728146 | 7.752583 | 7.742601 | 7.774924 | 7.765887 | 7.746341 | 7.768859 | 7.774801 | 7.776076 | 7.795484 | 7.792813 |
| GO:0030308 | negative regulation of cell growth | 10/301 | 213/20870 | 0.00109770692198521 | 0.0311635766602 | 0.0260068180201 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||TGFB2||RGS4||BCL11A||SLIT2||SEMA3D||SEMA6B||ST20||ENPP1 | 10 | 7.052177 | 7.441330 | 7.436574 | 7.052722 | 7.048665 | 7.046899 | 7.060386 | 7.454016 | 7.427094 | 7.448119 | 7.435938 | 7.438830 | 7.440390 | 7.444826 | 7.422148 |
| GO:0070234 | positive regulation of T cell apoptotic process | 3/301 | 15/20870 | 0.00118839074365309 | 0.0332491062409 | 0.0277472468827 | IDO1||ZC3H8||ADAM8 | 3 | 5.982379 | 7.345048 | 7.920634 | 5.977788 | 5.905611 | 6.008027 | 6.034881 | 7.397751 | 7.358919 | 7.336937 | 7.284257 | 7.882588 | 7.957425 | 7.900299 | 7.940966 |
| GO:0140374 | antiviral innate immune response | 3/301 | 15/20870 | 0.00118839074365309 | 0.0332491062409 | 0.0277472468827 | MX1||CXCL10||IFIT1 | 3 | 4.900979 | 5.046972 | 5.124223 | 4.795822 | 4.864043 | 4.908701 | 5.025581 | 5.128284 | 4.950729 | 4.995045 | 5.106199 | 5.077400 | 5.182885 | 5.091020 | 5.143121 |
| GO:0002444 | myeloid leukocyte mediated immunity | 7/301 | 112/20870 | 0.00120671318452054 | 0.0335188460823 | 0.0279723518199 | UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3||TREM1||C3||IL6||PTAFR | 7 | 7.072348 | 7.049993 | 7.145705 | 7.066636 | 7.078670 | 7.067592 | 7.076456 | 7.040091 | 7.057328 | 7.066608 | 7.035728 | 7.163854 | 7.150131 | 7.135636 | 7.132987 |
| GO:0048863 | stem cell differentiation | 10/301 | 217/20870 | 0.00126259212810571 | 0.0346047147554 | 0.0288785375663 | SEMA3F||LRP6||TGFB2||OSM||TBX2||LIF||FBXL17||EDNRA||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 10 | 5.389844 | 5.400133 | 5.344911 | 5.384560 | 5.397629 | 5.371653 | 5.405307 | 5.391471 | 5.402206 | 5.398743 | 5.408063 | 5.397166 | 5.331804 | 5.320690 | 5.328676 |
| GO:0071357 | cellular response to type I interferon | 5/301 | 56/20870 | 0.00126373084188371 | 0.0346047147554 | 0.0288785375663 | OAS2||IRF7||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 5 | 6.205650 | 6.317217 | 6.405068 | 6.266539 | 6.183641 | 6.217240 | 6.152704 | 6.308332 | 6.317802 | 6.334787 | 6.307781 | 6.378184 | 6.440934 | 6.399665 | 6.400776 |
| GO:0030500 | regulation of bone mineralization | 6/301 | 84/20870 | 0.00135668889082540 | 0.0368885620245 | 0.0307844677155 | TFAP2A||BMP6||S1PR1||SLC8A1||ISG15||ENPP1 | 6 | 5.770025 | 6.284620 | 6.413811 | 5.774023 | 5.761432 | 5.756851 | 5.787594 | 6.285719 | 6.273027 | 6.271988 | 6.307462 | 6.519271 | 6.382466 | 6.373194 | 6.374940 |
| GO:0003179 | heart valve morphogenesis | 5/301 | 57/20870 | 0.00136913744449759 | 0.0369667110014 | 0.0308496850762 | TIE1||TGFB2||HEY2||SLIT2||SCX | 5 | 5.022593 | 5.317228 | 5.402979 | 5.018614 | 5.038814 | 4.999868 | 5.032763 | 5.320845 | 5.275163 | 5.315881 | 5.355889 | 5.600484 | 5.353806 | 5.286795 | 5.350339 |
| GO:0035909 | aorta morphogenesis | 4/301 | 34/20870 | 0.00139854862817151 | 0.0374985850928 | 0.0312935478862 | MYLK||TGFB2||TBX2||HEY2 | 4 | 4.849908 | 5.212684 | 5.162394 | 4.861179 | 4.866511 | 4.824817 | 4.846765 | 5.216603 | 5.228938 | 5.214453 | 5.190473 | 5.154669 | 5.170649 | 5.149089 | 5.175009 |
| GO:2000402 | negative regulation of lymphocyte migration | 3/301 | 16/20870 | 0.00144709936439383 | 0.0385327630753 | 0.0321565964022 | RIPOR2||PADI2||KLRK1 | 3 | 5.036168 | 4.974601 | 4.946676 | 4.859458 | 5.071009 | 4.986520 | 5.205666 | 5.050510 | 4.855557 | 4.758408 | 5.194116 | 4.878914 | 5.014601 | 4.994194 | 4.894065 |
| GO:0048588 | developmental cell growth | 11/301 | 261/20870 | 0.00150569204698445 | 0.0398183355713 | 0.0332294402006 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||RASAL1||VEGFA||RGS4||BCL11A||UNC13A||SLIT2||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 11 | 6.541464 | 7.072718 | 7.056594 | 6.548389 | 6.539487 | 6.548687 | 6.529204 | 7.089044 | 7.063188 | 7.069948 | 7.068560 | 7.063816 | 7.062966 | 7.053498 | 7.046023 |
| GO:0032613 | interleukin-10 production | 6/301 | 86/20870 | 0.00153211061792071 | 0.0399221175249 | 0.0333160489494 | IL23A||IL6||TLR4||ISG15||PDCD1LG2||DLL1 | 6 | 6.688860 | 6.767729 | 6.757205 | 6.695196 | 6.674951 | 6.696874 | 6.688316 | 6.786186 | 6.771205 | 6.775370 | 6.737702 | 6.750809 | 6.764974 | 6.754207 | 6.758791 |
| GO:0032653 | regulation of interleukin-10 production | 6/301 | 86/20870 | 0.00153211061792071 | 0.0399221175249 | 0.0333160489494 | IL23A||IL6||TLR4||ISG15||PDCD1LG2||DLL1 | 6 | 6.688860 | 6.767729 | 6.757205 | 6.695196 | 6.674951 | 6.696874 | 6.688316 | 6.786186 | 6.771205 | 6.775370 | 6.737702 | 6.750809 | 6.764974 | 6.754207 | 6.758791 |
| GO:0050870 | positive regulation of T cell activation | 13/301 | 344/20870 | 0.00155805731534184 | 0.0399221175249 | 0.0333160489494 | IL23A||IL1A||CCR7||IL6||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||IGF2||EGR3||PDCD1LG2||HLA-DRA||KLRK1||HLA-DQA2||PIK3R6 | 13 | 6.995824 | 7.480704 | 7.631593 | 6.977580 | 7.006169 | 6.991785 | 7.007557 | 7.483981 | 7.458025 | 7.486059 | 7.494493 | 7.613003 | 7.633791 | 7.642305 | 7.637104 |
| GO:0048841 | regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance | 4/301 | 35/20870 | 0.00156127397299292 | 0.0399221175249 | 0.0333160489494 | SEMA3F||VEGFA||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 4 | 3.560108 | 4.311970 | 4.722278 | 3.557678 | 3.638773 | 3.550124 | 3.489957 | 4.221757 | 4.315348 | 4.269289 | 4.432882 | 4.856935 | 4.629569 | 4.785646 | 4.601209 |
| GO:0050863 | regulation of T cell activation | 16/301 | 475/20870 | 0.00156131565559854 | 0.0399221175249 | 0.0333160489494 | IL23A||RIPOR2||IL1A||TNFSF18||CCR7||IL6||ZC3H8||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||IGF2||EGR3||PDCD1LG2||HLA-DRA||KLRK1||HLA-DQA2||PIK3R6 | 16 | 6.783064 | 7.228927 | 7.360767 | 6.770467 | 6.794065 | 6.779549 | 6.788064 | 7.236627 | 7.210286 | 7.229772 | 7.238849 | 7.342147 | 7.364669 | 7.376748 | 7.359290 |
| GO:0002237 | response to molecule of bacterial origin | 15/301 | 431/20870 | 0.00158192280471272 | 0.0401829207171 | 0.0335336960196 | NR1H3||IL1A||CCR7||CMPK2||IL6||IL36G||TLR4||ANKRD1||BMP6||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||PTAFR||GNG12||PDCD1LG2 | 15 | 6.169403 | 6.492555 | 6.669737 | 6.173944 | 6.160385 | 6.175589 | 6.167645 | 6.499051 | 6.476312 | 6.496183 | 6.498550 | 6.676287 | 6.667607 | 6.672318 | 6.662702 |
| GO:0010574 | regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production | 5/301 | 59/20870 | 0.00159920729534040 | 0.0403564664530 | 0.0336785244653 | IL1A||C3||IL6||HPSE||SULF2 | 5 | 5.785178 | 7.227461 | 7.667874 | 5.762513 | 5.764509 | 5.768781 | 5.843306 | 7.224546 | 7.219845 | 7.231336 | 7.234075 | 7.663970 | 7.674578 | 7.675856 | 7.657009 |
| GO:0051058 | negative regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction | 5/301 | 60/20870 | 0.00172432736489605 | 0.0430288979189 | 0.0359087382679 | TGFB2||RASAL1||RIPOR2||TRIM67||SLIT2 | 5 | 5.601873 | 5.406877 | 5.308565 | 5.556470 | 5.661575 | 5.584049 | 5.603329 | 5.410586 | 5.446069 | 5.409341 | 5.360223 | 5.266798 | 5.309931 | 5.345630 | 5.310821 |
| GO:0006750 | glutathione biosynthetic process | 3/301 | 17/20870 | 0.00173854133005697 | 0.0430288979189 | 0.0359087382679 | GCLC||CHAC1||SLC7A11 | 3 | 5.514769 | 5.463751 | 5.452788 | 5.443808 | 5.597443 | 5.530728 | 5.482521 | 5.458210 | 5.433052 | 5.489677 | 5.473462 | 5.530396 | 5.269915 | 5.457789 | 5.537280 |
| GO:0060977 | coronary vasculature morphogenesis | 3/301 | 17/20870 | 0.00173854133005697 | 0.0430288979189 | 0.0359087382679 | VEGFA||HEY2||SPRED1 | 3 | 4.120714 | 4.935171 | 5.225778 | 4.126216 | 4.073076 | 4.159346 | 4.122906 | 4.916799 | 4.894875 | 4.956602 | 4.971120 | 5.216143 | 5.275885 | 5.223664 | 5.185960 |
| GO:0060485 | mesenchyme development | 12/301 | 308/20870 | 0.00181409158598640 | 0.0443478647014 | 0.0370094504699 | SEMA3F||LRP6||TGFB2||TBX2||HEY2||IL6||FBXL17||EDNRA||SEMA3D||SPRED1||SEMA6B||SCX | 12 | 6.184089 | 6.230759 | 6.345293 | 6.060676 | 6.141144 | 6.228540 | 6.295154 | 6.253430 | 6.283509 | 6.163574 | 6.219785 | 6.395732 | 6.296286 | 6.328877 | 6.358410 |
| GO:0030198 | extracellular matrix organization | 13/301 | 350/20870 | 0.00181480513411477 | 0.0443478647014 | 0.0370094504699 | TIE1||COL5A3||TGFB2||POMT1||IL6||MMP7||MMP13||ADAM8||CREB3L1||ADAMTS4||SULF2||COL6A6||SCX | 13 | 5.865514 | 6.452022 | 6.689373 | 5.872118 | 5.857190 | 5.879513 | 5.853075 | 6.454535 | 6.441630 | 6.457438 | 6.454432 | 6.674094 | 6.708282 | 6.692937 | 6.681951 |
| GO:0002673 | regulation of acute inflammatory response | 5/301 | 61/20870 | 0.00185647776169350 | 0.0449038672875 | 0.0374734491384 | OSM||C3||CCR7||IL6||ADAM8 | 5 | 5.569497 | 7.019327 | 7.406932 | 5.557655 | 5.584036 | 5.550844 | 5.585125 | 7.029043 | 7.013443 | 7.000129 | 7.034441 | 7.404685 | 7.401352 | 7.413375 | 7.408288 |
| GO:0043062 | extracellular structure organization | 13/301 | 351/20870 | 0.00186081812121254 | 0.0449038672875 | 0.0374734491384 | TIE1||COL5A3||TGFB2||POMT1||IL6||MMP7||MMP13||ADAM8||CREB3L1||ADAMTS4||SULF2||COL6A6||SCX | 13 | 5.865514 | 6.452022 | 6.689373 | 5.872118 | 5.857190 | 5.879513 | 5.853075 | 6.454535 | 6.441630 | 6.457438 | 6.454432 | 6.674094 | 6.708282 | 6.692937 | 6.681951 |
| GO:0071677 | positive regulation of mononuclear cell migration | 6/301 | 90/20870 | 0.00193421443111146 | 0.0463851050840 | 0.0387095807364 | TNFSF18||CCR7||PLA2G7||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10 | 6 | 6.560236 | 7.038053 | 7.291700 | 6.554000 | 6.556696 | 6.575274 | 6.554868 | 7.065931 | 7.027247 | 7.035358 | 7.023287 | 7.281159 | 7.306377 | 7.286293 | 7.292848 |
| GO:0043524 | negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process | 8/301 | 156/20870 | 0.00196311099422664 | 0.0467504419750 | 0.0390144639064 | GCLC||TYRO3||DNAJC5||NES||ADAM8||POU4F1||NR4A2||GPRASP2 | 8 | 6.794216 | 6.759210 | 6.791853 | 6.795511 | 6.805358 | 6.791429 | 6.784487 | 6.765461 | 6.771229 | 6.756534 | 6.743464 | 6.815584 | 6.762908 | 6.792648 | 6.795782 |
| GO:0045229 | external encapsulating structure organization | 13/301 | 354/20870 | 0.00200467847362715 | 0.0467504419750 | 0.0390144639064 | TIE1||COL5A3||TGFB2||POMT1||IL6||MMP7||MMP13||ADAM8||CREB3L1||ADAMTS4||SULF2||COL6A6||SCX | 13 | 5.857734 | 6.444575 | 6.681902 | 5.864312 | 5.849450 | 5.871732 | 5.845282 | 6.447081 | 6.434214 | 6.449969 | 6.446983 | 6.666888 | 6.700642 | 6.685448 | 6.674407 |
| GO:0002295 | T-helper cell lineage commitment | 3/301 | 18/20870 | 0.00206412205632017 | 0.0467504419750 | 0.0390144639064 | IL23A||TNFSF18||IL6 | 3 | 5.276806 | 5.040641 | 5.449066 | 5.307786 | 5.309357 | 5.244313 | 5.244337 | 5.031174 | 5.027947 | 5.143856 | 4.953115 | 5.456676 | 5.430368 | 5.424738 | 5.483719 |
| GO:0003184 | pulmonary valve morphogenesis | 3/301 | 18/20870 | 0.00206412205632017 | 0.0467504419750 | 0.0390144639064 | TGFB2||HEY2||SLIT2 | 3 | 4.232616 | 4.706080 | 4.796837 | 4.210548 | 4.371543 | 4.185157 | 4.153224 | 4.690082 | 4.653038 | 4.733839 | 4.745497 | 4.823770 | 4.891129 | 4.701730 | 4.763877 |
| GO:0048532 | anatomical structure arrangement | 3/301 | 18/20870 | 0.00206412205632017 | 0.0467504419750 | 0.0390144639064 | SEMA3F||TFAP2A||DLL1 | 3 | 5.615236 | 6.334214 | 6.514277 | 5.647236 | 5.579350 | 5.614392 | 5.619161 | 6.346050 | 6.368650 | 6.312205 | 6.309104 | 6.509704 | 6.465286 | 6.588466 | 6.490692 |
| GO:0070230 | positive regulation of lymphocyte apoptotic process | 3/301 | 18/20870 | 0.00206412205632017 | 0.0467504419750 | 0.0390144639064 | IDO1||ZC3H8||ADAM8 | 3 | 5.946520 | 7.158415 | 7.703125 | 5.973754 | 5.872431 | 5.948900 | 5.988256 | 7.216052 | 7.170553 | 7.146631 | 7.097906 | 7.660485 | 7.736627 | 7.685262 | 7.728770 |
| GO:2001135 | regulation of endocytic recycling | 3/301 | 18/20870 | 0.00206412205632017 | 0.0467504419750 | 0.0390144639064 | ZDHHC2||TAMALIN||INPP5F | 3 | 4.622255 | 4.731714 | 4.993392 | 4.470075 | 4.442102 | 5.060420 | 4.409055 | 4.719506 | 4.725555 | 4.772105 | 4.708876 | 4.949009 | 5.050422 | 4.906062 | 5.062008 |
| GO:0003206 | cardiac chamber morphogenesis | 7/301 | 123/20870 | 0.00206970296016891 | 0.0467504419750 | 0.0390144639064 | TGFB2||DNAH11||TBX2||HEY2||SLIT2||POU4F1||LY6E | 7 | 5.358853 | 5.347923 | 5.373261 | 5.380025 | 5.351924 | 5.325274 | 5.377509 | 5.369136 | 5.275014 | 5.425388 | 5.317756 | 5.439857 | 5.367461 | 5.366435 | 5.316603 |
| GO:0043523 | regulation of neuron apoptotic process | 10/301 | 232/20870 | 0.00207017039315389 | 0.0467504419750 | 0.0390144639064 | GCLC||TYRO3||TGFB2||DNAJC5||NES||TFAP2A||ADAM8||POU4F1||NR4A2||GPRASP2 | 10 | 6.793663 | 6.788725 | 6.793837 | 6.806502 | 6.797212 | 6.784822 | 6.786007 | 6.801845 | 6.788866 | 6.799196 | 6.764698 | 6.797415 | 6.781817 | 6.803667 | 6.792362 |
| GO:0001822 | kidney development | 12/301 | 313/20870 | 0.00207321410089640 | 0.0467504419750 | 0.0390144639064 | TGFB2||VEGFA||ID3||LIF||TFAP2A||FRAS1||SLIT2||BMP6||SERPINB7||GCNT1||SULF2||DLL1 | 12 | 5.313700 | 5.928408 | 6.215419 | 5.305195 | 5.310914 | 5.311929 | 5.326674 | 5.922038 | 5.909460 | 5.933580 | 5.948271 | 6.220793 | 6.217764 | 6.203933 | 6.219124 |
| GO:0050866 | negative regulation of cell activation | 11/301 | 272/20870 | 0.00208264077174240 | 0.0467504419750 | 0.0390144639064 | GCLC||NR1H3||CST7||TYRO3||RIPOR2||TNFSF18||ZC3H8||TNFRSF14||C1QTNF1||PDCD1LG2||HLA-F | 11 | 6.354064 | 6.460849 | 6.500415 | 6.371297 | 6.352250 | 6.346169 | 6.346395 | 6.464674 | 6.464858 | 6.443782 | 6.469942 | 6.494575 | 6.504199 | 6.523923 | 6.478590 |
| GO:0006936 | muscle contraction | 13/301 | 359/20870 | 0.00226477827525540 | 0.0505451382703 | 0.0421812369976 | MYLK||DMPK||TBX2||MKKS||CHRM3||BIN1||EDNRA||PTAFR||SSTR2||SLC8A1||TRDN||SULF2||TPM2 | 13 | 6.146835 | 6.216485 | 6.190454 | 6.142173 | 6.140606 | 6.143831 | 6.160641 | 6.208897 | 6.203021 | 6.220507 | 6.233328 | 6.188504 | 6.202393 | 6.160802 | 6.209637 |
| GO:0014033 | neural crest cell differentiation | 6/301 | 93/20870 | 0.00228466516961719 | 0.0506959322982 | 0.0423070785493 | SEMA3F||LRP6||FBXL17||EDNRA||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 6 | 4.969082 | 4.933599 | 4.978049 | 4.940692 | 5.007614 | 4.952206 | 4.974909 | 4.907705 | 4.940829 | 4.929759 | 4.955680 | 5.166949 | 4.931197 | 4.850325 | 4.944161 |
| GO:0035265 | organ growth | 9/301 | 197/20870 | 0.00231554033246751 | 0.0510874355638 | 0.0426337982417 | TGFB2||RGS4||TBX2||HEY2||MMP13||LY6E||IGF2||S1PR1||DLL1 | 9 | 5.851334 | 5.662966 | 5.628049 | 5.863925 | 5.853507 | 5.842570 | 5.845238 | 5.687634 | 5.636552 | 5.697497 | 5.628915 | 5.658538 | 5.605987 | 5.634920 | 5.612155 |
| GO:0071692 | protein localization to extracellular region | 14/301 | 404/20870 | 0.00233231657396297 | 0.0511389765670 | 0.0426768105540 | NR1H3||TGFB2||IL1A||RSAD2||IL6||IL1RN||TLR4||ANKRD1||FRMD4A||ADAM8||BMP6||NBL1||SCG2||SUCNR1 | 14 | 5.724655 | 6.095602 | 6.250917 | 5.716141 | 5.707922 | 5.718095 | 5.755984 | 6.106423 | 6.087913 | 6.093032 | 6.094978 | 6.255066 | 6.256899 | 6.247587 | 6.244079 |
| GO:0043368 | positive T cell selection | 4/301 | 39/20870 | 0.00234436644712552 | 0.0511389765670 | 0.0426768105540 | IL23A||TNFSF18||IL6||CD3G | 4 | 5.911802 | 6.526023 | 6.892950 | 5.925807 | 5.916277 | 5.894903 | 5.910046 | 6.492436 | 6.594525 | 6.510974 | 6.503869 | 6.892757 | 6.900996 | 6.875942 | 6.901956 |
| GO:0002697 | regulation of immune effector process | 16/301 | 495/20870 | 0.00236210397080585 | 0.0511636476975 | 0.0426973992563 | CFH||UNC13D||TGFB2||IL23A||NR4A3||TNFSF18||C3||RSAD2||IL6||TLR4||TNFRSF14||PTAFR||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||KLRK1||PIK3R6 | 16 | 6.951819 | 7.035090 | 7.140234 | 6.951089 | 6.942773 | 6.959646 | 6.953717 | 7.030065 | 7.034639 | 7.037544 | 7.038099 | 7.138561 | 7.144268 | 7.147196 | 7.130859 |
| GO:0030282 | bone mineralization | 7/301 | 126/20870 | 0.00237237316620516 | 0.0511636476975 | 0.0426973992563 | TFAP2A||MMP13||BMP6||S1PR1||SLC8A1||ISG15||ENPP1 | 7 | 5.491586 | 5.906368 | 6.043337 | 5.501186 | 5.482005 | 5.470059 | 5.512714 | 5.911681 | 5.894233 | 5.888442 | 5.930737 | 6.125675 | 6.022738 | 6.006765 | 6.014889 |
| GO:0001654 | eye development | 14/301 | 405/20870 | 0.00238525164090803 | 0.0511636476975 | 0.0426973992563 | TGFB2||SLC17A7||MEIS3||VEGFA||TBX2||NES||TFAP2A||MYO7A||BCAR3||SLC7A11||BMP6||IGFN1||SPRED1||DLL1 | 14 | 5.566526 | 5.655974 | 5.677901 | 5.562954 | 5.561568 | 5.562695 | 5.578818 | 5.673569 | 5.596770 | 5.715432 | 5.635433 | 5.690217 | 5.673376 | 5.685820 | 5.662022 |
| GO:0019184 | nonribosomal peptide biosynthetic process | 3/301 | 19/20870 | 0.00242516581848042 | 0.0514481605778 | 0.0429348326800 | GCLC||CHAC1||SLC7A11 | 3 | 5.334413 | 5.269146 | 5.255814 | 5.270770 | 5.412311 | 5.350432 | 5.300118 | 5.265791 | 5.236825 | 5.293223 | 5.280137 | 5.331038 | 5.079234 | 5.261107 | 5.337155 |
| GO:1903204 | negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced neuron death | 3/301 | 19/20870 | 0.00242516581848042 | 0.0514481605778 | 0.0429348326800 | NR4A3||MEAK7||SLC7A11 | 3 | 7.263371 | 7.275666 | 7.207338 | 7.252549 | 7.285753 | 7.242817 | 7.271979 | 7.276546 | 7.273666 | 7.245448 | 7.306359 | 7.200803 | 7.217930 | 7.234718 | 7.175231 |
| GO:0003018 | vascular process in circulatory system | 11/301 | 279/20870 | 0.00253532036945407 | 0.0534911035326 | 0.0446397218919 | GCLC||SLC7A8||VEGFA||ECE1||MKKS||CHRM3||SLIT2||EDNRA||BMP6||SLC15A2||SLC8A1 | 11 | 5.567830 | 5.758348 | 5.859198 | 5.560533 | 5.561477 | 5.562032 | 5.587103 | 5.770656 | 5.747336 | 5.736502 | 5.778496 | 5.873124 | 5.904289 | 5.813572 | 5.844235 |
| GO:0097484 | dendrite extension | 4/301 | 40/20870 | 0.00257567010554743 | 0.0540470775952 | 0.0451036967568 | CDKL3||RASAL1||BCL11A||UNC13A | 4 | 4.655744 | 4.245623 | 4.399023 | 4.443523 | 4.805488 | 4.734073 | 4.614216 | 4.162551 | 4.367065 | 4.210541 | 4.234264 | 4.332123 | 4.230167 | 4.546832 | 4.466497 |
| GO:0061564 | axon development | 16/301 | 500/20870 | 0.00260857129360322 | 0.0542989846686 | 0.0453139197837 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||NOTCH3||SCARF1||RPS6KA5||VEGFA||SLIT2||POU4F1||NR4A2||SEMA3D||CHODL||KALRN||SLITRK5||SEMA6B||INPP5F | 16 | 6.699779 | 6.992633 | 6.971034 | 6.701687 | 6.695849 | 6.713640 | 6.687817 | 6.999820 | 6.987789 | 6.993086 | 6.989809 | 6.978974 | 6.977423 | 6.969063 | 6.958587 |
| GO:0072001 | renal system development | 12/301 | 322/20870 | 0.00261580190322877 | 0.0542989846686 | 0.0453139197837 | TGFB2||VEGFA||ID3||LIF||TFAP2A||FRAS1||SLIT2||BMP6||SERPINB7||GCNT1||SULF2||DLL1 | 12 | 5.290168 | 5.901236 | 6.187906 | 5.283495 | 5.286894 | 5.287126 | 5.303075 | 5.895136 | 5.882358 | 5.906304 | 5.920867 | 6.194073 | 6.189687 | 6.176298 | 6.191500 |
| GO:0001947 | heart looping | 5/301 | 66/20870 | 0.00263082516363187 | 0.0543188019079 | 0.0453304577871 | ASB2||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||DLL1 | 5 | 5.926671 | 5.484374 | 5.611538 | 6.018006 | 5.740141 | 5.845296 | 6.078235 | 5.401453 | 5.400669 | 5.451636 | 5.666635 | 5.833975 | 5.375363 | 5.543513 | 5.654687 |
| GO:0050770 | regulation of axonogenesis | 8/301 | 165/20870 | 0.00278095462982285 | 0.0565684236273 | 0.0472078258218 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||SLIT2||SEMA3D||CHODL||SEMA6B | 8 | 6.723365 | 7.333213 | 7.328900 | 6.718138 | 6.721303 | 6.736091 | 6.717851 | 7.342649 | 7.334407 | 7.322255 | 7.333470 | 7.347963 | 7.336053 | 7.315105 | 7.316214 |
| GO:0010863 | positive regulation of phospholipase C activity | 4/301 | 41/20870 | 0.00282216271721080 | 0.0565684236273 | 0.0472078258218 | LPAR2||ITK||EDNRA||PTAFR | 4 | 5.100518 | 5.393897 | 5.511025 | 5.112848 | 5.049251 | 5.135169 | 5.103427 | 5.421259 | 5.367465 | 5.383176 | 5.403116 | 5.479027 | 5.511352 | 5.514770 | 5.538335 |
| GO:0030501 | positive regulation of bone mineralization | 4/301 | 41/20870 | 0.00282216271721080 | 0.0565684236273 | 0.0472078258218 | TFAP2A||BMP6||SLC8A1||ISG15 | 4 | 5.404097 | 5.897709 | 6.054317 | 5.382313 | 5.339993 | 5.390285 | 5.498973 | 5.884317 | 5.852163 | 5.881619 | 5.970032 | 6.270753 | 5.968861 | 5.961659 | 5.992203 |
| GO:1902622 | regulation of neutrophil migration | 4/301 | 41/20870 | 0.00282216271721080 | 0.0565684236273 | 0.0472078258218 | RIPOR2||CCR7||SLIT2||ADAM8 | 4 | 6.028842 | 6.915120 | 7.081765 | 6.036214 | 6.049726 | 6.032498 | 5.996394 | 6.912992 | 6.912336 | 6.924252 | 6.910862 | 7.091155 | 7.087080 | 7.083086 | 7.065610 |
| GO:0098586 | cellular response to virus | 6/301 | 97/20870 | 0.00282382243160968 | 0.0565684236273 | 0.0472078258218 | IFI6||OASL||IL6||CXCL10||IRF7||TLR7 | 6 | 6.015945 | 6.418838 | 6.713349 | 6.018593 | 5.992639 | 5.996828 | 6.054875 | 6.433678 | 6.408662 | 6.415064 | 6.417829 | 6.689992 | 6.716508 | 6.698090 | 6.748112 |
| GO:0048675 | axon extension | 7/301 | 130/20870 | 0.00282768861954446 | 0.0565684236273 | 0.0472078258218 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||SLIT2||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 7 | 5.779121 | 6.096581 | 6.083315 | 5.768538 | 5.769262 | 5.821176 | 5.756643 | 6.110228 | 6.106272 | 6.080006 | 6.089610 | 6.130725 | 6.087352 | 6.064812 | 6.049057 |
| GO:0003170 | heart valve development | 5/301 | 68/20870 | 0.00299794660470515 | 0.0596653187668 | 0.0497922656376 | TIE1||TGFB2||HEY2||SLIT2||SCX | 5 | 5.274832 | 5.422781 | 5.493210 | 5.277442 | 5.266424 | 5.234262 | 5.319895 | 5.458076 | 5.363874 | 5.435235 | 5.432234 | 5.635127 | 5.470208 | 5.409202 | 5.447801 |
| GO:0002275 | myeloid cell activation involved in immune response | 6/301 | 99/20870 | 0.00312662071250366 | 0.0619070901076 | 0.0516630823264 | UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3||DYSF||PTAFR||SUCNR1 | 6 | 7.864516 | 7.773410 | 7.768222 | 7.874934 | 7.871046 | 7.859512 | 7.852461 | 7.781936 | 7.764666 | 7.779493 | 7.767466 | 7.759819 | 7.777357 | 7.770891 | 7.764760 |
| GO:0060411 | cardiac septum morphogenesis | 5/301 | 69/20870 | 0.00319474370359205 | 0.0629331910182 | 0.0525193903152 | TGFB2||DNAH11||TBX2||HEY2||SLIT2 | 5 | 5.305853 | 5.123484 | 5.010316 | 5.313385 | 5.319038 | 5.293940 | 5.296891 | 5.141236 | 5.101923 | 5.132801 | 5.117664 | 5.006620 | 5.031887 | 4.996094 | 5.006421 |
| GO:0043373 | CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment | 3/301 | 21/20870 | 0.00325854886864949 | 0.0637379618829 | 0.0531909926045 | IL23A||TNFSF18||IL6 | 3 | 6.072576 | 6.710187 | 7.182880 | 6.095811 | 6.083034 | 6.046415 | 6.064560 | 6.708877 | 6.712303 | 6.716229 | 6.703307 | 7.178837 | 7.191958 | 7.165751 | 7.194788 |
| GO:0051897 | positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling | 7/301 | 134/20870 | 0.00334718617438910 | 0.0637379618829 | 0.0531909926045 | OSM||MEIS3||CCR7||ADAM8||IGF2||HPSE||C1QTNF1 | 7 | 6.766365 | 7.041645 | 7.141882 | 6.770462 | 6.751802 | 6.763832 | 6.779223 | 7.050084 | 7.035101 | 7.042175 | 7.039178 | 7.135973 | 7.153778 | 7.145290 | 7.132391 |
| GO:0051047 | positive regulation of secretion | 12/301 | 332/20870 | 0.00334886257251861 | 0.0637379618829 | 0.0531909926045 | UNC13D||TGFB2||IL1A||TLR4||ANKRD1||FRMD4A||ADAM8||BMP6||PTAFR||C1QTNF1||HLA-F||AQP1 | 12 | 6.868884 | 7.287749 | 7.336041 | 6.853945 | 6.884119 | 6.859826 | 6.877435 | 7.274641 | 7.273037 | 7.295519 | 7.307508 | 7.337381 | 7.340300 | 7.346100 | 7.320255 |
| GO:0032965 | regulation of collagen biosynthetic process | 4/301 | 43/20870 | 0.00336262371268519 | 0.0637379618829 | 0.0531909926045 | IL6||CREB3L1||SERPINB7||SCX | 4 | 5.757932 | 6.240186 | 6.348105 | 5.767016 | 5.738437 | 5.756282 | 5.769786 | 6.250020 | 6.193423 | 6.269952 | 6.246244 | 6.362729 | 6.359355 | 6.339540 | 6.330545 |
| GO:1900274 | regulation of phospholipase C activity | 4/301 | 43/20870 | 0.00336262371268519 | 0.0637379618829 | 0.0531909926045 | LPAR2||ITK||EDNRA||PTAFR | 4 | 5.047222 | 5.330556 | 5.438091 | 5.054808 | 5.004306 | 5.080067 | 5.048678 | 5.357047 | 5.310928 | 5.314886 | 5.338878 | 5.407321 | 5.438352 | 5.441575 | 5.464542 |
| GO:1905314 | semi-lunar valve development | 4/301 | 43/20870 | 0.00336262371268519 | 0.0637379618829 | 0.0531909926045 | TIE1||TGFB2||HEY2||SLIT2 | 4 | 5.134947 | 5.682283 | 5.761954 | 5.096705 | 5.171269 | 5.108187 | 5.162158 | 5.719722 | 5.593650 | 5.713099 | 5.699075 | 5.769549 | 5.821794 | 5.710387 | 5.743782 |
| GO:0010975 | regulation of neuron projection development | 15/301 | 467/20870 | 0.00339139800556119 | 0.0637379618829 | 0.0531909926045 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||SCARF1||VEGFA||TRIM67||BCL11A||HECW2||SLIT2||ANKRD1||SEMA3D||CHODL||GPRASP2||SEMA6B||INPP5F | 15 | 6.808027 | 7.178169 | 7.197585 | 6.797557 | 6.810909 | 6.812384 | 6.811208 | 7.181624 | 7.163874 | 7.183311 | 7.183771 | 7.193011 | 7.200222 | 7.202620 | 7.194466 |
| GO:0048568 | embryonic organ development | 15/301 | 467/20870 | 0.00339139800556119 | 0.0637379618829 | 0.0531909926045 | TGFB2||ASB2||VEGFA||ID3||TBX2||MKKS||LIF||NES||MICAL2||HEY2||TFAP2A||MYO7A||IGF2||SOCS3||DLL1 | 15 | 5.868354 | 5.882485 | 5.900488 | 5.902675 | 5.828683 | 5.856868 | 5.884105 | 5.844023 | 5.869426 | 5.911419 | 5.904051 | 5.913759 | 5.887843 | 5.900354 | 5.899879 |
| GO:0010573 | vascular endothelial growth factor production | 5/301 | 70/20870 | 0.00340067861898047 | 0.0637379618829 | 0.0531909926045 | IL1A||C3||IL6||HPSE||SULF2 | 5 | 5.641739 | 7.064632 | 7.491634 | 5.620867 | 5.617890 | 5.631798 | 5.695023 | 7.061407 | 7.058337 | 7.066884 | 7.071862 | 7.488513 | 7.496638 | 7.500112 | 7.481199 |
| GO:0061371 | determination of heart left/right asymmetry | 5/301 | 70/20870 | 0.00340067861898047 | 0.0637379618829 | 0.0531909926045 | ASB2||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||DLL1 | 5 | 5.903539 | 5.461077 | 5.588227 | 5.994410 | 5.719209 | 5.822983 | 6.053105 | 5.378291 | 5.381632 | 5.427134 | 5.640714 | 5.809260 | 5.353865 | 5.520382 | 5.631304 |
| GO:0007188 | adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | 10/301 | 249/20870 | 0.00344201630825666 | 0.0642010867931 | 0.0535774824285 | LPAR2||VIPR1||ADGRE3||CHRM3||EDNRA||CXCL10||CXCL11||S1PR1||ADGRE1||SSTR2 | 10 | 5.952474 | 5.873913 | 5.795681 | 5.963739 | 5.923301 | 5.976958 | 5.945334 | 5.876842 | 5.831276 | 5.924128 | 5.861845 | 5.768991 | 5.844665 | 5.808900 | 5.758546 |
| GO:0001558 | regulation of cell growth | 15/301 | 470/20870 | 0.00359836749038701 | 0.0667908437909 | 0.0557387022298 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||TGFB2||RASAL1||VEGFA||RGS4||BCL11A||ZNF639||UNC13A||SLIT2||SEMA3D||SEMA6B||ST20||ENPP1 | 15 | 6.777105 | 7.041326 | 7.048203 | 6.773361 | 6.774794 | 6.783777 | 6.776466 | 7.040798 | 7.044959 | 7.050341 | 7.029123 | 7.058850 | 7.049910 | 7.039215 | 7.044765 |
| GO:0060193 | positive regulation of lipase activity | 5/301 | 71/20870 | 0.00361598621321029 | 0.0667908437909 | 0.0557387022298 | NR1H3||LPAR2||ITK||EDNRA||PTAFR | 5 | 6.141738 | 6.597472 | 6.794899 | 6.129010 | 6.133777 | 6.141298 | 6.162636 | 6.628345 | 6.591616 | 6.587044 | 6.582421 | 6.772869 | 6.806730 | 6.786370 | 6.813268 |
| GO:0042116 | macrophage activation | 7/301 | 136/20870 | 0.00363275762654343 | 0.0667908437909 | 0.0557387022298 | NR1H3||CST7||CLU||DYSF||IL6||TLR4||SUCNR1 | 7 | 7.499987 | 7.394372 | 7.413584 | 7.515495 | 7.496253 | 7.498032 | 7.490043 | 7.405880 | 7.388325 | 7.395809 | 7.387398 | 7.397187 | 7.423566 | 7.423040 | 7.410382 |
| GO:0002221 | pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway | 9/301 | 211/20870 | 0.00365665060164686 | 0.0669115069808 | 0.0558393988109 | NR1H3||TYRO3||RSAD2||OASL||TLR4||SLC15A2||CLEC4E||IRF7||TLR7 | 9 | 5.906337 | 6.024744 | 6.033239 | 5.900664 | 5.906891 | 5.899967 | 5.917755 | 6.041689 | 6.022351 | 6.029214 | 6.005483 | 6.016428 | 6.029287 | 6.060481 | 6.026383 |
| GO:0002693 | positive regulation of cellular extravasation | 3/301 | 22/20870 | 0.00373315331840171 | 0.0669542304530 | 0.0558750526634 | RIPOR2||ADAM8||PTAFR | 3 | 6.320849 | 6.347110 | 6.312682 | 6.287633 | 6.393466 | 6.327525 | 6.271693 | 6.354837 | 6.328529 | 6.355785 | 6.349120 | 6.328703 | 6.319439 | 6.289846 | 6.312455 |
| GO:0003177 | pulmonary valve development | 3/301 | 22/20870 | 0.00373315331840171 | 0.0669542304530 | 0.0558750526634 | TGFB2||HEY2||SLIT2 | 3 | 4.801271 | 5.245316 | 5.302543 | 4.793697 | 4.868950 | 4.742173 | 4.797433 | 5.299106 | 5.137548 | 5.256883 | 5.282261 | 5.265551 | 5.411974 | 5.217633 | 5.307825 |
| GO:0006925 | inflammatory cell apoptotic process | 3/301 | 22/20870 | 0.00373315331840171 | 0.0669542304530 | 0.0558750526634 | IL6||SLC7A11||IRF7 | 3 | 6.694620 | 7.364915 | 7.612106 | 6.685404 | 6.674196 | 6.728043 | 6.690268 | 7.378116 | 7.357581 | 7.324267 | 7.398651 | 7.680239 | 7.567477 | 7.595039 | 7.603223 |
| GO:0035455 | response to interferon-alpha | 3/301 | 22/20870 | 0.00373315331840171 | 0.0669542304530 | 0.0558750526634 | IFIT3||IFIT2||IFITM1 | 3 | 5.821106 | 5.578908 | 5.883922 | 5.807601 | 5.850533 | 5.874784 | 5.748323 | 5.623158 | 5.542690 | 5.613245 | 5.534310 | 5.881404 | 5.939070 | 5.838244 | 5.875156 |
| GO:0048762 | mesenchymal cell differentiation | 10/301 | 252/20870 | 0.00374569121415375 | 0.0669542304530 | 0.0558750526634 | SEMA3F||LRP6||TGFB2||HEY2||IL6||FBXL17||EDNRA||SEMA3D||SPRED1||SEMA6B | 10 | 6.324772 | 6.375609 | 6.501172 | 6.192428 | 6.279764 | 6.374764 | 6.439951 | 6.399729 | 6.430675 | 6.305483 | 6.363555 | 6.554312 | 6.448350 | 6.484277 | 6.515632 |
| GO:0009855 | determination of bilateral symmetry | 7/301 | 137/20870 | 0.00378231107935403 | 0.0672972492045 | 0.0561613107635 | ASB2||DNAH11||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||NBL1||DLL1 | 7 | 5.520972 | 5.151353 | 5.189637 | 5.574602 | 5.388923 | 5.510581 | 5.600631 | 5.135722 | 5.068789 | 5.102793 | 5.288198 | 5.361721 | 5.012607 | 5.146511 | 5.215719 |
| GO:0007589 | body fluid secretion | 6/301 | 103/20870 | 0.00380410084537781 | 0.0673744649725 | 0.0562257493370 | NR1H3||OAS2||VEGFA||PRLR||CHRM3||AQP1 | 6 | 7.926009 | 7.899883 | 8.190955 | 7.913822 | 7.927196 | 7.938433 | 7.924480 | 7.901086 | 7.889879 | 7.901893 | 7.906624 | 8.190615 | 8.188419 | 8.197118 | 8.187650 |
| GO:0003143 | embryonic heart tube morphogenesis | 5/301 | 72/20870 | 0.00384090091843727 | 0.0677156093429 | 0.0565104432172 | ASB2||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||DLL1 | 5 | 5.760976 | 5.341903 | 5.466035 | 5.850648 | 5.582317 | 5.679465 | 5.907996 | 5.261594 | 5.267188 | 5.307746 | 5.515688 | 5.680548 | 5.235582 | 5.402072 | 5.509642 |
| GO:0009799 | specification of symmetry | 7/301 | 138/20870 | 0.00393649646512338 | 0.0690694633931 | 0.0576402697546 | ASB2||DNAH11||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||NBL1||DLL1 | 7 | 5.519609 | 5.132258 | 5.170220 | 5.572202 | 5.390883 | 5.509634 | 5.597022 | 5.116602 | 5.050088 | 5.083602 | 5.268870 | 5.342140 | 4.994940 | 5.126609 | 5.195424 |
| GO:0032733 | positive regulation of interleukin-10 production | 4/301 | 45/20870 | 0.00396950263590329 | 0.0690694633931 | 0.0576402697546 | IL23A||IL6||TLR4||ISG15 | 4 | 6.123655 | 6.082754 | 6.160663 | 6.112546 | 6.123494 | 6.123148 | 6.135342 | 6.125780 | 6.070320 | 6.091088 | 6.042546 | 6.142285 | 6.178075 | 6.171347 | 6.150647 |
| GO:0040013 | negative regulation of locomotion | 14/301 | 429/20870 | 0.00398574000424115 | 0.0690694633931 | 0.0576402697546 | SEMA3F||TIE1||RIPOR2||PADI2||TMEFF2||SLIT2||SEMA3D||NBL1||SPRED1||PIP5KL1||SEMA6B||IFITM1||KLRK1||EPPK1 | 14 | 5.985022 | 6.028788 | 6.081019 | 5.963603 | 5.984509 | 5.996950 | 5.994783 | 6.015514 | 6.051256 | 6.020886 | 6.027237 | 6.097205 | 6.080056 | 6.078662 | 6.068000 |
| GO:0030516 | regulation of axon extension | 6/301 | 104/20870 | 0.00398924898644633 | 0.0690694633931 | 0.0576402697546 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 6 | 5.517688 | 5.622604 | 5.650258 | 5.506426 | 5.494665 | 5.581578 | 5.486076 | 5.637342 | 5.652272 | 5.584583 | 5.615321 | 5.732168 | 5.648962 | 5.620174 | 5.596038 |
| GO:0050808 | synapse organization | 15/301 | 477/20870 | 0.00412182506389154 | 0.0710462793379 | 0.0592899742508 | SEMA3F||CDKL5||DLG3||ZDHHC2||PCDHB3||C3||LRRC4||UNC13A||UNC13C||SLC7A11||POU4F1||GPRASP2||IGFN1||SLITRK5||CACNB4 | 15 | 6.413203 | 6.546060 | 6.523341 | 6.400828 | 6.403773 | 6.432940 | 6.415051 | 6.556680 | 6.545067 | 6.544983 | 6.537444 | 6.537153 | 6.514216 | 6.511604 | 6.530231 |
| GO:0002363 | alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment | 3/301 | 23/20870 | 0.00424775585037836 | 0.0718545693947 | 0.0599645133977 | IL23A||TNFSF18||IL6 | 3 | 6.529438 | 6.937691 | 7.276676 | 6.545635 | 6.534691 | 6.506522 | 6.530620 | 6.948233 | 6.936205 | 6.932768 | 6.933504 | 7.269991 | 7.284146 | 7.261339 | 7.291039 |
| GO:0032740 | positive regulation of interleukin-17 production | 3/301 | 23/20870 | 0.00424775585037836 | 0.0718545693947 | 0.0599645133977 | OSM||IL23A||IL6 | 3 | 5.073505 | 6.265223 | 6.707285 | 4.991289 | 5.027139 | 5.107469 | 5.161920 | 6.278903 | 6.224967 | 6.296521 | 6.259528 | 6.710021 | 6.725694 | 6.717207 | 6.675718 |
| GO:0033081 | regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus | 3/301 | 23/20870 | 0.00424775585037836 | 0.0718545693947 | 0.0599645133977 | ZC3H8||ADAM8||EGR3 | 3 | 4.962352 | 4.803126 | 4.541773 | 5.062572 | 4.917952 | 4.972158 | 4.890704 | 4.893675 | 5.087911 | 4.601432 | 4.564353 | 4.477336 | 4.492549 | 4.514897 | 4.673603 |
| GO:0043369 | CD4-positive or CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment | 3/301 | 23/20870 | 0.00424775585037836 | 0.0718545693947 | 0.0599645133977 | IL23A||TNFSF18||IL6 | 3 | 6.018349 | 6.639212 | 7.106283 | 6.041728 | 6.027105 | 5.993252 | 6.010856 | 6.637974 | 6.641510 | 6.645369 | 6.631963 | 7.102466 | 7.115801 | 7.089176 | 7.117510 |
| GO:0030517 | negative regulation of axon extension | 4/301 | 46/20870 | 0.00429899133130445 | 0.0718545693947 | 0.0599645133977 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 4 | 4.929389 | 5.000838 | 5.127790 | 4.831987 | 4.949126 | 5.016061 | 4.914295 | 4.949342 | 4.987263 | 5.005162 | 5.059401 | 5.195199 | 5.047593 | 5.232501 | 5.024582 |
| GO:0032620 | interleukin-17 production | 4/301 | 46/20870 | 0.00429899133130445 | 0.0718545693947 | 0.0599645133977 | OSM||IL23A||IL6||TLR4 | 4 | 4.875735 | 5.794149 | 6.180722 | 4.834963 | 4.802089 | 4.924134 | 4.937185 | 5.811127 | 5.771835 | 5.807963 | 5.785306 | 6.182462 | 6.195109 | 6.189980 | 6.155006 |
| GO:0032660 | regulation of interleukin-17 production | 4/301 | 46/20870 | 0.00429899133130445 | 0.0718545693947 | 0.0599645133977 | OSM||IL23A||IL6||TLR4 | 4 | 4.875735 | 5.794149 | 6.180722 | 4.834963 | 4.802089 | 4.924134 | 4.937185 | 5.811127 | 5.771835 | 5.807963 | 5.785306 | 6.182462 | 6.195109 | 6.189980 | 6.155006 |
| GO:1902105 | regulation of leukocyte differentiation | 12/301 | 343/20870 | 0.00433852130759546 | 0.0720133337069 | 0.0600970063596 | IL23A||TNFSF18||LIF||TLR4||ZC3H8||ADAM8||POU4F1||EGR3||CSF1||IRF7||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 12 | 6.211933 | 6.325525 | 6.369325 | 6.211381 | 6.201776 | 6.229899 | 6.204507 | 6.326113 | 6.324473 | 6.330767 | 6.320728 | 6.357712 | 6.372746 | 6.382579 | 6.364141 |
| GO:0002831 | regulation of response to biotic stimulus | 15/301 | 480/20870 | 0.00436444446708434 | 0.0720133337069 | 0.0600970063596 | NR1H3||TYRO3||IL23A||POLR3G||OASL||TLR4||HERC5||ADAM8||BMP6||IRF7||IFIT1||ISG15||HLA-F||KLRK1||PIK3R6 | 15 | 6.389259 | 6.493147 | 6.557451 | 6.384971 | 6.379827 | 6.398865 | 6.393300 | 6.494210 | 6.499974 | 6.491998 | 6.486373 | 6.545333 | 6.565242 | 6.567513 | 6.551596 |
| GO:0042060 | wound healing | 15/301 | 480/20870 | 0.00436444446708434 | 0.0720133337069 | 0.0600970063596 | MYLK||TYRO3||TGFB2||VEGFA||IL1A||RREB1||DYSF||IL6||TLR4||ENTPD1||TMEFF2||SLC7A11||HPSE||C1QTNF1||EPPK1 | 15 | 6.978409 | 7.109664 | 7.095662 | 6.978778 | 6.989028 | 6.969385 | 6.976377 | 7.106101 | 7.116332 | 7.106093 | 7.110104 | 7.090382 | 7.089813 | 7.090852 | 7.111486 |
| GO:1903532 | positive regulation of secretion by cell | 11/301 | 302/20870 | 0.00461043561243814 | 0.0756958084432 | 0.0631701276311 | UNC13D||TGFB2||IL1A||TLR4||ANKRD1||FRMD4A||ADAM8||BMP6||PTAFR||C1QTNF1||HLA-F | 11 | 6.813598 | 7.254527 | 7.297597 | 6.803873 | 6.829614 | 6.799931 | 6.820767 | 7.241886 | 7.236237 | 7.262104 | 7.277504 | 7.300749 | 7.301649 | 7.309540 | 7.278264 |
| GO:0042551 | neuron maturation | 4/301 | 47/20870 | 0.00464644045611011 | 0.0756958084432 | 0.0631701276311 | SCARF1||BCL11A||C3||NR4A2 | 4 | 5.044541 | 5.080960 | 5.184688 | 5.069386 | 5.049049 | 5.046092 | 5.013074 | 5.080974 | 5.130001 | 5.072654 | 5.038731 | 5.155230 | 5.202261 | 5.167342 | 5.213126 |
| GO:0055010 | ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis | 4/301 | 47/20870 | 0.00464644045611011 | 0.0756958084432 | 0.0631701276311 | TGFB2||HEY2||POU4F1||LY6E | 4 | 5.275838 | 5.690701 | 5.862027 | 5.280602 | 5.273977 | 5.257738 | 5.290836 | 5.711790 | 5.658651 | 5.715877 | 5.675680 | 5.877714 | 5.883849 | 5.843453 | 5.842593 |
| GO:0051235 | maintenance of location | 12/301 | 347/20870 | 0.00475176169743976 | 0.0768996437478 | 0.0641747596102 | NR1H3||ARL2BP||C3||CCR7||B4GALNT1||IL6||NBL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||SLC8A1||TRDN||ENPP1 | 12 | 7.426636 | 7.749839 | 7.850864 | 7.422939 | 7.428875 | 7.422597 | 7.432112 | 7.739673 | 7.747848 | 7.759346 | 7.752416 | 7.836490 | 7.853340 | 7.858587 | 7.854937 |
| GO:0032147 | activation of protein kinase activity | 7/301 | 143/20870 | 0.00478008663545148 | 0.0768996437478 | 0.0641747596102 | TGFB2||IL23A||VEGFA||PRLR||MAS1||BORA||TNFSF15 | 7 | 6.334045 | 6.510020 | 6.748241 | 6.337533 | 6.334136 | 6.328275 | 6.336221 | 6.523206 | 6.482656 | 6.511207 | 6.522639 | 6.732452 | 6.750855 | 6.758414 | 6.751116 |
| GO:0062207 | regulation of pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway | 7/301 | 143/20870 | 0.00478008663545148 | 0.0768996437478 | 0.0641747596102 | NR1H3||TYRO3||RSAD2||OASL||TLR4||SLC15A2||IRF7 | 7 | 6.198028 | 6.160402 | 6.178307 | 6.161557 | 6.218202 | 6.187314 | 6.224164 | 6.169523 | 6.160904 | 6.156754 | 6.154382 | 6.154890 | 6.173106 | 6.213083 | 6.171511 |
| GO:0032727 | positive regulation of interferon-alpha production | 3/301 | 24/20870 | 0.00480331152215602 | 0.0769526381205 | 0.0642189847972 | TLR4||IRF7||TLR7 | 3 | 5.774877 | 5.907885 | 5.843070 | 5.917094 | 5.691373 | 5.774100 | 5.705693 | 5.915301 | 5.893756 | 5.895860 | 5.926365 | 5.842222 | 5.846881 | 5.871712 | 5.810815 |
| GO:0048844 | artery morphogenesis | 5/301 | 76/20870 | 0.00484129619969384 | 0.0772406802769 | 0.0644593634940 | MYLK||TGFB2||VEGFA||TBX2||HEY2 | 5 | 5.427385 | 5.263219 | 5.265700 | 5.421267 | 5.448736 | 5.394270 | 5.444614 | 5.278519 | 5.245820 | 5.272372 | 5.255932 | 5.266562 | 5.281437 | 5.246812 | 5.267778 |
| GO:0071214 | cellular response to abiotic stimulus | 12/301 | 349/20870 | 0.00496987221659866 | 0.0782992312435 | 0.0653427519013 | GCLC||MYLK||MAPK10||TLR4||MMP7||ANKRD1||BMP6||PTAFR||ST20||TLR7||AQP1||SCX | 12 | 6.140855 | 6.631044 | 6.846599 | 6.142715 | 6.128167 | 6.146464 | 6.145996 | 6.628027 | 6.650596 | 6.630151 | 6.615178 | 6.854955 | 6.850568 | 6.845606 | 6.835193 |
| GO:0104004 | cellular response to environmental stimulus | 12/301 | 349/20870 | 0.00496987221659866 | 0.0782992312435 | 0.0653427519013 | GCLC||MYLK||MAPK10||TLR4||MMP7||ANKRD1||BMP6||PTAFR||ST20||TLR7||AQP1||SCX | 12 | 6.140855 | 6.631044 | 6.846599 | 6.142715 | 6.128167 | 6.146464 | 6.145996 | 6.628027 | 6.650596 | 6.630151 | 6.615178 | 6.854955 | 6.850568 | 6.845606 | 6.835193 |
| GO:0051251 | positive regulation of lymphocyte activation | 15/301 | 487/20870 | 0.00497607710173217 | 0.0782992312435 | 0.0653427519013 | IL23A||IL1A||CCR7||IL6||TLR4||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||IGF2||EGR3||PDCD1LG2||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||KLRK1||HLA-DQA2||PIK3R6 | 15 | 6.959286 | 7.356554 | 7.481354 | 6.947489 | 6.961369 | 6.960980 | 6.967232 | 7.356074 | 7.335670 | 7.363333 | 7.370900 | 7.472665 | 7.483699 | 7.484321 | 7.484699 |
| GO:0010712 | regulation of collagen metabolic process | 4/301 | 48/20870 | 0.00501228571308204 | 0.0782992312435 | 0.0653427519013 | IL6||CREB3L1||SERPINB7||SCX | 4 | 6.363458 | 6.446176 | 6.522618 | 6.359932 | 6.361257 | 6.372888 | 6.359714 | 6.446867 | 6.404118 | 6.475386 | 6.457385 | 6.534364 | 6.532011 | 6.519481 | 6.504420 |
| GO:0050919 | negative chemotaxis | 4/301 | 48/20870 | 0.00501228571308204 | 0.0782992312435 | 0.0653427519013 | SEMA3F||SLIT2||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 4 | 5.370893 | 5.786846 | 5.775810 | 5.382672 | 5.389512 | 5.358796 | 5.352253 | 5.753190 | 5.745875 | 5.787770 | 5.857809 | 5.808175 | 5.758120 | 5.766344 | 5.770084 |
| GO:0031214 | biomineral tissue development | 8/301 | 182/20870 | 0.00502932125055482 | 0.0782992312435 | 0.0653427519013 | HEY2||TFAP2A||MMP13||BMP6||S1PR1||SLC8A1||ISG15||ENPP1 | 8 | 6.885619 | 7.603701 | 7.649232 | 6.891856 | 6.887066 | 6.875142 | 6.888355 | 7.612232 | 7.591168 | 7.600146 | 7.611153 | 7.672874 | 7.648902 | 7.632581 | 7.642263 |
| GO:0021675 | nerve development | 5/301 | 77/20870 | 0.00511773764556686 | 0.0793557632511 | 0.0662244554347 | SEMA3F||ATP8B1||TFAP2A||POU4F1||SULF2 | 5 | 6.475474 | 6.529834 | 6.490312 | 6.491308 | 6.451284 | 6.488931 | 6.470009 | 6.534466 | 6.496508 | 6.515760 | 6.571535 | 6.481735 | 6.456801 | 6.512423 | 6.509578 |
| GO:0009306 | protein secretion | 13/301 | 396/20870 | 0.00517843836381839 | 0.0799163731506 | 0.0666922990264 | NR1H3||TGFB2||IL1A||RSAD2||IL6||IL1RN||TLR4||ANKRD1||FRMD4A||ADAM8||BMP6||SCG2||SUCNR1 | 13 | 5.742177 | 6.119839 | 6.275706 | 5.733667 | 5.724838 | 5.735883 | 5.773828 | 6.130695 | 6.112294 | 6.117063 | 6.119241 | 6.278155 | 6.282004 | 6.273169 | 6.269464 |
| GO:0002367 | cytokine production involved in immune response | 8/301 | 183/20870 | 0.00519528869743519 | 0.0799163731506 | 0.0666922990264 | TGFB2||NR4A3||TREM1||RSAD2||IL6||TLR4||TNFRSF14||HLA-F | 8 | 7.287478 | 7.454017 | 7.611540 | 7.284063 | 7.282141 | 7.287778 | 7.295890 | 7.463194 | 7.450012 | 7.446416 | 7.456391 | 7.610256 | 7.621887 | 7.608480 | 7.605484 |
| GO:0035592 | establishment of protein localization to extracellular region | 13/301 | 397/20870 | 0.00528643772208587 | 0.0808222296426 | 0.0674482599098 | NR1H3||TGFB2||IL1A||RSAD2||IL6||IL1RN||TLR4||ANKRD1||FRMD4A||ADAM8||BMP6||SCG2||SUCNR1 | 13 | 5.742177 | 6.119839 | 6.275706 | 5.733667 | 5.724838 | 5.735883 | 5.773828 | 6.130695 | 6.112294 | 6.117063 | 6.119241 | 6.278155 | 6.282004 | 6.273169 | 6.269464 |
| GO:0051402 | neuron apoptotic process | 10/301 | 265/20870 | 0.00531543948687507 | 0.0808222296426 | 0.0674482599098 | GCLC||TYRO3||TGFB2||DNAJC5||NES||TFAP2A||ADAM8||POU4F1||NR4A2||GPRASP2 | 10 | 6.815024 | 6.829002 | 6.835089 | 6.824878 | 6.818686 | 6.806152 | 6.810305 | 6.838137 | 6.831323 | 6.833510 | 6.812908 | 6.836640 | 6.826780 | 6.840723 | 6.836175 |
| GO:0048511 | rhythmic process | 11/301 | 308/20870 | 0.00532895551672782 | 0.0808222296426 | 0.0674482599098 | NR1H3||TYRO3||TGFB2||PTGDS||MAPK10||ID3||BHLHE40||MMP7||SLIT2||FBXL17||EGR3 | 11 | 5.801782 | 5.690177 | 5.705362 | 5.666735 | 5.757558 | 5.833726 | 5.935555 | 5.706440 | 5.776889 | 5.605044 | 5.666935 | 5.735123 | 5.669420 | 5.705972 | 5.710174 |
| GO:0110148 | biomineralization | 8/301 | 184/20870 | 0.00536541295213763 | 0.0808222296426 | 0.0674482599098 | HEY2||TFAP2A||MMP13||BMP6||S1PR1||SLC8A1||ISG15||ENPP1 | 8 | 6.885619 | 7.603701 | 7.649232 | 6.891856 | 6.887066 | 6.875142 | 6.888355 | 7.612232 | 7.591168 | 7.600146 | 7.611153 | 7.672874 | 7.648902 | 7.632581 | 7.642263 |
| GO:1903706 | regulation of hemopoiesis | 14/301 | 444/20870 | 0.00536871743215093 | 0.0808222296426 | 0.0674482599098 | IL23A||TNFSF18||LIF||TLR4||ZC3H8||ADAM8||POU4F1||EGR3||CSF1||IRF7||ISG15||DLL1||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 14 | 6.491344 | 6.471937 | 6.500250 | 6.493742 | 6.486044 | 6.508227 | 6.477183 | 6.470828 | 6.476811 | 6.473327 | 6.466764 | 6.511073 | 6.496826 | 6.501062 | 6.491970 |
| GO:0006213 | pyrimidine nucleoside metabolic process | 3/301 | 25/20870 | 0.00540070842988738 | 0.0808222296426 | 0.0674482599098 | TYMP||AICDA||TK2 | 3 | 5.516339 | 5.397840 | 5.469795 | 5.883763 | 5.399628 | 5.491687 | 5.202696 | 5.245271 | 5.364498 | 5.457300 | 5.510373 | 5.538654 | 5.445730 | 5.459543 | 5.432879 |
| GO:1902932 | positive regulation of alcohol biosynthetic process | 3/301 | 25/20870 | 0.00540070842988738 | 0.0808222296426 | 0.0674482599098 | MAS1||BMP6||PTAFR | 3 | 4.381788 | 4.473384 | 4.467549 | 4.446040 | 4.290554 | 4.397359 | 4.388820 | 4.364394 | 4.500873 | 4.523111 | 4.499771 | 4.459936 | 4.350962 | 4.465533 | 4.584301 |
| GO:0007409 | axonogenesis | 14/301 | 445/20870 | 0.00547316286871478 | 0.0815902773595 | 0.0680892157738 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||NOTCH3||RPS6KA5||VEGFA||SLIT2||POU4F1||NR4A2||SEMA3D||CHODL||KALRN||SLITRK5||SEMA6B | 14 | 6.706691 | 7.075092 | 7.052465 | 6.709970 | 6.704755 | 6.716714 | 6.695238 | 7.083477 | 7.070655 | 7.076331 | 7.069863 | 7.062925 | 7.059990 | 7.049810 | 7.036991 |
| GO:0031016 | pancreas development | 5/301 | 79/20870 | 0.00570383758695401 | 0.0846168501884 | 0.0706149697860 | NR5A2||IL6||BMP6||IGF2||DLL1 | 5 | 5.249118 | 5.374213 | 5.120486 | 5.277125 | 5.236871 | 5.217500 | 5.264227 | 5.553471 | 5.370268 | 5.360538 | 5.189563 | 5.142092 | 5.086794 | 5.230366 | 5.014014 |
| GO:0002819 | regulation of adaptive immune response | 10/301 | 268/20870 | 0.00574193596202080 | 0.0846168501884 | 0.0706149697860 | IL23A||CD48||TNFSF18||C3||RSAD2||IL6||TNFRSF14||IRF7||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 10 | 6.622549 | 6.694593 | 6.867589 | 6.625359 | 6.608664 | 6.625595 | 6.630483 | 6.692887 | 6.689185 | 6.691891 | 6.704364 | 6.875898 | 6.861730 | 6.864857 | 6.867834 |
| GO:1903522 | regulation of blood circulation | 10/301 | 268/20870 | 0.00574193596202080 | 0.0846168501884 | 0.0706149697860 | TGFB2||DMPK||RGS4||ECE1||TBX2||CHRM3||HEY2||BIN1||SLC8A1||TRDN | 10 | 5.655865 | 5.727144 | 5.648960 | 5.661671 | 5.658549 | 5.652066 | 5.651147 | 5.756863 | 5.700573 | 5.749370 | 5.700809 | 5.628460 | 5.683841 | 5.658753 | 5.623968 |
| GO:0070169 | positive regulation of biomineral tissue development | 4/301 | 50/20870 | 0.00580086531151547 | 0.0851602318166 | 0.0710684359358 | TFAP2A||BMP6||SLC8A1||ISG15 | 4 | 5.395484 | 5.825398 | 5.988052 | 5.375158 | 5.340829 | 5.378017 | 5.483894 | 5.805834 | 5.777846 | 5.832373 | 5.883430 | 6.190571 | 5.914312 | 5.895266 | 5.931280 |
| GO:0050714 | positive regulation of protein secretion | 7/301 | 149/20870 | 0.00596439935004189 | 0.0872293404944 | 0.0727951611263 | TGFB2||IL1A||TLR4||ANKRD1||FRMD4A||ADAM8||BMP6 | 7 | 5.946678 | 6.133150 | 6.101263 | 5.912854 | 5.927966 | 5.932805 | 6.011049 | 6.135158 | 6.123133 | 6.143971 | 6.130261 | 6.112533 | 6.122965 | 6.081818 | 6.087329 |
| GO:0022617 | extracellular matrix disassembly | 5/301 | 80/20870 | 0.00601394937095776 | 0.0872927012078 | 0.0728480372952 | IL6||MMP7||MMP13||ADAM8||ADAMTS4 | 5 | 7.159245 | 7.964050 | 8.279879 | 7.146376 | 7.155856 | 7.171877 | 7.162750 | 7.951094 | 7.958658 | 7.980144 | 7.966143 | 8.265665 | 8.300565 | 8.283571 | 8.269453 |
| GO:1905330 | regulation of morphogenesis of an epithelium | 5/301 | 80/20870 | 0.00601394937095776 | 0.0872927012078 | 0.0728480372952 | VEGFA||TBX2||LIF||CXCL10||LBX2 | 5 | 5.583208 | 5.656009 | 5.793122 | 5.590278 | 5.571918 | 5.627294 | 5.542018 | 5.639111 | 5.579289 | 5.668841 | 5.732568 | 5.774253 | 5.801390 | 5.782519 | 5.813987 |
| GO:0002699 | positive regulation of immune effector process | 12/301 | 358/20870 | 0.00605233792970935 | 0.0875208866914 | 0.0730384640364 | UNC13D||IL23A||NR4A3||C3||RSAD2||IL6||TLR4||TNFRSF14||PTAFR||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||KLRK1 | 12 | 7.173213 | 7.253338 | 7.359120 | 7.173757 | 7.161917 | 7.180923 | 7.176188 | 7.245776 | 7.259197 | 7.256826 | 7.251514 | 7.357085 | 7.363547 | 7.364248 | 7.351564 |
| GO:0001655 | urogenital system development | 12/301 | 359/20870 | 0.00618331981977692 | 0.0890813351648 | 0.0743406990115 | TGFB2||VEGFA||ID3||LIF||TFAP2A||FRAS1||SLIT2||BMP6||SERPINB7||GCNT1||SULF2||DLL1 | 12 | 5.336162 | 5.866867 | 6.135755 | 5.323810 | 5.341859 | 5.332666 | 5.346211 | 5.858680 | 5.847297 | 5.879361 | 5.881841 | 6.141900 | 6.141322 | 6.124308 | 6.135421 |
| GO:0110151 | positive regulation of biomineralization | 4/301 | 51/20870 | 0.00622442811363137 | 0.0893402116979 | 0.0745567382345 | TFAP2A||BMP6||SLC8A1||ISG15 | 4 | 5.395484 | 5.825398 | 5.988052 | 5.375158 | 5.340829 | 5.378017 | 5.483894 | 5.805834 | 5.777846 | 5.832373 | 5.883430 | 6.190571 | 5.914312 | 5.895266 | 5.931280 |
| GO:0035050 | embryonic heart tube development | 5/301 | 81/20870 | 0.00633573519417096 | 0.0906010132766 | 0.0756089100560 | ASB2||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||DLL1 | 5 | 5.848880 | 5.502347 | 5.575999 | 5.926707 | 5.687842 | 5.801072 | 5.963629 | 5.447998 | 5.413585 | 5.456392 | 5.676104 | 5.764715 | 5.377997 | 5.522395 | 5.611578 |
| GO:0046425 | regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT | 6/301 | 115/20870 | 0.00649126421336617 | 0.0924825502871 | 0.0771791017950 | IL23A||PRLR||LIF||IL6||SOCS3||INPP5F | 6 | 5.669640 | 6.279741 | 6.450215 | 5.609689 | 5.835382 | 5.617872 | 5.602015 | 6.128900 | 6.283629 | 6.326817 | 6.368436 | 6.413048 | 6.430807 | 6.538762 | 6.414424 |
| GO:0021545 | cranial nerve development | 4/301 | 52/20870 | 0.00666804346807138 | 0.0930550327688 | 0.0776568533664 | SEMA3F||ATP8B1||TFAP2A||POU4F1 | 4 | 6.985456 | 7.020090 | 6.989089 | 6.999540 | 6.963420 | 6.996885 | 6.981693 | 7.024618 | 6.984697 | 7.002595 | 7.067131 | 6.976361 | 6.948932 | 7.017151 | 7.012832 |
| GO:0031295 | T cell costimulation | 4/301 | 52/20870 | 0.00666804346807138 | 0.0930550327688 | 0.0776568533664 | CCR7||TNFRSF14||PDCD1LG2||KLRK1 | 4 | 7.182266 | 8.312244 | 8.467593 | 7.116045 | 7.225266 | 7.142977 | 7.240895 | 8.311307 | 8.244887 | 8.328887 | 8.361404 | 8.416384 | 8.469725 | 8.506001 | 8.476816 |
| GO:0032964 | collagen biosynthetic process | 4/301 | 52/20870 | 0.00666804346807138 | 0.0930550327688 | 0.0776568533664 | IL6||CREB3L1||SERPINB7||SCX | 4 | 5.762595 | 6.091653 | 6.185586 | 5.780593 | 5.743103 | 5.749021 | 5.777282 | 6.099690 | 6.048812 | 6.120507 | 6.096652 | 6.200681 | 6.194655 | 6.178185 | 6.168598 |
| GO:2000404 | regulation of T cell migration | 4/301 | 52/20870 | 0.00666804346807138 | 0.0930550327688 | 0.0776568533664 | RIPOR2||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10 | 4 | 6.186461 | 6.621599 | 6.946718 | 6.196436 | 6.166113 | 6.199663 | 6.183391 | 6.651526 | 6.614479 | 6.605629 | 6.614326 | 6.938956 | 6.959389 | 6.916840 | 6.971097 |
| GO:0001958 | endochondral ossification | 3/301 | 27/20870 | 0.00672425644716349 | 0.0930550327688 | 0.0776568533664 | MMP13||BMP6||SCX | 3 | 7.244825 | 7.052118 | 7.209828 | 7.251630 | 7.245577 | 7.256453 | 7.225446 | 7.019664 | 7.035688 | 7.065886 | 7.086306 | 7.296545 | 7.184008 | 7.177715 | 7.177439 |
| GO:0003272 | endocardial cushion formation | 3/301 | 27/20870 | 0.00672425644716349 | 0.0930550327688 | 0.0776568533664 | TGFB2||TBX2||HEY2 | 3 | 4.937459 | 5.180784 | 5.161322 | 4.985038 | 4.936227 | 4.902322 | 4.924976 | 5.158598 | 5.180970 | 5.198358 | 5.184929 | 5.167972 | 5.209274 | 5.128986 | 5.137683 |
| GO:0036075 | replacement ossification | 3/301 | 27/20870 | 0.00672425644716349 | 0.0930550327688 | 0.0776568533664 | MMP13||BMP6||SCX | 3 | 7.244825 | 7.052118 | 7.209828 | 7.251630 | 7.245577 | 7.256453 | 7.225446 | 7.019664 | 7.035688 | 7.065886 | 7.086306 | 7.296545 | 7.184008 | 7.177715 | 7.177439 |
| GO:0090026 | positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis | 3/301 | 27/20870 | 0.00672425644716349 | 0.0930550327688 | 0.0776568533664 | TNFSF18||PLA2G7||CXCL10 | 3 | 5.607758 | 6.784540 | 7.360881 | 5.587972 | 5.583749 | 5.640973 | 5.617587 | 6.827417 | 6.796474 | 6.764883 | 6.748104 | 7.327919 | 7.386795 | 7.350279 | 7.377784 |
| GO:0050829 | defense response to Gram-negative bacterium | 6/301 | 116/20870 | 0.00676464131364857 | 0.0932795718286 | 0.0778442370717 | IL23A||TREM1||IL6||TLR4||TNFRSF14||AQP1 | 6 | 7.531399 | 7.503267 | 7.518604 | 7.537081 | 7.514659 | 7.542634 | 7.531071 | 7.471199 | 7.520783 | 7.516633 | 7.503929 | 7.518629 | 7.507151 | 7.542760 | 7.505570 |
| GO:0045926 | negative regulation of growth | 10/301 | 275/20870 | 0.00684113637245351 | 0.0939986744984 | 0.0784443470166 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||TGFB2||RGS4||BCL11A||SLIT2||SEMA3D||SEMA6B||ST20||ENPP1 | 10 | 6.806761 | 7.145667 | 7.136878 | 6.801786 | 6.807037 | 6.805978 | 6.812222 | 7.157245 | 7.130593 | 7.152712 | 7.141970 | 7.140997 | 7.139486 | 7.144236 | 7.122695 |
| GO:0007389 | pattern specification process | 14/301 | 458/20870 | 0.00698608616212062 | 0.0953723651766 | 0.0795907277377 | SEMA3F||LRP6||ASB2||MEIS3||DNAH11||TBX2||C3||MKKS||MICAL2||BHLHE40||HEY2||NBL1||HES4||DLL1 | 14 | 4.988622 | 4.837666 | 4.847364 | 5.007245 | 4.927980 | 4.961313 | 5.054777 | 4.828542 | 4.807132 | 4.833579 | 4.880414 | 4.905501 | 4.786360 | 4.827928 | 4.866944 |
| GO:0010770 | positive regulation of cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation | 5/301 | 83/20870 | 0.00701521670814443 | 0.0953723651766 | 0.0795907277377 | CDKL3||CDKL5||UNC13D||RREB1||GPRASP2 | 5 | 6.796929 | 6.888990 | 6.839691 | 6.776920 | 6.808959 | 6.827556 | 6.773577 | 6.890335 | 6.900863 | 6.877566 | 6.887100 | 6.869167 | 6.829819 | 6.835794 | 6.823553 |
| GO:0043299 | leukocyte degranulation | 5/301 | 83/20870 | 0.00701521670814443 | 0.0953723651766 | 0.0795907277377 | UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3||PTAFR||HLA-F | 5 | 7.187237 | 7.202795 | 7.359826 | 7.180229 | 7.202910 | 7.180582 | 7.185109 | 7.191379 | 7.212642 | 7.214070 | 7.192931 | 7.361491 | 7.369799 | 7.365675 | 7.342187 |
| GO:0048640 | negative regulation of developmental growth | 6/301 | 117/20870 | 0.00704627184399792 | 0.0954584406655 | 0.0796625599796 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||RGS4||BCL11A||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 6 | 6.986209 | 7.629540 | 7.606801 | 6.975902 | 6.994902 | 6.989950 | 6.984013 | 7.635137 | 7.610660 | 7.641925 | 7.630252 | 7.606357 | 7.608698 | 7.619955 | 7.592058 |
| GO:0046580 | negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction | 4/301 | 53/20870 | 0.00713210262782529 | 0.0962833854756 | 0.0803509979528 | TGFB2||RASAL1||RIPOR2||TRIM67 | 4 | 5.574361 | 5.287027 | 5.174879 | 5.556919 | 5.599308 | 5.557756 | 5.583017 | 5.315064 | 5.277469 | 5.332337 | 5.220713 | 5.113258 | 5.146535 | 5.214994 | 5.221821 |
| GO:0032963 | collagen metabolic process | 6/301 | 118/20870 | 0.00733629312087732 | 0.0986948701732 | 0.0823634448671 | IL6||MMP7||MMP13||CREB3L1||SERPINB7||SCX | 6 | 6.831889 | 7.581084 | 7.951351 | 6.832448 | 6.827435 | 6.842825 | 6.824782 | 7.566473 | 7.575126 | 7.596756 | 7.585804 | 7.941078 | 7.967024 | 7.954720 | 7.942429 |
| GO:0032967 | positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process | 3/301 | 28/20870 | 0.00745186812802841 | 0.0989198821159 | 0.0825512232055 | CREB3L1||SERPINB7||SCX | 3 | 5.979270 | 6.502374 | 6.593830 | 5.991040 | 5.956999 | 5.977436 | 5.991334 | 6.516043 | 6.448622 | 6.535123 | 6.508269 | 6.610643 | 6.607683 | 6.582918 | 6.573729 |
| GO:1902624 | positive regulation of neutrophil migration | 3/301 | 28/20870 | 0.00745186812802841 | 0.0989198821159 | 0.0825512232055 | RIPOR2||CCR7||ADAM8 | 3 | 6.346375 | 7.173406 | 7.370865 | 6.352391 | 6.363927 | 6.355846 | 6.312797 | 7.169119 | 7.171903 | 7.181035 | 7.171538 | 7.384011 | 7.373567 | 7.372595 | 7.353115 |
| GO:1903859 | regulation of dendrite extension | 3/301 | 28/20870 | 0.00745186812802841 | 0.0989198821159 | 0.0825512232055 | RASAL1||BCL11A||UNC13A | 3 | 4.157310 | 3.753846 | 3.916384 | 4.059320 | 4.420254 | 3.989345 | 4.121735 | 3.666191 | 3.949637 | 3.705717 | 3.674378 | 3.802446 | 3.767883 | 4.007482 | 4.065083 |
| GO:0071706 | tumor necrosis factor superfamily cytokine production | 9/301 | 236/20870 | 0.00749384932500513 | 0.0989198821159 | 0.0825512232055 | IL23A||OAS2||IL1A||CLU||IL6||TLR4||ADAM8||PTAFR||ORM1 | 9 | 6.623338 | 6.655584 | 6.666197 | 6.605558 | 6.629118 | 6.631928 | 6.626596 | 6.669656 | 6.653089 | 6.658259 | 6.641188 | 6.659852 | 6.672495 | 6.662921 | 6.669486 |
| GO:1903555 | regulation of tumor necrosis factor superfamily cytokine production | 9/301 | 236/20870 | 0.00749384932500513 | 0.0989198821159 | 0.0825512232055 | IL23A||OAS2||IL1A||CLU||IL6||TLR4||ADAM8||PTAFR||ORM1 | 9 | 6.623338 | 6.655584 | 6.666197 | 6.605558 | 6.629118 | 6.631928 | 6.626596 | 6.669656 | 6.653089 | 6.658259 | 6.641188 | 6.659852 | 6.672495 | 6.662921 | 6.669486 |
| GO:0031294 | lymphocyte costimulation | 4/301 | 54/20870 | 0.00761698726997544 | 0.0989198821159 | 0.0825512232055 | CCR7||TNFRSF14||PDCD1LG2||KLRK1 | 4 | 7.140886 | 8.269096 | 8.424221 | 7.074672 | 7.184157 | 7.101248 | 7.199566 | 8.268206 | 8.201557 | 8.285662 | 8.318454 | 8.373094 | 8.426261 | 8.462759 | 8.433327 |
| GO:0060337 | type I interferon signaling pathway | 4/301 | 54/20870 | 0.00761698726997544 | 0.0989198821159 | 0.0825512232055 | OAS2||IRF7||IFITM1||ISG15 | 4 | 6.237278 | 6.348637 | 6.435985 | 6.298176 | 6.215299 | 6.248825 | 6.184335 | 6.339735 | 6.349227 | 6.366194 | 6.339225 | 6.409050 | 6.471871 | 6.430557 | 6.431744 |
| GO:0001933 | negative regulation of protein phosphorylation | 12/301 | 369/20870 | 0.00762049537089578 | 0.0989198821159 | 0.0825512232055 | LRP6||PMEPA1||MAS1||SH3BP5||SLIT2||SPRED1||PIP5KL1||SOCS4||SLC8A1||SOCS3||ENPP1||INPP5F | 12 | 6.032821 | 6.185601 | 6.203968 | 6.023701 | 6.027057 | 6.048531 | 6.031868 | 6.188358 | 6.203869 | 6.188428 | 6.161424 | 6.214267 | 6.205364 | 6.196930 | 6.199249 |
| GO:0032479 | regulation of type I interferon production | 6/301 | 119/20870 | 0.00763484197630800 | 0.0989198821159 | 0.0825512232055 | OAS2||POLR3G||TLR4||IRF7||ISG15||TLR7 | 6 | 5.820879 | 6.047074 | 6.020074 | 5.870738 | 5.812729 | 5.807165 | 5.791631 | 6.033579 | 6.045094 | 6.064807 | 6.044639 | 6.001747 | 6.013553 | 6.063236 | 6.000851 |
| GO:0032606 | type I interferon production | 6/301 | 119/20870 | 0.00763484197630800 | 0.0989198821159 | 0.0825512232055 | OAS2||POLR3G||TLR4||IRF7||ISG15||TLR7 | 6 | 5.820879 | 6.047074 | 6.020074 | 5.870738 | 5.812729 | 5.807165 | 5.791631 | 6.033579 | 6.045094 | 6.064807 | 6.044639 | 6.001747 | 6.013553 | 6.063236 | 6.000851 |
| GO:0061387 | regulation of extent of cell growth | 6/301 | 119/20870 | 0.00763484197630800 | 0.0989198821159 | 0.0825512232055 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 6 | 6.998047 | 7.645060 | 7.641992 | 6.997533 | 6.994287 | 7.014953 | 6.985255 | 7.655425 | 7.644677 | 7.634411 | 7.645649 | 7.662612 | 7.647682 | 7.629857 | 7.627536 |
| GO:0043491 | protein kinase B signaling | 9/301 | 237/20870 | 0.00769424761204816 | 0.0993561539469 | 0.0829153034342 | TYRO3||OSM||MEIS3||CCR7||ADAM8||IGF2||HPSE||C1QTNF1||INPP5F | 9 | 6.531937 | 6.920281 | 7.110546 | 6.527215 | 6.523383 | 6.547952 | 6.529075 | 6.926434 | 6.926391 | 6.917007 | 6.911234 | 7.113213 | 7.120200 | 7.104037 | 7.104672 |
| GO:0042310 | vasoconstriction | 5/301 | 85/20870 | 0.00774403782294205 | 0.0996657667813 | 0.0831736834247 | ECE1||MKKS||CHRM3||EDNRA||SLC8A1 | 5 | 5.277312 | 5.527799 | 5.566753 | 5.320757 | 5.187545 | 5.243857 | 5.351372 | 5.525931 | 5.470767 | 5.463842 | 5.643387 | 5.589394 | 5.549933 | 5.482525 | 5.640550 |
| GO:0010720 | positive regulation of cell development | 11/301 | 325/20870 | 0.00785321387080048 | 0.1007350789208 | 0.0840660523117 | CDKL3||CDKL5||UNC13D||VEGFA||RREB1||LIF||IL6||BIN1||SLIT2||CHODL||GPRASP2 | 11 | 6.292204 | 6.499254 | 6.542211 | 6.289023 | 6.288810 | 6.324698 | 6.265668 | 6.498342 | 6.500440 | 6.487930 | 6.510215 | 6.560122 | 6.550220 | 6.533349 | 6.524887 |
| GO:0044106 | cellular amine metabolic process | 6/301 | 120/20870 | 0.00794205470459591 | 0.1015373285247 | 0.0847355505429 | TGFB2||IDO1||SLC7A11||NR4A2||GDPD1||LY6E | 6 | 6.846936 | 6.792147 | 6.946265 | 6.845360 | 6.847323 | 6.839843 | 6.855179 | 6.814648 | 6.792113 | 6.782138 | 6.779424 | 6.933505 | 6.958050 | 6.947467 | 6.945934 |
| GO:0007548 | sex differentiation | 10/301 | 282/20870 | 0.00809703721885150 | 0.1024316604866 | 0.0854818939052 | MAMLD1||TYRO3||TGFB2||VEGFA||TNFSF10||MKKS||MAS1||SLIT2||BMP6||SCX | 10 | 5.842749 | 5.751393 | 5.767538 | 5.847254 | 5.816638 | 5.838435 | 5.868195 | 5.717385 | 5.750213 | 5.748075 | 5.789003 | 5.759230 | 5.772116 | 5.754949 | 5.783679 |
| GO:0048545 | response to steroid hormone | 12/301 | 372/20870 | 0.00809923200705491 | 0.1024316604866 | 0.0854818939052 | NR1H3||TGFB2||PADI2||NR4A3||PMEPA1||IL6||IL1RN||SLIT2||BMP6||PTAFR||SSTR2||AQP1 | 12 | 7.413369 | 7.678497 | 7.704299 | 7.384395 | 7.402589 | 7.411168 | 7.454405 | 7.682874 | 7.672130 | 7.669086 | 7.689804 | 7.708122 | 7.692169 | 7.708356 | 7.708482 |
| GO:0002360 | T cell lineage commitment | 3/301 | 29/20870 | 0.00822424624471456 | 0.1024316604866 | 0.0854818939052 | IL23A||TNFSF18||IL6 | 3 | 6.460342 | 6.873947 | 7.197048 | 6.482032 | 6.465240 | 6.441129 | 6.452646 | 6.880702 | 6.869882 | 6.865632 | 6.879516 | 7.189817 | 7.202311 | 7.182359 | 7.213511 |
| GO:0010714 | positive regulation of collagen metabolic process | 3/301 | 29/20870 | 0.00822424624471456 | 0.1024316604866 | 0.0854818939052 | CREB3L1||SERPINB7||SCX | 3 | 5.933869 | 6.442770 | 6.534131 | 5.949398 | 5.910616 | 5.928630 | 5.946497 | 6.457392 | 6.389175 | 6.475128 | 6.447954 | 6.550116 | 6.547580 | 6.524288 | 6.514217 |
| GO:0021602 | cranial nerve morphogenesis | 3/301 | 29/20870 | 0.00822424624471456 | 0.1024316604866 | 0.0854818939052 | SEMA3F||ATP8B1||TFAP2A | 3 | 5.772104 | 5.528216 | 5.450904 | 5.740605 | 5.742866 | 5.742486 | 5.858859 | 5.564805 | 5.523246 | 5.505467 | 5.518659 | 5.412006 | 5.295725 | 5.576371 | 5.504323 |
| GO:0048843 | negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance | 3/301 | 29/20870 | 0.00822424624471456 | 0.1024316604866 | 0.0854818939052 | SEMA3F||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 3 | 3.512774 | 4.317263 | 4.629599 | 3.490920 | 3.610737 | 3.517096 | 3.426223 | 4.233298 | 4.324978 | 4.269763 | 4.433049 | 4.772307 | 4.481396 | 4.729512 | 4.512347 |
| GO:0072539 | T-helper 17 cell differentiation | 3/301 | 29/20870 | 0.00822424624471456 | 0.1024316604866 | 0.0854818939052 | IL23A||TNFSF18||IL6 | 3 | 4.408107 | 4.589005 | 5.156658 | 4.376470 | 4.470184 | 4.401870 | 4.381957 | 4.593954 | 4.585122 | 4.651677 | 4.522354 | 5.141030 | 5.165375 | 5.126043 | 5.193282 |
| GO:2000108 | positive regulation of leukocyte apoptotic process | 3/301 | 29/20870 | 0.00822424624471456 | 0.1024316604866 | 0.0854818939052 | IDO1||ZC3H8||ADAM8 | 3 | 5.726494 | 6.686068 | 7.156592 | 5.754002 | 5.689027 | 5.723925 | 5.738223 | 6.718949 | 6.709617 | 6.642206 | 6.672203 | 7.220066 | 7.144848 | 7.103615 | 7.155412 |
| GO:0045765 | regulation of angiogenesis | 12/301 | 374/20870 | 0.00843126778376099 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | TIE1||TGFB2||VEGFA||IL1A||C3||IL6||CREB3L1||SPRED1||CXCL10||DLL1||AQP1||PIK3R6 | 12 | 6.241914 | 6.547929 | 6.749057 | 6.233287 | 6.277729 | 6.231816 | 6.224207 | 6.528821 | 6.522943 | 6.548795 | 6.590192 | 6.745315 | 6.741261 | 6.778509 | 6.730696 |
| GO:0060562 | epithelial tube morphogenesis | 12/301 | 374/20870 | 0.00843126778376099 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | TIE1||TGFB2||ASB2||VEGFA||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||SLIT2||EDNRA||CXCL10||CSF1||DLL1 | 12 | 6.043643 | 6.103935 | 6.138692 | 6.061596 | 6.026406 | 6.029359 | 6.056865 | 6.091754 | 6.085899 | 6.102954 | 6.134643 | 6.162185 | 6.120738 | 6.129919 | 6.141592 |
| GO:0014031 | mesenchymal cell development | 5/301 | 87/20870 | 0.00852391999298912 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | SEMA3F||HEY2||EDNRA||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 5 | 4.951853 | 4.960999 | 4.987290 | 4.913891 | 4.989334 | 4.942070 | 4.961067 | 4.960549 | 4.939404 | 4.978718 | 4.965049 | 5.030476 | 5.008902 | 4.936475 | 4.971523 |
| GO:0008637 | apoptotic mitochondrial changes | 6/301 | 122/20870 | 0.00858301395268236 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | GCLC||IFIT2||CLU||TNFSF10||IFI6||CIDEB | 6 | 6.114069 | 6.998558 | 7.360316 | 6.105665 | 6.125233 | 6.106194 | 6.119083 | 7.024271 | 7.011843 | 6.993955 | 6.963440 | 7.345750 | 7.374286 | 7.359422 | 7.361664 |
| GO:0016081 | synaptic vesicle docking | 2/301 | 10/20870 | 0.00864304963946163 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | UNC13A||UNC13C | 2 | 3.592442 | 3.498035 | 3.612353 | 3.640979 | 3.569370 | 3.519188 | 3.636706 | 3.590346 | 3.482693 | 3.413469 | 3.500100 | 3.673726 | 3.679501 | 3.595470 | 3.492891 |
| GO:0033089 | positive regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus | 2/301 | 10/20870 | 0.00864304963946163 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | ADAM8||EGR3 | 2 | 4.409996 | 3.082641 | 3.339208 | 4.497600 | 4.300710 | 4.442518 | 4.391924 | 2.920665 | 3.292864 | 3.001452 | 3.088479 | 2.970012 | 3.080219 | 2.967496 | 4.032748 |
| GO:0045835 | negative regulation of meiotic nuclear division | 2/301 | 10/20870 | 0.00864304963946163 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | LIF||FBXO43 | 2 | 4.748253 | 4.857877 | 4.768262 | 4.648292 | 4.621431 | 5.074612 | 4.591836 | 4.932748 | 4.781659 | 4.866276 | 4.846805 | 4.545753 | 4.827949 | 4.683584 | 4.979511 |
| GO:0060947 | cardiac vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation | 2/301 | 10/20870 | 0.00864304963946163 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | VEGFA||HEY2 | 2 | 4.863570 | 5.701231 | 6.151092 | 4.891895 | 4.831732 | 4.908608 | 4.820055 | 5.643008 | 5.657970 | 5.730658 | 5.769543 | 6.161287 | 6.224036 | 6.089312 | 6.126305 |
| GO:0071281 | cellular response to iron ion | 2/301 | 10/20870 | 0.00864304963946163 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | TFAP2A||BMP6 | 2 | 9.488357 | 9.068959 | 9.092545 | 9.502985 | 9.473376 | 9.483463 | 9.493435 | 9.079404 | 9.076589 | 9.044637 | 9.074930 | 9.090774 | 9.094934 | 9.091229 | 9.093237 |
| GO:0097084 | vascular associated smooth muscle cell development | 2/301 | 10/20870 | 0.00864304963946163 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | VEGFA||HEY2 | 2 | 5.210167 | 5.754698 | 5.937543 | 5.206678 | 5.206845 | 5.208860 | 5.218254 | 5.728780 | 5.739434 | 5.785613 | 5.764287 | 5.959158 | 5.971040 | 5.913348 | 5.905518 |
| GO:0097278 | complement-dependent cytotoxicity | 2/301 | 10/20870 | 0.00864304963946163 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | CFH||C3 | 2 | 7.286853 | 7.918877 | 7.924676 | 7.298795 | 7.285132 | 7.256197 | 7.306777 | 7.883250 | 7.930751 | 7.945631 | 7.915136 | 7.960092 | 7.914987 | 7.916189 | 7.906830 |
| GO:2001225 | regulation of chloride transport | 2/301 | 10/20870 | 0.00864304963946163 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | ATP8B1||PTAFR | 2 | 3.307272 | 2.791255 | 3.973161 | 3.012530 | 3.010547 | 2.629133 | 4.111087 | 2.758005 | 2.710393 | 2.900521 | 2.789252 | 3.316844 | 2.769270 | 4.251171 | 4.754629 |
| GO:0003229 | ventricular cardiac muscle tissue development | 4/301 | 56/20870 | 0.00865071073011745 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | TGFB2||HEY2||POU4F1||LY6E | 4 | 5.866863 | 6.236064 | 6.235325 | 5.879959 | 5.875995 | 5.851176 | 5.860134 | 6.251604 | 6.216615 | 6.235519 | 6.240296 | 6.247827 | 6.239149 | 6.233869 | 6.220315 |
| GO:0003158 | endothelium development | 7/301 | 160/20870 | 0.00868681785352694 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | TIE1||VEGFA||HEY2||BMP6||CXCL10||S1PR1||DLL1 | 7 | 6.124621 | 6.380350 | 6.538615 | 6.128285 | 6.122771 | 6.131186 | 6.116196 | 6.396850 | 6.369503 | 6.370766 | 6.384110 | 6.535534 | 6.543536 | 6.539911 | 6.535465 |
| GO:1902107 | positive regulation of leukocyte differentiation | 8/301 | 200/20870 | 0.00870737221549391 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | IL23A||LIF||ADAM8||POU4F1||EGR3||CSF1||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 8 | 6.476182 | 6.507712 | 6.540292 | 6.477799 | 6.466920 | 6.492485 | 6.467374 | 6.499225 | 6.495061 | 6.523395 | 6.512994 | 6.533800 | 6.543618 | 6.543405 | 6.540323 |
| GO:1903708 | positive regulation of hemopoiesis | 8/301 | 200/20870 | 0.00870737221549391 | 0.1031262703191 | 0.0860615639381 | IL23A||LIF||ADAM8||POU4F1||EGR3||CSF1||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 8 | 6.476182 | 6.507712 | 6.540292 | 6.477799 | 6.466920 | 6.492485 | 6.467374 | 6.499225 | 6.495061 | 6.523395 | 6.512994 | 6.533800 | 6.543618 | 6.543405 | 6.540323 |
| GO:0031346 | positive regulation of cell projection organization | 12/301 | 376/20870 | 0.00877386206676026 | 0.1035959677057 | 0.0864535386652 | CDKL3||CDKL5||SCARF1||RIPOR2||VEGFA||TRIM67||RREB1||CCR7||SLIT2||ANKRD1||CHODL||GPRASP2 | 12 | 6.097707 | 6.118417 | 6.121833 | 6.074718 | 6.097595 | 6.123565 | 6.094532 | 6.103200 | 6.126920 | 6.116917 | 6.126502 | 6.129474 | 6.115664 | 6.128289 | 6.113837 |
| GO:0007202 | activation of phospholipase C activity | 3/301 | 30/20870 | 0.00904197544637975 | 0.1051538168629 | 0.0877536044431 | LPAR2||ITK||EDNRA | 3 | 5.350617 | 5.738821 | 5.857806 | 5.437565 | 5.266405 | 5.403341 | 5.287750 | 5.711161 | 5.718766 | 5.747347 | 5.777069 | 5.837506 | 5.877609 | 5.861390 | 5.854433 |
| GO:0040018 | positive regulation of multicellular organism growth | 3/301 | 30/20870 | 0.00904197544637975 | 0.1051538168629 | 0.0877536044431 | MKKS||IGF2||CSF1 | 3 | 6.628846 | 6.373293 | 6.551139 | 6.662429 | 6.477204 | 6.654720 | 6.710360 | 6.303844 | 6.329563 | 6.278529 | 6.562869 | 6.587956 | 6.532087 | 6.418305 | 6.655787 |
| GO:0061384 | heart trabecula morphogenesis | 3/301 | 30/20870 | 0.00904197544637975 | 0.1051538168629 | 0.0877536044431 | TGFB2||HEY2||S1PR1 | 3 | 4.785085 | 5.118994 | 5.168761 | 4.823983 | 4.780707 | 4.781156 | 4.753613 | 5.133061 | 5.103147 | 5.121656 | 5.117951 | 5.165809 | 5.173472 | 5.158116 | 5.177569 |
| GO:0090713 | immunological memory process | 3/301 | 30/20870 | 0.00904197544637975 | 0.1051538168629 | 0.0877536044431 | IL23A||TNFRSF14||HLA-DRA | 3 | 6.654950 | 6.912957 | 7.120824 | 6.669059 | 6.666988 | 6.631105 | 6.652330 | 6.903098 | 6.902138 | 6.933766 | 6.912602 | 7.119586 | 7.103230 | 7.113514 | 7.146609 |
| GO:1901623 | regulation of lymphocyte chemotaxis | 3/301 | 30/20870 | 0.00904197544637975 | 0.1051538168629 | 0.0877536044431 | PADI2||CXCL10||KLRK1 | 3 | 5.331382 | 6.806797 | 7.384849 | 5.331896 | 5.318961 | 5.369776 | 5.304067 | 6.792531 | 6.816729 | 6.794995 | 6.822694 | 7.365369 | 7.397622 | 7.380315 | 7.395856 |
| GO:0050878 | regulation of body fluid levels | 13/301 | 425/20870 | 0.00912074234810393 | 0.1052197153130 | 0.0878085984195 | NR1H3||TYRO3||OAS2||VEGFA||PRLR||CHRM3||IL6||TLR4||ENTPD1||SLC7A11||HPSE||C1QTNF1||AQP1 | 13 | 7.464846 | 7.545772 | 7.630280 | 7.466975 | 7.475555 | 7.455957 | 7.460823 | 7.540689 | 7.549589 | 7.543038 | 7.549748 | 7.626442 | 7.630149 | 7.628977 | 7.635538 |
| GO:0007015 | actin filament organization | 14/301 | 473/20870 | 0.00912816665268613 | 0.1052197153130 | 0.0878085984195 | ELMO3||RGS4||KPTN||MKKS||CCR7||MICAL2||BIN1||MYO7A||TMEFF2||SLIT2||JMY||S1PR1||NRAP||TPM2 | 14 | 7.144692 | 7.286794 | 7.233621 | 7.144469 | 7.137197 | 7.149576 | 7.147494 | 7.283421 | 7.279445 | 7.289739 | 7.294524 | 7.230421 | 7.227462 | 7.242004 | 7.234554 |
| GO:0007204 | positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration | 11/301 | 332/20870 | 0.00912939772852703 | 0.1052197153130 | 0.0878085984195 | LPAR2||LRP6||CCR7||EDNRA||CXCL10||CXCL11||S1PR1||C1QTNF1||SLC8A1||TRDN||CXCR3 | 11 | 5.949642 | 6.172375 | 6.250231 | 5.929427 | 5.942807 | 5.956690 | 5.969336 | 6.169274 | 6.169828 | 6.186256 | 6.164045 | 6.235167 | 6.273623 | 6.258018 | 6.233730 |
| GO:1901342 | regulation of vasculature development | 12/301 | 380/20870 | 0.00949161061381100 | 0.1090687755355 | 0.0910207396268 | TIE1||TGFB2||VEGFA||IL1A||C3||IL6||CREB3L1||SPRED1||CXCL10||DLL1||AQP1||PIK3R6 | 12 | 6.251151 | 6.546064 | 6.743063 | 6.243870 | 6.284544 | 6.243184 | 6.232455 | 6.527101 | 6.519475 | 6.547566 | 6.589097 | 6.740523 | 6.734932 | 6.772518 | 6.723824 |
| GO:0007009 | plasma membrane organization | 7/301 | 163/20870 | 0.00956616483987977 | 0.1095992950943 | 0.0914634720440 | TIE1||ATP8B1||TGFB2||CLU||DYSF||BIN1||TMEFF2 | 7 | 5.611517 | 5.680128 | 5.736310 | 5.558400 | 5.600561 | 5.645620 | 5.639795 | 5.700539 | 5.680151 | 5.665461 | 5.674129 | 5.705191 | 5.725845 | 5.691364 | 5.819340 |
| GO:0009308 | amine metabolic process | 6/301 | 125/20870 | 0.00961280250720186 | 0.1098077824861 | 0.0916374602135 | TGFB2||IDO1||SLC7A11||NR4A2||GDPD1||LY6E | 6 | 6.824354 | 6.769113 | 6.923273 | 6.822559 | 6.824638 | 6.817618 | 6.832562 | 6.791564 | 6.769068 | 6.759167 | 6.756386 | 6.910484 | 6.935003 | 6.924600 | 6.922901 |
| GO:0010518 | positive regulation of phospholipase activity | 4/301 | 58/20870 | 0.00977206908919670 | 0.1109704669217 | 0.0926077507184 | LPAR2||ITK||EDNRA||PTAFR | 4 | 5.654528 | 6.402815 | 6.730213 | 5.637712 | 5.642591 | 5.671074 | 5.666443 | 6.437836 | 6.396792 | 6.397820 | 6.378151 | 6.705741 | 6.742404 | 6.721011 | 6.751253 |
| GO:0035904 | aorta development | 4/301 | 58/20870 | 0.00977206908919670 | 0.1109704669217 | 0.0926077507184 | MYLK||TGFB2||TBX2||HEY2 | 4 | 4.759324 | 5.018253 | 5.000822 | 4.758823 | 4.776335 | 4.720913 | 4.780460 | 4.998626 | 5.008266 | 5.038438 | 5.027345 | 5.012656 | 5.041039 | 4.950551 | 4.997558 |
| GO:0051384 | response to glucocorticoid | 7/301 | 164/20870 | 0.00987324469817922 | 0.1117906093245 | 0.0932921809573 | IL6||IL1RN||SLIT2||BMP6||PTAFR||SSTR2||AQP1 | 7 | 7.619938 | 7.828363 | 7.895639 | 7.633119 | 7.625653 | 7.596398 | 7.624311 | 7.842042 | 7.797235 | 7.830745 | 7.842955 | 7.899900 | 7.885457 | 7.902971 | 7.894168 |
| GO:0033028 | myeloid cell apoptotic process | 3/301 | 31/20870 | 0.00990558560167553 | 0.1118288479768 | 0.0933240921106 | IL6||SLC7A11||IRF7 | 3 | 6.148633 | 6.691604 | 6.992364 | 6.130028 | 6.117230 | 6.191454 | 6.154708 | 6.696317 | 6.685662 | 6.657639 | 6.725967 | 7.074373 | 6.938500 | 6.966499 | 6.986473 |
| GO:1904892 | regulation of receptor signaling pathway via STAT | 6/301 | 126/20870 | 0.00997482397425168 | 0.1122822022291 | 0.0937024280656 | IL23A||PRLR||LIF||IL6||SOCS3||INPP5F | 6 | 5.755691 | 6.348644 | 6.508979 | 5.693925 | 5.897862 | 5.711779 | 5.709251 | 6.220946 | 6.342780 | 6.396299 | 6.426137 | 6.480404 | 6.495562 | 6.585954 | 6.471071 |
| GO:0007368 | determination of left/right symmetry | 6/301 | 127/20870 | 0.01034644396650773 | 0.1133376338071 | 0.0945832132618 | ASB2||DNAH11||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||DLL1 | 6 | 5.415775 | 4.967452 | 5.042614 | 5.476083 | 5.269347 | 5.380653 | 5.523967 | 4.943573 | 4.883474 | 4.923987 | 5.108417 | 5.240786 | 4.834982 | 4.994725 | 5.070404 |
| GO:0070228 | regulation of lymphocyte apoptotic process | 4/301 | 59/20870 | 0.01036645903784080 | 0.1133376338071 | 0.0945832132618 | IDO1||ZC3H8||ADAM8||CD3G | 4 | 5.544875 | 6.133252 | 6.497674 | 5.545535 | 5.528978 | 5.591867 | 5.511884 | 6.155087 | 6.164207 | 6.115084 | 6.097577 | 6.455850 | 6.528250 | 6.500867 | 6.504781 |
| GO:0002695 | negative regulation of leukocyte activation | 9/301 | 249/20870 | 0.01043098925792000 | 0.1133376338071 | 0.0945832132618 | NR1H3||CST7||TYRO3||RIPOR2||TNFSF18||ZC3H8||TNFRSF14||PDCD1LG2||HLA-F | 9 | 6.328193 | 6.440371 | 6.481696 | 6.347732 | 6.323586 | 6.322018 | 6.319255 | 6.445277 | 6.453660 | 6.414817 | 6.447417 | 6.475535 | 6.484924 | 6.514777 | 6.450819 |
| GO:0001672 | regulation of chromatin assembly or disassembly | 2/301 | 11/20870 | 0.01046377281157084 | 0.1133376338071 | 0.0945832132618 | PADI2||PARP10 | 2 | 4.921322 | 4.601067 | 4.723201 | 4.874122 | 4.924749 | 5.003169 | 4.879512 | 4.662344 | 4.401605 | 4.667853 | 4.655368 | 4.611738 | 4.675031 | 4.892191 | 4.698342 |
| GO:0002885 | positive regulation of hypersensitivity | 2/301 | 11/20870 | 0.01046377281157084 | 0.1133376338071 | 0.0945832132618 | C3||CCR7 | 2 | 6.077802 | 6.365278 | 6.595825 | 6.024389 | 6.072025 | 6.097534 | 6.115635 | 6.354474 | 6.358752 | 6.441462 | 6.302994 | 6.569322 | 6.581186 | 6.564995 | 6.665447 |
| GO:0030432 | peristalsis | 2/301 | 11/20870 | 0.01046377281157084 | 0.1133376338071 | 0.0945832132618 | TBX2||SSTR2 | 2 | 2.483383 | 2.537688 | 2.732217 | 2.250199 | 2.621278 | 2.444834 | 2.588139 | 2.277204 | 2.074634 | 3.088743 | 2.500552 | 2.947316 | 2.765924 | 2.559140 | 2.625389 |
| GO:0035457 | cellular response to interferon-alpha | 2/301 | 11/20870 | 0.01046377281157084 | 0.1133376338071 | 0.0945832132618 | IFIT3||IFIT2 | 2 | 4.469842 | 4.759321 | 4.541214 | 4.446833 | 4.446099 | 4.501286 | 4.484356 | 4.787323 | 4.721969 | 4.830228 | 4.693773 | 4.586731 | 4.517597 | 4.534772 | 4.524730 |
| GO:0045607 | regulation of inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation | 2/301 | 11/20870 | 0.01046377281157084 | 0.1133376338071 | 0.0945832132618 | HEY2||DLL1 | 2 | 4.361437 | 5.125127 | 5.308614 | 4.351755 | 4.343079 | 4.425103 | 4.323748 | 5.156179 | 5.098038 | 5.118596 | 5.127089 | 5.294168 | 5.315425 | 5.289838 | 5.334580 |
| GO:0045631 | regulation of mechanoreceptor differentiation | 2/301 | 11/20870 | 0.01046377281157084 | 0.1133376338071 | 0.0945832132618 | HEY2||DLL1 | 2 | 4.361437 | 5.125127 | 5.308614 | 4.351755 | 4.343079 | 4.425103 | 4.323748 | 5.156179 | 5.098038 | 5.118596 | 5.127089 | 5.294168 | 5.315425 | 5.289838 | 5.334580 |
| GO:0070099 | regulation of chemokine-mediated signaling pathway | 2/301 | 11/20870 | 0.01046377281157084 | 0.1133376338071 | 0.0945832132618 | PADI2||SLIT2 | 2 | 6.175663 | 7.230572 | 7.839868 | 6.158017 | 6.161026 | 6.199446 | 6.183760 | 7.271520 | 7.224462 | 7.213333 | 7.212151 | 7.811287 | 7.875228 | 7.797524 | 7.873701 |
| GO:0070243 | regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process | 2/301 | 11/20870 | 0.01046377281157084 | 0.1133376338071 | 0.0945832132618 | ZC3H8||ADAM8 | 2 | 4.680568 | 4.113621 | 3.929281 | 4.858937 | 4.620095 | 4.805608 | 4.392340 | 4.149237 | 4.161020 | 4.048460 | 4.092938 | 3.914509 | 3.962191 | 3.949237 | 3.890068 |
| GO:1902667 | regulation of axon guidance | 2/301 | 11/20870 | 0.01046377281157084 | 0.1133376338071 | 0.0945832132618 | VEGFA||SLIT2 | 2 | 3.925499 | 4.963967 | 5.265940 | 4.048300 | 3.922473 | 3.817409 | 3.904328 | 4.949947 | 4.830254 | 5.024392 | 5.041778 | 5.235284 | 5.349372 | 5.277808 | 5.196836 |
| GO:2000980 | regulation of inner ear receptor cell differentiation | 2/301 | 11/20870 | 0.01046377281157084 | 0.1133376338071 | 0.0945832132618 | HEY2||DLL1 | 2 | 4.361437 | 5.125127 | 5.308614 | 4.351755 | 4.343079 | 4.425103 | 4.323748 | 5.156179 | 5.098038 | 5.118596 | 5.127089 | 5.294168 | 5.315425 | 5.289838 | 5.334580 |
| GO:0003205 | cardiac chamber development | 7/301 | 166/20870 | 0.01050890259076704 | 0.1133376338071 | 0.0945832132618 | TGFB2||DNAH11||TBX2||HEY2||SLIT2||POU4F1||LY6E | 7 | 5.338606 | 5.445219 | 5.445528 | 5.357515 | 5.324943 | 5.309298 | 5.361992 | 5.460275 | 5.387506 | 5.515555 | 5.414248 | 5.490529 | 5.447360 | 5.445716 | 5.396988 |
| GO:0007519 | skeletal muscle tissue development | 7/301 | 166/20870 | 0.01050890259076704 | 0.1133376338071 | 0.0945832132618 | ASB2||RIPOR2||ANKRD1||IGF2||MYOZ2||DLL1||SCX | 7 | 6.693825 | 6.545554 | 6.511947 | 6.544035 | 6.629085 | 6.742611 | 6.841920 | 6.560104 | 6.614256 | 6.459720 | 6.543896 | 6.565481 | 6.444976 | 6.482676 | 6.551285 |
| GO:0016485 | protein processing | 9/301 | 250/20870 | 0.01068829241800345 | 0.1149512451975 | 0.0959298140786 | CST7||CPXM1||IL1R2||ECE1||CHAC1||ADAM19||CPM||CIDEB||ADAM8 | 9 | 6.389352 | 6.652940 | 6.724117 | 6.411379 | 6.384707 | 6.369933 | 6.391080 | 6.650371 | 6.639094 | 6.651131 | 6.670981 | 6.691675 | 6.731877 | 6.727978 | 6.744406 |
| GO:0046632 | alpha-beta T cell differentiation | 6/301 | 128/20870 | 0.01072779263060761 | 0.1150381615779 | 0.0960023480664 | IL23A||ITK||TNFSF18||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA | 6 | 5.960693 | 6.116935 | 6.252125 | 5.966932 | 5.979964 | 5.936783 | 5.958753 | 6.142276 | 6.120484 | 6.094553 | 6.110010 | 6.237789 | 6.255356 | 6.272237 | 6.242874 |
| GO:0045662 | negative regulation of myoblast differentiation | 3/301 | 32/20870 | 0.01081555365262419 | 0.1150381615779 | 0.0960023480664 | ID3||CXCL10||DLL1 | 3 | 5.576500 | 6.056171 | 6.284186 | 5.518534 | 5.582155 | 5.591425 | 5.612201 | 6.072702 | 6.015200 | 6.075349 | 6.060625 | 6.296012 | 6.286627 | 6.282973 | 6.271022 |
| GO:0050927 | positive regulation of positive chemotaxis | 3/301 | 32/20870 | 0.01081555365262419 | 0.1150381615779 | 0.0960023480664 | VEGFA||S1PR1||SCG2 | 3 | 4.705163 | 6.422350 | 6.860251 | 4.685507 | 4.726485 | 4.748921 | 4.658014 | 6.459330 | 6.380799 | 6.409915 | 6.438145 | 6.890080 | 6.863274 | 6.865000 | 6.821822 |
| GO:0090022 | regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis | 3/301 | 32/20870 | 0.01081555365262419 | 0.1150381615779 | 0.0960023480664 | RIPOR2||CCR7||SLIT2 | 3 | 5.657875 | 6.926377 | 7.150540 | 5.650823 | 5.672276 | 5.665221 | 5.642994 | 6.929289 | 6.920499 | 6.940616 | 6.914971 | 7.159624 | 7.158554 | 7.155299 | 7.128457 |
| GO:0051896 | regulation of protein kinase B signaling | 8/301 | 208/20870 | 0.01087011911393003 | 0.1152023228416 | 0.0961393449252 | OSM||MEIS3||CCR7||ADAM8||IGF2||HPSE||C1QTNF1||INPP5F | 8 | 6.629042 | 6.822867 | 6.886051 | 6.626384 | 6.620877 | 6.644734 | 6.624051 | 6.826956 | 6.828922 | 6.824158 | 6.811369 | 6.893800 | 6.896096 | 6.880397 | 6.873792 |
| GO:0021700 | developmental maturation | 10/301 | 295/20870 | 0.01089268754790628 | 0.1152023228416 | 0.0961393449252 | SCARF1||TGFB2||ZDHHC2||VEGFA||BCL11A||C3||UNC13A||UNC13C||NR4A2||S1PR1 | 10 | 5.792172 | 6.000048 | 5.995976 | 5.801077 | 5.786622 | 5.799641 | 5.781250 | 6.010811 | 5.990535 | 5.990709 | 6.008014 | 5.996693 | 6.008900 | 5.984271 | 5.993934 |
| GO:0043434 | response to peptide hormone | 13/301 | 435/20870 | 0.01092519012312431 | 0.1152023228416 | 0.0961393449252 | GCLC||LRP6||NR4A3||TNFSF10||MAS1||BCAR3||STAT4||MEAK7||NR4A2||IGF2||SOCS3||GCNT1||ENPP1 | 13 | 6.293396 | 6.426687 | 6.549312 | 6.310361 | 6.281340 | 6.293198 | 6.288528 | 6.435006 | 6.438967 | 6.427164 | 6.405376 | 6.551863 | 6.555622 | 6.553167 | 6.536518 |
| GO:0050769 | positive regulation of neurogenesis | 9/301 | 251/20870 | 0.01095033734340362 | 0.1152023228416 | 0.0961393449252 | CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||LIF||IL6||BIN1||SLIT2||CHODL||GPRASP2 | 9 | 5.781910 | 6.048327 | 6.170047 | 5.775312 | 5.773312 | 5.811535 | 5.767059 | 6.039635 | 6.043923 | 6.033215 | 6.076154 | 6.188475 | 6.183910 | 6.160144 | 6.147259 |
| GO:0045661 | regulation of myoblast differentiation | 4/301 | 60/20870 | 0.01098375415733686 | 0.1152398771779 | 0.0961706849989 | RIPOR2||ID3||CXCL10||DLL1 | 4 | 6.351379 | 6.373360 | 6.336127 | 6.318799 | 6.379252 | 6.360019 | 6.346776 | 6.383493 | 6.346653 | 6.360050 | 6.402604 | 6.463813 | 6.270487 | 6.288219 | 6.313736 |
| GO:0051781 | positive regulation of cell division | 5/301 | 93/20870 | 0.01118656181783845 | 0.1167332842667 | 0.0974169721889 | TGFB2||OSM||VEGFA||IL1A||IGF2 | 5 | 7.019321 | 7.618444 | 7.709894 | 7.031930 | 7.013600 | 7.010033 | 7.021624 | 7.626105 | 7.610421 | 7.611601 | 7.625572 | 7.701833 | 7.718304 | 7.696785 | 7.722493 |
| GO:0060191 | regulation of lipase activity | 5/301 | 93/20870 | 0.01118656181783845 | 0.1167332842667 | 0.0974169721889 | NR1H3||LPAR2||ITK||EDNRA||PTAFR | 5 | 7.107701 | 7.059619 | 7.142912 | 7.116355 | 7.094994 | 7.107962 | 7.111406 | 7.091189 | 7.037806 | 7.036435 | 7.072292 | 7.117030 | 7.153981 | 7.141198 | 7.159076 |
| GO:0050708 | regulation of protein secretion | 10/301 | 297/20870 | 0.01138077125296772 | 0.1184397784574 | 0.0988410861266 | NR1H3||TGFB2||IL1A||RSAD2||IL6||TLR4||ANKRD1||FRMD4A||ADAM8||BMP6 | 10 | 5.776595 | 6.222774 | 6.411609 | 5.759477 | 5.761327 | 5.777413 | 5.807643 | 6.233172 | 6.217699 | 6.219708 | 6.220465 | 6.418706 | 6.420702 | 6.403170 | 6.403766 |
| GO:0071496 | cellular response to external stimulus | 11/301 | 343/20870 | 0.01145209642628969 | 0.1188616782309 | 0.0991931724982 | GCLC||KPTN||TLR4||MMP7||ANKRD1||BMP6||NR4A2||TLR7||AQP1||SCX||NA | 11 | 6.010418 | 6.359386 | 6.463757 | 5.997343 | 6.002017 | 6.029995 | 6.012098 | 6.360154 | 6.379479 | 6.357214 | 6.340429 | 6.446509 | 6.490006 | 6.464134 | 6.454005 |
| GO:0070555 | response to interleukin-1 | 7/301 | 169/20870 | 0.01151750367055406 | 0.1192200581019 | 0.0994922498534 | GCLC||RPS6KA5||CCL22||IL1R2||IL6||IL1RN||ANKRD1 | 7 | 6.311247 | 7.098280 | 7.519906 | 6.330174 | 6.289815 | 6.301860 | 6.322780 | 7.103130 | 7.096875 | 7.107489 | 7.085532 | 7.505574 | 7.528914 | 7.527140 | 7.517878 |
| GO:0043551 | regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity | 4/301 | 61/20870 | 0.01162426478159252 | 0.1192988746214 | 0.0995580242959 | CCR7||SOCS4||SOCS3||PIK3R6 | 4 | 4.839493 | 5.278227 | 5.308499 | 4.822984 | 4.868137 | 4.827871 | 4.838552 | 5.229094 | 5.342438 | 5.267642 | 5.271400 | 5.258580 | 5.332636 | 5.380040 | 5.259043 |
| GO:0003180 | aortic valve morphogenesis | 3/301 | 33/20870 | 0.01177230542107212 | 0.1192988746214 | 0.0995580242959 | TIE1||HEY2||SLIT2 | 3 | 5.108734 | 5.699616 | 5.808454 | 5.045122 | 5.162383 | 5.097198 | 5.127670 | 5.707703 | 5.632935 | 5.741700 | 5.713896 | 5.848400 | 5.851474 | 5.761557 | 5.769914 |
| GO:0030201 | heparan sulfate proteoglycan metabolic process | 3/301 | 33/20870 | 0.01177230542107212 | 0.1192988746214 | 0.0995580242959 | DSE||HPSE||SULF2 | 3 | 4.820642 | 4.860302 | 4.795973 | 4.833371 | 4.758463 | 4.878271 | 4.809878 | 4.831572 | 4.774981 | 4.805486 | 5.016600 | 4.791528 | 4.793805 | 4.818352 | 4.779934 |
| GO:0032607 | interferon-alpha production | 3/301 | 33/20870 | 0.01177230542107212 | 0.1192988746214 | 0.0995580242959 | TLR4||IRF7||TLR7 | 3 | 5.706501 | 5.871299 | 5.780499 | 5.834586 | 5.623998 | 5.708641 | 5.649492 | 5.875132 | 5.859706 | 5.860332 | 5.889813 | 5.796241 | 5.781082 | 5.805112 | 5.738661 |
| GO:0032647 | regulation of interferon-alpha production | 3/301 | 33/20870 | 0.01177230542107212 | 0.1192988746214 | 0.0995580242959 | TLR4||IRF7||TLR7 | 3 | 5.706501 | 5.871299 | 5.780499 | 5.834586 | 5.623998 | 5.708641 | 5.649492 | 5.875132 | 5.859706 | 5.860332 | 5.889813 | 5.796241 | 5.781082 | 5.805112 | 5.738661 |
| GO:0045672 | positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation | 3/301 | 33/20870 | 0.01177230542107212 | 0.1192988746214 | 0.0995580242959 | IL23A||POU4F1||CSF1 | 3 | 7.066960 | 7.075585 | 7.078406 | 7.090333 | 7.037072 | 7.083640 | 7.056162 | 7.072660 | 7.083563 | 7.082471 | 7.063556 | 7.071790 | 7.088484 | 7.050464 | 7.102365 |
| GO:0048710 | regulation of astrocyte differentiation | 3/301 | 33/20870 | 0.01177230542107212 | 0.1192988746214 | 0.0995580242959 | LIF||IL6||BIN1 | 3 | 5.859461 | 5.572299 | 5.492805 | 5.857705 | 5.848985 | 5.856924 | 5.874115 | 5.604994 | 5.624816 | 5.491290 | 5.564501 | 5.505143 | 5.454358 | 5.494075 | 5.516881 |
| GO:0050926 | regulation of positive chemotaxis | 3/301 | 33/20870 | 0.01177230542107212 | 0.1192988746214 | 0.0995580242959 | VEGFA||S1PR1||SCG2 | 3 | 4.705163 | 6.422350 | 6.860251 | 4.685507 | 4.726485 | 4.748921 | 4.658014 | 6.459330 | 6.380799 | 6.409915 | 6.438145 | 6.890080 | 6.863274 | 6.865000 | 6.821822 |
| GO:0048592 | eye morphogenesis | 7/301 | 170/20870 | 0.01186876355006568 | 0.1199615080283 | 0.1001110091671 | VEGFA||TBX2||TFAP2A||MYO7A||BCAR3||IGFN1||DLL1 | 7 | 5.378324 | 5.428249 | 5.509259 | 5.366151 | 5.374430 | 5.358556 | 5.413534 | 5.485351 | 5.310961 | 5.553752 | 5.349409 | 5.530498 | 5.498399 | 5.534725 | 5.472526 |
| GO:0022408 | negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion | 9/301 | 255/20870 | 0.01204697513812740 | 0.1214448329199 | 0.1013488825005 | RIPOR2||VEGFA||TNFSF18||IL1RN||ZC3H8||BMP6||TNFRSF14||C1QTNF1||PDCD1LG2 | 9 | 5.997627 | 6.249814 | 6.351453 | 6.001997 | 6.008790 | 5.989227 | 5.990402 | 6.271760 | 6.250461 | 6.234724 | 6.242042 | 6.338953 | 6.357849 | 6.382736 | 6.325634 |
| GO:0008016 | regulation of heart contraction | 8/301 | 212/20870 | 0.01208962452511039 | 0.1215573965923 | 0.1014428198228 | TGFB2||DMPK||RGS4||TBX2||HEY2||BIN1||SLC8A1||TRDN | 8 | 5.763987 | 5.809291 | 5.721822 | 5.787988 | 5.753283 | 5.746787 | 5.767544 | 5.833943 | 5.764689 | 5.851899 | 5.784898 | 5.703279 | 5.747642 | 5.741431 | 5.694188 |
| GO:0043367 | CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation | 5/301 | 95/20870 | 0.01218709989216696 | 0.1222192017757 | 0.1019951135200 | IL23A||TNFSF18||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA | 5 | 5.514606 | 5.950347 | 6.203350 | 5.514968 | 5.509300 | 5.528353 | 5.505698 | 5.961070 | 5.946956 | 5.951124 | 5.942170 | 6.201356 | 6.215408 | 6.187318 | 6.209164 |
| GO:0014831 | gastro-intestinal system smooth muscle contraction | 2/301 | 12/20870 | 0.01243785954921031 | 0.1231348095372 | 0.1027592120921 | PTAFR||SULF2 | 2 | 4.001363 | 3.704619 | 3.624850 | 3.286678 | 3.237288 | 5.140430 | 3.263068 | 3.301967 | 4.527889 | 3.315872 | 3.211177 | 3.401263 | 4.282373 | 3.174644 | 3.363414 |
| GO:0042416 | dopamine biosynthetic process | 2/301 | 12/20870 | 0.01243785954921031 | 0.1231348095372 | 0.1027592120921 | TGFB2||NR4A2 | 2 | 5.920612 | 6.000821 | 5.911095 | 5.967417 | 5.916099 | 5.883791 | 5.913883 | 6.029927 | 5.982895 | 5.978048 | 6.011784 | 5.977909 | 5.856504 | 5.940806 | 5.865552 |
| GO:0060837 | blood vessel endothelial cell differentiation | 2/301 | 12/20870 | 0.01243785954921031 | 0.1231348095372 | 0.1027592120921 | HEY2||DLL1 | 2 | 4.720236 | 5.560177 | 5.716108 | 4.787642 | 4.721014 | 4.735149 | 4.632868 | 5.569405 | 5.562570 | 5.546670 | 5.561967 | 5.708879 | 5.744229 | 5.703834 | 5.707117 |
| GO:1903909 | regulation of receptor clustering | 2/301 | 12/20870 | 0.01243785954921031 | 0.1231348095372 | 0.1027592120921 | ZDHHC2||SLC7A11 | 2 | 7.600390 | 7.629509 | 7.655713 | 7.600337 | 7.608867 | 7.566503 | 7.625216 | 7.628709 | 7.613396 | 7.637584 | 7.638208 | 7.614926 | 7.631263 | 7.647368 | 7.726718 |
| GO:2000508 | regulation of dendritic cell chemotaxis | 2/301 | 12/20870 | 0.01243785954921031 | 0.1231348095372 | 0.1027592120921 | TNFSF18||CCR7 | 2 | 7.510140 | 7.693225 | 7.799136 | 7.509088 | 7.507145 | 7.524126 | 7.500093 | 7.722424 | 7.669162 | 7.689060 | 7.691750 | 7.794265 | 7.815597 | 7.798763 | 7.787770 |
| GO:0030522 | intracellular receptor signaling pathway | 10/301 | 302/20870 | 0.01267346214691001 | 0.1251463870824 | 0.1044379260511 | NR1H3||NR5A2||PADI2||NR4A3||PMEPA1||OASL||TLR4||NR4A2||SLC15A2||IRF7 | 10 | 5.952652 | 5.714175 | 5.713657 | 5.846344 | 5.906851 | 5.991911 | 6.056584 | 5.707049 | 5.776987 | 5.658098 | 5.712085 | 5.722753 | 5.670240 | 5.715672 | 5.744942 |
| GO:0010818 | T cell chemotaxis | 3/301 | 34/20870 | 0.01277621736877216 | 0.1255190210199 | 0.1047488987969 | CXCL10||CXCL11||CXCR3 | 3 | 4.907867 | 6.594400 | 7.177205 | 4.909270 | 4.844420 | 4.944955 | 4.930782 | 6.608934 | 6.606323 | 6.586649 | 6.575426 | 7.155445 | 7.196697 | 7.163180 | 7.193047 |
| GO:1902275 | regulation of chromatin organization | 3/301 | 34/20870 | 0.01277621736877216 | 0.1255190210199 | 0.1047488987969 | AICDA||PADI2||PARP10 | 3 | 5.921800 | 5.763254 | 5.909410 | 5.979939 | 5.850548 | 5.874002 | 5.977904 | 5.668893 | 5.802362 | 5.764258 | 5.813077 | 5.864377 | 5.862568 | 6.005520 | 5.900424 |
| GO:0001836 | release of cytochrome c from mitochondria | 4/301 | 63/20870 | 0.01297612067470501 | 0.1271593957488 | 0.1061178343181 | CLU||TNFSF10||IFI6||CIDEB | 4 | 6.488710 | 7.556811 | 8.006921 | 6.480954 | 6.481457 | 6.516530 | 6.475529 | 7.553293 | 7.579622 | 7.547295 | 7.546784 | 7.987190 | 8.022427 | 7.997311 | 8.020443 |
| GO:0045445 | myoblast differentiation | 5/301 | 97/20870 | 0.01324667744602242 | 0.1294820800483 | 0.1080561749827 | RIPOR2||ID3||TBX2||CXCL10||DLL1 | 5 | 7.149672 | 7.798108 | 7.936254 | 6.911815 | 7.096606 | 7.198732 | 7.355714 | 7.794604 | 7.809171 | 7.752359 | 7.835057 | 7.938778 | 7.877698 | 7.960711 | 7.966134 |
| GO:0043010 | camera-type eye development | 11/301 | 351/20870 | 0.01340712426694277 | 0.1307194616027 | 0.1090888021826 | TGFB2||SLC17A7||VEGFA||TBX2||NES||TFAP2A||BCAR3||SLC7A11||IGFN1||SPRED1||DLL1 | 11 | 5.606801 | 5.719921 | 5.757816 | 5.610993 | 5.592739 | 5.609224 | 5.614154 | 5.727138 | 5.684484 | 5.745920 | 5.721455 | 5.750711 | 5.765577 | 5.765032 | 5.749864 |
| GO:0045446 | endothelial cell differentiation | 6/301 | 135/20870 | 0.01368034904665195 | 0.1330474248593 | 0.1110315482747 | TIE1||VEGFA||HEY2||BMP6||S1PR1||DLL1 | 6 | 6.002602 | 6.331996 | 6.496598 | 6.004223 | 5.999611 | 6.013324 | 5.993175 | 6.344116 | 6.322843 | 6.325244 | 6.335681 | 6.495706 | 6.507534 | 6.497333 | 6.485735 |
| GO:0051271 | negative regulation of cellular component movement | 12/301 | 401/20870 | 0.01403828113679454 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | TIE1||RIPOR2||PADI2||BIN1||TMEFF2||SLIT2||NBL1||SPRED1||PIP5KL1||IFITM1||KLRK1||EPPK1 | 12 | 6.123294 | 6.155422 | 6.203008 | 6.105555 | 6.123014 | 6.126954 | 6.137470 | 6.145787 | 6.164423 | 6.156295 | 6.155121 | 6.213271 | 6.204057 | 6.199354 | 6.195288 |
| GO:0048708 | astrocyte differentiation | 5/301 | 99/20870 | 0.01436674415698657 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | LIF||IL6||BIN1||TLR4||DLL1 | 5 | 6.654910 | 6.405688 | 6.374199 | 6.649349 | 6.674452 | 6.653256 | 6.642384 | 6.419651 | 6.406255 | 6.393540 | 6.403185 | 6.381376 | 6.364708 | 6.374440 | 6.376223 |
| GO:0002866 | positive regulation of acute inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | C3||CCR7 | 2 | 6.330794 | 6.623816 | 6.714412 | 6.317729 | 6.326747 | 6.326106 | 6.352360 | 6.579231 | 6.572143 | 6.623293 | 6.715992 | 6.704462 | 6.668971 | 6.753568 | 6.729290 |
| GO:0003222 | ventricular trabecula myocardium morphogenesis | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 5.036119 | 5.564461 | 5.628252 | 5.068627 | 4.995246 | 5.047775 | 5.031833 | 5.576515 | 5.556433 | 5.564894 | 5.559921 | 5.627835 | 5.627186 | 5.628992 | 5.628992 |
| GO:0006534 | cysteine metabolic process | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | GCLC||SLC7A11 | 2 | 4.969490 | 4.971047 | 5.148321 | 4.943367 | 5.042348 | 4.993319 | 4.894719 | 5.007469 | 4.929318 | 4.994907 | 4.951098 | 5.278980 | 4.901471 | 5.080977 | 5.296380 |
| GO:0015816 | glycine transport | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | SLC7A8||RGS4 | 2 | 5.987676 | 5.557230 | 5.114983 | 6.013458 | 6.020522 | 5.974824 | 5.940473 | 5.511457 | 5.496058 | 5.552245 | 5.663167 | 5.024820 | 5.227848 | 5.044938 | 5.152858 |
| GO:0030157 | pancreatic juice secretion | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | NR1H3||AQP1 | 2 | 5.111559 | 5.108982 | 5.132382 | 5.164079 | 5.055607 | 5.109995 | 5.114510 | 4.990209 | 5.230904 | 4.999372 | 5.198490 | 5.040948 | 5.118656 | 5.153112 | 5.211548 |
| GO:0035745 | T-helper 2 cell cytokine production | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | RSAD2||IL6 | 2 | 7.384511 | 7.593189 | 7.620703 | 7.414393 | 7.391483 | 7.363180 | 7.368414 | 7.576706 | 7.590089 | 7.615629 | 7.590056 | 7.606482 | 7.596647 | 7.630359 | 7.648746 |
| GO:0036005 | response to macrophage colony-stimulating factor | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | TLR4||CSF1 | 2 | 6.017217 | 6.418859 | 6.472419 | 5.995139 | 6.003751 | 6.034405 | 6.035129 | 6.383415 | 6.555065 | 6.389356 | 6.338008 | 6.478535 | 6.461813 | 6.473140 | 6.476130 |
| GO:0036006 | cellular response to macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | TLR4||CSF1 | 2 | 6.017217 | 6.418859 | 6.472419 | 5.995139 | 6.003751 | 6.034405 | 6.035129 | 6.383415 | 6.555065 | 6.389356 | 6.338008 | 6.478535 | 6.461813 | 6.473140 | 6.476130 |
| GO:0046541 | saliva secretion | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | CHRM3||AQP1 | 2 | 6.187316 | 6.758237 | 6.970669 | 6.172806 | 6.215669 | 6.232041 | 6.126426 | 6.782755 | 6.770143 | 6.725034 | 6.754372 | 6.991749 | 6.937778 | 6.955572 | 6.996733 |
| GO:0048711 | positive regulation of astrocyte differentiation | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | LIF||BIN1 | 2 | 5.716237 | 5.719620 | 5.629212 | 5.727846 | 5.715190 | 5.678929 | 5.742223 | 5.623103 | 5.889203 | 5.633758 | 5.716380 | 5.655496 | 5.585228 | 5.648686 | 5.626398 |
| GO:0060700 | regulation of ribonuclease activity | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | OAS2||OASL | 2 | 7.078992 | 7.581162 | 7.521373 | 7.099133 | 7.035404 | 7.095132 | 7.085401 | 7.532875 | 7.652926 | 7.614527 | 7.520041 | 7.619440 | 7.486111 | 7.393660 | 7.575912 |
| GO:0060707 | trophoblast giant cell differentiation | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | LIF||SOCS3 | 2 | 3.441462 | 3.737264 | 3.881472 | 3.516572 | 3.451411 | 3.437059 | 3.356310 | 3.762400 | 3.730474 | 3.635240 | 3.815046 | 3.941876 | 3.874712 | 3.885121 | 3.821651 |
| GO:0061517 | macrophage proliferation | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | CLU||CSF1 | 2 | 6.608427 | 6.802642 | 6.890634 | 6.634378 | 6.574467 | 6.568948 | 6.654020 | 6.850114 | 6.785052 | 6.815040 | 6.758749 | 6.893882 | 6.878792 | 6.864188 | 6.924972 |
| GO:0072578 | neurotransmitter-gated ion channel clustering | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | ZDHHC2||SLC7A11 | 2 | 4.714759 | 4.314225 | 4.704366 | 4.672997 | 4.665376 | 4.704707 | 4.811192 | 4.414688 | 4.327009 | 4.310057 | 4.196855 | 4.697985 | 4.683090 | 4.709727 | 4.726317 |
| GO:1902510 | regulation of apoptotic DNA fragmentation | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | IL6||ST20 | 2 | 5.318935 | 5.253731 | 5.637551 | 5.195802 | 5.081997 | 5.561084 | 5.390026 | 5.252749 | 5.237537 | 5.281048 | 5.243202 | 5.747114 | 5.595242 | 5.585020 | 5.616852 |
| GO:2000551 | regulation of T-helper 2 cell cytokine production | 2/301 | 13/20870 | 0.01456053753136478 | 0.1354656274906 | 0.1130496014800 | RSAD2||IL6 | 2 | 7.384511 | 7.593189 | 7.620703 | 7.414393 | 7.391483 | 7.363180 | 7.368414 | 7.576706 | 7.590089 | 7.615629 | 7.590056 | 7.606482 | 7.596647 | 7.630359 | 7.648746 |
| GO:0002446 | neutrophil mediated immunity | 3/301 | 36/20870 | 0.01492679109259985 | 0.1368983656755 | 0.1142452588865 | TREM1||IL6||PTAFR | 3 | 7.756670 | 7.455149 | 7.634470 | 7.764936 | 7.759732 | 7.753660 | 7.748296 | 7.446537 | 7.455955 | 7.460575 | 7.457492 | 7.661153 | 7.636089 | 7.630109 | 7.610069 |
| GO:0003203 | endocardial cushion morphogenesis | 3/301 | 36/20870 | 0.01492679109259985 | 0.1368983656755 | 0.1142452588865 | TGFB2||TBX2||HEY2 | 3 | 4.760307 | 4.927568 | 4.917483 | 4.800012 | 4.764867 | 4.705326 | 4.769400 | 4.937409 | 4.909663 | 4.944056 | 4.918878 | 4.920211 | 4.964772 | 4.887404 | 4.896291 |
| GO:0031076 | embryonic camera-type eye development | 3/301 | 36/20870 | 0.01492679109259985 | 0.1368983656755 | 0.1142452588865 | TBX2||NES||TFAP2A | 3 | 5.456846 | 4.679160 | 4.340685 | 5.406306 | 5.402027 | 5.405088 | 5.603437 | 4.677701 | 4.713668 | 4.766357 | 4.550213 | 4.339583 | 4.428482 | 4.318324 | 4.271832 |
| GO:0036336 | dendritic cell migration | 3/301 | 36/20870 | 0.01492679109259985 | 0.1368983656755 | 0.1142452588865 | ASB2||TNFSF18||CCR7 | 3 | 6.839967 | 7.249036 | 7.515725 | 6.811613 | 6.814524 | 6.822957 | 6.908519 | 7.271495 | 7.242459 | 7.236448 | 7.245492 | 7.479034 | 7.585764 | 7.487057 | 7.508555 |
| GO:2000047 | regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin | 3/301 | 36/20870 | 0.01492679109259985 | 0.1368983656755 | 0.1142452588865 | VEGFA||ADAM19||BMP6 | 3 | 5.024370 | 5.064677 | 5.299132 | 5.080467 | 4.930406 | 5.012998 | 5.068776 | 5.056304 | 4.998871 | 5.114176 | 5.086826 | 5.327222 | 5.302820 | 5.263137 | 5.302621 |
| GO:0019915 | lipid storage | 5/301 | 100/20870 | 0.01494989913147221 | 0.1368983656755 | 0.1142452588865 | NR1H3||C3||B4GALNT1||IL6||ENPP1 | 5 | 5.965100 | 6.365150 | 6.586501 | 5.950311 | 5.979635 | 5.978623 | 5.951554 | 6.350357 | 6.397070 | 6.364029 | 6.348617 | 6.588130 | 6.576995 | 6.609362 | 6.571222 |
| GO:0060538 | skeletal muscle organ development | 7/301 | 178/20870 | 0.01496273253433486 | 0.1368983656755 | 0.1142452588865 | ASB2||RIPOR2||ANKRD1||IGF2||MYOZ2||DLL1||SCX | 7 | 6.641308 | 6.495251 | 6.465115 | 6.493755 | 6.581579 | 6.687975 | 6.785223 | 6.510618 | 6.562671 | 6.411110 | 6.492514 | 6.516309 | 6.402019 | 6.435732 | 6.503312 |
| GO:0071347 | cellular response to interleukin-1 | 6/301 | 138/20870 | 0.01510422235574642 | 0.1378661998003 | 0.1150529417219 | RPS6KA5||CCL22||IL1R2||IL6||IL1RN||ANKRD1 | 6 | 5.834284 | 6.978052 | 7.512751 | 5.907540 | 5.783254 | 5.811333 | 5.832041 | 6.983574 | 6.969931 | 6.989420 | 6.969179 | 7.498485 | 7.523174 | 7.522870 | 7.506316 |
| GO:0046854 | phosphatidylinositol phosphate biosynthetic process | 4/301 | 66/20870 | 0.01518516476602406 | 0.1379527556744 | 0.1151251748577 | PIP5KL1||SOCS4||SOCS3||PIK3R6 | 4 | 4.305245 | 4.167194 | 4.139442 | 4.391650 | 4.161720 | 4.424538 | 4.226333 | 4.143140 | 4.187534 | 4.193894 | 4.143421 | 4.194586 | 4.067117 | 4.250677 | 4.034405 |
| GO:1902475 | L-alpha-amino acid transmembrane transport | 4/301 | 66/20870 | 0.01518516476602406 | 0.1379527556744 | 0.1151251748577 | SLC7A8||SLC17A7||RGS4||SLC7A11 | 4 | 5.460095 | 5.801914 | 5.938199 | 5.442436 | 5.476058 | 5.477166 | 5.444337 | 5.809077 | 5.792097 | 5.807571 | 5.798845 | 5.920312 | 5.953682 | 5.951435 | 5.927071 |
| GO:0048771 | tissue remodeling | 7/301 | 179/20870 | 0.01538627454463501 | 0.1394516573165 | 0.1163760473959 | TIE1||IL23A||IL1A||LIF||IL6||ADAM8||S1PR1 | 7 | 7.257516 | 7.662479 | 7.735965 | 7.264963 | 7.257025 | 7.251685 | 7.256362 | 7.665469 | 7.644148 | 7.669264 | 7.670875 | 7.745964 | 7.736032 | 7.728981 | 7.732828 |
| GO:0019722 | calcium-mediated signaling | 8/301 | 222/20870 | 0.01557560041176308 | 0.1404077468412 | 0.1171739290560 | DMPK||NR5A2||CCR7||CHRM3||MCTP2||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||CXCR3 | 8 | 5.734995 | 6.117778 | 6.221294 | 5.708578 | 5.729865 | 5.761733 | 5.739298 | 6.131472 | 6.144581 | 6.113712 | 6.080549 | 6.250285 | 6.245799 | 6.198037 | 6.190029 |
| GO:0002720 | positive regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response | 6/301 | 139/20870 | 0.01560086076013090 | 0.1404077468412 | 0.1171739290560 | NR4A3||RSAD2||IL6||TLR4||TNFRSF14||HLA-F | 6 | 7.615110 | 7.716009 | 7.866412 | 7.616677 | 7.609552 | 7.613838 | 7.620351 | 7.722717 | 7.719775 | 7.707229 | 7.714268 | 7.865143 | 7.872912 | 7.865184 | 7.862387 |
| GO:0048593 | camera-type eye morphogenesis | 6/301 | 139/20870 | 0.01560086076013090 | 0.1404077468412 | 0.1171739290560 | VEGFA||TBX2||TFAP2A||BCAR3||IGFN1||DLL1 | 6 | 5.571101 | 5.591617 | 5.711624 | 5.565207 | 5.552275 | 5.557487 | 5.608743 | 5.616937 | 5.543560 | 5.621805 | 5.582807 | 5.679022 | 5.743201 | 5.731478 | 5.691807 |
| GO:0045580 | regulation of T cell differentiation | 7/301 | 180/20870 | 0.01581827901077845 | 0.1411911616019 | 0.1178277091191 | IL23A||TNFSF18||ZC3H8||ADAM8||EGR3||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 7 | 5.532778 | 5.688226 | 5.756855 | 5.541451 | 5.533799 | 5.545502 | 5.510100 | 5.702672 | 5.698218 | 5.681258 | 5.670526 | 5.745249 | 5.740396 | 5.794564 | 5.746536 |
| GO:1903034 | regulation of response to wounding | 7/301 | 180/20870 | 0.01581827901077845 | 0.1411911616019 | 0.1178277091191 | MYLK||SCARF1||RREB1||HPSE||C1QTNF1||INPP5F||EPPK1 | 7 | 7.273095 | 7.787198 | 7.772440 | 7.267360 | 7.282083 | 7.272867 | 7.270028 | 7.801719 | 7.772782 | 7.783383 | 7.790756 | 7.760881 | 7.774495 | 7.764897 | 7.789321 |
| GO:0030239 | myofibril assembly | 4/301 | 67/20870 | 0.01597088620001647 | 0.1411911616019 | 0.1178277091191 | ANKRD1||OBSCN||MYOZ2||NRAP | 4 | 6.778187 | 6.876137 | 6.824193 | 6.785224 | 6.779287 | 6.781045 | 6.767129 | 6.869478 | 6.860861 | 6.888067 | 6.885965 | 6.814770 | 6.837337 | 6.819151 | 6.825416 |
| GO:0043030 | regulation of macrophage activation | 4/301 | 67/20870 | 0.01597088620001647 | 0.1411911616019 | 0.1178277091191 | NR1H3||CST7||IL6||TLR4 | 4 | 6.826871 | 6.910631 | 6.972444 | 6.836861 | 6.832736 | 6.819810 | 6.817988 | 6.940540 | 6.893155 | 6.899220 | 6.909147 | 6.965988 | 6.977021 | 6.970941 | 6.975800 |
| GO:0050732 | negative regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | 4/301 | 67/20870 | 0.01597088620001647 | 0.1411911616019 | 0.1178277091191 | SH3BP5||SOCS4||SOCS3||INPP5F | 4 | 5.825950 | 6.054918 | 5.998604 | 5.810060 | 5.800193 | 5.873303 | 5.819126 | 6.022210 | 6.116683 | 6.035903 | 6.042994 | 6.000089 | 6.038332 | 5.999082 | 5.955728 |
| GO:0060113 | inner ear receptor cell differentiation | 4/301 | 67/20870 | 0.01597088620001647 | 0.1411911616019 | 0.1178277091191 | ATP8B1||HEY2||MYO7A||DLL1 | 4 | 4.613679 | 4.347960 | 4.439539 | 4.646341 | 4.585500 | 4.636770 | 4.584991 | 4.382407 | 4.305556 | 4.350497 | 4.352338 | 4.418870 | 4.398090 | 4.459455 | 4.480287 |
| GO:0032693 | negative regulation of interleukin-10 production | 3/301 | 37/20870 | 0.01607397420379369 | 0.1411911616019 | 0.1178277091191 | IL23A||PDCD1LG2||DLL1 | 3 | 7.247273 | 7.426243 | 7.442423 | 7.279060 | 7.210797 | 7.264159 | 7.234106 | 7.422633 | 7.451315 | 7.426749 | 7.403876 | 7.438272 | 7.440611 | 7.434680 | 7.456037 |
| GO:0045746 | negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway | 3/301 | 37/20870 | 0.01607397420379369 | 0.1411911616019 | 0.1178277091191 | CHAC1||HEY2||DLL1 | 3 | 6.668183 | 6.603428 | 6.712447 | 6.657048 | 6.663926 | 6.692369 | 6.659109 | 6.601699 | 6.589488 | 6.628369 | 6.593841 | 6.688667 | 6.731463 | 6.731701 | 6.697429 |
| GO:0070232 | regulation of T cell apoptotic process | 3/301 | 37/20870 | 0.01607397420379369 | 0.1411911616019 | 0.1178277091191 | IDO1||ZC3H8||ADAM8 | 3 | 5.700496 | 6.391441 | 6.812858 | 5.708519 | 5.673758 | 5.744110 | 5.674428 | 6.432610 | 6.404112 | 6.383796 | 6.343800 | 6.783967 | 6.842572 | 6.795109 | 6.828991 |
| GO:2000406 | positive regulation of T cell migration | 3/301 | 37/20870 | 0.01607397420379369 | 0.1411911616019 | 0.1178277091191 | ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10 | 3 | 6.333148 | 6.905518 | 7.250680 | 6.343683 | 6.304218 | 6.350565 | 6.333693 | 6.938336 | 6.897007 | 6.888448 | 6.897756 | 7.241508 | 7.265664 | 7.217649 | 7.277173 |
| GO:0002711 | positive regulation of T cell mediated immunity | 5/301 | 102/20870 | 0.01616329796115625 | 0.1411911616019 | 0.1178277091191 | IL23A||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 5 | 7.729962 | 7.750444 | 7.940777 | 7.740734 | 7.715547 | 7.731589 | 7.731861 | 7.755768 | 7.750560 | 7.743676 | 7.751745 | 7.936539 | 7.939691 | 7.937541 | 7.949300 |
| GO:0010769 | regulation of cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation | 5/301 | 102/20870 | 0.01616329796115625 | 0.1411911616019 | 0.1178277091191 | CDKL3||CDKL5||UNC13D||RREB1||GPRASP2 | 5 | 6.643695 | 6.758049 | 6.711960 | 6.630315 | 6.654560 | 6.674099 | 6.615099 | 6.740530 | 6.777198 | 6.760766 | 6.753457 | 6.732370 | 6.704856 | 6.704831 | 6.705591 |
| GO:0060840 | artery development | 5/301 | 102/20870 | 0.01616329796115625 | 0.1411911616019 | 0.1178277091191 | MYLK||TGFB2||VEGFA||TBX2||HEY2 | 5 | 5.162146 | 5.056479 | 5.066144 | 5.153565 | 5.181159 | 5.125344 | 5.187671 | 5.058045 | 5.031320 | 5.071781 | 5.064446 | 5.073533 | 5.099774 | 5.027026 | 5.063302 |
| GO:0002718 | regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response | 7/301 | 181/20870 | 0.01625882982283799 | 0.1417050608261 | 0.1182565714333 | TGFB2||NR4A3||RSAD2||IL6||TLR4||TNFRSF14||HLA-F | 7 | 7.326578 | 7.491935 | 7.648638 | 7.323246 | 7.321219 | 7.326671 | 7.335137 | 7.501182 | 7.487899 | 7.484795 | 7.493809 | 7.647032 | 7.658890 | 7.645842 | 7.642738 |
| GO:0008406 | gonad development | 8/301 | 224/20870 | 0.01635194179057726 | 0.1421956019221 | 0.1186659407799 | MAMLD1||TGFB2||VEGFA||TNFSF10||MKKS||MAS1||SLIT2||SCX | 8 | 5.998829 | 5.900595 | 5.923222 | 6.006524 | 5.973506 | 5.986564 | 6.028130 | 5.859074 | 5.907098 | 5.897382 | 5.937732 | 5.912868 | 5.925908 | 5.909040 | 5.944802 |
| GO:0032535 | regulation of cellular component size | 12/301 | 411/20870 | 0.01671427882499003 | 0.1434207179104 | 0.1196883320448 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||MKKS||CCR7||BIN1||SLIT2||JMY||SEMA3D||SEMA6B||AQP1 | 12 | 7.260839 | 7.533401 | 7.484570 | 7.261121 | 7.250393 | 7.265075 | 7.266710 | 7.536914 | 7.528452 | 7.533954 | 7.534273 | 7.492379 | 7.478632 | 7.483158 | 7.484074 |
| GO:0055002 | striated muscle cell development | 4/301 | 68/20870 | 0.01678169492472345 | 0.1434207179104 | 0.1196883320448 | ANKRD1||OBSCN||MYOZ2||NRAP | 4 | 6.738258 | 6.838879 | 6.787553 | 6.744911 | 6.739353 | 6.741805 | 6.726899 | 6.832363 | 6.823568 | 6.850925 | 6.848481 | 6.778841 | 6.800732 | 6.782278 | 6.788264 |
| GO:0062208 | positive regulation of pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway | 4/301 | 68/20870 | 0.01678169492472345 | 0.1434207179104 | 0.1196883320448 | NR1H3||RSAD2||OASL||TLR4 | 4 | 6.705381 | 6.850135 | 6.880798 | 6.658422 | 6.712091 | 6.710571 | 6.739259 | 6.846325 | 6.856172 | 6.855920 | 6.842071 | 6.863547 | 6.878712 | 6.891153 | 6.889611 |
| GO:0001768 | establishment of T cell polarity | 2/301 | 14/20870 | 0.01682713939741580 | 0.1434207179104 | 0.1196883320448 | RIPOR2||CCR7 | 2 | 6.845278 | 6.622525 | 6.714633 | 6.851050 | 6.904095 | 6.808720 | 6.815249 | 6.654775 | 6.593157 | 6.612120 | 6.629333 | 6.707692 | 6.696857 | 6.681901 | 6.770494 |
| GO:0002883 | regulation of hypersensitivity | 2/301 | 14/20870 | 0.01682713939741580 | 0.1434207179104 | 0.1196883320448 | C3||CCR7 | 2 | 5.907789 | 6.220389 | 6.445577 | 5.858222 | 5.908851 | 5.933741 | 5.929105 | 6.214904 | 6.214414 | 6.293654 | 6.155217 | 6.424247 | 6.427737 | 6.424560 | 6.504141 |
| GO:0043517 | positive regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator | 2/301 | 14/20870 | 0.01682713939741580 | 0.1434207179104 | 0.1196883320448 | ANKRD1||SPRED1 | 2 | 8.077853 | 7.765255 | 7.743476 | 7.480284 | 7.849799 | 8.245270 | 8.523900 | 7.777677 | 8.046435 | 7.448188 | 7.726454 | 7.813538 | 7.418472 | 7.805325 | 7.891615 |
| GO:0060732 | positive regulation of inositol phosphate biosynthetic process | 2/301 | 14/20870 | 0.01682713939741580 | 0.1434207179104 | 0.1196883320448 | MAS1||PTAFR | 2 | 3.058183 | 3.434306 | 3.478098 | 3.063951 | 3.045939 | 3.109110 | 3.012027 | 3.454327 | 3.470219 | 3.388505 | 3.422819 | 3.510617 | 3.391810 | 3.483484 | 3.522868 |
| GO:0072672 | neutrophil extravasation | 2/301 | 14/20870 | 0.01682713939741580 | 0.1434207179104 | 0.1196883320448 | RIPOR2||ADAM8 | 2 | 6.482685 | 6.023162 | 5.933160 | 6.495759 | 6.514033 | 6.494383 | 6.424974 | 6.020907 | 6.027790 | 6.008274 | 6.035536 | 5.962110 | 5.920243 | 5.915580 | 5.934252 |
| GO:1903624 | regulation of DNA catabolic process | 2/301 | 14/20870 | 0.01682713939741580 | 0.1434207179104 | 0.1196883320448 | IL6||ST20 | 2 | 5.318935 | 5.253731 | 5.637551 | 5.195802 | 5.081997 | 5.561084 | 5.390026 | 5.252749 | 5.237537 | 5.281048 | 5.243202 | 5.747114 | 5.595242 | 5.585020 | 5.616852 |
| GO:2000116 | regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | 9/301 | 270/20870 | 0.01689892760236875 | 0.1437153292351 | 0.1199341928840 | CST7||SENP1||VEGFA||TNFSF10||IFI6||CIDEB||ST20||TNFSF15||AQP1 | 9 | 6.649907 | 7.067745 | 7.279671 | 6.641847 | 6.649263 | 6.652587 | 6.655894 | 7.066817 | 7.064195 | 7.065916 | 7.074031 | 7.271571 | 7.285988 | 7.276579 | 7.284496 |
| GO:0030900 | forebrain development | 12/301 | 412/20870 | 0.01700167456883215 | 0.1442713527698 | 0.1203982090346 | TYRO3||MKKS||MAS1||SLIT2||SLC7A11||POU4F1||NR4A2||SEMA6B||GNG12||SSTR2||SLC8A1||AQP1 | 12 | 6.367768 | 6.227069 | 6.229521 | 6.376822 | 6.349890 | 6.374257 | 6.369947 | 6.246121 | 6.237507 | 6.198599 | 6.225606 | 6.246359 | 6.237452 | 6.214319 | 6.219720 |
| GO:0051783 | regulation of nuclear division | 6/301 | 142/20870 | 0.01715843275517158 | 0.1443955327677 | 0.1205018404836 | IL1A||LIF||BORA||FBXO43||IGF2||KNTC1 | 6 | 5.662291 | 5.952568 | 6.159581 | 5.601381 | 5.692330 | 5.736683 | 5.614449 | 5.995752 | 5.915919 | 5.950365 | 5.947110 | 6.129558 | 6.209200 | 6.157670 | 6.140595 |
| GO:0031960 | response to corticosteroid | 7/301 | 183/20870 | 0.01716590249685466 | 0.1443955327677 | 0.1205018404836 | IL6||IL1RN||SLIT2||BMP6||PTAFR||SSTR2||AQP1 | 7 | 7.809020 | 8.011991 | 8.041704 | 7.816524 | 7.814883 | 7.781620 | 7.822697 | 8.015651 | 7.981480 | 8.022205 | 8.028176 | 8.040623 | 8.033130 | 8.048381 | 8.044637 |
| GO:0048736 | appendage development | 7/301 | 183/20870 | 0.01716590249685466 | 0.1443955327677 | 0.1205018404836 | TGFB2||ECE1||TBX2||TFAP2A||FRAS1||SLC7A11||SCX | 7 | 4.716451 | 4.440635 | 4.416370 | 4.757729 | 4.683006 | 4.734652 | 4.689060 | 4.421093 | 4.382228 | 4.475460 | 4.481455 | 4.421443 | 4.421780 | 4.392948 | 4.429045 |
| GO:0060173 | limb development | 7/301 | 183/20870 | 0.01716590249685466 | 0.1443955327677 | 0.1205018404836 | TGFB2||ECE1||TBX2||TFAP2A||FRAS1||SLC7A11||SCX | 7 | 4.716451 | 4.440635 | 4.416370 | 4.757729 | 4.683006 | 4.734652 | 4.689060 | 4.421093 | 4.382228 | 4.475460 | 4.481455 | 4.421443 | 4.421780 | 4.392948 | 4.429045 |
| GO:0003176 | aortic valve development | 3/301 | 38/20870 | 0.01726936337615008 | 0.1446356008575 | 0.1207021835698 | TIE1||HEY2||SLIT2 | 3 | 5.217548 | 5.763977 | 5.844309 | 5.176965 | 5.252553 | 5.190599 | 5.248498 | 5.798331 | 5.674266 | 5.796770 | 5.782897 | 5.853613 | 5.905248 | 5.791439 | 5.824507 |
| GO:1903539 | protein localization to postsynaptic membrane | 3/301 | 38/20870 | 0.01726936337615008 | 0.1446356008575 | 0.1207021835698 | ZDHHC2||MAPK10||TAMALIN | 3 | 5.289112 | 4.882012 | 4.779118 | 5.260879 | 5.286552 | 5.300848 | 5.307723 | 4.891156 | 4.816758 | 4.900119 | 4.917965 | 4.857416 | 4.731074 | 4.799360 | 4.724504 |
| GO:0002285 | lymphocyte activation involved in immune response | 8/301 | 227/20870 | 0.01756832529226737 | 0.1460295383537 | 0.1218654607889 | UNC13D||IL23A||TNFSF18||IL6||TLR4||DLL1||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 8 | 7.127753 | 7.581987 | 7.580364 | 7.114479 | 7.134917 | 7.128587 | 7.132940 | 7.577709 | 7.560149 | 7.591407 | 7.598388 | 7.563207 | 7.578645 | 7.596730 | 7.582676 |
| GO:0010517 | regulation of phospholipase activity | 4/301 | 69/20870 | 0.01761781499986997 | 0.1460295383537 | 0.1218654607889 | LPAR2||ITK||EDNRA||PTAFR | 4 | 7.051673 | 7.107325 | 7.264823 | 7.062138 | 7.051385 | 7.054010 | 7.039065 | 7.130814 | 7.103937 | 7.103149 | 7.091106 | 7.249985 | 7.270170 | 7.256753 | 7.282170 |
| GO:0050771 | negative regulation of axonogenesis | 4/301 | 69/20870 | 0.01761781499986997 | 0.1460295383537 | 0.1218654607889 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 4 | 7.483640 | 8.267849 | 8.270682 | 7.473053 | 7.488482 | 7.490649 | 7.482309 | 8.273584 | 8.257624 | 8.265969 | 8.274155 | 8.275757 | 8.269962 | 8.273421 | 8.263558 |
| GO:0099173 | postsynapse organization | 7/301 | 184/20870 | 0.01763258852404686 | 0.1460295383537 | 0.1218654607889 | SEMA3F||CDKL5||DLG3||ZDHHC2||LRRC4||SLC7A11||GPRASP2 | 7 | 7.024079 | 7.169801 | 7.129353 | 7.000019 | 7.014710 | 7.047685 | 7.033446 | 7.182247 | 7.166801 | 7.178114 | 7.151847 | 7.132255 | 7.121838 | 7.116441 | 7.146695 |
| GO:0002224 | toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 6/301 | 143/20870 | 0.01770055010348050 | 0.1460295383537 | 0.1218654607889 | NR1H3||TYRO3||RSAD2||TLR4||IRF7||TLR7 | 6 | 6.177635 | 6.318958 | 6.333049 | 6.151076 | 6.182926 | 6.183990 | 6.192207 | 6.330152 | 6.319519 | 6.320848 | 6.305205 | 6.310870 | 6.329003 | 6.368750 | 6.322917 |
| GO:0035296 | regulation of tube diameter | 6/301 | 143/20870 | 0.01770055010348050 | 0.1460295383537 | 0.1218654607889 | GCLC||ECE1||MKKS||CHRM3||EDNRA||SLC8A1 | 6 | 5.791949 | 5.717745 | 5.699932 | 5.811481 | 5.752652 | 5.778672 | 5.823910 | 5.712324 | 5.693105 | 5.685630 | 5.778067 | 5.724127 | 5.685427 | 5.648048 | 5.740357 |
| GO:0097746 | blood vessel diameter maintenance | 6/301 | 143/20870 | 0.01770055010348050 | 0.1460295383537 | 0.1218654607889 | GCLC||ECE1||MKKS||CHRM3||EDNRA||SLC8A1 | 6 | 5.791949 | 5.717745 | 5.699932 | 5.811481 | 5.752652 | 5.778672 | 5.823910 | 5.712324 | 5.693105 | 5.685630 | 5.778067 | 5.724127 | 5.685427 | 5.648048 | 5.740357 |
| GO:0042326 | negative regulation of phosphorylation | 12/301 | 415/20870 | 0.01788624886035710 | 0.1472469229208 | 0.1228813999810 | LRP6||PMEPA1||MAS1||SH3BP5||SLIT2||SPRED1||PIP5KL1||SOCS4||SLC8A1||SOCS3||ENPP1||INPP5F | 12 | 6.006523 | 6.142311 | 6.150482 | 5.997279 | 6.004496 | 6.017013 | 6.007236 | 6.142900 | 6.158440 | 6.148325 | 6.119294 | 6.157147 | 6.150248 | 6.146820 | 6.147690 |
| GO:0010977 | negative regulation of neuron projection development | 6/301 | 144/20870 | 0.01825431406516622 | 0.1499572480970 | 0.1251432370738 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||BCL11A||SEMA3D||SEMA6B||INPP5F | 6 | 7.752259 | 8.283966 | 8.315068 | 7.737850 | 7.756592 | 7.753428 | 7.761059 | 8.286114 | 8.258898 | 8.295142 | 8.295404 | 8.303646 | 8.315670 | 8.326354 | 8.314512 |
| GO:0042698 | ovulation cycle | 4/301 | 70/20870 | 0.01847945962901479 | 0.1504823784363 | 0.1255814720466 | TYRO3||TGFB2||MMP7||SLIT2 | 4 | 5.147881 | 5.125965 | 5.246776 | 5.101113 | 5.100491 | 5.077741 | 5.300604 | 5.110070 | 5.136110 | 5.134948 | 5.122577 | 5.166887 | 5.419863 | 5.196007 | 5.189352 |
| GO:0051148 | negative regulation of muscle cell differentiation | 4/301 | 70/20870 | 0.01847945962901479 | 0.1504823784363 | 0.1255814720466 | RGS4||HEY2||IGF2||DLL1 | 4 | 7.125948 | 7.463748 | 7.405724 | 7.166999 | 7.108697 | 7.092101 | 7.134880 | 7.456738 | 7.480842 | 7.471186 | 7.445979 | 7.379462 | 7.431930 | 7.406779 | 7.404247 |
| GO:0060393 | regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation | 4/301 | 70/20870 | 0.01847945962901479 | 0.1504823784363 | 0.1255814720466 | TGFB2||PMEPA1||BMP6||RBPMS | 4 | 5.740781 | 5.835264 | 5.737383 | 5.785321 | 5.730417 | 5.735316 | 5.711022 | 5.839455 | 5.853813 | 5.829195 | 5.818355 | 5.777396 | 5.738823 | 5.731231 | 5.701056 |
| GO:0046475 | glycerophospholipid catabolic process | 3/301 | 39/20870 | 0.01851311312023545 | 0.1504823784363 | 0.1255814720466 | PLA2G7||GDPD1||INPP5F | 3 | 6.121258 | 5.569015 | 5.594125 | 6.071728 | 5.998646 | 6.312126 | 6.082920 | 5.571311 | 5.457618 | 5.515713 | 5.718259 | 5.506449 | 5.657262 | 5.611676 | 5.596990 |
| GO:0062237 | protein localization to postsynapse | 3/301 | 39/20870 | 0.01851311312023545 | 0.1504823784363 | 0.1255814720466 | ZDHHC2||MAPK10||TAMALIN | 3 | 5.289112 | 4.882012 | 4.779118 | 5.260879 | 5.286552 | 5.300848 | 5.307723 | 4.891156 | 4.816758 | 4.900119 | 4.917965 | 4.857416 | 4.731074 | 4.799360 | 4.724504 |
| GO:0051480 | regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration | 11/301 | 369/20870 | 0.01872211928244936 | 0.1518615599780 | 0.1267324350367 | LPAR2||LRP6||CCR7||EDNRA||CXCL10||CXCL11||S1PR1||C1QTNF1||SLC8A1||TRDN||CXCR3 | 11 | 5.887532 | 6.149454 | 6.227644 | 5.868168 | 5.876833 | 5.895937 | 5.908840 | 6.151203 | 6.143887 | 6.163341 | 6.139270 | 6.219154 | 6.249162 | 6.231237 | 6.210733 |
| GO:0035150 | regulation of tube size | 6/301 | 145/20870 | 0.01881983216677318 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | GCLC||ECE1||MKKS||CHRM3||EDNRA||SLC8A1 | 6 | 5.791949 | 5.717745 | 5.699932 | 5.811481 | 5.752652 | 5.778672 | 5.823910 | 5.712324 | 5.693105 | 5.685630 | 5.778067 | 5.724127 | 5.685427 | 5.648048 | 5.740357 |
| GO:0045137 | development of primary sexual characteristics | 8/301 | 230/20870 | 0.01884845465530790 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | MAMLD1||TGFB2||VEGFA||TNFSF10||MKKS||MAS1||SLIT2||SCX | 8 | 5.970867 | 5.872282 | 5.894724 | 5.978510 | 5.945728 | 5.958622 | 6.000022 | 5.830811 | 5.878664 | 5.868981 | 5.909578 | 5.884045 | 5.897946 | 5.880619 | 5.916015 |
| GO:0001767 | establishment of lymphocyte polarity | 2/301 | 15/20870 | 0.01923310072876390 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | RIPOR2||CCR7 | 2 | 6.734973 | 6.514245 | 6.606762 | 6.739697 | 6.794361 | 6.696849 | 6.706970 | 6.544817 | 6.486276 | 6.504740 | 6.520507 | 6.599718 | 6.589063 | 6.575302 | 6.661449 |
| GO:0002756 | MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 2/301 | 15/20870 | 0.01923310072876390 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | TLR4||IRF7 | 2 | 4.178210 | 4.299680 | 4.514763 | 4.218506 | 4.066157 | 4.288140 | 4.130138 | 4.358973 | 4.341245 | 4.267709 | 4.226791 | 4.623966 | 4.441056 | 4.415421 | 4.568176 |
| GO:0003188 | heart valve formation | 2/301 | 15/20870 | 0.01923310072876390 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | HEY2||SCX | 2 | 4.253389 | 4.463668 | 4.634780 | 4.354476 | 4.262225 | 4.201309 | 4.189573 | 4.384950 | 4.509930 | 4.527730 | 4.427307 | 4.625843 | 4.667992 | 4.615890 | 4.628849 |
| GO:0003356 | regulation of cilium beat frequency | 2/301 | 15/20870 | 0.01923310072876390 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | DNAH11||MKKS | 2 | 5.247883 | 4.276955 | 4.975722 | 5.671588 | 4.039029 | 5.161130 | 5.608956 | 3.509334 | 3.809730 | 3.382480 | 5.382176 | 5.073750 | 4.657420 | 4.217007 | 5.595515 |
| GO:0034154 | toll-like receptor 7 signaling pathway | 2/301 | 15/20870 | 0.01923310072876390 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | RSAD2||TLR7 | 2 | 5.263567 | 5.794357 | 5.750818 | 5.275334 | 5.283183 | 5.269647 | 5.225407 | 5.782218 | 5.795304 | 5.769426 | 5.829775 | 5.740212 | 5.715287 | 5.767181 | 5.779734 |
| GO:0035672 | oligopeptide transmembrane transport | 2/301 | 15/20870 | 0.01923310072876390 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | SLC7A11||SLC15A2 | 2 | 5.366803 | 5.061389 | 5.223737 | 5.378808 | 5.307921 | 5.409410 | 5.369200 | 5.052600 | 5.029937 | 5.034317 | 5.126587 | 5.229880 | 5.276016 | 5.198571 | 5.188873 |
| GO:0043320 | natural killer cell degranulation | 2/301 | 15/20870 | 0.01923310072876390 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | UNC13D||HLA-F | 2 | 7.268111 | 7.382921 | 7.480427 | 7.258637 | 7.278499 | 7.295826 | 7.238849 | 7.329211 | 7.459829 | 7.371523 | 7.367923 | 7.542634 | 7.454857 | 7.482741 | 7.439310 |
| GO:0060026 | convergent extension | 2/301 | 15/20870 | 0.01923310072876390 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | MKKS||LBX2 | 2 | 5.238987 | 4.779326 | 5.404219 | 5.462703 | 4.692302 | 5.161773 | 5.501763 | 4.320340 | 4.515430 | 4.679009 | 5.370852 | 5.390623 | 5.237743 | 5.040730 | 5.827615 |
| GO:0071474 | cellular hyperosmotic response | 2/301 | 15/20870 | 0.01923310072876390 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | MAPK10||AQP1 | 2 | 5.925469 | 6.609773 | 6.816139 | 5.926673 | 5.920381 | 5.878930 | 5.974303 | 6.769297 | 6.648437 | 6.470492 | 6.532650 | 6.865574 | 7.023178 | 6.691611 | 6.653712 |
| GO:1905208 | negative regulation of cardiocyte differentiation | 2/301 | 15/20870 | 0.01923310072876390 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | HEY2||DLL1 | 2 | 3.793243 | 3.586915 | 3.326382 | 3.946870 | 3.796661 | 3.716808 | 3.699162 | 3.472582 | 3.516458 | 3.938573 | 3.348757 | 3.316188 | 3.341438 | 3.468536 | 3.163113 |
| GO:0032640 | tumor necrosis factor production | 8/301 | 231/20870 | 0.01928961752623546 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | IL23A||OAS2||IL1A||CLU||IL6||TLR4||PTAFR||ORM1 | 8 | 6.665505 | 6.697249 | 6.707012 | 6.647415 | 6.671294 | 6.674347 | 6.668809 | 6.711712 | 6.694973 | 6.699892 | 6.682265 | 6.700235 | 6.713172 | 6.704014 | 6.710592 |
| GO:0032680 | regulation of tumor necrosis factor production | 8/301 | 231/20870 | 0.01928961752623546 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | IL23A||OAS2||IL1A||CLU||IL6||TLR4||PTAFR||ORM1 | 8 | 6.665505 | 6.697249 | 6.707012 | 6.647415 | 6.671294 | 6.674347 | 6.668809 | 6.711712 | 6.694973 | 6.699892 | 6.682265 | 6.700235 | 6.713172 | 6.704014 | 6.710592 |
| GO:0002763 | positive regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation | 4/301 | 71/20870 | 0.01936683117622700 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | IL23A||LIF||POU4F1||CSF1 | 4 | 6.748789 | 6.778638 | 6.809436 | 6.758624 | 6.726244 | 6.755078 | 6.754972 | 6.780707 | 6.769775 | 6.789587 | 6.774405 | 6.807255 | 6.810697 | 6.801764 | 6.817979 |
| GO:0002703 | regulation of leukocyte mediated immunity | 11/301 | 371/20870 | 0.01939725755304592 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | UNC13D||IL23A||C3||RSAD2||IL6||TLR4||PTAFR||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||KLRK1||PIK3R6 | 11 | 7.073264 | 7.098815 | 7.230841 | 7.077009 | 7.063587 | 7.077136 | 7.075282 | 7.099480 | 7.096186 | 7.101605 | 7.097981 | 7.223873 | 7.236857 | 7.236561 | 7.226025 |
| GO:0003279 | cardiac septum development | 5/301 | 107/20870 | 0.01947894643760250 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | TGFB2||DNAH11||TBX2||HEY2||SLIT2 | 5 | 5.106971 | 4.989370 | 4.918146 | 5.115149 | 5.096414 | 5.089517 | 5.126505 | 4.997060 | 4.959852 | 5.041398 | 4.957550 | 4.918652 | 4.945467 | 4.913731 | 4.894270 |
| GO:0006576 | cellular biogenic amine metabolic process | 5/301 | 107/20870 | 0.01947894643760250 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | TGFB2||IDO1||NR4A2||GDPD1||LY6E | 5 | 6.962120 | 6.892354 | 7.035375 | 6.964395 | 6.960111 | 6.953010 | 6.970903 | 6.909867 | 6.891070 | 6.881309 | 6.887010 | 7.021359 | 7.047143 | 7.039121 | 7.033755 |
| GO:0055017 | cardiac muscle tissue growth | 5/301 | 107/20870 | 0.01947894643760250 | 0.1519357822133 | 0.1267943754290 | TGFB2||RGS4||TBX2||HEY2||S1PR1 | 5 | 5.689330 | 5.248593 | 5.170425 | 5.708586 | 5.687263 | 5.670126 | 5.691086 | 5.282194 | 5.183204 | 5.336302 | 5.186792 | 5.237554 | 5.102102 | 5.183053 | 5.155680 |
| GO:0010955 | negative regulation of protein processing | 3/301 | 40/20870 | 0.01980533822953453 | 0.1520246737659 | 0.1268685577495 | CST7||IL1R2||CHAC1 | 3 | 6.243249 | 6.182845 | 6.087033 | 6.233701 | 6.257095 | 6.210014 | 6.271430 | 6.190480 | 6.136126 | 6.171873 | 6.231269 | 6.049491 | 6.096973 | 6.086442 | 6.114446 |
| GO:0032941 | secretion by tissue | 3/301 | 40/20870 | 0.01980533822953453 | 0.1520246737659 | 0.1268685577495 | NR1H3||CHRM3||AQP1 | 3 | 7.106286 | 7.325908 | 7.418304 | 7.063845 | 7.114252 | 7.124460 | 7.121748 | 7.305789 | 7.348721 | 7.328924 | 7.319860 | 7.399775 | 7.406457 | 7.417850 | 7.448646 |
| GO:0051281 | positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol | 3/301 | 40/20870 | 0.01980533822953453 | 0.1520246737659 | 0.1268685577495 | CXCL10||CXCL11||TRDN | 3 | 6.262425 | 6.297625 | 6.212333 | 6.219911 | 6.287994 | 6.274882 | 6.266006 | 6.309477 | 6.270063 | 6.327751 | 6.282501 | 6.218658 | 6.190904 | 6.218375 | 6.221184 |
| GO:0060412 | ventricular septum morphogenesis | 3/301 | 40/20870 | 0.01980533822953453 | 0.1520246737659 | 0.1268685577495 | TGFB2||HEY2||SLIT2 | 3 | 5.453584 | 4.964032 | 4.764651 | 5.449670 | 5.457141 | 5.460966 | 5.446513 | 4.964295 | 4.935784 | 4.990981 | 4.964538 | 4.776924 | 4.807251 | 4.737586 | 4.735611 |
| GO:0070528 | protein kinase C signaling | 3/301 | 40/20870 | 0.01980533822953453 | 0.1520246737659 | 0.1268685577495 | VEGFA||MAS1||ANKRD1 | 3 | 5.026988 | 4.274420 | 4.594142 | 4.995793 | 4.972939 | 5.041678 | 5.094528 | 4.252055 | 4.247629 | 4.252134 | 4.343587 | 4.642341 | 4.636973 | 4.553533 | 4.540722 |
| GO:1903318 | negative regulation of protein maturation | 3/301 | 40/20870 | 0.01980533822953453 | 0.1520246737659 | 0.1268685577495 | CST7||IL1R2||CHAC1 | 3 | 6.243249 | 6.182845 | 6.087033 | 6.233701 | 6.257095 | 6.210014 | 6.271430 | 6.190480 | 6.136126 | 6.171873 | 6.231269 | 6.049491 | 6.096973 | 6.086442 | 6.114446 |
| GO:1905207 | regulation of cardiocyte differentiation | 3/301 | 40/20870 | 0.01980533822953453 | 0.1520246737659 | 0.1268685577495 | TGFB2||HEY2||DLL1 | 3 | 5.713875 | 5.846879 | 6.015949 | 5.694814 | 5.688181 | 5.735901 | 5.735912 | 5.832582 | 5.799242 | 5.881936 | 5.872254 | 6.287653 | 5.891198 | 5.893902 | 5.952119 |
| GO:1905332 | positive regulation of morphogenesis of an epithelium | 3/301 | 40/20870 | 0.01980533822953453 | 0.1520246737659 | 0.1268685577495 | VEGFA||LIF||LBX2 | 3 | 5.614625 | 5.229497 | 5.509474 | 5.618665 | 5.605880 | 5.653936 | 5.579009 | 5.255941 | 5.155793 | 5.193774 | 5.307785 | 5.526430 | 5.494703 | 5.501648 | 5.514906 |
| GO:0051091 | positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity | 10/301 | 325/20870 | 0.02008606473108386 | 0.1538736030292 | 0.1284115374725 | LRP6||RPS6KA5||VEGFA||TNFSF18||CLU||TRIM22||IL6||TLR4||ADAM8||JMY | 10 | 5.904668 | 6.174479 | 6.226125 | 5.885586 | 5.916724 | 5.906002 | 5.910172 | 6.186488 | 6.172198 | 6.181892 | 6.157162 | 6.250454 | 6.220012 | 6.216694 | 6.217060 |
| GO:0048814 | regulation of dendrite morphogenesis | 4/301 | 72/20870 | 0.02028012119139112 | 0.1550525701385 | 0.1293954162936 | CDKL3||CDKL5||HECW2||GPRASP2 | 4 | 5.678884 | 6.013679 | 5.917770 | 5.644676 | 5.688448 | 5.656038 | 5.725015 | 6.053015 | 6.063345 | 5.937168 | 5.997701 | 5.990760 | 5.896452 | 5.901653 | 5.879589 |
| GO:0002761 | regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation | 6/301 | 148/20870 | 0.02058796131735691 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | IL23A||LIF||TLR4||POU4F1||CSF1||IRF7 | 6 | 6.240682 | 6.433897 | 6.457318 | 6.236880 | 6.218399 | 6.262680 | 6.244419 | 6.434210 | 6.448924 | 6.429835 | 6.422492 | 6.453121 | 6.465240 | 6.455422 | 6.455457 |
| GO:0045766 | positive regulation of angiogenesis | 7/301 | 190/20870 | 0.02062184808307870 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | TIE1||VEGFA||IL1A||C3||DLL1||AQP1||PIK3R6 | 7 | 6.565463 | 6.938777 | 7.218652 | 6.553478 | 6.560549 | 6.577946 | 6.569762 | 6.947213 | 6.931792 | 6.930656 | 6.945367 | 7.219419 | 7.216610 | 7.231556 | 7.206914 |
| GO:1904018 | positive regulation of vasculature development | 7/301 | 190/20870 | 0.02062184808307870 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | TIE1||VEGFA||IL1A||C3||DLL1||AQP1||PIK3R6 | 7 | 6.565463 | 6.938777 | 7.218652 | 6.553478 | 6.560549 | 6.577946 | 6.569762 | 6.947213 | 6.931792 | 6.930656 | 6.945367 | 7.219419 | 7.216610 | 7.231556 | 7.206914 |
| GO:0006898 | receptor-mediated endocytosis | 9/301 | 280/20870 | 0.02084343244198092 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | LRP6||SCARF1||SIGLEC1||VEGFA||CLU||C3||DLL1||ANKRD13B||INPP5F | 9 | 7.972519 | 7.873559 | 7.805430 | 7.978061 | 7.973798 | 7.969733 | 7.968464 | 7.878396 | 7.868358 | 7.864981 | 7.882431 | 7.799562 | 7.811251 | 7.803320 | 7.807560 |
| GO:0030100 | regulation of endocytosis | 8/301 | 235/20870 | 0.02112814333357783 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | NR1H3||SLC17A7||VEGFA||CLU||C3||BIN1||DLL1||ANKRD13B | 8 | 6.984958 | 6.851557 | 6.840165 | 6.987783 | 6.982599 | 6.982551 | 6.986891 | 6.866848 | 6.840252 | 6.841507 | 6.857448 | 6.830262 | 6.855877 | 6.831584 | 6.842790 |
| GO:0045823 | positive regulation of heart contraction | 3/301 | 41/20870 | 0.02114611524366531 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | TGFB2||RGS4||HEY2 | 3 | 6.205399 | 6.268940 | 6.179027 | 6.277411 | 6.169532 | 6.151991 | 6.219348 | 6.291801 | 6.190843 | 6.411273 | 6.168941 | 6.088422 | 6.263426 | 6.291890 | 6.057562 |
| GO:0050775 | positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis | 3/301 | 41/20870 | 0.02114611524366531 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | CDKL3||CDKL5||GPRASP2 | 3 | 5.710751 | 5.591781 | 5.518985 | 5.664566 | 5.690401 | 5.693116 | 5.791630 | 5.580223 | 5.611111 | 5.560013 | 5.615063 | 5.545174 | 5.485086 | 5.534096 | 5.510846 |
| GO:0061082 | myeloid leukocyte cytokine production | 3/301 | 41/20870 | 0.02114611524366531 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | TGFB2||NR4A3||TLR4 | 3 | 6.861031 | 7.273588 | 7.325636 | 6.823988 | 6.882606 | 6.863629 | 6.873212 | 7.275333 | 7.268888 | 7.273805 | 7.276315 | 7.331344 | 7.347967 | 7.325425 | 7.297347 |
| GO:0071526 | semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway | 3/301 | 41/20870 | 0.02114611524366531 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | SEMA3F||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 3 | 5.648104 | 5.839829 | 5.941177 | 5.630647 | 5.698963 | 5.633818 | 5.627764 | 5.785578 | 5.985327 | 5.763553 | 5.814050 | 5.945275 | 5.995734 | 5.976305 | 5.842619 |
| GO:0071542 | dopaminergic neuron differentiation | 3/301 | 41/20870 | 0.02114611524366531 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | LRP6||VEGFA||NR4A2 | 3 | 5.792056 | 6.061962 | 5.960927 | 5.804638 | 5.819500 | 5.791398 | 5.751812 | 6.232916 | 6.129595 | 5.876602 | 5.983051 | 6.118940 | 5.877713 | 5.898415 | 5.935752 |
| GO:0072538 | T-helper 17 type immune response | 3/301 | 41/20870 | 0.02114611524366531 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | IL23A||TNFSF18||IL6 | 3 | 4.618237 | 4.995449 | 5.389350 | 4.604135 | 4.619644 | 4.640564 | 4.608329 | 4.964986 | 4.987618 | 5.040340 | 4.987785 | 5.373640 | 5.398874 | 5.351614 | 5.432030 |
| GO:0051302 | regulation of cell division | 7/301 | 191/20870 | 0.02115231035092284 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | TGFB2||OSM||VEGFA||IL1A||KIF13A||IGF2||DLL1 | 7 | 6.626740 | 6.949014 | 6.985938 | 6.640494 | 6.631907 | 6.631482 | 6.602798 | 6.952018 | 6.951812 | 6.937934 | 6.954234 | 7.000120 | 6.992968 | 6.960770 | 6.989585 |
| GO:0003208 | cardiac ventricle morphogenesis | 4/301 | 73/20870 | 0.02121951044374628 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | TGFB2||HEY2||POU4F1||LY6E | 4 | 5.354371 | 5.639872 | 5.729537 | 5.400087 | 5.334401 | 5.284183 | 5.395667 | 5.653756 | 5.554229 | 5.751185 | 5.592585 | 5.824647 | 5.708943 | 5.728368 | 5.650725 |
| GO:0060389 | pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation | 4/301 | 73/20870 | 0.02121951044374628 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | TGFB2||PMEPA1||BMP6||RBPMS | 4 | 5.762541 | 5.799965 | 5.687507 | 5.798920 | 5.743170 | 5.743559 | 5.763800 | 5.802868 | 5.818912 | 5.793937 | 5.783913 | 5.728515 | 5.690526 | 5.682040 | 5.647801 |
| GO:0006874 | cellular calcium ion homeostasis | 13/301 | 476/20870 | 0.02137066427435622 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | MCUB||LPAR2||LRP6||DMPK||CCR7||EDNRA||CXCL10||CXCL11||S1PR1||C1QTNF1||SLC8A1||TRDN||CXCR3 | 13 | 6.436563 | 6.542101 | 6.607514 | 6.423633 | 6.445106 | 6.427204 | 6.450131 | 6.546655 | 6.539198 | 6.551944 | 6.530518 | 6.601171 | 6.624354 | 6.605553 | 6.598839 |
| GO:0030336 | negative regulation of cell migration | 11/301 | 377/20870 | 0.02153104735277196 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | TIE1||RIPOR2||PADI2||TMEFF2||SLIT2||NBL1||SPRED1||PIP5KL1||IFITM1||KLRK1||EPPK1 | 11 | 6.139376 | 6.158793 | 6.209196 | 6.118553 | 6.141069 | 6.145006 | 6.152651 | 6.153895 | 6.164580 | 6.158689 | 6.157988 | 6.221660 | 6.212110 | 6.202437 | 6.200480 |
| GO:0007173 | epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway | 5/301 | 110/20870 | 0.02166779341761424 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | RPS6KA5||IFI6||BCAR3||SOCS4||MVB12B | 5 | 5.791138 | 6.853263 | 7.309428 | 5.759031 | 5.791567 | 5.782949 | 5.830097 | 6.836234 | 6.874029 | 6.855889 | 6.846633 | 7.298352 | 7.317997 | 7.310086 | 7.311208 |
| GO:0050773 | regulation of dendrite development | 5/301 | 110/20870 | 0.02166779341761424 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | CDKL3||CDKL5||BCL11A||HECW2||GPRASP2 | 5 | 5.839519 | 6.197278 | 6.208023 | 5.823442 | 5.841569 | 5.796485 | 5.894782 | 6.226621 | 6.205310 | 6.201584 | 6.154643 | 6.224855 | 6.217618 | 6.223117 | 6.165676 |
| GO:0032946 | positive regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation | 7/301 | 192/20870 | 0.02169219045020887 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | IL23A||IL1A||IL6||TLR4||IGF2||CSF1||PDCD1LG2 | 7 | 6.499729 | 7.085221 | 7.284716 | 6.489001 | 6.505578 | 6.503048 | 6.501232 | 7.092848 | 7.082118 | 7.085875 | 7.080012 | 7.296786 | 7.284679 | 7.272267 | 7.285029 |
| GO:0002524 | hypersensitivity | 2/301 | 16/20870 | 0.02177395806653105 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | C3||CCR7 | 2 | 5.731787 | 6.026069 | 6.248126 | 5.679463 | 5.729018 | 5.762303 | 5.754913 | 6.019052 | 6.020780 | 6.099862 | 5.961197 | 6.223083 | 6.232331 | 6.231228 | 6.304351 |
| GO:0002830 | positive regulation of type 2 immune response | 2/301 | 16/20870 | 0.02177395806653105 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | RSAD2||IL6 | 2 | 6.588866 | 6.853889 | 6.989710 | 6.597722 | 6.594987 | 6.576562 | 6.586096 | 6.841908 | 6.861320 | 6.870537 | 6.841574 | 6.986491 | 6.968001 | 6.994973 | 7.009068 |
| GO:0003198 | epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation | 2/301 | 16/20870 | 0.02177395806653105 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 5.311725 | 5.461115 | 5.434158 | 5.361915 | 5.302107 | 5.292261 | 5.289402 | 5.449537 | 5.487548 | 5.474612 | 5.432120 | 5.425427 | 5.450359 | 5.427654 | 5.433058 |
| GO:0010649 | regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling | 2/301 | 16/20870 | 0.02177395806653105 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | SLC8A1||TRDN | 2 | 6.671494 | 6.491963 | 6.362288 | 6.636751 | 6.686030 | 6.691848 | 6.670713 | 6.519084 | 6.451228 | 6.505924 | 6.490720 | 6.380428 | 6.343266 | 6.365560 | 6.359655 |
| GO:0010919 | regulation of inositol phosphate biosynthetic process | 2/301 | 16/20870 | 0.02177395806653105 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | MAS1||PTAFR | 2 | 5.718006 | 5.587746 | 5.627047 | 5.703634 | 5.756762 | 5.735979 | 5.674285 | 5.560849 | 5.605777 | 5.607926 | 5.575877 | 5.630875 | 5.582028 | 5.700072 | 5.592214 |
| GO:0021783 | preganglionic parasympathetic fiber development | 2/301 | 16/20870 | 0.02177395806653105 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | SEMA3F||TFAP2A | 2 | 4.077459 | 5.112486 | 5.346244 | 4.117929 | 4.030313 | 4.145606 | 4.011535 | 5.131231 | 5.159844 | 5.075262 | 5.081901 | 5.361160 | 5.201582 | 5.544047 | 5.254003 |
| GO:0042976 | activation of Janus kinase activity | 2/301 | 16/20870 | 0.02177395806653105 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | IL23A||PRLR | 2 | 5.772345 | 6.952744 | 7.704637 | 5.744013 | 5.809601 | 5.785868 | 5.748883 | 6.967352 | 6.983567 | 6.941232 | 6.917959 | 7.677748 | 7.718078 | 7.693042 | 7.729112 |
| GO:0048569 | post-embryonic animal organ development | 2/301 | 16/20870 | 0.02177395806653105 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | VEGFA||MYO7A | 2 | 6.262054 | 7.243498 | 6.923780 | 6.229867 | 6.343917 | 6.409759 | 6.037525 | 7.389842 | 6.955288 | 7.225593 | 7.363391 | 7.348079 | 6.685665 | 6.881246 | 6.671003 |
| GO:0060413 | atrial septum morphogenesis | 2/301 | 16/20870 | 0.02177395806653105 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 4.455615 | 4.372817 | 4.112228 | 4.383744 | 4.355107 | 4.711072 | 4.338732 | 4.433202 | 4.395840 | 4.347352 | 4.311919 | 4.086022 | 4.110593 | 4.120370 | 4.131536 |
| GO:0061548 | ganglion development | 2/301 | 16/20870 | 0.02177395806653105 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | SEMA3F||RGS4 | 2 | 5.369110 | 5.855043 | 5.800782 | 5.391677 | 5.326915 | 5.481910 | 5.267099 | 5.889033 | 5.756994 | 5.791432 | 5.972737 | 5.809789 | 5.787140 | 5.800221 | 5.805876 |
| GO:0070242 | thymocyte apoptotic process | 2/301 | 16/20870 | 0.02177395806653105 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | ZC3H8||ADAM8 | 2 | 4.892350 | 4.497489 | 4.417645 | 5.026147 | 4.855728 | 4.938097 | 4.733390 | 4.570262 | 4.530503 | 4.421438 | 4.463130 | 4.361548 | 4.442475 | 4.418494 | 4.446479 |
| GO:0090594 | inflammatory response to wounding | 2/301 | 16/20870 | 0.02177395806653105 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | IL1A||TLR4 | 2 | 8.019222 | 7.580310 | 7.892328 | 8.009671 | 7.997653 | 8.029366 | 8.039824 | 7.586927 | 7.552031 | 7.613610 | 7.567940 | 7.901543 | 7.880740 | 7.899094 | 7.887837 |
| GO:0099638 | endosome to plasma membrane protein transport | 2/301 | 16/20870 | 0.02177395806653105 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | ZDHHC2||TAMALIN | 2 | 5.330655 | 5.308955 | 5.258350 | 5.414576 | 5.376965 | 5.315708 | 5.206894 | 5.330479 | 5.356723 | 5.181364 | 5.359904 | 5.373313 | 5.198475 | 5.273916 | 5.179569 |
| GO:2000048 | negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin | 2/301 | 16/20870 | 0.02177395806653105 | 0.1562625503622 | 0.1304051763679 | VEGFA||BMP6 | 2 | 5.747983 | 5.778849 | 6.038419 | 5.835422 | 5.651809 | 5.740559 | 5.758248 | 5.751953 | 5.688209 | 5.850273 | 5.819547 | 6.052230 | 6.048746 | 5.998633 | 6.053341 |
| GO:0062013 | positive regulation of small molecule metabolic process | 6/301 | 150/20870 | 0.02182737944589866 | 0.1563553099084 | 0.1304825866300 | NR1H3||NR4A3||MAS1||BMP6||IGF2||PTAFR | 6 | 8.108726 | 8.209219 | 8.383735 | 8.112826 | 8.109354 | 8.102207 | 8.110494 | 8.216754 | 8.199770 | 8.208709 | 8.211591 | 8.384591 | 8.383623 | 8.393581 | 8.373071 |
| GO:0003151 | outflow tract morphogenesis | 4/301 | 74/20870 | 0.02218516896327826 | 0.1580386298288 | 0.1318873610344 | TGFB2||VEGFA||TBX2||HEY2 | 4 | 5.713676 | 5.571854 | 5.549817 | 5.703702 | 5.748859 | 5.695682 | 5.705863 | 5.596612 | 5.514832 | 5.537463 | 5.635359 | 5.702776 | 5.522127 | 5.457855 | 5.504260 |
| GO:0042058 | regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway | 4/301 | 74/20870 | 0.02218516896327826 | 0.1580386298288 | 0.1318873610344 | IFI6||BCAR3||SOCS4||MVB12B | 4 | 5.779602 | 7.132688 | 7.674707 | 5.750577 | 5.784996 | 5.769159 | 5.812949 | 7.103296 | 7.166429 | 7.129090 | 7.131235 | 7.657724 | 7.687143 | 7.673702 | 7.680094 |
| GO:0043550 | regulation of lipid kinase activity | 4/301 | 74/20870 | 0.02218516896327826 | 0.1580386298288 | 0.1318873610344 | CCR7||SOCS4||SOCS3||PIK3R6 | 4 | 5.597439 | 5.805598 | 5.835996 | 5.595041 | 5.621030 | 5.582492 | 5.590905 | 5.775836 | 5.837911 | 5.811631 | 5.796301 | 5.810217 | 5.838649 | 5.872471 | 5.821880 |
| GO:0031345 | negative regulation of cell projection organization | 7/301 | 193/20870 | 0.02224156240263946 | 0.1581485680232 | 0.1319791073267 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||BCL11A||SLIT2||SEMA3D||SEMA6B||INPP5F | 7 | 7.468749 | 7.932533 | 7.962798 | 7.453308 | 7.475755 | 7.470617 | 7.475201 | 7.939258 | 7.907273 | 7.943196 | 7.940108 | 7.950758 | 7.962814 | 7.977468 | 7.960025 |
| GO:0007088 | regulation of mitotic nuclear division | 5/301 | 111/20870 | 0.02243148509508455 | 0.1589136953250 | 0.1326176260281 | IL1A||BORA||FBXO43||IGF2||KNTC1 | 5 | 5.305982 | 5.778009 | 5.992836 | 5.229765 | 5.349360 | 5.409479 | 5.226750 | 5.834842 | 5.743456 | 5.758171 | 5.773878 | 5.963659 | 6.042976 | 5.977601 | 5.985836 |
| GO:0010927 | cellular component assembly involved in morphogenesis | 5/301 | 111/20870 | 0.02243148509508455 | 0.1589136953250 | 0.1326176260281 | KNL1||ANKRD1||OBSCN||MYOZ2||NRAP | 5 | 6.100355 | 6.194081 | 6.143818 | 6.087510 | 6.105873 | 6.082959 | 6.124698 | 6.188646 | 6.189158 | 6.201104 | 6.197377 | 6.128747 | 6.182902 | 6.142576 | 6.120243 |
| GO:0001941 | postsynaptic membrane organization | 3/301 | 42/20870 | 0.02253548387290869 | 0.1593580645299 | 0.1329884637266 | ZDHHC2||LRRC4||SLC7A11 | 3 | 4.777663 | 4.687999 | 4.801147 | 4.774191 | 4.742716 | 4.811987 | 4.780920 | 4.660586 | 4.795169 | 4.649096 | 4.641544 | 4.805384 | 4.819704 | 4.768075 | 4.810890 |
| GO:0022604 | regulation of cell morphogenesis | 10/301 | 332/20870 | 0.02286962775806162 | 0.1614252884349 | 0.1347136160251 | CDKL3||CDKL5||UNC13D||RASAL1||VEGFA||BCL11A||RREB1||UNC13A||FGD2||GPRASP2 | 10 | 6.691990 | 6.856610 | 6.912560 | 6.671014 | 6.704392 | 6.706888 | 6.685369 | 6.841375 | 6.875864 | 6.853014 | 6.855973 | 6.920286 | 6.911164 | 6.916416 | 6.902313 |
| GO:0007411 | axon guidance | 8/301 | 239/20870 | 0.02308769357804639 | 0.1626671257388 | 0.1357499616642 | SEMA3F||NOTCH3||RPS6KA5||VEGFA||SLIT2||SEMA3D||KALRN||SEMA6B | 8 | 5.666853 | 5.802403 | 5.794646 | 5.694231 | 5.667709 | 5.663492 | 5.641492 | 5.790754 | 5.791520 | 5.804287 | 5.822817 | 5.789791 | 5.805864 | 5.800391 | 5.782425 |
| GO:1903201 | regulation of oxidative stress-induced cell death | 4/301 | 75/20870 | 0.02317725608959429 | 0.1630007026629 | 0.1360283403130 | NR4A3||TLR4||MEAK7||SLC7A11 | 4 | 7.204569 | 7.068441 | 7.021875 | 7.181378 | 7.205955 | 7.191758 | 7.238538 | 7.090299 | 7.048605 | 7.056391 | 7.078083 | 7.000828 | 7.052655 | 7.026453 | 7.006998 |
| GO:0046718 | viral entry into host cell | 7/301 | 195/20870 | 0.02336907317370705 | 0.1640508936794 | 0.1369047521239 | SIGLEC1||TYRO3||ZNF639||TRIM22||TNFRSF14||LY6E||IFITM1 | 7 | 7.009564 | 7.548432 | 7.729019 | 6.990850 | 7.020449 | 7.007320 | 7.019440 | 7.543839 | 7.524789 | 7.557716 | 7.567034 | 7.702282 | 7.736501 | 7.747486 | 7.729424 |
| GO:0097485 | neuron projection guidance | 8/301 | 240/20870 | 0.02359692288943185 | 0.1653497627515 | 0.1379886922620 | SEMA3F||NOTCH3||RPS6KA5||VEGFA||SLIT2||SEMA3D||KALRN||SEMA6B | 8 | 5.666853 | 5.802403 | 5.794646 | 5.694231 | 5.667709 | 5.663492 | 5.641492 | 5.790754 | 5.791520 | 5.804287 | 5.822817 | 5.789791 | 5.805864 | 5.800391 | 5.782425 |
| GO:0030224 | monocyte differentiation | 3/301 | 43/20870 | 0.02397344838492548 | 0.1664774895939 | 0.1389298097430 | VEGFA||CSF1||IRF7 | 3 | 6.034272 | 6.280025 | 6.421705 | 6.028715 | 6.036026 | 6.035033 | 6.037300 | 6.278000 | 6.277777 | 6.276164 | 6.288126 | 6.419035 | 6.421899 | 6.409179 | 6.436572 |
| GO:0042491 | inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation | 3/301 | 43/20870 | 0.02397344838492548 | 0.1664774895939 | 0.1389298097430 | HEY2||MYO7A||DLL1 | 3 | 4.876570 | 4.745547 | 4.739025 | 4.956176 | 4.885812 | 4.894045 | 4.763564 | 4.776147 | 4.709490 | 4.746161 | 4.749612 | 4.760654 | 4.749939 | 4.739885 | 4.705017 |
| GO:0044331 | cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin | 3/301 | 43/20870 | 0.02397344838492548 | 0.1664774895939 | 0.1389298097430 | VEGFA||ADAM19||BMP6 | 3 | 4.851608 | 4.892466 | 5.122465 | 4.892498 | 4.745039 | 4.846116 | 4.916848 | 4.869160 | 4.814726 | 4.979183 | 4.901859 | 5.151402 | 5.102502 | 5.134557 | 5.100755 |
| GO:0071470 | cellular response to osmotic stress | 3/301 | 43/20870 | 0.02397344838492548 | 0.1664774895939 | 0.1389298097430 | MYLK||MAPK10||AQP1 | 3 | 5.783734 | 6.105717 | 6.150980 | 5.765771 | 5.771252 | 5.779750 | 5.817592 | 6.213119 | 6.117835 | 6.021673 | 6.063065 | 6.180919 | 6.268863 | 6.088802 | 6.055672 |
| GO:1903524 | positive regulation of blood circulation | 3/301 | 43/20870 | 0.02397344838492548 | 0.1664774895939 | 0.1389298097430 | TGFB2||RGS4||HEY2 | 3 | 6.113901 | 6.170973 | 6.073633 | 6.160558 | 6.050736 | 6.138413 | 6.103523 | 6.181699 | 6.136420 | 6.297460 | 6.057829 | 5.980492 | 6.178053 | 6.172969 | 5.947332 |
| GO:0002705 | positive regulation of leukocyte mediated immunity | 8/301 | 241/20870 | 0.02411400126426313 | 0.1671528884763 | 0.1394934477368 | IL23A||C3||RSAD2||IL6||PTAFR||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||KLRK1 | 8 | 7.479918 | 7.446537 | 7.588700 | 7.486951 | 7.465610 | 7.487312 | 7.479691 | 7.447399 | 7.445292 | 7.447424 | 7.446031 | 7.582490 | 7.592623 | 7.587584 | 7.592078 |
| GO:1903036 | positive regulation of response to wounding | 4/301 | 76/20870 | 0.02419592052792211 | 0.1674148863194 | 0.1397120917743 | MYLK||SCARF1||RREB1||HPSE | 4 | 7.018771 | 6.817042 | 6.764483 | 7.021186 | 7.023741 | 7.001736 | 7.028278 | 6.830959 | 6.806435 | 6.810115 | 6.820532 | 6.737739 | 6.777121 | 6.781194 | 6.761475 |
| GO:0001780 | neutrophil homeostasis | 2/301 | 17/20870 | 0.02444534696472762 | 0.1674148863194 | 0.1397120917743 | IL6||SLC7A11 | 2 | 5.351840 | 5.318037 | 5.182900 | 5.357747 | 5.394840 | 5.336179 | 5.317443 | 5.339884 | 5.307906 | 5.294706 | 5.329219 | 5.172598 | 5.222743 | 5.182758 | 5.152592 |
| GO:0001921 | positive regulation of receptor recycling | 2/301 | 17/20870 | 0.02444534696472762 | 0.1674148863194 | 0.1397120917743 | ECE1||INPP5F | 2 | 5.947446 | 6.708350 | 6.924641 | 5.954703 | 5.878501 | 6.040934 | 5.910440 | 6.688817 | 6.792812 | 6.618533 | 6.727716 | 7.013368 | 6.803827 | 6.937055 | 6.936505 |
| GO:0006857 | oligopeptide transport | 2/301 | 17/20870 | 0.02444534696472762 | 0.1674148863194 | 0.1397120917743 | SLC7A11||SLC15A2 | 2 | 5.326397 | 4.975580 | 5.115115 | 5.316962 | 5.252942 | 5.326138 | 5.405469 | 5.017942 | 4.918062 | 4.930329 | 5.032391 | 5.120711 | 5.155368 | 5.097678 | 5.085722 |
| GO:0045651 | positive regulation of macrophage differentiation | 2/301 | 17/20870 | 0.02444534696472762 | 0.1674148863194 | 0.1397120917743 | LIF||CSF1 | 2 | 6.345269 | 6.535947 | 6.590476 | 6.315869 | 6.372249 | 6.306151 | 6.385173 | 6.539873 | 6.505117 | 6.569024 | 6.529043 | 6.609510 | 6.588643 | 6.617849 | 6.544798 |
| GO:0098969 | neurotransmitter receptor transport to postsynaptic membrane | 2/301 | 17/20870 | 0.02444534696472762 | 0.1674148863194 | 0.1397120917743 | MAPK10||TAMALIN | 2 | 4.941490 | 4.597417 | 4.696665 | 5.013505 | 4.960275 | 4.944620 | 4.842272 | 4.604700 | 4.532657 | 4.578109 | 4.670726 | 4.810046 | 4.661514 | 4.742924 | 4.560168 |
| GO:0030879 | mammary gland development | 6/301 | 154/20870 | 0.02445532138931222 | 0.1674148863194 | 0.1397120917743 | OAS2||VEGFA||PRLR||TBX2||RREB1||CSF1 | 6 | 7.316976 | 7.185490 | 7.468988 | 7.319311 | 7.312261 | 7.323865 | 7.312435 | 7.185449 | 7.171859 | 7.186188 | 7.198344 | 7.469390 | 7.473526 | 7.475637 | 7.457330 |
| GO:0008361 | regulation of cell size | 7/301 | 197/20870 | 0.02453541546274211 | 0.1676659099144 | 0.1399215775155 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||SEMA3D||SEMA6B||AQP1 | 7 | 6.824661 | 7.350700 | 7.323777 | 6.828054 | 6.818838 | 6.834497 | 6.817188 | 7.354405 | 7.357727 | 7.350828 | 7.339776 | 7.344610 | 7.324669 | 7.309593 | 7.315994 |
| GO:0001938 | positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation | 5/301 | 114/20870 | 0.02482656353180736 | 0.1693557628910 | 0.1413318039257 | VEGFA||BMP6||IGF2||SCG2||EGR3 | 5 | 6.312614 | 6.341194 | 6.384306 | 6.255805 | 6.305775 | 6.335025 | 6.352014 | 6.350018 | 6.332540 | 6.316728 | 6.365032 | 6.393580 | 6.369361 | 6.386094 | 6.388077 |
| GO:0007189 | adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | 6/301 | 155/20870 | 0.02514391198665461 | 0.1709166270783 | 0.1426343858250 | LPAR2||ADGRE3||CXCL10||CXCL11||S1PR1||ADGRE1 | 6 | 5.702701 | 5.494511 | 5.382007 | 5.701634 | 5.658925 | 5.745043 | 5.703916 | 5.489868 | 5.442564 | 5.568634 | 5.473963 | 5.344155 | 5.415593 | 5.434442 | 5.331100 |
| GO:0033135 | regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | 6/301 | 155/20870 | 0.02514391198665461 | 0.1709166270783 | 0.1426343858250 | OSM||VEGFA||LIF||IL6||BCAR3||INPP5F | 6 | 6.257306 | 6.544620 | 6.535690 | 6.267357 | 6.230341 | 6.262434 | 6.268754 | 6.554063 | 6.500617 | 6.582250 | 6.540354 | 6.530759 | 6.551608 | 6.568615 | 6.490606 |
| GO:0045214 | sarcomere organization | 3/301 | 44/20870 | 0.02545997895451823 | 0.1727609468249 | 0.1441735187860 | ANKRD1||OBSCN||MYOZ2 | 3 | 7.295596 | 7.467938 | 7.420005 | 7.295148 | 7.302775 | 7.300132 | 7.284257 | 7.461891 | 7.456659 | 7.476649 | 7.476444 | 7.409921 | 7.428526 | 7.419492 | 7.422018 |
| GO:0055074 | calcium ion homeostasis | 13/301 | 488/20870 | 0.02551560397026410 | 0.1728346437354 | 0.1442350207811 | MCUB||LPAR2||LRP6||DMPK||CCR7||EDNRA||CXCL10||CXCL11||S1PR1||C1QTNF1||SLC8A1||TRDN||CXCR3 | 13 | 6.407836 | 6.510355 | 6.575953 | 6.394688 | 6.416059 | 6.398454 | 6.421960 | 6.514765 | 6.507406 | 6.520452 | 6.498703 | 6.569744 | 6.592854 | 6.573748 | 6.567328 |
| GO:0060419 | heart growth | 5/301 | 115/20870 | 0.02565998622810020 | 0.1735082431291 | 0.1447971570545 | TGFB2||RGS4||TBX2||HEY2||S1PR1 | 5 | 5.761527 | 5.380365 | 5.271618 | 5.782891 | 5.768077 | 5.734449 | 5.760262 | 5.411187 | 5.340548 | 5.446779 | 5.319241 | 5.330313 | 5.203265 | 5.287789 | 5.262180 |
| GO:0045055 | regulated exocytosis | 8/301 | 244/20870 | 0.02571287949454776 | 0.1735619365882 | 0.1448419656474 | UNC13D||DNAJC5||PTGDS||NR4A3||UNC13A||UNC13C||PTAFR||HLA-F | 8 | 6.302876 | 6.350492 | 6.436217 | 6.296753 | 6.312733 | 6.305871 | 6.296081 | 6.351382 | 6.376586 | 6.346668 | 6.326897 | 6.448015 | 6.428194 | 6.441539 | 6.427008 |
| GO:0002753 | cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway | 4/301 | 78/20870 | 0.02631352337272858 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | OASL||TLR4||SLC15A2||IRF7 | 4 | 5.170636 | 5.209260 | 5.202277 | 5.255074 | 5.129622 | 5.146196 | 5.148177 | 5.240772 | 5.199269 | 5.230019 | 5.165800 | 5.182638 | 5.215033 | 5.173320 | 5.237213 |
| GO:0042093 | T-helper cell differentiation | 4/301 | 78/20870 | 0.02631352337272858 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | IL23A||TNFSF18||IL6||HLA-DRA | 4 | 5.117749 | 5.245153 | 5.412241 | 5.115985 | 5.139379 | 5.123888 | 5.091327 | 5.243213 | 5.243851 | 5.267848 | 5.225382 | 5.420758 | 5.415577 | 5.384348 | 5.427897 |
| GO:0070227 | lymphocyte apoptotic process | 4/301 | 78/20870 | 0.02631352337272858 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | IDO1||ZC3H8||ADAM8||CD3G | 4 | 6.760241 | 6.991674 | 7.006653 | 6.764290 | 6.751313 | 6.769188 | 6.756107 | 6.993818 | 7.006921 | 6.981283 | 6.984536 | 6.983665 | 7.008230 | 7.017634 | 7.016821 |
| GO:0045088 | regulation of innate immune response | 10/301 | 340/20870 | 0.02638179413165011 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | NR1H3||TYRO3||POLR3G||TLR4||ADAM8||IRF7||ISG15||HLA-F||KLRK1||PIK3R6 | 10 | 6.512926 | 6.583926 | 6.637182 | 6.520870 | 6.492084 | 6.524780 | 6.513748 | 6.577911 | 6.598551 | 6.578880 | 6.580259 | 6.622853 | 6.649551 | 6.651658 | 6.624414 |
| GO:0033138 | positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | 5/301 | 116/20870 | 0.02651112789091332 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | OSM||VEGFA||LIF||IL6||BCAR3 | 5 | 6.257759 | 6.679962 | 6.687806 | 6.284228 | 6.240078 | 6.250415 | 6.255942 | 6.695900 | 6.627208 | 6.719368 | 6.675781 | 6.680053 | 6.695607 | 6.733400 | 6.640629 |
| GO:0045936 | negative regulation of phosphate metabolic process | 13/301 | 491/20870 | 0.02663871921870902 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | LRP6||TGFB2||PMEPA1||MAS1||SH3BP5||SLIT2||SPRED1||PIP5KL1||SOCS4||SLC8A1||SOCS3||ENPP1||INPP5F | 13 | 6.038521 | 6.182274 | 6.171592 | 6.032231 | 6.033230 | 6.048416 | 6.040150 | 6.188236 | 6.195753 | 6.180981 | 6.163933 | 6.179181 | 6.173690 | 6.166127 | 6.167330 |
| GO:0019932 | second-messenger-mediated signaling | 10/301 | 341/20870 | 0.02684652116783450 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | DMPK||VEGFA||NR5A2||CCR7||CHRM3||MCTP2||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||CXCR3||AQP1 | 10 | 6.899841 | 6.813305 | 6.685522 | 6.889876 | 6.901854 | 6.904255 | 6.903331 | 6.819035 | 6.825452 | 6.810751 | 6.797836 | 6.693749 | 6.701205 | 6.679588 | 6.667310 |
| GO:0060249 | anatomical structure homeostasis | 10/301 | 341/20870 | 0.02684652116783450 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | TYRO3||VEGFA||MKKS||IL6||TLR4||ADAM8||S1PR1||CSF1||ABCA4||SCX | 10 | 7.373075 | 7.683837 | 7.739456 | 7.386480 | 7.363548 | 7.369312 | 7.372861 | 7.692763 | 7.673219 | 7.681359 | 7.687931 | 7.743822 | 7.749470 | 7.731455 | 7.732999 |
| GO:0002691 | regulation of cellular extravasation | 3/301 | 45/20870 | 0.02699501297727648 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | RIPOR2||ADAM8||PTAFR | 3 | 5.759084 | 5.763159 | 5.708084 | 5.738329 | 5.814243 | 5.768632 | 5.713159 | 5.776962 | 5.743294 | 5.768251 | 5.763919 | 5.724497 | 5.717232 | 5.682234 | 5.708019 |
| GO:0007528 | neuromuscular junction development | 3/301 | 45/20870 | 0.02699501297727648 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | UNC13A||UNC13C||CACNB4 | 3 | 5.081211 | 5.146435 | 5.232635 | 5.098198 | 5.046734 | 5.092540 | 5.086809 | 5.119819 | 5.212343 | 5.093387 | 5.157413 | 5.214344 | 5.254079 | 5.222105 | 5.239680 |
| GO:0061462 | protein localization to lysosome | 3/301 | 45/20870 | 0.02699501297727648 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | KPTN||CLU||MEAK7 | 3 | 7.326723 | 7.734299 | 7.637939 | 7.323614 | 7.393484 | 7.272505 | 7.314660 | 7.667417 | 7.711959 | 7.751232 | 7.803123 | 7.641819 | 7.604023 | 7.693586 | 7.610584 |
| GO:0010563 | negative regulation of phosphorus metabolic process | 13/301 | 492/20870 | 0.02702105611416883 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | LRP6||TGFB2||PMEPA1||MAS1||SH3BP5||SLIT2||SPRED1||PIP5KL1||SOCS4||SLC8A1||SOCS3||ENPP1||INPP5F | 13 | 6.044223 | 6.190876 | 6.177102 | 6.040795 | 6.037082 | 6.050187 | 6.048785 | 6.197561 | 6.199644 | 6.199017 | 6.167023 | 6.179999 | 6.181584 | 6.178317 | 6.168470 |
| GO:0043087 | regulation of GTPase activity | 11/301 | 391/20870 | 0.02717487881904364 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | CDKL5||CCL22||RASAL1||RIPOR2||RGS4||MKKS||CCR7||BCAR3||FGD2||S1PR1||KLRK1 | 11 | 5.628103 | 5.898395 | 6.030590 | 5.635304 | 5.606877 | 5.623614 | 5.646323 | 5.899140 | 5.923795 | 5.867187 | 5.902893 | 6.053783 | 6.017906 | 6.022098 | 6.028303 |
| GO:0007250 | activation of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activity | 2/301 | 18/20870 | 0.02724300007827852 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | MAS1||TNFSF15 | 2 | 7.234015 | 7.214207 | 7.703364 | 7.267607 | 7.201634 | 7.234911 | 7.231148 | 7.210545 | 7.188251 | 7.244098 | 7.213387 | 7.684156 | 7.716129 | 7.702096 | 7.710869 |
| GO:0021756 | striatum development | 2/301 | 18/20870 | 0.02724300007827852 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | MKKS||SLC7A11 | 2 | 4.666160 | 4.194633 | 4.741165 | 4.959659 | 3.796540 | 4.548500 | 5.050672 | 3.840297 | 3.787575 | 3.798839 | 4.963168 | 4.782091 | 4.534767 | 4.272711 | 5.207704 |
| GO:0035743 | CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell cytokine production | 2/301 | 18/20870 | 0.02724300007827852 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | RSAD2||IL6 | 2 | 6.600709 | 7.922506 | 8.388983 | 6.626701 | 6.599524 | 6.585678 | 6.590584 | 7.918833 | 7.917185 | 7.927209 | 7.926770 | 8.383505 | 8.381310 | 8.396979 | 8.394078 |
| GO:0042117 | monocyte activation | 2/301 | 18/20870 | 0.02724300007827852 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | DYSF||CSF1 | 2 | 6.390316 | 6.088780 | 5.890569 | 6.399689 | 6.365416 | 6.441351 | 6.353177 | 6.058658 | 6.097573 | 6.070828 | 6.127097 | 5.927638 | 5.852106 | 5.919301 | 5.861666 |
| GO:0042532 | negative regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | 2/301 | 18/20870 | 0.02724300007827852 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | SOCS3||INPP5F | 2 | 5.341215 | 5.715130 | 5.591127 | 5.266043 | 5.148794 | 5.682060 | 5.203783 | 5.633675 | 5.978695 | 5.638572 | 5.572931 | 5.494829 | 5.642902 | 5.599565 | 5.622755 |
| GO:0048486 | parasympathetic nervous system development | 2/301 | 18/20870 | 0.02724300007827852 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | SEMA3F||TFAP2A | 2 | 4.077459 | 5.112486 | 5.346244 | 4.117929 | 4.030313 | 4.145606 | 4.011535 | 5.131231 | 5.159844 | 5.075262 | 5.081901 | 5.361160 | 5.201582 | 5.544047 | 5.254003 |
| GO:0051447 | negative regulation of meiotic cell cycle | 2/301 | 18/20870 | 0.02724300007827852 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | LIF||FBXO43 | 2 | 4.643743 | 4.744738 | 4.691910 | 4.621967 | 4.594194 | 4.830335 | 4.508743 | 4.784420 | 4.667871 | 4.794679 | 4.728453 | 4.549656 | 4.753018 | 4.637353 | 4.813243 |
| GO:0051798 | positive regulation of hair follicle development | 2/301 | 18/20870 | 0.02724300007827852 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | TGFB2||HPSE | 2 | 4.186179 | 4.908999 | 4.957456 | 4.125070 | 4.155718 | 4.219224 | 4.241649 | 4.879020 | 4.922125 | 4.889309 | 4.944597 | 4.946410 | 4.923008 | 4.988873 | 4.970678 |
| GO:0060391 | positive regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction | 2/301 | 18/20870 | 0.02724300007827852 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | BMP6||RBPMS | 2 | 6.007202 | 6.109621 | 6.060456 | 6.060298 | 6.007106 | 5.950803 | 6.008523 | 6.172907 | 6.041369 | 6.118754 | 6.102410 | 6.089384 | 6.108317 | 6.033531 | 6.008318 |
| GO:1903540 | establishment of protein localization to postsynaptic membrane | 2/301 | 18/20870 | 0.02724300007827852 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | MAPK10||TAMALIN | 2 | 4.941490 | 4.597417 | 4.696665 | 5.013505 | 4.960275 | 4.944620 | 4.842272 | 4.604700 | 4.532657 | 4.578109 | 4.670726 | 4.810046 | 4.661514 | 4.742924 | 4.560168 |
| GO:0006275 | regulation of DNA replication | 5/301 | 117/20870 | 0.02738009467872207 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | AICDA||ID3||CHTF18||MAS1||BCAR3 | 5 | 5.470837 | 5.878838 | 5.829461 | 5.547409 | 5.451762 | 5.484229 | 5.395770 | 5.870072 | 5.922980 | 5.844383 | 5.876798 | 5.827337 | 5.799366 | 5.870686 | 5.819511 |
| GO:0014823 | response to activity | 4/301 | 79/20870 | 0.02741270661463656 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | GCLC||MAS1||IL6||BMP6 | 4 | 6.395808 | 6.579776 | 6.654967 | 6.360643 | 6.390598 | 6.424297 | 6.406933 | 6.565256 | 6.596584 | 6.578898 | 6.578193 | 6.636158 | 6.639424 | 6.650433 | 6.693133 |
| GO:0042490 | mechanoreceptor differentiation | 4/301 | 79/20870 | 0.02741270661463656 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | ATP8B1||HEY2||MYO7A||DLL1 | 4 | 4.585445 | 4.314638 | 4.406932 | 4.619310 | 4.555216 | 4.608906 | 4.557167 | 4.348769 | 4.271955 | 4.317890 | 4.318896 | 4.385872 | 4.365257 | 4.426626 | 4.448486 |
| GO:0070613 | regulation of protein processing | 4/301 | 79/20870 | 0.02741270661463656 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | CST7||IL1R2||CHAC1||ADAM8 | 4 | 6.955941 | 7.022213 | 7.075418 | 6.960819 | 6.959055 | 6.938506 | 6.965239 | 7.018914 | 6.998283 | 7.041142 | 7.030164 | 7.033965 | 7.088019 | 7.076691 | 7.102103 |
| GO:0001894 | tissue homeostasis | 9/301 | 294/20870 | 0.02742519285336883 | 0.1764811160114 | 0.1472780970599 | VEGFA||MKKS||IL6||TLR4||ADAM8||S1PR1||CSF1||ABCA4||SCX | 9 | 7.528322 | 7.829531 | 7.880072 | 7.544260 | 7.520898 | 7.520836 | 7.527167 | 7.837533 | 7.823708 | 7.827247 | 7.829599 | 7.887449 | 7.888801 | 7.869036 | 7.874904 |
| GO:0044409 | entry into host | 7/301 | 202/20870 | 0.02762477131904865 | 0.1774696207368 | 0.1481030300510 | SIGLEC1||TYRO3||ZNF639||TRIM22||TNFRSF14||LY6E||IFITM1 | 7 | 6.963782 | 7.570005 | 7.761065 | 6.946249 | 6.973817 | 6.961391 | 6.973498 | 7.566539 | 7.544129 | 7.582557 | 7.586412 | 7.737420 | 7.769336 | 7.778784 | 7.758391 |
| GO:0060047 | heart contraction | 8/301 | 248/20870 | 0.02795788153478663 | 0.1793112634648 | 0.1496399289701 | TGFB2||DMPK||RGS4||TBX2||HEY2||BIN1||SLC8A1||TRDN | 8 | 5.976623 | 5.946827 | 5.831944 | 5.992463 | 5.966246 | 5.960926 | 5.986613 | 5.963627 | 5.911290 | 5.980319 | 5.931061 | 5.805033 | 5.852265 | 5.843251 | 5.826782 |
| GO:2000146 | negative regulation of cell motility | 11/301 | 393/20870 | 0.02806078404023186 | 0.1796727813919 | 0.1499416251150 | TIE1||RIPOR2||PADI2||TMEFF2||SLIT2||NBL1||SPRED1||PIP5KL1||IFITM1||KLRK1||EPPK1 | 11 | 6.112849 | 6.135097 | 6.185429 | 6.093816 | 6.113578 | 6.117027 | 6.126774 | 6.129035 | 6.143281 | 6.133156 | 6.134877 | 6.197207 | 6.187070 | 6.180461 | 6.176894 |
| GO:0001570 | vasculogenesis | 4/301 | 80/20870 | 0.02853895699588277 | 0.1808875737038 | 0.1509554010026 | TIE1||VEGFA||HEY2||SPRED1 | 4 | 5.985505 | 5.942943 | 5.823531 | 5.954346 | 5.968513 | 6.019222 | 5.999046 | 5.959412 | 5.912496 | 5.933054 | 5.966173 | 5.820676 | 5.851213 | 5.814036 | 5.807815 |
| GO:0002294 | CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation involved in immune response | 4/301 | 80/20870 | 0.02853895699588277 | 0.1808875737038 | 0.1509554010026 | IL23A||TNFSF18||IL6||HLA-DRA | 4 | 5.328474 | 5.438681 | 5.567450 | 5.314256 | 5.336688 | 5.342323 | 5.320449 | 5.451465 | 5.429311 | 5.459815 | 5.413674 | 5.571168 | 5.577039 | 5.547069 | 5.574327 |
| GO:1901184 | regulation of ERBB signaling pathway | 4/301 | 80/20870 | 0.02853895699588277 | 0.1808875737038 | 0.1509554010026 | IFI6||BCAR3||SOCS4||MVB12B | 4 | 5.882000 | 7.099155 | 7.603495 | 5.864011 | 5.882229 | 5.870719 | 5.910601 | 7.073172 | 7.130939 | 7.094602 | 7.097315 | 7.587163 | 7.616828 | 7.603696 | 7.606139 |
| GO:0003197 | endocardial cushion development | 3/301 | 46/20870 | 0.02857845634792566 | 0.1808875737038 | 0.1509554010026 | TGFB2||TBX2||HEY2 | 3 | 5.628087 | 5.234160 | 5.090604 | 5.631044 | 5.647343 | 5.582392 | 5.650545 | 5.254103 | 5.206178 | 5.247614 | 5.228260 | 5.108126 | 5.129208 | 5.063049 | 5.060839 |
| GO:0060976 | coronary vasculature development | 3/301 | 46/20870 | 0.02857845634792566 | 0.1808875737038 | 0.1509554010026 | VEGFA||HEY2||SPRED1 | 3 | 4.469001 | 4.677686 | 4.844313 | 4.443768 | 4.465609 | 4.466222 | 4.499845 | 4.631132 | 4.655538 | 4.731922 | 4.690152 | 4.837957 | 4.902595 | 4.801671 | 4.833153 |
| GO:0061383 | trabecula morphogenesis | 3/301 | 46/20870 | 0.02857845634792566 | 0.1808875737038 | 0.1509554010026 | TGFB2||HEY2||S1PR1 | 3 | 5.479124 | 5.508562 | 5.476157 | 5.517226 | 5.490570 | 5.457800 | 5.449897 | 5.529870 | 5.476645 | 5.474030 | 5.552119 | 5.534643 | 5.459818 | 5.439556 | 5.468838 |
| GO:0089718 | amino acid import across plasma membrane | 3/301 | 46/20870 | 0.02857845634792566 | 0.1808875737038 | 0.1509554010026 | SLC7A8||RGS4||SLC7A11 | 3 | 5.595740 | 6.056980 | 6.199560 | 5.598958 | 5.603016 | 5.602605 | 5.578235 | 6.077495 | 6.044488 | 6.058647 | 6.047055 | 6.186223 | 6.198303 | 6.224175 | 6.189229 |
| GO:1903531 | negative regulation of secretion by cell | 6/301 | 160/20870 | 0.02878084599073662 | 0.1818704523244 | 0.1517756388623 | NR1H3||OSM||LIF||RSAD2||FRMD4A||HLA-F | 6 | 5.678927 | 6.190605 | 6.364650 | 5.651743 | 5.661294 | 5.718916 | 5.682827 | 6.192159 | 6.196059 | 6.181747 | 6.192416 | 6.359174 | 6.388597 | 6.360069 | 6.350475 |
| GO:0010721 | negative regulation of cell development | 7/301 | 204/20870 | 0.02893129740096782 | 0.1822246970067 | 0.1520712652947 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||VEGFA||BCL11A||IL6||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 7 | 7.368388 | 7.770591 | 7.822686 | 7.373570 | 7.358970 | 7.369136 | 7.371833 | 7.780174 | 7.768816 | 7.769639 | 7.763687 | 7.822047 | 7.821267 | 7.829588 | 7.817817 |
| GO:0070665 | positive regulation of leukocyte proliferation | 7/301 | 204/20870 | 0.02893129740096782 | 0.1822246970067 | 0.1520712652947 | IL23A||IL1A||IL6||TLR4||IGF2||CSF1||PDCD1LG2 | 7 | 6.465650 | 7.081973 | 7.284519 | 6.452772 | 6.473916 | 6.470602 | 6.465220 | 7.089399 | 7.079571 | 7.082400 | 7.076491 | 7.295635 | 7.285329 | 7.274622 | 7.282410 |
| GO:0045582 | positive regulation of T cell differentiation | 5/301 | 119/20870 | 0.02917190726246532 | 0.1834409347563 | 0.1530862474377 | IL23A||ADAM8||EGR3||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 5 | 5.580094 | 5.803337 | 5.915946 | 5.577824 | 5.577722 | 5.603946 | 5.560550 | 5.794698 | 5.787333 | 5.823165 | 5.807894 | 5.923261 | 5.903398 | 5.919892 | 5.917154 |
| GO:0002287 | alpha-beta T cell activation involved in immune response | 4/301 | 81/20870 | 0.02969237111545224 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | IL23A||TNFSF18||IL6||HLA-DRA | 4 | 5.302077 | 5.412282 | 5.541013 | 5.287967 | 5.309979 | 5.316230 | 5.293949 | 5.425024 | 5.403048 | 5.433293 | 5.387309 | 5.544644 | 5.550556 | 5.520517 | 5.548137 |
| GO:0002293 | alpha-beta T cell differentiation involved in immune response | 4/301 | 81/20870 | 0.02969237111545224 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | IL23A||TNFSF18||IL6||HLA-DRA | 4 | 5.302077 | 5.412282 | 5.541013 | 5.287967 | 5.309979 | 5.316230 | 5.293949 | 5.425024 | 5.403048 | 5.433293 | 5.387309 | 5.544644 | 5.550556 | 5.520517 | 5.548137 |
| GO:0051279 | regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol | 4/301 | 81/20870 | 0.02969237111545224 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | CXCL10||CXCL11||SLC8A1||TRDN | 4 | 6.859665 | 7.044578 | 7.095172 | 6.824047 | 6.886643 | 6.868958 | 6.858290 | 7.028093 | 7.051955 | 7.064140 | 7.033837 | 7.081058 | 7.084892 | 7.110951 | 7.103570 |
| GO:1903317 | regulation of protein maturation | 4/301 | 81/20870 | 0.02969237111545224 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | CST7||IL1R2||CHAC1||ADAM8 | 4 | 6.911538 | 6.977239 | 7.023153 | 6.916887 | 6.915415 | 6.893302 | 6.920390 | 6.974891 | 6.953712 | 6.995662 | 6.984362 | 6.981729 | 7.036064 | 7.024220 | 7.049703 |
| GO:0045637 | regulation of myeloid cell differentiation | 8/301 | 251/20870 | 0.02972831718653384 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | IL23A||LIF||TLR4||POU4F1||CSF1||IRF7||ISG15||DLL1 | 8 | 6.685134 | 6.633946 | 6.636374 | 6.687340 | 6.676999 | 6.704535 | 6.671443 | 6.631713 | 6.649126 | 6.627145 | 6.627689 | 6.661882 | 6.632116 | 6.623566 | 6.627616 |
| GO:0022600 | digestive system process | 5/301 | 120/20870 | 0.03009494433019882 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | NR1H3||TYMP||CHRM3||TLR4||AQP1 | 5 | 5.075117 | 5.259658 | 5.362867 | 5.038947 | 5.072219 | 5.161469 | 5.023842 | 5.230411 | 5.316097 | 5.224715 | 5.265564 | 5.380060 | 5.346753 | 5.335826 | 5.388162 |
| GO:0016082 | synaptic vesicle priming | 2/301 | 19/20870 | 0.03016274528531361 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | UNC13A||UNC13C | 2 | 4.531569 | 4.223391 | 4.435710 | 4.303379 | 4.663800 | 4.594942 | 4.539343 | 4.141094 | 4.410936 | 4.254900 | 4.062615 | 4.766029 | 4.241884 | 4.232356 | 4.435557 |
| GO:0031290 | retinal ganglion cell axon guidance | 2/301 | 19/20870 | 0.03016274528531361 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | VEGFA||SLIT2 | 2 | 7.235275 | 7.317215 | 7.227011 | 7.280014 | 7.203676 | 7.257923 | 7.197779 | 7.292665 | 7.279886 | 7.320551 | 7.373940 | 7.201908 | 7.235174 | 7.233915 | 7.236755 |
| GO:0043116 | negative regulation of vascular permeability | 2/301 | 19/20870 | 0.03016274528531361 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | VEGFA||SLIT2 | 2 | 3.582712 | 4.358291 | 4.512626 | 3.544192 | 3.680703 | 3.597474 | 3.502287 | 4.260456 | 4.283990 | 4.407375 | 4.470865 | 4.532327 | 4.559518 | 4.461625 | 4.495131 |
| GO:0048791 | calcium ion-regulated exocytosis of neurotransmitter | 2/301 | 19/20870 | 0.03016274528531361 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | UNC13A||UNC13C | 2 | 4.247731 | 4.494508 | 4.592804 | 4.274309 | 4.238411 | 4.256067 | 4.221602 | 4.412503 | 4.618486 | 4.553281 | 4.380381 | 4.564744 | 4.557995 | 4.599260 | 4.647467 |
| GO:0098877 | neurotransmitter receptor transport to plasma membrane | 2/301 | 19/20870 | 0.03016274528531361 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | MAPK10||TAMALIN | 2 | 4.947108 | 4.790621 | 4.868467 | 5.019105 | 4.976028 | 4.931151 | 4.857197 | 4.782443 | 4.735815 | 4.711009 | 4.923679 | 4.965847 | 4.812952 | 4.909054 | 4.778261 |
| GO:2000319 | regulation of T-helper 17 cell differentiation | 2/301 | 19/20870 | 0.03016274528531361 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | IL23A||TNFSF18 | 2 | 4.063405 | 4.626088 | 5.424420 | 4.055325 | 4.018246 | 4.098066 | 4.080739 | 4.663766 | 4.618826 | 4.631723 | 4.589041 | 5.414615 | 5.411473 | 5.391850 | 5.478267 |
| GO:0031018 | endocrine pancreas development | 3/301 | 47/20870 | 0.03021018470418580 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | IL6||BMP6||DLL1 | 3 | 5.220447 | 5.376914 | 5.111455 | 5.260866 | 5.221087 | 5.122736 | 5.272349 | 5.627950 | 5.402216 | 5.382006 | 5.034482 | 5.132635 | 5.073295 | 5.278432 | 4.941079 |
| GO:0044058 | regulation of digestive system process | 3/301 | 47/20870 | 0.03021018470418580 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | NR1H3||TYMP||AQP1 | 3 | 4.567004 | 5.096842 | 5.412671 | 4.533179 | 4.608678 | 4.701827 | 4.408427 | 5.075374 | 5.180092 | 4.980379 | 5.143575 | 5.473024 | 5.390034 | 5.353479 | 5.431371 |
| GO:0045124 | regulation of bone resorption | 3/301 | 47/20870 | 0.03021018470418580 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | IL6||ADAM8||S1PR1 | 3 | 8.038177 | 8.863591 | 8.868947 | 8.054675 | 8.038588 | 8.023636 | 8.035640 | 8.872665 | 8.852354 | 8.859116 | 8.870133 | 8.868711 | 8.875685 | 8.863518 | 8.867848 |
| GO:0048483 | autonomic nervous system development | 3/301 | 47/20870 | 0.03021018470418580 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | SEMA3F||TFAP2A||EDNRA | 3 | 5.257472 | 5.476424 | 5.517197 | 5.276077 | 5.193032 | 5.343118 | 5.212847 | 5.507960 | 5.433992 | 5.432792 | 5.528386 | 5.525642 | 5.524792 | 5.557947 | 5.458607 |
| GO:2000403 | positive regulation of lymphocyte migration | 3/301 | 47/20870 | 0.03021018470418580 | 0.1848518591804 | 0.1542637006915 | ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10 | 3 | 6.291937 | 7.032010 | 7.407349 | 6.297781 | 6.276838 | 6.306987 | 6.285958 | 7.051304 | 7.040173 | 7.024024 | 7.012229 | 7.395224 | 7.424561 | 7.387464 | 7.421786 |
| GO:0003407 | neural retina development | 4/301 | 82/20870 | 0.03087303540487281 | 0.1880138638773 | 0.1569024761320 | TGFB2||SLC17A7||TFAP2A||IGFN1 | 4 | 4.337612 | 4.628119 | 4.725250 | 4.282059 | 4.240685 | 4.204096 | 4.589961 | 4.640743 | 4.620882 | 4.655950 | 4.594159 | 4.763935 | 4.717834 | 4.729117 | 4.689117 |
| GO:0014032 | neural crest cell development | 4/301 | 82/20870 | 0.03087303540487281 | 0.1880138638773 | 0.1569024761320 | SEMA3F||EDNRA||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 4 | 4.978407 | 4.957180 | 4.972616 | 4.936692 | 5.022980 | 4.962746 | 4.989789 | 4.958358 | 4.935037 | 4.974747 | 4.960299 | 5.021459 | 4.994368 | 4.917527 | 4.954963 |
| GO:0072527 | pyrimidine-containing compound metabolic process | 4/301 | 82/20870 | 0.03087303540487281 | 0.1880138638773 | 0.1569024761320 | TYMP||AICDA||CMPK2||TK2 | 4 | 5.685847 | 5.705329 | 5.618070 | 5.730442 | 5.636040 | 5.714500 | 5.660347 | 5.684500 | 5.680114 | 5.771447 | 5.683179 | 5.661120 | 5.595214 | 5.602765 | 5.612258 |
| GO:2001234 | negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | 8/301 | 253/20870 | 0.03095063181856696 | 0.1881895896874 | 0.1570491239066 | GCLC||MEIS3||IL1A||CLU||IFI6||NR4A2||CREB3L1||SCG2 | 8 | 6.815446 | 7.233419 | 7.423857 | 6.808282 | 6.817896 | 6.808706 | 6.826819 | 7.247408 | 7.232476 | 7.226386 | 7.227308 | 7.421444 | 7.427218 | 7.422438 | 7.424321 |
| GO:0002573 | myeloid leukocyte differentiation | 8/301 | 254/20870 | 0.03157454039639638 | 0.1916812900479 | 0.1599630389827 | IL23A||VEGFA||CCR7||LIF||TLR4||POU4F1||CSF1||IRF7 | 8 | 6.275507 | 6.841037 | 7.043956 | 6.281349 | 6.269913 | 6.272736 | 6.278000 | 6.842299 | 6.844590 | 6.838706 | 6.838542 | 7.035573 | 7.048174 | 7.046426 | 7.045619 |
| GO:0031032 | actomyosin structure organization | 7/301 | 208/20870 | 0.03166843398223133 | 0.1919494876066 | 0.1601868568448 | MKKS||TMEFF2||ANKRD1||OBSCN||S1PR1||MYOZ2||NRAP | 7 | 6.462103 | 6.496682 | 6.471869 | 6.479004 | 6.443769 | 6.462687 | 6.462738 | 6.477513 | 6.488840 | 6.492754 | 6.527143 | 6.478740 | 6.458425 | 6.464875 | 6.485279 |
| GO:0045861 | negative regulation of proteolysis | 11/301 | 401/20870 | 0.03181303448614075 | 0.1922659613178 | 0.1604509624160 | NR1H3||CST7||VEGFA||IL1R2||C3||IFI6||CHAC1||BIN1||SERPINB7||SERPINA9||AQP1 | 11 | 7.058927 | 7.208575 | 7.335159 | 7.059433 | 7.070524 | 7.042346 | 7.063258 | 7.203792 | 7.215419 | 7.200094 | 7.214930 | 7.345212 | 7.322787 | 7.334988 | 7.337561 |
| GO:0062012 | regulation of small molecule metabolic process | 10/301 | 351/20870 | 0.03182024068428981 | 0.1922659613178 | 0.1604509624160 | NR1H3||NR4A3||MAS1||ETFBKMT||SLC7A11||BMP6||IGF2||PTAFR||C1QTNF1||ENPP1 | 10 | 7.090962 | 7.196825 | 7.340098 | 7.095723 | 7.092364 | 7.081580 | 7.094140 | 7.207215 | 7.188663 | 7.196695 | 7.194666 | 7.340654 | 7.341216 | 7.352112 | 7.326292 |
| GO:0042398 | cellular modified amino acid biosynthetic process | 3/301 | 48/20870 | 0.03189004463692604 | 0.1923866599112 | 0.1605516885422 | GCLC||CHAC1||SLC7A11 | 3 | 5.463333 | 5.635905 | 5.665958 | 5.456121 | 5.502185 | 5.470077 | 5.423851 | 5.627516 | 5.631891 | 5.618150 | 5.665618 | 5.723884 | 5.585694 | 5.677871 | 5.672946 |
| GO:0051209 | release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol | 5/301 | 122/20870 | 0.03199572643928478 | 0.1927230885836 | 0.1608324470493 | CCR7||CXCL10||CXCL11||SLC8A1||TRDN | 5 | 6.374554 | 6.640410 | 6.753994 | 6.332828 | 6.386319 | 6.364799 | 6.413072 | 6.631214 | 6.649141 | 6.653561 | 6.627549 | 6.726271 | 6.786226 | 6.754304 | 6.748539 |
| GO:0070527 | platelet aggregation | 4/301 | 83/20870 | 0.03208102622496033 | 0.1929358913623 | 0.1610100365217 | TYRO3||IL6||SLC7A11||C1QTNF1 | 4 | 8.269893 | 8.348471 | 8.306964 | 8.268450 | 8.269810 | 8.273250 | 8.268058 | 8.356203 | 8.343625 | 8.349908 | 8.344111 | 8.309875 | 8.310223 | 8.307667 | 8.300067 |
| GO:0051962 | positive regulation of nervous system development | 9/301 | 303/20870 | 0.03235973233229059 | 0.1941226405505 | 0.1620004096908 | CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||LIF||IL6||BIN1||SLIT2||CHODL||GPRASP2 | 9 | 5.665316 | 5.901375 | 6.022676 | 5.655747 | 5.651492 | 5.705767 | 5.647479 | 5.893107 | 5.902068 | 5.884922 | 5.925088 | 6.038328 | 6.038785 | 6.011984 | 6.001234 |
| GO:0045619 | regulation of lymphocyte differentiation | 7/301 | 209/20870 | 0.03237891233218035 | 0.1941226405505 | 0.1620004096908 | IL23A||TNFSF18||ZC3H8||ADAM8||EGR3||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 7 | 6.038167 | 6.123967 | 6.187839 | 6.043859 | 6.035408 | 6.050254 | 6.023004 | 6.119992 | 6.124163 | 6.127036 | 6.124668 | 6.172250 | 6.182268 | 6.216126 | 6.180319 |
| GO:0038127 | ERBB signaling pathway | 5/301 | 123/20870 | 0.03297363730955042 | 0.1951098102562 | 0.1628242285730 | RPS6KA5||IFI6||BCAR3||SOCS4||MVB12B | 5 | 5.817586 | 6.779536 | 7.199713 | 5.793256 | 5.813949 | 5.814225 | 5.848370 | 6.764999 | 6.799107 | 6.780947 | 6.772869 | 7.189859 | 7.209164 | 7.200495 | 7.199270 |
| GO:0051283 | negative regulation of sequestering of calcium ion | 5/301 | 123/20870 | 0.03297363730955042 | 0.1951098102562 | 0.1628242285730 | CCR7||CXCL10||CXCL11||SLC8A1||TRDN | 5 | 6.362496 | 6.628138 | 6.743663 | 6.320449 | 6.373004 | 6.352428 | 6.402851 | 6.618605 | 6.637222 | 6.640958 | 6.615596 | 6.717335 | 6.775620 | 6.742793 | 6.738300 |
| GO:0002281 | macrophage activation involved in immune response | 2/301 | 20/20870 | 0.03320050384313580 | 0.1951098102562 | 0.1628242285730 | DYSF||SUCNR1 | 2 | 8.031764 | 7.575672 | 7.440085 | 8.055681 | 8.016553 | 8.046169 | 8.008110 | 7.599607 | 7.574504 | 7.571342 | 7.556908 | 7.430992 | 7.454445 | 7.425616 | 7.449086 |
| GO:0002864 | regulation of acute inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus | 2/301 | 20/20870 | 0.03320050384313580 | 0.1951098102562 | 0.1628242285730 | C3||CCR7 | 2 | 6.131732 | 6.502103 | 6.582760 | 6.118627 | 6.139623 | 6.121010 | 6.147462 | 6.467138 | 6.458650 | 6.490596 | 6.588289 | 6.582560 | 6.535012 | 6.613553 | 6.598713 |
| GO:0010759 | positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis | 2/301 | 20/20870 | 0.03320050384313580 | 0.1951098102562 | 0.1628242285730 | TNFSF18||CSF1 | 2 | 5.410188 | 7.332517 | 7.835762 | 5.391503 | 5.416954 | 5.429237 | 5.402777 | 7.342604 | 7.354626 | 7.326889 | 7.305479 | 7.816173 | 7.842679 | 7.823474 | 7.860309 |
| GO:0032793 | positive regulation of CREB transcription factor activity | 2/301 | 20/20870 | 0.03320050384313580 | 0.1951098102562 | 0.1628242285730 | RPS6KA5||VEGFA | 2 | 5.023928 | 4.590887 | 4.955732 | 4.930178 | 4.825575 | 5.066218 | 5.240073 | 4.628371 | 4.496790 | 4.585236 | 4.648482 | 5.196897 | 4.879778 | 4.777315 | 4.934907 |
| GO:0043031 | negative regulation of macrophage activation | 2/301 | 20/20870 | 0.03320050384313580 | 0.1951098102562 | 0.1628242285730 | NR1H3||CST7 | 2 | 6.893245 | 6.050031 | 6.222192 | 6.907578 | 6.885190 | 6.901596 | 6.878423 | 6.108693 | 5.990077 | 6.036638 | 6.062165 | 6.200006 | 6.211192 | 6.216567 | 6.260273 |
| GO:0043117 | positive regulation of vascular permeability | 2/301 | 20/20870 | 0.03320050384313580 | 0.1951098102562 | 0.1628242285730 | VEGFA||BMP6 | 2 | 5.430123 | 5.867302 | 6.103735 | 5.316165 | 5.456129 | 5.438547 | 5.503128 | 5.888232 | 5.773414 | 5.889556 | 5.913929 | 6.113866 | 6.134758 | 6.086644 | 6.078989 |
| GO:0044320 | cellular response to leptin stimulus | 2/301 | 20/20870 | 0.03320050384313580 | 0.1951098102562 | 0.1628242285730 | NR4A3||MKKS | 2 | 5.262948 | 6.227197 | 6.545675 | 5.444461 | 4.812824 | 5.189700 | 5.505949 | 6.109763 | 6.134681 | 6.195426 | 6.443896 | 6.568677 | 6.480798 | 6.414255 | 6.702677 |
| GO:0051900 | regulation of mitochondrial depolarization | 2/301 | 20/20870 | 0.03320050384313580 | 0.1951098102562 | 0.1628242285730 | GCLC||IFI6 | 2 | 6.989019 | 7.116914 | 7.472577 | 6.993969 | 6.975691 | 6.975585 | 7.010539 | 7.122846 | 7.114001 | 7.092411 | 7.138022 | 7.472528 | 7.498151 | 7.475961 | 7.443136 |
| GO:0071731 | response to nitric oxide | 2/301 | 20/20870 | 0.03320050384313580 | 0.1951098102562 | 0.1628242285730 | CCR7||AQP1 | 2 | 5.850262 | 5.853824 | 5.906735 | 5.816714 | 5.864592 | 5.873211 | 5.845884 | 5.877977 | 5.831082 | 5.847946 | 5.857890 | 5.881253 | 5.921102 | 5.926800 | 5.897319 |
| GO:1904948 | midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation | 2/301 | 20/20870 | 0.03320050384313580 | 0.1951098102562 | 0.1628242285730 | LRP6||NR4A2 | 2 | 5.898548 | 5.803933 | 5.719691 | 5.910356 | 5.902666 | 5.916364 | 5.864237 | 5.845832 | 5.697439 | 5.729147 | 5.931178 | 5.766600 | 5.664791 | 5.692980 | 5.751981 |
| GO:2000846 | regulation of corticosteroid hormone secretion | 2/301 | 20/20870 | 0.03320050384313580 | 0.1951098102562 | 0.1628242285730 | BMP6||C1QTNF1 | 2 | 4.776408 | 4.338458 | 4.218381 | 4.632586 | 4.625017 | 5.122403 | 4.661551 | 4.241047 | 4.646723 | 4.197675 | 4.218237 | 4.220383 | 4.374363 | 4.125688 | 4.139299 |
| GO:0050678 | regulation of epithelial cell proliferation | 11/301 | 404/20870 | 0.03330821756336325 | 0.1951967509611 | 0.1628967828602 | TIE1||TGFB2||VEGFA||NR4A3||RREB1||BMP6||IGF2||SCG2||EGR3||SULF2||EPPK1 | 11 | 6.550636 | 6.488721 | 6.496551 | 6.533092 | 6.546963 | 6.559938 | 6.562360 | 6.495356 | 6.480067 | 6.480394 | 6.498966 | 6.508409 | 6.493153 | 6.491648 | 6.492926 |
| GO:0001892 | embryonic placenta development | 4/301 | 84/20870 | 0.03331640996720199 | 0.1951967509611 | 0.1628967828602 | LIF||HEY2||IGF2||SOCS3 | 4 | 5.681145 | 5.541264 | 5.489409 | 5.689233 | 5.678030 | 5.673979 | 5.683291 | 5.551913 | 5.520472 | 5.550148 | 5.542306 | 5.501334 | 5.474859 | 5.469385 | 5.511625 |
| GO:0046434 | organophosphate catabolic process | 6/301 | 166/20870 | 0.03358234559490884 | 0.1964567217302 | 0.1639482613493 | TYMP||ENTPD1||PLA2G7||GDPD1||ENPP1||INPP5F | 6 | 5.365716 | 5.334582 | 5.369260 | 5.341711 | 5.346851 | 5.427807 | 5.344664 | 5.340501 | 5.281896 | 5.353391 | 5.361208 | 5.349904 | 5.422295 | 5.330151 | 5.373043 |
| GO:0003015 | heart process | 8/301 | 258/20870 | 0.03415626103307207 | 0.1995118363823 | 0.1664978342579 | TGFB2||DMPK||RGS4||TBX2||HEY2||BIN1||SLC8A1||TRDN | 8 | 6.021966 | 5.981119 | 5.874177 | 6.035226 | 6.012749 | 6.009327 | 6.030392 | 5.995000 | 5.946307 | 6.016085 | 5.966096 | 5.853643 | 5.896397 | 5.880496 | 5.865816 |
| GO:0045670 | regulation of osteoclast differentiation | 4/301 | 85/20870 | 0.03457924315951113 | 0.2016774287596 | 0.1683050776137 | IL23A||TLR4||POU4F1||CSF1 | 4 | 6.265077 | 6.449269 | 6.496369 | 6.282149 | 6.231550 | 6.283022 | 6.262985 | 6.450188 | 6.451818 | 6.446922 | 6.448142 | 6.490192 | 6.508814 | 6.477337 | 6.508887 |
| GO:0010811 | positive regulation of cell-substrate adhesion | 5/301 | 125/20870 | 0.03498488133811004 | 0.2021508076056 | 0.1687001246148 | UNC13D||VEGFA||RREB1||CCR7||CSF1 | 5 | 6.459516 | 6.567584 | 6.521191 | 6.455073 | 6.467569 | 6.489603 | 6.425064 | 6.597064 | 6.592890 | 6.547346 | 6.531931 | 6.568958 | 6.510775 | 6.508601 | 6.495308 |
| GO:0032755 | positive regulation of interleukin-6 production | 5/301 | 125/20870 | 0.03498488133811004 | 0.2021508076056 | 0.1687001246148 | IL1A||IL6||TLR4||PTAFR||TLR7 | 5 | 6.626086 | 7.045453 | 7.203516 | 6.601843 | 6.627876 | 6.632266 | 6.642054 | 7.046914 | 7.051063 | 7.054926 | 7.028769 | 7.201900 | 7.205297 | 7.207020 | 7.199837 |
| GO:0042752 | regulation of circadian rhythm | 5/301 | 125/20870 | 0.03498488133811004 | 0.2021508076056 | 0.1687001246148 | NR1H3||PTGDS||MAPK10||BHLHE40||FBXL17 | 5 | 5.497395 | 5.413841 | 5.310421 | 5.485313 | 5.514516 | 5.511822 | 5.477568 | 5.478054 | 5.472907 | 5.347346 | 5.351546 | 5.375237 | 5.290517 | 5.292420 | 5.281494 |
| GO:0045639 | positive regulation of myeloid cell differentiation | 5/301 | 125/20870 | 0.03498488133811004 | 0.2021508076056 | 0.1687001246148 | IL23A||LIF||POU4F1||CSF1||ISG15 | 5 | 6.366791 | 6.350778 | 6.348035 | 6.375312 | 6.357400 | 6.370529 | 6.363859 | 6.350116 | 6.337014 | 6.361007 | 6.354869 | 6.346828 | 6.354898 | 6.340101 | 6.350272 |
| GO:0051282 | regulation of sequestering of calcium ion | 5/301 | 125/20870 | 0.03498488133811004 | 0.2021508076056 | 0.1687001246148 | CCR7||CXCL10||CXCL11||SLC8A1||TRDN | 5 | 6.333710 | 6.597494 | 6.714075 | 6.292513 | 6.346704 | 6.321646 | 6.372754 | 6.586920 | 6.606973 | 6.610960 | 6.584935 | 6.689810 | 6.744640 | 6.711536 | 6.709778 |
| GO:0046661 | male sex differentiation | 6/301 | 168/20870 | 0.03529131201115080 | 0.2021508076056 | 0.1687001246148 | MAMLD1||TGFB2||TNFSF10||MAS1||BMP6||SCX | 6 | 6.181467 | 6.068088 | 6.036733 | 6.181027 | 6.183370 | 6.173579 | 6.187856 | 6.038373 | 6.076179 | 6.069785 | 6.087556 | 6.021937 | 6.049837 | 6.040093 | 6.034926 |
| GO:1903169 | regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport | 6/301 | 168/20870 | 0.03529131201115080 | 0.2021508076056 | 0.1687001246148 | BIN1||CXCL10||CXCL11||CACNB4||SLC8A1||TRDN | 6 | 6.286846 | 6.416217 | 6.438195 | 6.253496 | 6.295994 | 6.297428 | 6.299956 | 6.411435 | 6.422636 | 6.428355 | 6.402300 | 6.427489 | 6.432418 | 6.455112 | 6.437610 |
| GO:0046631 | alpha-beta T cell activation | 7/301 | 213/20870 | 0.03532726975843301 | 0.2021508076056 | 0.1687001246148 | IL23A||ITK||TNFSF18||RSAD2||IL6||TNFRSF14||HLA-DRA | 7 | 6.095098 | 6.398089 | 6.533305 | 6.076253 | 6.108603 | 6.087966 | 6.107315 | 6.413558 | 6.405750 | 6.387427 | 6.385423 | 6.520254 | 6.529949 | 6.541580 | 6.541328 |
| GO:0050679 | positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation | 7/301 | 213/20870 | 0.03532726975843301 | 0.2021508076056 | 0.1687001246148 | VEGFA||NR4A3||RREB1||BMP6||IGF2||SCG2||EGR3 | 7 | 6.316795 | 6.421907 | 6.443504 | 6.270707 | 6.313852 | 6.341601 | 6.339890 | 6.442113 | 6.412020 | 6.402369 | 6.430792 | 6.440154 | 6.442276 | 6.451302 | 6.440256 |
| GO:0010543 | regulation of platelet activation | 3/301 | 50/20870 | 0.03539340739223060 | 0.2021508076056 | 0.1687001246148 | IL6||TLR4||C1QTNF1 | 3 | 7.941995 | 8.047195 | 7.901950 | 7.966550 | 7.954560 | 7.928360 | 7.917984 | 8.047370 | 8.019963 | 8.056683 | 8.064375 | 7.881028 | 7.911379 | 7.913245 | 7.901922 |
| GO:0043303 | mast cell degranulation | 3/301 | 50/20870 | 0.03539340739223060 | 0.2021508076056 | 0.1687001246148 | UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3 | 3 | 6.175841 | 6.330756 | 6.388635 | 6.146274 | 6.219992 | 6.136258 | 6.199129 | 6.312298 | 6.317341 | 6.365463 | 6.327319 | 6.426316 | 6.388110 | 6.372339 | 6.367026 |
| GO:0046189 | phenol-containing compound biosynthetic process | 3/301 | 50/20870 | 0.03539340739223060 | 0.2021508076056 | 0.1687001246148 | TGFB2||SLC7A11||NR4A2 | 3 | 4.959367 | 5.209994 | 5.323676 | 5.006730 | 4.914401 | 4.984297 | 4.930047 | 5.211665 | 5.224583 | 5.208080 | 5.195499 | 5.339387 | 5.260683 | 5.335479 | 5.357270 |
| GO:1902930 | regulation of alcohol biosynthetic process | 3/301 | 50/20870 | 0.03539340739223060 | 0.2021508076056 | 0.1687001246148 | MAS1||BMP6||PTAFR | 3 | 5.408384 | 5.292439 | 5.333992 | 5.411311 | 5.399270 | 5.430772 | 5.391881 | 5.254458 | 5.297941 | 5.327613 | 5.288801 | 5.341199 | 5.283136 | 5.355318 | 5.355099 |
| GO:2000677 | regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding | 3/301 | 50/20870 | 0.03539340739223060 | 0.2021508076056 | 0.1687001246148 | LIF||HEY2||POU4F1 | 3 | 8.423895 | 8.622563 | 8.553514 | 8.431501 | 8.422475 | 8.420071 | 8.421506 | 8.640026 | 8.598157 | 8.622006 | 8.629734 | 8.554447 | 8.543989 | 8.570865 | 8.544590 |
| GO:0007193 | adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | 4/301 | 86/20870 | 0.03586957257609467 | 0.2031203852343 | 0.1695092624497 | CHRM3||EDNRA||S1PR1||SSTR2 | 4 | 6.467867 | 6.540758 | 6.479904 | 6.491192 | 6.458658 | 6.466971 | 6.454365 | 6.548047 | 6.513303 | 6.562944 | 6.538286 | 6.478447 | 6.507557 | 6.466866 | 6.466358 |
| GO:0061053 | somite development | 4/301 | 86/20870 | 0.03586957257609467 | 0.2031203852343 | 0.1695092624497 | LRP6||RAD51B||DLL1||SCX | 4 | 4.220715 | 4.550462 | 4.493704 | 4.217183 | 4.189809 | 4.200013 | 4.274365 | 4.541865 | 4.502455 | 4.545917 | 4.609561 | 4.477641 | 4.503591 | 4.465531 | 4.527262 |
| GO:0050673 | epithelial cell proliferation | 12/301 | 461/20870 | 0.03616613527538106 | 0.2031203852343 | 0.1695092624497 | TIE1||TGFB2||VEGFA||NR4A3||RREB1||IL6||BMP6||IGF2||SCG2||EGR3||SULF2||EPPK1 | 12 | 6.582981 | 6.507500 | 6.527053 | 6.568557 | 6.577974 | 6.594289 | 6.590956 | 6.509471 | 6.500502 | 6.505473 | 6.514515 | 6.533748 | 6.527447 | 6.523667 | 6.523326 |
| GO:0002824 | positive regulation of adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains | 6/301 | 169/20870 | 0.03616642152062057 | 0.2031203852343 | 0.1695092624497 | IL23A||C3||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 6 | 7.042252 | 7.094023 | 7.273653 | 7.046124 | 7.022029 | 7.050766 | 7.049895 | 7.093804 | 7.089025 | 7.097052 | 7.096198 | 7.268534 | 7.274633 | 7.267916 | 7.283476 |
| GO:0003215 | cardiac right ventricle morphogenesis | 2/301 | 21/20870 | 0.03635228857729224 | 0.2031203852343 | 0.1695092624497 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 4.211541 | 4.455770 | 4.401028 | 4.194392 | 4.318180 | 4.162510 | 4.165388 | 4.471037 | 4.429673 | 4.480821 | 4.440940 | 4.370415 | 4.398638 | 4.425419 | 4.409086 |
| GO:0006309 | apoptotic DNA fragmentation | 2/301 | 21/20870 | 0.03635228857729224 | 0.2031203852343 | 0.1695092624497 | IL6||ST20 | 2 | 4.836157 | 4.813109 | 5.033060 | 4.881399 | 4.591210 | 4.997963 | 4.844230 | 4.719616 | 5.062729 | 4.754881 | 4.682449 | 5.130370 | 5.009745 | 4.980271 | 5.007123 |
| GO:0006883 | cellular sodium ion homeostasis | 2/301 | 21/20870 | 0.03635228857729224 | 0.2031203852343 | 0.1695092624497 | IL1A||SLC8A1 | 2 | 5.909610 | 6.394340 | 6.494889 | 5.940987 | 5.887541 | 5.896307 | 5.913027 | 6.457301 | 6.360939 | 6.407236 | 6.349356 | 6.535694 | 6.534813 | 6.490199 | 6.415560 |
| GO:0009713 | catechol-containing compound biosynthetic process | 2/301 | 21/20870 | 0.03635228857729224 | 0.2031203852343 | 0.1695092624497 | TGFB2||NR4A2 | 2 | 5.612519 | 5.683365 | 5.591401 | 5.662369 | 5.606876 | 5.576186 | 5.603280 | 5.710282 | 5.672926 | 5.658466 | 5.691260 | 5.658111 | 5.537811 | 5.620198 | 5.545938 |
| GO:0030449 | regulation of complement activation | 2/301 | 21/20870 | 0.03635228857729224 | 0.2031203852343 | 0.1695092624497 | CFH||C3 | 2 | 6.982943 | 7.775467 | 8.204463 | 6.967684 | 6.938871 | 7.004902 | 7.018946 | 7.773668 | 7.763854 | 7.781640 | 7.782625 | 8.208927 | 8.202383 | 8.196963 | 8.209543 |
| GO:0034501 | protein localization to kinetochore | 2/301 | 21/20870 | 0.03635228857729224 | 0.2031203852343 | 0.1695092624497 | KNL1||KNTC1 | 2 | 5.226302 | 5.280739 | 4.953890 | 4.747516 | 5.477361 | 5.576506 | 4.935764 | 5.620301 | 5.148980 | 5.046527 | 5.239410 | 4.794106 | 5.243805 | 4.667762 | 5.040910 |
| GO:0042423 | catecholamine biosynthetic process | 2/301 | 21/20870 | 0.03635228857729224 | 0.2031203852343 | 0.1695092624497 | TGFB2||NR4A2 | 2 | 5.612519 | 5.683365 | 5.591401 | 5.662369 | 5.606876 | 5.576186 | 5.603280 | 5.710282 | 5.672926 | 5.658466 | 5.691260 | 5.658111 | 5.537811 | 5.620198 | 5.545938 |
| GO:0043382 | positive regulation of memory T cell differentiation | 2/301 | 21/20870 | 0.03635228857729224 | 0.2031203852343 | 0.1695092624497 | IL23A||HLA-DRA | 2 | 5.090538 | 5.514804 | 6.157185 | 5.101634 | 5.082837 | 5.079862 | 5.097698 | 5.540707 | 5.513952 | 5.499632 | 5.504577 | 6.203384 | 6.123509 | 6.097680 | 6.201141 |
| GO:0050930 | induction of positive chemotaxis | 2/301 | 21/20870 | 0.03635228857729224 | 0.2031203852343 | 0.1695092624497 | VEGFA||SCG2 | 2 | 5.338691 | 7.095520 | 7.557496 | 5.315716 | 5.382251 | 5.361173 | 5.293912 | 7.100495 | 7.066071 | 7.101473 | 7.113607 | 7.584529 | 7.564674 | 7.567053 | 7.512735 |
| GO:0070424 | regulation of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing signaling pathway | 2/301 | 21/20870 | 0.03635228857729224 | 0.2031203852343 | 0.1695092624497 | TLR4||SLC15A2 | 2 | 4.553025 | 4.996628 | 5.102419 | 4.536977 | 4.490111 | 4.601692 | 4.580782 | 4.980895 | 4.928395 | 4.951289 | 5.118277 | 5.065538 | 5.113627 | 5.092213 | 5.137324 |
| GO:1903083 | protein localization to condensed chromosome | 2/301 | 21/20870 | 0.03635228857729224 | 0.2031203852343 | 0.1695092624497 | KNL1||KNTC1 | 2 | 5.226302 | 5.280739 | 4.953890 | 4.747516 | 5.477361 | 5.576506 | 4.935764 | 5.620301 | 5.148980 | 5.046527 | 5.239410 | 4.794106 | 5.243805 | 4.667762 | 5.040910 |
| GO:2001236 | regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | 6/301 | 170/20870 | 0.03705536022686041 | 0.2052754075051 | 0.1713076847757 | GCLC||IL1A||TNFSF10||G0S2||IFI6||SCG2 | 6 | 6.154727 | 6.532931 | 6.733162 | 6.139381 | 6.176819 | 6.157369 | 6.145053 | 6.568086 | 6.537441 | 6.515855 | 6.509613 | 6.726409 | 6.719311 | 6.722908 | 6.763578 |
| GO:0003231 | cardiac ventricle development | 5/301 | 127/20870 | 0.03707048227537260 | 0.2052754075051 | 0.1713076847757 | TGFB2||HEY2||SLIT2||POU4F1||LY6E | 5 | 5.486494 | 5.620956 | 5.609957 | 5.509271 | 5.468330 | 5.456317 | 5.511237 | 5.635970 | 5.556212 | 5.699131 | 5.588483 | 5.664861 | 5.608406 | 5.618392 | 5.545673 |
| GO:0030326 | embryonic limb morphogenesis | 5/301 | 127/20870 | 0.03707048227537260 | 0.2052754075051 | 0.1713076847757 | TGFB2||ECE1||TBX2||TFAP2A||FRAS1 | 5 | 4.821744 | 4.445817 | 4.407007 | 4.864167 | 4.814715 | 4.834488 | 4.772054 | 4.427613 | 4.383273 | 4.477641 | 4.492186 | 4.410915 | 4.426711 | 4.362681 | 4.426770 |
| GO:0035113 | embryonic appendage morphogenesis | 5/301 | 127/20870 | 0.03707048227537260 | 0.2052754075051 | 0.1713076847757 | TGFB2||ECE1||TBX2||TFAP2A||FRAS1 | 5 | 4.821744 | 4.445817 | 4.407007 | 4.864167 | 4.814715 | 4.834488 | 4.772054 | 4.427613 | 4.383273 | 4.477641 | 4.492186 | 4.410915 | 4.426711 | 4.362681 | 4.426770 |
| GO:0002292 | T cell differentiation involved in immune response | 4/301 | 87/20870 | 0.03718743535118410 | 0.2052754075051 | 0.1713076847757 | IL23A||TNFSF18||IL6||HLA-DRA | 4 | 6.969962 | 7.030557 | 6.943086 | 6.986912 | 6.979059 | 6.966182 | 6.947384 | 7.042873 | 7.011824 | 7.035066 | 7.032282 | 6.934007 | 6.947392 | 6.941680 | 6.949215 |
| GO:0010827 | regulation of glucose transmembrane transport | 4/301 | 87/20870 | 0.03718743535118410 | 0.2052754075051 | 0.1713076847757 | NR4A3||C3||EDNRA||ENPP1 | 4 | 5.540374 | 6.128971 | 6.386774 | 5.594565 | 5.523431 | 5.484164 | 5.557030 | 6.108648 | 6.094301 | 6.196863 | 6.113814 | 6.369731 | 6.387896 | 6.410590 | 6.378559 |
| GO:0050772 | positive regulation of axonogenesis | 4/301 | 87/20870 | 0.03718743535118410 | 0.2052754075051 | 0.1713076847757 | CDKL5||VEGFA||SLIT2||CHODL | 4 | 5.798321 | 5.892479 | 5.949100 | 5.805137 | 5.781027 | 5.826953 | 5.779643 | 5.863308 | 5.898738 | 5.877477 | 5.929527 | 6.003770 | 5.983761 | 5.900193 | 5.905745 |
| GO:0002279 | mast cell activation involved in immune response | 3/301 | 51/20870 | 0.03721646859714305 | 0.2052754075051 | 0.1713076847757 | UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3 | 3 | 6.175841 | 6.330756 | 6.388635 | 6.146274 | 6.219992 | 6.136258 | 6.199129 | 6.312298 | 6.317341 | 6.365463 | 6.327319 | 6.426316 | 6.388110 | 6.372339 | 6.367026 |
| GO:0045622 | regulation of T-helper cell differentiation | 3/301 | 51/20870 | 0.03721646859714305 | 0.2052754075051 | 0.1713076847757 | IL23A||TNFSF18||HLA-DRA | 3 | 4.633120 | 4.892817 | 5.278020 | 4.629354 | 4.630398 | 4.662372 | 4.609865 | 4.906684 | 4.904776 | 4.901950 | 4.857277 | 5.306810 | 5.274119 | 5.237526 | 5.292695 |
| GO:0048661 | positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation | 5/301 | 128/20870 | 0.03814132331784271 | 0.2100765325680 | 0.1753143489390 | NR4A3||IL6||TLR4||PTAFR||S1PR1 | 5 | 6.189971 | 7.126800 | 7.569422 | 6.177253 | 6.181564 | 6.198589 | 6.202318 | 7.112646 | 7.148320 | 7.123188 | 7.122807 | 7.555134 | 7.578146 | 7.559407 | 7.584786 |
| GO:0045123 | cellular extravasation | 4/301 | 88/20870 | 0.03853285909638791 | 0.2116292588494 | 0.1766101395434 | RIPOR2||ADAM8||PTAFR||GCNT1 | 4 | 5.767693 | 5.718455 | 5.703601 | 5.775817 | 5.795632 | 5.768984 | 5.729541 | 5.738192 | 5.708352 | 5.732699 | 5.694130 | 5.727665 | 5.704898 | 5.683935 | 5.697557 |
| GO:0048864 | stem cell development | 4/301 | 88/20870 | 0.03853285909638791 | 0.2116292588494 | 0.1766101395434 | SEMA3F||EDNRA||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 4 | 5.000886 | 5.032544 | 5.021061 | 4.958073 | 5.041309 | 4.985406 | 5.017378 | 5.034289 | 5.008182 | 5.043151 | 5.044262 | 5.064935 | 5.039417 | 4.972789 | 5.005430 |
| GO:0030856 | regulation of epithelial cell differentiation | 6/301 | 172/20870 | 0.03887494700688625 | 0.2125550125236 | 0.1773827051445 | VEGFA||LIF||HEY2||BMP6||SPRED1||DLL1 | 6 | 5.743443 | 6.721937 | 7.161137 | 5.721815 | 5.729725 | 5.769769 | 5.751968 | 6.727973 | 6.706969 | 6.719445 | 6.733227 | 7.151570 | 7.171491 | 7.163720 | 7.157693 |
| GO:0002448 | mast cell mediated immunity | 3/301 | 52/20870 | 0.03908678033973928 | 0.2125550125236 | 0.1773827051445 | UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3 | 3 | 6.101107 | 6.252720 | 6.311006 | 6.071178 | 6.145388 | 6.062700 | 6.123485 | 6.234562 | 6.238867 | 6.287387 | 6.249462 | 6.348695 | 6.309917 | 6.295751 | 6.288913 |
| GO:0006509 | membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis | 3/301 | 52/20870 | 0.03908678033973928 | 0.2125550125236 | 0.1773827051445 | ADAM19||MMP7||ADAM8 | 3 | 6.906476 | 7.286239 | 7.620515 | 6.914053 | 6.872464 | 6.907095 | 6.931652 | 7.294412 | 7.265060 | 7.298403 | 7.286852 | 7.615938 | 7.620628 | 7.626124 | 7.619352 |
| GO:0043114 | regulation of vascular permeability | 3/301 | 52/20870 | 0.03908678033973928 | 0.2125550125236 | 0.1773827051445 | VEGFA||SLIT2||BMP6 | 3 | 5.055736 | 5.307147 | 5.509436 | 4.975295 | 5.102704 | 5.072088 | 5.069723 | 5.313674 | 5.253065 | 5.326626 | 5.333828 | 5.514726 | 5.541448 | 5.501289 | 5.479584 |
| GO:0072132 | mesenchyme morphogenesis | 3/301 | 52/20870 | 0.03908678033973928 | 0.2125550125236 | 0.1773827051445 | TGFB2||TBX2||HEY2 | 3 | 4.554165 | 4.821391 | 4.789295 | 4.594076 | 4.560120 | 4.497716 | 4.563062 | 4.815286 | 4.829796 | 4.824713 | 4.815716 | 4.797031 | 4.819923 | 4.760592 | 4.778965 |
| GO:0072583 | clathrin-dependent endocytosis | 3/301 | 52/20870 | 0.03908678033973928 | 0.2125550125236 | 0.1773827051445 | SIGLEC1||DLL1||INPP5F | 3 | 6.003525 | 5.926088 | 5.817089 | 6.007806 | 6.005886 | 6.036701 | 5.962745 | 5.935122 | 5.939291 | 5.899070 | 5.930520 | 5.853698 | 5.780899 | 5.781834 | 5.850197 |
| GO:0090199 | regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria | 3/301 | 52/20870 | 0.03908678033973928 | 0.2125550125236 | 0.1773827051445 | CLU||TNFSF10||CIDEB | 3 | 6.522961 | 7.678090 | 8.078593 | 6.506216 | 6.527330 | 6.549673 | 6.508195 | 7.677122 | 7.702806 | 7.666915 | 7.665202 | 8.058348 | 8.096166 | 8.064402 | 8.095042 |
| GO:0051208 | sequestering of calcium ion | 5/301 | 129/20870 | 0.03923093316437352 | 0.2125773504858 | 0.1774013467569 | CCR7||CXCL10||CXCL11||SLC8A1||TRDN | 5 | 6.654962 | 6.835494 | 6.951887 | 6.627353 | 6.664358 | 6.644838 | 6.682701 | 6.829102 | 6.839694 | 6.847207 | 6.825874 | 6.934032 | 6.978690 | 6.951071 | 6.943371 |
| GO:0007623 | circadian rhythm | 7/301 | 218/20870 | 0.03925606083822646 | 0.2125773504858 | 0.1774013467569 | NR1H3||PTGDS||MAPK10||ID3||BHLHE40||FBXL17||EGR3 | 7 | 5.499668 | 5.434424 | 5.386804 | 5.490301 | 5.525421 | 5.497044 | 5.485575 | 5.465333 | 5.465570 | 5.399215 | 5.406204 | 5.430754 | 5.360310 | 5.390307 | 5.364754 |
| GO:0051250 | negative regulation of lymphocyte activation | 7/301 | 218/20870 | 0.03925606083822646 | 0.2125773504858 | 0.1774013467569 | TYRO3||RIPOR2||TNFSF18||ZC3H8||TNFRSF14||PDCD1LG2||HLA-F | 7 | 6.288625 | 6.486106 | 6.517849 | 6.311208 | 6.283835 | 6.280138 | 6.279077 | 6.495741 | 6.506332 | 6.460807 | 6.481141 | 6.515426 | 6.522679 | 6.550563 | 6.481900 |
| GO:0014821 | phasic smooth muscle contraction | 2/301 | 22/20870 | 0.03961420210318129 | 0.2136179250285 | 0.1782697333694 | TBX2||SSTR2 | 2 | 3.488398 | 3.143634 | 2.965806 | 2.998897 | 3.121637 | 4.308482 | 3.066995 | 2.780556 | 3.671586 | 3.156202 | 2.770058 | 2.983769 | 3.379684 | 2.632662 | 2.750567 |
| GO:0043576 | regulation of respiratory gaseous exchange | 2/301 | 22/20870 | 0.03961420210318129 | 0.2136179250285 | 0.1782697333694 | MTG1||NR4A2 | 2 | 4.869987 | 4.570612 | 4.309606 | 4.780696 | 4.957194 | 4.771414 | 4.959141 | 4.588739 | 4.662113 | 4.524794 | 4.501366 | 4.300746 | 4.276972 | 4.331133 | 4.328889 |
| GO:1903978 | regulation of microglial cell activation | 2/301 | 22/20870 | 0.03961420210318129 | 0.2136179250285 | 0.1782697333694 | CST7||IL6 | 2 | 7.834352 | 7.651241 | 7.643217 | 7.840944 | 7.843477 | 7.838891 | 7.813899 | 7.684312 | 7.634767 | 7.646934 | 7.638411 | 7.617858 | 7.650380 | 7.650802 | 7.653529 |
| GO:0032609 | interferon-gamma production | 6/301 | 173/20870 | 0.03980570043163539 | 0.2140152253818 | 0.1786012908829 | IL23A||CCR7||TLR4||ISG15||TLR7||PDCD1LG2 | 6 | 5.954904 | 6.763087 | 7.010921 | 5.937037 | 5.951001 | 5.962239 | 5.969133 | 6.769602 | 6.760008 | 6.760871 | 6.761847 | 7.007215 | 7.009838 | 7.017886 | 7.008722 |
| GO:0032649 | regulation of interferon-gamma production | 6/301 | 173/20870 | 0.03980570043163539 | 0.2140152253818 | 0.1786012908829 | IL23A||CCR7||TLR4||ISG15||TLR7||PDCD1LG2 | 6 | 5.954904 | 6.763087 | 7.010921 | 5.937037 | 5.951001 | 5.962239 | 5.969133 | 6.769602 | 6.760008 | 6.760871 | 6.761847 | 7.007215 | 7.009838 | 7.017886 | 7.008722 |
| GO:0015850 | organic hydroxy compound transport | 9/301 | 315/20870 | 0.03985416913999922 | 0.2140152253818 | 0.1786012908829 | NR1H3||LRP6||ATP8B1||CLU||BMP6||LY6E||C1QTNF1||ABCA4||AQP1 | 9 | 7.054628 | 7.423600 | 7.417493 | 7.055060 | 7.044995 | 7.064995 | 7.053392 | 7.439227 | 7.413087 | 7.417700 | 7.424252 | 7.414298 | 7.425648 | 7.419145 | 7.410839 |
| GO:0002708 | positive regulation of lymphocyte mediated immunity | 7/301 | 219/20870 | 0.04007474293848831 | 0.2146027496332 | 0.1790915952036 | IL23A||C3||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||KLRK1 | 7 | 7.105533 | 7.147672 | 7.320474 | 7.113305 | 7.086217 | 7.112538 | 7.109900 | 7.149311 | 7.140883 | 7.147175 | 7.153291 | 7.316640 | 7.321805 | 7.314959 | 7.328452 |
| GO:0071902 | positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity | 7/301 | 219/20870 | 0.04007474293848831 | 0.2146027496332 | 0.1790915952036 | VEGFA||TLR4||ETAA1||FGD2||ADAM8||IGF2||PIK3R6 | 7 | 6.193468 | 6.586935 | 6.623764 | 6.165574 | 6.216115 | 6.200727 | 6.190990 | 6.590825 | 6.582560 | 6.593870 | 6.580442 | 6.631243 | 6.624221 | 6.623024 | 6.616528 |
| GO:0043406 | positive regulation of MAP kinase activity | 5/301 | 130/20870 | 0.04033936282824298 | 0.2157206092519 | 0.1800244782290 | VEGFA||TLR4||FGD2||ADAM8||PIK3R6 | 5 | 6.011789 | 6.577173 | 6.729670 | 6.002882 | 6.013198 | 6.008174 | 6.022827 | 6.585047 | 6.545631 | 6.597341 | 6.580163 | 6.720435 | 6.747185 | 6.726647 | 6.724264 |
| GO:0002821 | positive regulation of adaptive immune response | 6/301 | 174/20870 | 0.04075049373826538 | 0.2176177819135 | 0.1816077183269 | IL23A||C3||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 6 | 6.992599 | 7.038285 | 7.216001 | 6.996384 | 6.971419 | 7.001031 | 7.001351 | 7.038486 | 7.033134 | 7.041738 | 7.039768 | 7.211004 | 7.216868 | 7.210282 | 7.225795 |
| GO:0033059 | cellular pigmentation | 3/301 | 53/20870 | 0.04100406100245414 | 0.2180670516949 | 0.1819826456844 | MKKS||KIF13A||MYO7A | 3 | 5.833529 | 6.209712 | 6.283957 | 5.868005 | 5.730198 | 5.823245 | 5.906714 | 6.183501 | 6.204927 | 6.168852 | 6.279058 | 6.286531 | 6.312480 | 6.210555 | 6.323591 |
| GO:0043300 | regulation of leukocyte degranulation | 3/301 | 53/20870 | 0.04100406100245414 | 0.2180670516949 | 0.1819826456844 | UNC13D||PTAFR||HLA-F | 3 | 7.541638 | 7.407206 | 7.526517 | 7.538806 | 7.544234 | 7.539167 | 7.544336 | 7.401114 | 7.409784 | 7.419500 | 7.398331 | 7.513167 | 7.541168 | 7.545026 | 7.506312 |
| GO:0046427 | positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT | 3/301 | 53/20870 | 0.04100406100245414 | 0.2180670516949 | 0.1819826456844 | IL23A||PRLR||IL6 | 3 | 5.725356 | 6.486721 | 6.943779 | 5.662405 | 5.787917 | 5.679746 | 5.767295 | 6.485419 | 6.523527 | 6.504987 | 6.431309 | 6.907455 | 6.966530 | 6.939927 | 6.960466 |
| GO:0097194 | execution phase of apoptosis | 4/301 | 90/20870 | 0.04130645305806788 | 0.2193730608765 | 0.1830725444302 | IL6||CIDEB||CASP6||ST20 | 4 | 5.198550 | 4.975955 | 5.108583 | 5.216964 | 5.155026 | 5.199253 | 5.221998 | 4.923795 | 5.065957 | 4.974590 | 4.935105 | 5.087075 | 5.109132 | 5.126956 | 5.110891 |
| GO:0032944 | regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation | 9/301 | 319/20870 | 0.04259411497767730 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | IL23A||IL1A||TNFSF18||IL6||TLR4||TNFRSF14||IGF2||CSF1||PDCD1LG2 | 9 | 6.471003 | 6.938423 | 7.093530 | 6.479618 | 6.470844 | 6.467631 | 6.465880 | 6.950110 | 6.933453 | 6.932690 | 6.937372 | 7.108094 | 7.092809 | 7.090250 | 7.082850 |
| GO:0034103 | regulation of tissue remodeling | 4/301 | 91/20870 | 0.04273463198691517 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | IL23A||IL6||ADAM8||S1PR1 | 4 | 7.684410 | 8.357842 | 8.387111 | 7.693721 | 7.688567 | 7.671813 | 7.683447 | 8.366902 | 8.341618 | 8.356541 | 8.366161 | 8.387959 | 8.393669 | 8.382486 | 8.384306 |
| GO:0050886 | endocrine process | 4/301 | 91/20870 | 0.04273463198691517 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | ECE1||BMP6||C1QTNF1||SUCNR1 | 4 | 6.624538 | 7.181033 | 7.386978 | 6.589790 | 6.631672 | 6.645405 | 6.630688 | 7.175161 | 7.189297 | 7.173521 | 7.186088 | 7.371289 | 7.402390 | 7.383074 | 7.390981 |
| GO:0002833 | positive regulation of response to biotic stimulus | 8/301 | 270/20870 | 0.04275101431642532 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | POLR3G||OASL||TLR4||ADAM8||BMP6||IRF7||HLA-F||KLRK1 | 8 | 6.718297 | 6.851326 | 6.903447 | 6.726898 | 6.704696 | 6.726252 | 6.715226 | 6.847132 | 6.866264 | 6.849307 | 6.842489 | 6.894129 | 6.913163 | 6.904465 | 6.901967 |
| GO:0010524 | positive regulation of calcium ion transport into cytosol | 3/301 | 54/20870 | 0.04296800651612937 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | CXCL10||CXCL11||TRDN | 3 | 6.064229 | 6.103617 | 6.031970 | 6.024337 | 6.088554 | 6.071482 | 6.071752 | 6.117239 | 6.075290 | 6.133949 | 6.087236 | 6.038367 | 6.013192 | 6.034084 | 6.042066 |
| GO:0014888 | striated muscle adaptation | 3/301 | 54/20870 | 0.04296800651612937 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | HEY2||MYOZ2||INPP5F | 3 | 5.955420 | 6.495690 | 6.622659 | 5.862830 | 5.945549 | 6.089127 | 5.914257 | 6.513167 | 6.523951 | 6.473877 | 6.471006 | 6.548354 | 6.671846 | 6.543365 | 6.718916 |
| GO:0043090 | amino acid import | 3/301 | 54/20870 | 0.04296800651612937 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | SLC7A8||RGS4||SLC7A11 | 3 | 5.454766 | 5.873985 | 5.996914 | 5.459197 | 5.458350 | 5.461883 | 5.439528 | 5.879985 | 5.857280 | 5.888638 | 5.869848 | 5.982757 | 5.992556 | 6.022405 | 5.989618 |
| GO:0060350 | endochondral bone morphogenesis | 3/301 | 54/20870 | 0.04296800651612937 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | MMP13||BMP6||SCX | 3 | 6.854102 | 6.743652 | 6.831972 | 6.858450 | 6.848982 | 6.874552 | 6.834125 | 6.724407 | 6.730393 | 6.757373 | 6.762064 | 6.896092 | 6.811887 | 6.808677 | 6.809282 |
| GO:0070231 | T cell apoptotic process | 3/301 | 54/20870 | 0.04296800651612937 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | IDO1||ZC3H8||ADAM8 | 3 | 7.160800 | 7.388849 | 7.377775 | 7.172243 | 7.150718 | 7.162712 | 7.157444 | 7.397621 | 7.395373 | 7.382160 | 7.380160 | 7.363480 | 7.374521 | 7.379272 | 7.393664 |
| GO:0071320 | cellular response to cAMP | 3/301 | 54/20870 | 0.04296800651612937 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | PTAFR||SLC8A1||AQP1 | 3 | 5.844349 | 6.001199 | 5.931247 | 5.846813 | 5.834661 | 5.852290 | 5.843578 | 6.003667 | 6.010866 | 5.996274 | 5.993928 | 5.903130 | 5.933610 | 5.939075 | 5.948770 |
| GO:1903202 | negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced cell death | 3/301 | 54/20870 | 0.04296800651612937 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | NR4A3||MEAK7||SLC7A11 | 3 | 7.347866 | 7.232588 | 7.152716 | 7.337780 | 7.353952 | 7.343112 | 7.356538 | 7.253850 | 7.211207 | 7.213491 | 7.251240 | 7.147751 | 7.147702 | 7.166678 | 7.148643 |
| GO:1903573 | negative regulation of response to endoplasmic reticulum stress | 3/301 | 54/20870 | 0.04296800651612937 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | NR1H3||CLU||CREB3L1 | 3 | 6.664166 | 6.845278 | 6.851352 | 6.689158 | 6.642800 | 6.629944 | 6.693682 | 6.850665 | 6.841620 | 6.824079 | 6.864452 | 6.850668 | 6.865734 | 6.851059 | 6.837810 |
| GO:0006359 | regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III | 2/301 | 23/20870 | 0.04298243507963873 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | POLR3G||ZC3H8 | 2 | 4.913519 | 4.816326 | 4.599466 | 4.885296 | 4.974016 | 4.908182 | 4.884727 | 4.665943 | 4.888425 | 4.767575 | 4.928656 | 4.529771 | 4.588951 | 4.713987 | 4.558207 |
| GO:0009162 | deoxyribonucleoside monophosphate metabolic process | 2/301 | 23/20870 | 0.04298243507963873 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | TYMP||TK2 | 2 | 6.503523 | 6.514961 | 6.551498 | 6.640259 | 6.450080 | 6.484590 | 6.429505 | 6.422268 | 6.427848 | 6.611896 | 6.587170 | 6.508765 | 6.552378 | 6.560002 | 6.583830 |
| GO:0010002 | cardioblast differentiation | 2/301 | 23/20870 | 0.04298243507963873 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | TGFB2||TBX2 | 2 | 4.637362 | 5.251156 | 5.341397 | 4.641873 | 4.626202 | 4.672537 | 4.608058 | 5.249873 | 5.272543 | 5.249088 | 5.232842 | 5.343744 | 5.342956 | 5.338656 | 5.340226 |
| GO:0010866 | regulation of triglyceride biosynthetic process | 2/301 | 23/20870 | 0.04298243507963873 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | NR1H3||C3 | 2 | 5.753788 | 6.342248 | 6.718601 | 5.700473 | 5.696876 | 5.848376 | 5.764139 | 6.264485 | 6.376490 | 6.427778 | 6.294401 | 6.704573 | 6.736106 | 6.689974 | 6.743085 |
| GO:0033630 | positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin | 2/301 | 23/20870 | 0.04298243507963873 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | TGFB2||LIF | 2 | 6.012547 | 6.835321 | 7.232580 | 6.001767 | 6.001976 | 6.180003 | 5.847128 | 6.793268 | 6.907411 | 6.820764 | 6.817216 | 7.293148 | 7.235562 | 7.165331 | 7.233443 |
| GO:0035930 | corticosteroid hormone secretion | 2/301 | 23/20870 | 0.04298243507963873 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | BMP6||C1QTNF1 | 2 | 4.900164 | 4.324849 | 4.176387 | 4.787936 | 4.779527 | 5.190633 | 4.798600 | 4.231449 | 4.613532 | 4.190041 | 4.220728 | 4.162628 | 4.320541 | 4.075589 | 4.135257 |
| GO:0036303 | lymph vessel morphogenesis | 2/301 | 23/20870 | 0.04298243507963873 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | TIE1||VEGFA | 2 | 4.209226 | 4.270085 | 4.698661 | 4.273930 | 4.124797 | 4.175186 | 4.257868 | 4.280987 | 4.223645 | 4.293035 | 4.281662 | 4.749729 | 4.775710 | 4.641330 | 4.621728 |
| GO:0045061 | thymic T cell selection | 2/301 | 23/20870 | 0.04298243507963873 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | CCR7||CD3G | 2 | 5.208982 | 5.784782 | 5.878862 | 5.196361 | 5.213031 | 5.232521 | 5.193680 | 5.773636 | 5.956695 | 5.678529 | 5.714041 | 5.882573 | 5.883862 | 5.860107 | 5.888736 |
| GO:0051904 | pigment granule transport | 2/301 | 23/20870 | 0.04298243507963873 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | MKKS||MYO7A | 2 | 5.111898 | 4.785770 | 5.027363 | 5.269465 | 4.610605 | 5.020748 | 5.421479 | 4.647623 | 4.664442 | 4.597649 | 5.157859 | 5.162003 | 4.813096 | 4.759427 | 5.302000 |
| GO:0060384 | innervation | 2/301 | 23/20870 | 0.04298243507963873 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | POU4F1||SULF2 | 2 | 4.304211 | 4.807729 | 4.764785 | 4.293576 | 4.300301 | 4.337765 | 4.284630 | 4.859007 | 4.750897 | 4.808674 | 4.810309 | 4.751876 | 4.805114 | 4.738912 | 4.762380 |
| GO:0072574 | hepatocyte proliferation | 2/301 | 23/20870 | 0.04298243507963873 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | IL6||SULF2 | 2 | 5.132624 | 5.426863 | 5.609398 | 5.152714 | 5.148159 | 5.113437 | 5.115735 | 5.403709 | 5.390468 | 5.485664 | 5.425758 | 5.575489 | 5.669173 | 5.554649 | 5.635369 |
| GO:0072575 | epithelial cell proliferation involved in liver morphogenesis | 2/301 | 23/20870 | 0.04298243507963873 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | IL6||SULF2 | 2 | 5.132624 | 5.426863 | 5.609398 | 5.152714 | 5.148159 | 5.113437 | 5.115735 | 5.403709 | 5.390468 | 5.485664 | 5.425758 | 5.575489 | 5.669173 | 5.554649 | 5.635369 |
| GO:0098719 | sodium ion import across plasma membrane | 2/301 | 23/20870 | 0.04298243507963873 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | SLC9A9||SLC8A1 | 2 | 4.731198 | 4.658042 | 4.426408 | 4.754697 | 4.665666 | 4.755659 | 4.746820 | 4.695622 | 4.644703 | 4.582843 | 4.705720 | 4.466300 | 4.435468 | 4.442451 | 4.359197 |
| GO:2000831 | regulation of steroid hormone secretion | 2/301 | 23/20870 | 0.04298243507963873 | 0.2203920077589 | 0.1839228821958 | BMP6||C1QTNF1 | 2 | 4.776408 | 4.338458 | 4.218381 | 4.632586 | 4.625017 | 5.122403 | 4.661551 | 4.241047 | 4.646723 | 4.197675 | 4.218237 | 4.220383 | 4.374363 | 4.125688 | 4.139299 |
| GO:0051604 | protein maturation | 9/301 | 320/20870 | 0.04329844280259606 | 0.2217178881443 | 0.1850293639798 | CST7||CPXM1||IL1R2||ECE1||CHAC1||ADAM19||CPM||CIDEB||ADAM8 | 9 | 6.284683 | 6.493426 | 6.547877 | 6.305258 | 6.285386 | 6.267471 | 6.280360 | 6.493030 | 6.481752 | 6.490531 | 6.508266 | 6.520551 | 6.560737 | 6.545844 | 6.563969 |
| GO:0051701 | biological process involved in interaction with host | 8/301 | 271/20870 | 0.04352620472567249 | 0.2225889754249 | 0.1857563090488 | SIGLEC1||TYRO3||ZNF639||TRIM22||TNFRSF14||LY6E||IFIT1||IFITM1 | 8 | 6.813541 | 7.327520 | 7.489966 | 6.797911 | 6.819338 | 6.814197 | 6.822596 | 7.325415 | 7.301972 | 7.341725 | 7.340612 | 7.468064 | 7.493699 | 7.506031 | 7.491808 |
| GO:0006937 | regulation of muscle contraction | 6/301 | 177/20870 | 0.04366957274889373 | 0.2229906667315 | 0.1860915309274 | DMPK||CHRM3||BIN1||PTAFR||SSTR2||SLC8A1 | 6 | 5.822259 | 5.959863 | 5.951519 | 5.807004 | 5.851251 | 5.827080 | 5.803192 | 5.970979 | 5.946916 | 5.973563 | 5.947778 | 5.948269 | 5.972385 | 5.948661 | 5.936525 |
| GO:0022612 | gland morphogenesis | 5/301 | 133/20870 | 0.04377801745207607 | 0.2229906667315 | 0.1860915309274 | TGFB2||TBX2||IL6||CSF1||SULF2 | 5 | 5.543181 | 6.025654 | 6.084659 | 5.541444 | 5.557896 | 5.544233 | 5.529003 | 6.002327 | 5.996419 | 6.068008 | 6.034722 | 6.063664 | 6.112672 | 6.071990 | 6.089821 |
| GO:0045621 | positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation | 5/301 | 133/20870 | 0.04377801745207607 | 0.2229906667315 | 0.1860915309274 | IL23A||ADAM8||EGR3||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 5 | 6.186728 | 6.283402 | 6.393304 | 6.184396 | 6.181771 | 6.210609 | 6.169830 | 6.266982 | 6.266984 | 6.305654 | 6.293594 | 6.384878 | 6.393897 | 6.401677 | 6.392714 |
| GO:0050918 | positive chemotaxis | 4/301 | 92/20870 | 0.04419038956705457 | 0.2242038030465 | 0.1871039248423 | VEGFA||CXCL10||S1PR1||SCG2 | 4 | 6.226448 | 7.169410 | 7.555031 | 6.257498 | 6.249088 | 6.217001 | 6.180948 | 7.186656 | 7.170088 | 7.152184 | 7.168506 | 7.548332 | 7.576217 | 7.557330 | 7.537970 |
| GO:0060349 | bone morphogenesis | 4/301 | 92/20870 | 0.04419038956705457 | 0.2242038030465 | 0.1871039248423 | TFAP2A||MMP13||BMP6||SCX | 4 | 6.476732 | 6.321962 | 6.357541 | 6.478513 | 6.471536 | 6.490864 | 6.465892 | 6.304878 | 6.311028 | 6.333084 | 6.338578 | 6.415053 | 6.337832 | 6.336403 | 6.339314 |
| GO:1900407 | regulation of cellular response to oxidative stress | 4/301 | 92/20870 | 0.04419038956705457 | 0.2242038030465 | 0.1871039248423 | NR4A3||TLR4||MEAK7||SLC7A11 | 4 | 7.046024 | 6.909637 | 6.859705 | 7.020583 | 7.050656 | 7.032682 | 7.079489 | 6.938074 | 6.885426 | 6.900065 | 6.914460 | 6.841292 | 6.890037 | 6.863862 | 6.843091 |
| GO:0001763 | morphogenesis of a branching structure | 7/301 | 224/20870 | 0.04433513496811416 | 0.2246429870235 | 0.1874704353328 | TIE1||VEGFA||BCL11A||SLIT2||EDNRA||CSF1||SOCS3 | 7 | 5.843938 | 5.982091 | 6.021256 | 5.849376 | 5.833882 | 5.856607 | 5.835762 | 5.968087 | 5.959452 | 6.010969 | 5.989304 | 6.012331 | 6.028587 | 6.019362 | 6.024690 |
| GO:0042476 | odontogenesis | 5/301 | 134/20870 | 0.04496215206406200 | 0.2258272859838 | 0.1884587637226 | TGFB2||ID3||TFAP2A||CSF1||AQP1 | 5 | 6.017998 | 5.835435 | 5.868677 | 6.022324 | 6.031803 | 6.012652 | 6.005071 | 5.845414 | 5.801806 | 5.839345 | 5.854619 | 5.853025 | 5.852456 | 5.921166 | 5.846752 |
| GO:0043500 | muscle adaptation | 5/301 | 134/20870 | 0.04496215206406200 | 0.2258272859838 | 0.1884587637226 | RGS4||NR4A3||HEY2||MYOZ2||INPP5F | 5 | 6.446864 | 6.894953 | 7.095112 | 6.425886 | 6.437649 | 6.466302 | 6.457270 | 6.908015 | 6.892237 | 6.915527 | 6.863482 | 7.055136 | 7.114799 | 7.080167 | 7.129178 |
| GO:0002369 | T cell cytokine production | 3/301 | 55/20870 | 0.04497829135497165 | 0.2258272859838 | 0.1884587637226 | RSAD2||IL6||HLA-F | 3 | 8.141697 | 8.135255 | 8.324739 | 8.152936 | 8.127606 | 8.138644 | 8.147474 | 8.146610 | 8.129612 | 8.124857 | 8.139842 | 8.318101 | 8.329585 | 8.321506 | 8.329729 |
| GO:0002724 | regulation of T cell cytokine production | 3/301 | 55/20870 | 0.04497829135497165 | 0.2258272859838 | 0.1884587637226 | RSAD2||IL6||HLA-F | 3 | 8.141697 | 8.135255 | 8.324739 | 8.152936 | 8.127606 | 8.138644 | 8.147474 | 8.146610 | 8.129612 | 8.124857 | 8.139842 | 8.318101 | 8.329585 | 8.321506 | 8.329729 |
| GO:0007595 | lactation | 3/301 | 55/20870 | 0.04497829135497165 | 0.2258272859838 | 0.1884587637226 | OAS2||VEGFA||PRLR | 3 | 8.377586 | 8.226688 | 8.591859 | 8.373050 | 8.374554 | 8.389857 | 8.372814 | 8.231675 | 8.205802 | 8.232398 | 8.236674 | 8.596970 | 8.594120 | 8.598137 | 8.578120 |
| GO:0010676 | positive regulation of cellular carbohydrate metabolic process | 3/301 | 55/20870 | 0.04497829135497165 | 0.2258272859838 | 0.1884587637226 | MAS1||IGF2||PTAFR | 3 | 5.041876 | 4.980304 | 4.865896 | 5.063021 | 5.042194 | 5.037712 | 5.024309 | 4.955872 | 5.112348 | 4.898651 | 4.945218 | 4.855306 | 4.861267 | 4.890401 | 4.856323 |
| GO:0010862 | positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation | 3/301 | 55/20870 | 0.04497829135497165 | 0.2258272859838 | 0.1884587637226 | TGFB2||BMP6||RBPMS | 3 | 6.012736 | 6.118374 | 6.006134 | 6.036983 | 6.002929 | 5.998132 | 6.012589 | 6.137328 | 6.096792 | 6.131957 | 6.107025 | 6.033158 | 6.021711 | 6.011366 | 5.957130 |
| GO:0090257 | regulation of muscle system process | 8/301 | 273/20870 | 0.04510432452644753 | 0.2261659701255 | 0.1887414044777 | DMPK||RGS4||NR4A3||CHRM3||BIN1||PTAFR||SSTR2||SLC8A1 | 8 | 5.809372 | 6.026312 | 6.023131 | 5.806839 | 5.824204 | 5.810233 | 5.796074 | 6.048548 | 6.012416 | 6.052715 | 5.990650 | 5.990478 | 6.057576 | 6.012827 | 6.030805 |
| GO:0051346 | negative regulation of hydrolase activity | 11/301 | 425/20870 | 0.04519066015459584 | 0.2263049790621 | 0.1888574110632 | CST7||TGFB2||VEGFA||C3||MKKS||IFI6||BIN1||SERPINB7||SERPINA9||KLRK1||AQP1 | 11 | 6.395884 | 6.687003 | 6.931931 | 6.399867 | 6.392319 | 6.382738 | 6.408489 | 6.682180 | 6.677934 | 6.660712 | 6.726370 | 6.927848 | 6.930623 | 6.927344 | 6.941860 |
| GO:0060021 | roof of mouth development | 4/301 | 93/20870 | 0.04567370766814291 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | TGFB2||TBX2||TFAP2A||FRAS1 | 4 | 4.525875 | 4.568036 | 4.559184 | 4.532794 | 4.479763 | 4.476173 | 4.610637 | 4.540012 | 4.564881 | 4.605366 | 4.561108 | 4.615738 | 4.516870 | 4.523758 | 4.578075 |
| GO:0033002 | muscle cell proliferation | 8/301 | 274/20870 | 0.04590731726034457 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | TGFB2||NR4A3||TBX2||HEY2||IL6||TLR4||PTAFR||S1PR1 | 8 | 6.076940 | 6.649712 | 6.928076 | 6.061496 | 6.080649 | 6.087042 | 6.078452 | 6.642044 | 6.652460 | 6.645689 | 6.658599 | 6.932138 | 6.926831 | 6.909828 | 6.943304 |
| GO:0035710 | CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation | 5/301 | 135/20870 | 0.04616529833396237 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | IL23A||TNFSF18||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA | 5 | 5.937874 | 6.337003 | 6.550608 | 5.945117 | 5.943876 | 5.933473 | 5.928967 | 6.343940 | 6.330447 | 6.344782 | 6.328768 | 6.549884 | 6.551690 | 6.536360 | 6.564362 |
| GO:0003148 | outflow tract septum morphogenesis | 2/301 | 24/20870 | 0.04645326449395534 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | TGFB2||TBX2 | 2 | 5.094409 | 5.429163 | 5.415526 | 5.111959 | 5.122787 | 5.037485 | 5.103876 | 5.448517 | 5.405605 | 5.431727 | 5.430480 | 5.415289 | 5.469933 | 5.380836 | 5.394439 |
| GO:0003283 | atrial septum development | 2/301 | 24/20870 | 0.04645326449395534 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 4.174400 | 3.988908 | 3.823233 | 4.125637 | 4.060434 | 4.328298 | 4.169516 | 4.094585 | 3.986375 | 3.968819 | 3.899003 | 3.777871 | 3.816963 | 3.861701 | 3.835110 |
| GO:0003323 | type B pancreatic cell development | 2/301 | 24/20870 | 0.04645326449395534 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | BMP6||DLL1 | 2 | 5.349178 | 5.607302 | 5.274811 | 5.397344 | 5.350454 | 5.201598 | 5.436508 | 5.948960 | 5.627226 | 5.620071 | 5.113174 | 5.270013 | 5.208571 | 5.530679 | 5.047357 |
| GO:0009219 | pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotide metabolic process | 2/301 | 24/20870 | 0.04645326449395534 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | TYMP||CMPK2 | 2 | 5.163576 | 5.306216 | 5.485603 | 5.077396 | 5.260734 | 5.047788 | 5.255031 | 5.242309 | 5.168445 | 5.506700 | 5.284885 | 5.479426 | 5.465773 | 5.445330 | 5.549730 |
| GO:0021544 | subpallium development | 2/301 | 24/20870 | 0.04645326449395534 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | MKKS||SLC7A11 | 2 | 4.484185 | 4.017245 | 4.551993 | 4.773762 | 3.628300 | 4.373266 | 4.861803 | 3.686967 | 3.613827 | 3.630404 | 4.768922 | 4.584523 | 4.348099 | 4.089790 | 5.019915 |
| GO:0035994 | response to muscle stretch | 2/301 | 24/20870 | 0.04645326449395534 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | ANKRD1||SLC8A1 | 2 | 6.370742 | 6.279647 | 6.257761 | 6.478978 | 6.299652 | 6.374656 | 6.323011 | 6.317597 | 6.236382 | 6.236650 | 6.325443 | 6.201351 | 6.248874 | 6.254197 | 6.323959 |
| GO:0040037 | negative regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway | 2/301 | 24/20870 | 0.04645326449395534 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | CREB3L1||SULF2 | 2 | 5.181479 | 4.840343 | 4.330696 | 5.178155 | 5.169489 | 5.171711 | 5.206261 | 4.733949 | 4.891359 | 5.042308 | 4.663821 | 4.279979 | 4.266171 | 4.263692 | 4.498909 |
| GO:0043380 | regulation of memory T cell differentiation | 2/301 | 24/20870 | 0.04645326449395534 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | IL23A||HLA-DRA | 2 | 5.063518 | 5.489776 | 6.019321 | 5.054322 | 5.071058 | 5.061376 | 5.067262 | 5.516454 | 5.481194 | 5.483207 | 5.477913 | 6.054309 | 5.992986 | 5.981092 | 6.047451 |
| GO:0051797 | regulation of hair follicle development | 2/301 | 24/20870 | 0.04645326449395534 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | TGFB2||HPSE | 2 | 4.042852 | 4.594912 | 4.610354 | 4.066094 | 4.052484 | 3.993280 | 4.058402 | 4.535460 | 4.645025 | 4.601628 | 4.595432 | 4.610335 | 4.600981 | 4.629441 | 4.600468 |
| GO:0051882 | mitochondrial depolarization | 2/301 | 24/20870 | 0.04645326449395534 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | GCLC||IFI6 | 2 | 6.906059 | 6.977989 | 7.313671 | 6.910547 | 6.905844 | 6.885515 | 6.922087 | 6.977564 | 6.982258 | 6.959076 | 6.992853 | 7.311872 | 7.340215 | 7.319827 | 7.282167 |
| GO:0051905 | establishment of pigment granule localization | 2/301 | 24/20870 | 0.04645326449395534 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | MKKS||MYO7A | 2 | 5.044762 | 4.717240 | 4.957576 | 5.201338 | 4.545334 | 4.953927 | 5.353932 | 4.577970 | 4.595517 | 4.528689 | 5.090687 | 5.091985 | 4.743185 | 4.690025 | 5.232247 |
| GO:0072576 | liver morphogenesis | 2/301 | 24/20870 | 0.04645326449395534 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | IL6||SULF2 | 2 | 5.263311 | 5.494438 | 5.640342 | 5.279837 | 5.298052 | 5.253570 | 5.220612 | 5.435330 | 5.484700 | 5.544190 | 5.511335 | 5.592282 | 5.700338 | 5.602030 | 5.663963 |
| GO:0090023 | positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis | 2/301 | 24/20870 | 0.04645326449395534 | 0.2278984170409 | 0.1901871766415 | RIPOR2||CCR7 | 2 | 5.899857 | 7.157033 | 7.404800 | 5.899143 | 5.909383 | 5.907732 | 5.883019 | 7.154793 | 7.154249 | 7.170262 | 7.148741 | 7.415538 | 7.408799 | 7.409943 | 7.384727 |
| GO:0001755 | neural crest cell migration | 3/301 | 56/20870 | 0.04703456950354831 | 0.2292935263298 | 0.1913514317522 | SEMA3F||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 3 | 4.069158 | 4.658383 | 4.853435 | 4.029672 | 4.097643 | 4.063279 | 4.085119 | 4.636337 | 4.650195 | 4.639945 | 4.705956 | 4.919487 | 4.914189 | 4.750417 | 4.822902 |
| GO:0030225 | macrophage differentiation | 3/301 | 56/20870 | 0.04703456950354831 | 0.2292935263298 | 0.1913514317522 | VEGFA||LIF||CSF1 | 3 | 6.257597 | 7.601574 | 8.065272 | 6.241846 | 6.278126 | 6.246873 | 6.263259 | 7.586710 | 7.618600 | 7.600652 | 7.600156 | 8.055283 | 8.070195 | 8.070476 | 8.065080 |
| GO:0043113 | receptor clustering | 3/301 | 56/20870 | 0.04703456950354831 | 0.2292935263298 | 0.1913514317522 | DLG3||ZDHHC2||SLC7A11 | 3 | 7.522231 | 7.315387 | 7.439628 | 7.530452 | 7.522804 | 7.516154 | 7.519476 | 7.314480 | 7.323310 | 7.326793 | 7.296779 | 7.421370 | 7.436845 | 7.436240 | 7.463734 |
| GO:0046850 | regulation of bone remodeling | 3/301 | 56/20870 | 0.04703456950354831 | 0.2292935263298 | 0.1913514317522 | IL6||ADAM8||S1PR1 | 3 | 7.881770 | 8.697904 | 8.703058 | 7.897632 | 7.882298 | 7.867119 | 7.879868 | 8.707051 | 8.686582 | 8.693299 | 8.704587 | 8.702764 | 8.709918 | 8.697403 | 8.702119 |
| GO:0051784 | negative regulation of nuclear division | 3/301 | 56/20870 | 0.04703456950354831 | 0.2292935263298 | 0.1913514317522 | LIF||FBXO43||KNTC1 | 3 | 5.262392 | 5.281345 | 5.145398 | 5.112951 | 5.346699 | 5.434569 | 5.128650 | 5.391860 | 5.202631 | 5.242834 | 5.281095 | 5.065876 | 5.310211 | 5.058083 | 5.132843 |
| GO:0010565 | regulation of cellular ketone metabolic process | 5/301 | 136/20870 | 0.04738748208582076 | 0.2307226586801 | 0.1925440799956 | NR1H3||NR4A3||ETFBKMT||SLC7A11||BMP6 | 5 | 5.658630 | 6.246699 | 6.512403 | 5.650169 | 5.645612 | 5.657915 | 5.680574 | 6.239947 | 6.233320 | 6.237710 | 6.275427 | 6.502725 | 6.533288 | 6.513171 | 6.500192 |
| GO:0021537 | telencephalon development | 8/301 | 276/20870 | 0.04754132019082580 | 0.2311801476786 | 0.1929258665042 | MKKS||MAS1||SLIT2||SLC7A11||SEMA6B||GNG12||SLC8A1||AQP1 | 8 | 5.575680 | 5.623185 | 5.673891 | 5.569255 | 5.571542 | 5.577726 | 5.584152 | 5.656746 | 5.629393 | 5.567463 | 5.637595 | 5.705874 | 5.688244 | 5.644014 | 5.656594 |
| GO:0007163 | establishment or maintenance of cell polarity | 7/301 | 228/20870 | 0.04794610511501183 | 0.2328552350303 | 0.1943237706151 | DLG3||RIPOR2||CCR7||FRMD4A||CD3G||ALPK2||AQP1 | 7 | 7.615744 | 7.642623 | 7.501273 | 7.612419 | 7.622415 | 7.615570 | 7.612548 | 7.647505 | 7.653718 | 7.633829 | 7.635345 | 7.507507 | 7.504182 | 7.495574 | 7.497799 |
| GO:0032868 | response to insulin | 8/301 | 277/20870 | 0.04837238845859044 | 0.2346303917571 | 0.1958051852311 | GCLC||TNFSF10||BCAR3||MEAK7||IGF2||SOCS3||GCNT1||ENPP1 | 8 | 5.611671 | 6.056072 | 6.161850 | 5.670777 | 5.595986 | 5.580421 | 5.597785 | 6.068491 | 6.078060 | 6.050065 | 6.027149 | 6.178164 | 6.169508 | 6.170918 | 6.128284 |
| GO:0009395 | phospholipid catabolic process | 3/301 | 57/20870 | 0.04913647539647215 | 0.2374417165279 | 0.1981513091214 | PLA2G7||GDPD1||INPP5F | 3 | 6.225747 | 6.015379 | 6.059739 | 6.172637 | 6.175824 | 6.342858 | 6.204815 | 6.039536 | 5.945119 | 6.008830 | 6.065259 | 6.035653 | 6.104048 | 6.070148 | 6.027833 |
| GO:0030857 | negative regulation of epithelial cell differentiation | 3/301 | 57/20870 | 0.04913647539647215 | 0.2374417165279 | 0.1981513091214 | VEGFA||SPRED1||DLL1 | 3 | 5.730974 | 7.536729 | 8.128533 | 5.713525 | 5.725506 | 5.778565 | 5.705161 | 7.529831 | 7.526804 | 7.529112 | 7.560895 | 8.118945 | 8.133928 | 8.132614 | 8.128595 |
| GO:0048260 | positive regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis | 3/301 | 57/20870 | 0.04913647539647215 | 0.2374417165279 | 0.1981513091214 | VEGFA||CLU||C3 | 3 | 8.393233 | 8.222049 | 8.235492 | 8.402438 | 8.389618 | 8.392888 | 8.387945 | 8.235167 | 8.223802 | 8.206734 | 8.222350 | 8.228934 | 8.249537 | 8.221040 | 8.242285 |
| GO:0071805 | potassium ion transmembrane transport | 7/301 | 230/20870 | 0.04981988885920054 | 0.2384432144275 | 0.1989870852554 | KCNC4||RGS4||BIN1||KCNS3||SLC9A9||KCNIP1||AQP1 | 7 | 5.609447 | 5.900892 | 5.931626 | 5.592249 | 5.588070 | 5.639520 | 5.617352 | 5.924600 | 5.879491 | 5.910666 | 5.888368 | 5.909113 | 5.987488 | 5.916444 | 5.911976 |
GO: MF
| ID | Description | GeneRatio | BgRatio | pvalue | p.adjust | qvalue | geneID | Count | No-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgKDN-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgwt-inf_Log2MeanTPM | log2TPM_No-inf_1 | log2TPM_No-inf_2 | log2TPM_No-inf_3 | log2TPM_No-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0005125 | cytokine activity | 19/306 | 286/20678 | 0.00000005862371 | 0.00002450341 | 0.0000229374 | TGFB2||OSM||CCL22||IL23A||VEGFA||IL1A||TNFSF18||TNFSF10||LIF||IL6||IL36G||IL1RN||BMP6||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||SCG2||TNFSF15||CSF1 | 19 | 7.027925 | 7.899978 | 8.123290 | 7.033845 | 7.023726 | 7.027537 | 7.026573 | 7.909586 | 7.884917 | 7.906682 | 7.898601 | 8.125205 | 8.127085 | 8.122796 | 8.118056 |
| GO:0005126 | cytokine receptor binding | 20/306 | 324/20678 | 0.00000008751217 | 0.00002450341 | 0.0000229374 | TGFB2||OSM||CCL22||IL23A||VEGFA||PRLR||IL1A||TNFSF18||TNFSF10||LIF||NES||IL6||IL36G||IL1RN||CXCL1||SPRED1||CXCL10||CXCL11||TNFSF15||CSF1 | 20 | 5.249355 | 6.199512 | 6.565369 | 5.253601 | 5.256485 | 5.240748 | 5.246532 | 6.201147 | 6.171475 | 6.229478 | 6.195358 | 6.571697 | 6.563335 | 6.569093 | 6.557309 |
| GO:0008083 | growth factor activity | 10/306 | 164/20678 | 0.00017157415897 | 0.03202717634 | 0.0299803267 | TYMP||TGFB2||OSM||VEGFA||LIF||IL6||BMP6||CXCL1||IGF2||CSF1 | 10 | 6.564895 | 6.333211 | 6.513167 | 6.571109 | 6.564066 | 6.567302 | 6.557068 | 6.331334 | 6.304736 | 6.348731 | 6.347606 | 6.509150 | 6.517083 | 6.508832 | 6.517579 |
| GO:0038187 | pattern recognition receptor activity | 4/306 | 26/20678 | 0.00054363218032 | 0.07610850525 | 0.0712444278 | TLR4||CLEC4E||PTAFR||TLR7 | 4 | 5.185544 | 5.113231 | 4.888125 | 5.086531 | 5.184477 | 5.267138 | 5.198302 | 5.109280 | 5.112831 | 5.137487 | 5.092975 | 4.897892 | 4.844611 | 4.976414 | 4.828945 |
| GO:0019207 | kinase regulator activity | 11/306 | 257/20678 | 0.00163134944842 | 0.14606840758 | 0.1367332086 | LRP6||MOB3B||SH3BP5||ETAA1||SPRED1||IGF2||CXCL10||SOCS4||SOCS3||INKA1||PIK3R6 | 11 | 6.379871 | 6.468260 | 6.457381 | 6.358024 | 6.399825 | 6.385843 | 6.375468 | 6.460618 | 6.498363 | 6.467491 | 6.446062 | 6.463768 | 6.459648 | 6.448748 | 6.457319 |
| GO:0005149 | interleukin-1 receptor binding | 3/306 | 17/20678 | 0.00187091141648 | 0.14606840758 | 0.1367332086 | IL1A||IL36G||IL1RN | 3 | 4.667378 | 7.263311 | 7.948052 | 4.700509 | 4.556703 | 4.683424 | 4.723173 | 7.226743 | 7.221571 | 7.316887 | 7.285803 | 7.961882 | 7.939553 | 7.950509 | 7.940147 |
| GO:0046935 | 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase regulator activity | 3/306 | 17/20678 | 0.00187091141648 | 0.14606840758 | 0.1367332086 | SOCS4||SOCS3||PIK3R6 | 3 | 3.314612 | 3.529455 | 3.720929 | 3.511497 | 3.156408 | 3.144337 | 3.410830 | 3.295765 | 3.842160 | 3.434046 | 3.487745 | 3.425983 | 3.528388 | 4.225582 | 3.554512 |
| GO:0045236 | CXCR chemokine receptor binding | 3/306 | 18/20678 | 0.00222066372888 | 0.14606840758 | 0.1367332086 | CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11 | 3 | 3.548332 | 7.195972 | 7.649166 | 3.521617 | 3.603004 | 3.418267 | 3.640450 | 7.194877 | 7.153837 | 7.223717 | 7.210506 | 7.673348 | 7.656225 | 7.666252 | 7.599678 |
| GO:0043394 | proteoglycan binding | 4/306 | 39/20678 | 0.00257228584831 | 0.14606840758 | 0.1367332086 | CFH||COL5A3||SLIT2||HPSE | 4 | 6.978910 | 7.319367 | 7.669985 | 6.976605 | 6.967437 | 6.990599 | 6.980904 | 7.319367 | 7.321249 | 7.311065 | 7.325748 | 7.664853 | 7.683679 | 7.662386 | 7.668929 |
| GO:0008569 | minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity | 3/306 | 19/20678 | 0.00260836442111 | 0.14606840758 | 0.1367332086 | DNAH11||DNHD1||DNAH17 | 3 | 4.716565 | 4.640867 | 4.628409 | 4.636547 | 4.823245 | 4.706530 | 4.693499 | 4.423348 | 4.541914 | 4.505030 | 5.015048 | 4.432911 | 5.004897 | 4.503801 | 4.494402 |
| GO:0008237 | metallopeptidase activity | 9/306 | 205/20678 | 0.00357802791424 | 0.18215414836 | 0.1705127178 | CPXM1||ECE1||ADAM19||CPM||MMP7||MMP13||ADAM8||ADAMTS4||AMZ1 | 9 | 6.014354 | 6.796519 | 7.088932 | 6.032626 | 5.991229 | 6.039862 | 5.993013 | 6.784057 | 6.799839 | 6.802180 | 6.799926 | 7.076710 | 7.103349 | 7.101408 | 7.074007 |
| GO:0035014 | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulator activity | 3/306 | 22/20678 | 0.00401182509807 | 0.18721850458 | 0.1752534122 | SOCS4||SOCS3||PIK3R6 | 3 | 3.602610 | 3.648351 | 3.674326 | 3.730235 | 3.516198 | 3.512830 | 3.639611 | 3.493669 | 3.832515 | 3.577856 | 3.667270 | 3.459860 | 3.521721 | 4.062781 | 3.568884 |
| GO:0030215 | semaphorin receptor binding | 3/306 | 24/20678 | 0.00515902243763 | 0.22223481270 | 0.2080318359 | SEMA3F||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 3 | 3.902182 | 4.316143 | 4.613858 | 3.617337 | 4.285885 | 3.765519 | 3.850578 | 4.215067 | 4.477010 | 4.056240 | 4.472618 | 4.765756 | 4.704461 | 4.551257 | 4.407327 |
| GO:0019210 | kinase inhibitor activity | 5/306 | 83/20678 | 0.00779373046791 | 0.26491418647 | 0.2479835806 | LRP6||SH3BP5||SPRED1||SOCS3||INKA1 | 5 | 6.645116 | 6.616318 | 6.512385 | 6.635448 | 6.647064 | 6.671039 | 6.626527 | 6.591853 | 6.661162 | 6.630573 | 6.580257 | 6.559030 | 6.511801 | 6.454750 | 6.522027 |
| GO:0019955 | cytokine binding | 7/306 | 153/20678 | 0.00785574450139 | 0.26491418647 | 0.2479835806 | PRLR||IL1R2||CCR7||IL1RN||TNFRSF14||NBL1||CXCR3 | 7 | 5.946169 | 6.087673 | 6.112773 | 5.932731 | 5.966770 | 5.940101 | 5.944851 | 6.088577 | 6.073802 | 6.094018 | 6.094200 | 6.106540 | 6.128636 | 6.096226 | 6.119479 |
| GO:0045499 | chemorepellent activity | 3/306 | 28/20678 | 0.00799493807775 | 0.26491418647 | 0.2479835806 | SEMA3F||SEMA3D||SEMA6B | 3 | 2.889007 | 3.697833 | 4.011858 | 2.779890 | 3.108649 | 2.841956 | 2.800487 | 3.630288 | 3.640326 | 3.612046 | 3.890086 | 4.213582 | 3.959987 | 3.898596 | 3.954089 |
| GO:0004693 | cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity | 3/306 | 30/20678 | 0.00969563060547 | 0.26491418647 | 0.2479835806 | CDKL3||CDKL5||CDK3 | 3 | 5.298881 | 4.959319 | 5.065250 | 5.164291 | 5.453142 | 5.384180 | 5.171217 | 5.063474 | 5.068066 | 4.898773 | 4.787857 | 4.974226 | 5.046859 | 5.126999 | 5.108007 |
| GO:0051959 | dynein light intermediate chain binding | 3/306 | 30/20678 | 0.00969563060547 | 0.26491418647 | 0.2479835806 | DNAH11||DNHD1||DNAH17 | 3 | 5.398381 | 5.320899 | 5.202385 | 5.368925 | 5.466237 | 5.344925 | 5.410487 | 5.276504 | 5.279077 | 5.301836 | 5.421207 | 5.109994 | 5.352574 | 5.145610 | 5.189206 |
| GO:0097472 | cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity | 3/306 | 30/20678 | 0.00969563060547 | 0.26491418647 | 0.2479835806 | CDKL3||CDKL5||CDK3 | 3 | 5.298881 | 4.959319 | 5.065250 | 5.164291 | 5.453142 | 5.384180 | 5.171217 | 5.063474 | 5.068066 | 4.898773 | 4.787857 | 4.974226 | 5.046859 | 5.126999 | 5.108007 |
| GO:0004879 | nuclear receptor activity | 4/306 | 57/20678 | 0.01004227443497 | 0.26491418647 | 0.2479835806 | NR1H3||NR5A2||NR4A3||NR4A2 | 4 | 4.581180 | 4.349347 | 4.457578 | 4.569707 | 4.579661 | 4.571762 | 4.603341 | 4.293215 | 4.334194 | 4.416867 | 4.350348 | 4.454964 | 4.468156 | 4.451003 | 4.456134 |
| GO:0098531 | ligand-activated transcription factor activity | 4/306 | 57/20678 | 0.01004227443497 | 0.26491418647 | 0.2479835806 | NR1H3||NR5A2||NR4A3||NR4A2 | 4 | 4.581180 | 4.349347 | 4.457578 | 4.569707 | 4.579661 | 4.571762 | 4.603341 | 4.293215 | 4.334194 | 4.416867 | 4.350348 | 4.454964 | 4.468156 | 4.451003 | 4.456134 |
| GO:0004222 | metalloendopeptidase activity | 6/306 | 124/20678 | 0.01042156020711 | 0.26491418647 | 0.2479835806 | ECE1||ADAM19||MMP7||MMP13||ADAM8||ADAMTS4 | 6 | 6.210903 | 7.260648 | 7.615709 | 6.226690 | 6.183908 | 6.252671 | 6.179043 | 7.246223 | 7.257907 | 7.275293 | 7.263018 | 7.597136 | 7.637325 | 7.621793 | 7.606255 |
| GO:0005031 | tumor necrosis factor-activated receptor activity | 2/306 | 11/20678 | 0.01099190741236 | 0.26491418647 | 0.2479835806 | TNFRSF14||TNFRSF18 | 2 | 4.842933 | 5.372980 | 5.666966 | 4.789753 | 4.846950 | 4.769312 | 4.958168 | 5.506027 | 5.186969 | 5.365562 | 5.414907 | 5.551987 | 5.820757 | 5.600163 | 5.680410 |
| GO:0030165 | PDZ domain binding | 5/306 | 91/20678 | 0.01135346513424 | 0.26491418647 | 0.2479835806 | DLG3||MPP3||TAMALIN||GNG12||SSTR2 | 5 | 4.914966 | 5.427006 | 5.346718 | 4.960124 | 4.899069 | 4.892070 | 4.907602 | 5.411226 | 5.416376 | 5.453288 | 5.426768 | 5.364937 | 5.356385 | 5.333569 | 5.331695 |
| GO:0008009 | chemokine activity | 4/306 | 63/20678 | 0.01413947809884 | 0.30746744190 | 0.2878172670 | CCL22||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11 | 4 | 4.661476 | 7.336671 | 7.908591 | 4.742723 | 4.658529 | 4.658808 | 4.581323 | 7.367746 | 7.337433 | 7.330670 | 7.310246 | 7.893723 | 7.922333 | 7.914025 | 7.904122 |
| GO:0031432 | titin binding | 2/306 | 13/20678 | 0.01528790834729 | 0.30746744190 | 0.2878172670 | ANKRD1||OBSCN | 2 | 6.982809 | 6.688038 | 6.610090 | 6.938936 | 6.994435 | 7.030297 | 6.965973 | 6.722391 | 6.650202 | 6.690852 | 6.687802 | 6.643586 | 6.599990 | 6.603379 | 6.592859 |
| GO:0140333 | glycerophospholipid flippase activity | 2/306 | 13/20678 | 0.01528790834729 | 0.30746744190 | 0.2878172670 | ATP8B1||ABCA4 | 2 | 5.210164 | 6.279542 | 6.804522 | 5.165758 | 5.181228 | 5.118706 | 5.362796 | 6.275393 | 6.268867 | 6.325958 | 6.246782 | 6.733212 | 6.798323 | 6.795249 | 6.887116 |
| GO:0042379 | chemokine receptor binding | 5/306 | 99/20678 | 0.01588608501313 | 0.30746744190 | 0.2878172670 | CCL22||NES||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11 | 5 | 4.960000 | 7.002930 | 7.501374 | 4.977735 | 5.007770 | 4.932893 | 4.919889 | 7.023783 | 7.001988 | 7.002238 | 6.983428 | 7.489150 | 7.517183 | 7.504270 | 7.494738 |
| GO:0045505 | dynein intermediate chain binding | 3/306 | 36/20678 | 0.01597983369885 | 0.30746744190 | 0.2878172670 | DNAH11||DNHD1||DNAH17 | 3 | 5.749721 | 5.635463 | 5.577273 | 5.705178 | 5.835796 | 5.699277 | 5.754452 | 5.580347 | 5.610929 | 5.692264 | 5.655787 | 5.552975 | 5.591305 | 5.668656 | 5.490361 |
| GO:0005035 | death receptor activity | 2/306 | 14/20678 | 0.01766340045884 | 0.30746744190 | 0.2878172670 | TNFRSF14||TNFRSF18 | 2 | 4.438676 | 5.033390 | 5.311963 | 4.383641 | 4.430584 | 4.367348 | 4.564671 | 5.142883 | 4.859113 | 5.027450 | 5.088651 | 5.221594 | 5.450305 | 5.250112 | 5.314908 |
| GO:0005313 | L-glutamate transmembrane transporter activity | 2/306 | 14/20678 | 0.01766340045884 | 0.30746744190 | 0.2878172670 | SLC17A7||SLC7A11 | 2 | 3.319892 | 4.378169 | 4.829708 | 3.116802 | 3.423419 | 3.326203 | 3.393755 | 4.369826 | 4.478923 | 4.376922 | 4.280121 | 4.767941 | 4.883984 | 4.852011 | 4.812280 |
| GO:0035259 | glucocorticoid receptor binding | 2/306 | 14/20678 | 0.01766340045884 | 0.30746744190 | 0.2878172670 | NR4A3||NR4A2 | 2 | 5.124789 | 5.049466 | 5.093991 | 5.041331 | 5.307804 | 5.128561 | 5.001880 | 4.985711 | 5.050248 | 5.119361 | 5.039398 | 5.117134 | 5.099654 | 5.115941 | 5.041942 |
| GO:0071889 | 14-3-3 protein binding | 3/306 | 38/20678 | 0.01847770639002 | 0.30746744190 | 0.2878172670 | TMCC3||RIPOR2||HLA-F | 3 | 5.455387 | 5.275619 | 5.139190 | 5.446714 | 5.444791 | 5.484922 | 5.444713 | 5.218470 | 5.285647 | 5.259602 | 5.336226 | 5.094956 | 5.125198 | 5.194759 | 5.140026 |
| GO:0042277 | peptide binding | 13/306 | 456/20678 | 0.01886620088081 | 0.30746744190 | 0.2878172670 | SLC7A8||TGFB2||PRLR||VIPR1||ECE1||CLU||MAS1||TLR4||GPRASP2||SSTR2||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA2 | 13 | 6.819496 | 6.712047 | 6.753334 | 6.831306 | 6.818768 | 6.822265 | 6.805528 | 6.715463 | 6.705464 | 6.720228 | 6.706981 | 6.750071 | 6.758847 | 6.753321 | 6.751083 |
| GO:0019887 | protein kinase regulator activity | 8/306 | 225/20678 | 0.01921671511877 | 0.30746744190 | 0.2878172670 | MOB3B||SH3BP5||ETAA1||SPRED1||IGF2||CXCL10||SOCS3||INKA1 | 8 | 6.468845 | 6.590818 | 6.579669 | 6.447788 | 6.489949 | 6.477025 | 6.460260 | 6.581821 | 6.620173 | 6.592507 | 6.568266 | 6.590594 | 6.583326 | 6.566227 | 6.578419 |
| GO:0045125 | bioactive lipid receptor activity | 2/306 | 15/20678 | 0.02018398725221 | 0.31397313503 | 0.2939071828 | LPAR2||S1PR1 | 2 | 5.331686 | 4.791168 | 4.766586 | 5.400657 | 5.270543 | 5.321087 | 5.331465 | 4.867460 | 4.712571 | 4.826595 | 4.752950 | 4.780396 | 4.781425 | 4.814602 | 4.686803 |
| GO:0015172 | acidic amino acid transmembrane transporter activity | 2/306 | 16/20678 | 0.02284488353298 | 0.32655921306 | 0.3056888874 | SLC17A7||SLC7A11 | 2 | 4.307768 | 5.331940 | 5.707775 | 4.222413 | 4.358705 | 4.337994 | 4.308253 | 5.367213 | 5.367962 | 5.321147 | 5.269164 | 5.692808 | 5.706936 | 5.732552 | 5.698484 |
| GO:0019992 | diacylglycerol binding | 2/306 | 16/20678 | 0.02284488353298 | 0.32655921306 | 0.3056888874 | UNC13A||UNC13C | 2 | 4.102010 | 3.401241 | 3.447882 | 4.137163 | 3.998879 | 4.102582 | 4.164032 | 3.367514 | 3.469705 | 3.441311 | 3.321678 | 3.474574 | 3.381820 | 3.471003 | 3.462135 |
| GO:0140327 | flippase activity | 2/306 | 16/20678 | 0.02284488353298 | 0.32655921306 | 0.3056888874 | ATP8B1||ABCA4 | 2 | 5.743486 | 6.380439 | 6.758364 | 5.728775 | 5.720428 | 5.682410 | 5.837657 | 6.381842 | 6.374500 | 6.414781 | 6.349888 | 6.697661 | 6.750665 | 6.751668 | 6.830343 |
| GO:0008201 | heparin binding | 7/306 | 190/20678 | 0.02332565807558 | 0.32655921306 | 0.3056888874 | CFH||COL5A3||VEGFA||MMP7||SLIT2||CXCL10||CXCL11 | 7 | 6.508431 | 6.299913 | 6.294777 | 6.517174 | 6.523999 | 6.495402 | 6.496935 | 6.326440 | 6.293638 | 6.275829 | 6.303280 | 6.301488 | 6.301536 | 6.283628 | 6.292378 |
| GO:0003777 | microtubule motor activity | 4/306 | 75/20678 | 0.02516984762338 | 0.34188550865 | 0.3200356829 | DNAH11||KIF13A||DNHD1||DNAH17 | 4 | 4.339185 | 4.202411 | 4.199648 | 4.302409 | 4.401760 | 4.345764 | 4.304538 | 4.173902 | 4.178539 | 4.189044 | 4.266188 | 4.136409 | 4.255843 | 4.123237 | 4.276553 |
| GO:0019215 | intermediate filament binding | 2/306 | 17/20678 | 0.02564141314852 | 0.34188550865 | 0.3200356829 | NES||EPPK1 | 2 | 6.596582 | 7.443379 | 7.434451 | 6.520412 | 6.578306 | 6.713362 | 6.566998 | 7.465580 | 7.439522 | 7.453645 | 7.414264 | 7.423171 | 7.468159 | 7.429441 | 7.416474 |
| GO:0004860 | protein kinase inhibitor activity | 4/306 | 78/20678 | 0.02855181066922 | 0.36360554142 | 0.3403675933 | SH3BP5||SPRED1||SOCS3||INKA1 | 4 | 6.707662 | 6.669604 | 6.557976 | 6.698608 | 6.708902 | 6.733758 | 6.688993 | 6.644657 | 6.713707 | 6.684557 | 6.634087 | 6.606703 | 6.557064 | 6.499539 | 6.566572 |
| GO:0019966 | interleukin-1 binding | 2/306 | 18/20678 | 0.02856900682597 | 0.36360554142 | 0.3403675933 | IL1R2||IL1RN | 2 | 6.676983 | 6.664422 | 6.968790 | 6.625348 | 6.618725 | 6.749964 | 6.709574 | 6.664882 | 6.687014 | 6.634842 | 6.670458 | 6.980478 | 6.985989 | 6.951443 | 6.956948 |
| GO:0008528 | G protein-coupled peptide receptor activity | 6/306 | 157/20678 | 0.02959874705523 | 0.36833996335 | 0.3447994394 | VIPR1||CCR7||MAS1||EDNRA||SSTR2||CXCR3 | 6 | 3.638332 | 3.752104 | 3.885854 | 3.611672 | 3.645398 | 3.633970 | 3.661829 | 3.723287 | 3.750270 | 3.796529 | 3.737276 | 3.894663 | 3.871764 | 3.823318 | 3.950758 |
| GO:0035497 | cAMP response element binding | 2/306 | 19/20678 | 0.03162320005007 | 0.38497808757 | 0.3603742248 | NR4A3||CREB3L1 | 2 | 5.117081 | 4.907905 | 4.967326 | 4.963030 | 5.217397 | 5.238284 | 5.030309 | 4.926371 | 4.913373 | 4.900623 | 4.891008 | 5.118329 | 4.907010 | 4.968959 | 4.861809 |
| GO:0015291 | secondary active transmembrane transporter activity | 8/306 | 252/20678 | 0.03451851546486 | 0.40085816582 | 0.3752394109 | SLC7A8||SLC17A7||SLC7A11||SLC15A2||SLC16A5||SLC9A9||SLC8A1||SLC28A3 | 8 | 5.031071 | 5.584843 | 5.775846 | 5.024249 | 5.032715 | 5.032178 | 5.035117 | 5.591952 | 5.561017 | 5.613192 | 5.572668 | 5.753384 | 5.783816 | 5.806457 | 5.759107 |
| GO:0001653 | peptide receptor activity | 6/306 | 163/20678 | 0.03462141276480 | 0.40085816582 | 0.3752394109 | VIPR1||CCR7||MAS1||EDNRA||SSTR2||CXCR3 | 6 | 3.760204 | 3.879727 | 3.982451 | 3.735982 | 3.765504 | 3.758210 | 3.780761 | 3.856444 | 3.877825 | 3.921890 | 3.861830 | 3.990254 | 3.970367 | 3.930640 | 4.036527 |
| GO:0003774 | cytoskeletal motor activity | 5/306 | 122/20678 | 0.03514529567584 | 0.40085816582 | 0.3752394109 | DNAH11||KIF13A||MYO7A||DNHD1||DNAH17 | 5 | 5.949503 | 5.828285 | 5.697691 | 5.950690 | 5.984361 | 5.947046 | 5.915082 | 5.822943 | 5.813219 | 5.815085 | 5.861365 | 5.656999 | 5.742658 | 5.668436 | 5.720913 |
| GO:0005539 | glycosaminoglycan binding | 8/306 | 254/20678 | 0.03590719664801 | 0.40085816582 | 0.3752394109 | CFH||COL5A3||VEGFA||MMP7||SLIT2||CXCL10||CXCL11||SULF2 | 8 | 6.417068 | 6.357197 | 6.351249 | 6.421047 | 6.419984 | 6.406393 | 6.420794 | 6.388797 | 6.333918 | 6.344204 | 6.361269 | 6.359493 | 6.352182 | 6.344249 | 6.349028 |
| GO:0030246 | carbohydrate binding | 9/306 | 302/20678 | 0.03650672581611 | 0.40085816582 | 0.3752394109 | CLEC2D||SIGLEC1||GNPNAT1||CHODL||SIGLEC11||CLEC4E||ENPP1||HLA-DRA||KLRK1 | 9 | 6.635478 | 7.044478 | 7.227307 | 6.613737 | 6.632989 | 6.641023 | 6.653868 | 7.048465 | 7.008982 | 7.052544 | 7.067277 | 7.200853 | 7.232867 | 7.246835 | 7.228288 |
| GO:0038024 | cargo receptor activity | 4/306 | 85/20678 | 0.03744783328637 | 0.40181820910 | 0.3761380980 | LRP6||SCARF1||LGALS3BP||ENPP1 | 4 | 6.867957 | 6.622084 | 6.725321 | 6.864025 | 6.866021 | 6.877156 | 6.864587 | 6.621038 | 6.631704 | 6.617576 | 6.617971 | 6.707260 | 6.730850 | 6.738414 | 6.724579 |
| GO:0005516 | calmodulin binding | 7/306 | 211/20678 | 0.03802922336111 | 0.40181820910 | 0.3761380980 | MYLK||RGS4||UNC13A||MYO7A||UNC13C||OBSCN||SLC8A1 | 7 | 6.150507 | 6.023623 | 6.071251 | 6.005946 | 6.085327 | 6.214651 | 6.280191 | 6.030741 | 6.094214 | 5.945817 | 6.019882 | 6.086290 | 6.001331 | 6.084674 | 6.110367 |
| GO:0030506 | ankyrin binding | 2/306 | 22/20678 | 0.04150225973515 | 0.43039380466 | 0.4028874337 | OBSCN||SLC8A1 | 2 | 6.042239 | 6.703988 | 6.801084 | 6.135937 | 5.990295 | 6.065654 | 5.971119 | 6.730601 | 6.658746 | 6.714562 | 6.711038 | 6.853557 | 6.865191 | 6.791578 | 6.687188 |
| GO:0005158 | insulin receptor binding | 2/306 | 23/20678 | 0.04502022903605 | 0.44518097209 | 0.4167295566 | IGF2||ENPP1 | 2 | 5.215575 | 5.284451 | 5.223240 | 5.330824 | 5.186801 | 5.145087 | 5.192702 | 5.341299 | 5.267697 | 5.271707 | 5.255525 | 5.058289 | 5.262614 | 5.429350 | 5.113571 |
| GO:0016493 | C-C chemokine receptor activity | 2/306 | 23/20678 | 0.04502022903605 | 0.44518097209 | 0.4167295566 | CCR7||CXCR3 | 2 | 3.038659 | 3.754420 | 4.322256 | 2.919140 | 3.137207 | 3.079256 | 3.009912 | 3.738342 | 3.732681 | 3.801532 | 3.744057 | 4.319468 | 4.307749 | 4.323771 | 4.337878 |
| GO:0005044 | scavenger receptor activity | 3/306 | 54/20678 | 0.04577977256992 | 0.44518097209 | 0.4167295566 | SCARF1||LGALS3BP||ENPP1 | 3 | 5.353983 | 5.208113 | 4.962286 | 5.343645 | 5.322524 | 5.416344 | 5.331500 | 5.193558 | 5.268263 | 5.185758 | 5.183139 | 4.965924 | 4.951660 | 4.953254 | 4.978145 |
| GO:0061629 | RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding | 9/306 | 316/20678 | 0.04635518657775 | 0.44518097209 | 0.4167295566 | PADI2||NR4A3||MKKS||BHLHE40||OASL||HEY2||ANKRD1||NR4A2||DLL1 | 9 | 6.568060 | 6.484247 | 6.496104 | 6.517868 | 6.541529 | 6.582167 | 6.628229 | 6.485173 | 6.534666 | 6.443117 | 6.472511 | 6.527318 | 6.462839 | 6.480338 | 6.513016 |
| GO:0042056 | chemoattractant activity | 3/306 | 55/20678 | 0.04790909138529 | 0.44518097209 | 0.4167295566 | VEGFA||CXCL10||SCG2 | 3 | 6.337513 | 7.322712 | 7.809817 | 6.350566 | 6.353775 | 6.319545 | 6.325858 | 7.360046 | 7.308144 | 7.311095 | 7.310908 | 7.790920 | 7.848302 | 7.792629 | 7.806669 |
| GO:0017075 | syntaxin-1 binding | 2/306 | 24/20678 | 0.04864397509046 | 0.44518097209 | 0.4167295566 | UNC13A||UNC13C | 2 | 4.980885 | 4.570165 | 4.500080 | 5.079819 | 4.888311 | 4.990862 | 4.957956 | 4.462390 | 4.681774 | 4.646989 | 4.476066 | 4.510391 | 4.578561 | 4.399500 | 4.506218 |
| GO:0019957 | C-C chemokine binding | 2/306 | 24/20678 | 0.04864397509046 | 0.44518097209 | 0.4167295566 | CCR7||CXCR3 | 2 | 3.640821 | 4.066142 | 4.522569 | 3.574701 | 3.698347 | 3.616594 | 3.670477 | 4.060938 | 4.039107 | 4.111371 | 4.052106 | 4.516259 | 4.497160 | 4.544338 | 4.532085 |
| GO:0001228 | DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | 12/306 | 472/20678 | 0.04928789333819 | 0.44518097209 | 0.4167295566 | NR1H3||MEIS3||NR5A2||NR4A3||ZNF639||RREB1||TFAP2A||POU4F1||NR4A2||CREB3L1||EGR3||SCX | 12 | 4.912267 | 4.761573 | 4.763319 | 4.920159 | 4.926356 | 4.906366 | 4.895995 | 4.746435 | 4.753124 | 4.797681 | 4.748432 | 4.789066 | 4.741287 | 4.760984 | 4.761538 |
GO: CC
| ID | Description | GeneRatio | BgRatio | pvalue | p.adjust | qvalue | geneID | Count | No-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgKDN-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgwt-inf_Log2MeanTPM | log2TPM_No-inf_1 | log2TPM_No-inf_2 | log2TPM_No-inf_3 | log2TPM_No-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0032421 | stereocilium bundle | 5/318 | 64/21916 | 0.002360750 | 0.3358818 | 0.3189170 | ATP8B1||RIPOR2||KPTN||MKKS||MYO7A | 5 | 5.253838 | 4.713979 | 4.699130 | 5.311518 | 5.034454 | 5.221536 | 5.420448 | 4.599918 | 4.566129 | 4.619373 | 5.020700 | 4.723474 | 4.487282 | 4.539488 | 4.991093 |
| GO:0098862 | cluster of actin-based cell projections | 8/318 | 173/21916 | 0.003857190 | 0.3358818 | 0.3189170 | ATP8B1||RIPOR2||KPTN||MKKS||MYO7A||SLC7A11||SLC28A3||AQP1 | 8 | 6.501373 | 6.704585 | 6.650843 | 6.509458 | 6.467189 | 6.492188 | 6.535792 | 6.678063 | 6.681613 | 6.722779 | 6.735023 | 6.617392 | 6.686907 | 6.624950 | 6.672884 |
| GO:0031093 | platelet alpha granule lumen | 5/318 | 72/21916 | 0.003944295 | 0.3358818 | 0.3189170 | TGFB2||VEGFA||CLU||IGF2||ORM1 | 5 | 8.528156 | 8.699732 | 8.705178 | 8.531235 | 8.515663 | 8.527919 | 8.537715 | 8.697935 | 8.679128 | 8.708487 | 8.713140 | 8.702369 | 8.705107 | 8.708898 | 8.704332 |
| GO:0031674 | I band | 7/318 | 149/21916 | 0.006168541 | 0.3358818 | 0.3189170 | BIN1||ANKRD1||OBSCN||IGFN1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 7 | 6.346202 | 6.424762 | 6.462992 | 6.351345 | 6.351773 | 6.360966 | 6.320399 | 6.449467 | 6.431277 | 6.397184 | 6.420623 | 6.461008 | 6.519820 | 6.430041 | 6.439401 |
| GO:0005942 | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex | 3/318 | 29/21916 | 0.008363788 | 0.3358818 | 0.3189170 | SOCS4||SOCS3||PIK3R6 | 3 | 4.176091 | 4.156162 | 4.220437 | 4.347026 | 4.086497 | 4.043879 | 4.207476 | 4.163010 | 4.182984 | 4.243611 | 4.026407 | 4.098643 | 4.213144 | 4.367429 | 4.189435 |
| GO:0034774 | secretory granule lumen | 12/318 | 375/21916 | 0.009028052 | 0.3358818 | 0.3189170 | UNC13D||TGFB2||LGALS3BP||ALDOC||VEGFA||PADI2||CLU||C3||CXCL1||IGF2||HPSE||ORM1 | 12 | 8.436455 | 8.447697 | 8.395265 | 8.437495 | 8.435584 | 8.433819 | 8.438915 | 8.448437 | 8.441748 | 8.444915 | 8.455652 | 8.391704 | 8.399398 | 8.394334 | 8.395614 |
| GO:0032420 | stereocilium | 4/318 | 57/21916 | 0.009397494 | 0.3358818 | 0.3189170 | ATP8B1||RIPOR2||KPTN||MYO7A | 4 | 5.077734 | 4.639863 | 4.395503 | 5.033079 | 5.071587 | 5.069546 | 5.134857 | 4.638059 | 4.604766 | 4.655468 | 4.660502 | 4.373280 | 4.272266 | 4.423996 | 4.502808 |
| GO:0060205 | cytoplasmic vesicle lumen | 12/318 | 378/21916 | 0.009577591 | 0.3358818 | 0.3189170 | UNC13D||TGFB2||LGALS3BP||ALDOC||VEGFA||PADI2||CLU||C3||CXCL1||IGF2||HPSE||ORM1 | 12 | 8.426076 | 8.436916 | 8.384382 | 8.427130 | 8.425277 | 8.423340 | 8.428551 | 8.437583 | 8.431075 | 8.434085 | 8.444886 | 8.380846 | 8.388490 | 8.383482 | 8.384700 |
| GO:0031983 | vesicle lumen | 12/318 | 380/21916 | 0.009958169 | 0.3358818 | 0.3189170 | UNC13D||TGFB2||LGALS3BP||ALDOC||VEGFA||PADI2||CLU||C3||CXCL1||IGF2||HPSE||ORM1 | 12 | 8.420441 | 8.431309 | 8.378769 | 8.421495 | 8.419641 | 8.417706 | 8.422918 | 8.431972 | 8.425474 | 8.428471 | 8.439282 | 8.375238 | 8.382878 | 8.377869 | 8.379080 |
| GO:0031526 | brush border membrane | 4/318 | 60/21916 | 0.011216778 | 0.3358818 | 0.3189170 | ATP8B1||SLC7A11||SLC28A3||AQP1 | 4 | 5.639202 | 6.199464 | 6.264040 | 5.600369 | 5.665384 | 5.597865 | 5.690907 | 6.183530 | 6.175233 | 6.255422 | 6.182178 | 6.223050 | 6.269019 | 6.270565 | 6.292642 |
| GO:0018995 | host cellular component | 2/318 | 12/21916 | 0.012583468 | 0.3358818 | 0.3189170 | IFIT1||AQP1 | 2 | 4.699807 | 5.103641 | 5.122732 | 4.692708 | 4.630690 | 4.757211 | 4.715725 | 5.023581 | 5.128245 | 5.138109 | 5.121707 | 5.143922 | 5.122115 | 5.125565 | 5.098971 |
| GO:0043657 | host cell | 2/318 | 12/21916 | 0.012583468 | 0.3358818 | 0.3189170 | IFIT1||AQP1 | 2 | 4.699807 | 5.103641 | 5.122732 | 4.692708 | 4.630690 | 4.757211 | 4.715725 | 5.023581 | 5.128245 | 5.138109 | 5.121707 | 5.143922 | 5.122115 | 5.125565 | 5.098971 |
| GO:0060198 | clathrin-sculpted vesicle | 2/318 | 12/21916 | 0.012583468 | 0.3358818 | 0.3189170 | DNAJC5||SLC17A7 | 2 | 6.846899 | 7.891887 | 7.759805 | 6.838690 | 6.881782 | 6.799170 | 6.866590 | 7.922606 | 7.937875 | 7.880587 | 7.823784 | 7.765173 | 7.723156 | 7.742763 | 7.806781 |
| GO:0030018 | Z disc | 6/318 | 138/21916 | 0.015532453 | 0.3474508 | 0.3299018 | BIN1||OBSCN||IGFN1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 6 | 6.212302 | 6.180270 | 6.192808 | 6.222049 | 6.216031 | 6.230193 | 6.180437 | 6.209304 | 6.199036 | 6.144907 | 6.166927 | 6.191429 | 6.258411 | 6.157164 | 6.161947 |
| GO:0030017 | sarcomere | 8/318 | 223/21916 | 0.016516405 | 0.3474508 | 0.3299018 | BIN1||ANKRD1||OBSCN||IGFN1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP||TPM2 | 8 | 6.636453 | 6.764775 | 6.765147 | 6.636738 | 6.638843 | 6.652087 | 6.617938 | 6.770014 | 6.765068 | 6.757543 | 6.766448 | 6.761675 | 6.798342 | 6.736631 | 6.763269 |
| GO:0031091 | platelet alpha granule | 5/318 | 102/21916 | 0.016560505 | 0.3474508 | 0.3299018 | TGFB2||VEGFA||CLU||IGF2||ORM1 | 5 | 8.153683 | 8.283769 | 8.282526 | 8.155263 | 8.143585 | 8.153545 | 8.162279 | 8.281917 | 8.264316 | 8.294130 | 8.294503 | 8.279105 | 8.284792 | 8.285595 | 8.280601 |
| GO:0042583 | chromaffin granule | 2/318 | 14/21916 | 0.017022088 | 0.3474508 | 0.3299018 | DNAJC5||CLU | 2 | 6.314415 | 7.258579 | 7.635363 | 6.376547 | 6.285599 | 6.268293 | 6.324810 | 7.243039 | 7.325448 | 7.230280 | 7.233398 | 7.638138 | 7.632621 | 7.626958 | 7.643682 |
| GO:0099092 | postsynaptic density, intracellular component | 2/318 | 15/21916 | 0.019454759 | 0.3750445 | 0.3561017 | CDKL5||DLG3 | 2 | 6.212840 | 6.067298 | 6.021486 | 6.179883 | 6.173715 | 6.265585 | 6.230196 | 6.079097 | 5.981420 | 6.076277 | 6.128498 | 6.009992 | 5.967361 | 6.107525 | 5.997197 |
| GO:0098831 | presynaptic active zone cytoplasmic component | 2/318 | 16/21916 | 0.022023586 | 0.4022202 | 0.3819048 | UNC13A||UNC13C | 2 | 5.245667 | 5.046205 | 4.952603 | 5.259639 | 5.197580 | 5.351459 | 5.167050 | 5.088658 | 4.936941 | 4.964786 | 5.181014 | 5.019159 | 4.887405 | 5.000820 | 4.898189 |
| GO:0031253 | cell projection membrane | 11/318 | 381/21916 | 0.024012253 | 0.4166126 | 0.3955703 | CDKL5||ATP8B1||SLC7A8||GABRA4||RIPOR2||KCNC4||FGD2||SLC7A11||SLC28A3||CYS1||AQP1 | 11 | 7.118246 | 7.202003 | 7.062144 | 7.108490 | 7.116858 | 7.128702 | 7.118861 | 7.205486 | 7.193766 | 7.205614 | 7.203114 | 7.070672 | 7.062486 | 7.054717 | 7.060654 |
| GO:0030016 | myofibril | 8/318 | 243/21916 | 0.026006933 | 0.4297336 | 0.4080286 | BIN1||ANKRD1||OBSCN||IGFN1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP||TPM2 | 8 | 6.786878 | 6.912449 | 6.899446 | 6.786531 | 6.790892 | 6.796598 | 6.773391 | 6.914978 | 6.911257 | 6.907115 | 6.916431 | 6.894584 | 6.930116 | 6.875154 | 6.897390 |
| GO:0032994 | protein-lipid complex | 3/318 | 46/21916 | 0.029030253 | 0.4528221 | 0.4299509 | CLU||BIN1||PLA2G7 | 3 | 6.737914 | 6.965766 | 6.945774 | 6.750629 | 6.695471 | 6.742312 | 6.762353 | 7.006611 | 6.905755 | 6.943474 | 7.004708 | 6.925593 | 6.971880 | 6.955959 | 6.929154 |
| GO:0099091 | postsynaptic specialization, intracellular component | 2/318 | 19/21916 | 0.030503118 | 0.4528221 | 0.4299509 | CDKL5||DLG3 | 2 | 6.035866 | 6.099226 | 6.110515 | 6.012641 | 6.012888 | 6.076489 | 6.040494 | 6.111726 | 6.047490 | 6.088494 | 6.147371 | 6.083864 | 6.087050 | 6.199148 | 6.068167 |
| GO:0043292 | contractile fiber | 8/318 | 252/21916 | 0.031319110 | 0.4528221 | 0.4299509 | BIN1||ANKRD1||OBSCN||IGFN1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP||TPM2 | 8 | 6.793588 | 6.911653 | 6.889428 | 6.785860 | 6.812933 | 6.799491 | 6.775797 | 6.915529 | 6.906190 | 6.907514 | 6.917346 | 6.882530 | 6.922195 | 6.861309 | 6.891015 |
| GO:0030136 | clathrin-coated vesicle | 8/318 | 258/21916 | 0.035247368 | 0.4598902 | 0.4366620 | UNC13D||DNAJC5||SLC17A7||ECE1||CD3G||INPP5F||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA2 | 8 | 6.246599 | 6.270767 | 6.202458 | 6.253468 | 6.205043 | 6.277734 | 6.249199 | 6.254797 | 6.281630 | 6.294444 | 6.251746 | 6.200572 | 6.199275 | 6.172144 | 6.237101 |
| GO:0030672 | synaptic vesicle membrane | 5/318 | 125/21916 | 0.035783961 | 0.4598902 | 0.4366620 | DNAJC5||SLC17A7||UNC13A||UNC13C||MCTP2 | 5 | 5.096839 | 5.230273 | 5.155012 | 5.129843 | 5.073680 | 5.099038 | 5.084174 | 5.226951 | 5.258005 | 5.233362 | 5.202228 | 5.179571 | 5.147152 | 5.143189 | 5.149847 |
| GO:0099501 | exocytic vesicle membrane | 5/318 | 125/21916 | 0.035783961 | 0.4598902 | 0.4366620 | DNAJC5||SLC17A7||UNC13A||UNC13C||MCTP2 | 5 | 5.096839 | 5.230273 | 5.155012 | 5.129843 | 5.073680 | 5.099038 | 5.084174 | 5.226951 | 5.258005 | 5.233362 | 5.202228 | 5.179571 | 5.147152 | 5.143189 | 5.149847 |
| GO:0030139 | endocytic vesicle | 12/318 | 464/21916 | 0.039265557 | 0.4632932 | 0.4398931 | LPAR2||SCARF1||NCF2||DYSF||ADAM8||CD3G||CLEC4E||TLR7||INPP5F||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA2 | 12 | 7.197556 | 7.306449 | 7.317735 | 7.193661 | 7.215347 | 7.194137 | 7.186919 | 7.286518 | 7.301287 | 7.312716 | 7.324998 | 7.316560 | 7.319094 | 7.317275 | 7.318011 |
| GO:0060076 | excitatory synapse | 3/318 | 52/21916 | 0.039689104 | 0.4632932 | 0.4398931 | SLC17A7||LRRC4||UNC13C | 3 | 4.887296 | 5.170210 | 5.416894 | 4.806266 | 4.911940 | 4.978489 | 4.846529 | 5.169848 | 5.159634 | 5.193719 | 5.157351 | 5.416951 | 5.367445 | 5.463949 | 5.417617 |
| GO:0005767 | secondary lysosome | 2/318 | 22/21916 | 0.040054165 | 0.4632932 | 0.4398931 | NCF2||ADAM8 | 2 | 9.403337 | 10.080943 | 10.331757 | 9.387422 | 9.403642 | 9.410974 | 9.411179 | 10.064605 | 10.079370 | 10.082272 | 10.097339 | 10.306066 | 10.342651 | 10.334900 | 10.343094 |
| GO:0030315 | T-tubule | 3/318 | 53/21916 | 0.041633223 | 0.4660235 | 0.4424855 | DYSF||BIN1||SLC8A1 | 3 | 5.286890 | 5.269391 | 5.278904 | 5.293800 | 5.326069 | 5.304097 | 5.221476 | 5.303102 | 5.223029 | 5.301507 | 5.248279 | 5.292796 | 5.297791 | 5.300899 | 5.222686 |
| GO:0005858 | axonemal dynein complex | 2/318 | 23/21916 | 0.043457266 | 0.4712397 | 0.4474383 | DNHD1||DNAH17 | 2 | 2.866515 | 3.097293 | 3.062716 | 2.342501 | 2.990863 | 2.719089 | 3.257942 | 2.002417 | 2.907049 | 1.744075 | 4.276133 | 1.947668 | 4.371475 | 2.313370 | 1.961637 |
| GO:0035327 | transcriptionally active chromatin | 2/318 | 24/21916 | 0.046963701 | 0.4873002 | 0.4626875 | PADI2||ZC3H8 | 2 | 4.699002 | 4.876220 | 4.965400 | 4.751904 | 4.727627 | 4.656892 | 4.657105 | 4.890730 | 4.895410 | 4.844506 | 4.873685 | 5.274693 | 4.880365 | 4.801077 | 4.854157 |
| GO:0030286 | dynein complex | 3/318 | 56/21916 | 0.047746989 | 0.4873002 | 0.4626875 | DNAH11||DNHD1||DNAH17 | 3 | 5.648873 | 5.491517 | 5.374830 | 5.618408 | 5.687397 | 5.626381 | 5.662230 | 5.443779 | 5.496828 | 5.483815 | 5.540012 | 5.288177 | 5.429742 | 5.429776 | 5.346684 |
KEGG
| ID | Description | GeneRatio | BgRatio | pvalue | p.adjust | qvalue | geneID | Count | No-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgKDN-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgwt-inf_Log2MeanTPM | log2TPM_No-inf_1 | log2TPM_No-inf_2 | log2TPM_No-inf_3 | log2TPM_No-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa04060 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | 23/156 | 295/8212 | 0.000000006578002 | 0.000001572143 | 0.000001322525 | TGFB2||OSM||CCL22||IL23A||PRLR||IL1A||IL1R2||TNFSF18||TNFSF10||CCR7||LIF||IL6||IL36G||IL1RN||BMP6||TNFRSF14||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||TNFSF15||CSF1||CXCR3||TNFRSF18 | 23 | 5.086895 | 6.202895 | 6.595424 | 5.076743 | 5.101743 | 5.074889 | 5.094023 | 6.217429 | 6.181225 | 6.212603 | 6.200054 | 6.586842 | 6.593162 | 6.583248 | 6.618186 |
| hsa05164 | Influenza A | 14/156 | 171/8212 | 0.000004123677075 | 0.000492779410 | 0.000414538064 | OAS2||IL1A||TNFSF10||RSAD2||IL6||TLR4||MX1||CXCL10||SOCS3||IRF7||TLR7||HLA-DRA||IRF9||HLA-DQA1 | 14 | 6.876102 | 7.191024 | 7.321240 | 6.899589 | 6.869638 | 6.870578 | 6.864337 | 7.200377 | 7.187613 | 7.197474 | 7.178529 | 7.325638 | 7.331922 | 7.315561 | 7.311752 |
| hsa05323 | Rheumatoid arthritis | 10/156 | 93/8212 | 0.000009581034728 | 0.000763289100 | 0.000642097415 | TGFB2||IL23A||VEGFA||IL1A||IL6||TLR4||CXCL1||CSF1||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 10 | 6.988702 | 7.855870 | 8.211933 | 6.981703 | 6.984825 | 6.985874 | 7.002318 | 7.860418 | 7.846485 | 7.856672 | 7.859860 | 8.207121 | 8.224023 | 8.211271 | 8.205243 |
| hsa04061 | Viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor | 10/156 | 100/8212 | 0.000018319935109 | 0.001094616123 | 0.000920817791 | CCL22||TNFSF10||CCR7||IL6||TNFRSF14||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||CSF1||CXCR3 | 10 | 4.413663 | 6.576132 | 7.088386 | 4.409913 | 4.389610 | 4.420417 | 4.434344 | 6.587527 | 6.565820 | 6.581568 | 6.569508 | 7.078842 | 7.101224 | 7.091849 | 7.081520 |
| hsa05321 | Inflammatory bowel disease | 8/156 | 65/8212 | 0.000028559394861 | 0.001365139074 | 0.001148388299 | TGFB2||IL23A||IL1A||IL6||TLR4||STAT4||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 8 | 6.139674 | 6.709631 | 7.013545 | 6.189569 | 6.133551 | 6.114257 | 6.120078 | 6.706348 | 6.693349 | 6.732409 | 6.706138 | 7.018634 | 7.018068 | 7.010635 | 7.006807 |
| hsa04668 | TNF signaling pathway | 9/156 | 112/8212 | 0.000264973461545 | 0.010221910918 | 0.008598920878 | RPS6KA5||MAPK10||LIF||IL6||CREB3L1||CXCL1||CXCL10||CSF1||SOCS3 | 9 | 5.672874 | 6.796137 | 7.307626 | 5.689898 | 5.688634 | 5.659989 | 5.652590 | 6.792082 | 6.790702 | 6.805525 | 6.796191 | 7.285020 | 7.314741 | 7.320371 | 7.310122 |
| hsa05162 | Measles | 10/156 | 139/8212 | 0.000299386512253 | 0.010221910918 | 0.008598920878 | MAPK10||OAS2||IL1A||IL6||TLR4||MX1||CD3G||IRF7||TLR7||IRF9 | 10 | 5.935125 | 6.374623 | 6.459455 | 5.977544 | 5.945791 | 5.911978 | 5.903998 | 6.405019 | 6.390110 | 6.357606 | 6.344949 | 6.465403 | 6.465188 | 6.447725 | 6.459433 |
| hsa05169 | Epstein-Barr virus infection | 12/156 | 202/8212 | 0.000446795596745 | 0.013348018453 | 0.011228678813 | MAPK10||OAS2||IL6||ENTPD1||CD3G||CXCL10||IRF7||ISG15||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||IRF9||HLA-DQA1 | 12 | 6.719375 | 6.720722 | 6.775605 | 6.747556 | 6.715192 | 6.715007 | 6.699316 | 6.726912 | 6.715704 | 6.721937 | 6.718308 | 6.772559 | 6.789228 | 6.768539 | 6.772005 |
| hsa05140 | Leishmaniasis | 7/156 | 77/8212 | 0.000615945847204 | 0.016356784165 | 0.013759725943 | TGFB2||IL1A||NCF2||C3||TLR4||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 7 | 8.514126 | 8.491293 | 8.456718 | 8.518474 | 8.518236 | 8.512755 | 8.507007 | 8.497518 | 8.483024 | 8.496188 | 8.488392 | 8.451958 | 8.461460 | 8.459096 | 8.454338 |
| hsa05332 | Graft-versus-host disease | 5/156 | 42/8212 | 0.001119164226784 | 0.026748025020 | 0.022501091296 | IL1A||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA1 | 5 | 6.308038 | 7.169955 | 7.692298 | 6.265930 | 6.314128 | 6.331948 | 6.319280 | 7.172058 | 7.164992 | 7.177910 | 7.164821 | 7.692447 | 7.696712 | 7.684128 | 7.695869 |
| hsa04658 | Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | 7/156 | 92/8212 | 0.001770645814767 | 0.038471304521 | 0.032363000059 | NOTCH3||MAPK10||STAT4||CD3G||DLL1||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 7 | 5.783866 | 5.674545 | 5.646206 | 5.831371 | 5.784118 | 5.775333 | 5.743257 | 5.653619 | 5.664670 | 5.707478 | 5.671847 | 5.629796 | 5.666706 | 5.615631 | 5.671900 |
| hsa05152 | Tuberculosis | 10/156 | 180/8212 | 0.002209220090814 | 0.044000300142 | 0.037014126083 | TGFB2||MAPK10||IL23A||IL1A||C3||IL6||TLR4||CLEC4E||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 10 | 7.287533 | 7.426140 | 7.541544 | 7.301719 | 7.296681 | 7.278032 | 7.273501 | 7.426307 | 7.410039 | 7.423270 | 7.444730 | 7.525855 | 7.545638 | 7.540690 | 7.553850 |
| hsa04640 | Hematopoietic cell lineage | 7/156 | 99/8212 | 0.002694809667454 | 0.046632046417 | 0.039228015263 | IL1A||IL1R2||IL6||CD3G||CSF1||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 7 | 5.814938 | 6.519575 | 6.860708 | 5.832844 | 5.799393 | 5.835409 | 5.791576 | 6.525016 | 6.530718 | 6.499022 | 6.523338 | 6.874949 | 6.842844 | 6.882556 | 6.842015 |
| hsa04380 | Osteoclast differentiation | 8/156 | 128/8212 | 0.002955090660678 | 0.046632046417 | 0.039228015263 | TGFB2||MAPK10||IL1A||NCF2||CSF1||SOCS3||IRF9||LILRA6 | 8 | 6.586307 | 6.815743 | 6.924388 | 6.590097 | 6.588715 | 6.585986 | 6.580411 | 6.816030 | 6.812978 | 6.833909 | 6.799852 | 6.920005 | 6.933660 | 6.912408 | 6.931375 |
| hsa05160 | Hepatitis C | 9/156 | 157/8212 | 0.002957982551764 | 0.046632046417 | 0.039228015263 | NR1H3||OAS2||RSAD2||MX1||CXCL10||SOCS3||IRF7||IFIT1||IRF9 | 9 | 5.986245 | 6.230674 | 6.181634 | 6.020419 | 5.970485 | 5.994002 | 5.959309 | 6.265731 | 6.235998 | 6.216332 | 6.203877 | 6.185915 | 6.175414 | 6.174209 | 6.190931 |
| hsa05133 | Pertussis | 6/156 | 76/8212 | 0.003121810638763 | 0.046632046417 | 0.039228015263 | MAPK10||IL23A||IL1A||C3||IL6||TLR4 | 6 | 7.142965 | 7.419720 | 7.664698 | 7.162268 | 7.132486 | 7.150798 | 7.126021 | 7.423793 | 7.402581 | 7.429621 | 7.422741 | 7.659481 | 7.654946 | 7.691610 | 7.652409 |
| hsa04620 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 7/156 | 104/8212 | 0.003554613571679 | 0.047197369091 | 0.039703578491 | MAPK10||IL6||TLR4||CXCL10||CXCL11||IRF7||TLR7 | 7 | 6.857067 | 7.864424 | 8.031730 | 6.900834 | 6.841592 | 6.849210 | 6.835700 | 7.871990 | 7.853207 | 7.867530 | 7.864901 | 8.028003 | 8.039847 | 8.027727 | 8.031310 |
| hsa04625 | C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | 7/156 | 104/8212 | 0.003554613571679 | 0.047197369091 | 0.039703578491 | CCL22||MAPK10||IL23A||IL6||CLEC4E||EGR3||IRF9 | 7 | 6.660317 | 6.874663 | 6.963941 | 6.688233 | 6.675412 | 6.641058 | 6.635878 | 6.880213 | 6.846659 | 6.865132 | 6.905995 | 6.942256 | 6.949467 | 6.973618 | 6.989921 |
| hsa05167 | Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection | 10/156 | 194/8212 | 0.003798431284347 | 0.047780267208 | 0.040193926610 | MAPK10||VEGFA||C3||IL6||CXCL1||GNG12||IRF7||HLA-F||IRF9||PIK3R6 | 10 | 6.652857 | 6.720990 | 6.687743 | 6.659124 | 6.656846 | 6.656189 | 6.639180 | 6.736921 | 6.712207 | 6.726891 | 6.707755 | 6.705342 | 6.688463 | 6.673428 | 6.683554 |
| hsa04630 | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | 9/156 | 166/8212 | 0.004284193388182 | 0.051196110989 | 0.043067417744 | OSM||IL23A||PRLR||LIF||IL6||STAT4||SOCS4||SOCS3||IRF9 | 9 | 5.798479 | 5.855192 | 5.789364 | 5.809397 | 5.811975 | 5.780190 | 5.792120 | 5.834596 | 5.876643 | 5.859921 | 5.849279 | 5.774185 | 5.786034 | 5.759564 | 5.836503 |
| hsa05171 | Coronavirus disease - COVID-19 | 11/156 | 232/8212 | 0.004602734809259 | 0.051360241446 | 0.043205488289 | MAPK10||OAS2||C3||MAS1||IL6||TLR4||MX1||CXCL10||ISG15||TLR7||IRF9 | 11 | 9.634707 | 9.683136 | 9.511494 | 9.640896 | 9.636472 | 9.633881 | 9.627548 | 9.686777 | 9.686507 | 9.689459 | 9.669714 | 9.510125 | 9.510608 | 9.512799 | 9.512442 |
| hsa00240 | Pyrimidine metabolism | 5/156 | 58/8212 | 0.004727720969883 | 0.051360241446 | 0.043205488289 | TYMP||CMPK2||ENTPD1||TK2||ENPP1 | 5 | 5.663223 | 5.922748 | 5.895341 | 5.720022 | 5.590887 | 5.682031 | 5.656899 | 5.890995 | 5.877082 | 6.009137 | 5.910023 | 5.871476 | 5.901632 | 5.888278 | 5.919548 |
| hsa04940 | Type I diabetes mellitus | 4/156 | 43/8212 | 0.008698031659129 | 0.090383894197 | 0.076033137158 | IL1A||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA1 | 4 | 6.290782 | 7.126277 | 7.599910 | 6.262364 | 6.279570 | 6.310261 | 6.310346 | 7.127999 | 7.124381 | 7.129783 | 7.122936 | 7.596629 | 7.603877 | 7.593160 | 7.605936 |
| hsa05166 | Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection | 10/156 | 222/8212 | 0.009608619829068 | 0.095685839131 | 0.080493262603 | TGFB2||MAPK10||IL1R2||IL6||MMP7||CREB3L1||CD3G||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA1 | 10 | 6.874949 | 6.831572 | 6.922154 | 6.872693 | 6.880821 | 6.869892 | 6.876367 | 6.850533 | 6.828733 | 6.826301 | 6.820542 | 6.918281 | 6.940231 | 6.918827 | 6.911113 |
| hsa04062 | Chemokine signaling pathway | 9/156 | 192/8212 | 0.010800666582979 | 0.103254372533 | 0.086860097573 | CCL22||ITK||CCR7||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||GNG12||CXCR3||PIK3R6 | 9 | 5.744445 | 6.272208 | 6.473053 | 5.766626 | 5.746681 | 5.725173 | 5.738988 | 6.282292 | 6.289842 | 6.285769 | 6.230113 | 6.454515 | 6.490275 | 6.496459 | 6.450373 |
| hsa05161 | Hepatitis B | 8/156 | 162/8212 | 0.011904492026650 | 0.109429753630 | 0.092054978830 | TGFB2||MAPK10||IL6||TLR4||STAT4||CREB3L1||EGR3||IRF7 | 8 | 5.662220 | 6.472859 | 6.778320 | 5.695498 | 5.669496 | 5.645200 | 5.637980 | 6.471337 | 6.457282 | 6.485151 | 6.477522 | 6.769592 | 6.786408 | 6.782144 | 6.775077 |
| hsa05142 | Chagas disease | 6/156 | 102/8212 | 0.012874301030134 | 0.113961405415 | 0.095867114883 | TGFB2||MAPK10||C3||IL6||TLR4||CD3G | 6 | 6.410152 | 6.924750 | 7.204108 | 6.443648 | 6.389860 | 6.409609 | 6.396896 | 6.926460 | 6.915543 | 6.933661 | 6.923278 | 7.195763 | 7.213088 | 7.209741 | 7.197765 |
| hsa04672 | Intestinal immune network for IgA production | 4/156 | 49/8212 | 0.013683357375662 | 0.116797229028 | 0.098252678900 | AICDA||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 4 | 5.069841 | 5.611385 | 5.857128 | 5.022695 | 5.108456 | 5.084618 | 5.062215 | 5.618492 | 5.586828 | 5.609954 | 5.629919 | 5.890235 | 5.871043 | 5.837469 | 5.828908 |
| hsa05144 | Malaria | 4/156 | 50/8212 | 0.014658602711991 | 0.120807105109 | 0.101625884501 | TGFB2||IL6||TLR4||KLRK1 | 4 | 7.726214 | 8.321494 | 8.580880 | 7.712012 | 7.735215 | 7.729228 | 7.728296 | 8.320206 | 8.306614 | 8.328778 | 8.330258 | 8.578562 | 8.590995 | 8.587655 | 8.566181 |
| hsa04659 | Th17 cell differentiation | 6/156 | 108/8212 | 0.016686491086316 | 0.128647463536 | 0.108221385314 | MAPK10||IL23A||IL6||CD3G||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 6 | 6.245807 | 6.773038 | 6.950252 | 6.273823 | 6.247195 | 6.235188 | 6.226582 | 6.768169 | 6.758660 | 6.797266 | 6.767762 | 6.948426 | 6.957724 | 6.942009 | 6.952801 |
| hsa04931 | Insulin resistance | 6/156 | 108/8212 | 0.016686491086316 | 0.128647463536 | 0.108221385314 | NR1H3||MAPK10||IL6||CREB3L1||SOCS3||CPT1B | 6 | 5.325164 | 5.342827 | 5.398927 | 5.359087 | 5.335342 | 5.277837 | 5.327184 | 5.429146 | 5.387219 | 5.295675 | 5.252404 | 5.472379 | 5.464855 | 5.335105 | 5.316218 |
| hsa05145 | Toxoplasmosis | 6/156 | 112/8212 | 0.019622648470894 | 0.146556655767 | 0.123287034801 | TGFB2||MAPK10||TLR4||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1||PIK3R6 | 6 | 5.940853 | 6.228837 | 6.173066 | 5.966540 | 5.954670 | 5.910110 | 5.931440 | 6.233031 | 6.213901 | 6.243990 | 6.224256 | 6.172722 | 6.169936 | 6.186094 | 6.163415 |
| hsa01232 | Nucleotide metabolism | 5/156 | 85/8212 | 0.022546827226435 | 0.159682315169 | 0.134328659754 | TYMP||CMPK2||ENTPD1||TK2||ENPP1 | 5 | 5.806245 | 6.030504 | 6.034363 | 5.845179 | 5.786694 | 5.798723 | 5.793648 | 6.004169 | 6.023671 | 6.066529 | 6.026935 | 6.004500 | 6.069966 | 6.052243 | 6.009669 |
| hsa05134 | Legionellosis | 4/156 | 57/8212 | 0.022716312618141 | 0.159682315169 | 0.134328659754 | C3||IL6||TLR4||CXCL1 | 4 | 8.633757 | 8.745687 | 8.719390 | 8.643546 | 8.638199 | 8.629330 | 8.623873 | 8.757228 | 8.734623 | 8.747546 | 8.743261 | 8.713532 | 8.720996 | 8.724871 | 8.718136 |
| hsa05165 | Human papillomavirus infection | 12/156 | 331/8212 | 0.023517761803979 | 0.160592716319 | 0.135094511415 | NOTCH3||DLG3||VEGFA||OASL||HEY2||MX1||CREB3L1||ISG15||HES4||HLA-F||COL6A6||IRF9 | 12 | 6.488302 | 6.944573 | 6.974719 | 6.509168 | 6.479664 | 6.487422 | 6.476731 | 6.951878 | 6.938578 | 6.943178 | 6.944627 | 6.973654 | 6.984916 | 6.974091 | 6.966152 |
| hsa05410 | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | 5/156 | 90/8212 | 0.028036949922247 | 0.186134195317 | 0.156580626759 | TGFB2||IL6||CACNB4||SLC8A1||TPM2 | 5 | 7.862435 | 8.122709 | 8.135054 | 7.858884 | 7.861014 | 7.878763 | 7.850938 | 8.126422 | 8.125935 | 8.126128 | 8.112302 | 8.142216 | 8.144767 | 8.122269 | 8.130850 |
| hsa04514 | Cell adhesion molecules | 7/156 | 157/8212 | 0.029809193695336 | 0.192551278194 | 0.161978833451 | SIGLEC1||LRRC4||SLITRK5||PDCD1LG2||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA1 | 7 | 6.712245 | 6.768462 | 6.883147 | 6.708076 | 6.721809 | 6.718045 | 6.700955 | 6.766351 | 6.765418 | 6.781290 | 6.760705 | 6.885242 | 6.896058 | 6.882683 | 6.868473 |
| hsa04657 | IL-17 signaling pathway | 5/156 | 94/8212 | 0.032992127938485 | 0.207503120455 | 0.174556687985 | MAPK10||IL6||MMP13||CXCL1||CXCL10 | 5 | 6.027005 | 7.544981 | 7.949861 | 6.090109 | 5.991013 | 6.034467 | 5.990099 | 7.549537 | 7.548306 | 7.547971 | 7.534052 | 7.953893 | 7.949889 | 7.954820 | 7.940802 |
| hsa05330 | Allograft rejection | 3/156 | 38/8212 | 0.034929476989851 | 0.209612566245 | 0.176331205253 | HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA1 | 3 | 6.418458 | 6.394930 | 6.666126 | 6.373850 | 6.428928 | 6.442445 | 6.427657 | 6.388855 | 6.399116 | 6.409975 | 6.381616 | 6.669858 | 6.676428 | 6.632023 | 6.685622 |
| hsa05150 | Staphylococcus aureus infection | 5/156 | 96/8212 | 0.035662063326345 | 0.209612566245 | 0.176331205253 | CFH||C3||PTAFR||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 5 | 7.423417 | 7.294302 | 7.510582 | 7.420281 | 7.430177 | 7.425441 | 7.417738 | 7.289489 | 7.300136 | 7.308147 | 7.279272 | 7.495206 | 7.519631 | 7.523427 | 7.503882 |
| hsa04623 | Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | 4/156 | 66/8212 | 0.036403567358890 | 0.209612566245 | 0.176331205253 | POLR3G||IL6||CXCL10||IRF7 | 4 | 5.411037 | 6.447396 | 6.971146 | 5.543759 | 5.325416 | 5.387395 | 5.378227 | 6.438311 | 6.481011 | 6.450045 | 6.419523 | 6.960680 | 6.983765 | 6.963761 | 6.976258 |
| hsa04151 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 12/156 | 354/8212 | 0.036835681097431 | 0.209612566245 | 0.176331205253 | LPAR2||OSM||VEGFA||PRLR||IL6||TLR4||CREB3L1||IGF2||GNG12||CSF1||COL6A6||PIK3R6 | 12 | 6.682235 | 7.106428 | 7.061342 | 6.692412 | 6.679574 | 6.677568 | 6.679339 | 7.112024 | 7.103687 | 7.101792 | 7.108187 | 7.064362 | 7.057127 | 7.064505 | 7.059359 |
| hsa04068 | FoxO signaling pathway | 6/156 | 131/8212 | 0.038369454427017 | 0.213262781583 | 0.179401855460 | TGFB2||MAPK10||TNFSF10||IL6||FBXO25||S1PR1 | 6 | 5.340607 | 5.552049 | 5.565552 | 5.325722 | 5.362787 | 5.329550 | 5.344074 | 5.568159 | 5.518641 | 5.572826 | 5.547940 | 5.578851 | 5.578285 | 5.548056 | 5.556768 |
| hsa04933 | AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications | 5/156 | 100/8212 | 0.041393168184557 | 0.224840163548 | 0.189141031657 | TGFB2||MAPK10||VEGFA||IL1A||IL6 | 5 | 5.429300 | 6.280544 | 6.560890 | 5.466875 | 5.421012 | 5.412004 | 5.416632 | 6.291995 | 6.244208 | 6.303474 | 6.281815 | 6.559388 | 6.571371 | 6.557948 | 6.554799 |
| hsa05219 | Bladder cancer | 3/156 | 41/8212 | 0.042371655251002 | 0.225040569000 | 0.189309617613 | TYMP||RPS6KA5||VEGFA | 3 | 5.785975 | 7.785006 | 8.247497 | 5.753419 | 5.821909 | 5.772336 | 5.795323 | 7.790786 | 7.767380 | 7.790772 | 7.790941 | 8.242380 | 8.252307 | 8.252203 | 8.243067 |
| hsa04917 | Prolactin signaling pathway | 4/156 | 70/8212 | 0.043728589788738 | 0.226065212394 | 0.190171572637 | MAPK10||PRLR||SOCS4||SOCS3 | 4 | 5.140994 | 5.162325 | 5.115609 | 5.188564 | 5.164605 | 5.082294 | 5.126270 | 5.267508 | 5.222366 | 5.078886 | 5.070089 | 5.135737 | 5.047477 | 5.172269 | 5.104052 |
| hsa05146 | Amoebiasis | 5/156 | 102/8212 | 0.044456338838928 | 0.226065212394 | 0.190171572637 | TGFB2||IL1R2||IL6||TLR4||CXCL1 | 5 | 6.869948 | 7.094771 | 7.380173 | 6.896037 | 6.853879 | 6.879305 | 6.850076 | 7.079874 | 7.086348 | 7.111230 | 7.101420 | 7.376689 | 7.384154 | 7.391924 | 7.367815 |
| hsa04622 | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | 4/156 | 71/8212 | 0.045680126788610 | 0.227448964635 | 0.191335618786 | MAPK10||CXCL10||IRF7||ISG15 | 4 | 5.078174 | 5.655759 | 5.885765 | 5.253145 | 5.017187 | 5.060039 | 4.965610 | 5.645235 | 5.635874 | 5.683744 | 5.657733 | 5.892111 | 5.890083 | 5.910739 | 5.849437 |
ORA: Down-regulated DEGs
Please Click HERE to download a Microsoft .excel that contains all of the “ORT: Down-regulated DEGs” results.
GO: BP
| ID | Description | GeneRatio | BgRatio | pvalue | p.adjust | qvalue | geneID | Count | No-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgKDN-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgwt-inf_Log2MeanTPM | log2TPM_No-inf_1 | log2TPM_No-inf_2 | log2TPM_No-inf_3 | log2TPM_No-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0051607 | defense response to virus | 20/204 | 306/20870 | 0.00000000002447426 | 0.00000003945251 | 0.00000003222874 | UNC13D||IL23A||OAS2||AICDA||IFIT3||IFIT2||IFI6||TRIM22||RSAD2||OASL||IL6||IFI44L||HERC5||MX1||CXCL10||IRF7||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15||IRF9 | 20 | 5.560236 | 5.626557 | 5.751936 | 5.591743 | 5.556254 | 5.557421 | 5.534953 | 5.625001 | 5.617580 | 5.653544 | 5.609725 | 5.736605 | 5.757706 | 5.763703 | 5.749587 |
| GO:0140546 | defense response to symbiont | 20/204 | 306/20870 | 0.00000000002447426 | 0.00000003945251 | 0.00000003222874 | UNC13D||IL23A||OAS2||AICDA||IFIT3||IFIT2||IFI6||TRIM22||RSAD2||OASL||IL6||IFI44L||HERC5||MX1||CXCL10||IRF7||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15||IRF9 | 20 | 5.560236 | 5.626557 | 5.751936 | 5.591743 | 5.556254 | 5.557421 | 5.534953 | 5.625001 | 5.617580 | 5.653544 | 5.609725 | 5.736605 | 5.757706 | 5.763703 | 5.749587 |
| GO:0009615 | response to virus | 22/204 | 420/20870 | 0.00000000017266763 | 0.00000018556015 | 0.00000015158401 | UNC13D||CCL22||IL23A||OAS2||AICDA||IFIT3||IFIT2||IFI6||TRIM22||RSAD2||OASL||IL6||IFI44L||IFI44||HERC5||MX1||CXCL10||IRF7||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15||IRF9 | 22 | 6.641763 | 6.626694 | 6.615414 | 6.651325 | 6.644070 | 6.633737 | 6.637860 | 6.625735 | 6.620015 | 6.635351 | 6.625631 | 6.600811 | 6.619182 | 6.620456 | 6.621107 |
| GO:0030595 | leukocyte chemotaxis | 17/204 | 268/20870 | 0.00000000128840464 | 0.00000096249944 | 0.00000078626538 | CCL22||RIPOR2||VEGFA||PADI2||TREM1||CCR7||IL6||PLA2G7||ADAM8||NBL1||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||SCG2||CSF1||CXCR3||CD300H | 17 | 7.083536 | 7.379525 | 7.502467 | 7.090422 | 7.081914 | 7.077300 | 7.084476 | 7.376976 | 7.376392 | 7.376521 | 7.388176 | 7.496692 | 7.516555 | 7.504886 | 7.491614 |
| GO:0050900 | leukocyte migration | 21/204 | 428/20870 | 0.00000000149271006 | 0.00000096249944 | 0.00000078626538 | ASB2||CCL22||RIPOR2||VEGFA||PADI2||TREM1||CCR7||IL6||PLA2G7||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||NBL1||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||PTAFR||SCG2||CSF1||CXCR3||TNFRSF18||CD300H | 21 | 6.964052 | 7.305350 | 7.475330 | 6.970243 | 6.965686 | 6.958039 | 6.962212 | 7.304248 | 7.301741 | 7.306149 | 7.309253 | 7.466529 | 7.487203 | 7.478769 | 7.468725 |
| GO:0045071 | negative regulation of viral genome replication | 9/204 | 65/20870 | 0.00000001359792030 | 0.00000730661584 | 0.00000596877133 | OAS2||AICDA||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||PARP10||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 9 | 5.757779 | 6.079732 | 6.570917 | 5.753978 | 5.749926 | 5.824677 | 5.699782 | 6.081680 | 6.074060 | 6.102637 | 6.060226 | 6.529888 | 6.594232 | 6.548119 | 6.609949 |
| GO:0060326 | cell chemotaxis | 18/204 | 360/20870 | 0.00000001755863990 | 0.00000808700786 | 0.00000660627324 | CCL22||RIPOR2||VEGFA||PADI2||TREM1||CCR7||IL6||PLA2G7||ADAM8||NBL1||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||SCG2||EGR3||CSF1||CXCR3||CD300H | 18 | 7.420946 | 7.632148 | 7.698801 | 7.423195 | 7.417902 | 7.420298 | 7.422383 | 7.636151 | 7.625448 | 7.630074 | 7.636888 | 7.692880 | 7.705452 | 7.703822 | 7.693002 |
| GO:0097529 | myeloid leukocyte migration | 15/204 | 256/20870 | 0.00000003600141109 | 0.00001450856867 | 0.00001185204349 | CCL22||RIPOR2||VEGFA||TREM1||CCR7||IL6||PLA2G7||ADAM8||NBL1||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||SCG2||CSF1||CD300H | 15 | 7.248137 | 7.517777 | 7.632278 | 7.260379 | 7.250545 | 7.245304 | 7.236213 | 7.516295 | 7.511541 | 7.521235 | 7.522015 | 7.625159 | 7.637097 | 7.637789 | 7.629028 |
| GO:0071674 | mononuclear cell migration | 14/204 | 242/20870 | 0.00000012189334784 | 0.00004366490594 | 0.00003566984284 | ASB2||CCL22||RIPOR2||PADI2||CCR7||IL6||PLA2G7||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||NBL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||CSF1||CXCR3 | 14 | 6.373474 | 6.821085 | 6.973271 | 6.357472 | 6.375267 | 6.368280 | 6.392648 | 6.830046 | 6.825929 | 6.813798 | 6.814497 | 6.962104 | 6.996159 | 6.976565 | 6.957947 |
| GO:0002685 | regulation of leukocyte migration | 14/204 | 248/20870 | 0.00000016471509211 | 0.00005310414570 | 0.00004338075373 | RIPOR2||VEGFA||PADI2||CCR7||IL6||PLA2G7||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||NBL1||CXCL10||PTAFR||CSF1||CXCR3||TNFRSF18 | 14 | 6.529385 | 6.937917 | 7.103903 | 6.528496 | 6.534993 | 6.527518 | 6.526518 | 6.945217 | 6.929019 | 6.940867 | 6.936517 | 7.097605 | 7.116149 | 7.108173 | 7.093577 |
| GO:0045069 | regulation of viral genome replication | 9/204 | 94/20870 | 0.00000035442897217 | 0.00010387990966 | 0.00008485945343 | OAS2||AICDA||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||PARP10||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 9 | 7.015155 | 7.333250 | 7.500881 | 6.848251 | 6.923270 | 7.096989 | 7.169076 | 7.330894 | 7.386915 | 7.275220 | 7.337798 | 7.516515 | 7.459509 | 7.506431 | 7.520255 |
| GO:1903900 | regulation of viral life cycle | 12/204 | 198/20870 | 0.00000060646397482 | 0.00016293665457 | 0.00013310288289 | TYRO3||OAS2||AICDA||TRIM22||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||LY6E||PARP10||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 12 | 7.017875 | 7.565773 | 7.729136 | 6.888556 | 6.978128 | 7.058979 | 7.134253 | 7.563604 | 7.568045 | 7.544530 | 7.586601 | 7.715019 | 7.708984 | 7.744274 | 7.747855 |
| GO:0097530 | granulocyte migration | 11/204 | 164/20870 | 0.00000066270558662 | 0.00016435098548 | 0.00013425824921 | CCL22||RIPOR2||TREM1||CCR7||ADAM8||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||SCG2||CSF1||CD300H | 11 | 7.293974 | 7.623455 | 7.756631 | 7.312537 | 7.298990 | 7.289358 | 7.274750 | 7.626991 | 7.616015 | 7.622286 | 7.628496 | 7.751006 | 7.760856 | 7.753954 | 7.760682 |
| GO:0002687 | positive regulation of leukocyte migration | 11/204 | 166/20870 | 0.00000074763037190 | 0.00017216859422 | 0.00014064445041 | RIPOR2||VEGFA||CCR7||IL6||PLA2G7||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10||PTAFR||CSF1||TNFRSF18 | 11 | 6.700125 | 7.126714 | 7.342652 | 6.692622 | 6.700521 | 6.709761 | 6.697543 | 7.136872 | 7.119055 | 7.134460 | 7.116353 | 7.337292 | 7.355210 | 7.343590 | 7.334428 |
| GO:0048525 | negative regulation of viral process | 10/204 | 136/20870 | 0.00000093207404008 | 0.00020033378035 | 0.00016365257883 | OAS2||AICDA||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||LY6E||PARP10||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 10 | 6.035323 | 6.193514 | 6.493518 | 6.024200 | 6.029903 | 6.046859 | 6.040222 | 6.207102 | 6.166709 | 6.205415 | 6.194466 | 6.459978 | 6.502713 | 6.476658 | 6.533644 |
| GO:0071621 | granulocyte chemotaxis | 10/204 | 140/20870 | 0.00000121607467879 | 0.00024503904778 | 0.00020017229252 | CCL22||RIPOR2||TREM1||CCR7||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||SCG2||CSF1||CD300H | 10 | 7.424814 | 7.762995 | 7.909668 | 7.443832 | 7.427076 | 7.419814 | 7.408304 | 7.768665 | 7.753959 | 7.762184 | 7.767128 | 7.902981 | 7.913695 | 7.907341 | 7.914625 |
| GO:0050792 | regulation of viral process | 12/204 | 214/20870 | 0.00000138003060995 | 0.00026171874626 | 0.00021379793103 | TYRO3||OAS2||AICDA||TRIM22||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||LY6E||PARP10||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 12 | 6.927273 | 7.454784 | 7.611930 | 6.807328 | 6.889759 | 6.966385 | 7.035581 | 7.451268 | 7.458534 | 7.434163 | 7.474873 | 7.599560 | 7.592454 | 7.626699 | 7.628649 |
| GO:0018108 | peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | 16/204 | 415/20870 | 0.00000349279917635 | 0.00062559914136 | 0.00051105166896 | TIE1||TYRO3||OSM||IL23A||VEGFA||ITK||PRLR||LIF||SH3BP5||IL6||BMP6||TNFRSF14||IGF2||SOCS3||TNFRSF18||INPP5F | 16 | 5.987589 | 6.181374 | 6.314010 | 5.971469 | 5.978780 | 6.007471 | 5.992376 | 6.173270 | 6.180880 | 6.188769 | 6.182535 | 6.301529 | 6.331648 | 6.320809 | 6.301823 |
| GO:0018212 | peptidyl-tyrosine modification | 16/204 | 418/20870 | 0.00000382832605201 | 0.00064960648377 | 0.00053066325663 | TIE1||TYRO3||OSM||IL23A||VEGFA||ITK||PRLR||LIF||SH3BP5||IL6||BMP6||TNFRSF14||IGF2||SOCS3||TNFRSF18||INPP5F | 16 | 5.985509 | 6.183163 | 6.312752 | 5.970084 | 5.976266 | 6.005153 | 5.990279 | 6.175220 | 6.183022 | 6.190207 | 6.184161 | 6.300541 | 6.330266 | 6.319296 | 6.300683 |
| GO:0019058 | viral life cycle | 15/204 | 390/20870 | 0.00000732029468890 | 0.00118003150385 | 0.00096396722693 | SIGLEC1||TYRO3||OAS2||AICDA||TRIM22||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||TNFRSF14||LY6E||PARP10||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15||MVB12B | 15 | 6.869392 | 7.291442 | 7.420550 | 6.819818 | 6.847786 | 6.890617 | 6.917380 | 7.286220 | 7.302263 | 7.275597 | 7.301516 | 7.410232 | 7.409469 | 7.434755 | 7.427576 |
| GO:0050920 | regulation of chemotaxis | 12/204 | 255/20870 | 0.00000839879986686 | 0.00128941575099 | 0.00105332317127 | SEMA3F||RIPOR2||VEGFA||PADI2||CCR7||IL6||PLA2G7||NBL1||SEMA6B||CXCL10||SCG2||CSF1 | 12 | 6.966195 | 7.294631 | 7.384699 | 6.957606 | 6.962347 | 6.976834 | 6.967920 | 7.303045 | 7.289229 | 7.291965 | 7.294247 | 7.386540 | 7.384670 | 7.392520 | 7.375009 |
| GO:1990266 | neutrophil migration | 9/204 | 138/20870 | 0.00000882233105011 | 0.00129287251389 | 0.00105614699940 | CCL22||RIPOR2||TREM1||CCR7||ADAM8||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||CD300H | 9 | 7.466107 | 7.769987 | 7.906780 | 7.485791 | 7.469490 | 7.461899 | 7.446977 | 7.774027 | 7.762321 | 7.768201 | 7.775362 | 7.899851 | 7.911220 | 7.904569 | 7.911449 |
| GO:0071222 | cellular response to lipopolysaccharide | 12/204 | 258/20870 | 0.00000945022874161 | 0.00132467554187 | 0.00108212687924 | NR1H3||IL1A||CMPK2||IL6||IL36G||ANKRD1||BMP6||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||PTAFR||PDCD1LG2 | 12 | 5.602065 | 6.377258 | 6.668393 | 5.611467 | 5.588703 | 5.617768 | 5.590093 | 6.386363 | 6.356848 | 6.388852 | 6.376751 | 6.679675 | 6.668113 | 6.671684 | 6.653981 |
| GO:0048638 | regulation of developmental growth | 14/204 | 351/20870 | 0.00000988625902932 | 0.00132805412960 | 0.00108488684611 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||RASAL1||VEGFA||BCL11A||TBX2||MKKS||UNC13A||IGF2||SEMA6B||CSF1||DLL1||EPPK1 | 14 | 6.357096 | 6.788540 | 6.800863 | 6.354830 | 6.359589 | 6.364061 | 6.349865 | 6.795691 | 6.779266 | 6.784518 | 6.794619 | 6.819812 | 6.796535 | 6.792004 | 6.794930 |
| GO:0002688 | regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis | 9/204 | 142/20870 | 0.00001111769564937 | 0.00140486044411 | 0.00114762989133 | RIPOR2||VEGFA||PADI2||CCR7||IL6||PLA2G7||NBL1||CXCL10||CSF1 | 9 | 6.076542 | 6.859043 | 7.116823 | 6.076534 | 6.074316 | 6.082915 | 6.072378 | 6.865076 | 6.850966 | 6.859792 | 6.860302 | 7.117342 | 7.129369 | 7.120158 | 7.100271 |
| GO:0019079 | viral genome replication | 9/204 | 143/20870 | 0.00001176527046863 | 0.00140486044411 | 0.00114762989133 | OAS2||AICDA||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||PARP10||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 9 | 6.920573 | 7.227896 | 7.334749 | 6.832214 | 6.856751 | 6.968867 | 7.016349 | 7.225237 | 7.277339 | 7.181354 | 7.226052 | 7.347382 | 7.299879 | 7.342903 | 7.348270 |
| GO:0071675 | regulation of mononuclear cell migration | 9/204 | 143/20870 | 0.00001176527046863 | 0.00140486044411 | 0.00114762989133 | RIPOR2||PADI2||CCR7||PLA2G7||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||NBL1||CXCL10||CSF1 | 9 | 6.306448 | 6.836272 | 7.029916 | 6.293792 | 6.312521 | 6.310631 | 6.308773 | 6.855976 | 6.829151 | 6.827363 | 6.832411 | 7.018807 | 7.044757 | 7.033000 | 7.022960 |
| GO:0072676 | lymphocyte migration | 9/204 | 144/20870 | 0.00001244476666523 | 0.00143292599031 | 0.00117055662393 | CCL22||RIPOR2||PADI2||CCR7||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10||CXCL11||CXCR3 | 9 | 6.183495 | 6.609464 | 6.861102 | 6.177270 | 6.206504 | 6.185118 | 6.164768 | 6.633184 | 6.611576 | 6.593453 | 6.599319 | 6.851927 | 6.874761 | 6.855241 | 6.862375 |
| GO:1990868 | response to chemokine | 8/204 | 111/20870 | 0.00001355865554941 | 0.00145710351638 | 0.00119030723455 | CCL22||RIPOR2||PADI2||CCR7||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||CXCR3 | 8 | 5.397966 | 6.654542 | 7.075181 | 5.397572 | 5.402568 | 5.469729 | 5.317995 | 6.655483 | 6.672483 | 6.653831 | 6.636143 | 7.095145 | 7.077760 | 7.060078 | 7.067502 |
| GO:1990869 | cellular response to chemokine | 8/204 | 111/20870 | 0.00001355865554941 | 0.00145710351638 | 0.00119030723455 | CCL22||RIPOR2||PADI2||CCR7||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||CXCR3 | 8 | 5.397966 | 6.654542 | 7.075181 | 5.397572 | 5.402568 | 5.469729 | 5.317995 | 6.655483 | 6.672483 | 6.653831 | 6.636143 | 7.095145 | 7.077760 | 7.060078 | 7.067502 |
| GO:0071219 | cellular response to molecule of bacterial origin | 12/204 | 271/20870 | 0.00001545743486531 | 0.00160757322599 | 0.00131322587548 | NR1H3||IL1A||CMPK2||IL6||IL36G||ANKRD1||BMP6||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||PTAFR||PDCD1LG2 | 12 | 5.657281 | 6.366285 | 6.642598 | 5.664427 | 5.645436 | 5.673761 | 5.645290 | 6.375781 | 6.346713 | 6.375987 | 6.366461 | 6.653174 | 6.642004 | 6.645670 | 6.629441 |
| GO:0030593 | neutrophil chemotaxis | 8/204 | 118/20870 | 0.00002119263519285 | 0.00208101266747 | 0.00169997835118 | CCL22||RIPOR2||TREM1||CCR7||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||CD300H | 8 | 7.613547 | 7.929617 | 8.079746 | 7.633389 | 7.614432 | 7.609215 | 7.596911 | 7.935661 | 7.920295 | 7.928298 | 7.934164 | 8.071592 | 8.084285 | 8.078248 | 8.084819 |
| GO:1903039 | positive regulation of leukocyte cell-cell adhesion | 14/204 | 376/20870 | 0.00002130068797346 | 0.00208101266747 | 0.00169997835118 | IL23A||IL1A||NR4A3||CCR7||IL6||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||IGF2||PTAFR||EGR3||PDCD1LG2||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA2||PIK3R6 | 14 | 7.134261 | 7.528899 | 7.683683 | 7.128002 | 7.140414 | 7.129619 | 7.138964 | 7.531380 | 7.506780 | 7.534895 | 7.542296 | 7.663628 | 7.687476 | 7.695529 | 7.687901 |
| GO:1903131 | mononuclear cell differentiation | 16/204 | 494/20870 | 0.00003028677244015 | 0.00268945271358 | 0.00219701276262 | TYRO3||IL23A||AICDA||VEGFA||ITK||IL1A||CCR7||RSAD2||IL6||ADAM8||EGR3||CSF1||IRF7||DLL1||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 16 | 6.875889 | 7.116099 | 7.185286 | 6.875768 | 6.879741 | 6.864678 | 6.883302 | 7.123233 | 7.097082 | 7.115901 | 7.127988 | 7.162259 | 7.190503 | 7.203323 | 7.184755 |
| GO:0016032 | viral process | 16/204 | 495/20870 | 0.00003103201378114 | 0.00268945271358 | 0.00219701276262 | SIGLEC1||TYRO3||OAS2||AICDA||TRIM22||RSAD2||OASL||MX1||TNFRSF14||LY6E||PARP10||IRF7||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15||MVB12B | 16 | 6.733532 | 7.133900 | 7.242622 | 6.695006 | 6.716146 | 6.751977 | 6.769809 | 7.131411 | 7.149174 | 7.116366 | 7.138452 | 7.235311 | 7.233209 | 7.255327 | 7.246533 |
| GO:0050730 | regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | 12/204 | 291/20870 | 0.00003118165347786 | 0.00268945271358 | 0.00219701276262 | OSM||IL23A||VEGFA||LIF||SH3BP5||IL6||BMP6||TNFRSF14||IGF2||SOCS3||TNFRSF18||INPP5F | 12 | 6.316631 | 6.553299 | 6.700355 | 6.305630 | 6.306290 | 6.336436 | 6.317951 | 6.543305 | 6.553231 | 6.558849 | 6.557758 | 6.688453 | 6.718361 | 6.707917 | 6.686440 |
| GO:0034340 | response to type I interferon | 6/204 | 62/20870 | 0.00003158834788130 | 0.00268945271358 | 0.00219701276262 | OAS2||MX1||IRF7||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 6 | 6.109724 | 6.209027 | 6.304528 | 6.164978 | 6.087404 | 6.121653 | 6.062812 | 6.206713 | 6.207351 | 6.219084 | 6.202910 | 6.276904 | 6.343399 | 6.297391 | 6.299601 |
| GO:0022409 | positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion | 15/204 | 442/20870 | 0.00003169950468855 | 0.00268945271358 | 0.00219701276262 | IL23A||IL1A||NR4A3||CCR7||ADAM19||IL6||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||IGF2||PTAFR||EGR3||PDCD1LG2||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA2||PIK3R6 | 15 | 7.045654 | 7.430617 | 7.584441 | 7.039326 | 7.049736 | 7.041211 | 7.052303 | 7.431501 | 7.410633 | 7.435991 | 7.444132 | 7.565485 | 7.589960 | 7.594064 | 7.588083 |
| GO:0071216 | cellular response to biotic stimulus | 12/204 | 296/20870 | 0.00003680863007091 | 0.00304284675253 | 0.00248570020074 | NR1H3||IL1A||CMPK2||IL6||IL36G||ANKRD1||BMP6||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||PTAFR||PDCD1LG2 | 12 | 5.794434 | 6.426580 | 6.644484 | 5.799828 | 5.791211 | 5.805826 | 5.780749 | 6.447456 | 6.421047 | 6.421054 | 6.416554 | 6.660395 | 6.639708 | 6.644972 | 6.632718 |
| GO:0002526 | acute inflammatory response | 8/204 | 129/20870 | 0.00004029746563988 | 0.00324797573057 | 0.00265326997450 | OSM||IL1A||TREM1||C3||CCR7||IL6||ADAM8||ORM1 | 8 | 5.093333 | 6.183311 | 6.528774 | 5.088652 | 5.120144 | 5.090694 | 5.073447 | 6.190058 | 6.177013 | 6.174808 | 6.191286 | 6.535760 | 6.519521 | 6.523342 | 6.536397 |
| GO:0042509 | regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | 7/204 | 96/20870 | 0.00004394717190338 | 0.00345574834674 | 0.00282299933510 | OSM||IL23A||LIF||IL6||SOCS3||TNFRSF18||INPP5F | 7 | 5.369853 | 6.178940 | 6.489370 | 5.328404 | 5.309394 | 5.497311 | 5.336278 | 6.143899 | 6.229540 | 6.166586 | 6.174354 | 6.460776 | 6.512806 | 6.493595 | 6.489824 |
| GO:0002675 | positive regulation of acute inflammatory response | 5/204 | 41/20870 | 0.00004782723118028 | 0.00367130936489 | 0.00299909103792 | OSM||C3||CCR7||IL6||ADAM8 | 5 | 5.273196 | 7.293729 | 7.731690 | 5.262571 | 5.236677 | 5.286657 | 5.305942 | 7.297693 | 7.280986 | 7.277485 | 7.318385 | 7.728485 | 7.726545 | 7.743463 | 7.728200 |
| GO:0007260 | tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | 7/204 | 99/20870 | 0.00005355255826177 | 0.00401519646130 | 0.00328001225877 | OSM||IL23A||LIF||IL6||SOCS3||TNFRSF18||INPP5F | 7 | 5.344823 | 6.153502 | 6.462323 | 5.301251 | 5.282661 | 5.470930 | 5.316527 | 6.116720 | 6.202408 | 6.146338 | 6.147207 | 6.433296 | 6.485402 | 6.467647 | 6.462461 |
| GO:0070098 | chemokine-mediated signaling pathway | 7/204 | 102/20870 | 0.00006481253147674 | 0.00474899094275 | 0.00387944865442 | CCL22||PADI2||CCR7||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||CXCR3 | 7 | 4.942244 | 6.645200 | 7.142348 | 4.944161 | 4.952342 | 5.057979 | 4.803196 | 6.636484 | 6.670499 | 6.651517 | 6.621847 | 7.167052 | 7.146340 | 7.126767 | 7.128866 |
| GO:0007259 | receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT | 9/204 | 184/20870 | 0.00008550361414798 | 0.00612585893362 | 0.00500421152277 | OSM||IL23A||PRLR||LIF||IL6||STAT4||SOCS3||TNFRSF18||INPP5F | 9 | 5.589713 | 6.053650 | 6.164930 | 5.547856 | 5.685969 | 5.566337 | 5.554183 | 5.937499 | 6.044536 | 6.107077 | 6.118430 | 6.137024 | 6.160410 | 6.229970 | 6.130139 |
| GO:1903037 | regulation of leukocyte cell-cell adhesion | 15/204 | 490/20870 | 0.00010115195487147 | 0.00708943266317 | 0.00579135448715 | IL23A||RIPOR2||IL1A||NR4A3||CCR7||IL6||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||IGF2||PTAFR||EGR3||PDCD1LG2||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA2||PIK3R6 | 15 | 6.936365 | 7.303898 | 7.444103 | 6.932850 | 6.943994 | 6.930473 | 6.938105 | 7.310322 | 7.286927 | 7.304984 | 7.313213 | 7.423541 | 7.448678 | 7.461237 | 7.442700 |
| GO:0002690 | positive regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis | 7/204 | 111/20870 | 0.00011070693780379 | 0.00759402483999 | 0.00620355561893 | RIPOR2||VEGFA||CCR7||IL6||PLA2G7||CXCL10||CSF1 | 7 | 6.272371 | 7.033161 | 7.322300 | 6.268483 | 6.267044 | 6.284230 | 6.269661 | 7.039208 | 7.034702 | 7.038458 | 7.020195 | 7.323246 | 7.330962 | 7.324932 | 7.309977 |
| GO:0002444 | myeloid leukocyte mediated immunity | 7/204 | 112/20870 | 0.00011712202838206 | 0.00778248557916 | 0.00635750911553 | UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3||TREM1||C3||IL6||PTAFR | 7 | 7.072348 | 7.049993 | 7.145705 | 7.066636 | 7.078670 | 7.067592 | 7.076456 | 7.040091 | 7.057328 | 7.066608 | 7.035728 | 7.163854 | 7.150131 | 7.135636 | 7.132987 |
| GO:0048639 | positive regulation of developmental growth | 9/204 | 192/20870 | 0.00011828219397606 | 0.00778248557916 | 0.00635750911553 | CDKL5||RASAL1||VEGFA||TBX2||MKKS||UNC13A||IGF2||CSF1||DLL1 | 9 | 5.723141 | 5.696969 | 5.794108 | 5.747433 | 5.687361 | 5.742920 | 5.714038 | 5.673784 | 5.697045 | 5.644597 | 5.769473 | 5.865573 | 5.780096 | 5.707169 | 5.818944 |
| GO:0097696 | receptor signaling pathway via STAT | 9/204 | 195/20870 | 0.00013301930193398 | 0.00843774730087 | 0.00689279213360 | OSM||IL23A||PRLR||LIF||IL6||STAT4||SOCS3||TNFRSF18||INPP5F | 9 | 5.657043 | 6.123086 | 6.232478 | 5.612609 | 5.744271 | 5.635968 | 5.631580 | 6.019147 | 6.108569 | 6.176352 | 6.182320 | 6.209691 | 6.230804 | 6.291405 | 6.196161 |
| GO:0072678 | T cell migration | 6/204 | 80/20870 | 0.00013347553112419 | 0.00843774730087 | 0.00689279213360 | RIPOR2||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10||CXCL11||CXCR3 | 6 | 6.385685 | 6.833325 | 7.076395 | 6.388676 | 6.389117 | 6.396296 | 6.368501 | 6.851643 | 6.835841 | 6.830466 | 6.815115 | 7.075563 | 7.090227 | 7.057311 | 7.082273 |
| GO:0048247 | lymphocyte chemotaxis | 6/204 | 81/20870 | 0.00014299314332926 | 0.00871815292554 | 0.00712185536754 | CCL22||PADI2||ADAM8||CXCL10||CXCL11||CXCR3 | 6 | 5.169438 | 6.501941 | 6.991191 | 5.178518 | 5.199111 | 5.183710 | 5.114990 | 6.516897 | 6.502618 | 6.484426 | 6.503640 | 6.972994 | 7.002812 | 6.992502 | 6.996287 |
| GO:2000659 | regulation of interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway | 3/204 | 11/20870 | 0.00014331951149314 | 0.00871815292554 | 0.00712185536754 | IL1R2||IL6||IL1RN | 3 | 3.234978 | 4.777036 | 5.770857 | 3.225098 | 3.244225 | 3.152400 | 3.313622 | 4.791825 | 4.858920 | 4.713185 | 4.739902 | 5.766636 | 5.797825 | 5.750789 | 5.767777 |
| GO:0050870 | positive regulation of T cell activation | 12/204 | 344/20870 | 0.00015349307330608 | 0.00916410496924 | 0.00748615339984 | IL23A||IL1A||CCR7||IL6||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||IGF2||EGR3||PDCD1LG2||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA2||PIK3R6 | 12 | 6.995824 | 7.480704 | 7.631593 | 6.977580 | 7.006169 | 6.991785 | 7.007557 | 7.483981 | 7.458025 | 7.486059 | 7.494493 | 7.613003 | 7.633791 | 7.642305 | 7.637104 |
| GO:0071260 | cellular response to mechanical stimulus | 6/204 | 83/20870 | 0.00016363796358544 | 0.00959215990181 | 0.00783583128978 | GCLC||MMP7||ANKRD1||BMP6||AQP1||SCX | 6 | 6.230437 | 6.758638 | 7.021425 | 6.211382 | 6.258688 | 6.225537 | 6.225721 | 6.774458 | 6.786468 | 6.737634 | 6.735292 | 7.024497 | 7.064101 | 7.010771 | 6.985200 |
| GO:0010575 | positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production | 4/204 | 29/20870 | 0.00017382186131307 | 0.01000717287274 | 0.00817485520687 | IL1A||C3||IL6||SULF2 | 4 | 5.703219 | 7.368466 | 7.853234 | 5.666546 | 5.678995 | 5.687635 | 5.777032 | 7.370343 | 7.351860 | 7.380938 | 7.370572 | 7.850991 | 7.857488 | 7.859208 | 7.845206 |
| GO:0032496 | response to lipopolysaccharide | 13/204 | 405/20870 | 0.00018608968508297 | 0.01052549376680 | 0.00859827132184 | NR1H3||IL1A||CCR7||CMPK2||IL6||IL36G||ANKRD1||BMP6||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||PTAFR||PDCD1LG2 | 13 | 5.566540 | 6.198817 | 6.422688 | 5.565015 | 5.559973 | 5.577813 | 5.563298 | 6.204943 | 6.175767 | 6.211016 | 6.203288 | 6.431125 | 6.420027 | 6.427059 | 6.412472 |
| GO:0001960 | negative regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway | 6/204 | 86/20870 | 0.00019895047008685 | 0.01104846379570 | 0.00902548531306 | NR1H3||IL1R2||PADI2||IL6||IL1RN||ISG15 | 6 | 5.669144 | 5.952244 | 6.322585 | 5.666857 | 5.651667 | 5.695160 | 5.662533 | 5.941380 | 5.997181 | 5.911598 | 5.957491 | 6.303233 | 6.350566 | 6.291838 | 6.343819 |
| GO:0060560 | developmental growth involved in morphogenesis | 10/204 | 253/20870 | 0.00020218962901569 | 0.01104846379570 | 0.00902548531306 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||RASAL1||VEGFA||BCL11A||TBX2||UNC13A||SEMA6B||CSF1 | 10 | 6.482581 | 7.027302 | 7.018547 | 6.476873 | 6.488104 | 6.494033 | 6.471202 | 7.040377 | 7.025811 | 7.016528 | 7.026393 | 7.030795 | 7.024533 | 7.007574 | 7.011161 |
| GO:0071357 | cellular response to type I interferon | 5/204 | 56/20870 | 0.00021650300486746 | 0.01163342812821 | 0.00950334242418 | OAS2||IRF7||IFIT1||IFITM1||ISG15 | 5 | 6.205650 | 6.317217 | 6.405068 | 6.266539 | 6.183641 | 6.217240 | 6.152704 | 6.308332 | 6.317802 | 6.334787 | 6.307781 | 6.378184 | 6.440934 | 6.399665 | 6.400776 |
| GO:0070498 | interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway | 4/204 | 31/20870 | 0.00022678471805942 | 0.01198613001678 | 0.00979146444495 | RPS6KA5||IL1R2||IL6||IL1RN | 4 | 4.740669 | 6.436546 | 7.068193 | 5.033984 | 4.593082 | 4.640330 | 4.649826 | 6.419250 | 6.409836 | 6.473960 | 6.442287 | 7.053658 | 7.086068 | 7.071143 | 7.061699 |
| GO:0050921 | positive regulation of chemotaxis | 8/204 | 166/20870 | 0.00023433084918502 | 0.01218520415762 | 0.00995408802480 | RIPOR2||VEGFA||CCR7||IL6||PLA2G7||CXCL10||SCG2||CSF1 | 8 | 7.456660 | 7.768956 | 7.868716 | 7.459116 | 7.454369 | 7.457555 | 7.455594 | 7.785538 | 7.757483 | 7.768973 | 7.763681 | 7.868117 | 7.869256 | 7.875686 | 7.861769 |
| GO:0030098 | lymphocyte differentiation | 13/204 | 418/20870 | 0.00025279289589104 | 0.01293657613258 | 0.01056788346732 | TYRO3||IL23A||AICDA||ITK||IL1A||CCR7||RSAD2||IL6||ADAM8||EGR3||DLL1||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 13 | 6.937395 | 7.197329 | 7.255879 | 6.939574 | 6.942872 | 6.928987 | 6.938109 | 7.204619 | 7.176714 | 7.196633 | 7.211119 | 7.234240 | 7.254569 | 7.277203 | 7.257184 |
| GO:0050731 | positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | 9/204 | 213/20870 | 0.00025743248731508 | 0.01296816154850 | 0.01059368557997 | OSM||IL23A||VEGFA||LIF||IL6||BMP6||TNFRSF14||IGF2||TNFRSF18 | 9 | 5.838362 | 6.322641 | 6.532059 | 5.823351 | 5.834913 | 5.845496 | 5.849543 | 6.320142 | 6.308163 | 6.331898 | 6.330237 | 6.530388 | 6.539696 | 6.538069 | 6.519999 |
| GO:0060761 | negative regulation of response to cytokine stimulus | 6/204 | 91/20870 | 0.00027090465177807 | 0.01343687072819 | 0.01097657390686 | NR1H3||IL1R2||PADI2||IL6||IL1RN||ISG15 | 6 | 5.680620 | 5.905343 | 6.251259 | 5.669947 | 5.673035 | 5.707293 | 5.671873 | 5.893734 | 5.950267 | 5.867514 | 5.908609 | 6.234732 | 6.272570 | 6.224982 | 6.272109 |
| GO:0001959 | regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway | 8/204 | 172/20870 | 0.00029801778600900 | 0.01455771730444 | 0.01189219299194 | NR1H3||IL1R2||PADI2||IL6||IL1RN||CSF1||IRF7||ISG15 | 8 | 6.143792 | 6.408319 | 6.567647 | 6.165788 | 6.118197 | 6.144452 | 6.146335 | 6.400884 | 6.414432 | 6.407992 | 6.409934 | 6.555778 | 6.585737 | 6.558324 | 6.570553 |
| GO:0016322 | neuron remodeling | 3/204 | 14/20870 | 0.00030939591265109 | 0.01488794660279 | 0.01216195716344 | SCARF1||BCL11A||C3 | 3 | 5.157256 | 5.238382 | 5.628451 | 5.129045 | 5.203289 | 5.163032 | 5.132417 | 5.144691 | 5.263294 | 5.323261 | 5.216374 | 5.585647 | 5.638377 | 5.643342 | 5.645596 |
| GO:0002673 | regulation of acute inflammatory response | 5/204 | 61/20870 | 0.00032413947625591 | 0.01536802458013 | 0.01255413265623 | OSM||C3||CCR7||IL6||ADAM8 | 5 | 5.569497 | 7.019327 | 7.406932 | 5.557655 | 5.584036 | 5.550844 | 5.585125 | 7.029043 | 7.013443 | 7.000129 | 7.034441 | 7.404685 | 7.401352 | 7.413375 | 7.408288 |
| GO:0002237 | response to molecule of bacterial origin | 13/204 | 431/20870 | 0.00033899985645365 | 0.01583964546676 | 0.01293939955526 | NR1H3||IL1A||CCR7||CMPK2||IL6||IL36G||ANKRD1||BMP6||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||PTAFR||PDCD1LG2 | 13 | 6.169403 | 6.492555 | 6.669737 | 6.173944 | 6.160385 | 6.175589 | 6.167645 | 6.499051 | 6.476312 | 6.496183 | 6.498550 | 6.676287 | 6.667607 | 6.672318 | 6.662702 |
| GO:1901215 | negative regulation of neuron death | 10/204 | 271/20870 | 0.00034980180135001 | 0.01608877737074 | 0.01314291530024 | GCLC||TYRO3||NR4A3||MEAK7||SLC7A11||ADAM8||NR4A2||GPRASP2||CSF1||HLA-F | 10 | 6.660277 | 6.647098 | 6.666824 | 6.657500 | 6.671901 | 6.657017 | 6.654625 | 6.664565 | 6.662085 | 6.630941 | 6.630431 | 6.690614 | 6.647747 | 6.665139 | 6.663467 |
| GO:1903557 | positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor superfamily cytokine production | 7/204 | 134/20870 | 0.00035431240487666 | 0.01608877737074 | 0.01314291530024 | IL23A||OAS2||IL1A||IL6||ADAM8||PTAFR||ORM1 | 7 | 6.945545 | 6.969009 | 6.967670 | 6.934640 | 6.951059 | 6.946531 | 6.949890 | 6.977096 | 6.969071 | 6.977675 | 6.952044 | 6.964348 | 6.975949 | 6.967790 | 6.962555 |
| GO:0048608 | reproductive structure development | 13/204 | 435/20870 | 0.00037011389112723 | 0.01657287756936 | 0.01353837654386 | MAMLD1||TYRO3||VEGFA||TNFSF10||C3||MKKS||LIF||MAS1||ADAM19||BMP6||IGF2||SOCS3||SCX | 13 | 6.580551 | 6.867529 | 6.858255 | 6.584500 | 6.574636 | 6.579344 | 6.583703 | 6.856055 | 6.861273 | 6.871650 | 6.881011 | 6.856086 | 6.860630 | 6.852650 | 6.863632 |
| GO:0140374 | antiviral innate immune response | 3/204 | 15/20870 | 0.00038396478816163 | 0.01695756817854 | 0.01385263013670 | MX1||CXCL10||IFIT1 | 3 | 4.900979 | 5.046972 | 5.124223 | 4.795822 | 4.864043 | 4.908701 | 5.025581 | 5.128284 | 4.950729 | 4.995045 | 5.106199 | 5.077400 | 5.182885 | 5.091020 | 5.143121 |
| GO:0061458 | reproductive system development | 13/204 | 438/20870 | 0.00039501695314688 | 0.01720992779656 | 0.01405878259991 | MAMLD1||TYRO3||VEGFA||TNFSF10||C3||MKKS||LIF||MAS1||ADAM19||BMP6||IGF2||SOCS3||SCX | 13 | 6.580987 | 6.863292 | 6.855412 | 6.587091 | 6.574751 | 6.575495 | 6.586562 | 6.851415 | 6.856561 | 6.868235 | 6.876822 | 6.851425 | 6.856951 | 6.852335 | 6.860917 |
| GO:0001947 | heart looping | 5/204 | 66/20870 | 0.00046810105708009 | 0.02012210410702 | 0.01643773817283 | ASB2||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||DLL1 | 5 | 5.926671 | 5.484374 | 5.611538 | 6.018006 | 5.740141 | 5.845296 | 6.078235 | 5.401453 | 5.400669 | 5.451636 | 5.666635 | 5.833975 | 5.375363 | 5.543513 | 5.654687 |
| GO:0060759 | regulation of response to cytokine stimulus | 8/204 | 185/20870 | 0.00048503998130363 | 0.02057590657530 | 0.01680844921360 | NR1H3||IL1R2||PADI2||IL6||IL1RN||CSF1||IRF7||ISG15 | 8 | 6.098369 | 6.343913 | 6.491184 | 6.115623 | 6.078461 | 6.098809 | 6.100341 | 6.335759 | 6.351400 | 6.343531 | 6.344921 | 6.480960 | 6.504025 | 6.485259 | 6.494383 |
| GO:1990138 | neuron projection extension | 8/204 | 189/20870 | 0.00055868002972550 | 0.02337907387892 | 0.01909835537582 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||RASAL1||VEGFA||BCL11A||UNC13A||SEMA6B | 8 | 5.638871 | 5.883867 | 5.871944 | 5.630839 | 5.640238 | 5.670590 | 5.613214 | 5.902922 | 5.893765 | 5.860380 | 5.878037 | 5.908730 | 5.873230 | 5.855632 | 5.849444 |
| GO:0006750 | glutathione biosynthetic process | 3/204 | 17/20870 | 0.00056562275513520 | 0.02337907387892 | 0.01909835537582 | GCLC||CHAC1||SLC7A11 | 3 | 5.514769 | 5.463751 | 5.452788 | 5.443808 | 5.597443 | 5.530728 | 5.482521 | 5.458210 | 5.433052 | 5.489677 | 5.473462 | 5.530396 | 5.269915 | 5.457789 | 5.537280 |
| GO:0061371 | determination of heart left/right asymmetry | 5/204 | 70/20870 | 0.00061426756501986 | 0.02478423222979 | 0.02024622862705 | ASB2||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||DLL1 | 5 | 5.903539 | 5.461077 | 5.588227 | 5.994410 | 5.719209 | 5.822983 | 6.053105 | 5.378291 | 5.381632 | 5.427134 | 5.640714 | 5.809260 | 5.353865 | 5.520382 | 5.631304 |
| GO:0097484 | dendrite extension | 4/204 | 40/20870 | 0.00061499335557800 | 0.02478423222979 | 0.02024622862705 | CDKL3||RASAL1||BCL11A||UNC13A | 4 | 4.655744 | 4.245623 | 4.399023 | 4.443523 | 4.805488 | 4.734073 | 4.614216 | 4.162551 | 4.367065 | 4.210541 | 4.234264 | 4.332123 | 4.230167 | 4.546832 | 4.466497 |
| GO:0048532 | anatomical structure arrangement | 3/204 | 18/20870 | 0.00067387488193286 | 0.02682188418953 | 0.02191078563478 | SEMA3F||TFAP2A||DLL1 | 3 | 5.615236 | 6.334214 | 6.514277 | 5.647236 | 5.579350 | 5.614392 | 5.619161 | 6.346050 | 6.368650 | 6.312205 | 6.309104 | 6.509704 | 6.465286 | 6.588466 | 6.490692 |
| GO:0003143 | embryonic heart tube morphogenesis | 5/204 | 72/20870 | 0.00069902148899511 | 0.02748347903073 | 0.02245124217543 | ASB2||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||DLL1 | 5 | 5.760976 | 5.341903 | 5.466035 | 5.850648 | 5.582317 | 5.679465 | 5.907996 | 5.261594 | 5.267188 | 5.307746 | 5.515688 | 5.680548 | 5.235582 | 5.402072 | 5.509642 |
| GO:0030217 | T cell differentiation | 10/204 | 297/20870 | 0.00071351188129158 | 0.02771520849740 | 0.02264054187687 | IL23A||ITK||IL1A||CCR7||RSAD2||IL6||ADAM8||EGR3||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 10 | 7.003079 | 7.104962 | 7.138221 | 7.019186 | 7.003417 | 6.996776 | 6.992796 | 7.115935 | 7.098678 | 7.096434 | 7.108717 | 7.128401 | 7.132917 | 7.151941 | 7.139517 |
| GO:0150063 | visual system development | 12/204 | 409/20870 | 0.00072860250232398 | 0.02796445794634 | 0.02284415364429 | SLC17A7||MEIS3||VEGFA||TBX2||C3||TFAP2A||MYO7A||BCAR3||SLC7A11||BMP6||IGFN1||DLL1 | 12 | 5.587874 | 5.647851 | 5.673829 | 5.587981 | 5.582263 | 5.581722 | 5.599459 | 5.663903 | 5.589786 | 5.709747 | 5.625201 | 5.685402 | 5.669156 | 5.681667 | 5.658938 |
| GO:0019184 | nonribosomal peptide biosynthetic process | 3/204 | 19/20870 | 0.00079448460782537 | 0.02958196079355 | 0.02416549102307 | GCLC||CHAC1||SLC7A11 | 3 | 5.334413 | 5.269146 | 5.255814 | 5.270770 | 5.412311 | 5.350432 | 5.300118 | 5.265791 | 5.236825 | 5.293223 | 5.280137 | 5.331038 | 5.079234 | 5.261107 | 5.337155 |
| GO:1903204 | negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced neuron death | 3/204 | 19/20870 | 0.00079448460782537 | 0.02958196079355 | 0.02416549102307 | NR4A3||MEAK7||SLC7A11 | 3 | 7.263371 | 7.275666 | 7.207338 | 7.252549 | 7.285753 | 7.242817 | 7.271979 | 7.276546 | 7.273666 | 7.245448 | 7.306359 | 7.200803 | 7.217930 | 7.234718 | 7.175231 |
| GO:0032965 | regulation of collagen biosynthetic process | 4/204 | 43/20870 | 0.00081171252130573 | 0.02958196079355 | 0.02416549102307 | IL6||CREB3L1||SERPINB7||SCX | 4 | 5.757932 | 6.240186 | 6.348105 | 5.767016 | 5.738437 | 5.756282 | 5.769786 | 6.250020 | 6.193423 | 6.269952 | 6.246244 | 6.362729 | 6.359355 | 6.339540 | 6.330545 |
| GO:0016485 | protein processing | 9/204 | 250/20870 | 0.00082004622720980 | 0.02958196079355 | 0.02416549102307 | CST7||CPXM1||IL1R2||ECE1||CHAC1||ADAM19||CPM||CIDEB||ADAM8 | 9 | 6.389352 | 6.652940 | 6.724117 | 6.411379 | 6.384707 | 6.369933 | 6.391080 | 6.650371 | 6.639094 | 6.651131 | 6.670981 | 6.691675 | 6.731877 | 6.727978 | 6.744406 |
| GO:0050863 | regulation of T cell activation | 13/204 | 475/20870 | 0.00083985280864309 | 0.02958196079355 | 0.02416549102307 | IL23A||RIPOR2||IL1A||CCR7||IL6||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||IGF2||EGR3||PDCD1LG2||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA2||PIK3R6 | 13 | 6.783064 | 7.228927 | 7.360767 | 6.770467 | 6.794065 | 6.779549 | 6.788064 | 7.236627 | 7.210286 | 7.229772 | 7.238849 | 7.342147 | 7.364669 | 7.376748 | 7.359290 |
| GO:2000401 | regulation of lymphocyte migration | 5/204 | 75/20870 | 0.00084216508523673 | 0.02958196079355 | 0.02416549102307 | RIPOR2||PADI2||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10 | 5 | 6.294099 | 6.806183 | 7.081653 | 6.286496 | 6.295707 | 6.292113 | 6.302036 | 6.826790 | 6.807991 | 6.785054 | 6.804592 | 7.067437 | 7.102129 | 7.071048 | 7.085740 |
| GO:0003007 | heart morphogenesis | 9/204 | 251/20870 | 0.00084349057025909 | 0.02958196079355 | 0.02416549102307 | ASB2||VEGFA||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||ANKRD1||LY6E||DLL1||ALPK2 | 9 | 5.463710 | 5.405228 | 5.436223 | 5.506568 | 5.413688 | 5.422336 | 5.509429 | 5.410453 | 5.338387 | 5.427200 | 5.442679 | 5.474634 | 5.393899 | 5.443675 | 5.431528 |
| GO:0042692 | muscle cell differentiation | 12/204 | 416/20870 | 0.00084415024596971 | 0.02958196079355 | 0.02416549102307 | ASB2||DMPK||RIPOR2||VEGFA||TBX2||ANKRD1||OBSCN||IGF2||CXCL10||LBX2||DLL1||ALPK2 | 12 | 6.738567 | 6.895861 | 6.878914 | 6.746115 | 6.740953 | 6.738072 | 6.729074 | 6.891816 | 6.896176 | 6.891990 | 6.903433 | 6.866854 | 6.888438 | 6.876309 | 6.883962 |
| GO:0046425 | regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT | 6/204 | 115/20870 | 0.00094256710663674 | 0.03267565969674 | 0.02669273232377 | IL23A||PRLR||LIF||IL6||SOCS3||INPP5F | 6 | 5.669640 | 6.279741 | 6.450215 | 5.609689 | 5.835382 | 5.617872 | 5.602015 | 6.128900 | 6.283629 | 6.326817 | 6.368436 | 6.413048 | 6.430807 | 6.538762 | 6.414424 |
| GO:0048880 | sensory system development | 12/204 | 422/20870 | 0.00095502248746812 | 0.03275523935742 | 0.02675774091428 | SLC17A7||MEIS3||VEGFA||TBX2||C3||TFAP2A||MYO7A||BCAR3||SLC7A11||BMP6||IGFN1||DLL1 | 12 | 5.574649 | 5.634690 | 5.660676 | 5.574735 | 5.569061 | 5.568460 | 5.586269 | 5.650799 | 5.576628 | 5.696528 | 5.612041 | 5.672276 | 5.656021 | 5.668505 | 5.645749 |
| GO:0042531 | positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | 5/204 | 78/20870 | 0.00100608847266779 | 0.03401219488084 | 0.02778454733964 | OSM||IL23A||LIF||IL6||TNFRSF18 | 5 | 5.242150 | 6.198981 | 6.616334 | 5.219377 | 5.261998 | 5.259830 | 5.226891 | 6.178163 | 6.201619 | 6.203829 | 6.212094 | 6.600526 | 6.627838 | 6.619485 | 6.617350 |
| GO:0051146 | striated muscle cell differentiation | 10/204 | 311/20870 | 0.00101277007089350 | 0.03401219488084 | 0.02778454733964 | ASB2||DMPK||RIPOR2||VEGFA||ANKRD1||OBSCN||IGF2||CXCL10||DLL1||ALPK2 | 10 | 6.972553 | 7.131860 | 7.118249 | 6.977810 | 6.973775 | 6.971540 | 6.967065 | 7.139389 | 7.120579 | 7.131006 | 7.136394 | 7.108150 | 7.124123 | 7.118417 | 7.122251 |
| GO:0071887 | leukocyte apoptotic process | 6/204 | 117/20870 | 0.00103100314452884 | 0.03426756843259 | 0.02799316188401 | CCR7||IDO1||IL6||SLC7A11||ADAM8||IRF7 | 6 | 6.518892 | 6.817712 | 6.915426 | 6.517505 | 6.505317 | 6.533467 | 6.519139 | 6.820596 | 6.829244 | 6.800531 | 6.820326 | 6.924253 | 6.901047 | 6.916621 | 6.919678 |
| GO:0051251 | positive regulation of lymphocyte activation | 13/204 | 487/20870 | 0.00105353191683449 | 0.03465904999872 | 0.02831296300666 | IL23A||IL1A||CCR7||IL6||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||IGF2||EGR3||PDCD1LG2||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA2||PIK3R6 | 13 | 6.959286 | 7.356554 | 7.481354 | 6.947489 | 6.961369 | 6.960980 | 6.967232 | 7.356074 | 7.335670 | 7.363333 | 7.370900 | 7.472665 | 7.483699 | 7.484321 | 7.484699 |
| GO:1905330 | regulation of morphogenesis of an epithelium | 5/204 | 80/20870 | 0.00112780295697026 | 0.03668972368808 | 0.02997181946832 | VEGFA||TBX2||LIF||CXCL10||LBX2 | 5 | 5.583208 | 5.656009 | 5.793122 | 5.590278 | 5.571918 | 5.627294 | 5.542018 | 5.639111 | 5.579289 | 5.668841 | 5.732568 | 5.774253 | 5.801390 | 5.782519 | 5.813987 |
| GO:0042551 | neuron maturation | 4/204 | 47/20870 | 0.00113801872481632 | 0.03668972368808 | 0.02997181946832 | SCARF1||BCL11A||C3||NR4A2 | 4 | 5.044541 | 5.080960 | 5.184688 | 5.069386 | 5.049049 | 5.046092 | 5.013074 | 5.080974 | 5.130001 | 5.072654 | 5.038731 | 5.155230 | 5.202261 | 5.167342 | 5.213126 |
| GO:0035050 | embryonic heart tube development | 5/204 | 81/20870 | 0.00119259307628875 | 0.03794151780530 | 0.03099440954318 | ASB2||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||DLL1 | 5 | 5.848880 | 5.502347 | 5.575999 | 5.926707 | 5.687842 | 5.801072 | 5.963629 | 5.447998 | 5.413585 | 5.456392 | 5.676104 | 5.764715 | 5.377997 | 5.522395 | 5.611578 |
| GO:0010712 | regulation of collagen metabolic process | 4/204 | 48/20870 | 0.00123207604574381 | 0.03794151780530 | 0.03099440954318 | IL6||CREB3L1||SERPINB7||SCX | 4 | 6.363458 | 6.446176 | 6.522618 | 6.359932 | 6.361257 | 6.372888 | 6.359714 | 6.446867 | 6.404118 | 6.475386 | 6.457385 | 6.534364 | 6.532011 | 6.519481 | 6.504420 |
| GO:0002693 | positive regulation of cellular extravasation | 3/204 | 22/20870 | 0.00123568839006086 | 0.03794151780530 | 0.03099440954318 | RIPOR2||ADAM8||PTAFR | 3 | 6.320849 | 6.347110 | 6.312682 | 6.287633 | 6.393466 | 6.327525 | 6.271693 | 6.354837 | 6.328529 | 6.355785 | 6.349120 | 6.328703 | 6.319439 | 6.289846 | 6.312455 |
| GO:0006925 | inflammatory cell apoptotic process | 3/204 | 22/20870 | 0.00123568839006086 | 0.03794151780530 | 0.03099440954318 | IL6||SLC7A11||IRF7 | 3 | 6.694620 | 7.364915 | 7.612106 | 6.685404 | 6.674196 | 6.728043 | 6.690268 | 7.378116 | 7.357581 | 7.324267 | 7.398651 | 7.680239 | 7.567477 | 7.595039 | 7.603223 |
| GO:0035455 | response to interferon-alpha | 3/204 | 22/20870 | 0.00123568839006086 | 0.03794151780530 | 0.03099440954318 | IFIT3||IFIT2||IFITM1 | 3 | 5.821106 | 5.578908 | 5.883922 | 5.807601 | 5.850533 | 5.874784 | 5.748323 | 5.623158 | 5.542690 | 5.613245 | 5.534310 | 5.881404 | 5.939070 | 5.838244 | 5.875156 |
| GO:0010770 | positive regulation of cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation | 5/204 | 83/20870 | 0.00133038230699467 | 0.03979295349393 | 0.03250684655930 | CDKL3||CDKL5||UNC13D||RREB1||GPRASP2 | 5 | 6.796929 | 6.888990 | 6.839691 | 6.776920 | 6.808959 | 6.827556 | 6.773577 | 6.890335 | 6.900863 | 6.877566 | 6.887100 | 6.869167 | 6.829819 | 6.835794 | 6.823553 |
| GO:0043299 | leukocyte degranulation | 5/204 | 83/20870 | 0.00133038230699467 | 0.03979295349393 | 0.03250684655930 | UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3||PTAFR||HLA-F | 5 | 7.187237 | 7.202795 | 7.359826 | 7.180229 | 7.202910 | 7.180582 | 7.185109 | 7.191379 | 7.212642 | 7.214070 | 7.192931 | 7.361491 | 7.369799 | 7.365675 | 7.342187 |
| GO:0002819 | regulation of adaptive immune response | 9/204 | 268/20870 | 0.00133301457113663 | 0.03979295349393 | 0.03250684655930 | IL23A||CD48||C3||RSAD2||IL6||TNFRSF14||IRF7||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 9 | 6.622549 | 6.694593 | 6.867589 | 6.625359 | 6.608664 | 6.625595 | 6.630483 | 6.692887 | 6.689185 | 6.691891 | 6.704364 | 6.875898 | 6.861730 | 6.864857 | 6.867834 |
| GO:0070555 | response to interleukin-1 | 7/204 | 169/20870 | 0.00139704115022117 | 0.04097861658036 | 0.03347541422360 | GCLC||RPS6KA5||CCL22||IL1R2||IL6||IL1RN||ANKRD1 | 7 | 6.311247 | 7.098280 | 7.519906 | 6.330174 | 6.289815 | 6.301860 | 6.322780 | 7.103130 | 7.096875 | 7.107489 | 7.085532 | 7.505574 | 7.528914 | 7.527140 | 7.517878 |
| GO:2000116 | regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | 9/204 | 270/20870 | 0.00140318571991464 | 0.04097861658036 | 0.03347541422360 | CST7||SENP1||VEGFA||TNFSF10||IFI6||CIDEB||ST20||TNFSF15||AQP1 | 9 | 6.649907 | 7.067745 | 7.279671 | 6.641847 | 6.649263 | 6.652587 | 6.655894 | 7.066817 | 7.064195 | 7.065916 | 7.074031 | 7.271571 | 7.285988 | 7.276579 | 7.284496 |
| GO:0032740 | positive regulation of interleukin-17 production | 3/204 | 23/20870 | 0.00141086428052720 | 0.04097861658036 | 0.03347541422360 | OSM||IL23A||IL6 | 3 | 5.073505 | 6.265223 | 6.707285 | 4.991289 | 5.027139 | 5.107469 | 5.161920 | 6.278903 | 6.224967 | 6.296521 | 6.259528 | 6.710021 | 6.725694 | 6.717207 | 6.675718 |
| GO:0048592 | eye morphogenesis | 7/204 | 170/20870 | 0.00144521037712392 | 0.04160141299864 | 0.03398417634929 | VEGFA||TBX2||TFAP2A||MYO7A||BCAR3||IGFN1||DLL1 | 7 | 5.378324 | 5.428249 | 5.509259 | 5.366151 | 5.374430 | 5.358556 | 5.413534 | 5.485351 | 5.310961 | 5.553752 | 5.349409 | 5.530498 | 5.498399 | 5.534725 | 5.472526 |
| GO:0050866 | negative regulation of cell activation | 9/204 | 272/20870 | 0.00147630332655148 | 0.04212037101595 | 0.03440811292997 | GCLC||NR1H3||CST7||TYRO3||RIPOR2||TNFRSF14||C1QTNF1||PDCD1LG2||HLA-F | 9 | 6.354064 | 6.460849 | 6.500415 | 6.371297 | 6.352250 | 6.346169 | 6.346395 | 6.464674 | 6.464858 | 6.443782 | 6.469942 | 6.494575 | 6.504199 | 6.523923 | 6.478590 |
| GO:1904892 | regulation of receptor signaling pathway via STAT | 6/204 | 126/20870 | 0.00151038096047755 | 0.04271463347877 | 0.03489356567973 | IL23A||PRLR||LIF||IL6||SOCS3||INPP5F | 6 | 5.755691 | 6.348644 | 6.508979 | 5.693925 | 5.897862 | 5.711779 | 5.709251 | 6.220946 | 6.342780 | 6.396299 | 6.426137 | 6.480404 | 6.495562 | 6.585954 | 6.471071 |
| GO:0032613 | interleukin-10 production | 5/204 | 86/20870 | 0.00155863042364467 | 0.04331917660199 | 0.03538741669654 | IL23A||IL6||ISG15||PDCD1LG2||DLL1 | 5 | 6.688860 | 6.767729 | 6.757205 | 6.695196 | 6.674951 | 6.696874 | 6.688316 | 6.786186 | 6.771205 | 6.775370 | 6.737702 | 6.750809 | 6.764974 | 6.754207 | 6.758791 |
| GO:0032653 | regulation of interleukin-10 production | 5/204 | 86/20870 | 0.00155863042364467 | 0.04331917660199 | 0.03538741669654 | IL23A||IL6||ISG15||PDCD1LG2||DLL1 | 5 | 6.688860 | 6.767729 | 6.757205 | 6.695196 | 6.674951 | 6.696874 | 6.688316 | 6.786186 | 6.771205 | 6.775370 | 6.737702 | 6.750809 | 6.764974 | 6.754207 | 6.758791 |
| GO:0009612 | response to mechanical stimulus | 8/204 | 223/20870 | 0.00162217661879274 | 0.04467083002471 | 0.03649158179503 | GCLC||MKKS||MMP7||ANKRD1||BMP6||CXCL10||AQP1||SCX | 8 | 6.655237 | 6.745157 | 6.970231 | 6.666085 | 6.641408 | 6.654020 | 6.659321 | 6.741952 | 6.755465 | 6.732665 | 6.750443 | 6.958360 | 6.992760 | 6.959574 | 6.969966 |
| GO:0022604 | regulation of cell morphogenesis | 10/204 | 332/20870 | 0.00164815752572600 | 0.04467083002471 | 0.03649158179503 | CDKL3||CDKL5||UNC13D||RASAL1||VEGFA||BCL11A||RREB1||UNC13A||FGD2||GPRASP2 | 10 | 6.691990 | 6.856610 | 6.912560 | 6.671014 | 6.704392 | 6.706888 | 6.685369 | 6.841375 | 6.875864 | 6.853014 | 6.855973 | 6.920286 | 6.911164 | 6.916416 | 6.902313 |
| GO:0032964 | collagen biosynthetic process | 4/204 | 52/20870 | 0.00166293864052642 | 0.04467083002471 | 0.03649158179503 | IL6||CREB3L1||SERPINB7||SCX | 4 | 5.762595 | 6.091653 | 6.185586 | 5.780593 | 5.743103 | 5.749021 | 5.777282 | 6.099690 | 6.048812 | 6.120507 | 6.096652 | 6.200681 | 6.194655 | 6.178185 | 6.168598 |
| GO:2000404 | regulation of T cell migration | 4/204 | 52/20870 | 0.00166293864052642 | 0.04467083002471 | 0.03649158179503 | RIPOR2||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10 | 4 | 6.186461 | 6.621599 | 6.946718 | 6.196436 | 6.166113 | 6.199663 | 6.183391 | 6.651526 | 6.614479 | 6.605629 | 6.614326 | 6.938956 | 6.959389 | 6.916840 | 6.971097 |
| GO:0050727 | regulation of inflammatory response | 12/204 | 451/20870 | 0.00167654169757756 | 0.04467083002471 | 0.03649158179503 | NR1H3||CST7||TYRO3||OSM||IL23A||C3||CCR7||MAS1||IL6||PLA2G7||ADAM8||SOCS3 | 12 | 6.961617 | 7.265227 | 7.431958 | 6.968246 | 6.953033 | 6.959322 | 6.965819 | 7.266837 | 7.266331 | 7.261073 | 7.266661 | 7.424592 | 7.429126 | 7.447251 | 7.426750 |
| GO:0032760 | positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production | 6/204 | 130/20870 | 0.00177104133251871 | 0.04680194472164 | 0.03823248847249 | IL23A||OAS2||IL1A||IL6||PTAFR||ORM1 | 6 | 6.994096 | 7.017190 | 7.014912 | 6.982806 | 6.999592 | 6.995382 | 6.998544 | 7.025849 | 7.017466 | 7.025846 | 6.999438 | 7.011258 | 7.022897 | 7.015287 | 7.010171 |
| GO:1902932 | positive regulation of alcohol biosynthetic process | 3/204 | 25/20870 | 0.00180615814341092 | 0.04734190125493 | 0.03867357873183 | MAS1||BMP6||PTAFR | 3 | 4.381788 | 4.473384 | 4.467549 | 4.446040 | 4.290554 | 4.397359 | 4.388820 | 4.364394 | 4.500873 | 4.523111 | 4.499771 | 4.459936 | 4.350962 | 4.465533 | 4.584301 |
| GO:0050729 | positive regulation of inflammatory response | 7/204 | 178/20870 | 0.00187889720337564 | 0.04885132728777 | 0.03990662820752 | OSM||IL23A||C3||CCR7||IL6||PLA2G7||ADAM8 | 7 | 6.793309 | 7.009496 | 7.176289 | 6.789639 | 6.782989 | 6.791134 | 6.809343 | 7.015028 | 7.013241 | 7.005118 | 7.004568 | 7.176094 | 7.170422 | 7.194368 | 7.164097 |
| GO:0071677 | positive regulation of mononuclear cell migration | 5/204 | 90/20870 | 0.00190616778818040 | 0.04895699818326 | 0.03999295071651 | CCR7||PLA2G7||ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10 | 5 | 6.560236 | 7.038053 | 7.291700 | 6.554000 | 6.556696 | 6.575274 | 6.554868 | 7.065931 | 7.027247 | 7.035358 | 7.023287 | 7.281159 | 7.306377 | 7.286293 | 7.292848 |
| GO:0060337 | type I interferon signaling pathway | 4/204 | 54/20870 | 0.00191333181485440 | 0.04895699818326 | 0.03999295071651 | OAS2||IRF7||IFITM1||ISG15 | 4 | 6.237278 | 6.348637 | 6.435985 | 6.298176 | 6.215299 | 6.248825 | 6.184335 | 6.339735 | 6.349227 | 6.366194 | 6.339225 | 6.409050 | 6.471871 | 6.430557 | 6.431744 |
| GO:2000106 | regulation of leukocyte apoptotic process | 5/204 | 91/20870 | 0.00200124122634333 | 0.05080316310024 | 0.04150108204153 | CCR7||IDO1||SLC7A11||ADAM8||IRF7 | 5 | 5.558441 | 5.968834 | 6.255261 | 5.539445 | 5.545848 | 5.599333 | 5.548339 | 5.982514 | 5.989858 | 5.943547 | 5.958943 | 6.279237 | 6.238724 | 6.251816 | 6.250961 |
| GO:0071676 | negative regulation of mononuclear cell migration | 3/204 | 26/20870 | 0.00202714175646491 | 0.05105863299096 | 0.04170977528516 | RIPOR2||PADI2||NBL1 | 3 | 4.676758 | 5.186923 | 5.170907 | 4.536051 | 4.695201 | 4.626895 | 4.832547 | 5.205356 | 5.122000 | 5.087299 | 5.321626 | 5.137248 | 5.218877 | 5.178128 | 5.147978 |
| GO:1901214 | regulation of neuron death | 11/204 | 401/20870 | 0.00204898635954567 | 0.05114877870758 | 0.04178341528221 | GCLC||TYRO3||NR4A3||TFAP2A||MEAK7||SLC7A11||ADAM8||NR4A2||GPRASP2||CSF1||HLA-F | 11 | 6.798750 | 6.788936 | 6.861117 | 6.807417 | 6.797212 | 6.784975 | 6.805288 | 6.804616 | 6.797819 | 6.786815 | 6.766201 | 6.857545 | 6.869633 | 6.861318 | 6.855933 |
| GO:0051897 | positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling | 6/204 | 134/20870 | 0.00206449187453198 | 0.05114877870758 | 0.04178341528221 | OSM||MEIS3||CCR7||ADAM8||IGF2||C1QTNF1 | 6 | 6.766365 | 7.041645 | 7.141882 | 6.770462 | 6.751802 | 6.763832 | 6.779223 | 7.050084 | 7.035101 | 7.042175 | 7.039178 | 7.135973 | 7.153778 | 7.145290 | 7.132391 |
| GO:0045927 | positive regulation of growth | 9/204 | 286/20870 | 0.00207831576014052 | 0.05114877870758 | 0.04178341528221 | CDKL5||RASAL1||VEGFA||TBX2||MKKS||UNC13A||IGF2||CSF1||DLL1 | 9 | 6.505582 | 6.565097 | 6.621309 | 6.504711 | 6.487772 | 6.530368 | 6.499140 | 6.536409 | 6.571365 | 6.557081 | 6.594902 | 6.650268 | 6.616818 | 6.587276 | 6.630150 |
| GO:0007517 | muscle organ development | 10/204 | 345/20870 | 0.00218204712443500 | 0.05324127032502 | 0.04349277078268 | ASB2||RIPOR2||LIF||ANKRD1||LY6E||IGF2||CXCL10||EGR3||DLL1||SCX | 10 | 6.097461 | 5.908065 | 5.860493 | 5.987651 | 6.043297 | 6.130406 | 6.217864 | 5.916200 | 5.962478 | 5.837111 | 5.913683 | 5.911265 | 5.805662 | 5.834083 | 5.888516 |
| GO:0002548 | monocyte chemotaxis | 5/204 | 93/20870 | 0.00220171646965998 | 0.05324127032502 | 0.04349277078268 | CCL22||IL6||PLA2G7||NBL1||CXCL10 | 5 | 6.015285 | 7.089481 | 7.407922 | 6.029063 | 5.976965 | 6.024432 | 6.030003 | 7.075836 | 7.122358 | 7.084625 | 7.074580 | 7.394666 | 7.415928 | 7.428812 | 7.391958 |
| GO:0001654 | eye development | 11/204 | 405/20870 | 0.00221288158298781 | 0.05324127032502 | 0.04349277078268 | SLC17A7||MEIS3||VEGFA||TBX2||TFAP2A||MYO7A||BCAR3||SLC7A11||BMP6||IGFN1||DLL1 | 11 | 5.566526 | 5.655974 | 5.677901 | 5.562954 | 5.561568 | 5.562695 | 5.578818 | 5.673569 | 5.596770 | 5.715432 | 5.635433 | 5.690217 | 5.673376 | 5.685820 | 5.662022 |
| GO:1903203 | regulation of oxidative stress-induced neuron death | 3/204 | 27/20870 | 0.00226423213185493 | 0.05407321772667 | 0.04417238825654 | NR4A3||MEAK7||SLC7A11 | 3 | 7.159159 | 7.063772 | 7.004184 | 7.123006 | 7.155292 | 7.113820 | 7.240995 | 7.075713 | 7.057194 | 7.035909 | 7.085771 | 6.968164 | 7.092505 | 6.996210 | 6.955830 |
| GO:0009855 | determination of bilateral symmetry | 6/204 | 137/20870 | 0.00230763026684240 | 0.05470441161985 | 0.04468801027585 | ASB2||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||NBL1||DLL1 | 6 | 5.520972 | 5.151353 | 5.189637 | 5.574602 | 5.388923 | 5.510581 | 5.600631 | 5.135722 | 5.068789 | 5.102793 | 5.288198 | 5.361721 | 5.012607 | 5.146511 | 5.215719 |
| GO:0043491 | protein kinase B signaling | 8/204 | 237/20870 | 0.00237074445385576 | 0.05551038269756 | 0.04534640770188 | TYRO3||OSM||MEIS3||CCR7||ADAM8||IGF2||C1QTNF1||INPP5F | 8 | 6.531937 | 6.920281 | 7.110546 | 6.527215 | 6.523383 | 6.547952 | 6.529075 | 6.926434 | 6.926391 | 6.917007 | 6.911234 | 7.113213 | 7.120200 | 7.104037 | 7.104672 |
| GO:0009799 | specification of symmetry | 6/204 | 138/20870 | 0.00239328262871012 | 0.05551038269756 | 0.04534640770188 | ASB2||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||NBL1||DLL1 | 6 | 5.519609 | 5.132258 | 5.170220 | 5.572202 | 5.390883 | 5.509634 | 5.597022 | 5.116602 | 5.050088 | 5.083602 | 5.268870 | 5.342140 | 4.994940 | 5.126609 | 5.195424 |
| GO:0071347 | cellular response to interleukin-1 | 6/204 | 138/20870 | 0.00239328262871012 | 0.05551038269756 | 0.04534640770188 | RPS6KA5||CCL22||IL1R2||IL6||IL1RN||ANKRD1 | 6 | 5.834284 | 6.978052 | 7.512751 | 5.907540 | 5.783254 | 5.811333 | 5.832041 | 6.983574 | 6.969931 | 6.989420 | 6.969179 | 7.498485 | 7.523174 | 7.522870 | 7.506316 |
| GO:0048593 | camera-type eye morphogenesis | 6/204 | 139/20870 | 0.00248130623270093 | 0.05676540626680 | 0.04637163591470 | VEGFA||TBX2||TFAP2A||BCAR3||IGFN1||DLL1 | 6 | 5.571101 | 5.591617 | 5.711624 | 5.565207 | 5.552275 | 5.557487 | 5.608743 | 5.616937 | 5.543560 | 5.621805 | 5.582807 | 5.679022 | 5.743201 | 5.731478 | 5.691807 |
| GO:0032967 | positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process | 3/204 | 28/20870 | 0.00251782043925334 | 0.05676540626680 | 0.04637163591470 | CREB3L1||SERPINB7||SCX | 3 | 5.979270 | 6.502374 | 6.593830 | 5.991040 | 5.956999 | 5.977436 | 5.991334 | 6.516043 | 6.448622 | 6.535123 | 6.508269 | 6.610643 | 6.607683 | 6.582918 | 6.573729 |
| GO:1902624 | positive regulation of neutrophil migration | 3/204 | 28/20870 | 0.00251782043925334 | 0.05676540626680 | 0.04637163591470 | RIPOR2||CCR7||ADAM8 | 3 | 6.346375 | 7.173406 | 7.370865 | 6.352391 | 6.363927 | 6.355846 | 6.312797 | 7.169119 | 7.171903 | 7.181035 | 7.171538 | 7.384011 | 7.373567 | 7.372595 | 7.353115 |
| GO:1903859 | regulation of dendrite extension | 3/204 | 28/20870 | 0.00251782043925334 | 0.05676540626680 | 0.04637163591470 | RASAL1||BCL11A||UNC13A | 3 | 4.157310 | 3.753846 | 3.916384 | 4.059320 | 4.420254 | 3.989345 | 4.121735 | 3.666191 | 3.949637 | 3.705717 | 3.674378 | 3.802446 | 3.767883 | 4.007482 | 4.065083 |
| GO:0098586 | cellular response to virus | 5/204 | 97/20870 | 0.00264599934485936 | 0.05894700344866 | 0.04815378171234 | IFI6||OASL||IL6||CXCL10||IRF7 | 5 | 6.015945 | 6.418838 | 6.713349 | 6.018593 | 5.992639 | 5.996828 | 6.054875 | 6.433678 | 6.408662 | 6.415064 | 6.417829 | 6.689992 | 6.716508 | 6.698090 | 6.748112 |
| GO:0010574 | regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production | 4/204 | 59/20870 | 0.00265115245038948 | 0.05894700344866 | 0.04815378171234 | IL1A||C3||IL6||SULF2 | 4 | 5.785178 | 7.227461 | 7.667874 | 5.762513 | 5.764509 | 5.768781 | 5.843306 | 7.224546 | 7.219845 | 7.231336 | 7.234075 | 7.663970 | 7.674578 | 7.675856 | 7.657009 |
| GO:0045766 | positive regulation of angiogenesis | 7/204 | 190/20870 | 0.00271120392415260 | 0.05946205069026 | 0.04857452358203 | TIE1||VEGFA||IL1A||C3||DLL1||AQP1||PIK3R6 | 7 | 6.565463 | 6.938777 | 7.218652 | 6.553478 | 6.560549 | 6.577946 | 6.569762 | 6.947213 | 6.931792 | 6.930656 | 6.945367 | 7.219419 | 7.216610 | 7.231556 | 7.206914 |
| GO:1904018 | positive regulation of vasculature development | 7/204 | 190/20870 | 0.00271120392415260 | 0.05946205069026 | 0.04857452358203 | TIE1||VEGFA||IL1A||C3||DLL1||AQP1||PIK3R6 | 7 | 6.565463 | 6.938777 | 7.218652 | 6.553478 | 6.560549 | 6.577946 | 6.569762 | 6.947213 | 6.931792 | 6.930656 | 6.945367 | 7.219419 | 7.216610 | 7.231556 | 7.206914 |
| GO:0010714 | positive regulation of collagen metabolic process | 3/204 | 29/20870 | 0.00278828181363106 | 0.06013500901777 | 0.04912426294974 | CREB3L1||SERPINB7||SCX | 3 | 5.933869 | 6.442770 | 6.534131 | 5.949398 | 5.910616 | 5.928630 | 5.946497 | 6.457392 | 6.389175 | 6.475128 | 6.447954 | 6.550116 | 6.547580 | 6.524288 | 6.514217 |
| GO:0021602 | cranial nerve morphogenesis | 3/204 | 29/20870 | 0.00278828181363106 | 0.06013500901777 | 0.04912426294974 | SEMA3F||ATP8B1||TFAP2A | 3 | 5.772104 | 5.528216 | 5.450904 | 5.740605 | 5.742866 | 5.742486 | 5.858859 | 5.564805 | 5.523246 | 5.505467 | 5.518659 | 5.412006 | 5.295725 | 5.576371 | 5.504323 |
| GO:0002831 | regulation of response to biotic stimulus | 12/204 | 480/20870 | 0.00279784471236522 | 0.06013500901777 | 0.04912426294974 | NR1H3||TYRO3||IL23A||OASL||HERC5||ADAM8||BMP6||IRF7||IFIT1||ISG15||HLA-F||PIK3R6 | 12 | 6.389259 | 6.493147 | 6.557451 | 6.384971 | 6.379827 | 6.398865 | 6.393300 | 6.494210 | 6.499974 | 6.491998 | 6.486373 | 6.545333 | 6.565242 | 6.567513 | 6.551596 |
| GO:0002699 | positive regulation of immune effector process | 10/204 | 358/20870 | 0.00284732501513257 | 0.06061837875584 | 0.04951912748044 | UNC13D||IL23A||NR4A3||C3||RSAD2||IL6||TNFRSF14||PTAFR||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 10 | 7.173213 | 7.253338 | 7.359120 | 7.173757 | 7.161917 | 7.180923 | 7.176188 | 7.245776 | 7.259197 | 7.256826 | 7.251514 | 7.357085 | 7.363547 | 7.364248 | 7.351564 |
| GO:0062207 | regulation of pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway | 6/204 | 143/20870 | 0.00285793845250844 | 0.06061837875584 | 0.04951912748044 | NR1H3||TYRO3||RSAD2||OASL||SLC15A2||IRF7 | 6 | 6.198028 | 6.160402 | 6.178307 | 6.161557 | 6.218202 | 6.187314 | 6.224164 | 6.169523 | 6.160904 | 6.156754 | 6.154382 | 6.154890 | 6.173106 | 6.213083 | 6.171511 |
| GO:0051960 | regulation of nervous system development | 12/204 | 482/20870 | 0.00289348682816145 | 0.06097125185616 | 0.04980738936402 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||TYMP||CST7||VEGFA||LIF||BHLHE40||IL6||GPRASP2||SEMA6B||DLL1 | 12 | 6.577894 | 6.809045 | 6.837024 | 6.576770 | 6.570407 | 6.590360 | 6.573960 | 6.812935 | 6.805163 | 6.801111 | 6.816917 | 6.842026 | 6.842129 | 6.833468 | 6.830436 |
| GO:0019915 | lipid storage | 5/204 | 100/20870 | 0.00301940698605461 | 0.06321148131844 | 0.05163743184627 | NR1H3||C3||B4GALNT1||IL6||ENPP1 | 5 | 5.965100 | 6.365150 | 6.586501 | 5.950311 | 5.979635 | 5.978623 | 5.951554 | 6.350357 | 6.397070 | 6.364029 | 6.348617 | 6.588130 | 6.576995 | 6.609362 | 6.571222 |
| GO:0040018 | positive regulation of multicellular organism growth | 3/204 | 30/20870 | 0.00307597569383431 | 0.06340197798379 | 0.05179304849009 | MKKS||IGF2||CSF1 | 3 | 6.628846 | 6.373293 | 6.551139 | 6.662429 | 6.477204 | 6.654720 | 6.710360 | 6.303844 | 6.329563 | 6.278529 | 6.562869 | 6.587956 | 6.532087 | 6.418305 | 6.655787 |
| GO:0090713 | immunological memory process | 3/204 | 30/20870 | 0.00307597569383431 | 0.06340197798379 | 0.05179304849009 | IL23A||TNFRSF14||HLA-DRA | 3 | 6.654950 | 6.912957 | 7.120824 | 6.669059 | 6.666988 | 6.631105 | 6.652330 | 6.903098 | 6.902138 | 6.933766 | 6.912602 | 7.119586 | 7.103230 | 7.113514 | 7.146609 |
| GO:0045860 | positive regulation of protein kinase activity | 11/204 | 423/20870 | 0.00308750327030229 | 0.06340197798379 | 0.05179304849009 | IL23A||VEGFA||PRLR||CCR7||MAS1||FGD2||ADAM8||IGF2||TNFSF15||CSF1||PIK3R6 | 11 | 6.274199 | 6.602494 | 6.691660 | 6.255130 | 6.281147 | 6.282518 | 6.277831 | 6.606546 | 6.600187 | 6.607268 | 6.595944 | 6.695335 | 6.694364 | 6.681821 | 6.695074 |
| GO:0002711 | positive regulation of T cell mediated immunity | 5/204 | 102/20870 | 0.00328857381818302 | 0.06668152194857 | 0.05447210654150 | IL23A||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 5 | 7.729962 | 7.750444 | 7.940777 | 7.740734 | 7.715547 | 7.731589 | 7.731861 | 7.755768 | 7.750560 | 7.743676 | 7.751745 | 7.936539 | 7.939691 | 7.937541 | 7.949300 |
| GO:0010769 | regulation of cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation | 5/204 | 102/20870 | 0.00328857381818302 | 0.06668152194857 | 0.05447210654150 | CDKL3||CDKL5||UNC13D||RREB1||GPRASP2 | 5 | 6.643695 | 6.758049 | 6.711960 | 6.630315 | 6.654560 | 6.674099 | 6.615099 | 6.740530 | 6.777198 | 6.760766 | 6.753457 | 6.732370 | 6.704856 | 6.704831 | 6.705591 |
| GO:0033028 | myeloid cell apoptotic process | 3/204 | 31/20870 | 0.00338124615552447 | 0.06770892922615 | 0.05531139510377 | IL6||SLC7A11||IRF7 | 3 | 6.148633 | 6.691604 | 6.992364 | 6.130028 | 6.117230 | 6.191454 | 6.154708 | 6.696317 | 6.685662 | 6.657639 | 6.725967 | 7.074373 | 6.938500 | 6.966499 | 6.986473 |
| GO:0036475 | neuron death in response to oxidative stress | 3/204 | 31/20870 | 0.00338124615552447 | 0.06770892922615 | 0.05531139510377 | NR4A3||MEAK7||SLC7A11 | 3 | 7.030682 | 6.963978 | 6.907817 | 6.993185 | 7.025891 | 6.988656 | 7.111588 | 6.977667 | 6.955835 | 6.937140 | 6.984781 | 6.872430 | 6.992624 | 6.902024 | 6.860435 |
| GO:0007589 | body fluid secretion | 5/204 | 103/20870 | 0.00342944328912824 | 0.06825015533426 | 0.05575352247823 | NR1H3||OAS2||VEGFA||PRLR||AQP1 | 5 | 7.926009 | 7.899883 | 8.190955 | 7.913822 | 7.927196 | 7.938433 | 7.924480 | 7.901086 | 7.889879 | 7.901893 | 7.906624 | 8.190615 | 8.188419 | 8.197118 | 8.187650 |
| GO:0030516 | regulation of axon extension | 5/204 | 104/20870 | 0.00357460003191866 | 0.06984584618802 | 0.05705704164896 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||SEMA6B | 5 | 5.517688 | 5.622604 | 5.650258 | 5.506426 | 5.494665 | 5.581578 | 5.486076 | 5.637342 | 5.652272 | 5.584583 | 5.615321 | 5.732168 | 5.648962 | 5.620174 | 5.596038 |
| GO:0002697 | regulation of immune effector process | 12/204 | 495/20870 | 0.00358196626396345 | 0.06984584618802 | 0.05705704164896 | CFH||UNC13D||IL23A||NR4A3||C3||RSAD2||IL6||TNFRSF14||PTAFR||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||PIK3R6 | 12 | 6.951819 | 7.035090 | 7.140234 | 6.951089 | 6.942773 | 6.959646 | 6.953717 | 7.030065 | 7.034639 | 7.037544 | 7.038099 | 7.138561 | 7.144268 | 7.147196 | 7.130859 |
| GO:1902107 | positive regulation of leukocyte differentiation | 7/204 | 200/20870 | 0.00359981510720386 | 0.06984584618802 | 0.05705704164896 | IL23A||LIF||ADAM8||EGR3||CSF1||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 7 | 6.476182 | 6.507712 | 6.540292 | 6.477799 | 6.466920 | 6.492485 | 6.467374 | 6.499225 | 6.495061 | 6.523395 | 6.512994 | 6.533800 | 6.543618 | 6.543405 | 6.540323 |
| GO:1903708 | positive regulation of hemopoiesis | 7/204 | 200/20870 | 0.00359981510720386 | 0.06984584618802 | 0.05705704164896 | IL23A||LIF||ADAM8||EGR3||CSF1||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 7 | 6.476182 | 6.507712 | 6.540292 | 6.477799 | 6.466920 | 6.492485 | 6.467374 | 6.499225 | 6.495061 | 6.523395 | 6.512994 | 6.533800 | 6.543618 | 6.543405 | 6.540323 |
| GO:0062013 | positive regulation of small molecule metabolic process | 6/204 | 150/20870 | 0.00361794550663757 | 0.06984584618802 | 0.05705704164896 | NR1H3||NR4A3||MAS1||BMP6||IGF2||PTAFR | 6 | 8.108726 | 8.209219 | 8.383735 | 8.112826 | 8.109354 | 8.102207 | 8.110494 | 8.216754 | 8.199770 | 8.208709 | 8.211591 | 8.384591 | 8.383623 | 8.393581 | 8.373071 |
| GO:0048545 | response to steroid hormone | 10/204 | 372/20870 | 0.00373584371428692 | 0.07169261985036 | 0.05856567025781 | NR1H3||PADI2||NR4A3||PMEPA1||IL6||IL1RN||BMP6||PTAFR||SSTR2||AQP1 | 10 | 7.413369 | 7.678497 | 7.704299 | 7.384395 | 7.402589 | 7.411168 | 7.454405 | 7.682874 | 7.672130 | 7.669086 | 7.689804 | 7.708122 | 7.692169 | 7.708356 | 7.708482 |
| GO:0043434 | response to peptide hormone | 11/204 | 435/20870 | 0.00381160053016184 | 0.07271361011386 | 0.05939971676403 | GCLC||NR4A3||TNFSF10||MAS1||BCAR3||STAT4||MEAK7||NR4A2||IGF2||SOCS3||ENPP1 | 11 | 6.293396 | 6.426687 | 6.549312 | 6.310361 | 6.281340 | 6.293198 | 6.288528 | 6.435006 | 6.438967 | 6.427164 | 6.405376 | 6.551863 | 6.555622 | 6.553167 | 6.536518 |
| GO:0045765 | regulation of angiogenesis | 10/204 | 374/20870 | 0.00387897684472638 | 0.07356365498469 | 0.06009411805267 | TIE1||VEGFA||IL1A||C3||IL6||CREB3L1||CXCL10||DLL1||AQP1||PIK3R6 | 10 | 6.241914 | 6.547929 | 6.749057 | 6.233287 | 6.277729 | 6.231816 | 6.224207 | 6.528821 | 6.522943 | 6.548795 | 6.590192 | 6.745315 | 6.741261 | 6.778509 | 6.730696 |
| GO:0002366 | leukocyte activation involved in immune response | 9/204 | 316/20870 | 0.00402591791790198 | 0.07401236728184 | 0.06046067093482 | UNC13D||PTGDS||IL23A||NR4A3||IL6||PTAFR||DLL1||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 9 | 7.202099 | 7.465457 | 7.488595 | 7.195496 | 7.208659 | 7.200276 | 7.203932 | 7.462114 | 7.448913 | 7.476119 | 7.474515 | 7.474166 | 7.491117 | 7.499973 | 7.489006 |
| GO:0016081 | synaptic vesicle docking | 2/204 | 10/20870 | 0.00406333405982792 | 0.07401236728184 | 0.06046067093482 | UNC13A||UNC13C | 2 | 3.592442 | 3.498035 | 3.612353 | 3.640979 | 3.569370 | 3.519188 | 3.636706 | 3.590346 | 3.482693 | 3.413469 | 3.500100 | 3.673726 | 3.679501 | 3.595470 | 3.492891 |
| GO:0033089 | positive regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus | 2/204 | 10/20870 | 0.00406333405982792 | 0.07401236728184 | 0.06046067093482 | ADAM8||EGR3 | 2 | 4.409996 | 3.082641 | 3.339208 | 4.497600 | 4.300710 | 4.442518 | 4.391924 | 2.920665 | 3.292864 | 3.001452 | 3.088479 | 2.970012 | 3.080219 | 2.967496 | 4.032748 |
| GO:0045835 | negative regulation of meiotic nuclear division | 2/204 | 10/20870 | 0.00406333405982792 | 0.07401236728184 | 0.06046067093482 | LIF||FBXO43 | 2 | 4.748253 | 4.857877 | 4.768262 | 4.648292 | 4.621431 | 5.074612 | 4.591836 | 4.932748 | 4.781659 | 4.866276 | 4.846805 | 4.545753 | 4.827949 | 4.683584 | 4.979511 |
| GO:0071281 | cellular response to iron ion | 2/204 | 10/20870 | 0.00406333405982792 | 0.07401236728184 | 0.06046067093482 | TFAP2A||BMP6 | 2 | 9.488357 | 9.068959 | 9.092545 | 9.502985 | 9.473376 | 9.483463 | 9.493435 | 9.079404 | 9.076589 | 9.044637 | 9.074930 | 9.090774 | 9.094934 | 9.091229 | 9.093237 |
| GO:0097278 | complement-dependent cytotoxicity | 2/204 | 10/20870 | 0.00406333405982792 | 0.07401236728184 | 0.06046067093482 | CFH||C3 | 2 | 7.286853 | 7.918877 | 7.924676 | 7.298795 | 7.285132 | 7.256197 | 7.306777 | 7.883250 | 7.930751 | 7.945631 | 7.915136 | 7.960092 | 7.914987 | 7.916189 | 7.906830 |
| GO:2001225 | regulation of chloride transport | 2/204 | 10/20870 | 0.00406333405982792 | 0.07401236728184 | 0.06046067093482 | ATP8B1||PTAFR | 2 | 3.307272 | 2.791255 | 3.973161 | 3.012530 | 3.010547 | 2.629133 | 4.111087 | 2.758005 | 2.710393 | 2.900521 | 2.789252 | 3.316844 | 2.769270 | 4.251171 | 4.754629 |
| GO:0030879 | mammary gland development | 6/204 | 154/20870 | 0.00411453932519141 | 0.07452401564279 | 0.06087863626037 | OAS2||VEGFA||PRLR||TBX2||RREB1||CSF1 | 6 | 7.316976 | 7.185490 | 7.468988 | 7.319311 | 7.312261 | 7.323865 | 7.312435 | 7.185449 | 7.171859 | 7.186188 | 7.198344 | 7.469390 | 7.473526 | 7.475637 | 7.457330 |
| GO:0033135 | regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | 6/204 | 155/20870 | 0.00424619397370856 | 0.07626622414739 | 0.06230184563693 | OSM||VEGFA||LIF||IL6||BCAR3||INPP5F | 6 | 6.257306 | 6.544620 | 6.535690 | 6.267357 | 6.230341 | 6.262434 | 6.268754 | 6.554063 | 6.500617 | 6.582250 | 6.540354 | 6.530759 | 6.551608 | 6.568615 | 6.490606 |
| GO:0048588 | developmental cell growth | 8/204 | 261/20870 | 0.00425803980971798 | 0.07626622414739 | 0.06230184563693 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||RASAL1||VEGFA||BCL11A||UNC13A||SEMA6B | 8 | 6.541464 | 7.072718 | 7.056594 | 6.548389 | 6.539487 | 6.548687 | 6.529204 | 7.089044 | 7.063188 | 7.069948 | 7.068560 | 7.063816 | 7.062966 | 7.053498 | 7.046023 |
| GO:0070997 | neuron death | 11/204 | 442/20870 | 0.00429304443748357 | 0.07636605903725 | 0.06238340071542 | GCLC||TYRO3||NR4A3||TFAP2A||MEAK7||SLC7A11||ADAM8||NR4A2||GPRASP2||CSF1||HLA-F | 11 | 6.786417 | 6.797651 | 6.862524 | 6.793626 | 6.785303 | 6.773363 | 6.793281 | 6.810926 | 6.806311 | 6.792834 | 6.780333 | 6.858997 | 6.870636 | 6.861435 | 6.858997 |
| GO:1901342 | regulation of vasculature development | 10/204 | 380/20870 | 0.00433462190476898 | 0.07636605903725 | 0.06238340071542 | TIE1||VEGFA||IL1A||C3||IL6||CREB3L1||CXCL10||DLL1||AQP1||PIK3R6 | 10 | 6.251151 | 6.546064 | 6.743063 | 6.243870 | 6.284544 | 6.243184 | 6.232455 | 6.527101 | 6.519475 | 6.547566 | 6.589097 | 6.740523 | 6.734932 | 6.772518 | 6.723824 |
| GO:0002263 | cell activation involved in immune response | 9/204 | 320/20870 | 0.00436797075960362 | 0.07636605903725 | 0.06238340071542 | UNC13D||PTGDS||IL23A||NR4A3||IL6||PTAFR||DLL1||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 9 | 7.190609 | 7.454633 | 7.480262 | 7.187405 | 7.194502 | 7.189759 | 7.190760 | 7.448742 | 7.439798 | 7.463402 | 7.466425 | 7.466895 | 7.481588 | 7.488833 | 7.483638 |
| GO:0051604 | protein maturation | 9/204 | 320/20870 | 0.00436797075960362 | 0.07636605903725 | 0.06238340071542 | CST7||CPXM1||IL1R2||ECE1||CHAC1||ADAM19||CPM||CIDEB||ADAM8 | 9 | 6.284683 | 6.493426 | 6.547877 | 6.305258 | 6.285386 | 6.267471 | 6.280360 | 6.493030 | 6.481752 | 6.490531 | 6.508266 | 6.520551 | 6.560737 | 6.545844 | 6.563969 |
| GO:0010818 | T cell chemotaxis | 3/204 | 34/20870 | 0.00440573417522603 | 0.07636605903725 | 0.06238340071542 | CXCL10||CXCL11||CXCR3 | 3 | 4.907867 | 6.594400 | 7.177205 | 4.909270 | 4.844420 | 4.944955 | 4.930782 | 6.608934 | 6.606323 | 6.586649 | 6.575426 | 7.155445 | 7.196697 | 7.163180 | 7.193047 |
| GO:1902275 | regulation of chromatin organization | 3/204 | 34/20870 | 0.00440573417522603 | 0.07636605903725 | 0.06238340071542 | AICDA||PADI2||PARP10 | 3 | 5.921800 | 5.763254 | 5.909410 | 5.979939 | 5.850548 | 5.874002 | 5.977904 | 5.668893 | 5.802362 | 5.764258 | 5.813077 | 5.864377 | 5.862568 | 6.005520 | 5.900424 |
| GO:0051896 | regulation of protein kinase B signaling | 7/204 | 208/20870 | 0.00445783899896310 | 0.07685600498747 | 0.06278363735100 | OSM||MEIS3||CCR7||ADAM8||IGF2||C1QTNF1||INPP5F | 7 | 6.629042 | 6.822867 | 6.886051 | 6.626384 | 6.620877 | 6.644734 | 6.624051 | 6.826956 | 6.828922 | 6.824158 | 6.811369 | 6.893800 | 6.896096 | 6.880397 | 6.873792 |
| GO:0050773 | regulation of dendrite development | 5/204 | 110/20870 | 0.00453961465188916 | 0.07784956190261 | 0.06359527356678 | CDKL3||CDKL5||BCL11A||HECW2||GPRASP2 | 5 | 5.839519 | 6.197278 | 6.208023 | 5.823442 | 5.841569 | 5.796485 | 5.894782 | 6.226621 | 6.205310 | 6.201584 | 6.154643 | 6.224855 | 6.217618 | 6.223117 | 6.165676 |
| GO:0048841 | regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance | 3/204 | 35/20870 | 0.00478445579990767 | 0.08116664109276 | 0.06630499412762 | SEMA3F||VEGFA||SEMA6B | 3 | 3.560108 | 4.311970 | 4.722278 | 3.557678 | 3.638773 | 3.550124 | 3.489957 | 4.221757 | 4.315348 | 4.269289 | 4.432882 | 4.856935 | 4.629569 | 4.785646 | 4.601209 |
| GO:0002221 | pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway | 7/204 | 211/20870 | 0.00481654074627203 | 0.08116664109276 | 0.06630499412762 | NR1H3||TYRO3||RSAD2||OASL||SLC15A2||CLEC4E||IRF7 | 7 | 5.906337 | 6.024744 | 6.033239 | 5.900664 | 5.906891 | 5.899967 | 5.917755 | 6.041689 | 6.022351 | 6.029214 | 6.005483 | 6.016428 | 6.029287 | 6.060481 | 6.026383 |
| GO:0006939 | smooth muscle contraction | 5/204 | 112/20870 | 0.00489884689645611 | 0.08116664109276 | 0.06630499412762 | TBX2||MKKS||PTAFR||SSTR2||SULF2 | 5 | 5.189384 | 5.098388 | 5.046867 | 5.215527 | 5.081595 | 5.228004 | 5.227220 | 5.057299 | 5.051013 | 5.083644 | 5.196740 | 5.061834 | 5.042258 | 4.964162 | 5.115161 |
| GO:0010573 | vascular endothelial growth factor production | 4/204 | 70/20870 | 0.00491489661613744 | 0.08116664109276 | 0.06630499412762 | IL1A||C3||IL6||SULF2 | 4 | 5.641739 | 7.064632 | 7.491634 | 5.620867 | 5.617890 | 5.631798 | 5.695023 | 7.061407 | 7.058337 | 7.066884 | 7.071862 | 7.488513 | 7.496638 | 7.500112 | 7.481199 |
| GO:0001672 | regulation of chromatin assembly or disassembly | 2/204 | 11/20870 | 0.00493444840390232 | 0.08116664109276 | 0.06630499412762 | PADI2||PARP10 | 2 | 4.921322 | 4.601067 | 4.723201 | 4.874122 | 4.924749 | 5.003169 | 4.879512 | 4.662344 | 4.401605 | 4.667853 | 4.655368 | 4.611738 | 4.675031 | 4.892191 | 4.698342 |
| GO:0002885 | positive regulation of hypersensitivity | 2/204 | 11/20870 | 0.00493444840390232 | 0.08116664109276 | 0.06630499412762 | C3||CCR7 | 2 | 6.077802 | 6.365278 | 6.595825 | 6.024389 | 6.072025 | 6.097534 | 6.115635 | 6.354474 | 6.358752 | 6.441462 | 6.302994 | 6.569322 | 6.581186 | 6.564995 | 6.665447 |
| GO:0030432 | peristalsis | 2/204 | 11/20870 | 0.00493444840390232 | 0.08116664109276 | 0.06630499412762 | TBX2||SSTR2 | 2 | 2.483383 | 2.537688 | 2.732217 | 2.250199 | 2.621278 | 2.444834 | 2.588139 | 2.277204 | 2.074634 | 3.088743 | 2.500552 | 2.947316 | 2.765924 | 2.559140 | 2.625389 |
| GO:0035457 | cellular response to interferon-alpha | 2/204 | 11/20870 | 0.00493444840390232 | 0.08116664109276 | 0.06630499412762 | IFIT3||IFIT2 | 2 | 4.469842 | 4.759321 | 4.541214 | 4.446833 | 4.446099 | 4.501286 | 4.484356 | 4.787323 | 4.721969 | 4.830228 | 4.693773 | 4.586731 | 4.517597 | 4.534772 | 4.524730 |
| GO:0050679 | positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation | 7/204 | 213/20870 | 0.00506748469455289 | 0.08293183073725 | 0.06774697678745 | VEGFA||NR4A3||RREB1||BMP6||IGF2||SCG2||EGR3 | 7 | 6.316795 | 6.421907 | 6.443504 | 6.270707 | 6.313852 | 6.341601 | 6.339890 | 6.442113 | 6.412020 | 6.402369 | 6.430792 | 6.440154 | 6.442276 | 6.451302 | 6.440256 |
| GO:0060193 | positive regulation of lipase activity | 4/204 | 71/20870 | 0.00516918180113464 | 0.08309456452082 | 0.06787991394511 | NR1H3||LPAR2||ITK||PTAFR | 4 | 6.141738 | 6.597472 | 6.794899 | 6.129010 | 6.133777 | 6.141298 | 6.162636 | 6.628345 | 6.591616 | 6.587044 | 6.582421 | 6.772869 | 6.806730 | 6.786370 | 6.813268 |
| GO:0002446 | neutrophil mediated immunity | 3/204 | 36/20870 | 0.00518225520523356 | 0.08309456452082 | 0.06787991394511 | TREM1||IL6||PTAFR | 3 | 7.756670 | 7.455149 | 7.634470 | 7.764936 | 7.759732 | 7.753660 | 7.748296 | 7.446537 | 7.455955 | 7.460575 | 7.457492 | 7.661153 | 7.636089 | 7.630109 | 7.610069 |
| GO:0090025 | regulation of monocyte chemotaxis | 3/204 | 36/20870 | 0.00518225520523356 | 0.08309456452082 | 0.06787991394511 | PLA2G7||NBL1||CXCL10 | 3 | 5.346606 | 6.610486 | 7.089980 | 5.322819 | 5.340878 | 5.373943 | 5.348315 | 6.637457 | 6.626141 | 6.587109 | 6.590571 | 7.053950 | 7.120402 | 7.092342 | 7.092453 |
| GO:2000047 | regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin | 3/204 | 36/20870 | 0.00518225520523356 | 0.08309456452082 | 0.06787991394511 | VEGFA||ADAM19||BMP6 | 3 | 5.024370 | 5.064677 | 5.299132 | 5.080467 | 4.930406 | 5.012998 | 5.068776 | 5.056304 | 4.998871 | 5.114176 | 5.086826 | 5.327222 | 5.302820 | 5.263137 | 5.302621 |
| GO:0002274 | myeloid leukocyte activation | 8/204 | 270/20870 | 0.00520629715670160 | 0.08309456452082 | 0.06787991394511 | NR1H3||CST7||UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3||IL6||PTAFR||CSF1 | 8 | 7.156141 | 7.253265 | 7.302597 | 7.160392 | 7.159133 | 7.159988 | 7.144991 | 7.263031 | 7.238600 | 7.256622 | 7.254695 | 7.303072 | 7.303569 | 7.299709 | 7.304035 |
| GO:0001938 | positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation | 5/204 | 114/20870 | 0.00527780935346011 | 0.08382097219485 | 0.06847331606097 | VEGFA||BMP6||IGF2||SCG2||EGR3 | 5 | 6.312614 | 6.341194 | 6.384306 | 6.255805 | 6.305775 | 6.335025 | 6.352014 | 6.350018 | 6.332540 | 6.316728 | 6.365032 | 6.393580 | 6.369361 | 6.386094 | 6.388077 |
| GO:0048814 | regulation of dendrite morphogenesis | 4/204 | 72/20870 | 0.00543213240773108 | 0.08584899452218 | 0.07013000662613 | CDKL3||CDKL5||HECW2||GPRASP2 | 4 | 5.678884 | 6.013679 | 5.917770 | 5.644676 | 5.688448 | 5.656038 | 5.725015 | 6.053015 | 6.063345 | 5.937168 | 5.997701 | 5.990760 | 5.896452 | 5.901653 | 5.879589 |
| GO:0051047 | positive regulation of secretion | 9/204 | 332/20870 | 0.00553171686773343 | 0.08637529426058 | 0.07055994065560 | UNC13D||IL1A||ANKRD1||ADAM8||BMP6||PTAFR||C1QTNF1||HLA-F||AQP1 | 9 | 6.868884 | 7.287749 | 7.336041 | 6.853945 | 6.884119 | 6.859826 | 6.877435 | 7.274641 | 7.273037 | 7.295519 | 7.307508 | 7.337381 | 7.340300 | 7.346100 | 7.320255 |
| GO:0051384 | response to glucocorticoid | 6/204 | 164/20870 | 0.00557520648699379 | 0.08637529426058 | 0.07055994065560 | IL6||IL1RN||BMP6||PTAFR||SSTR2||AQP1 | 6 | 7.619938 | 7.828363 | 7.895639 | 7.633119 | 7.625653 | 7.596398 | 7.624311 | 7.842042 | 7.797235 | 7.830745 | 7.842955 | 7.899900 | 7.885457 | 7.902971 | 7.894168 |
| GO:0007389 | pattern specification process | 11/204 | 458/20870 | 0.00557624303459663 | 0.08637529426058 | 0.07055994065560 | SEMA3F||ASB2||MEIS3||TBX2||C3||MKKS||MICAL2||BHLHE40||NBL1||HES4||DLL1 | 11 | 4.988622 | 4.837666 | 4.847364 | 5.007245 | 4.927980 | 4.961313 | 5.054777 | 4.828542 | 4.807132 | 4.833579 | 4.880414 | 4.905501 | 4.786360 | 4.827928 | 4.866944 |
| GO:0032693 | negative regulation of interleukin-10 production | 3/204 | 37/20870 | 0.00559939097408876 | 0.08637529426058 | 0.07055994065560 | IL23A||PDCD1LG2||DLL1 | 3 | 7.247273 | 7.426243 | 7.442423 | 7.279060 | 7.210797 | 7.264159 | 7.234106 | 7.422633 | 7.451315 | 7.426749 | 7.403876 | 7.438272 | 7.440611 | 7.434680 | 7.456037 |
| GO:2000406 | positive regulation of T cell migration | 3/204 | 37/20870 | 0.00559939097408876 | 0.08637529426058 | 0.07055994065560 | ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10 | 3 | 6.333148 | 6.905518 | 7.250680 | 6.343683 | 6.304218 | 6.350565 | 6.333693 | 6.938336 | 6.897007 | 6.888448 | 6.897756 | 7.241508 | 7.265664 | 7.217649 | 7.277173 |
| GO:0033138 | positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | 5/204 | 116/20870 | 0.00567706594539859 | 0.08674341520363 | 0.07086065849532 | OSM||VEGFA||LIF||IL6||BCAR3 | 5 | 6.257759 | 6.679962 | 6.687806 | 6.284228 | 6.240078 | 6.250415 | 6.255942 | 6.695900 | 6.627208 | 6.719368 | 6.675781 | 6.680053 | 6.695607 | 6.733400 | 6.640629 |
| GO:0050829 | defense response to Gram-negative bacterium | 5/204 | 116/20870 | 0.00567706594539859 | 0.08674341520363 | 0.07086065849532 | IL23A||TREM1||IL6||TNFRSF14||AQP1 | 5 | 7.531399 | 7.503267 | 7.518604 | 7.537081 | 7.514659 | 7.542634 | 7.531071 | 7.471199 | 7.520783 | 7.516633 | 7.503929 | 7.518629 | 7.507151 | 7.542760 | 7.505570 |
| GO:0050673 | epithelial cell proliferation | 11/204 | 461/20870 | 0.00584746331732536 | 0.08817733542286 | 0.07203202730443 | TIE1||VEGFA||NR4A3||RREB1||IL6||BMP6||IGF2||SCG2||EGR3||SULF2||EPPK1 | 11 | 6.582981 | 6.507500 | 6.527053 | 6.568557 | 6.577974 | 6.594289 | 6.590956 | 6.509471 | 6.500502 | 6.505473 | 6.514515 | 6.533748 | 6.527447 | 6.523667 | 6.523326 |
| GO:0014831 | gastro-intestinal system smooth muscle contraction | 2/204 | 12/20870 | 0.00588339465761052 | 0.08817733542286 | 0.07203202730443 | PTAFR||SULF2 | 2 | 4.001363 | 3.704619 | 3.624850 | 3.286678 | 3.237288 | 5.140430 | 3.263068 | 3.301967 | 4.527889 | 3.315872 | 3.211177 | 3.401263 | 4.282373 | 3.174644 | 3.363414 |
| GO:0016188 | synaptic vesicle maturation | 2/204 | 12/20870 | 0.00588339465761052 | 0.08817733542286 | 0.07203202730443 | UNC13A||UNC13C | 2 | 4.908614 | 4.639784 | 4.287201 | 5.122540 | 4.865178 | 4.756257 | 4.864728 | 4.489816 | 4.575248 | 4.987353 | 4.438974 | 4.343697 | 4.240954 | 4.364620 | 4.192524 |
| GO:0021559 | trigeminal nerve development | 2/204 | 12/20870 | 0.00588339465761052 | 0.08817733542286 | 0.07203202730443 | SEMA3F||TFAP2A | 2 | 3.428781 | 4.669453 | 5.076681 | 3.524273 | 3.280369 | 3.557952 | 3.332843 | 4.563748 | 4.772439 | 4.660441 | 4.673606 | 5.148156 | 4.829537 | 5.391023 | 4.864456 |
| GO:0007519 | skeletal muscle tissue development | 6/204 | 166/20870 | 0.00590766267101073 | 0.08817733542286 | 0.07203202730443 | ASB2||RIPOR2||ANKRD1||IGF2||DLL1||SCX | 6 | 6.693825 | 6.545554 | 6.511947 | 6.544035 | 6.629085 | 6.742611 | 6.841920 | 6.560104 | 6.614256 | 6.459720 | 6.543896 | 6.565481 | 6.444976 | 6.482676 | 6.551285 |
| GO:0050767 | regulation of neurogenesis | 10/204 | 398/20870 | 0.00595932025830630 | 0.08853847240912 | 0.07232703995286 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||LIF||BHLHE40||IL6||GPRASP2||SEMA6B||DLL1 | 10 | 6.699334 | 6.976764 | 7.013124 | 6.699380 | 6.690117 | 6.709653 | 6.698122 | 6.979491 | 6.972709 | 6.969557 | 6.985248 | 7.019339 | 7.019133 | 7.008736 | 7.005234 |
| GO:0032963 | collagen metabolic process | 5/204 | 118/20870 | 0.00609717576662443 | 0.09017107647522 | 0.07366071351084 | IL6||MMP7||CREB3L1||SERPINB7||SCX | 5 | 6.831889 | 7.581084 | 7.951351 | 6.832448 | 6.827435 | 6.842825 | 6.824782 | 7.566473 | 7.575126 | 7.596756 | 7.585804 | 7.941078 | 7.967024 | 7.954720 | 7.942429 |
| GO:0045861 | negative regulation of proteolysis | 10/204 | 401/20870 | 0.00627104441341414 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | NR1H3||CST7||VEGFA||IL1R2||C3||IFI6||CHAC1||SERPINB7||SERPINA9||AQP1 | 10 | 7.058927 | 7.208575 | 7.335159 | 7.059433 | 7.070524 | 7.042346 | 7.063258 | 7.203792 | 7.215419 | 7.200094 | 7.214930 | 7.345212 | 7.322787 | 7.334988 | 7.337561 |
| GO:0045582 | positive regulation of T cell differentiation | 5/204 | 119/20870 | 0.00631522389406597 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | IL23A||ADAM8||EGR3||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 5 | 5.580094 | 5.803337 | 5.915946 | 5.577824 | 5.577722 | 5.603946 | 5.560550 | 5.794698 | 5.787333 | 5.823165 | 5.807894 | 5.923261 | 5.903398 | 5.919892 | 5.917154 |
| GO:0061387 | regulation of extent of cell growth | 5/204 | 119/20870 | 0.00631522389406597 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||SEMA6B | 5 | 6.998047 | 7.645060 | 7.641992 | 6.997533 | 6.994287 | 7.014953 | 6.985255 | 7.655425 | 7.644677 | 7.634411 | 7.645649 | 7.662612 | 7.647682 | 7.629857 | 7.627536 |
| GO:0010975 | regulation of neuron projection development | 11/204 | 467/20870 | 0.00642107972775609 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||SCARF1||VEGFA||BCL11A||HECW2||ANKRD1||GPRASP2||SEMA6B||INPP5F | 11 | 6.808027 | 7.178169 | 7.197585 | 6.797557 | 6.810909 | 6.812384 | 6.811208 | 7.181624 | 7.163874 | 7.183311 | 7.183771 | 7.193011 | 7.200222 | 7.202620 | 7.194466 |
| GO:0048568 | embryonic organ development | 11/204 | 467/20870 | 0.00642107972775609 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | ASB2||VEGFA||TBX2||MKKS||LIF||MICAL2||TFAP2A||MYO7A||IGF2||SOCS3||DLL1 | 11 | 5.868354 | 5.882485 | 5.900488 | 5.902675 | 5.828683 | 5.856868 | 5.884105 | 5.844023 | 5.869426 | 5.911419 | 5.904051 | 5.913759 | 5.887843 | 5.900354 | 5.899879 |
| GO:0002824 | positive regulation of adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains | 6/204 | 169/20870 | 0.00643315815079573 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | IL23A||C3||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 6 | 7.042252 | 7.094023 | 7.273653 | 7.046124 | 7.022029 | 7.050766 | 7.049895 | 7.093804 | 7.089025 | 7.097052 | 7.096198 | 7.268534 | 7.274633 | 7.267916 | 7.283476 |
| GO:0050678 | regulation of epithelial cell proliferation | 10/204 | 404/20870 | 0.00659533748794995 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | TIE1||VEGFA||NR4A3||RREB1||BMP6||IGF2||SCG2||EGR3||SULF2||EPPK1 | 10 | 6.550636 | 6.488721 | 6.496551 | 6.533092 | 6.546963 | 6.559938 | 6.562360 | 6.495356 | 6.480067 | 6.480394 | 6.498966 | 6.508409 | 6.493153 | 6.491648 | 6.492926 |
| GO:0071692 | protein localization to extracellular region | 10/204 | 404/20870 | 0.00659533748794995 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | NR1H3||IL1A||RSAD2||IL6||IL1RN||ANKRD1||ADAM8||BMP6||NBL1||SCG2 | 10 | 5.724655 | 6.095602 | 6.250917 | 5.716141 | 5.707922 | 5.718095 | 5.755984 | 6.106423 | 6.087913 | 6.093032 | 6.094978 | 6.255066 | 6.256899 | 6.247587 | 6.244079 |
| GO:2001236 | regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | 6/204 | 170/20870 | 0.00661564404495447 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | GCLC||IL1A||TNFSF10||G0S2||IFI6||SCG2 | 6 | 6.154727 | 6.532931 | 6.733162 | 6.139381 | 6.176819 | 6.157369 | 6.145053 | 6.568086 | 6.537441 | 6.515855 | 6.509613 | 6.726409 | 6.719311 | 6.722908 | 6.763578 |
| GO:0007548 | sex differentiation | 8/204 | 282/20870 | 0.00671249198219008 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | MAMLD1||TYRO3||VEGFA||TNFSF10||MKKS||MAS1||BMP6||SCX | 8 | 5.842749 | 5.751393 | 5.767538 | 5.847254 | 5.816638 | 5.838435 | 5.868195 | 5.717385 | 5.750213 | 5.748075 | 5.789003 | 5.759230 | 5.772116 | 5.754949 | 5.783679 |
| GO:0030278 | regulation of ossification | 5/204 | 121/20870 | 0.00676764989821145 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | TFAP2A||BMP6||CSF1||ISG15||ENPP1 | 5 | 5.476861 | 5.907544 | 6.012849 | 5.477983 | 5.478199 | 5.462590 | 5.488553 | 5.908816 | 5.895155 | 5.899927 | 5.926083 | 6.108199 | 5.985694 | 5.973039 | 5.980073 |
| GO:0071496 | cellular response to external stimulus | 9/204 | 343/20870 | 0.00679715306531987 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | GCLC||KPTN||MMP7||ANKRD1||BMP6||NR4A2||AQP1||SCX||NA | 9 | 6.010418 | 6.359386 | 6.463757 | 5.997343 | 6.002017 | 6.029995 | 6.012098 | 6.360154 | 6.379479 | 6.357214 | 6.340429 | 6.446509 | 6.490006 | 6.464134 | 6.454005 |
| GO:0021675 | nerve development | 4/204 | 77/20870 | 0.00688130456318189 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | SEMA3F||ATP8B1||TFAP2A||SULF2 | 4 | 6.475474 | 6.529834 | 6.490312 | 6.491308 | 6.451284 | 6.488931 | 6.470009 | 6.534466 | 6.496508 | 6.515760 | 6.571535 | 6.481735 | 6.456801 | 6.512423 | 6.509578 |
| GO:0002866 | positive regulation of acute inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus | 2/204 | 13/20870 | 0.00690858318696989 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | C3||CCR7 | 2 | 6.330794 | 6.623816 | 6.714412 | 6.317729 | 6.326747 | 6.326106 | 6.352360 | 6.579231 | 6.572143 | 6.623293 | 6.715992 | 6.704462 | 6.668971 | 6.753568 | 6.729290 |
| GO:0006534 | cysteine metabolic process | 2/204 | 13/20870 | 0.00690858318696989 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | GCLC||SLC7A11 | 2 | 4.969490 | 4.971047 | 5.148321 | 4.943367 | 5.042348 | 4.993319 | 4.894719 | 5.007469 | 4.929318 | 4.994907 | 4.951098 | 5.278980 | 4.901471 | 5.080977 | 5.296380 |
| GO:0030157 | pancreatic juice secretion | 2/204 | 13/20870 | 0.00690858318696989 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | NR1H3||AQP1 | 2 | 5.111559 | 5.108982 | 5.132382 | 5.164079 | 5.055607 | 5.109995 | 5.114510 | 4.990209 | 5.230904 | 4.999372 | 5.198490 | 5.040948 | 5.118656 | 5.153112 | 5.211548 |
| GO:0035745 | T-helper 2 cell cytokine production | 2/204 | 13/20870 | 0.00690858318696989 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | RSAD2||IL6 | 2 | 7.384511 | 7.593189 | 7.620703 | 7.414393 | 7.391483 | 7.363180 | 7.368414 | 7.576706 | 7.590089 | 7.615629 | 7.590056 | 7.606482 | 7.596647 | 7.630359 | 7.648746 |
| GO:0060700 | regulation of ribonuclease activity | 2/204 | 13/20870 | 0.00690858318696989 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | OAS2||OASL | 2 | 7.078992 | 7.581162 | 7.521373 | 7.099133 | 7.035404 | 7.095132 | 7.085401 | 7.532875 | 7.652926 | 7.614527 | 7.520041 | 7.619440 | 7.486111 | 7.393660 | 7.575912 |
| GO:0060707 | trophoblast giant cell differentiation | 2/204 | 13/20870 | 0.00690858318696989 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | LIF||SOCS3 | 2 | 3.441462 | 3.737264 | 3.881472 | 3.516572 | 3.451411 | 3.437059 | 3.356310 | 3.762400 | 3.730474 | 3.635240 | 3.815046 | 3.941876 | 3.874712 | 3.885121 | 3.821651 |
| GO:1902510 | regulation of apoptotic DNA fragmentation | 2/204 | 13/20870 | 0.00690858318696989 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | IL6||ST20 | 2 | 5.318935 | 5.253731 | 5.637551 | 5.195802 | 5.081997 | 5.561084 | 5.390026 | 5.252749 | 5.237537 | 5.281048 | 5.243202 | 5.747114 | 5.595242 | 5.585020 | 5.616852 |
| GO:2000551 | regulation of T-helper 2 cell cytokine production | 2/204 | 13/20870 | 0.00690858318696989 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | RSAD2||IL6 | 2 | 7.384511 | 7.593189 | 7.620703 | 7.414393 | 7.391483 | 7.363180 | 7.368414 | 7.576706 | 7.590089 | 7.615629 | 7.590056 | 7.606482 | 7.596647 | 7.630359 | 7.648746 |
| GO:0010955 | negative regulation of protein processing | 3/204 | 40/20870 | 0.00696920627541369 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | CST7||IL1R2||CHAC1 | 3 | 6.243249 | 6.182845 | 6.087033 | 6.233701 | 6.257095 | 6.210014 | 6.271430 | 6.190480 | 6.136126 | 6.171873 | 6.231269 | 6.049491 | 6.096973 | 6.086442 | 6.114446 |
| GO:0048846 | axon extension involved in axon guidance | 3/204 | 40/20870 | 0.00696920627541369 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | SEMA3F||VEGFA||SEMA6B | 3 | 3.987081 | 4.985164 | 5.259509 | 3.987477 | 4.051329 | 3.977565 | 3.929330 | 4.935403 | 4.978454 | 4.973460 | 5.050906 | 5.342861 | 5.198263 | 5.285411 | 5.206571 |
| GO:0070528 | protein kinase C signaling | 3/204 | 40/20870 | 0.00696920627541369 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | VEGFA||MAS1||ANKRD1 | 3 | 5.026988 | 4.274420 | 4.594142 | 4.995793 | 4.972939 | 5.041678 | 5.094528 | 4.252055 | 4.247629 | 4.252134 | 4.343587 | 4.642341 | 4.636973 | 4.553533 | 4.540722 |
| GO:1902284 | neuron projection extension involved in neuron projection guidance | 3/204 | 40/20870 | 0.00696920627541369 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | SEMA3F||VEGFA||SEMA6B | 3 | 3.987081 | 4.985164 | 5.259509 | 3.987477 | 4.051329 | 3.977565 | 3.929330 | 4.935403 | 4.978454 | 4.973460 | 5.050906 | 5.342861 | 5.198263 | 5.285411 | 5.206571 |
| GO:1903318 | negative regulation of protein maturation | 3/204 | 40/20870 | 0.00696920627541369 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | CST7||IL1R2||CHAC1 | 3 | 6.243249 | 6.182845 | 6.087033 | 6.233701 | 6.257095 | 6.210014 | 6.271430 | 6.190480 | 6.136126 | 6.171873 | 6.231269 | 6.049491 | 6.096973 | 6.086442 | 6.114446 |
| GO:1905332 | positive regulation of morphogenesis of an epithelium | 3/204 | 40/20870 | 0.00696920627541369 | 0.09170906543646 | 0.07491709603044 | VEGFA||LIF||LBX2 | 3 | 5.614625 | 5.229497 | 5.509474 | 5.618665 | 5.605880 | 5.653936 | 5.579009 | 5.255941 | 5.155793 | 5.193774 | 5.307785 | 5.526430 | 5.494703 | 5.501648 | 5.514906 |
| GO:0008637 | apoptotic mitochondrial changes | 5/204 | 122/20870 | 0.00700216392417943 | 0.09176819712014 | 0.07496540067735 | GCLC||IFIT2||TNFSF10||IFI6||CIDEB | 5 | 6.114069 | 6.998558 | 7.360316 | 6.105665 | 6.125233 | 6.106194 | 6.119083 | 7.024271 | 7.011843 | 6.993955 | 6.963440 | 7.345750 | 7.374286 | 7.359422 | 7.361664 |
| GO:0050922 | negative regulation of chemotaxis | 4/204 | 78/20870 | 0.00719888381131778 | 0.09396437816878 | 0.07675946002948 | SEMA3F||PADI2||NBL1||SEMA6B | 4 | 5.201034 | 5.754280 | 5.821285 | 5.074499 | 5.176163 | 5.309193 | 5.234136 | 5.707682 | 5.787820 | 5.744532 | 5.775754 | 5.852782 | 5.819427 | 5.813701 | 5.798685 |
| GO:0051235 | maintenance of location | 9/204 | 347/20870 | 0.00730863426418700 | 0.09429487635102 | 0.07702944385211 | NR1H3||C3||CCR7||B4GALNT1||IL6||NBL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||ENPP1 | 9 | 7.426636 | 7.749839 | 7.850864 | 7.422939 | 7.428875 | 7.422597 | 7.432112 | 7.739673 | 7.747848 | 7.759346 | 7.752416 | 7.836490 | 7.853340 | 7.858587 | 7.854937 |
| GO:0002821 | positive regulation of adaptive immune response | 6/204 | 174/20870 | 0.00738332725448861 | 0.09429487635102 | 0.07702944385211 | IL23A||C3||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 6 | 6.992599 | 7.038285 | 7.216001 | 6.996384 | 6.971419 | 7.001031 | 7.001351 | 7.038486 | 7.033134 | 7.041738 | 7.039768 | 7.211004 | 7.216868 | 7.210282 | 7.225795 |
| GO:0010863 | positive regulation of phospholipase C activity | 3/204 | 41/20870 | 0.00746601398566192 | 0.09429487635102 | 0.07702944385211 | LPAR2||ITK||PTAFR | 3 | 5.100518 | 5.393897 | 5.511025 | 5.112848 | 5.049251 | 5.135169 | 5.103427 | 5.421259 | 5.367465 | 5.383176 | 5.403116 | 5.479027 | 5.511352 | 5.514770 | 5.538335 |
| GO:0030501 | positive regulation of bone mineralization | 3/204 | 41/20870 | 0.00746601398566192 | 0.09429487635102 | 0.07702944385211 | TFAP2A||BMP6||ISG15 | 3 | 5.404097 | 5.897709 | 6.054317 | 5.382313 | 5.339993 | 5.390285 | 5.498973 | 5.884317 | 5.852163 | 5.881619 | 5.970032 | 6.270753 | 5.968861 | 5.961659 | 5.992203 |
| GO:0050775 | positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis | 3/204 | 41/20870 | 0.00746601398566192 | 0.09429487635102 | 0.07702944385211 | CDKL3||CDKL5||GPRASP2 | 3 | 5.710751 | 5.591781 | 5.518985 | 5.664566 | 5.690401 | 5.693116 | 5.791630 | 5.580223 | 5.611111 | 5.560013 | 5.615063 | 5.545174 | 5.485086 | 5.534096 | 5.510846 |
| GO:1902622 | regulation of neutrophil migration | 3/204 | 41/20870 | 0.00746601398566192 | 0.09429487635102 | 0.07702944385211 | RIPOR2||CCR7||ADAM8 | 3 | 6.028842 | 6.915120 | 7.081765 | 6.036214 | 6.049726 | 6.032498 | 5.996394 | 6.912992 | 6.912336 | 6.924252 | 6.910862 | 7.091155 | 7.087080 | 7.083086 | 7.065610 |
| GO:0014706 | striated muscle tissue development | 10/204 | 412/20870 | 0.00752410599717155 | 0.09429487635102 | 0.07702944385211 | ASB2||RIPOR2||VEGFA||TBX2||ANKRD1||LY6E||IGF2||DLL1||ALPK2||SCX | 10 | 6.260378 | 6.232633 | 6.214179 | 6.178880 | 6.233292 | 6.288843 | 6.335703 | 6.254565 | 6.261037 | 6.191347 | 6.222512 | 6.225862 | 6.182874 | 6.206607 | 6.240723 |
| GO:0014823 | response to activity | 4/204 | 79/20870 | 0.00752598921496914 | 0.09429487635102 | 0.07702944385211 | GCLC||MAS1||IL6||BMP6 | 4 | 6.395808 | 6.579776 | 6.654967 | 6.360643 | 6.390598 | 6.424297 | 6.406933 | 6.565256 | 6.596584 | 6.578898 | 6.578193 | 6.636158 | 6.639424 | 6.650433 | 6.693133 |
| GO:0031016 | pancreas development | 4/204 | 79/20870 | 0.00752598921496914 | 0.09429487635102 | 0.07702944385211 | IL6||BMP6||IGF2||DLL1 | 4 | 5.249118 | 5.374213 | 5.120486 | 5.277125 | 5.236871 | 5.217500 | 5.264227 | 5.553471 | 5.370268 | 5.360538 | 5.189563 | 5.142092 | 5.086794 | 5.230366 | 5.014014 |
| GO:0070613 | regulation of protein processing | 4/204 | 79/20870 | 0.00752598921496914 | 0.09429487635102 | 0.07702944385211 | CST7||IL1R2||CHAC1||ADAM8 | 4 | 6.955941 | 7.022213 | 7.075418 | 6.960819 | 6.959055 | 6.938506 | 6.965239 | 7.018914 | 6.998283 | 7.041142 | 7.030164 | 7.033965 | 7.088019 | 7.076691 | 7.102103 |
| GO:0071214 | cellular response to abiotic stimulus | 9/204 | 349/20870 | 0.00757517772174727 | 0.09429487635102 | 0.07702944385211 | GCLC||MAPK10||MMP7||ANKRD1||BMP6||PTAFR||ST20||AQP1||SCX | 9 | 6.140855 | 6.631044 | 6.846599 | 6.142715 | 6.128167 | 6.146464 | 6.145996 | 6.628027 | 6.650596 | 6.630151 | 6.615178 | 6.854955 | 6.850568 | 6.845606 | 6.835193 |
| GO:0104004 | cellular response to environmental stimulus | 9/204 | 349/20870 | 0.00757517772174727 | 0.09429487635102 | 0.07702944385211 | GCLC||MAPK10||MMP7||ANKRD1||BMP6||PTAFR||ST20||AQP1||SCX | 9 | 6.140855 | 6.631044 | 6.846599 | 6.142715 | 6.128167 | 6.146464 | 6.145996 | 6.628027 | 6.650596 | 6.630151 | 6.615178 | 6.854955 | 6.850568 | 6.845606 | 6.835193 |
| GO:0030198 | extracellular matrix organization | 9/204 | 350/20870 | 0.00771120601297884 | 0.09560479412771 | 0.07809951511935 | TIE1||COL5A3||IL6||MMP7||ADAM8||CREB3L1||SULF2||COL6A6||SCX | 9 | 5.865514 | 6.452022 | 6.689373 | 5.872118 | 5.857190 | 5.879513 | 5.853075 | 6.454535 | 6.441630 | 6.457438 | 6.454432 | 6.674094 | 6.708282 | 6.692937 | 6.681951 |
| GO:0010811 | positive regulation of cell-substrate adhesion | 5/204 | 125/20870 | 0.00773971813502889 | 0.09560479412771 | 0.07809951511935 | UNC13D||VEGFA||RREB1||CCR7||CSF1 | 5 | 6.459516 | 6.567584 | 6.521191 | 6.455073 | 6.467569 | 6.489603 | 6.425064 | 6.597064 | 6.592890 | 6.547346 | 6.531931 | 6.568958 | 6.510775 | 6.508601 | 6.495308 |
| GO:0043062 | extracellular structure organization | 9/204 | 351/20870 | 0.00784909334821998 | 0.09562679811182 | 0.07811749016448 | TIE1||COL5A3||IL6||MMP7||ADAM8||CREB3L1||SULF2||COL6A6||SCX | 9 | 5.865514 | 6.452022 | 6.689373 | 5.872118 | 5.857190 | 5.879513 | 5.853075 | 6.454535 | 6.441630 | 6.457438 | 6.454432 | 6.674094 | 6.708282 | 6.692937 | 6.681951 |
| GO:0062012 | regulation of small molecule metabolic process | 9/204 | 351/20870 | 0.00784909334821998 | 0.09562679811182 | 0.07811749016448 | NR1H3||NR4A3||MAS1||SLC7A11||BMP6||IGF2||PTAFR||C1QTNF1||ENPP1 | 9 | 7.090962 | 7.196825 | 7.340098 | 7.095723 | 7.092364 | 7.081580 | 7.094140 | 7.207215 | 7.188663 | 7.196695 | 7.194666 | 7.340654 | 7.341216 | 7.352112 | 7.326292 |
| GO:0033077 | T cell differentiation in thymus | 4/204 | 80/20870 | 0.00786273586012697 | 0.09562679811182 | 0.07811749016448 | IL1A||CCR7||ADAM8||EGR3 | 4 | 7.747139 | 7.764042 | 7.784824 | 7.764975 | 7.728146 | 7.752583 | 7.742601 | 7.774924 | 7.765887 | 7.746341 | 7.768859 | 7.774801 | 7.776076 | 7.795484 | 7.792813 |
| GO:0001768 | establishment of T cell polarity | 2/204 | 14/20870 | 0.00800844773268970 | 0.09562679811182 | 0.07811749016448 | RIPOR2||CCR7 | 2 | 6.845278 | 6.622525 | 6.714633 | 6.851050 | 6.904095 | 6.808720 | 6.815249 | 6.654775 | 6.593157 | 6.612120 | 6.629333 | 6.707692 | 6.696857 | 6.681901 | 6.770494 |
| GO:0002883 | regulation of hypersensitivity | 2/204 | 14/20870 | 0.00800844773268970 | 0.09562679811182 | 0.07811749016448 | C3||CCR7 | 2 | 5.907789 | 6.220389 | 6.445577 | 5.858222 | 5.908851 | 5.933741 | 5.929105 | 6.214904 | 6.214414 | 6.293654 | 6.155217 | 6.424247 | 6.427737 | 6.424560 | 6.504141 |
| GO:0060732 | positive regulation of inositol phosphate biosynthetic process | 2/204 | 14/20870 | 0.00800844773268970 | 0.09562679811182 | 0.07811749016448 | MAS1||PTAFR | 2 | 3.058183 | 3.434306 | 3.478098 | 3.063951 | 3.045939 | 3.109110 | 3.012027 | 3.454327 | 3.470219 | 3.388505 | 3.422819 | 3.510617 | 3.391810 | 3.483484 | 3.522868 |
| GO:0072540 | T-helper 17 cell lineage commitment | 2/204 | 14/20870 | 0.00800844773268970 | 0.09562679811182 | 0.07811749016448 | IL23A||IL6 | 2 | 4.674476 | 4.538319 | 5.240682 | 4.653474 | 4.768468 | 4.664098 | 4.606990 | 4.528096 | 4.529847 | 4.649054 | 4.438484 | 5.246967 | 5.213392 | 5.216386 | 5.284828 |
| GO:0072672 | neutrophil extravasation | 2/204 | 14/20870 | 0.00800844773268970 | 0.09562679811182 | 0.07811749016448 | RIPOR2||ADAM8 | 2 | 6.482685 | 6.023162 | 5.933160 | 6.495759 | 6.514033 | 6.494383 | 6.424974 | 6.020907 | 6.027790 | 6.008274 | 6.035536 | 5.962110 | 5.920243 | 5.915580 | 5.934252 |
| GO:1903624 | regulation of DNA catabolic process | 2/204 | 14/20870 | 0.00800844773268970 | 0.09562679811182 | 0.07811749016448 | IL6||ST20 | 2 | 5.318935 | 5.253731 | 5.637551 | 5.195802 | 5.081997 | 5.561084 | 5.390026 | 5.252749 | 5.237537 | 5.281048 | 5.243202 | 5.747114 | 5.595242 | 5.585020 | 5.616852 |
| GO:1903317 | regulation of protein maturation | 4/204 | 81/20870 | 0.00820923678396273 | 0.09735325119367 | 0.07952782894298 | CST7||IL1R2||CHAC1||ADAM8 | 4 | 6.911538 | 6.977239 | 7.023153 | 6.916887 | 6.915415 | 6.893302 | 6.920390 | 6.974891 | 6.953712 | 6.995662 | 6.984362 | 6.981729 | 7.036064 | 7.024220 | 7.049703 |
| GO:0060538 | skeletal muscle organ development | 6/204 | 178/20870 | 0.00821342565901941 | 0.09735325119367 | 0.07952782894298 | ASB2||RIPOR2||ANKRD1||IGF2||DLL1||SCX | 6 | 6.641308 | 6.495251 | 6.465115 | 6.493755 | 6.581579 | 6.687975 | 6.785223 | 6.510618 | 6.562671 | 6.411110 | 6.492514 | 6.516309 | 6.402019 | 6.435732 | 6.503312 |
| GO:0007368 | determination of left/right symmetry | 5/204 | 127/20870 | 0.00826042874371021 | 0.09735621031195 | 0.07953024624543 | ASB2||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||DLL1 | 5 | 5.415775 | 4.967452 | 5.042614 | 5.476083 | 5.269347 | 5.380653 | 5.523967 | 4.943573 | 4.883474 | 4.923987 | 5.108417 | 5.240786 | 4.834982 | 4.994725 | 5.070404 |
| GO:0045229 | external encapsulating structure organization | 9/204 | 354/20870 | 0.00827406998308787 | 0.09735621031195 | 0.07953024624543 | TIE1||COL5A3||IL6||MMP7||ADAM8||CREB3L1||SULF2||COL6A6||SCX | 9 | 5.857734 | 6.444575 | 6.681902 | 5.864312 | 5.849450 | 5.871732 | 5.845282 | 6.447081 | 6.434214 | 6.449969 | 6.446983 | 6.666888 | 6.700642 | 6.685448 | 6.674407 |
| GO:0048771 | tissue remodeling | 6/204 | 179/20870 | 0.00843101804819771 | 0.09821320925694 | 0.08023032831425 | TIE1||IL23A||IL1A||LIF||IL6||ADAM8 | 6 | 7.257516 | 7.662479 | 7.735965 | 7.264963 | 7.257025 | 7.251685 | 7.256362 | 7.665469 | 7.644148 | 7.669264 | 7.670875 | 7.745964 | 7.736032 | 7.728981 | 7.732828 |
| GO:0043281 | regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process | 7/204 | 235/20870 | 0.00851975169248136 | 0.09821320925694 | 0.08023032831425 | SENP1||VEGFA||TNFSF10||IFI6||ST20||TNFSF15||AQP1 | 7 | 6.750586 | 7.174296 | 7.391106 | 6.741058 | 6.750070 | 6.751755 | 6.759403 | 7.173101 | 7.170046 | 7.170791 | 7.183208 | 7.382472 | 7.398222 | 7.387198 | 7.396472 |
| GO:0030224 | monocyte differentiation | 3/204 | 43/20870 | 0.00852112494300526 | 0.09821320925694 | 0.08023032831425 | VEGFA||CSF1||IRF7 | 3 | 6.034272 | 6.280025 | 6.421705 | 6.028715 | 6.036026 | 6.035033 | 6.037300 | 6.278000 | 6.277777 | 6.276164 | 6.288126 | 6.419035 | 6.421899 | 6.409179 | 6.436572 |
| GO:0044331 | cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin | 3/204 | 43/20870 | 0.00852112494300526 | 0.09821320925694 | 0.08023032831425 | VEGFA||ADAM19||BMP6 | 3 | 4.851608 | 4.892466 | 5.122465 | 4.892498 | 4.745039 | 4.846116 | 4.916848 | 4.869160 | 4.814726 | 4.979183 | 4.901859 | 5.151402 | 5.102502 | 5.134557 | 5.100755 |
| GO:1900274 | regulation of phospholipase C activity | 3/204 | 43/20870 | 0.00852112494300526 | 0.09821320925694 | 0.08023032831425 | LPAR2||ITK||PTAFR | 3 | 5.047222 | 5.330556 | 5.438091 | 5.054808 | 5.004306 | 5.080067 | 5.048678 | 5.357047 | 5.310928 | 5.314886 | 5.338878 | 5.407321 | 5.438352 | 5.441575 | 5.464542 |
| GO:0046632 | alpha-beta T cell differentiation | 5/204 | 128/20870 | 0.00852968318608682 | 0.09821320925694 | 0.08023032831425 | IL23A||ITK||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA | 5 | 5.960693 | 6.116935 | 6.252125 | 5.966932 | 5.979964 | 5.936783 | 5.958753 | 6.142276 | 6.120484 | 6.094553 | 6.110010 | 6.237789 | 6.255356 | 6.272237 | 6.242874 |
| GO:0071706 | tumor necrosis factor superfamily cytokine production | 7/204 | 236/20870 | 0.00870958037277817 | 0.09957335858807 | 0.08134143371665 | IL23A||OAS2||IL1A||IL6||ADAM8||PTAFR||ORM1 | 7 | 6.623338 | 6.655584 | 6.666197 | 6.605558 | 6.629118 | 6.631928 | 6.626596 | 6.669656 | 6.653089 | 6.658259 | 6.641188 | 6.659852 | 6.672495 | 6.662921 | 6.669486 |
| GO:1903555 | regulation of tumor necrosis factor superfamily cytokine production | 7/204 | 236/20870 | 0.00870958037277817 | 0.09957335858807 | 0.08134143371665 | IL23A||OAS2||IL1A||IL6||ADAM8||PTAFR||ORM1 | 7 | 6.623338 | 6.655584 | 6.666197 | 6.605558 | 6.629118 | 6.631928 | 6.626596 | 6.669656 | 6.653089 | 6.658259 | 6.641188 | 6.659852 | 6.672495 | 6.662921 | 6.669486 |
| GO:0070527 | platelet aggregation | 4/204 | 83/20870 | 0.00893194323804185 | 0.10175471731253 | 0.08312338471854 | TYRO3||IL6||SLC7A11||C1QTNF1 | 4 | 8.269893 | 8.348471 | 8.306964 | 8.268450 | 8.269810 | 8.273250 | 8.268058 | 8.356203 | 8.343625 | 8.349908 | 8.344111 | 8.309875 | 8.310223 | 8.307667 | 8.300067 |
| GO:0048675 | axon extension | 5/204 | 130/20870 | 0.00908631329580553 | 0.10207234148509 | 0.08338285176822 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||SEMA6B | 5 | 5.779121 | 6.096581 | 6.083315 | 5.768538 | 5.769262 | 5.821176 | 5.756643 | 6.110228 | 6.106272 | 6.080006 | 6.089610 | 6.130725 | 6.087352 | 6.064812 | 6.049057 |
| GO:0001767 | establishment of lymphocyte polarity | 2/204 | 15/20870 | 0.00918144510877093 | 0.10207234148509 | 0.08338285176822 | RIPOR2||CCR7 | 2 | 6.734973 | 6.514245 | 6.606762 | 6.739697 | 6.794361 | 6.696849 | 6.706970 | 6.544817 | 6.486276 | 6.504740 | 6.520507 | 6.599718 | 6.589063 | 6.575302 | 6.661449 |
| GO:0035672 | oligopeptide transmembrane transport | 2/204 | 15/20870 | 0.00918144510877093 | 0.10207234148509 | 0.08338285176822 | SLC7A11||SLC15A2 | 2 | 5.366803 | 5.061389 | 5.223737 | 5.378808 | 5.307921 | 5.409410 | 5.369200 | 5.052600 | 5.029937 | 5.034317 | 5.126587 | 5.229880 | 5.276016 | 5.198571 | 5.188873 |
| GO:0043320 | natural killer cell degranulation | 2/204 | 15/20870 | 0.00918144510877093 | 0.10207234148509 | 0.08338285176822 | UNC13D||HLA-F | 2 | 7.268111 | 7.382921 | 7.480427 | 7.258637 | 7.278499 | 7.295826 | 7.238849 | 7.329211 | 7.459829 | 7.371523 | 7.367923 | 7.542634 | 7.454857 | 7.482741 | 7.439310 |
| GO:0060026 | convergent extension | 2/204 | 15/20870 | 0.00918144510877093 | 0.10207234148509 | 0.08338285176822 | MKKS||LBX2 | 2 | 5.238987 | 4.779326 | 5.404219 | 5.462703 | 4.692302 | 5.161773 | 5.501763 | 4.320340 | 4.515430 | 4.679009 | 5.370852 | 5.390623 | 5.237743 | 5.040730 | 5.827615 |
| GO:0070234 | positive regulation of T cell apoptotic process | 2/204 | 15/20870 | 0.00918144510877093 | 0.10207234148509 | 0.08338285176822 | IDO1||ADAM8 | 2 | 5.982379 | 7.345048 | 7.920634 | 5.977788 | 5.905611 | 6.008027 | 6.034881 | 7.397751 | 7.358919 | 7.336937 | 7.284257 | 7.882588 | 7.957425 | 7.900299 | 7.940966 |
| GO:0071474 | cellular hyperosmotic response | 2/204 | 15/20870 | 0.00918144510877093 | 0.10207234148509 | 0.08338285176822 | MAPK10||AQP1 | 2 | 5.925469 | 6.609773 | 6.816139 | 5.926673 | 5.920381 | 5.878930 | 5.974303 | 6.769297 | 6.648437 | 6.470492 | 6.532650 | 6.865574 | 7.023178 | 6.691611 | 6.653712 |
| GO:0050878 | regulation of body fluid levels | 10/204 | 425/20870 | 0.00924555339169093 | 0.10243183551482 | 0.08367652228617 | NR1H3||TYRO3||OAS2||VEGFA||PRLR||IL6||ENTPD1||SLC7A11||C1QTNF1||AQP1 | 10 | 7.464846 | 7.545772 | 7.630280 | 7.466975 | 7.475555 | 7.455957 | 7.460823 | 7.540689 | 7.549589 | 7.543038 | 7.549748 | 7.626442 | 7.630149 | 7.628977 | 7.635538 |
| GO:0030500 | regulation of bone mineralization | 4/204 | 84/20870 | 0.00930836440244141 | 0.10245419906158 | 0.08369479105788 | TFAP2A||BMP6||ISG15||ENPP1 | 4 | 5.770025 | 6.284620 | 6.413811 | 5.774023 | 5.761432 | 5.756851 | 5.787594 | 6.285719 | 6.273027 | 6.271988 | 6.307462 | 6.519271 | 6.382466 | 6.373194 | 6.374940 |
| GO:0002367 | cytokine production involved in immune response | 6/204 | 183/20870 | 0.00934290773080138 | 0.10245419906158 | 0.08369479105788 | NR4A3||TREM1||RSAD2||IL6||TNFRSF14||HLA-F | 6 | 7.287478 | 7.454017 | 7.611540 | 7.284063 | 7.282141 | 7.287778 | 7.295890 | 7.463194 | 7.450012 | 7.446416 | 7.456391 | 7.610256 | 7.621887 | 7.608480 | 7.605484 |
| GO:0031960 | response to corticosteroid | 6/204 | 183/20870 | 0.00934290773080138 | 0.10245419906158 | 0.08369479105788 | IL6||IL1RN||BMP6||PTAFR||SSTR2||AQP1 | 6 | 7.809020 | 8.011991 | 8.041704 | 7.816524 | 7.814883 | 7.781620 | 7.822697 | 8.015651 | 7.981480 | 8.022205 | 8.028176 | 8.040623 | 8.033130 | 8.048381 | 8.044637 |
| GO:0002691 | regulation of cellular extravasation | 3/204 | 45/20870 | 0.00965939761430983 | 0.10520911455586 | 0.08594528033785 | RIPOR2||ADAM8||PTAFR | 3 | 5.759084 | 5.763159 | 5.708084 | 5.738329 | 5.814243 | 5.768632 | 5.713159 | 5.776962 | 5.743294 | 5.768251 | 5.763919 | 5.724497 | 5.717232 | 5.682234 | 5.708019 |
| GO:0032733 | positive regulation of interleukin-10 production | 3/204 | 45/20870 | 0.00965939761430983 | 0.10520911455586 | 0.08594528033785 | IL23A||IL6||ISG15 | 3 | 6.123655 | 6.082754 | 6.160663 | 6.112546 | 6.123494 | 6.123148 | 6.135342 | 6.125780 | 6.070320 | 6.091088 | 6.042546 | 6.142285 | 6.178075 | 6.171347 | 6.150647 |
| GO:0002705 | positive regulation of leukocyte mediated immunity | 7/204 | 241/20870 | 0.00970568341449750 | 0.10535731760384 | 0.08606634734387 | IL23A||C3||RSAD2||IL6||PTAFR||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 7 | 7.479918 | 7.446537 | 7.588700 | 7.486951 | 7.465610 | 7.487312 | 7.479691 | 7.447399 | 7.445292 | 7.447424 | 7.446031 | 7.582490 | 7.592623 | 7.587584 | 7.592078 |
| GO:0030522 | intracellular receptor signaling pathway | 8/204 | 302/20870 | 0.00992790894338765 | 0.10704875730261 | 0.08744808370483 | NR1H3||PADI2||NR4A3||PMEPA1||OASL||NR4A2||SLC15A2||IRF7 | 8 | 5.952652 | 5.714175 | 5.713657 | 5.846344 | 5.906851 | 5.991911 | 6.056584 | 5.707049 | 5.776987 | 5.658098 | 5.712085 | 5.722753 | 5.670240 | 5.715672 | 5.744942 |
| GO:1903532 | positive regulation of secretion by cell | 8/204 | 302/20870 | 0.00992790894338765 | 0.10704875730261 | 0.08744808370483 | UNC13D||IL1A||ANKRD1||ADAM8||BMP6||PTAFR||C1QTNF1||HLA-F | 8 | 6.813598 | 7.254527 | 7.297597 | 6.803873 | 6.829614 | 6.799931 | 6.820767 | 7.241886 | 7.236237 | 7.262104 | 7.277504 | 7.300749 | 7.301649 | 7.309540 | 7.278264 |
| GO:0045621 | positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation | 5/204 | 133/20870 | 0.00996751428834306 | 0.10711755355206 | 0.08750428333135 | IL23A||ADAM8||EGR3||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 5 | 6.186728 | 6.283402 | 6.393304 | 6.184396 | 6.181771 | 6.210609 | 6.169830 | 6.266982 | 6.266984 | 6.305654 | 6.293594 | 6.384878 | 6.393897 | 6.401677 | 6.392714 |
| GO:0030517 | negative regulation of axon extension | 3/204 | 46/20870 | 0.01026011527627292 | 0.10739169652657 | 0.08772823060907 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||SEMA6B | 3 | 4.929389 | 5.000838 | 5.127790 | 4.831987 | 4.949126 | 5.016061 | 4.914295 | 4.949342 | 4.987263 | 5.005162 | 5.059401 | 5.195199 | 5.047593 | 5.232501 | 5.024582 |
| GO:0032620 | interleukin-17 production | 3/204 | 46/20870 | 0.01026011527627292 | 0.10739169652657 | 0.08772823060907 | OSM||IL23A||IL6 | 3 | 4.875735 | 5.794149 | 6.180722 | 4.834963 | 4.802089 | 4.924134 | 4.937185 | 5.811127 | 5.771835 | 5.807963 | 5.785306 | 6.182462 | 6.195109 | 6.189980 | 6.155006 |
| GO:0032660 | regulation of interleukin-17 production | 3/204 | 46/20870 | 0.01026011527627292 | 0.10739169652657 | 0.08772823060907 | OSM||IL23A||IL6 | 3 | 4.875735 | 5.794149 | 6.180722 | 4.834963 | 4.802089 | 4.924134 | 4.937185 | 5.811127 | 5.771835 | 5.807963 | 5.785306 | 6.182462 | 6.195109 | 6.189980 | 6.155006 |
| GO:0060537 | muscle tissue development | 10/204 | 432/20870 | 0.01028960306256449 | 0.10739169652657 | 0.08772823060907 | ASB2||RIPOR2||VEGFA||TBX2||ANKRD1||LY6E||IGF2||DLL1||ALPK2||SCX | 10 | 6.237649 | 6.207868 | 6.183220 | 6.157958 | 6.211851 | 6.265188 | 6.311046 | 6.227633 | 6.234946 | 6.167794 | 6.200135 | 6.194990 | 6.152260 | 6.174392 | 6.210572 |
| GO:0045055 | regulated exocytosis | 7/204 | 244/20870 | 0.01034194197748633 | 0.10739169652657 | 0.08772823060907 | UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3||UNC13A||UNC13C||PTAFR||HLA-F | 7 | 6.302876 | 6.350492 | 6.436217 | 6.296753 | 6.312733 | 6.305871 | 6.296081 | 6.351382 | 6.376586 | 6.346668 | 6.326897 | 6.448015 | 6.428194 | 6.441539 | 6.427008 |
| GO:0002524 | hypersensitivity | 2/204 | 16/20870 | 0.01042605490471945 | 0.10739169652657 | 0.08772823060907 | C3||CCR7 | 2 | 5.731787 | 6.026069 | 6.248126 | 5.679463 | 5.729018 | 5.762303 | 5.754913 | 6.019052 | 6.020780 | 6.099862 | 5.961197 | 6.223083 | 6.232331 | 6.231228 | 6.304351 |
| GO:0002830 | positive regulation of type 2 immune response | 2/204 | 16/20870 | 0.01042605490471945 | 0.10739169652657 | 0.08772823060907 | RSAD2||IL6 | 2 | 6.588866 | 6.853889 | 6.989710 | 6.597722 | 6.594987 | 6.576562 | 6.586096 | 6.841908 | 6.861320 | 6.870537 | 6.841574 | 6.986491 | 6.968001 | 6.994973 | 7.009068 |
| GO:0010919 | regulation of inositol phosphate biosynthetic process | 2/204 | 16/20870 | 0.01042605490471945 | 0.10739169652657 | 0.08772823060907 | MAS1||PTAFR | 2 | 5.718006 | 5.587746 | 5.627047 | 5.703634 | 5.756762 | 5.735979 | 5.674285 | 5.560849 | 5.605777 | 5.607926 | 5.575877 | 5.630875 | 5.582028 | 5.700072 | 5.592214 |
| GO:0021783 | preganglionic parasympathetic fiber development | 2/204 | 16/20870 | 0.01042605490471945 | 0.10739169652657 | 0.08772823060907 | SEMA3F||TFAP2A | 2 | 4.077459 | 5.112486 | 5.346244 | 4.117929 | 4.030313 | 4.145606 | 4.011535 | 5.131231 | 5.159844 | 5.075262 | 5.081901 | 5.361160 | 5.201582 | 5.544047 | 5.254003 |
| GO:0042976 | activation of Janus kinase activity | 2/204 | 16/20870 | 0.01042605490471945 | 0.10739169652657 | 0.08772823060907 | IL23A||PRLR | 2 | 5.772345 | 6.952744 | 7.704637 | 5.744013 | 5.809601 | 5.785868 | 5.748883 | 6.967352 | 6.983567 | 6.941232 | 6.917959 | 7.677748 | 7.718078 | 7.693042 | 7.729112 |
| GO:0048569 | post-embryonic animal organ development | 2/204 | 16/20870 | 0.01042605490471945 | 0.10739169652657 | 0.08772823060907 | VEGFA||MYO7A | 2 | 6.262054 | 7.243498 | 6.923780 | 6.229867 | 6.343917 | 6.409759 | 6.037525 | 7.389842 | 6.955288 | 7.225593 | 7.363391 | 7.348079 | 6.685665 | 6.881246 | 6.671003 |
| GO:2000048 | negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin | 2/204 | 16/20870 | 0.01042605490471945 | 0.10739169652657 | 0.08772823060907 | VEGFA||BMP6 | 2 | 5.747983 | 5.778849 | 6.038419 | 5.835422 | 5.651809 | 5.740559 | 5.758248 | 5.751953 | 5.688209 | 5.850273 | 5.819547 | 6.052230 | 6.048746 | 5.998633 | 6.053341 |
| GO:2000402 | negative regulation of lymphocyte migration | 2/204 | 16/20870 | 0.01042605490471945 | 0.10739169652657 | 0.08772823060907 | RIPOR2||PADI2 | 2 | 5.036168 | 4.974601 | 4.946676 | 4.859458 | 5.071009 | 4.986520 | 5.205666 | 5.050510 | 4.855557 | 4.758408 | 5.194116 | 4.878914 | 5.014601 | 4.994194 | 4.894065 |
| GO:0031018 | endocrine pancreas development | 3/204 | 47/20870 | 0.01088207640478134 | 0.11102472888929 | 0.09069605318042 | IL6||BMP6||DLL1 | 3 | 5.220447 | 5.376914 | 5.111455 | 5.260866 | 5.221087 | 5.122736 | 5.272349 | 5.627950 | 5.402216 | 5.382006 | 5.034482 | 5.132635 | 5.073295 | 5.278432 | 4.941079 |
| GO:0044058 | regulation of digestive system process | 3/204 | 47/20870 | 0.01088207640478134 | 0.11102472888929 | 0.09069605318042 | NR1H3||TYMP||AQP1 | 3 | 4.567004 | 5.096842 | 5.412671 | 4.533179 | 4.608678 | 4.701827 | 4.408427 | 5.075374 | 5.180092 | 4.980379 | 5.143575 | 5.473024 | 5.390034 | 5.353479 | 5.431371 |
| GO:2000403 | positive regulation of lymphocyte migration | 3/204 | 47/20870 | 0.01088207640478134 | 0.11102472888929 | 0.09069605318042 | ADAM8||TNFRSF14||CXCL10 | 3 | 6.291937 | 7.032010 | 7.407349 | 6.297781 | 6.276838 | 6.306987 | 6.285958 | 7.051304 | 7.040173 | 7.024024 | 7.012229 | 7.395224 | 7.424561 | 7.387464 | 7.421786 |
| GO:0002703 | regulation of leukocyte mediated immunity | 9/204 | 371/20870 | 0.01102202512376398 | 0.11209782018617 | 0.09157266099836 | UNC13D||IL23A||C3||RSAD2||IL6||PTAFR||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||PIK3R6 | 9 | 7.073264 | 7.098815 | 7.230841 | 7.077009 | 7.063587 | 7.077136 | 7.075282 | 7.099480 | 7.096186 | 7.101605 | 7.097981 | 7.223873 | 7.236857 | 7.236561 | 7.226025 |
| GO:0071375 | cellular response to peptide hormone stimulus | 8/204 | 308/20870 | 0.01108515926342487 | 0.11238538825560 | 0.09180757523035 | GCLC||NR4A3||MAS1||BCAR3||NR4A2||IGF2||SOCS3||ENPP1 | 8 | 5.869198 | 6.212030 | 6.282201 | 5.899483 | 5.864987 | 5.860027 | 5.851836 | 6.200682 | 6.232350 | 6.227155 | 6.187459 | 6.284584 | 6.271316 | 6.303880 | 6.268755 |
| GO:0001936 | regulation of endothelial cell proliferation | 6/204 | 191/20870 | 0.01137450170830568 | 0.11470385488742 | 0.09370152962268 | TIE1||VEGFA||BMP6||IGF2||SCG2||EGR3 | 6 | 6.113266 | 6.124685 | 6.179434 | 6.072907 | 6.109632 | 6.125935 | 6.143649 | 6.127969 | 6.118327 | 6.101500 | 6.150506 | 6.232740 | 6.151278 | 6.157667 | 6.174610 |
| GO:0002695 | negative regulation of leukocyte activation | 7/204 | 249/20870 | 0.01146916009133584 | 0.11470385488742 | 0.09370152962268 | NR1H3||CST7||TYRO3||RIPOR2||TNFRSF14||PDCD1LG2||HLA-F | 7 | 6.328193 | 6.440371 | 6.481696 | 6.347732 | 6.323586 | 6.322018 | 6.319255 | 6.445277 | 6.453660 | 6.414817 | 6.447417 | 6.475535 | 6.484924 | 6.514777 | 6.450819 |
| GO:0032728 | positive regulation of interferon-beta production | 3/204 | 48/20870 | 0.01152540976205049 | 0.11470385488742 | 0.09370152962268 | OAS2||IRF7||ISG15 | 3 | 5.923571 | 5.867557 | 5.780233 | 6.001191 | 5.893480 | 5.916145 | 5.880373 | 5.858144 | 5.885684 | 5.824393 | 5.900836 | 5.750266 | 5.757130 | 5.878066 | 5.730746 |
| GO:0042398 | cellular modified amino acid biosynthetic process | 3/204 | 48/20870 | 0.01152540976205049 | 0.11470385488742 | 0.09370152962268 | GCLC||CHAC1||SLC7A11 | 3 | 5.463333 | 5.635905 | 5.665958 | 5.456121 | 5.502185 | 5.470077 | 5.423851 | 5.627516 | 5.631891 | 5.618150 | 5.665618 | 5.723884 | 5.585694 | 5.677871 | 5.672946 |
| GO:0060562 | epithelial tube morphogenesis | 9/204 | 374/20870 | 0.01157063065191842 | 0.11470385488742 | 0.09370152962268 | TIE1||ASB2||VEGFA||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||CXCL10||CSF1||DLL1 | 9 | 6.043643 | 6.103935 | 6.138692 | 6.061596 | 6.026406 | 6.029359 | 6.056865 | 6.091754 | 6.085899 | 6.102954 | 6.134643 | 6.162185 | 6.120738 | 6.129919 | 6.141592 |
| GO:0001503 | ossification | 10/204 | 440/20870 | 0.01159037090888420 | 0.11470385488742 | 0.09370152962268 | IL6||TFAP2A||BMP6||CREB3L1||IGF2||CSF1||IFITM1||ISG15||ENPP1||SCX | 10 | 6.712685 | 7.184369 | 7.294757 | 6.676108 | 6.691892 | 6.725123 | 6.756290 | 7.180044 | 7.200688 | 7.168587 | 7.187967 | 7.300947 | 7.282735 | 7.292662 | 7.302599 |
| GO:0032946 | positive regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation | 6/204 | 192/20870 | 0.01164871950839968 | 0.11470385488742 | 0.09370152962268 | IL23A||IL1A||IL6||IGF2||CSF1||PDCD1LG2 | 6 | 6.499729 | 7.085221 | 7.284716 | 6.489001 | 6.505578 | 6.503048 | 6.501232 | 7.092848 | 7.082118 | 7.085875 | 7.080012 | 7.296786 | 7.284679 | 7.272267 | 7.285029 |
| GO:0001780 | neutrophil homeostasis | 2/204 | 17/20870 | 0.01174077919133070 | 0.11470385488742 | 0.09370152962268 | IL6||SLC7A11 | 2 | 5.351840 | 5.318037 | 5.182900 | 5.357747 | 5.394840 | 5.336179 | 5.317443 | 5.339884 | 5.307906 | 5.294706 | 5.329219 | 5.172598 | 5.222743 | 5.182758 | 5.152592 |
| GO:0001921 | positive regulation of receptor recycling | 2/204 | 17/20870 | 0.01174077919133070 | 0.11470385488742 | 0.09370152962268 | ECE1||INPP5F | 2 | 5.947446 | 6.708350 | 6.924641 | 5.954703 | 5.878501 | 6.040934 | 5.910440 | 6.688817 | 6.792812 | 6.618533 | 6.727716 | 7.013368 | 6.803827 | 6.937055 | 6.936505 |
| GO:0006857 | oligopeptide transport | 2/204 | 17/20870 | 0.01174077919133070 | 0.11470385488742 | 0.09370152962268 | SLC7A11||SLC15A2 | 2 | 5.326397 | 4.975580 | 5.115115 | 5.316962 | 5.252942 | 5.326138 | 5.405469 | 5.017942 | 4.918062 | 4.930329 | 5.032391 | 5.120711 | 5.155368 | 5.097678 | 5.085722 |
| GO:0045651 | positive regulation of macrophage differentiation | 2/204 | 17/20870 | 0.01174077919133070 | 0.11470385488742 | 0.09370152962268 | LIF||CSF1 | 2 | 6.345269 | 6.535947 | 6.590476 | 6.315869 | 6.372249 | 6.306151 | 6.385173 | 6.539873 | 6.505117 | 6.569024 | 6.529043 | 6.609510 | 6.588643 | 6.617849 | 6.544798 |
| GO:0098969 | neurotransmitter receptor transport to postsynaptic membrane | 2/204 | 17/20870 | 0.01174077919133070 | 0.11470385488742 | 0.09370152962268 | MAPK10||TAMALIN | 2 | 4.941490 | 4.597417 | 4.696665 | 5.013505 | 4.960275 | 4.944620 | 4.842272 | 4.604700 | 4.532657 | 4.578109 | 4.670726 | 4.810046 | 4.661514 | 4.742924 | 4.560168 |
| GO:0002720 | positive regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response | 5/204 | 139/20870 | 0.01190255515804737 | 0.11593304480225 | 0.09470565433434 | NR4A3||RSAD2||IL6||TNFRSF14||HLA-F | 5 | 7.615110 | 7.716009 | 7.866412 | 7.616677 | 7.609552 | 7.613838 | 7.620351 | 7.722717 | 7.719775 | 7.707229 | 7.714268 | 7.865143 | 7.872912 | 7.865184 | 7.862387 |
| GO:0031346 | positive regulation of cell projection organization | 9/204 | 376/20870 | 0.01194757214751690 | 0.11602100181806 | 0.09477750638265 | CDKL3||CDKL5||SCARF1||RIPOR2||VEGFA||RREB1||CCR7||ANKRD1||GPRASP2 | 9 | 6.097707 | 6.118417 | 6.121833 | 6.074718 | 6.097595 | 6.123565 | 6.094532 | 6.103200 | 6.126920 | 6.116917 | 6.126502 | 6.129474 | 6.115664 | 6.128289 | 6.113837 |
| GO:1903706 | regulation of hemopoiesis | 10/204 | 444/20870 | 0.01228574066972392 | 0.11894663038796 | 0.09716745110052 | IL23A||LIF||ADAM8||EGR3||CSF1||IRF7||ISG15||DLL1||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 10 | 6.491344 | 6.471937 | 6.500250 | 6.493742 | 6.486044 | 6.508227 | 6.477183 | 6.470828 | 6.476811 | 6.473327 | 6.466764 | 6.511073 | 6.496826 | 6.501062 | 6.491970 |
| GO:2001234 | negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | 7/204 | 253/20870 | 0.01243306392525764 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | GCLC||MEIS3||IL1A||IFI6||NR4A2||CREB3L1||SCG2 | 7 | 6.815446 | 7.233419 | 7.423857 | 6.808282 | 6.817896 | 6.808706 | 6.826819 | 7.247408 | 7.232476 | 7.226386 | 7.227308 | 7.421444 | 7.427218 | 7.422438 | 7.424321 |
| GO:0046718 | viral entry into host cell | 6/204 | 195/20870 | 0.01249934499660855 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | SIGLEC1||TYRO3||TRIM22||TNFRSF14||LY6E||IFITM1 | 6 | 7.009564 | 7.548432 | 7.729019 | 6.990850 | 7.020449 | 7.007320 | 7.019440 | 7.543839 | 7.524789 | 7.557716 | 7.567034 | 7.702282 | 7.736501 | 7.747486 | 7.729424 |
| GO:0048738 | cardiac muscle tissue development | 7/204 | 254/20870 | 0.01268290053910267 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | ASB2||VEGFA||TBX2||ANKRD1||LY6E||DLL1||ALPK2 | 7 | 5.985579 | 6.073793 | 6.097059 | 5.989234 | 6.003624 | 5.982907 | 5.966304 | 6.101736 | 6.053971 | 6.080963 | 6.057990 | 6.097368 | 6.092846 | 6.096002 | 6.102004 |
| GO:0043303 | mast cell degranulation | 3/204 | 50/20870 | 0.01287665722555269 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3 | 3 | 6.175841 | 6.330756 | 6.388635 | 6.146274 | 6.219992 | 6.136258 | 6.199129 | 6.312298 | 6.317341 | 6.365463 | 6.327319 | 6.426316 | 6.388110 | 6.372339 | 6.367026 |
| GO:0045778 | positive regulation of ossification | 3/204 | 50/20870 | 0.01287665722555269 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | TFAP2A||BMP6||ISG15 | 3 | 5.216938 | 5.671167 | 5.812508 | 5.186478 | 5.175406 | 5.189679 | 5.311830 | 5.664976 | 5.625390 | 5.652354 | 5.739454 | 6.026046 | 5.733032 | 5.723540 | 5.744379 |
| GO:0070169 | positive regulation of biomineral tissue development | 3/204 | 50/20870 | 0.01287665722555269 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | TFAP2A||BMP6||ISG15 | 3 | 5.395484 | 5.825398 | 5.988052 | 5.375158 | 5.340829 | 5.378017 | 5.483894 | 5.805834 | 5.777846 | 5.832373 | 5.883430 | 6.190571 | 5.914312 | 5.895266 | 5.931280 |
| GO:1902930 | regulation of alcohol biosynthetic process | 3/204 | 50/20870 | 0.01287665722555269 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | MAS1||BMP6||PTAFR | 3 | 5.408384 | 5.292439 | 5.333992 | 5.411311 | 5.399270 | 5.430772 | 5.391881 | 5.254458 | 5.297941 | 5.327613 | 5.288801 | 5.341199 | 5.283136 | 5.355318 | 5.355099 |
| GO:0022408 | negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion | 7/204 | 255/20870 | 0.01293633646848527 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | RIPOR2||VEGFA||IL1RN||BMP6||TNFRSF14||C1QTNF1||PDCD1LG2 | 7 | 5.997627 | 6.249814 | 6.351453 | 6.001997 | 6.008790 | 5.989227 | 5.990402 | 6.271760 | 6.250461 | 6.234724 | 6.242042 | 6.338953 | 6.357849 | 6.382736 | 6.325634 |
| GO:0008361 | regulation of cell size | 6/204 | 197/20870 | 0.01309012536828824 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||SEMA6B||AQP1 | 6 | 6.824661 | 7.350700 | 7.323777 | 6.828054 | 6.818838 | 6.834497 | 6.817188 | 7.354405 | 7.357727 | 7.350828 | 7.339776 | 7.344610 | 7.324669 | 7.309593 | 7.315994 |
| GO:0002295 | T-helper cell lineage commitment | 2/204 | 18/20870 | 0.01312414223000540 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | IL23A||IL6 | 2 | 5.276806 | 5.040641 | 5.449066 | 5.307786 | 5.309357 | 5.244313 | 5.244337 | 5.031174 | 5.027947 | 5.143856 | 4.953115 | 5.456676 | 5.430368 | 5.424738 | 5.483719 |
| GO:0007250 | activation of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activity | 2/204 | 18/20870 | 0.01312414223000540 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | MAS1||TNFSF15 | 2 | 7.234015 | 7.214207 | 7.703364 | 7.267607 | 7.201634 | 7.234911 | 7.231148 | 7.210545 | 7.188251 | 7.244098 | 7.213387 | 7.684156 | 7.716129 | 7.702096 | 7.710869 |
| GO:0021756 | striatum development | 2/204 | 18/20870 | 0.01312414223000540 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | MKKS||SLC7A11 | 2 | 4.666160 | 4.194633 | 4.741165 | 4.959659 | 3.796540 | 4.548500 | 5.050672 | 3.840297 | 3.787575 | 3.798839 | 4.963168 | 4.782091 | 4.534767 | 4.272711 | 5.207704 |
| GO:0035743 | CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell cytokine production | 2/204 | 18/20870 | 0.01312414223000540 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | RSAD2||IL6 | 2 | 6.600709 | 7.922506 | 8.388983 | 6.626701 | 6.599524 | 6.585678 | 6.590584 | 7.918833 | 7.917185 | 7.927209 | 7.926770 | 8.383505 | 8.381310 | 8.396979 | 8.394078 |
| GO:0042532 | negative regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | 2/204 | 18/20870 | 0.01312414223000540 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | SOCS3||INPP5F | 2 | 5.341215 | 5.715130 | 5.591127 | 5.266043 | 5.148794 | 5.682060 | 5.203783 | 5.633675 | 5.978695 | 5.638572 | 5.572931 | 5.494829 | 5.642902 | 5.599565 | 5.622755 |
| GO:0048486 | parasympathetic nervous system development | 2/204 | 18/20870 | 0.01312414223000540 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | SEMA3F||TFAP2A | 2 | 4.077459 | 5.112486 | 5.346244 | 4.117929 | 4.030313 | 4.145606 | 4.011535 | 5.131231 | 5.159844 | 5.075262 | 5.081901 | 5.361160 | 5.201582 | 5.544047 | 5.254003 |
| GO:0051447 | negative regulation of meiotic cell cycle | 2/204 | 18/20870 | 0.01312414223000540 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | LIF||FBXO43 | 2 | 4.643743 | 4.744738 | 4.691910 | 4.621967 | 4.594194 | 4.830335 | 4.508743 | 4.784420 | 4.667871 | 4.794679 | 4.728453 | 4.549656 | 4.753018 | 4.637353 | 4.813243 |
| GO:0070230 | positive regulation of lymphocyte apoptotic process | 2/204 | 18/20870 | 0.01312414223000540 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | IDO1||ADAM8 | 2 | 5.946520 | 7.158415 | 7.703125 | 5.973754 | 5.872431 | 5.948900 | 5.988256 | 7.216052 | 7.170553 | 7.146631 | 7.097906 | 7.660485 | 7.736627 | 7.685262 | 7.728770 |
| GO:1903540 | establishment of protein localization to postsynaptic membrane | 2/204 | 18/20870 | 0.01312414223000540 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | MAPK10||TAMALIN | 2 | 4.941490 | 4.597417 | 4.696665 | 5.013505 | 4.960275 | 4.944620 | 4.842272 | 4.604700 | 4.532657 | 4.578109 | 4.670726 | 4.810046 | 4.661514 | 4.742924 | 4.560168 |
| GO:2001135 | regulation of endocytic recycling | 2/204 | 18/20870 | 0.01312414223000540 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | TAMALIN||INPP5F | 2 | 4.622255 | 4.731714 | 4.993392 | 4.470075 | 4.442102 | 5.060420 | 4.409055 | 4.719506 | 4.725555 | 4.772105 | 4.708876 | 4.949009 | 5.050422 | 4.906062 | 5.062008 |
| GO:0051781 | positive regulation of cell division | 4/204 | 93/20870 | 0.01316634332004548 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | OSM||VEGFA||IL1A||IGF2 | 4 | 7.019321 | 7.618444 | 7.709894 | 7.031930 | 7.013600 | 7.010033 | 7.021624 | 7.626105 | 7.610421 | 7.611601 | 7.625572 | 7.701833 | 7.718304 | 7.696785 | 7.722493 |
| GO:0060191 | regulation of lipase activity | 4/204 | 93/20870 | 0.01316634332004548 | 0.11991042616900 | 0.09795477545868 | NR1H3||LPAR2||ITK||PTAFR | 4 | 7.107701 | 7.059619 | 7.142912 | 7.116355 | 7.094994 | 7.107962 | 7.111406 | 7.091189 | 7.037806 | 7.036435 | 7.072292 | 7.117030 | 7.153981 | 7.141198 | 7.159076 |
| GO:0032147 | activation of protein kinase activity | 5/204 | 143/20870 | 0.01332561937463896 | 0.12101914609531 | 0.09886048828865 | IL23A||VEGFA||PRLR||MAS1||TNFSF15 | 5 | 6.334045 | 6.510020 | 6.748241 | 6.337533 | 6.334136 | 6.328275 | 6.336221 | 6.523206 | 6.482656 | 6.511207 | 6.522639 | 6.732452 | 6.750855 | 6.758414 | 6.751116 |
| GO:0002279 | mast cell activation involved in immune response | 3/204 | 51/20870 | 0.01358477858678822 | 0.12268158589301 | 0.10021853464291 | UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3 | 3 | 6.175841 | 6.330756 | 6.388635 | 6.146274 | 6.219992 | 6.136258 | 6.199129 | 6.312298 | 6.317341 | 6.365463 | 6.327319 | 6.426316 | 6.388110 | 6.372339 | 6.367026 |
| GO:0110151 | positive regulation of biomineralization | 3/204 | 51/20870 | 0.01358477858678822 | 0.12268158589301 | 0.10021853464291 | TFAP2A||BMP6||ISG15 | 3 | 5.395484 | 5.825398 | 5.988052 | 5.375158 | 5.340829 | 5.378017 | 5.483894 | 5.805834 | 5.777846 | 5.832373 | 5.883430 | 6.190571 | 5.914312 | 5.895266 | 5.931280 |
| GO:0010977 | negative regulation of neuron projection development | 5/204 | 144/20870 | 0.01369853954301055 | 0.12336338404097 | 0.10077549525614 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||BCL11A||SEMA6B||INPP5F | 5 | 7.752259 | 8.283966 | 8.315068 | 7.737850 | 7.756592 | 7.753428 | 7.761059 | 8.286114 | 8.258898 | 8.295142 | 8.295404 | 8.303646 | 8.315670 | 8.326354 | 8.314512 |
| GO:0001101 | response to acid chemical | 5/204 | 145/20870 | 0.01407843169043324 | 0.12575082121930 | 0.10272579165819 | GCLC||MAPK10||VEGFA||BCL11A||MEAK7 | 5 | 6.153207 | 6.325818 | 6.373629 | 6.170058 | 6.149815 | 6.143530 | 6.149286 | 6.322204 | 6.338808 | 6.321366 | 6.320817 | 6.373810 | 6.376725 | 6.371241 | 6.372735 |
| GO:0043367 | CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation | 4/204 | 95/20870 | 0.01414270655089108 | 0.12575082121930 | 0.10272579165819 | IL23A||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA | 4 | 5.514606 | 5.950347 | 6.203350 | 5.514968 | 5.509300 | 5.528353 | 5.505698 | 5.961070 | 5.946956 | 5.951124 | 5.942170 | 6.201356 | 6.215408 | 6.187318 | 6.209164 |
| GO:0002448 | mast cell mediated immunity | 3/204 | 52/20870 | 0.01431468715492669 | 0.12575082121930 | 0.10272579165819 | UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3 | 3 | 6.101107 | 6.252720 | 6.311006 | 6.071178 | 6.145388 | 6.062700 | 6.123485 | 6.234562 | 6.238867 | 6.287387 | 6.249462 | 6.348695 | 6.309917 | 6.295751 | 6.288913 |
| GO:0006509 | membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis | 3/204 | 52/20870 | 0.01431468715492669 | 0.12575082121930 | 0.10272579165819 | ADAM19||MMP7||ADAM8 | 3 | 6.906476 | 7.286239 | 7.620515 | 6.914053 | 6.872464 | 6.907095 | 6.931652 | 7.294412 | 7.265060 | 7.298403 | 7.286852 | 7.615938 | 7.620628 | 7.626124 | 7.619352 |
| GO:0021545 | cranial nerve development | 3/204 | 52/20870 | 0.01431468715492669 | 0.12575082121930 | 0.10272579165819 | SEMA3F||ATP8B1||TFAP2A | 3 | 6.985456 | 7.020090 | 6.989089 | 6.999540 | 6.963420 | 6.996885 | 6.981693 | 7.024618 | 6.984697 | 7.002595 | 7.067131 | 6.976361 | 6.948932 | 7.017151 | 7.012832 |
| GO:0031295 | T cell costimulation | 3/204 | 52/20870 | 0.01431468715492669 | 0.12575082121930 | 0.10272579165819 | CCR7||TNFRSF14||PDCD1LG2 | 3 | 7.182266 | 8.312244 | 8.467593 | 7.116045 | 7.225266 | 7.142977 | 7.240895 | 8.311307 | 8.244887 | 8.328887 | 8.361404 | 8.416384 | 8.469725 | 8.506001 | 8.476816 |
| GO:0045058 | T cell selection | 3/204 | 52/20870 | 0.01431468715492669 | 0.12575082121930 | 0.10272579165819 | IL23A||CCR7||IL6 | 3 | 6.107984 | 6.495746 | 6.753945 | 6.117611 | 6.114680 | 6.093755 | 6.105772 | 6.496879 | 6.535857 | 6.469469 | 6.479891 | 6.747602 | 6.761850 | 6.738915 | 6.767238 |
| GO:0071622 | regulation of granulocyte chemotaxis | 3/204 | 52/20870 | 0.01431468715492669 | 0.12575082121930 | 0.10272579165819 | RIPOR2||CCR7||CSF1 | 3 | 5.614424 | 7.047197 | 7.399781 | 5.597395 | 5.627873 | 5.627832 | 5.604334 | 7.054750 | 7.049132 | 7.054644 | 7.030122 | 7.397294 | 7.408564 | 7.393420 | 7.399803 |
| GO:0072583 | clathrin-dependent endocytosis | 3/204 | 52/20870 | 0.01431468715492669 | 0.12575082121930 | 0.10272579165819 | SIGLEC1||DLL1||INPP5F | 3 | 6.003525 | 5.926088 | 5.817089 | 6.007806 | 6.005886 | 6.036701 | 5.962745 | 5.935122 | 5.939291 | 5.899070 | 5.930520 | 5.853698 | 5.780899 | 5.781834 | 5.850197 |
| GO:0002709 | regulation of T cell mediated immunity | 5/204 | 146/20870 | 0.01446534974144222 | 0.12665445056127 | 0.10346396607820 | IL23A||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 5 | 7.338600 | 7.381863 | 7.566192 | 7.347790 | 7.326033 | 7.339127 | 7.341365 | 7.389565 | 7.380533 | 7.371402 | 7.385889 | 7.558374 | 7.570219 | 7.563848 | 7.572285 |
| GO:0016082 | synaptic vesicle priming | 2/204 | 19/20870 | 0.01457469018555602 | 0.12665445056127 | 0.10346396607820 | UNC13A||UNC13C | 2 | 4.531569 | 4.223391 | 4.435710 | 4.303379 | 4.663800 | 4.594942 | 4.539343 | 4.141094 | 4.410936 | 4.254900 | 4.062615 | 4.766029 | 4.241884 | 4.232356 | 4.435557 |
| GO:0048791 | calcium ion-regulated exocytosis of neurotransmitter | 2/204 | 19/20870 | 0.01457469018555602 | 0.12665445056127 | 0.10346396607820 | UNC13A||UNC13C | 2 | 4.247731 | 4.494508 | 4.592804 | 4.274309 | 4.238411 | 4.256067 | 4.221602 | 4.412503 | 4.618486 | 4.553281 | 4.380381 | 4.564744 | 4.557995 | 4.599260 | 4.647467 |
| GO:0098877 | neurotransmitter receptor transport to plasma membrane | 2/204 | 19/20870 | 0.01457469018555602 | 0.12665445056127 | 0.10346396607820 | MAPK10||TAMALIN | 2 | 4.947108 | 4.790621 | 4.868467 | 5.019105 | 4.976028 | 4.931151 | 4.857197 | 4.782443 | 4.735815 | 4.711009 | 4.923679 | 4.965847 | 4.812952 | 4.909054 | 4.778261 |
| GO:0044409 | entry into host | 6/204 | 202/20870 | 0.01465222933568449 | 0.12698598757593 | 0.10373479852259 | SIGLEC1||TYRO3||TRIM22||TNFRSF14||LY6E||IFITM1 | 6 | 6.963782 | 7.570005 | 7.761065 | 6.946249 | 6.973817 | 6.961391 | 6.973498 | 7.566539 | 7.544129 | 7.582557 | 7.586412 | 7.737420 | 7.769336 | 7.778784 | 7.758391 |
| GO:0010720 | positive regulation of cell development | 8/204 | 325/20870 | 0.01490543314624673 | 0.12883409239544 | 0.10524451455315 | CDKL3||CDKL5||UNC13D||VEGFA||RREB1||LIF||IL6||GPRASP2 | 8 | 6.292204 | 6.499254 | 6.542211 | 6.289023 | 6.288810 | 6.324698 | 6.265668 | 6.498342 | 6.500440 | 6.487930 | 6.510215 | 6.560122 | 6.550220 | 6.533349 | 6.524887 |
| GO:0002686 | negative regulation of leukocyte migration | 3/204 | 53/20870 | 0.01506646282729115 | 0.12918690466805 | 0.10553272674659 | RIPOR2||PADI2||NBL1 | 3 | 5.243829 | 5.921022 | 5.972915 | 5.234779 | 5.247548 | 5.197981 | 5.293395 | 5.939672 | 5.875789 | 5.882870 | 5.983082 | 5.968219 | 6.009292 | 5.972744 | 5.940574 |
| GO:0043300 | regulation of leukocyte degranulation | 3/204 | 53/20870 | 0.01506646282729115 | 0.12918690466805 | 0.10553272674659 | UNC13D||PTAFR||HLA-F | 3 | 7.541638 | 7.407206 | 7.526517 | 7.538806 | 7.544234 | 7.539167 | 7.544336 | 7.401114 | 7.409784 | 7.419500 | 7.398331 | 7.513167 | 7.541168 | 7.545026 | 7.506312 |
| GO:0046427 | positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT | 3/204 | 53/20870 | 0.01506646282729115 | 0.12918690466805 | 0.10553272674659 | IL23A||PRLR||IL6 | 3 | 5.725356 | 6.486721 | 6.943779 | 5.662405 | 5.787917 | 5.679746 | 5.767295 | 6.485419 | 6.523527 | 6.504987 | 6.431309 | 6.907455 | 6.966530 | 6.939927 | 6.960466 |
| GO:0034121 | regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 4/204 | 97/20870 | 0.01516383532946827 | 0.12933387593176 | 0.10565278750858 | NR1H3||TYRO3||RSAD2||IRF7 | 4 | 6.500946 | 6.470880 | 6.507974 | 6.463998 | 6.523264 | 6.493287 | 6.522411 | 6.481338 | 6.471824 | 6.468069 | 6.462222 | 6.482349 | 6.501525 | 6.553100 | 6.493899 |
| GO:0045445 | myoblast differentiation | 4/204 | 97/20870 | 0.01516383532946827 | 0.12933387593176 | 0.10565278750858 | RIPOR2||TBX2||CXCL10||DLL1 | 4 | 7.149672 | 7.798108 | 7.936254 | 6.911815 | 7.096606 | 7.198732 | 7.355714 | 7.794604 | 7.809171 | 7.752359 | 7.835057 | 7.938778 | 7.877698 | 7.960711 | 7.966134 |
| GO:0010721 | negative regulation of cell development | 6/204 | 204/20870 | 0.01531191235795855 | 0.12956851822063 | 0.10584446669322 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||VEGFA||BCL11A||IL6||SEMA6B | 6 | 7.368388 | 7.770591 | 7.822686 | 7.373570 | 7.358970 | 7.369136 | 7.371833 | 7.780174 | 7.768816 | 7.769639 | 7.763687 | 7.822047 | 7.821267 | 7.829588 | 7.817817 |
| GO:0055001 | muscle cell development | 6/204 | 204/20870 | 0.01531191235795855 | 0.12956851822063 | 0.10584446669322 | ASB2||RIPOR2||VEGFA||ANKRD1||OBSCN||ALPK2 | 6 | 6.420787 | 6.557195 | 6.527652 | 6.429272 | 6.410019 | 6.426920 | 6.416855 | 6.556308 | 6.549533 | 6.571219 | 6.551618 | 6.485159 | 6.545349 | 6.542804 | 6.536461 |
| GO:0070665 | positive regulation of leukocyte proliferation | 6/204 | 204/20870 | 0.01531191235795855 | 0.12956851822063 | 0.10584446669322 | IL23A||IL1A||IL6||IGF2||CSF1||PDCD1LG2 | 6 | 6.465650 | 7.081973 | 7.284519 | 6.452772 | 6.473916 | 6.470602 | 6.465220 | 7.089399 | 7.079571 | 7.082400 | 7.076491 | 7.295635 | 7.285329 | 7.274622 | 7.282410 |
| GO:0031349 | positive regulation of defense response | 9/204 | 393/20870 | 0.01553249043359939 | 0.13109096638200 | 0.10708815394011 | OSM||IL23A||C3||CCR7||IL6||PLA2G7||ADAM8||IRF7||HLA-F | 9 | 6.666897 | 6.862931 | 6.986268 | 6.669884 | 6.655852 | 6.670364 | 6.671431 | 6.864474 | 6.870248 | 6.859265 | 6.857704 | 6.993580 | 6.986632 | 6.985856 | 6.978968 |
| GO:0001935 | endothelial cell proliferation | 6/204 | 205/20870 | 0.01564936565410679 | 0.13166841237589 | 0.10755986932365 | TIE1||VEGFA||BMP6||IGF2||SCG2||EGR3 | 6 | 6.464006 | 6.423099 | 6.490990 | 6.433776 | 6.454320 | 6.486170 | 6.481138 | 6.415997 | 6.419909 | 6.418189 | 6.438194 | 6.524657 | 6.475448 | 6.479647 | 6.483664 |
| GO:2000117 | negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | 4/204 | 98/20870 | 0.01569138067978771 | 0.13166841237589 | 0.10755986932365 | CST7||VEGFA||IFI6||AQP1 | 4 | 6.327927 | 7.125131 | 7.563158 | 6.340417 | 6.319821 | 6.333062 | 6.318289 | 7.112274 | 7.129173 | 7.117603 | 7.141299 | 7.541698 | 7.567590 | 7.566555 | 7.576559 |
| GO:0031294 | lymphocyte costimulation | 3/204 | 54/20870 | 0.01584017641625803 | 0.13166841237589 | 0.10755986932365 | CCR7||TNFRSF14||PDCD1LG2 | 3 | 7.140886 | 8.269096 | 8.424221 | 7.074672 | 7.184157 | 7.101248 | 7.199566 | 8.268206 | 8.201557 | 8.285662 | 8.318454 | 8.373094 | 8.426261 | 8.462759 | 8.433327 |
| GO:1903202 | negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced cell death | 3/204 | 54/20870 | 0.01584017641625803 | 0.13166841237589 | 0.10755986932365 | NR4A3||MEAK7||SLC7A11 | 3 | 7.347866 | 7.232588 | 7.152716 | 7.337780 | 7.353952 | 7.343112 | 7.356538 | 7.253850 | 7.211207 | 7.213491 | 7.251240 | 7.147751 | 7.147702 | 7.166678 | 7.148643 |
| GO:0002864 | regulation of acute inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus | 2/204 | 20/20870 | 0.01609099084246326 | 0.13166841237589 | 0.10755986932365 | C3||CCR7 | 2 | 6.131732 | 6.502103 | 6.582760 | 6.118627 | 6.139623 | 6.121010 | 6.147462 | 6.467138 | 6.458650 | 6.490596 | 6.588289 | 6.582560 | 6.535012 | 6.613553 | 6.598713 |
| GO:0032793 | positive regulation of CREB transcription factor activity | 2/204 | 20/20870 | 0.01609099084246326 | 0.13166841237589 | 0.10755986932365 | RPS6KA5||VEGFA | 2 | 5.023928 | 4.590887 | 4.955732 | 4.930178 | 4.825575 | 5.066218 | 5.240073 | 4.628371 | 4.496790 | 4.585236 | 4.648482 | 5.196897 | 4.879778 | 4.777315 | 4.934907 |
| GO:0043031 | negative regulation of macrophage activation | 2/204 | 20/20870 | 0.01609099084246326 | 0.13166841237589 | 0.10755986932365 | NR1H3||CST7 | 2 | 6.893245 | 6.050031 | 6.222192 | 6.907578 | 6.885190 | 6.901596 | 6.878423 | 6.108693 | 5.990077 | 6.036638 | 6.062165 | 6.200006 | 6.211192 | 6.216567 | 6.260273 |
| GO:0043117 | positive regulation of vascular permeability | 2/204 | 20/20870 | 0.01609099084246326 | 0.13166841237589 | 0.10755986932365 | VEGFA||BMP6 | 2 | 5.430123 | 5.867302 | 6.103735 | 5.316165 | 5.456129 | 5.438547 | 5.503128 | 5.888232 | 5.773414 | 5.889556 | 5.913929 | 6.113866 | 6.134758 | 6.086644 | 6.078989 |
| GO:0044320 | cellular response to leptin stimulus | 2/204 | 20/20870 | 0.01609099084246326 | 0.13166841237589 | 0.10755986932365 | NR4A3||MKKS | 2 | 5.262948 | 6.227197 | 6.545675 | 5.444461 | 4.812824 | 5.189700 | 5.505949 | 6.109763 | 6.134681 | 6.195426 | 6.443896 | 6.568677 | 6.480798 | 6.414255 | 6.702677 |
| GO:0051900 | regulation of mitochondrial depolarization | 2/204 | 20/20870 | 0.01609099084246326 | 0.13166841237589 | 0.10755986932365 | GCLC||IFI6 | 2 | 6.989019 | 7.116914 | 7.472577 | 6.993969 | 6.975691 | 6.975585 | 7.010539 | 7.122846 | 7.114001 | 7.092411 | 7.138022 | 7.472528 | 7.498151 | 7.475961 | 7.443136 |
| GO:0071731 | response to nitric oxide | 2/204 | 20/20870 | 0.01609099084246326 | 0.13166841237589 | 0.10755986932365 | CCR7||AQP1 | 2 | 5.850262 | 5.853824 | 5.906735 | 5.816714 | 5.864592 | 5.873211 | 5.845884 | 5.877977 | 5.831082 | 5.847946 | 5.857890 | 5.881253 | 5.921102 | 5.926800 | 5.897319 |
| GO:2000846 | regulation of corticosteroid hormone secretion | 2/204 | 20/20870 | 0.01609099084246326 | 0.13166841237589 | 0.10755986932365 | BMP6||C1QTNF1 | 2 | 4.776408 | 4.338458 | 4.218381 | 4.632586 | 4.625017 | 5.122403 | 4.661551 | 4.241047 | 4.646723 | 4.197675 | 4.218237 | 4.220383 | 4.374363 | 4.125688 | 4.139299 |
| GO:0002275 | myeloid cell activation involved in immune response | 4/204 | 99/20870 | 0.01623034556611425 | 0.13187851253443 | 0.10773150005261 | UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3||PTAFR | 4 | 7.864516 | 7.773410 | 7.768222 | 7.874934 | 7.871046 | 7.859512 | 7.852461 | 7.781936 | 7.764666 | 7.779493 | 7.767466 | 7.759819 | 7.777357 | 7.770891 | 7.764760 |
| GO:0002437 | inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus | 4/204 | 99/20870 | 0.01623034556611425 | 0.13187851253443 | 0.10773150005261 | C3||CCR7||IL36G||IL1RN | 4 | 6.786089 | 6.818603 | 6.869548 | 6.788688 | 6.791068 | 6.785625 | 6.778946 | 6.798850 | 6.794647 | 6.843494 | 6.836759 | 6.879056 | 6.865481 | 6.867425 | 6.866187 |
| GO:0009306 | protein secretion | 9/204 | 396/20870 | 0.01623938259186363 | 0.13187851253443 | 0.10773150005261 | NR1H3||IL1A||RSAD2||IL6||IL1RN||ANKRD1||ADAM8||BMP6||SCG2 | 9 | 5.742177 | 6.119839 | 6.275706 | 5.733667 | 5.724838 | 5.735883 | 5.773828 | 6.130695 | 6.112294 | 6.117063 | 6.119241 | 6.278155 | 6.282004 | 6.273169 | 6.269464 |
| GO:0031099 | regeneration | 6/204 | 207/20870 | 0.01633967429139410 | 0.13235957265190 | 0.10812447785524 | SCARF1||NR4A3||IL6||SULF2||INPP5F||EPPK1 | 6 | 7.736482 | 7.973425 | 7.975148 | 7.733468 | 7.736395 | 7.740750 | 7.735307 | 7.977339 | 7.969452 | 7.975067 | 7.971828 | 7.973467 | 7.977270 | 7.969857 | 7.979979 |
| GO:0035592 | establishment of protein localization to extracellular region | 9/204 | 397/20870 | 0.01648018442227232 | 0.13242989861367 | 0.10818192710311 | NR1H3||IL1A||RSAD2||IL6||IL1RN||ANKRD1||ADAM8||BMP6||SCG2 | 9 | 5.742177 | 6.119839 | 6.275706 | 5.733667 | 5.724838 | 5.735883 | 5.773828 | 6.130695 | 6.112294 | 6.117063 | 6.119241 | 6.278155 | 6.282004 | 6.273169 | 6.269464 |
| GO:0010675 | regulation of cellular carbohydrate metabolic process | 5/204 | 151/20870 | 0.01650716467301456 | 0.13242989861367 | 0.10818192710311 | MAS1||IGF2||PTAFR||C1QTNF1||ENPP1 | 5 | 5.365206 | 5.399264 | 5.295010 | 5.388048 | 5.390462 | 5.320559 | 5.360659 | 5.436526 | 5.436141 | 5.393640 | 5.328051 | 5.306740 | 5.285787 | 5.333567 | 5.252737 |
| GO:0072006 | nephron development | 5/204 | 151/20870 | 0.01650716467301456 | 0.13242989861367 | 0.10818192710311 | VEGFA||LIF||SERPINB7||SULF2||DLL1 | 5 | 5.001678 | 5.149752 | 5.195884 | 4.983659 | 4.986909 | 5.028245 | 5.007456 | 5.146124 | 5.124102 | 5.125070 | 5.202304 | 5.282959 | 5.180791 | 5.143637 | 5.172263 |
| GO:0002369 | T cell cytokine production | 3/204 | 55/20870 | 0.01663588986927290 | 0.13242989861367 | 0.10818192710311 | RSAD2||IL6||HLA-F | 3 | 8.141697 | 8.135255 | 8.324739 | 8.152936 | 8.127606 | 8.138644 | 8.147474 | 8.146610 | 8.129612 | 8.124857 | 8.139842 | 8.318101 | 8.329585 | 8.321506 | 8.329729 |
| GO:0002724 | regulation of T cell cytokine production | 3/204 | 55/20870 | 0.01663588986927290 | 0.13242989861367 | 0.10818192710311 | RSAD2||IL6||HLA-F | 3 | 8.141697 | 8.135255 | 8.324739 | 8.152936 | 8.127606 | 8.138644 | 8.147474 | 8.146610 | 8.129612 | 8.124857 | 8.139842 | 8.318101 | 8.329585 | 8.321506 | 8.329729 |
| GO:0007595 | lactation | 3/204 | 55/20870 | 0.01663588986927290 | 0.13242989861367 | 0.10818192710311 | OAS2||VEGFA||PRLR | 3 | 8.377586 | 8.226688 | 8.591859 | 8.373050 | 8.374554 | 8.389857 | 8.372814 | 8.231675 | 8.205802 | 8.232398 | 8.236674 | 8.596970 | 8.594120 | 8.598137 | 8.578120 |
| GO:0010676 | positive regulation of cellular carbohydrate metabolic process | 3/204 | 55/20870 | 0.01663588986927290 | 0.13242989861367 | 0.10818192710311 | MAS1||IGF2||PTAFR | 3 | 5.041876 | 4.980304 | 4.865896 | 5.063021 | 5.042194 | 5.037712 | 5.024309 | 4.955872 | 5.112348 | 4.898651 | 4.945218 | 4.855306 | 4.861267 | 4.890401 | 4.856323 |
| GO:2001233 | regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | 9/204 | 398/20870 | 0.01672359773197846 | 0.13280019479778 | 0.10848442189632 | GCLC||MEIS3||IL1A||TNFSF10||G0S2||IFI6||NR4A2||CREB3L1||SCG2 | 9 | 7.078580 | 7.295578 | 7.372311 | 7.072281 | 7.089881 | 7.074178 | 7.077914 | 7.307049 | 7.293703 | 7.292375 | 7.289122 | 7.369889 | 7.373619 | 7.367315 | 7.378395 |
| GO:0043255 | regulation of carbohydrate biosynthetic process | 4/204 | 100/20870 | 0.01678080134028341 | 0.13292703567831 | 0.10858803815696 | MAS1||IGF2||PTAFR||ENPP1 | 4 | 5.490983 | 5.532621 | 5.447122 | 5.513267 | 5.499606 | 5.435771 | 5.513863 | 5.585300 | 5.586582 | 5.529984 | 5.422525 | 5.475989 | 5.434460 | 5.492659 | 5.382901 |
| GO:0018105 | peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | 8/204 | 333/20870 | 0.01700130080188438 | 0.13434361221881 | 0.10974523892238 | OSM||RPS6KA5||DMPK||VEGFA||LIF||IL6||BCAR3||INPP5F | 8 | 5.696622 | 5.877913 | 5.865941 | 5.691937 | 5.702300 | 5.684107 | 5.708026 | 5.891593 | 5.861210 | 5.889192 | 5.869426 | 5.875042 | 5.872262 | 5.885133 | 5.830731 |
| GO:0030225 | macrophage differentiation | 3/204 | 56/20870 | 0.01745365648498882 | 0.13695515826522 | 0.11187860976217 | VEGFA||LIF||CSF1 | 3 | 6.257597 | 7.601574 | 8.065272 | 6.241846 | 6.278126 | 6.246873 | 6.263259 | 7.586710 | 7.618600 | 7.600652 | 7.600156 | 8.055283 | 8.070195 | 8.070476 | 8.065080 |
| GO:0051701 | biological process involved in interaction with host | 7/204 | 271/20870 | 0.01750276704656153 | 0.13695515826522 | 0.11187860976217 | SIGLEC1||TYRO3||TRIM22||TNFRSF14||LY6E||IFIT1||IFITM1 | 7 | 6.813541 | 7.327520 | 7.489966 | 6.797911 | 6.819338 | 6.814197 | 6.822596 | 7.325415 | 7.301972 | 7.341725 | 7.340612 | 7.468064 | 7.493699 | 7.506031 | 7.491808 |
| GO:0001558 | regulation of cell growth | 10/204 | 470/20870 | 0.01760016305057822 | 0.13695515826522 | 0.11187860976217 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||RASAL1||VEGFA||BCL11A||UNC13A||SEMA6B||ST20||ENPP1 | 10 | 6.777105 | 7.041326 | 7.048203 | 6.773361 | 6.774794 | 6.783777 | 6.776466 | 7.040798 | 7.044959 | 7.050341 | 7.029123 | 7.058850 | 7.049910 | 7.039215 | 7.044765 |
| GO:0006309 | apoptotic DNA fragmentation | 2/204 | 21/20870 | 0.01767163332454436 | 0.13695515826522 | 0.11187860976217 | IL6||ST20 | 2 | 4.836157 | 4.813109 | 5.033060 | 4.881399 | 4.591210 | 4.997963 | 4.844230 | 4.719616 | 5.062729 | 4.754881 | 4.682449 | 5.130370 | 5.009745 | 4.980271 | 5.007123 |
| GO:0030449 | regulation of complement activation | 2/204 | 21/20870 | 0.01767163332454436 | 0.13695515826522 | 0.11187860976217 | CFH||C3 | 2 | 6.982943 | 7.775467 | 8.204463 | 6.967684 | 6.938871 | 7.004902 | 7.018946 | 7.773668 | 7.763854 | 7.781640 | 7.782625 | 8.208927 | 8.202383 | 8.196963 | 8.209543 |
| GO:0043373 | CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment | 2/204 | 21/20870 | 0.01767163332454436 | 0.13695515826522 | 0.11187860976217 | IL23A||IL6 | 2 | 6.072576 | 6.710187 | 7.182880 | 6.095811 | 6.083034 | 6.046415 | 6.064560 | 6.708877 | 6.712303 | 6.716229 | 6.703307 | 7.178837 | 7.191958 | 7.165751 | 7.194788 |
| GO:0043382 | positive regulation of memory T cell differentiation | 2/204 | 21/20870 | 0.01767163332454436 | 0.13695515826522 | 0.11187860976217 | IL23A||HLA-DRA | 2 | 5.090538 | 5.514804 | 6.157185 | 5.101634 | 5.082837 | 5.079862 | 5.097698 | 5.540707 | 5.513952 | 5.499632 | 5.504577 | 6.203384 | 6.123509 | 6.097680 | 6.201141 |
| GO:0050930 | induction of positive chemotaxis | 2/204 | 21/20870 | 0.01767163332454436 | 0.13695515826522 | 0.11187860976217 | VEGFA||SCG2 | 2 | 5.338691 | 7.095520 | 7.557496 | 5.315716 | 5.382251 | 5.361173 | 5.293912 | 7.100495 | 7.066071 | 7.101473 | 7.113607 | 7.584529 | 7.564674 | 7.567053 | 7.512735 |
| GO:0042102 | positive regulation of T cell proliferation | 5/204 | 154/20870 | 0.01781985439394201 | 0.13777268720880 | 0.11254644880384 | IL23A||IL1A||IL6||IGF2||PDCD1LG2 | 5 | 6.723341 | 7.312114 | 7.524096 | 6.709496 | 6.725721 | 6.731653 | 6.726398 | 7.322835 | 7.311717 | 7.316507 | 7.297273 | 7.514701 | 7.531280 | 7.521976 | 7.528369 |
| GO:0007189 | adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | 5/204 | 155/20870 | 0.01827230974128311 | 0.14093283877009 | 0.11512797525231 | LPAR2||ADGRE3||CXCL10||CXCL11||ADGRE1 | 5 | 5.702701 | 5.494511 | 5.382007 | 5.701634 | 5.658925 | 5.745043 | 5.703916 | 5.489868 | 5.442564 | 5.568634 | 5.473963 | 5.344155 | 5.415593 | 5.434442 | 5.331100 |
| GO:0070167 | regulation of biomineral tissue development | 4/204 | 103/20870 | 0.01850179367677140 | 0.14195037804801 | 0.11595920264990 | TFAP2A||BMP6||ISG15||ENPP1 | 4 | 5.646468 | 6.123353 | 6.249280 | 5.653459 | 5.636137 | 5.633277 | 5.662791 | 6.121930 | 6.110899 | 6.119527 | 6.140891 | 6.347994 | 6.223707 | 6.206922 | 6.213765 |
| GO:0030308 | negative regulation of cell growth | 6/204 | 213/20870 | 0.01853632418058727 | 0.14195037804801 | 0.11595920264990 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||BCL11A||SEMA6B||ST20||ENPP1 | 6 | 7.052177 | 7.441330 | 7.436574 | 7.052722 | 7.048665 | 7.046899 | 7.060386 | 7.454016 | 7.427094 | 7.448119 | 7.435938 | 7.438830 | 7.440390 | 7.444826 | 7.422148 |
| GO:0046631 | alpha-beta T cell activation | 6/204 | 213/20870 | 0.01853632418058727 | 0.14195037804801 | 0.11595920264990 | IL23A||ITK||RSAD2||IL6||TNFRSF14||HLA-DRA | 6 | 6.095098 | 6.398089 | 6.533305 | 6.076253 | 6.108603 | 6.087966 | 6.107315 | 6.413558 | 6.405750 | 6.387427 | 6.385423 | 6.520254 | 6.529949 | 6.541580 | 6.541328 |
| GO:0043524 | negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process | 5/204 | 156/20870 | 0.01873228897872274 | 0.14311113665261 | 0.11690742585374 | GCLC||TYRO3||ADAM8||NR4A2||GPRASP2 | 5 | 6.794216 | 6.759210 | 6.791853 | 6.795511 | 6.805358 | 6.791429 | 6.784487 | 6.765461 | 6.771229 | 6.756534 | 6.743464 | 6.815584 | 6.762908 | 6.792648 | 6.795782 |
| GO:0010518 | positive regulation of phospholipase activity | 3/204 | 58/20870 | 0.01915552042532558 | 0.14481928950049 | 0.11830281517899 | LPAR2||ITK||PTAFR | 3 | 5.654528 | 6.402815 | 6.730213 | 5.637712 | 5.642591 | 5.671074 | 5.666443 | 6.437836 | 6.396792 | 6.397820 | 6.378151 | 6.705741 | 6.742404 | 6.721011 | 6.751253 |
| GO:0046006 | regulation of activated T cell proliferation | 3/204 | 58/20870 | 0.01915552042532558 | 0.14481928950049 | 0.11830281517899 | IL23A||IGF2||PDCD1LG2 | 3 | 6.995556 | 7.134087 | 7.127719 | 6.994221 | 6.995652 | 6.993197 | 6.999146 | 7.155602 | 7.116443 | 7.149663 | 7.114152 | 7.107670 | 7.151293 | 7.141028 | 7.110388 |
| GO:1903307 | positive regulation of regulated secretory pathway | 3/204 | 58/20870 | 0.01915552042532558 | 0.14481928950049 | 0.11830281517899 | UNC13D||PTAFR||HLA-F | 3 | 7.417680 | 7.167955 | 7.289319 | 7.406565 | 7.425838 | 7.418980 | 7.419270 | 7.159061 | 7.153311 | 7.186791 | 7.172425 | 7.277023 | 7.285496 | 7.316582 | 7.277812 |
| GO:1904894 | positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via STAT | 3/204 | 58/20870 | 0.01915552042532558 | 0.14481928950049 | 0.11830281517899 | IL23A||PRLR||IL6 | 3 | 5.883099 | 6.607145 | 7.001051 | 5.817080 | 5.928486 | 5.845836 | 5.937276 | 6.610681 | 6.622384 | 6.631517 | 6.563037 | 6.976271 | 7.024478 | 6.995757 | 7.007271 |
| GO:0060249 | anatomical structure homeostasis | 8/204 | 341/20870 | 0.01930196177498698 | 0.14481928950049 | 0.11830281517899 | TYRO3||VEGFA||MKKS||IL6||ADAM8||CSF1||ABCA4||SCX | 8 | 7.373075 | 7.683837 | 7.739456 | 7.386480 | 7.363548 | 7.369312 | 7.372861 | 7.692763 | 7.673219 | 7.681359 | 7.687931 | 7.743822 | 7.749470 | 7.731455 | 7.732999 |
| GO:0014821 | phasic smooth muscle contraction | 2/204 | 22/20870 | 0.01931522781799273 | 0.14481928950049 | 0.11830281517899 | TBX2||SSTR2 | 2 | 3.488398 | 3.143634 | 2.965806 | 2.998897 | 3.121637 | 4.308482 | 3.066995 | 2.780556 | 3.671586 | 3.156202 | 2.770058 | 2.983769 | 3.379684 | 2.632662 | 2.750567 |
| GO:0043576 | regulation of respiratory gaseous exchange | 2/204 | 22/20870 | 0.01931522781799273 | 0.14481928950049 | 0.11830281517899 | MTG1||NR4A2 | 2 | 4.869987 | 4.570612 | 4.309606 | 4.780696 | 4.957194 | 4.771414 | 4.959141 | 4.588739 | 4.662113 | 4.524794 | 4.501366 | 4.300746 | 4.276972 | 4.331133 | 4.328889 |
| GO:1903978 | regulation of microglial cell activation | 2/204 | 22/20870 | 0.01931522781799273 | 0.14481928950049 | 0.11830281517899 | CST7||IL6 | 2 | 7.834352 | 7.651241 | 7.643217 | 7.840944 | 7.843477 | 7.838891 | 7.813899 | 7.684312 | 7.634767 | 7.646934 | 7.638411 | 7.617858 | 7.650380 | 7.650802 | 7.653529 |
| GO:0032868 | response to insulin | 7/204 | 277/20870 | 0.01947659164114783 | 0.14569032819272 | 0.11901436631128 | GCLC||TNFSF10||BCAR3||MEAK7||IGF2||SOCS3||ENPP1 | 7 | 5.611671 | 6.056072 | 6.161850 | 5.670777 | 5.595986 | 5.580421 | 5.597785 | 6.068491 | 6.078060 | 6.050065 | 6.027149 | 6.178164 | 6.169508 | 6.170918 | 6.128284 |
| GO:0110149 | regulation of biomineralization | 4/204 | 105/20870 | 0.01970778300880283 | 0.14707845467681 | 0.12014832623788 | TFAP2A||BMP6||ISG15||ENPP1 | 4 | 5.646468 | 6.123353 | 6.249280 | 5.653459 | 5.636137 | 5.633277 | 5.662791 | 6.121930 | 6.110899 | 6.119527 | 6.140891 | 6.347994 | 6.223707 | 6.206922 | 6.213765 |
| GO:1902105 | regulation of leukocyte differentiation | 8/204 | 343/20870 | 0.01991028086893037 | 0.14818334398442 | 0.12105090983708 | IL23A||LIF||ADAM8||EGR3||CSF1||IRF7||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 8 | 6.211933 | 6.325525 | 6.369325 | 6.211381 | 6.201776 | 6.229899 | 6.204507 | 6.326113 | 6.324473 | 6.330767 | 6.320728 | 6.357712 | 6.372746 | 6.382579 | 6.364141 |
| GO:0002920 | regulation of humoral immune response | 3/204 | 59/20870 | 0.02003968299541138 | 0.14818334398442 | 0.12105090983708 | CFH||C3||CCR7 | 3 | 6.347585 | 7.173142 | 7.557957 | 6.323986 | 6.316016 | 6.358235 | 6.390870 | 7.168830 | 7.153014 | 7.180426 | 7.190034 | 7.561245 | 7.551538 | 7.558388 | 7.560635 |
| GO:0006953 | acute-phase response | 3/204 | 59/20870 | 0.02003968299541138 | 0.14818334398442 | 0.12105090983708 | IL1A||IL6||ORM1 | 3 | 4.477817 | 6.283921 | 6.888269 | 4.487096 | 4.554332 | 4.435619 | 4.430753 | 6.264953 | 6.262098 | 6.279962 | 6.327707 | 6.895921 | 6.878363 | 6.897119 | 6.881575 |
| GO:0007566 | embryo implantation | 3/204 | 59/20870 | 0.02003968299541138 | 0.14818334398442 | 0.12105090983708 | VEGFA||PRLR||LIF | 3 | 8.632078 | 9.346680 | 9.559276 | 8.633365 | 8.637192 | 8.629107 | 8.628630 | 9.344852 | 9.338694 | 9.354106 | 9.349024 | 9.552029 | 9.564920 | 9.558990 | 9.561135 |
| GO:0006898 | receptor-mediated endocytosis | 7/204 | 280/20870 | 0.02051980119102859 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | SCARF1||SIGLEC1||VEGFA||C3||DLL1||ANKRD13B||INPP5F | 7 | 7.972519 | 7.873559 | 7.805430 | 7.978061 | 7.973798 | 7.969733 | 7.968464 | 7.878396 | 7.868358 | 7.864981 | 7.882431 | 7.799562 | 7.811251 | 7.803320 | 7.807560 |
| GO:0003158 | endothelium development | 5/204 | 160/20870 | 0.02064834271317039 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | TIE1||VEGFA||BMP6||CXCL10||DLL1 | 5 | 6.124621 | 6.380350 | 6.538615 | 6.128285 | 6.122771 | 6.131186 | 6.116196 | 6.396850 | 6.369503 | 6.370766 | 6.384110 | 6.535534 | 6.543536 | 6.539911 | 6.535465 |
| GO:1903531 | negative regulation of secretion by cell | 5/204 | 160/20870 | 0.02064834271317039 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | NR1H3||OSM||LIF||RSAD2||HLA-F | 5 | 5.678927 | 6.190605 | 6.364650 | 5.651743 | 5.661294 | 5.718916 | 5.682827 | 6.192159 | 6.196059 | 6.181747 | 6.192416 | 6.359174 | 6.388597 | 6.360069 | 6.350475 |
| GO:0002708 | positive regulation of lymphocyte mediated immunity | 6/204 | 219/20870 | 0.02092720184243188 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | IL23A||C3||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 6 | 7.105533 | 7.147672 | 7.320474 | 7.113305 | 7.086217 | 7.112538 | 7.109900 | 7.149311 | 7.140883 | 7.147175 | 7.153291 | 7.316640 | 7.321805 | 7.314959 | 7.328452 |
| GO:0001954 | positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion | 3/204 | 60/20870 | 0.02094602962518693 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | VEGFA||CCR7||CSF1 | 3 | 5.961514 | 6.209230 | 6.051735 | 5.954466 | 5.961055 | 6.006645 | 5.922641 | 6.250579 | 6.288437 | 6.162690 | 6.129494 | 6.175614 | 6.019959 | 5.998299 | 6.005538 |
| GO:0045661 | regulation of myoblast differentiation | 3/204 | 60/20870 | 0.02094602962518693 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | RIPOR2||CXCL10||DLL1 | 3 | 6.351379 | 6.373360 | 6.336127 | 6.318799 | 6.379252 | 6.360019 | 6.346776 | 6.383493 | 6.346653 | 6.360050 | 6.402604 | 6.463813 | 6.270487 | 6.288219 | 6.313736 |
| GO:0002363 | alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment | 2/204 | 23/20870 | 0.02102040529775134 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | IL23A||IL6 | 2 | 6.529438 | 6.937691 | 7.276676 | 6.545635 | 6.534691 | 6.506522 | 6.530620 | 6.948233 | 6.936205 | 6.932768 | 6.933504 | 7.269991 | 7.284146 | 7.261339 | 7.291039 |
| GO:0010866 | regulation of triglyceride biosynthetic process | 2/204 | 23/20870 | 0.02102040529775134 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | NR1H3||C3 | 2 | 5.753788 | 6.342248 | 6.718601 | 5.700473 | 5.696876 | 5.848376 | 5.764139 | 6.264485 | 6.376490 | 6.427778 | 6.294401 | 6.704573 | 6.736106 | 6.689974 | 6.743085 |
| GO:0033081 | regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus | 2/204 | 23/20870 | 0.02102040529775134 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | ADAM8||EGR3 | 2 | 4.962352 | 4.803126 | 4.541773 | 5.062572 | 4.917952 | 4.972158 | 4.890704 | 4.893675 | 5.087911 | 4.601432 | 4.564353 | 4.477336 | 4.492549 | 4.514897 | 4.673603 |
| GO:0035930 | corticosteroid hormone secretion | 2/204 | 23/20870 | 0.02102040529775134 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | BMP6||C1QTNF1 | 2 | 4.900164 | 4.324849 | 4.176387 | 4.787936 | 4.779527 | 5.190633 | 4.798600 | 4.231449 | 4.613532 | 4.190041 | 4.220728 | 4.162628 | 4.320541 | 4.075589 | 4.135257 |
| GO:0036303 | lymph vessel morphogenesis | 2/204 | 23/20870 | 0.02102040529775134 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | TIE1||VEGFA | 2 | 4.209226 | 4.270085 | 4.698661 | 4.273930 | 4.124797 | 4.175186 | 4.257868 | 4.280987 | 4.223645 | 4.293035 | 4.281662 | 4.749729 | 4.775710 | 4.641330 | 4.621728 |
| GO:0043369 | CD4-positive or CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment | 2/204 | 23/20870 | 0.02102040529775134 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | IL23A||IL6 | 2 | 6.018349 | 6.639212 | 7.106283 | 6.041728 | 6.027105 | 5.993252 | 6.010856 | 6.637974 | 6.641510 | 6.645369 | 6.631963 | 7.102466 | 7.115801 | 7.089176 | 7.117510 |
| GO:0051904 | pigment granule transport | 2/204 | 23/20870 | 0.02102040529775134 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | MKKS||MYO7A | 2 | 5.111898 | 4.785770 | 5.027363 | 5.269465 | 4.610605 | 5.020748 | 5.421479 | 4.647623 | 4.664442 | 4.597649 | 5.157859 | 5.162003 | 4.813096 | 4.759427 | 5.302000 |
| GO:0072574 | hepatocyte proliferation | 2/204 | 23/20870 | 0.02102040529775134 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | IL6||SULF2 | 2 | 5.132624 | 5.426863 | 5.609398 | 5.152714 | 5.148159 | 5.113437 | 5.115735 | 5.403709 | 5.390468 | 5.485664 | 5.425758 | 5.575489 | 5.669173 | 5.554649 | 5.635369 |
| GO:0072575 | epithelial cell proliferation involved in liver morphogenesis | 2/204 | 23/20870 | 0.02102040529775134 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | IL6||SULF2 | 2 | 5.132624 | 5.426863 | 5.609398 | 5.152714 | 5.148159 | 5.113437 | 5.115735 | 5.403709 | 5.390468 | 5.485664 | 5.425758 | 5.575489 | 5.669173 | 5.554649 | 5.635369 |
| GO:2000831 | regulation of steroid hormone secretion | 2/204 | 23/20870 | 0.02102040529775134 | 0.14993315637157 | 0.12248033082202 | BMP6||C1QTNF1 | 2 | 4.776408 | 4.338458 | 4.218381 | 4.632586 | 4.625017 | 5.122403 | 4.661551 | 4.241047 | 4.646723 | 4.197675 | 4.218237 | 4.220383 | 4.374363 | 4.125688 | 4.139299 |
| GO:0034109 | homotypic cell-cell adhesion | 4/204 | 108/20870 | 0.02160593810030590 | 0.15353313587584 | 0.12542115252754 | TYRO3||IL6||SLC7A11||C1QTNF1 | 4 | 8.252127 | 8.713106 | 8.793356 | 8.233653 | 8.261647 | 8.249157 | 8.263850 | 8.715835 | 8.692376 | 8.717778 | 8.726218 | 8.774321 | 8.799770 | 8.801678 | 8.797488 |
| GO:0048732 | gland development | 10/204 | 486/20870 | 0.02162036094529560 | 0.15353313587584 | 0.12542115252754 | OAS2||VEGFA||PRLR||TBX2||RREB1||IL6||LY6E||IGF2||CSF1||SULF2 | 10 | 6.789015 | 6.742562 | 6.852602 | 6.791342 | 6.791500 | 6.788470 | 6.784738 | 6.740882 | 6.729279 | 6.754878 | 6.745094 | 6.845770 | 6.862396 | 6.854684 | 6.847499 |
| GO:0043551 | regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity | 3/204 | 61/20870 | 0.02187457347975169 | 0.15465707214631 | 0.12633929558250 | CCR7||SOCS3||PIK3R6 | 3 | 4.839493 | 5.278227 | 5.308499 | 4.822984 | 4.868137 | 4.827871 | 4.838552 | 5.229094 | 5.342438 | 5.267642 | 5.271400 | 5.258580 | 5.332636 | 5.380040 | 5.259043 |
| GO:0050798 | activated T cell proliferation | 3/204 | 61/20870 | 0.02187457347975169 | 0.15465707214631 | 0.12633929558250 | IL23A||IGF2||PDCD1LG2 | 3 | 6.922846 | 7.035181 | 7.028363 | 6.922994 | 6.921987 | 6.923930 | 6.922470 | 7.057012 | 7.017494 | 7.055774 | 7.009801 | 7.012929 | 7.051102 | 7.037881 | 7.011143 |
| GO:0090596 | sensory organ morphogenesis | 7/204 | 284/20870 | 0.02197057958962280 | 0.15499594878981 | 0.12661612376652 | VEGFA||TBX2||TFAP2A||MYO7A||BCAR3||IGFN1||DLL1 | 7 | 5.720957 | 5.697255 | 5.633814 | 5.771858 | 5.701349 | 5.723265 | 5.685891 | 5.694369 | 5.659482 | 5.787554 | 5.643237 | 5.626640 | 5.624983 | 5.670273 | 5.612697 |
| GO:0007605 | sensory perception of sound | 5/204 | 163/20870 | 0.02216653215043594 | 0.15603689880569 | 0.12746647538587 | ATP8B1||RIPOR2||MKKS||TFAP2A||MYO7A | 5 | 6.336595 | 6.164728 | 6.087281 | 6.397966 | 6.289795 | 6.332040 | 6.324445 | 6.097552 | 6.179758 | 6.175821 | 6.203591 | 6.063446 | 6.053322 | 6.087136 | 6.143519 |
| GO:0010951 | negative regulation of endopeptidase activity | 7/204 | 285/20870 | 0.02234411353406222 | 0.15623955971968 | 0.12763202899916 | CST7||VEGFA||C3||IFI6||SERPINB7||SERPINA9||AQP1 | 7 | 6.691406 | 7.090156 | 7.407347 | 6.693975 | 6.694483 | 6.686278 | 6.690874 | 7.077069 | 7.088082 | 7.082821 | 7.112402 | 7.393232 | 7.411212 | 7.409968 | 7.414879 |
| GO:0043010 | camera-type eye development | 8/204 | 351/20870 | 0.02248064854405817 | 0.15623955971968 | 0.12763202899916 | SLC17A7||VEGFA||TBX2||TFAP2A||BCAR3||SLC7A11||IGFN1||DLL1 | 8 | 5.606801 | 5.719921 | 5.757816 | 5.610993 | 5.592739 | 5.609224 | 5.614154 | 5.727138 | 5.684484 | 5.745920 | 5.721455 | 5.750711 | 5.765577 | 5.765032 | 5.749864 |
| GO:0002689 | negative regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis | 2/204 | 24/20870 | 0.02278581725718124 | 0.15623955971968 | 0.12763202899916 | PADI2||NBL1 | 2 | 5.337415 | 6.362109 | 6.417702 | 5.385567 | 5.332261 | 5.301012 | 5.329521 | 6.374623 | 6.273780 | 6.342872 | 6.451500 | 6.431345 | 6.452768 | 6.393225 | 6.392549 |
| GO:0003323 | type B pancreatic cell development | 2/204 | 24/20870 | 0.02278581725718124 | 0.15623955971968 | 0.12763202899916 | BMP6||DLL1 | 2 | 5.349178 | 5.607302 | 5.274811 | 5.397344 | 5.350454 | 5.201598 | 5.436508 | 5.948960 | 5.627226 | 5.620071 | 5.113174 | 5.270013 | 5.208571 | 5.530679 | 5.047357 |
| GO:0009219 | pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotide metabolic process | 2/204 | 24/20870 | 0.02278581725718124 | 0.15623955971968 | 0.12763202899916 | TYMP||CMPK2 | 2 | 5.163576 | 5.306216 | 5.485603 | 5.077396 | 5.260734 | 5.047788 | 5.255031 | 5.242309 | 5.168445 | 5.506700 | 5.284885 | 5.479426 | 5.465773 | 5.445330 | 5.549730 |
| GO:0021544 | subpallium development | 2/204 | 24/20870 | 0.02278581725718124 | 0.15623955971968 | 0.12763202899916 | MKKS||SLC7A11 | 2 | 4.484185 | 4.017245 | 4.551993 | 4.773762 | 3.628300 | 4.373266 | 4.861803 | 3.686967 | 3.613827 | 3.630404 | 4.768922 | 4.584523 | 4.348099 | 4.089790 | 5.019915 |
| GO:0040037 | negative regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway | 2/204 | 24/20870 | 0.02278581725718124 | 0.15623955971968 | 0.12763202899916 | CREB3L1||SULF2 | 2 | 5.181479 | 4.840343 | 4.330696 | 5.178155 | 5.169489 | 5.171711 | 5.206261 | 4.733949 | 4.891359 | 5.042308 | 4.663821 | 4.279979 | 4.266171 | 4.263692 | 4.498909 |
| GO:0043380 | regulation of memory T cell differentiation | 2/204 | 24/20870 | 0.02278581725718124 | 0.15623955971968 | 0.12763202899916 | IL23A||HLA-DRA | 2 | 5.063518 | 5.489776 | 6.019321 | 5.054322 | 5.071058 | 5.061376 | 5.067262 | 5.516454 | 5.481194 | 5.483207 | 5.477913 | 6.054309 | 5.992986 | 5.981092 | 6.047451 |
| GO:0051882 | mitochondrial depolarization | 2/204 | 24/20870 | 0.02278581725718124 | 0.15623955971968 | 0.12763202899916 | GCLC||IFI6 | 2 | 6.906059 | 6.977989 | 7.313671 | 6.910547 | 6.905844 | 6.885515 | 6.922087 | 6.977564 | 6.982258 | 6.959076 | 6.992853 | 7.311872 | 7.340215 | 7.319827 | 7.282167 |
| GO:0051905 | establishment of pigment granule localization | 2/204 | 24/20870 | 0.02278581725718124 | 0.15623955971968 | 0.12763202899916 | MKKS||MYO7A | 2 | 5.044762 | 4.717240 | 4.957576 | 5.201338 | 4.545334 | 4.953927 | 5.353932 | 4.577970 | 4.595517 | 4.528689 | 5.090687 | 5.091985 | 4.743185 | 4.690025 | 5.232247 |
| GO:0072576 | liver morphogenesis | 2/204 | 24/20870 | 0.02278581725718124 | 0.15623955971968 | 0.12763202899916 | IL6||SULF2 | 2 | 5.263311 | 5.494438 | 5.640342 | 5.279837 | 5.298052 | 5.253570 | 5.220612 | 5.435330 | 5.484700 | 5.544190 | 5.511335 | 5.592282 | 5.700338 | 5.602030 | 5.663963 |
| GO:0090023 | positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis | 2/204 | 24/20870 | 0.02278581725718124 | 0.15623955971968 | 0.12763202899916 | RIPOR2||CCR7 | 2 | 5.899857 | 7.157033 | 7.404800 | 5.899143 | 5.909383 | 5.907732 | 5.883019 | 7.154793 | 7.154249 | 7.170262 | 7.148741 | 7.415538 | 7.408799 | 7.409943 | 7.384727 |
| GO:0040014 | regulation of multicellular organism growth | 3/204 | 62/20870 | 0.02282532029403522 | 0.15623955971968 | 0.12763202899916 | MKKS||IGF2||CSF1 | 3 | 6.211869 | 6.538392 | 6.686140 | 6.187601 | 6.196982 | 6.224199 | 6.238121 | 6.515218 | 6.495582 | 6.527949 | 6.612055 | 6.689292 | 6.679095 | 6.672895 | 6.703095 |
| GO:0007173 | epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway | 4/204 | 110/20870 | 0.02293144500336202 | 0.15663342942974 | 0.12795378099557 | RPS6KA5||IFI6||BCAR3||MVB12B | 4 | 5.791138 | 6.853263 | 7.309428 | 5.759031 | 5.791567 | 5.782949 | 5.830097 | 6.836234 | 6.874029 | 6.855889 | 6.846633 | 7.298352 | 7.317997 | 7.310086 | 7.311208 |
| GO:0010876 | lipid localization | 10/204 | 491/20870 | 0.02300399386012854 | 0.15679677844620 | 0.12808722073671 | NR1H3||ATP8B1||C3||B4GALNT1||IL6||BMP6||C1QTNF1||ENPP1||ABCA4||CPT1B | 10 | 6.305107 | 6.746477 | 6.814569 | 6.300824 | 6.305427 | 6.315222 | 6.298900 | 6.755885 | 6.749069 | 6.741575 | 6.739322 | 6.816326 | 6.827331 | 6.816426 | 6.798042 |
| GO:0008406 | gonad development | 6/204 | 224/20870 | 0.02307294179580668 | 0.15693494588540 | 0.12820008965825 | MAMLD1||VEGFA||TNFSF10||MKKS||MAS1||SCX | 6 | 5.998829 | 5.900595 | 5.923222 | 6.006524 | 5.973506 | 5.986564 | 6.028130 | 5.859074 | 5.907098 | 5.897382 | 5.937732 | 5.912868 | 5.925908 | 5.909040 | 5.944802 |
| GO:0050770 | regulation of axonogenesis | 5/204 | 165/20870 | 0.02321791558326336 | 0.15758854703251 | 0.12873401615363 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||SEMA6B | 5 | 6.723365 | 7.333213 | 7.328900 | 6.718138 | 6.721303 | 6.736091 | 6.717851 | 7.342649 | 7.334407 | 7.322255 | 7.333470 | 7.347963 | 7.336053 | 7.315105 | 7.316214 |
| GO:0046434 | organophosphate catabolic process | 5/204 | 166/20870 | 0.02375550107743269 | 0.16085035188335 | 0.13139858313052 | TYMP||ENTPD1||PLA2G7||ENPP1||INPP5F | 5 | 5.365716 | 5.334582 | 5.369260 | 5.341711 | 5.346851 | 5.427807 | 5.344664 | 5.340501 | 5.281896 | 5.353391 | 5.361208 | 5.349904 | 5.422295 | 5.330151 | 5.373043 |
| GO:0001836 | release of cytochrome c from mitochondria | 3/204 | 63/20870 | 0.02379826856338704 | 0.16085035188335 | 0.13139858313052 | TNFSF10||IFI6||CIDEB | 3 | 6.488710 | 7.556811 | 8.006921 | 6.480954 | 6.481457 | 6.516530 | 6.475529 | 7.553293 | 7.579622 | 7.547295 | 7.546784 | 7.987190 | 8.022427 | 7.997311 | 8.020443 |
| GO:0018209 | peptidyl-serine modification | 8/204 | 356/20870 | 0.02420144871319871 | 0.16323320219948 | 0.13334513252681 | OSM||RPS6KA5||DMPK||VEGFA||LIF||IL6||BCAR3||INPP5F | 8 | 5.669837 | 5.845624 | 5.825921 | 5.665012 | 5.675756 | 5.658700 | 5.679782 | 5.857739 | 5.830017 | 5.856561 | 5.837982 | 5.834542 | 5.832783 | 5.843581 | 5.792239 |
| GO:0002285 | lymphocyte activation involved in immune response | 6/204 | 227/20870 | 0.02442898223970230 | 0.16325735938630 | 0.13336486652231 | UNC13D||IL23A||IL6||DLL1||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 6 | 7.127753 | 7.581987 | 7.580364 | 7.114479 | 7.134917 | 7.128587 | 7.132940 | 7.577709 | 7.560149 | 7.591407 | 7.598388 | 7.563207 | 7.578645 | 7.596730 | 7.582676 |
| GO:0006213 | pyrimidine nucleoside metabolic process | 2/204 | 25/20870 | 0.02461013544098738 | 0.16325735938630 | 0.13336486652231 | TYMP||AICDA | 2 | 5.516339 | 5.397840 | 5.469795 | 5.883763 | 5.399628 | 5.491687 | 5.202696 | 5.245271 | 5.364498 | 5.457300 | 5.510373 | 5.538654 | 5.445730 | 5.459543 | 5.432879 |
| GO:0006957 | complement activation, alternative pathway | 2/204 | 25/20870 | 0.02461013544098738 | 0.16325735938630 | 0.13336486652231 | CFH||C3 | 2 | 6.145612 | 4.351469 | 4.766251 | 6.118457 | 6.176842 | 6.097968 | 6.187204 | 4.171027 | 4.320418 | 4.581415 | 4.301668 | 4.723949 | 4.795893 | 4.681337 | 4.857506 |
| GO:0043379 | memory T cell differentiation | 2/204 | 25/20870 | 0.02461013544098738 | 0.16325735938630 | 0.13336486652231 | IL23A||HLA-DRA | 2 | 5.013526 | 5.381853 | 5.897194 | 4.989623 | 5.015504 | 5.011070 | 5.037508 | 5.400283 | 5.361447 | 5.378547 | 5.386860 | 5.935622 | 5.874719 | 5.855147 | 5.921782 |
| GO:0044321 | response to leptin | 2/204 | 25/20870 | 0.02461013544098738 | 0.16325735938630 | 0.13336486652231 | NR4A3||MKKS | 2 | 5.103949 | 6.170954 | 6.395751 | 5.257424 | 4.738718 | 5.053252 | 5.300481 | 6.090311 | 6.091342 | 6.141892 | 6.344713 | 6.421967 | 6.343762 | 6.279800 | 6.525735 |
| GO:0045649 | regulation of macrophage differentiation | 2/204 | 25/20870 | 0.02461013544098738 | 0.16325735938630 | 0.13336486652231 | LIF||CSF1 | 2 | 6.051462 | 6.274382 | 6.282797 | 6.019016 | 6.077054 | 6.023288 | 6.085228 | 6.234431 | 6.371276 | 6.266769 | 6.220147 | 6.309835 | 6.278609 | 6.304407 | 6.237199 |
| GO:0060706 | cell differentiation involved in embryonic placenta development | 2/204 | 25/20870 | 0.02461013544098738 | 0.16325735938630 | 0.13336486652231 | LIF||SOCS3 | 2 | 4.347104 | 4.456810 | 4.426516 | 4.409908 | 4.339097 | 4.305543 | 4.331783 | 4.470258 | 4.435463 | 4.437651 | 4.483276 | 4.478120 | 4.393983 | 4.430244 | 4.402213 |
| GO:1903861 | positive regulation of dendrite extension | 2/204 | 25/20870 | 0.02461013544098738 | 0.16325735938630 | 0.13336486652231 | RASAL1||UNC13A | 2 | 4.111397 | 3.524411 | 3.726524 | 4.027506 | 4.394276 | 3.907265 | 4.070141 | 3.432185 | 3.709664 | 3.483486 | 3.454773 | 3.527354 | 3.540637 | 3.841653 | 3.949041 |
| GO:0002886 | regulation of myeloid leukocyte mediated immunity | 3/204 | 64/20870 | 0.02479340973073578 | 0.16346411650694 | 0.13353376632505 | UNC13D||C3||PTAFR | 3 | 7.663772 | 7.582702 | 7.636802 | 7.661307 | 7.661427 | 7.664884 | 7.667461 | 7.572831 | 7.591990 | 7.600812 | 7.564890 | 7.626070 | 7.649075 | 7.643593 | 7.628337 |
| GO:0045576 | mast cell activation | 3/204 | 64/20870 | 0.02479340973073578 | 0.16346411650694 | 0.13353376632505 | UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3 | 3 | 6.006186 | 6.143352 | 6.223481 | 5.913050 | 6.034550 | 6.047543 | 6.025646 | 6.132645 | 6.096989 | 6.172277 | 6.170179 | 6.255933 | 6.198507 | 6.174433 | 6.263094 |
| GO:1903670 | regulation of sprouting angiogenesis | 3/204 | 64/20870 | 0.02479340973073578 | 0.16346411650694 | 0.13353376632505 | VEGFA||CREB3L1||DLL1 | 3 | 6.037408 | 6.705179 | 6.790540 | 6.039851 | 6.011833 | 6.099612 | 5.996166 | 6.714777 | 6.699631 | 6.695477 | 6.710747 | 6.784410 | 6.816057 | 6.798168 | 6.763005 |
| GO:0046661 | male sex differentiation | 5/204 | 168/20870 | 0.02485464550403184 | 0.16353342266326 | 0.13359038249428 | MAMLD1||TNFSF10||MAS1||BMP6||SCX | 5 | 6.181467 | 6.068088 | 6.036733 | 6.181027 | 6.183370 | 6.173579 | 6.187856 | 6.038373 | 6.076179 | 6.069785 | 6.087556 | 6.021937 | 6.049837 | 6.040093 | 6.034926 |
| GO:2001237 | negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | 4/204 | 113/20870 | 0.02501076726465874 | 0.16422548607181 | 0.13415572879446 | GCLC||IL1A||IFI6||SCG2 | 4 | 6.120285 | 6.721642 | 7.010013 | 6.106758 | 6.104943 | 6.138078 | 6.131068 | 6.750638 | 6.749031 | 6.693181 | 6.692594 | 7.010096 | 7.007162 | 7.004633 | 7.018127 |
| GO:0040013 | negative regulation of locomotion | 9/204 | 429/20870 | 0.02564715932759731 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | SEMA3F||TIE1||RIPOR2||PADI2||NBL1||PIP5KL1||SEMA6B||IFITM1||EPPK1 | 9 | 5.985022 | 6.028788 | 6.081019 | 5.963603 | 5.984509 | 5.996950 | 5.994783 | 6.015514 | 6.051256 | 6.020886 | 6.027237 | 6.097205 | 6.080056 | 6.078662 | 6.068000 |
| GO:0061564 | axon development | 10/204 | 500/20870 | 0.02565479893138183 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||NOTCH3||SCARF1||RPS6KA5||VEGFA||NR4A2||SEMA6B||INPP5F | 10 | 6.699779 | 6.992633 | 6.971034 | 6.701687 | 6.695849 | 6.713640 | 6.687817 | 6.999820 | 6.987789 | 6.993086 | 6.989809 | 6.978974 | 6.977423 | 6.969063 | 6.958587 |
| GO:1905954 | positive regulation of lipid localization | 4/204 | 114/20870 | 0.02572832937052051 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | NR1H3||C3||BMP6||C1QTNF1 | 4 | 7.316384 | 8.054836 | 8.116543 | 7.312870 | 7.309790 | 7.333590 | 7.309144 | 8.064396 | 8.046472 | 8.052101 | 8.056314 | 8.113077 | 8.126400 | 8.112714 | 8.113938 |
| GO:0046847 | filopodium assembly | 3/204 | 65/20870 | 0.02581072837036993 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | RIPOR2||CCR7||FGD2 | 3 | 5.783306 | 5.992210 | 6.120889 | 5.734662 | 5.751912 | 5.740645 | 5.899431 | 5.989506 | 6.007899 | 5.986483 | 5.984832 | 6.123376 | 6.170010 | 6.093564 | 6.095274 |
| GO:1900076 | regulation of cellular response to insulin stimulus | 3/204 | 65/20870 | 0.02581072837036993 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | IGF2||SOCS3||ENPP1 | 3 | 5.551786 | 6.350582 | 6.660823 | 5.768696 | 5.484542 | 5.461113 | 5.468974 | 6.286188 | 6.413618 | 6.377490 | 6.321680 | 6.662863 | 6.653353 | 6.722406 | 6.602138 |
| GO:0045137 | development of primary sexual characteristics | 6/204 | 230/20870 | 0.02583740771368586 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | MAMLD1||VEGFA||TNFSF10||MKKS||MAS1||SCX | 6 | 5.970867 | 5.872282 | 5.894724 | 5.978510 | 5.945728 | 5.958622 | 6.000022 | 5.830811 | 5.878664 | 5.868981 | 5.909578 | 5.884045 | 5.897946 | 5.880619 | 5.916015 |
| GO:0001894 | tissue homeostasis | 7/204 | 294/20870 | 0.02590573264519716 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | VEGFA||MKKS||IL6||ADAM8||CSF1||ABCA4||SCX | 7 | 7.528322 | 7.829531 | 7.880072 | 7.544260 | 7.520898 | 7.520836 | 7.527167 | 7.837533 | 7.823708 | 7.827247 | 7.829599 | 7.887449 | 7.888801 | 7.869036 | 7.874904 |
| GO:0032640 | tumor necrosis factor production | 6/204 | 231/20870 | 0.02631865096958647 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | IL23A||OAS2||IL1A||IL6||PTAFR||ORM1 | 6 | 6.665505 | 6.697249 | 6.707012 | 6.647415 | 6.671294 | 6.674347 | 6.668809 | 6.711712 | 6.694973 | 6.699892 | 6.682265 | 6.700235 | 6.713172 | 6.704014 | 6.710592 |
| GO:0032680 | regulation of tumor necrosis factor production | 6/204 | 231/20870 | 0.02631865096958647 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | IL23A||OAS2||IL1A||IL6||PTAFR||ORM1 | 6 | 6.665505 | 6.697249 | 6.707012 | 6.647415 | 6.671294 | 6.674347 | 6.668809 | 6.711712 | 6.694973 | 6.699892 | 6.682265 | 6.700235 | 6.713172 | 6.704014 | 6.710592 |
| GO:0010466 | negative regulation of peptidase activity | 7/204 | 295/20870 | 0.02632406612852047 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | CST7||VEGFA||C3||IFI6||SERPINB7||SERPINA9||AQP1 | 7 | 6.670724 | 7.043102 | 7.357822 | 6.672918 | 6.674009 | 6.663204 | 6.672737 | 7.029986 | 7.039857 | 7.036871 | 7.065442 | 7.343933 | 7.359749 | 7.360828 | 7.366679 |
| GO:0021700 | developmental maturation | 7/204 | 295/20870 | 0.02632406612852047 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | SCARF1||VEGFA||BCL11A||C3||UNC13A||UNC13C||NR4A2 | 7 | 5.792172 | 6.000048 | 5.995976 | 5.801077 | 5.786622 | 5.799641 | 5.781250 | 6.010811 | 5.990535 | 5.990709 | 6.008014 | 5.996693 | 6.008900 | 5.984271 | 5.993934 |
| GO:0044344 | cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus | 4/204 | 115/20870 | 0.02645818391290955 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | GCLC||CREB3L1||EGR3||SULF2 | 4 | 5.246147 | 6.190199 | 6.503992 | 5.254702 | 5.228596 | 5.273654 | 5.227117 | 6.207821 | 6.167902 | 6.202298 | 6.182423 | 6.504013 | 6.504830 | 6.490012 | 6.516988 |
| GO:0001919 | regulation of receptor recycling | 2/204 | 26/20870 | 0.02649205158136423 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | ECE1||INPP5F | 2 | 5.691512 | 6.322401 | 6.477397 | 5.706136 | 5.618238 | 5.778727 | 5.657968 | 6.292605 | 6.396114 | 6.252656 | 6.344185 | 6.555049 | 6.364187 | 6.480983 | 6.502688 |
| GO:0002888 | positive regulation of myeloid leukocyte mediated immunity | 2/204 | 26/20870 | 0.02649205158136423 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | C3||PTAFR | 2 | 8.769425 | 8.612487 | 8.687096 | 8.772914 | 8.762785 | 8.776155 | 8.765808 | 8.606512 | 8.623218 | 8.623074 | 8.596971 | 8.670055 | 8.698948 | 8.687796 | 8.691431 |
| GO:0032069 | regulation of nuclease activity | 2/204 | 26/20870 | 0.02649205158136423 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | OAS2||OASL | 2 | 7.857192 | 8.061326 | 7.988332 | 7.857265 | 7.852200 | 7.850110 | 7.869119 | 8.059665 | 8.071679 | 8.079442 | 8.034113 | 8.014859 | 7.998478 | 7.945539 | 7.993532 |
| GO:0033032 | regulation of myeloid cell apoptotic process | 2/204 | 26/20870 | 0.02649205158136423 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | SLC7A11||IRF7 | 2 | 5.604607 | 5.620847 | 5.681423 | 5.540579 | 5.587453 | 5.664559 | 5.622957 | 5.607806 | 5.601874 | 5.577430 | 5.693582 | 5.939419 | 5.469808 | 5.640206 | 5.635662 |
| GO:0048596 | embryonic camera-type eye morphogenesis | 2/204 | 26/20870 | 0.02649205158136423 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | TBX2||TFAP2A | 2 | 6.050810 | 5.109998 | 4.741950 | 5.995727 | 6.002362 | 5.975930 | 6.215678 | 5.107769 | 5.136306 | 5.176441 | 5.014594 | 4.727350 | 4.874505 | 4.727961 | 4.627112 |
| GO:0048643 | positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue development | 2/204 | 26/20870 | 0.02649205158136423 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | IGF2||DLL1 | 2 | 6.315360 | 6.404646 | 6.429363 | 6.336031 | 6.261816 | 6.388196 | 6.271747 | 6.423328 | 6.349900 | 6.303087 | 6.531853 | 6.740505 | 6.264678 | 6.260628 | 6.396629 |
| GO:0051875 | pigment granule localization | 2/204 | 26/20870 | 0.02649205158136423 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | MKKS||MYO7A | 2 | 4.955701 | 4.644991 | 4.869208 | 5.109719 | 4.469295 | 4.875381 | 5.251644 | 4.513202 | 4.523399 | 4.455835 | 5.013490 | 4.990947 | 4.657657 | 4.635029 | 5.130050 |
| GO:0060669 | embryonic placenta morphogenesis | 2/204 | 26/20870 | 0.02649205158136423 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | IGF2||SOCS3 | 2 | 6.002919 | 6.064823 | 6.018500 | 6.012557 | 5.972401 | 6.031074 | 5.994991 | 6.045070 | 6.039116 | 6.096745 | 6.077587 | 5.998844 | 6.002172 | 5.977280 | 6.092940 |
| GO:0090715 | immunological memory formation process | 2/204 | 26/20870 | 0.02649205158136423 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | IL23A||HLA-DRA | 2 | 5.104549 | 5.365006 | 5.841635 | 5.076611 | 5.126610 | 5.097147 | 5.117314 | 5.370821 | 5.346002 | 5.372212 | 5.370822 | 5.878459 | 5.817877 | 5.800951 | 5.867778 |
| GO:1901739 | regulation of myoblast fusion | 2/204 | 26/20870 | 0.02649205158136423 | 0.16649195769653 | 0.13600720848789 | RIPOR2||CXCL10 | 2 | 6.708865 | 6.989308 | 6.892407 | 6.666347 | 6.728922 | 6.711272 | 6.728030 | 6.970200 | 7.001357 | 6.986180 | 6.999280 | 6.873365 | 6.902724 | 6.896394 | 6.896970 |
| GO:2001056 | positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | 5/204 | 171/20870 | 0.02656382761167675 | 0.16661824945534 | 0.13611037617124 | SENP1||TNFSF10||CIDEB||ST20||TNFSF15 | 5 | 6.836997 | 7.067851 | 7.119499 | 6.820312 | 6.840246 | 6.837985 | 6.849291 | 7.074030 | 7.057546 | 7.069027 | 7.070746 | 7.118759 | 7.127291 | 7.112358 | 7.119551 |
| GO:0043523 | regulation of neuron apoptotic process | 6/204 | 232/20870 | 0.02680582225712294 | 0.16743723875376 | 0.13677940817615 | GCLC||TYRO3||TFAP2A||ADAM8||NR4A2||GPRASP2 | 6 | 6.793663 | 6.788725 | 6.793837 | 6.806502 | 6.797212 | 6.784822 | 6.786007 | 6.801845 | 6.788866 | 6.799196 | 6.764698 | 6.797415 | 6.781817 | 6.803667 | 6.792362 |
| GO:0043277 | apoptotic cell clearance | 3/204 | 66/20870 | 0.02685020236839122 | 0.16743723875376 | 0.13677940817615 | NR1H3||TYRO3||C3 | 3 | 6.728644 | 6.604731 | 6.504254 | 6.738927 | 6.700993 | 6.750185 | 6.724000 | 6.590213 | 6.633551 | 6.635277 | 6.558462 | 6.480038 | 6.534849 | 6.492706 | 6.508838 |
| GO:0046854 | phosphatidylinositol phosphate biosynthetic process | 3/204 | 66/20870 | 0.02685020236839122 | 0.16743723875376 | 0.13677940817615 | PIP5KL1||SOCS3||PIK3R6 | 3 | 4.305245 | 4.167194 | 4.139442 | 4.391650 | 4.161720 | 4.424538 | 4.226333 | 4.143140 | 4.187534 | 4.193894 | 4.143421 | 4.194586 | 4.067117 | 4.250677 | 4.034405 |
| GO:0050708 | regulation of protein secretion | 7/204 | 297/20870 | 0.02717454302533350 | 0.16913267705343 | 0.13816441099245 | NR1H3||IL1A||RSAD2||IL6||ANKRD1||ADAM8||BMP6 | 7 | 5.776595 | 6.222774 | 6.411609 | 5.759477 | 5.761327 | 5.777413 | 5.807643 | 6.233172 | 6.217699 | 6.219708 | 6.220465 | 6.418706 | 6.420702 | 6.403170 | 6.403766 |
| GO:0044706 | multi-multicellular organism process | 6/204 | 233/20870 | 0.02729894734206747 | 0.16957958811334 | 0.13852949244469 | VEGFA||PRLR||LIF||IDO1||MMP7||PTAFR | 6 | 7.223620 | 7.782630 | 7.974730 | 7.220573 | 7.223915 | 7.230206 | 7.219763 | 7.790082 | 7.774198 | 7.782030 | 7.784165 | 7.972666 | 7.987828 | 7.973599 | 7.964731 |
| GO:0001906 | cell killing | 8/204 | 365/20870 | 0.02752851646006743 | 0.17037170942098 | 0.13917657599951 | CFH||UNC13D||IL23A||TREM1||C3||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||PIK3R6 | 8 | 7.769209 | 7.804550 | 7.832920 | 7.782937 | 7.761866 | 7.771567 | 7.760355 | 7.787204 | 7.817717 | 7.803874 | 7.809234 | 7.837912 | 7.829927 | 7.839944 | 7.823839 |
| GO:0035051 | cardiocyte differentiation | 5/204 | 173/20870 | 0.02774398614088553 | 0.17037170942098 | 0.13917657599951 | ASB2||VEGFA||TBX2||DLL1||ALPK2 | 5 | 6.170644 | 6.297204 | 6.341258 | 6.167455 | 6.183230 | 6.172871 | 6.158914 | 6.330029 | 6.269110 | 6.300944 | 6.288053 | 6.342822 | 6.338910 | 6.339986 | 6.343309 |
| GO:0052126 | movement in host environment | 6/204 | 234/20870 | 0.02779805157008185 | 0.17037170942098 | 0.13917657599951 | SIGLEC1||TYRO3||TRIM22||TNFRSF14||LY6E||IFITM1 | 6 | 6.922312 | 7.476393 | 7.644214 | 6.904943 | 6.930867 | 6.919291 | 6.933968 | 7.472790 | 7.451476 | 7.489512 | 7.491438 | 7.622160 | 7.651080 | 7.658847 | 7.644508 |
| GO:0010883 | regulation of lipid storage | 3/204 | 67/20870 | 0.02791180309989220 | 0.17037170942098 | 0.13917657599951 | NR1H3||C3||IL6 | 3 | 5.997637 | 5.958566 | 5.915502 | 5.992463 | 5.981176 | 6.029930 | 5.986470 | 5.929815 | 5.997250 | 5.981552 | 5.924249 | 5.919280 | 5.911111 | 5.933996 | 5.897377 |
| GO:0043030 | regulation of macrophage activation | 3/204 | 67/20870 | 0.02791180309989220 | 0.17037170942098 | 0.13917657599951 | NR1H3||CST7||IL6 | 3 | 6.826871 | 6.910631 | 6.972444 | 6.836861 | 6.832736 | 6.819810 | 6.817988 | 6.940540 | 6.893155 | 6.899220 | 6.909147 | 6.965988 | 6.977021 | 6.970941 | 6.975800 |
| GO:0046626 | regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway | 3/204 | 67/20870 | 0.02791180309989220 | 0.17037170942098 | 0.13917657599951 | IGF2||SOCS3||ENPP1 | 3 | 5.580350 | 6.190692 | 6.517827 | 5.789583 | 5.527885 | 5.467517 | 5.513725 | 6.123437 | 6.265701 | 6.225027 | 6.143915 | 6.517910 | 6.507125 | 6.580049 | 6.463824 |
| GO:0050732 | negative regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | 3/204 | 67/20870 | 0.02791180309989220 | 0.17037170942098 | 0.13917657599951 | SH3BP5||SOCS3||INPP5F | 3 | 5.825950 | 6.054918 | 5.998604 | 5.810060 | 5.800193 | 5.873303 | 5.819126 | 6.022210 | 6.116683 | 6.035903 | 6.042994 | 6.000089 | 6.038332 | 5.999082 | 5.955728 |
| GO:0060113 | inner ear receptor cell differentiation | 3/204 | 67/20870 | 0.02791180309989220 | 0.17037170942098 | 0.13917657599951 | ATP8B1||MYO7A||DLL1 | 3 | 4.613679 | 4.347960 | 4.439539 | 4.646341 | 4.585500 | 4.636770 | 4.584991 | 4.382407 | 4.305556 | 4.350497 | 4.352338 | 4.418870 | 4.398090 | 4.459455 | 4.480287 |
| GO:0006275 | regulation of DNA replication | 4/204 | 117/20870 | 0.02795491137831906 | 0.17037170942098 | 0.13917657599951 | AICDA||CHTF18||MAS1||BCAR3 | 4 | 5.470837 | 5.878838 | 5.829461 | 5.547409 | 5.451762 | 5.484229 | 5.395770 | 5.870072 | 5.922980 | 5.844383 | 5.876798 | 5.827337 | 5.799366 | 5.870686 | 5.819511 |
| GO:0048640 | negative regulation of developmental growth | 4/204 | 117/20870 | 0.02795491137831906 | 0.17037170942098 | 0.13917657599951 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||BCL11A||SEMA6B | 4 | 6.986209 | 7.629540 | 7.606801 | 6.975902 | 6.994902 | 6.989950 | 6.984013 | 7.635137 | 7.610660 | 7.641925 | 7.630252 | 7.606357 | 7.608698 | 7.619955 | 7.592058 |
| GO:0030100 | regulation of endocytosis | 6/204 | 235/20870 | 0.02830315986381812 | 0.17068754839988 | 0.13943458472525 | NR1H3||SLC17A7||VEGFA||C3||DLL1||ANKRD13B | 6 | 6.984958 | 6.851557 | 6.840165 | 6.987783 | 6.982599 | 6.982551 | 6.986891 | 6.866848 | 6.840252 | 6.841507 | 6.857448 | 6.830262 | 6.855877 | 6.831584 | 6.842790 |
| GO:0001958 | endochondral ossification | 2/204 | 27/20870 | 0.02843027713732498 | 0.17068754839988 | 0.13943458472525 | BMP6||SCX | 2 | 7.244825 | 7.052118 | 7.209828 | 7.251630 | 7.245577 | 7.256453 | 7.225446 | 7.019664 | 7.035688 | 7.065886 | 7.086306 | 7.296545 | 7.184008 | 7.177715 | 7.177439 |
| GO:0034698 | response to gonadotropin | 2/204 | 27/20870 | 0.02843027713732498 | 0.17068754839988 | 0.13943458472525 | GCLC||MAS1 | 2 | 4.316251 | 5.295173 | 5.559585 | 4.303157 | 4.327942 | 4.340473 | 4.292935 | 5.300759 | 5.275579 | 5.323212 | 5.280653 | 5.588826 | 5.502921 | 5.541933 | 5.602509 |
| GO:0036075 | replacement ossification | 2/204 | 27/20870 | 0.02843027713732498 | 0.17068754839988 | 0.13943458472525 | BMP6||SCX | 2 | 7.244825 | 7.052118 | 7.209828 | 7.251630 | 7.245577 | 7.256453 | 7.225446 | 7.019664 | 7.035688 | 7.065886 | 7.086306 | 7.296545 | 7.184008 | 7.177715 | 7.177439 |
| GO:0038095 | Fc-epsilon receptor signaling pathway | 2/204 | 27/20870 | 0.02843027713732498 | 0.17068754839988 | 0.13943458472525 | MAPK10||NR4A3 | 2 | 8.000621 | 8.049118 | 7.862210 | 8.025929 | 8.014901 | 7.992140 | 7.968849 | 8.050494 | 8.046168 | 8.049877 | 8.049929 | 7.843453 | 7.869537 | 7.879240 | 7.856359 |
| GO:0071624 | positive regulation of granulocyte chemotaxis | 2/204 | 27/20870 | 0.02843027713732498 | 0.17068754839988 | 0.13943458472525 | RIPOR2||CCR7 | 2 | 5.899857 | 7.157033 | 7.404800 | 5.899143 | 5.909383 | 5.907732 | 5.883019 | 7.154793 | 7.154249 | 7.170262 | 7.148741 | 7.415538 | 7.408799 | 7.409943 | 7.384727 |
| GO:0090026 | positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis | 2/204 | 27/20870 | 0.02843027713732498 | 0.17068754839988 | 0.13943458472525 | PLA2G7||CXCL10 | 2 | 5.607758 | 6.784540 | 7.360881 | 5.587972 | 5.583749 | 5.640973 | 5.617587 | 6.827417 | 6.796474 | 6.764883 | 6.748104 | 7.327919 | 7.386795 | 7.350279 | 7.377784 |
| GO:0099637 | neurotransmitter receptor transport | 2/204 | 27/20870 | 0.02843027713732498 | 0.17068754839988 | 0.13943458472525 | MAPK10||TAMALIN | 2 | 4.940121 | 4.834742 | 4.893468 | 5.012651 | 4.943511 | 4.928595 | 4.872251 | 4.810511 | 4.774399 | 4.764497 | 4.978975 | 4.966300 | 4.852653 | 4.923211 | 4.827472 |
| GO:0008286 | insulin receptor signaling pathway | 4/204 | 118/20870 | 0.02872184946995746 | 0.17211755147053 | 0.14060275361736 | BCAR3||IGF2||SOCS3||ENPP1 | 4 | 5.241544 | 5.758304 | 5.989787 | 5.406378 | 5.207382 | 5.155174 | 5.183364 | 5.736677 | 5.838131 | 5.763815 | 5.690607 | 6.013980 | 5.960947 | 6.035382 | 5.946992 |
| GO:0048562 | embryonic organ morphogenesis | 7/204 | 301/20870 | 0.02893129740096781 | 0.17215741772334 | 0.14063532034211 | ASB2||TBX2||MKKS||MICAL2||TFAP2A||MYO7A||DLL1 | 7 | 5.996030 | 5.795372 | 5.762239 | 6.051121 | 5.938756 | 5.985882 | 6.006103 | 5.740204 | 5.790235 | 5.816812 | 5.832545 | 5.796257 | 5.728977 | 5.766682 | 5.756237 |
| GO:0009880 | embryonic pattern specification | 3/204 | 68/20870 | 0.02899549560290812 | 0.17215741772334 | 0.14063532034211 | SEMA3F||MEIS3||DLL1 | 3 | 5.069472 | 5.071108 | 5.038026 | 5.089040 | 5.053436 | 5.083965 | 5.051036 | 5.064458 | 5.014399 | 5.043402 | 5.158118 | 5.049346 | 5.005368 | 5.015055 | 5.081091 |
| GO:0033619 | membrane protein proteolysis | 3/204 | 68/20870 | 0.02899549560290812 | 0.17215741772334 | 0.14063532034211 | ADAM19||MMP7||ADAM8 | 3 | 6.803657 | 7.331102 | 7.626446 | 6.809674 | 6.776982 | 6.802306 | 6.825245 | 7.334137 | 7.310668 | 7.346808 | 7.332560 | 7.625100 | 7.628326 | 7.630654 | 7.621688 |
| GO:0035914 | skeletal muscle cell differentiation | 3/204 | 68/20870 | 0.02899549560290812 | 0.17215741772334 | 0.14063532034211 | ASB2||ANKRD1||SCX | 3 | 6.820993 | 6.623263 | 6.712625 | 6.469763 | 6.671104 | 6.928404 | 7.128388 | 6.626545 | 6.815808 | 6.430628 | 6.594026 | 6.822395 | 6.545841 | 6.668864 | 6.796681 |
| GO:0062208 | positive regulation of pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway | 3/204 | 68/20870 | 0.02899549560290812 | 0.17215741772334 | 0.14063532034211 | NR1H3||RSAD2||OASL | 3 | 6.705381 | 6.850135 | 6.880798 | 6.658422 | 6.712091 | 6.710571 | 6.739259 | 6.846325 | 6.856172 | 6.855920 | 6.842071 | 6.863547 | 6.878712 | 6.891153 | 6.889611 |
| GO:0001818 | negative regulation of cytokine production | 9/204 | 439/20870 | 0.02913666369456324 | 0.17267758042513 | 0.14106024102902 | RPS6KA5||IL23A||IL1R2||CCR7||IL6||PDCD1LG2||DLL1||HLA-F||ORM1 | 9 | 6.908329 | 7.113037 | 7.095793 | 6.914223 | 6.898061 | 6.916366 | 6.904589 | 7.124587 | 7.102655 | 7.105696 | 7.119095 | 7.090401 | 7.103271 | 7.094926 | 7.094543 |
| GO:0010517 | regulation of phospholipase activity | 3/204 | 69/20870 | 0.03010123874919282 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | LPAR2||ITK||PTAFR | 3 | 7.051673 | 7.107325 | 7.264823 | 7.062138 | 7.051385 | 7.054010 | 7.039065 | 7.130814 | 7.103937 | 7.103149 | 7.091106 | 7.249985 | 7.270170 | 7.256753 | 7.282170 |
| GO:0032608 | interferon-beta production | 3/204 | 69/20870 | 0.03010123874919282 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | OAS2||IRF7||ISG15 | 3 | 5.699115 | 5.620393 | 5.547004 | 5.784642 | 5.655594 | 5.687674 | 5.664866 | 5.617127 | 5.630948 | 5.591712 | 5.641305 | 5.527149 | 5.524719 | 5.627528 | 5.505431 |
| GO:0032648 | regulation of interferon-beta production | 3/204 | 69/20870 | 0.03010123874919282 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | OAS2||IRF7||ISG15 | 3 | 5.699115 | 5.620393 | 5.547004 | 5.784642 | 5.655594 | 5.687674 | 5.664866 | 5.617127 | 5.630948 | 5.591712 | 5.641305 | 5.527149 | 5.524719 | 5.627528 | 5.505431 |
| GO:0050771 | negative regulation of axonogenesis | 3/204 | 69/20870 | 0.03010123874919282 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||SEMA6B | 3 | 7.483640 | 8.267849 | 8.270682 | 7.473053 | 7.488482 | 7.490649 | 7.482309 | 8.273584 | 8.257624 | 8.265969 | 8.274155 | 8.275757 | 8.269962 | 8.273421 | 8.263558 |
| GO:0044106 | cellular amine metabolic process | 4/204 | 120/20870 | 0.03029302131981026 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | IDO1||SLC7A11||NR4A2||LY6E | 4 | 6.846936 | 6.792147 | 6.946265 | 6.845360 | 6.847323 | 6.839843 | 6.855179 | 6.814648 | 6.792113 | 6.782138 | 6.779424 | 6.933505 | 6.958050 | 6.947467 | 6.945934 |
| GO:0001945 | lymph vessel development | 2/204 | 28/20870 | 0.03042354303717665 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | TIE1||VEGFA | 2 | 4.304992 | 4.324277 | 4.629322 | 4.379286 | 4.263999 | 4.245313 | 4.327454 | 4.330419 | 4.301292 | 4.339327 | 4.325797 | 4.666273 | 4.713757 | 4.575262 | 4.556176 |
| GO:0006972 | hyperosmotic response | 2/204 | 28/20870 | 0.03042354303717665 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | MAPK10||AQP1 | 2 | 7.902378 | 7.757443 | 8.082715 | 7.906888 | 7.885665 | 7.900942 | 7.915851 | 7.817387 | 7.778385 | 7.688682 | 7.742211 | 8.086075 | 8.157879 | 8.040945 | 8.042821 |
| GO:0009435 | NAD biosynthetic process | 2/204 | 28/20870 | 0.03042354303717665 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | IDO1||PARP10 | 2 | 5.110512 | 4.748948 | 4.976853 | 5.259804 | 5.163897 | 4.969832 | 5.030711 | 4.769046 | 4.713898 | 4.763468 | 4.748744 | 4.968755 | 4.927337 | 4.958510 | 5.049949 |
| GO:0015813 | L-glutamate transmembrane transport | 2/204 | 28/20870 | 0.03042354303717665 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | SLC17A7||SLC7A11 | 2 | 5.077390 | 5.823594 | 5.845832 | 5.065012 | 5.080643 | 5.098487 | 5.065153 | 5.841488 | 5.816100 | 5.839491 | 5.796832 | 5.834984 | 5.840762 | 5.862066 | 5.845373 |
| GO:0032958 | inositol phosphate biosynthetic process | 2/204 | 28/20870 | 0.03042354303717665 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | MAS1||PTAFR | 2 | 5.212731 | 5.067277 | 5.050582 | 5.178466 | 5.237815 | 5.282288 | 5.148625 | 5.093352 | 5.052812 | 5.064949 | 5.057651 | 5.071875 | 4.997100 | 5.105931 | 5.024985 |
| GO:0035929 | steroid hormone secretion | 2/204 | 28/20870 | 0.03042354303717665 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | BMP6||C1QTNF1 | 2 | 4.651221 | 4.088170 | 3.961786 | 4.540676 | 4.533891 | 4.939005 | 4.548238 | 3.994797 | 4.372829 | 3.952793 | 3.989842 | 3.949204 | 4.099030 | 3.868944 | 3.919637 |
| GO:0044766 | multi-organism transport | 2/204 | 28/20870 | 0.03042354303717665 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | SIGLEC1||IFIT1 | 2 | 6.156746 | 6.857154 | 7.222997 | 6.138324 | 6.154825 | 6.144711 | 6.188601 | 6.837643 | 6.905956 | 6.824942 | 6.858750 | 7.222794 | 7.234383 | 7.212807 | 7.221924 |
| GO:0045655 | regulation of monocyte differentiation | 2/204 | 28/20870 | 0.03042354303717665 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | CSF1||IRF7 | 2 | 6.065140 | 6.032282 | 6.136033 | 6.061073 | 6.070927 | 6.071496 | 6.057010 | 6.020688 | 6.033272 | 6.011302 | 6.063331 | 6.122628 | 6.127471 | 6.122153 | 6.171293 |
| GO:0045844 | positive regulation of striated muscle tissue development | 2/204 | 28/20870 | 0.03042354303717665 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | IGF2||DLL1 | 2 | 6.094885 | 6.177046 | 6.201767 | 6.109129 | 6.053996 | 6.169988 | 6.042864 | 6.187739 | 6.128709 | 6.092039 | 6.291720 | 6.513854 | 6.040985 | 6.046140 | 6.152184 |
| GO:0048636 | positive regulation of muscle organ development | 2/204 | 28/20870 | 0.03042354303717665 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | IGF2||DLL1 | 2 | 6.094885 | 6.177046 | 6.201767 | 6.109129 | 6.053996 | 6.169988 | 6.042864 | 6.187739 | 6.128709 | 6.092039 | 6.291720 | 6.513854 | 6.040985 | 6.046140 | 6.152184 |
| GO:1902579 | multi-organism localization | 2/204 | 28/20870 | 0.03042354303717665 | 0.17515268348546 | 0.14308215165229 | SIGLEC1||IFIT1 | 2 | 6.156746 | 6.857154 | 7.222997 | 6.138324 | 6.154825 | 6.144711 | 6.188601 | 6.837643 | 6.905956 | 6.824942 | 6.858750 | 7.222794 | 7.234383 | 7.212807 | 7.221924 |
| GO:0044403 | biological process involved in symbiotic interaction | 8/204 | 373/20870 | 0.03074194975398995 | 0.17667031373772 | 0.14432190315130 | SIGLEC1||TYRO3||TREM1||TRIM22||TNFRSF14||LY6E||IFIT1||IFITM1 | 8 | 6.902122 | 7.395820 | 7.548096 | 6.899555 | 6.906464 | 6.899141 | 6.903316 | 7.389374 | 7.387939 | 7.401602 | 7.404294 | 7.530752 | 7.548769 | 7.559691 | 7.553012 |
| GO:0060042 | retina morphogenesis in camera-type eye | 3/204 | 70/20870 | 0.03122898541186691 | 0.17914990919548 | 0.14634748361208 | TFAP2A||IGFN1||DLL1 | 3 | 4.714610 | 5.297449 | 5.756285 | 4.608783 | 4.649712 | 4.649710 | 4.927121 | 5.245697 | 5.340457 | 5.362179 | 5.237184 | 5.746755 | 5.794535 | 5.718749 | 5.764052 |
| GO:0002456 | T cell mediated immunity | 5/204 | 179/20870 | 0.03148255818642109 | 0.18028377902846 | 0.14727374138997 | IL23A||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 5 | 7.252122 | 7.346730 | 7.483279 | 7.259104 | 7.246120 | 7.252621 | 7.250613 | 7.353232 | 7.343602 | 7.339912 | 7.350137 | 7.480327 | 7.487123 | 7.478612 | 7.487033 |
| GO:0071774 | response to fibroblast growth factor | 4/204 | 122/20870 | 0.03191409205100648 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | GCLC||CREB3L1||EGR3||SULF2 | 4 | 5.277294 | 6.195187 | 6.497489 | 5.284277 | 5.262162 | 5.300092 | 5.262290 | 6.211895 | 6.173947 | 6.206972 | 6.187614 | 6.496110 | 6.499574 | 6.484270 | 6.509885 |
| GO:0045580 | regulation of T cell differentiation | 5/204 | 180/20870 | 0.03213483924790745 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | IL23A||ADAM8||EGR3||HLA-DRA||PIK3R6 | 5 | 5.532778 | 5.688226 | 5.756855 | 5.541451 | 5.533799 | 5.545502 | 5.510100 | 5.702672 | 5.698218 | 5.681258 | 5.670526 | 5.745249 | 5.740396 | 5.794564 | 5.746536 |
| GO:0048469 | cell maturation | 5/204 | 180/20870 | 0.03213483924790745 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | SCARF1||VEGFA||BCL11A||C3||NR4A2 | 5 | 5.213382 | 5.372522 | 5.368306 | 5.208887 | 5.205846 | 5.240460 | 5.197971 | 5.417772 | 5.349167 | 5.345561 | 5.376426 | 5.368551 | 5.353382 | 5.383990 | 5.367136 |
| GO:1903034 | regulation of response to wounding | 5/204 | 180/20870 | 0.03213483924790745 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | SCARF1||RREB1||C1QTNF1||INPP5F||EPPK1 | 5 | 7.273095 | 7.787198 | 7.772440 | 7.267360 | 7.282083 | 7.272867 | 7.270028 | 7.801719 | 7.772782 | 7.783383 | 7.790756 | 7.760881 | 7.774495 | 7.764897 | 7.789321 |
| GO:0048511 | rhythmic process | 7/204 | 308/20870 | 0.03218784965549765 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | NR1H3||TYRO3||PTGDS||MAPK10||BHLHE40||MMP7||EGR3 | 7 | 5.801782 | 5.690177 | 5.705362 | 5.666735 | 5.757558 | 5.833726 | 5.935555 | 5.706440 | 5.776889 | 5.605044 | 5.666935 | 5.735123 | 5.669420 | 5.705972 | 5.710174 |
| GO:0048872 | homeostasis of number of cells | 7/204 | 308/20870 | 0.03218784965549765 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | VEGFA||CCR7||IL6||SLC7A11||GPRASP2||CSF1||ISG15 | 7 | 7.133257 | 7.101995 | 7.029263 | 7.132886 | 7.133271 | 7.128116 | 7.138735 | 7.097183 | 7.111722 | 7.095436 | 7.103581 | 7.036197 | 7.022288 | 7.045670 | 7.012674 |
| GO:0002763 | positive regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation | 3/204 | 71/20870 | 0.03237868262998747 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | IL23A||LIF||CSF1 | 3 | 6.748789 | 6.778638 | 6.809436 | 6.758624 | 6.726244 | 6.755078 | 6.754972 | 6.780707 | 6.769775 | 6.789587 | 6.774405 | 6.807255 | 6.810697 | 6.801764 | 6.817979 |
| GO:0002313 | mature B cell differentiation involved in immune response | 2/204 | 29/20870 | 0.03247059942410594 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | IL6||DLL1 | 2 | 7.705129 | 8.908139 | 9.074725 | 7.604933 | 7.745328 | 7.695945 | 7.768885 | 8.904907 | 8.849516 | 8.925165 | 8.951046 | 9.023596 | 9.080695 | 9.112146 | 9.081052 |
| GO:0002360 | T cell lineage commitment | 2/204 | 29/20870 | 0.03247059942410594 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | IL23A||IL6 | 2 | 6.460342 | 6.873947 | 7.197048 | 6.482032 | 6.465240 | 6.441129 | 6.452646 | 6.880702 | 6.869882 | 6.865632 | 6.879516 | 7.189817 | 7.202311 | 7.182359 | 7.213511 |
| GO:0036003 | positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to stress | 2/204 | 29/20870 | 0.03247059942410594 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | VEGFA||CREB3L1 | 2 | 6.016916 | 6.314735 | 6.472235 | 6.037693 | 6.014428 | 5.995389 | 6.019839 | 6.347558 | 6.290897 | 6.314085 | 6.305799 | 6.452893 | 6.515000 | 6.464003 | 6.456163 |
| GO:0038083 | peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation | 2/204 | 29/20870 | 0.03247059942410594 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | VEGFA||ITK | 2 | 4.789909 | 5.031604 | 5.259949 | 4.813836 | 4.805674 | 4.757386 | 4.782068 | 5.018935 | 4.970687 | 5.169904 | 4.956813 | 5.287240 | 5.284765 | 5.260195 | 5.206132 |
| GO:0048843 | negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance | 2/204 | 29/20870 | 0.03247059942410594 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | SEMA3F||SEMA6B | 2 | 3.512774 | 4.317263 | 4.629599 | 3.490920 | 3.610737 | 3.517096 | 3.426223 | 4.233298 | 4.324978 | 4.269763 | 4.433049 | 4.772307 | 4.481396 | 4.729512 | 4.512347 |
| GO:0072539 | T-helper 17 cell differentiation | 2/204 | 29/20870 | 0.03247059942410594 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | IL23A||IL6 | 2 | 4.408107 | 4.589005 | 5.156658 | 4.376470 | 4.470184 | 4.401870 | 4.381957 | 4.593954 | 4.585122 | 4.651677 | 4.522354 | 5.141030 | 5.165375 | 5.126043 | 5.193282 |
| GO:0072677 | eosinophil migration | 2/204 | 29/20870 | 0.03247059942410594 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | ADAM8||SCG2 | 2 | 4.531901 | 7.185498 | 7.852392 | 4.484303 | 4.550569 | 4.564861 | 4.526586 | 7.202571 | 7.217448 | 7.181733 | 7.139036 | 7.820399 | 7.874729 | 7.848485 | 7.865365 |
| GO:1901863 | positive regulation of muscle tissue development | 2/204 | 29/20870 | 0.03247059942410594 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | IGF2||DLL1 | 2 | 6.094885 | 6.177046 | 6.201767 | 6.109129 | 6.053996 | 6.169988 | 6.042864 | 6.187739 | 6.128709 | 6.092039 | 6.291720 | 6.513854 | 6.040985 | 6.046140 | 6.152184 |
| GO:2000108 | positive regulation of leukocyte apoptotic process | 2/204 | 29/20870 | 0.03247059942410594 | 0.18080347589519 | 0.14769828153643 | IDO1||ADAM8 | 2 | 5.726494 | 6.686068 | 7.156592 | 5.754002 | 5.689027 | 5.723925 | 5.738223 | 6.718949 | 6.709617 | 6.642206 | 6.672203 | 7.220066 | 7.144848 | 7.103615 | 7.155412 |
| GO:0038127 | ERBB signaling pathway | 4/204 | 123/20870 | 0.03274339591692541 | 0.18198413772473 | 0.14866276367614 | RPS6KA5||IFI6||BCAR3||MVB12B | 4 | 5.817586 | 6.779536 | 7.199713 | 5.793256 | 5.813949 | 5.814225 | 5.848370 | 6.764999 | 6.799107 | 6.780947 | 6.772869 | 7.189859 | 7.209164 | 7.200495 | 7.199270 |
| GO:0002718 | regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response | 5/204 | 181/20870 | 0.03279552854158382 | 0.18198413772473 | 0.14866276367614 | NR4A3||RSAD2||IL6||TNFRSF14||HLA-F | 5 | 7.326578 | 7.491935 | 7.648638 | 7.323246 | 7.321219 | 7.326671 | 7.335137 | 7.501182 | 7.487899 | 7.484795 | 7.493809 | 7.647032 | 7.658890 | 7.645842 | 7.642738 |
| GO:0002706 | regulation of lymphocyte mediated immunity | 7/204 | 311/20870 | 0.03365579186476843 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | IL23A||C3||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||PIK3R6 | 7 | 6.853314 | 6.916634 | 7.072982 | 6.858268 | 6.836771 | 6.858986 | 6.859103 | 6.922097 | 6.906552 | 6.913770 | 6.924049 | 7.064706 | 7.077007 | 7.075776 | 7.074406 |
| GO:0002822 | regulation of adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains | 6/204 | 245/20870 | 0.03368964157352868 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | IL23A||C3||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 6 | 6.727586 | 6.802310 | 6.970964 | 6.730342 | 6.711636 | 6.733177 | 6.735069 | 6.801436 | 6.796620 | 6.799164 | 6.811971 | 6.981579 | 6.968472 | 6.958331 | 6.975372 |
| GO:0048736 | appendage development | 5/204 | 183/20870 | 0.03414222715484159 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | ECE1||TBX2||TFAP2A||SLC7A11||SCX | 5 | 4.716451 | 4.440635 | 4.416370 | 4.757729 | 4.683006 | 4.734652 | 4.689060 | 4.421093 | 4.382228 | 4.475460 | 4.481455 | 4.421443 | 4.421780 | 4.392948 | 4.429045 |
| GO:0060173 | limb development | 5/204 | 183/20870 | 0.03414222715484159 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | ECE1||TBX2||TFAP2A||SLC7A11||SCX | 5 | 4.716451 | 4.440635 | 4.416370 | 4.757729 | 4.683006 | 4.734652 | 4.689060 | 4.421093 | 4.382228 | 4.475460 | 4.481455 | 4.421443 | 4.421780 | 4.392948 | 4.429045 |
| GO:0009308 | amine metabolic process | 4/204 | 125/20870 | 0.03443963542553875 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | IDO1||SLC7A11||NR4A2||LY6E | 4 | 6.824354 | 6.769113 | 6.923273 | 6.822559 | 6.824638 | 6.817618 | 6.832562 | 6.791564 | 6.769068 | 6.759167 | 6.756386 | 6.910484 | 6.935003 | 6.924600 | 6.922901 |
| GO:0042752 | regulation of circadian rhythm | 4/204 | 125/20870 | 0.03443963542553875 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | NR1H3||PTGDS||MAPK10||BHLHE40 | 4 | 5.497395 | 5.413841 | 5.310421 | 5.485313 | 5.514516 | 5.511822 | 5.477568 | 5.478054 | 5.472907 | 5.347346 | 5.351546 | 5.375237 | 5.290517 | 5.292420 | 5.281494 |
| GO:0045639 | positive regulation of myeloid cell differentiation | 4/204 | 125/20870 | 0.03443963542553875 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | IL23A||LIF||CSF1||ISG15 | 4 | 6.366791 | 6.350778 | 6.348035 | 6.375312 | 6.357400 | 6.370529 | 6.363859 | 6.350116 | 6.337014 | 6.361007 | 6.354869 | 6.346828 | 6.354898 | 6.340101 | 6.350272 |
| GO:0000737 | DNA catabolic process, endonucleolytic | 2/204 | 30/20870 | 0.03457021540483966 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | IL6||ST20 | 2 | 5.065031 | 5.037691 | 5.132702 | 5.093486 | 4.931268 | 5.154853 | 5.071352 | 4.995764 | 5.172546 | 5.018749 | 4.954098 | 5.172079 | 5.115243 | 5.126744 | 5.115985 |
| GO:0002068 | glandular epithelial cell development | 2/204 | 30/20870 | 0.03457021540483966 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | BMP6||DLL1 | 2 | 5.531032 | 5.773592 | 5.582932 | 5.524185 | 5.525131 | 5.449474 | 5.620231 | 6.043144 | 5.774826 | 5.779734 | 5.432500 | 5.585774 | 5.551554 | 5.737223 | 5.441581 |
| GO:0002468 | dendritic cell antigen processing and presentation | 2/204 | 30/20870 | 0.03457021540483966 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | CCR7||HLA-DRA | 2 | 5.160835 | 5.539716 | 6.162471 | 5.022226 | 5.199160 | 5.107806 | 5.299352 | 5.584281 | 5.510518 | 5.558857 | 5.503642 | 6.212503 | 6.131797 | 6.158566 | 6.145716 |
| GO:0003309 | type B pancreatic cell differentiation | 2/204 | 30/20870 | 0.03457021540483966 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | BMP6||DLL1 | 2 | 5.241813 | 5.484274 | 5.170005 | 5.282160 | 5.241693 | 5.106252 | 5.327790 | 5.819235 | 5.502349 | 5.497278 | 5.004306 | 5.170401 | 5.111786 | 5.415154 | 4.942418 |
| GO:0005979 | regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process | 2/204 | 30/20870 | 0.03457021540483966 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | IGF2||ENPP1 | 2 | 5.217585 | 5.438985 | 5.155266 | 5.307457 | 5.211131 | 5.043479 | 5.293281 | 5.628544 | 5.478203 | 5.487321 | 5.113368 | 5.188133 | 5.121672 | 5.286319 | 5.011067 |
| GO:0007202 | activation of phospholipase C activity | 2/204 | 30/20870 | 0.03457021540483966 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | LPAR2||ITK | 2 | 5.350617 | 5.738821 | 5.857806 | 5.437565 | 5.266405 | 5.403341 | 5.287750 | 5.711161 | 5.718766 | 5.747347 | 5.777069 | 5.837506 | 5.877609 | 5.861390 | 5.854433 |
| GO:0010962 | regulation of glucan biosynthetic process | 2/204 | 30/20870 | 0.03457021540483966 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | IGF2||ENPP1 | 2 | 5.217585 | 5.438985 | 5.155266 | 5.307457 | 5.211131 | 5.043479 | 5.293281 | 5.628544 | 5.478203 | 5.487321 | 5.113368 | 5.188133 | 5.121672 | 5.286319 | 5.011067 |
| GO:0030262 | apoptotic nuclear changes | 2/204 | 30/20870 | 0.03457021540483966 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | IL6||ST20 | 2 | 5.560699 | 5.198097 | 5.370687 | 5.587166 | 5.437261 | 5.587614 | 5.623726 | 5.138335 | 5.316113 | 5.177558 | 5.153365 | 5.419732 | 5.343906 | 5.354362 | 5.363549 |
| GO:0043302 | positive regulation of leukocyte degranulation | 2/204 | 30/20870 | 0.03457021540483966 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | PTAFR||HLA-F | 2 | 8.170683 | 7.856675 | 8.001338 | 8.171028 | 8.173323 | 8.170007 | 8.168371 | 7.851911 | 7.851557 | 7.873745 | 7.849349 | 7.976475 | 8.015941 | 8.018079 | 7.994456 |
| GO:0046426 | negative regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT | 2/204 | 30/20870 | 0.03457021540483966 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | SOCS3||INPP5F | 2 | 5.883192 | 6.392594 | 6.088795 | 5.825816 | 6.193033 | 5.808554 | 5.648451 | 5.941513 | 6.363305 | 6.497529 | 6.671359 | 6.050788 | 5.962916 | 6.389993 | 5.900083 |
| GO:0051491 | positive regulation of filopodium assembly | 2/204 | 30/20870 | 0.03457021540483966 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | RIPOR2||CCR7 | 2 | 5.592927 | 6.055857 | 6.211526 | 5.598149 | 5.573619 | 5.599295 | 5.600475 | 6.025052 | 6.075571 | 6.044195 | 6.077931 | 6.273093 | 6.138371 | 6.216049 | 6.215423 |
| GO:0090200 | positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria | 2/204 | 30/20870 | 0.03457021540483966 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | TNFSF10||CIDEB | 2 | 6.049907 | 7.889589 | 8.440117 | 6.039256 | 6.075341 | 6.055704 | 6.028899 | 7.876195 | 7.902992 | 7.891870 | 7.887170 | 8.422578 | 8.447996 | 8.441520 | 8.448225 |
| GO:1901623 | regulation of lymphocyte chemotaxis | 2/204 | 30/20870 | 0.03457021540483966 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | PADI2||CXCL10 | 2 | 5.331382 | 6.806797 | 7.384849 | 5.331896 | 5.318961 | 5.369776 | 5.304067 | 6.792531 | 6.816729 | 6.794995 | 6.822694 | 7.365369 | 7.397622 | 7.380315 | 7.395856 |
| GO:1903672 | positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis | 2/204 | 30/20870 | 0.03457021540483966 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | VEGFA||DLL1 | 2 | 6.659356 | 7.456890 | 7.550192 | 6.655649 | 6.637379 | 6.726233 | 6.615764 | 7.456112 | 7.469085 | 7.450514 | 7.451775 | 7.556934 | 7.580287 | 7.550485 | 7.512236 |
| GO:0001822 | kidney development | 7/204 | 313/20870 | 0.03465885749638875 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | VEGFA||LIF||TFAP2A||BMP6||SERPINB7||SULF2||DLL1 | 7 | 5.313700 | 5.928408 | 6.215419 | 5.305195 | 5.310914 | 5.311929 | 5.326674 | 5.922038 | 5.909460 | 5.933580 | 5.948271 | 6.220793 | 6.217764 | 6.203933 | 6.219124 |
| GO:0001916 | positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity | 3/204 | 73/20870 | 0.03474368868471972 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | IL23A||HLA-DRA||HLA-F | 3 | 8.482814 | 8.180112 | 8.259281 | 8.486891 | 8.471313 | 8.487194 | 8.485799 | 8.187655 | 8.182029 | 8.168210 | 8.182480 | 8.255091 | 8.260914 | 8.251131 | 8.269919 |
| GO:0006109 | regulation of carbohydrate metabolic process | 5/204 | 184/20870 | 0.03482828192267238 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | MAS1||IGF2||PTAFR||C1QTNF1||ENPP1 | 5 | 5.394518 | 5.531945 | 5.476133 | 5.412792 | 5.414288 | 5.350822 | 5.399254 | 5.563899 | 5.550574 | 5.535042 | 5.476742 | 5.489119 | 5.472087 | 5.506738 | 5.435636 |
| GO:0050954 | sensory perception of mechanical stimulus | 5/204 | 184/20870 | 0.03482828192267238 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | ATP8B1||RIPOR2||MKKS||TFAP2A||MYO7A | 5 | 6.184853 | 6.017609 | 5.953843 | 6.242813 | 6.141350 | 6.184275 | 6.169057 | 5.955463 | 6.024788 | 6.032869 | 6.055397 | 5.936360 | 5.922025 | 5.949580 | 6.005992 |
| GO:0097191 | extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | 6/204 | 247/20870 | 0.03484125935118077 | 0.18505472841550 | 0.15117112788807 | GCLC||IL1A||TNFSF10||G0S2||IFI6||SCG2 | 6 | 6.022110 | 6.373653 | 6.527441 | 6.003498 | 6.034585 | 6.026802 | 6.023374 | 6.402348 | 6.375292 | 6.377595 | 6.338661 | 6.530237 | 6.517321 | 6.519644 | 6.542423 |
| GO:0030282 | bone mineralization | 4/204 | 126/20870 | 0.03530660285712765 | 0.18721790725556 | 0.15293822775023 | TFAP2A||BMP6||ISG15||ENPP1 | 4 | 5.491586 | 5.906368 | 6.043337 | 5.501186 | 5.482005 | 5.470059 | 5.512714 | 5.911681 | 5.894233 | 5.888442 | 5.930737 | 6.125675 | 6.022738 | 6.006765 | 6.014889 |
| GO:0051048 | negative regulation of secretion | 5/204 | 185/20870 | 0.03552283581882679 | 0.18798981191036 | 0.15356879633007 | NR1H3||OSM||LIF||RSAD2||HLA-F | 5 | 5.667970 | 6.195364 | 6.379548 | 5.644101 | 5.648112 | 5.704547 | 5.674307 | 6.192649 | 6.204968 | 6.180980 | 6.202733 | 6.372883 | 6.403842 | 6.371142 | 6.370050 |
| GO:1901653 | cellular response to peptide | 8/204 | 384/20870 | 0.03556879195574499 | 0.18798981191036 | 0.15356879633007 | GCLC||NR4A3||MAS1||BCAR3||NR4A2||IGF2||SOCS3||ENPP1 | 8 | 5.985379 | 6.256252 | 6.304066 | 6.011784 | 5.984318 | 5.972470 | 5.972588 | 6.252794 | 6.266245 | 6.268177 | 6.237583 | 6.311011 | 6.292998 | 6.325167 | 6.286772 |
| GO:0015850 | organic hydroxy compound transport | 7/204 | 315/20870 | 0.03568162590398852 | 0.18827751540828 | 0.15380382119352 | NR1H3||ATP8B1||BMP6||LY6E||C1QTNF1||ABCA4||AQP1 | 7 | 7.054628 | 7.423600 | 7.417493 | 7.055060 | 7.044995 | 7.064995 | 7.053392 | 7.439227 | 7.413087 | 7.417700 | 7.424252 | 7.414298 | 7.425648 | 7.419145 | 7.410839 |
| GO:0006749 | glutathione metabolic process | 3/204 | 74/20870 | 0.03595886386809036 | 0.18881331776991 | 0.15424151791182 | GCLC||CHAC1||SLC7A11 | 3 | 7.022389 | 7.125127 | 6.996845 | 6.998422 | 7.027206 | 7.039401 | 7.024221 | 7.124544 | 7.120854 | 7.126432 | 7.128668 | 7.006494 | 6.959893 | 6.990465 | 7.029637 |
| GO:0042058 | regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway | 3/204 | 74/20870 | 0.03595886386809036 | 0.18881331776991 | 0.15424151791182 | IFI6||BCAR3||MVB12B | 3 | 5.779602 | 7.132688 | 7.674707 | 5.750577 | 5.784996 | 5.769159 | 5.812949 | 7.103296 | 7.166429 | 7.129090 | 7.131235 | 7.657724 | 7.687143 | 7.673702 | 7.680094 |
| GO:0043550 | regulation of lipid kinase activity | 3/204 | 74/20870 | 0.03595886386809036 | 0.18881331776991 | 0.15424151791182 | CCR7||SOCS3||PIK3R6 | 3 | 5.597439 | 5.805598 | 5.835996 | 5.595041 | 5.621030 | 5.582492 | 5.590905 | 5.775836 | 5.837911 | 5.811631 | 5.796301 | 5.810217 | 5.838649 | 5.872471 | 5.821880 |
| GO:0007188 | adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | 6/204 | 249/20870 | 0.03601803028601019 | 0.18881647096276 | 0.15424409375370 | LPAR2||ADGRE3||CXCL10||CXCL11||ADGRE1||SSTR2 | 6 | 5.952474 | 5.873913 | 5.795681 | 5.963739 | 5.923301 | 5.976958 | 5.945334 | 5.876842 | 5.831276 | 5.924128 | 5.861845 | 5.768991 | 5.844665 | 5.808900 | 5.758546 |
| GO:0006959 | humoral immune response | 8/204 | 386/20870 | 0.03649849028528172 | 0.19003062673440 | 0.15523593708028 | CFH||TREM1||C3||CCR7||IL6||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11 | 8 | 7.241684 | 7.602668 | 7.712654 | 7.251976 | 7.227700 | 7.234852 | 7.252051 | 7.581766 | 7.605475 | 7.611300 | 7.611921 | 7.732040 | 7.699158 | 7.718724 | 7.700434 |
| GO:0002438 | acute inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus | 2/204 | 31/20870 | 0.03672117880134411 | 0.19003062673440 | 0.15523593708028 | C3||CCR7 | 2 | 5.696193 | 6.349841 | 6.480971 | 5.670491 | 5.695995 | 5.692586 | 5.725174 | 6.326373 | 6.311382 | 6.351131 | 6.408568 | 6.483579 | 6.450933 | 6.507311 | 6.481506 |
| GO:0002863 | positive regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus | 2/204 | 31/20870 | 0.03672117880134411 | 0.19003062673440 | 0.15523593708028 | C3||CCR7 | 2 | 7.291821 | 7.653552 | 7.708634 | 7.302586 | 7.297231 | 7.273480 | 7.293818 | 7.637247 | 7.627083 | 7.667484 | 7.681716 | 7.694036 | 7.676737 | 7.731347 | 7.731628 |
| GO:0010888 | negative regulation of lipid storage | 2/204 | 31/20870 | 0.03672117880134411 | 0.19003062673440 | 0.15523593708028 | NR1H3||IL6 | 2 | 5.716110 | 5.632448 | 5.713524 | 5.692819 | 5.692599 | 5.762448 | 5.715445 | 5.596601 | 5.776347 | 5.579305 | 5.567261 | 5.717764 | 5.705967 | 5.745262 | 5.684434 |
| GO:0019359 | nicotinamide nucleotide biosynthetic process | 2/204 | 31/20870 | 0.03672117880134411 | 0.19003062673440 | 0.15523593708028 | IDO1||PARP10 | 2 | 5.362089 | 5.072028 | 5.236448 | 5.484479 | 5.330753 | 5.250998 | 5.372240 | 5.095308 | 5.132730 | 5.030618 | 5.026679 | 5.256552 | 5.222196 | 5.187478 | 5.277932 |
| GO:0019363 | pyridine nucleotide biosynthetic process | 2/204 | 31/20870 | 0.03672117880134411 | 0.19003062673440 | 0.15523593708028 | IDO1||PARP10 | 2 | 5.362089 | 5.072028 | 5.236448 | 5.484479 | 5.330753 | 5.250998 | 5.372240 | 5.095308 | 5.132730 | 5.030618 | 5.026679 | 5.256552 | 5.222196 | 5.187478 | 5.277932 |
| GO:0035066 | positive regulation of histone acetylation | 2/204 | 31/20870 | 0.03672117880134411 | 0.19003062673440 | 0.15523593708028 | RPS6KA5||LIF | 2 | 5.086219 | 6.607498 | 7.179867 | 5.050960 | 5.195141 | 5.006793 | 5.085190 | 6.620769 | 6.565526 | 6.624672 | 6.618215 | 7.162734 | 7.195393 | 7.176444 | 7.184701 |
| GO:0048679 | regulation of axon regeneration | 2/204 | 31/20870 | 0.03672117880134411 | 0.19003062673440 | 0.15523593708028 | SCARF1||INPP5F | 2 | 9.031149 | 9.684207 | 9.680920 | 9.025821 | 9.034504 | 9.046150 | 9.017969 | 9.694678 | 9.672942 | 9.683639 | 9.685485 | 9.679528 | 9.687037 | 9.672045 | 9.685025 |
| GO:0032481 | positive regulation of type I interferon production | 3/204 | 75/20870 | 0.03719572260876194 | 0.19047239755854 | 0.15559681947612 | OAS2||IRF7||ISG15 | 3 | 6.149076 | 6.440955 | 6.415428 | 6.196729 | 6.147805 | 6.133283 | 6.117257 | 6.423921 | 6.440046 | 6.457462 | 6.442195 | 6.387141 | 6.408484 | 6.473429 | 6.390976 |
| GO:0045669 | positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation | 3/204 | 75/20870 | 0.03719572260876194 | 0.19047239755854 | 0.15559681947612 | IL6||BMP6||IFITM1 | 3 | 5.850394 | 6.146271 | 6.232834 | 5.826446 | 5.840629 | 5.874743 | 5.859295 | 6.129613 | 6.144624 | 6.105667 | 6.203373 | 6.345485 | 6.180250 | 6.176245 | 6.222766 |
| GO:0045913 | positive regulation of carbohydrate metabolic process | 3/204 | 75/20870 | 0.03719572260876194 | 0.19047239755854 | 0.15559681947612 | MAS1||IGF2||PTAFR | 3 | 4.957818 | 4.996778 | 4.940409 | 4.981161 | 4.960104 | 4.945236 | 4.944464 | 4.982769 | 5.086926 | 4.943328 | 4.969920 | 4.931937 | 4.934314 | 4.971380 | 4.923534 |
| GO:0046596 | regulation of viral entry into host cell | 3/204 | 75/20870 | 0.03719572260876194 | 0.19047239755854 | 0.15559681947612 | TRIM22||LY6E||IFITM1 | 3 | 7.625252 | 8.428973 | 8.610281 | 7.551352 | 7.667547 | 7.603568 | 7.675022 | 8.431546 | 8.367657 | 8.446891 | 8.467869 | 8.563536 | 8.618928 | 8.631541 | 8.626101 |
| GO:1903201 | regulation of oxidative stress-induced cell death | 3/204 | 75/20870 | 0.03719572260876194 | 0.19047239755854 | 0.15559681947612 | NR4A3||MEAK7||SLC7A11 | 3 | 7.204569 | 7.068441 | 7.021875 | 7.181378 | 7.205955 | 7.191758 | 7.238538 | 7.090299 | 7.048605 | 7.056391 | 7.078083 | 7.000828 | 7.052655 | 7.026453 | 7.006998 |
| GO:0045637 | regulation of myeloid cell differentiation | 6/204 | 251/20870 | 0.03722010250058252 | 0.19047239755854 | 0.15559681947612 | IL23A||LIF||CSF1||IRF7||ISG15||DLL1 | 6 | 6.685134 | 6.633946 | 6.636374 | 6.687340 | 6.676999 | 6.704535 | 6.671443 | 6.631713 | 6.649126 | 6.627145 | 6.627689 | 6.661882 | 6.632116 | 6.623566 | 6.627616 |
| GO:0050769 | positive regulation of neurogenesis | 6/204 | 251/20870 | 0.03722010250058252 | 0.19047239755854 | 0.15559681947612 | CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||LIF||IL6||GPRASP2 | 6 | 5.781910 | 6.048327 | 6.170047 | 5.775312 | 5.773312 | 5.811535 | 5.767059 | 6.039635 | 6.043923 | 6.033215 | 6.076154 | 6.188475 | 6.183910 | 6.160144 | 6.147259 |
| GO:0032944 | regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation | 7/204 | 319/20870 | 0.03778677199604834 | 0.19306585248060 | 0.15771541168423 | IL23A||IL1A||IL6||TNFRSF14||IGF2||CSF1||PDCD1LG2 | 7 | 6.471003 | 6.938423 | 7.093530 | 6.479618 | 6.470844 | 6.467631 | 6.465880 | 6.950110 | 6.933453 | 6.932690 | 6.937372 | 7.108094 | 7.092809 | 7.090250 | 7.082850 |
| GO:0042129 | regulation of T cell proliferation | 6/204 | 253/20870 | 0.03844761679213974 | 0.19515627060564 | 0.15942307334965 | IL23A||IL1A||IL6||TNFRSF14||IGF2||PDCD1LG2 | 6 | 6.411051 | 6.933307 | 7.134707 | 6.410779 | 6.417388 | 6.411856 | 6.404150 | 6.956830 | 6.922828 | 6.931145 | 6.922149 | 7.127281 | 7.139483 | 7.141385 | 7.130631 |
| GO:0043087 | regulation of GTPase activity | 8/204 | 391/20870 | 0.03889423687868527 | 0.19515627060564 | 0.15942307334965 | CDKL5||CCL22||RASAL1||RIPOR2||MKKS||CCR7||BCAR3||FGD2 | 8 | 5.628103 | 5.898395 | 6.030590 | 5.635304 | 5.606877 | 5.623614 | 5.646323 | 5.899140 | 5.923795 | 5.867187 | 5.902893 | 6.053783 | 6.017906 | 6.022098 | 6.028303 |
| GO:0043406 | positive regulation of MAP kinase activity | 4/204 | 130/20870 | 0.03890040087474888 | 0.19515627060564 | 0.15942307334965 | VEGFA||FGD2||ADAM8||PIK3R6 | 4 | 6.011789 | 6.577173 | 6.729670 | 6.002882 | 6.013198 | 6.008174 | 6.022827 | 6.585047 | 6.545631 | 6.597341 | 6.580163 | 6.720435 | 6.747185 | 6.726647 | 6.724264 |
| GO:0002726 | positive regulation of T cell cytokine production | 2/204 | 32/20870 | 0.03892229590552952 | 0.19515627060564 | 0.15942307334965 | RSAD2||IL6 | 2 | 8.513535 | 8.485796 | 8.678677 | 8.525804 | 8.501076 | 8.511088 | 8.516063 | 8.494988 | 8.485017 | 8.474899 | 8.488205 | 8.675948 | 8.677864 | 8.678342 | 8.682545 |
| GO:0002828 | regulation of type 2 immune response | 2/204 | 32/20870 | 0.03892229590552952 | 0.19515627060564 | 0.15942307334965 | RSAD2||IL6 | 2 | 6.375473 | 6.462089 | 6.567095 | 6.396683 | 6.378514 | 6.358989 | 6.367431 | 6.438010 | 6.465724 | 6.494837 | 6.449148 | 6.568563 | 6.553154 | 6.567961 | 6.578588 |
| GO:0006921 | cellular component disassembly involved in execution phase of apoptosis | 2/204 | 32/20870 | 0.03892229590552952 | 0.19515627060564 | 0.15942307334965 | IL6||ST20 | 2 | 5.530002 | 5.161362 | 5.336231 | 5.553583 | 5.414913 | 5.551710 | 5.593553 | 5.102672 | 5.275676 | 5.142845 | 5.117652 | 5.376716 | 5.313779 | 5.317818 | 5.335745 |
| GO:0035767 | endothelial cell chemotaxis | 2/204 | 32/20870 | 0.03892229590552952 | 0.19515627060564 | 0.15942307334965 | VEGFA||EGR3 | 2 | 9.243718 | 9.330775 | 9.276338 | 9.240609 | 9.238669 | 9.252667 | 9.242887 | 9.345276 | 9.315340 | 9.331137 | 9.331190 | 9.271794 | 9.270530 | 9.288263 | 9.274695 |
| GO:0045662 | negative regulation of myoblast differentiation | 2/204 | 32/20870 | 0.03892229590552952 | 0.19515627060564 | 0.15942307334965 | CXCL10||DLL1 | 2 | 5.576500 | 6.056171 | 6.284186 | 5.518534 | 5.582155 | 5.591425 | 5.612201 | 6.072702 | 6.015200 | 6.075349 | 6.060625 | 6.296012 | 6.286627 | 6.282973 | 6.271022 |
| GO:0048641 | regulation of skeletal muscle tissue development | 2/204 | 32/20870 | 0.03892229590552952 | 0.19515627060564 | 0.15942307334965 | IGF2||DLL1 | 2 | 6.348893 | 6.647076 | 6.714533 | 6.352996 | 6.307197 | 6.391340 | 6.342792 | 6.674550 | 6.582051 | 6.603659 | 6.723623 | 6.908544 | 6.640091 | 6.616068 | 6.674041 |
| GO:0050927 | positive regulation of positive chemotaxis | 2/204 | 32/20870 | 0.03892229590552952 | 0.19515627060564 | 0.15942307334965 | VEGFA||SCG2 | 2 | 4.705163 | 6.422350 | 6.860251 | 4.685507 | 4.726485 | 4.748921 | 4.658014 | 6.459330 | 6.380799 | 6.409915 | 6.438145 | 6.890080 | 6.863274 | 6.865000 | 6.821822 |
| GO:0061036 | positive regulation of cartilage development | 2/204 | 32/20870 | 0.03892229590552952 | 0.19515627060564 | 0.15942307334965 | BMP6||SCX | 2 | 4.459215 | 3.776641 | 3.843298 | 4.511087 | 4.507912 | 4.438618 | 4.374906 | 3.708464 | 3.810083 | 3.824967 | 3.760162 | 3.847998 | 3.781354 | 3.814107 | 3.925722 |
| GO:0090022 | regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis | 2/204 | 32/20870 | 0.03892229590552952 | 0.19515627060564 | 0.15942307334965 | RIPOR2||CCR7 | 2 | 5.657875 | 6.926377 | 7.150540 | 5.650823 | 5.672276 | 5.665221 | 5.642994 | 6.929289 | 6.920499 | 6.940616 | 6.914971 | 7.159624 | 7.158554 | 7.155299 | 7.128457 |
| GO:0002573 | myeloid leukocyte differentiation | 6/204 | 254/20870 | 0.03907095670148741 | 0.19559746025714 | 0.15978348098581 | IL23A||VEGFA||CCR7||LIF||CSF1||IRF7 | 6 | 6.275507 | 6.841037 | 7.043956 | 6.281349 | 6.269913 | 6.272736 | 6.278000 | 6.842299 | 6.844590 | 6.838706 | 6.838542 | 7.035573 | 7.048174 | 7.046426 | 7.045619 |
| GO:0072001 | renal system development | 7/204 | 322/20870 | 0.03941825991809837 | 0.19703018600922 | 0.16095387403522 | VEGFA||LIF||TFAP2A||BMP6||SERPINB7||SULF2||DLL1 | 7 | 5.290168 | 5.901236 | 6.187906 | 5.283495 | 5.286894 | 5.287126 | 5.303075 | 5.895136 | 5.882358 | 5.906304 | 5.920867 | 6.194073 | 6.189687 | 6.176298 | 6.191500 |
| GO:0050671 | positive regulation of lymphocyte proliferation | 5/204 | 191/20870 | 0.03986972727686814 | 0.19867078939818 | 0.16229408223660 | IL23A||IL1A||IL6||IGF2||PDCD1LG2 | 5 | 6.513967 | 7.098230 | 7.296430 | 6.503281 | 6.519574 | 6.517444 | 6.515513 | 7.105967 | 7.094620 | 7.098839 | 7.093461 | 7.308644 | 7.296613 | 7.283715 | 7.296641 |
| GO:0051302 | regulation of cell division | 5/204 | 191/20870 | 0.03986972727686814 | 0.19867078939818 | 0.16229408223660 | OSM||VEGFA||IL1A||IGF2||DLL1 | 5 | 6.626740 | 6.949014 | 6.985938 | 6.640494 | 6.631907 | 6.631482 | 6.602798 | 6.952018 | 6.951812 | 6.937934 | 6.954234 | 7.000120 | 6.992968 | 6.960770 | 6.989585 |
| GO:0002753 | cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway | 3/204 | 78/20870 | 0.04103557810345195 | 0.20142608398762 | 0.16454488119924 | OASL||SLC15A2||IRF7 | 3 | 5.170636 | 5.209260 | 5.202277 | 5.255074 | 5.129622 | 5.146196 | 5.148177 | 5.240772 | 5.199269 | 5.230019 | 5.165800 | 5.182638 | 5.215033 | 5.173320 | 5.237213 |
| GO:0035924 | cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus | 3/204 | 78/20870 | 0.04103557810345195 | 0.20142608398762 | 0.16454488119924 | VEGFA||EGR3||DLL1 | 3 | 6.186134 | 6.417356 | 6.492260 | 6.219597 | 6.186500 | 6.197744 | 6.139511 | 6.429893 | 6.430472 | 6.384117 | 6.424431 | 6.471456 | 6.552112 | 6.455251 | 6.488335 |
| GO:0042093 | T-helper cell differentiation | 3/204 | 78/20870 | 0.04103557810345195 | 0.20142608398762 | 0.16454488119924 | IL23A||IL6||HLA-DRA | 3 | 5.117749 | 5.245153 | 5.412241 | 5.115985 | 5.139379 | 5.123888 | 5.091327 | 5.243213 | 5.243851 | 5.267848 | 5.225382 | 5.420758 | 5.415577 | 5.384348 | 5.427897 |
| GO:0048644 | muscle organ morphogenesis | 3/204 | 78/20870 | 0.04103557810345195 | 0.20142608398762 | 0.16454488119924 | LIF||ANKRD1||LY6E | 3 | 5.132797 | 5.309763 | 5.435590 | 5.108064 | 5.102638 | 5.103870 | 5.213506 | 5.331057 | 5.294131 | 5.327240 | 5.286083 | 5.439355 | 5.466459 | 5.421010 | 5.414979 |
| GO:0010743 | regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation | 2/204 | 33/20870 | 0.04117239123692314 | 0.20142608398762 | 0.16454488119924 | NR1H3||CSF1 | 2 | 6.084653 | 6.104573 | 5.962847 | 6.105236 | 6.077590 | 6.088988 | 6.066512 | 6.110942 | 6.097336 | 6.121057 | 6.088744 | 5.955709 | 5.978972 | 5.981461 | 5.934743 |
| GO:0030201 | heparan sulfate proteoglycan metabolic process | 2/204 | 33/20870 | 0.04117239123692314 | 0.20142608398762 | 0.16454488119924 | DSE||SULF2 | 2 | 4.820642 | 4.860302 | 4.795973 | 4.833371 | 4.758463 | 4.878271 | 4.809878 | 4.831572 | 4.774981 | 4.805486 | 5.016600 | 4.791528 | 4.793805 | 4.818352 | 4.779934 |
| GO:0035456 | response to interferon-beta | 2/204 | 33/20870 | 0.04117239123692314 | 0.20142608398762 | 0.16454488119924 | XAF1||IFITM1 | 2 | 6.342222 | 6.025942 | 6.299906 | 6.332319 | 6.394615 | 6.333625 | 6.306876 | 6.052162 | 6.022565 | 6.040214 | 5.988019 | 6.258982 | 6.315207 | 6.365883 | 6.256724 |
| GO:0035883 | enteroendocrine cell differentiation | 2/204 | 33/20870 | 0.04117239123692314 | 0.20142608398762 | 0.16454488119924 | BMP6||DLL1 | 2 | 5.180825 | 5.437495 | 5.125683 | 5.219887 | 5.183219 | 5.045317 | 5.265629 | 5.767959 | 5.453985 | 5.449835 | 4.968558 | 5.125164 | 5.067188 | 5.366153 | 4.905937 |
| GO:0043171 | peptide catabolic process | 2/204 | 33/20870 | 0.04117239123692314 | 0.20142608398762 | 0.16454488119924 | ECE1||CHAC1 | 2 | 6.373581 | 6.741037 | 6.928462 | 6.368881 | 6.374436 | 6.428890 | 6.320056 | 6.772249 | 6.742508 | 6.705814 | 6.742807 | 6.966122 | 6.882426 | 6.961607 | 6.901843 |
| GO:0045672 | positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation | 2/204 | 33/20870 | 0.04117239123692314 | 0.20142608398762 | 0.16454488119924 | IL23A||CSF1 | 2 | 7.066960 | 7.075585 | 7.078406 | 7.090333 | 7.037072 | 7.083640 | 7.056162 | 7.072660 | 7.083563 | 7.082471 | 7.063556 | 7.071790 | 7.088484 | 7.050464 | 7.102365 |
| GO:0048710 | regulation of astrocyte differentiation | 2/204 | 33/20870 | 0.04117239123692314 | 0.20142608398762 | 0.16454488119924 | LIF||IL6 | 2 | 5.859461 | 5.572299 | 5.492805 | 5.857705 | 5.848985 | 5.856924 | 5.874115 | 5.604994 | 5.624816 | 5.491290 | 5.564501 | 5.505143 | 5.454358 | 5.494075 | 5.516881 |
| GO:0050926 | regulation of positive chemotaxis | 2/204 | 33/20870 | 0.04117239123692314 | 0.20142608398762 | 0.16454488119924 | VEGFA||SCG2 | 2 | 4.705163 | 6.422350 | 6.860251 | 4.685507 | 4.726485 | 4.748921 | 4.658014 | 6.459330 | 6.380799 | 6.409915 | 6.438145 | 6.890080 | 6.863274 | 6.865000 | 6.821822 |
| GO:0002702 | positive regulation of production of molecular mediator of immune response | 5/204 | 193/20870 | 0.04138751048274409 | 0.20186586050888 | 0.16490413444992 | NR4A3||RSAD2||IL6||TNFRSF14||HLA-F | 5 | 7.103839 | 7.264981 | 7.406160 | 7.101572 | 7.088609 | 7.112989 | 7.112053 | 7.266337 | 7.265386 | 7.261595 | 7.266599 | 7.404209 | 7.411691 | 7.404616 | 7.404110 |
| GO:0031345 | negative regulation of cell projection organization | 5/204 | 193/20870 | 0.04138751048274409 | 0.20186586050888 | 0.16490413444992 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||BCL11A||SEMA6B||INPP5F | 5 | 7.468749 | 7.932533 | 7.962798 | 7.453308 | 7.475755 | 7.470617 | 7.475201 | 7.939258 | 7.907273 | 7.943196 | 7.940108 | 7.950758 | 7.962814 | 7.977468 | 7.960025 |
| GO:0045444 | fat cell differentiation | 6/204 | 258/20870 | 0.04162856896570580 | 0.20260785434246 | 0.16551026889279 | NR4A3||RREB1||MKKS||IL6||NR4A2||ENPP1 | 6 | 5.426686 | 5.400187 | 5.399313 | 5.454257 | 5.407518 | 5.400619 | 5.443624 | 5.401391 | 5.345429 | 5.353565 | 5.495380 | 5.393983 | 5.419807 | 5.387443 | 5.395810 |
| GO:0022612 | gland morphogenesis | 4/204 | 133/20870 | 0.04172816851221910 | 0.20260785434246 | 0.16551026889279 | TBX2||IL6||CSF1||SULF2 | 4 | 5.543181 | 6.025654 | 6.084659 | 5.541444 | 5.557896 | 5.544233 | 5.529003 | 6.002327 | 5.996419 | 6.068008 | 6.034722 | 6.063664 | 6.112672 | 6.071990 | 6.089821 |
| GO:0035270 | endocrine system development | 4/204 | 133/20870 | 0.04172816851221910 | 0.20260785434246 | 0.16551026889279 | IL6||BMP6||LY6E||DLL1 | 4 | 5.413428 | 5.200001 | 5.022361 | 5.404365 | 5.413551 | 5.362884 | 5.470850 | 5.330573 | 5.206485 | 5.221131 | 5.025403 | 5.044480 | 5.015732 | 5.092647 | 4.931881 |
| GO:0042490 | mechanoreceptor differentiation | 3/204 | 79/20870 | 0.04235832503326046 | 0.20535825549960 | 0.16775707041269 | ATP8B1||MYO7A||DLL1 | 3 | 4.585445 | 4.314638 | 4.406932 | 4.619310 | 4.555216 | 4.608906 | 4.557167 | 4.348769 | 4.271955 | 4.317890 | 4.318896 | 4.385872 | 4.365257 | 4.426626 | 4.448486 |
| GO:0001659 | temperature homeostasis | 5/204 | 195/20870 | 0.04293990018917246 | 0.20750551443757 | 0.16951116531370 | NR1H3||VEGFA||PRLR||IL1A||G0S2 | 5 | 5.911761 | 5.866731 | 6.008145 | 5.884871 | 5.890799 | 5.922931 | 5.947551 | 5.851267 | 5.861142 | 5.888678 | 5.865577 | 6.012223 | 6.034524 | 6.001813 | 5.983550 |
| GO:0002440 | production of molecular mediator of immune response | 9/204 | 472/20870 | 0.04299378983234232 | 0.20750551443757 | 0.16951116531370 | AICDA||NR4A3||TREM1||RSAD2||IL6||TNFRSF14||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA2 | 9 | 6.541621 | 6.740258 | 6.877389 | 6.537033 | 6.532875 | 6.548984 | 6.547528 | 6.739298 | 6.736994 | 6.734320 | 6.750368 | 6.875284 | 6.880775 | 6.880014 | 6.873472 |
| GO:0010039 | response to iron ion | 2/204 | 34/20870 | 0.04347030730327928 | 0.20750551443757 | 0.16951116531370 | TFAP2A||BMP6 | 2 | 8.219269 | 7.880241 | 7.899104 | 8.231866 | 8.202869 | 8.212294 | 8.229845 | 7.896364 | 7.885271 | 7.858082 | 7.880977 | 7.899586 | 7.902316 | 7.895077 | 7.899427 |
| GO:0032816 | positive regulation of natural killer cell activation | 2/204 | 34/20870 | 0.04347030730327928 | 0.20750551443757 | 0.16951116531370 | IL23A||HLA-F | 2 | 7.162674 | 7.161341 | 7.101896 | 7.188458 | 7.123869 | 7.178257 | 7.159276 | 7.159650 | 7.185661 | 7.160644 | 7.139030 | 7.104312 | 7.120606 | 7.065666 | 7.116350 |
| GO:0033238 | regulation of cellular amine metabolic process | 2/204 | 34/20870 | 0.04347030730327928 | 0.20750551443757 | 0.16951116531370 | SLC7A11||NR4A2 | 2 | 8.198027 | 7.960199 | 8.150450 | 8.195217 | 8.200896 | 8.198182 | 8.197808 | 7.969907 | 7.958739 | 7.958995 | 7.953103 | 8.131147 | 8.167609 | 8.156939 | 8.145850 |
| GO:0042104 | positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation | 2/204 | 34/20870 | 0.04347030730327928 | 0.20750551443757 | 0.16951116531370 | IL23A||IGF2 | 2 | 7.432329 | 7.614432 | 7.605994 | 7.419812 | 7.447136 | 7.425538 | 7.436678 | 7.624616 | 7.602278 | 7.630778 | 7.599803 | 7.594091 | 7.631608 | 7.597116 | 7.600848 |
| GO:0048048 | embryonic eye morphogenesis | 2/204 | 34/20870 | 0.04347030730327928 | 0.20750551443757 | 0.16951116531370 | TBX2||TFAP2A | 2 | 5.741480 | 4.806202 | 4.490057 | 5.685245 | 5.692176 | 5.671241 | 5.904137 | 4.810383 | 4.824720 | 4.871861 | 4.713273 | 4.569351 | 4.578190 | 4.440620 | 4.360628 |
| GO:0072525 | pyridine-containing compound biosynthetic process | 2/204 | 34/20870 | 0.04347030730327928 | 0.20750551443757 | 0.16951116531370 | IDO1||PARP10 | 2 | 5.309907 | 5.145190 | 5.348850 | 5.432832 | 5.277535 | 5.209487 | 5.310609 | 5.127652 | 5.222441 | 5.122002 | 5.105732 | 5.380042 | 5.326660 | 5.301180 | 5.385755 |
| GO:1904996 | positive regulation of leukocyte adhesion to vascular endothelial cell | 2/204 | 34/20870 | 0.04347030730327928 | 0.20750551443757 | 0.16951116531370 | IL6||PTAFR | 2 | 7.975716 | 7.807143 | 7.948354 | 8.015851 | 7.966284 | 7.966467 | 7.953468 | 7.812469 | 7.788850 | 7.812505 | 7.814593 | 7.919363 | 7.960946 | 7.963911 | 7.948766 |
| GO:0035710 | CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation | 4/204 | 135/20870 | 0.04367643536536304 | 0.20750551443757 | 0.16951116531370 | IL23A||RSAD2||IL6||HLA-DRA | 4 | 5.937874 | 6.337003 | 6.550608 | 5.945117 | 5.943876 | 5.933473 | 5.928967 | 6.343940 | 6.330447 | 6.344782 | 6.328768 | 6.549884 | 6.551690 | 6.536360 | 6.564362 |
| GO:0045446 | endothelial cell differentiation | 4/204 | 135/20870 | 0.04367643536536304 | 0.20750551443757 | 0.16951116531370 | TIE1||VEGFA||BMP6||DLL1 | 4 | 6.002602 | 6.331996 | 6.496598 | 6.004223 | 5.999611 | 6.013324 | 5.993175 | 6.344116 | 6.322843 | 6.325244 | 6.335681 | 6.495706 | 6.507534 | 6.497333 | 6.485735 |
| GO:0002294 | CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation involved in immune response | 3/204 | 80/20870 | 0.04370230902701896 | 0.20750551443757 | 0.16951116531370 | IL23A||IL6||HLA-DRA | 3 | 5.328474 | 5.438681 | 5.567450 | 5.314256 | 5.336688 | 5.342323 | 5.320449 | 5.451465 | 5.429311 | 5.459815 | 5.413674 | 5.571168 | 5.577039 | 5.547069 | 5.574327 |
| GO:0022617 | extracellular matrix disassembly | 3/204 | 80/20870 | 0.04370230902701896 | 0.20750551443757 | 0.16951116531370 | IL6||MMP7||ADAM8 | 3 | 7.159245 | 7.964050 | 8.279879 | 7.146376 | 7.155856 | 7.171877 | 7.162750 | 7.951094 | 7.958658 | 7.980144 | 7.966143 | 8.265665 | 8.300565 | 8.283571 | 8.269453 |
| GO:1901184 | regulation of ERBB signaling pathway | 3/204 | 80/20870 | 0.04370230902701896 | 0.20750551443757 | 0.16951116531370 | IFI6||BCAR3||MVB12B | 3 | 5.882000 | 7.099155 | 7.603495 | 5.864011 | 5.882229 | 5.870719 | 5.910601 | 7.073172 | 7.130939 | 7.094602 | 7.097315 | 7.587163 | 7.616828 | 7.603696 | 7.606139 |
| GO:0061448 | connective tissue development | 6/204 | 262/20870 | 0.04428967998695390 | 0.20998518864403 | 0.17153681010427 | MKKS||BMP6||SERPINB7||CSF1||SULF2||SCX | 6 | 6.095395 | 6.042240 | 6.279315 | 6.101091 | 6.057263 | 6.105755 | 6.116763 | 6.034553 | 6.021797 | 6.040486 | 6.071656 | 6.301367 | 6.271190 | 6.254910 | 6.289361 |
| GO:1905952 | regulation of lipid localization | 5/204 | 197/20870 | 0.04452699338828932 | 0.21046788209992 | 0.17193112218036 | NR1H3||C3||IL6||BMP6||C1QTNF1 | 5 | 7.009643 | 7.641647 | 7.694137 | 7.006126 | 6.996048 | 7.028010 | 7.008203 | 7.648707 | 7.635400 | 7.634508 | 7.647911 | 7.689472 | 7.704715 | 7.692719 | 7.689589 |
| GO:0031589 | cell-substrate adhesion | 8/204 | 402/20870 | 0.04453071978415246 | 0.21046788209992 | 0.17193112218036 | COL5A3||SIGLEC1||TYRO3||UNC13D||VEGFA||RREB1||CCR7||CSF1 | 8 | 6.833107 | 7.161844 | 7.221972 | 6.819355 | 6.838695 | 6.843922 | 6.830339 | 7.153955 | 7.151054 | 7.173612 | 7.168630 | 7.207712 | 7.229021 | 7.228773 | 7.222279 |
| GO:0006909 | phagocytosis | 7/204 | 331/20870 | 0.04458733358382392 | 0.21046788209992 | 0.17193112218036 | NR1H3||TYRO3||UNC13D||ELMO3||NCF2||C3||MYO7A | 7 | 7.211427 | 7.269065 | 7.295502 | 7.212014 | 7.216168 | 7.220221 | 7.197200 | 7.263564 | 7.279756 | 7.272051 | 7.260812 | 7.283501 | 7.308381 | 7.298493 | 7.291516 |
| GO:0010565 | regulation of cellular ketone metabolic process | 4/204 | 136/20870 | 0.04466948746299488 | 0.21054740874371 | 0.17199608746139 | NR1H3||NR4A3||SLC7A11||BMP6 | 4 | 5.658630 | 6.246699 | 6.512403 | 5.650169 | 5.645612 | 5.657915 | 5.680574 | 6.239947 | 6.233320 | 6.237710 | 6.275427 | 6.502725 | 6.533288 | 6.513171 | 6.500192 |
| GO:0002287 | alpha-beta T cell activation involved in immune response | 3/204 | 81/20870 | 0.04506742719021338 | 0.21180376860240 | 0.17302240728850 | IL23A||IL6||HLA-DRA | 3 | 5.302077 | 5.412282 | 5.541013 | 5.287967 | 5.309979 | 5.316230 | 5.293949 | 5.425024 | 5.403048 | 5.433293 | 5.387309 | 5.544644 | 5.550556 | 5.520517 | 5.548137 |
| GO:0002293 | alpha-beta T cell differentiation involved in immune response | 3/204 | 81/20870 | 0.04506742719021338 | 0.21180376860240 | 0.17302240728850 | IL23A||IL6||HLA-DRA | 3 | 5.302077 | 5.412282 | 5.541013 | 5.287967 | 5.309979 | 5.316230 | 5.293949 | 5.425024 | 5.403048 | 5.433293 | 5.387309 | 5.544644 | 5.550556 | 5.520517 | 5.548137 |
| GO:0002335 | mature B cell differentiation | 2/204 | 35/20870 | 0.04581490436408962 | 0.21252841966881 | 0.17361437443234 | IL6||DLL1 | 2 | 7.473989 | 8.675283 | 8.838847 | 7.377130 | 7.509870 | 7.466312 | 7.537572 | 8.671119 | 8.617736 | 8.692699 | 8.717704 | 8.789567 | 8.846455 | 8.874429 | 8.843635 |
| GO:0006308 | DNA catabolic process | 2/204 | 35/20870 | 0.04581490436408962 | 0.21252841966881 | 0.17361437443234 | IL6||ST20 | 2 | 5.077142 | 5.106886 | 5.144777 | 5.102766 | 4.968107 | 5.151012 | 5.080508 | 5.077064 | 5.190877 | 5.136814 | 5.016931 | 5.173209 | 5.121124 | 5.123965 | 5.160102 |
| GO:0019362 | pyridine nucleotide metabolic process | 2/204 | 35/20870 | 0.04581490436408962 | 0.21252841966881 | 0.17361437443234 | IDO1||PARP10 | 2 | 5.311845 | 5.029503 | 5.187925 | 5.419453 | 5.272553 | 5.221762 | 5.326140 | 5.064221 | 5.089956 | 4.985796 | 4.974648 | 5.206519 | 5.177726 | 5.137849 | 5.228027 |
| GO:0040020 | regulation of meiotic nuclear division | 2/204 | 35/20870 | 0.04581490436408962 | 0.21252841966881 | 0.17361437443234 | LIF||FBXO43 | 2 | 6.627167 | 6.461508 | 6.650992 | 6.583440 | 6.618433 | 6.678420 | 6.626770 | 6.463521 | 6.417972 | 6.509185 | 6.453884 | 6.606713 | 6.711291 | 6.676285 | 6.606838 |
| GO:0046496 | nicotinamide nucleotide metabolic process | 2/204 | 35/20870 | 0.04581490436408962 | 0.21252841966881 | 0.17361437443234 | IDO1||PARP10 | 2 | 5.311845 | 5.029503 | 5.187925 | 5.419453 | 5.272553 | 5.221762 | 5.326140 | 5.064221 | 5.089956 | 4.985796 | 4.974648 | 5.206519 | 5.177726 | 5.137849 | 5.228027 |
| GO:0060142 | regulation of syncytium formation by plasma membrane fusion | 2/204 | 35/20870 | 0.04581490436408962 | 0.21252841966881 | 0.17361437443234 | RIPOR2||CXCL10 | 2 | 7.551797 | 7.635005 | 7.476922 | 7.553839 | 7.538368 | 7.564637 | 7.550221 | 7.630068 | 7.651216 | 7.633598 | 7.625005 | 7.464306 | 7.491004 | 7.457608 | 7.494409 |
| GO:0070050 | neuron cellular homeostasis | 2/204 | 35/20870 | 0.04581490436408962 | 0.21252841966881 | 0.17361437443234 | TYRO3||IL6 | 2 | 4.439205 | 5.057895 | 5.197909 | 4.556321 | 4.138165 | 4.596447 | 4.422687 | 5.080751 | 4.830621 | 5.159551 | 5.137567 | 5.061636 | 5.247266 | 5.358250 | 5.105226 |
| GO:0070570 | regulation of neuron projection regeneration | 2/204 | 35/20870 | 0.04581490436408962 | 0.21252841966881 | 0.17361437443234 | SCARF1||INPP5F | 2 | 8.974053 | 9.616156 | 9.609370 | 8.969636 | 8.976768 | 8.988363 | 8.961311 | 9.627292 | 9.604748 | 9.615068 | 9.617429 | 9.608716 | 9.615110 | 9.600305 | 9.613305 |
| GO:0090330 | regulation of platelet aggregation | 2/204 | 35/20870 | 0.04581490436408962 | 0.21252841966881 | 0.17361437443234 | IL6||C1QTNF1 | 2 | 5.411943 | 5.691619 | 5.695705 | 5.397221 | 5.464820 | 5.394618 | 5.389784 | 5.663800 | 5.699914 | 5.676514 | 5.725480 | 5.685663 | 5.728023 | 5.750886 | 5.614538 |
| GO:0003012 | muscle system process | 9/204 | 478/20870 | 0.04592059261812743 | 0.21271263017362 | 0.17376485591433 | DMPK||NR4A3||TBX2||MKKS||PTAFR||SSTR2||SULF2||TPM2||INPP5F | 9 | 6.197495 | 6.441757 | 6.510739 | 6.186866 | 6.189210 | 6.206639 | 6.207142 | 6.438655 | 6.432809 | 6.455249 | 6.440222 | 6.495510 | 6.526803 | 6.488041 | 6.532097 |
| GO:0051402 | neuron apoptotic process | 6/204 | 265/20870 | 0.04635393728852964 | 0.21303885841274 | 0.17403135162227 | GCLC||TYRO3||TFAP2A||ADAM8||NR4A2||GPRASP2 | 6 | 6.815024 | 6.829002 | 6.835089 | 6.824878 | 6.818686 | 6.806152 | 6.810305 | 6.838137 | 6.831323 | 6.833510 | 6.812908 | 6.836640 | 6.826780 | 6.840723 | 6.836175 |
| GO:0003407 | neural retina development | 3/204 | 82/20870 | 0.04645357241444147 | 0.21303885841274 | 0.17403135162227 | SLC17A7||TFAP2A||IGFN1 | 3 | 4.337612 | 4.628119 | 4.725250 | 4.282059 | 4.240685 | 4.204096 | 4.589961 | 4.640743 | 4.620882 | 4.655950 | 4.594159 | 4.763935 | 4.717834 | 4.729117 | 4.689117 |
| GO:0009791 | post-embryonic development | 3/204 | 82/20870 | 0.04645357241444147 | 0.21303885841274 | 0.17403135162227 | VEGFA||MYO7A||NR4A2 | 3 | 5.302220 | 5.339301 | 5.260233 | 5.300953 | 5.319365 | 5.264945 | 5.322890 | 5.338200 | 5.367922 | 5.296403 | 5.353691 | 5.217863 | 5.290880 | 5.293105 | 5.237587 |
| GO:0032418 | lysosome localization | 3/204 | 82/20870 | 0.04645357241444147 | 0.21303885841274 | 0.17403135162227 | UNC13D||PTGDS||NR4A3 | 3 | 5.825519 | 5.971743 | 6.003800 | 5.798242 | 5.860776 | 5.794034 | 5.847819 | 5.959439 | 5.969997 | 5.989060 | 5.968316 | 6.030478 | 5.997198 | 6.001158 | 5.985991 |
| GO:0050688 | regulation of defense response to virus | 3/204 | 82/20870 | 0.04645357241444147 | 0.21303885841274 | 0.17403135162227 | IL23A||HERC5||IFIT1 | 3 | 5.566940 | 5.841213 | 5.829224 | 5.552230 | 5.589663 | 5.550520 | 5.574978 | 5.869929 | 5.813811 | 5.846435 | 5.834103 | 5.818413 | 5.826154 | 5.826576 | 5.845614 |
| GO:0052372 | modulation by symbiont of entry into host | 3/204 | 82/20870 | 0.04645357241444147 | 0.21303885841274 | 0.17403135162227 | TRIM22||LY6E||IFITM1 | 3 | 7.443874 | 8.358396 | 8.554527 | 7.374790 | 7.483778 | 7.422613 | 7.491190 | 8.361926 | 8.297768 | 8.381481 | 8.390602 | 8.516170 | 8.564287 | 8.573684 | 8.563275 |
| GO:0072527 | pyrimidine-containing compound metabolic process | 3/204 | 82/20870 | 0.04645357241444147 | 0.21303885841274 | 0.17403135162227 | TYMP||AICDA||CMPK2 | 3 | 5.685847 | 5.705329 | 5.618070 | 5.730442 | 5.636040 | 5.714500 | 5.660347 | 5.684500 | 5.680114 | 5.771447 | 5.683179 | 5.661120 | 5.595214 | 5.602765 | 5.612258 |
| GO:0042060 | wound healing | 9/204 | 480/20870 | 0.04692509983357097 | 0.21489562764692 | 0.17554814560944 | TYRO3||VEGFA||IL1A||RREB1||IL6||ENTPD1||SLC7A11||C1QTNF1||EPPK1 | 9 | 6.978409 | 7.109664 | 7.095662 | 6.978778 | 6.989028 | 6.969385 | 6.976377 | 7.106101 | 7.116332 | 7.106093 | 7.110104 | 7.090382 | 7.089813 | 7.090852 | 7.111486 |
| GO:0031100 | animal organ regeneration | 3/204 | 83/20870 | 0.04786063350855646 | 0.21736099870631 | 0.17756210616533 | NR4A3||IL6||SULF2 | 3 | 7.821569 | 7.843173 | 7.883526 | 7.819912 | 7.814464 | 7.829437 | 7.822422 | 7.849106 | 7.848446 | 7.840090 | 7.835004 | 7.880776 | 7.887317 | 7.876704 | 7.889270 |
| GO:0001881 | receptor recycling | 2/204 | 36/20870 | 0.04820506019696350 | 0.21736099870631 | 0.17756210616533 | ECE1||INPP5F | 2 | 5.591746 | 6.019278 | 6.160480 | 5.581524 | 5.504585 | 5.656403 | 5.620105 | 5.987120 | 6.081513 | 5.963086 | 6.042408 | 6.215886 | 6.076246 | 6.164071 | 6.182062 |
| GO:0006536 | glutamate metabolic process | 2/204 | 36/20870 | 0.04820506019696350 | 0.21736099870631 | 0.17756210616533 | GCLC||SLC7A11 | 2 | 5.151995 | 5.108462 | 5.078198 | 5.103526 | 5.192035 | 5.160417 | 5.150609 | 5.151442 | 5.071351 | 5.138285 | 5.070852 | 5.104132 | 4.979020 | 5.068190 | 5.155729 |
| GO:0010842 | retina layer formation | 2/204 | 36/20870 | 0.04820506019696350 | 0.21736099870631 | 0.17756210616533 | TFAP2A||IGFN1 | 2 | 4.613550 | 3.335987 | 3.172344 | 4.433551 | 4.447039 | 4.441769 | 5.034228 | 3.091992 | 3.692049 | 3.316504 | 3.166377 | 3.295096 | 3.104868 | 3.135040 | 3.146743 |
| GO:0031076 | embryonic camera-type eye development | 2/204 | 36/20870 | 0.04820506019696350 | 0.21736099870631 | 0.17756210616533 | TBX2||TFAP2A | 2 | 5.456846 | 4.679160 | 4.340685 | 5.406306 | 5.402027 | 5.405088 | 5.603437 | 4.677701 | 4.713668 | 4.766357 | 4.550213 | 4.339583 | 4.428482 | 4.318324 | 4.271832 |
| GO:0034123 | positive regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 2/204 | 36/20870 | 0.04820506019696350 | 0.21736099870631 | 0.17756210616533 | NR1H3||RSAD2 | 2 | 7.195816 | 7.343995 | 7.377260 | 7.157270 | 7.202605 | 7.204055 | 7.218602 | 7.335847 | 7.355137 | 7.355023 | 7.329795 | 7.358523 | 7.374439 | 7.384520 | 7.391349 |
| GO:0036336 | dendritic cell migration | 2/204 | 36/20870 | 0.04820506019696350 | 0.21736099870631 | 0.17756210616533 | ASB2||CCR7 | 2 | 6.839967 | 7.249036 | 7.515725 | 6.811613 | 6.814524 | 6.822957 | 6.908519 | 7.271495 | 7.242459 | 7.236448 | 7.245492 | 7.479034 | 7.585764 | 7.487057 | 7.508555 |
| GO:0046627 | negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway | 2/204 | 36/20870 | 0.04820506019696350 | 0.21736099870631 | 0.17756210616533 | SOCS3||ENPP1 | 2 | 5.094512 | 6.388420 | 6.880795 | 5.336334 | 5.023273 | 4.900906 | 5.081874 | 6.363763 | 6.423073 | 6.461560 | 6.300119 | 6.842803 | 6.901968 | 6.944825 | 6.830625 |
| GO:0046629 | gamma-delta T cell activation | 2/204 | 36/20870 | 0.04820506019696350 | 0.21736099870631 | 0.17756210616533 | ITK||EGR3 | 2 | 4.717576 | 4.778049 | 4.503579 | 4.741944 | 4.687546 | 4.743200 | 4.696717 | 4.762456 | 4.751434 | 4.760447 | 4.836234 | 4.495408 | 4.509823 | 4.502594 | 4.506453 |
| GO:1904893 | negative regulation of receptor signaling pathway via STAT | 2/204 | 36/20870 | 0.04820506019696350 | 0.21736099870631 | 0.17756210616533 | SOCS3||INPP5F | 2 | 5.864990 | 6.336179 | 6.028080 | 5.808220 | 6.163349 | 5.798270 | 5.637357 | 5.892988 | 6.305945 | 6.441550 | 6.610543 | 5.991055 | 5.905608 | 6.326962 | 5.837963 |
| GO:2000758 | positive regulation of peptidyl-lysine acetylation | 2/204 | 36/20870 | 0.04820506019696350 | 0.21736099870631 | 0.17756210616533 | RPS6KA5||LIF | 2 | 5.100186 | 6.446327 | 6.973483 | 5.082484 | 5.196911 | 5.023121 | 5.092763 | 6.458088 | 6.406861 | 6.463176 | 6.456465 | 6.956084 | 6.989582 | 6.969542 | 6.978515 |
| GO:0016358 | dendrite development | 6/204 | 268/20870 | 0.04847718629012581 | 0.21828274944045 | 0.17831508394280 | CDKL3||CDKL5||SCARF1||BCL11A||HECW2||GPRASP2 | 6 | 5.929218 | 6.165223 | 6.159750 | 5.923984 | 5.918659 | 5.944941 | 5.929154 | 6.174659 | 6.167257 | 6.164179 | 6.154725 | 6.205492 | 6.153111 | 6.146418 | 6.132924 |
| GO:0001892 | embryonic placenta development | 3/204 | 84/20870 | 0.04928849532730143 | 0.22131770046688 | 0.18079433412829 | LIF||IGF2||SOCS3 | 3 | 5.681145 | 5.541264 | 5.489409 | 5.689233 | 5.678030 | 5.673979 | 5.683291 | 5.551913 | 5.520472 | 5.550148 | 5.542306 | 5.501334 | 5.474859 | 5.469385 | 5.511625 |
| GO:0051881 | regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential | 3/204 | 84/20870 | 0.04928849532730143 | 0.22131770046688 | 0.18079433412829 | GCLC||IFI6||PIP5KL1 | 3 | 6.478243 | 6.645826 | 6.739769 | 6.474798 | 6.478121 | 6.465051 | 6.494840 | 6.652445 | 6.659223 | 6.633548 | 6.637935 | 6.738612 | 6.745573 | 6.757637 | 6.716952 |
| GO:0007369 | gastrulation | 5/204 | 203/20870 | 0.04949725460403823 | 0.22149165119515 | 0.18093643440324 | NR4A3||MKKS||IL1RN||LBX2||SCX | 5 | 6.904212 | 7.200482 | 7.399317 | 6.920874 | 6.881535 | 6.907291 | 6.906867 | 7.169832 | 7.198907 | 7.209952 | 7.222710 | 7.385572 | 7.400649 | 7.402966 | 7.407987 |
| GO:0032535 | regulation of cellular component size | 8/204 | 411/20870 | 0.04952459648871932 | 0.22149165119515 | 0.18093643440324 | SEMA3F||CDKL3||CDKL5||VEGFA||MKKS||CCR7||SEMA6B||AQP1 | 8 | 7.260839 | 7.533401 | 7.484570 | 7.261121 | 7.250393 | 7.265075 | 7.266710 | 7.536914 | 7.528452 | 7.533954 | 7.534273 | 7.492379 | 7.478632 | 7.483158 | 7.484074 |
| GO:0070663 | regulation of leukocyte proliferation | 7/204 | 339/20870 | 0.04953333762769857 | 0.22149165119515 | 0.18093643440324 | IL23A||IL1A||IL6||TNFRSF14||IGF2||CSF1||PDCD1LG2 | 7 | 6.470859 | 6.940560 | 7.098709 | 6.474344 | 6.472503 | 6.469099 | 6.467481 | 6.952635 | 6.935748 | 6.935876 | 6.937911 | 7.112761 | 7.097807 | 7.094395 | 7.089773 |
| GO:0055007 | cardiac muscle cell differentiation | 4/204 | 141/20870 | 0.04982362772568379 | 0.22248112989973 | 0.18174473913057 | ASB2||VEGFA||DLL1||ALPK2 | 4 | 6.239376 | 6.455472 | 6.522829 | 6.243461 | 6.248645 | 6.244930 | 6.220294 | 6.487416 | 6.429362 | 6.455785 | 6.448717 | 6.521595 | 6.522963 | 6.522675 | 6.524082 |
GO: MF
| ID | Description | GeneRatio | BgRatio | pvalue | p.adjust | qvalue | geneID | Count | No-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgKDN-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgwt-inf_Log2MeanTPM | log2TPM_No-inf_1 | log2TPM_No-inf_2 | log2TPM_No-inf_3 | log2TPM_No-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0005125 | cytokine activity | 17/206 | 286/20678 | 0.000000004580116 | 0.000001891588 | 0.000001697054 | OSM||CCL22||IL23A||VEGFA||IL1A||TNFSF10||LIF||IL6||IL36G||IL1RN||BMP6||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||SCG2||TNFSF15||CSF1 | 17 | 7.027925 | 7.899978 | 8.123290 | 7.033845 | 7.023726 | 7.027537 | 7.026573 | 7.909586 | 7.884917 | 7.906682 | 7.898601 | 8.125205 | 8.127085 | 8.122796 | 8.118056 |
| GO:0005126 | cytokine receptor binding | 16/206 | 324/20678 | 0.000000172362332 | 0.000035592822 | 0.000031932390 | OSM||CCL22||IL23A||VEGFA||PRLR||IL1A||TNFSF10||LIF||IL6||IL36G||IL1RN||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||TNFSF15||CSF1 | 16 | 5.249355 | 6.199512 | 6.565369 | 5.253601 | 5.256485 | 5.240748 | 5.246532 | 6.201147 | 6.171475 | 6.229478 | 6.195358 | 6.571697 | 6.563335 | 6.569093 | 6.557309 |
| GO:0008083 | growth factor activity | 9/206 | 164/20678 | 0.000040566352124 | 0.005584634476 | 0.005010300332 | TYMP||OSM||VEGFA||LIF||IL6||BMP6||CXCL1||IGF2||CSF1 | 9 | 6.564895 | 6.333211 | 6.513167 | 6.571109 | 6.564066 | 6.567302 | 6.557068 | 6.331334 | 6.304736 | 6.348731 | 6.347606 | 6.509150 | 6.517083 | 6.508832 | 6.517579 |
| GO:0005149 | interleukin-1 receptor binding | 3/206 | 17/20678 | 0.000597713186621 | 0.058811871471 | 0.052763549784 | IL1A||IL36G||IL1RN | 3 | 4.667378 | 7.263311 | 7.948052 | 4.700509 | 4.556703 | 4.683424 | 4.723173 | 7.226743 | 7.221571 | 7.316887 | 7.285803 | 7.961882 | 7.939553 | 7.950509 | 7.940147 |
| GO:0045236 | CXCR chemokine receptor binding | 3/206 | 18/20678 | 0.000712008129194 | 0.058811871471 | 0.052763549784 | CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11 | 3 | 3.548332 | 7.195972 | 7.649166 | 3.521617 | 3.603004 | 3.418267 | 3.640450 | 7.194877 | 7.153837 | 7.223717 | 7.210506 | 7.673348 | 7.656225 | 7.666252 | 7.599678 |
| GO:0019955 | cytokine binding | 7/206 | 153/20678 | 0.000874579812789 | 0.060200243780 | 0.054009139316 | PRLR||IL1R2||CCR7||IL1RN||TNFRSF14||NBL1||CXCR3 | 7 | 5.946169 | 6.087673 | 6.112773 | 5.932731 | 5.966770 | 5.940101 | 5.944851 | 6.088577 | 6.073802 | 6.094018 | 6.094200 | 6.106540 | 6.128636 | 6.096226 | 6.119479 |
| GO:0004693 | cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity | 3/206 | 30/20678 | 0.003244664995110 | 0.165283935273 | 0.148285829530 | CDKL3||CDKL5||CDK3 | 3 | 5.298881 | 4.959319 | 5.065250 | 5.164291 | 5.453142 | 5.384180 | 5.171217 | 5.063474 | 5.068066 | 4.898773 | 4.787857 | 4.974226 | 5.046859 | 5.126999 | 5.108007 |
| GO:0097472 | cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity | 3/206 | 30/20678 | 0.003244664995110 | 0.165283935273 | 0.148285829530 | CDKL3||CDKL5||CDK3 | 3 | 5.298881 | 4.959319 | 5.065250 | 5.164291 | 5.453142 | 5.384180 | 5.171217 | 5.063474 | 5.068066 | 4.898773 | 4.787857 | 4.974226 | 5.046859 | 5.126999 | 5.108007 |
| GO:0008009 | chemokine activity | 4/206 | 63/20678 | 0.003601829097961 | 0.165283935273 | 0.148285829530 | CCL22||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11 | 4 | 4.661476 | 7.336671 | 7.908591 | 4.742723 | 4.658529 | 4.658808 | 4.581323 | 7.367746 | 7.337433 | 7.330670 | 7.310246 | 7.893723 | 7.922333 | 7.914025 | 7.904122 |
| GO:0008237 | metallopeptidase activity | 7/206 | 205/20678 | 0.004564829685681 | 0.188527466019 | 0.169138952564 | CPXM1||ECE1||ADAM19||CPM||MMP7||ADAM8||AMZ1 | 7 | 6.014354 | 6.796519 | 7.088932 | 6.032626 | 5.991229 | 6.039862 | 5.993013 | 6.784057 | 6.799839 | 6.802180 | 6.799926 | 7.076710 | 7.103349 | 7.101408 | 7.074007 |
| GO:0005031 | tumor necrosis factor-activated receptor activity | 2/206 | 11/20678 | 0.005120061584356 | 0.192235039485 | 0.172465232315 | TNFRSF14||TNFRSF18 | 2 | 4.842933 | 5.372980 | 5.666966 | 4.789753 | 4.846950 | 4.769312 | 4.958168 | 5.506027 | 5.186969 | 5.365562 | 5.414907 | 5.551987 | 5.820757 | 5.600163 | 5.680410 |
| GO:0071889 | 14-3-3 protein binding | 3/206 | 38/20678 | 0.006360184558058 | 0.201802025554 | 0.181048331834 | TMCC3||RIPOR2||HLA-F | 3 | 5.455387 | 5.275619 | 5.139190 | 5.446714 | 5.444791 | 5.484922 | 5.444713 | 5.218470 | 5.285647 | 5.259602 | 5.336226 | 5.094956 | 5.125198 | 5.194759 | 5.140026 |
| GO:0031432 | titin binding | 2/206 | 13/20678 | 0.007166687324437 | 0.201802025554 | 0.181048331834 | ANKRD1||OBSCN | 2 | 6.982809 | 6.688038 | 6.610090 | 6.938936 | 6.994435 | 7.030297 | 6.965973 | 6.722391 | 6.650202 | 6.690852 | 6.687802 | 6.643586 | 6.599990 | 6.603379 | 6.592859 |
| GO:0140333 | glycerophospholipid flippase activity | 2/206 | 13/20678 | 0.007166687324437 | 0.201802025554 | 0.181048331834 | ATP8B1||ABCA4 | 2 | 5.210164 | 6.279542 | 6.804522 | 5.165758 | 5.181228 | 5.118706 | 5.362796 | 6.275393 | 6.268867 | 6.325958 | 6.246782 | 6.733212 | 6.798323 | 6.795249 | 6.887116 |
| GO:0005035 | death receptor activity | 2/206 | 14/20678 | 0.008306620906600 | 0.201802025554 | 0.181048331834 | TNFRSF14||TNFRSF18 | 2 | 4.438676 | 5.033390 | 5.311963 | 4.383641 | 4.430584 | 4.367348 | 4.564671 | 5.142883 | 4.859113 | 5.027450 | 5.088651 | 5.221594 | 5.450305 | 5.250112 | 5.314908 |
| GO:0005313 | L-glutamate transmembrane transporter activity | 2/206 | 14/20678 | 0.008306620906600 | 0.201802025554 | 0.181048331834 | SLC17A7||SLC7A11 | 2 | 3.319892 | 4.378169 | 4.829708 | 3.116802 | 3.423419 | 3.326203 | 3.393755 | 4.369826 | 4.478923 | 4.376922 | 4.280121 | 4.767941 | 4.883984 | 4.852011 | 4.812280 |
| GO:0035259 | glucocorticoid receptor binding | 2/206 | 14/20678 | 0.008306620906600 | 0.201802025554 | 0.181048331834 | NR4A3||NR4A2 | 2 | 5.124789 | 5.049466 | 5.093991 | 5.041331 | 5.307804 | 5.128561 | 5.001880 | 4.985711 | 5.050248 | 5.119361 | 5.039398 | 5.117134 | 5.099654 | 5.115941 | 5.041942 |
| GO:0015172 | acidic amino acid transmembrane transporter activity | 2/206 | 16/20678 | 0.010811587790862 | 0.215980013183 | 0.193768228980 | SLC17A7||SLC7A11 | 2 | 4.307768 | 5.331940 | 5.707775 | 4.222413 | 4.358705 | 4.337994 | 4.308253 | 5.367213 | 5.367962 | 5.321147 | 5.269164 | 5.692808 | 5.706936 | 5.732552 | 5.698484 |
| GO:0019992 | diacylglycerol binding | 2/206 | 16/20678 | 0.010811587790862 | 0.215980013183 | 0.193768228980 | UNC13A||UNC13C | 2 | 4.102010 | 3.401241 | 3.447882 | 4.137163 | 3.998879 | 4.102582 | 4.164032 | 3.367514 | 3.469705 | 3.441311 | 3.321678 | 3.474574 | 3.381820 | 3.471003 | 3.462135 |
| GO:0140327 | flippase activity | 2/206 | 16/20678 | 0.010811587790862 | 0.215980013183 | 0.193768228980 | ATP8B1||ABCA4 | 2 | 5.743486 | 6.380439 | 6.758364 | 5.728775 | 5.720428 | 5.682410 | 5.837657 | 6.381842 | 6.374500 | 6.414781 | 6.349888 | 6.697661 | 6.750665 | 6.751668 | 6.830343 |
| GO:0008201 | heparin binding | 6/206 | 190/20678 | 0.012105208136339 | 0.215980013183 | 0.193768228980 | CFH||COL5A3||VEGFA||MMP7||CXCL10||CXCL11 | 6 | 6.508431 | 6.299913 | 6.294777 | 6.517174 | 6.523999 | 6.495402 | 6.496935 | 6.326440 | 6.293638 | 6.275829 | 6.303280 | 6.301488 | 6.301536 | 6.283628 | 6.292378 |
| GO:0046935 | 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase regulator activity | 2/206 | 17/20678 | 0.012173437738095 | 0.215980013183 | 0.193768228980 | SOCS3||PIK3R6 | 2 | 3.314612 | 3.529455 | 3.720929 | 3.511497 | 3.156408 | 3.144337 | 3.410830 | 3.295765 | 3.842160 | 3.434046 | 3.487745 | 3.425983 | 3.528388 | 4.225582 | 3.554512 |
| GO:0019966 | interleukin-1 binding | 2/206 | 18/20678 | 0.013606116439207 | 0.215980013183 | 0.193768228980 | IL1R2||IL1RN | 2 | 6.676983 | 6.664422 | 6.968790 | 6.625348 | 6.618725 | 6.749964 | 6.709574 | 6.664882 | 6.687014 | 6.634842 | 6.670458 | 6.980478 | 6.985989 | 6.951443 | 6.956948 |
| GO:0005539 | glycosaminoglycan binding | 7/206 | 254/20678 | 0.013948793014398 | 0.215980013183 | 0.193768228980 | CFH||COL5A3||VEGFA||MMP7||CXCL10||CXCL11||SULF2 | 7 | 6.417068 | 6.357197 | 6.351249 | 6.421047 | 6.419984 | 6.406393 | 6.420794 | 6.388797 | 6.333918 | 6.344204 | 6.361269 | 6.359493 | 6.352182 | 6.344249 | 6.349028 |
| GO:0061629 | RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding | 8/206 | 316/20678 | 0.014183143817775 | 0.215980013183 | 0.193768228980 | PADI2||NR4A3||MKKS||BHLHE40||OASL||ANKRD1||NR4A2||DLL1 | 8 | 6.568060 | 6.484247 | 6.496104 | 6.517868 | 6.541529 | 6.582167 | 6.628229 | 6.485173 | 6.534666 | 6.443117 | 6.472511 | 6.527318 | 6.462839 | 6.480338 | 6.513016 |
| GO:0106310 | protein serine kinase activity | 9/206 | 380/20678 | 0.014249520470021 | 0.215980013183 | 0.193768228980 | CDKL3||CDKL5||RPS6KA5||DMPK||MAPK10||OBSCN||ALPK2||CDK3||NA | 9 | 4.947383 | 4.898755 | 4.890008 | 4.959976 | 4.965606 | 4.928952 | 4.934656 | 4.929947 | 4.891870 | 4.898069 | 4.874574 | 4.878448 | 4.901268 | 4.910559 | 4.869373 |
| GO:0008569 | minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity | 2/206 | 19/20678 | 0.015108091723016 | 0.215980013183 | 0.193768228980 | DNHD1||DNAH17 | 2 | 4.716565 | 4.640867 | 4.628409 | 4.636547 | 4.823245 | 4.706530 | 4.693499 | 4.423348 | 4.541914 | 4.505030 | 5.015048 | 4.432911 | 5.004897 | 4.503801 | 4.494402 |
| GO:0035497 | cAMP response element binding | 2/206 | 19/20678 | 0.015108091723016 | 0.215980013183 | 0.193768228980 | NR4A3||CREB3L1 | 2 | 5.117081 | 4.907905 | 4.967326 | 4.963030 | 5.217397 | 5.238284 | 5.030309 | 4.926371 | 4.913373 | 4.900623 | 4.891008 | 5.118329 | 4.907010 | 4.968959 | 4.861809 |
| GO:0070851 | growth factor receptor binding | 5/206 | 145/20678 | 0.015165666785222 | 0.215980013183 | 0.193768228980 | VEGFA||IL1A||IL6||IL36G||IL1RN | 5 | 5.544798 | 6.161478 | 6.395765 | 5.573276 | 5.532491 | 5.552890 | 5.519964 | 6.136474 | 6.154743 | 6.186860 | 6.167367 | 6.389364 | 6.397634 | 6.419822 | 6.375885 |
| GO:0005044 | scavenger receptor activity | 3/206 | 54/20678 | 0.016654675206799 | 0.223526619146 | 0.200538728022 | SCARF1||LGALS3BP||ENPP1 | 3 | 5.353983 | 5.208113 | 4.962286 | 5.343645 | 5.322524 | 5.416344 | 5.331500 | 5.193558 | 5.268263 | 5.185758 | 5.183139 | 4.965924 | 4.951660 | 4.953254 | 4.978145 |
| GO:0042379 | chemokine receptor binding | 4/206 | 99/20678 | 0.017277027470299 | 0.223526619146 | 0.200538728022 | CCL22||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11 | 4 | 4.960000 | 7.002930 | 7.501374 | 4.977735 | 5.007770 | 4.932893 | 4.919889 | 7.023783 | 7.001988 | 7.002238 | 6.983428 | 7.489150 | 7.517183 | 7.504270 | 7.494738 |
| GO:0042056 | chemoattractant activity | 3/206 | 55/20678 | 0.017488968753229 | 0.223526619146 | 0.200538728022 | VEGFA||CXCL10||SCG2 | 3 | 6.337513 | 7.322712 | 7.809817 | 6.350566 | 6.353775 | 6.319545 | 6.325858 | 7.360046 | 7.308144 | 7.311095 | 7.310908 | 7.790920 | 7.848302 | 7.792629 | 7.806669 |
| GO:0004896 | cytokine receptor activity | 4/206 | 100/20678 | 0.017860480464474 | 0.223526619146 | 0.200538728022 | PRLR||IL1R2||CCR7||CXCR3 | 4 | 5.732659 | 5.812155 | 5.812118 | 5.735133 | 5.745732 | 5.717985 | 5.731651 | 5.798175 | 5.816464 | 5.820422 | 5.813463 | 5.807582 | 5.809943 | 5.794605 | 5.836026 |
| GO:0004879 | nuclear receptor activity | 3/206 | 57/20678 | 0.019226475991753 | 0.226872416703 | 0.203540437567 | NR1H3||NR4A3||NR4A2 | 3 | 4.581180 | 4.349347 | 4.457578 | 4.569707 | 4.579661 | 4.571762 | 4.603341 | 4.293215 | 4.334194 | 4.416867 | 4.350348 | 4.454964 | 4.468156 | 4.451003 | 4.456134 |
| GO:0098531 | ligand-activated transcription factor activity | 3/206 | 57/20678 | 0.019226475991753 | 0.226872416703 | 0.203540437567 | NR1H3||NR4A3||NR4A2 | 3 | 4.581180 | 4.349347 | 4.457578 | 4.569707 | 4.579661 | 4.571762 | 4.603341 | 4.293215 | 4.334194 | 4.416867 | 4.350348 | 4.454964 | 4.468156 | 4.451003 | 4.456134 |
| GO:0035014 | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulator activity | 2/206 | 22/20678 | 0.020014822099730 | 0.229614486866 | 0.206000508161 | SOCS3||PIK3R6 | 2 | 3.602610 | 3.648351 | 3.674326 | 3.730235 | 3.516198 | 3.512830 | 3.639611 | 3.493669 | 3.832515 | 3.577856 | 3.667270 | 3.459860 | 3.521721 | 4.062781 | 3.568884 |
| GO:0005158 | insulin receptor binding | 2/206 | 23/20678 | 0.021779122190523 | 0.232119771583 | 0.208248144762 | IGF2||ENPP1 | 2 | 5.215575 | 5.284451 | 5.223240 | 5.330824 | 5.186801 | 5.145087 | 5.192702 | 5.341299 | 5.267697 | 5.271707 | 5.255525 | 5.058289 | 5.262614 | 5.429350 | 5.113571 |
| GO:0016493 | C-C chemokine receptor activity | 2/206 | 23/20678 | 0.021779122190523 | 0.232119771583 | 0.208248144762 | CCR7||CXCR3 | 2 | 3.038659 | 3.754420 | 4.322256 | 2.919140 | 3.137207 | 3.079256 | 3.009912 | 3.738342 | 3.732681 | 3.801532 | 3.744057 | 4.319468 | 4.307749 | 4.323771 | 4.337878 |
| GO:0140297 | DNA-binding transcription factor binding | 9/206 | 414/20678 | 0.023370732245286 | 0.232119771583 | 0.208248144762 | PADI2||NR4A3||MKKS||BHLHE40||OASL||ANKRD1||NR4A2||DLL1||SCX | 9 | 6.727065 | 6.716925 | 6.661799 | 6.700682 | 6.690169 | 6.745570 | 6.770355 | 6.720883 | 6.757266 | 6.677250 | 6.711174 | 6.694367 | 6.627478 | 6.650541 | 6.673939 |
| GO:0017075 | syntaxin-1 binding | 2/206 | 24/20678 | 0.023605400499994 | 0.232119771583 | 0.208248144762 | UNC13A||UNC13C | 2 | 4.980885 | 4.570165 | 4.500080 | 5.079819 | 4.888311 | 4.990862 | 4.957956 | 4.462390 | 4.681774 | 4.646989 | 4.476066 | 4.510391 | 4.578561 | 4.399500 | 4.506218 |
| GO:0019957 | C-C chemokine binding | 2/206 | 24/20678 | 0.023605400499994 | 0.232119771583 | 0.208248144762 | CCR7||CXCR3 | 2 | 3.640821 | 4.066142 | 4.522569 | 3.574701 | 3.698347 | 3.616594 | 3.670477 | 4.060938 | 4.039107 | 4.111371 | 4.052106 | 4.516259 | 4.497160 | 4.544338 | 4.532085 |
| GO:0030215 | semaphorin receptor binding | 2/206 | 24/20678 | 0.023605400499994 | 0.232119771583 | 0.208248144762 | SEMA3F||SEMA6B | 2 | 3.902182 | 4.316143 | 4.613858 | 3.617337 | 4.285885 | 3.765519 | 3.850578 | 4.215067 | 4.477010 | 4.056240 | 4.472618 | 4.765756 | 4.704461 | 4.551257 | 4.407327 |
| GO:0051019 | mitogen-activated protein kinase binding | 2/206 | 25/20678 | 0.025492259755151 | 0.236083913902 | 0.211804607349 | MICAL2||PTAFR | 2 | 5.693548 | 5.829042 | 5.888342 | 5.694458 | 5.741684 | 5.682691 | 5.653965 | 5.853313 | 5.781792 | 5.853231 | 5.826657 | 5.934832 | 5.829335 | 5.903652 | 5.883511 |
| GO:0070412 | R-SMAD binding | 2/206 | 25/20678 | 0.025492259755151 | 0.236083913902 | 0.211804607349 | PMEPA1||ANKRD1 | 2 | 6.943678 | 6.438415 | 6.600192 | 6.236909 | 6.661804 | 7.135221 | 7.452414 | 6.414268 | 6.854269 | 5.964975 | 6.382918 | 6.707521 | 6.193060 | 6.624558 | 6.803850 |
| GO:1901681 | sulfur compound binding | 7/206 | 289/20678 | 0.026128980611504 | 0.236083913902 | 0.211804607349 | CFH||COL5A3||VEGFA||MMP7||CXCL10||CXCL11||ENPP1 | 7 | 6.135902 | 6.014510 | 6.000495 | 6.132525 | 6.137247 | 6.133854 | 6.139970 | 6.039129 | 6.007962 | 5.993500 | 6.017069 | 6.017102 | 6.001256 | 5.984514 | 5.998924 |
| GO:0001637 | G protein-coupled chemoattractant receptor activity | 2/206 | 26/20678 | 0.027438324133848 | 0.236083913902 | 0.211804607349 | CCR7||CXCR3 | 2 | 2.946615 | 3.783798 | 4.329393 | 2.815363 | 3.054967 | 2.985720 | 2.919661 | 3.777548 | 3.759349 | 3.828295 | 3.769012 | 4.335326 | 4.318352 | 4.325064 | 4.338737 |
| GO:0004950 | chemokine receptor activity | 2/206 | 26/20678 | 0.027438324133848 | 0.236083913902 | 0.211804607349 | CCR7||CXCR3 | 2 | 2.946615 | 3.783798 | 4.329393 | 2.815363 | 3.054967 | 2.985720 | 2.919661 | 3.777548 | 3.759349 | 3.828295 | 3.769012 | 4.335326 | 4.318352 | 4.325064 | 4.338737 |
| GO:0038187 | pattern recognition receptor activity | 2/206 | 26/20678 | 0.027438324133848 | 0.236083913902 | 0.211804607349 | CLEC4E||PTAFR | 2 | 5.185544 | 5.113231 | 4.888125 | 5.086531 | 5.184477 | 5.267138 | 5.198302 | 5.109280 | 5.112831 | 5.137487 | 5.092975 | 4.897892 | 4.844611 | 4.976414 | 4.828945 |
| GO:0043425 | bHLH transcription factor binding | 2/206 | 27/20678 | 0.029442238979491 | 0.248156014256 | 0.222635190565 | BHLHE40||SCX | 2 | 5.451292 | 4.925343 | 5.071777 | 5.498269 | 5.467147 | 5.491828 | 5.342486 | 4.872171 | 4.933893 | 4.999056 | 4.892985 | 5.172903 | 5.046365 | 5.047617 | 5.015072 |
| GO:0045499 | chemorepellent activity | 2/206 | 28/20678 | 0.031502670519255 | 0.260212058489 | 0.233451368901 | SEMA3F||SEMA6B | 2 | 2.889007 | 3.697833 | 4.011858 | 2.779890 | 3.108649 | 2.841956 | 2.800487 | 3.630288 | 3.640326 | 3.612046 | 3.890086 | 4.213582 | 3.959987 | 3.898596 | 3.954089 |
| GO:0140326 | ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity | 2/206 | 29/20678 | 0.033618305585772 | 0.272242356999 | 0.244244449251 | ATP8B1||ABCA4 | 2 | 5.519581 | 5.946472 | 6.276271 | 5.520501 | 5.502493 | 5.462820 | 5.589582 | 5.946181 | 5.963191 | 5.954469 | 5.921717 | 6.230972 | 6.248004 | 6.291798 | 6.332151 |
| GO:0004222 | metalloendopeptidase activity | 4/206 | 124/20678 | 0.035627452778062 | 0.278875143478 | 0.250195107696 | ECE1||ADAM19||MMP7||ADAM8 | 4 | 6.210903 | 7.260648 | 7.615709 | 6.226690 | 6.183908 | 6.252671 | 6.179043 | 7.246223 | 7.257907 | 7.275293 | 7.263018 | 7.597136 | 7.637325 | 7.621793 | 7.606255 |
| GO:0051959 | dynein light intermediate chain binding | 2/206 | 30/20678 | 0.035787851342248 | 0.278875143478 | 0.250195107696 | DNHD1||DNAH17 | 2 | 5.398381 | 5.320899 | 5.202385 | 5.368925 | 5.466237 | 5.344925 | 5.410487 | 5.276504 | 5.279077 | 5.301836 | 5.421207 | 5.109994 | 5.352574 | 5.145610 | 5.189206 |
| GO:0004181 | metallocarboxypeptidase activity | 2/206 | 31/20678 | 0.038010035010971 | 0.290706378880 | 0.260809596956 | CPXM1||CPM | 2 | 4.856683 | 4.299396 | 4.729433 | 4.980075 | 5.051704 | 4.676317 | 4.677964 | 4.146962 | 4.466839 | 4.218597 | 4.344376 | 4.525169 | 4.766792 | 5.064144 | 4.485879 |
| GO:0005112 | Notch binding | 2/206 | 32/20678 | 0.040283603605166 | 0.302493241617 | 0.271384276919 | CHAC1||DLL1 | 2 | 4.389195 | 4.681506 | 4.736246 | 4.343594 | 4.434214 | 4.436847 | 4.339044 | 4.664719 | 4.698945 | 4.668522 | 4.693524 | 4.683672 | 4.754584 | 4.725617 | 4.779358 |
| GO:0019956 | chemokine binding | 2/206 | 33/20678 | 0.042607323664166 | 0.314229012023 | 0.281913118981 | CCR7||CXCR3 | 2 | 6.123398 | 6.295656 | 6.217447 | 6.098247 | 6.134175 | 6.145740 | 6.114974 | 6.305440 | 6.270633 | 6.296715 | 6.309521 | 6.224334 | 6.222174 | 6.216809 | 6.206404 |
| GO:0140375 | immune receptor activity | 7/206 | 323/20678 | 0.043514644811021 | 0.314991748849 | 0.282597414540 | PRLR||IL1R2||CCR7||CXCR3||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA2||LILRA6 | 7 | 6.766883 | 6.999792 | 6.945789 | 6.786634 | 6.780244 | 6.753646 | 6.746608 | 7.004616 | 6.991503 | 6.997668 | 7.005337 | 6.936372 | 6.944951 | 6.944303 | 6.957451 |
| GO:0019207 | kinase regulator activity | 6/206 | 257/20678 | 0.044236129378279 | 0.314991748849 | 0.282597414540 | MOB3B||SH3BP5||IGF2||CXCL10||SOCS3||PIK3R6 | 6 | 6.379871 | 6.468260 | 6.457381 | 6.358024 | 6.399825 | 6.385843 | 6.375468 | 6.460618 | 6.498363 | 6.467491 | 6.446062 | 6.463768 | 6.459648 | 6.448748 | 6.457319 |
| GO:0001228 | DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | 9/206 | 472/20678 | 0.047463385591785 | 0.332243699142 | 0.298075142343 | NR1H3||MEIS3||NR4A3||RREB1||TFAP2A||NR4A2||CREB3L1||EGR3||SCX | 9 | 4.912267 | 4.761573 | 4.763319 | 4.920159 | 4.926356 | 4.906366 | 4.895995 | 4.746435 | 4.753124 | 4.797681 | 4.748432 | 4.789066 | 4.741287 | 4.760984 | 4.761538 |
| GO:0046332 | SMAD binding | 3/206 | 82/20678 | 0.048662756517147 | 0.334961974026 | 0.300513864808 | PMEPA1||ANKRD1||CREB3L1 | 3 | 6.315982 | 5.831523 | 5.806154 | 6.033035 | 6.171260 | 6.422875 | 6.574958 | 5.832053 | 6.007977 | 5.645353 | 5.817888 | 5.889819 | 5.598417 | 5.811493 | 5.904698 |
| GO:0045505 | dynein intermediate chain binding | 2/206 | 36/20678 | 0.049867345444699 | 0.337389704359 | 0.302691922861 | DNHD1||DNAH17 | 2 | 5.749721 | 5.635463 | 5.577273 | 5.705178 | 5.835796 | 5.699277 | 5.754452 | 5.580347 | 5.610929 | 5.692264 | 5.655787 | 5.552975 | 5.591305 | 5.668656 | 5.490361 |
GO: CC
| ID | Description | GeneRatio | BgRatio | pvalue | p.adjust | qvalue | geneID | Count | No-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgKDN-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgwt-inf_Log2MeanTPM | log2TPM_No-inf_1 | log2TPM_No-inf_2 | log2TPM_No-inf_3 | log2TPM_No-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0098862 | cluster of actin-based cell projections | 8/215 | 173/21916 | 0.0003188435 | 0.0526845 | 0.04980289 | ATP8B1||RIPOR2||KPTN||MKKS||MYO7A||SLC7A11||SLC28A3||AQP1 | 8 | 6.501373 | 6.704585 | 6.650843 | 6.509458 | 6.467189 | 6.492188 | 6.535792 | 6.678063 | 6.681613 | 6.722779 | 6.735023 | 6.617392 | 6.686907 | 6.624950 | 6.672884 |
| GO:0032421 | stereocilium bundle | 5/215 | 64/21916 | 0.0004132117 | 0.0526845 | 0.04980289 | ATP8B1||RIPOR2||KPTN||MKKS||MYO7A | 5 | 5.253838 | 4.713979 | 4.699130 | 5.311518 | 5.034454 | 5.221536 | 5.420448 | 4.599918 | 4.566129 | 4.619373 | 5.020700 | 4.723474 | 4.487282 | 4.539488 | 4.991093 |
| GO:0032420 | stereocilium | 4/215 | 57/21916 | 0.0023693010 | 0.1822537 | 0.17228521 | ATP8B1||RIPOR2||KPTN||MYO7A | 4 | 5.077734 | 4.639863 | 4.395503 | 5.033079 | 5.071587 | 5.069546 | 5.134857 | 4.638059 | 4.604766 | 4.655468 | 4.660502 | 4.373280 | 4.272266 | 4.423996 | 4.502808 |
| GO:0031526 | brush border membrane | 4/215 | 60/21916 | 0.0028588811 | 0.1822537 | 0.17228521 | ATP8B1||SLC7A11||SLC28A3||AQP1 | 4 | 5.639202 | 6.199464 | 6.264040 | 5.600369 | 5.665384 | 5.597865 | 5.690907 | 6.183530 | 6.175233 | 6.255422 | 6.182178 | 6.223050 | 6.269019 | 6.270565 | 6.292642 |
| GO:0018995 | host cellular component | 2/215 | 12/21916 | 0.0059259783 | 0.2518541 | 0.23807878 | IFIT1||AQP1 | 2 | 4.699807 | 5.103641 | 5.122732 | 4.692708 | 4.630690 | 4.757211 | 4.715725 | 5.023581 | 5.128245 | 5.138109 | 5.121707 | 5.143922 | 5.122115 | 5.125565 | 5.098971 |
| GO:0043657 | host cell | 2/215 | 12/21916 | 0.0059259783 | 0.2518541 | 0.23807878 | IFIT1||AQP1 | 2 | 4.699807 | 5.103641 | 5.122732 | 4.692708 | 4.630690 | 4.757211 | 4.715725 | 5.023581 | 5.128245 | 5.138109 | 5.121707 | 5.143922 | 5.122115 | 5.125565 | 5.098971 |
| GO:0098831 | presynaptic active zone cytoplasmic component | 2/215 | 16/21916 | 0.0105004190 | 0.3072337 | 0.29042941 | UNC13A||UNC13C | 2 | 5.245667 | 5.046205 | 4.952603 | 5.259639 | 5.197580 | 5.351459 | 5.167050 | 5.088658 | 4.936941 | 4.964786 | 5.181014 | 5.019159 | 4.887405 | 5.000820 | 4.898189 |
| GO:0034774 | secretory granule lumen | 9/215 | 375/21916 | 0.0120547567 | 0.3072337 | 0.29042941 | UNC13D||LGALS3BP||ALDOC||VEGFA||PADI2||C3||CXCL1||IGF2||ORM1 | 9 | 8.436455 | 8.447697 | 8.395265 | 8.437495 | 8.435584 | 8.433819 | 8.438915 | 8.448437 | 8.441748 | 8.444915 | 8.455652 | 8.391704 | 8.399398 | 8.394334 | 8.395614 |
| GO:0060205 | cytoplasmic vesicle lumen | 9/215 | 378/21916 | 0.0126434006 | 0.3072337 | 0.29042941 | UNC13D||LGALS3BP||ALDOC||VEGFA||PADI2||C3||CXCL1||IGF2||ORM1 | 9 | 8.426076 | 8.436916 | 8.384382 | 8.427130 | 8.425277 | 8.423340 | 8.428551 | 8.437583 | 8.431075 | 8.434085 | 8.444886 | 8.380846 | 8.388490 | 8.383482 | 8.384700 |
| GO:0031983 | vesicle lumen | 9/215 | 380/21916 | 0.0130475669 | 0.3072337 | 0.29042941 | UNC13D||LGALS3BP||ALDOC||VEGFA||PADI2||C3||CXCL1||IGF2||ORM1 | 9 | 8.420441 | 8.431309 | 8.378769 | 8.421495 | 8.419641 | 8.417706 | 8.422918 | 8.431972 | 8.425474 | 8.428471 | 8.439282 | 8.375238 | 8.382878 | 8.377869 | 8.379080 |
| GO:0031253 | cell projection membrane | 9/215 | 381/21916 | 0.0132532198 | 0.3072337 | 0.29042941 | CDKL5||ATP8B1||RIPOR2||KCNC4||FGD2||SLC7A11||SLC28A3||CYS1||AQP1 | 9 | 7.118246 | 7.202003 | 7.062144 | 7.108490 | 7.116858 | 7.128702 | 7.118861 | 7.205486 | 7.193766 | 7.205614 | 7.203114 | 7.070672 | 7.062486 | 7.054717 | 7.060654 |
| GO:0005767 | secondary lysosome | 2/215 | 22/21916 | 0.0194499727 | 0.3854116 | 0.36433126 | NCF2||ADAM8 | 2 | 9.403337 | 10.080943 | 10.331757 | 9.387422 | 9.403642 | 9.410974 | 9.411179 | 10.064605 | 10.079370 | 10.082272 | 10.097339 | 10.306066 | 10.342651 | 10.334900 | 10.343094 |
| GO:0070820 | tertiary granule | 6/215 | 215/21916 | 0.0196484324 | 0.3854116 | 0.36433126 | ALDOC||ADGRE3||ADAM8||CXCL1||PTAFR||ORM1 | 6 | 8.121496 | 8.430838 | 8.626014 | 8.122786 | 8.125538 | 8.111685 | 8.125929 | 8.425310 | 8.424005 | 8.430037 | 8.443912 | 8.612511 | 8.636341 | 8.621554 | 8.633524 |
| GO:0005858 | axonemal dynein complex | 2/215 | 23/21916 | 0.0211665018 | 0.3855327 | 0.36444578 | DNHD1||DNAH17 | 2 | 2.866515 | 3.097293 | 3.062716 | 2.342501 | 2.990863 | 2.719089 | 3.257942 | 2.002417 | 2.907049 | 1.744075 | 4.276133 | 1.947668 | 4.371475 | 2.313370 | 1.961637 |
| GO:0005903 | brush border | 4/215 | 116/21916 | 0.0275338604 | 0.4232036 | 0.40005624 | ATP8B1||SLC7A11||SLC28A3||AQP1 | 4 | 6.813153 | 7.102732 | 7.053689 | 6.810119 | 6.807626 | 6.803590 | 6.831119 | 7.083803 | 7.092115 | 7.132785 | 7.101746 | 7.009108 | 7.104128 | 7.044175 | 7.055740 |
| GO:1904724 | tertiary granule lumen | 3/215 | 68/21916 | 0.0292755899 | 0.4232036 | 0.40005624 | ALDOC||CXCL1||ORM1 | 3 | 8.655019 | 9.250434 | 9.589405 | 8.654336 | 8.648802 | 8.660469 | 8.656445 | 9.237089 | 9.249175 | 9.242296 | 9.272913 | 9.571272 | 9.601071 | 9.584578 | 9.600486 |
| GO:0005942 | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex | 2/215 | 29/21916 | 0.0326912743 | 0.4232036 | 0.40005624 | SOCS3||PIK3R6 | 2 | 4.176091 | 4.156162 | 4.220437 | 4.347026 | 4.086497 | 4.043879 | 4.207476 | 4.163010 | 4.182984 | 4.243611 | 4.026407 | 4.098643 | 4.213144 | 4.367429 | 4.189435 |
| GO:0031045 | dense core granule | 2/215 | 29/21916 | 0.0326912743 | 0.4232036 | 0.40005624 | ADAM8||SCG2 | 2 | 4.641476 | 4.722914 | 4.555833 | 4.541590 | 4.527581 | 4.865493 | 4.604688 | 4.533711 | 5.040867 | 4.616682 | 4.644866 | 4.565889 | 4.508880 | 4.548842 | 4.598283 |
| GO:0031093 | platelet alpha granule lumen | 3/215 | 72/21916 | 0.0338704514 | 0.4232036 | 0.40005624 | VEGFA||IGF2||ORM1 | 3 | 8.528156 | 8.699732 | 8.705178 | 8.531235 | 8.515663 | 8.527919 | 8.537715 | 8.697935 | 8.679128 | 8.708487 | 8.713140 | 8.702369 | 8.705107 | 8.708898 | 8.704332 |
| GO:0030672 | synaptic vesicle membrane | 4/215 | 125/21916 | 0.0348520614 | 0.4232036 | 0.40005624 | SLC17A7||UNC13A||UNC13C||MCTP2 | 4 | 5.096839 | 5.230273 | 5.155012 | 5.129843 | 5.073680 | 5.099038 | 5.084174 | 5.226951 | 5.258005 | 5.233362 | 5.202228 | 5.179571 | 5.147152 | 5.143189 | 5.149847 |
| GO:0099501 | exocytic vesicle membrane | 4/215 | 125/21916 | 0.0348520614 | 0.4232036 | 0.40005624 | SLC17A7||UNC13A||UNC13C||MCTP2 | 4 | 5.096839 | 5.230273 | 5.155012 | 5.129843 | 5.073680 | 5.099038 | 5.084174 | 5.226951 | 5.258005 | 5.233362 | 5.202228 | 5.179571 | 5.147152 | 5.143189 | 5.149847 |
| GO:0030139 | endocytic vesicle | 9/215 | 464/21916 | 0.0401419087 | 0.4493490 | 0.42477160 | LPAR2||SCARF1||NCF2||ADAM8||CLEC4E||INPP5F||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA2 | 9 | 7.197556 | 7.306449 | 7.317735 | 7.193661 | 7.215347 | 7.194137 | 7.186919 | 7.286518 | 7.301287 | 7.312716 | 7.324998 | 7.316560 | 7.319094 | 7.317275 | 7.318011 |
| GO:0030658 | transport vesicle membrane | 7/215 | 324/21916 | 0.0412575262 | 0.4493490 | 0.42477160 | SLC17A7||UNC13A||UNC13C||MCTP2||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA2 | 7 | 6.635296 | 6.399305 | 6.396546 | 6.645769 | 6.626119 | 6.633033 | 6.636192 | 6.402164 | 6.403266 | 6.391328 | 6.400430 | 6.407983 | 6.396535 | 6.383184 | 6.398375 |
| GO:0030136 | clathrin-coated vesicle | 6/215 | 258/21916 | 0.0422916699 | 0.4493490 | 0.42477160 | UNC13D||SLC17A7||ECE1||INPP5F||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA2 | 6 | 6.246599 | 6.270767 | 6.202458 | 6.253468 | 6.205043 | 6.277734 | 6.249199 | 6.254797 | 6.281630 | 6.294444 | 6.251746 | 6.200572 | 6.199275 | 6.172144 | 6.237101 |
| GO:0005788 | endoplasmic reticulum lumen | 7/215 | 334/21916 | 0.0472178663 | 0.4737333 | 0.44782218 | COL5A3||IL23A||C3||IL6||CERCAM||SCG2||CSF1 | 7 | 7.499002 | 7.838528 | 7.907398 | 7.497426 | 7.498539 | 7.499147 | 7.500892 | 7.835631 | 7.820649 | 7.840636 | 7.856960 | 7.900386 | 7.912799 | 7.906081 | 7.910297 |
| GO:0048786 | presynaptic active zone | 3/215 | 83/21916 | 0.0483022179 | 0.4737333 | 0.44782218 | SLC17A7||UNC13A||UNC13C | 3 | 5.089132 | 5.342616 | 5.406120 | 5.058599 | 5.114353 | 5.129530 | 5.052470 | 5.358811 | 5.296191 | 5.350968 | 5.363488 | 5.398508 | 5.365096 | 5.429534 | 5.430348 |
KEGG
| ID | Description | GeneRatio | BgRatio | pvalue | p.adjust | qvalue | geneID | Count | No-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgKDN-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgwt-inf_Log2MeanTPM | log2TPM_No-inf_1 | log2TPM_No-inf_2 | log2TPM_No-inf_3 | log2TPM_No-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa04060 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | 21/105 | 295/8212 | 0.00000000009476502 | 0.00000002009018 | 0.00000001645919 | OSM||CCL22||IL23A||PRLR||IL1A||IL1R2||TNFSF10||CCR7||LIF||IL6||IL36G||IL1RN||BMP6||TNFRSF14||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||TNFSF15||CSF1||CXCR3||TNFRSF18 | 21 | 5.086895 | 6.202895 | 6.595424 | 5.076743 | 5.101743 | 5.074889 | 5.094023 | 6.217429 | 6.181225 | 6.212603 | 6.200054 | 6.586842 | 6.593162 | 6.583248 | 6.618186 |
| hsa04061 | Viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor | 10/105 | 100/8212 | 0.00000050350304971 | 0.00005337132327 | 0.00004372526484 | CCL22||TNFSF10||CCR7||IL6||TNFRSF14||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||CSF1||CXCR3 | 10 | 4.413663 | 6.576132 | 7.088386 | 4.409913 | 4.389610 | 4.420417 | 4.434344 | 6.587527 | 6.565820 | 6.581568 | 6.569508 | 7.078842 | 7.101224 | 7.091849 | 7.081520 |
| hsa05164 | Influenza A | 12/105 | 171/8212 | 0.00000164302252609 | 0.00011610692518 | 0.00009512235677 | OAS2||IL1A||TNFSF10||RSAD2||IL6||MX1||CXCL10||SOCS3||IRF7||HLA-DRA||IRF9||HLA-DQA1 | 12 | 6.876102 | 7.191024 | 7.321240 | 6.899589 | 6.869638 | 6.870578 | 6.864337 | 7.200377 | 7.187613 | 7.197474 | 7.178529 | 7.325638 | 7.331922 | 7.315561 | 7.311752 |
| hsa04668 | TNF signaling pathway | 9/105 | 112/8212 | 0.00001190873123220 | 0.00063116275531 | 0.00051708964561 | RPS6KA5||MAPK10||LIF||IL6||CREB3L1||CXCL1||CXCL10||CSF1||SOCS3 | 9 | 5.672874 | 6.796137 | 7.307626 | 5.689898 | 5.688634 | 5.659989 | 5.652590 | 6.792082 | 6.790702 | 6.805525 | 6.796191 | 7.285020 | 7.314741 | 7.320371 | 7.310122 |
| hsa05323 | Rheumatoid arthritis | 8/105 | 93/8212 | 0.00002265433442677 | 0.00096054377970 | 0.00078694003798 | IL23A||VEGFA||IL1A||IL6||CXCL1||CSF1||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 8 | 6.988702 | 7.855870 | 8.211933 | 6.981703 | 6.984825 | 6.985874 | 7.002318 | 7.860418 | 7.846485 | 7.856672 | 7.859860 | 8.207121 | 8.224023 | 8.211271 | 8.205243 |
| hsa05169 | Epstein-Barr virus infection | 11/105 | 202/8212 | 0.00005015587248787 | 0.00177217416124 | 0.00145188051939 | MAPK10||OAS2||IL6||ENTPD1||CXCL10||IRF7||ISG15||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||IRF9||HLA-DQA1 | 11 | 6.719375 | 6.720722 | 6.775605 | 6.747556 | 6.715192 | 6.715007 | 6.699316 | 6.726912 | 6.715704 | 6.721937 | 6.718308 | 6.772559 | 6.789228 | 6.768539 | 6.772005 |
| hsa05321 | Inflammatory bowel disease | 6/105 | 65/8212 | 0.00016968804928371 | 0.00427276465971 | 0.00350052715418 | IL23A||IL1A||IL6||STAT4||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 6 | 6.139674 | 6.709631 | 7.013545 | 6.189569 | 6.133551 | 6.114257 | 6.120078 | 6.706348 | 6.693349 | 6.732409 | 6.706138 | 7.018634 | 7.018068 | 7.010635 | 7.006807 |
| hsa05160 | Hepatitis C | 9/105 | 157/8212 | 0.00017029407640873 | 0.00427276465971 | 0.00350052715418 | NR1H3||OAS2||RSAD2||MX1||CXCL10||SOCS3||IRF7||IFIT1||IRF9 | 9 | 5.986245 | 6.230674 | 6.181634 | 6.020419 | 5.970485 | 5.994002 | 5.959309 | 6.265731 | 6.235998 | 6.216332 | 6.203877 | 6.185915 | 6.175414 | 6.174209 | 6.190931 |
| hsa05332 | Graft-versus-host disease | 5/105 | 42/8212 | 0.00018139095253495 | 0.00427276465971 | 0.00350052715418 | IL1A||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA1 | 5 | 6.308038 | 7.169955 | 7.692298 | 6.265930 | 6.314128 | 6.331948 | 6.319280 | 7.172058 | 7.164992 | 7.177910 | 7.164821 | 7.692447 | 7.696712 | 7.684128 | 7.695869 |
| hsa04625 | C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | 7/105 | 104/8212 | 0.00035137394622766 | 0.00744912766003 | 0.00610281064501 | CCL22||MAPK10||IL23A||IL6||CLEC4E||EGR3||IRF9 | 7 | 6.660317 | 6.874663 | 6.963941 | 6.688233 | 6.675412 | 6.641058 | 6.635878 | 6.880213 | 6.846659 | 6.865132 | 6.905995 | 6.942256 | 6.949467 | 6.973618 | 6.989921 |
| hsa05167 | Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection | 9/105 | 194/8212 | 0.00080963428133996 | 0.01560386069492 | 0.01278369917905 | MAPK10||VEGFA||C3||IL6||CXCL1||IRF7||HLA-F||IRF9||PIK3R6 | 9 | 6.652857 | 6.720990 | 6.687743 | 6.659124 | 6.656846 | 6.656189 | 6.639180 | 6.736921 | 6.712207 | 6.726891 | 6.707755 | 6.705342 | 6.688463 | 6.673428 | 6.683554 |
| hsa04658 | Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | 6/105 | 92/8212 | 0.00110937131305718 | 0.01884368514089 | 0.01543797442029 | NOTCH3||MAPK10||STAT4||DLL1||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 6 | 5.783866 | 5.674545 | 5.646206 | 5.831371 | 5.784118 | 5.775333 | 5.743257 | 5.653619 | 5.664670 | 5.707478 | 5.671847 | 5.629796 | 5.666706 | 5.615631 | 5.671900 |
| hsa04380 | Osteoclast differentiation | 7/105 | 128/8212 | 0.00121778247202719 | 0.01884368514089 | 0.01543797442029 | MAPK10||IL1A||NCF2||CSF1||SOCS3||IRF9||LILRA6 | 7 | 6.586307 | 6.815743 | 6.924388 | 6.590097 | 6.588715 | 6.585986 | 6.580411 | 6.816030 | 6.812978 | 6.833909 | 6.799852 | 6.920005 | 6.933660 | 6.912408 | 6.931375 |
| hsa04630 | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | 8/105 | 166/8212 | 0.00124439430175681 | 0.01884368514089 | 0.01543797442029 | OSM||IL23A||PRLR||LIF||IL6||STAT4||SOCS3||IRF9 | 8 | 5.798479 | 5.855192 | 5.789364 | 5.809397 | 5.811975 | 5.780190 | 5.792120 | 5.834596 | 5.876643 | 5.859921 | 5.849279 | 5.774185 | 5.786034 | 5.759564 | 5.836503 |
| hsa04640 | Hematopoietic cell lineage | 6/105 | 99/8212 | 0.00162237992762074 | 0.02292963631037 | 0.01878545179350 | IL1A||IL1R2||IL6||CSF1||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 6 | 5.814938 | 6.519575 | 6.860708 | 5.832844 | 5.799393 | 5.835409 | 5.791576 | 6.525016 | 6.530718 | 6.499022 | 6.523338 | 6.874949 | 6.842844 | 6.882556 | 6.842015 |
| hsa05162 | Measles | 7/105 | 139/8212 | 0.00196059456579725 | 0.02500806652106 | 0.02048823721934 | MAPK10||OAS2||IL1A||IL6||MX1||IRF7||IRF9 | 7 | 5.935125 | 6.374623 | 6.459455 | 5.977544 | 5.945791 | 5.911978 | 5.903998 | 6.405019 | 6.390110 | 6.357606 | 6.344949 | 6.465403 | 6.465188 | 6.447725 | 6.459433 |
| hsa05152 | Tuberculosis | 8/105 | 180/8212 | 0.00208174901203883 | 0.02500806652106 | 0.02048823721934 | MAPK10||IL23A||IL1A||C3||IL6||CLEC4E||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 8 | 7.287533 | 7.426140 | 7.541544 | 7.301719 | 7.296681 | 7.278032 | 7.273501 | 7.426307 | 7.410039 | 7.423270 | 7.444730 | 7.525855 | 7.545638 | 7.540690 | 7.553850 |
| hsa04940 | Type I diabetes mellitus | 4/105 | 43/8212 | 0.00212332640273142 | 0.02500806652106 | 0.02048823721934 | IL1A||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA1 | 4 | 6.290782 | 7.126277 | 7.599910 | 6.262364 | 6.279570 | 6.310261 | 6.310346 | 7.127999 | 7.124381 | 7.129783 | 7.122936 | 7.596629 | 7.603877 | 7.593160 | 7.605936 |
| hsa04931 | Insulin resistance | 6/105 | 108/8212 | 0.00252632218005666 | 0.02818843695642 | 0.02309380386201 | NR1H3||MAPK10||IL6||CREB3L1||SOCS3||CPT1B | 6 | 5.325164 | 5.342827 | 5.398927 | 5.359087 | 5.335342 | 5.277837 | 5.327184 | 5.429146 | 5.387219 | 5.295675 | 5.252404 | 5.472379 | 5.464855 | 5.335105 | 5.316218 |
| hsa05133 | Pertussis | 5/105 | 76/8212 | 0.00279535148679220 | 0.02826174634986 | 0.02315386369278 | MAPK10||IL23A||IL1A||C3||IL6 | 5 | 7.142965 | 7.419720 | 7.664698 | 7.162268 | 7.132486 | 7.150798 | 7.126021 | 7.423793 | 7.402581 | 7.429621 | 7.422741 | 7.659481 | 7.654946 | 7.691610 | 7.652409 |
| hsa05171 | Coronavirus disease - COVID-19 | 9/105 | 232/8212 | 0.00279951261012754 | 0.02826174634986 | 0.02315386369278 | MAPK10||OAS2||C3||MAS1||IL6||MX1||CXCL10||ISG15||IRF9 | 9 | 9.634707 | 9.683136 | 9.511494 | 9.640896 | 9.636472 | 9.633881 | 9.627548 | 9.686777 | 9.686507 | 9.689459 | 9.669714 | 9.510125 | 9.510608 | 9.512799 | 9.512442 |
| hsa05140 | Leishmaniasis | 5/105 | 77/8212 | 0.00295958390360050 | 0.02851962670742 | 0.02336513608106 | IL1A||NCF2||C3||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 5 | 8.514126 | 8.491293 | 8.456718 | 8.518474 | 8.518236 | 8.512755 | 8.507007 | 8.497518 | 8.483024 | 8.496188 | 8.488392 | 8.451958 | 8.461460 | 8.459096 | 8.454338 |
| hsa04062 | Chemokine signaling pathway | 8/105 | 192/8212 | 0.00310774728240782 | 0.02864532277698 | 0.02346811448958 | CCL22||ITK||CCR7||CXCL1||CXCL10||CXCL11||CXCR3||PIK3R6 | 8 | 5.744445 | 6.272208 | 6.473053 | 5.766626 | 5.746681 | 5.725173 | 5.738988 | 6.282292 | 6.289842 | 6.285769 | 6.230113 | 6.454515 | 6.490275 | 6.496459 | 6.450373 |
| hsa04672 | Intestinal immune network for IgA production | 4/105 | 49/8212 | 0.00343819288670509 | 0.03037070383256 | 0.02488165904852 | AICDA||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 4 | 5.069841 | 5.611385 | 5.857128 | 5.022695 | 5.108456 | 5.084618 | 5.062215 | 5.618492 | 5.586828 | 5.609954 | 5.629919 | 5.890235 | 5.871043 | 5.837469 | 5.828908 |
| hsa00240 | Pyrimidine metabolism | 4/105 | 58/8212 | 0.00630768151829251 | 0.05348913927512 | 0.04382178739024 | TYMP||CMPK2||ENTPD1||ENPP1 | 4 | 5.663223 | 5.922748 | 5.895341 | 5.720022 | 5.590887 | 5.682031 | 5.656899 | 5.890995 | 5.877082 | 6.009137 | 5.910023 | 5.871476 | 5.901632 | 5.888278 | 5.919548 |
| hsa05166 | Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection | 8/105 | 222/8212 | 0.00740482754200854 | 0.05942542968798 | 0.04868518321011 | MAPK10||IL1R2||IL6||MMP7||CREB3L1||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA1 | 8 | 6.874949 | 6.831572 | 6.922154 | 6.872693 | 6.880821 | 6.869892 | 6.876367 | 6.850533 | 6.828733 | 6.826301 | 6.820542 | 6.918281 | 6.940231 | 6.918827 | 6.911113 |
| hsa05150 | Staphylococcus aureus infection | 5/105 | 96/8212 | 0.00756833302629927 | 0.05942542968798 | 0.04868518321011 | CFH||C3||PTAFR||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 5 | 7.423417 | 7.294302 | 7.510582 | 7.420281 | 7.430177 | 7.425441 | 7.417738 | 7.289489 | 7.300136 | 7.308147 | 7.279272 | 7.495206 | 7.519631 | 7.523427 | 7.503882 |
| hsa05165 | Human papillomavirus infection | 10/105 | 331/8212 | 0.00956162506951858 | 0.07239516124064 | 0.05931083219814 | NOTCH3||VEGFA||OASL||MX1||CREB3L1||ISG15||HES4||HLA-F||COL6A6||IRF9 | 10 | 6.488302 | 6.944573 | 6.974719 | 6.509168 | 6.479664 | 6.487422 | 6.476731 | 6.951878 | 6.938578 | 6.943178 | 6.944627 | 6.973654 | 6.984916 | 6.974091 | 6.966152 |
| hsa04620 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 5/105 | 104/8212 | 0.01051237386782264 | 0.07684907793029 | 0.06295977089622 | MAPK10||IL6||CXCL10||CXCL11||IRF7 | 5 | 6.857067 | 7.864424 | 8.031730 | 6.900834 | 6.841592 | 6.849210 | 6.835700 | 7.871990 | 7.853207 | 7.867530 | 7.864901 | 8.028003 | 8.039847 | 8.027727 | 8.031310 |
| hsa04659 | Th17 cell differentiation | 5/105 | 108/8212 | 0.01224402886214387 | 0.08437779859804 | 0.06912778931816 | MAPK10||IL23A||IL6||HLA-DRA||HLA-DQA1 | 5 | 6.245807 | 6.773038 | 6.950252 | 6.273823 | 6.247195 | 6.235188 | 6.226582 | 6.768169 | 6.758660 | 6.797266 | 6.767762 | 6.948426 | 6.957724 | 6.942009 | 6.952801 |
| hsa05330 | Allograft rejection | 3/105 | 38/8212 | 0.01238861507866246 | 0.08437779859804 | 0.06912778931816 | HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA1 | 3 | 6.418458 | 6.394930 | 6.666126 | 6.373850 | 6.428928 | 6.442445 | 6.427657 | 6.388855 | 6.399116 | 6.409975 | 6.381616 | 6.669858 | 6.676428 | 6.632023 | 6.685622 |
| hsa04622 | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | 4/105 | 71/8212 | 0.01273627148649680 | 0.08437779859804 | 0.06912778931816 | MAPK10||CXCL10||IRF7||ISG15 | 4 | 5.078174 | 5.655759 | 5.885765 | 5.253145 | 5.017187 | 5.060039 | 4.965610 | 5.645235 | 5.635874 | 5.683744 | 5.657733 | 5.892111 | 5.890083 | 5.910739 | 5.849437 |
| hsa04151 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 10/105 | 354/8212 | 0.01482188304728154 | 0.09496159022652 | 0.07779872089064 | LPAR2||OSM||VEGFA||PRLR||IL6||CREB3L1||IGF2||CSF1||COL6A6||PIK3R6 | 10 | 6.682235 | 7.106428 | 7.061342 | 6.692412 | 6.679574 | 6.677568 | 6.679339 | 7.112024 | 7.103687 | 7.101792 | 7.108187 | 7.064362 | 7.057127 | 7.064505 | 7.059359 |
| hsa05219 | Bladder cancer | 3/105 | 41/8212 | 0.01522968899859216 | 0.09496159022652 | 0.07779872089064 | TYMP||RPS6KA5||VEGFA | 3 | 5.785975 | 7.785006 | 8.247497 | 5.753419 | 5.821909 | 5.772336 | 5.795323 | 7.790786 | 7.767380 | 7.790772 | 7.790941 | 8.242380 | 8.252307 | 8.252203 | 8.243067 |
| hsa05161 | Hepatitis B | 6/105 | 162/8212 | 0.01740353019875800 | 0.10541566863248 | 0.08636338294121 | MAPK10||IL6||STAT4||CREB3L1||EGR3||IRF7 | 6 | 5.662220 | 6.472859 | 6.778320 | 5.695498 | 5.669496 | 5.645200 | 5.637980 | 6.471337 | 6.457282 | 6.485151 | 6.477522 | 6.769592 | 6.786408 | 6.782144 | 6.775077 |
| hsa01232 | Nucleotide metabolism | 4/105 | 85/8212 | 0.02319209146127183 | 0.13657564971638 | 0.11189166933070 | TYMP||CMPK2||ENTPD1||ENPP1 | 4 | 5.806245 | 6.030504 | 6.034363 | 5.845179 | 5.786694 | 5.798723 | 5.793648 | 6.004169 | 6.023671 | 6.066529 | 6.026935 | 6.004500 | 6.069966 | 6.052243 | 6.009669 |
| hsa05320 | Autoimmune thyroid disease | 3/105 | 53/8212 | 0.02999446018849599 | 0.17186015026922 | 0.14079903075681 | HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA1 | 3 | 6.582899 | 6.449079 | 6.721810 | 6.538144 | 6.598146 | 6.602397 | 6.591978 | 6.452077 | 6.451726 | 6.461307 | 6.431036 | 6.725605 | 6.737020 | 6.683541 | 6.740365 |
| hsa04621 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 6/105 | 186/8212 | 0.03166042969351016 | 0.17210669537302 | 0.14100101656678 | MAPK10||OAS2||IL6||CXCL1||IRF7||IRF9 | 6 | 6.251026 | 6.673795 | 6.903518 | 6.256704 | 6.230573 | 6.253792 | 6.262828 | 6.675522 | 6.663632 | 6.680139 | 6.675837 | 6.887584 | 6.928398 | 6.903037 | 6.894722 |
| hsa04657 | IL-17 signaling pathway | 4/105 | 94/8212 | 0.03204146620358956 | 0.17210669537302 | 0.14100101656678 | MAPK10||IL6||CXCL1||CXCL10 | 4 | 6.027005 | 7.544981 | 7.949861 | 6.090109 | 5.991013 | 6.034467 | 5.990099 | 7.549537 | 7.548306 | 7.547971 | 7.534052 | 7.953893 | 7.949889 | 7.954820 | 7.940802 |
| hsa05418 | Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis | 5/105 | 139/8212 | 0.03247296139113651 | 0.17210669537302 | 0.14100101656678 | MAPK10||VEGFA||IL1A||IL1R2||NCF2 | 5 | 7.507613 | 7.993529 | 8.178245 | 7.513409 | 7.506042 | 7.499707 | 7.511257 | 7.993641 | 7.987546 | 7.995633 | 7.997278 | 8.185120 | 8.179293 | 8.173023 | 8.175514 |
| hsa04936 | Alcoholic liver disease | 5/105 | 142/8212 | 0.03513226541803356 | 0.18165951874691 | 0.14882731178371 | MAPK10||C3||IL6||CXCL1||CPT1B | 5 | 5.251329 | 6.067098 | 6.318194 | 5.334877 | 5.203956 | 5.272543 | 5.189231 | 6.096152 | 6.065185 | 6.054370 | 6.052255 | 6.339150 | 6.312327 | 6.319752 | 6.301281 |
| hsa05134 | Legionellosis | 3/105 | 57/8212 | 0.03612706096442739 | 0.18235564105854 | 0.14939762052959 | C3||IL6||CXCL1 | 3 | 8.633757 | 8.745687 | 8.719390 | 8.643546 | 8.638199 | 8.629330 | 8.623873 | 8.757228 | 8.734623 | 8.747546 | 8.743261 | 8.713532 | 8.720996 | 8.724871 | 8.718136 |
| hsa04933 | AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications | 4/105 | 100/8212 | 0.03890460138701573 | 0.19180873241971 | 0.15714220878476 | MAPK10||VEGFA||IL1A||IL6 | 4 | 5.429300 | 6.280544 | 6.560890 | 5.466875 | 5.421012 | 5.412004 | 5.416632 | 6.291995 | 6.244208 | 6.303474 | 6.281815 | 6.559388 | 6.571371 | 6.557948 | 6.554799 |
| hsa05416 | Viral myocarditis | 3/105 | 60/8212 | 0.04111745637361714 | 0.19811138070925 | 0.16230574884323 | HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA1 | 3 | 8.629517 | 8.684178 | 8.733628 | 8.630005 | 8.630168 | 8.635000 | 8.622868 | 8.684843 | 8.684491 | 8.694392 | 8.672906 | 8.748068 | 8.747613 | 8.717254 | 8.721292 |
| hsa04145 | Phagosome | 5/105 | 152/8212 | 0.04495369819016803 | 0.21178186702924 | 0.17350550178661 | NCF2||C3||HLA-DRA||HLA-F||HLA-DQA1 | 5 | 7.969877 | 8.135376 | 8.191084 | 7.967865 | 7.981784 | 7.965055 | 7.964736 | 8.118348 | 8.128772 | 8.146742 | 8.147433 | 8.190491 | 8.193412 | 8.203015 | 8.177301 |
| hsa05203 | Viral carcinogenesis | 6/105 | 204/8212 | 0.04631250648659249 | 0.21344024728603 | 0.17486415492649 | C3||CREB3L1||EGR3||IRF7||HLA-F||IRF9 | 6 | 6.324310 | 6.494961 | 6.506808 | 6.338654 | 6.321486 | 6.325139 | 6.311831 | 6.505354 | 6.490414 | 6.499818 | 6.484163 | 6.491878 | 6.524211 | 6.503087 | 6.507869 |
| hsa04932 | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | 5/105 | 155/8212 | 0.04819098372933095 | 0.21737209682166 | 0.17808538220245 | NR1H3||MAPK10||IL1A||IL6||SOCS3 | 5 | 8.461942 | 8.357088 | 8.625355 | 8.467846 | 8.454478 | 8.467956 | 8.457439 | 8.361560 | 8.353789 | 8.360478 | 8.352501 | 8.629958 | 8.635326 | 8.623253 | 8.612786 |
ORA: Up-regulated DEGs
Please Click HERE to download a Microsoft .excel that contains all of the “ORT: Up-regulated DEGs” results.
GO: BP
| ID | Description | GeneRatio | BgRatio | pvalue | p.adjust | qvalue | geneID | Count | No-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgKDN-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgwt-inf_Log2MeanTPM | log2TPM_No-inf_1 | log2TPM_No-inf_2 | log2TPM_No-inf_3 | log2TPM_No-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0060415 | muscle tissue morphogenesis | 5/97 | 71/20870 | 0.00001996614 | 0.03170975 | 0.02797216 | MYLK||TGFB2||HEY2||POU4F1||S1PR1 | 5 | 5.136792 | 5.345375 | 5.480612 | 5.136975 | 5.127562 | 5.129204 | 5.153284 | 5.371145 | 5.326653 | 5.361982 | 5.321068 | 5.487305 | 5.506067 | 5.465273 | 5.463378 |
| GO:0048644 | muscle organ morphogenesis | 5/97 | 78/20870 | 0.00003155427 | 0.03170975 | 0.02797216 | MYLK||TGFB2||HEY2||POU4F1||S1PR1 | 5 | 5.132797 | 5.309763 | 5.435590 | 5.108064 | 5.102638 | 5.103870 | 5.213506 | 5.331057 | 5.294131 | 5.327240 | 5.286083 | 5.439355 | 5.466459 | 5.421010 | 5.414979 |
| GO:0055001 | muscle cell development | 7/97 | 204/20870 | 0.00004697741 | 0.03170975 | 0.02797216 | RGS4||HEY2||DYSF||BIN1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 7 | 6.420787 | 6.557195 | 6.527652 | 6.429272 | 6.410019 | 6.426920 | 6.416855 | 6.556308 | 6.549533 | 6.571219 | 6.551618 | 6.485159 | 6.545349 | 6.542804 | 6.536461 |
| GO:0003184 | pulmonary valve morphogenesis | 3/97 | 18/20870 | 0.00007549783 | 0.03822078 | 0.03371574 | TGFB2||HEY2||SLIT2 | 3 | 4.232616 | 4.706080 | 4.796837 | 4.210548 | 4.371543 | 4.185157 | 4.153224 | 4.690082 | 4.653038 | 4.733839 | 4.745497 | 4.823770 | 4.891129 | 4.701730 | 4.763877 |
| GO:0003177 | pulmonary valve development | 3/97 | 22/20870 | 0.00014057380 | 0.04193470 | 0.03699191 | TGFB2||HEY2||SLIT2 | 3 | 4.801271 | 5.245316 | 5.302543 | 4.793697 | 4.868950 | 4.742173 | 4.797433 | 5.299106 | 5.137548 | 5.256883 | 5.282261 | 5.265551 | 5.411974 | 5.217633 | 5.307825 |
| GO:0048762 | mesenchymal cell differentiation | 7/97 | 252/20870 | 0.00017560477 | 0.04193470 | 0.03699191 | LRP6||TGFB2||HEY2||FBXL17||EDNRA||SEMA3D||SPRED1 | 7 | 6.324772 | 6.375609 | 6.501172 | 6.192428 | 6.279764 | 6.374764 | 6.439951 | 6.399729 | 6.430675 | 6.305483 | 6.363555 | 6.554312 | 6.448350 | 6.484277 | 6.515632 |
| GO:0060537 | muscle tissue development | 9/97 | 432/20870 | 0.00018371314 | 0.04193470 | 0.03699191 | MYLK||TGFB2||RGS4||HEY2||POU4F1||S1PR1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 9 | 6.237649 | 6.207868 | 6.183220 | 6.157958 | 6.211851 | 6.265188 | 6.311046 | 6.227633 | 6.234946 | 6.167794 | 6.200135 | 6.194990 | 6.152260 | 6.174392 | 6.210572 |
| GO:0048738 | cardiac muscle tissue development | 7/97 | 254/20870 | 0.00018432876 | 0.04193470 | 0.03699191 | TGFB2||RGS4||HEY2||POU4F1||S1PR1||SLC8A1||NRAP | 7 | 5.985579 | 6.073793 | 6.097059 | 5.989234 | 6.003624 | 5.982907 | 5.966304 | 6.101736 | 6.053971 | 6.080963 | 6.057990 | 6.097368 | 6.092846 | 6.096002 | 6.102004 |
| GO:0055008 | cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis | 4/97 | 61/20870 | 0.00018678115 | 0.04193470 | 0.03699191 | TGFB2||HEY2||POU4F1||S1PR1 | 4 | 5.058301 | 5.439267 | 5.604533 | 5.063918 | 5.048990 | 5.049971 | 5.070211 | 5.458373 | 5.412763 | 5.465666 | 5.419521 | 5.617371 | 5.622961 | 5.587772 | 5.589679 |
| GO:0007517 | muscle organ development | 8/97 | 345/20870 | 0.00020708492 | 0.04193470 | 0.03699191 | MYLK||TGFB2||ID3||HEY2||POU4F1||CHODL||S1PR1||MYOZ2 | 8 | 6.097461 | 5.908065 | 5.860493 | 5.987651 | 6.043297 | 6.130406 | 6.217864 | 5.916200 | 5.962478 | 5.837111 | 5.913683 | 5.911265 | 5.805662 | 5.834083 | 5.888516 |
| GO:0014829 | vascular associated smooth muscle contraction | 3/97 | 26/20870 | 0.00023415361 | 0.04267339 | 0.03764353 | CHRM3||EDNRA||SLC8A1 | 3 | 6.009656 | 6.025296 | 6.055758 | 6.087553 | 5.843585 | 5.981768 | 6.110497 | 6.000249 | 5.918640 | 5.937114 | 6.224125 | 6.097685 | 6.001633 | 5.916596 | 6.192327 |
| GO:1903522 | regulation of blood circulation | 7/97 | 268/20870 | 0.00025571506 | 0.04267339 | 0.03764353 | TGFB2||RGS4||CHRM3||HEY2||BIN1||SLC8A1||TRDN | 7 | 5.655865 | 5.727144 | 5.648960 | 5.661671 | 5.658549 | 5.652066 | 5.651147 | 5.756863 | 5.700573 | 5.749370 | 5.700809 | 5.628460 | 5.683841 | 5.658753 | 5.623968 |
| GO:0003206 | cardiac chamber morphogenesis | 5/97 | 123/20870 | 0.00027395264 | 0.04267339 | 0.03764353 | TGFB2||DNAH11||HEY2||SLIT2||POU4F1 | 5 | 5.358853 | 5.347923 | 5.373261 | 5.380025 | 5.351924 | 5.325274 | 5.377509 | 5.369136 | 5.275014 | 5.425388 | 5.317756 | 5.439857 | 5.367461 | 5.366435 | 5.316603 |
| GO:0060411 | cardiac septum morphogenesis | 4/97 | 69/20870 | 0.00030076252 | 0.04350315 | 0.03837549 | TGFB2||DNAH11||HEY2||SLIT2 | 4 | 5.305853 | 5.123484 | 5.010316 | 5.313385 | 5.319038 | 5.293940 | 5.296891 | 5.141236 | 5.101923 | 5.132801 | 5.117664 | 5.006620 | 5.031887 | 4.996094 | 5.006421 |
| GO:0061384 | heart trabecula morphogenesis | 3/97 | 30/20870 | 0.00036074633 | 0.04870075 | 0.04296046 | TGFB2||HEY2||S1PR1 | 3 | 4.785085 | 5.118994 | 5.168761 | 4.823983 | 4.780707 | 4.781156 | 4.753613 | 5.133061 | 5.103147 | 5.121656 | 5.117951 | 5.165809 | 5.173472 | 5.158116 | 5.177569 |
| GO:0003012 | muscle system process | 9/97 | 478/20870 | 0.00038657936 | 0.04892645 | 0.04315955 | MYLK||RGS4||CHRM3||HEY2||BIN1||EDNRA||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||TRDN | 9 | 6.197495 | 6.441757 | 6.510739 | 6.186866 | 6.189210 | 6.206639 | 6.207142 | 6.438655 | 6.432809 | 6.455249 | 6.440222 | 6.495510 | 6.526803 | 6.488041 | 6.532097 |
| GO:0008016 | regulation of heart contraction | 6/97 | 212/20870 | 0.00046919425 | 0.05588931 | 0.04930171 | TGFB2||RGS4||HEY2||BIN1||SLC8A1||TRDN | 6 | 5.763987 | 5.809291 | 5.721822 | 5.787988 | 5.753283 | 5.746787 | 5.767544 | 5.833943 | 5.764689 | 5.851899 | 5.784898 | 5.703279 | 5.747642 | 5.741431 | 5.694188 |
| GO:0035909 | aorta morphogenesis | 3/97 | 34/20870 | 0.00052459048 | 0.05901643 | 0.05206024 | MYLK||TGFB2||HEY2 | 3 | 4.849908 | 5.212684 | 5.162394 | 4.861179 | 4.866511 | 4.824817 | 4.846765 | 5.216603 | 5.228938 | 5.214453 | 5.190473 | 5.154669 | 5.170649 | 5.149089 | 5.175009 |
| GO:0060485 | mesenchyme development | 7/97 | 308/20870 | 0.00058873824 | 0.06274710 | 0.05535118 | LRP6||TGFB2||HEY2||FBXL17||EDNRA||SEMA3D||SPRED1 | 7 | 6.184089 | 6.230759 | 6.345293 | 6.060676 | 6.141144 | 6.228540 | 6.295154 | 6.253430 | 6.283509 | 6.163574 | 6.219785 | 6.395732 | 6.296286 | 6.328877 | 6.358410 |
| GO:0014706 | striated muscle tissue development | 8/97 | 412/20870 | 0.00067378788 | 0.06822102 | 0.06017990 | TGFB2||RGS4||HEY2||POU4F1||S1PR1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 8 | 6.260378 | 6.232633 | 6.214179 | 6.178880 | 6.233292 | 6.288843 | 6.335703 | 6.254565 | 6.261037 | 6.191347 | 6.222512 | 6.225862 | 6.182874 | 6.206607 | 6.240723 |
| GO:0060412 | ventricular septum morphogenesis | 3/97 | 40/20870 | 0.00084883588 | 0.07474476 | 0.06593469 | TGFB2||HEY2||SLIT2 | 3 | 5.453584 | 4.964032 | 4.764651 | 5.449670 | 5.457141 | 5.460966 | 5.446513 | 4.964295 | 4.935784 | 4.990981 | 4.964538 | 4.776924 | 4.807251 | 4.737586 | 4.735611 |
| GO:0045823 | positive regulation of heart contraction | 3/97 | 41/20870 | 0.00091277693 | 0.07474476 | 0.06593469 | TGFB2||RGS4||HEY2 | 3 | 6.205399 | 6.268940 | 6.179027 | 6.277411 | 6.169532 | 6.151991 | 6.219348 | 6.291801 | 6.190843 | 6.411273 | 6.168941 | 6.088422 | 6.263426 | 6.291890 | 6.057562 |
| GO:0014033 | neural crest cell differentiation | 4/97 | 93/20870 | 0.00093303483 | 0.07474476 | 0.06593469 | LRP6||FBXL17||EDNRA||SEMA3D | 4 | 4.969082 | 4.933599 | 4.978049 | 4.940692 | 5.007614 | 4.952206 | 4.974909 | 4.907705 | 4.940829 | 4.929759 | 4.955680 | 5.166949 | 4.931197 | 4.850325 | 4.944161 |
| GO:0007009 | plasma membrane organization | 5/97 | 163/20870 | 0.00098769185 | 0.07474476 | 0.06593469 | TGFB2||CLU||DYSF||BIN1||TMEFF2 | 5 | 5.611517 | 5.680128 | 5.736310 | 5.558400 | 5.600561 | 5.645620 | 5.639795 | 5.700539 | 5.680151 | 5.665461 | 5.674129 | 5.705191 | 5.725845 | 5.691364 | 5.819340 |
| GO:1903524 | positive regulation of blood circulation | 3/97 | 43/20870 | 0.00104963910 | 0.07474476 | 0.06593469 | TGFB2||RGS4||HEY2 | 3 | 6.113901 | 6.170973 | 6.073633 | 6.160558 | 6.050736 | 6.138413 | 6.103523 | 6.181699 | 6.136420 | 6.297460 | 6.057829 | 5.980492 | 6.178053 | 6.172969 | 5.947332 |
| GO:1905314 | semi-lunar valve development | 3/97 | 43/20870 | 0.00104963910 | 0.07474476 | 0.06593469 | TGFB2||HEY2||SLIT2 | 3 | 5.134947 | 5.682283 | 5.761954 | 5.096705 | 5.171269 | 5.108187 | 5.162158 | 5.719722 | 5.593650 | 5.713099 | 5.699075 | 5.769549 | 5.821794 | 5.710387 | 5.743782 |
| GO:0060047 | heart contraction | 6/97 | 248/20870 | 0.00106317255 | 0.07474476 | 0.06593469 | TGFB2||RGS4||HEY2||BIN1||SLC8A1||TRDN | 6 | 5.976623 | 5.946827 | 5.831944 | 5.992463 | 5.966246 | 5.960926 | 5.986613 | 5.963627 | 5.911290 | 5.980319 | 5.931061 | 5.805033 | 5.852265 | 5.843251 | 5.826782 |
| GO:0003205 | cardiac chamber development | 5/97 | 166/20870 | 0.00107145384 | 0.07474476 | 0.06593469 | TGFB2||DNAH11||HEY2||SLIT2||POU4F1 | 5 | 5.338606 | 5.445219 | 5.445528 | 5.357515 | 5.324943 | 5.309298 | 5.361992 | 5.460275 | 5.387506 | 5.515555 | 5.414248 | 5.490529 | 5.447360 | 5.445716 | 5.396988 |
| GO:0003007 | heart morphogenesis | 6/97 | 251/20870 | 0.00113091072 | 0.07474476 | 0.06593469 | TGFB2||DNAH11||HEY2||SLIT2||POU4F1||S1PR1 | 6 | 5.463710 | 5.405228 | 5.436223 | 5.506568 | 5.413688 | 5.422336 | 5.509429 | 5.410453 | 5.338387 | 5.427200 | 5.442679 | 5.474634 | 5.393899 | 5.443675 | 5.431528 |
| GO:0055013 | cardiac muscle cell development | 4/97 | 98/20870 | 0.00113412566 | 0.07474476 | 0.06593469 | RGS4||HEY2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 4 | 5.945223 | 6.258170 | 6.307760 | 5.964091 | 5.934841 | 5.953567 | 5.928106 | 6.285736 | 6.251448 | 6.277588 | 6.216912 | 6.221514 | 6.339425 | 6.333967 | 6.332797 |
| GO:0014820 | tonic smooth muscle contraction | 2/97 | 11/20870 | 0.00114424075 | 0.07474476 | 0.06593469 | MYLK||EDNRA | 2 | 5.720665 | 4.611351 | 5.134876 | 6.004231 | 4.903833 | 5.644211 | 6.061771 | 4.063136 | 4.076069 | 3.961246 | 5.603306 | 5.250248 | 4.799330 | 4.416075 | 5.735773 |
| GO:0050920 | regulation of chemotaxis | 6/97 | 255/20870 | 0.00122632715 | 0.07532123 | 0.06644321 | TNFSF18||SLIT2||SEMA3D||S1PR1||SUCNR1||KLRK1 | 6 | 6.966195 | 7.294631 | 7.384699 | 6.957606 | 6.962347 | 6.976834 | 6.967920 | 7.303045 | 7.289229 | 7.291965 | 7.294247 | 7.386540 | 7.384670 | 7.392520 | 7.375009 |
| GO:0061383 | trabecula morphogenesis | 3/97 | 46/20870 | 0.00127816487 | 0.07532123 | 0.06644321 | TGFB2||HEY2||S1PR1 | 3 | 5.479124 | 5.508562 | 5.476157 | 5.517226 | 5.490570 | 5.457800 | 5.449897 | 5.529870 | 5.476645 | 5.474030 | 5.552119 | 5.534643 | 5.459818 | 5.439556 | 5.468838 |
| GO:0035051 | cardiocyte differentiation | 5/97 | 173/20870 | 0.00128731164 | 0.07532123 | 0.06644321 | TGFB2||RGS4||HEY2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 5 | 6.170644 | 6.297204 | 6.341258 | 6.167455 | 6.183230 | 6.172871 | 6.158914 | 6.330029 | 6.269110 | 6.300944 | 6.288053 | 6.342822 | 6.338910 | 6.339986 | 6.343309 |
| GO:0003015 | heart process | 6/97 | 258/20870 | 0.00130184844 | 0.07532123 | 0.06644321 | TGFB2||RGS4||HEY2||BIN1||SLC8A1||TRDN | 6 | 6.021966 | 5.981119 | 5.874177 | 6.035226 | 6.012749 | 6.009327 | 6.030392 | 5.995000 | 5.946307 | 6.016085 | 5.966096 | 5.853643 | 5.896397 | 5.880496 | 5.865816 |
| GO:0055010 | ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis | 3/97 | 47/20870 | 0.00136073782 | 0.07595816 | 0.06700507 | TGFB2||HEY2||POU4F1 | 3 | 5.275838 | 5.690701 | 5.862027 | 5.280602 | 5.273977 | 5.257738 | 5.290836 | 5.711790 | 5.658651 | 5.715877 | 5.675680 | 5.877714 | 5.883849 | 5.843453 | 5.842593 |
| GO:0055006 | cardiac cell development | 4/97 | 104/20870 | 0.00141337484 | 0.07595816 | 0.06700507 | RGS4||HEY2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 4 | 5.878818 | 6.209550 | 6.262842 | 5.894643 | 5.871785 | 5.885605 | 5.863032 | 6.235121 | 6.202495 | 6.227293 | 6.172461 | 6.179771 | 6.292754 | 6.286859 | 6.288889 |
| GO:0032728 | positive regulation of interferon-beta production | 3/97 | 48/20870 | 0.00144659136 | 0.07595816 | 0.06700507 | POLR3G||TLR4||TLR7 | 3 | 5.923571 | 5.867557 | 5.780233 | 6.001191 | 5.893480 | 5.916145 | 5.880373 | 5.858144 | 5.885684 | 5.824393 | 5.900836 | 5.750266 | 5.757130 | 5.878066 | 5.730746 |
| GO:0002027 | regulation of heart rate | 4/97 | 107/20870 | 0.00156956202 | 0.07595816 | 0.06700507 | RGS4||HEY2||BIN1||SLC8A1 | 4 | 5.776837 | 5.615765 | 5.494030 | 5.767448 | 5.766783 | 5.797067 | 5.775841 | 5.619735 | 5.602998 | 5.632498 | 5.607644 | 5.490906 | 5.507589 | 5.486258 | 5.491277 |
| GO:0003279 | cardiac septum development | 4/97 | 107/20870 | 0.00156956202 | 0.07595816 | 0.06700507 | TGFB2||DNAH11||HEY2||SLIT2 | 4 | 5.106971 | 4.989370 | 4.918146 | 5.115149 | 5.096414 | 5.089517 | 5.126505 | 4.997060 | 4.959852 | 5.041398 | 4.957550 | 4.918652 | 4.945467 | 4.913731 | 4.894270 |
| GO:0055017 | cardiac muscle tissue growth | 4/97 | 107/20870 | 0.00156956202 | 0.07595816 | 0.06700507 | TGFB2||RGS4||HEY2||S1PR1 | 4 | 5.689330 | 5.248593 | 5.170425 | 5.708586 | 5.687263 | 5.670126 | 5.691086 | 5.282194 | 5.183204 | 5.336302 | 5.186792 | 5.237554 | 5.102102 | 5.183053 | 5.155680 |
| GO:0003222 | ventricular trabecula myocardium morphogenesis | 2/97 | 13/20870 | 0.00161293876 | 0.07595816 | 0.06700507 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 5.036119 | 5.564461 | 5.628252 | 5.068627 | 4.995246 | 5.047775 | 5.031833 | 5.576515 | 5.556433 | 5.564894 | 5.559921 | 5.627835 | 5.627186 | 5.628992 | 5.628992 |
| GO:0015816 | glycine transport | 2/97 | 13/20870 | 0.00161293876 | 0.07595816 | 0.06700507 | SLC7A8||RGS4 | 2 | 5.987676 | 5.557230 | 5.114983 | 6.013458 | 6.020522 | 5.974824 | 5.940473 | 5.511457 | 5.496058 | 5.552245 | 5.663167 | 5.024820 | 5.227848 | 5.044938 | 5.152858 |
| GO:0006939 | smooth muscle contraction | 4/97 | 112/20870 | 0.00185594526 | 0.08541566 | 0.07534783 | MYLK||CHRM3||EDNRA||SLC8A1 | 4 | 5.189384 | 5.098388 | 5.046867 | 5.215527 | 5.081595 | 5.228004 | 5.227220 | 5.057299 | 5.051013 | 5.083644 | 5.196740 | 5.061834 | 5.042258 | 4.964162 | 5.115161 |
| GO:0060419 | heart growth | 4/97 | 115/20870 | 0.00204413574 | 0.09198611 | 0.08114382 | TGFB2||RGS4||HEY2||S1PR1 | 4 | 5.761527 | 5.380365 | 5.271618 | 5.782891 | 5.768077 | 5.734449 | 5.760262 | 5.411187 | 5.340548 | 5.446779 | 5.319241 | 5.330313 | 5.203265 | 5.287789 | 5.262180 |
| GO:0003229 | ventricular cardiac muscle tissue development | 3/97 | 56/20870 | 0.00225707186 | 0.09535245 | 0.08411338 | TGFB2||HEY2||POU4F1 | 3 | 5.866863 | 6.236064 | 6.235325 | 5.879959 | 5.875995 | 5.851176 | 5.860134 | 6.251604 | 6.216615 | 6.235519 | 6.240296 | 6.247827 | 6.239149 | 6.233869 | 6.220315 |
| GO:0035265 | organ growth | 5/97 | 197/20870 | 0.00227525860 | 0.09535245 | 0.08411338 | TGFB2||RGS4||HEY2||MMP13||S1PR1 | 5 | 5.851334 | 5.662966 | 5.628049 | 5.863925 | 5.853507 | 5.842570 | 5.845238 | 5.687634 | 5.636552 | 5.697497 | 5.628915 | 5.658538 | 5.605987 | 5.634920 | 5.612155 |
| GO:0051924 | regulation of calcium ion transport | 6/97 | 290/20870 | 0.00234771263 | 0.09535245 | 0.08411338 | MYLK||RGS4||BIN1||CACNB4||SLC8A1||TRDN | 6 | 6.105368 | 6.430538 | 6.549169 | 6.078962 | 6.106049 | 6.117839 | 6.118270 | 6.436966 | 6.429969 | 6.427000 | 6.428197 | 6.540515 | 6.547437 | 6.557895 | 6.550776 |
| GO:0003179 | heart valve morphogenesis | 3/97 | 57/20870 | 0.00237449791 | 0.09535245 | 0.08411338 | TGFB2||HEY2||SLIT2 | 3 | 5.022593 | 5.317228 | 5.402979 | 5.018614 | 5.038814 | 4.999868 | 5.032763 | 5.320845 | 5.275163 | 5.315881 | 5.355889 | 5.600484 | 5.353806 | 5.286795 | 5.350339 |
| GO:0003198 | epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation | 2/97 | 16/20870 | 0.00245901288 | 0.09535245 | 0.08411338 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 5.311725 | 5.461115 | 5.434158 | 5.361915 | 5.302107 | 5.292261 | 5.289402 | 5.449537 | 5.487548 | 5.474612 | 5.432120 | 5.425427 | 5.450359 | 5.427654 | 5.433058 |
| GO:0010649 | regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling | 2/97 | 16/20870 | 0.00245901288 | 0.09535245 | 0.08411338 | SLC8A1||TRDN | 2 | 6.671494 | 6.491963 | 6.362288 | 6.636751 | 6.686030 | 6.691848 | 6.670713 | 6.519084 | 6.451228 | 6.505924 | 6.490720 | 6.380428 | 6.343266 | 6.365560 | 6.359655 |
| GO:0060413 | atrial septum morphogenesis | 2/97 | 16/20870 | 0.00245901288 | 0.09535245 | 0.08411338 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 4.455615 | 4.372817 | 4.112228 | 4.383744 | 4.355107 | 4.711072 | 4.338732 | 4.433202 | 4.395840 | 4.347352 | 4.311919 | 4.086022 | 4.110593 | 4.120370 | 4.131536 |
| GO:0035904 | aorta development | 3/97 | 58/20870 | 0.00249564437 | 0.09535245 | 0.08411338 | MYLK||TGFB2||HEY2 | 3 | 4.759324 | 5.018253 | 5.000822 | 4.758823 | 4.776335 | 4.720913 | 4.780460 | 4.998626 | 5.008266 | 5.038438 | 5.027345 | 5.012656 | 5.041039 | 4.950551 | 4.997558 |
| GO:0110053 | regulation of actin filament organization | 6/97 | 299/20870 | 0.00273229239 | 0.10047125 | 0.08862883 | RGS4||BIN1||TMEFF2||SLIT2||JMY||S1PR1 | 6 | 7.380699 | 7.491806 | 7.423087 | 7.382483 | 7.369704 | 7.378980 | 7.391544 | 7.493731 | 7.480977 | 7.491560 | 7.500886 | 7.424966 | 7.410849 | 7.430505 | 7.425954 |
| GO:0051058 | negative regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction | 3/97 | 60/20870 | 0.00274925588 | 0.10047125 | 0.08862883 | TGFB2||TRIM67||SLIT2 | 3 | 5.601873 | 5.406877 | 5.308565 | 5.556470 | 5.661575 | 5.584049 | 5.603329 | 5.410586 | 5.446069 | 5.409341 | 5.360223 | 5.266798 | 5.309931 | 5.345630 | 5.310821 |
| GO:0060977 | coronary vasculature morphogenesis | 2/97 | 17/20870 | 0.00277846425 | 0.10047125 | 0.08862883 | HEY2||SPRED1 | 2 | 4.120714 | 4.935171 | 5.225778 | 4.126216 | 4.073076 | 4.159346 | 4.122906 | 4.916799 | 4.894875 | 4.956602 | 4.971120 | 5.216143 | 5.275885 | 5.223664 | 5.185960 |
| GO:0003231 | cardiac ventricle development | 4/97 | 127/20870 | 0.00292925051 | 0.10406548 | 0.09179941 | TGFB2||HEY2||SLIT2||POU4F1 | 4 | 5.486494 | 5.620956 | 5.609957 | 5.509271 | 5.468330 | 5.456317 | 5.511237 | 5.635970 | 5.556212 | 5.699131 | 5.588483 | 5.664861 | 5.608406 | 5.618392 | 5.545673 |
| GO:0051798 | positive regulation of hair follicle development | 2/97 | 18/20870 | 0.00311633505 | 0.10880308 | 0.09597859 | TGFB2||HPSE | 2 | 4.186179 | 4.908999 | 4.957456 | 4.125070 | 4.155718 | 4.219224 | 4.241649 | 4.879020 | 4.922125 | 4.889309 | 4.944597 | 4.946410 | 4.923008 | 4.988873 | 4.970678 |
| GO:0042692 | muscle cell differentiation | 7/97 | 416/20870 | 0.00327980523 | 0.11256959 | 0.09930115 | RGS4||HEY2||DYSF||BIN1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 7 | 6.738567 | 6.895861 | 6.878914 | 6.746115 | 6.740953 | 6.738072 | 6.729074 | 6.891816 | 6.896176 | 6.891990 | 6.903433 | 6.866854 | 6.888438 | 6.876309 | 6.883962 |
| GO:0048863 | stem cell differentiation | 5/97 | 217/20870 | 0.00344800038 | 0.11637001 | 0.10265363 | LRP6||TGFB2||FBXL17||EDNRA||SEMA3D | 5 | 5.389844 | 5.400133 | 5.344911 | 5.384560 | 5.397629 | 5.371653 | 5.405307 | 5.391471 | 5.402206 | 5.398743 | 5.408063 | 5.397166 | 5.331804 | 5.320690 | 5.328676 |
| GO:1902903 | regulation of supramolecular fiber organization | 7/97 | 423/20870 | 0.00359405720 | 0.11931092 | 0.10524789 | RGS4||CLU||BIN1||TMEFF2||SLIT2||JMY||S1PR1 | 7 | 7.205364 | 7.315211 | 7.239423 | 7.205749 | 7.199496 | 7.204191 | 7.211992 | 7.316925 | 7.309574 | 7.316544 | 7.317787 | 7.243820 | 7.228794 | 7.242861 | 7.242167 |
| GO:0042116 | macrophage activation | 4/97 | 136/20870 | 0.00374393502 | 0.12228175 | 0.10786855 | CLU||DYSF||TLR4||SUCNR1 | 4 | 7.499987 | 7.394372 | 7.413584 | 7.515495 | 7.496253 | 7.498032 | 7.490043 | 7.405880 | 7.388325 | 7.395809 | 7.387398 | 7.397187 | 7.423566 | 7.423040 | 7.410382 |
| GO:0002281 | macrophage activation involved in immune response | 2/97 | 20/20870 | 0.00384663800 | 0.12315004 | 0.10863450 | DYSF||SUCNR1 | 2 | 8.031764 | 7.575672 | 7.440085 | 8.055681 | 8.016553 | 8.046169 | 8.008110 | 7.599607 | 7.574504 | 7.571342 | 7.556908 | 7.430992 | 7.454445 | 7.425616 | 7.449086 |
| GO:0003170 | heart valve development | 3/97 | 68/20870 | 0.00392005060 | 0.12315004 | 0.10863450 | TGFB2||HEY2||SLIT2 | 3 | 5.274832 | 5.422781 | 5.493210 | 5.277442 | 5.266424 | 5.234262 | 5.319895 | 5.458076 | 5.363874 | 5.435235 | 5.432234 | 5.635127 | 5.470208 | 5.409202 | 5.447801 |
| GO:0032608 | interferon-beta production | 3/97 | 69/20870 | 0.00408456370 | 0.12315004 | 0.10863450 | POLR3G||TLR4||TLR7 | 3 | 5.699115 | 5.620393 | 5.547004 | 5.784642 | 5.655594 | 5.687674 | 5.664866 | 5.617127 | 5.630948 | 5.591712 | 5.641305 | 5.527149 | 5.524719 | 5.627528 | 5.505431 |
| GO:0032648 | regulation of interferon-beta production | 3/97 | 69/20870 | 0.00408456370 | 0.12315004 | 0.10863450 | POLR3G||TLR4||TLR7 | 3 | 5.699115 | 5.620393 | 5.547004 | 5.784642 | 5.655594 | 5.687674 | 5.664866 | 5.617127 | 5.630948 | 5.591712 | 5.641305 | 5.527149 | 5.524719 | 5.627528 | 5.505431 |
| GO:0003215 | cardiac right ventricle morphogenesis | 2/97 | 21/20870 | 0.00423872465 | 0.12315004 | 0.10863450 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 4.211541 | 4.455770 | 4.401028 | 4.194392 | 4.318180 | 4.162510 | 4.165388 | 4.471037 | 4.429673 | 4.480821 | 4.440940 | 4.370415 | 4.398638 | 4.425419 | 4.409086 |
| GO:0034501 | protein localization to kinetochore | 2/97 | 21/20870 | 0.00423872465 | 0.12315004 | 0.10863450 | KNL1||KNTC1 | 2 | 5.226302 | 5.280739 | 4.953890 | 4.747516 | 5.477361 | 5.576506 | 4.935764 | 5.620301 | 5.148980 | 5.046527 | 5.239410 | 4.794106 | 5.243805 | 4.667762 | 5.040910 |
| GO:1903083 | protein localization to condensed chromosome | 2/97 | 21/20870 | 0.00423872465 | 0.12315004 | 0.10863450 | KNL1||KNTC1 | 2 | 5.226302 | 5.280739 | 4.953890 | 4.747516 | 5.477361 | 5.576506 | 4.935764 | 5.620301 | 5.148980 | 5.046527 | 5.239410 | 4.794106 | 5.243805 | 4.667762 | 5.040910 |
| GO:0055007 | cardiac muscle cell differentiation | 4/97 | 141/20870 | 0.00425703829 | 0.12315004 | 0.10863450 | RGS4||HEY2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 4 | 6.239376 | 6.455472 | 6.522829 | 6.243461 | 6.248645 | 6.244930 | 6.220294 | 6.487416 | 6.429362 | 6.455785 | 6.448717 | 6.521595 | 6.522963 | 6.522675 | 6.524082 |
| GO:0071805 | potassium ion transmembrane transport | 5/97 | 230/20870 | 0.00441177919 | 0.12582891 | 0.11099762 | RGS4||BIN1||KCNS3||SLC9A9||KCNIP1 | 5 | 5.609447 | 5.900892 | 5.931626 | 5.592249 | 5.588070 | 5.639520 | 5.617352 | 5.924600 | 5.879491 | 5.910666 | 5.888368 | 5.909113 | 5.987488 | 5.916444 | 5.911976 |
| GO:0003208 | cardiac ventricle morphogenesis | 3/97 | 73/20870 | 0.00478437179 | 0.13431154 | 0.11848040 | TGFB2||HEY2||POU4F1 | 3 | 5.354371 | 5.639872 | 5.729537 | 5.400087 | 5.334401 | 5.284183 | 5.395667 | 5.653756 | 5.554229 | 5.751185 | 5.592585 | 5.824647 | 5.708943 | 5.728368 | 5.650725 |
| GO:0010959 | regulation of metal ion transport | 7/97 | 449/20870 | 0.00496624081 | 0.13431154 | 0.11848040 | MYLK||RGS4||BIN1||KCNIP1||CACNB4||SLC8A1||TRDN | 7 | 6.664644 | 6.783921 | 6.854500 | 6.653363 | 6.664472 | 6.667373 | 6.673294 | 6.788515 | 6.782877 | 6.779838 | 6.784441 | 6.846035 | 6.863731 | 6.854534 | 6.853645 |
| GO:0003281 | ventricular septum development | 3/97 | 74/20870 | 0.00496991113 | 0.13431154 | 0.11848040 | TGFB2||HEY2||SLIT2 | 3 | 5.172478 | 4.852460 | 4.716743 | 5.188186 | 5.145845 | 5.166345 | 5.189097 | 4.857430 | 4.809842 | 4.925027 | 4.814559 | 4.718241 | 4.754334 | 4.733179 | 4.659507 |
| GO:0006359 | regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III | 2/97 | 23/20870 | 0.00507591345 | 0.13431154 | 0.11848040 | POLR3G||ZC3H8 | 2 | 4.913519 | 4.816326 | 4.599466 | 4.885296 | 4.974016 | 4.908182 | 4.884727 | 4.665943 | 4.888425 | 4.767575 | 4.928656 | 4.529771 | 4.588951 | 4.713987 | 4.558207 |
| GO:0098719 | sodium ion import across plasma membrane | 2/97 | 23/20870 | 0.00507591345 | 0.13431154 | 0.11848040 | SLC9A9||SLC8A1 | 2 | 4.731198 | 4.658042 | 4.426408 | 4.754697 | 4.665666 | 4.755659 | 4.746820 | 4.695622 | 4.644703 | 4.582843 | 4.705720 | 4.466300 | 4.435468 | 4.442451 | 4.359197 |
| GO:0032481 | positive regulation of type I interferon production | 3/97 | 75/20870 | 0.00515974239 | 0.13431154 | 0.11848040 | POLR3G||TLR4||TLR7 | 3 | 6.149076 | 6.440955 | 6.415428 | 6.196729 | 6.147805 | 6.133283 | 6.117257 | 6.423921 | 6.440046 | 6.457462 | 6.442195 | 6.387141 | 6.408484 | 6.473429 | 6.390976 |
| GO:0000086 | G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle | 4/97 | 149/20870 | 0.00517348142 | 0.13431154 | 0.11848040 | NES||FBXL17||CCDC57||RAD51B | 4 | 5.455843 | 5.482812 | 5.391862 | 5.439798 | 5.461787 | 5.471495 | 5.450095 | 5.481873 | 5.493939 | 5.476736 | 5.478636 | 5.391706 | 5.390618 | 5.398458 | 5.386639 |
| GO:0048844 | artery morphogenesis | 3/97 | 76/20870 | 0.00535389290 | 0.13469122 | 0.11881534 | MYLK||TGFB2||HEY2 | 3 | 5.427385 | 5.263219 | 5.265700 | 5.421267 | 5.448736 | 5.394270 | 5.444614 | 5.278519 | 5.245820 | 5.272372 | 5.255932 | 5.266562 | 5.281437 | 5.246812 | 5.267778 |
| GO:0002689 | negative regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis | 2/97 | 24/20870 | 0.00552067718 | 0.13469122 | 0.11881534 | SLIT2||KLRK1 | 2 | 5.337415 | 6.362109 | 6.417702 | 5.385567 | 5.332261 | 5.301012 | 5.329521 | 6.374623 | 6.273780 | 6.342872 | 6.451500 | 6.431345 | 6.452768 | 6.393225 | 6.392549 |
| GO:0003283 | atrial septum development | 2/97 | 24/20870 | 0.00552067718 | 0.13469122 | 0.11881534 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 4.174400 | 3.988908 | 3.823233 | 4.125637 | 4.060434 | 4.328298 | 4.169516 | 4.094585 | 3.986375 | 3.968819 | 3.899003 | 3.777871 | 3.816963 | 3.861701 | 3.835110 |
| GO:0032727 | positive regulation of interferon-alpha production | 2/97 | 24/20870 | 0.00552067718 | 0.13469122 | 0.11881534 | TLR4||TLR7 | 2 | 5.774877 | 5.907885 | 5.843070 | 5.917094 | 5.691373 | 5.774100 | 5.705693 | 5.915301 | 5.893756 | 5.895860 | 5.926365 | 5.842222 | 5.846881 | 5.871712 | 5.810815 |
| GO:0051797 | regulation of hair follicle development | 2/97 | 24/20870 | 0.00552067718 | 0.13469122 | 0.11881534 | TGFB2||HPSE | 2 | 4.042852 | 4.594912 | 4.610354 | 4.066094 | 4.052484 | 3.993280 | 4.058402 | 4.535460 | 4.645025 | 4.601628 | 4.595432 | 4.610335 | 4.600981 | 4.629441 | 4.600468 |
| GO:0050922 | negative regulation of chemotaxis | 3/97 | 78/20870 | 0.00575525773 | 0.13874282 | 0.12238938 | SLIT2||SEMA3D||KLRK1 | 3 | 5.201034 | 5.754280 | 5.821285 | 5.074499 | 5.176163 | 5.309193 | 5.234136 | 5.707682 | 5.787820 | 5.744532 | 5.775754 | 5.852782 | 5.819427 | 5.813701 | 5.798685 |
| GO:0003181 | atrioventricular valve morphogenesis | 2/97 | 25/20870 | 0.00598266345 | 0.14252816 | 0.12572854 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 4.587283 | 4.412297 | 4.262452 | 4.633584 | 4.574387 | 4.524970 | 4.613811 | 4.424931 | 4.406758 | 4.442411 | 4.374209 | 4.226665 | 4.281954 | 4.275614 | 4.264942 |
| GO:0006816 | calcium ion transport | 7/97 | 469/20870 | 0.00626599769 | 0.14754239 | 0.13015175 | MCUB||MYLK||RGS4||BIN1||CACNB4||SLC8A1||TRDN | 7 | 6.336581 | 6.499218 | 6.523439 | 6.317832 | 6.345606 | 6.328339 | 6.354266 | 6.508287 | 6.497116 | 6.496080 | 6.495351 | 6.512157 | 6.535361 | 6.524774 | 6.521366 |
| GO:0071676 | negative regulation of mononuclear cell migration | 2/97 | 26/20870 | 0.00646170593 | 0.14830758 | 0.13082675 | SLIT2||KLRK1 | 2 | 4.676758 | 5.186923 | 5.170907 | 4.536051 | 4.695201 | 4.626895 | 4.832547 | 5.205356 | 5.122000 | 5.087299 | 5.321626 | 5.137248 | 5.218877 | 5.178128 | 5.147978 |
| GO:0007015 | actin filament organization | 7/97 | 473/20870 | 0.00655387815 | 0.14830758 | 0.13082675 | RGS4||BIN1||TMEFF2||SLIT2||JMY||S1PR1||NRAP | 7 | 7.144692 | 7.286794 | 7.233621 | 7.144469 | 7.137197 | 7.149576 | 7.147494 | 7.283421 | 7.279445 | 7.289739 | 7.294524 | 7.230421 | 7.227462 | 7.242004 | 7.234554 |
| GO:0006936 | muscle contraction | 6/97 | 359/20870 | 0.00661722740 | 0.14830758 | 0.13082675 | MYLK||CHRM3||BIN1||EDNRA||SLC8A1||TRDN | 6 | 6.146835 | 6.216485 | 6.190454 | 6.142173 | 6.140606 | 6.143831 | 6.160641 | 6.208897 | 6.203021 | 6.220507 | 6.233328 | 6.188504 | 6.202393 | 6.160802 | 6.209637 |
| GO:0006813 | potassium ion transport | 5/97 | 255/20870 | 0.00678122833 | 0.14830758 | 0.13082675 | RGS4||BIN1||KCNS3||SLC9A9||KCNIP1 | 5 | 5.618174 | 5.877205 | 5.904475 | 5.599571 | 5.601974 | 5.646154 | 5.624500 | 5.895495 | 5.857488 | 5.889336 | 5.866156 | 5.883845 | 5.955711 | 5.892616 | 5.884472 |
| GO:0044839 | cell cycle G2/M phase transition | 4/97 | 161/20870 | 0.00678244800 | 0.14830758 | 0.13082675 | NES||FBXL17||CCDC57||RAD51B | 4 | 5.686309 | 5.783447 | 5.708318 | 5.674420 | 5.681805 | 5.703078 | 5.685777 | 5.770310 | 5.811333 | 5.794980 | 5.756537 | 5.724747 | 5.700416 | 5.681945 | 5.725703 |
| GO:0050808 | synapse organization | 7/97 | 477/20870 | 0.00685152883 | 0.14830758 | 0.13082675 | DLG3||ZDHHC2||PCDHB3||LRRC4||POU4F1||SLITRK5||CACNB4 | 7 | 6.413203 | 6.546060 | 6.523341 | 6.400828 | 6.403773 | 6.432940 | 6.415051 | 6.556680 | 6.545067 | 6.544983 | 6.537444 | 6.537153 | 6.514216 | 6.511604 | 6.530231 |
| GO:0003272 | endocardial cushion formation | 2/97 | 27/20870 | 0.00695763947 | 0.14830758 | 0.13082675 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 4.937459 | 5.180784 | 5.161322 | 4.985038 | 4.936227 | 4.902322 | 4.924976 | 5.158598 | 5.180970 | 5.198358 | 5.184929 | 5.167972 | 5.209274 | 5.128986 | 5.137683 |
| GO:0071459 | protein localization to chromosome, centromeric region | 2/97 | 27/20870 | 0.00695763947 | 0.14830758 | 0.13082675 | KNL1||KNTC1 | 2 | 5.160617 | 5.159195 | 4.852605 | 4.777258 | 5.367007 | 5.449543 | 4.939369 | 5.448816 | 5.036983 | 4.994543 | 5.110426 | 4.705957 | 5.084023 | 4.650794 | 4.927392 |
| GO:0086064 | cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction | 2/97 | 27/20870 | 0.00695763947 | 0.14830758 | 0.13082675 | SLC8A1||TRDN | 2 | 6.681948 | 6.707657 | 6.667075 | 6.673402 | 6.693705 | 6.691295 | 6.669228 | 6.735730 | 6.669623 | 6.727931 | 6.696386 | 6.695268 | 6.679436 | 6.664178 | 6.628574 |
| GO:0042310 | vasoconstriction | 3/97 | 85/20870 | 0.00729980478 | 0.15118416 | 0.13336427 | CHRM3||EDNRA||SLC8A1 | 3 | 5.277312 | 5.527799 | 5.566753 | 5.320757 | 5.187545 | 5.243857 | 5.351372 | 5.525931 | 5.470767 | 5.463842 | 5.643387 | 5.589394 | 5.549933 | 5.482525 | 5.640550 |
| GO:0003171 | atrioventricular valve development | 2/97 | 28/20870 | 0.00747030003 | 0.15118416 | 0.13336427 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 4.587283 | 4.412297 | 4.262452 | 4.633584 | 4.574387 | 4.524970 | 4.613811 | 4.424931 | 4.406758 | 4.442411 | 4.374209 | 4.226665 | 4.281954 | 4.275614 | 4.264942 |
| GO:0007252 | I-kappaB phosphorylation | 2/97 | 28/20870 | 0.00747030003 | 0.15118416 | 0.13336427 | TLR4||TLR7 | 2 | 5.325879 | 5.642814 | 5.614551 | 5.285701 | 5.349840 | 5.322711 | 5.344388 | 5.661642 | 5.623771 | 5.672439 | 5.612534 | 5.611393 | 5.628568 | 5.613258 | 5.604880 |
| GO:0007193 | adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | 3/97 | 86/20870 | 0.00753851035 | 0.15118416 | 0.13336427 | CHRM3||EDNRA||S1PR1 | 3 | 6.467867 | 6.540758 | 6.479904 | 6.491192 | 6.458658 | 6.466971 | 6.454365 | 6.548047 | 6.513303 | 6.562944 | 6.538286 | 6.478447 | 6.507557 | 6.466866 | 6.466358 |
| GO:0035637 | multicellular organismal signaling | 4/97 | 166/20870 | 0.00754054341 | 0.15118416 | 0.13336427 | BIN1||S1PR1||SLC8A1||TRDN | 4 | 5.883262 | 6.079329 | 6.061595 | 5.884124 | 5.884022 | 5.906430 | 5.858065 | 6.099695 | 6.061221 | 6.072884 | 6.083239 | 6.076127 | 6.070026 | 6.054236 | 6.045789 |
| GO:0050921 | positive regulation of chemotaxis | 4/97 | 166/20870 | 0.00754054341 | 0.15118416 | 0.13336427 | TNFSF18||SLIT2||S1PR1||SUCNR1 | 4 | 7.456660 | 7.768956 | 7.868716 | 7.459116 | 7.454369 | 7.457555 | 7.455594 | 7.785538 | 7.757483 | 7.768973 | 7.763681 | 7.868117 | 7.869256 | 7.875686 | 7.861769 |
| GO:0014031 | mesenchymal cell development | 3/97 | 87/20870 | 0.00778179408 | 0.15282111 | 0.13480828 | HEY2||EDNRA||SEMA3D | 3 | 4.951853 | 4.960999 | 4.987290 | 4.913891 | 4.989334 | 4.942070 | 4.961067 | 4.960549 | 4.939404 | 4.978718 | 4.965049 | 5.030476 | 5.008902 | 4.936475 | 4.971523 |
| GO:1903169 | regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport | 4/97 | 168/20870 | 0.00785878658 | 0.15282111 | 0.13480828 | BIN1||CACNB4||SLC8A1||TRDN | 4 | 6.286846 | 6.416217 | 6.438195 | 6.253496 | 6.295994 | 6.297428 | 6.299956 | 6.411435 | 6.422636 | 6.428355 | 6.402300 | 6.427489 | 6.432418 | 6.455112 | 6.437610 |
| GO:0010460 | positive regulation of heart rate | 2/97 | 29/20870 | 0.00799952471 | 0.15282111 | 0.13480828 | RGS4||HEY2 | 2 | 5.697794 | 5.657925 | 5.556025 | 5.695800 | 5.679907 | 5.730312 | 5.684616 | 5.631005 | 5.699075 | 5.637010 | 5.663606 | 5.516304 | 5.573468 | 5.564969 | 5.568627 |
| GO:0010934 | macrophage cytokine production | 2/97 | 29/20870 | 0.00799952471 | 0.15282111 | 0.13480828 | TGFB2||TLR4 | 2 | 7.500706 | 7.920827 | 7.979307 | 7.473390 | 7.517408 | 7.506320 | 7.505333 | 7.926607 | 7.907585 | 7.922458 | 7.926575 | 7.985078 | 8.004175 | 7.973909 | 7.953600 |
| GO:0010935 | regulation of macrophage cytokine production | 2/97 | 29/20870 | 0.00799952471 | 0.15282111 | 0.13480828 | TGFB2||TLR4 | 2 | 7.500706 | 7.920827 | 7.979307 | 7.473390 | 7.517408 | 7.506320 | 7.505333 | 7.926607 | 7.907585 | 7.922458 | 7.926575 | 7.985078 | 8.004175 | 7.973909 | 7.953600 |
| GO:0030595 | leukocyte chemotaxis | 5/97 | 268/20870 | 0.00831280047 | 0.15732169 | 0.13877838 | TGFB2||TNFSF18||SLIT2||S1PR1||KLRK1 | 5 | 7.083536 | 7.379525 | 7.502467 | 7.090422 | 7.081914 | 7.077300 | 7.084476 | 7.376976 | 7.376392 | 7.376521 | 7.388176 | 7.496692 | 7.516555 | 7.504886 | 7.491614 |
| GO:0001837 | epithelial to mesenchymal transition | 4/97 | 172/20870 | 0.00852152820 | 0.15875167 | 0.14003981 | LRP6||TGFB2||HEY2||SPRED1 | 4 | 6.673082 | 6.739168 | 6.870254 | 6.525321 | 6.618260 | 6.730041 | 6.803178 | 6.769649 | 6.800028 | 6.661878 | 6.721347 | 6.901150 | 6.817933 | 6.870410 | 6.890115 |
| GO:0003209 | cardiac atrium morphogenesis | 2/97 | 30/20870 | 0.00854515173 | 0.15875167 | 0.14003981 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 5.075007 | 5.116722 | 5.094526 | 5.059942 | 5.044132 | 5.148024 | 5.045342 | 5.141032 | 5.110680 | 5.133477 | 5.080943 | 5.086400 | 5.103101 | 5.097628 | 5.090919 |
| GO:0032956 | regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization | 6/97 | 381/20870 | 0.00874144945 | 0.16092214 | 0.14195445 | RGS4||BIN1||TMEFF2||SLIT2||JMY||S1PR1 | 6 | 7.171243 | 7.304843 | 7.252829 | 7.170926 | 7.163243 | 7.163725 | 7.186948 | 7.308641 | 7.297172 | 7.303830 | 7.309695 | 7.249499 | 7.250654 | 7.258618 | 7.252529 |
| GO:1904062 | regulation of cation transmembrane transport | 6/97 | 382/20870 | 0.00884836840 | 0.16142294 | 0.14239622 | RGS4||BIN1||KCNIP1||CACNB4||SLC8A1||TRDN | 6 | 7.053934 | 7.397851 | 7.494543 | 7.044368 | 7.058307 | 7.048591 | 7.064385 | 7.394874 | 7.395689 | 7.400980 | 7.399853 | 7.495597 | 7.491813 | 7.497545 | 7.493212 |
| GO:1902430 | negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation | 2/97 | 31/20870 | 0.00910702046 | 0.16465818 | 0.14525013 | CLU||BIN1 | 2 | 6.366579 | 6.197854 | 6.107329 | 6.425016 | 6.310863 | 6.308478 | 6.417628 | 6.236258 | 6.230240 | 6.167572 | 6.155532 | 6.104633 | 6.109860 | 6.109981 | 6.104835 |
| GO:0050729 | positive regulation of inflammatory response | 4/97 | 178/20870 | 0.00958267886 | 0.16906954 | 0.14914153 | TNFSF18||TLR4||TLR7||SUCNR1 | 4 | 6.793309 | 7.009496 | 7.176289 | 6.789639 | 6.782989 | 6.791134 | 6.809343 | 7.015028 | 7.013241 | 7.005118 | 7.004568 | 7.176094 | 7.170422 | 7.194368 | 7.164097 |
| GO:1902904 | negative regulation of supramolecular fiber organization | 4/97 | 178/20870 | 0.00958267886 | 0.16906954 | 0.14914153 | CLU||TMEFF2||SLIT2||S1PR1 | 4 | 7.634726 | 7.723697 | 7.666446 | 7.638768 | 7.623543 | 7.638411 | 7.638124 | 7.719121 | 7.722707 | 7.724610 | 7.728334 | 7.678054 | 7.641730 | 7.669393 | 7.676312 |
| GO:0010880 | regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum | 2/97 | 32/20870 | 0.00968497133 | 0.16906954 | 0.14914153 | SLC8A1||TRDN | 2 | 6.409211 | 6.298736 | 6.163736 | 6.386528 | 6.422232 | 6.409000 | 6.418815 | 6.327434 | 6.259090 | 6.326495 | 6.280716 | 6.170778 | 6.145074 | 6.161996 | 6.176896 |
| GO:0060317 | cardiac epithelial to mesenchymal transition | 2/97 | 32/20870 | 0.00968497133 | 0.16906954 | 0.14914153 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 5.714426 | 5.779608 | 5.669254 | 5.724275 | 5.717125 | 5.693434 | 5.722660 | 5.772491 | 5.792455 | 5.789082 | 5.764217 | 5.663751 | 5.679343 | 5.680613 | 5.653129 |
| GO:0003018 | vascular process in circulatory system | 5/97 | 279/20870 | 0.00978416912 | 0.16934139 | 0.14938133 | SLC7A8||CHRM3||SLIT2||EDNRA||SLC8A1 | 5 | 5.567830 | 5.758348 | 5.859198 | 5.560533 | 5.561477 | 5.562032 | 5.587103 | 5.770656 | 5.747336 | 5.736502 | 5.778496 | 5.873124 | 5.904289 | 5.813572 | 5.844235 |
| GO:0031349 | positive regulation of defense response | 6/97 | 393/20870 | 0.01008727569 | 0.17016347 | 0.15010651 | POLR3G||TNFSF18||TLR4||TLR7||SUCNR1||KLRK1 | 6 | 6.666897 | 6.862931 | 6.986268 | 6.669884 | 6.655852 | 6.670364 | 6.671431 | 6.864474 | 6.870248 | 6.859265 | 6.857704 | 6.993580 | 6.986632 | 6.985856 | 6.978968 |
| GO:0003180 | aortic valve morphogenesis | 2/97 | 33/20870 | 0.01027884592 | 0.17016347 | 0.15010651 | HEY2||SLIT2 | 2 | 5.108734 | 5.699616 | 5.808454 | 5.045122 | 5.162383 | 5.097198 | 5.127670 | 5.707703 | 5.632935 | 5.741700 | 5.713896 | 5.848400 | 5.851474 | 5.761557 | 5.769914 |
| GO:0032607 | interferon-alpha production | 2/97 | 33/20870 | 0.01027884592 | 0.17016347 | 0.15010651 | TLR4||TLR7 | 2 | 5.706501 | 5.871299 | 5.780499 | 5.834586 | 5.623998 | 5.708641 | 5.649492 | 5.875132 | 5.859706 | 5.860332 | 5.889813 | 5.796241 | 5.781082 | 5.805112 | 5.738661 |
| GO:0032647 | regulation of interferon-alpha production | 2/97 | 33/20870 | 0.01027884592 | 0.17016347 | 0.15010651 | TLR4||TLR7 | 2 | 5.706501 | 5.871299 | 5.780499 | 5.834586 | 5.623998 | 5.708641 | 5.649492 | 5.875132 | 5.859706 | 5.860332 | 5.889813 | 5.796241 | 5.781082 | 5.805112 | 5.738661 |
| GO:0042634 | regulation of hair cycle | 2/97 | 33/20870 | 0.01027884592 | 0.17016347 | 0.15010651 | TGFB2||HPSE | 2 | 4.164418 | 4.584924 | 4.552373 | 4.140701 | 4.323786 | 3.997517 | 4.176992 | 4.500846 | 4.720908 | 4.566138 | 4.542034 | 4.596908 | 4.592222 | 4.539946 | 4.477189 |
| GO:0031214 | biomineral tissue development | 4/97 | 182/20870 | 0.01033585499 | 0.17016347 | 0.15010651 | HEY2||MMP13||S1PR1||SLC8A1 | 4 | 6.885619 | 7.603701 | 7.649232 | 6.891856 | 6.887066 | 6.875142 | 6.888355 | 7.612232 | 7.591168 | 7.600146 | 7.611153 | 7.672874 | 7.648902 | 7.632581 | 7.642263 |
| GO:0050767 | regulation of neurogenesis | 6/97 | 398/20870 | 0.01068946576 | 0.17376810 | 0.15328627 | HEY2||BIN1||SLIT2||POU4F1||SEMA3D||CHODL | 6 | 6.699334 | 6.976764 | 7.013124 | 6.699380 | 6.690117 | 6.709653 | 6.698122 | 6.979491 | 6.972709 | 6.969557 | 6.985248 | 7.019339 | 7.019133 | 7.008736 | 7.005234 |
| GO:0110148 | biomineralization | 4/97 | 184/20870 | 0.01072642569 | 0.17376810 | 0.15328627 | HEY2||MMP13||S1PR1||SLC8A1 | 4 | 6.885619 | 7.603701 | 7.649232 | 6.891856 | 6.887066 | 6.875142 | 6.888355 | 7.612232 | 7.591168 | 7.600146 | 7.611153 | 7.672874 | 7.648902 | 7.632581 | 7.642263 |
| GO:0010644 | cell communication by electrical coupling | 2/97 | 34/20870 | 0.01088848688 | 0.17499354 | 0.15436727 | SLC8A1||TRDN | 2 | 6.471368 | 6.491964 | 6.458616 | 6.461656 | 6.480151 | 6.480483 | 6.463069 | 6.522653 | 6.455270 | 6.508014 | 6.480994 | 6.483884 | 6.468677 | 6.454422 | 6.426870 |
| GO:1901214 | regulation of neuron death | 6/97 | 401/20870 | 0.01106282369 | 0.17639542 | 0.15560391 | TGFB2||DNAJC5||CLU||NES||TLR4||POU4F1 | 6 | 6.798750 | 6.788936 | 6.861117 | 6.807417 | 6.797212 | 6.784975 | 6.805288 | 6.804616 | 6.797819 | 6.786815 | 6.766201 | 6.857545 | 6.869633 | 6.861318 | 6.855933 |
| GO:0098739 | import across plasma membrane | 4/97 | 187/20870 | 0.01132999473 | 0.17663121 | 0.15581191 | SLC7A8||RGS4||SLC9A9||SLC8A1 | 4 | 5.250968 | 5.664121 | 5.822667 | 5.229243 | 5.228642 | 5.223836 | 5.319891 | 5.723017 | 5.667652 | 5.643839 | 5.619942 | 5.814205 | 5.934678 | 5.786035 | 5.748950 |
| GO:1901379 | regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport | 3/97 | 100/20870 | 0.01136938645 | 0.17663121 | 0.15581191 | RGS4||BIN1||KCNIP1 | 3 | 6.366091 | 6.669085 | 6.672497 | 6.349819 | 6.364830 | 6.371448 | 6.378114 | 6.681195 | 6.661721 | 6.669900 | 6.663443 | 6.653230 | 6.725881 | 6.634019 | 6.675216 |
| GO:0051497 | negative regulation of stress fiber assembly | 2/97 | 35/20870 | 0.01151373798 | 0.17663121 | 0.15581191 | TMEFF2||S1PR1 | 2 | 6.681374 | 6.626885 | 6.784070 | 6.702413 | 6.683928 | 6.679217 | 6.659616 | 6.586103 | 6.652542 | 6.598342 | 6.668856 | 6.838666 | 6.704959 | 6.796904 | 6.792495 |
| GO:1901380 | negative regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport | 2/97 | 35/20870 | 0.01151373798 | 0.17663121 | 0.15581191 | RGS4||BIN1 | 2 | 4.917868 | 4.899288 | 4.686021 | 4.916336 | 4.872562 | 4.868987 | 5.009116 | 4.872102 | 4.871612 | 4.941523 | 4.910727 | 4.639670 | 4.759370 | 4.679801 | 4.662404 |
| GO:1902992 | negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process | 2/97 | 35/20870 | 0.01151373798 | 0.17663121 | 0.15581191 | CLU||BIN1 | 2 | 6.521372 | 6.380580 | 6.290529 | 6.539070 | 6.540507 | 6.456223 | 6.547758 | 6.405818 | 6.401964 | 6.354904 | 6.358863 | 6.332228 | 6.272637 | 6.281095 | 6.275327 |
| GO:0007416 | synapse assembly | 4/97 | 189/20870 | 0.01174430096 | 0.17881360 | 0.15773707 | PCDHB3||LRRC4||POU4F1||SLITRK5 | 4 | 4.832902 | 4.855313 | 4.892863 | 4.824128 | 4.815039 | 4.859977 | 4.832071 | 4.833385 | 4.892767 | 4.815464 | 4.878253 | 5.012097 | 4.859931 | 4.827299 | 4.864951 |
| GO:0060840 | artery development | 3/97 | 102/20870 | 0.01199263453 | 0.17965510 | 0.15847938 | MYLK||TGFB2||HEY2 | 3 | 5.162146 | 5.056479 | 5.066144 | 5.153565 | 5.181159 | 5.125344 | 5.187671 | 5.058045 | 5.031320 | 5.071781 | 5.064446 | 5.073533 | 5.099774 | 5.027026 | 5.063302 |
| GO:0061337 | cardiac conduction | 3/97 | 102/20870 | 0.01199263453 | 0.17965510 | 0.15847938 | BIN1||SLC8A1||TRDN | 3 | 6.186420 | 6.372945 | 6.316695 | 6.198875 | 6.190978 | 6.186399 | 6.169266 | 6.403011 | 6.343588 | 6.369917 | 6.374649 | 6.327866 | 6.326510 | 6.311556 | 6.300672 |
| GO:0003203 | endocardial cushion morphogenesis | 2/97 | 36/20870 | 0.01215444404 | 0.17965510 | 0.15847938 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 4.760307 | 4.927568 | 4.917483 | 4.800012 | 4.764867 | 4.705326 | 4.769400 | 4.937409 | 4.909663 | 4.944056 | 4.918878 | 4.920211 | 4.964772 | 4.887404 | 4.896291 |
| GO:0090025 | regulation of monocyte chemotaxis | 2/97 | 36/20870 | 0.01215444404 | 0.17965510 | 0.15847938 | TNFSF18||SLIT2 | 2 | 5.346606 | 6.610486 | 7.089980 | 5.322819 | 5.340878 | 5.373943 | 5.348315 | 6.637457 | 6.626141 | 6.587109 | 6.590571 | 7.053950 | 7.120402 | 7.092342 | 7.092453 |
| GO:0070167 | regulation of biomineral tissue development | 3/97 | 103/20870 | 0.01231149893 | 0.18065786 | 0.15936395 | HEY2||S1PR1||SLC8A1 | 3 | 5.646468 | 6.123353 | 6.249280 | 5.653459 | 5.636137 | 5.633277 | 5.662791 | 6.121930 | 6.110899 | 6.119527 | 6.140891 | 6.347994 | 6.223707 | 6.206922 | 6.213765 |
| GO:0003230 | cardiac atrium development | 2/97 | 37/20870 | 0.01281045100 | 0.18662707 | 0.16462957 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 4.919683 | 4.912933 | 4.899355 | 4.907580 | 4.878059 | 4.970618 | 4.920920 | 4.955398 | 4.899893 | 4.927574 | 4.867391 | 4.885096 | 4.905291 | 4.910794 | 4.896106 |
| GO:0110149 | regulation of biomineralization | 3/97 | 105/20870 | 0.01296376540 | 0.18751161 | 0.16540985 | HEY2||S1PR1||SLC8A1 | 3 | 5.646468 | 6.123353 | 6.249280 | 5.653459 | 5.636137 | 5.633277 | 5.662791 | 6.121930 | 6.110899 | 6.119527 | 6.140891 | 6.347994 | 6.223707 | 6.206922 | 6.213765 |
| GO:0003176 | aortic valve development | 2/97 | 38/20870 | 0.01348160584 | 0.19091085 | 0.16840843 | HEY2||SLIT2 | 2 | 5.217548 | 5.763977 | 5.844309 | 5.176965 | 5.252553 | 5.190599 | 5.248498 | 5.798331 | 5.674266 | 5.796770 | 5.782897 | 5.853613 | 5.905248 | 5.791439 | 5.824507 |
| GO:0014808 | release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum | 2/97 | 38/20870 | 0.01348160584 | 0.19091085 | 0.16840843 | SLC8A1||TRDN | 2 | 6.275683 | 6.581553 | 6.666616 | 6.255376 | 6.284461 | 6.273833 | 6.288830 | 6.608582 | 6.576808 | 6.602350 | 6.537392 | 6.657328 | 6.672069 | 6.670841 | 6.666180 |
| GO:0032232 | negative regulation of actin filament bundle assembly | 2/97 | 38/20870 | 0.01348160584 | 0.19091085 | 0.16840843 | TMEFF2||S1PR1 | 2 | 6.487484 | 6.429991 | 6.589037 | 6.507362 | 6.488623 | 6.485132 | 6.468558 | 6.390203 | 6.454855 | 6.401174 | 6.472066 | 6.644841 | 6.509282 | 6.601940 | 6.596748 |
| GO:0032970 | regulation of actin filament-based process | 6/97 | 422/20870 | 0.01393954519 | 0.19384937 | 0.17100059 | RGS4||BIN1||TMEFF2||SLIT2||JMY||S1PR1 | 6 | 7.130650 | 7.262474 | 7.210825 | 7.131016 | 7.124432 | 7.123685 | 7.143381 | 7.267252 | 7.254657 | 7.261000 | 7.266949 | 7.207033 | 7.210462 | 7.215627 | 7.210162 |
| GO:0045860 | positive regulation of protein kinase activity | 6/97 | 423/20870 | 0.01408840114 | 0.19384937 | 0.17100059 | DLG3||TGFB2||CLU||BORA||TLR4||ETAA1 | 6 | 6.274199 | 6.602494 | 6.691660 | 6.255130 | 6.281147 | 6.282518 | 6.277831 | 6.606546 | 6.600187 | 6.607268 | 6.595944 | 6.695335 | 6.694364 | 6.681821 | 6.695074 |
| GO:0043368 | positive T cell selection | 2/97 | 39/20870 | 0.01416775661 | 0.19384937 | 0.17100059 | TNFSF18||CD3G | 2 | 5.911802 | 6.526023 | 6.892950 | 5.925807 | 5.916277 | 5.894903 | 5.910046 | 6.492436 | 6.594525 | 6.510974 | 6.503869 | 6.892757 | 6.900996 | 6.875942 | 6.901956 |
| GO:0097106 | postsynaptic density organization | 2/97 | 39/20870 | 0.01416775661 | 0.19384937 | 0.17100059 | DLG3||LRRC4 | 2 | 4.161661 | 4.021441 | 3.997897 | 4.119026 | 4.119118 | 4.172726 | 4.232707 | 4.105628 | 3.937854 | 4.074354 | 3.960809 | 4.044561 | 3.941155 | 3.857822 | 4.133067 |
| GO:1903514 | release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by endoplasmic reticulum | 2/97 | 39/20870 | 0.01416775661 | 0.19384937 | 0.17100059 | SLC8A1||TRDN | 2 | 6.275683 | 6.581553 | 6.666616 | 6.255376 | 6.284461 | 6.273833 | 6.288830 | 6.608582 | 6.576808 | 6.602350 | 6.537392 | 6.657328 | 6.672069 | 6.670841 | 6.666180 |
| GO:0050900 | leukocyte migration | 6/97 | 428/20870 | 0.01484941274 | 0.19480554 | 0.17184406 | TGFB2||TNFSF18||SLIT2||S1PR1||GCNT1||KLRK1 | 6 | 6.964052 | 7.305350 | 7.475330 | 6.970243 | 6.965686 | 6.958039 | 6.962212 | 7.304248 | 7.301741 | 7.306149 | 7.309253 | 7.466529 | 7.487203 | 7.478769 | 7.468725 |
| GO:0010719 | negative regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition | 2/97 | 40/20870 | 0.01486875244 | 0.19480554 | 0.17184406 | TGFB2||SPRED1 | 2 | 5.603443 | 5.392907 | 5.167444 | 5.658487 | 5.567011 | 5.624285 | 5.561720 | 5.381548 | 5.477059 | 5.353172 | 5.356302 | 5.173017 | 5.111754 | 5.189874 | 5.193643 |
| GO:0048846 | axon extension involved in axon guidance | 2/97 | 40/20870 | 0.01486875244 | 0.19480554 | 0.17184406 | SLIT2||SEMA3D | 2 | 3.987081 | 4.985164 | 5.259509 | 3.987477 | 4.051329 | 3.977565 | 3.929330 | 4.935403 | 4.978454 | 4.973460 | 5.050906 | 5.342861 | 5.198263 | 5.285411 | 5.206571 |
| GO:1902284 | neuron projection extension involved in neuron projection guidance | 2/97 | 40/20870 | 0.01486875244 | 0.19480554 | 0.17184406 | SLIT2||SEMA3D | 2 | 3.987081 | 4.985164 | 5.259509 | 3.987477 | 4.051329 | 3.977565 | 3.929330 | 4.935403 | 4.978454 | 4.973460 | 5.050906 | 5.342861 | 5.198263 | 5.285411 | 5.206571 |
| GO:1905207 | regulation of cardiocyte differentiation | 2/97 | 40/20870 | 0.01486875244 | 0.19480554 | 0.17184406 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 5.713875 | 5.846879 | 6.015949 | 5.694814 | 5.688181 | 5.735901 | 5.735912 | 5.832582 | 5.799242 | 5.881936 | 5.872254 | 6.287653 | 5.891198 | 5.893902 | 5.952119 |
| GO:0010927 | cellular component assembly involved in morphogenesis | 3/97 | 111/20870 | 0.01503759143 | 0.19480554 | 0.17184406 | KNL1||MYOZ2||NRAP | 3 | 6.100355 | 6.194081 | 6.143818 | 6.087510 | 6.105873 | 6.082959 | 6.124698 | 6.188646 | 6.189158 | 6.201104 | 6.197377 | 6.128747 | 6.182902 | 6.142576 | 6.120243 |
| GO:0051146 | striated muscle cell differentiation | 5/97 | 311/20870 | 0.01506409890 | 0.19480554 | 0.17184406 | RGS4||HEY2||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 5 | 6.972553 | 7.131860 | 7.118249 | 6.977810 | 6.973775 | 6.971540 | 6.967065 | 7.139389 | 7.120579 | 7.131006 | 7.136394 | 7.108150 | 7.124123 | 7.118417 | 7.122251 |
| GO:1904063 | negative regulation of cation transmembrane transport | 3/97 | 112/20870 | 0.01540038904 | 0.19480554 | 0.17184406 | RGS4||BIN1||TRDN | 3 | 5.898150 | 6.940368 | 7.377047 | 5.888333 | 5.886945 | 5.885543 | 5.931264 | 6.937786 | 6.930118 | 6.950177 | 6.943318 | 7.363780 | 7.385219 | 7.381916 | 7.377183 |
| GO:0001822 | kidney development | 5/97 | 313/20870 | 0.01544665719 | 0.19480554 | 0.17184406 | TGFB2||ID3||FRAS1||SLIT2||GCNT1 | 5 | 5.313700 | 5.928408 | 6.215419 | 5.305195 | 5.310914 | 5.311929 | 5.326674 | 5.922038 | 5.909460 | 5.933580 | 5.948271 | 6.220793 | 6.217764 | 6.203933 | 6.219124 |
| GO:0043267 | negative regulation of potassium ion transport | 2/97 | 41/20870 | 0.01558444349 | 0.19480554 | 0.17184406 | RGS4||BIN1 | 2 | 5.396839 | 5.280127 | 5.200853 | 5.391336 | 5.408706 | 5.368342 | 5.418470 | 5.233702 | 5.275825 | 5.333981 | 5.275231 | 5.179024 | 5.222901 | 5.244745 | 5.155013 |
| GO:0061082 | myeloid leukocyte cytokine production | 2/97 | 41/20870 | 0.01558444349 | 0.19480554 | 0.17184406 | TGFB2||TLR4 | 2 | 6.861031 | 7.273588 | 7.325636 | 6.823988 | 6.882606 | 6.863629 | 6.873212 | 7.275333 | 7.268888 | 7.273805 | 7.276315 | 7.331344 | 7.347967 | 7.325425 | 7.297347 |
| GO:0099084 | postsynaptic specialization organization | 2/97 | 41/20870 | 0.01558444349 | 0.19480554 | 0.17184406 | DLG3||LRRC4 | 2 | 4.161661 | 4.021441 | 3.997897 | 4.119026 | 4.119118 | 4.172726 | 4.232707 | 4.105628 | 3.937854 | 4.074354 | 3.960809 | 4.044561 | 3.941155 | 3.857822 | 4.133067 |
| GO:1901998 | toxin transport | 2/97 | 41/20870 | 0.01558444349 | 0.19480554 | 0.17184406 | LRP6||SLC7A8 | 2 | 6.421541 | 6.772399 | 6.720016 | 6.378935 | 6.369246 | 6.450254 | 6.484488 | 6.778060 | 6.775017 | 6.761738 | 6.774728 | 6.747788 | 6.698877 | 6.731317 | 6.701496 |
| GO:1902742 | apoptotic process involved in development | 2/97 | 41/20870 | 0.01558444349 | 0.19480554 | 0.17184406 | TGFB2||SLIT2 | 2 | 5.092179 | 5.522684 | 5.687414 | 5.139054 | 5.146334 | 5.060193 | 5.019168 | 5.590244 | 5.522615 | 5.493963 | 5.481438 | 5.569994 | 5.781199 | 5.688418 | 5.702203 |
| GO:1901216 | positive regulation of neuron death | 3/97 | 113/20870 | 0.01576811020 | 0.19589217 | 0.17280260 | TGFB2||CLU||TLR4 | 3 | 7.255214 | 7.111594 | 7.147196 | 7.269573 | 7.248218 | 7.233679 | 7.269070 | 7.147678 | 7.113360 | 7.113640 | 7.070667 | 7.124890 | 7.177035 | 7.152289 | 7.134020 |
| GO:0043266 | regulation of potassium ion transport | 3/97 | 114/20870 | 0.01614076171 | 0.19846387 | 0.17507118 | RGS4||BIN1||KCNIP1 | 3 | 6.370344 | 6.645795 | 6.652886 | 6.354646 | 6.375421 | 6.375165 | 6.376032 | 6.654432 | 6.640860 | 6.649207 | 6.638624 | 6.635272 | 6.701067 | 6.621279 | 6.652662 |
| GO:0031032 | actomyosin structure organization | 4/97 | 208/20870 | 0.01617112984 | 0.19846387 | 0.17507118 | TMEFF2||S1PR1||MYOZ2||NRAP | 4 | 6.462103 | 6.496682 | 6.471869 | 6.479004 | 6.443769 | 6.462687 | 6.462738 | 6.477513 | 6.488840 | 6.492754 | 6.527143 | 6.478740 | 6.458425 | 6.464875 | 6.485279 |
| GO:0001941 | postsynaptic membrane organization | 2/97 | 42/20870 | 0.01631468098 | 0.19901945 | 0.17556128 | ZDHHC2||LRRC4 | 2 | 4.777663 | 4.687999 | 4.801147 | 4.774191 | 4.742716 | 4.811987 | 4.780920 | 4.660586 | 4.795169 | 4.649096 | 4.641544 | 4.805384 | 4.819704 | 4.768075 | 4.810890 |
| GO:0001503 | ossification | 6/97 | 440/20870 | 0.01679201502 | 0.20361575 | 0.17961582 | BCAP29||TGFB2||ID3||MMP13||S1PR1||SLC8A1 | 6 | 6.712685 | 7.184369 | 7.294757 | 6.676108 | 6.691892 | 6.725123 | 6.756290 | 7.180044 | 7.200688 | 7.168587 | 7.187967 | 7.300947 | 7.282735 | 7.292662 | 7.302599 |
| GO:0070997 | neuron death | 6/97 | 442/20870 | 0.01713206846 | 0.20650261 | 0.18216241 | TGFB2||DNAJC5||CLU||NES||TLR4||POU4F1 | 6 | 6.786417 | 6.797651 | 6.862524 | 6.793626 | 6.785303 | 6.773363 | 6.793281 | 6.810926 | 6.806311 | 6.792834 | 6.780333 | 6.858997 | 6.870636 | 6.861435 | 6.858997 |
| GO:0072001 | renal system development | 5/97 | 322/20870 | 0.01724877608 | 0.20667912 | 0.18231811 | TGFB2||ID3||FRAS1||SLIT2||GCNT1 | 5 | 5.290168 | 5.901236 | 6.187906 | 5.283495 | 5.286894 | 5.287126 | 5.303075 | 5.895136 | 5.882358 | 5.906304 | 5.920867 | 6.194073 | 6.189687 | 6.176298 | 6.191500 |
| GO:0030308 | negative regulation of cell growth | 4/97 | 213/20870 | 0.01748821270 | 0.20831547 | 0.18376159 | TGFB2||RGS4||SLIT2||SEMA3D | 4 | 7.052177 | 7.441330 | 7.436574 | 7.052722 | 7.048665 | 7.046899 | 7.060386 | 7.454016 | 7.427094 | 7.448119 | 7.435938 | 7.438830 | 7.440390 | 7.444826 | 7.422148 |
| GO:0007409 | axonogenesis | 6/97 | 445/20870 | 0.01765103332 | 0.20902539 | 0.18438783 | SLIT2||POU4F1||SEMA3D||CHODL||KALRN||SLITRK5 | 6 | 6.706691 | 7.075092 | 7.052465 | 6.709970 | 6.704755 | 6.716714 | 6.695238 | 7.083477 | 7.070655 | 7.076331 | 7.069863 | 7.062925 | 7.059990 | 7.049810 | 7.036991 |
| GO:0051091 | positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity | 5/97 | 325/20870 | 0.01787924214 | 0.20919039 | 0.18453338 | LRP6||TNFSF18||CLU||TLR4||JMY | 5 | 5.904668 | 6.174479 | 6.226125 | 5.885586 | 5.916724 | 5.906002 | 5.910172 | 6.186488 | 6.172198 | 6.181892 | 6.157162 | 6.250454 | 6.220012 | 6.216694 | 6.217060 |
| GO:0032479 | regulation of type I interferon production | 3/97 | 119/20870 | 0.01807818154 | 0.20919039 | 0.18453338 | POLR3G||TLR4||TLR7 | 3 | 5.820879 | 6.047074 | 6.020074 | 5.870738 | 5.812729 | 5.807165 | 5.791631 | 6.033579 | 6.045094 | 6.064807 | 6.044639 | 6.001747 | 6.013553 | 6.063236 | 6.000851 |
| GO:0032606 | type I interferon production | 3/97 | 119/20870 | 0.01807818154 | 0.20919039 | 0.18453338 | POLR3G||TLR4||TLR7 | 3 | 5.820879 | 6.047074 | 6.020074 | 5.870738 | 5.812729 | 5.807165 | 5.791631 | 6.033579 | 6.045094 | 6.064807 | 6.044639 | 6.001747 | 6.013553 | 6.063236 | 6.000851 |
| GO:0034766 | negative regulation of ion transmembrane transport | 3/97 | 119/20870 | 0.01807818154 | 0.20919039 | 0.18453338 | RGS4||BIN1||TRDN | 3 | 5.883932 | 6.873759 | 7.281101 | 5.877700 | 5.872958 | 5.877507 | 5.907305 | 6.870991 | 6.863807 | 6.881374 | 6.878798 | 7.267840 | 7.288800 | 7.288411 | 7.279250 |
| GO:0022602 | ovulation cycle process | 2/97 | 45/20870 | 0.01859119984 | 0.21269593 | 0.18762573 | TGFB2||SLIT2 | 2 | 5.113905 | 5.375167 | 5.474475 | 5.126248 | 5.102859 | 5.139985 | 5.085926 | 5.359464 | 5.377551 | 5.385633 | 5.377892 | 5.458030 | 5.467721 | 5.489580 | 5.482360 |
| GO:0070296 | sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ion transport | 2/97 | 45/20870 | 0.01859119984 | 0.21269593 | 0.18762573 | SLC8A1||TRDN | 2 | 6.626914 | 7.078404 | 7.114463 | 6.622386 | 6.645081 | 6.620387 | 6.619647 | 7.102988 | 7.072573 | 7.083322 | 7.054302 | 7.105354 | 7.116238 | 7.120757 | 7.115458 |
| GO:0030278 | regulation of ossification | 3/97 | 121/20870 | 0.01888785141 | 0.21367541 | 0.18848976 | TGFB2||S1PR1||SLC8A1 | 3 | 5.476861 | 5.907544 | 6.012849 | 5.477983 | 5.478199 | 5.462590 | 5.488553 | 5.908816 | 5.895155 | 5.899927 | 5.926083 | 6.108199 | 5.985694 | 5.973039 | 5.980073 |
| GO:2000060 | positive regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | 3/97 | 121/20870 | 0.01888785141 | 0.21367541 | 0.18848976 | TRIM67||CLU||SOCS4 | 3 | 6.462668 | 6.521540 | 6.472418 | 6.473169 | 6.463582 | 6.441671 | 6.472028 | 6.549941 | 6.514985 | 6.521325 | 6.499443 | 6.489928 | 6.473505 | 6.480627 | 6.445227 |
| GO:0003197 | endocardial cushion development | 2/97 | 46/20870 | 0.01937815597 | 0.21477542 | 0.18946011 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 5.628087 | 5.234160 | 5.090604 | 5.631044 | 5.647343 | 5.582392 | 5.650545 | 5.254103 | 5.206178 | 5.247614 | 5.228260 | 5.108126 | 5.129208 | 5.063049 | 5.060839 |
| GO:0060976 | coronary vasculature development | 2/97 | 46/20870 | 0.01937815597 | 0.21477542 | 0.18946011 | HEY2||SPRED1 | 2 | 4.469001 | 4.677686 | 4.844313 | 4.443768 | 4.465609 | 4.466222 | 4.499845 | 4.631132 | 4.655538 | 4.731922 | 4.690152 | 4.837957 | 4.902595 | 4.801671 | 4.833153 |
| GO:0089718 | amino acid import across plasma membrane | 2/97 | 46/20870 | 0.01937815597 | 0.21477542 | 0.18946011 | SLC7A8||RGS4 | 2 | 5.595740 | 6.056980 | 6.199560 | 5.598958 | 5.603016 | 5.602605 | 5.578235 | 6.077495 | 6.044488 | 6.058647 | 6.047055 | 6.186223 | 6.198303 | 6.224175 | 6.189229 |
| GO:0007204 | positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration | 5/97 | 332/20870 | 0.01940933423 | 0.21477542 | 0.18946011 | LRP6||EDNRA||S1PR1||SLC8A1||TRDN | 5 | 5.949642 | 6.172375 | 6.250231 | 5.929427 | 5.942807 | 5.956690 | 5.969336 | 6.169274 | 6.169828 | 6.186256 | 6.164045 | 6.235167 | 6.273623 | 6.258018 | 6.233730 |
| GO:1902106 | negative regulation of leukocyte differentiation | 3/97 | 123/20870 | 0.01971739839 | 0.21699854 | 0.19142120 | TNFSF18||TLR4||ZC3H8 | 3 | 5.667102 | 5.972864 | 5.999954 | 5.672093 | 5.672684 | 5.684411 | 5.638820 | 5.999576 | 6.007861 | 5.927590 | 5.954938 | 5.972219 | 6.003958 | 6.037993 | 5.984792 |
| GO:0070588 | calcium ion transmembrane transport | 5/97 | 334/20870 | 0.01986185350 | 0.21740677 | 0.19178131 | MCUB||BIN1||CACNB4||SLC8A1||TRDN | 5 | 5.799483 | 6.116079 | 6.179095 | 5.770873 | 5.797390 | 5.795118 | 5.833848 | 6.119702 | 6.123328 | 6.118607 | 6.102593 | 6.164131 | 6.199960 | 6.178938 | 6.173108 |
| GO:0019722 | calcium-mediated signaling | 4/97 | 222/20870 | 0.02002399570 | 0.21800318 | 0.19230742 | NR5A2||CHRM3||MYOZ2||SLC8A1 | 4 | 5.734995 | 6.117778 | 6.221294 | 5.708578 | 5.729865 | 5.761733 | 5.739298 | 6.131472 | 6.144581 | 6.113712 | 6.080549 | 6.250285 | 6.245799 | 6.198037 | 6.190029 |
| GO:0050919 | negative chemotaxis | 2/97 | 48/20870 | 0.02099337962 | 0.22618643 | 0.19952612 | SLIT2||SEMA3D | 2 | 5.370893 | 5.786846 | 5.775810 | 5.382672 | 5.389512 | 5.358796 | 5.352253 | 5.753190 | 5.745875 | 5.787770 | 5.857809 | 5.808175 | 5.758120 | 5.766344 | 5.770084 |
| GO:0030282 | bone mineralization | 3/97 | 126/20870 | 0.02099903683 | 0.22618643 | 0.19952612 | MMP13||S1PR1||SLC8A1 | 3 | 5.491586 | 5.906368 | 6.043337 | 5.501186 | 5.482005 | 5.470059 | 5.512714 | 5.911681 | 5.894233 | 5.888442 | 5.930737 | 6.125675 | 6.022738 | 6.006765 | 6.014889 |
| GO:1903707 | negative regulation of hemopoiesis | 3/97 | 127/20870 | 0.02143620908 | 0.22967367 | 0.20260232 | TNFSF18||TLR4||ZC3H8 | 3 | 5.706113 | 6.032117 | 6.055751 | 5.705868 | 5.711113 | 5.729606 | 5.677379 | 6.060592 | 6.062720 | 5.984527 | 6.019185 | 6.023919 | 6.060753 | 6.101142 | 6.035977 |
| GO:0006383 | transcription by RNA polymerase III | 2/97 | 49/20870 | 0.02182136287 | 0.23135215 | 0.20408296 | POLR3G||ZC3H8 | 2 | 5.400729 | 5.488279 | 5.401070 | 5.397373 | 5.415629 | 5.383344 | 5.406373 | 5.428784 | 5.478158 | 5.556785 | 5.486492 | 5.359785 | 5.368768 | 5.410928 | 5.462495 |
| GO:0015804 | neutral amino acid transport | 2/97 | 49/20870 | 0.02182136287 | 0.23135215 | 0.20408296 | SLC7A8||RGS4 | 2 | 5.511313 | 5.831276 | 6.009021 | 5.531865 | 5.504722 | 5.511679 | 5.496749 | 5.828447 | 5.838519 | 5.828678 | 5.829437 | 5.990671 | 6.017045 | 6.029333 | 5.998715 |
| GO:0007041 | lysosomal transport | 3/97 | 129/20870 | 0.02232550020 | 0.23384495 | 0.20628194 | CLU||BIN1||KIF13A | 3 | 6.529647 | 6.613533 | 6.555435 | 6.522955 | 6.583252 | 6.500940 | 6.510001 | 6.570819 | 6.579088 | 6.638274 | 6.663818 | 6.560253 | 6.534890 | 6.596804 | 6.528796 |
| GO:0043279 | response to alkaloid | 3/97 | 129/20870 | 0.02232550020 | 0.23384495 | 0.20628194 | RGS4||CASP6||SLC8A1 | 3 | 7.356732 | 7.109093 | 7.302523 | 7.380113 | 7.342714 | 7.356000 | 7.347816 | 7.126982 | 7.113338 | 7.100944 | 7.094898 | 7.309481 | 7.299444 | 7.299984 | 7.301159 |
| GO:0043254 | regulation of protein-containing complex assembly | 6/97 | 470/20870 | 0.02240292398 | 0.23384495 | 0.20628194 | TNFSF18||CLU||BIN1||TLR4||SLIT2||JMY | 6 | 7.125195 | 7.278433 | 7.205978 | 7.127188 | 7.116246 | 7.124231 | 7.133064 | 7.285951 | 7.274412 | 7.278200 | 7.275139 | 7.203237 | 7.205530 | 7.210104 | 7.205031 |
| GO:0045778 | positive regulation of ossification | 2/97 | 50/20870 | 0.02266273923 | 0.23414310 | 0.20654494 | TGFB2||SLC8A1 | 2 | 5.216938 | 5.671167 | 5.812508 | 5.186478 | 5.175406 | 5.189679 | 5.311830 | 5.664976 | 5.625390 | 5.652354 | 5.739454 | 6.026046 | 5.733032 | 5.723540 | 5.744379 |
| GO:2000677 | regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding | 2/97 | 50/20870 | 0.02266273923 | 0.23414310 | 0.20654494 | HEY2||POU4F1 | 2 | 8.423895 | 8.622563 | 8.553514 | 8.431501 | 8.422475 | 8.420071 | 8.421506 | 8.640026 | 8.598157 | 8.622006 | 8.629734 | 8.554447 | 8.543989 | 8.570865 | 8.544590 |
| GO:0043523 | regulation of neuron apoptotic process | 4/97 | 232/20870 | 0.02309529464 | 0.23740087 | 0.20941873 | TGFB2||DNAJC5||NES||POU4F1 | 4 | 6.793663 | 6.788725 | 6.793837 | 6.806502 | 6.797212 | 6.784822 | 6.786007 | 6.801845 | 6.788866 | 6.799196 | 6.764698 | 6.797415 | 6.781817 | 6.803667 | 6.792362 |
| GO:0045581 | negative regulation of T cell differentiation | 2/97 | 51/20870 | 0.02351736905 | 0.24051855 | 0.21216893 | TNFSF18||ZC3H8 | 2 | 5.581972 | 5.625313 | 5.688652 | 5.626898 | 5.597297 | 5.552608 | 5.549642 | 5.667128 | 5.714358 | 5.547926 | 5.565147 | 5.637358 | 5.669075 | 5.776453 | 5.667812 |
| GO:0006874 | cellular calcium ion homeostasis | 6/97 | 476/20870 | 0.02366050501 | 0.24076645 | 0.21238761 | MCUB||LRP6||EDNRA||S1PR1||SLC8A1||TRDN | 6 | 6.436563 | 6.542101 | 6.607514 | 6.423633 | 6.445106 | 6.427204 | 6.450131 | 6.546655 | 6.539198 | 6.551944 | 6.530518 | 6.601171 | 6.624354 | 6.605553 | 6.598839 |
| GO:0006469 | negative regulation of protein kinase activity | 4/97 | 235/20870 | 0.02406958762 | 0.24325052 | 0.21457888 | LRP6||SPRED1||SOCS4||SLC8A1 | 4 | 6.133470 | 6.297710 | 6.345009 | 6.135586 | 6.129489 | 6.120752 | 6.147918 | 6.296857 | 6.319208 | 6.298758 | 6.275689 | 6.345131 | 6.346600 | 6.337804 | 6.350472 |
| GO:0045058 | T cell selection | 2/97 | 52/20870 | 0.02438511367 | 0.24325052 | 0.21457888 | TNFSF18||CD3G | 2 | 6.107984 | 6.495746 | 6.753945 | 6.117611 | 6.114680 | 6.093755 | 6.105772 | 6.496879 | 6.535857 | 6.469469 | 6.479891 | 6.747602 | 6.761850 | 6.738915 | 6.767238 |
| GO:0071622 | regulation of granulocyte chemotaxis | 2/97 | 52/20870 | 0.02438511367 | 0.24325052 | 0.21457888 | TNFSF18||SLIT2 | 2 | 5.614424 | 7.047197 | 7.399781 | 5.597395 | 5.627873 | 5.627832 | 5.604334 | 7.054750 | 7.049132 | 7.054644 | 7.030122 | 7.397294 | 7.408564 | 7.393420 | 7.399803 |
| GO:0072132 | mesenchyme morphogenesis | 2/97 | 52/20870 | 0.02438511367 | 0.24325052 | 0.21457888 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 4.554165 | 4.821391 | 4.789295 | 4.594076 | 4.560120 | 4.497716 | 4.563062 | 4.815286 | 4.829796 | 4.824713 | 4.815716 | 4.797031 | 4.819923 | 4.760592 | 4.778965 |
| GO:0042060 | wound healing | 6/97 | 480/20870 | 0.02452484165 | 0.24335490 | 0.21467096 | MYLK||TGFB2||DYSF||TLR4||TMEFF2||HPSE | 6 | 6.978409 | 7.109664 | 7.095662 | 6.978778 | 6.989028 | 6.969385 | 6.976377 | 7.106101 | 7.116332 | 7.106093 | 7.110104 | 7.090382 | 7.089813 | 7.090852 | 7.111486 |
| GO:0043500 | muscle adaptation | 3/97 | 134/20870 | 0.02463592804 | 0.24335490 | 0.21467096 | RGS4||HEY2||MYOZ2 | 3 | 6.446864 | 6.894953 | 7.095112 | 6.425886 | 6.437649 | 6.466302 | 6.457270 | 6.908015 | 6.892237 | 6.915527 | 6.863482 | 7.055136 | 7.114799 | 7.080167 | 7.129178 |
| GO:0051960 | regulation of nervous system development | 6/97 | 482/20870 | 0.02496486877 | 0.24480056 | 0.21594622 | HEY2||BIN1||SLIT2||POU4F1||SEMA3D||CHODL | 6 | 6.577894 | 6.809045 | 6.837024 | 6.576770 | 6.570407 | 6.590360 | 6.573960 | 6.812935 | 6.805163 | 6.801111 | 6.816917 | 6.842026 | 6.842129 | 6.833468 | 6.830436 |
| GO:0002686 | negative regulation of leukocyte migration | 2/97 | 53/20870 | 0.02526583542 | 0.24480056 | 0.21594622 | SLIT2||KLRK1 | 2 | 5.243829 | 5.921022 | 5.972915 | 5.234779 | 5.247548 | 5.197981 | 5.293395 | 5.939672 | 5.875789 | 5.882870 | 5.983082 | 5.968219 | 6.009292 | 5.972744 | 5.940574 |
| GO:0046580 | negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction | 2/97 | 53/20870 | 0.02526583542 | 0.24480056 | 0.21594622 | TGFB2||TRIM67 | 2 | 5.574361 | 5.287027 | 5.174879 | 5.556919 | 5.599308 | 5.557756 | 5.583017 | 5.315064 | 5.277469 | 5.332337 | 5.220713 | 5.113258 | 5.146535 | 5.214994 | 5.221821 |
| GO:0071312 | cellular response to alkaloid | 2/97 | 53/20870 | 0.02526583542 | 0.24480056 | 0.21594622 | CASP6||SLC8A1 | 2 | 5.184194 | 5.396679 | 5.367594 | 5.123611 | 5.208043 | 5.314654 | 5.079205 | 5.409243 | 5.485563 | 5.375477 | 5.310930 | 5.352145 | 5.357034 | 5.386454 | 5.374482 |
| GO:0001655 | urogenital system development | 5/97 | 359/20870 | 0.02611140008 | 0.24786597 | 0.21865032 | TGFB2||ID3||FRAS1||SLIT2||GCNT1 | 5 | 5.336162 | 5.866867 | 6.135755 | 5.323810 | 5.341859 | 5.332666 | 5.346211 | 5.858680 | 5.847297 | 5.879361 | 5.881841 | 6.141900 | 6.141322 | 6.124308 | 6.135421 |
| GO:0014888 | striated muscle adaptation | 2/97 | 54/20870 | 0.02615939760 | 0.24786597 | 0.21865032 | HEY2||MYOZ2 | 2 | 5.955420 | 6.495690 | 6.622659 | 5.862830 | 5.945549 | 6.089127 | 5.914257 | 6.513167 | 6.523951 | 6.473877 | 6.471006 | 6.548354 | 6.671846 | 6.543365 | 6.718916 |
| GO:0043090 | amino acid import | 2/97 | 54/20870 | 0.02615939760 | 0.24786597 | 0.21865032 | SLC7A8||RGS4 | 2 | 5.454766 | 5.873985 | 5.996914 | 5.459197 | 5.458350 | 5.461883 | 5.439528 | 5.879985 | 5.857280 | 5.888638 | 5.869848 | 5.982757 | 5.992556 | 6.022405 | 5.989618 |
| GO:1903170 | negative regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport | 2/97 | 54/20870 | 0.02615939760 | 0.24786597 | 0.21865032 | BIN1||TRDN | 2 | 6.262135 | 6.276505 | 6.155776 | 6.242537 | 6.244562 | 6.255772 | 6.304777 | 6.310189 | 6.239438 | 6.294570 | 6.260754 | 6.169577 | 6.151783 | 6.166969 | 6.134503 |
| GO:0055074 | calcium ion homeostasis | 6/97 | 488/20870 | 0.02631667280 | 0.24786597 | 0.21865032 | MCUB||LRP6||EDNRA||S1PR1||SLC8A1||TRDN | 6 | 6.407836 | 6.510355 | 6.575953 | 6.394688 | 6.416059 | 6.398454 | 6.421960 | 6.514765 | 6.507406 | 6.520452 | 6.498703 | 6.569744 | 6.592854 | 6.573748 | 6.567328 |
| GO:0060326 | cell chemotaxis | 5/97 | 360/20870 | 0.02638473436 | 0.24786597 | 0.21865032 | TGFB2||TNFSF18||SLIT2||S1PR1||KLRK1 | 5 | 7.420946 | 7.632148 | 7.698801 | 7.423195 | 7.417902 | 7.420298 | 7.422383 | 7.636151 | 7.625448 | 7.630074 | 7.636888 | 7.692880 | 7.705452 | 7.703822 | 7.693002 |
| GO:0071674 | mononuclear cell migration | 4/97 | 242/20870 | 0.02643903674 | 0.24786597 | 0.21865032 | TNFSF18||SLIT2||S1PR1||KLRK1 | 4 | 6.373474 | 6.821085 | 6.973271 | 6.357472 | 6.375267 | 6.368280 | 6.392648 | 6.830046 | 6.825929 | 6.813798 | 6.814497 | 6.962104 | 6.996159 | 6.976565 | 6.957947 |
| GO:0045936 | negative regulation of phosphate metabolic process | 6/97 | 491/20870 | 0.02701056330 | 0.25141271 | 0.22177901 | LRP6||TGFB2||SLIT2||SPRED1||SOCS4||SLC8A1 | 6 | 6.038521 | 6.182274 | 6.171592 | 6.032231 | 6.033230 | 6.048416 | 6.040150 | 6.188236 | 6.195753 | 6.180981 | 6.163933 | 6.179181 | 6.173690 | 6.166127 | 6.167330 |
| GO:0010862 | positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation | 2/97 | 55/20870 | 0.02706566445 | 0.25141271 | 0.22177901 | TGFB2||RBPMS | 2 | 6.012736 | 6.118374 | 6.006134 | 6.036983 | 6.002929 | 5.998132 | 6.012589 | 6.137328 | 6.096792 | 6.131957 | 6.107025 | 6.033158 | 6.021711 | 6.011366 | 5.957130 |
| GO:0010563 | negative regulation of phosphorus metabolic process | 6/97 | 492/20870 | 0.02724454415 | 0.25191873 | 0.22222539 | LRP6||TGFB2||SLIT2||SPRED1||SOCS4||SLC8A1 | 6 | 6.044223 | 6.190876 | 6.177102 | 6.040795 | 6.037082 | 6.050187 | 6.048785 | 6.197561 | 6.199644 | 6.199017 | 6.167023 | 6.179999 | 6.181584 | 6.178317 | 6.168470 |
| GO:0071621 | granulocyte chemotaxis | 3/97 | 140/20870 | 0.02757273598 | 0.25347352 | 0.22359691 | TGFB2||TNFSF18||SLIT2 | 3 | 7.424814 | 7.762995 | 7.909668 | 7.443832 | 7.427076 | 7.419814 | 7.408304 | 7.768665 | 7.753959 | 7.762184 | 7.767128 | 7.902981 | 7.913695 | 7.907341 | 7.914625 |
| GO:0043113 | receptor clustering | 2/97 | 56/20870 | 0.02798450122 | 0.25347352 | 0.22359691 | DLG3||ZDHHC2 | 2 | 7.522231 | 7.315387 | 7.439628 | 7.530452 | 7.522804 | 7.516154 | 7.519476 | 7.314480 | 7.323310 | 7.326793 | 7.296779 | 7.421370 | 7.436845 | 7.436240 | 7.463734 |
| GO:0097720 | calcineurin-mediated signaling | 2/97 | 56/20870 | 0.02798450122 | 0.25347352 | 0.22359691 | NR5A2||MYOZ2 | 2 | 5.107129 | 5.267931 | 5.062145 | 5.052548 | 5.130209 | 5.260249 | 4.969525 | 5.358145 | 5.467228 | 5.119737 | 5.091605 | 5.308850 | 4.962546 | 4.962324 | 4.983679 |
| GO:0098657 | import into cell | 4/97 | 248/20870 | 0.02857794767 | 0.25347352 | 0.22359691 | SLC7A8||RGS4||SLC9A9||SLC8A1 | 4 | 6.475903 | 6.655369 | 6.707137 | 6.467966 | 6.463259 | 6.471745 | 6.500350 | 6.689171 | 6.654131 | 6.648953 | 6.628561 | 6.716239 | 6.754576 | 6.688844 | 6.667413 |
| GO:0002688 | regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis | 3/97 | 142/20870 | 0.02859142341 | 0.25347352 | 0.22359691 | TNFSF18||SLIT2||KLRK1 | 3 | 6.076542 | 6.859043 | 7.116823 | 6.076534 | 6.074316 | 6.082915 | 6.072378 | 6.865076 | 6.850966 | 6.859792 | 6.860302 | 7.117342 | 7.129369 | 7.120158 | 7.100271 |
| GO:0008333 | endosome to lysosome transport | 2/97 | 57/20870 | 0.02891577406 | 0.25347352 | 0.22359691 | BIN1||KIF13A | 2 | 5.499983 | 5.307439 | 5.200880 | 5.496380 | 5.498552 | 5.525969 | 5.478632 | 5.342100 | 5.300912 | 5.278507 | 5.307512 | 5.188114 | 5.222505 | 5.167417 | 5.224681 |
| GO:1902003 | regulation of amyloid-beta formation | 2/97 | 57/20870 | 0.02891577406 | 0.25347352 | 0.22359691 | CLU||BIN1 | 2 | 7.013870 | 6.583804 | 6.316860 | 7.103021 | 6.977058 | 6.934322 | 7.035487 | 6.603651 | 6.546269 | 6.660431 | 6.520817 | 6.258691 | 6.347385 | 6.395112 | 6.261562 |
| GO:0001933 | negative regulation of protein phosphorylation | 5/97 | 369/20870 | 0.02892757374 | 0.25347352 | 0.22359691 | LRP6||SLIT2||SPRED1||SOCS4||SLC8A1 | 5 | 6.032821 | 6.185601 | 6.203968 | 6.023701 | 6.027057 | 6.048531 | 6.031868 | 6.188358 | 6.203869 | 6.188428 | 6.161424 | 6.214267 | 6.205364 | 6.196930 | 6.199249 |
| GO:0051480 | regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration | 5/97 | 369/20870 | 0.02892757374 | 0.25347352 | 0.22359691 | LRP6||EDNRA||S1PR1||SLC8A1||TRDN | 5 | 5.887532 | 6.149454 | 6.227644 | 5.868168 | 5.876833 | 5.895937 | 5.908840 | 6.151203 | 6.143887 | 6.163341 | 6.139270 | 6.219154 | 6.249162 | 6.231237 | 6.210733 |
| GO:0007188 | adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | 4/97 | 249/20870 | 0.02894418214 | 0.25347352 | 0.22359691 | VIPR1||CHRM3||EDNRA||S1PR1 | 4 | 5.952474 | 5.873913 | 5.795681 | 5.963739 | 5.923301 | 5.976958 | 5.945334 | 5.876842 | 5.831276 | 5.924128 | 5.861845 | 5.768991 | 5.844665 | 5.808900 | 5.758546 |
| GO:0035296 | regulation of tube diameter | 3/97 | 143/20870 | 0.02910820538 | 0.25347352 | 0.22359691 | CHRM3||EDNRA||SLC8A1 | 3 | 5.791949 | 5.717745 | 5.699932 | 5.811481 | 5.752652 | 5.778672 | 5.823910 | 5.712324 | 5.693105 | 5.685630 | 5.778067 | 5.724127 | 5.685427 | 5.648048 | 5.740357 |
| GO:0071675 | regulation of mononuclear cell migration | 3/97 | 143/20870 | 0.02910820538 | 0.25347352 | 0.22359691 | TNFSF18||SLIT2||KLRK1 | 3 | 6.306448 | 6.836272 | 7.029916 | 6.293792 | 6.312521 | 6.310631 | 6.308773 | 6.855976 | 6.829151 | 6.827363 | 6.832411 | 7.018807 | 7.044757 | 7.033000 | 7.022960 |
| GO:0097746 | blood vessel diameter maintenance | 3/97 | 143/20870 | 0.02910820538 | 0.25347352 | 0.22359691 | CHRM3||EDNRA||SLC8A1 | 3 | 5.791949 | 5.717745 | 5.699932 | 5.811481 | 5.752652 | 5.778672 | 5.823910 | 5.712324 | 5.693105 | 5.685630 | 5.778067 | 5.724127 | 5.685427 | 5.648048 | 5.740357 |
| GO:0061564 | axon development | 6/97 | 500/20870 | 0.02916510126 | 0.25347352 | 0.22359691 | SLIT2||POU4F1||SEMA3D||CHODL||KALRN||SLITRK5 | 6 | 6.699779 | 6.992633 | 6.971034 | 6.701687 | 6.695849 | 6.713640 | 6.687817 | 6.999820 | 6.987789 | 6.993086 | 6.989809 | 6.978974 | 6.977423 | 6.969063 | 6.958587 |
| GO:0045429 | positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process | 2/97 | 58/20870 | 0.02985935012 | 0.25839822 | 0.22794115 | CLU||TLR4 | 2 | 6.361274 | 7.326808 | 7.575610 | 6.363151 | 6.364814 | 6.349160 | 6.367900 | 7.341078 | 7.317396 | 7.324156 | 7.324496 | 7.577014 | 7.578909 | 7.579355 | 7.567128 |
| GO:0035150 | regulation of tube size | 3/97 | 145/20870 | 0.03015662475 | 0.25986028 | 0.22923087 | CHRM3||EDNRA||SLC8A1 | 3 | 5.791949 | 5.717745 | 5.699932 | 5.811481 | 5.752652 | 5.778672 | 5.823910 | 5.712324 | 5.693105 | 5.685630 | 5.778067 | 5.724127 | 5.685427 | 5.648048 | 5.740357 |
| GO:0045620 | negative regulation of lymphocyte differentiation | 2/97 | 59/20870 | 0.03081509747 | 0.26218728 | 0.23128359 | TNFSF18||ZC3H8 | 2 | 5.694872 | 5.632517 | 5.665165 | 5.734165 | 5.710849 | 5.660153 | 5.673116 | 5.663706 | 5.716044 | 5.556418 | 5.588457 | 5.624478 | 5.641249 | 5.748171 | 5.643400 |
| GO:0070228 | regulation of lymphocyte apoptotic process | 2/97 | 59/20870 | 0.03081509747 | 0.26218728 | 0.23128359 | ZC3H8||CD3G | 2 | 5.544875 | 6.133252 | 6.497674 | 5.545535 | 5.528978 | 5.591867 | 5.511884 | 6.155087 | 6.164207 | 6.115084 | 6.097577 | 6.455850 | 6.528250 | 6.500867 | 6.504781 |
| GO:1904407 | positive regulation of nitric oxide metabolic process | 2/97 | 59/20870 | 0.03081509747 | 0.26218728 | 0.23128359 | CLU||TLR4 | 2 | 6.331673 | 7.294084 | 7.539658 | 6.334638 | 6.336602 | 6.318873 | 6.336504 | 7.307685 | 7.284530 | 7.292785 | 7.291236 | 7.540659 | 7.542896 | 7.543222 | 7.531826 |
| GO:0006865 | amino acid transport | 3/97 | 147/20870 | 0.03122481974 | 0.26456176 | 0.23337819 | XK||SLC7A8||RGS4 | 3 | 5.045325 | 5.341450 | 5.461883 | 5.034088 | 5.047258 | 5.057115 | 5.042743 | 5.348130 | 5.333500 | 5.360700 | 5.323190 | 5.454439 | 5.463996 | 5.463789 | 5.465282 |
| GO:0050714 | positive regulation of protein secretion | 3/97 | 149/20870 | 0.03231274834 | 0.27263881 | 0.24050322 | TGFB2||TLR4||FRMD4A | 3 | 5.946678 | 6.133150 | 6.101263 | 5.912854 | 5.927966 | 5.932805 | 6.011049 | 6.135158 | 6.123133 | 6.143971 | 6.130261 | 6.112533 | 6.122965 | 6.081818 | 6.087329 |
| GO:0010639 | negative regulation of organelle organization | 5/97 | 381/20870 | 0.03255299609 | 0.27302152 | 0.24084082 | CLU||TMEFF2||SLIT2||S1PR1||KNTC1 | 5 | 6.867299 | 6.952895 | 6.893483 | 6.853072 | 6.859343 | 6.894957 | 6.861452 | 6.949524 | 6.962476 | 6.949726 | 6.949813 | 6.894918 | 6.887851 | 6.891243 | 6.899891 |
| GO:0060038 | cardiac muscle cell proliferation | 2/97 | 61/20870 | 0.03276258299 | 0.27302152 | 0.24084082 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 5.539579 | 4.964494 | 4.874466 | 5.508065 | 5.576366 | 5.545856 | 5.527148 | 4.980012 | 4.932582 | 4.960071 | 4.984729 | 5.121295 | 4.723295 | 4.761308 | 4.857518 |
| GO:0086065 | cell communication involved in cardiac conduction | 2/97 | 61/20870 | 0.03276258299 | 0.27302152 | 0.24084082 | SLC8A1||TRDN | 2 | 6.120321 | 6.012732 | 5.925185 | 6.121845 | 6.134638 | 6.116154 | 6.108521 | 6.038226 | 5.982020 | 6.025249 | 6.004806 | 5.935398 | 5.946519 | 5.924627 | 5.893662 |
| GO:0090303 | positive regulation of wound healing | 2/97 | 62/20870 | 0.03375406198 | 0.28013105 | 0.24711235 | MYLK||HPSE | 2 | 6.839015 | 6.909663 | 6.835825 | 6.836788 | 6.841810 | 6.813790 | 6.863246 | 6.914843 | 6.902738 | 6.903553 | 6.917456 | 6.808928 | 6.854560 | 6.851471 | 6.827862 |
| GO:0033673 | negative regulation of kinase activity | 4/97 | 263/20870 | 0.03436614843 | 0.28289208 | 0.24954794 | LRP6||SPRED1||SOCS4||SLC8A1 | 4 | 6.097471 | 6.249402 | 6.289295 | 6.100688 | 6.093109 | 6.084907 | 6.111050 | 6.246538 | 6.269411 | 6.251154 | 6.230235 | 6.282973 | 6.290508 | 6.286878 | 6.296785 |
| GO:0098656 | anion transmembrane transport | 4/97 | 263/20870 | 0.03436614843 | 0.28289208 | 0.24954794 | SLC7A8||GABRA4||RGS4||SLC9A9 | 4 | 5.209073 | 5.519635 | 5.573521 | 5.205451 | 5.213475 | 5.210911 | 5.206438 | 5.548032 | 5.496807 | 5.526392 | 5.506774 | 5.551402 | 5.564773 | 5.608497 | 5.568782 |
| GO:0051402 | neuron apoptotic process | 4/97 | 265/20870 | 0.03518583684 | 0.28846688 | 0.25446565 | TGFB2||DNAJC5||NES||POU4F1 | 4 | 6.815024 | 6.829002 | 6.835089 | 6.824878 | 6.818686 | 6.806152 | 6.810305 | 6.838137 | 6.831323 | 6.833510 | 6.812908 | 6.836640 | 6.826780 | 6.840723 | 6.836175 |
| GO:0010656 | negative regulation of muscle cell apoptotic process | 2/97 | 64/20870 | 0.03577185135 | 0.29208871 | 0.25766058 | LRP6||HEY2 | 2 | 5.603622 | 5.565721 | 5.655176 | 5.663860 | 5.591719 | 5.608068 | 5.548471 | 5.467673 | 5.693133 | 5.525901 | 5.566581 | 5.671301 | 5.674819 | 5.642600 | 5.631511 |
| GO:0043524 | negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process | 3/97 | 156/20870 | 0.03627518792 | 0.29382902 | 0.25919576 | DNAJC5||NES||POU4F1 | 3 | 6.794216 | 6.759210 | 6.791853 | 6.795511 | 6.805358 | 6.791429 | 6.784487 | 6.765461 | 6.771229 | 6.756534 | 6.743464 | 6.815584 | 6.762908 | 6.792648 | 6.795782 |
| GO:1903052 | positive regulation of proteolysis involved in cellular protein catabolic process | 3/97 | 156/20870 | 0.03627518792 | 0.29382902 | 0.25919576 | TRIM67||CLU||SOCS4 | 3 | 6.615801 | 6.592000 | 6.493209 | 6.625567 | 6.618247 | 6.610671 | 6.608658 | 6.610412 | 6.594460 | 6.599939 | 6.562753 | 6.500690 | 6.494583 | 6.504426 | 6.472932 |
| GO:0061951 | establishment of protein localization to plasma membrane | 2/97 | 65/20870 | 0.03679790806 | 0.29569748 | 0.26084398 | ZDHHC2||KIF13A | 2 | 6.079894 | 6.117911 | 6.018599 | 6.113097 | 6.084206 | 6.063442 | 6.058182 | 6.141150 | 6.121747 | 6.088208 | 6.120040 | 6.045655 | 6.038944 | 5.999136 | 5.989846 |
| GO:1904645 | response to amyloid-beta | 2/97 | 65/20870 | 0.03679790806 | 0.29569748 | 0.26084398 | TLR4||MMP13 | 2 | 5.799971 | 7.183600 | 7.707549 | 5.768915 | 5.812112 | 5.787784 | 5.830317 | 7.209094 | 7.203620 | 7.166937 | 7.153983 | 7.711528 | 7.704072 | 7.705714 | 7.708872 |
| GO:0002274 | myeloid leukocyte activation | 4/97 | 270/20870 | 0.03728463488 | 0.29842445 | 0.26324953 | CLU||DYSF||TLR4||SUCNR1 | 4 | 7.156141 | 7.253265 | 7.302597 | 7.160392 | 7.159133 | 7.159988 | 7.144991 | 7.263031 | 7.238600 | 7.256622 | 7.254695 | 7.303072 | 7.303569 | 7.299709 | 7.304035 |
| GO:0034205 | amyloid-beta formation | 2/97 | 66/20870 | 0.03783523851 | 0.30045631 | 0.26504190 | CLU||BIN1 | 2 | 6.907160 | 6.530045 | 6.302227 | 6.979527 | 6.874225 | 6.846295 | 6.924997 | 6.548957 | 6.493120 | 6.588672 | 6.486993 | 6.268521 | 6.321702 | 6.362488 | 6.253589 |
| GO:1902475 | L-alpha-amino acid transmembrane transport | 2/97 | 66/20870 | 0.03783523851 | 0.30045631 | 0.26504190 | SLC7A8||RGS4 | 2 | 5.460095 | 5.801914 | 5.938199 | 5.442436 | 5.476058 | 5.477166 | 5.444337 | 5.809077 | 5.792097 | 5.807571 | 5.798845 | 5.920312 | 5.953682 | 5.951435 | 5.927071 |
| GO:0031334 | positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly | 4/97 | 272/20870 | 0.03814401134 | 0.30172509 | 0.26616113 | CLU||BIN1||TLR4||JMY | 4 | 6.876794 | 7.090604 | 7.015008 | 6.863995 | 6.873729 | 6.883604 | 6.885745 | 7.103417 | 7.090127 | 7.090214 | 7.078549 | 7.012867 | 7.026201 | 7.016632 | 7.004248 |
| GO:0090257 | regulation of muscle system process | 4/97 | 273/20870 | 0.03857795873 | 0.30333238 | 0.26757897 | RGS4||CHRM3||BIN1||SLC8A1 | 4 | 5.809372 | 6.026312 | 6.023131 | 5.806839 | 5.824204 | 5.810233 | 5.796074 | 6.048548 | 6.012416 | 6.052715 | 5.990650 | 5.990478 | 6.057576 | 6.012827 | 6.030805 |
| GO:0034763 | negative regulation of transmembrane transport | 3/97 | 160/20870 | 0.03864679155 | 0.30333238 | 0.26757897 | RGS4||BIN1||TRDN | 3 | 6.220686 | 7.085963 | 7.441251 | 6.235085 | 6.212238 | 6.201732 | 6.233413 | 7.078065 | 7.068201 | 7.114275 | 7.082898 | 7.427340 | 7.450801 | 7.454519 | 7.432155 |
| GO:0030239 | myofibril assembly | 2/97 | 67/20870 | 0.03888371811 | 0.30386485 | 0.26804868 | MYOZ2||NRAP | 2 | 6.778187 | 6.876137 | 6.824193 | 6.785224 | 6.779287 | 6.781045 | 6.767129 | 6.869478 | 6.860861 | 6.888067 | 6.885965 | 6.814770 | 6.837337 | 6.819151 | 6.825416 |
| GO:0033002 | muscle cell proliferation | 4/97 | 274/20870 | 0.03901474663 | 0.30386485 | 0.26804868 | TGFB2||HEY2||TLR4||S1PR1 | 4 | 6.076940 | 6.649712 | 6.928076 | 6.061496 | 6.080649 | 6.087042 | 6.078452 | 6.642044 | 6.652460 | 6.645689 | 6.658599 | 6.932138 | 6.926831 | 6.909828 | 6.943304 |
| GO:0051271 | negative regulation of cellular component movement | 5/97 | 401/20870 | 0.03920450260 | 0.30417287 | 0.26832039 | BIN1||TMEFF2||SLIT2||SPRED1||KLRK1 | 5 | 6.123294 | 6.155422 | 6.203008 | 6.105555 | 6.123014 | 6.126954 | 6.137470 | 6.145787 | 6.164423 | 6.156295 | 6.155121 | 6.213271 | 6.204057 | 6.199354 | 6.195288 |
| GO:0045926 | negative regulation of growth | 4/97 | 275/20870 | 0.03945437569 | 0.30494317 | 0.26899990 | TGFB2||RGS4||SLIT2||SEMA3D | 4 | 6.806761 | 7.145667 | 7.136878 | 6.801786 | 6.807037 | 6.805978 | 6.812222 | 7.157245 | 7.130593 | 7.152712 | 7.141970 | 7.140997 | 7.139486 | 7.144236 | 7.122695 |
| GO:0055002 | striated muscle cell development | 2/97 | 68/20870 | 0.03994322319 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | MYOZ2||NRAP | 2 | 6.738258 | 6.838879 | 6.787553 | 6.744911 | 6.739353 | 6.741805 | 6.726899 | 6.832363 | 6.823568 | 6.850925 | 6.848481 | 6.778841 | 6.800732 | 6.782278 | 6.788264 |
| GO:0007187 | G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger | 2/97 | 69/20870 | 0.04101363093 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | VIPR1||CHRM3 | 2 | 4.485119 | 4.138710 | 4.043465 | 4.497935 | 4.475090 | 4.483719 | 4.483640 | 4.069692 | 4.026933 | 4.005234 | 4.413279 | 4.026356 | 3.987348 | 4.159065 | 3.994326 |
| GO:0097530 | granulocyte migration | 3/97 | 164/20870 | 0.04109580794 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TGFB2||TNFSF18||SLIT2 | 3 | 7.293974 | 7.623455 | 7.756631 | 7.312537 | 7.298990 | 7.289358 | 7.274750 | 7.626991 | 7.616015 | 7.622286 | 7.628496 | 7.751006 | 7.760856 | 7.753954 | 7.760682 |
| GO:0050770 | regulation of axonogenesis | 3/97 | 165/20870 | 0.04172008843 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | SLIT2||SEMA3D||CHODL | 3 | 6.723365 | 7.333213 | 7.328900 | 6.718138 | 6.721303 | 6.736091 | 6.717851 | 7.342649 | 7.334407 | 7.322255 | 7.333470 | 7.347963 | 7.336053 | 7.315105 | 7.316214 |
| GO:0042698 | ovulation cycle | 2/97 | 70/20870 | 0.04209481943 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TGFB2||SLIT2 | 2 | 5.147881 | 5.125965 | 5.246776 | 5.101113 | 5.100491 | 5.077741 | 5.300604 | 5.110070 | 5.136110 | 5.134948 | 5.122577 | 5.166887 | 5.419863 | 5.196007 | 5.189352 |
| GO:0051148 | negative regulation of muscle cell differentiation | 2/97 | 70/20870 | 0.04209481943 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | RGS4||HEY2 | 2 | 7.125948 | 7.463748 | 7.405724 | 7.166999 | 7.108697 | 7.092101 | 7.134880 | 7.456738 | 7.480842 | 7.471186 | 7.445979 | 7.379462 | 7.431930 | 7.406779 | 7.404247 |
| GO:0060393 | regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation | 2/97 | 70/20870 | 0.04209481943 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TGFB2||RBPMS | 2 | 5.740781 | 5.835264 | 5.737383 | 5.785321 | 5.730417 | 5.735316 | 5.711022 | 5.839455 | 5.853813 | 5.829195 | 5.818355 | 5.777396 | 5.738823 | 5.731231 | 5.701056 |
| GO:1902991 | regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process | 2/97 | 70/20870 | 0.04209481943 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | CLU||BIN1 | 2 | 6.892296 | 6.505321 | 6.266837 | 6.962393 | 6.891465 | 6.817111 | 6.894558 | 6.521332 | 6.477066 | 6.562227 | 6.458403 | 6.222228 | 6.295668 | 6.341654 | 6.203478 |
| GO:0042326 | negative regulation of phosphorylation | 5/97 | 415/20870 | 0.04432172159 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | LRP6||SLIT2||SPRED1||SOCS4||SLC8A1 | 5 | 6.006523 | 6.142311 | 6.150482 | 5.997279 | 6.004496 | 6.017013 | 6.007236 | 6.142900 | 6.158440 | 6.148325 | 6.119294 | 6.157147 | 6.150248 | 6.146820 | 6.147690 |
| GO:0060389 | pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation | 2/97 | 73/20870 | 0.04540186338 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TGFB2||RBPMS | 2 | 5.762541 | 5.799965 | 5.687507 | 5.798920 | 5.743170 | 5.743559 | 5.763800 | 5.802868 | 5.818912 | 5.793937 | 5.783913 | 5.728515 | 5.690526 | 5.682040 | 5.647801 |
| GO:0003056 | regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle contraction | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | CHRM3 | 1 | 6.362179 | 6.734403 | 6.715189 | 6.338125 | 6.416194 | 6.352689 | 6.340290 | 6.789354 | 6.707358 | 6.682098 | 6.756383 | 6.721954 | 6.744724 | 6.689864 | 6.703626 |
| GO:0010693 | negative regulation of alkaline phosphatase activity | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TGFB2 | 1 | 3.804314 | 5.554536 | 5.768530 | 3.477539 | 4.510317 | 3.550307 | 3.355882 | 5.466405 | 5.398265 | 5.404396 | 5.888826 | 6.103574 | 5.597254 | 5.687418 | 5.624834 |
| GO:0015803 | branched-chain amino acid transport | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | SLC7A8 | 1 | 5.032701 | 5.782909 | 6.233599 | 5.025399 | 5.039876 | 5.038964 | 5.026502 | 5.809234 | 5.785366 | 5.790945 | 5.745338 | 6.206421 | 6.254354 | 6.278360 | 6.193605 |
| GO:0015808 | L-alanine transport | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | SLC7A8 | 1 | 5.015991 | 5.866229 | 6.241192 | 4.991117 | 5.050838 | 5.051448 | 4.968719 | 5.889209 | 5.851107 | 5.874126 | 5.850098 | 6.220174 | 6.264858 | 6.275584 | 6.202886 |
| GO:0035524 | proline transmembrane transport | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | SLC7A8 | 1 | 4.578684 | 5.450052 | 5.435551 | 4.483690 | 4.591891 | 4.674492 | 4.558143 | 5.441280 | 5.430798 | 5.468318 | 5.459511 | 5.475482 | 5.400969 | 5.442573 | 5.422132 |
| GO:0035907 | dorsal aorta development | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | HEY2 | 1 | 5.241509 | 5.604715 | 5.581316 | 5.276860 | 5.236748 | 5.219278 | 5.232504 | 5.613086 | 5.607589 | 5.627399 | 5.570170 | 5.579454 | 5.602684 | 5.568516 | 5.574377 |
| GO:0042439 | ethanolamine-containing compound metabolic process | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | GDPD1 | 1 | 4.399427 | 3.960950 | 3.848012 | 4.537595 | 4.312814 | 4.402982 | 4.333444 | 3.918769 | 3.767784 | 4.023674 | 4.111112 | 3.888727 | 3.802555 | 3.794846 | 3.902618 |
| GO:0044557 | relaxation of smooth muscle | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | SLC8A1 | 1 | 7.235858 | 6.587386 | 6.302705 | 7.238746 | 7.219404 | 7.239452 | 7.245695 | 6.593075 | 6.596577 | 6.564481 | 6.595168 | 6.312320 | 6.333881 | 6.314864 | 6.248320 |
| GO:0044848 | biological phase | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TGFB2 | 1 | 5.913394 | 5.964566 | 5.783907 | 5.926815 | 5.857814 | 6.035314 | 5.824533 | 6.011947 | 5.828074 | 5.863211 | 6.134143 | 5.830717 | 5.740367 | 5.789667 | 5.773410 |
| GO:0051890 | regulation of cardioblast differentiation | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TGFB2 | 1 | 4.485483 | 4.231893 | 3.929203 | 4.247052 | 4.607863 | 4.495541 | 4.565195 | 4.349117 | 4.349309 | 4.324572 | 3.843944 | 3.986068 | 3.849380 | 4.085816 | 3.775523 |
| GO:0060947 | cardiac vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | HEY2 | 1 | 4.863570 | 5.701231 | 6.151092 | 4.891895 | 4.831732 | 4.908608 | 4.820055 | 5.643008 | 5.657970 | 5.730658 | 5.769543 | 6.161287 | 6.224036 | 6.089312 | 6.126305 |
| GO:0070391 | response to lipoteichoic acid | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TLR4 | 1 | 6.549034 | 6.068223 | 5.917629 | 6.737103 | 6.461608 | 6.505269 | 6.474187 | 6.119374 | 6.047576 | 6.076028 | 6.028280 | 5.819456 | 6.002847 | 5.939225 | 5.902917 |
| GO:0071223 | cellular response to lipoteichoic acid | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TLR4 | 1 | 6.549034 | 6.068223 | 5.917629 | 6.737103 | 6.461608 | 6.505269 | 6.474187 | 6.119374 | 6.047576 | 6.076028 | 6.028280 | 5.819456 | 6.002847 | 5.939225 | 5.902917 |
| GO:0071672 | negative regulation of smooth muscle cell chemotaxis | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | SLIT2 | 1 | 7.435694 | 6.958423 | 6.810686 | 7.045637 | 7.357320 | 7.709592 | 7.547666 | 6.881927 | 7.057638 | 7.100480 | 6.769030 | 6.752028 | 6.797495 | 6.754377 | 6.931334 |
| GO:0097084 | vascular associated smooth muscle cell development | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | HEY2 | 1 | 5.210167 | 5.754698 | 5.937543 | 5.206678 | 5.206845 | 5.208860 | 5.218254 | 5.728780 | 5.739434 | 5.785613 | 5.764287 | 5.959158 | 5.971040 | 5.913348 | 5.905518 |
| GO:0097119 | postsynaptic density protein 95 clustering | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | LRRC4 | 1 | 3.258283 | 2.274978 | 2.223348 | 3.192700 | 3.223584 | 3.474370 | 3.116864 | 2.348336 | 2.359156 | 2.243295 | 2.138084 | 2.146075 | 2.211388 | 2.295105 | 2.236863 |
| GO:1903960 | negative regulation of anion transmembrane transport | 1/97 | 10/20870 | 0.04552766202 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | RGS4 | 1 | 5.783936 | 5.429656 | 5.218200 | 5.829901 | 5.796766 | 5.764963 | 5.742605 | 5.466261 | 5.406965 | 5.393915 | 5.450251 | 5.146292 | 5.264614 | 5.237606 | 5.221636 |
| GO:0051494 | negative regulation of cytoskeleton organization | 3/97 | 171/20870 | 0.04556601464 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TMEFF2||SLIT2||S1PR1 | 3 | 7.561287 | 7.643066 | 7.586154 | 7.567467 | 7.546649 | 7.567883 | 7.563046 | 7.628224 | 7.647783 | 7.650351 | 7.645803 | 7.604502 | 7.558105 | 7.583189 | 7.598376 |
| GO:0003151 | outflow tract morphogenesis | 2/97 | 74/20870 | 0.04652497317 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TGFB2||HEY2 | 2 | 5.713676 | 5.571854 | 5.549817 | 5.703702 | 5.748859 | 5.695682 | 5.705863 | 5.596612 | 5.514832 | 5.537463 | 5.635359 | 5.702776 | 5.522127 | 5.457855 | 5.504260 |
| GO:0050730 | regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | 4/97 | 291/20870 | 0.04687501429 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | DLG3||ARL2BP||TNFSF18||SOCS4 | 4 | 6.316631 | 6.553299 | 6.700355 | 6.305630 | 6.306290 | 6.336436 | 6.317951 | 6.543305 | 6.553231 | 6.558849 | 6.557758 | 6.688453 | 6.718361 | 6.707917 | 6.686440 |
| GO:0007034 | vacuolar transport | 3/97 | 175/20870 | 0.04822463419 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | CLU||BIN1||KIF13A | 3 | 6.332794 | 6.383742 | 6.317339 | 6.318665 | 6.376711 | 6.323210 | 6.311658 | 6.344149 | 6.360086 | 6.395902 | 6.433190 | 6.318164 | 6.302646 | 6.355164 | 6.292597 |
| GO:0050435 | amyloid-beta metabolic process | 2/97 | 76/20870 | 0.04880162863 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | CLU||BIN1 | 2 | 6.735048 | 6.376908 | 6.152448 | 6.796952 | 6.707200 | 6.673122 | 6.759779 | 6.405949 | 6.339414 | 6.435464 | 6.323859 | 6.129363 | 6.167181 | 6.200231 | 6.111378 |
| GO:1903036 | positive regulation of response to wounding | 2/97 | 76/20870 | 0.04880162863 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | MYLK||HPSE | 2 | 7.018771 | 6.817042 | 6.764483 | 7.021186 | 7.023741 | 7.001736 | 7.028278 | 6.830959 | 6.806435 | 6.810115 | 6.820532 | 6.737739 | 6.777121 | 6.781194 | 6.761475 |
| GO:0051348 | negative regulation of transferase activity | 4/97 | 296/20870 | 0.04934306772 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | LRP6||SPRED1||SOCS4||SLC8A1 | 4 | 7.111370 | 7.090983 | 7.001868 | 7.111699 | 7.110611 | 7.099276 | 7.123789 | 7.102195 | 7.104768 | 7.096207 | 7.060320 | 7.018075 | 6.978782 | 6.999094 | 7.011212 |
| GO:0006937 | regulation of muscle contraction | 3/97 | 177/20870 | 0.04958206629 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | CHRM3||BIN1||SLC8A1 | 3 | 5.822259 | 5.959863 | 5.951519 | 5.807004 | 5.851251 | 5.827080 | 5.803192 | 5.970979 | 5.946916 | 5.973563 | 5.947778 | 5.948269 | 5.972385 | 5.948661 | 5.936525 |
| GO:0040013 | negative regulation of locomotion | 5/97 | 429/20870 | 0.04982362344 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TMEFF2||SLIT2||SEMA3D||SPRED1||KLRK1 | 5 | 5.985022 | 6.028788 | 6.081019 | 5.963603 | 5.984509 | 5.996950 | 5.994783 | 6.015514 | 6.051256 | 6.020886 | 6.027237 | 6.097205 | 6.080056 | 6.078662 | 6.068000 |
| GO:0030032 | lamellipodium assembly | 2/97 | 77/20870 | 0.04995494167 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | SLIT2||S1PR1 | 2 | 6.630531 | 6.833061 | 6.685150 | 6.617610 | 6.651201 | 6.622538 | 6.630547 | 6.810975 | 6.843310 | 6.835881 | 6.841844 | 6.673741 | 6.692524 | 6.691743 | 6.682508 |
| GO:0001967 | suckling behavior | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | POU4F1 | 1 | 6.052965 | 5.935444 | 6.046972 | 6.113527 | 6.045568 | 5.786017 | 6.230777 | 5.928240 | 5.910614 | 5.964294 | 5.938105 | 5.925034 | 6.018967 | 6.189317 | 6.042023 |
| GO:0006971 | hypotonic response | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | MYLK | 1 | 5.094631 | 5.293144 | 5.158410 | 5.091974 | 5.024605 | 5.089627 | 5.168699 | 5.298435 | 5.310230 | 5.256875 | 5.306410 | 5.162015 | 5.128774 | 5.250464 | 5.087356 |
| GO:0009120 | deoxyribonucleoside metabolic process | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TK2 | 1 | 5.981734 | 5.847316 | 5.530175 | 6.406273 | 5.756093 | 6.002158 | 5.638703 | 5.703326 | 5.885148 | 5.907649 | 5.883939 | 5.483518 | 5.617049 | 5.473285 | 5.542276 |
| GO:0015074 | DNA integration | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | GIN1 | 1 | 3.642483 | 3.888418 | 3.579613 | 3.674453 | 3.569550 | 3.663844 | 3.659654 | 4.030510 | 3.859663 | 3.830303 | 3.823067 | 3.249881 | 3.392391 | 3.855128 | 3.737426 |
| GO:0021889 | olfactory bulb interneuron differentiation | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | SLIT2 | 1 | 4.559662 | 5.706965 | 5.757230 | 4.388544 | 4.666256 | 4.555009 | 4.614000 | 5.700772 | 5.669353 | 5.713057 | 5.743693 | 5.796553 | 5.797842 | 5.687468 | 5.744221 |
| GO:0033539 | fatty acid beta-oxidation using acyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | ETFBKMT | 1 | 6.017627 | 5.247070 | 5.191278 | 5.960552 | 6.090253 | 6.024643 | 5.991840 | 5.294340 | 5.283533 | 5.185329 | 5.222319 | 5.222312 | 5.102615 | 5.218599 | 5.218070 |
| GO:0033690 | positive regulation of osteoblast proliferation | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | HPSE | 1 | 4.533483 | 4.634247 | 4.349331 | 4.589692 | 4.503553 | 4.587534 | 4.448239 | 4.569048 | 4.644224 | 4.691465 | 4.629606 | 4.282172 | 4.194322 | 4.334838 | 4.560158 |
| GO:0045348 | positive regulation of MHC class II biosynthetic process | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TLR4 | 1 | 5.699651 | 4.587101 | 4.683317 | 5.722645 | 5.699171 | 5.706339 | 5.669947 | 4.582838 | 4.599426 | 4.585306 | 4.580760 | 4.674495 | 4.677658 | 4.681723 | 4.699264 |
| GO:0045607 | regulation of inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | HEY2 | 1 | 4.361437 | 5.125127 | 5.308614 | 4.351755 | 4.343079 | 4.425103 | 4.323748 | 5.156179 | 5.098038 | 5.118596 | 5.127089 | 5.294168 | 5.315425 | 5.289838 | 5.334580 |
| GO:0045631 | regulation of mechanoreceptor differentiation | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | HEY2 | 1 | 4.361437 | 5.125127 | 5.308614 | 4.351755 | 4.343079 | 4.425103 | 4.323748 | 5.156179 | 5.098038 | 5.118596 | 5.127089 | 5.294168 | 5.315425 | 5.289838 | 5.334580 |
| GO:0045945 | positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | ZC3H8 | 1 | 4.401437 | 4.377104 | 4.143179 | 4.532723 | 4.363527 | 4.348051 | 4.353015 | 4.233896 | 4.169540 | 4.435247 | 4.624878 | 4.006971 | 4.068630 | 4.435616 | 4.016199 |
| GO:0046349 | amino sugar biosynthetic process | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | GNPNAT1 | 1 | 4.107039 | 4.489401 | 4.519193 | 4.052670 | 4.292409 | 4.063380 | 4.001850 | 4.597077 | 4.380294 | 4.399568 | 4.567624 | 4.224564 | 4.438476 | 4.640767 | 4.722342 |
| GO:0048103 | somatic stem cell division | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TGFB2 | 1 | 5.183451 | 5.332671 | 5.226056 | 5.165576 | 5.148333 | 5.177695 | 5.240510 | 5.350582 | 5.314466 | 5.323985 | 5.341374 | 5.220128 | 5.242921 | 5.225201 | 5.215826 |
| GO:0055015 | ventricular cardiac muscle cell development | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | HEY2 | 1 | 6.572149 | 7.580778 | 7.700619 | 6.455488 | 6.605312 | 6.736215 | 6.473623 | 7.629963 | 7.632699 | 7.501359 | 7.554923 | 7.636629 | 7.770009 | 7.621482 | 7.767554 |
| GO:0060159 | regulation of dopamine receptor signaling pathway | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | RGS4 | 1 | 3.730729 | 5.028223 | 4.827771 | 3.694510 | 3.761440 | 3.701261 | 3.764232 | 5.022889 | 4.882641 | 5.039944 | 5.154560 | 4.819389 | 4.906543 | 4.742740 | 4.837704 |
| GO:0060315 | negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TRDN | 1 | 7.110587 | 6.984001 | 6.858529 | 7.090638 | 7.128940 | 7.106701 | 7.115798 | 7.013272 | 6.930733 | 7.025270 | 6.964736 | 6.878447 | 6.843562 | 6.860433 | 6.851440 |
| GO:0061314 | Notch signaling involved in heart development | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | HEY2 | 1 | 4.265294 | 4.956845 | 5.088597 | 4.296817 | 4.312798 | 4.261623 | 4.186692 | 4.938890 | 4.968976 | 4.960457 | 4.958889 | 5.059166 | 5.117553 | 5.056669 | 5.119722 |
| GO:0070099 | regulation of chemokine-mediated signaling pathway | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | SLIT2 | 1 | 6.175663 | 7.230572 | 7.839868 | 6.158017 | 6.161026 | 6.199446 | 6.183760 | 7.271520 | 7.224462 | 7.213333 | 7.212151 | 7.811287 | 7.875228 | 7.797524 | 7.873701 |
| GO:0070243 | regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | ZC3H8 | 1 | 4.680568 | 4.113621 | 3.929281 | 4.858937 | 4.620095 | 4.805608 | 4.392340 | 4.149237 | 4.161020 | 4.048460 | 4.092938 | 3.914509 | 3.962191 | 3.949237 | 3.890068 |
| GO:0070327 | thyroid hormone transport | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | SLC7A8 | 1 | 4.101015 | 6.003004 | 6.370282 | 4.037117 | 4.116636 | 4.144705 | 4.103451 | 5.922621 | 5.969387 | 6.021996 | 6.092465 | 6.333720 | 6.463430 | 6.396779 | 6.280697 |
| GO:0071313 | cellular response to caffeine | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | SLC8A1 | 1 | 5.222174 | 4.588939 | 4.057371 | 5.253833 | 5.207084 | 5.220833 | 5.206430 | 4.599914 | 4.620142 | 4.556575 | 4.578345 | 4.090576 | 3.978905 | 4.023380 | 4.131791 |
| GO:0099566 | regulation of postsynaptic cytosolic calcium ion concentration | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | SLC8A1 | 1 | 4.528427 | 4.224932 | 3.898793 | 4.523245 | 4.527317 | 4.560393 | 4.502151 | 4.244477 | 4.215500 | 4.197301 | 4.241922 | 3.994011 | 3.915964 | 3.900124 | 3.776737 |
| GO:1901844 | regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TRDN | 1 | 6.986310 | 6.831074 | 6.734987 | 6.951361 | 7.005365 | 7.004029 | 6.983829 | 6.857469 | 6.790812 | 6.848310 | 6.826795 | 6.751262 | 6.716940 | 6.736984 | 6.734556 |
| GO:1902337 | regulation of apoptotic process involved in morphogenesis | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TGFB2 | 1 | 5.379215 | 5.844444 | 5.957053 | 5.420034 | 5.347584 | 5.311775 | 5.433938 | 5.957911 | 5.710028 | 5.833022 | 5.865955 | 5.863017 | 6.018342 | 5.920034 | 6.020607 |
| GO:1902667 | regulation of axon guidance | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | SLIT2 | 1 | 3.925499 | 4.963967 | 5.265940 | 4.048300 | 3.922473 | 3.817409 | 3.904328 | 4.949947 | 4.830254 | 5.024392 | 5.041778 | 5.235284 | 5.349372 | 5.277808 | 5.196836 |
| GO:1904464 | regulation of matrix metallopeptidase secretion | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TLR4 | 1 | 5.665081 | 5.994895 | 5.821606 | 5.710554 | 5.620606 | 5.625624 | 5.701148 | 6.045111 | 5.956542 | 5.991946 | 5.984552 | 5.823959 | 5.751352 | 5.856445 | 5.852230 |
| GO:1990773 | matrix metallopeptidase secretion | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TLR4 | 1 | 5.665081 | 5.994895 | 5.821606 | 5.710554 | 5.620606 | 5.625624 | 5.701148 | 6.045111 | 5.956542 | 5.991946 | 5.984552 | 5.823959 | 5.751352 | 5.856445 | 5.852230 |
| GO:2000320 | negative regulation of T-helper 17 cell differentiation | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | TNFSF18 | 1 | 4.533716 | 4.639803 | 4.945277 | 4.539547 | 4.516508 | 4.528562 | 4.550032 | 4.698760 | 4.601351 | 4.633376 | 4.623894 | 4.866839 | 4.959792 | 4.928207 | 5.021928 |
| GO:2000980 | regulation of inner ear receptor cell differentiation | 1/97 | 11/20870 | 0.04996600415 | 0.30521164 | 0.26923673 | HEY2 | 1 | 4.361437 | 5.125127 | 5.308614 | 4.351755 | 4.343079 | 4.425103 | 4.323748 | 5.156179 | 5.098038 | 5.118596 | 5.127089 | 5.294168 | 5.315425 | 5.289838 | 5.334580 |
GO: MF
| ID | Description | GeneRatio | BgRatio | pvalue | p.adjust | qvalue | geneID | Count | No-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgKDN-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgwt-inf_Log2MeanTPM | log2TPM_No-inf_1 | log2TPM_No-inf_2 | log2TPM_No-inf_3 | log2TPM_No-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0038187 | pattern recognition receptor activity | 2/100 | 26/20678 | 0.006977061 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | TLR4||TLR7 | 2 | 5.185544 | 5.113231 | 4.888125 | 5.086531 | 5.184477 | 5.267138 | 5.198302 | 5.109280 | 5.112831 | 5.137487 | 5.092975 | 4.897892 | 4.844611 | 4.976414 | 4.828945 |
| GO:0019210 | kinase inhibitor activity | 3/100 | 83/20678 | 0.007623202 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | LRP6||SPRED1||INKA1 | 3 | 6.645116 | 6.616318 | 6.512385 | 6.635448 | 6.647064 | 6.671039 | 6.626527 | 6.591853 | 6.661162 | 6.630573 | 6.580257 | 6.559030 | 6.511801 | 6.454750 | 6.522027 |
| GO:0003953 | NAD+ nucleosidase activity | 2/100 | 28/20678 | 0.008064112 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | TLR4||TLR7 | 2 | 4.017484 | 4.118424 | 3.955228 | 3.946638 | 4.144276 | 4.055495 | 3.911794 | 4.153356 | 4.097295 | 4.129744 | 4.092442 | 3.965690 | 3.930462 | 3.984087 | 3.940053 |
| GO:0003779 | actin binding | 7/100 | 473/20678 | 0.008090445 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | MYLK||KLHL4||BIN1||FBXO25||JMY||MYOZ2||NRAP | 7 | 7.572857 | 7.590704 | 7.494889 | 7.572138 | 7.575566 | 7.574588 | 7.569128 | 7.586274 | 7.583073 | 7.591845 | 7.601558 | 7.484076 | 7.495969 | 7.499268 | 7.500187 |
| GO:0019207 | kinase regulator activity | 5/100 | 257/20678 | 0.008246040 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | LRP6||ETAA1||SPRED1||SOCS4||INKA1 | 5 | 6.379871 | 6.468260 | 6.457381 | 6.358024 | 6.399825 | 6.385843 | 6.375468 | 6.460618 | 6.498363 | 6.467491 | 6.446062 | 6.463768 | 6.459648 | 6.448748 | 6.457319 |
| GO:0004435 | phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C activity | 2/100 | 29/20678 | 0.008634344 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | CHRM3||EDNRA | 2 | 4.837572 | 6.067854 | 6.778932 | 4.874352 | 4.786320 | 4.969282 | 4.707029 | 6.097976 | 6.073703 | 6.028549 | 6.070325 | 6.739428 | 6.809057 | 6.744391 | 6.820968 |
| GO:0015491 | cation:cation antiporter activity | 2/100 | 29/20678 | 0.008634344 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | SLC9A9||SLC8A1 | 2 | 4.345415 | 4.604245 | 4.972112 | 4.377862 | 4.302753 | 4.309796 | 4.389150 | 4.646779 | 4.584416 | 4.600680 | 4.584193 | 4.950073 | 4.989153 | 5.003754 | 4.944590 |
| GO:0004629 | phospholipase C activity | 2/100 | 31/20678 | 0.009827315 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | CHRM3||EDNRA | 2 | 6.189761 | 6.834813 | 7.324639 | 6.218679 | 6.208334 | 6.234615 | 6.093135 | 6.843171 | 6.825560 | 6.818472 | 6.851802 | 7.309084 | 7.362483 | 7.283408 | 7.342305 |
| GO:0008081 | phosphoric diester hydrolase activity | 3/100 | 97/20678 | 0.011654095 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | CHRM3||EDNRA||GDPD1 | 3 | 5.436871 | 5.849042 | 6.190031 | 5.448217 | 5.458923 | 5.460833 | 5.377907 | 5.842019 | 5.835458 | 5.840302 | 5.877990 | 6.178370 | 6.211300 | 6.166298 | 6.203693 |
| GO:0030291 | protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity | 2/100 | 36/20678 | 0.013107741 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | SPRED1||INKA1 | 2 | 6.554962 | 6.429224 | 6.297552 | 6.536837 | 6.581593 | 6.630691 | 6.465632 | 6.407190 | 6.467057 | 6.417981 | 6.423947 | 6.367290 | 6.251955 | 6.280772 | 6.287634 |
| GO:0001540 | amyloid-beta binding | 3/100 | 102/20678 | 0.013339269 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | TGFB2||CLU||TLR4 | 3 | 7.635777 | 7.136525 | 7.116347 | 7.639714 | 7.642079 | 7.639968 | 7.621251 | 7.131804 | 7.140211 | 7.149964 | 7.123991 | 7.102058 | 7.127357 | 7.117359 | 7.118498 |
| GO:0015298 | solute:cation antiporter activity | 2/100 | 38/20678 | 0.014535446 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | SLC9A9||SLC8A1 | 2 | 4.479612 | 4.682781 | 4.927593 | 4.609066 | 4.403791 | 4.414822 | 4.481392 | 4.693757 | 4.590809 | 4.832621 | 4.600672 | 4.915472 | 4.936487 | 4.956035 | 4.901788 |
| GO:0043394 | proteoglycan binding | 2/100 | 39/20678 | 0.015273370 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | SLIT2||HPSE | 2 | 6.978910 | 7.319367 | 7.669985 | 6.976605 | 6.967437 | 6.990599 | 6.980904 | 7.319367 | 7.321249 | 7.311065 | 7.325748 | 7.664853 | 7.683679 | 7.662386 | 7.668929 |
| GO:0004620 | phospholipase activity | 3/100 | 115/20678 | 0.018341178 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | CHRM3||EDNRA||GDPD1 | 3 | 5.855870 | 6.035028 | 6.336607 | 5.867127 | 5.871151 | 5.871813 | 5.812532 | 6.015304 | 6.007194 | 6.058100 | 6.058732 | 6.316658 | 6.339061 | 6.358629 | 6.331765 |
| GO:0048156 | tau protein binding | 2/100 | 46/20678 | 0.020872610 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | CLU||BIN1 | 2 | 7.810484 | 7.971530 | 7.919484 | 7.820033 | 7.814878 | 7.792962 | 7.813915 | 8.008001 | 7.977946 | 7.980969 | 7.917704 | 7.935685 | 7.924624 | 7.933021 | 7.884010 |
| GO:0008375 | acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity | 2/100 | 48/20678 | 0.022606925 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | ALG13||GCNT1 | 2 | 5.906773 | 5.327096 | 5.284337 | 5.898202 | 5.991789 | 5.809504 | 5.921731 | 5.308056 | 5.301925 | 5.276856 | 5.417449 | 5.332514 | 5.295231 | 5.263151 | 5.244910 |
| GO:0016799 | hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing N-glycosyl compounds | 2/100 | 50/20678 | 0.024398690 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | TLR4||TLR7 | 2 | 4.803269 | 4.692443 | 4.612846 | 4.805390 | 4.833924 | 4.845847 | 4.724860 | 4.697764 | 4.711181 | 4.670520 | 4.690009 | 4.636213 | 4.583542 | 4.607671 | 4.623424 |
| GO:0019902 | phosphatase binding | 4/100 | 230/20678 | 0.025525509 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | DLG3||SIGLEC11||SPRED1||MYOZ2 | 4 | 5.892670 | 5.823652 | 5.736694 | 5.909395 | 5.890996 | 5.881635 | 5.888508 | 5.824396 | 5.804181 | 5.832535 | 5.833307 | 5.742296 | 5.732068 | 5.749588 | 5.722681 |
| GO:0016298 | lipase activity | 3/100 | 141/20678 | 0.031070830 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | CHRM3||EDNRA||GDPD1 | 3 | 5.735480 | 5.885006 | 6.162292 | 5.740386 | 5.751872 | 5.749386 | 5.699667 | 5.854580 | 5.889033 | 5.901181 | 5.894782 | 6.143884 | 6.166378 | 6.186485 | 6.152059 |
| GO:0015459 | potassium channel regulator activity | 2/100 | 57/20678 | 0.031104463 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | KCNS3||KCNIP1 | 2 | 6.075316 | 6.004015 | 5.923688 | 6.087481 | 6.077667 | 6.049208 | 6.086575 | 6.059735 | 5.956815 | 5.998955 | 5.998684 | 5.943618 | 5.915755 | 5.906449 | 5.928659 |
| GO:0099106 | ion channel regulator activity | 3/100 | 145/20678 | 0.033351545 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | MCUB||KCNS3||KCNIP1 | 3 | 6.319826 | 6.239209 | 6.163487 | 6.307882 | 6.334039 | 6.304489 | 6.332633 | 6.261744 | 6.211009 | 6.238826 | 6.244796 | 6.173396 | 6.169410 | 6.161583 | 6.149442 |
| GO:0015291 | secondary active transmembrane transporter activity | 4/100 | 252/20678 | 0.034059191 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | SLC7A8||SLC16A5||SLC9A9||SLC8A1 | 4 | 5.031071 | 5.584843 | 5.775846 | 5.024249 | 5.032715 | 5.032178 | 5.035117 | 5.591952 | 5.561017 | 5.613192 | 5.572668 | 5.753384 | 5.783816 | 5.806457 | 5.759107 |
| GO:0016247 | channel regulator activity | 3/100 | 151/20678 | 0.036931950 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | MCUB||KCNS3||KCNIP1 | 3 | 6.283899 | 6.215798 | 6.140889 | 6.274761 | 6.296313 | 6.270126 | 6.294213 | 6.238078 | 6.189728 | 6.216217 | 6.218759 | 6.154624 | 6.148544 | 6.134061 | 6.126150 |
| GO:0016798 | hydrolase activity, acting on glycosyl bonds | 3/100 | 154/20678 | 0.038793364 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | TLR4||HPSE||TLR7 | 3 | 5.680795 | 5.434214 | 5.507820 | 5.675598 | 5.685469 | 5.710870 | 5.650597 | 5.423201 | 5.462219 | 5.415341 | 5.435655 | 5.507164 | 5.496996 | 5.519944 | 5.507085 |
| GO:0008173 | RNA methyltransferase activity | 2/100 | 67/20678 | 0.041776888 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | RNMT||TRMT10A | 2 | 4.373587 | 4.385120 | 4.328590 | 4.406695 | 4.418720 | 4.300135 | 4.365841 | 4.347970 | 4.386635 | 4.379504 | 4.425320 | 4.253163 | 4.299108 | 4.437121 | 4.318508 |
| GO:0015079 | potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity | 3/100 | 163/20678 | 0.044659229 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | KCNS3||SLC9A9||KCNIP1 | 3 | 4.707356 | 4.892651 | 4.988806 | 4.677009 | 4.655116 | 4.778527 | 4.715711 | 4.960257 | 4.829501 | 4.927385 | 4.849426 | 4.989387 | 5.011724 | 5.026152 | 4.925940 |
| GO:0008757 | S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase activity | 3/100 | 165/20678 | 0.046019540 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | RNMT||ETFBKMT||TRMT10A | 3 | 4.746394 | 4.727203 | 4.701216 | 4.797649 | 4.729525 | 4.660624 | 4.793483 | 4.713965 | 4.711901 | 4.734367 | 4.748266 | 4.678327 | 4.674251 | 4.751239 | 4.699737 |
| GO:0004726 | non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine phosphatase activity | 1/100 | 10/20678 | 0.047331677 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | PTPN4 | 1 | 5.761513 | 5.820458 | 5.602319 | 5.624595 | 5.913728 | 5.729345 | 5.763412 | 5.687706 | 6.051019 | 5.720763 | 5.793356 | 5.533194 | 5.619645 | 5.604401 | 5.649518 |
| GO:0005432 | calcium:sodium antiporter activity | 1/100 | 10/20678 | 0.047331677 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | SLC8A1 | 1 | 5.082498 | 5.531455 | 5.970075 | 5.118181 | 5.069270 | 5.078785 | 5.063117 | 5.588927 | 5.538637 | 5.508812 | 5.487423 | 5.942854 | 5.965165 | 6.033757 | 5.936446 |
| GO:0035197 | siRNA binding | 1/100 | 10/20678 | 0.047331677 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | TLR7 | 1 | 4.704384 | 5.149196 | 4.938711 | 4.755787 | 4.705203 | 4.750179 | 4.601093 | 4.754934 | 5.693350 | 5.141657 | 4.802107 | 4.743656 | 5.076338 | 4.679096 | 5.190953 |
| GO:0071936 | coreceptor activity involved in Wnt signaling pathway | 1/100 | 10/20678 | 0.047331677 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | LRP6 | 1 | 4.598391 | 3.582315 | 3.437011 | 4.610653 | 4.602899 | 4.651577 | 4.525576 | 3.648508 | 3.448936 | 3.547475 | 3.673459 | 3.253025 | 3.272224 | 3.459102 | 3.714688 |
| GO:0099186 | structural constituent of postsynapse | 1/100 | 10/20678 | 0.047331677 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | DLG3 | 1 | 10.083763 | 10.200666 | 10.178443 | 10.088964 | 10.080012 | 10.081101 | 10.084959 | 10.205597 | 10.198761 | 10.211975 | 10.186207 | 10.193782 | 10.180092 | 10.177556 | 10.162169 |
| GO:0098960 | postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor activity | 2/100 | 73/20678 | 0.048745248 | 0.2848612 | 0.2654956 | GABRA4||CHRM3 | 2 | 3.310628 | 2.905699 | 1.724926 | 3.220936 | 3.380974 | 3.174030 | 3.448977 | 3.033733 | 3.380132 | 1.853361 | 2.956218 | 1.433998 | 1.354223 | 1.307753 | 2.456394 |
GO: CC
| ID | Description | GeneRatio | BgRatio | pvalue | p.adjust | qvalue | geneID | Count | No-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgKDN-inf_Log2MeanTPM | pgwt-inf_Log2MeanTPM | log2TPM_No-inf_1 | log2TPM_No-inf_2 | log2TPM_No-inf_3 | log2TPM_No-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgKDN-inf_4 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_1 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_2 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_3 | log2TPM_pgwt-inf_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0042583 | chromaffin granule | 2/103 | 14/21916 | 0.001918534 | 0.1899717 | 0.1731344 | DNAJC5||CLU | 2 | 6.314415 | 7.258579 | 7.635363 | 6.376547 | 6.285599 | 6.268293 | 6.324810 | 7.243039 | 7.325448 | 7.230280 | 7.233398 | 7.638138 | 7.632621 | 7.626958 | 7.643682 |
| GO:0030315 | T-tubule | 3/103 | 53/21916 | 0.001991322 | 0.1899717 | 0.1731344 | DYSF||BIN1||SLC8A1 | 3 | 5.286890 | 5.269391 | 5.278904 | 5.293800 | 5.326069 | 5.304097 | 5.221476 | 5.303102 | 5.223029 | 5.301507 | 5.248279 | 5.292796 | 5.297791 | 5.300899 | 5.222686 |
| GO:0034702 | ion channel complex | 6/103 | 307/21916 | 0.003303679 | 0.1899717 | 0.1731344 | MCUB||DLG3||GABRA4||KCNS3||KCNIP1||CACNB4 | 6 | 5.385716 | 5.454007 | 5.408961 | 5.374404 | 5.402208 | 5.402324 | 5.363524 | 5.482086 | 5.468705 | 5.434987 | 5.429571 | 5.408709 | 5.391078 | 5.410424 | 5.425426 |
| GO:0034703 | cation channel complex | 5/103 | 222/21916 | 0.003995965 | 0.1899717 | 0.1731344 | MCUB||DLG3||KCNS3||KCNIP1||CACNB4 | 5 | 5.412118 | 5.217064 | 5.220823 | 5.411896 | 5.440739 | 5.410689 | 5.384600 | 5.240122 | 5.197734 | 5.225334 | 5.204676 | 5.236884 | 5.197035 | 5.227254 | 5.221819 |
| GO:0030018 | Z disc | 4/103 | 138/21916 | 0.004111941 | 0.1899717 | 0.1731344 | BIN1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 4 | 6.212302 | 6.180270 | 6.192808 | 6.222049 | 6.216031 | 6.230193 | 6.180437 | 6.209304 | 6.199036 | 6.144907 | 6.166927 | 6.191429 | 6.258411 | 6.157164 | 6.161947 |
| GO:0031674 | I band | 4/103 | 149/21916 | 0.005391276 | 0.2075641 | 0.1891676 | BIN1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 4 | 6.346202 | 6.424762 | 6.462992 | 6.351345 | 6.351773 | 6.360966 | 6.320399 | 6.449467 | 6.431277 | 6.397184 | 6.420623 | 6.461008 | 6.519820 | 6.430041 | 6.439401 |
| GO:0009898 | cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | 4/103 | 184/21916 | 0.011160156 | 0.3011409 | 0.2744505 | PTPN4||GNG12||KCNIP1||CACNB4 | 4 | 6.284069 | 6.366974 | 6.324494 | 6.283775 | 6.287552 | 6.289591 | 6.275317 | 6.372873 | 6.359550 | 6.377962 | 6.357407 | 6.325526 | 6.334699 | 6.319588 | 6.318106 |
| GO:1902495 | transmembrane transporter complex | 6/103 | 406/21916 | 0.012363082 | 0.3011409 | 0.2744505 | MCUB||DLG3||GABRA4||KCNS3||KCNIP1||CACNB4 | 6 | 8.616839 | 8.435853 | 8.690301 | 8.622629 | 8.616702 | 8.615030 | 8.612978 | 8.445579 | 8.428429 | 8.431045 | 8.438299 | 8.694717 | 8.694029 | 8.690007 | 8.682416 |
| GO:1990351 | transporter complex | 6/103 | 421/21916 | 0.014555655 | 0.3011409 | 0.2744505 | MCUB||DLG3||GABRA4||KCNS3||KCNIP1||CACNB4 | 6 | 8.514339 | 8.333789 | 8.586910 | 8.520472 | 8.513979 | 8.511676 | 8.511209 | 8.343623 | 8.326436 | 8.328989 | 8.336046 | 8.592242 | 8.588647 | 8.587484 | 8.579237 |
| GO:0043198 | dendritic shaft | 2/103 | 40/21916 | 0.015190668 | 0.3011409 | 0.2744505 | DLG3||SLC8A1 | 2 | 5.178076 | 5.068939 | 4.903863 | 5.217446 | 5.143056 | 5.144509 | 5.205676 | 5.051241 | 5.105912 | 5.070020 | 5.047844 | 4.867417 | 4.858003 | 4.899950 | 4.986489 |
| GO:0098562 | cytoplasmic side of membrane | 4/103 | 213/21916 | 0.018171685 | 0.3011409 | 0.2744505 | PTPN4||GNG12||KCNIP1||CACNB4 | 4 | 7.498378 | 7.488148 | 7.319017 | 7.503329 | 7.500555 | 7.490677 | 7.498918 | 7.485478 | 7.475508 | 7.500615 | 7.490876 | 7.316580 | 7.321602 | 7.321873 | 7.316005 |
| GO:0032994 | protein-lipid complex | 2/103 | 46/21916 | 0.019793376 | 0.3011409 | 0.2744505 | CLU||BIN1 | 2 | 6.737914 | 6.965766 | 6.945774 | 6.750629 | 6.695471 | 6.742312 | 6.762353 | 7.006611 | 6.905755 | 6.943474 | 7.004708 | 6.925593 | 6.971880 | 6.955959 | 6.929154 |
| GO:0030017 | sarcomere | 4/103 | 223/21916 | 0.021103738 | 0.3011409 | 0.2744505 | BIN1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 4 | 6.636453 | 6.764775 | 6.765147 | 6.636738 | 6.638843 | 6.652087 | 6.617938 | 6.770014 | 6.765068 | 6.757543 | 6.766448 | 6.761675 | 6.798342 | 6.736631 | 6.763269 |
| GO:0034451 | centriolar satellite | 3/103 | 127/21916 | 0.022086314 | 0.3011409 | 0.2744505 | KLHL4||DYSF||CCDC57 | 3 | 5.226652 | 4.979873 | 4.986846 | 5.260622 | 5.202640 | 5.231026 | 5.211634 | 4.928466 | 5.007880 | 4.967338 | 5.014166 | 5.055994 | 4.964136 | 4.965432 | 4.959546 |
| GO:0005874 | microtubule | 6/103 | 466/21916 | 0.022735484 | 0.3011409 | 0.2744505 | DNAH11||KIF13A||SPACA9||CCDC57||SLC8A1||KNTC1 | 6 | 5.995520 | 5.914429 | 5.787386 | 5.970396 | 6.006944 | 5.993878 | 6.010521 | 5.914055 | 5.897489 | 5.934807 | 5.911118 | 5.764952 | 5.793851 | 5.802290 | 5.788184 |
| GO:0099055 | integral component of postsynaptic membrane | 3/103 | 129/21916 | 0.023000689 | 0.3011409 | 0.2744505 | GABRA4||LRRC4||SLC8A1 | 3 | 4.569696 | 5.133361 | 5.317102 | 4.573499 | 4.565123 | 4.577073 | 4.563041 | 5.169127 | 5.113170 | 5.126603 | 5.123909 | 5.293728 | 5.318580 | 5.335639 | 5.320150 |
| GO:0014704 | intercalated disc | 2/103 | 50/21916 | 0.023144981 | 0.3011409 | 0.2744505 | SLC8A1||NRAP | 2 | 5.876005 | 6.411734 | 6.529996 | 5.892795 | 5.864119 | 5.893310 | 5.853370 | 6.487573 | 6.412954 | 6.353346 | 6.389702 | 6.579531 | 6.649054 | 6.456074 | 6.423734 |
| GO:0001669 | acrosomal vesicle | 3/103 | 130/21916 | 0.023465521 | 0.3011409 | 0.2744505 | POMT1||KNL1||SPACA9 | 3 | 6.367226 | 6.186927 | 6.289764 | 6.359964 | 6.368277 | 6.383712 | 6.356802 | 6.154922 | 6.187815 | 6.198926 | 6.205521 | 6.285181 | 6.291615 | 6.317529 | 6.264226 |
| GO:0098936 | intrinsic component of postsynaptic membrane | 3/103 | 134/21916 | 0.025375801 | 0.3085163 | 0.2811723 | GABRA4||LRRC4||SLC8A1 | 3 | 4.687177 | 5.167081 | 5.339540 | 4.683220 | 4.681297 | 4.705303 | 4.678732 | 5.200170 | 5.144398 | 5.163749 | 5.159422 | 5.311585 | 5.339390 | 5.362136 | 5.344593 |
| GO:0030016 | myofibril | 4/103 | 243/21916 | 0.027798625 | 0.3210741 | 0.2926171 | BIN1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 4 | 6.786878 | 6.912449 | 6.899446 | 6.786531 | 6.790892 | 6.796598 | 6.773391 | 6.914978 | 6.911257 | 6.907115 | 6.916431 | 6.894584 | 6.930116 | 6.875154 | 6.897390 |
| GO:0043292 | contractile fiber | 4/103 | 252/21916 | 0.031180767 | 0.3217259 | 0.2932111 | BIN1||MYOZ2||SLC8A1||NRAP | 4 | 6.793588 | 6.911653 | 6.889428 | 6.785860 | 6.812933 | 6.799491 | 6.775797 | 6.915529 | 6.906190 | 6.907514 | 6.917346 | 6.882530 | 6.922195 | 6.861309 | 6.891015 |
| GO:0042383 | sarcolemma | 3/103 | 149/21916 | 0.033262897 | 0.3217259 | 0.2932111 | DYSF||BIN1||SLC8A1 | 3 | 5.698017 | 5.967760 | 6.021574 | 5.679001 | 5.729058 | 5.734307 | 5.647922 | 5.986496 | 5.994709 | 5.940635 | 5.948441 | 6.074641 | 6.075496 | 5.964442 | 5.967593 |
| GO:0005657 | replication fork | 2/103 | 61/21916 | 0.033446490 | 0.3217259 | 0.2932111 | ETAA1||RAD51B | 2 | 5.053381 | 4.967238 | 5.036011 | 4.953020 | 4.991467 | 5.138938 | 5.121174 | 4.955548 | 5.028646 | 5.016735 | 4.862049 | 5.083063 | 5.079086 | 5.018277 | 4.960123 |
| GO:0019005 | SCF ubiquitin ligase complex | 2/103 | 62/21916 | 0.034457432 | 0.3217259 | 0.2932111 | FBXL17||FBXO25 | 2 | 5.176964 | 5.155757 | 5.025169 | 5.233712 | 5.169827 | 5.122378 | 5.179769 | 5.239827 | 5.047948 | 5.019968 | 5.295656 | 5.029440 | 5.193323 | 4.942708 | 4.918871 |
| GO:0099572 | postsynaptic specialization | 5/103 | 387/21916 | 0.035975550 | 0.3217259 | 0.2932111 | DLG3||ZDHHC2||GABRA4||LRRC4||SLC8A1 | 5 | 8.058160 | 8.058136 | 7.946571 | 8.068372 | 8.059517 | 8.058407 | 8.046260 | 8.068682 | 8.067352 | 8.062344 | 8.033887 | 7.947661 | 7.947193 | 7.936408 | 7.954960 |
| GO:0099699 | integral component of synaptic membrane | 3/103 | 163/21916 | 0.041643068 | 0.3217259 | 0.2932111 | GABRA4||LRRC4||SLC8A1 | 3 | 4.923186 | 5.475799 | 5.584857 | 4.915440 | 4.925950 | 4.927960 | 4.923362 | 5.504117 | 5.440361 | 5.456257 | 5.501388 | 5.579398 | 5.578716 | 5.605488 | 5.575627 |
| GO:0016529 | sarcoplasmic reticulum | 2/103 | 71/21916 | 0.044072460 | 0.3217259 | 0.2932111 | POMT1||TRDN | 2 | 6.209622 | 6.369883 | 6.438491 | 6.253972 | 6.190705 | 6.229104 | 6.163017 | 6.364839 | 6.357121 | 6.382554 | 6.374887 | 6.448429 | 6.427687 | 6.441035 | 6.436733 |
| GO:0031093 | platelet alpha granule lumen | 2/103 | 72/21916 | 0.045195856 | 0.3217259 | 0.2932111 | TGFB2||CLU | 2 | 8.528156 | 8.699732 | 8.705178 | 8.531235 | 8.515663 | 8.527919 | 8.537715 | 8.697935 | 8.679128 | 8.708487 | 8.713140 | 8.702369 | 8.705107 | 8.708898 | 8.704332 |
| GO:0005916 | fascia adherens | 1/103 | 10/21916 | 0.046025285 | 0.3217259 | 0.2932111 | NRAP | 1 | 6.675374 | 6.926290 | 6.873798 | 6.688862 | 6.614127 | 6.761953 | 6.631909 | 6.893700 | 6.877528 | 6.926918 | 7.003717 | 6.880147 | 6.850868 | 6.887647 | 6.876268 |
| GO:0034704 | calcium channel complex | 2/103 | 73/21916 | 0.046329807 | 0.3217259 | 0.2932111 | MCUB||CACNB4 | 2 | 5.938847 | 5.615343 | 5.550352 | 5.941564 | 5.984370 | 5.926477 | 5.901723 | 5.668271 | 5.588075 | 5.611637 | 5.591956 | 5.562151 | 5.548523 | 5.554409 | 5.536200 |
| GO:0005876 | spindle microtubule | 2/103 | 74/21916 | 0.047474191 | 0.3217259 | 0.2932111 | CCDC57||KNTC1 | 2 | 5.634431 | 5.555925 | 5.434264 | 5.604501 | 5.659756 | 5.623782 | 5.649038 | 5.521290 | 5.566350 | 5.536704 | 5.598156 | 5.402579 | 5.425903 | 5.448941 | 5.458976 |
KEGG
No significcant functional terms were enriched under the threshold of P<0.05
Help
2-2. Summary Plot
GSEA
GO: BP
GO: MF
GO: CC
KEGG
ORA: All DEGs
GO: BP
GO: MF
GO: CC
KEGG
ORA: Down-regulated DEGs
GO: BP
GO: MF
GO: CC
KEGG
ORA: Up-regulated DEGs
GO: BP
GO: MF
GO: CC
KEGG
No results under this category
ORA: Overlapped Terms
GO: BP
Summary Plot
Venn Plot
List
| Intersection Combination | Overlapped Functional Terms |
|---|---|
| Up-Regulated ∪ Down-Regulated | GO:0048644||GO:0055001||GO:0060537||GO:0048738||GO:0007517||GO:0003012||GO:0014706||GO:0003007||GO:0050920||GO:0035051||GO:0032728||GO:0006939||GO:0042692||GO:0032608||GO:0032648||GO:0055007||GO:0032481||GO:0002689||GO:0050922||GO:0071676||GO:0050921||GO:0030595||GO:0050729||GO:0031349||GO:0050767||GO:1901214||GO:0090025||GO:0070167||GO:0110149||GO:0045860||GO:0050900||GO:0048846||GO:1902284||GO:0051146||GO:0001822||GO:0001503||GO:0070997||GO:0072001||GO:0030308||GO:0030278||GO:0030282||GO:0045778||GO:0043523||GO:0045058||GO:0071622||GO:0042060||GO:0051960||GO:0002686||GO:0060326||GO:0071674||GO:0071621||GO:0002688||GO:0007188||GO:0071675||GO:0061564||GO:0051402||GO:0043524||GO:0002274||GO:0097530||GO:0050770||GO:0050730||GO:0040013 |
| All ∪ Down-Regulated | GO:0030595||GO:0050900||GO:0051607||GO:0140546||GO:0009615||GO:0060326||GO:0071674||GO:0050920||GO:0097529||GO:0097530||GO:0071621||GO:0002685||GO:0045071||GO:0045069||GO:0002688||GO:0071675||GO:0018108||GO:0007517||GO:0018212||GO:0003007||GO:1990266||GO:0002687||GO:0050921||GO:0050730||GO:1903900||GO:0072676||GO:0030593||GO:0055001||GO:0042509||GO:0042692||GO:0007260||GO:0050792||GO:0048638||GO:0048644||GO:0060537||GO:0048738||GO:0071260||GO:0048525||GO:0071676||GO:0014706||GO:1990868||GO:1990869||GO:0006939||GO:0019079||GO:0051146||GO:0010575||GO:0019058||GO:0050729||GO:0032728||GO:0050731||GO:0007259||GO:1901214||GO:0060560||GO:0071222||GO:1903131||GO:0070098||GO:0097696||GO:0042531||GO:0050922||GO:1903557||GO:0045860||GO:0072678||GO:0090025||GO:0071219||GO:1901215||GO:0048247||GO:0002690||GO:0035051||GO:0003012||GO:0050767||GO:0051960||GO:0001960||GO:0070997||GO:0048846||GO:1902284||GO:0034340||GO:1903037||GO:0002675||GO:0071887||GO:0016032||GO:0060761||GO:2000106||GO:0002689||GO:0060759||GO:0030278||GO:0071216||GO:0002548||GO:1903039||GO:0030217||GO:0030098||GO:0009612||GO:1990138||GO:0048880||GO:2000659||GO:0032608||GO:0032648||GO:0048639||GO:1903203||GO:0002526||GO:0002274||GO:0016188||GO:0021559||GO:0032760||GO:0048608||GO:0031349||GO:0061458||GO:0001503||GO:0002366||GO:0070167||GO:0022409||GO:0032481||GO:2000401||GO:0045778||GO:0002263||GO:0110149||GO:0032496||GO:0045058||GO:0071622||GO:0001959||GO:0050727||GO:0150063||GO:0016322||GO:0072540||GO:0045927||GO:0036475||GO:0070498||GO:0002686||GO:0055007||GO:0033077||GO:0030308||GO:0070234||GO:0140374||GO:0002444||GO:0071357||GO:0030500||GO:2000402||GO:0048588||GO:0032613||GO:0032653||GO:0050870||GO:0048841||GO:0050863||GO:0002237||GO:0010574||GO:0006750||GO:0030198||GO:0002673||GO:0043062||GO:0071677||GO:0043524||GO:0045229||GO:0002295||GO:0048532||GO:0070230||GO:2001135||GO:0043523||GO:0001822||GO:0050866||GO:0071692||GO:0002697||GO:0030282||GO:0001654||GO:0019184||GO:1903204||GO:0097484||GO:0061564||GO:0072001||GO:0001947||GO:0050770||GO:0010863||GO:0030501||GO:1902622||GO:0098586||GO:0048675||GO:0002275||GO:0043373||GO:0051897||GO:0051047||GO:0032965||GO:1900274||GO:0010975||GO:0048568||GO:0010573||GO:0061371||GO:0007188||GO:0001558||GO:0060193||GO:0002221||GO:0002693||GO:0006925||GO:0035455||GO:0009855||GO:0007589||GO:0003143||GO:0009799||GO:0032733||GO:0040013||GO:0030516||GO:0002363||GO:0032740||GO:0033081||GO:0043369||GO:0030517||GO:0032620||GO:0032660||GO:1902105||GO:0002831||GO:0042060||GO:1903532||GO:0042551||GO:0051235||GO:0032147||GO:0062207||GO:0071214||GO:0104004||GO:0051251||GO:0010712||GO:0021675||GO:0009306||GO:0002367||GO:0035592||GO:0051402||GO:0048511||GO:1903706||GO:0006213||GO:1902932||GO:0031016||GO:0002819||GO:0070169||GO:0022617||GO:1905330||GO:0002699||GO:0110151||GO:0035050||GO:0046425||GO:0021545||GO:0031295||GO:0032964||GO:2000404||GO:0001958||GO:0036075||GO:0090026||GO:0050829||GO:0007389||GO:0010770||GO:0043299||GO:0048640||GO:0032963||GO:0032967||GO:1902624||GO:1903859||GO:0071706||GO:1903555||GO:0031294||GO:0060337||GO:0061387||GO:0043491||GO:0010720||GO:0044106||GO:0007548||GO:0048545||GO:0002360||GO:0010714||GO:0021602||GO:0048843||GO:0072539||GO:2000108||GO:0045765||GO:0060562||GO:0008637||GO:0016081||GO:0033089||GO:0045835||GO:0071281||GO:0097278||GO:2001225||GO:0003158||GO:1902107||GO:1903708||GO:0031346||GO:0007202||GO:0040018||GO:0090713||GO:1901623||GO:0050878||GO:1901342||GO:0009308||GO:0010518||GO:0051384||GO:0033028||GO:1904892||GO:0007368||GO:0002695||GO:0001672||GO:0002885||GO:0030432||GO:0035457||GO:0007519||GO:0016485||GO:0046632||GO:0045662||GO:0050927||GO:0090022||GO:0051896||GO:0021700||GO:0043434||GO:0050769||GO:0045661||GO:0051781||GO:0060191||GO:0050708||GO:0071496||GO:0070555||GO:0043551||GO:0030201||GO:0045672||GO:0048710||GO:0050926||GO:0048592||GO:0022408||GO:0043367||GO:0014831||GO:0030522||GO:0010818||GO:1902275||GO:0001836||GO:0045445||GO:0043010||GO:0045446||GO:0002866||GO:0006534||GO:0030157||GO:0035745||GO:0060700||GO:0060707||GO:1902510||GO:2000551||GO:0002446||GO:0031076||GO:0036336||GO:2000047||GO:0019915||GO:0060538||GO:0071347||GO:0046854||GO:0048771||GO:0002720||GO:0048593||GO:0045580||GO:1903034||GO:0043030||GO:0050732||GO:0060113||GO:0032693||GO:2000406||GO:0002711||GO:0010769||GO:0002718||GO:0008406||GO:0032535||GO:0062208||GO:0001768||GO:0002883||GO:0060732||GO:0072672||GO:1903624||GO:2000116||GO:0031960||GO:0048736||GO:0060173||GO:0002285||GO:0010517||GO:0050771||GO:0010977||GO:0045137||GO:0001767||GO:0035672||GO:0043320||GO:0060026||GO:0071474||GO:0032640||GO:0032680||GO:0002763||GO:0002703||GO:0010955||GO:0070528||GO:1903318||GO:1905332||GO:0048814||GO:0045766||GO:1904018||GO:0006898||GO:0030100||GO:0050775||GO:0051302||GO:0007173||GO:0050773||GO:0032946||GO:0002524||GO:0002830||GO:0010919||GO:0021783||GO:0042976||GO:0048569||GO:2000048||GO:0062013||GO:0042058||GO:0043550||GO:0031345||GO:0022604||GO:1903201||GO:0046718||GO:0030224||GO:0044331||GO:0002705||GO:0001780||GO:0001921||GO:0006857||GO:0045651||GO:0098969||GO:0030879||GO:0008361||GO:0001938||GO:0007189||GO:0033135||GO:0045055||GO:0002753||GO:0042093||GO:0033138||GO:0060249||GO:0002691||GO:0043087||GO:0007250||GO:0021756||GO:0035743||GO:0042532||GO:0048486||GO:0051447||GO:1903540||GO:0006275||GO:0014823||GO:0042490||GO:0070613||GO:0001894||GO:0044409||GO:0002294||GO:1901184||GO:1903531||GO:0010721||GO:0070665||GO:0045582||GO:0002287||GO:0002293||GO:1903317||GO:0045637||GO:0016082||GO:0048791||GO:0098877||GO:0031018||GO:0044058||GO:2000403||GO:0003407||GO:0072527||GO:2001234||GO:0002573||GO:0045861||GO:0062012||GO:0042398||GO:0070527||GO:0038127||GO:0002864||GO:0032793||GO:0043031||GO:0043117||GO:0044320||GO:0051900||GO:0071731||GO:2000846||GO:0050678||GO:0001892||GO:0046434||GO:0010811||GO:0042752||GO:0045639||GO:0046661||GO:0046631||GO:0050679||GO:0043303||GO:1902930||GO:0050673||GO:0002824||GO:0006309||GO:0030449||GO:0043382||GO:0050930||GO:2001236||GO:0002279||GO:0002448||GO:0006509||GO:0072583||GO:0014821||GO:0043576||GO:1903978||GO:0015850||GO:0002708||GO:0043406||GO:0002821||GO:0043300||GO:0046427||GO:0032944||GO:1903202||GO:0010866||GO:0035930||GO:0036303||GO:0051904||GO:0072574||GO:0072575||GO:2000831||GO:0051604||GO:0051701||GO:0022612||GO:0045621||GO:0002369||GO:0002724||GO:0007595||GO:0010676||GO:0035710||GO:0003323||GO:0009219||GO:0021544||GO:0040037||GO:0043380||GO:0051882||GO:0051905||GO:0072576||GO:0090023||GO:0030225||GO:0010565||GO:0032868 |
| All ∪ Up-Regulated | GO:0030595||GO:0050900||GO:0060326||GO:0071674||GO:0050920||GO:0097530||GO:0071621||GO:0002688||GO:0071675||GO:0007517||GO:0003007||GO:0050921||GO:0050730||GO:0055001||GO:0042692||GO:0048644||GO:0060537||GO:0048738||GO:0071676||GO:0014706||GO:0006939||GO:0051146||GO:0050729||GO:0032728||GO:0060415||GO:1901214||GO:0050922||GO:0045860||GO:0090025||GO:0035051||GO:0003012||GO:0050767||GO:0051960||GO:0055008||GO:0070997||GO:0048846||GO:1902284||GO:0002689||GO:0030278||GO:0014820||GO:0032608||GO:0032648||GO:0014829||GO:0055013||GO:0002274||GO:0031349||GO:0001503||GO:0070167||GO:0032481||GO:0045778||GO:0055006||GO:0110149||GO:0045058||GO:0071622||GO:0002686||GO:0055007||GO:0030308||GO:0048863||GO:0003179||GO:0035909||GO:0051058||GO:0060977||GO:0060485||GO:0043524||GO:0003184||GO:0003206||GO:0043523||GO:0001822||GO:0006936||GO:0014033||GO:0035265||GO:0043368||GO:0030282||GO:0003018||GO:0061564||GO:0072001||GO:0050770||GO:0003170||GO:0060411||GO:1905314||GO:0007188||GO:0042116||GO:0003177||GO:0048762||GO:0040013||GO:0050808||GO:0042060||GO:0055010||GO:0032727||GO:0048844||GO:0050919||GO:0031214||GO:0051402||GO:0110148||GO:0007409||GO:1903522||GO:0050714||GO:0001655||GO:0003272||GO:0045926||GO:0046580||GO:0001933||GO:0032479||GO:0032606||GO:0042310||GO:0014031||GO:0060947||GO:0097084||GO:0003229||GO:0061384||GO:0007015||GO:0007204||GO:0007009||GO:0035904||GO:0070228||GO:0045607||GO:0045631||GO:0070099||GO:0070243||GO:1902667||GO:2000980||GO:0003205||GO:0003180||GO:0032607||GO:0032647||GO:0008016||GO:0051271||GO:0003222||GO:0015816||GO:0003203||GO:1902475||GO:0019722||GO:0030239||GO:0060840||GO:0055002||GO:0003176||GO:0035296||GO:0097746||GO:0042326||GO:0042698||GO:0051148||GO:0060393||GO:0051480||GO:0035150||GO:0003279||GO:0055017||GO:0060412||GO:1905207||GO:0051091||GO:0045823||GO:0061082||GO:0003208||GO:0060389||GO:0006874||GO:0003198||GO:0010649||GO:0060413||GO:0003151||GO:0010927||GO:0001941||GO:1903524||GO:1903036||GO:0055074||GO:0060419||GO:0045936||GO:0010563||GO:0051798||GO:0060047||GO:0003197||GO:0060976||GO:0061383||GO:0089718||GO:0031032||GO:0002281||GO:0003015||GO:1903169||GO:2000677||GO:0007193||GO:0003215||GO:0034501||GO:1903083||GO:0003231||GO:0072132||GO:0014888||GO:0043090||GO:0006359||GO:0098719||GO:0006937||GO:0043500||GO:0010862||GO:0090257||GO:0033002||GO:0003283||GO:0051797||GO:0043113||GO:0071805 |
| All ∪ Down-Regulated ∪ Up-Regulated | GO:0030595||GO:0050900||GO:0060326||GO:0071674||GO:0050920||GO:0097530||GO:0071621||GO:0002688||GO:0071675||GO:0007517||GO:0003007||GO:0050921||GO:0050730||GO:0055001||GO:0042692||GO:0048644||GO:0060537||GO:0048738||GO:0071676||GO:0014706||GO:0006939||GO:0051146||GO:0050729||GO:0032728||GO:1901214||GO:0050922||GO:0045860||GO:0090025||GO:0035051||GO:0003012||GO:0050767||GO:0051960||GO:0070997||GO:0048846||GO:1902284||GO:0002689||GO:0030278||GO:0032608||GO:0032648||GO:0002274||GO:0031349||GO:0001503||GO:0070167||GO:0032481||GO:0045778||GO:0110149||GO:0045058||GO:0071622||GO:0002686||GO:0055007||GO:0030308||GO:0043524||GO:0043523||GO:0001822||GO:0030282||GO:0061564||GO:0072001||GO:0050770||GO:0007188||GO:0040013||GO:0042060||GO:0051402 |
GO: MF
Summary Plot
Venn Plot
List
| Intersection Combination | Overlapped Functional Terms |
|---|---|
| Up-Regulated ∪ Down-Regulated | GO:0038187||GO:0019207 |
| All ∪ Down-Regulated | GO:0005125||GO:0005126||GO:0008083||GO:0038187||GO:0019207||GO:0005149||GO:0046935||GO:0045236||GO:0008569||GO:0008237||GO:0035014||GO:0030215||GO:0019955||GO:0045499||GO:0004693||GO:0051959||GO:0097472||GO:0004879||GO:0098531||GO:0004222||GO:0005031||GO:0008009||GO:0031432||GO:0140333||GO:0042379||GO:0045505||GO:0005035||GO:0005313||GO:0035259||GO:0071889||GO:0015172||GO:0019992||GO:0140327||GO:0008201||GO:0019966||GO:0035497||GO:0005539||GO:0005158||GO:0016493||GO:0005044||GO:0061629||GO:0042056||GO:0017075||GO:0019957||GO:0001228 |
| All ∪ Up-Regulated | GO:0038187||GO:0019207||GO:0043394||GO:0019210||GO:0015291 |
| All ∪ Down-Regulated ∪ Up-Regulated | GO:0038187||GO:0019207 |
GO: CC
Summary Plot
Venn Plot
List
| Intersection Combination | Overlapped Functional Terms |
|---|---|
| Up-Regulated ∪ Down-Regulated | GO:0031093 |
| All ∪ Down-Regulated | GO:0032421||GO:0098862||GO:0031093||GO:0005942||GO:0034774||GO:0032420||GO:0060205||GO:0031983||GO:0031526||GO:0018995||GO:0043657||GO:0098831||GO:0031253||GO:0030136||GO:0030672||GO:0099501||GO:0030139||GO:0005767||GO:0005858 |
| All ∪ Up-Regulated | GO:0031093||GO:0031674||GO:0030018||GO:0030017||GO:0042583||GO:0030016||GO:0032994||GO:0043292||GO:0030315 |
| All ∪ Down-Regulated ∪ Up-Regulated | GO:0031093 |
KEGG
Summary Plot
Venn Plot
List
| Intersection Combination | Overlapped Functional Terms |
|---|---|
| Up-Regulated ∪ Down-Regulated | |
| All ∪ Down-Regulated | hsa04060||hsa05164||hsa05323||hsa04061||hsa05321||hsa04668||hsa05162||hsa05169||hsa05140||hsa05332||hsa04658||hsa05152||hsa04640||hsa04380||hsa05160||hsa05133||hsa04620||hsa04625||hsa05167||hsa04630||hsa05171||hsa00240||hsa04940||hsa05166||hsa04062||hsa05161||hsa04672||hsa04659||hsa04931||hsa01232||hsa05134||hsa05165||hsa04657||hsa05330||hsa05150||hsa04151||hsa04933||hsa05219||hsa04622 |
| All ∪ Up-Regulated | |
| All ∪ Down-Regulated ∪ Up-Regulated |
Help
3. Isoform Switch Analysis
Alternative Splicing Events
Amount of Event
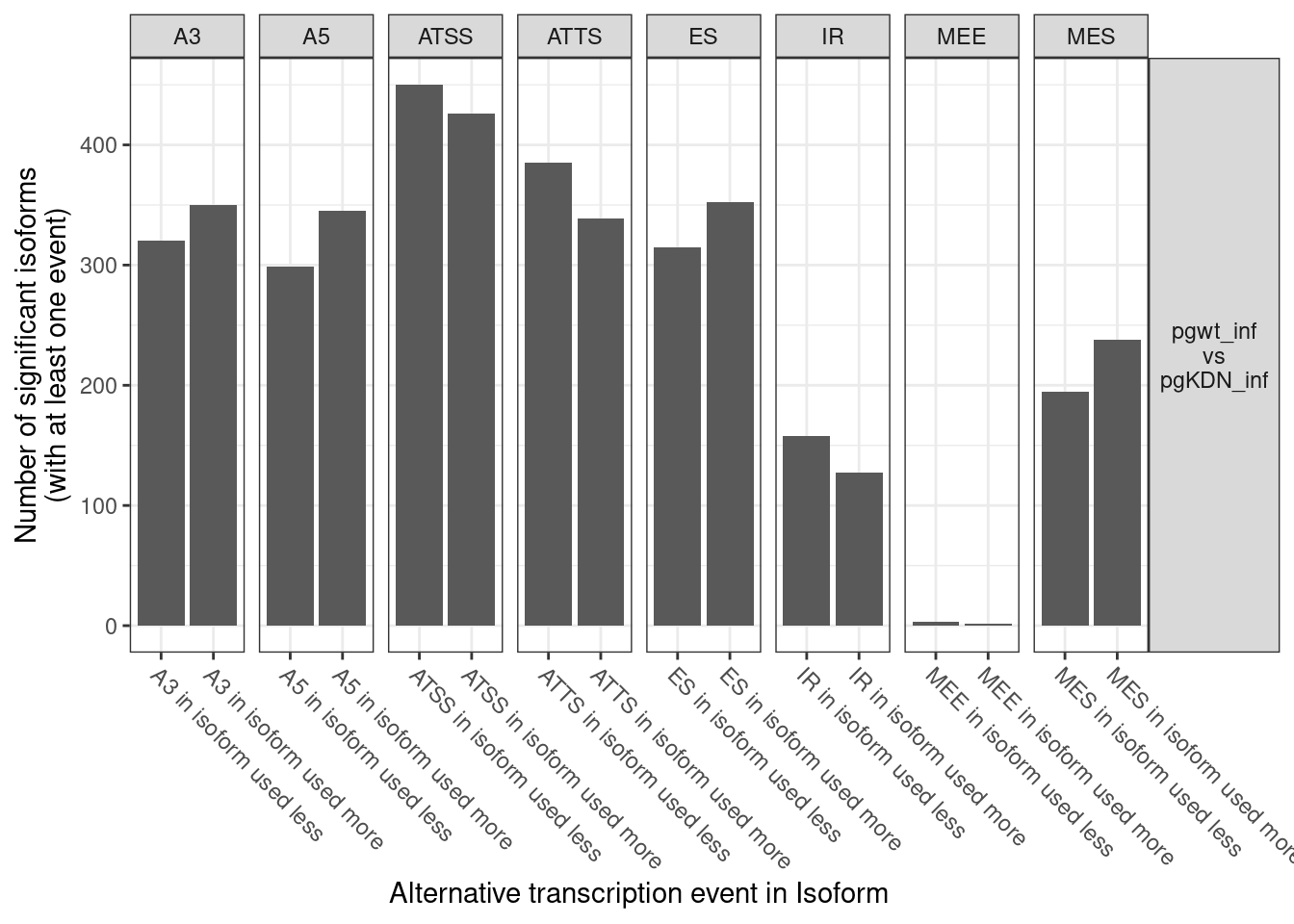
Enrichment Analysis
This below result summarizes the uneven usage within each comparison by for each alternative splicing type calculate the fraction of events being gains (as opposed to loss) and perform a statistical analysis of this fraction.
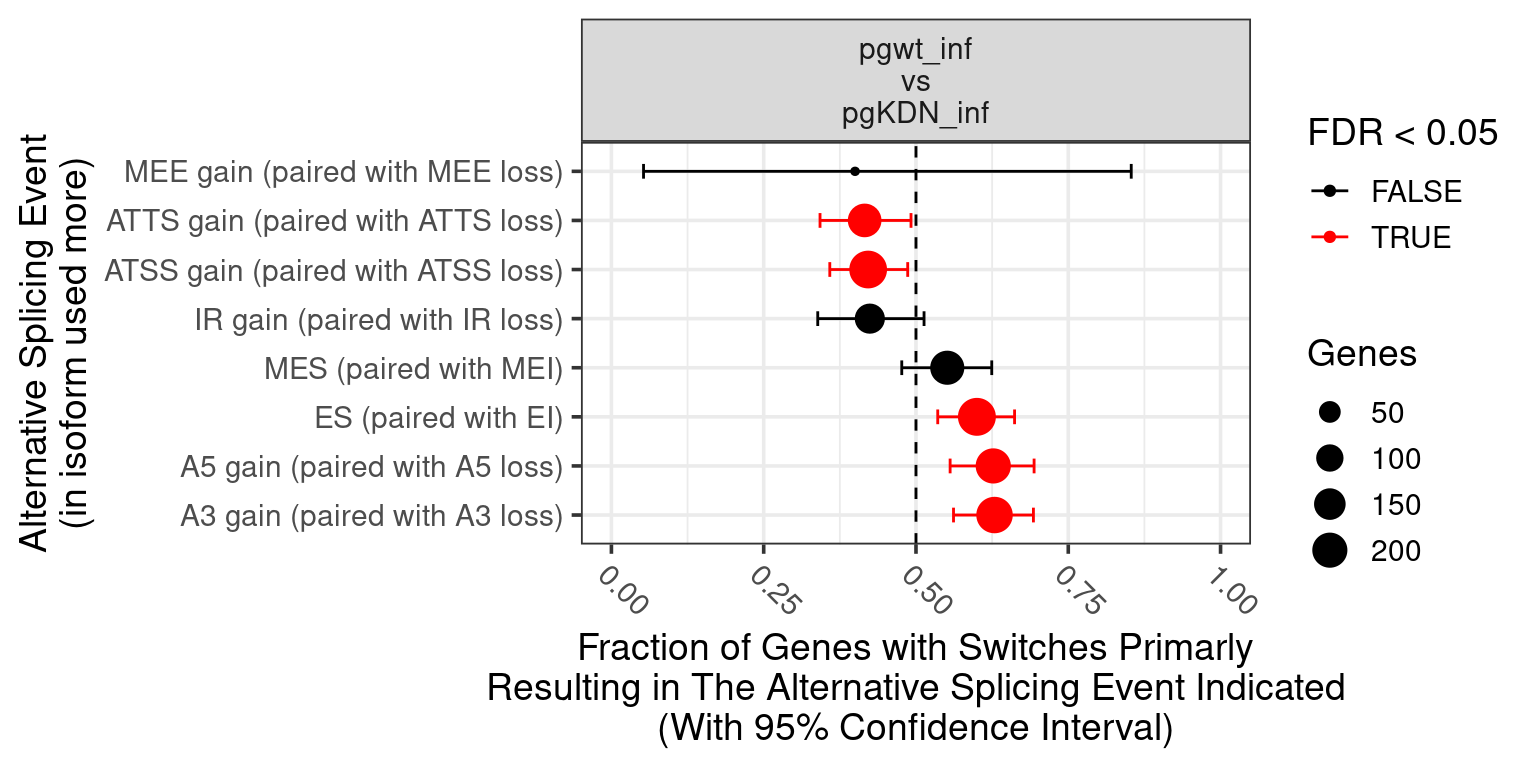
Comparison Analysis
This below result answered the question: How does the isoform usage of all isoforms utilizing a particular splicing type change - in other words is all isoforms or only a subset of isoforms that are affected.
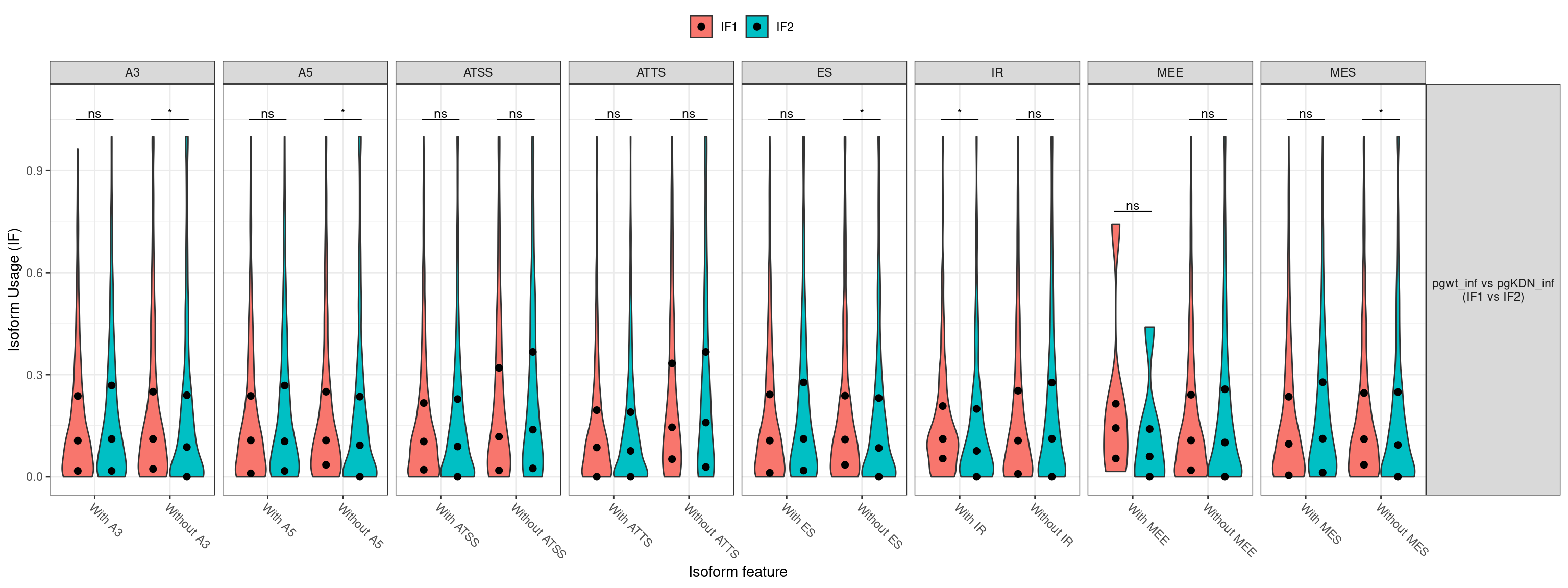
- Please note that:
- The the dots in the violin plots above indicate 25th, 50th (median) and 75th percentiles (just like the box in a boxplot would).
- The analysis provided here should only be expected to give a result when splicing is (severely) affected.
Abbreviations
- Abbreviations:
- IR : Intron Retention.
- A5 : Alternative 5’ donor site (changes in the 5’end of the upstream exon).
- A3 : Alternative 3’ acceptor site (changes in the 3’end of the downstream exon).
- ATSS : Alternative Transcription Start Site.
- ATTS : Alternative Transcription Termination Site.
- ES : Exon Skipping (EI means Exon Inclusion).
- MES : Multiple Exon Skipping. Skipping of >1 consecutive exons. (MEI means Multiple Exon Inclusion).
- MEE : Mutually Exclusive Exons.
Alternative Splicing Consequence
Amount of Event
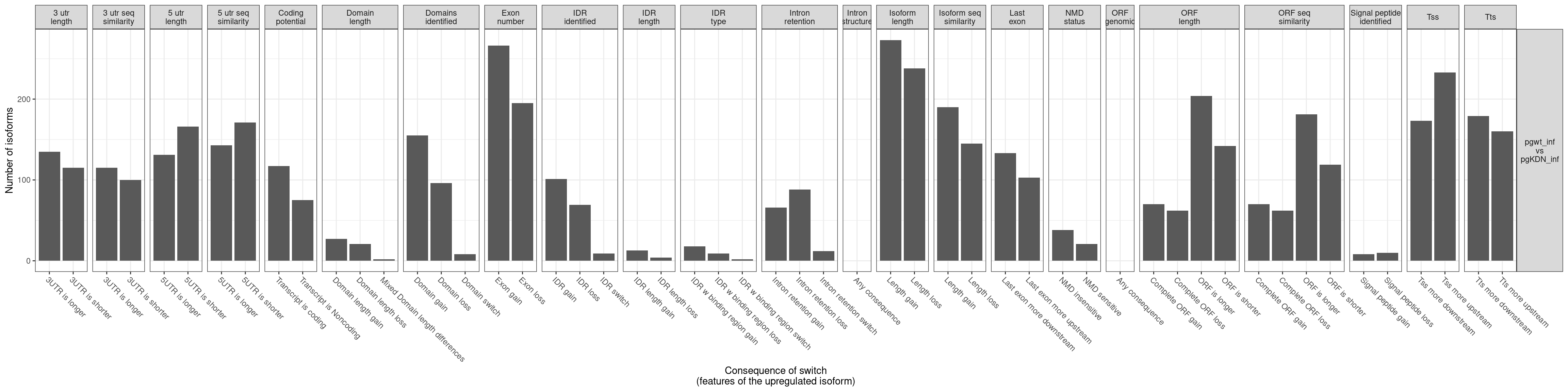
Enrichment Analysis
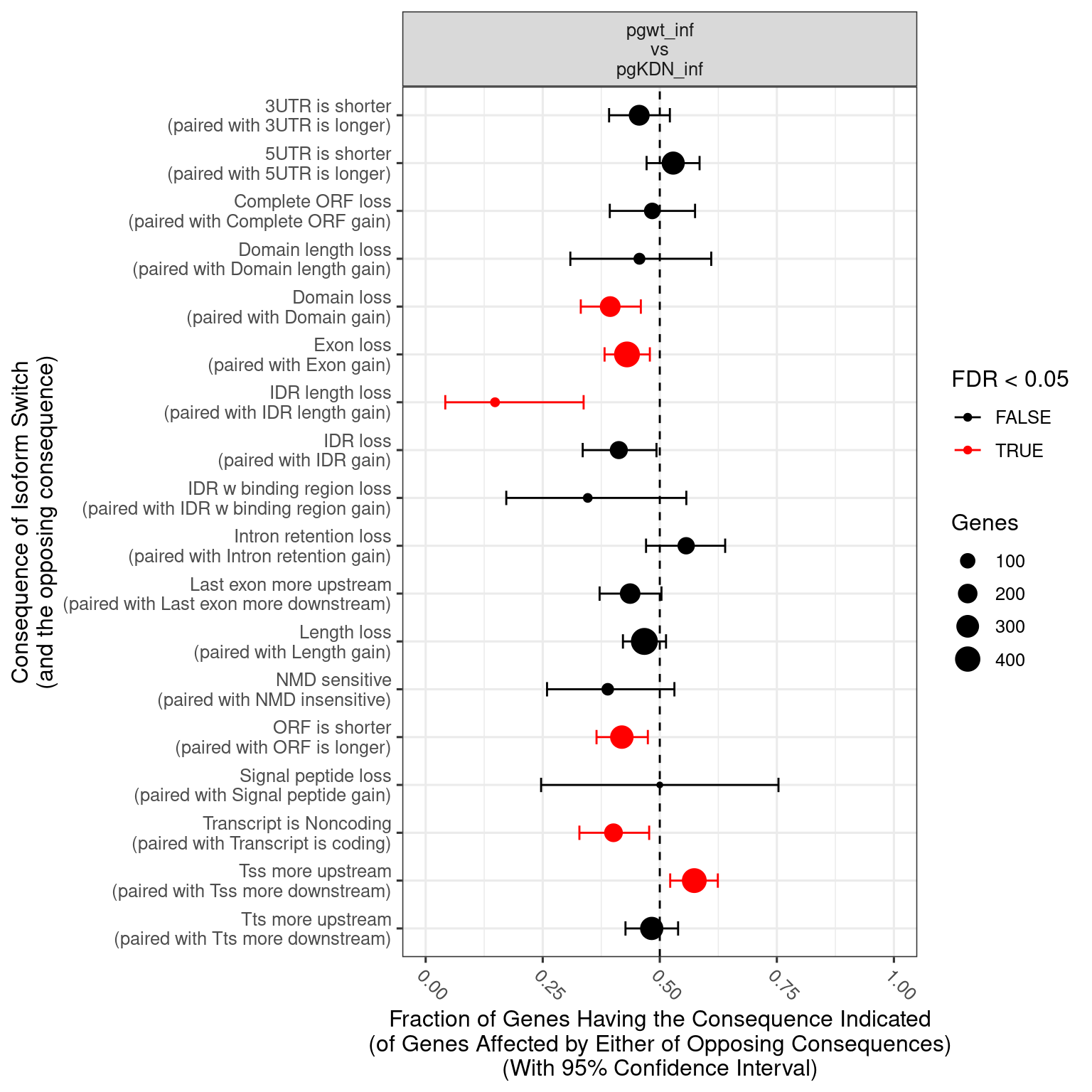
Comparison Analysis
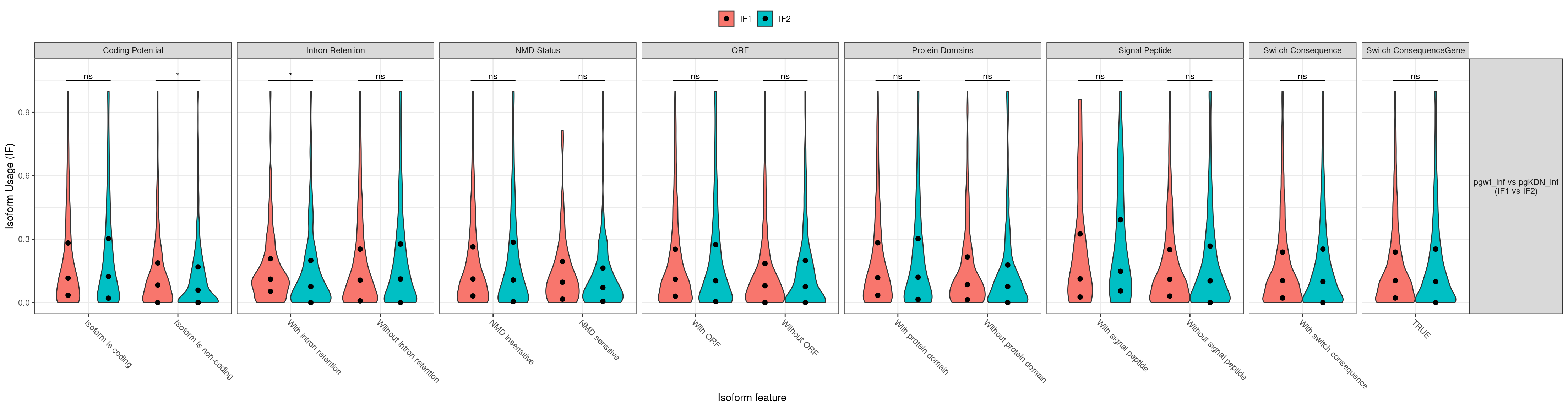
- Please note that:
- The the dots in the violin plots above indicate 25th, 50th (median) and 75th percentiles (just like the box in a boxplot would).
- The analysis provided here should only be expected to give a result when splicing is (severely) affected.
Abbreviations
- Abbreviations:
- tss : Test transcripts for whether they use different Transcription Start Site (TSS) (more than ntCutoff from each other).
- tts : Test transcripts for whether they use different Transcription Termination Site (TTS) (more than ntCutoff from each other).
- last_exon : Test whether transcripts utilizes different last exons (defined as the last exon of each transcript is non-overlapping).
- isoform_seq_similarity : Test whether the isoform nucleotide sequences are different (as described above). Reported as different if the measured JCsim is smaller than ntJCsimCutoff and the length difference of the aligned and combined region is larger than ntCutoff.
- isoform_length : Test transcripts for differences in isoform length. Only reported if the difference is larger than indicated by the ntCutoff and ntFracCutoff. Please * note that this is a less powerful analysis than implemented in ‘isoform_seq_similarity’ as two equally long sequences might be very different.
- exon_number : Test transcripts for differences in exon number.
- intron_structure : Test transcripts for differences in intron structure, e.g. usage of exon-exon junctions. This analysis corresponds to analyzing whether all introns in one isoform is also found in the other isoforms.
- intron_retention : Test for differences in intron retentions (and their genomic positions). Require that analyzeIntronRetention have been run.
- isoform_class_code : Test transcripts for differences in the transcript classification provide by cufflinks. For a updated list of class codes see http://cole-trapnell-lab.github.io/cufflinks/cuffcompare/#transfrag-class-codes.
- coding_potential : Test transcripts for differences in coding potential, as indicated by the CPAT or CPC2 analysis. Requires that analyzeCPAT or analyzeCPC2 have been used to add external conding potential analysis to the switchAnalyzeRlist.
- ORF_seq_similarity : Test whether the amino acid sequences of the ORFs are different (as described above). Reported as different if the measured JCsim is smaller than AaJCsimCutoff and the length difference of the aligned and combined region is larger than AaCutoff. Requires that least one of the isoforms are annotated with a ORF either via identifyORF or by supplying a GTF file and setting addAnnotatedORFs=TRUE when creating the switchAnalyzeRlist.
- ORF_genomic : Test transcripts for differences in genomic position of the Open Reading Frames (ORF). Requires that least one of the isoforms are annotated with an ORF either via identifyORF or by supplying a GTF file and settingaddAnnotatedORFs=TRUE when creating the switchAnalyzeRlist.
- ORF_length : Test transcripts for differences in length of Open Reading Frames (ORF). Note that this is a less powerful analysis than implemented in ORF_seq_similarity as two equally long sequences might be very different. Only reported if the difference is larger than indicated by the ntCutoff and ntFracCutoff. Requires that least one of the isoforms are annotated with a ORF either via identifyORF or by supplying a GTF file and setting addAnnotatedORFs=TRUE when creating the switchAnalyzeRlist.
- 5_utr_seq_similarity : Test whether the isoform nucleotide sequences of the 5’ UnTranslated Region (UTR) are different (as described above). The 5’UTR is defined as the region from the transcript start to the ORF start. Reported as different if the measured JCsim is smaller than ntJCsimCutoff and the length difference of the aligned and combined region is larger than ntCutoff. Requires that both the isoforms are annotated with an ORF either via identifyORF or by supplying a GTF file and setting addAnnotatedORFs=TRUE when creating the switchAnalyzeRlist.
- 5_utr_length : Test transcripts for differences in the length of the 5’ UnTranslated Region (UTR). The 5’UTR is defined as the region from the transcript start to the ORF start. Note that this is a less powerful analysis than implemented in ‘5_utr_seq_similarity’ as two equally long sequences might be very different. Only reported if the difference is larger than indicated by the ntCutoff and ntFracCutoff. Requires that both the isoforms are annotated with a ORF either via identifyORF or by supplying a GTF file and setting addAnnotatedORFs=TRUE when creating the switchAnalyzeRlist.
- 3_utr_seq_similarity : Test whether the isoform nucleotide sequences of the 3’ UnTranslated Region (UTR) are different (as described above). The 3’UTR is defined as the region from the end of the ORF to the transcript end. Reported as different if the measured JCsim is smaller than ntJCsimCutoff and the length difference of the aligned and combined region is larger than ntCutoff. Requires that both the isoforms are annotated with a ORF either via identifyORF or by supplying a GTF file and setting addAnnotatedORFs=TRUE when creating the switchAnalyzeRlist.
- 3_utr_length : Test transcripts for differences in the length of the 3’ UnTranslated Regions (UTR). The 3’UTR is defined as the region from the end of the ORF to the transcript end. Note that this is a less powerful analysis than implemented in 3_utr_seq_similarity as two equally long sequences might be very different. Requires that identifyORF have been used to predict NMD sensitivity or that the ORF was imported though one of the dedicated import functions implemented in isoformSwitchAnalyzeR. Only reported if the difference is larger than indicated by the ntCutoff and ntFracCutoff. Requires that both the isoforms are annotated with a ORF either via identifyORF or by supplying a GTF file and setting addAnnotatedORFs=TRUE when creating the switchAnalyzeRlist.
- NMD_status : Test transcripts for differences in sensitivity to Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD). Requires that both the isoforms have been annotated with PTC either via identifyORF or by supplying a GTF file and setting addAnnotatedORFs=TRUE when creating the switchAnalyzeRlist.
- domains_identified : Test transcripts for differences in the name and order of which domains are identified by the Pfam in the transcripts. Requires that analyzePFAM have been used to add external Pfam analysis to the switchAnalyzeRlist. Requires that both the isoforms are annotated with a ORF either via identifyORF or by supplying a GTF file and setting addAnnotatedORFs=TRUE when creating the switchAnalyzeRlist.
- domain_length : Test transcripts for differences in the length of overlapping domains of the same type (same hmm_name) thereby enabling analysis of protein domain truncation. Do however note that a small difference in length is will likely not truncate the protein domain. The length difference, measured in AA, must be larger than AaCutoff and AaFracCutoff .Requires that analyzePFAM have been used to add external Pfam analysis to the switchAnalyzeRlist. Requires that both the isoforms are annotated with a ORF either via identifyORF or by supplying a GTF file and setting addAnnotatedORFs=TRUE when creating the switchAnalyzeRlist.
- genomic_domain_position : Test transcripts for differences in the genomic position of the domains identified by the Pfam analysis (Will be different unless the two isoforms have the same domains at the same genomic location). Requires that analyzePFAM have been used to add external Pfam analysis to the switchAnalyzeRlist. Requires that both the isoforms are annotated with a ORF either via identifyORF or by supplying a GTF file and setting addAnnotatedORFs=TRUE when creating the switchAnalyzeRlist (and are thereby also affected by removeNoncodinORFs=TRUE in analyzeCPAT).
- IDR_identified : Test for differences in isoform IDRs. Specifically the two isoforms are analyzed for whether they contain IDRs which do not overlap in genomic coordinates. Requires that analyzeNetSurfP2 or analyzeIUPred2A have been used to add external IDR analysis to the switchAnalyzeRlist.
- IDR_length : Test for differences in the length of overlapping (in genomic coordinates) IDRs. The length difference, measured in AA, must be larger than AaCutoff and AaFracCutoff. Requires that analyzeNetSurfP2 or analyzeIUPred2A have been used to add external IDR analysis to the switchAnalyzeRlist.
- IDR_type : Test for differences in IDR type. Specifically the two isoforms are tested for overlapping IDRs (genomic coordinates) and overlapping IDRs are compared with regards to their IDR type (IDR vs IDR w binding site). Only available if analyzeIUPred2A was used to add external IDR analysis to the switchAnalyzeRlist.
- signal_peptide_identified : Test transcripts for differences in whether a signal peptide was identified or not by the SignalP analysis. Requires that analyzeSignalP have been used to add external SignalP analysis to the switchAnalyzeRlist. Requires that both the isoforms are annotated with a ORF either via analyzeORF or by supplying a GTF file and setting addAnnotatedORFs=TRUE when creating the switchAnalyzeRlist (and are thereby also affected by removeNoncodinORFs=TRUE in analyzeCPAT).
Volcano Plot
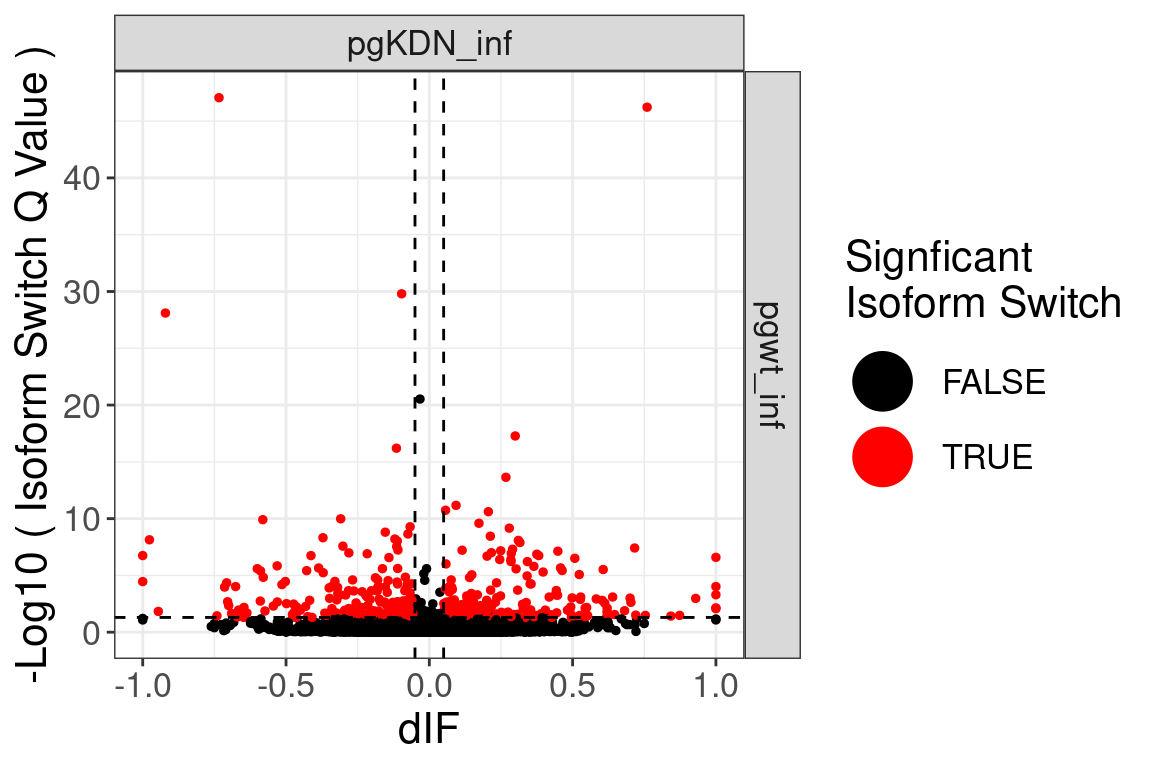
Spreadsheet
| iso_ref | gene_ref | isoform_id | gene_id | gene_name | condition_1 | condition_2 | IF1 | IF2 | dIF | isoform_switch_q_value | has.consequences |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| isoComp_00407444 | geneComp_00088656 | ENST00000674427 | ENSG00000180953 | ST20 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.734 | 0.000 | -0.734 | 0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008693102 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00410581 | geneComp_00089240 | ENST00000542727 | ENSG00000184445 | KNTC1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.760 | 0.760 | 0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000059450128 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00411330 | geneComp_00089380 | ENST00000567831 | ENSG00000185164 | NOMO2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.096 | 0.000 | -0.096 | 0.000000000000000000000000000001597026522795678723662098 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00308611 | geneComp_00075079 | MSTRG.23522.48 | ENSG00000006837 | CDKL3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.921 | 0.000 | -0.921 | 0.000000000000000000000000000078944233604896478076805844 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00358859 | geneComp_00081355 | ENST00000554546 | ENSG00000133961 | NUMB | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.300 | 0.300 | 0.000000000000000005267291892827672136187608340433072576 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00421613 | geneComp_00091294 | ENST00000464126 | ENSG00000204463 | BAG6 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.115 | 0.000 | -0.115 | 0.000000000000000062853187622461725341955872161937227510 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00374340 | geneComp_00083401 | MSTRG.27533.2 | ENSG00000147475 | ERLIN2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.267 | 0.267 | 0.000000000000022912869256175792890478486448870307971257 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00355536 | geneComp_00080938 | MSTRG.14496.8 | ENSG00000130816 | DNMT1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.093 | 0.093 | 0.000000000006805879646163393213948334488226071651607862 | |
| isoComp_00396781 | geneComp_00086729 | ENST00000302190 | ENSG00000169439 | SDC2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.916 | 0.973 | 0.057 | 0.000000000018332745363129656466838305156033701870388342 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00396208 | geneComp_00086631 | ENST00000381571 | ENSG00000169019 | COMMD8 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.794 | 1.000 | 0.206 | 0.000000000024347281742136570512348245777078242779722927 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00329489 | geneComp_00077528 | MSTRG.10565.18 | ENSG00000102858 | MGRN1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.309 | 0.000 | -0.309 | 0.000000000103324702514694225826301373744416827252234903 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00442861 | geneComp_00100553 | ENST00000292538 | ENSG00000257923 | CUX1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.581 | 0.000 | -0.581 | 0.000000000123143922808698247021233280141183034223084647 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00356516 | geneComp_00081060 | ENST00000578232 | ENSG00000131748 | STARD3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.173 | 0.173 | 0.000000000255744986801359145119754245862675814948694608 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00391850 | geneComp_00086024 | ENST00000532344 | ENSG00000166337 | TAF10 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.067 | 0.000 | -0.067 | 0.000000000522625482082539182056456327759913146890902169 | |
| isoComp_00327008 | geneComp_00077190 | ENST00000556007 | ENSG00000100575 | TIMM9 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.279 | 0.279 | 0.000000000691492754962659750839518176234723897954914662 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00336461 | geneComp_00078377 | ENST00000589769 | ENSG00000108883 | EFTUD2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.154 | 0.000 | -0.154 | 0.000000001562969279415427458665095500258551686201258235 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00355805 | geneComp_00080974 | ENST00000465158 | ENSG00000131051 | RBM39 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.075 | 0.000 | -0.075 | 0.000000002256287143827684761267419905083654596555930993 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00377942 | geneComp_00083896 | ENST00000538489 | ENSG00000152332 | UHMK1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.213 | 0.213 | 0.000000003531840432639746880691551171008342457913187218 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00351724 | geneComp_00080418 | ENST00000469302 | ENSG00000126216 | TUBGCP3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.371 | 0.000 | -0.371 | 0.000000004805786246460858791140989792600030083846718298 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00390871 | geneComp_00085860 | ENST00000447677 | ENSG00000165637 | VDAC2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.120 | 0.000 | -0.120 | 0.000000006235725303620802479478790427596182621705622751 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00438129 | geneComp_00098257 | MSTRG.4585.1 | ENSG00000247151 | CSTF3-DT | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.977 | 0.000 | -0.977 | 0.000000007289022957412077436383583922512030550677764040 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00311057 | geneComp_00075356 | ENST00000523045 | ENSG00000025770 | NCAPH2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.311 | 0.311 | 0.000000008273347673960917487110216486830005511166064025 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00370800 | geneComp_00082895 | ENST00000532105 | ENSG00000143575 | HAX1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.112 | 0.000 | -0.112 | 0.000000009322770674506622605562082702589099536538697066 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00398702 | geneComp_00087078 | ENST00000485122 | ENSG00000171311 | EXOSC1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.316 | 0.316 | 0.000000012647534233445748313552339976446187153058531294 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00340529 | geneComp_00078908 | ENST00000504133 | ENSG00000113360 | DROSHA | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.302 | 0.000 | -0.302 | 0.000000026452423073521589695937181185847464348626090214 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00410914 | geneComp_00089302 | ENST00000497630 | ENSG00000184787 | UBE2G2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.114 | 0.000 | -0.114 | 0.000000029006472573232634136649782971399680331359149932 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00406209 | geneComp_00088369 | ENST00000431792 | ENSG00000179029 | TMEM107 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.716 | 0.716 | 0.000000038542445738287073828075009022942065683992041158 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00311312 | geneComp_00075379 | MSTRG.22664.16 | ENSG00000028310 | BRD9 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.291 | 0.291 | 0.000000049593527135598207739063044167601712608473008004 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00322751 | geneComp_00076682 | ENST00000538223 | ENSG00000089053 | ANAPC5 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.109 | 0.000 | -0.109 | 0.000000057816396335128910036170332914853831063339839602 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00409125 | geneComp_00088963 | ENST00000498644 | ENSG00000182979 | MTA1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.114 | 0.114 | 0.000000060483339497675344926246748539916398001992092759 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00322462 | geneComp_00076642 | MSTRG.18118.1 | ENSG00000088325 | TPX2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.249 | 0.249 | 0.000000067728769805842297185953786598650028238921549928 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00407442 | geneComp_00088656 | ENST00000485386 | ENSG00000180953 | ST20 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.129 | 0.577 | 0.449 | 0.000000073797754556688003882936272102149866114473297785 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00341487 | geneComp_00079031 | ENST00000471751 | ENSG00000114520 | SNX4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.217 | 0.217 | 0.000000099151274601803264092937889671169893190949551354 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00312019 | geneComp_00075463 | ENST00000511050 | ENSG00000039319 | ZFYVE16 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.281 | 0.000 | -0.281 | 0.000000103103860181181237149026109350957725041553203482 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00424477 | geneComp_00092103 | ENST00000223136 | ENSG00000214253 | FIS1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.598 | 0.884 | 0.286 | 0.000000115149095384018475112043234688530279896667707362 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00438290 | geneComp_00098293 | ENST00000697437 | ENSG00000247774 | PCED1B-AS1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.217 | 0.000 | -0.217 | 0.000000123451120764344634720766427649074614691926399246 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00398800 | geneComp_00087104 | ENST00000306058 | ENSG00000171456 | ASXL1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.375 | 0.375 | 0.000000136008745801811643510783873638192442712124829995 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00455128 | geneComp_00108587 | ENST00000675225 | ENSG00000288612 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 1.000 | 0.000 | -1.000 | 0.000000179725739145519661761423411971971830780603340827 | TRUE | |
| isoComp_00378202 | geneComp_00083943 | MSTRG.16051.3 | ENSG00000152683 | SLC30A6 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.382 | 0.382 | 0.000000180321485438798406722554746282882742747233351110 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00381967 | geneComp_00084485 | ENST00000539736 | ENSG00000157895 | C12orf43 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.413 | 0.000 | -0.413 | 0.000000180321485438798406722554746282882742747233351110 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00413986 | geneComp_00089879 | MSTRG.783.5 | ENSG00000187815 | ZFP69 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.202 | 0.202 | 0.000000202366456337327072963419983923916145585053527611 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00455129 | geneComp_00108587 | ENST00000676390 | ENSG00000288612 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.000000256081481121306949769823651727462809901680884650 | TRUE | |
| isoComp_00437092 | geneComp_00097934 | MSTRG.18747.1 | ENSG00000243927 | MRPS6 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.141 | 0.000 | -0.141 | 0.000000268036672125579312671181603580650154583508992800 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00346882 | geneComp_00079711 | ENST00000239231 | ENSG00000120137 | PANK3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.492 | 1.000 | 0.508 | 0.000000312079871963171098302820740538754407111809996422 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00319081 | geneComp_00076245 | ENST00000221283 | ENSG00000076944 | STXBP2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.454 | 0.700 | 0.246 | 0.000000402765060723283312660531006038633350385680387262 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00416992 | geneComp_00090456 | ENST00000370406 | ENSG00000197021 | EOLA2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.284 | 0.284 | 0.000000410854602206810261632268085549291036784325115150 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00355223 | geneComp_00080906 | ENST00000372350 | ENSG00000130713 | EXOSC2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.285 | 0.285 | 0.000000604520297748443428936099535569992369232750206720 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00447913 | geneComp_00103505 | ENST00000612022 | ENSG00000269556 | TMEM185A | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.342 | 0.342 | 0.000000604520297748443428936099535569992369232750206720 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00345920 | geneComp_00079585 | MSTRG.15838.10 | ENSG00000119185 | ITGB1BP1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.058 | 0.058 | 0.000000978269755285860380543861043733944171663097222336 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00375382 | geneComp_00083538 | ENST00000492266 | ENSG00000148824 | MTG1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.531 | 0.000 | -0.531 | 0.000001444004766624514417801337755331569923100687447004 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00335291 | geneComp_00078239 | ENST00000468544 | ENSG00000107833 | NPM3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.365 | 0.365 | 0.000001580219436430649460661383536030921703741114470176 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00409940 | geneComp_00089109 | ENST00000488860 | ENSG00000183763 | TRAIP | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.458 | 0.458 | 0.000002179284545539202737736645190680384587267326423898 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00420416 | geneComp_00091016 | ENST00000531313 | ENSG00000198945 | L3MBTL3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.386 | 0.000 | -0.386 | 0.000002220590041624383716926515591749691225231799762696 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00308961 | geneComp_00075124 | MSTRG.12946.10 | ENSG00000008294 | SPAG9 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.110 | 0.000 | -0.110 | 0.000002456076604530435665666191977218879571864817989990 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00327608 | geneComp_00077249 | ENST00000419198 | ENSG00000100908 | EMC9 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.600 | 0.000 | -0.600 | 0.000002545432730911401680742693620640437757174368016422 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00370117 | geneComp_00082804 | ENST00000495447 | ENSG00000143198 | MGST3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.164 | 0.000 | -0.164 | 0.000002545432730911401680742693620640437757174368016422 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00421966 | geneComp_00091357 | MSTRG.15522.49 | ENSG00000204673 | AKT1S1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.006 | 0.309 | 0.303 | 0.000002645830960548055526561882222491561833521700464189 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00401473 | geneComp_00087511 | ENST00000591241 | ENSG00000173581 | CCDC106 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.607 | 0.607 | 0.000003016496050989191873381665282005670292164722923189 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00376736 | geneComp_00083717 | MSTRG.22690.3 | ENSG00000150756 | ATPSCKMT | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.464 | 0.464 | 0.000003716557268503014874655226637556459934330632677302 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00402374 | geneComp_00087677 | MSTRG.14471.11 | ENSG00000174652 | ZNF266 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.428 | 0.000 | -0.428 | 0.000003795670906118581705562938996556532345039158826694 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00397775 | geneComp_00086897 | MSTRG.19646.2 | ENSG00000170364 | SETMAR | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.589 | 0.000 | -0.589 | 0.000004026435000521514813161087775750246464667725376785 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00348068 | geneComp_00079897 | ENST00000369717 | ENSG00000121933 | TMIGD3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.397 | 0.397 | 0.000005038970552715478844294384047630686040974978823215 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00336894 | geneComp_00078426 | ENST00000510408 | ENSG00000109381 | ELF2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.370 | 0.000 | -0.370 | 0.000005783444465516560728860200740752972592417791020125 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00423871 | geneComp_00091937 | ENST00000416649 | ENSG00000213672 | NCKIPSD | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.523 | 0.523 | 0.000008361628172176142868312308242817465497864759527147 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00311219 | geneComp_00075372 | ENST00000696693 | ENSG00000027697 | IFNGR1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.118 | 0.266 | 0.148 | 0.000008794375680393897324401038251284745683733490295708 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00377542 | geneComp_00083830 | MSTRG.6295.4 | ENSG00000151743 | AMN1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.341 | 0.341 | 0.000011133963569408087686913796932053344335145084187388 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00388125 | geneComp_00085409 | ENST00000471012 | ENSG00000163874 | ZC3H12A | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.084 | 0.000 | -0.084 | 0.000014353226195971129531148841040888441966671962291002 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00406207 | geneComp_00088369 | ENST00000316425 | ENSG00000179029 | TMEM107 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.580 | 0.000 | -0.580 | 0.000014772742233960760909676317165217795945864054374397 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00341927 | geneComp_00079084 | ENST00000264963 | ENSG00000114988 | LMAN2L | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.860 | 1.000 | 0.140 | 0.000015381190684837115769615506488676714980101678520441 | |
| isoComp_00396210 | geneComp_00086631 | MSTRG.21714.2 | ENSG00000169019 | COMMD8 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.188 | 0.000 | -0.188 | 0.000016139979837685153167027574117042831858270801603794 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00329520 | geneComp_00077532 | ENST00000219150 | ENSG00000102879 | CORO1A | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.846 | 0.923 | 0.076 | 0.000024973399090192804526070619042243947660608682781458 | |
| isoComp_00355866 | geneComp_00080978 | ENST00000624538 | ENSG00000131089 | ARHGEF9 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.268 | 0.000 | -0.268 | 0.000024973399090192804526070619042243947660608682781458 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00369690 | geneComp_00082724 | MSTRG.184.21 | ENSG00000142599 | RERE | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.180 | 0.000 | -0.180 | 0.000024973399090192804526070619042243947660608682781458 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00333508 | geneComp_00077989 | ENST00000522223 | ENSG00000105808 | RASA4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.144 | 0.000 | -0.144 | 0.000028752612507503743575739199589413885860267328098416 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00319459 | geneComp_00076288 | ENST00000398654 | ENSG00000078043 | PIAS2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.329 | 0.000 | -0.329 | 0.000033774863295183426171054003050997494028706569224596 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00398561 | geneComp_00087051 | ENST00000470245 | ENSG00000171169 | NAIF1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.502 | 0.000 | -0.502 | 0.000034401616931782161182100387986082523639197461307049 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00362608 | geneComp_00081830 | ENST00000259205 | ENSG00000136688 | IL36G | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 1.000 | 0.000 | -1.000 | 0.000034861369443573488611023969419022705551469698548317 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00424189 | geneComp_00092036 | ENST00000554977 | ENSG00000213983 | AP1G2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.112 | 0.000 | -0.112 | 0.000038403769537053239154812678268768877387628890573978 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00350170 | geneComp_00080188 | ENST00000416795 | ENSG00000124508 | BTN2A2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.707 | 0.000 | -0.707 | 0.000044765225178454383283405126903176096675451844930649 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00400967 | geneComp_00087427 | ENST00000533715 | ENSG00000173137 | ADCK5 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.235 | 0.235 | 0.000044765225178454383283405126903176096675451844930649 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00409120 | geneComp_00088963 | ENST00000481012 | ENSG00000182979 | MTA1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.062 | 0.000 | -0.062 | 0.000054795681412008273255577484039946511984453536570072 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00310929 | geneComp_00075339 | ENST00000526521 | ENSG00000023697 | DERA | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.352 | 0.352 | 0.000055167584780575880333466226579375302208063658326864 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00340854 | geneComp_00078951 | ENST00000513318 | ENSG00000113716 | HMGXB3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.077 | 0.000 | -0.077 | 0.000056428579569010638226477655221557938602927606552839 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00346976 | geneComp_00079732 | MSTRG.23674.7 | ENSG00000120318 | ARAP3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.355 | 0.355 | 0.000056428579569010638226477655221557938602927606552839 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00330100 | geneComp_00077592 | ENST00000645024 | ENSG00000103197 | TSC2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.111 | 0.000 | -0.111 | 0.000056470427333697616049165007856558418097847606986761 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00339213 | geneComp_00078712 | ENST00000645988 | ENSG00000111817 | DSE | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.514 | 0.000 | -0.514 | 0.000064289858901515089975413352885169615547056309878826 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00343358 | geneComp_00079242 | MSTRG.16469.18 | ENSG00000116001 | TIA1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.070 | 0.070 | 0.000094594093273461311074251645081290007510688155889511 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00310906 | geneComp_00075334 | ENST00000310271 | ENSG00000023330 | ALAS1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.296 | 0.119 | -0.177 | 0.000095255341361251503204746193809171472821617498993874 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00312137 | geneComp_00075475 | ENST00000416372 | ENSG00000040608 | RTN4R | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.000095255341361251503204746193809171472821617498993874 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00342879 | geneComp_00079194 | ENST00000393352 | ENSG00000115641 | FHL2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.676 | 0.000 | -0.676 | 0.000095255341361251503204746193809171472821617498993874 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00387066 | geneComp_00085249 | ENST00000682957 | ENSG00000163359 | COL6A3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.153 | 0.000 | -0.153 | 0.000099976772583442919295655670897104982941527850925922 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00418165 | geneComp_00090645 | ENST00000561564 | ENSG00000197774 | EME2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.342 | 0.000 | -0.342 | 0.000099976772583442919295655670897104982941527850925922 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00351280 | geneComp_00080348 | ENST00000398425 | ENSG00000125814 | NAPB | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.714 | 0.000 | -0.714 | 0.000106343395623394594258839807032757107663201168179512 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00348580 | geneComp_00079951 | ENST00000309315 | ENSG00000122515 | ZMIZ2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.070 | 0.070 | 0.000111333710516118555562507796974358598163235001266003 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00411333 | geneComp_00089380 | ENST00000620440 | ENSG00000185164 | NOMO2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.837 | 0.915 | 0.078 | 0.000111333710516118555562507796974358598163235001266003 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00392840 | geneComp_00086177 | ENST00000679624 | ENSG00000166949 | SMAD3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.320 | 0.000 | -0.320 | 0.000113992717082785337961992055966220505069941282272339 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00317996 | geneComp_00076128 | ENST00000464166 | ENSG00000073792 | IGF2BP2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.180 | 0.000 | -0.180 | 0.000115480752335223415313419925709581548289861530065536 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00406952 | geneComp_00088521 | ENST00000582437 | ENSG00000180011 | PTGR3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.349 | 0.000 | -0.349 | 0.000125793273251225540525916057887911847501527518033981 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00412252 | geneComp_00089534 | ENST00000543660 | ENSG00000185864 | NPIPB4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.081 | 0.000 | -0.081 | 0.000142984448366435150986480939749867502541746944189072 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00392766 | geneComp_00086164 | ENST00000353703 | ENSG00000166913 | YWHAB | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.900 | 0.956 | 0.057 | 0.000148685074844403044853208273323730281845200806856155 | |
| isoComp_00376062 | geneComp_00083619 | MSTRG.4849.1 | ENSG00000149541 | B3GAT3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.080 | 0.080 | 0.000173968965749568896250742966458346927538514137268066 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00356328 | geneComp_00081036 | ENST00000431508 | ENSG00000131503 | ANKHD1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.214 | 0.214 | 0.000196943685130912711500617007231994648464024066925049 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00432572 | geneComp_00095813 | MSTRG.24431.5 | ENSG00000234127 | TRIM26 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.686 | 0.995 | 0.308 | 0.000197177981341403930513542230862356063880724832415581 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00320696 | geneComp_00076428 | ENST00000262188 | ENSG00000082014 | SMARCD3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.443 | 0.443 | 0.000213441676956824911504453923249968738673487678170204 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00327293 | geneComp_00077222 | ENST00000554691 | ENSG00000100731 | PCNX1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.282 | 0.000 | -0.282 | 0.000219088467900734257861466991457177755364682525396347 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00326301 | geneComp_00077103 | ENST00000337554 | ENSG00000100300 | TSPO | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.940 | 0.738 | -0.202 | 0.000222357895985734620083323909156547415477689355611801 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00342357 | geneComp_00079139 | ENST00000317610 | ENSG00000115310 | RTN4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.930 | 0.845 | -0.086 | 0.000222357895985734620083323909156547415477689355611801 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00338068 | geneComp_00078571 | ENST00000537407 | ENSG00000110801 | PSMD9 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.069 | 0.069 | 0.000230600091344301989793041940401963074691593647003174 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00351548 | geneComp_00080402 | ENST00000425525 | ENSG00000126001 | CEP250 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.182 | 0.000 | -0.182 | 0.000231480417378966538870591063137283072137506678700447 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00414251 | geneComp_00089956 | ENST00000468582 | ENSG00000188186 | LAMTOR4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.317 | 0.053 | -0.263 | 0.000233472235640395329179033745425897450331831350922585 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00332092 | geneComp_00077808 | ENST00000291270 | ENSG00000104936 | DMPK | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.234 | 0.000 | -0.234 | 0.000271975068706483357437730941086329039535485208034515 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00360288 | geneComp_00081546 | MSTRG.7287.6 | ENSG00000135090 | TAOK3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.070 | 0.070 | 0.000283673752759040721706934595758298200962599366903305 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00433267 | geneComp_00096135 | ENST00000525101 | ENSG00000235173 | HGH1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.147 | 0.000 | -0.147 | 0.000312595803256492934737997835270562063669785857200623 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00417313 | geneComp_00090497 | ENST00000577724 | ENSG00000197170 | PSMD12 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.067 | 0.000 | -0.067 | 0.000346482237562565817921844679716514292522333562374115 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00344684 | geneComp_00079418 | ENST00000310955 | ENSG00000117399 | CDC20 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.628 | 0.774 | 0.147 | 0.000385936228109495457500727200184087450907099992036819 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00370813 | geneComp_00082896 | ENST00000468845 | ENSG00000143578 | CREB3L4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.319 | 0.000 | -0.319 | 0.000385936228109495457500727200184087450907099992036819 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00362609 | geneComp_00081830 | ENST00000376489 | ENSG00000136688 | IL36G | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.000503117034376904834029609059342647015000693500041962 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00343301 | geneComp_00079238 | ENST00000407351 | ENSG00000115970 | THADA | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.014 | 0.454 | 0.440 | 0.000512390682219018627971407475740761583438143134117126 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00334605 | geneComp_00078143 | ENST00000413712 | ENSG00000106771 | TMEM245 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.168 | 0.168 | 0.000512687135727971023298199515494388833758421242237091 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00399033 | geneComp_00087138 | ENST00000424679 | ENSG00000171606 | ZNF274 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.311 | 0.000 | -0.311 | 0.000522721289055538373795328777049462587456218898296356 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00393345 | geneComp_00086247 | MSTRG.13437.7 | ENSG00000167302 | TEPSIN | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.292 | 0.000 | -0.292 | 0.000533337301813669915039051172556128221913240849971771 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00314895 | geneComp_00075786 | ENST00000261369 | ENSG00000064652 | SNX24 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.447 | 0.447 | 0.000560203383325555653686478319031039063702337443828583 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00401077 | geneComp_00087445 | ENST00000672303 | ENSG00000173214 | MFSD4B | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.221 | 0.000 | -0.221 | 0.000579451782821344347010339426162772724637761712074280 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00322912 | geneComp_00076702 | ENST00000261735 | ENSG00000089248 | ERP29 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.645 | 0.893 | 0.249 | 0.000635093644981895894159606985596155936946161091327667 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00330852 | geneComp_00077673 | ENST00000220325 | ENSG00000103966 | EHD4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.865 | 0.996 | 0.130 | 0.000648371988889706357857278806733347664703615009784698 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00315626 | geneComp_00075873 | ENST00000334379 | ENSG00000066651 | TRMT11 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.047 | 0.687 | 0.640 | 0.000795828193478416282859166930307992515736259520053864 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00323316 | geneComp_00076745 | ENST00000261233 | ENSG00000090376 | IRAK3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.159 | 0.687 | 0.528 | 0.000800627155323075843061653156240708995028398931026459 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00367549 | geneComp_00082483 | ENST00000696327 | ENSG00000140598 | EFL1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.418 | 0.418 | 0.000800627155323075843061653156240708995028398931026459 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00402946 | geneComp_00087768 | ENST00000376285 | ENSG00000175198 | PCCA | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.216 | 0.000 | -0.216 | 0.000824275706324491372507801134617011484806425869464874 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00326357 | geneComp_00077112 | MSTRG.19332.4 | ENSG00000100320 | RBFOX2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.235 | 0.235 | 0.000910434156623220257158191071056307919207029044628143 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00350751 | geneComp_00080280 | ENST00000245457 | ENSG00000125384 | PTGER2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.502 | 1.000 | 0.498 | 0.000951111897373095138523424463272704088012687861919403 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00402826 | geneComp_00087751 | MSTRG.12072.12 | ENSG00000175106 | TVP23C | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.701 | 0.701 | 0.000995800117412382794837566457601951697142794728279114 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00381263 | geneComp_00084393 | ENST00000568738 | ENSG00000157045 | NTAN1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.368 | 0.020 | -0.348 | 0.001037150354089922017764013872920259018428623676300049 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00452723 | geneComp_00106869 | ENST00000684111 | ENSG00000284308 | C2orf81 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.929 | 0.929 | 0.001058180445194159460114979864897577499505132436752319 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00353875 | geneComp_00080719 | ENST00000250024 | ENSG00000129173 | E2F8 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.417 | 1.000 | 0.583 | 0.001174831786609827500439395819853416469413787126541138 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00318732 | geneComp_00076204 | ENST00000660898 | ENSG00000075711 | DLG1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.175 | 0.000 | -0.175 | 0.001209978047785886584239434249354872008552774786949158 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00441493 | geneComp_00099831 | ENST00000531742 | ENSG00000254873 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.868 | 1.000 | 0.132 | 0.001247080564948739936359523028386320220306515693664551 | TRUE | |
| isoComp_00368632 | geneComp_00082599 | MSTRG.11925.18 | ENSG00000141503 | MINK1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.207 | 0.000 | -0.207 | 0.001301027559964388399110779559464390331413596868515015 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00354676 | geneComp_00080835 | ENST00000526092 | ENSG00000130270 | ATP8B3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.527 | 0.527 | 0.001304719886863798519391344221673989522969350218772888 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00398346 | geneComp_00087007 | ENST00000418871 | ENSG00000170949 | ZNF160 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.323 | 0.000 | -0.323 | 0.001428127197780924622846909777251767081907019019126892 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00403549 | geneComp_00087868 | ENST00000322623 | ENSG00000175792 | RUVBL1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.911 | 0.998 | 0.087 | 0.001428127197780924622846909777251767081907019019126892 | |
| isoComp_00358587 | geneComp_00081331 | MSTRG.23717.20 | ENSG00000133706 | LARS1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.075 | 0.000 | -0.075 | 0.001440286532443147988341580756355142511893063783645630 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00393471 | geneComp_00086264 | ENST00000472468 | ENSG00000167397 | VKORC1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.060 | 0.000 | -0.060 | 0.001521028524188803264516334223799276514910161495208740 | |
| isoComp_00393728 | geneComp_00086290 | ENST00000686151 | ENSG00000167548 | KMT2D | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.001549354466055172501598446999082625552546232938766479 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00320707 | geneComp_00076428 | ENST00000496530 | ENSG00000082014 | SMARCD3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.417 | 0.000 | -0.417 | 0.001560186786129301060241370002756866597337648272514343 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00363554 | geneComp_00081972 | ENST00000477052 | ENSG00000137411 | VARS2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.603 | 0.603 | 0.001560186786129301060241370002756866597337648272514343 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00368429 | geneComp_00082574 | ENST00000542420 | ENSG00000141380 | SS18 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.001 | 0.079 | 0.078 | 0.001643574353994392469452412441910382767673581838607788 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00323892 | geneComp_00076818 | ENST00000554373 | ENSG00000092036 | HAUS4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.091 | 0.000 | -0.091 | 0.001737702330117001483025807040405652514891698956489563 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00406596 | geneComp_00088449 | ENST00000618878 | ENSG00000179528 | LBX2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.590 | 0.000 | -0.590 | 0.001813483056133688908415080298652810597559437155723572 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00391047 | geneComp_00085888 | ENST00000354185 | ENSG00000165732 | DDX21 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.828 | 0.982 | 0.154 | 0.001977986196182097630713592195661476580426096916198730 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00383801 | geneComp_00084757 | ENST00000439227 | ENSG00000160211 | G6PD | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.111 | 0.000 | -0.111 | 0.002023272757011647816210997419261730101425200700759888 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00341256 | geneComp_00079007 | ENST00000232424 | ENSG00000114315 | HES1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.917 | 1.000 | 0.083 | 0.002070359035326790452663514585651682864408940076828003 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00434483 | geneComp_00096711 | ENST00000606165 | ENSG00000237187 | NR2F1-AS1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.803 | 0.099 | -0.704 | 0.002070359035326790452663514585651682864408940076828003 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00434713 | geneComp_00096798 | ENST00000585768 | ENSG00000237491 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.530 | 0.000 | -0.530 | 0.002170350051410110687327703615778773382771760225296021 | TRUE | |
| isoComp_00311207 | geneComp_00075372 | ENST00000367739 | ENSG00000027697 | IFNGR1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.789 | 0.619 | -0.170 | 0.002178151085678932397105000973169808275997638702392578 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00316756 | geneComp_00076001 | MSTRG.14147.5 | ENSG00000070423 | RNF126 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.067 | 0.067 | 0.002178151085678932397105000973169808275997638702392578 | |
| isoComp_00441576 | geneComp_00099876 | MSTRG.23636.9 | ENSG00000254996 | ANKHD1-EIF4EBP3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.155 | 0.000 | -0.155 | 0.002248313802375872822586488908314095169771462678909302 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00332135 | geneComp_00077811 | MSTRG.15523.5 | ENSG00000104946 | TBC1D17 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.002287165459768208172069980932405997009482234716415405 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00406050 | geneComp_00088348 | ENST00000372433 | ENSG00000178922 | HYI | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.231 | 0.231 | 0.002302639854840247187611756984892963373567909002304077 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00333792 | geneComp_00078029 | MSTRG.25743.6 | ENSG00000106003 | LFNG | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.127 | 0.000 | -0.127 | 0.002329913057884392020568942172076276619918644428253174 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00431640 | geneComp_00095387 | MSTRG.22592.1 | ENSG00000232648 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.703 | 0.703 | 0.002347906913937234350819860395631621940992772579193115 | TRUE | |
| isoComp_00368101 | geneComp_00082537 | ENST00000582565 | ENSG00000141027 | NCOR1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.157 | 0.000 | -0.157 | 0.002378572529570759878231323014574627450201660394668579 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00346152 | geneComp_00079614 | ENST00000398805 | ENSG00000119471 | HSDL2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.642 | 0.980 | 0.338 | 0.002415284940385456751571480182860796048771589994430542 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00324013 | geneComp_00076828 | ENST00000553700 | ENSG00000092148 | HECTD1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.076 | 0.076 | 0.002542190349949723440770021909429488005116581916809082 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00387701 | geneComp_00085348 | ENST00000417128 | ENSG00000163681 | SLMAP | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.256 | 0.000 | -0.256 | 0.002650731165361087590670585711905005155131220817565918 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00404343 | geneComp_00088032 | ENST00000582953 | ENSG00000176927 | EFCAB5 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.612 | 0.612 | 0.002815259714068491913446790064767810690682381391525269 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00417489 | geneComp_00090527 | ENST00000478032 | ENSG00000197323 | TRIM33 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.143 | 0.143 | 0.002848613248866638508055570966348568617831915616989136 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00416001 | geneComp_00090315 | ENST00000548571 | ENSG00000196465 | MYL6B | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.864 | 0.915 | 0.051 | 0.002973470785296486451620978641585679724812507629394531 | |
| isoComp_00424664 | geneComp_00092178 | ENST00000489234 | ENSG00000214655 | ZSWIM8 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.088 | 0.000 | -0.088 | 0.002973470785296486451620978641585679724812507629394531 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00408703 | geneComp_00088885 | ENST00000514322 | ENSG00000182552 | RWDD4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.138 | 0.138 | 0.002979216115159530591655068221257351979147642850875854 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00350752 | geneComp_00080280 | ENST00000557436 | ENSG00000125384 | PTGER2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.498 | 0.000 | -0.498 | 0.003040046174369996981323716056522243889048695564270020 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00401342 | geneComp_00087494 | MSTRG.20096.4 | ENSG00000173473 | SMARCC1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.078 | 0.000 | -0.078 | 0.003040046174369996981323716056522243889048695564270020 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00393531 | geneComp_00086272 | ENST00000591446 | ENSG00000167470 | MIDN | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.545 | 0.071 | -0.473 | 0.003323124095982059322818003010979737155139446258544922 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00414247 | geneComp_00089956 | ENST00000341942 | ENSG00000188186 | LAMTOR4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.407 | 0.733 | 0.325 | 0.003469888426406835153781305081110986066050827503204346 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00412398 | geneComp_00089567 | ENST00000414675 | ENSG00000186001 | LRCH3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.150 | 0.150 | 0.003491587619490924693232969389100617263466119766235352 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00356272 | geneComp_00081025 | ENST00000590720 | ENSG00000131467 | PSME3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.867 | 0.979 | 0.112 | 0.003744659522031246797618697641496510186698287725448608 | |
| isoComp_00330140 | geneComp_00077595 | MSTRG.10730.10 | ENSG00000103222 | ABCC1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.098 | 0.000 | -0.098 | 0.004058075531901606490536860150086795329116284847259521 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00337779 | geneComp_00078543 | ENST00000531190 | ENSG00000110455 | ACCS | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.149 | 0.000 | -0.149 | 0.004171226545833009100028299087625782703980803489685059 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00311781 | geneComp_00075432 | ENST00000262768 | ENSG00000035862 | TIMP2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.960 | 0.745 | -0.215 | 0.004331955193188053408748228179092620848678052425384521 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00334972 | geneComp_00078192 | ENST00000371605 | ENSG00000107331 | ABCA2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.006 | 0.186 | 0.180 | 0.004494522175169135200234471483327070018276572227478027 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00423869 | geneComp_00091937 | ENST00000294129 | ENSG00000213672 | NCKIPSD | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.821 | 0.121 | -0.700 | 0.004494522175169135200234471483327070018276572227478027 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00326305 | geneComp_00077103 | ENST00000583777 | ENSG00000100300 | TSPO | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.021 | 0.209 | 0.188 | 0.004997449345375318784101548175158313824795186519622803 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00327302 | geneComp_00077222 | MSTRG.8750.11 | ENSG00000100731 | PCNX1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.217 | 0.217 | 0.004997449345375318784101548175158313824795186519622803 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00332852 | geneComp_00077900 | ENST00000222005 | ENSG00000105401 | CDC37 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.734 | 0.862 | 0.128 | 0.004997449345375318784101548175158313824795186519622803 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00368905 | geneComp_00082620 | ENST00000413392 | ENSG00000141570 | CBX8 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.544 | 0.000 | -0.544 | 0.004997449345375318784101548175158313824795186519622803 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00393605 | geneComp_00086280 | ENST00000562275 | ENSG00000167522 | ANKRD11 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.004 | 0.088 | 0.085 | 0.004997449345375318784101548175158313824795186519622803 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00403347 | geneComp_00087829 | ENST00000376991 | ENSG00000175550 | DRAP1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.124 | 0.124 | 0.004997449345375318784101548175158313824795186519622803 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00405938 | geneComp_00088324 | ENST00000563119 | ENSG00000178761 | FAM219B | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.138 | 0.006 | -0.132 | 0.004997449345375318784101548175158313824795186519622803 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00384417 | geneComp_00084830 | ENST00000396091 | ENSG00000160746 | ANO10 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.459 | 0.028 | -0.431 | 0.005392688698702855637501230035013577435165643692016602 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00336103 | geneComp_00078331 | MSTRG.12185.1 | ENSG00000108591 | DRG2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.196 | 0.196 | 0.005528574659871990891468751527781932963989675045013428 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00387969 | geneComp_00085383 | ENST00000491924 | ENSG00000163795 | ZNF513 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.113 | 0.113 | 0.005632143540694753772180014550485793733969330787658691 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00329442 | geneComp_00077524 | ENST00000650833 | ENSG00000102796 | DHRS12 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.464 | 0.000 | -0.464 | 0.005694345710387432001053920060940072289668023586273193 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00370852 | geneComp_00082902 | ENST00000609492 | ENSG00000143622 | RIT1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.080 | 0.000 | -0.080 | 0.005850040321111382203567163884372348547913134098052979 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00415142 | geneComp_00090155 | MSTRG.16862.28 | ENSG00000189223 | PAX8-AS1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.493 | 0.493 | 0.005971952314487437817047688071170341572724282741546631 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00408673 | geneComp_00088880 | ENST00000375036 | ENSG00000182534 | MXRA7 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.079 | 0.000 | -0.079 | 0.006003016512132816097369047980691902921535074710845947 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00336822 | geneComp_00078424 | ENST00000503418 | ENSG00000109332 | UBE2D3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.070 | 0.070 | 0.006189707003193499305904179408344134571962058544158936 | |
| isoComp_00339577 | geneComp_00078764 | ENST00000504364 | ENSG00000112200 | ZNF451 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.091 | 0.000 | -0.091 | 0.006288963262919267799277989183792669791728258132934570 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00421377 | geneComp_00091258 | MSTRG.24510.12 | ENSG00000204348 | DXO | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.238 | 0.000 | -0.238 | 0.006528372415450161420080732455062388908118009567260742 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00373399 | geneComp_00083269 | MSTRG.25000.2 | ENSG00000146281 | PM20D2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.647 | 0.000 | -0.647 | 0.006537314657138900385324742359216543263755738735198975 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00329042 | geneComp_00077457 | ENST00000652476 | ENSG00000102125 | TAFAZZIN | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.103 | 0.000 | -0.103 | 0.006657581917895414279351395947514902218244969844818115 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00397380 | geneComp_00086820 | ENST00000385049 | ENSG00000169964 | TMEM42 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.549 | 0.549 | 0.006657581917895414279351395947514902218244969844818115 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00332083 | geneComp_00077806 | MSTRG.14629.8 | ENSG00000104915 | STX10 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.214 | 0.214 | 0.006740915884106310831946906603207025909796357154846191 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00409403 | geneComp_00089010 | ENST00000329600 | ENSG00000183208 | GDPGP1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.007174485269354075912817680915622986503876745700836182 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00448560 | geneComp_00103937 | MSTRG.20727.1 | ENSG00000271270 | TMCC1-DT | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.544 | 0.544 | 0.007493271724998410397711179342650211765430867671966553 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00380713 | geneComp_00084324 | MSTRG.3931.2 | ENSG00000156398 | SFXN2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.621 | 0.621 | 0.007677459790500022404624580474319373024627566337585449 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00446549 | geneComp_00102754 | ENST00000577785 | ENSG00000266714 | MYO15B | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.071 | 0.000 | -0.071 | 0.007894737625386574753072466137382434681057929992675781 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00309329 | geneComp_00075161 | ENST00000580759 | ENSG00000010244 | ZNF207 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.117 | 0.117 | 0.008059012546624392397953684508138394448906183242797852 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00400873 | geneComp_00087413 | ENST00000526257 | ENSG00000173039 | RELA | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.281 | 0.000 | -0.281 | 0.008189246042682929091482968431137123843654990196228027 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00351720 | geneComp_00080418 | ENST00000261965 | ENSG00000126216 | TUBGCP3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.468 | 0.796 | 0.328 | 0.008394779944054714393431027019687462598085403442382812 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00368287 | geneComp_00082559 | ENST00000572925 | ENSG00000141258 | SGSM2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.340 | 0.000 | -0.340 | 0.008394779944054714393431027019687462598085403442382812 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00419132 | geneComp_00090786 | MSTRG.7179.5 | ENSG00000198324 | PHETA1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.104 | 0.104 | 0.008394779944054714393431027019687462598085403442382812 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00371126 | geneComp_00082928 | ENST00000272139 | ENSG00000143793 | C1orf35 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.070 | 0.070 | 0.008398868653853164625844307522584131220355629920959473 | |
| isoComp_00313319 | geneComp_00075610 | ENST00000649697 | ENSG00000053438 | NNAT | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.008435890307409392788184909761639573844149708747863770 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00366322 | geneComp_00082338 | ENST00000665585 | ENSG00000139618 | BRCA2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.265 | 0.000 | -0.265 | 0.008654780516516399901938427774439333006739616394042969 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00327458 | geneComp_00077235 | MSTRG.8988.6 | ENSG00000100815 | TRIP11 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.457 | 0.000 | -0.457 | 0.008962795075894982102515662347741454141214489936828613 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00391568 | geneComp_00085979 | ENST00000554989 | ENSG00000166165 | CKB | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.205 | 0.205 | 0.009704597689262225990169952183350687846541404724121094 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00335623 | geneComp_00078276 | ENST00000225174 | ENSG00000108179 | PPIF | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.857 | 0.909 | 0.052 | 0.010476110759252626331017310690185695420950651168823242 | |
| isoComp_00361036 | geneComp_00081634 | ENST00000491526 | ENSG00000135540 | NHSL1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.354 | 0.354 | 0.010838889628432732056828591282737761503085494041442871 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00327953 | geneComp_00077292 | ENST00000470551 | ENSG00000101152 | DNAJC5 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.815 | 0.149 | -0.666 | 0.011139906338170895566674900578618689905852079391479492 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00320794 | geneComp_00076439 | MSTRG.24880.8 | ENSG00000082269 | FAM135A | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.019 | 0.424 | 0.405 | 0.011337372801066555177973427248616644646972417831420898 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00374383 | geneComp_00083406 | ENST00000520973 | ENSG00000147526 | TACC1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.100 | 0.000 | -0.100 | 0.011387022491218425426784399689950078027322888374328613 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00360391 | geneComp_00081561 | ENST00000433078 | ENSG00000135185 | TMEM243 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.734 | 0.284 | -0.450 | 0.011508853589744195630717449319035949883982539176940918 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00361555 | geneComp_00081702 | ENST00000392086 | ENSG00000135924 | DNAJB2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.073 | 0.555 | 0.482 | 0.011508853589744195630717449319035949883982539176940918 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00406281 | geneComp_00088387 | ENST00000588025 | ENSG00000179115 | FARSA | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.007 | 0.095 | 0.088 | 0.011508853589744195630717449319035949883982539176940918 | |
| isoComp_00438538 | geneComp_00098359 | ENST00000649424 | ENSG00000248323 | LUCAT1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.064 | 0.000 | -0.064 | 0.011721376365872447286586854886536457343026995658874512 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00390870 | geneComp_00085860 | ENST00000332211 | ENSG00000165637 | VDAC2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.776 | 0.928 | 0.152 | 0.011840543998928240720935889385145856067538261413574219 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00353731 | geneComp_00080699 | ENST00000249822 | ENSG00000128989 | ARPP19 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.869 | 0.573 | -0.296 | 0.011945719405557905443138189127694204216822981834411621 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00413982 | geneComp_00089879 | MSTRG.783.1 | ENSG00000187815 | ZFP69 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.136 | 0.008 | -0.128 | 0.012443813838267576629692534595506003824993968009948730 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00332860 | geneComp_00077900 | ENST00000591248 | ENSG00000105401 | CDC37 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.168 | 0.072 | -0.097 | 0.012661131318276503190944914933879772434011101722717285 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00389350 | geneComp_00085601 | ENST00000506963 | ENSG00000164466 | SFXN1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.212 | 0.011 | -0.201 | 0.012661131318276503190944914933879772434011101722717285 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00348467 | geneComp_00079941 | ENST00000484939 | ENSG00000122432 | SPATA1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.681 | 0.681 | 0.012840444912026256069070839771484315861016511917114258 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00323560 | geneComp_00076771 | ENST00000315183 | ENSG00000090905 | TNRC6A | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.193 | 0.000 | -0.193 | 0.013131833589684116514462175473454408347606658935546875 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00330615 | geneComp_00077649 | ENST00000566703 | ENSG00000103549 | RNF40 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.057 | 0.000 | -0.057 | 0.013131833589684116514462175473454408347606658935546875 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00332413 | geneComp_00077848 | ENST00000576442 | ENSG00000105176 | URI1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.262 | 0.000 | -0.262 | 0.013131833589684116514462175473454408347606658935546875 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00336119 | geneComp_00078333 | ENST00000583951 | ENSG00000108599 | AKAP10 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.490 | 0.490 | 0.013131833589684116514462175473454408347606658935546875 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00418284 | geneComp_00090666 | ENST00000529503 | ENSG00000197858 | GPAA1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.071 | 0.071 | 0.013131833589684116514462175473454408347606658935546875 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00432170 | geneComp_00095599 | MSTRG.2762.6 | ENSG00000233384 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.573 | 0.000 | -0.573 | 0.013520329721955564108992753347138204844668507575988770 | TRUE | |
| isoComp_00432569 | geneComp_00095813 | ENST00000453195 | ENSG00000234127 | TRIM26 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.177 | 0.000 | -0.177 | 0.013533233359229011535940223609486565692350268363952637 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00372635 | geneComp_00083150 | MSTRG.22305.8 | ENSG00000145391 | SETD7 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.123 | 0.123 | 0.013556038684594120397042260606212948914617300033569336 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00356327 | geneComp_00081036 | ENST00000421706 | ENSG00000131503 | ANKHD1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.150 | 0.150 | 0.013649639069972283045295569081645226106047630310058594 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00336188 | geneComp_00078340 | ENST00000581806 | ENSG00000108654 | DDX5 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.025 | 0.088 | 0.063 | 0.014320514401040075613824598121937015093863010406494141 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00387989 | geneComp_00085385 | MSTRG.16020.13 | ENSG00000163803 | PLB1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.476 | 0.007 | -0.469 | 0.014627165228311447137121703576667641755193471908569336 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00386341 | geneComp_00085126 | MSTRG.2734.10 | ENSG00000162819 | BROX | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.239 | 0.000 | -0.239 | 0.014664473537562868268868676580041210399940609931945801 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00423060 | geneComp_00091643 | ENST00000383768 | ENSG00000206559 | ZCWPW2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 1.000 | 0.054 | -0.946 | 0.014753419465975230878695967362546070944517850875854492 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00386920 | geneComp_00085218 | MSTRG.16434.17 | ENSG00000163219 | ARHGAP25 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.338 | 0.000 | -0.338 | 0.015023245978431538222297447759956412483006715774536133 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00318265 | geneComp_00076159 | ENST00000265198 | ENSG00000074706 | IPCEF1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.010 | 0.151 | 0.141 | 0.015532378064664042680020905606852466007694602012634277 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00413116 | geneComp_00089696 | MSTRG.13190.3 | ENSG00000186665 | C17orf58 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.380 | 1.000 | 0.620 | 0.015908253179047683600888518640203983522951602935791016 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00389707 | geneComp_00085666 | ENST00000522839 | ENSG00000164758 | MED30 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.056 | 0.000 | -0.056 | 0.015949947103961342048661364856343425344675779342651367 | |
| isoComp_00400579 | geneComp_00087386 | ENST00000530534 | ENSG00000172890 | NADSYN1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.068 | 0.000 | -0.068 | 0.015949947103961342048661364856343425344675779342651367 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00410588 | geneComp_00089240 | MSTRG.7382.7 | ENSG00000184445 | KNTC1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.228 | 0.040 | -0.187 | 0.016037576145962399720712454609383712522685527801513672 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00332501 | geneComp_00077857 | ENST00000476247 | ENSG00000105221 | AKT2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.187 | 0.187 | 0.016497977279896717389684468457744515035301446914672852 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00345802 | geneComp_00079567 | MSTRG.15896.4 | ENSG00000118960 | HS1BP3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.274 | 0.274 | 0.016922297332580139850310985139003605581820011138916016 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00386348 | geneComp_00085126 | MSTRG.2734.7 | ENSG00000162819 | BROX | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.045 | 0.296 | 0.251 | 0.017592355729317932927502354800708417315036058425903320 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00390512 | geneComp_00085792 | ENST00000452248 | ENSG00000165283 | STOML2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.014 | 0.182 | 0.168 | 0.018039066142985355628569621444512449670583009719848633 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00314149 | geneComp_00075704 | MSTRG.6030.3 | ENSG00000060138 | YBX3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.158 | 0.158 | 0.019133837672947864860795164076989749446511268615722656 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00326506 | geneComp_00077130 | MSTRG.19466.43 | ENSG00000100359 | SGSM3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.197 | 0.005 | -0.192 | 0.019133837672947864860795164076989749446511268615722656 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00354206 | geneComp_00080765 | ENST00000531430 | ENSG00000129559 | NEDD8 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.105 | 0.009 | -0.096 | 0.019189899992204117323835177444379951339215040206909180 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00317162 | geneComp_00076041 | ENST00000557372 | ENSG00000071537 | SEL1L | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.237 | 0.000 | -0.237 | 0.019225334094227754244688100015991949476301670074462891 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00432234 | geneComp_00095622 | ENST00000667843 | ENSG00000233461 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.063 | 0.507 | 0.444 | 0.019737995579406961144108834105281857773661613464355469 | TRUE | |
| isoComp_00385591 | geneComp_00084986 | ENST00000525004 | ENSG00000162191 | UBXN1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.109 | 0.000 | -0.109 | 0.019841696349305194824186315827319049276411533355712891 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00364935 | geneComp_00082148 | ENST00000479093 | ENSG00000138363 | ATIC | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.119 | 0.119 | 0.020214793479131517445201993155023956205695867538452148 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00385204 | geneComp_00084933 | MSTRG.12764.2 | ENSG00000161692 | DBF4B | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.330 | 0.006 | -0.324 | 0.020418937229990403309232149808849499095231294631958008 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00413024 | geneComp_00089685 | ENST00000412224 | ENSG00000186615 | KTN1-AS1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.636 | 0.000 | -0.636 | 0.020422860646168449622050999892053368967026472091674805 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00425827 | geneComp_00092671 | ENST00000481223 | ENSG00000221978 | CCNL2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.124 | 0.010 | -0.114 | 0.020422860646168449622050999892053368967026472091674805 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00372069 | geneComp_00083058 | ENST00000273179 | ENSG00000144677 | CTDSPL | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.365 | 0.000 | -0.365 | 0.020813251318076465834483457228998304344713687896728516 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00332023 | geneComp_00077799 | ENST00000596426 | ENSG00000104894 | CD37 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.084 | 0.084 | 0.021025051883805937619209558420152461621910333633422852 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00382364 | geneComp_00084558 | ENST00000289473 | ENSG00000158517 | NCF1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.815 | 0.914 | 0.100 | 0.021025051883805937619209558420152461621910333633422852 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00407193 | geneComp_00088580 | ENST00000591169 | ENSG00000180448 | ARHGAP45 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.027 | 0.159 | 0.133 | 0.021440551749885166515907641837657138239592313766479492 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00325162 | geneComp_00076959 | MSTRG.14190.20 | ENSG00000099622 | CIRBP | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.129 | 0.000 | -0.129 | 0.021782003905788965836265447251207660883665084838867188 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00322583 | geneComp_00076657 | ENST00000556597 | ENSG00000088808 | PPP1R13B | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.241 | 0.000 | -0.241 | 0.021835362858638990291026971135579515248537063598632812 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00384323 | geneComp_00084822 | ENST00000368450 | ENSG00000160691 | SHC1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.257 | 0.000 | -0.257 | 0.021854405449889861834389392925004358403384685516357422 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00353678 | geneComp_00080694 | ENST00000487418 | ENSG00000128928 | IVD | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.459 | 0.724 | 0.265 | 0.022036985635802096988866694005082536023110151290893555 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00310115 | geneComp_00075242 | MSTRG.10973.41 | ENSG00000013364_ENSG00000280893 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.690 | 0.000 | -0.690 | 0.022100158657021352209826048351715144235640764236450195 | TRUE | |
| isoComp_00333438 | geneComp_00077981 | ENST00000300540 | ENSG00000105750 | ZNF85 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.371 | 0.016 | -0.355 | 0.022279368724786998562370499143980850931257009506225586 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00412559 | geneComp_00089596 | ENST00000698764 | ENSG00000186141 | POLR3C | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.057 | 0.000 | -0.057 | 0.022279368724786998562370499143980850931257009506225586 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00395755 | geneComp_00086563 | MSTRG.22781.6 | ENSG00000168685 | IL7R | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.107 | 0.000 | -0.107 | 0.022562406454880699208098704389158228877931833267211914 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00361948 | geneComp_00081746 | MSTRG.7828.4 | ENSG00000136144 | RCBTB1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.142 | 0.142 | 0.023225563271096875267440751144931709859520196914672852 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00373529 | geneComp_00083289 | ENST00000492456 | ENSG00000146463 | ZMYM4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.101 | 0.000 | -0.101 | 0.023225563271096875267440751144931709859520196914672852 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00374624 | geneComp_00083440 | ENST00000449291 | ENSG00000147813 | NAPRT | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.441 | 0.637 | 0.195 | 0.023225563271096875267440751144931709859520196914672852 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00314388 | geneComp_00075731 | MSTRG.22920.2 | ENSG00000062194 | GPBP1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.121 | 0.121 | 0.023380253575066636817503251677408115938305854797363281 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00327607 | geneComp_00077249 | ENST00000216799 | ENSG00000100908 | EMC9 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.028 | 0.418 | 0.390 | 0.023394312325749570119493014885847514960914850234985352 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00386885 | geneComp_00085211 | MSTRG.16949.3 | ENSG00000163166 | IWS1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.164 | 0.010 | -0.155 | 0.023523024154025691523361984991424833424389362335205078 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00395866 | geneComp_00086579 | ENST00000381885 | ENSG00000168781 | PPIP5K1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.122 | 0.000 | -0.122 | 0.023523024154025691523361984991424833424389362335205078 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00360254 | geneComp_00081541 | ENST00000376588 | ENSG00000135069 | PSAT1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 1.000 | 0.804 | -0.196 | 0.023525930425368171694522345660516293719410896301269531 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00331036 | geneComp_00077693 | ENST00000565727 | ENSG00000104164 | BLOC1S6 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.217 | 0.217 | 0.025017037221422511183988035554648377001285552978515625 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00339338 | geneComp_00078732 | ENST00000229633 | ENSG00000111911 | HINT3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 1.000 | 0.853 | -0.147 | 0.025017037221422511183988035554648377001285552978515625 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00350632 | geneComp_00080257 | MSTRG.11318.7 | ENSG00000125149 | PHAF1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.358 | 0.358 | 0.025017037221422511183988035554648377001285552978515625 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00350019 | geneComp_00080164 | ENST00000286448 | ENSG00000124333 | VAMP7 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.987 | 0.839 | -0.148 | 0.025057781226846678052089245625211333390325307846069336 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00354868 | geneComp_00080862 | ENST00000404554 | ENSG00000130414 | NDUFA10 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.237 | 0.237 | 0.025367331476952029861715587344406230840831995010375977 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00361418 | geneComp_00081686 | ENST00000367553 | ENSG00000135838 | NPL | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.228 | 0.228 | 0.025393976050296186014465504854342725593596696853637695 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00342948 | geneComp_00079200 | ENST00000470482 | ENSG00000115677 | HDLBP | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.070 | 0.000 | -0.070 | 0.025496686414423708200160945125389844179153442382812500 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00439665 | geneComp_00098905 | ENST00000520222 | ENSG00000250479 | CHCHD10 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.225 | 0.000 | -0.225 | 0.025496686414423708200160945125389844179153442382812500 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00408256 | geneComp_00088812 | ENST00000333213 | ENSG00000182173 | TSEN54 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.472 | 0.779 | 0.307 | 0.026614966316367866250303109154629055410623550415039062 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00344687 | geneComp_00079418 | ENST00000482046 | ENSG00000117399 | CDC20 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.221 | 0.109 | -0.113 | 0.026832522962495022195161809008823183830827474594116211 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00407787 | geneComp_00088723 | ENST00000376955 | ENSG00000181513 | ACBD4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.492 | 0.015 | -0.478 | 0.027063363307314722283614116804528748616576194763183594 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00379564 | geneComp_00084147 | ENST00000284881 | ENSG00000154642 | C21orf91 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.669 | 0.965 | 0.295 | 0.027206885051365991418093059905913833063095808029174805 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00408863 | geneComp_00088914 | ENST00000421017 | ENSG00000182718 | ANXA2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.620 | 0.508 | -0.112 | 0.027733549895551649899783086539173382334411144256591797 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00424478 | geneComp_00092103 | ENST00000442303 | ENSG00000214253 | FIS1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.159 | 0.000 | -0.159 | 0.027733549895551649899783086539173382334411144256591797 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00448344 | geneComp_00103782 | ENST00000604841 | ENSG00000270647 | TAF15 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.081 | 0.000 | -0.081 | 0.027733549895551649899783086539173382334411144256591797 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00335973 | geneComp_00078314 | ENST00000397786 | ENSG00000108510 | MED13 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.702 | 0.987 | 0.285 | 0.027872257544823517139143120857625035569071769714355469 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00345149 | geneComp_00079483 | ENST00000236671 | ENSG00000117984 | CTSD | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.585 | 0.690 | 0.104 | 0.027872257544823517139143120857625035569071769714355469 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00346974 | geneComp_00079732 | MSTRG.23674.4 | ENSG00000120318 | ARAP3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.116 | 0.000 | -0.116 | 0.027872257544823517139143120857625035569071769714355469 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00373398 | geneComp_00083269 | ENST00000275072 | ENSG00000146281 | PM20D2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.353 | 1.000 | 0.647 | 0.027872257544823517139143120857625035569071769714355469 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00382945 | geneComp_00084633 | ENST00000355938 | ENSG00000159199 | ATP5MC1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.531 | 0.775 | 0.244 | 0.027872257544823517139143120857625035569071769714355469 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00309995 | geneComp_00075227 | ENST00000517738 | ENSG00000012232 | EXTL3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.052 | 0.476 | 0.424 | 0.028663244768125907546707509254702017642557621002197266 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00399737 | geneComp_00087253 | ENST00000559876 | ENSG00000172183 | ISG20 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.091 | 0.091 | 0.028760501489271013408899335672685992904007434844970703 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00396238 | geneComp_00086636 | ENST00000687481 | ENSG00000169032 | MAP2K1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.229 | 0.032 | -0.197 | 0.029004549133952919198753406249124964233487844467163086 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00411381 | geneComp_00089390 | ENST00000680011 | ENSG00000185201 | IFITM2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.104 | 0.000 | -0.104 | 0.029004549133952919198753406249124964233487844467163086 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00354990 | geneComp_00080870 | MSTRG.14791.4 | ENSG00000130511 | SSBP4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.146 | 0.000 | -0.146 | 0.029176445639769846979172385204037709627300500869750977 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00409908 | geneComp_00089102 | MSTRG.6767.33 | ENSG00000183735 | TBK1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.343 | 0.343 | 0.029349107511004918213970427132153417915105819702148438 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00411205 | geneComp_00089354 | ENST00000328649 | ENSG00000185043 | CIB1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.097 | 0.000 | -0.097 | 0.030306555297937139148434226854078588075935840606689453 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00418517 | geneComp_00090698 | ENST00000487858 | ENSG00000197965 | MPZL1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.085 | 0.085 | 0.030409363985418706721741699539052206091582775115966797 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00371908 | geneComp_00083036 | ENST00000422242 | ENSG00000144566 | RAB5A | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.222 | 0.000 | -0.222 | 0.030519035013165083519703912884324381593614816665649414 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00395974 | geneComp_00086597 | ENST00000541144 | ENSG00000168876 | ANKRD49 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.153 | 0.000 | -0.153 | 0.030985419624596853560571929619982256554067134857177734 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00413984 | geneComp_00089879 | MSTRG.783.3 | ENSG00000187815 | ZFP69 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.159 | 0.159 | 0.030985419624596853560571929619982256554067134857177734 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00440913 | geneComp_00099489 | MSTRG.27200.1 | ENSG00000253853 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.720 | 0.720 | 0.031095604175394180729297133325417235027998685836791992 | TRUE | |
| isoComp_00347434 | geneComp_00079800 | MSTRG.27434.5 | ENSG00000120885 | CLU | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.496 | 0.496 | 0.031316155863444231077785673278413014486432075500488281 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00351786 | geneComp_00080429 | ENST00000586618 | ENSG00000126254 | RBM42 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.179 | 0.000 | -0.179 | 0.031909302208040606074757050691914628259837627410888672 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00370107 | geneComp_00082804 | ENST00000367884 | ENSG00000143198 | MGST3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.173 | 0.173 | 0.031909302208040606074757050691914628259837627410888672 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00420496 | geneComp_00091027 | MSTRG.3421.3 | ENSG00000198964 | SGMS1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.817 | 0.141 | -0.676 | 0.032456431115077247206990307404339546337723731994628906 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00346883 | geneComp_00079711 | ENST00000520504 | ENSG00000120137 | PANK3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.283 | 0.000 | -0.283 | 0.033040077318369054371061110941809602081775665283203125 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00425573 | geneComp_00092568 | ENST00000613899 | ENSG00000219626 | FAM228B | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.359 | 0.000 | -0.359 | 0.033040077318369054371061110941809602081775665283203125 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00309478 | geneComp_00075178 | MSTRG.5915.12 | ENSG00000010610 | CD4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.037 | 0.205 | 0.168 | 0.033105697531342702377710196515181451104581356048583984 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00337112 | geneComp_00078453 | ENST00000508803 | ENSG00000109685 | NSD2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.086 | 0.490 | 0.404 | 0.033105697531342702377710196515181451104581356048583984 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00343132 | geneComp_00079216 | ENST00000498486 | ENSG00000115827 | DCAF17 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.264 | 0.000 | -0.264 | 0.033105697531342702377710196515181451104581356048583984 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00397495 | geneComp_00086842 | ENST00000429602 | ENSG00000170085 | SIMC1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.138 | 0.891 | 0.754 | 0.033105697531342702377710196515181451104581356048583984 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00400197 | geneComp_00087337 | ENST00000307980 | ENSG00000172613 | RAD9A | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.092 | 0.617 | 0.525 | 0.033105697531342702377710196515181451104581356048583984 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00418415 | geneComp_00090683 | ENST00000645742 | ENSG00000197912 | SPG7 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.131 | 0.131 | 0.033105697531342702377710196515181451104581356048583984 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00419978 | geneComp_00090933 | ENST00000589204 | ENSG00000198796 | ALPK2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.047 | 0.921 | 0.873 | 0.033105697531342702377710196515181451104581356048583984 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00328834 | geneComp_00077429 | ENST00000371144 | ENSG00000101972 | STAG2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.222 | 0.000 | -0.222 | 0.033501943615602179649126668437020271085202693939208984 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00398676 | geneComp_00087076 | ENST00000393760 | ENSG00000171307 | ZDHHC16 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.121 | 0.000 | -0.121 | 0.033830823322365137506562149383171345107257366180419922 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00365630 | geneComp_00082232 | ENST00000502833 | ENSG00000138777 | PPA2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.173 | 0.173 | 0.033940458087241526241584210765722673386335372924804688 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00330897 | geneComp_00077677 | MSTRG.9496.6 | ENSG00000104043 | ATP8B4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.152 | 0.152 | 0.033942133802681948018253876853123074397444725036621094 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00364729 | geneComp_00082113 | ENST00000369905 | ENSG00000138107 | ACTR1A | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.980 | 0.797 | -0.182 | 0.033942133802681948018253876853123074397444725036621094 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00368788 | geneComp_00082612 | ENST00000314028 | ENSG00000141551 | CSNK1D | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.163 | 0.033 | -0.130 | 0.033942133802681948018253876853123074397444725036621094 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00379940 | geneComp_00084206 | ENST00000359980 | ENSG00000155256 | ZFYVE27 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.373 | 0.373 | 0.033942133802681948018253876853123074397444725036621094 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00382328 | geneComp_00084549 | ENST00000674085 | ENSG00000158473 | CD1D | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.098 | 0.650 | 0.552 | 0.033942133802681948018253876853123074397444725036621094 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00365266 | geneComp_00082192 | ENST00000563081 | ENSG00000138629 | UBL7 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.210 | 0.210 | 0.034099078875119821774308803696840186603367328643798828 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00411958 | geneComp_00089486 | ENST00000446924 | ENSG00000185658 | BRWD1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.116 | 0.116 | 0.034099078875119821774308803696840186603367328643798828 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00340594 | geneComp_00078917 | ENST00000507716 | ENSG00000113407 | TARS1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.123 | 0.000 | -0.123 | 0.035882798729004815319054699784828699193894863128662109 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00362328 | geneComp_00081798 | ENST00000588455 | ENSG00000136448 | NMT1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.178 | 0.000 | -0.178 | 0.035958634166534345077970158399693900719285011291503906 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00316154 | geneComp_00075934 | ENST00000684414 | ENSG00000068366 | ACSL4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.082 | 0.197 | 0.115 | 0.036012641072609402614901341621589381247758865356445312 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00402637 | geneComp_00087722 | ENST00000534941 | ENSG00000174928 | C3orf33 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 1.000 | 0.259 | -0.741 | 0.036012641072609402614901341621589381247758865356445312 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00310878 | geneComp_00075331 | ENST00000440274 | ENSG00000023228 | NDUFS1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.253 | 0.253 | 0.036606361574270954162280133914464386180043220520019531 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00333200 | geneComp_00077947 | ENST00000683912 | ENSG00000105643 | ARRDC2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.286 | 0.286 | 0.036606361574270954162280133914464386180043220520019531 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00311782 | geneComp_00075432 | ENST00000585421 | ENSG00000035862 | TIMP2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.032 | 0.249 | 0.216 | 0.037154559627801987675699280089247622527182102203369141 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00382627 | geneComp_00084599 | ENST00000462914 | ENSG00000158863 | FHIP2B | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.207 | 0.016 | -0.191 | 0.037154559627801987675699280089247622527182102203369141 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00384780 | geneComp_00084874 | ENST00000520969 | ENSG00000161013 | MGAT4B | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.215 | 0.037 | -0.178 | 0.037185138925999658421339688629814190790057182312011719 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00309043 | geneComp_00075136 | ENST00000530538 | ENSG00000008517 | IL32 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.523 | 0.523 | 0.037942649193550351260917352647084044292569160461425781 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00347969 | geneComp_00079879 | ENST00000497275 | ENSG00000121769 | FABP3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.157 | 1.000 | 0.843 | 0.038007370788181747689460365791092044673860073089599609 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00332408 | geneComp_00077848 | ENST00000570704 | ENSG00000105176 | URI1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.048 | 0.287 | 0.239 | 0.038050578019850359035025633147597545757889747619628906 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00363706 | geneComp_00081990 | ENST00000527495 | ENSG00000137500 | CCDC90B | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.206 | 0.000 | -0.206 | 0.038273179095959071471799717301109922118484973907470703 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00343960 | geneComp_00079323 | ENST00000616327 | ENSG00000116685 | KIAA2013 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.166 | 0.021 | -0.145 | 0.038520458000970744794067002203519223257899284362792969 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00323971 | geneComp_00076826 | ENST00000554776 | ENSG00000092108 | SCFD1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.229 | 0.229 | 0.038553412864505476331800082334666512906551361083984375 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00359560 | geneComp_00081453 | MSTRG.23895.7 | ENSG00000134516 | DOCK2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.168 | 0.168 | 0.039459110705893848947134472382458625361323356628417969 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00353930 | geneComp_00080726 | ENST00000575813 | ENSG00000129219 | PLD2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.258 | 0.258 | 0.039645566778083188297365779817482689395546913146972656 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00408574 | geneComp_00088863 | MSTRG.13459.1 | ENSG00000182446 | NPLOC4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.202 | 0.000 | -0.202 | 0.039728169563148299503474447647022316232323646545410156 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00389908 | geneComp_00085693 | ENST00000482202 | ENSG00000164897 | TMUB1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.052 | 0.284 | 0.232 | 0.039760727318488335579882431147780152969062328338623047 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00346799 | geneComp_00079698 | ENST00000361432 | ENSG00000119979 | DENND10 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.112 | 0.737 | 0.625 | 0.039958130701072944179763624106271890923380851745605469 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00349959 | geneComp_00080160 | ENST00000506115 | ENSG00000124275 | MTRR | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.209 | 0.209 | 0.040724101291364091237401368061910034157335758209228516 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00359486 | geneComp_00081443 | ENST00000447032 | ENSG00000134453 | RBM17 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.252 | 0.000 | -0.252 | 0.040724101291364091237401368061910034157335758209228516 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00416383 | geneComp_00090362 | MSTRG.19719.5 | ENSG00000196639 | HRH1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.646 | 0.000 | -0.646 | 0.040724101291364091237401368061910034157335758209228516 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00419578 | geneComp_00090861 | ENST00000535004 | ENSG00000198598 | MMP17 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.202 | 0.202 | 0.040724101291364091237401368061910034157335758209228516 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00346151 | geneComp_00079614 | ENST00000398803 | ENSG00000119471 | HSDL2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.308 | 0.020 | -0.288 | 0.041092812455728940090882161939589423127472400665283203 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00312731 | geneComp_00075547 | ENST00000647414 | ENSG00000048707 | VPS13D | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.319 | 0.000 | -0.319 | 0.041572967313296620150975257956815767101943492889404297 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00328849 | geneComp_00077429 | MSTRG.30426.27 | ENSG00000101972 | STAG2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.257 | 0.257 | 0.041572967313296620150975257956815767101943492889404297 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00386748 | geneComp_00085193 | ENST00000510099 | ENSG00000163110 | PDLIM5 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.135 | 0.000 | -0.135 | 0.041647137809413689590876117563311709091067314147949219 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00397694 | geneComp_00086883 | ENST00000573928 | ENSG00000170296 | GABARAP | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.450 | 0.872 | 0.422 | 0.041647137809413689590876117563311709091067314147949219 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00444521 | geneComp_00101579 | MSTRG.11439.11 | ENSG00000260537 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.714 | 1.000 | 0.286 | 0.041659152913390798400605774531868519261479377746582031 | TRUE | |
| isoComp_00392829 | geneComp_00086176 | ENST00000567690 | ENSG00000166946 | CCNDBP1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.241 | 0.000 | -0.241 | 0.041806201824715165382695403195612016133964061737060547 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00353974 | geneComp_00080733 | ENST00000572836 | ENSG00000129255 | MPDU1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.054 | 0.054 | 0.041837483816452775142735731606080662459135055541992188 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00314692 | geneComp_00075765 | ENST00000545303 | ENSG00000064115 | TM7SF3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.041909495209869931930946052034414606168866157531738281 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00436382 | geneComp_00097589 | ENST00000626852 | ENSG00000242086 | MUC20-OT1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.067 | 0.000 | -0.067 | 0.042020649858562270084760825739067513495683670043945312 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00311746 | geneComp_00075428 | ENST00000557867 | ENSG00000035664 | DAPK2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.199 | 0.000 | -0.199 | 0.042035858391750689777577321137869148515164852142333984 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00357217 | geneComp_00081148 | MSTRG.25055.24 | ENSG00000132424 | PNISR | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.115 | 0.115 | 0.042035858391750689777577321137869148515164852142333984 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00370071 | geneComp_00082796 | ENST00000431969 | ENSG00000143178 | TBX19 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.044 | 0.663 | 0.619 | 0.042035858391750689777577321137869148515164852142333984 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00377504 | geneComp_00083826 | ENST00000403733 | ENSG00000151718 | WWC2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.362 | 0.000 | -0.362 | 0.042035858391750689777577321137869148515164852142333984 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00392530 | geneComp_00086121 | ENST00000551678 | ENSG00000166783 | MARF1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.073 | 0.073 | 0.042035858391750689777577321137869148515164852142333984 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00405936 | geneComp_00088324 | ENST00000357635 | ENSG00000178761 | FAM219B | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.119 | 0.485 | 0.366 | 0.042035858391750689777577321137869148515164852142333984 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00334982 | geneComp_00078192 | ENST00000479446 | ENSG00000107331 | ABCA2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.059 | 0.000 | -0.059 | 0.042196728353524212695724315835832385346293449401855469 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00398942 | geneComp_00087123 | MSTRG.22817.5 | ENSG00000171522 | PTGER4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.078 | 0.000 | -0.078 | 0.042272046615361512367226026753996848128736019134521484 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00364394 | geneComp_00082071 | ENST00000538653 | ENSG00000137936 | BCAR3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.424 | 0.000 | -0.424 | 0.042280435613208711131960626516956835985183715820312500 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00421365 | geneComp_00091258 | ENST00000337523 | ENSG00000204348 | DXO | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.248 | 0.248 | 0.042523799461465859594877514382460503838956356048583984 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00387821 | geneComp_00085359 | ENST00000684493 | ENSG00000163703 | CRELD1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.042803673227848920701532620114448945969343185424804688 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00382432 | geneComp_00084568 | ENST00000689921 | ENSG00000158615 | PPP1R15B | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.146 | 0.146 | 0.042997408060949295072195042166640632785856723785400391 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00393528 | geneComp_00086272 | ENST00000300952 | ENSG00000167470 | MIDN | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.051 | 0.596 | 0.545 | 0.042997408060949295072195042166640632785856723785400391 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00375792 | geneComp_00083585 | MSTRG.5248.2 | ENSG00000149269 | PAK1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.053 | 0.302 | 0.249 | 0.043858318709387236755681271915818797424435615539550781 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00391632 | geneComp_00085991 | ENST00000603946 | ENSG00000166197 | NOLC1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.276 | 0.276 | 0.043969286990992548225243297110864659771323204040527344 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00311638 | geneComp_00075413 | ENST00000564915 | ENSG00000033800 | PIAS1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.251 | 0.000 | -0.251 | 0.044050732405774131739129018114908831194043159484863281 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00335893 | geneComp_00078307 | ENST00000583697 | ENSG00000108465 | CDK5RAP3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.015 | 0.130 | 0.115 | 0.044050732405774131739129018114908831194043159484863281 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00313696 | geneComp_00075654 | ENST00000266041 | ENSG00000055955 | ITIH4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.019 | 0.540 | 0.521 | 0.044296677159402421397604854291785159148275852203369141 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00386232 | geneComp_00085106 | MSTRG.2089.31 | ENSG00000162735 | PEX19 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.006 | 0.099 | 0.093 | 0.044296677159402421397604854291785159148275852203369141 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00358214 | geneComp_00081286 | MSTRG.14223.2 | ENSG00000133243 | BTBD2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.198 | 0.000 | -0.198 | 0.044431567159553396473281594580839737318456172943115234 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00339943 | geneComp_00078824 | ENST00000480286 | ENSG00000112651 | MRPL2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.189 | 0.000 | -0.189 | 0.044755448253227872457138403206045040860772132873535156 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00430267 | geneComp_00094721 | ENST00000435388 | ENSG00000230337 | EXOSC10-AS1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 1.000 | 0.330 | -0.670 | 0.045318810597867381639858308517432305961847305297851562 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00385139 | geneComp_00084921 | ENST00000352268 | ENSG00000161642 | ZNF385A | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.248 | 0.248 | 0.045982569082819363392999889583734329789876937866210938 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00407569 | geneComp_00088677 | ENST00000470543 | ENSG00000181061 | HIGD1A | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.023 | 0.140 | 0.117 | 0.046120715761095248952372571693558711558580398559570312 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00308699 | geneComp_00075089 | MSTRG.12064.5 | ENSG00000007237 | GAS7 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.284 | 0.284 | 0.046266913108964531631261962729695369489490985870361328 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00353738 | geneComp_00080699 | ENST00000566423 | ENSG00000128989 | ARPP19 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.032 | 0.255 | 0.223 | 0.046266913108964531631261962729695369489490985870361328 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00367289 | geneComp_00082457 | ENST00000440863 | ENSG00000140474 | ULK3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.224 | 0.224 | 0.046266913108964531631261962729695369489490985870361328 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00411398 | geneComp_00089392 | MSTRG.9092.3 | ENSG00000185215 | TNFAIP2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.086 | 0.086 | 0.046266913108964531631261962729695369489490985870361328 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00335101 | geneComp_00078210 | MSTRG.4005.2 | ENSG00000107581 | EIF3A | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.013 | 0.111 | 0.099 | 0.046564797073771944935227651285458705388009548187255859 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00381966 | geneComp_00084485 | ENST00000538296 | ENSG00000157895 | C12orf43 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.336 | 0.336 | 0.046564797073771944935227651285458705388009548187255859 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00386447 | geneComp_00085144 | ENST00000295008 | ENSG00000162910 | MRPL55 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.089 | 0.333 | 0.244 | 0.046564797073771944935227651285458705388009548187255859 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00421014 | geneComp_00091196 | ENST00000409547 | ENSG00000204120 | GIGYF2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.112 | 0.005 | -0.107 | 0.046564797073771944935227651285458705388009548187255859 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00373707 | geneComp_00083317 | ENST00000456769 | ENSG00000146826 | TRAPPC14 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.257 | 0.257 | 0.047512689078425755784262918268723296932876110076904297 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00319251 | geneComp_00076259 | MSTRG.10897.2 | ENSG00000077238 | IL4R | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.221 | 0.221 | 0.047676465135664973515883247046076576225459575653076172 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00335720 | geneComp_00078291 | ENST00000545893 | ENSG00000108352 | RAPGEFL1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.476 | 0.000 | -0.476 | 0.048323226212038036808671392918768106028437614440917969 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00377132 | geneComp_00083776 | ENST00000534048 | ENSG00000151348 | EXT2 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.059 | 0.375 | 0.316 | 0.048798115046622958512756440541124902665615081787109375 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00369985 | geneComp_00082778 | ENST00000490870 | ENSG00000143106 | PSMA5 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.749 | 0.424 | -0.324 | 0.049157094642091940517314441194685059599578380584716797 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00312653 | geneComp_00075535 | MSTRG.25891.39 | ENSG00000048052 | HDAC9 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.012 | 0.148 | 0.136 | 0.049222983737008840776638862735126167535781860351562500 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00338650 | geneComp_00078643 | ENST00000548055 | ENSG00000111344 | RASAL1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.534 | 0.534 | 0.049485844138703369288201372455660020932555198669433594 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00328283 | geneComp_00077344 | ENST00000465985 | ENSG00000101347 | SAMHD1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.056 | 0.000 | -0.056 | 0.049661806567928984401660841285774949938058853149414062 | |
| isoComp_00345344 | geneComp_00079510 | MSTRG.1806.6 | ENSG00000118292 | C1orf54 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.061 | 0.241 | 0.180 | 0.049661806567928984401660841285774949938058853149414062 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00430166 | geneComp_00094661 | MSTRG.19510.3 | ENSG00000230107 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.492 | 0.028 | -0.464 | 0.049661806567928984401660841285774949938058853149414062 | TRUE | |
| isoComp_00457799 | geneComp_00109907 | ENST00000685034 | ENSG00000291152 | SBDSP1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.528 | 0.118 | -0.409 | 0.049661806567928984401660841285774949938058853149414062 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00349862 | geneComp_00080134 | MSTRG.18312.6 | ENSG00000124193 | SRSF6 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.055 | 0.005 | -0.050 | 0.049695852436159142218041750993506866507232189178466797 | |
| isoComp_00316530 | geneComp_00075975 | ENST00000286371 | ENSG00000069849 | ATP1B3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.894 | 0.950 | 0.056 | 0.049945898569307652092863492043761652894318103790283203 | |
| isoComp_00353071 | geneComp_00080598 | ENST00000514888 | ENSG00000128050 | PAICS | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.005 | 0.092 | 0.086 | 0.049945898569307652092863492043761652894318103790283203 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00354227 | geneComp_00080767 | MSTRG.8143.4 | ENSG00000129566 | TEP1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.103 | 0.103 | 0.049945898569307652092863492043761652894318103790283203 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00356890 | geneComp_00081109 | ENST00000651735 | ENSG00000132170 | PPARG | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.496 | 0.496 | 0.049945898569307652092863492043761652894318103790283203 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00373979 | geneComp_00083356 | ENST00000470832 | ENSG00000147130 | ZMYM3 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.187 | 0.000 | -0.187 | 0.049945898569307652092863492043761652894318103790283203 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00377540 | geneComp_00083830 | ENST00000541931 | ENSG00000151743 | AMN1 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.284 | 0.018 | -0.266 | 0.049945898569307652092863492043761652894318103790283203 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00379894 | geneComp_00084198 | ENST00000522894 | ENSG00000155100 | OTUD6B | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.170 | 0.000 | -0.170 | 0.049945898569307652092863492043761652894318103790283203 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00380418 | geneComp_00084276 | ENST00000519515 | ENSG00000155975 | VPS37A | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.145 | 0.145 | 0.049945898569307652092863492043761652894318103790283203 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00384421 | geneComp_00084830 | ENST00000451430 | ENSG00000160746 | ANO10 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.353 | 0.353 | 0.049945898569307652092863492043761652894318103790283203 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00385240 | geneComp_00084937 | ENST00000429001 | ENSG00000161813 | LARP4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.417 | 0.000 | -0.417 | 0.049945898569307652092863492043761652894318103790283203 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00385415 | geneComp_00084964 | ENST00000563088 | ENSG00000161999 | JMJD8 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.058 | 0.058 | 0.049945898569307652092863492043761652894318103790283203 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00406619 | geneComp_00088451 | MSTRG.30504.3 | ENSG00000179542 | SLITRK4 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.038 | 0.372 | 0.334 | 0.049945898569307652092863492043761652894318103790283203 | TRUE |
| isoComp_00413502 | geneComp_00089781 | ENST00000544078 | ENSG00000187186 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.792 | 0.145 | -0.647 | 0.049945898569307652092863492043761652894318103790283203 | TRUE | |
| isoComp_00457778 | geneComp_00109905 | ENST00000608531 | ENSG00000291150 | LSP1P5 | pgwt_inf | pgKDN_inf | 0.000 | 0.427 | 0.427 | 0.049945898569307652092863492043761652894318103790283203 | TRUE |
- Note:
- The comparisons made can be identified as “from ‘condition_1’ to ‘condition_2’”, meaning ‘condition_1’ is considered the ground state and ‘condition_2’ the changed state. This also means that a positive dIF value indicates that the isoform usage is increased in ‘condition_2’ compared to ‘condition_1’. Since the ‘isoformFeatures’ entry is the most relevant part of the switchAnalyzeRlist object, the most-used standard methods have also been implemented to work directly on isoformFeatures.
Help
Please Click HERE to learn more details about the results of IsoformSwitchAnalyzeR.
4. Circular RNA Analysis
Volcano Plot
No significantly changed circRNA was detected.
Details of sig. circRNA
No significantly changed circRNA was detected.
Annotation of sig. circRNA
No significantly changed circRNA was detected.